If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

AP®︎/College US History
Course: ap®︎/college us history > unit 10, ap us history periods and themes.
- AP US History multiple choice example 1
- AP US History multiple choice example 2
- AP US History short answer example 1
- AP US History short answer example 2
- AP US History DBQ example 1
- AP US History DBQ example 2
- AP US History DBQ example 3
- AP US History DBQ example 4
- AP US History long essay example 1
- AP US History long essay example 2
- AP US History long essay example 3
- Preparing for the AP US History Exam (5/4/2016)
- AP US History Exam Prep Session (5/1/2017)
AP US history periods and themes
Example ap us history problems, key terms, documents, and court cases to know, primary documents:.
John Winthrop, “City on a Hill” / “A Model of Christian Charity”
Jonathan Edwards, “Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God”
Thomas Jefferson, “Declaration of Independence”
James Madison, “Constitution of the United States”
Elizabeth Cady Stanton and Susan B. Anthony, “Declaration of Sentiments”
Frederick Douglass, “What to the Slave is the Fourth of July?”
Harriet Beecher Stowe, “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” (main ideas)
Abraham Lincoln, “House Divided” speech, Second Inaugural Address
Sojourner Truth, “Ain’t I a Woman?”
Andrew Carnegie, “The Gospel of Wealth” (main ideas)
Josiah Strong, “Our Country” (main ideas)
Upton Sinclair “The Jungle” (main ideas)
Franklin Delano Roosevelt, First Inaugural Address, December 8 1941 address
George Kennan, “Long Telegram”
Martin Luther King Jr. “Letter from Birmingham Jail”, “I Have a Dream” speech
Betty Friedan “The Feminine Mystique” (main ideas)
Ronald Reagan “Evil Empire” speech
Supreme Court cases:
Marbury v. Madison
Dred Scott v. Sanford
Plessy v. Ferguson
Brown v. Board of Education
Roe v. Wade
Bush v. Gore
Foreign policy doctrines:
Monroe Doctrine
Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine
Truman Doctrine
Nixon Doctrine
Bush Doctrine
virgin soil epidemic
salutary neglect / benign neglect
mercantilism
Anti-Federalist
isolationism
judicial review
Democratic-Republican
Jacksonian Democracy
nullification
popular sovereignty
Emancipation
Jim Crow segregation
sharecropping
mass production
labor union
imperialism
self-determination
prohibition
laissez-faire economics
liberalism (economics/politics)
Soviet Union
containment
Domino Theory
non-violent protest (Civil Rights)
Vietnamization
conservatism
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page


How to write an introduction for a history essay

Every essay needs to begin with an introductory paragraph. It needs to be the first paragraph the marker reads.
While your introduction paragraph might be the first of the paragraphs you write, this is not the only way to do it.
You can choose to write your introduction after you have written the rest of your essay.
This way, you will know what you have argued, and this might make writing the introduction easier.
Either approach is fine. If you do write your introduction first, ensure that you go back and refine it once you have completed your essay.
What is an ‘introduction paragraph’?
An introductory paragraph is a single paragraph at the start of your essay that prepares your reader for the argument you are going to make in your body paragraphs .
It should provide all of the necessary historical information about your topic and clearly state your argument so that by the end of the paragraph, the marker knows how you are going to structure the rest of your essay.
In general, you should never use quotes from sources in your introduction.
Introduction paragraph structure
While your introduction paragraph does not have to be as long as your body paragraphs , it does have a specific purpose, which you must fulfil.
A well-written introduction paragraph has the following four-part structure (summarised by the acronym BHES).
B – Background sentences
H – Hypothesis
E – Elaboration sentences
S - Signpost sentence
Each of these elements are explained in further detail, with examples, below:
1. Background sentences
The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis , your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about.
Background sentences explain the important historical period, dates, people, places, events and concepts that will be mentioned later in your essay. This information should be drawn from your background research .
Example background sentences:
Middle Ages (Year 8 Level)
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15 th and 16 th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges.
WWI (Year 9 Level)
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe.
Civil Rights (Year 10 Level)
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success.
Ancient Rome (Year 11/12 Level)
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times.
2. Hypothesis
Once you have provided historical context for your essay in your background sentences, you need to state your hypothesis .
A hypothesis is a single sentence that clearly states the argument that your essay will be proving in your body paragraphs .
A good hypothesis contains both the argument and the reasons in support of your argument.
Example hypotheses:
Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery.
Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare.
The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders.
Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1 st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state.
3. Elaboration sentences
Once you have stated your argument in your hypothesis , you need to provide particular information about how you’re going to prove your argument.
Your elaboration sentences should be one or two sentences that provide specific details about how you’re going to cover the argument in your three body paragraphs.
You might also briefly summarise two or three of your main points.
Finally, explain any important key words, phrases or concepts that you’ve used in your hypothesis, you’ll need to do this in your elaboration sentences.
Example elaboration sentences:
By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period.
Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined.
The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results.
While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period.
4. Signpost sentence
The final sentence of your introduction should prepare the reader for the topic of your first body paragraph. The main purpose of this sentence is to provide cohesion between your introductory paragraph and you first body paragraph .
Therefore, a signpost sentence indicates where you will begin proving the argument that you set out in your hypothesis and usually states the importance of the first point that you’re about to make.
Example signpost sentences:
The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20 th century.
The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Putting it all together
Once you have written all four parts of the BHES structure, you should have a completed introduction paragraph. In the examples above, we have shown each part separately. Below you will see the completed paragraphs so that you can appreciate what an introduction should look like.
Example introduction paragraphs:
Castles were an important component of Medieval Britain from the time of the Norman conquest in 1066 until they were phased out in the 15th and 16th centuries. Initially introduced as wooden motte and bailey structures on geographical strongpoints, they were rapidly replaced by stone fortresses which incorporated sophisticated defensive designs to improve the defenders’ chances of surviving prolonged sieges. Medieval castles were designed with features that nullified the superior numbers of besieging armies, but were ultimately made obsolete by the development of gunpowder artillery. By the height of the Middle Ages, feudal lords were investing significant sums of money by incorporating concentric walls and guard towers to maximise their defensive potential. These developments were so successful that many medieval armies avoided sieges in the late period. The early development of castles is best understood when examining their military purpose.
The First World War began in 1914 following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The subsequent declarations of war from most of Europe drew other countries into the conflict, including Australia. The Australian Imperial Force joined the war as part of Britain’s armed forces and were dispatched to locations in the Middle East and Western Europe. Australian soldiers’ opinion of the First World War changed from naïve enthusiasm to pessimistic realism as a result of the harsh realities of modern industrial warfare. Following Britain's official declaration of war on Germany, young Australian men voluntarily enlisted into the army, which was further encouraged by government propaganda about the moral justifications for the conflict. However, following the initial engagements on the Gallipoli peninsula, enthusiasm declined. The naïve attitudes of those who volunteered in 1914 can be clearly seen in the personal letters and diaries that they themselves wrote.
The 1967 Referendum sought to amend the Australian Constitution in order to change the legal standing of the indigenous people in Australia. The fact that 90% of Australians voted in favour of the proposed amendments has been attributed to a series of significant events and people who were dedicated to the referendum’s success. The success of the 1967 Referendum was a direct result of the efforts of First Nations leaders such as Charles Perkins, Faith Bandler and the Federal Council for the Advancement of Aborigines and Torres Strait Islanders. The political activity of key indigenous figures and the formation of activism organisations focused on indigenous resulted in a wider spread of messages to the general Australian public. The generation of powerful images and speeches has been frequently cited by modern historians as crucial to the referendum results. The significance of these people is evident when examining the lack of political representation the indigenous people experience in the early half of the 20th century.
In the late second century BC, the Roman novus homo Gaius Marius became one of the most influential men in the Roman Republic. Marius gained this authority through his victory in the Jugurthine War, with his defeat of Jugurtha in 106 BC, and his triumph over the invading Germanic tribes in 101 BC, when he crushed the Teutones at the Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC) and the Cimbri at the Battle of Vercellae (101 BC). Marius also gained great fame through his election to the consulship seven times. Gaius Marius was the most one of the most significant personalities in the 1st century BC due to his effect on the political, military and social structures of the Roman state. While Marius is best known for his military reforms, it is the subsequent impacts of this reform on the way other Romans approached the attainment of magistracies and how public expectations of military leaders changed that had the longest impacts on the late republican period. The origin of Marius’ later achievements was his military reform in 107 BC, which occurred when he was first elected as consul.
Additional resources

What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
Module 4: Imperial Reforms and Colonial Protests (1763-1774)
Historical thesis statements, learning objectives.
- Recognize and create high-quality historical thesis statements
Some consider all writing a form of argument—or at least of persuasion. After all, even if you’re writing a letter or an informative essay, you’re implicitly trying to persuade your audience to care about what you’re saying. Your thesis statement represents the main idea—or point—about a topic or issue that you make in an argument. For example, let’s say that your topic is social media. A thesis statement about social media could look like one of the following sentences:
- Social media are hurting the communication skills of young Americans.
- Social media are useful tools for social movements.
A basic thesis sentence has two main parts: a claim and support for that claim.
- The Immigration Act of 1965 effectively restructured the United States’ immigration policies in such a way that no group, minority or majority, was singled out by being discriminated against or given preferential treatment in terms of its ability to immigrate to America.
Identifying the Thesis Statement
A thesis consists of a specific topic and an angle on the topic. All of the other ideas in the text support and develop the thesis. The thesis statement is often found in the introduction, sometimes after an initial “hook” or interesting story; sometimes, however, the thesis is not explicitly stated until the end of an essay, and sometimes it is not stated at all. In those instances, there is an implied thesis statement. You can generally extract the thesis statement by looking for a few key sentences and ideas.
Most readers expect to see the point of your argument (the thesis statement) within the first few paragraphs. This does not mean that it has to be placed there every time. Some writers place it at the very end, slowly building up to it throughout their work, to explain a point after the fact. For history essays, most professors will expect to see a clearly discernible thesis sentence in the introduction. Note that many history papers also include a topic sentence, which clearly state what the paper is about
Thesis statements vary based on the rhetorical strategy of the essay, but thesis statements typically share the following characteristics:
- Presents the main idea
- Most often is one sentence
- Tells the reader what to expect
- Is a summary of the essay topic
- Usually worded to have an argumentative edge
- Written in the third person
This video explains thesis statements and gives a few clear examples of how a good thesis should both make a claim and forecast specific ways that the essay will support that claim.
You can view the transcript for “Thesis Statement – Writing Tutorials, US History, Dr. Robert Scafe” here (opens in new window) .
Writing a Thesis Statement
A good basic structure for a thesis statement is “they say, I say.” What is the prevailing view, and how does your position differ from it? However, avoid limiting the scope of your writing with an either/or thesis under the assumption that your view must be strictly contrary to their view.
Following are some typical thesis statements:
- Although many readers believe Romeo and Juliet to be a tale about the ill fate of two star-crossed lovers, it can also be read as an allegory concerning a playwright and his audience.
- The “War on Drugs” has not only failed to reduce the frequency of drug-related crimes in America but actually enhanced the popular image of dope peddlers by romanticizing them as desperate rebels fighting for a cause.
- The bulk of modern copyright law was conceived in the age of commercial printing, long before the Internet made it so easy for the public to compose and distribute its own texts. Therefore, these laws should be reviewed and revised to better accommodate modern readers and writers.
- The usual moral justification for capital punishment is that it deters crime by frightening would-be criminals. However, the statistics tell a different story.
- If students really want to improve their writing, they must read often, practice writing, and receive quality feedback from their peers.
- Plato’s dialectical method has much to offer those engaged in online writing, which is far more conversational in nature than print.
Thesis Problems to Avoid
Although you have creative control over your thesis sentence, you still should try to avoid the following problems, not for stylistic reasons, but because they indicate a problem in the thinking that underlies the thesis sentence.
- Hospice workers need support. This is a thesis sentence; it has a topic (hospice workers) and an argument (need support). But the argument is very broad. When the argument in a thesis sentence is too broad, the writer may not have carefully thought through the specific support for the rest of the writing. A thesis argument that’s too broad makes it easy to fall into the trap of offering information that deviates from that argument.
- Hospice workers have a 55% turnover rate compared to the general health care population’s 25% turnover rate. This sentence really isn’t a thesis sentence at all, because there’s no argument to support it. A narrow statistic, or a narrow statement of fact, doesn’t offer the writer’s own ideas or analysis about a topic.
Let’s see some examples of potential theses related to the following prompt:
- Bad thesis : The relationship between the American colonists and the British government changed after the French & Indian War.
- Better thesis : The relationship between the American colonists and the British government was strained following the Revolutionary war.
- Best thesis : Due to the heavy debt acquired by the British government during the French & Indian War, the British government increased efforts to tax the colonists, causing American opposition and resistance that strained the relationship between the colonists and the crown.
Practice identifying strong thesis statements in the following interactive.
Supporting Evidence for Thesis Statements
A thesis statement doesn’t mean much without supporting evidence. Oftentimes in a history class, you’ll be expected to defend your thesis, or your argument, using primary source documents. Sometimes these documents are provided to you, and sometimes you’ll need to go find evidence on your own. When the documents are provided for you and you are asked to answer questions about them, it is called a document-based question, or DBQ. You can think of a DBQ like a miniature research paper, where the research has been done for you. DBQs are often used on standardized tests, like this DBQ from the 2004 U.S. History AP exam , which asked students about the altered political, economic, and ideological relations between Britain and the colonies because of the French & Indian War. In this question, students were given 8 documents (A through H) and expected to use these documents to defend and support their argument. For example, here is a possible thesis statement for this essay:
- The French & Indian War altered the political, economic, and ideological relations between the colonists and the British government because it changed the nature of British rule over the colonies, sowed the seeds of discontent, and led to increased taxation from the British.
Now, to defend this thesis statement, you would add evidence from the documents. The thesis statement can also help structure your argument. With the thesis statement above, we could expect the essay to follow this general outline:
- Introduction—introduce how the French and Indian War altered political, economic, and ideological relations between the colonists and the British
- Show the changing map from Doc A and greater administrative responsibility and increased westward expansion
- Discuss Doc B, frustrations from the Iroquois Confederacy and encroachment onto Native lands
- Could also mention Doc F and the result in greater administrative costs
- Use Doc D and explain how a colonial soldier notices disparities between how they are treated when compared to the British
- Use General Washington’s sentiments in Doc C to discuss how these attitudes of reverence shifted after the war. Could mention how the war created leadership opportunities and gave military experience to colonists.
- Use Doc E to highlight how the sermon showed optimism about Britain ruling the colonies after the war
- Highlight some of the political, economic, and ideological differences related to increased taxation caused by the War
- Use Doc F, the British Order in Council Statement, to indicate the need for more funding to pay for the cost of war
- Explain Doc G, frustration from Benjamin Franklin about the Stamp Act and efforts to repeal it
- Use Doc H, the newspaper masthead saying “farewell to liberty”, to highlight the change in sentiments and colonial anger over the Stamp Act
As an example, to argue that the French & Indian War sowed the seeds of discontent, you could mention Document D, from a Massachusetts soldier diary, who wrote, “And we, being here within stone walls, are not likely to get liquors or clothes at this time of the year; and though we be Englishmen born, we are debarred [denied] Englishmen’s liberty.” This shows how colonists began to see their identity as Americans as distinct from those from the British mainland.
Remember, a strong thesis statement is one that supports the argument of your writing. It should have a clear purpose and objective, and although you may revise it as you write, it’s a good idea to start with a strong thesis statement the give your essay direction and organization. You can check the quality of your thesis statement by answering the following questions:
- If a specific prompt was provided, does the thesis statement answer the question prompt?
- Does the thesis statement make sense?
- Is the thesis statement historically accurate?
- Does the thesis statement provide clear and cohesive reasoning?
- Is the thesis supportable by evidence?
thesis statement : a statement of the topic of the piece of writing and the angle the writer has on that topic
- Thesis Statements. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/englishcomp1/wp-admin/post.php?post=576&action=edit . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Thesis Examples. Authored by : Cody Chun, Kieran O'Neil, Kylie Young, Julie Nelson Christoph. Provided by : The University of Puget Sound. Located at : https://soundwriting.pugetsound.edu/universal/thesis-dev-six-steps.html . Project : Sound Writing. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Writing Practice: Building Thesis Statements. Provided by : The Bill of Rights Institute, OpenStax, and contributing authors. Located at : https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:L3kRHhAr@7/1-22-%F0%9F%93%9D-Writing-Practice-Building-Thesis-Statements . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].
- Thesis Statement - Writing Tutorials, US History, Dr. Robert Scafe. Provided by : OU Office of Digital Learning. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2hjAk8JI0IY&t=310s . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
19 Standards of Historical Writing
In this chapter, you will learn the basic expectations for writing an undergrad history research paper. At this point in your college career, you’ve likely had a great deal of instruction about writing and you may be wondering why this chapter is here. There are at least three reasons:
- For some of you, those lessons about writing came before you were ready to appreciate or implement them. If you know your writing skills are weak, you should not only pay close attention to this chapter, but also submit early drafts of your work to the History Tutoring Center (at UTA) or another writing coach. Only practice and multiple drafts will improve those skills.
- Those of you who were paying attention in composition courses know the basics, but may lack a good understanding of the format and approach of scholarly writing in history. Other disciplines permit more generalities and relaxed associations than history, which is oriented toward specific contexts and (often, but not always) linear narratives. Moreover, because historians work in a subject often read by non-academics, they place a greater emphasis on clearing up jargon and avoiding convoluted sentence structure. In other words, the standards of historical writing are high and the guidelines that follow will help you reach them.
- Every writer, no matter how confident or experienced, faces writing blocks. Going back to the fundamental structures and explanations may help you get past the blank screen by supplying prompts to help you get started.
As you read the following guide, keep in mind that it represents only our perspective on the basic standards. In all writing, even history research papers, there is room for stylistic variation and elements of a personal style. But one of the standards of historical writing is that only those who fully understand the rules can break them successfully. If you regularly violate the rule against passive voice verb construction or the need for full subject-predicate sentences, you cannot claim the use of sentence fragments or passive voice verbs is “just your style.” Those who normally observe those grammatical rules, in contrast, might on occasion violate them for effect. The best approach is first to demonstrate to your instructor that you can follow rules of grammar and essay structure before you experiment or stray too far from the advice below.
Introductions
Introductions are nearly impossible to get right the first time. Thus, one of the best strategies for writing an introduction to your history essay is to keep it “bare bones” in the first draft, initially working only toward a version that covers the basic requirements. After you’ve written the full paper (and realized what you’re really trying to say, which usually differs from your initial outline), you can come back to the intro and re-draft it accordingly. However, don’t use the likelihood of re-writing your first draft to avoid writing one. Introductions provide templates not only for your readers, but also for you, the writer. A decent “bare bones” introduction can minimize writer’s block as a well-written thesis statement provides a road map for each section of the paper.
So what are the basic requirements? In an introduction, you must:
- Pose a worthwhile question or problem that engages your reader
- Establish that your sources are appropriate for answering the question, and thus that you are a trustworthy guide without unfair biases
- Convince your reader that they will be able to follow your explanation by laying out a clear thesis statement.
Engaging readers in an introduction
When you initiated your research, you asked questions as a part of the process of narrowing your topic (see the “Choosing and Narrowing a Topic” chapter for more info). If all went according to plan, the information you found as you evaluated your primary sources allowed you to narrow your question further, as well as arrive at a plausible answer, or explanation for the problem you posed. (If it didn’t, you’ll need to repeat the process, and either vary your questions or expand your sources. Consult your instructor, who can help identify what contribution your research into a set of primary sources can achieve.) The key task for your introduction is to frame your narrowed research question—or, in the words of some composition instructors, the previously assumed truth that your inquiries have destabilized—in a way that captures the attention of your readers. Common approaches to engaging readers include:
- Telling a short story (or vignette) from your research that illustrates the tension between what readers might have assumed before reading your paper and what you have found to be plausible instead.
- Stating directly what others believe to be true about your topic—perhaps using a quote from a scholar of the subject—and then pointing immediately to an aspect of your research that puts that earlier explanation into doubt.
- Revealing your most unexpected finding, before moving to explain the source that leads you to make the claim, then turning to the ways in which this finding expands our understanding of your topic.
What you do NOT want to do is begin with a far-reaching transhistorical claim about human nature or an open-ended rhetorical question about the nature of history. Grand and thus unprovable claims about “what history tells us” do not inspire confidence in readers. Moreover, such broadly focused beginnings require too much “drilling down” to get to your specific area of inquiry, words that risk losing readers’ interest. Last, beginning with generic ideas is not common to the discipline. Typical essay structures in history do not start broadly and steadily narrow over the course of the essay, like a giant inverted triangle. If thinking in terms of a geometric shape helps you to conceptualize what a good introduction does, think of your introduction as the top tip of a diamond instead. In analytical essays based on research, many history scholars begin with the specific circumstances that need explaining, then broaden out into the larger implications of their findings, before returning to the specifics in their conclusions—following the shape of a diamond.
Clear Thesis Statements
Under the standards of good scholarly writing in the United States—and thus those that should guide your paper—your introduction contains the main argument you will make in your essay. Elsewhere—most commonly in European texts—scholars sometimes build to their argument and reveal it fully only in the conclusion. Do not follow this custom in your essay. Include a well-written thesis statement somewhere in your introduction; it can be the first sentence of your essay, toward the end of the first paragraph, or even a page or so in, should you begin by setting the stage with a vignette. Wherever you place it, make sure your thesis statement meets the following standards:
A good thesis statement :
- Could be debated by informed scholars : Your claim should not be so obvious as to be logically impossible to argue against. Avoid the history equivalent of “the sky was blue.”
- Can be proven with the evidence at hand : In the allotted number of pages, you will need to introduce and explain at least three ways in which you can support your claim, each built on its own pieces of evidence. Making an argument about the role of weather on the outcome of the Civil War might be intriguing, given that such a claim questions conventional explanations for the Union’s victory. But a great deal of weather occurred in four years and Civil War scholars have established many other arguments you would need to counter, making such an argument impossible to establish in the length of even a long research paper. But narrowing the claim—to a specific battle or from a single viewpoint—could make such an argument tenable. Often in student history papers, the thesis incorporates the main primary source into the argument. For example, “As his journal and published correspondence between 1861 and 1864 reveal, Colonel Mustard believed that a few timely shifts in Tennessee’s weather could have altered the outcome of the war.”
- Is specific without being insignificant : Along with avoiding the obvious, stay away from the arcane. “Between 1861 and 1864, January proved to be the worst month for weather in Central Tennessee.” Though this statement about the past is debatable and possible to support with evidence about horrible weather in January and milder-by-comparison weather in other months, it lacks import because it’s not connected to knowledge that concerns historians. Thesis statements should either explicitly or implicitly speak to current historical knowledge—which they can do by refining, reinforcing, nuancing, or expanding what (an)other scholar(s) wrote about a critical event or person.
- P rovide s a “roadmap” to readers : Rather than just state your main argument, considering outlining the key aspects of it, each of which will form a main section of the body of the paper. When you echo these points in transitions between sections, readers will realize they’ve completed one aspect of your argument and are beginning a new part of it. To demonstrate this practice by continuing the fictional Colonel Mustard example above: “As his journal and published correspondence between 1861 and 1864 reveals, Colonel Mustard believed that Tennessee’s weather was critical to the outcome of the Civil War. He linked both winter storms and spring floods in Tennessee to the outcome of key battles and highlighted the weather’s role in tardy supply transport in the critical year of 1863.” Such a thesis cues the reader that evidence and explanations about 1) winter storms; 2) spring floods; and 3) weather-slowed supply transport that will form the main elements of the essay.
Thesis Statement Practice
More Thesis Statement Practice
The Body of the Paper
What makes a good paragraph.
While an engaging introduction and solid conclusion are important, the key to drafting a good essay is to write good paragraphs. That probably seems obvious, but too many students treat paragraphs as just a collection of a few sentences without considering the logic and rules that make a good paragraph. In essence, in a research paper such as the type required in a history course, for each paragraph you should follow the same rules as the paper itself. That is, a good paragraph has a topic sentence, evidence that builds to make a point, and a conclusion that ties the point to the larger argument of the paper. On one hand, given that it has so much work to do, paragraphs are three sentences , at a minimum . On the other hand, because paragraphs should be focused to making a single point, they are seldom more than six to seven sentences . Though rules about number of sentences are not hard and fast, keeping the guidelines in mind can help you construct tightly focused paragraphs in which your evidence is fully explained.
Topic sentences
The first sentence of every paragraph in a research paper (or very occasionally the second) should state a claim that you will defend in the paragraph . Every sentence in the paragraph should contribute to that topic. If you read back over your paragraph and find that you have included several different ideas, the paragraph lacks focus. Go back, figure out the job that this paragraph needs to do—showing why an individual is important, establishing that many accept an argument that you plan on countering, explaining why a particular primary source can help answer your research question, etc. Then rework your topic sentence until it correctly frames the point you need to make. Next, cut out (and likely move) the sentences that don’t contribute to that outcome. The sentences you removed may well help you construct the next paragraph, as they could be important ideas, just not ones that fit with the topic of the current paragraph. Every sentence needs to be located in a paragraph with a topic sentence that alerts the reader about what’s to come.
Transitions/Bridges/Conclusion sentences in paragraphs
All good writers help their readers by including transition sentences or phrases in their paragraphs, often either at the paragraph’s end or as an initial phrase in the topic sentence. A transition sentence can either connect two sections of the paper or provide a bridge from one paragraph to the next. These sentences clarify how the evidence discussed in the paragraph ties into the thesis of the paper and help readers follow the argument. Such a sentence is characterized by a clause that summarizes the info above, and points toward the agenda of the next paragraph. For example, if the current section of your paper focused on the negative aspects of your subject’s early career, but your thesis maintains he was a late-developing military genius, a transition between part one (on the negative early career) and part two (discussing your first piece of evidence revealing genius) might note that “These initial disastrous strategies were not a good predictor of General Smith’s mature years, however, as his 1841 experience reveals.” Such a sentence underscores for the reader what has just been argued (General Smith had a rough start) and sets up what’s to come (1841 was a critical turning point).
Explaining Evidence
Just as transitional sentences re-state points already made for clarity’s sake, “stitching” phrases or sentences that set-up and/or follow quotations from sources provide a certain amount of repetition. Re-stating significant points of analysis using different terms is one way you explain your evidence. Another way is by never allowing a quote from a source to stand on its own, as though its meaning was self-evident. It isn’t and indeed, what you, the writer, believes to be obvious seldom is. When in doubt, explain more.
For more about when to use a quotation and how to set it up see “How to quote” in the next section on Notes and Quotation.”
Conclusio ns
There exists one basic rule for conclusions: Summarize the paper you have written . Do not introduce new ideas, launch briefly into a second essay based on a different thesis, or claim a larger implication based on research not yet completed. This final paragraph is NOT a chance to comment on “what history tells us” or other lessons for humankind. Your conclusion should rest, more or less, on your thesis, albeit using different language from the introduction and evolved, or enriched, by examples discussed throughout the paper. Keep your conclusion relevant and short, and you’ll be fine.
For a checklist of things you need before you write or a rubric to evaluate your writing click here
How History is Made: A Student’s Guide to Reading, Writing, and Thinking in the Discipline Copyright © 2022 by Stephanie Cole; Kimberly Breuer; Scott W. Palmer; and Brandon Blakeslee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Tool in School: Quizlet
- Posted May 22, 2018
- By Lory Hough

When 15-year-old Andrew Sutherland created a software program in 2005 to help him study 111 French terms for a test on animals, little did he imagine that the program would eventually become one of the fastest-growing free education tools, with 30 million monthly users from 130 countries.
“Quizlet has absolutely become a valuable tool,” Sutherland says. “In the United States, half of all high school students and a third of all college students use us every month. That’s not something I expected to happen when I made it in high school, and it speaks to how essential it has become.”
Part of the appeal is that Quizlet takes a simple idea — picture paper flash cards — but gives it a modern twist. Online users create study sets (terms and definitions) or use study sets created by others, including classmates. They then have multiple ways to study the information: virtual flashcards or typing in answers to written or audio prompts. There are also two games: match (drag the correct answer) and gravity (type the correct answer as asteroids fall).
The online format is key, he says. “The appeal of a digital learning tool is that it can ask much more dynamic questions than what you can do with paper. Quizlet can figure out what material you’re struggling with and just focus on that. It can also verify what you know and coach you to only stop studying when it thinks you’re ready.”
Recently, they launched Quizlet Live for students to work in teams during class. Teacher feedback was key, he says, but adds, “My favorite type of feedback is hearing from teachers about new-use cases. The other day I was at a chocolate store and wearing my Quizlet shirt. The woman there said she uses Quizlet to train all their new employees about their chocolate. I want that job!”

Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Can Tablets Transform Teaching?

For Note Taking, Low-Tech Is Often Best

Harnessing AI's Powers For All
Visiting Professor Seiji Isotani explores how behavioral science and technology can make a positive impact on education
The Essay: History and Definition
Attempts at Defining Slippery Literary Form
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
"One damned thing after another" is how Aldous Huxley described the essay: "a literary device for saying almost everything about almost anything."
As definitions go, Huxley's is no more or less exact than Francis Bacon's "dispersed meditations," Samuel Johnson's "loose sally of the mind" or Edward Hoagland's "greased pig."
Since Montaigne adopted the term "essay" in the 16th century to describe his "attempts" at self-portrayal in prose , this slippery form has resisted any sort of precise, universal definition. But that won't an attempt to define the term in this brief article.
In the broadest sense, the term "essay" can refer to just about any short piece of nonfiction -- an editorial, feature story, critical study, even an excerpt from a book. However, literary definitions of a genre are usually a bit fussier.
One way to start is to draw a distinction between articles , which are read primarily for the information they contain, and essays, in which the pleasure of reading takes precedence over the information in the text . Although handy, this loose division points chiefly to kinds of reading rather than to kinds of texts. So here are some other ways that the essay might be defined.
Standard definitions often stress the loose structure or apparent shapelessness of the essay. Johnson, for example, called the essay "an irregular, indigested piece, not a regular and orderly performance."
True, the writings of several well-known essayists ( William Hazlitt and Ralph Waldo Emerson , for instance, after the fashion of Montaigne) can be recognized by the casual nature of their explorations -- or "ramblings." But that's not to say that anything goes. Each of these essayists follows certain organizing principles of his own.
Oddly enough, critics haven't paid much attention to the principles of design actually employed by successful essayists. These principles are rarely formal patterns of organization , that is, the "modes of exposition" found in many composition textbooks. Instead, they might be described as patterns of thought -- progressions of a mind working out an idea.
Unfortunately, the customary divisions of the essay into opposing types -- formal and informal, impersonal and familiar -- are also troublesome. Consider this suspiciously neat dividing line drawn by Michele Richman:
Post-Montaigne, the essay split into two distinct modalities: One remained informal, personal, intimate, relaxed, conversational and often humorous; the other, dogmatic, impersonal, systematic and expository .
The terms used here to qualify the term "essay" are convenient as a kind of critical shorthand, but they're imprecise at best and potentially contradictory. Informal can describe either the shape or the tone of the work -- or both. Personal refers to the stance of the essayist, conversational to the language of the piece, and expository to its content and aim. When the writings of particular essayists are studied carefully, Richman's "distinct modalities" grow increasingly vague.
But as fuzzy as these terms might be, the qualities of shape and personality, form and voice, are clearly integral to an understanding of the essay as an artful literary kind.
Many of the terms used to characterize the essay -- personal, familiar, intimate, subjective, friendly, conversational -- represent efforts to identify the genre's most powerful organizing force: the rhetorical voice or projected character (or persona ) of the essayist.
In his study of Charles Lamb , Fred Randel observes that the "principal declared allegiance" of the essay is to "the experience of the essayistic voice." Similarly, British author Virginia Woolf has described this textual quality of personality or voice as "the essayist's most proper but most dangerous and delicate tool."
Similarly, at the beginning of "Walden, " Henry David Thoreau reminds the reader that "it is ... always the first person that is speaking." Whether expressed directly or not, there's always an "I" in the essay -- a voice shaping the text and fashioning a role for the reader.
Fictional Qualities
The terms "voice" and "persona" are often used interchangeably to suggest the rhetorical nature of the essayist himself on the page. At times an author may consciously strike a pose or play a role. He can, as E.B. White confirms in his preface to "The Essays," "be any sort of person, according to his mood or his subject matter."
In "What I Think, What I Am," essayist Edward Hoagland points out that "the artful 'I' of an essay can be as chameleon as any narrator in fiction." Similar considerations of voice and persona lead Carl H. Klaus to conclude that the essay is "profoundly fictive":
It seems to convey the sense of human presence that is indisputably related to its author's deepest sense of self, but that is also a complex illusion of that self -- an enactment of it as if it were both in the process of thought and in the process of sharing the outcome of that thought with others.
But to acknowledge the fictional qualities of the essay isn't to deny its special status as nonfiction.
Reader's Role
A basic aspect of the relationship between a writer (or a writer's persona) and a reader (the implied audience ) is the presumption that what the essayist says is literally true. The difference between a short story, say, and an autobiographical essay lies less in the narrative structure or the nature of the material than in the narrator's implied contract with the reader about the kind of truth being offered.
Under the terms of this contract, the essayist presents experience as it actually occurred -- as it occurred, that is, in the version by the essayist. The narrator of an essay, the editor George Dillon says, "attempts to convince the reader that its model of experience of the world is valid."
In other words, the reader of an essay is called on to join in the making of meaning. And it's up to the reader to decide whether to play along. Viewed in this way, the drama of an essay might lie in the conflict between the conceptions of self and world that the reader brings to a text and the conceptions that the essayist tries to arouse.
At Last, a Definition—of Sorts
With these thoughts in mind, the essay might be defined as a short work of nonfiction, often artfully disordered and highly polished, in which an authorial voice invites an implied reader to accept as authentic a certain textual mode of experience.
Sure. But it's still a greased pig.
Sometimes the best way to learn exactly what an essay is -- is to read some great ones. You'll find more than 300 of them in this collection of Classic British and American Essays and Speeches .
- What is a Familiar Essay in Composition?
- What Does "Persona" Mean?
- What Are the Different Types and Characteristics of Essays?
- What Is a Personal Essay (Personal Statement)?
- The Writer's Voice in Literature and Rhetoric
- Rhetorical Analysis Definition and Examples
- Point of View in Grammar and Composition
- What Is Colloquial Style or Language?
- What Is Literary Journalism?
- Definition and Examples of Formal Essays
- What Is Expository Writing?
- First-Person Point of View
- The Difference Between an Article and an Essay
- An Introduction to Literary Nonfiction
- Third-Person Point of View
Self-Paced Courses : Explore American history with top historians at your own time and pace!
- AP US History Study Guide
- History U: Courses for High School Students
- History School: Summer Enrichment
- Lesson Plans
- Classroom Resources
- Spotlights on Primary Sources
- Professional Development (Academic Year)
- Professional Development (Summer)
- Book Breaks
- Inside the Vault
- Self-Paced Courses
- Browse All Resources
- Search by Issue
- Search by Essay
- Become a Member (Free)
- Monthly Offer (Free for Members)
- Program Information
- Scholarships and Financial Aid
- Applying and Enrolling
- Eligibility (In-Person)
- EduHam Online
- Hamilton Cast Read Alongs
- Official Website
- Press Coverage
- Veterans Legacy Program
- The Declaration at 250
- Black Lives in the Founding Era
- Celebrating American Historical Holidays
- Browse All Programs
- Donate Items to the Collection
- Search Our Catalog
- Research Guides
- Rights and Reproductions
- See Our Documents on Display
- Bring an Exhibition to Your Organization
- Interactive Exhibitions Online
- About the Transcription Program
- Civil War Letters
- Founding Era Newspapers
- College Fellowships in American History
- Scholarly Fellowship Program
- Richard Gilder History Prize
- David McCullough Essay Prize
- Affiliate School Scholarships
- Nominate a Teacher
- Eligibility
- State Winners
- National Winners
- Gilder Lehrman Lincoln Prize
- Gilder Lehrman Military History Prize
- George Washington Prize
- Frederick Douglass Book Prize
- Our Mission and History
- Annual Report
- Contact Information
- Student Advisory Council
- Teacher Advisory Council
- Board of Trustees
- Remembering Richard Gilder
- President's Council
- Scholarly Advisory Board
- Internships
- Our Partners
- Press Releases
Period 3: 1754–1800 (AP US History)
Period 3: 1754-1800.
British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles over the new nation’s social, political, and economic identity. Topics may include:
The Seven Years’ War
The american revolution, the articles of confederation, the creation and ratification of the constitution, developing an american identity, immigration to and migration within america.
Image Source : A detail from A View of Part of the Town of Boston in New-England and Brittish Ships of War Landing Their Troops, 1768 , a broadside by Paul Revere and Christian Remick, printed in Boston, 1770. (The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC02873)
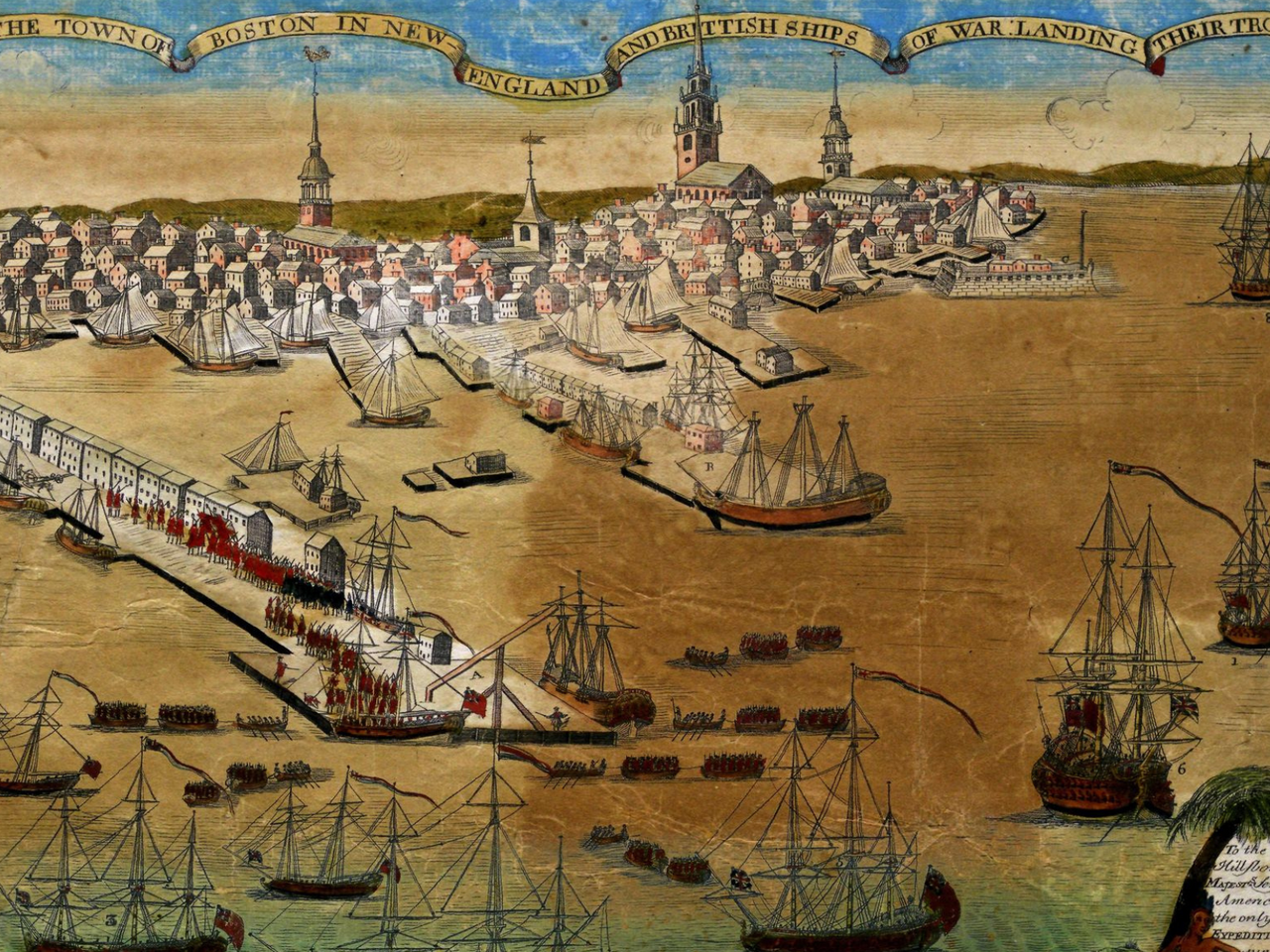

10–17% Exam Weighting
Resources by Period:
- Period 1: 1491–1607
- Period 2: 1607–1754
- Period 3: 1754–1800
- Period 4: 1800–1848
- Period 5: 1844–1877
- Period 6: 1865–1898
- Period 7: 1890–1945
- Period 8: 1945–1980
- Period 9: 1980–Present
Key Concepts
3.1 : British attempts to assert tighter control over its North American colonies and the colonial resolve to pursue self-government led to a colonial independence movement and the Revolutionary War.
3.2 : The American Revolution’s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government.
3.3 : Migration within North America and competition over resources, boundaries, and trade intensified conflicts among peoples and nations.

The state of the English colonies
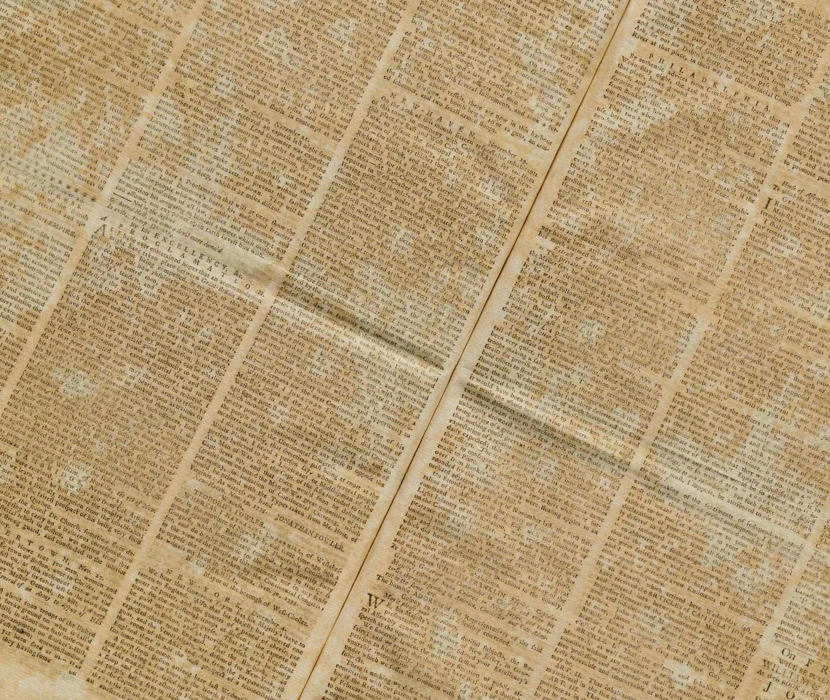
Newspaper article drumming up support for the British in the French and Indian War
- Primary Source

Proclamation of 1763
Proclamation limiting White settlement and interaction with Indigenous peoples

The French and Indian War
By andrew robertson.
Watch a discussion of how Americans' view of themselves as British changed.
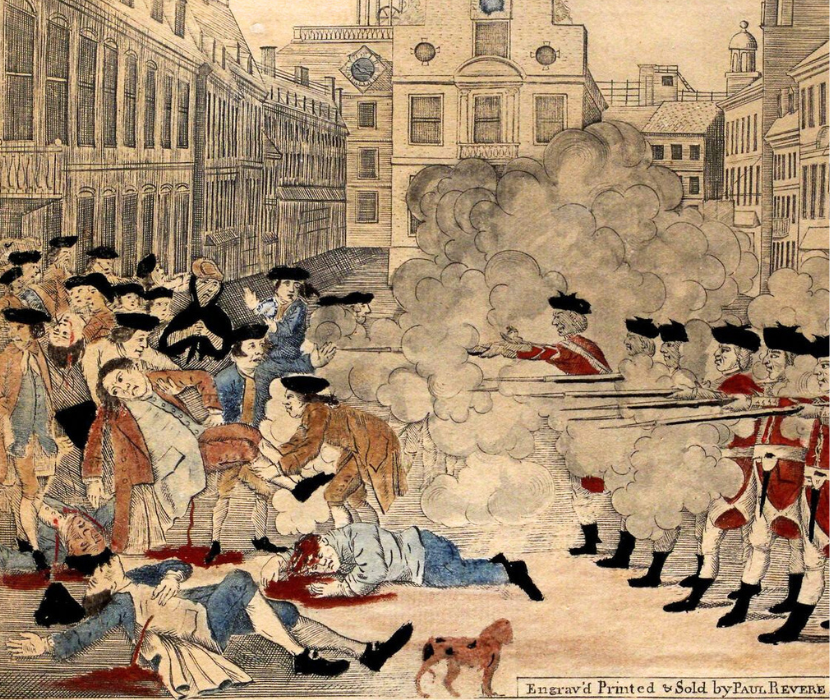

The Bloody Massacre
Paul Revere's propaganda representing the Boston "Massacre"
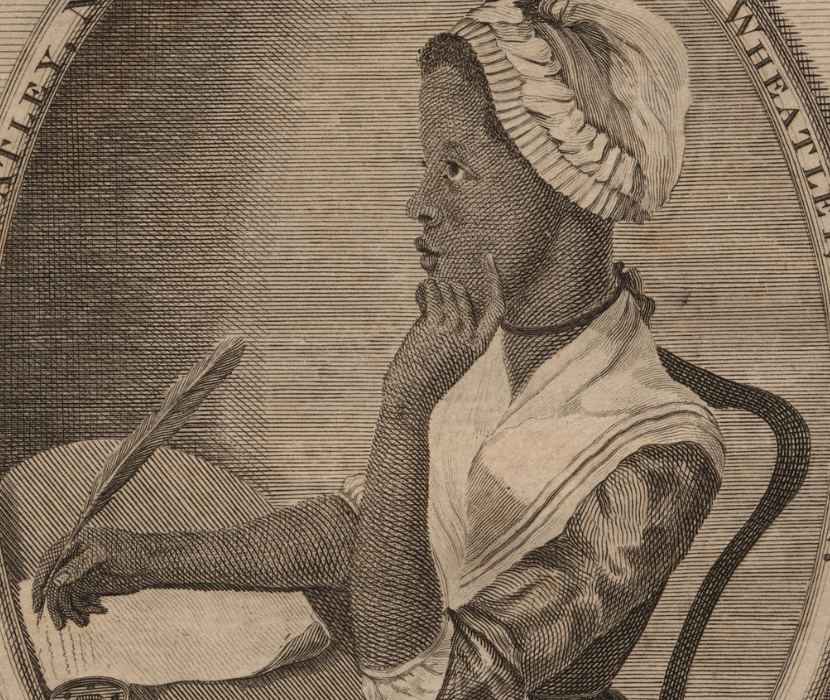

Poem on tyranny and slavery
Poem by Phillis Wheatley published in her 1773 book of poetry
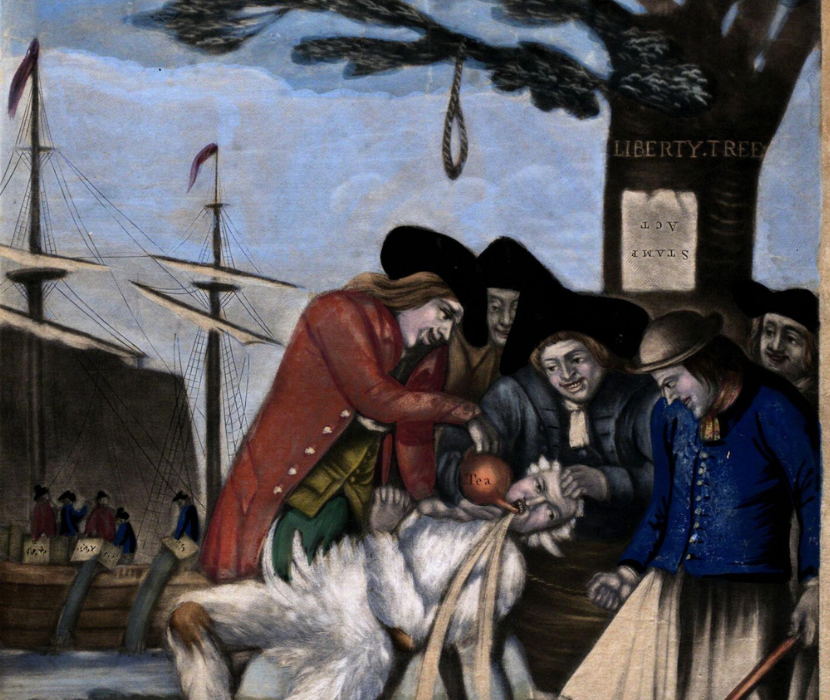
Unruly Americans in the Revolution
By woody holton.
Learn about the role of ordinary citizens in the fight for independence.

The American Revolution, 1763–1783
By pauline maier.
Learn more about the American Revolution from a timeline and a comprehensive essay.

The Stamp Act
Tax requiring colonists to pay for a stamp on printed materials to help subsidize British troops in the colonies

A report on reaction to the Stamp Act
Merchant and rising politician from Nova Scotia covers colonial impressions of the new tax

Taxation and Representation
By gordon s. wood.
Watch a discussion of the connection between taxation and representation in the leadup to the Revolutionary War.

The Battles of Lexington and Concord
Broadside detailing the “Bloody Butchery by the British Troops"

Lord Dunmore's Proclamation
The British threat to free enslaved Virginians

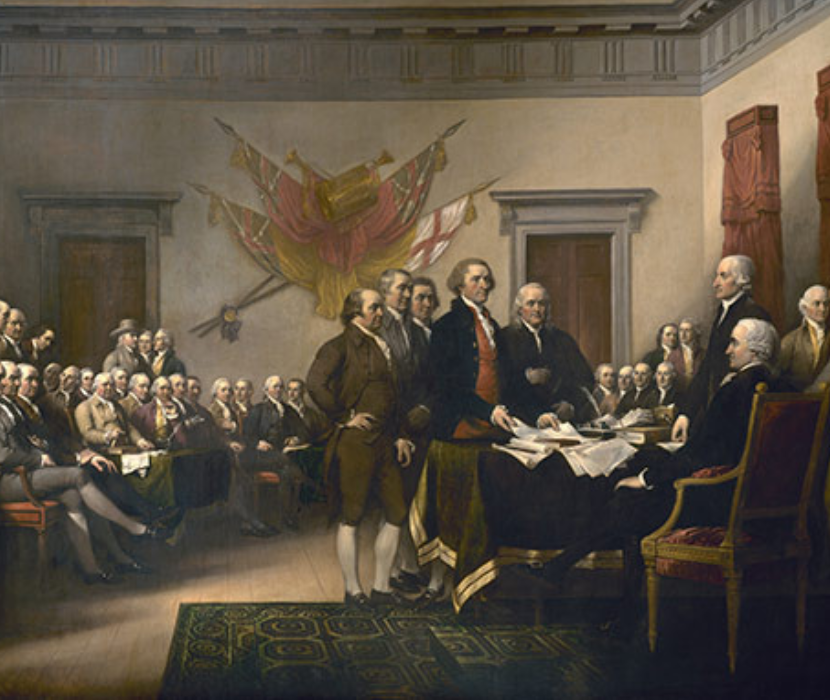
The Declaration of Independence
A unique copy printed in South Carolina by patriotic printer Peter Timothy

The Indians’ War of Independence
By colin g. calloway.
Learn about the role of American Indians during the Revolutionary War.
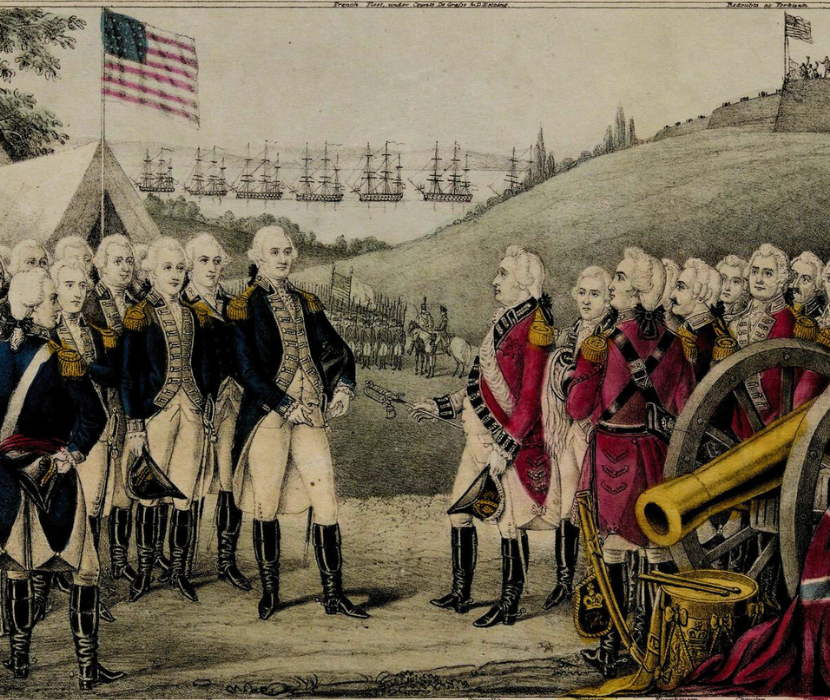

by James Kirby Martin
Learn the reasons for Cornwallis's loss at Yorktown and America’s victory in the War for Independence.

Watch a discussion of why the British were blamed for the Revolutionary War.
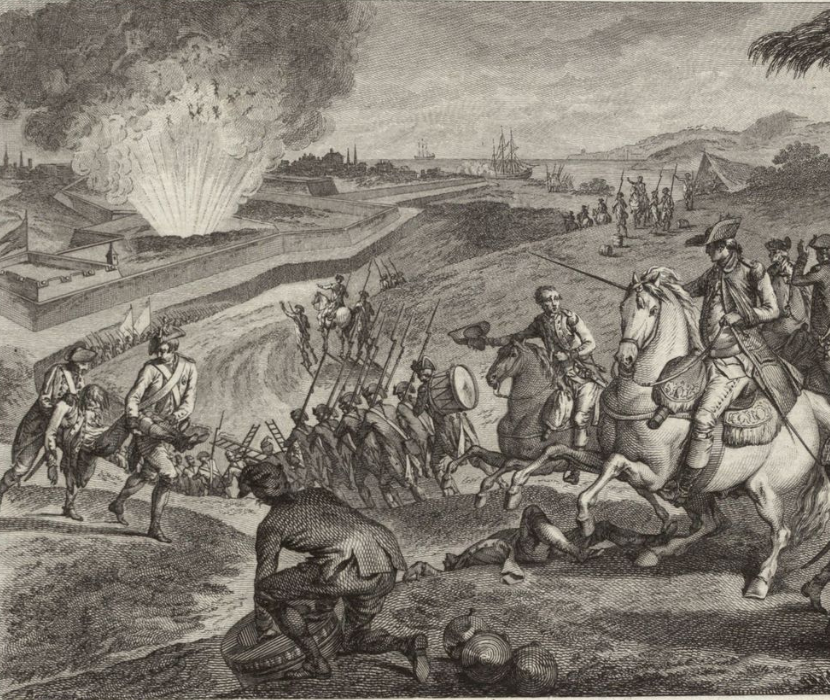

The Siege of Pensacola
By kathleen duval.
Read about Bernardo de Gálvez's efforts to recruit free Black men and Native Americans for Spain's fight against the British.

Lockean Liberalism and the American Revolution
By isaac kramnick.
Learn about the influence of Enlightenment philosopher John Locke.


Understanding the Articles of Confederation
By denver brunsman.
Watch a discussion of the context and key components of the Articles of Confederation.

Establishment of the first US government balancing state and national interests
George Washington on the Constitutional Convention
Letter to Henry Knox discussing Shays’ Rebellion and the upcoming Constitutional Convention

Two versions of the Preamble to the Constitution
Drafts showing the shift from a confederation of states to a united country

Ratification of the US Constitution in New York
Broadside of the Constitution with Washington’s letter of support

Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists
By carol berkin.
Watch a discussion of the arguments between the Federalists and Anti-Federalists.

Calling the Constitutional Convention
Watch a discussion of why the Constitutional Convention was called.
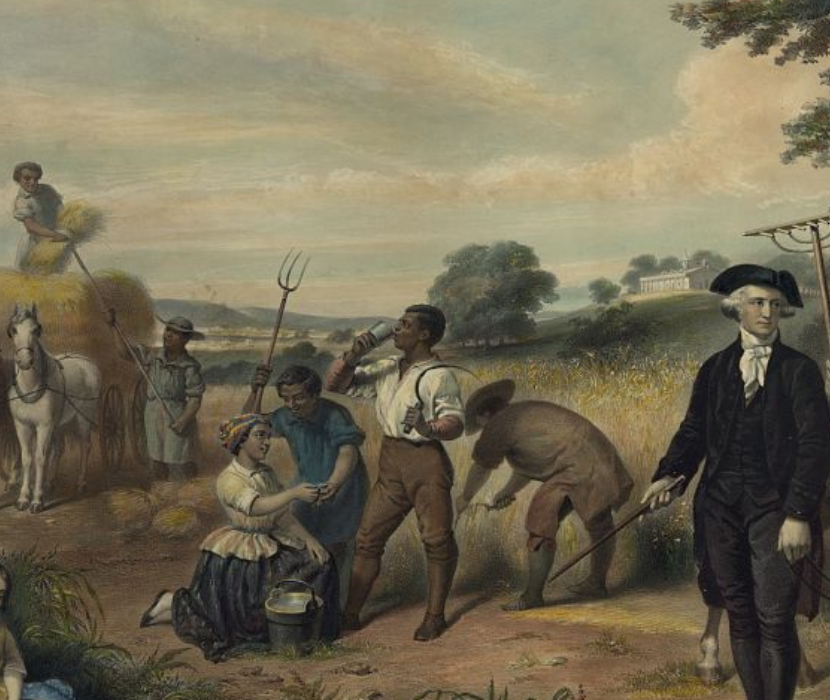

Slavery and the American Revolution
By james oliver horton.
Watch a discussion on the American Revolution in relation to African enslavement.
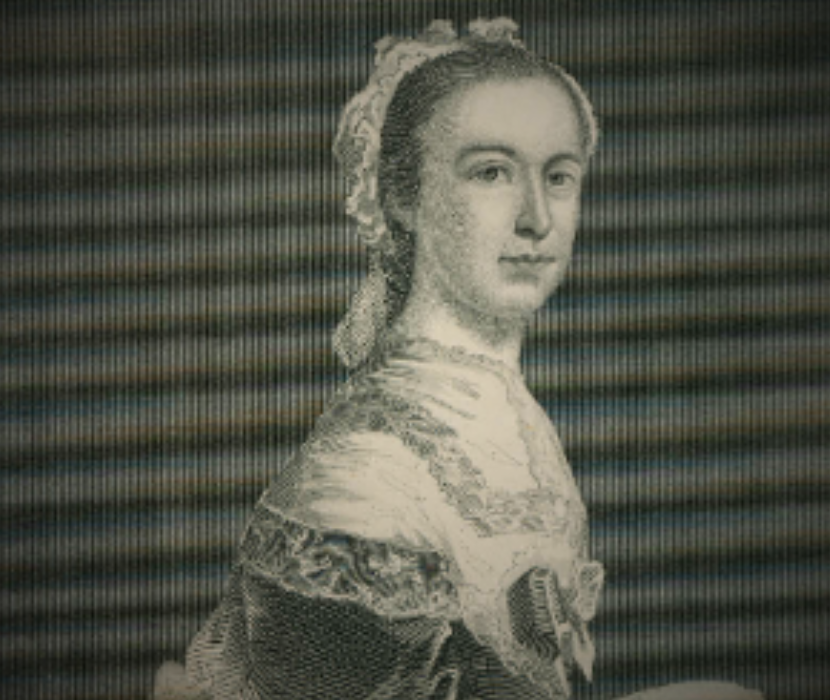

The Legal Status of Women, 1776–1830
By marylynn salmon.
Learn about the rights of women in the founding era.
George Washington on the abolition of slavery
Letter to John Francis Mercer describing Washington's private views on slavery

Hamilton’s Report on the Subject of Manufactures
A report advocating tariffs to protect American industry from foreign competition

Washington's Most Significant Act
Watch a discussion of the importance of George Washington stepping down as general.

George Washington’s reluctance to become president
Letter to Henry Knox as Washington prepares to travel to his inauguration

George Washington’s First Inaugural Address
Washington explaining the fundamental principle of the American democratic revolution

The Righteous Revolution of Mercy Otis Warren
By ray raphael.
Explore the role of writer Mercy Otis Warren in the fight for independence and equality.
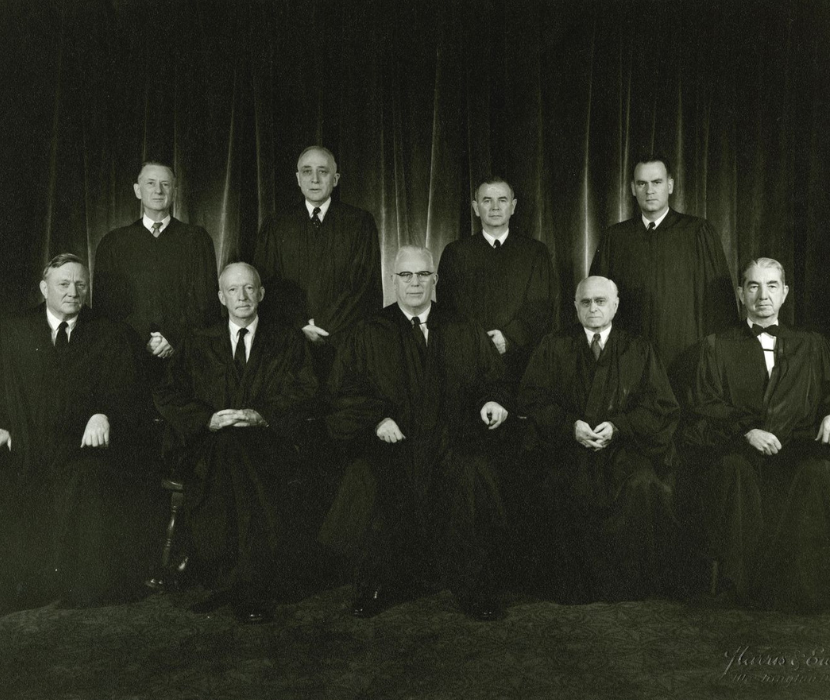

The Supreme Court Then and Now
By a. e. dick howard.
Read about the development of judicial review through US history.

Women and the Revolution
Watch a discussion of the significance of women in the leadup to the American Revolution.

The Significance of the American Revolution
Watch a discussion of the transformative nature of the American Revolution

The League of the Iroquois
By matthew dennis.
Learn about the Six Nations and Tripartite Agreement.

A Nation of Immigrants from the Outset
By james basker and sofia melnychuck.
Learn about the economic and religious diversity of the Continental Congress and signers of the Declaration of Independence.

Receipt for land purchased from the Six Nations
Document outlining the acquisition of land with Native leaders' names
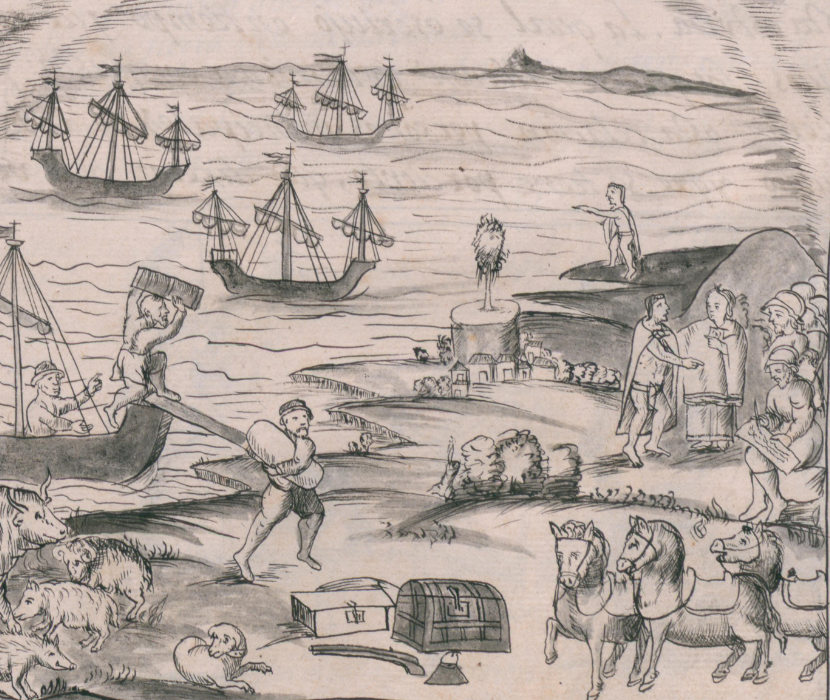

Hispanics in the United States: Origins and Destinies
By rubén g. rumbaut.
Read about Spanish migration to the Americas from the sixteenth to eighteenth centuries.

The impact of Horse Culture
By elliott west.
Read the return of the horse to the Americas, indigenous migration, and the hunting of buffalo.

Early America’s Jewish Settlers
By eli faber.
Read about the causes and consequences of early Jewish migration to North America.
American History Timeline: 1754-1800
Image citations.
Listed in order of appearance in the sections above
- Maryland Gazette, May 22, 1755. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC08719.
- George III. Proclamation, October 7, 1763. Broadside. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC05214.
- Leonard, Ephraim. "To Joseph Hall, 'Captain of a military foot Company in the Town of Taunton,'" August 11, 1757. Manuscript. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC01450.199.01.
- Revere, Paul. The Bloody Massacre perpetrated in King-Street Boston on March 5th 1770 by a party of the 29th Reg. Boston, 1770. Broadside. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC01868.
- Unidentified Artist. A Portrait of Phyllis Wheatley. 1773, Engraving on Paper. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC06154.
- Dawe, Philip. The Bostonian's Paying the Excise-man, or Tarring & Feathering. London, 1774. Engraving. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC04961.01.
- Trumball, John. Declaration of Independence. Washington D.C., 1826. Oil on Canvas, U.S. Capitol Rotunda.
- Stamp Act, 1765, 5 Geo. 3, c. 1. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00769. Hinshelwood, Archibald. Letter to Joshua Mauger, August 19, 1765. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC03902.061.
- US Congress. Instructions to the Commanders of private Ships or Vessels of War, which shall have Commissions or Letters of Marque and Reprisal, authorising them to make Captures of British Vessels and Cargoes, April 3, 1776. s.l., ca. 1777-1778. Broadside. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00038.02.
- Russell, Ezekiel. Bloody Butchery by the British Troops. Salem, MA, 1775. Broadside. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC04810.
- Pennsylvania Journal and Weekly Advertiser, No. 1674 (January 4, 1774) - No. 1725 (December 27, 1775) [with gaps]. Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC01706_00124.
- Continental Congress. Declaration of Independence, 1776. Washington DC, 1823. Facsimile engraving by William J. Stone. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00154.02.
- Baillie, James S. Surrender of Cornwallis. New York, 1845. Lithograph. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC02918.02.
- Pendleton, Edmund. Letter to James Madison, April 17, 1765. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00099.026.
- Godefroy, François. Recueil d'estampes représentant les différents evenémens de la Guerre qui a procuré l'indépendance aux Etats Unis de l'Amérique. Paris, ca. 1784. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC06551.
- Locke, John. Essay Concerning Humane Understanding. London: Eliz. Holt, 1690. The Gilder Institute of American History. GLC00320.
- Continental Congress. Articles of Confederation. Lancaster, PA, 1777. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC04759.
- Continental Congress. Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union between the States of New-Hampshire, Massachusetts-Bay, Rhode-Island and Providence Plantations, Connecticut, New-York, New-Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. Boston, MA, 1777. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00268.
- Washington, George. Letter to Henry Knox, February 3, 1787. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC02437.09410.
- Constitutional Convention. Committee of Detail. US Constitution [printing of first draft], August 6, 1787. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00819.01.
- Constitutional Convention. US Constitution. Albany, NY, 1788. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC07866.
- Carrington, Edward. Letter to Henry Knox, March 13, 1788. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC02437.03821.
- Pendleton, Edmund. Letter to James Madison, August 12, 1787. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00099.123.
- Régnier, Claude, engraver. Life of George Washington--The Farmer. Lemercier. Paris, ca. 1853. Lithograph based on a painting by Junius Brutus Stearns. Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division.
- Unidentified artist, engraver. Mercy Warren. s.l., n.d. Engraving based on a painting by John Singleton Copley. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC08878.0726.
- Hamilton, Alexander. Report of the Secretary of the Treasury of the United States, on the Subject of Manufactures. New York, 1791. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00891.
- Washington, George. Farewell Address. In Claypoole's American Daily Advertiser, September 19, 1796. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC00185.
- Washington, George. Letter to Henry Knox, April 1, 1789. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC02437.09410.
- Washington, George. First Inaugural Address. Gazette of the United States, May 2, 1789. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC03518.
- Warren, Mercy Otis. Letter to Catharine Macaulay, December 29, 1774. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC01800.01.
- Harris & Ewing. Supreme Court Justices. Washington DC, ca. 1940. Photograph. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC02929.01.
- Rogers, J., engraver. Moll Pitcher at the Battle of Monmouth. New York, 1856. Engraving based on a painting by D. M. Carter. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC08878.0067.
- Trumbull, John, painter, Washington Lays Down His Sword. Washington D.C., 1826. Oil on Canvas. Capital Rotunda, Architect of the Capital.
- Cusick, David (Tuscarora). Three Iroquois: Atotárho Protected by Black Snakes, Flanked by Deganawida(?) Offering Wampum and Hiawatha(?). ca. 1827. Watercolor and ink over graphite on paper. Collections of the New-York Historical Society.
- Sadd, Henry S., engraver. The First Prayer in Congress. New York, John Neale, 1848. Engraving based on a painting by T. H. Matteson. Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division.
- Iroquois Nation. Six Nations. Receipt for land sale signed with the totems of fourteen Indigenous leaders. [Lancaster, PA], 1769. The Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History, GLC02548.
- Sahagún, Bernardino de. Historia general de las coasas de nueva España [General History of the Things of New Spain]: The Florentine Codex. s.l., 1577. Library of Congress.
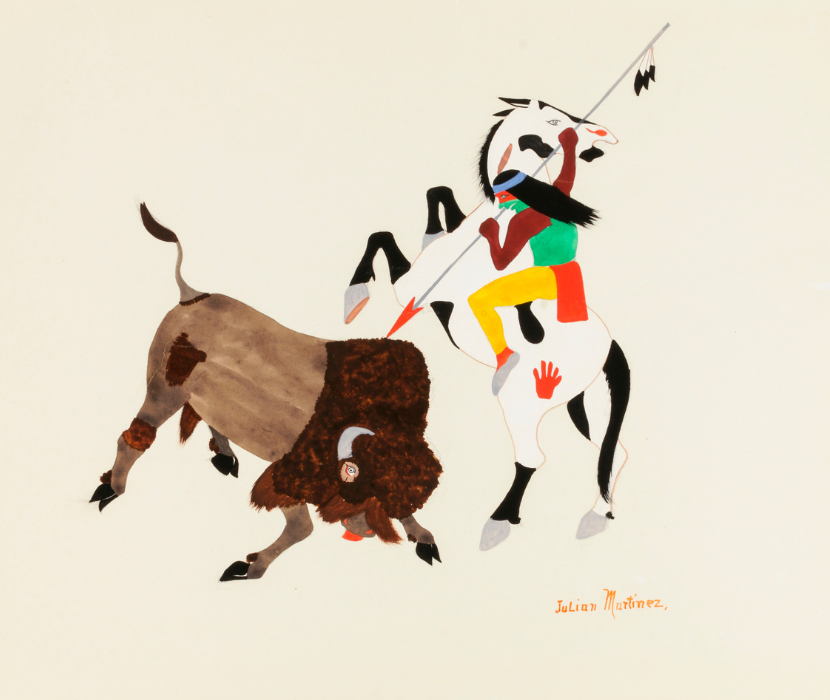
- Martinez, Julian. Buffalo Hunter, ca. 1920-1925, watercolor, ink, and pencil on paperboard, sheet: 11 1/8 x 14 1/4 in. (28.4 x 36.2 cm), Smithsonian American Art Museum, Corbin-Henderson Collection, Gift of Alice H. Rossin, 1979.144.84
- Lazarus, Emma. "The New Colossus." 1883. Manuscript bound in journal. Courtesy of the American Jewish Historical Society, New York and Newton Centre, Massachusetts.
Stay up to date, and subscribe to our quarterly newsletter.
Learn how the Institute impacts history education through our work guiding teachers, energizing students, and supporting research.
Chapter 13 Introductory Essay: 1945-1960

Written by: Patrick Allitt, Emory University
By the end of this section, you will:.
- Explain the context for societal change from 1945 to 1960
- Explain the extent to which the events of the period from 1945 to 1960 reshaped national identity
Introduction
World War II ended in 1945. The United States and the Soviet Union had cooperated to defeat Nazi Germany, but they mistrusted each other. Joseph Stalin, the Soviet dictator, believed the Americans had waited too long before launching the D-Day invasion of France in 1944, leaving his people to bear the full brunt of the German war machine. It was true that Soviet casualties were more than 20 million, whereas American casualties in all theaters of war were fewer than half a million.
On the other hand, Harry Truman, Franklin Roosevelt’s vice president, who had become president after Roosevelt’s death in April 1945, believed Stalin had betrayed a promise made to Roosevelt at the Yalta summit in February 1945. That promise was to permit all the nations of Europe to become independent and self-governing at the war’s end. Instead, Stalin installed Soviet puppet governments in Poland, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Rumania, Hungary, and Bulgaria, the parts of Europe his armies had recaptured from the Nazis.
These tensions between the two countries set the stage for the Cold War that came to dominate foreign and domestic policy during the postwar era. The world’s two superpowers turned from allies into ideological and strategic enemies as they struggled to protect and spread their systems around the world, while at the same time developing arsenals of nuclear weapons that could destroy it. Domestically, the United States emerged from the war as the world’s unchallenged economic powerhouse and enjoyed great prosperity from pent-up consumer demand and industrial dominance. Americans generally supported preserving the New Deal welfare state and the postwar anti-communist crusade. While millions of white middle-class Americans moved to settle down in the suburbs, African Americans had fought a war against racism abroad and were prepared to challenge it at home.
The Truman Doctrine and the Cold War
Journalists nicknamed the deteriorating relationship between the two great powers a “ cold war ,” and the name stuck. In the short run, America possessed the great advantage of being the only possessor of nuclear weapons as a result of the Manhattan Project. It had used two of them against the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki to end the war in the Far East, with destructive power so fearsome it deterred Soviet aggression. But after nearly four years of war, Truman was reluctant to risk a future conflict. Instead, with congressional support, he pledged to keep American forces in Europe to prevent any more Soviet advances. This was the “ Truman Doctrine ,” a dramatic contrast with the American decision after World War I to withdraw from European affairs. (See the Harry S. Truman, “Truman Doctrine” Address, March 1947 Primary Source.)

President Harry Truman pictured here in his official presidential portrait pledged to counter Soviet geopolitical expansion with his “Truman Doctrine.”
The National Security Act, passed by Congress in 1947, reorganized the relationship between the military forces and the government. It created the National Security Council (NSC), the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), and the office of Secretary of Defense. The Air Force, previously a branch of the U.S. Army, now became independent, a reflection of its new importance in an era of nuclear weapons. Eventually, NSC-68, a secret memorandum from 1950, was used to authorize large increases in American military strength and aid to its allies, aiming to ensure a high degree of readiness for war against the Soviet Union.
What made the Soviet Union tick? George Kennan, an American diplomat at the U.S. Embassy in Moscow who knew the Soviets as well as anyone in American government, wrote an influential article titled “The Sources of Soviet Conduct.” Originally sent from Moscow as a long telegram, it was later published in the journal Foreign Affairs under the byline “X” and impressed nearly all senior American policy makers in Washington, DC. The Soviets, said Kennan, believed capitalism and communism could not coexist and that they would be perpetually at war until one was destroyed. According to Kennan, the Soviets believed communism was destined to dominate the world. They were disciplined and patient, however, and understood “the logic of force.” Therefore, said Kennan, the United States must be equally patient, keeping watch everywhere to “contain” the threat.
Containment became the guiding principle of U.S. anti-Soviet policy, under which the United States deployed military, economic, and cultural resources to halt Soviet expansion. In 1948, the United States gave more than $12 billion to Western Europe to relieve suffering and help rebuild and integrate the economies through the Marshall Plan. The Europeans would thus not turn to communism in their desperation and America would promote mutual prosperity through trade. The Berlin crisis of 1948–1949 was the policy’s first great test. (See the George Kennan (“Mr. X”), “Sources of Soviet Conduct,” July 1947 Primary Source.)
Berlin, jointly occupied by the major powers, lay inside Soviet-dominated East Germany, but access roads led to it from the West. In June 1948, Soviet forces cut these roads, hoping the Americans would permit the whole of Berlin to fall into the Soviet sphere rather than risk war. Truman and his advisors, recognizing the symbolic importance of Berlin but reluctant to fire the first shot, responded by having supplies flown into West Berlin, using aircraft that had dropped bombs on Berlin just three years earlier. Grateful Berliners called them the “raisin bombers” in tribute to one of the foods they brought.
After 11 months, recognizing their plan had failed, the Soviets relented. West Berlin remained part of West Germany, making the first test of containment a success. On the other hand, the United States was powerless to prevent a complete Communist takeover in Czechoslovakia, whose government had shown some elements of independence from Moscow’s direction. (See The Berlin Airlift Narrative.)
Alarm about the Czech situation hastened the American decision to begin re-arming West Germany, where an imperfect and incomplete process of “de-Nazification” had taken place. The United States also supervised the creation in 1949 of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), an alliance of Western nations to forestall Soviet aggression in central Europe. The U.S. government also continued research on and development of new and more powerful nuclear weapons. Americans were dismayed to learn, in 1949, that the Soviets had successfully tested an atomic bomb of their own, greatly facilitated by information provided by Soviet spies. Europe and much of the world were divided between the world’s two superpowers and their allies.

U.S. Secretary of State Dean Acheson along with the foreign ministers of Canada and 10 European nations gathered to sign the North Atlantic Treaty on April 4 1949 founding NATO.
Postwar Uncertainty
The postwar years were politically volatile ones all over the world, due to widespread decolonization. Britain, though allied with the United States during World War II, had been weakened by the conflict and could no longer dominate its remote colonies. The British Empire was shrinking drastically, and this made the Truman Doctrine all the more necessary. In 1947, an economically desperate Britain reluctantly granted India and Pakistan the independence their citizens had sought for years. Britain’s African colonies gained independence in the 1950s and early 1960s. The United States and the Soviet Union each struggled to win over the former British colonies to their own ideological side of the Cold War. (See the Who Was Responsible for Starting the Cold War? Point-Counterpoint and Winston Churchill, “Sinews of Peace,” March 1946 Primary Source.)
Israel came into existence on May 14, 1948, on land that had been a British-controlled mandate since the end of World War I. The Zionist movement, founded in the 1890s by Austro-Hungarian journalist Theodore Herzl, had encouraged European Jews to immigrate to Palestine. There, they would buy land, become farmers, and eventually create a Jewish state. Tens of thousands, indeed, had migrated there and prospered between 1900 and 1945. Widespread sympathy for the Jews, six million of whom had been exterminated in the Nazi Holocaust, prompted the new United Nations to authorize the partition of Palestine into two states, one Jewish and one Arab. From the very beginning, these two states were at war, with all the neighboring Arab states uniting to threaten Israel’s survival. President Truman supported Israel, however, and in the ensuing decades, most American politicians, and virtually all the American Jewish population, supported and strengthened it.
In 1949, a decades-long era of chaos, conquest, and revolution in China ended with the triumph of Mao Zedong, leader of a Communist army. Against him, America had backed Chiang Kai-Shek, the Chinese Nationalist leader, whose defeated forces fled to the offshore island of Taiwan. American anti-communist politicians in Washington, DC, pointed to the growing “red” (Communist) areas of the map as evidence that communism was winning the struggle for the world. Domestically, Truman and the Democrats endured charges that they had “lost” China to communism.
War in Korea
Korea, one of the many parts of Asia that Japan had conquered in the earlier twentieth century but then lost in 1945, was now partitioned into a pro-Communist North and an anti-Communist South. In June 1950, the Truman administration was taken by surprise when North Korea attacked the South, overpowering its army and forcing the survivors back into a small area of the country’s southeast, the Pusan perimeter. Truman and his advisors quickly concluded they should apply the containment principle to Asia and procured a resolution of support from the United Nations, which was unanimous because the Soviet representatives were not present in the Security Council during the vote. See the Truman Intervenes in Korea Decision Point.)

U.S. troops were sent to Korea shortly after Truman’s decision to apply containment to the region. Pictured is a U.S. gun crew near the Kum River in July 1950.
An American invasion force led by General Douglas MacArthur thus made a daring counterattack, landing at Inchon, near Seoul on the west coast of the Korean peninsula, on September 15, 1950. At once, this attack turned the tables in the war, forcing the North Koreans into retreat. Rather than simply restore the old boundary, however, MacArthur’s force advanced deep into North Korea, ultimately approaching the Chinese border. At this point, in October 1950, Mao Zedong sent tens of thousands of Chinese Communist soldiers into the conflict on the side of North Korea. They turned the tide of the war once again, forcing the American forces to fall back in disarray.
After a brutal winter of hard fighting in Korea, the front lines stabilized around the 38th parallel . MacArthur, already a hero of World War II in the Pacific, had burnished his reputation at Inchon. In April 1951, however, he crossed the line in civil-military relations that bars soldiers from dabbling in politics by publicly criticizing one of President Truman’s strategic decisions not to expand the war against the Chinese. MacArthur was so popular in America, he had come to think the rules no longer applied to him, but they did. Truman fired him with no hesitation, replacing him with the equally competent but less egotistical General Matthew Ridgway. The war dragged on in a stalemate. Only in 1953, after the inauguration of President Dwight D. Eisenhower, was a truce declared between the two Koreas. It has held uneasily ever since. (See The Korean War and The Battle of Chosin Reservoir Narrative.)
Prosperity and the Baby Boom
The late 1940s and early 1950s were paradoxical. They were years of great geopolitical stress, danger, and upheaval, yet they were also a time of prosperity and opportunity for millions of ordinary American citizens. Far more babies were born each year than in the 1930s, resulting in the large “ baby boom ” generation. Millions of new houses were built to meet a need accumulated over the long years of the Great Depression and the war. Suburbs expanded around every city, creating far better and less-crowded living conditions than ever before. Levittown housing developments were just one example of the planned communities with mass-produced homes across the country that made homeownership within the reach of many, though mostly white families, thanks to cheap loans for returning veterans (See the Levittown Videos, 1947–1957 Primary Source). Wages and living standards increased, and more American consumers found they could afford their own homes, cars, refrigerators, air conditioners, and even television sets—TV was then a new and exciting technology. The entire nation breathed a sigh of relief on discovering that peace did not bring a return of depression-era conditions and widespread unemployment. (See The Sound of the Suburbs Lesson.)

Television became a staple in U.S. households during the 1940s and 1950s.
Full employment during the war years had strengthened trade unions, but for patriotic reasons, nearly all industrial workers had cooperated with their employers. Now that the war was over, a rash of strikes for better pay and working conditions broke out. In 1945, Truman expanded presidential power by seizing coal mines, arguing it was in the national interest because coal supplied electricity. He then forced the United Mine Workers to end their strike the following year.
Although coal miners won their demands, the power of organized labor waned over the next few decades. Republican members of Congress, whose party had triumphed in the 1946 mid-term elections, passed the Taft-Hartley Act in 1947, aiming to curb the power of unions by banning the closed shop, allowing states to protect the right to work outside the union, setting regulations to limit labor strikes and excluding supporters of the Communist Party and other social radicals from their leadership. Truman vetoed the act, but Congress overrode the veto. In 1952, Truman attempted to again seize a key industry and forestall a strike among steelworkers. However, the Supreme Court decided in Youngstown Sheet & Tube Co. v. Sawyer (1952) that Truman lacked the constitutional authority to seize private property, and steelworkers won significant concessions.
Watch this BRI AP U.S. History Exam Study Guide about the Post-WWII Boom: Transition to a Consumer Economy to explore the post-World War II economic boom in the United States and its impacts on society.
Joseph McCarthy and the Red Scare
Fear of communism, not only abroad but at home, was one of the postwar era’s great obsessions. Ever since the Russian Revolution of 1917, a small and dedicated American Communist Party had aimed to overthrow capitalism and create a Communist America. Briefly popular during the crisis of the Great Depression and again when Stalin was an American ally in World War II, the party shrank during the early Cold War years. Rising politicians like the young California congressman Richard Nixon nevertheless discovered that anti-Communism was a useful issue for gaining visibility. Nixon helped win publicity for the House Committee on Un-American Activities (HUAC), whose hearings urged former communists to expose their old comrades in the name of national security, especially in government and Hollywood. In 1947, President Truman issued Executive Order No. 9835, establishing loyalty boards investigating the communist sympathies of 2.5 million federal employees. (See The Postwar Red Scare and the Cold War Spy Cases Narratives.)
The most unscrupulous anti-communist was Senator Joseph R. McCarthy (R-WI), who used fear of communism as a powerful political issue during the early Cold War. He made reckless allegations that the government was riddled with communists and their sympathizers, even including Secretary of State George Marshall. Intimidating all critics by accusing them of being part of a great communist conspiracy, McCarthy finally overplayed his hand in publicly televised hearings by accusing the U.S. Army of knowingly harboring communists among its senior officers. The Senate censured him in December 1954, after which his influence evaporated, but for four years, he had been one of the most important figures in American political life. Although he was correct that the Soviets had spies in the U.S. government, McCarthy created a climate of fear and ruined the lives of innocent people for his own political gain during what became known as the “Second Red Scare.” (See the McCarthyism DBQ Lesson.)

Senator Joseph McCarthy (left) is pictured with his lawyer Roy Cohn during the 1950s McCarthy-Army clash.
Be sure to check out this BRI Homework Help video about The Rise and Fall of Joseph McCarthy to learn more about Joseph McCarthy and his battle against communists in the U.S. government.
Several highly publicized spy cases commanded national attention. Klaus Fuchs and other scientists with detailed knowledge of the Manhattan Project were caught passing nuclear secrets to the Soviet Union. In 1950, Alger Hiss was prosecuted for perjury before Congress and accused of sharing State Department documents with the Soviets. Julius and Ethel Rosenberg were tried for espionage in 1951 and executed two years later. Julius was convicted of running a spy ring associated with selling atomic secrets to the Russians, though the case against Ethel’s direct involvement was thinner.
From Truman to Eisenhower
After the 1946 midterm election, in which Republicans won a majority in the House and the Senate, the Democratic President Truman struggled to advance his domestic program, called the Fair Deal in an echo of Franklin Roosevelt’s New Deal. For instance, Truman was the first American president to propose a system of universal health care, but the Republican Congress voted it down because they opposed the cost and regulations associated with the government program and called it “socialized medicine.” Truman did succeed in other areas. He was able to encourage Congress to pass the Employment Act of 1946, committing the government to ensuring full employment. By executive order, he desegregated the American armed forces and commissioned a report on African American civil rights. He thus played an important role in helping advance the early growth of the civil rights movement.
Truman seemed certain to lose his re-election bid in 1948. The Republicans had an attractive candidate in Thomas Dewey, and Truman’s own Democratic Party was splintering three ways. Former Vice President Henry Wallace led a Progressive breakaway, advocating a less confrontational approach to the Cold War. Strom Thurmond, a South Carolina senator, led the southern “Dixiecrat” breakaway by opposing any breach in racial segregation. The Chicago Daily Tribune was so sure Dewey would win that it prematurely printed its front page with the headline “Dewey Defeats Truman.” One of the most famous photographs in the history of American journalism shows Truman, who had upset the pollsters by winning, holding a copy of this newspaper aloft and grinning broadly.

President Truman is pictured here holding the Chicago Daily Tribune with its inaccurate 1948 headline.
Four years later, exhausted by Korea and the fierce stresses of the early Cold War, Truman declined to run for another term. Both parties hoped to attract the popular Supreme Allied commander, Dwight D. Eisenhower, to be their candidate. He accepted the Republicans’ invitation, defeated Adlai Stevenson in November 1952, and won against the same rival again in 1956.
Rather than roll back the New Deal, which had greatly increased the size and reach of the federal government since 1933, Eisenhower accepted most of it as a permanent part of the system, in line with his philosophy of “Modern Republicanism.” He worked with Congress to balance the budget but signed bills for the expansion of Social Security and unemployment benefits, a national highway system, federal aid to education, and the creation of National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). In foreign policy, he recognized that for the foreseeable future, the Cold War was here to stay and that each side’s possession of nuclear weapons deterred an attack by the other. The two sides’ nuclear arsenals escalated during the 1950s, soon reaching a condition known as “ mutually assured destruction ,” which carried the ominous acronym MAD and would supposedly prevent a nuclear war.
At the same time, Eisenhower and Secretary of State John Foster Dulles supported the “New Look” foreign policy, which increased reliance on nuclear weapons rather than the more flexible but costly buildup of conventional armed forces. Despite the Cold War consensus about containment, Eisenhower did not send troops when the Vietnamese defeated the French in Vietnam; when mainland China bombed the Taiwanese islands of Quemoy and Matsu; when the British, French, and Egypt fought over the Suez Canal in 1956; or when the Soviets cracked down on Hungary. Instead, Eisenhower assumed financial responsibility for the French war effort in Vietnam and sent hundreds of military advisers there over the next several years. (See the Dwight D. Eisenhower, Farewell Address, January 1961 Primary Source.)
Birth of the Civil Rights Movement
Encouraged by early signs of a change in national racial policy and by the Supreme Court’s decision in Brown v. Board of Education (1954) , African American organizations intensified their efforts to challenge southern segregation. Martin Luther King Jr., then a spellbinding young preacher in Montgomery, Alabama, led a Montgomery bus boycott that began in December 1955. Inspired by the refusal of Rosa Parks to give up her seat on a city bus, African Americans refused to ride Montgomery’s buses unless the company abandoned its policy of forcing them to ride at the back and to give up their seats to whites when the bus was crowded. After a year, the boycott succeeded. King went on to create the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC), which practiced nonviolent resistance as a tactic, attracting press attention, embarrassing the agents of segregation, and promoting racial integration. (See the Rosa Parks, Martin Luther King Jr., and the Montgomery Bus Boycott Narrative and the Rosa Parks’s Account of the Montgomery Bus Boycott (Radio Interview), April 1956 Primary Source.)
In 1957, Congress passed the first federal protection of civil rights since Reconstruction and empowered the federal government to protect black voting rights. However, the bill was watered down and did not lead to significant change. In August, black students tried to attend high school in Little Rock, Arkansas, but were blocked by National Guard troops. Over the next few weeks, angry crowds assembled and threatened these students. President Eisenhower decided to send in federal troops to protect the nine black students. In the postwar era, African Americans won some victories in the fight for equality, but many southern whites began a campaign of massive resistance to that goal.
Check out this BRI Homework Help video about Brown v. Board of Education to learn more about the details of the case.
Thus, the pace of school desegregation across the south remained very slow. White southerners in Congress promised massive resistance to the policy. When it came to the point, however, only one county, Prince Edward County, Virginia, actually closed down its public schools rather than permit them to be desegregated. Other districts, gradually and reluctantly, eventually undertook integration, but widespread discrimination persisted, especially in the South.
Mexican Americans, like African Americans, suffered from racial discrimination. Under the bracero program, inaugurated during the 1940s, Mexicans were permitted to enter the United States temporarily to work, mainly as farm laborers in the western states, but they too were treated by whites as second-class citizens. They were guest workers, and the program was not intended to put them on a path to U.S. citizenship. (See The Little Rock Nine Narrative.)

Pictured are Mexican workers waiting to gain legal employment and enter the United States as part of the “ bracero ” program begun in the 1940s.
The Space Race
The desegregation of schools was only one aspect of public concern about education in the 1950s. The Soviet Union launched an artificial orbiting satellite, “Sputnik,” in 1957 and ignited the “ Space Race .” Most Americans were horrified, understanding that a rocket able to carry a satellite into space could also carry a warhead to the United States. Congress reacted by passing the National Defense Education Act in August 1958, devoting $1 billion of federal funds to education in science, engineering, and technology in the hope of improving the nation’s scientific talent pool.
NASA had been created earlier that same year to coordinate programs related to rocketry and space travel. NASA managed to catch up with the Soviet space program in the ensuing years and later triumphed by placing the first person on the moon in 1969. Better space rockets meant better military missiles. NASA programs also stimulated useful technological discoveries in materials, navigation, and computers. (See the Sputnik and NASA Narrative and the Was Federal Spending on the Space Race Justified? Point-Counterpoint.)
Another major initiative, also defense related, of the Eisenhower years was the decision to build the interstate highway system. As a young officer just after World War I, Eisenhower had been part of an Army truck convoy that attempted to cross the United States. Terrible roads meant that the convoy took 62 days, with many breakdowns and 21 injuries to the soldiers, an experience Eisenhower never forgot. He had also been impressed by the high quality of Germany’s autobahns near the war’s end. A comprehensive national system across the United States would permit military convoys to move quickly and efficiently. Commerce, the trucking industry, and tourism would benefit too, a belief borne out over the next 35 years while the system was built; it was declared finished in 1992. See The National Highway Act Narrative and the Nam Paik, Electronic Superhighway , 1995 Primary Source.)
New Roles for Women
American women, especially in the large and growing middle class, were in a paradoxical situation in the 1950s. In one sense, they were the most materially privileged generation of women in world history, wealthier than any predecessors. More had gained college education than ever before, and millions were marrying young, raising their children with advice from Dr. Spock’s best-selling Common Sense Book of Baby and Child Care (1946), and enjoying labor-saving domestic devices and modern conveniences like washing machines, toasters, and electric ovens. Affluence meant many middle-class women were driving cars of their own. This 1950s advertisement for Ford automobiles persuaded women to become a “two Ford family.” At the same time, however, some suffered various forms of depression and anxiety, seeking counseling, often medicating themselves, and feeling a lack of purpose in their lives.
This situation was noticed by Betty Friedan, a popular journalist in the 1950s whose book The Feminine Mystique , published in 1963, helped ignite the new feminist movement. Its principal claim was that in America in the 1950s, women lacked fulfilling careers of their own, and material abundance was no substitute. (See the Dr. Benjamin Spock and the Baby Boom Narrative.) A feminist movement emerged in the 1960s and 1970s seeking greater equality. In the postwar period, however, not all women shared the same experiences. Millions of working-class and poor women of all races continued to work in factories, retail, domestic, or offices as they had before and during the war. Whether married or single, these women generally did not share in the postwar affluence enjoyed by middle-class, mostly white, women who were in the vanguard of the feminist movement for equal rights for women.
By 1960, the United States was, without question, in a superior position to its great rival the Soviet Union—richer, stronger, healthier, better fed, much freer, and much more powerful. Nevertheless Eisenhower, in his farewell address, warned against the dangers of an overdeveloped “military-industrial complex,” in which American traditions of democracy, decentralization, and civilian control would be swallowed up by the demands of the defense industry and a large, governmental national security apparatus. He had no easy remedies to offer and remained acutely aware that the Cold War continued to threaten the future of the world.

Timeline of events in the postwar period from 1945 to 1960.
Additional Chapter Resources
- Eleanor Roosevelt and the United Nations Narrative
- The G.I. Bill Narrative
- Jackie Robinson Narrative
- The Murder of Emmett Till Narrative
- The Nixon-Khrushchev Kitchen Debate Narrative
- William F. Buckley Jr. and the Conservative Movement Narrative
- Truman Fires General Douglas MacArthur Decision Point
- Eisenhower and the Suez Canal Crisis Point-Counterpoint
- Richard Nixon “Checkers” Speech September 1952 Primary Source
- Critics of Postwar Culture: Jack Kerouac On the Road (Excerpts) 1957 Primary Source
- Kennedy vs. Nixon: TV and Politics Lesson
Review Questions
1. The major deterrent to Soviet aggression in Europe immediately after World War II was
- that the Soviets lost 20 million people during the war
- the Truman Doctrine
- the United States’ possession of atomic power
- the presence of U.S. troops in western Europe after World War II was over
2. Why did the United States maintain large armed forces in Europe after World War II?
- To stop renewed German aggression
- To halt Soviet aggression despite the wartime alliance
- To help the British relinquish their empire
- To maintain high levels of employment at home
3. The memorandum NSC-68 authorized
- the formation of the CIA
- the creation of the Department of Defense
- increases in the size of U.S. military forces
- the formation of an independent air force
4. The United States’ first successful application of its policy of containment occurred in
- Prague Czechoslovakia
- Moscow U.S.S.R.
- Berlin Germany
- Bombay India
5. During the late 1940s the Truman Administration supported all the following countries except
- Republic of Korea
- People’s Republic of China
6. When North Korea invaded South Korea the Truman Administration resolved to apply which strategy?
- The Truman Doctrine
- Containment
- A plan similar to the Berlin Airlift
- The bracero program
7. Events in which European country led the United States to allow the re-arming of West Germany?
- East Germany
- Czechoslovakia
8. The Taft-Hartley Act was most likely passed as a result of
- fear of labor involvement in radical politics and activities
- concern that strong labor unions could rekindle a depression
- fear that labor would restrict the freedom of workers
- desire to make the labor strike illegal
9. Why was it reasonable to expect Truman to lose the presidential election of 1948?
- McCarthyism was creating widespread dislike of the Democratic Party.
- Truman had been unable to win the Korean War.
- The Democratic Party split into three rival branches including one dedicated to racial segregation.
- The Democrats had controlled Congress since 1933.
10. Why were many middle-class women dissatisfied with their lives in the 1950s?
- They were excluded from most career opportunities.
- The cost of living was too high.
- Fear of losing their traditional roles caused them constant anxiety.
- They opposed the early civil rights movement.
11. All the following were Cold War based initiatives by the Eisenhower Administration except
- the creation of NASA
- the National Defense Highway Act
- the National Defense Education Act
- the Taft-Hartley Act
12. Anti-communist crusader Senator Joseph McCarthy overplayed his advantage in the Red Scare when he
- claimed members of the president’s Cabinet were known communists
- charged Martin Luther King Jr. with being a communist
- asserted the U.S. Army knowingly protected known communists in its leadership
- hinted that President Eisenhower could be a communist
13. As a presidential candidate Dwight Eisenhower recognized the significance of all the following except
- the success of some New Deal programs
- the Cold War’s impact on U.S. foreign policy
- racial integration
- mutually assured destruction (MAD)
14. Which of the following statements most accurately describes the United States’ foreign policy during 1945-1960?
- The United States distanced itself from the global free-market economy.
- The United States based its foreign policy on unilateral decision-making.
- The Cold War was based on military policy only.
- The United States formed military alliances in reaction to the Soviet Union’s aggression.
15. Betty Friedan gained prominence by
- supporting women’s traditional role at home
- promoting the child-rearing ideas of Dr. Benjamin Spock
- researching and writing about the unfulfilling domestic role of educated women
- encouraging more women to attend college
16. Before leaving the office of the presidency Dwight D. Eisenhower warned the nation of the danger of
- falling behind in the space race
- having fewer nuclear weapons than the Soviet Union
- allowing the growth of the military-industrial complex
- overlooking communists within the federal government
Free Response Questions
- Explain President Harry Truman’s reaction to the Taft-Hartley Act.
- Describe President Truman’s role in advancing civil rights.
- Describe Dwight D. Eisenhower’s reaction to the New Deal programs still in existence when he was elected president.
- Explain the main reason for the United States’ military participation in Korea.
AP Practice Questions

Political cartoon by Clifford Berryman regarding civil rights and the 1948 election.
1. The main topic of public debate at the time this political cartoon was published was the
- deployment of U.S. troops in Korea
- dropping of the atomic bomb on Japan
- integration of the U.S. military
2. Which of the following groups would most likely support the sentiments expressed in the political cartoon?
- Progressives who argued for prohibition
- William Lloyd Garrison and like-minded abolitionists
- Antebellum reformers in favor of free public education
- Members of the America First Committee
“It would be an unspeakable tragedy if these countries which have struggled so long against overwhelming odds should lose that victory for which they sacrificed so much. Collapse of free institutions and loss of independence would be disastrous not only for them but for the world. Discouragement and possibly failure would quickly be the lot of neighboring peoples striving to maintain their freedom and independence. Should we fail to aid Greece and Turkey in this fateful hour the effect will be far reaching to the West as well as to the East. We must take immediate and resolute action. I therefore ask the Congress to provide authority for assistance to Greece and Turkey in the amount of $400 0 000 for the period ending June 30 1948.”
President Harry S. Truman The Truman Doctrine Speech March 12 1947
3. President Truman’s speech was most likely intended to increase the public’s awareness of
- rising tensions over oil reserves in the Middle East
- the Cold War and the struggle against Communism in Europe
- the United States’ need for access to the Black Sea
- the need to rebuild Europe after World War II
4. The immediate outcome of the event described in the excerpt was that
- the United States unilaterally rebuilt Europe
- worldwide freedom of the seas was guaranteed for all nations
- the United States’ foreign policy of containment was successfully implemented
- Europe was not as vital to U.S. interests as initially believed
5. Based on the ideas in the excerpt which of the following observations of U.S. foreign policy in the post World War II years is true?
- The United States was making a major shift in foreign policy from its stance after World War I.
- More people opposed the idea of U.S. involvement in world affairs.
- A majority believed that U.S. foreign policy was being dictated by the United Nations.
- The United States needed to reassert the “Good Neighbor Policy” but with a focus on Europe.
“Women especially educated women such as you have a unique opportunity to influence us man and boy and to play a direct part in the unfolding drama of our free society. But I am told that nowadays the young wife or mother is short of time for the subtle arts that things are not what they used to be; that once immersed in the very pressing and particular problems of domesticity many women feel frustrated and far apart from the great issues and stirring debates for which their education has given them understanding and relish. . . . There is often a sense of contraction of closing horizons and lost opportunities. They had hoped to play their part in the crisis of the age. . . . The point is that . . . women “never had it so good” as you do. And in spite of the difficulties of domesticity you have a way to participate actively in the crisis in addition to keeping yourself and those about you straight on the difference between means and ends mind and spirit reason and emotion . . . In modern America the home is not the boundary of a woman’s life. . . . But even more important is the fact surely that what you have learned and can learn will fit you for the primary task of making homes and whole human beings in whom the rational values of freedom tolerance charity and free inquiry can take root.”
Adlai Stevenson “A Purpose for Modern Women” from his Commencement Address at Smith College 1955
6. Which of the following best mirrors the sentiments expressed by Adlai Stevenson in the provided excerpt?
- Women should be prepared to return to a more traditional role in society.
- The ideals espoused by Republican Motherhood should be upheld.
- The United States would not have won World War II if women had not worked in factories.
- Women had the opportunity to influence the next generation of citizens.
7. The reference that “many women feel frustrated and far apart from the great issues and stirring debates for which their education has given them understanding and relish” is a reference to the ideas espoused by
- Martin Luther King Jr.
- Betty Friedan
- Dr. Benjamin Spock
Primary Sources
Eisenhower Dwight D. “Eisenhower’s Farewell Address to the Nation.” http://mcadams.posc.mu.edu/ike.htm
Eisenhower Dwight D. “Interstate Highway System.” Eisenhower proposes the interstate highway system to Congress. https://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/documents/special-message-the-congress-regarding-national-highway-program
“‘Enemies from Within’: Senator Joseph R. McCarthy’s Accusations of Disloyalty.” McCarthy’s speech in Wheeling West Virginia. http://historymatters.gmu.edu/d/6456
Friedan Betty. The Feminine Mystique . New York: W. W. Norton 1963.
Hamilton Shane and Sarah Phillips. Kitchen Debate and Cold War Consumer Politics: A Brief History with Documents . Boston: Bedford Books 2014.
Kennan George F. American Diplomacy . New York: Signet/Penguin Publishing 1952.
King Martin Luther Jr. “(1955) Martin Luther King Jr. ‘The Montgomery Bus Boycott.'” http://www.blackpast.org/1955-martin-luther-king-jr-montgomery-bus-boycott
King Martin Luther Jr. Stride Toward Freedom: The Montgomery Story . New York: Harper & Brothers Publishers 1958.
MacLean Nancy. American Women’s Movement 1945-2000: A Brief History with Documents . Boston: Bedford Books 2009.
Marshall George C. “The ‘Marshall Plan’ speech at Harvard University 5 June 1947.” http://www.oecd.org/general/themarshallplanspeechatharvarduniversity5june1947.htm
Martin Waldo E. Jr. Brown v. Board of Education: A Brief History with Documents . Boston: Bedford Books 1998.
Schrecker Ellen W. The Age of McCarthyism: A Brief History with Documents . Boston: Bedford Books 2016.
Story Ronald and Bruce Laurie. Rise of Conservatism in America 1945-2000: A Brief History with Documents. Boston: Bedford Books 2008.
Truman Harry. “A Report to the National Security Council – NSC 68 April 12 1950.” https://www.trumanlibrary.gov/library/research-files/report-national-security-council-nsc-68
Truman Harry. “The Fateful Hour (1947)” speech. http://www.americanrhetoric.com/speeches/harrystrumantrumandoctrine.html
Suggested Resources
Ambrose Stephen and Douglas Brinkley. Rise to Globalism: American Foreign Policy since 1938. Ninth ed. New York: Penguin 2010.
Branch Taylor. Parting the Waters: America in the King Years 1954-63 . New York: Simon and Schuster 1988.
Brands H.W. American Dreams: The United States Since 1945 . New York: Penguin 2010.
Brands H.W. The General vs. the President: MacArthur and Truman at the Brink of Nuclear War . New York: Anchor 2016.
Cadbury Deborah. Space Race: The Epic Battle Between American and the Soviet Union for Dominion of Space. New York: Harper 2007.
Cohen Lizabeth A. A Consumers’ Republic: The Politics of Mass Consumption in Postwar America . New York: Vintage 2003.
Coontz Stephanie. The Way We Never Were: American Families and the Nostalgia Trap . New York: Basic Books 2016.
Dallek Robert. Harry S. Truman . New York: Times Books 2008.
Diggins John Patrick. The Proud Decades: America in War and Peace 1941-1960 . New York: W. W. Norton 1989.
Fried Richard. Nightmare in Red: The McCarthy Era in Perspective . Oxford: Oxford University Press 1991.
Gaddis John Lewis. The Cold War: A New History . New York: Penguin 2005.
Halberstam David. The Coldest Winter: America and the Korean War. New York: Hyperion 2007.
Hitchcock William I. The Age of Eisenhower: America and the World in the 1950s. New York: Simon and Schuster 2018.
Johnson Paul. Eisenhower: A Life. New York: Penguin 2015.
Lewis Tom. Divided Highways: Building the Interstate Highways Transforming American Life. Ithaca NY: Cornell University Press 2013.
May Elaine Tyler. Homeward Bound: American Families in the Cold War Era . New York: Basic 2008.
McCullough David. Truman. New York: Simon and Schuster 1993.
Patterson James T. Grand Expectations: The United States 1945-1974. Oxford: Oxford University Press 1996.
Whitfield Stephen J. The Culture of the Cold War. Baltimore MD: Johns Hopkins University Press 1996.
Related Content

Life, Liberty, and the Pursuit of Happiness
In our resource history is presented through a series of narratives, primary sources, and point-counterpoint debates that invites students to participate in the ongoing conversation about the American experiment.
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
The Holocaust
By: History.com Editors
Updated: April 11, 2023 | Original: October 14, 2009

The Holocaust was the state-sponsored persecution and mass murder of millions of European Jews, Romani people, the intellectually disabled, political dissidents and homosexuals by the German Nazi regime between 1933 and 1945. The word “holocaust,” from the Greek words “holos” (whole) and “kaustos” (burned), was historically used to describe a sacrificial offering burned on an altar.
After years of Nazi rule in Germany, dictator Adolf Hitler’s “Final Solution”—now known as the Holocaust—came to fruition during World War II, with mass killing centers in concentration camps. About six million Jews and some five million others, targeted for racial, political, ideological and behavioral reasons, died in the Holocaust—more than one million of those who perished were children.
Historical Anti-Semitism
Anti-Semitism in Europe did not begin with Adolf Hitler . Though use of the term itself dates only to the 1870s, there is evidence of hostility toward Jews long before the Holocaust—even as far back as the ancient world, when Roman authorities destroyed the Jewish temple in Jerusalem and forced Jews to leave Palestine .
The Enlightenment , during the 17th and 18th centuries, emphasized religious tolerance, and in the 19th century Napoleon Bonaparte and other European rulers enacted legislation that ended long-standing restrictions on Jews. Anti-Semitic feeling endured, however, in many cases taking on a racial character rather than a religious one.
Did you know? Even in the early 21st century, the legacy of the Holocaust endures. Swiss government and banking institutions have in recent years acknowledged their complicity with the Nazis and established funds to aid Holocaust survivors and other victims of human rights abuses, genocide or other catastrophes.
Hitler's Rise to Power
The roots of Adolf Hitler’s particularly virulent brand of anti-Semitism are unclear. Born in Austria in 1889, he served in the German army during World War I . Like many anti-Semites in Germany, he blamed the Jews for the country’s defeat in 1918.
Soon after World War I ended, Hitler joined the National German Workers’ Party, which became the National Socialist German Workers’ Party (NSDAP), known to English speakers as the Nazis. While imprisoned for treason for his role in the Beer Hall Putsch of 1923, Hitler wrote the memoir and propaganda tract “ Mein Kampf ” (or “my struggle”), in which he predicted a general European war that would result in “the extermination of the Jewish race in Germany.”
Hitler was obsessed with the idea of the superiority of the “pure” German race, which he called “Aryan,” and with the need for “Lebensraum,” or living space, for that race to expand. In the decade after he was released from prison, Hitler took advantage of the weakness of his rivals to enhance his party’s status and rise from obscurity to power.
On January 30, 1933, he was named chancellor of Germany. After the death of President Paul von Hindenburg in 1934, Hitler anointed himself Fuhrer , becoming Germany’s supreme ruler.
Concentration Camps
The twin goals of racial purity and territorial expansion were the core of Hitler’s worldview, and from 1933 onward they would combine to form the driving force behind his foreign and domestic policy.
At first, the Nazis reserved their harshest persecution for political opponents such as Communists or Social Democrats. The first official concentration camp opened at Dachau (near Munich) in March 1933, and many of the first prisoners sent there were Communists.
Like the network of concentration camps that followed, becoming the killing grounds of the Holocaust, Dachau was under the control of Heinrich Himmler , head of the elite Nazi guard, the Schutzstaffel (SS) and later chief of the German police.
By July 1933, German concentration camps ( Konzentrationslager in German, or KZ) held some 27,000 people in “protective custody.” Huge Nazi rallies and symbolic acts such as the public burning of books by Jews, Communists, liberals and foreigners helped drive home the desired message of party strength and unity.
In 1933, Jews in Germany numbered around 525,000—just one percent of the total German population. During the next six years, Nazis undertook an “Aryanization” of Germany, dismissing non-Aryans from civil service, liquidating Jewish-owned businesses and stripping Jewish lawyers and doctors of their clients.
Nuremberg Laws
Under the Nuremberg Laws of 1935, anyone with three or four Jewish grandparents was considered a Jew, while those with two Jewish grandparents were designated Mischlinge (half-breeds).
Under the Nuremberg Laws, Jews became routine targets for stigmatization and persecution. This culminated in Kristallnacht , or the “Night of Broken Glass” in November 1938, when German synagogues were burned and windows in Jewish home and shops were smashed; some 100 Jews were killed and thousands more arrested.
From 1933 to 1939, hundreds of thousands of Jews who were able to leave Germany did, while those who remained lived in a constant state of uncertainty and fear.

HISTORY Vault: Third Reich: The Rise
Rare and never-before-seen amateur films offer a unique perspective on the rise of Nazi Germany from Germans who experienced it. How were millions of people so vulnerable to fascism?
Euthanasia Program
In September 1939, Germany invaded the western half of Poland , starting World War II . German police soon forced tens of thousands of Polish Jews from their homes and into ghettoes, giving their confiscated properties to ethnic Germans (non-Jews outside Germany who identified as German), Germans from the Reich or Polish gentiles.
Surrounded by high walls and barbed wire, the Jewish ghettoes in Poland functioned like captive city-states, governed by Jewish Councils. In addition to widespread unemployment, poverty and hunger, overpopulation and poor sanitation made the ghettoes breeding grounds for disease such as typhus.
Meanwhile, beginning in the fall of 1939, Nazi officials selected around 70,000 Germans institutionalized for mental illness or physical disabilities to be gassed to death in the so-called Euthanasia Program.
After prominent German religious leaders protested, Hitler put an end to the program in August 1941, though killings of the disabled continued in secrecy, and by 1945 some 275,000 people deemed handicapped from all over Europe had been killed. In hindsight, it seems clear that the Euthanasia Program functioned as a pilot for the Holocaust.

'Final Solution'
Throughout the spring and summer of 1940, the German army expanded Hitler’s empire in Europe, conquering Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg and France. Beginning in 1941, Jews from all over the continent, as well as hundreds of thousands of European Romani people, were transported to Polish ghettoes.
The German invasion of the Soviet Union in June 1941 marked a new level of brutality in warfare. Mobile killing units of Himmler’s SS called Einsatzgruppen would murder more than 500,000 Soviet Jews and others (usually by shooting) over the course of the German occupation.
A memorandum dated July 31, 1941, from Hitler’s top commander Hermann Goering to Reinhard Heydrich, chief of the SD (the security service of the SS), referred to the need for an Endlösung ( Final Solution ) to “the Jewish question.”

Yellow Stars
Beginning in September 1941, every person designated as a Jew in German-held territory was marked with a yellow, six-pointed star, making them open targets. Tens of thousands were soon being deported to the Polish ghettoes and German-occupied cities in the USSR.
Since June 1941, experiments with mass killing methods had been ongoing at the concentration camp of Auschwitz , near Krakow, Poland. That August, 500 officials gassed 500 Soviet POWs to death with the pesticide Zyklon-B. The SS soon placed a huge order for the gas with a German pest-control firm, an ominous indicator of the coming Holocaust.
Holocaust Death Camps
Beginning in late 1941, the Germans began mass transports from the ghettoes in Poland to the concentration camps, starting with those people viewed as the least useful: the sick, old and weak and the very young.
The first mass gassings began at the camp of Belzec, near Lublin, on March 17, 1942. Five more mass killing centers were built at camps in occupied Poland, including Chelmno, Sobibor, Treblinka, Majdanek and the largest of all, Auschwitz.
From 1942 to 1945, Jews were deported to the camps from all over Europe, including German-controlled territory as well as those countries allied with Germany. The heaviest deportations took place during the summer and fall of 1942, when more than 300,000 people were deported from the Warsaw ghetto alone.
Warsaw Ghetto Uprising
Amid the deportations, disease and constant hunger, incarcerated people in the Warsaw Ghetto rose up in armed revolt.
The Warsaw Ghetto Uprising from April 19-May 16, 1943, ended in the death of 7,000 Jews, with 50,000 survivors sent to extermination camps. But the resistance fighters had held off the Nazis for almost a month, and their revolt inspired revolts at camps and ghettos across German-occupied Europe.
Though the Nazis tried to keep operation of the camps secret, the scale of the killing made this virtually impossible. Eyewitnesses brought reports of Nazi atrocities in Poland to the Allied governments, who were harshly criticized after the war for their failure to respond, or to publicize news of the mass slaughter.
This lack of action was likely mostly due to the Allied focus on winning the war at hand, but was also partly a result of the general incomprehension with which news of the Holocaust was met and the denial and disbelief that such atrocities could be occurring on such a scale.
'Angel of Death'
At Auschwitz alone, more than 2 million people were murdered in a process resembling a large-scale industrial operation. A large population of Jewish and non-Jewish inmates worked in the labor camp there; though only Jews were gassed, thousands of others died of starvation or disease.
In 1943, eugenics advocate Josef Mengele arrived in Auschwitz to begin his infamous experiments on Jewish prisoners. His special area of focus was conducting medical experiments on twins , injecting them with everything from petrol to chloroform under the guise of giving them medical treatment. His actions earned him the nickname “the Angel of Death.”
Nazi Rule Ends
By the spring of 1945, German leadership was dissolving amid internal dissent, with Goering and Himmler both seeking to distance themselves from Hitler and take power.
In his last will and political testament, dictated in a German bunker that April 29, Hitler blamed the war on “International Jewry and its helpers” and urged the German leaders and people to follow “the strict observance of the racial laws and with merciless resistance against the universal poisoners of all peoples”—the Jews.
The following day, Hitler died by suicide . Germany’s formal surrender in World War II came barely a week later, on May 8, 1945.
German forces had begun evacuating many of the death camps in the fall of 1944, sending inmates under guard to march further from the advancing enemy’s front line. These so-called “death marches” continued all the way up to the German surrender, resulting in the deaths of some 250,000 to 375,000 people.
In his classic book Survival in Auschwitz , the Italian-Jewish author Primo Levi described his own state of mind, as well as that of his fellow inmates in Auschwitz on the day before Soviet troops liberated the camp in January 1945: “We lay in a world of death and phantoms. The last trace of civilization had vanished around and inside us. The work of bestial degradation, begun by the victorious Germans, had been carried to conclusion by the Germans in defeat.”
Legacy of the Holocaust
The wounds of the Holocaust—known in Hebrew as “Shoah,” or catastrophe—were slow to heal. Survivors of the camps found it nearly impossible to return home, as in many cases they had lost their entire family and been denounced by their non-Jewish neighbors. As a result, the late 1940s saw an unprecedented number of refugees, POWs and other displaced populations moving across Europe.
In an effort to punish the villains of the Holocaust, the Allies held the Nuremberg Trials of 1945-46, which brought Nazi atrocities to horrifying light. Increasing pressure on the Allied powers to create a homeland for Jewish survivors of the Holocaust would lead to a mandate for the creation of Israel in 1948.
Over the decades that followed, ordinary Germans struggled with the Holocaust’s bitter legacy, as survivors and the families of victims sought restitution of wealth and property confiscated during the Nazi years.
Beginning in 1953, the German government made payments to individual Jews and to the Jewish people as a way of acknowledging the German people’s responsibility for the crimes committed in their name.
The Holocaust. The National WWII Museum . What Was The Holocaust? Imperial War Museums . Introduction to the Holocaust. United States Holocaust Memorial Museum . Holocaust Remembrance. Council of Europe . Outreach Programme on the Holocaust. United Nations .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
The Shenandoah County School Board’s Terrible History Lesson

O n May 10, 2024, 161 years to the day after General Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson’s last breath fighting for the Confederate insurrection intended to continue enslavement of human beings in America, the Shenandoah County School Board voted 5-1 to restore his name on a high school in rural Virginia.
More than 50 concerned community members, students, and parents, including one of the first African Americans to integrate Stonewall Jackson High School in 1963, and hundreds of their supporters, continued to advocate a new reckoning of the county’s heritage of enslavement, segregation, and racial injustice. They affirmed the names a community committee selected in 2021 renaming the school as Mountain View High and another school named after Confederate generals Turner Ashby and Robert E. Lee as Honey Run Elementary.
But the school board heard none of it. Instead, the board sided with those idolizing the faith and loyalty of “heroes” like Jackson, condemning pandemic-related processes that did not take into account the voices of “we the people,” and complaining about “woke outsiders.” At the end of the board meeting, the board had delivered a disgraceful new chapter in our community’s history and a terrible lesson for the children they are sworn to educate.
Historians will debate the consequences of the board’s vote and perhaps whether the nation’s current political mood has rekindled racial tensions. But the school board members and their embittered supporters made it clear that the shadows of our segregated past still loom large.
For context, we should look at 2020, particularly the 8 minutes and 46 seconds of video that emblazoned the truth of racial injustice in America. After George Floyd’s murder by police in May of that year, national, state, and local leaders across the nation took up resolutions against racism, including Shenandoah County’s Board of Supervisors and the county School Board.
At around the same time in our mountain-cradled county, another incident reminded us of America’s lingering racial unrest: an encounter between a white mob and a black pastor in Edinburg, Va. On June 1, 2020, Pastor McCray approached a couple illegally dumping a refrigerator on his property, asking them to leave. They left, returned with three more people and began “attacking him physically, saying ‘they don’t give a darn’ about ‘my black life and the Black Lives Matter stuff,’ and telling him they would ‘kill’ him,” according to Associated Press reports. McCray put distance between himself and the mob by brandishing a gun that he was legally licensed to carry. When the police arrived, they arrested the Black man with the gun.
The Shenandoah County Sheriff later apologized for the incident, but it reinforces the need for formal resolutions against racism and leaders willing to make difficult decisions for a more inclusive community. The Shenandoah County School Board at the time agreed. They chose action, encouraged by then-Department of Education secretary Atif Qarni and then-Governor Ralph Northam, both of whom supported statewide removal of Confederate leaders’ names of public schools.
The 2020 school board, tying in as the next step to its June “Resolution condemning racism and affirming the division’s commitment to an inclusive school environment for all,” retired the names of Confederate leaders, and developed a process for community and student input into choosing more unifying public school names. On September 10, 2020, the then school board reaffirmed the foregoing motion, as well as moving forward with renaming the schools on southern campus. Community committees met during the next three months, with new names chosen at the January 14, 2021 meeting, after seven months of public input.
By 2024, recently elected school board members focused their arguments for restoration on the former board’s “secret” process during the COVID “plan-demic,” stating that community input was not taken into account at the time. Two years before, three current school board members ran on a campaign to restore the school’s Confederate leader names, an attempt that ended at the June 9, 2022 school board meeting with a 3-3 stalemate. The current board consists of three more new school board members, elected in the fall of 2023. Like many school boards around the nation, ours has committed to reversing civil rights often under the lost-cause banner of Confederate pride.
The memory of Stonewall Jackson High School as a whites-only public institution until its integration in 1963 is not a distant echo of history but an agonizing experience for many Black residents of Shenandoah County. These individuals are not just statistics in history books; they are our neighbors, friends, and family—and they were intentionally harmed in Shenandoah County as the Civil Rights movement gained momentum in the 1950s.
Read More: Confederate Monuments and Other Disputed Memorials Have Come Down in Cities Across America. What Should Take Their Place?
And now again in 2024. Dozens of citizens, alum, parents, and current students of the schools addressed the board, offering poignant testimony about lived experiences with institutionalized discrimination or in support of others who had. Approximately two-thirds of the speakers opposed back-naming the schools. For them, returning to Confederate leader names makes the damage linger.
Aliyah Ogle, a student who represented her school in three sports this year and would be attending the renamed high school next year, said it best: “I'm a black student and if the name is restored, I would have to represent a man that fought for my ancestors to be slaves. That makes me feel like I'm disrespecting my ancestors and going against what my family and I believe, which is that we should all be treated equally, and that slavery was a cruel and awful thing.”
Most of the board members could not have cared less about the county’s 252 year history. They were more concerned for judging the 2020 school board’s actions and recognizing the Confederate heritage of the county. Their brand of leadership consisted of telling the people they represent that we all have problems of one kind or another; it’s time to move on. “War is hell,” said Dennis Barlow, chairman of the Shenandoah County School Board. They were joined by two dozen pro-Confederacy speakers, claiming there is no evident racism in Shenandoah County, and never has been.
Board member Tom Streett used his decision to discuss pro-slavery General Jackson. “When you read about this man — who he was, what he stood for, his character, his loyalty, his leadership, how Godly a man he was — those standards that he had were much higher than any leadership of the school system in 2020,” Streett said.
Streett, however, neglected to mention that even Jackson’s descendants have weighed in on this legacy issue. For the past seven years, the general’s great-great grandsons, William Jackson Christian and Warren Edmund Christian, have said they support removing Confederate statues and other monuments—including in Shenandoah County this week—as “part of a larger project of actively mending the racial disparities that hundreds of years of white supremacy have wrought.” They added that they were “ashamed to benefit from white supremacy while our black family and friends suffer.”
Yet Shenandoah County’s school board and its grievance agenda does nothing to provide historical context, advance dialogue, or heal the feelings of well-meaning citizens. Using the same policy the 2021 school board used to name Mountain View and Honey Run, the 2024 board defiantly focused on undoing the decision and giving voice to the people they wanted to hear. The decision unfairly places our children as pawns on a rhetorical battlefield, keeping the board’s focus on vengeance and political control—not due process or heritage. But it’s more dangerous than just talk and hard feelings: The county remains on the radar of the Southern Poverty Law Center , which tracks white supremacists, including ongoing activity by the Patriot Front. To address this reality, we need better, sensible leadership from our school board. But for now, we must live with a stark reminder that elections have consequences.
Looking ahead, the many good people of our county will strive to ensure that our complete history, good and bad, remains available to students and the public. We must find a way to truly honor our whole heritage without insisting that students salute pro-slavery traitors or the treatment of their ancestors as subhuman property for almost 400 years.
If the U.S. Department of Defense can rename military bases once emblazoned with Confederate leaders’ names, then our public schools can do the same. After all, these are the spaces where the first lessons of civic duties are learned. History is complicated, no doubt, but there’s no better place to examine complex issues than in a good school. Other nations and communities reckon with difficult pasts. In Germany, for example, students still learn about Adolf Hitler, but they are not forced to wear sports jerseys and school-pride t-shirts that glorify symbols or names associated with murderous war crimes.
Our fight for what’s right in Shenandoah County is not over. We will continue to oppose historical injustices and help all constituencies in our community learn from the lessons of our past. As it has throughout our nation’s history, the work of decent people striving for a better, more united America will go on. We hope the school board here can find a way to join us along the way.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Javier Milei’s Radical Plan to Transform Argentina
- The New Face of Doctor Who
- How Private Donors Shape Birth-Control Choices
- What Happens if Trump Is Convicted ? Your Questions, Answered
- The Deadly Digital Frontiers at the Border
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- The 31 Most Anticipated Movies of Summer 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]

IMAGES
COMMENTS
History Essay. Intro paragraph. Periods of transition during human history have changed the way that people live forever. From the hunter- gathers during the forging period to the informational period of time where people have developed technology, the ways of life have dramatically changed. Three other periods of transition, the horticultural ...
We've put together some video examples of how to tackle each section of the AP US history exam. Find them here: Multiple choice section: How to approach multiple choice questions. Short answer section: How to approach short answer questions. Document-based essay: How to approach the DBQ. Long essay: How to approach the long essay question/LE.
History & Literature emphasizes primary source texts such as novels, films, songs, monuments, speeches, poems, archival documents, and other first-hand or original works. Most writing assignments in History & Literature will encourage you to anchor your writing in a primary source base and engage with the context in which it was produced.
1. Background sentences. The first two or three sentences of your introduction should provide a general introduction to the historical topic which your essay is about. This is done so that when you state your hypothesis, your reader understands the specific point you are arguing about. Background sentences explain the important historical ...
Purpose. The purpose of this guide is to provide you with the basics for writing undergraduate history essays and papers. It is a guide only, and its step by step approach is only one possible model; it does not replace consultation with your professor, TA, or instructor about writing questions and getting feedback, nor the excellent tutoring services provided by the Rutgers Writing Center ...
Many history essays have a natural chronological focus. Arguments that seek to explain what happened at a place and time, or demonstrate what led up to an event, as well as essays that focus on an individual's importance, can be organized chronologically. Intro; Early phase or antecedents; Middle years or main event; Later years or impact ...
Thesis statements vary based on the rhetorical strategy of the essay, but thesis statements typically share the following characteristics: Presents the main idea. Most often is one sentence. Tells the reader what to expect. Is a summary of the essay topic. Usually worded to have an argumentative edge.
Typical essay structures in history do not start broadly and steadily narrow over the course of the essay, like a giant inverted triangle. If thinking in terms of a geometric shape helps you to conceptualize what a good introduction does, think of your introduction as the top tip of a diamond instead. In analytical essays based on research ...
Download free-response questions from this year's exam and past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at ssd@info ...
If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected]. The 2020 free-response questions are available in the AP Classroom question bank. Download free-response questions from past AP World History exams ...
Step 2: Plan Your Response. Next, take time to plan your response. Check your plan against the long essay question requirements. See the sample plan that a high-scoring writer might make; scoring requirements are written in bold for reference. Step 3: Action! Write Your Response & Step 4: Proofread.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like In a brief essay, explain who Martin Luther was, what were his grievances against the Catholic Church, how did he believe you could obtain salvation, and what technological innovation help him to spread his message?, The Muslim historian Ibn-Khaldūn made the argument that history was cyclical, argued that civilizations go ...
Quizlet has become one of the most used tools these days for teaching and learning. When 15-year-old Andrew Sutherland created a software program in 2005 to help him study 111 French terms for a test on animals, little did he imagine that the program would eventually become one of the fastest-growing free education tools, with 30 million ...
Exam questions assess the course concepts and skills outlined in the course framework. For more information, download the AP U.S. History Course and Exam Description (CED).. Scoring rubrics - general scoring criteria for the document-based and long essay questions, regardless of specific question prompt - are available in the course and exam description (CED).
Meaning. In the broadest sense, the term "essay" can refer to just about any short piece of nonfiction -- an editorial, feature story, critical study, even an excerpt from a book. However, literary definitions of a genre are usually a bit fussier. One way to start is to draw a distinction between articles, which are read primarily for the ...
Period 3: 1754-1800. British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles over the new nation's social, political, and economic identity. Topics may include: Image Source: A detail from A View of Part of the Town of Boston in New ...
Essay Questions for Midterm Examination. Prepare for this examination by carefully drafting an answer for each of the following essay questions. One of these will appear on the exam. But all of the other questions will also be represented on the exam through terms or short answer questions pertinent to that. issue.
World War II ended in 1945. The United States and the Soviet Union had cooperated to defeat Nazi Germany, but they mistrusted each other. Joseph Stalin, the Soviet dictator, believed the Americans had waited too long before launching the D-Day invasion of France in 1944, leaving his people to bear the full brunt of the German war machine.
Learn how the Bill of Rights, the first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution, was drafted, ratified and protects the rights of U.S. citizens.
The Holocaust. Updated: April 11, 2023 | Original: October 14, 2009. The Holocaust was the state-sponsored persecution and mass murder of millions of European Jews, Romani people, the ...
At the end of the board meeting, the board had delivered a disgraceful new chapter in our community's history and a terrible lesson for the children they are sworn to educate. Historians will ...
Download free-response questions from this year's exam and past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at ssd@info ...