- Home |
- About |
- Contact Us |
- Privacy |
- Copyright |
- Shop |
- 🔍 Search Site
- Easter Color By Number Sheets
- Printable Easter Dot to Dot
- Easter Worksheets for kids
- Kindergarten
- All Generated Sheets
- Place Value Generated Sheets
- Addition Generated Sheets
- Subtraction Generated Sheets
- Multiplication Generated Sheets
- Division Generated Sheets
- Money Generated Sheets
- Negative Numbers Generated Sheets
- Fraction Generated Sheets
- Place Value Zones
- Number Bonds
- Addition & Subtraction
- Times Tables
- Fraction & Percent Zones
- All Calculators
- Fraction Calculators
- Percent calculators
- Area & Volume Calculators
- Age Calculator
- Height Calculator
- Roman Numeral Calculator
- Coloring Pages
- Fun Math Sheets
- Math Puzzles
- Mental Math Sheets
- Online Times Tables
- Online Addition & Subtraction
- Math Grab Packs
- All Math Quizzes
- 1st Grade Quizzes
- 2nd Grade Quizzes
- 3rd Grade Quizzes
- 4th Grade Quizzes
- 5th Grade Quizzes
- 6th Grade Math Quizzes
- Place Value
- Rounding Numbers
- Comparing Numbers
- Number Lines
- Prime Numbers
- Negative Numbers
- Roman Numerals
- Subtraction
- Add & Subtract
- Multiplication
- Fraction Worksheets
- Learning Fractions
- Fraction Printables
- Percent Worksheets & Help
- All Geometry
- 2d Shapes Worksheets
- 3d Shapes Worksheets
- Shape Properties
- Geometry Cheat Sheets
- Printable Shapes
- Coordinates
- Measurement
- Math Conversion
- Statistics Worksheets
- Bar Graph Worksheets
- Venn Diagrams
- All Word Problems
- Finding all possibilities
- Logic Problems
- Ratio Word Problems
- All UK Maths Sheets
- Year 1 Maths Worksheets
- Year 2 Maths Worksheets
- Year 3 Maths Worksheets
- Year 4 Maths Worksheets
- Year 5 Maths Worksheets
- Year 6 Maths Worksheets
- All AU Maths Sheets
- Kindergarten Maths Australia
- Year 1 Maths Australia
- Year 2 Maths Australia
- Year 3 Maths Australia
- Year 4 Maths Australia
- Year 5 Maths Australia
- Meet the Sallies
- Certificates

Mean Median Mode Range Worksheets and Help
Welcome to the Math Salamanders Mean Median Mode Range Worksheets. Here you will find a wide range of free printable Worksheets, which will help your child learn how to find the mean, median, mode and range of a set of data points.
These worksheets are aimed at students in 5th and 6th grade.
For full functionality of this site it is necessary to enable JavaScript.
Here are the instructions how to enable JavaScript in your web browser .
Mean Median Mode Range Quicklinks
Quicklinks to ...
- Median Help
Mean Median Mode Range Worksheets
- Mean Median Mode Range Online Quiz
- More related Math resources
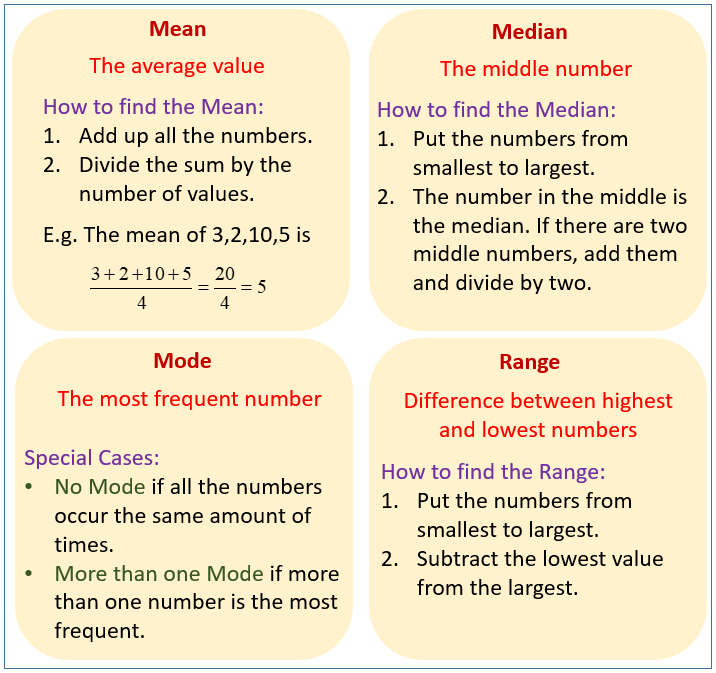
What is the Mean?
The mean is the average of a set of numbers.
It is found by adding up the set of numbers and then dividing the total by the number of data points in the set.
How to find the mean
Step 1) Add up all the numbers in the set.
Step 2) Divide the total by the total number of data points in the set.
Example 1) Find the mean of 5, 7, 8 and 4
Step 1) Add up the numbers to give a total of 5+7+8+4=24
Step 2) Divide the total by the number of data points. 24 ÷ 4 = 6
Answer: the mean is 6.
Example 2) Find the mean of 8, 2, 5, 7 and 13
Step 1) Add up the numbers to give a total of 8+2+5+7+13=35
Step 2) Divide by the number of data points. 35 ÷ 5 = 7
Answer: the mean is 7.
What is the Median?
The median is the midpoint (or middle value) of a set of numbers.
It is found by ordering the set of numbers and then finding the middle value in the set.
How to find the median
Step 1) Order the numbers in the set from smallest to largest.
Step 2) Find the middle number.
- If there is an odd number of values in the set, then the median is the middle value.
- If there is an even number of values in the set, then the median is the average of the two middle values.
Example 1) Find the median of 5, 7, 8, 2 and 4
Step 1) Put the numbers in order: 2, 4, 5, 7, 8
Step 2) There is an odd number of values in the set so the median is the middle value which is 5.
Answer: the median is 5.
Example 2) Find the median of 23, 27, 16, 31
Step 1) Put the numbers in order: 16, 23, 27, 31
Step 2) There is an even number of values in the set, so the median is the average of the middle two values.
(23+27) ÷ 2 = 25
Answer: the mean is 25
Example 3) Find the median of 7, -4, 9, -7, -2, 5
Step 1) Order the numbers: -7, -4, -2, 5, 7, 9
To get the average, simply add the two values together and divide by 2:
(-2 + 5) ÷ 2 = 1.5
Answer: the mean is 1.5
What is the Mode?
The mode is the most common (or the data point that appears most often) in a set of data.
It can be found by putting the data into an ordered list and seeing which data point occurs most often.
How to find the mode
Step 1) Put the data into an ordered list.
Step 2) Check that you have got the same number of data points.
Step 3) The mode is the data point which is the most common.
Finding the Mode Examples
Example 1) Find the mode of 3, 6, 4, 3, 2, 4, 7, 8, 6, 3, 9
This gives us: 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9
Step 2) Check the number of data points in both lists is the same.
Both lists have 11 data points.
Step 3) The mode is the number which occurs most often.
Answer: the mode is 3.
Example 2) Find the mode of 0.6, 0.3, 0.4, 0.2, 0.4, 0.7, 0.6, 0.1, 0.4, 0.9
This gives us: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.4, 0.4, 0.6, 0.6, 0.7, 0.9
Both lists have 10 data points.
Answer: the mode is 0.4.
Back to Top
What is the Range?
The range is the gap between the smallest and largest data point.
It is found by putting the data into an ordered list and find the difference between the largest and smallest amount.
How to find the range
Step 3) The range is the difference between the largest and smallest data point.
To find the range simply subtract the smallest number from the largest number.
Finding the Range Examples
Example 1) Find the range of 14, 21, 9, 32, 27, 15, 12, 30
This gives us: 9, 12, 14, 15, 21, 27, 30, 32
Both lists have 8 data points.
Step 3) The range is the difference or gap between the largest and smallest numbers.
Answer: the range is 32-9=23.
Example 2) Find the range of 6, 2, -7, 2, -5, 11, 3, -4, 0, 9
This gives us: -7, -5, -4, 0, 2, 2, 3, 6, 9, 11
Answer: the range is 11-(-7)=18.
These printable mean median mode range worksheets have been carefully graded to ensure a progression in the level of difficulty.
Sheets 1, 2 and 3 are designed for 5th graders involve ordering and calculating using positive integers and decimals.
Sheets 4, 5 and 6 are designed for 6th graders and involve ordering and calculating with positive and negative numbers and decimals.
The first sheet involve finding the mean, median, mode and range of some positive whole numbers.
The 2nd sheet involves the use of decimals to 1dp.
The 3rd sheet is similar to the 2nd sheet but has many more data points.
The 4th sheet involves decimals and negative numbers.
The 5th and 6th sheets are similar to the 4th sheets but with increased number of data points.
- Mean Median Mode and Range Sheet 1
- PDF version
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 2
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 3
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 4
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 5
- Median Mean Mode and Range Sheet 6
Mean Median Mode Range Problems
These printable mean median mode range problem sheets will help your child to use and apply their skills to solve problems.
The first problem sheet is more suitable for 5th grade and the second sheet is aimed at 6th graders.
- Median Mean Mode and Range Problems 1
- Median Mean Mode and Range Problems 2
Mean Median Mode Range Walkthrough Video
This short video walkthrough shows the problems from our Median Mean Mode and Range Problems Sheet 2 being solved and has been produced by the West Explains Best math channel.
If you would like some support in solving the problems on these sheets, check out the video!
More Recommended Math Worksheets
Take a look at some more of our worksheets similar to these.
- Mean Worksheets
The sheets in this section will help you to find the mean of a range of numbers, including negative numbers and decimals.
There are a range of sheets involving finding the mean, and also finding a missing data point when the mean is given.
- Median Worksheets
The sheets in this section will help you to find the median of a range of numbers, including negative numbers and decimals.
On some of the easier sheets, only odd numbers of data points have been used.
On the harder sheets, both odd and even numbers of data points have been included.
- Mode and Range Worksheets
The sheets in this section will help you to find the mode and range of a set of numbers, including negative numbers and decimals.
There are easier sheets involving fewer data points, and harder ones with more data points.
The sheets in this section will help you to solve problems involving bar graphs and picture graphs.
There are a range of sheet involving reading and interpreting graphs as well as drawing your own graphs.
- Box Plot Worksheets
Here are our selection of box plot worksheets to help you practice creating and interpreting box plots.
Mean, Median, Mode and Range Online Quiz
Our quizzes have been created using Google Forms.
At the end of the quiz, you will get the chance to see your results by clicking 'See Score'.
This will take you to a new webpage where your results will be shown. You can print a copy of your results from this page, either as a pdf or as a paper copy.
For incorrect responses, we have added some helpful learning points to explain which answer was correct and why.
We do not collect any personal data from our quizzes, except in the 'First Name' and 'Group/Class' fields which are both optional and only used for teachers to identify students within their educational setting.
We also collect the results from the quizzes which we use to help us to develop our resources and give us insight into future resources to create.
For more information on the information we collect, please take a look at our Privacy Policy
We would be grateful for any feedback on our quizzes, please let us know using our Contact Us link, or use the Facebook Comments form at the bottom of the page.
This quick quiz tests your knowledge and skill at finding and using the mean, median, mode and range of a set of data.
How to Print or Save these sheets 🖶
Need help with printing or saving? Follow these 3 steps to get your worksheets printed perfectly!
- How to Print support
Return to 6th Grade Math Worksheets
Return to Statistics Hub page
Return from Mean Median Mode Range to Math Salamanders Homepage
Math-Salamanders.com
The Math Salamanders hope you enjoy using these free printable Math worksheets and all our other Math games and resources.
We welcome any comments about our site or worksheets on the Facebook comments box at the bottom of every page.
New! Comments
TOP OF PAGE
© 2010-2024 Math Salamanders Limited. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy

Mean, Mode, Median, Range Practice Questions
Click here for questions, click here for answers.
averages, average, means, modes, medians, ranges
GCSE Revision Cards

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024

Child Login
- Kindergarten
- Number charts
- Skip Counting
- Place Value
- Number Lines
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Word Problems
- Comparing Numbers
- Ordering Numbers
- Odd and Even
- Prime and Composite
- Roman Numerals
- Ordinal Numbers
- In and Out Boxes
- Number System Conversions
- More Number Sense Worksheets
- Size Comparison
- Measuring Length
- Metric Unit Conversion
- Customary Unit Conversion
- Temperature
- More Measurement Worksheets
- Writing Checks
- Profit and Loss
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Tally Marks
- Mean, Median, Mode, Range
- Mean Absolute Deviation
- Stem-and-leaf Plot
- Box-and-whisker Plot
- Permutation and Combination
- Probability
- Venn Diagram
- More Statistics Worksheets
- Shapes - 2D
- Shapes - 3D
- Lines, Rays and Line Segments
- Points, Lines and Planes
- Transformation
- Quadrilateral
- Ordered Pairs
- Midpoint Formula
- Distance Formula
- Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines
- Scale Factor
- Surface Area
- Pythagorean Theorem
- More Geometry Worksheets
- Converting between Fractions and Decimals
- Significant Figures
- Convert between Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
- Proportions
- Direct and Inverse Variation
- Order of Operations
- Squaring Numbers
- Square Roots
- Scientific Notations
- Speed, Distance, and Time
- Absolute Value
- More Pre-Algebra Worksheets
- Translating Algebraic Phrases
- Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
- Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Identities
- Quadratic Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Polynomials
- Inequalities
- Sequence and Series
- Complex Numbers
- More Algebra Worksheets
- Trigonometry
- Math Workbooks
- English Language Arts
- Summer Review Packets
- Social Studies
- Holidays and Events
- Worksheets >
- Statistics >
- Mean, Median, Mode and Range
Central Tendency Worksheets: Mean, Median, Mode and Range
Mean, median, mode and range worksheets contain printable practice pages to determine the mean, median, mode, range, lower quartile and upper quartile for the given set of data. The pdf exercises are curated for students of grade 3 through grade 8. Interesting word problems are included in each section. Sample some of these worksheets for free!
Finding Average
Average or mean worksheets have plentiful exercises to find the average of numbers, numbers with practical units and decimals.
(49 Worksheets)

Finding Range
Identify the maximum and minimum values to find the range of the given data. Word problems are included for practice.
- Download the set

Finding Median
In these worksheets, 3rd grade and 4th grade children identify the median (middle value) of the represented data. Two word problems included.

Finding Quartiles
Determine the first (lower) quartile, second (median) quartile and the third (upper) quartile of the given data. One word problem included in each pdf worksheet for 5th grade and 6th grade students.

Mean, Median, Mode and Range: Level 1
These printable central tendency worksheets contain a mixed review of mean, median, mode and range concepts. Around 8 data are used in level 1.

Mean, Median, Mode and Range: Level 2
Find the mean, median, mode and range of each set of data. Each sheet has six problems with around 15 data.

Word Problems: Level 1
This exclusive section has five word problems to find the mean, median, mode and range of the given data.

Word Problems: Level 2
A variety of informative data are included as word problems in these central tendency worksheet pdfs requires 7th grade and 8th grade students to determine the values of mean, median, mode and range.
Related Worksheets
» Line Plot
» Mean Absolute Deviation
» Stem and Leaf Plot
» Box and Whisker Plot
Become a Member
Membership Information
Privacy Policy
What's New?
Printing Help
Testimonial
Copyright © 2024 - Math Worksheets 4 Kids
This is a members-only feature!

If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Statistics and probability
Course: statistics and probability > unit 3.
- Statistics intro: Mean, median, & mode
- Mean, median, & mode example
Mean, median, and mode
Calculating the mean.
- Calculating the median
- Choosing the "best" measure of center
Mean, median, and mode review
Practice problems.
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi
Finding the median
- Arrange the data points from smallest to largest.
- If the number of data points is odd, the median is the middle data point in the list.
- If the number of data points is even, the median is the average of the two middle data points in the list.
Finding the mode
Practice problem, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Mean, Median, Mode and Range
These lessons help GMAT students review mean, median, mode and range.
Related Pages Mean Median Mode Central Tendency More Statistics Lessons
The following diagrams show how to find the mean, median, mode and range. Scroll down the page for examples and solutions.
Statistics: The Average
Introduction to descriptive statistics and central tendency. Ways to measure the average of a set: median, mean, mode
Mean, Median, and Mode
Learn about Mean, Median, and Mode Mean, median and mode are measures of central tendency. Mean: add together and divide by how many there are. Median: the middle number when the data is listed in order from smallest to largest. If there are 2 middle number, add them and divide by 2. Mode: the most frequent number.
Example: Find the mean, median and mode of this set of data. 35,8,12,50,55,22,34,22,34
Mean, Median and Mode
This lesson shows how to calculate Mean, Median and Mode and some tricks to help you remember the differences of these methods of finding the Center.
The mean is the average. To calculate the mean, you add add the values and divide by the number of values.
- If you had 20 pencils in one box and 30 pencils in a second box, what is the average number of pencils in your boxes?
- Your grades out of 20 are all listed below. What is your average grade out of 20? 15, 16, 20, 12, 18, 20, 17
The median is the center. List the numbers in order and pick the center one. If there are an even number of numbers find the mean of the two middle numbers.
The mode is the number that shows up the most. There can be more than one mode. If the values all appear the same number of times, there is no mode.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.

- HW Guidelines
- Study Skills Quiz
- Find Local Tutors
- Demo MathHelp.com
- Join MathHelp.com
Select a Course Below
- ACCUPLACER Math
- Math Placement Test
- PRAXIS Math
- + more tests
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- Pre-Algebra
- College Pre-Algebra
- Introductory Algebra
- Intermediate Algebra
- College Algebra
Mean, Median, Mode, and Range
Mean, median, and mode are three kinds of "averages". There are many "averages" in statistics, but these are, I think, the three most common, and are certainly the three you are most likely to encounter in your pre-statistics courses, if the topic comes up at all.
Why do we need different kinds of averages?
The average that we're used to is found by adding all the values in a data set, and then dividing the sum by the number of values in that data set; but this average might be misleading.
Content Continues Below
MathHelp.com
Median, Mode, and Range
A typical example would be the case where nearly every person in a given population lives on about two dollars a day, but there is a small elite with incomes in the millions. The numerical average can mislead by suggesting that the average (in this case, we mean "typical") person earns a few tens of thousands per year.
Advertisement
But this does not accurately reflect what we mean when we're trying to discuss the "average" income. This is why the average income is almost always expressed by a different sort of average.
What are the three averages?
The three averages are:
- The "mean" is the "average" you're used to, where you add up all the numbers and then divide by the number of numbers.
- The "median" is the "middle" value in the list of numbers. To find the median, your numbers have to be listed in numerical order from smallest to largest, so you may have to rewrite your list before you can find the median.
- The "mode" is the value that occurs most often. If no number in the list is repeated, then there is no mode for the list.
The "range" of a list a numbers is just the difference between the largest and smallest values. It expresses "spread", being how far the values are distributed (or how concentrated they are).
- Find the mean, median, mode, and range for the following list of values:
13, 18, 13, 14, 13, 16, 14, 21, 13
The mean is the usual average, so I'll add and then divide:
(13 + 18 + 13 + 14 + 13 + 16 + 14 + 21 + 13) ÷ 9 = 15
Note that the mean, in this case, isn't a value from the original list. This is a common result. You should not assume that your mean will be one of your original numbers; you should not be surprised when it isn't.
The median is the middle value, so first I'll have to rewrite the list in numerical order:
13, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 16, 18, 21
There are nine numbers in the list, so the middle one will be the (9 + 1) ÷ 2 = 10 ÷ 2 = 5 th number:
So the median is 14 .
The mode is the number that is repeated more often than any other, so 13 , I see from my listing above, is the mode.
The largest value in the list is 21 , and the smallest is 13 , so the range is 21 − 13 = 8 .
mean: 15 median: 14 mode: 13 range: 8
Note: The formula for the place to find the median is " ( [the number of data points] + 1) ÷ 2 ", but you don't have to use this formula. You can just count in from both ends of the list until you meet in the middle, if you prefer, especially if your list is short. Either way will work.

The mean is the usual average:
(1 + 2 + 4 + 7) ÷ 4 = 14 ÷ 4 = 3.5
The median is the middle number. In this example, the numbers are already listed in numerical order, so I don't have to rewrite the list. But there is no "middle" number, because there are an even number of numbers.
Because of this, the median of the list will be the mean (that is, the usual average) of the middle two values within the list. The middle two numbers are 2 and 4 , so:
(2 + 4) ÷ 2 = 6 ÷ 2 = 3
So the median of this list is 3 , a value that isn't in the list at all.
The mode is the number that is repeated most often, but all the numbers in this list appear only once, so there is no mode.
The largest value in the list is 7 , the smallest is 1 , and their difference is 6 , so the range is 6 .
mean: 3.5 median: 3 mode: none range: 6
The values in the list above were all whole numbers, but the mean of the list was a decimal value. Getting a decimal value for the mean (or for the median, if you have an even number of data points) is perfectly okay; don't round your answers to try to match the format of the other numbers.
8, 9, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 12, 13
The mean is the usual average, so I'll add up and then divide:
(8 + 9 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 11 + 11 + 11 + 12 + 13) ÷ 10 = 105 ÷ 10 = 10.5
The median is the middle value. In a list of ten values, that will be the (10 + 1) ÷ 2 = 5.5 -th value; the formula is reminding me, with that "point-five", that I'll need to average the fifth and sixth numbers to find the median. The fifth and sixth numbers are the last 10 and the first 11 , so:
(10 + 11) ÷ 2 = 21 ÷ 2 = 10.5
The mode is the number repeated most often. This list has two values that are repeated three times; namely, 10 and 11 , each repeated three times.
The largest value is 13 and the smallest is 8 , so the range is 13 − 8 = 5 .
mean: 10.5 median: 10.5 modes: 10 and 11 range: 5
As you can see, it is possible for two of the averages (the mean and the median, in this case) to have the same value. But this is not usual, and you should not expect it.
Note: Depending on your text or your instructor, the above data set may be viewed as having no mode rather than having two modes, because no single solitary number was repeated more often than any other. I've seen books that go either way on this; there doesn't seem to be a consensus on the "right" definition of "mode" in the above case. So if you're not certain how you should answer the "mode" part of the above example, ask your instructor before the next test.
How can I keep straight which average is which?
About the only hard part of finding the mean, median, and mode is keeping straight which "average" is which. Use this list:
- mean: regular meaning of "average"
- median: middle value
- mode: most often
(In the above, I've used the term "average" rather casually. The technical definition of what we commonly refer to as the "average" is technically called "the arithmetic mean": adding up the values and then dividing by the number of values. Since you're probably more familiar with the concept of "average" than with "measure of central tendency", I used the more comfortable term.)
- A student has gotten the following grades on his tests: 87, 95, 76, and 88 . He wants an 85 or better overall for the course. Assuming all tests are evenly weighted, what is the minimum grade he must get on the last test in order to achieve that overall average?
The minimum grade for the last test is what I need to find. To find the average of all his grades (the known ones, plus the unknown one), I have to add up all the grades, and then divide by the number of grades. Since I don't have a score for the last test yet, I'll use a variable to stand for this unknown value: " x ". Then, setting the expression for the average equal to the desired average, the computation is:
(87 + 95 + 76 + 88 + x ) ÷ 5 = 85
Multiplying through by 5 and simplifying, I get:
87 + 95 + 76 + 88 + x = 425
346 + x = 425
This is the score that he needs on the last test in order to get the overall grade that he is wanting. (If I doubt myself, I can always plug this value into the formula for the average, and confirm that I get 85 as the result.)
He needs to get at least a 79 on the last test.
You can use the Mathway widget below to practice finding the median. Try the entered exercise, or type in your own exercise. Or try entering any list of numbers, and then selecting the option — mean, median, mode, etc — from what the widget offers you. Then click the button to compare your answer to Mathway's.
Please accept "preferences" cookies in order to enable this widget.
(Click here to be taken directly to the Mathway site, if you'd like to check out their software or get further info.)
URL: https://www.purplemath.com/modules/meanmode.htm
Standardized Test Prep
College math, homeschool math, share this page.
- Terms of Use
- About Purplemath
- About the Author
- Tutoring from PM
- Advertising
- Linking to PM
- Site licencing
Visit Our Profiles
Mean, Median, Mode and Range
The mean, the median and the mode are three different measures of average which we can use. The range is a measure of how spread out data is.
The mode is the value that appears most often.
The median is the middle number (when the numbers are in order).
To calculate the mean add up all the numbers and then divide by how many numbers there are.
The range is the difference between the biggest number and the smallest number.
Example 1: Here are a list of 7 numbers: 7 4 7 9 5 1 2 Find: a) The mode b) The median c) The mean d) The range
a) The mode is the most common number The only number that appears more than once is 7 The mode is 7
b) The median is the middle number (but only when the numbers are in order) We have to put the numbers in order: 1 2 4 5 7 7 9 We can now find the middle number:
The median is 5
c) To find the mean we need to add up all the numbers then divide by how many numbers there are:
1 + 2 + 4 + 5 + 7 + 7 + 9 ⁄ 7 = 35 ⁄ 7 = 5
The mean is 5
d) To find the range we take the smallest number away from the biggest number 9 - 1 = 8 The range is 8
Example 2: Here are a list of 8 numbers: 6 6 13 5 11 11 11 9 Find: a) The mode b) The median c) The mean d) The range
a) The mode is the most common number 11 appears three times, that is more than any other number The mode is 11
b) To find the median (the middle number) we need to put the numbers in order: 5 6 6 9 11 11 11 13
We can see that there is not one middle number, we have 9 and 11 in the middle. When this happens the median is half way between the two middle numbers, the middle of 9 and 11 is 10. We can work this out by adding 9 and 11 and then dividing by 2.
9 + 11 ⁄ 2 = 10 The median is 10
5 + 6 + 6 + 9 + 11 + 11 + 11 + 13 ⁄ 8 = 72 ⁄ 8 = 9
The mean is 9
d) To find the range we take the smallest number away from the biggest number 13 - 5 = 8 The range is 8
Calculate the mode, the median, the mean and the range:

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage

Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
All about Averages

About Average Age 11 to 14 Challenge Level
Unequal Averages Age 11 to 14 Challenge Level
Wipeout Age 11 to 16 Challenge Level
The Lives of Presidents Age 11 to 16 Challenge Level
- Statistics - Stage 3
- Statistics - Stage 4
You may also like
Patterns in Number Sequences
These resources are designed to get you thinking about number sequences and patterns.
Secondary Student Latest
Latest list for the Lower Secondary Student page
Curriculum Topics
Problems organised by curriculum topic for lower secondary students.

Addition (Basic)
Addition (Multi-Digit)
Algebra & Pre-Algebra
Comparing Numbers
Daily Math Review
Division (Basic)
Division (Long Division)
Hundreds Charts
Measurement
Multiplication (Basic)
Multiplication (Multi-Digit)
Order of Operations
Place Value
Probability
Skip Counting
Subtraction
Telling Time
Word Problems (Daily)
More Math Worksheets
Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension Gr. 1
Reading Comprehension Gr. 2
Reading Comprehension Gr. 3
Reading Comprehension Gr. 4
Reading Comprehension Gr. 5
Reading Comprehension Gr. 6
Reading & Writing
Reading Worksheets
Cause & Effect
Fact & Opinion
Fix the Sentences
Graphic Organizers
Synonyms & Antonyms
Writing Prompts
Writing Story Pictures
Writing Worksheets
More ELA Worksheets
Consonant Sounds
Vowel Sounds
Consonant Blends
Consonant Digraphs
Word Families
More Phonics Worksheets
Early Literacy
Build Sentences
Sight Word Units
Sight Words (Individual)
More Early Literacy
Punctuation
Subjects and Predicates
More Grammar Worksheets
Spelling Lists
Spelling Grade 1
Spelling Grade 2
Spelling Grade 3
Spelling Grade 4
Spelling Grade 5
Spelling Grade 6
More Spelling Worksheets
Chapter Books
Charlotte's Web
Magic Tree House #1
Boxcar Children
More Literacy Units
Animal (Vertebrate) Groups
Butterfly Life Cycle
Electricity
Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas)
Simple Machines
Space - Solar System
More Science Worksheets
Social Studies
Maps (Geography)
Maps (Map Skills)
More Social Studies
Mother's Day
Father's Day
More Holiday Worksheets
Puzzles & Brain Teasers
Brain Teasers
Logic: Addition Squares
Mystery Graph Pictures
Number Detective
Lost in the USA
More Thinking Puzzles
Teacher Helpers
Teaching Tools
Award Certificates
More Teacher Helpers
Pre-K and Kindergarten
Alphabet (ABCs)
Numbers and Counting
Shapes (Basic)
More Kindergarten
Worksheet Generator
Word Search Generator
Multiple Choice Generator
Fill-in-the-Blanks Generator
More Generator Tools
Full Website Index
Mean, Median, Mode, and Range Worksheets
Worksheets for calculating the mean (average), median, mode, and range.
Basic Level

Logged in members can use the Super Teacher Worksheets filing cabinet to save their favorite worksheets.
Quickly access your most used files AND your custom generated worksheets!
Please login to your account or become a member and join our community today to utilize this helpful feature.

Advanced Level
These worksheets focus only on calculating the mean, or average.
Pictures of Worksheets
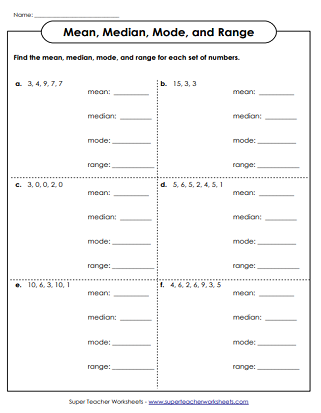
PDF with answer key:
PDF no answer key:
- Math Article
Mean Median Mode Questions
Mean, Median and Mode are three measures of central tendency, and these are the important topics in statistics. In this article, you will get mean, median, and mode questions and answers, along with some practice questions. These questions and answers will help you to practise for the board exams. Also, these questions cover various types of problems asked on mean, median and mode for Classes 9 and 10.
What is the mean formula?
As we know, the mean is the average of the given data set. This can be calculated using the formula given below.
Mean for ungrouped data = Sum of observations/Number of observations
Click here to get more information about mean .
What is the formula for the median?
The median is the middlemost data value of an ordered data set. This can be estimated using the formulas given below.
When n is odd:
Median = (n + 1)/2th observation
When n is even:
Median = [(n/2)th observation + {(n/2)+1}th observation]/2
Learn more about median here.
What is the mode?
Mode is the most frequently occurring value in the data set.
Get more information about mode here.
Mean Median Mode Questions and Answers
1. Find the mean of the first 10 odd integers.
First 10 odd integers: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19
Mean = Sum of the first 10 odd integers/Number of such integers
= (1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + 9 + 11 + 13 + 15 + 17 + 19)/10
Therefore, the mean of the first 10 odd integers is 10.
2. What is the median of the following data set?
32, 6, 21, 10, 8, 11, 12, 36, 17, 16, 15, 18, 40, 24, 21, 23, 24, 24, 29, 16, 32, 31, 10, 30, 35, 32, 18, 39, 12, 20
The ascending order of the given data set is:
6, 8, 10, 10, 11, 12, 12, 15, 16, 16, 17, 18, 18, 20, 21, 21, 23, 24, 24, 24, 29, 30, 31, 32, 32, 32, 35, 36, 39, 40
Number of values in the data set = n = 30
n/2 = 30/2 = 15
15th data value = 21
(n/2) +1 = 16
16th data value = 21
= (15th data value + 16th data value)/2
= (21 + 21)/2
3. Identify the mode for the following data set:
21, 19, 62, 21, 66, 28, 66, 48, 79, 59, 28, 62, 63, 63, 48, 66, 59, 66, 94, 79, 19 94
Let us write the given data set in ascending order as follows:
19, 19, 21, 21, 28, 28, 48, 48, 59, 59, 62, 62, 63, 63, 66, 66, 66, 66, 79, 79, 94, 94
Here, we can observe that the number 66 occurred the maximum number of times.
Thus, the mode of the given data set is 66.
4. Consider the following frequency distribution. Calculate the mean weight of students.
The given distribution has discontinuous class intervals, so we need to make them continuous.
Here, ∑f i = 40 and ∑f i d i = 35
By Assumed mean method,
Mean = a + (∑f i d i /∑f i )
= 43 + (35/40)
= 43 + 0.875
Therefore, the mean weight of the students is 43.875 kg.
5. Find the mean for the following distribution.
Mean = ∑f i x i /∑f i
6. Calculate the median marks of students from the following distribution.
N/2 = 90/2 = 45
Cumulative frequency greater and nearer to 45 is 47, which lies in the interval 40 – 50
Median class is 40 – 50.
Lower limit of the median class = l = 40
Class size = h = 10
Frequency of the median class = f = 20
Cumulative frequency of the class preceding the median class = cf = 27
As we know,
Median = 40 + [(45 – 27)/20] × 10
= 40 + (18/2)
Hence, the median marks of the students = 49.
7. The given distribution shows the number of runs scored by some top batsmen of the world in one-day international cricket matches.
Find the mode of the above distribution.
From the given,
Modal class = 4000 – 5000
Lower limit of the modal class = l = 4000
Class width (h) = 1000
Frequency of the modal class = f 1 = 18,
Frequency of the class preceding the modal class = f 0 = 4
Frequency of the class succeeding the modal class = f 2 = 9
Mode = l + [(f 1 – f 0 )/ (2f 1 – f 0 – f 2 )] × h
Mode = 4000 + [(18 – 4)/(36 – 4 – 9)] × 1000
= 4000 + (14000/23)
= 4000 + 608.695
= 4608.7 (approximately)
Thus, the mode of the given data is 4608.7 runs
8. If the median of a distribution given below is 28.5, then find the value of x and y.
N/2 = 60/2 = 30
Median of the given data = 28.5
Median class is 20 – 30 with a cumulative frequency = 25 + x.
Lower limit of median class = l = 20
Cumulative frequency of the class preceding the median class = cf = 5 + x
28.5 = 20 + [(30 − 5 − x)/ 20] × 10
28.5 – 20 = (25 – x)/2
8.5 × 2 = 25 – x
17 = 25 – x
x = 25 – 17
Therefore, x = 8
60 = 5 + 20 + 15 + 5 + x + y
60 = 5 + 20 + 15 + 5 + 8 + y
y = 60 – 53
Therefore, the value of x = 8 and y = 7.
9. For a moderately skewed distribution, the mean and median are respectively 26.8 and 27.9. What is the mode of the distribution?
Mean = 26.8
Median = 27.9
Using the relationship between mean, median and mode,
Mode = 3 Median – 2 Mean
= 3 × 27.9 – 2 × 26.8
= 83.7 – 53.6
Therefore, the mode of the distribution is 30.1.
10. If the mean of the given frequency distribution is 35, then find the missing frequency y. Also, calculate the median and mode for the distribution.
Given that the mean of the distribution is 35.
So, (430 + 45y)/(14 + y) = 35
430 + 45y = (14 + y)35
430 + 45y = 490 + 35y
45y – 35y = 490 – 430
Thus, the missing frequency is 6.
Now, we can calculate the mode as follows:
Mode = 30 + [(7 – 4)/(14 – 4 – 6)] × 10
= 30 + (30/4)
Now, using the formula Mode = 3Median – 2 Mean, we can get the value of median.
37.5 = 3 Median – 2 (35)
3 Median = 37.5 + 70
Median = 107.7/3
Recommended Videos

Practice Questions on Mean Median Mode
1. Find the mean, median and mode of the following data:
23, 18, 24, 23, 31, 37, 28, 30, 25, 40, 35, 35, 27, 25
2. The mileage (km per litre) of 50 cars of the same model was tested by a manufacturer, and details are tabulated as given below:
Find the mean mileage.
The manufacturer claimed that the mileage of the model was 16 km/litre. Do you agree with this claim?
3. Find the median of the following frequency distribution.
4. Calculate the mode for the following distribution.
5. Suppose the mean and median of distribution are 10.14 and 8, respectively. Find the mode of the distribution using the empirical relationship between mean, median and mode.
Keep visiting byjus.com to get solved questions on various Maths topics. Also, download BYJU’S – The Learning App today!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Mean, Median, Mode and Range -- Sorted Sets (Sets of 5 from 10 to 99) (A)
Welcome to The Mean, Median, Mode and Range -- Sorted Sets (Sets of 5 from 10 to 99) (A) Math Worksheet from the Statistics Worksheets Page at Math-Drills.com. This math worksheet was created or last revised on 2013-02-16 and has been viewed 48 times this week and 1,834 times this month. It may be printed, downloaded or saved and used in your classroom, home school, or other educational environment to help someone learn math.
Teacher s can use math worksheets as test s, practice assignment s or teaching tool s (for example in group work , for scaffolding or in a learning center ). Parent s can work with their children to give them extra practice , to help them learn a new math skill or to keep their skills fresh over school breaks . Student s can use math worksheets to master a math skill through practice, in a study group or for peer tutoring .
Use the buttons below to print, open, or download the PDF version of the Mean, Median, Mode and Range -- Sorted Sets (Sets of 5 from 10 to 99) (A) math worksheet . The size of the PDF file is 35070 bytes . Preview images of the first and second (if there is one) pages are shown. If there are more versions of this worksheet, the other versions will be available below the preview images. For more like this, use the search bar to look for some or all of these keywords: math, statistics, data, management, mean, median, mode, range .
Print Full Version
Open Full Version
Download Full Version
Print Student Version
Open Student Version
Download Student Version
The Print button initiates your browser's print dialog. The Open button opens the complete PDF file in a new browser tab. The Download button initiates a download of the PDF math worksheet. Teacher versions include both the question page and the answer key. Student versions, if present, include only the question page.

Other Versions:
More Statistics Worksheets
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.
Mean, Median, Mode, Range Calculator
Please provide numbers separated by comma to calculate.
Related Statistics Calculator | Standard Deviation Calculator | Sample Size Calculator
The word mean, which is a homonym for multiple other words in the English language, is similarly ambiguous even in the area of mathematics. Depending on the context, whether mathematical or statistical, what is meant by the "mean" changes. In its simplest mathematical definition regarding data sets, the mean used is the arithmetic mean, also referred to as mathematical expectation, or average. In this form, the mean refers to an intermediate value between a discrete set of numbers, namely, the sum of all values in the data set, divided by the total number of values. The equation for calculating the arithmetic mean is virtually identical to that for calculating the statistical concepts of population and sample mean, with slight variations in the variables used:
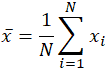
The mean is often denoted as x̄ , pronounced "x bar," and even in other uses when the variable is not x , the bar notation is a common indicator of some form of the mean. In the specific case of the population mean, rather than using the variable x̄ , the Greek symbol mu, or μ , is used. Similarly, or rather confusingly, the sample mean in statistics is often indicated with a capital X̄ . Given the data set 10, 2, 38, 23, 38, 23, 21, applying the summation above yields:
As previously mentioned, this is one of the simplest definitions of the mean, and some others include the weighted arithmetic mean (which only differs in that certain values in the data set contribute more value than others), and geometric mean . Proper understanding of given situations and contexts can often provide a person with the tools necessary to determine what statistically relevant method to use. In general, mean, median, mode and range should ideally all be computed and analyzed for a given sample or data set since they elucidate different aspects of the given data, and if considered alone, can lead to misrepresentations of the data, as will be demonstrated in the following sections.
The statistical concept of the median is a value that divides a data sample, population, or probability distribution into two halves. Finding the median essentially involves finding the value in a data sample that has a physical location between the rest of the numbers. Note that when calculating the median of a finite list of numbers, the order of the data samples is important. Conventionally, the values are listed in ascending order, but there is no real reason that listing the values in descending order would provide different results. In the case where the total number of values in a data sample is odd, the median is simply the number in the middle of the list of all values. When the data sample contains an even number of values, the median is the mean of the two middle values. While this can be confusing, simply remember that even though the median sometimes involves the computation of a mean, when this case arises, it will involve only the two middle values, while a mean involves all the values in the data sample. In the odd cases where there are only two data samples or there is an even number of samples where all the values are the same, the mean and median will be the same. Given the same data set as before, the median would be acquired in the following manner:
2,10,21, 23 ,23,38,38
After listing the data in ascending order, and determining that there are an odd number of values, it is clear that 23 is the median given this case. If there were another value added to the data set:
2,10,21, 23 , 23 ,38,38,1027892
Since there are an even number of values, the median will be the average of the two middle numbers, in this case, 23 and 23, the mean of which is 23. Note that in this particular data set, the addition of an outlier (a value well outside the expected range of values), the value 1,027,892, has no real effect on the data set. If, however, the mean is computed for this data set, the result is 128,505.875. This value is clearly not a good representation of the seven other values in the data set that are far smaller and closer in value than the average and the outlier. This is the main advantage of using the median in describing statistical data when compared to the mean. While both, as well as other statistical values, should be calculated when describing data, if only one can be used, the median can provide a better estimate of a typical value in a given data set when there are extremely large variations between values.
In statistics, the mode is the value in a data set that has the highest number of recurrences. It is possible for a data set to be multimodal, meaning that it has more than one mode. For example:
2,10,21,23,23,38,38
Both 23 and 38 appear twice each, making them both a mode for the data set above.
Similar to mean and median, the mode is used as a way to express information about random variables and populations. Unlike mean and median, however, the mode is a concept that can be applied to non-numerical values such as the brand of tortilla chips most commonly purchased from a grocery store. For example, when comparing the brands Tostitos, Mission, and XOCHiTL, if it is found that in the sale of tortilla chips, XOCHiTL is the mode and sells in a 3:2:1 ratio compared to Tostitos and Mission brand tortilla chips respectively, the ratio could be used to determine how many bags of each brand to stock. In the case where 24 bags of tortilla chips sell during a given period, the store would stock 12 bags of XOCHiTL chips, 8 of Tostitos, and 4 of Mission if using the mode. If, however, the store simply used an average and sold 8 bags of each, it could potentially lose 4 sales if a customer desired only XOCHiTL chips and not any other brand. As is evident from this example, it is important to take all manners of statistical values into account when attempting to draw conclusions about any data sample.
The range of a data set in statistics is the difference between the largest and the smallest values. While range does have different meanings within different areas of statistics and mathematics, this is its most basic definition, and is what is used by the provided calculator. Using the same example:
2,10,21,23,23,38,38 38 - 2 = 36
The range in this example is 36. Similar to the mean, range can be significantly affected by extremely large or small values. Using the same example as previously:
The range, in this case, would be 1,027,890 compared to 36 in the previous case. As such, it is important to extensively analyze data sets to ensure that outliers are accounted for.
Word Problems: When to Use Mean, Median, and Mode - Expii
Word problems: when to use mean, median, and mode, explanations (4).

(Video) Word Problems: When to Use Mean, Median, and Mode
by Anusha Rahman

This video by Anusha Rahman goes over three examples of when to use mean, median, and mode in word problems.
Example 1: Jessie’s math teacher said that their final class grade is based on the average of all exam grades. Jessie has gotten a 93,87,71, and 97 on her math exams. What measure of central tendency will she use to calculate the average? What is the average?
We know that when we see the word average , we're talking about the mean ! So, we will be using mean to solve this problem.
Mean=93+87+71+974 =3484 =87
So, we know that Jessie's average score on her math exams was 87!
Example 2: Meghan wants to get an accurate picture of household salary in her neighborhood. The salaries for people in her neighborhood are: 87,000;94,000;103,000;97,000; and 55,000. What measure of central tendency will most accurate describe the data?
At first glance, we can see that there is an outlier at 55,000. At outlier is going to mess with the mean, and mode (the frequency) is not going to give us a lot of information. So, we will use the median, or the middle value.
Step 1: Put the salaries in numerical order, from least to greatest.
55,000,87,000,94,000,97,000,103,000
Step 2: Cross of the numbers evenly from each side until you're left with a middle number.
In this case, the median is 94,000.
Example 3: At her birthday party, Charlotte asks everyone to go around and say their favorite Taylor Swift song. In order, people respond with:
All Too Well, Shake it Off, Black Space, New Romantics, All Too Well, New Romantics, All Too Well, and Mr Perfectly Fine
Charlotte wants to know which song is the most popular. What measure of central tendency should she use?
Because the question is asking for the most popular song, we know we are looking for the mode ! We also know that the mean and median cannot be used for nominal or qualitative data.
Our first step is to make a frequency table with the data.
SongFrequencyAll Too Well3Shake It Off1Blank Space1New Romantics2Mr. Perfectly Fine1
From this frequency table, we can see that All Too Well has the highest frequency, so that is the mode of the data set, and it is the most popular song!
When solving word problems with central tendency, it's important to understand the pros and cons of each type . Let's break them down.
PRO: asymmetrical data (with an outlier)
CON: doesn't work with qualitative or nominal data
PRO: symmetrical data (no outlier)
PRO: big data sets
CON: highly affected by outliers
PRO: working with qualitative or nominal data
PRO: very easy to look at and read graphs/charts
CON: very limited in what it tells you
Related Lessons
(video) understanding and calculating measures of central tendency.
by Nurse Killam
This video by Nurse Killam explains when to use mean, median, and mode.
She starts with the definition of a normal distribution . All of the measures of central tendency work best with a normal distribution.
The mean is the average of a data set. We find the mean by adding all of the values, and dividing the sum by the number of values. The mean gets more accurate with more values.
Mean Benefits
- Best measure for symmetrical distributions
- Influenced by all data
- Most reliable
- Good for interval and ratio data
Mean Limitations
- Works best with no outliers
The median is the middle value of a set. We find this by ordering the data, then finding the literal middle number. Even sized sets will have two numbers that share the middle. The median of these sets is the average of those two numbers.
Median Benefits
- Good for asymmetrical data
- Works for ordinal, interval, and ratio data
Median Limitations
- Does not account for extreme scores
- Not algebraically defined
- Not appropriate for nominal data
The mode is the value that occurs the most in a set. We find this by ordering the set and finding the number that repeats the most.
Mode Benefits
- The only appropriate measure for nominal data
- Can also be used for ordinal, interval, and ratio data
Mode Limitations
- Cannot be used if all scores are different
- There can be several modes
- Cannot be used for further calculations
Using the Measures of Central Tendency: Media, Median, and Mode
When you're faced with word problems where you're asking to look into the distribution of a dataset, it can feel intimidating to figure out whether to use mean, median, or mode. The good news is that because each measure is different, they each have their own advantages and disadvantages!

Image source: by Anusha Rahman
Let's go through some example problems.
Which measure of central tendency is the most effective way to analyze the following dataset? 4,7,9,10,11,18,2,20,15,350,14

When to Use Mean, Median, and Mode
Three extremely important measures of central tendency (part of statistics ) are mean , median , and mode . You can find the mean, median, and mode of most data sets. Sometimes, it is more advantageous to only focus on one or two of these measures of central tendency, depending on your data set. Let's find out when we should use the mean, median, or mode to accurately describe a data set.
The mean is the average value in a data set. We can calculate the mean using the following formula:
mean=sum of all valuestotal number of values
Advantages:
The mean is the best measure for symmetrical data distributions. It is affected by all of the data points, and the more data points you know, the more accurate the mean will be. The mean is helpful when working with interval and ratio data.
Limitations:
Outliers can really throw off the mean. For example, say we have the data set {1,4,5,6,6,7,8,8,9}. The average of this data set is 1+4+5+6+6+7+8+8+99=549=6. But, what if we had an outlier in the set? What if our new set was {1,4,5,6,6,7,8,8,9,4946}? When our new mean would be 1+4+5+6+6+7+8+8+9+494610=500010=500. See how much an outlier can throw off the mean?
The median is the value separating the first half of the data set with the second half. To find the median of a data set, first put the data set in order. Then, if there are an odd number of values, cross an equal amount of values off from the beginning of the list and the end of the list. The remaining data point in the middle of your list is the median! If there are an even number of values in your set, the median will be the average of the two middle values.
The median is helpful when describing asymmetrical data , and it also works for ordinal, ratio, or interval data. It is easy to find, especially if your data is in order. Also, it is not usually too affected by outliers.
Limitations
However, the fact that the median is not usually affected by outliers means that we can't use it to account for these extreme values. Also, the median is not helpful when we are working with nominal or qualitative data. Think about it ... how can you order a list of colors and find the middle color?
The mode of a data set is the value that occurs most frequently. We can find the mode by putting the data in order, and then identifying which value(s) repeat the most. Frequency tables , histograms , and frequency distributions can be helpful in identifying the mode.
Finding the mode can be especially helpful when we are working with qualitative data or nominal data , but it can also be used when we have ordinal, ratio, or interval data. It's easy to spot on a graph, frequency table, or even an ordered set of data. It is not usually affected by outliers.
There can be many modes, so finding the mode may not say much about how the data is distributed. On the other hand, if all the data points only occur once, there is no real mode. The mode is unstable, and can be easily influenced by certain changes in the data. Adding just one new data point can change the mode!
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Problem Solving Averages and Range
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
29 January 2018
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Many thanks for your resources, extremely useful especially focusing on literacy in Maths.
Really helpful set of questions, thank you
JulieHallas
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

COMMENTS
This post will share key information, formulas, and vocabulary so that you can use math to determine the mean, median, mode, and range of any data set and understand what these values represent. After working through two examples, you will also have access to a free mean, median, and mode pdf practice worksheet that includes an answer key.
To find the range: Range is equal to maximum value minus minimum value which gives us: 12 − 2 = 10. Example 3: Find the mean, median, mode and range for the following list of values. To determine the value of the mean, obtain the total of all the numbers and then divide by the number of numbers in the list.
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Step 1) Put the data into an ordered list. This gives us: 9, 12, 14, 15, 21, 27, 30, 32. Step 2) Check the number of data points in both lists is the same. Both lists have 8 data points. Step 3) The range is the difference or gap between the largest and smallest numbers. Answer: the range is 32-9=23.
averages, average, means, modes, medians, ranges. Practice Questions. Previous: Area of a Triangle Practice Questions
These printable central tendency worksheets contain a mixed review of mean, median, mode and range concepts. Around 8 data are used in level 1. Download the set. Mean, Median, Mode and Range: Level 2. Find the mean, median, mode and range of each set of data. Each sheet has six problems with around 15 data. Download the set.
Mean: The "average" number; found by adding all data points and dividing by the number of data points. Example: The mean of 4 , 1 , and 7 is ( 4 + 1 + 7) / 3 = 12 / 3 = 4 . Median: The middle number; found by ordering all data points and picking out the one in the middle (or if there are two middle numbers, taking the mean of those two numbers).
Mean, median and mode are measures of central tendency. Mean: add together and divide by how many there are. Median: the middle number when the data is listed in order from smallest to largest. If there are 2 middle number, add them and divide by 2. Mode: the most frequent number. Find the mean, median and mode of this set of data.
Because of this, the median of the list will be the mean (that is, the usual average) of the middle two values within the list. The middle two numbers are 2 and 4, so: (2 + 4) ÷ 2 = 6 ÷ 2 = 3. So the median of this list is 3, a value that isn't in the list at all. The mode is the number that is repeated most often, but all the numbers in this ...
The mode is 7. b) The median is the middle number (but only when the numbers are in order) We have to put the numbers in order: 1 2 4 5 7 7 9. We can now find the middle number: The median is 5. c) To find the mean we need to add up all the numbers then divide by how many numbers there are: 1 + 2 + 4 + 5 + 7 + 7 + 9 7 = 35 7 = 5.
Follow us. Learn how to find the mean, median, mode, and range of a data set in this free, interactive math lesson. Practice, get feedback, and have fun learning!
The mean of a data set tells us on average how much gas cost in the year 2000. We can find the mean by adding all of the numbers up and dividing by 12, which is the number of months in the year ...
All about Averages. How well do you really understand mean, median and mode? In these puzzling problems we invite you to be playful with numbers and discover how averages change when data sets are tweaked. About Average. Age 11 to 14. Challenge Level. Can you find sets of numbers which satisfy each of our mean, median, mode and range conditions?
Find the median, range, mode, and mean. Use the data on the line plot to answer the range, median, mean, and mode questions. With this worksheet, students will find the median of each set of numbers and solve a word problem that involves reading a table. Find the range for each set of numbers. Includes a word problem.
Getting Started with Mean, Median, Mode and Range Problems. The worksheets on this page require kids to calculate the mean, median, range and mode for small sets of numbers, all of which are easy enough to add up on paper without the aid of a calculator. These are great practice tools for introducing concepts like mean or median because the ...
Mean = 26.8. Median = 27.9. Using the relationship between mean, median and mode, Mode = 3 Median - 2 Mean = 3 × 27.9 - 2 × 26.8 = 83.7 - 53.6 = 30.1. Therefore, the mode of the distribution is 30.1. 10. If the mean of the given frequency distribution is 35, then find the missing frequency y. Also, calculate the median and mode for the ...
Welcome to The Mean, Median, Mode and Range -- Sorted Sets (Sets of 5 from 10 to 99) (A) Math Worksheet from the Statistics Worksheets Page at Math-Drills.com. This math worksheet was created or last revised on 2013-02-16 and has been viewed 759 times this week and 1,561 times this month. It may be printed, downloaded or saved and used in your classroom, home school, or other educational ...
These Mean Mode Median and Range Worksheets are great for practicing how to compute mean, mode, median, and range for data sets of numbers. These Mean Mode Median and Range Worksheets will generate 10 Mean Mode Median and Range problems per worksheet. These Mean Mode Median and Range Worksheets are perfect for mastering the math topic of means ...
The mean is the arithmetic average, and it is probably the measure of central tendency that you are most familiar. Calculating the mean is very simple. You just add up all of the values and divide by the number of observations in your dataset. The calculation of the mean incorporates all values in the data.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Find the mode of the following numbers. {33,60,33,60,33,57}, Find the range of the following numbers. {69,51,39,27,39}, Find the mean of the following numbers. {12,68,48,36} and more.
Using the same example as previously: 2,10,21, 23, 23 ,38,38,1027892. The range, in this case, would be 1,027,890 compared to 36 in the previous case. As such, it is important to extensively analyze data sets to ensure that outliers are accounted for. This calculator determines the mean, median, mode, and range of a given data set.
At outlier is going to mess with the mean, and mode (the frequency) is not going to give us a lot of information. So, we will use the median, or the middle value. Step 1: Put the salaries in numerical order, from least to greatest. 55,000,87,000,94,000,97,000,103,000. Step 2: Cross of the numbers evenly from each side until you're left with a ...
Problem Solving Averages and Range. Subject: Mathematics. Age range: 11-14. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. docx, 15.19 KB. A mixed bag of problem solving style questions on mean, median, mode and range. Suitable for key stage 3 and key stage 4 student. Answers are included too.