Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.

How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Writing a Research Proposal
- First Online: 10 April 2022
Cite this chapter

- Fahimeh Tabatabaei 3 &
- Lobat Tayebi 3
1101 Accesses
A research proposal is a roadmap that brings the researcher closer to the objectives, takes the research topic from a purely subjective mind, and manifests an objective plan. It shows us what steps we need to take to reach the objective, what questions we should answer, and how much time we need. It is a framework based on which you can perform your research in a well-organized and timely manner. In other words, by writing a research proposal, you get a map that shows the direction to the destination (answering the research question). If the proposal is poorly prepared, after spending a lot of energy and money, you may realize that the result of the research has nothing to do with the initial objective, and the study may end up nowhere. Therefore, writing the proposal shows that the researcher is aware of the proper research and can justify the significance of his/her idea.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
A. Gholipour, E.Y. Lee, S.K. Warfield, The anatomy and art of writing a successful grant application: A practical step-by-step approach. Pediatr. Radiol. 44 (12), 1512–1517 (2014)
Article Google Scholar
L.S. Marshall, Research commentary: Grant writing: Part I first things first …. J. Radiol. Nurs. 31 (4), 154–155 (2012)
E.K. Proctor, B.J. Powell, A.A. Baumann, A.M. Hamilton, R.L. Santens, Writing implementation research grant proposals: Ten key ingredients. Implement. Sci. 7 (1), 96 (2012)
K.C. Chung, M.J. Shauver, Fundamental principles of writing a successful grant proposal. J. Hand Surg. Am. 33 (4), 566–572 (2008)
A.A. Monte, A.M. Libby, Introduction to the specific aims page of a grant proposal. Kline JA, editor. Acad. Emerg. Med. 25 (9), 1042–1047 (2018)
P. Kan, M.R. Levitt, W.J. Mack, R.M. Starke, K.N. Sheth, F.C. Albuquerque, et al., National Institutes of Health grant opportunities for the neurointerventionalist: Preparation and choosing the right mechanism. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 13 (3), 287–289 (2021)
A.M. Goldstein, S. Balaji, A.A. Ghaferi, A. Gosain, M. Maggard-Gibbons, B. Zuckerbraun, et al., An algorithmic approach to an impactful specific aims page. Surgery 169 (4), 816–820 (2021)
S. Engberg, D.Z. Bliss, Writing a grant proposal—Part 1. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (3), 157–162 (2005)
D.Z. Bliss, K. Savik, Writing a grant proposal—Part 2. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (4), 226–229 (2005)
D.Z. Bliss, Writing a grant proposal—Part 6. J. Wound Ostomy Cont. Nurs. 32 (6), 365–367 (2005)
J.C. Liu, M.A. Pynnonen, M. St John, E.L. Rosenthal, M.E. Couch, C.E. Schmalbach, Grant-writing pearls and pitfalls. Otolaryngol. Neck. Surg. 154 (2), 226–232 (2016)
R.J. Santen, E.J. Barrett, H.M. Siragy, L.S. Farhi, L. Fishbein, R.M. Carey, The jewel in the crown: Specific aims section of investigator-initiated grant proposals. J. Endocr. Soc. 1 (9), 1194–1202 (2017)
O.J. Arthurs, Think it through first: Questions to consider in writing a successful grant application. Pediatr. Radiol. 44 (12), 1507–1511 (2014)
M. Monavarian, Basics of scientific and technical writing. MRS Bull. 46 (3), 284–286 (2021)
Additional Resources
https://grants.nih.gov
https://grants.nih.gov/grants/oer.htm
https://www.ninr.nih.gov
https://www.niaid.nih.gov
http://www.grantcentral.com
http://www.saem.org/research
http://www.cfda.gov
http://www.ahrq.gov
http://www.nsf/gov
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Dentistry, Marquette University, Milwaukee, WI, USA
Fahimeh Tabatabaei & Lobat Tayebi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Tabatabaei, F., Tayebi, L. (2022). Writing a Research Proposal. In: Research Methods in Dentistry. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98028-3_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-98028-3_4
Published : 10 April 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-98027-6
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-98028-3
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
- Research Tips and Tools
Advanced Research Methods
- Writing a Research Proposal
- What Is Research?
- Library Research
What Is a Research Proposal?
Reference books.
- Writing the Research Paper
- Presenting the Research Paper
When applying for a research grant or scholarship, or, just before you start a major research project, you may be asked to write a preliminary document that includes basic information about your future research. This is the information that is usually needed in your proposal:
- The topic and goal of the research project.
- The kind of result expected from the research.
- The theory or framework in which the research will be done and presented.
- What kind of methods will be used (statistical, empirical, etc.).
- Short reference on the preliminary scholarship and why your research project is needed; how will it continue/justify/disprove the previous scholarship.
- How much will the research project cost; how will it be budgeted (what for the money will be spent).
- Why is it you who can do this research and not somebody else.
Most agencies that offer scholarships or grants provide information about the required format of the proposal. It may include filling out templates, types of information they need, suggested/maximum length of the proposal, etc.
Research proposal formats vary depending on the size of the planned research, the number of participants, the discipline, the characteristics of the research, etc. The following outline assumes an individual researcher. This is just a SAMPLE; several other ways are equally good and can be successful. If possible, discuss your research proposal with an expert in writing, a professor, your colleague, another student who already wrote successful proposals, etc.
- Author, author's affiliation
- Explain the topic and why you chose it. If possible explain your goal/outcome of the research . How much time you need to complete the research?
- Give a brief summary of previous scholarship and explain why your topic and goals are important.
- Relate your planned research to previous scholarship. What will your research add to our knowledge of the topic.
- Break down the main topic into smaller research questions. List them one by one and explain why these questions need to be investigated. Relate them to previous scholarship.
- Include your hypothesis into the descriptions of the detailed research issues if you have one. Explain why it is important to justify your hypothesis.
- This part depends of the methods conducted in the research process. List the methods; explain how the results will be presented; how they will be assessed.
- Explain what kind of results will justify or disprove your hypothesis.
- Explain how much money you need.
- Explain the details of the budget (how much you want to spend for what).
- Describe why your research is important.
- List the sources you have used for writing the research proposal, including a few main citations of the preliminary scholarship.
- << Previous: Library Research
- Next: Writing the Research Paper >>
- Last Updated: Aug 22, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/research-methods
- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
- {{item.title}} {{item.title}} 0" aria-label="Find options under this page" @click="mobchildshow(true, item.title)" class="more-menu">
- {{subitem.title}}
Writing a research proposal
How to write a research proposal.
For many subjects, writing a research proposal is a key part of your postgraduate research degree application. This is your opportunity to demonstrate your knowledge and how you want to contribute to the subject.
We use the proposal to match your interest with an appropriate supervisor to make sure you have the best support during your degree. We are looking for originality and relevance when assessing the overall quality of your application, including your suitability for this level of study.
We highly recommend that you explore which academic researchers are working in your subject area and contact them first with any questions, this is a good opportunity to firm up your ideas, further explore the topic and talk with others in your field.
What is a research proposal?
A research proposal is a concise and coherent document, usually between 1500 – 2000 words, maximum 4 x A4 pages. You should outline your proposed research project, why it is of relevance (rationale), what research questions are you going to ask, what you hope to achieve (aims and objectives) and how you plan to carry out your research (methodology).
Step-by-step
This page is your comprehensive guide to writing a research proposal and will cover seven key elements of a proposal:
Working title
You should include a title for your thesis in the proposal.
Your title may change as you further your research, but at this stage it's important to state succinctly what your research will cover.
Introduction
Briefly identify your idea, what is your ‘research question’?
It could be the theory you want to test, or a more open question. It would be useful to give examples, 3-5 research questions from recently completed PhDs in a relevant field. You should discuss the context around your research topic, such as current debates and issues. The important thing here is that you introduce your research project with clarity and in a way that stimulates your reader’s interest.
Demonstrate the significance of your research project.
To do this, explain why your research is important, what makes it original and how it will contribute to existing knowledge within its field.
Aims and objectives
What are you hoping to achieve with your research?
Try and produce four or five bullet points of objectives for each aim, which demonstrate your understanding of how to meet your research aims. You can use the SMART acronym to support you in creating objectives, which involves making your objectives: specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time specific.
Literature Review
Demonstrate your knowledge and awareness of relevant literature
A literature review is a discussion and evaluation of academic literature or a relevant body of knowledge (for practice-based research). You should use this section of your proposal to show that you are familiar with work in your chosen topic area and that your research will contribute something new and/or meaningful to it.
Methodology
Explain how you plan to carry out your research
The methodology section of your research proposal is where you explain how you plan to carry out your research. This should include the research techniques and methods you will use, why these are most appropriate and how you will implement them. You should also include a discussion of the research strategy (general approach) you will adopt, with appropriate justification, including the analytical approach. The section should also contain the range of research findings that will be gathered from the research and how you will analyse or evaluate this. For practice based research, include how will your portfolio of artefacts, code, software, compositions, computer games etc. articulate the originality of your research?
Reference all the materials you used in the preparation your proposal
You may also list references that you didn't directly draw upon, to demonstrate awareness of literature relating to your proposed material.
Support from academic staff in drafting your research proposal
Your research proposal will be read by academics with an interest in your field of research. You are therefore encouraged to contact members of academic staff informally prior to submitting your application to discuss to your research proposal. This can often speed up the applications process, as you can identify the member(s) of staff you have spoken to on your research degree application form.
Use the Huddersfield Research Portal to browse academic staff profiles and search using key words to find staff members who share your research interests.
Changing aspects of your research proposal after gaining a place as a research student
Your research proposal is your starting point, and we understand that as your idea develop s , your proposed research is likely to change. As such, you will not be obliged to adhere to the specifics of your proposal if you are offered a place as a research degree candidate at Huddersfield. However, as the proposal is the foundation of your working relationship with your supervisor(s), you will need to discuss any changes with them first.
Useful tips for writing a research proposal
- Maintain a focus in your proposal: Your research proposal should be clear and concise, outlining your research idea and its benefits to your chosen field of study, in a way that the reader can clearly understand. Remember, your proposal is just the starting point and an outline and does not need to be overly complicated.
- Share your proposal: Ask someone you trust (a friend, family member, tutor) to read your proposal and provide some feedback. Do they understand what your research is about? Do they think your aims and objectives are achievable? Does your research engage them?
- Align your proposal topic with University research themes: Whilst it is important to choose a research topic that you are passionate about, your proposal will be assessed (in part) on its fit with our University research themes. You therefore need to choose a topic which aligns with topics of interest to the University or academic school you hoping to work within and make it clear how your project matches up with them.
- Be realistic in your proposal: Your proposal is assessed not only on its quality, originality and fit with our research themes but also the likelihood of completion, so make sure that the scope of your research project is reasonable and realistic .
- Take your time when writing your proposal: There are a lot of elements to a high-quality research proposal, so take the time to ensure that you meet them all. At the University of Huddersfield, there are three opportunities for enrolling onto a research degree programme during the academic year (October, January, and April), meaning less time pressure when working on your proposal and application.
Once you have written your proposal, what next?
Once you have written your research proposal you will need to complete an application form. Look at our how to apply webpage for more information.

How to apply for a research degree
Our step-by-step guide will help you to make the most out of your application for a research degree

Scholarships and funding
Explore our funding options, including scholarships and Doctoral Loans.

Writing a Research Proposal
- Parts of a Research Proposal
- Structure of a Research Proposal

Common Proposal Writing Mistakes
Preventing common writing mistakes.
- Proposal Writing Resources
According to Wong (2002) and Locke et al. (2007), there are common mistakes that people make when writing a research proposal:
- Not providing context to the research question(s).
- Not citing significant studies ("landmark studies") in the field that changed others' understanding of the topic.
- Not accurately presenting other research done on the topic.
- Not staying focused on the primary research question.
- Not focusing on the study's primary objective or paying too much attention to minor things (not focusing on the big picture).
- Trying to change the reader's opinions on topics that are not relevant to understanding the project.
- Using the proposal to take a stance on a particular political or social issue.
- Failing to have a clear sense of direction (proposals should flow like a research paper).
- Making the proposal too long or too short.
- Using APA style improperly.
- Using too many citations (only use what you need).
- Not proofreading for grammar and spelling errors.
Making these mistakes can reduce the probability of gaining the favor of your evaluators, so it is critical that you avoid these common mistakes!
Below are some tips that will help you avoid making common proposal writing mistakes (Wallwork and Southern, 2020):
- If you feel overwhelmed with the thought of writing a proposal, start with creating an outline. This will place your main ideas on paper and prevent you from getting sidetracked. You can use the outline as a guide to write your proposal once it is complete.
- Make an effort to "sell" your work. Many people assume reviewers will automatically understand the importance of your proposed study, but you should assume that they know nothing about your topic.
- Make sure your proposal follows the instructions and guidelines of your assignment prompt or instructions. This includes having proper document formatting.
- Ensure that your proposal is visually pleasing and easy to read. Reviewers will not want to spend time on your proposal if it is not easy to follow.
- Check spelling and grammar on your own before or after using a proofreading service. Language editing programs like Grammarly can improve the quality of your writing, but it may not catch everything that should be edited or changed.
- << Previous: Structure of a Research Proposal
- Next: Proposal Writing Resources >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2023 10:46 AM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/writingaresearchproposal
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Research Grant Proposal Writing Course for Students in Higher Institutions
Genevieve dable-tupas.
1 Research Center, College of Medicine, Davao Medical School Foundation Inc., Davao, The Philippines.
Victoria Toralba-Lupase
2 Graduate School, Davao Medical School Foundation, Inc., Davao City, Philippines.
Juan C. Puyana
3 MD, FRCSC, FACS, FACCP. School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Professor of Surgery, Critical Care Medicine, and Clinical Translational Science, Director for Global Health-Surgery, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, United States. Editorial Board Member, IJMS.
Mihnea-Alexandru Găman
4 Carol Davila” University of Medicine and Pharmacy. Department of Hematology, Center of Hematology and Bone Marrow Transplantation, Fundeni Clinical Institute. Alumnus, Society of Students in Medicine of Bucharest (SSMB), Bucharest, Romania. Scientific Editor, IJMS.
Research grant proposals have become part of the everyday life of every scientist working in the field of life sciences. Although most early career researchers begin working on research grant proposals during their doctorate, laying the foundation of this complicated task should occur during their undergraduate training. This editorial serves as an introduction into research grant proposal writing for students enrolled in higher education and tackles subjects such as choosing a research topic and writing a successful grant application, as well as possible challenges and funding opportunities that we considered appropriate for students and early career researchers.
Introduction
Writing a research proposal is already a big challenge in itself. How much more if you write a research proposal to seek funding? Can we do it? How? The answers to these questions are provided in this editorial. While it is true that writing a research proposal is indeed a challenging task, it does not mean that it is impossible. It does take time and a lot of effort, but once you have done it, getting someone to fund it, is not much of a problem anymore. A lot of funding agencies, local, national and international are willing to fund research projects that are sound, innovative and have the potential to help improve the way we do things, the environment and the community.
So where do we start? We begin by conceptualizing a research question that seeks to answer or clarify a certain need or problem. The research question can come from daily experiences and challenges. It can be a local, national or global issue or problem that needs to be clarified, improved or addressed. An example of a global problem that needs solutions would be climate change. In developing and tropical countries like the Philippines, research on Dengue Fever can be considered relevant. Most recently is the emergence of a new infectious viral disease, the novel Coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19). Ideas that would seek to address these problems are good research topics to work on. Since these problems pose great impact for society, naturally, many agencies would support research innovations that offer potential solutions to such. This is where we start.
Choosing a Research Topic
In everyday life, we are confronted with so many problems. So how do we choose? You can approach this issue in several ways. Firstly, you may consider thinking about your potential beneficiaries. Who do you want to help? What subset of the population do you want to benefit from your project? For example, if you want to help the earthquake victims, then think of disaster related activities that can help improve the way we deal with natural calamities or disaster preparedness. Such ideas may address problems that have occurred before, during or after the disaster. In particular, you can think of ways on how to streamline the approach of distributing relief goods for the affected community so that these goods reach the victims in the earliest time possible while minimizing expenses. Secondly, you may opt to look for funding opportunities first that are in line with your expertise, then think of a particular problem you want to address. For example, you may just search the World Wide Web: look for legitimate websites like for the Philippines, Department of Health (DOH) or Department of Science and Technology (DOST) and scroll down on funding opportunities. 1 These websites usually give details on the research topics they prefer to fund. Choose a topic you are most interested in and that suits your expertise and write about it. These funding sites also have their own research proposal templates which you need to follow.
Writing the Research Proposal
Generally, the major components of a research proposal are the following: Introduction, Methodology, Results (Dummy tables), Timetable and Budget ( Figure 1 ). The following section presents the general contents of a research proposal as well as instructions on how to write each component. Normally, since we are still proposing something, we use the future tense especially in the Methodology section. There may be variations depending on the funding institution. Nevertheless, this section will just serve as a guide on how to develop your research proposal.

Major Components of a Research Proposal.
Preliminaries
Write the title of your research proposal. Some funding agencies may have specific formats for you to follow. There is no ideal number of words that should make up a research title although some sources advise to limit it to 10 to 15 words. 2 In our opinion, researchers should not limit themselves with a specific number of words but that the title should be as concise as possible, yet adequate enough to describe the contents and purpose of your research. Firstly, a good title predicts the content of the research paper. Secondly, a good title should be interesting to the reader. Thirdly, it should reflect the tone of the writing. Fourthly and finally, it should contain important keywords that will make it easier to be located during a keyword search. Avoid phrases like “A study on…” or “Analysis of…”; research titles are usually in the form of a phrase or less commonly a question. 2
Table of Contents
Arrange this section with main headings and subheadings with the following major parts, namely: Introduction, Methodology and Results. The Results section will only include dummy tables. Other important parts include the preliminaries, references, appendices, and curriculum vitae. 3
List of Tables
List the number and titles of tables as they appear in the body of the research proposal. The first table may start in the Methodology. 3
List of Figures
Make a list of figures and arrange in this section as they appear in the body of the research. The first figure may start in the Methodology. 3
Body of a Full-Blown Research Proposal
The full-blown proposal contains only three parts: Introduction, Methodology and Results (dummy tables only). 3
This part justifies the need to answer the main question you are designed to answer. It gives a clear idea about the seriousness of the problem. It sets the scene of the setting of the study that is to interest the reader. It starts with general ideas then moves down to specifics. This contains the background, review of related literature, theoretical framework, conceptual framework, objectives, hypothesis, and significance of the study. 3
Background of the Study
Writing the background of your study is like writing an interesting story that will engage your reader. Start with a brief provocative problem statement that is applicable to the theme of the study. This one statement should catch the attention of the reader. Include convincing arguments that will support the statement on the seriousness and urgency of the problem. Follow with facts/statistics that portray the problematic situation (global, national, regional, and local setting). Present a resume of events/programs/projects that have been done by various public and private sectors to address the problem. Indicate a firm stand on the need to bridge the gap between existing facts and the problematic situation. Indicate what should be done and what data are needed to address the problem. Present the rationale on the need to conduct the study. 4 – 5 The length of the write-up should not exceed three pages in double space setting. 3
Review of Related Literature
This section provides information on the background of the problem, theories that explain the existence of the problem and determinants, and previous studies done. Acquaint the reader with existing studies as to what has been found, who has done the work, when and where the latest studies have been conducted. Provide the reader with information on what research methods were utilized and provide information on what problems were met and how were they resolved. Use sub-headings and use past tense. 6 – 7 Establish the theoretical and conceptual framework for the research.
- Theoretical Framework - Make use of a theory or theories to explain why a phenomenon exists and how the different factors which brought about the phenomenon are interrelated. The purpose of the theoretical framework is to develop and present a unified explanation of related ideas and to provide the foundation on which the study will build and develop. 3 , 8
- Conceptual Framework - Make a diagram to present how different variables in the study are related to each other. It has the same function as the theoretical framework but instead of using theories, it uses constructs which are specific and well-defined. Explain how the different variables are related to each other. 3 , 8
These are statements of purpose for which the investigation is conducted. These serve as guides in the specification of variables, selection of research methods, determination of the data to be collected and planning of analysis of results.
For a quantitative study, state the General Objective by transforming the problem statement from an interrogative form to a declarative statement, usually introduced by the phrase “to determine”. State the specific objectives which are specific activities/questions that are desired to be done to answer the general objectives. These are statements of the specific outcomes expected in the study. 3 , 9
In a qualitative study, the objectives appear as a) “Grand Tour Question” as the main aim which is written in a declarative statement; and b) the sub-problems which are in the interrogative form. 3 , 10 Although the focus of this editorial is quantitative research, it is also good to note this distinction between quantitative and qualitative research in terms of objective formulation.
This section appears in the proposal only if the study determines relationship(s) or difference(s) between variables. This is an educated guess, an assertion or proposition about the interrelationship or about differences between two or more variables. If your study does not test causal relationships or differences between variables, do not use a hypothesis (e.g., in purely descriptive, diagnostic, or exploratory investigations). There are two types of hypotheses, the Null Hypothesis (statement of denial of an existence, attribute, relationship, difference, or an effect) and Alternative Hypothesis (statement of relationship, difference or an effect). Of these two, use the null hypothesis because errors in accepting or rejecting the hypothesis can be easily avoided. 3 , 11
Significance of the Study
State the value of the study or justification for making the study. Make a list of potential users and indicate the specific contribution of the results (findings, conclusions, recommendations) to these beneficiaries of the study. (Note: In the final research write-up, you have to integrate significance in the Discussion). 3
Methodology
This section provides a detailed description of the basic research plan or procedure on how the study will be done so that it will be reproduced by a competent colleague or that the procedures are needed to judge the validity of its answer. This may be a place to begin writing then return to introduction when a flow of words has already started. Include in this section the following parts: research design, setting, population, variables and measures (dependent and independent variables), sampling (design, randomization and estimation of sample size), data collection procedures and ethical considerations. 3 In the proposal, this chapter is written in future tense. In the final write-up, it is written in past tense.
Research Design
This refers to the plan of action, approach or strategy to be used in the study. Define the research design used, whether it is descriptive, cross-sectional, case-control, cohort or experimental, quasi-experimental, etc. Indicate who has the authority of such definition and cite the reference. 3
Describe the study area or the venue where the study will be conducted (e.g., hospital, university, research centre, etc.). Provide a justification for choosing the study area. A map may be shown when necessary. 3
Indicate the number and significant characteristics of the participants. Provide inclusion criteria (specific characteristics that make the participants qualified to participate in the study) and exclusion criteria (specific characteristics that render a certain segment of the population to be ineligible to be included in the study). 3
Variables and Measures
Variables are characteristics that are measured numerically (e.g. blood pressure) or in terms of categories (e.g. presence or absence of a disease, smoker or non-smoker, etc.). If your study determines a relationship between variables, write the dependent variable first. A dependent variable “hangs on” to another variable or is a putative effect of one or more variables. Then write the independent variable(s). This/these characteristic(s) is/are the assumed cause(s) or reason(s) for any variation of a dependent variable which is usually the problem in the study. 3
Specify the categories or classes of the dependent and independent variables in terms of scales of measurement. These maybe written in a form of a nominal (two or more categories that are qualitatively different from each other (e.g. place of delivery such as hospital and home); ordinal (ranked categories, e.g. severity of a disease); interval (zero does not indicate absence of attribute and equal differences between any pair of numbers in the scale indicate equal differences but not in the amounts of the attribute such as temperature); and ratio (zero indicates absence of attribute and equal differences between any pair of numbers is the same as that between the amounts of attribute being measured (e.g. hemoglobin concentration or scores in the examination). 3
Explain the process of choosing the samples that will represent the entire population. Include in this section three issues about sampling: i.e., sampling design, randomization, and estimation of sample size if appropriate.
Sampling design:
Explain the entire procedure on how the participants will be chosen. Choose the appropriate sampling design. There are two basic types of sampling designs namely non-probability or non-random or judgmental sampling (e.g. accidental and purposive) and probability sampling (e.g. simple random, systematic, stratified random, stratified systematic, cluster, two-stage and multi-stage designs). State the sampling frame, whether a spot map or a list will be used. 3
Randomization:
Describe the randomization procedure if needed in the study. This refers to the procedure where each participant is assigned to a treatment group or control group by chance (e.g. by random numbers) to reduce the influence of extraneous factors. 3
Estimation of sample size:
Show how sample size is derived using some formula for estimation of sample size. This is used to consider the availability of human resources and logistics. 3
Data Collection Procedure
Explain in detail how pre-testing or pilot testing will be conducted including the number of participants, recruitment, setting, and instrument to be pre-tested, procedures to be used in pre-testing. 3
Explain in detail how the data will be gathered, whether through observation method using instruments (like tape measure or weighing scale); personal interview using a structured interview schedule, self-administered interview, key informant interview and/or focus group discussion. Describe the instrument in terms of number and content of questions to be used, type of scale, how these are organized, and the method of validation. Attach a copy of the instrument in the appendix. Also describe here when the study will start and when it will end. Describe the enumerators in terms of their educational attainment, employment status, experience as interviewers/observers, method and duration of training for the study. 3
Data Analysis
Indicate the type of statistical test(s), decision making criteria (alpha level) and computer software that will be used in the study. Refer to the specific objectives as a guide in the identification of appropriate statistical tools. (Note: In the final research write-up, integrate data analysis in the Results. 3
Limitations of the Study
The limitations of the study should provide information on certain conditions which are beyond the control of the investigator. (Note: In the final paper, integrate limitations of the study in the Discussion). 3
Ethical Considerations
Describe the ethical issues that will be observed to protect the rights, safety, privacy, and sensitivity of laboratory animals and/or human participants as well as the researchers themselves, the community and the environment. If the study deals with human participants, state clearly how informed consent is obtained. This means that the participants will give their consent (by signing in the informed consent form) after they have been informed of the nature of the study, their roles in the study, risks and inconveniences, benefits for participation, compensation, provision for illness/injury, whom to contact, voluntariness of participation, and confidentially that must be carried out to secure their anonymity and privacy. Guidelines for ethical considerations can be accessed from the manual of the Research Ethics Committee of the institution in accordance with internationally approved ethical standards in the conduct of human research. 12 If the study deals with animals, it should be stated that extreme care must be observed in every step from the time these are purchased to the time that they are disposed of. These guidelines should be available and well stipulated in the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) Manual. 13 Take into consideration that any research project you conduct must also adhere to the local regulations, national law and the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008. 14 Do not forget to disclose any possible conflicts of interest or competing interests: research funding, honoraria from pharmaceutical companies, personal fees, payments for partaking in advisory boards, etc.
The results section of a research proposal will only contain the Dummy tables and/or figures which should be left empty until data have been collected and analyzed. The dummy tables and/or figures will depend on the specific objectives of your research. Roughly, there should be at least one table and/or figure per specific objective. 3
For example, if one specific objective states: To determine and compare the demographic data of the participants in the treatment and control group. For this type of objective, a table summarizing the demographic data of your population would be most appropriate.
Timetables or Gantt charts provide a visual presentation of the specific tasks that will be undertaken in the research project and their relative timing or expected length of time from start to completion of each task. 15 This gives the reader an idea on the chronological activities to be undertaken from the beginning to the end of the research project ( Table 2 ).
Sample Timetable for a One-Year Research Project.
| Activities | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signing of MOA | X | |||||||||||
| Hiring and Appointment of personnel | X | |||||||||||
| IACUC Clearance | X | |||||||||||
| Procurement | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Solvent Partitioning | X | |||||||||||
| In vivo screening of bloactivity | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Phytochemical Testing | X | X | ||||||||||
| Acutte Toxicity Testing | X | X | ||||||||||
| In vitro toxicity testing | X | |||||||||||
| In vitro efficacy studies | X | X | ||||||||||
| Standardization of bloactive calabash fractions | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Formulation of Tablet | X | |||||||||||
| Structure Elucidation | X | X | X | |||||||||
| Data Analysis | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Reporting of Findings | X |
A budget plan is a crucial part of every research proposal. If a funding agency has already been identified, just check the website and you will surely find a budget template which will serve as your guide. Generally, the basic parts of a budget proposal consist of the following: Personnel Services, Maintenance and Operating Expenses, and Supplies or Capital Outlay but the format may vary according to the preferred budget format of the funder. Personnel Services include honoraria of the researchers and salaries of research assistants who will help conduct the study. Maintenance and other operating expenses (MOOE) includes repairs and maintenance of facilities and equipment, supplies and materials, travelling and communication expenses and all expenses pertaining to the data collection and completion of the research. 16
A good budget proposal is often a reflection of well-planned research activities. It provides information on how the requested funds will be spent. As much as possible, the amount reflected in the budget should be based on actual costs. Additionally, some funders may require budget justification or explanations aside from the costing. 16 Please find below ( Table 3 ) an example of a budget proposal of one of our funded research projects.
Actual Example of a Budget Proposal for Funding.
| Item | Details | Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Salaries | One (1) URA II @ P 33,306.00 × 12mos | 399,672.00 |
| One (1) URA I @ P27,525.60 × 12mos | 330,307.20 | |
| One (1) Laboratory Aide I @ P 14,113.20 × 12 mos | 169,358.40 | |
| Honoraria | One (1) Project Leader @8,800 × 12 months | 105,600.00 |
| One (1) Project Staff III @7,500 × 12 months | 72,000.00 | |
| One (1) Project Staff II @6,000 × 12 months | 90,000.00 | |
| 1,166,937.60 | ||
| Traveling Expenses | Airfare, Accommodation, Per Diem allowance during sample collection and reporting | 350,000.00 |
| Communication Expenses | Monthly Prepaid cellphone load, internet | 10,000.00 |
| Repair and Maintenance of Facilities | Repair and calibration of equipment | 200,000.00 |
| Transportation and Delivery Expenses | Local Transportation, courier | 60,000.00 |
| Supplies and Materials Expenses | Office Supplies | 80,000.00 |
| Laboratory supplies | 1,420,000.00 | |
| Trainig and Extension Expenses | Training of URAs on XO inhibition assay at UP Diliman | 80,000.00 |
| Training of other DMSF Faculty and Personnel on TLDC SOP | 70,000.00 | |
| Rental Expenses | Vehicle Rental during sample collection, coordination meetings, etc. | 100,000.00 |
| Representation Expenses | Food during meetings and reporting | 30,000.00 |
| Professional Services | Consultancy (plant Authentication) @ P3,000 × 6 consultations | 18,000.00 |
| Consultancy (Sample Collection and Laboratory Analysis) @P3,000 × 4 consultations | 12,000.00 | |
| Consultancy (Auditor) @ P3,000 × 1 consultation | 9,000.00 | |
| Consultancy (Biostatistics) @P3,000 × 4 consultations | 12,000.00 | |
| Labor (field assistants for collection, transport, and processing) | 59,000.00 | |
| Other Maintenance and Operating Expenses | Analytical Services (Cytotoxicity testing by orthogonal assays) | 1,000,000.00 |
| Subtotal MOOE | 3,510,000.00 | |
| Honorarium for two (2) Proyects Support Staff Lever 2 @ P1,500/qtr x 4 qtr | 12,000.00 | |
| Honorarium for two (2) Proyects Support Staff Lever 1 @ P1,000/qtr x 4 qtr | 8,000.00 | |
| DOST Monitoring Costs | 80,000.00 | |
| Utilies | 250,770.00 | |
| Subtotal Indirect Cost | 350,770.00 | |
| Ultra-Low Freezer | 1,000,000.00 | |
| Recirculating chiler | 300,000.00 | |
| Rotary Evaporator with vacuum pump | 500,000.00 | |
| Vacuum concentrator | 1,200,000.00 | |
| Freeze dryer | 1,200,000.00 | |
| Heating mantle | 60,000.00 | |
| Grinder | 50,000.00 | |
| GPS tracker | 40,000.00 | |
| Subtotal CO/EO | 4,350,000.00 | |
| 9,377,707.60 |
Legend: Budget in Romanian leu. 1 Romanian leu equals 0.2 USD.
Writing a research proposal for funding is a very challenging and demanding job. Even if you are convinced that the problem or issue you want to address is relevant and has a big potential to change or improve the way we do things, we can never say 100% that it will be funded. The decision whether our proposal will be funded or not remains in the hands of the funding agency. To increase our chance to be funded, we need to seek guidance from the funding agencies themselves. We need to determine what types of research they prefer and what their needs are. Priority issues or problems that need solutions are usually included in the research agenda of the funding agency which we can access from their websites. Once we have set our goals on what research proposal we are going to pursue, we work on it to the best of our abilities. If ever we fail to get the funding the first time we submit our proposal, it does not mean we give up right away. Usually, the funding agencies will give their comments and recommendations on how to improve our proposal. If their recommendations are doable, then we can work on them, improve our proposal, and submit again. Hard work and perseverance will usually get you somewhere. We can also opt to submit our proposal to another funding agency, but we have to submit to only one funding agency at a time. Do not make the mistake of sending your proposal to several funding agencies at one time. This is not a good research practice.
Funding Opportunities for Students
Although the opportunities to receive funding as a student are small, opportunities may arise at any time during an aspiring young researcher’s career. In many instances, students should take into consideration that the first research proposal and grant that they present to the scientific world is their graduation thesis. Most of the time, their investigation is financed by their university or by research grants obtained by their supervisors and (or) coordinators. However, there are still some opportunities to apply for financing from professional societies. Fortunately, most international societies offer free membership for students, and we encourage you to join as many societies as possible and benefit from free lectures, workshops, or participation in congresses, as well as apply for travel and (or) accommodation grants as to partake in scientific events.
For example, the Association for Medical Education in Europe (AMEE) offers several awards and grants for students interested in medical education. The Student Initiatives Grant consists of a funding opportunity of £2000 ( https://amee.org/awards-prizes/student-initiatives-grant ) for students who would like to coordinate a project in the field of medical education. Another AMEE change to receive an imbursement (£10000) is the Research Grant Awards for an educational research project. 17 – 18 In addition, the pharmaceutical company AMGEN finances an undergraduate summer research program in Science and Biotechnology ( AMGEN Scholars Program ) for undergraduates willing to partake in a short research internship in a top-notch university in the United States, Canada, Europe, Australia or Asia, such as Harvard University, Yale University, Cambridge University, The Pasteur Institute, The Karolinska Institute, The University of Tokyo or The University of Melbourne. The AMGEN Foundation does not ask for previous experience in research for the students who want to apply. More details can be obtained at the following website: https://amgenscholars.com/ . 19
In addition, the American Society of Hematology (ASH) offers awards for Medical Students and Early-Career Investigators who are aspiring to conduct research in the field of Hematology or who want to pursue specialty training in Hematology. More information can be obtained at the following address: https://www.hematology.org/awards/medical-student . 20
In terms of courses and lectures, the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) organizes annual five-day courses for medical students who are interested in the field of Oncology. Some of the topics tackled during these scientific meetings are Breast Cancer, Colorectal Cancer, Lung Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Melanoma and other malignancies. Please access https://www.esmo.org/meetings/esmo-eso-courses-on-medical-oncology-for-medical-students to discover this opportunity. 21
Further Recommended Readings and Training Opportunities
Although there are less opportunities for students enrolled in higher education to submit grant applications and receive funding for their ideas, there are sufficient chances to receive free training in the field before starting to get involved in research projects. For example, Elsevier’s Researcher Academy ( https://researcheracademy.elsevier.com ) offers several free webinars and e-learning opportunities for researchers who want to improve their grasp of knowledge. The e-learning modules are focused on research preparation (funding, management of data, research collaborations), writing for research (manuscript preparation and book writing), the basics of the publication process, peer-review and methods to communicate your research findings. 22
Another opportunity for students to get involved in the process of manuscript and grant evaluation is The Web of Science Academy ( https://clarivate.com/webofsciencegroup/solutions/web-of-science-academy/ ) a peer-review training course available for free which enables researchers to become certified peer-reviewers. Applicants are mentored by experts in their field of research and the course is divided in 10 modules: introductory modules, an overview of peer-review and scientific journals, ethics, how to evaluate different sections of a paper (introduction, methodology, data and results, discussions, conclusions) and how to structure a review. 23
In summary, we have given you a guide on how to make a research proposal for funding from conceptualization to execution to facing the challenges and more. 24 Writing a research proposal for funding is hard work and very challenging. However, if you succeed, it is also very rewarding, not as much financially but more so on the potential of improving the lives of the people in the community and in contributing to the body of knowledge which can benefit humanity.
Sample Table of Contents. 3
| Table of Contents | Page |
|---|---|
| Title Page | |
| List of Tables | |
| List of Figures | |
| Introduction | |
| Background | |
| Review of Related Literature | |
| Theoretical framework | |
| Conceptual framework | |
| Objectives | |
| Significance of the Study | |
| Methodology | |
| Research Design | |
| Setting | |
| Population | |
| Variables and Measures | |
| Sampling | |
| Sampling Design | |
| Randomization | |
| Estimation of Sample size | |
| Data collection Procedure | |
| Data Analysis | |
| Limitations of the Study | |
| Ethical Consideration | |
| Results (Dummy Tables) | |
| Timetable | |
| Budget | |
| References | |
| Curriculum Vitae | |
| Appendices |
Acknowledgments
M.-A.G. acknowledges the support of the Society of Students in Medicine of Bucharest (SSMB) - research grant competition for students, contract no. 231/29.03.2017.
Dr. Juan C. Puyana work is partially funded by the National Institute of Health (NIH) of the United States with the grant 5UG3HL151595. The opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not reflect the view of the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Health and Human Services, or the United States government.
Conflict of Interest Statement & Funding
The Authors have no financial relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
Published on November 6, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023.
A problem statement is a concise and concrete summary of the research problem you seek to address. It should:
- Contextualize the problem. What do we already know?
- Describe the exact issue your research will address. What do we still need to know?
- Show the relevance of the problem. Why do we need to know more about this?
- Set the objectives of the research. What will you do to find out more?
Table of contents
When should you write a problem statement, step 1: contextualize the problem, step 2: show why it matters, step 3: set your aims and objectives.
Problem statement example
Other interesting articles
Frequently asked questions about problem statements.
There are various situations in which you might have to write a problem statement.
In the business world, writing a problem statement is often the first step in kicking off an improvement project. In this case, the problem statement is usually a stand-alone document.
In academic research, writing a problem statement can help you contextualize and understand the significance of your research problem. It is often several paragraphs long, and serves as the basis for your research proposal . Alternatively, it can be condensed into just a few sentences in your introduction .
A problem statement looks different depending on whether you’re dealing with a practical, real-world problem or a theoretical issue. Regardless, all problem statements follow a similar process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The problem statement should frame your research problem, giving some background on what is already known.
Practical research problems
For practical research, focus on the concrete details of the situation:
- Where and when does the problem arise?
- Who does the problem affect?
- What attempts have been made to solve the problem?
Theoretical research problems
For theoretical research, think about the scientific, social, geographical and/or historical background:
- What is already known about the problem?
- Is the problem limited to a certain time period or geographical area?
- How has the problem been defined and debated in the scholarly literature?
The problem statement should also address the relevance of the research. Why is it important that the problem is addressed?
Don’t worry, this doesn’t mean you have to do something groundbreaking or world-changing. It’s more important that the problem is researchable, feasible, and clearly addresses a relevant issue in your field.
Practical research is directly relevant to a specific problem that affects an organization, institution, social group, or society more broadly. To make it clear why your research problem matters, you can ask yourself:
- What will happen if the problem is not solved?
- Who will feel the consequences?
- Does the problem have wider relevance? Are similar issues found in other contexts?
Sometimes theoretical issues have clear practical consequences, but sometimes their relevance is less immediately obvious. To identify why the problem matters, ask:
- How will resolving the problem advance understanding of the topic?
- What benefits will it have for future research?
- Does the problem have direct or indirect consequences for society?
Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it.
The research aim is the overall purpose of your research. It is generally written in the infinitive form:
- The aim of this study is to determine …
- This project aims to explore …
- This research aims to investigate …
The research objectives are the concrete steps you will take to achieve the aim:
- Qualitative methods will be used to identify …
- This work will use surveys to collect …
- Using statistical analysis, the research will measure …
The aims and objectives should lead directly to your research questions.
Learn how to formulate research questions
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
You can use these steps to write your own problem statement, like the example below.
Step 1: Contextualize the problem A family-owned shoe manufacturer has been in business in New England for several generations, employing thousands of local workers in a variety of roles, from assembly to supply-chain to customer service and retail. Employee tenure in the past always had an upward trend, with the average employee staying at the company for 10+ years. However, in the past decade, the trend has reversed, with some employees lasting only a few months, and others leaving abruptly after many years.
Step 2: Show why it matters As the perceived loyalty of their employees has long been a source of pride for the company, they employed an outside consultant firm to see why there was so much turnover. The firm focused on the new hires, concluding that a rival shoe company located in the next town offered higher hourly wages and better “perks”, such as pizza parties. They claimed this was what was leading employees to switch. However, to gain a fuller understanding of why the turnover persists even after the consultant study, in-depth qualitative research focused on long-term employees is also needed. Focusing on why established workers leave can help develop a more telling reason why turnover is so high, rather than just due to salaries. It can also potentially identify points of change or conflict in the company’s culture that may cause workers to leave.
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives This project aims to better understand why established workers choose to leave the company. Qualitative methods such as surveys and interviews will be conducted comparing the views of those who have worked 10+ years at the company and chose to stay, compared with those who chose to leave.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 20). How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/problem-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to define a research problem | ideas & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Organizing Academic Research Papers: Writing a Research Proposal
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The goal of a research proposal is to present and justify a research idea you have and to present the practical ways in which you think this research should be conducted. The forms and procedures for such research are defined by the field of study, so guidelines for research proposals are generally more exacting and less formal than a project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews and must provide persuasive evidence that there is a need for the research study being proposed. In addition to providing rationale for the proposed research, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and/or benefits derived from the study.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.
How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study.
- Help learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to ensure a research problem has not already been answered [or you may determine the problem has been answered ineffectively] and, in so doing, become familiar with scholarship related to your topic.
- Improve your general research and writing skills.
- Practice identifying what logical steps must be taken to accomplish one's research goals.
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of doing scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a complete research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the results of the study and your analysis of those results. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing. It is, therefore, important that your writing is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succient in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to research.
- Why do you want to do it? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of study. Be sure to answer the "So what? question.
- How are you going to do it? Be sure that what you propose is doable.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise; being "all over the map" without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review.
- Failure to delimit the contextual boundaries of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.].
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research.
- Failure to stay focused on the research question; going off on unrelated tangents.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing. Poor grammar.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal . The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal . Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal . International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing a traditional research paper, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout the social sciences. Most proposals are between ten and fifteen pages in length. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study, and why?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on my topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In the end, your research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and highlight enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like--"Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
In general your proposal should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write your doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to sense your passion for the topic and be excited about its possible outcomes.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in one to three paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Why is this important research, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes from the study?
II. Background and Significance
This section can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and flow of your proposal. This is where you explain the context of your project and outline why it's important. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the research problem; instead, you must choose what is relevant to help explain your goals for the study.
To that end, while there are no hard and fast rules, you should attempt to deal with some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction.
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing. Answer the "So what? question [i.e., why should anyone care].
- Describe the major issues or problems to be addressed by your research.
- Explain how you plan to go about conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to the analysis of your topic.
- Set the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus.
- Provide definitions of key concepts or terms, if necessary.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methods they've used, and what is your understanding of their findings. Assess what you believe is still missing, and state how previous research has failed to examine the issue that your study addresses.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your study in relation to that of other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically describing materials one at a time.
To help frame your proposal's literature review, here are the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite : keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches and controversies expressed in the literature: what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, etc.] .
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, or synthesize what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research . As a consequence, the reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. The objective here is to ensure that the reader is convinced that your overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem. Your design and methods should be absolutely and unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to collect information, about the techniques you will use to analyze it, and about tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places or times].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover these issues:
- Specify the research operations you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results of these operations in relation to your research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while doing it.
- Keep in mind that a methodology is not just a list of research tasks; it is an argument as to why these tasks add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to perform does not demonstrate that they add up to the best feasible approach.
- Be sure to anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to get around them.
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, it doesn't mean that you can skip talking about the process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results of your study will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to the theoretical framework that frames the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the "real world"?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented, and what innovations will come about?
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief recap of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why your research study is unique, why it advances knowledge, and why the research problem is worth investigating.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study was done,
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempted to answer,
- The research design and methods used,
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem, and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so speak with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- lists only the literature that you actually used or cited in your proposal.
- Bibliography -- lists everything you used or cited in your proposal with additional citations of any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to make sure the project will complement and not duplicate the efforts of other researchers. Start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [i.e., education=APA; history=Chicago, etc]. This section normally does not count towards the total length of your proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal . Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences. Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal . The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. Developing and Writing a Research Proposal. In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills. Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal . Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal . International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books . The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal . University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Policy Memo
- Next: Acknowledgements >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

EFL students’ difficulties in writing a research proposal

International Journal of Humanities and Innovation (IJHI)
This study aims to investigate EFL students’ difficulties in writing a research proposal by using Swales’ Create-A-Research-Space (cars) model and try to find out the students’ problems. This study was used as a qualitative research design. The subject of this study are twenty students and the instrument are students writing the research proposal, interview for the students and lecturer. The result of this research is the students’ problem in writing for their introduction for move 1 (75%) and for move 2 (55%), there are 4 (four) students having problems how to face the criteria for inclusion and exclusion from review was not justified and the literature review was not topic focused. Related to methodology, the choice of paradigm, methodology, data collection, and data analysis was not justified to answer the research questions (20%). Next, a detailed description of the research procedures, as well as an explanation of the reason for doing so, was not provided (15%). Continued to th...
Related Papers
Acitya : Journal of Teaching and Education
Yanti Sri Rezeki
Teuku Zulfikar
PIONEER: Journal of Language and Literature
Nina Inayati
Generating ideas plays the key role in the initial phase of writing process, but not many empirical research is available in the literature that address the problems that students face in generating ideas, especially during research proposal writing. The current study aims to find out students’ problems in generating ideas in writing the research proposal. This descriptive study mainly collected the data through survey and interview involving seventh semester students who were in their initial phase of drafting research proposal for their final projects. The data were then analyzed and presented using descriptive quantitative method. The findings indicate that most of the students’ reported facing problems when generating ideas during the initial phase of research writing. Data analysis show that the problems range from the topic development, theoretical frameworks identification, relevant theory search, trusted sources evaluation, research ideas and relevant theory connection, as w...
European Journal of Special Education Research
Fawaz Qasem
Research, by its nature, is a critical challenging task requires in depth knowledge of the subject matter, planning, care, and hard work. From the students' point of view, this paper attempts to explore the challenges that are faced by undergraduates when they are writing proposals and research projects at the early stages. The study target group comprised undergraduates in the final year in the College of Science and Arts, Al-Namas, University of Bisha, Saudi Arabia. Around 60 subjects participated in this study and they were from Department of English and Department of Computer Science who conducted their research projects in English as Second Language (ESL). The Research tools of the study include questionnaire and informal interviews with students and teachers of the target groups. Clearly, the results from study showed that around 70 % of the participants who are writing research or conducting research projects in English is one of the predominant challenges for them. Around 50% prefer to conduct their research in L1. The study explored various and common challenges/difficulties during writing the research proposals and projects such as: difficulty in deciding the topic for research, lack of good knowledge of the methodology, inability of finding modern, specialized and related references, lack of interest in research, lack of understanding of the subject matter, lack of time, and research guiding. The study also attempts to give some suggestions/recommendations for developing the process of writing research proposals and research projects.
kheryadi kheryadi
This research aims to investigate the students' ability and problems in writing introduction section of research proposal. This study has been conducted in an undergraduate English study program a University in Banten. The documentation/selection of students' research proposal was conducted by choosing nine students' research proposals from fifty seven students to represent different levels of achievement. It uses text analysis and in-depth interview to investigate the students' performance in writing a research proposal. These findings implicate that most students faced difficulties in presenting arguments in terms of justifications. Second, most students were not aware that there are standard models in writing a research proposal, especially in terms of its elements and linguistic features, which are widely accepted in the field of English Language Teaching (ELT). This study supports the extensive research into academic writing that emphasizes the importance of explicit teaching of the structure of specific written genres, particularly a research proposal, to second-language students.
International Journal of Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences
IJHASS Journal
The current study aims at investigating the difficulties encountering Jordanian EFL students in the writing problem statement section. The study grouped those difficulties into two main categories, namely academic skills difficulties and language skills difficulties. It has been noticed that undergraduate as well as postgraduate students, lack the required skills enabling them to conduct a well-constructed research article, which sparkles the idea of this study. In addition, no previous study has examined the challenges encountered by Jordanian EFL students when conducting a research paper in general and the problem statement section in particular. For the purpose of collecting the required data of the present study, twenty Jordanian EFL students had a teaching program about research writing skills. They were introduced thoroughly to all sections of the research article, with special emphasis on the research problem, section which is the main concern of this study following that the participants were given a month period to accomplish their research papers before submission. The results of the study reveal that the participants lack the academic skills enabling them to conduct a well-constructed problem statement section. More specifically, the vast majority of the participants fail to provide an overview of their topics and to identify their research gap within the current literature. The study also shows that the participants face serious grammatical errors when writing research problem section. It could be concluded that conducting a scholarly research article in general and problem statement, in particular, is a demanding issue and need to be further highlighted by researchers and academicians to identify the challenges facing learners.
Allure Journal
ikariya sugesti
Learning strategies assist students in revealing their individual learning style, recognizing their identity as “learners”, and being conscious of their learning obstacles. The current study aimed to investigate the strategies in writing research background encountered by English Department students at one of Cirebon’s institutions throughout the academic year 2021/2022. This study employed a qualitative technique with a case study design, with thirty students participating as respondents. The data was gathered via a questionnaire and an interview. There are two research instruments in this research, especially close-ended questionnaire and semi-structured interview.The instruments were also distributed in Bahasa Indonesia. According to the findings, students adopted strategies such as reviewing the references of journal articles. This causes students to use strategies to reduce these difficulties, including reading reference journals or articles. The score using this strategy is 95...
Zimbabwe Journal of Educational Research
morrin phiri
Advances in Language and Literary Studies
MIRRAH DIYANA MAZNUN
This study was conducted to investigate the difficulties encountered by undergraduate ESL students in writing the introduction section of their project reports. Five introduction sections of bachelor of arts students, majoring in English language, were analyzed and a lecturer was interviewed regarding the areas of the students’ weaknesses. Swales’ create-a-research-space (cars) model was used as the analytical framework of the study. The results revealed that students confronted problems in writing their introduction for each move especially for move 2, which consists of counter claiming, indicating research gap, raising questions from previous research and continuing tradition. It was also found that the students had difficulty in writing the background of the study, theoretical framework, and statement of the problem which indicated their unawareness of the appropriate rhetorical structure of the introduction section.
norizan razak
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Loquen: English Studies Journal
Education India: A Quarterly Refereed Journal of Dialogues on Education
Shubham kumar Sanu , Vishwa Raj Sharma , Dr Mukesh Kumar , Smriti Shreya
Open University Research Sessions
Dr. Inoka Deepthinee Dediwala
S M Mukarram Jahan
IOSR Journal of Research & Method in Education (IOSRJRME)
Selviana Napitupulu
Journal Academica, Volume 1, July 2010, p. 1-5. [ISSN 2026 559X]
Hungarian Educational Research Journal
chahrazed hamzaoui
abasynuniv.edu.pk
Flora Maleki
International Journal of Learning, Teaching and Educational Research
Hendrikus Male
Language Circle: Journal of Language and Literature
ngudi wahyuni
Anas Iftikhar
The Scientific Journal of Cihan University – Sulaimaniya
Barham S Abdulrahman
European Diabetes Nursing
Shamim Hosen
The Indian Review of World Literature in English
Muhammad Javed
Stevejobs.education
Dr. David Annan
Roger Hurcombe
The Educational Review, USA
maria Fareed
International Journal of Multicultural and Multireligious Understanding
Journal of Information Management and Practices
Nareen Hashmi
Review of Applied Management and Social Sciences
hassan raza
Renaldi Bimantoro
IOSR Journals
Studies in Linguistics and Literature
Md. A M I R Hossain
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Open access
- Published: 04 September 2024
Insights into research activities of senior dental students in the Middle East: A multicenter preliminary study
- Mohammad S. Alrashdan 1 , 2 ,
- Abubaker Qutieshat 3 , 4 ,
- Mohamed El-Kishawi 5 ,
- Abdulghani Alarabi 6 ,
- Lina Khasawneh 7 &
- Sausan Al Kawas 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 967 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Despite the increasing recognition of the importance of research in undergraduate dental education, limited studies have explored the nature of undergraduate research activities in dental schools in the Middle East region. This study aimed to evaluate the research experience of final year dental students from three dental schools in the Middle East.
A descriptive, cross-sectional study was conducted among final-year dental students from three institutions, namely Jordan University of Science and Technology, University of Sharjah (UAE), and Oman Dental College. Participants were asked about the nature and scope of their research projects, the processes involved in the research, and their perceived benefits of engaging in research.
A total of 369 respondents completed the questionnaire. Cross-sectional studies represented the most common research type (50.4%), with public health (29.3%) and dental education (27.9%) being the predominant domains. More than half of research proposals were developed via discussions with instructors (55.0%), and literature reviews primarily utilized PubMed (70.2%) and Google Scholar (68.5%). Regarding statistical analysis, it was usually carried out with instructor’s assistance (45.2%) or using specialized software (45.5%). The students typically concluded their projects with a manuscript (58.4%), finding the discussion section most challenging to write (42.0%). The research activity was considered highly beneficial, especially in terms of teamwork and communication skills, as well as data interpretation skills, with 74.1% of students reporting a positive impact on their research perspectives.
Conclusions
The research experience was generally positive among surveyed dental students. However, there is a need for more diversity in research domains, especially in qualitative studies, greater focus on guiding students in research activities s, especially in manuscript writing and publication. The outcomes of this study could provide valuable insights for dental schools seeking to improve their undergraduate research activities.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The importance of research training for undergraduate dental students cannot be overstressed and many reports have thoroughly discussed the necessity of incorporating research components in the dental curricula [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. A structured research training is crucial to ensure that dental graduates will adhere to evidence-based practices and policies in their future career and are able to critically appraise the overwhelming amount of dental and relevant medical literature so that only rigorous scientific outcomes are adopted. Furthermore, a sound research background is imperative for dental graduates to overcome some of the reported barriers to scientific evidence uptake. This includes the lack of familiarity or uncertain applicability and the lack of agreement with available evidence [ 5 ]. There is even evidence that engagement in research activities can improve the academic achievements of students [ 6 ]. Importantly, many accreditation bodies around the globe require a distinct research component with clear learning outcomes to be present in the curriculum of the dental schools [ 1 ].
Research projects and courses have become fundamental elements of modern biomedical education worldwide. The integration of research training in biomedical academic programs has evolved over the years, reflecting the growing recognition of research as a cornerstone of evidence-based practice [ 7 ]. Notwithstanding the numerous opportunities presented by the inclusion of research training in biomedical programs, it poses significant challenges such as limited resources, varying levels of student preparedness, and the need for faculty development in research mentorship [ 8 , 9 ]. Addressing these challenges is essential to maximize the benefits of research training and to ensure that all students can engage meaningfully in research activities.
While there are different models for incorporating research training into biomedical programs, including dentistry, almost all models share the common goals of equipping students with basic research skills and techniques, critical thinking training and undertaking research projects either as an elective or a summer training course, or more commonly as a compulsory course required for graduation [ 2 , 4 , 10 ].
Dental colleges in the Middle East region are not an exception and most of these colleges are continuously striving to update their curricula to improve the undergraduate research component and cultivate a research-oriented academic teaching environment. Despite these efforts, there remains a significant gap in our understanding of the nature and scope of student-led research in these institutions, the challenges they face, and the perceived benefits of their research experiences. Furthermore, a common approach in most studies in this domain is to confine data collection to a single center from a single country, which in turn limits the value of the outcomes. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to conduct studies with representative samples and preferably multiple institutions in order to address the existing knowledge gaps, to provide valuable insights that can inform future curricular improvements and to support the development of more effective research training programs in dental education across the region. Accordingly, this study was designed and conducted to elucidate some of these knowledge gaps.
The faculty of dentistry at Jordan University of Science and Technology (JUST) is the biggest in Jordan and adopts a five-year bachelor’s program in dental surgery (BDS). The faculty is home to more than 1600 undergraduate and 75 postgraduate students. The college of dental medicine at the University of Sharjah (UoS) is also the biggest in the UAE, with both undergraduate and postgraduate programs, local and international accreditation and follows a (1 + 5) program structure, whereby students need to finish a foundation year and then qualify for the five-year BDS program. Furthermore, the UoS dental college applies an integrated stream-based curriculum. Finally, Oman Dental College (ODC) is the sole dental school in Oman and represents an independent college that does not belong to a university body.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the research experience of final year dental students from three major dental schools in the Middle East, namely JUST from Jordan, UoS from the UAE, and ODC from Oman. Furthermore, the hypothesis of this study was that research activities conducted at dental schools has no perceived benefit for final year dental students.
The rationale for selecting these three dental schools stems from the diversity in the dental curriculum and program structure as well as the fact that final year BDS students are required to conduct a research project as a prerequisite for graduation in the three schools. Furthermore, the authors from these dental schools have a strong scholarly record and have been collaborating in a variety of academic and research activities.
Materials and methods
The current study is a population-based descriptive cross-sectional observational study. The study was conducted using an online self-administered questionnaire and targeted final-year dental students at three dental schools in the Middle East region: JUST from Jordan, UoS from the UAE, and ODC from Oman. The study took place in the period from January to June 2023.
For inclusion in the study, participants should have been final-year dental students at the three participating schools, have finished their research project and agreed to participate. Exclusion criteria included any students not in their final year, those who have not conducted or finished their research projects and those who refused to participate.
The study was approved by the institutional review board of JUST (Reference: 724–2022), the research ethics committee of the UoS (Reference: REC-22-02-22-3) as well as ODC (Reference: ODC-MA-2022-166). The study adhered to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines [ 11 ]. The checklist is available as a supplementary file.
Sample size determination was based on previous studies with a similar design and was further confirmed with a statistical formula. A close look at the relevant literature reveals that such studies were either targeting a single dental or medical school or multiple schools and the sample size generally ranged from 158 to 360 [ 4 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 ]. Furthermore, to confirm the sample size, the following 2-step formula for finite population sample size calculation was used [ 13 ]:
Wherein Z is the confidence level at 95% =1.96, P is the population proportion = 0.5, and E is the margin of error = 0.05. Based on this formula, the resultant initial sample size was 384.
Wherein n is the initial sample size = 384, N is the total population size (total number of final year dental students in the 3 schools) = 443. Based on this formula, the adjusted sample size was 206.
An online, self-administered questionnaire comprising 13 questions was designed to assess the research experience of final year dental students in the participating schools. The questionnaire was initially prepared by the first three authors and was then reviewed and approved by the other authors. The questionnaire was developed following an extensive review of relevant literature to identify the most critical aspects of research projects conducted at the dental or medical schools and the most common challenges experienced by students with regards to research project design, research components, attributes, analysis, interpretation, drafting, writing, and presentation of the final outcomes.
The questionnaire was then pretested for both face and content validity. Face validity was assessed by a pilot study that evaluated clarity, validity, and comprehensiveness in a small cohort of 30 students. Content validity was assessed by the authors, who are all experienced academics with remarkable research profiles and experience in supervising undergraduate and postgraduate research projects. The authors critically evaluated each item and made the necessary changes whenever required. Furthermore, Cronbach’s alpha was used to assess the internal consistency/ reliability of the questionnaire and the correlation between the questionnaire items was found to be 0.79. Thereafter, online invitations along with the questionnaire were sent out to a total of 443 students, 280 from JUST, 96 from UoS and 67 from ODC, which represented the total number of final year students at the three schools. A first reminder was sent 2 weeks later, and a second reminder was sent after another 2 weeks.
In addition to basic demographic details, the questionnaire comprised questions related to the type of study conducted, the scope of the research project, whether the research project was proposed by the students or the instructors or both, the literature review part of the project, the statistical analysis performed, the final presentation of the project, the writing up of the resultant manuscript if applicable, the perceived benefits of the research project and finally suggestions to improve the research component for future students.
The outcomes of the study were the students’ research experience in terms of research design, literature review, data collection, analysis, interpretation and presentation, students’ perceived benefits from research, students’ perspective towards research in their future career and students’ suggestions to improve their research experience.
The exposures were the educational and clinical experience of students, research supervision by mentors and faculty members, and participation in extracurricular activities, while the predictors were the academic performance of students, previous research experience and self-motivation.
The collected responses were entered into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet and analyzed using SPSS Statistics software, version 20.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive data were presented as frequencies and percentages. For this study, only descriptive statistics were carried out as the aim was not to compare and contrast the three schools but rather to provide an overview of the research activities at the participating dental schools.
The heatmap generated to represent the answers for question 11 (perceived benefits of the research activity) was created using Python programming language (Python 3.11) and the pandas, seaborn, and matplotlib libraries. The heatmap was customized to highlight the count and percentage of responses in each component, with the highest values shown in red and the lowest values shown in blue.
Potentially eligible participants in this study were all final year dental students at the three dental schools (443 students, 280 from JUST, 96 from UoS and 67 from ODC). All potentially eligible participants were confirmed to be eligible and were invited to participate in the study.
The total number of participants included in the study, i.e. the total number of students who completed the questionnaire and whose responses were analyzed, was 369 (223 from JUST, 80 from UoS and 66 from ODC). The overall response rate was 83.3% (79.6% from JUST, 83.3% from UoS and 98.5% from ODC).
The highest proportion of participants were from JUST ( n = 223, 60.4%), followed by UoS ( n = 80, 21.7%), and then ODC ( n = 66, 17.9%). The majority of the participants were females ( n = 296, 80.4%), while males represented a smaller proportion ( n = 73, 19.6%). It is noteworthy that these proportions reflect the size of the cohorts in each college.
With regards to the type of study, half of final-year dental students in the 3 colleges participated in observational cross-sectional studies (i.e., population-based studies) ( n = 186, 50.4%), while literature review projects were the second most common type ( n = 83, 22.5%), followed by experimental studies ( n = 55, 14.9%). Longitudinal studies randomized controlled trials, and other types of studies (e.g., qualitative studies, case reports) were less common, with ( n = 5, 1.4%), ( n = 10, 2.7%), and ( n = 30, 8.1%) participation rates, respectively. Distribution of study types within each college is shown Fig. 1 .
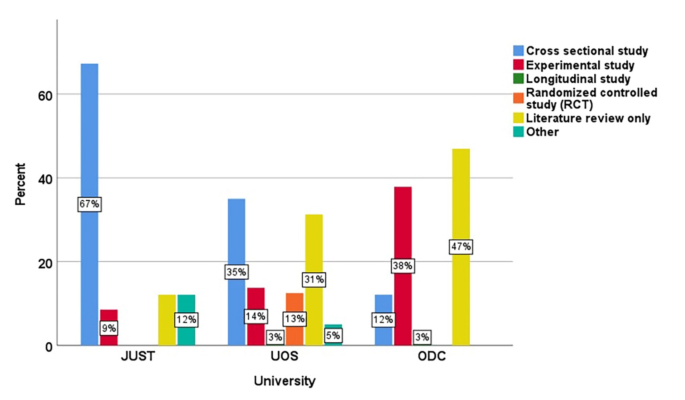
Distribution in percent of study types within each college. JUST: Jordan University of Science and Technology, UOS: University of Sharjah, ODC: Oman Dental College
The most common scope of research projects among final-year dental students was in public health/health services ( n = 108, 29.3%) followed by dental education/attitudes of students or faculty ( n = 103, 27.9%) (Fig. 2 ). Biomaterials/dental materials ( n = 62, 16.8%) and restorative dentistry ( n = 41, 11.1%) were also popular research areas. Oral diagnostic sciences (oral medicine/oral pathology/oral radiology) ( n = 28, 7.6%), oral surgery ( n = 12, 3.2%) and other research areas ( n = 15, 4.1%) were less common among the participants. Thirty-two students (8.7%) were engaged in more than one research project.
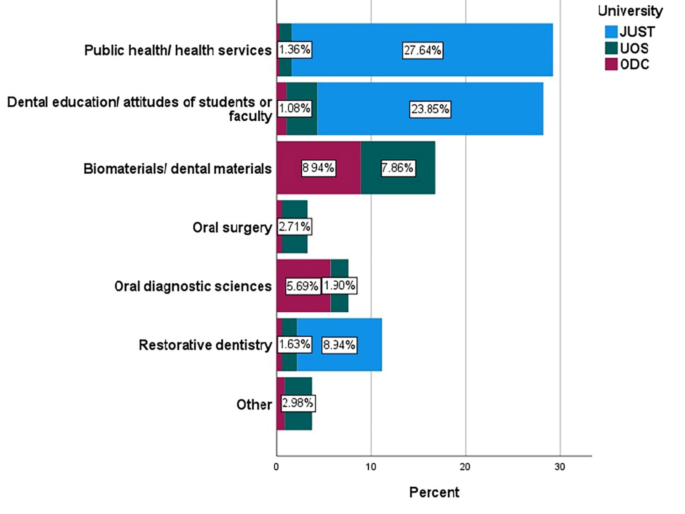
Percentages of the scope of research projects among final-year dental students. JUST: Jordan University of Science and Technology, UOS: University of Sharjah, ODC: Oman Dental College
The majority of research projects were proposed through a discussion and agreement between the students and the instructor (55.0%). Instructors proposed the topic for 36.6% of the research projects, while students proposed the topic for the remaining 8.4% of the projects.
Most dental students (79.1%) performed the literature review for their research projects using internet search engines. Material provided by the instructor was used for the literature review by 15.5% of the students, while 5.4% of the students did not perform a literature review. More than half of the students ( n = 191, 51.7%) used multiple search engines in their literature search. The most popular search engines for literature review among dental students were PubMed (70.2% of cases) and Google Scholar (68.5% of cases). Scopus was used by 12.8% of students, while other search engines were used by 15.6% of students.
The majority of dental students ( n = 276, 74.8%) did not utilize the university library to gain access to the required material for their research. In contrast, 93 students (25.2%) reported using the university library for this purpose.
Dental students performed statistical analysis in their projects primarily by receiving help from the instructor ( n = 167, 45.2%) or using specialized software ( n = 168, 45.5%). A smaller percentage of students ( n = 34, 9.4%) consulted a professional statistician for assistance with statistical analysis. at the end of the research project, 58.4% of students ( n = 215) presented their work in the form of a manuscript or scientific paper. Other methods of presenting the work included PowerPoint presentations ( n = 80, 21.7%) and discussions with the instructor ( n = 74, 19.8%).
For those students who prepared a manuscript at the conclusion of their project, the most difficult part of the writing-up was the discussion section ( n = 155, 42.0%), followed by the methodology section ( n = 120, 32.5%), a finding that was common across the three colleges. Fewer students found the introduction ( n = 13, 3.6%) and conclusion ( n = 10, 2.7%) sections to be challenging. Additionally, 71 students (19.2%) were not sure which part of the manuscript was the most difficult to prepare (Fig. 3 ).
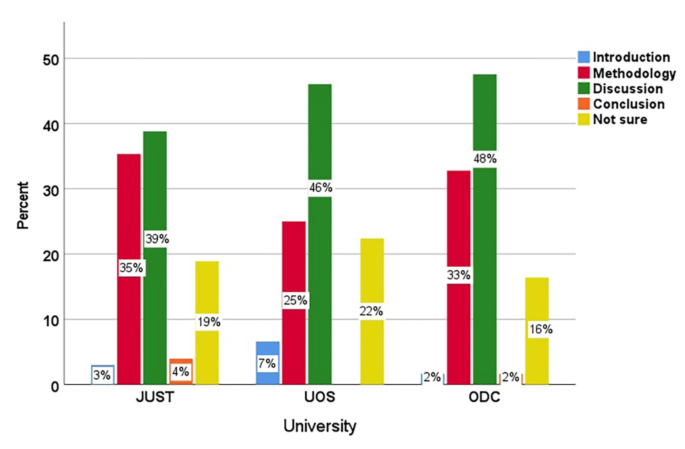
Percentages of the most difficult part reported by dental students during the writing-up of their projects. JUST: Jordan University of Science and Technology, UOS: University of Sharjah, ODC: Oman Dental College
The dental students’ perceived benefits from the research activity were evaluated across seven components, including literature review skills, research design skills, data collection and interpretation, manuscript writing, publication, teamwork and effective communication, and engagement in continuing professional development.
The majority of students found the research activity to be beneficial or highly beneficial in most of the areas, with the highest ratings observed in teamwork and effective communication, where 33.5% rated it as beneficial and 32.7% rated it as highly beneficial. Similarly, in the area of data collection and interpretation, 33.0% rated it as beneficial and 27.5% rated it as highly beneficial. In the areas of literature review skills and research design skills, 28.6% and 34.0% of students rated the research activity as beneficial, while 25.3% and 22.7% rated it as highly beneficial, respectively. Students also perceived the research activity to be helpful for the manuscript writing, with 27.9% rating it as beneficial and 19.2% rating it as highly beneficial.
When it comes to publication, students’ perceptions were more variable, with 22.0% rating it as beneficial and 11.3% rating it as highly beneficial. A notable 29.9% rated it as neutral, and 17.9% reported no benefit. Finally, in terms of engaging in continuing professional development, 26.8% of students rated the research activity as beneficial and 26.2% rated it as highly beneficial (Fig. 4 ).
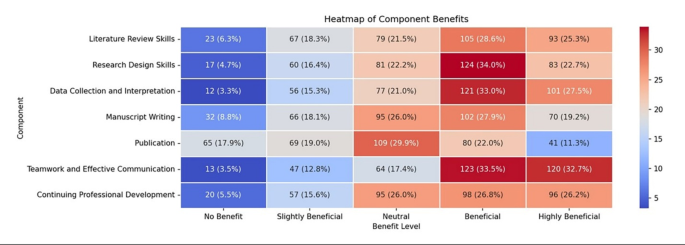
Heatmap of the dental students’ perceived benefits from the research activity
The research course’s impact on students’ perspectives towards being engaged in research activities or pursuing a research career after graduation was predominantly positive, wherein 274 students (74.1%) reported a positive impact on their research perspectives. However, 79 students (21.5%) felt that the course had no impact on their outlook towards research engagement or a research career. A small percentage of students ( n = 16, 4.4%) indicated that the course had a negative impact on their perspective towards research activities or a research career after graduation.
Finally, when students were asked about their suggestions to improve research activities, they indicated the need for more training and orientation ( n = 127, 34.6%) as well as to allow more time for students to finish their research projects ( n = 87, 23.6%). Participation in competitions and more generous funding were believed to be less important factors to improve students` research experience ( n = 78, 21.2% and n = 63, 17.1%, respectively). Other factors such as external collaborations and engagement in research groups were even less important from the students` perspective (Fig. 5 ).
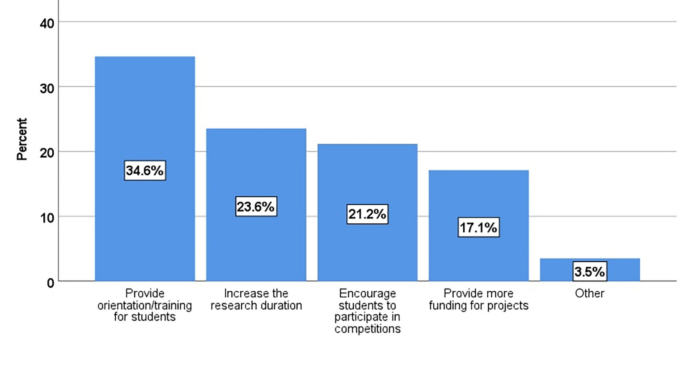
Precentages of dental students’ suggestions to improve research activities at their colleges
To the best of our knowledge, this report is the first to provide a comprehensive overview of the research experience of dental students from three leading dental colleges in the Middle East region, which is home to more than 50 dental schools according to the latest SCImago Institutions Ranking ® ( https://www.scimagoir.com ). The reasonable sample size and different curricular structure across the participating colleges enhanced the value of our findings not only for dental colleges in the Middle East, but also to any dental college seeking to improve and update its undergraduate research activities. However, it is noteworthy that since the study has included only three dental schools, the generalizability of the current findings would be limited, and the outcomes are preliminary in nature.
Cross-sectional (epidemiological) studies and literature reviews represented the most common types of research among our cohort of students, which can be attributed to the feasibility, shorter time and low cost required to conduct such research projects. On the contrary, longitudinal studies and randomized trials, both known to be time consuming and meticulous, were the least common types. These findings concur with previous reports, which demonstrated that epidemiological studies are popular among undergraduate research projects [ 4 , 10 ]. In a retrospective study, Nalliah et al. also demonstrated a remarkable increase in epidemiological research concurrent with a decline in the clinical research in dental students` projects over a period of 4 years [ 4 ]. However, literature reviews, whether systematic or scoping, were not as common in some dental schools as in our cohort. For instance, a report from Sweden showed that literature reviews accounted for less than 10% of total dental students` projects [ 14 ]. Overall, qualitative research was seldom performed among our cohort, which is in agreement with a general trend in dental research that has been linked to the low level of competence and experience of dental educators to train students in qualitative research, as this requires special training in social research [ 15 , 16 ].
In terms of the research topics, public health research, research in dental education and attitudinal research were the most prevalent among our respondents. In agreement with our results, research in health care appears common in dental students` projects [ 12 ]. In general, these research domains may reflect the underlying interests of the faculty supervisors, who, in our case, were actively engaged in the selection of the research topic for more than 90% of the projects. Other areas of research, such as clinical dentistry and basic dental research are also widely reported [ 4 , 10 , 14 , 17 ].
The selection of a research domain is a critical step in undergraduate research projects, and a systematic approach in identifying research gaps and selecting appropriate research topics is indispensable and should always be given an utmost attention by supervisors [ 18 ].
More than half of the projects in the current report were reasonably selected based on a discussion between the students and the supervisor, whereas 36% were selected by the supervisors. Otuyemi et al. reported that about half of undergraduate research topics in a Nigerian dental school were selected by students themselves, however, a significant proportion of these projects (20%) were subsequently modified by supervisors [ 19 ]. The autonomy in selecting the research topic was discussed in a Swedish report, which suggested that such approach can enhance the learning experience of students, their motivation and creativity [ 20 ]. Flexibility in selecting the research topic as well as the faculty supervisor, whenever feasible, should be offered to students in order to improve their research experience and gain better outcomes [ 12 ].
Pubmed and Google Scholar were the most widely used search engines for performing a literature review. This finding is consistent with recent reviews which classify these two search systems as the most commonly used ones in biomedical research despite some critical limitations [ 21 , 22 ]. It is noteworthy that students should be competent in critical appraisal of available literature to perform the literature review efficiently. Interestingly, only 25% of students used their respective university library`s access to the search engines, which means that most students retrieved only open access publications for their literature reviews, a finding that requires attention from faculty mentors to guide students to utilize the available library services to widen their accessibility to available literature.
Statistical analysis has classically been viewed as a perceived obstacle for undergraduate students to undertake research in general [ 23 , 24 ] and recent literature has highlighted the crucial need of biomedical students to develop necessary competencies in biostatistics during their studies [ 25 ]. One obvious advantage of conducting research in our cohort is that 45.5% of students used a specialized software to analyze their data, which means that they did have at least an overview of how data are processed and analyzed to reach their final results and inferences. Unfortunately, the remaining 54.5% of students were, partially or completely, dependent on the supervisor or a professional statistician for data analysis. It is noteworthy that the research projects were appropriately tailored to the undergraduate level, focusing on fundamental statistical analysis methods. Therefore, consulting a professional statistician for more complex analyses was done only if indicated, which explains the small percentage of students who consulted a professional statistician.
Over half of participating students (58.4%) prepared a manuscript at the end of their research projects and for these students, the discussion section was identified as the most challenging to prepare, followed by the methodology section. These findings can be explained by the students’ lack of knowledge and experience related to conducting and writing-up scientific research. The same was reported by Habib et al. who found dental students’ research knowledge to be less than that of medical students [ 26 ]. The skills of critical thinking and scientific writing are believed to be of paramount importance to biomedical students and several strategies have been proposed to enhance these skills especially for both English and non-English speaking students [ 27 , 28 , 29 ].
Dental students in the current study reported positive attitude towards research and found the research activity to be beneficial in several aspects of their education, with the most significant benefits in the areas of teamwork, effective communication, data collection and interpretation, literature review skills, and research design skills. Similar findings were reported by previous studies with most of participating students reporting a positive impact of their research experience [ 4 , 10 , 12 , 30 ]. Furthermore, 74% of students found that their research experience had a positive impact on their perspectives towards engagement in research in the future. This particular finding may be promising in resolving a general lack of interest in research by dental students, as shown in a previous report from one of the participating colleges in this study (JUST), which demonstrated that only 2% of students may consider a research career in the future [ 31 ].
Notably, only 11.3% of our students perceived their research experience as being highly beneficial with regards to publication. Students` attitudes towards publishing their research appear inconsistent in literature and ranges from highly positive rates in developed countries [ 4 ] to relatively low rates in developing countries [ 8 , 32 , 33 ]. This can be attributed to lack of motivation and poor training in scientific writing skills, a finding that has prompted researchers to propose strategies to tackle such a gap as mentioned in the previous section.
Finally, key suggestions by the students to improve the research experience were the provision of more training and orientation, more time to conduct the research, as well as participation in competitions and more funding opportunities. These findings are generally in agreement with previous studies which demonstrated that dental students perceived these factors as potential barriers to improving their research experience [ 8 , 10 , 17 , 30 , 34 ].
A major limitation of the current study is the inclusion of only three dental schools from the Middle East which my limit the generalizability and validity of the findings. Furthermore, the cross-sectional nature of the study would not allow definitive conclusions to be drawn as students’ perspectives were not evaluated before and after the research project. Potential confounders in the study include the socioeconomic status of the students, the teaching environment, previous research experience, and self-motivation. Moreover, potential sources of bias include variations in the available resources and funding to students’ projects and variations in the quality of supervision provided. Another potential source of bias is the non-response bias whereby students with low academic performance or those who were not motivated might not respond to the questionnaire. This potential source of bias was managed by sending multiple reminders to students and aiming for the highest response rate and largest sample size possible.
In conclusion, the current study evaluated the key aspects of dental students’ research experience at three dental colleges in the Middle East. While there were several perceived benefits, some aspects need further reinforcement and revision including the paucity of qualitative and clinical research, the need for more rigorous supervision from mentors with focus on scientific writing skills and research presentation opportunities. Within the limitations of the current study, these outcomes can help in designing future larger scale studies and provide valuable guidance for dental colleges to foster the research component in their curricula. Further studies with larger and more representative samples are required to validate these findings and to explore other relevant elements in undergraduate dental research activities.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Emrick JJ, Gullard A. Integrating research into dental student training: a global necessity. J Dent Res. 2013;92(12):1053–5.
Article Google Scholar
Ramachandra SS. A comprehensive template for inclusion of research in the undergraduate dental curriculum. Health Professions Educ. 2020;6(2):264–70.
Al Sweleh FS. Integrating scientific research into undergraduate curriculum: a new direction in dental education. J Health Spec. 2016;4(1):42–5.
Nalliah RP, Lee MK, Da Silva JD, Allareddy V. Impact of a research requirement in a dental school curriculum. J Dent Educ. 2014;78(10):1364–71.
Lang ES, Wyer PC, Haynes RB. Knowledge translation: closing the evidence-to-practice gap. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;49(3):355–63.
Fechheimer M, Webber K, Kleiber PB. How well do undergraduate research programs promote engagement and success of students? CBE Life Sci Educ. 2011;10(2):156–63.
Kingsley K, O’Malley S, Stewart T, Howard KM. Research enrichment: evaluation of structured research in the curriculum for dental medicine students as part of the vertical and horizontal integration of biomedical training and discovery. BMC Med Educ. 2008;8:1–10.
Alsaleem SA, Alkhairi MAY, Alzahrani MAA, Alwadai MI, Alqahtani SSA, Alaseri YFY, et al. Challenges and Barriers toward Medical Research among Medical and Dental students at King Khalid University, Abha, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Front Public Health. 2021;9:706778.
Soe HHK, Than NN, Lwin H, Htay MNNN, Phyu KL, Abas AL. Knowledge, attitudes, and barriers toward research: the perspectives of undergraduate medical and dental students. J Educ Health Promotion. 2018;7(1):23.
Amir LR, Soekanto SA, Julia V, Wahono NA, Maharani DA. Impact of Undergraduate Research as a compulsory course in the Dentistry Study Program Universitas Indonesia. Dent J (Basel). 2022;10(11).
Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The strengthening the reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007;370(9596):1453–7.
Van der Groen TA, Olsen BR, Park SE. Effects of a Research Requirement for Dental students: a retrospective analysis of students’ perspectives across ten years. J Dent Educ. 2018;82(11):1171–7.
Althubaiti A. Sample size determination: a practical guide for health researchers. J Gen Family Med. 2023;24(2):72–8.
Franzén C. The undergraduate degree project–preparing dental students for professional work and postgraduate studies? Eur J Dent Educ. 2014;18(4):207–13.
Edmunds S, Brown G. Doing qualitative research in dentistry and dental education. Eur J Dent Educ. 2012;16(2):110–7.
Moreno X. Research training in dental undergraduate curriculum in Chile. J Oral Res. 2014;3(2):95–9.
Liu H, Gong Z, Ye C, Gan X, Chen S, Li L, et al. The picture of undergraduate dental basic research education: a scoping review. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):569.
Omar A, Elliott E, Sharma S. How to undertake research as a dental undergraduate. BDJ Student. 2021;28(3):17–8.
Otuyemi OD, Olaniyi EA. A 5-year retrospective evaluation of undergraduate dental research projects in a Nigerian University: graduates’ perceptions of their learning experiences. Eur J Dent Educ. 2020;24(2):292–300.
Franzén C, Brown G. Undergraduate degree projects in the Swedish dental schools: a documentary analysis. Eur J Dent Educ. 2013;17(2):122–6.
Thakre SB, Golawar SH, Thakr SS, Gawande AV. Search engines use for effective literature search in biomedical research. 2014.
Gusenbauer M, Haddaway NR. Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Res Synthesis Methods. 2020;11(2):181–217.
Lorton L, Rethman MP. Statistics: curse of the writing class. J Endod. 1990;16(1):13–8.
Leppink J. Helping medical students in their study of statistics: a flexible approach. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2017;12(1):1–7.
Google Scholar
Oster RA, Enders FT. The Importance of Statistical Competencies for Medical Research Learners. J Stat Educ. 2018;26(2):137–42.
Habib SR, AlOtaibi SS, Abdullatif FA, AlAhmad IM. Knowledge and attitude of undergraduate Dental students towards Research. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2018;30(3):443–8.
Florek AG, Dellavalle RP. Case reports in medical education: a platform for training medical students, residents, and fellows in scientific writing and critical thinking. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:86.
Wortman-Wunder E, Wefes I. Scientific writing workshop improves confidence in critical writing skills among trainees in the Biomedical sciences. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2020;21(1).
Barroga E, Mitoma H. Critical thinking and scientific writing skills of Non-anglophone Medical students: a model of Training Course. J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(3):e18.
Kyaw Soe HH, Than NN, Lwin H, Nu Htay MNN, Phyu KL, Abas AL. Knowledge, attitudes, and barriers toward research: the perspectives of undergraduate medical and dental students. J Educ Health Promot. 2018;7:23.
Alrashdan MS, Alazzam M, Alkhader M, Phillips C. Career perspectives of senior dental students from different backgrounds at a single Middle Eastern institution. BMC Med Educ. 2018;18(1):283.
Chellaiyan VG, Manoharan A, Jasmine M, Liaquathali F. Medical research: perception and barriers to its practice among medical school students of Chennai. J Educ Health Promot. 2019;8:134.
Jeelani W, Aslam SM, Elahi A. Current trends in undergraduate medical and dental research: a picture from Pakistan. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2014;26(2):162–6.
Yu W, Sun Y, Miao M, Li L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, et al. Eleven-year experience implementing a dental undergraduate research programme in a prestigious dental school in China: lessons learned and future prospects. Eur J Dent Educ. 2021;25(2):246–60.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge final year dental students at the three participating colleges for their time completing the questionnaire.
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Oral and Craniofacial Health Sciences, College of Dental Medicine, University of Sharjah, P.O.Box: 27272, Sharjah, UAE
Mohammad S. Alrashdan & Sausan Al Kawas
Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Jordan
Mohammad S. Alrashdan
Department of Adult Restorative Dentistry, Oman Dental College, Muscat, Sultanate of Oman
Abubaker Qutieshat
Department of Restorative Dentistry, Dundee Dental Hospital & School, University of Dundee, Dundee, UK
Preventive and Restorative Dentistry Department, College of Dental Medicine, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, UAE
Mohamed El-Kishawi
Clinical Sciences Department, College of Dentistry, Ajman University, Ajman, UAE
Abdulghani Alarabi
Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Jordan
Lina Khasawneh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.A.: Conceptualization, data curation, project administration; supervision, validation, writing - original draft; writing - review and editing. A.Q: Conceptualization, data curation, project administration; writing - review and editing. M.E: Conceptualization, data curation, project administration; validation, writing - original draft; writing - review and editing. A.A.: data curation, writing - original draft; writing - review and editing. L.K.: Conceptualization, data curation, validation, writing - original draft; writing - review and editing. S.A: Conceptualization, writing - review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mohammad S. Alrashdan .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The current study was approved by the institutional review board of Jordan University of Science and Technology (Reference: 724–2022), the research ethics committee of the University of Sharjah (Reference: REC-22-02-22-3) and Oman Dental College (Reference: ODC-MA-2022-166).
Informed consent
Agreement to the invitation to fill out the questionnaire was considered as an implied consent to participate.
Consent for publication
not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Alrashdan, M.S., Qutieshat, A., El-Kishawi, M. et al. Insights into research activities of senior dental students in the Middle East: A multicenter preliminary study. BMC Med Educ 24 , 967 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05955-5
Download citation
Received : 12 August 2023
Accepted : 24 August 2024
Published : 04 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05955-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Dental research
- Dental education
- Undergraduate
- Literature review
- Publication
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Bar Standards Board consults on revised proposals to promote equality, diversity and inclusion at the Bar
The Bar Standards Board (BSB) has today launched a public consultation on new rules to promote equality, diversity and inclusion at the Bar. Despite improvements in diversity in recent years, there remain significant challenges for the Bar in promoting access to the profession, in retaining qualified practitioners and in addressing bullying, discrimination and harassment. The regulator is therefore asking for a further step change in the profession’s approach to equality, diversity and inclusion.
The consultation document seeks views on a number of proposals. In particular, a change to Core Duty 8 would place a positive obligation on barristers to “act in a way that advances equality, diversity, and inclusion” when providing legal services, The BSB also proposes to take a more outcomes focused approach to these equality rules, but to retain prescriptive requirements where necessary for transparency and accountability. These proposals have been informed by engagement activities with the profession, the Inns, the BSB Race Equality, Disability, and Religion and Belief Task Forces , as well as through research and data on the current inequalities within the profession and the extent to which the current rules have had an impact on tackling inequalities.
In addition to the wider public consultation on these proposed changes, the BSB plans to engage separately with those stakeholders who are likely to be impacted by these proposals through a series of targeted engagement sessions, including, for example the Inns of Court and Circuits across England and Wales, the specialist Bar Associations, and equalities groups who represent those who face barriers at the Bar. The public consultation will be open until 5PM on Friday 29 November and you can access the full consultation document here and you can respond to the consultation questions here .
Commenting on the launch of the consultation, BSB Director General Mark Neale said:
“We want to ensure that the Bar is as inclusive as possible and that it is truly representative of the society it serves. Regulation alone cannot achieve that, but regulation can help by supporting barristers to challenge practices which work against diversity and inclusion. We hope that you will take this opportunity to share your views with us, so we can ensure our proposals are fully informed by your experience.”
Notes to editors
About the Bar Standards Board
Our mission is to regulate barristers and specialised legal services businesses in England and Wales in the public interest. For more information about what we do visit: http://bit.ly/1gwui8t
Contact: For all media enquiries call: 07432 713 328 or email [email protected] .
- Consultations
- Equality and diversity

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Overview: 8 Research Proposal Killers. The research topic is too broad (or just poorly articulated). The research aims, objectives and questions don't align. The research topic is not well justified. The study has a weak theoretical foundation. The research design is not well articulated well enough. Poor writing and sloppy presentation.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
"Crafting a Research Proposal." The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. "Writing a Research Proposal." In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning. Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. "Writing a Research Proposal."
This qualitative study delves closely into students' challenges of writing specific sections (i.e., introduction, literature review, and method) of their research proposal and coping strategies ...
Remember, your research proposal should demonstrate: the feasibility and logical foundations of your project. a well-focussed research question, set of research objectives, or hypothesis. the width and depth of the academic literature on your topic. understanding of current issues or debates on your topic.
Research proposals, like all other kinds of academic writing, are written in a formal, objective tone. Keep in mind that being concise is a key component of academic writing; formal does not mean flowery. Adhere to the structure outlined above. Your reader knows how a research proposal is supposed to read and expects it to fit this template.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components: Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
A research proposal is a roadmap that brings the researcher closer to the objectives, takes the research topic from a purely subjective mind, and manifests an objective plan. It shows us what steps we need to take to reach the objective, what questions we should answer, and how much time we need. It is a framework based on which you can perform ...
Budget: Explain how much money you need. Explain the details of the budget (how much you want to spend for what). Conclusion: Describe why your research is important. References: List the sources you have used for writing the research proposal, including a few main citations of the preliminary scholarship. Date.
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Complete the sentence: "The purpose of this study is …". Formulate your research questions. Let your answers guide you. Determine what kind of design and methodology can best answer your research questions. If your questions include words such as "explore," "understand," and "generate," it's an indication that your study is ...
Useful tips for writing a research proposal. Maintain a focus in your proposal: Your research proposal should be clear and concise, outlining your research idea and its benefits to your chosen field of study, in a way that the reader can clearly understand. Remember, your proposal is just the starting point and an outline and does not need to ...
According to Wong (2002) and Locke et al. (2007), there are common mistakes that people make when writing a research proposal: Not providing context to the research question(s). Not citing significant studies ("landmark studies") in the field that changed others' understanding of the topic. Not accurately presenting other research done on the ...
Challenges. Writing a research proposal for funding is a very challenging and demanding job. Even if you are convinced that the problem or issue you want to address is relevant and has a big potential to change or improve the way we do things, we can never say 100% that it will be funded. The decision whether our proposal will be funded or not ...
Step 3: Set your aims and objectives. Finally, the problem statement should frame how you intend to address the problem. Your goal here should not be to find a conclusive solution, but rather to propose more effective approaches to tackling or understanding it. The research aim is the overall purpose of your research.
The writing thesis challenges were lack of knowledge related to writing a scientific paper, skill in designing research methodology, and lack of r esources related to the thesis's topic.
II. Research Proposal Writing A. Introduction. A research proposal is commonly written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project when enrolling for a research-based postgraduate degree. Graduate and post-graduate students also embark on a university dissertation to obtain a degree or get that Ph.D. Although it is just a course ...
1. Introduction. Although writing effectively can lead to fruitful academic upshots (Mousavi & Kashefian-Naeeini, Citation 2011), writing thesis is not an easy task for many students.Most of them face with challenges of writing up their theses particularly their literature review section (Boote & Beile, Citation 2005; Fergie et al., Citation 2011). ...
Research, by its nature, is a critical challenging task requires in depth knowledge of the subject matter, planning, care, and hard work. From the students' point of view, this paper attempts to explore the challenges that are faced by undergraduates when they are writing proposals and research projects at the early stages.
From the students' point of view, this paper attempts to explore the challenges that are faced by undergraduates when they are writing proposals and research projects at the early stages.
In general your proposal should include the following sections: I. Introduction. In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write your doctoral dissertation.
Research, by its nature, is a critical challenging task requires in depth knowledge of the subject matter, planning, care, and hard work. From the students' point of view, this paper attempts to explore the challenges that are faced by undergraduates when they are writing proposals and research projects at the early stages.
Early on at the department/school - lack of robust startup funding, guidance to write winning grant proposals, research support and resources, mentorship and a concrete and working model to include junior faculty into more senior research for national and local networking to support transition/starting up in terms of productivity."
The importance of research training for undergraduate dental students cannot be overstressed and many reports have thoroughly discussed the necessity of incorporating research components in the dental curricula [1,2,3,4].A structured research training is crucial to ensure that dental graduates will adhere to evidence-based practices and policies in their future career and are able to ...
The Bar Standards Board (BSB) has today launched a public consultation on new rules to promote equality, diversity and inclusion at the Bar. Despite improvements in diversity in recent years, there remain significant challenges for the Bar in promoting access to the profession, in retaining qualified practitioners and in addressing bullying, discrimination and harassment.