Welcome to Africa Online & Publications Library

What are the qualities of a 'good' research topic?

At some point as a student, you will have to write research papers including your thesis, internship reports etc. One of the first and most important steps would be to come up with a research topic.
To make sure your research topic is researchable, you will have to consider the following:
1. Length of your research topic. It should neither be too short nor too long. Schools, for example, usually have thesis writing regulations and may define the number of words to use but I would recommend a research topic of 7 to 15 words.
2. A general rule is that your research topic should be precise, meaningful and unambiguous. In other words, it should be attractive, expressive and parsimonious.
3. A research topic should also be simple enough for your readers to understand. Keep in mind that you are writing to an audience that goes beyond your field of study.
4. Avoid abbreviation(s) in a research topic. A reader may find it difficult to know the full meaning of the abbreviation(s) . For example, CC in a topic such as "Using CC to promote social cohesion" could mean Creative Commons or Cameroon Cup etc.
5. I would also recommend you always write your research topic in SENTENCE CASE. Avoid writing in all capital letters or capitalising each word except otherwise stated.
6. A research topic should be well-defined. If a research topic is not well-defined, it will make it difficult for you to frame your research questions, objectives and hypotheses.
7. A 'good' research topic should address a problem in the society and in most cases, it should be a contemporary issue that is well-founded.
Despite other considerations, a 'good' research topic have the above-mentioned qualities.
Support the Library, Give Today..
Copyright © Africa Online & Publications Library 2021. All rights reserved. Tech support by WhileSmart Support.

- Spartanburg Community College Library
- SCC Research Guides
- Choosing a Research Topic
- What Makes a Good Research Topic?
Before diving into how to choose a research topic, it is important to think about what are some elements of a good research topic. Of course, this will depend specifically on your research project, but a good research topic will always:
- Relate to the assignment itself. Even when you have a choice for your research topic, you still want to make sure your chosen topic lines up with your class assignment sheet.
- A topic that is too broad will give you too many sources, and it will be hard to focus your research.
- A topic that is too narrow will not give you enough sources, if you can find any sources at all.
- Is debatable. This is important if you are researching a topic that you will have to argue a position for. Good topics have more than one side to the issue and cannot be resolved with a simple yes or no.
- Should be interesting to you! It's more fun to do research on a topic that you are interested in as opposed to one you are not interested in.
Remember, it is common and normal if your research topic changes as you start brainstorming and doing some background research on your topic.
Start with a General Idea
As an example, let's say you were writing a paper about issues relating to college students
- << Previous: Choosing a Research Topic
- Next: 1. Concept Mapping >>
- 1. Concept Mapping
- 2. Background Research
- 3. Narrow Your Topic / Thesis Statements
Questions? Ask a Librarian

- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 9:31 AM
- URL: https://libguides.sccsc.edu/chooseatopic
Giles Campus | 864.592.4764 | Toll Free 866.542.2779 | Contact Us
Copyright © 2024 Spartanburg Community College. All rights reserved.
Info for Library Staff | Guide Search
Return to SCC Website

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2.3 Choosing a Research Topic
Many researchers assume that choosing a topic is a linear process; however, in reality, it is more complex, and the research idea may need to be refined before the topic is finally chosen. Watch the video below that explains the process of choosing a research topic.
Choosing a research idea video by Bunmi Malau-Aduli and Faith Alele, used under a CC BY NC ND 4.0 licence
Techniques for finding and choosing a research topic
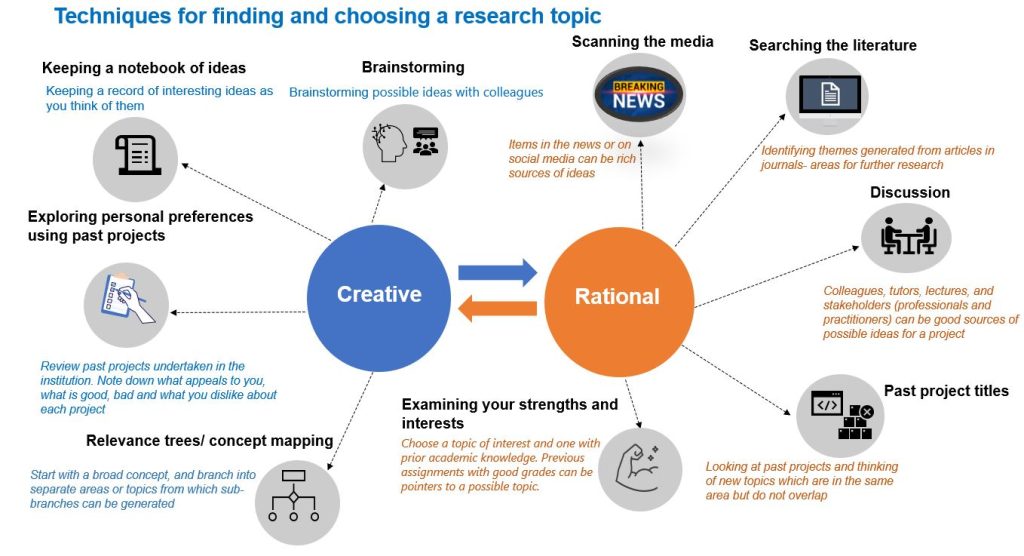
There are two main approaches to finding and choosing a research topic– rational (logical) and creative (intuitive). 2,3 The creative approach requires techniques such as brainstorming, keeping a record of the ideas, using relevance trees and exploring personal preferences. 3,4 The rational approach, on the other hand, involves techniques such as reviewing the literature to identify knowledge gaps, discussing the ideas with subject experts, peers or stakeholders, using past project titles, scanning the media and identifying one’s strengths and interests. 3,4 It is also imperative to engage in critical reflection throughout the process to ensure that the topic is relevant. As a result of this process, the topic may not only be refined but may change substantially. It is important to note that diverse techniques can be used simultaneously or iteratively to decide on a research topic. 3 Figure 2.2 portrays the different techniques.
Attributes of a good research topic
As a researcher, it is important to ensure that your chosen research topic is of obvious value and benefit, financially viable and within your capabilities and interests. 5 As indicated in Table 2.1, ways of assessing your capability include deciding if the topic is achievable within the time frame, whether the project will be current at completion and whether you have access to the required data. 4 Furthermore, there is a need for the topic to be linked to theory, emphasising the role and importance of literature. 4 This implies that the topic should be set in the context of existing literature, i.e. reading and identifying research already undertaken on that topic to guide the decision-making process about the topic selection. Also, the literature aids the refinement of research ideas and prevents research that repeats what has already been done. 6 The proposed research should provide fresh insight into the topic, the aims and objectives should be clear, 7 and the findings should be of similar value irrespective of the outcome (symmetrical). 4 Finally, the research topic should match the researcher’s career goals. 4 While this may not be the case in all instances, it is important to give it considerable thought, especially for those undertaking a dissertation. A checklist of the attributes of a good research topic is listed in Table 2.1 and serves as a guide when choosing a topic.
Table 2.1 Attributes of a good research topic. Adapted from Saunders, et al. 2003 3
Refining the research topic/idea
Remember that a research idea can be generated using rational and/or creative techniques. However, at the onset, the developed idea may be too broad or too specific and may need to be refined. Refining a research idea involves the steps outlined in Figure 2.3. First, a research topic is picked, and the topic is tested by reading the literature. If the topic is too broad, it needs to be made more focused, and if it is too specific, it needs to be broadened. The literature search and discussion with subject experts could be useful in refining the topic. 2
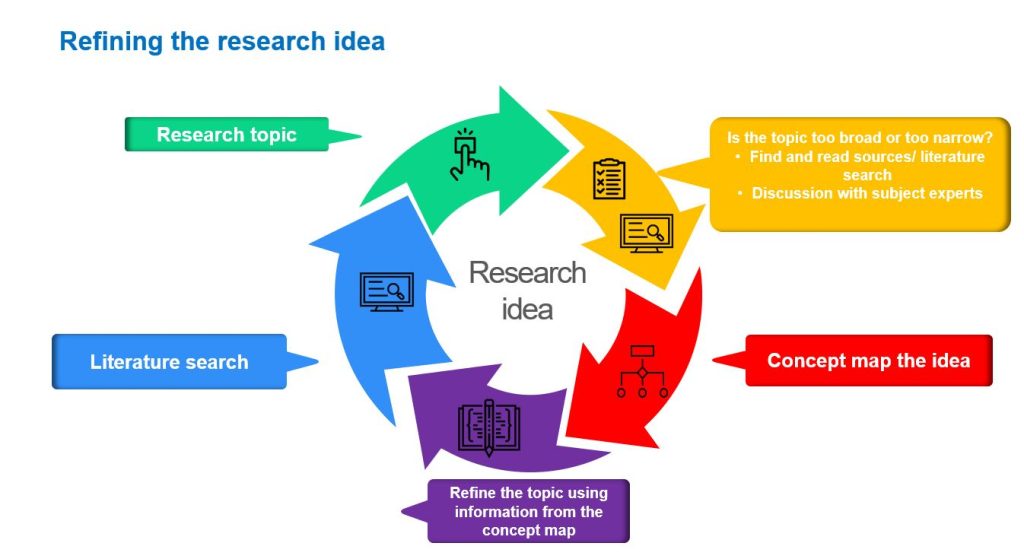
A useful way of refining the research idea/topic is to use a concept map based on the findings from the literature or discussions to identify contextual factors or areas related to the topic. 3 Let us return to our previous example of obesity as your research topic which was depicted in the video. A concept map that utilised the 5Ws and H (who, what, where, when, why and how) questions is presented in Figure 2.4 to facilitate in-depth analysis and refinement of the research topic. It is important to note that concept maps can be complex as each theme can be branched into further subthemes.

The refined topic can be further tested by searching the literature to ensure that the idea is novel and has not been previously answered. The Delphi technique is an alternative technique that could also be used to refine the topic and generate possible research questions. 8 The Delphi technique entails selecting a more focused research idea via contributions from a group of people who are either working on or interested in the research topic. 8 The Delphi consists of four distinct phases. In the first phase, participants can provide whatever information they deem pertinent, which explores the topic under investigation. The second stage is ascertaining how the entire group perceives the topic/idea. 8 The third step is utilised to investigate any substantial disputes and identify the root causes of any identified differences. A final assessment of all the information acquired is done in the fourth step. 8
An Introduction to Research Methods for Undergraduate Health Profession Students Copyright © 2023 by Faith Alele and Bunmi Malau-Aduli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
81k Accesses
28 Citations
71 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others

Good Qualitative Research: Opening up the Debate
Beyond qualitative/quantitative structuralism: the positivist qualitative research and the paradigmatic disclaimer.

What is Qualitative in Research
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
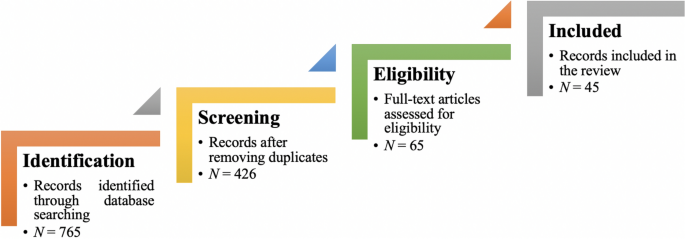
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
1000+ FREE Research Topics & Title Ideas
If you’re at the start of your research journey and are trying to figure out which research topic you want to focus on, you’ve come to the right place. Select your area of interest below to view a comprehensive collection of potential research ideas.

Research Topic FAQs
What (exactly) is a research topic.
A research topic is the subject of a research project or study – for example, a dissertation or thesis. A research topic typically takes the form of a problem to be solved, or a question to be answered.
A good research topic should be specific enough to allow for focused research and analysis. For example, if you are interested in studying the effects of climate change on agriculture, your research topic could focus on how rising temperatures have impacted crop yields in certain regions over time.
To learn more about the basics of developing a research topic, consider our free research topic ideation webinar.
What constitutes a good research topic?
A strong research topic comprises three important qualities : originality, value and feasibility.
- Originality – a good topic explores an original area or takes a novel angle on an existing area of study.
- Value – a strong research topic provides value and makes a contribution, either academically or practically.
- Feasibility – a good research topic needs to be practical and manageable, given the resource constraints you face.
To learn more about what makes for a high-quality research topic, check out this post .
What's the difference between a research topic and research problem?
A research topic and a research problem are two distinct concepts that are often confused. A research topic is a broader label that indicates the focus of the study , while a research problem is an issue or gap in knowledge within the broader field that needs to be addressed.
To illustrate this distinction, consider a student who has chosen “teenage pregnancy in the United Kingdom” as their research topic. This research topic could encompass any number of issues related to teenage pregnancy such as causes, prevention strategies, health outcomes for mothers and babies, etc.
Within this broad category (the research topic) lies potential areas of inquiry that can be explored further – these become the research problems . For example:
- What factors contribute to higher rates of teenage pregnancy in certain communities?
- How do different types of parenting styles affect teen pregnancy rates?
- What interventions have been successful in reducing teenage pregnancies?
Simply put, a key difference between a research topic and a research problem is scope ; the research topic provides an umbrella under which multiple questions can be asked, while the research problem focuses on one specific question or set of questions within that larger context.
How can I find potential research topics for my project?
There are many steps involved in the process of finding and choosing a high-quality research topic for a dissertation or thesis. We cover these steps in detail in this video (also accessible below).
How can I find quality sources for my research topic?
Finding quality sources is an essential step in the topic ideation process. To do this, you should start by researching scholarly journals, books, and other academic publications related to your topic. These sources can provide reliable information on a wide range of topics. Additionally, they may contain data or statistics that can help support your argument or conclusions.
Identifying Relevant Sources
When searching for relevant sources, it’s important to look beyond just published material; try using online databases such as Google Scholar or JSTOR to find articles from reputable journals that have been peer-reviewed by experts in the field.
You can also use search engines like Google or Bing to locate websites with useful information about your topic. However, be sure to evaluate any website before citing it as a source—look for evidence of authorship (such as an “About Us” page) and make sure the content is up-to-date and accurate before relying on it.
Evaluating Sources
Once you’ve identified potential sources for your research project, take some time to evaluate them thoroughly before deciding which ones will best serve your purpose. Consider factors such as author credibility (are they an expert in their field?), publication date (is the source current?), objectivity (does the author present both sides of an issue?) and relevance (how closely does this source relate to my specific topic?).
By researching the current literature on your topic, you can identify potential sources that will help to provide quality information. Once you’ve identified these sources, it’s time to look for a gap in the research and determine what new knowledge could be gained from further study.
How can I find a good research gap?
Finding a strong gap in the literature is an essential step when looking for potential research topics. We explain what research gaps are and how to find them in this post.
How should I evaluate potential research topics/ideas?
When evaluating potential research topics, it is important to consider the factors that make for a strong topic (we discussed these earlier). Specifically:
- Originality
- Feasibility
So, when you have a list of potential topics or ideas, assess each of them in terms of these three criteria. A good topic should take a unique angle, provide value (either to academia or practitioners), and be practical enough for you to pull off, given your limited resources.
Finally, you should also assess whether this project could lead to potential career opportunities such as internships or job offers down the line. Make sure that you are researching something that is relevant enough so that it can benefit your professional development in some way. Additionally, consider how each research topic aligns with your career goals and interests; researching something that you are passionate about can help keep motivation high throughout the process.
How can I assess the feasibility of a research topic?
When evaluating the feasibility and practicality of a research topic, it is important to consider several factors.
First, you should assess whether or not the research topic is within your area of competence. Of course, when you start out, you are not expected to be the world’s leading expert, but do should at least have some foundational knowledge.
Time commitment
When considering a research topic, you should think about how much time will be required for completion. Depending on your field of study, some topics may require more time than others due to their complexity or scope.
Additionally, if you plan on collaborating with other researchers or institutions in order to complete your project, additional considerations must be taken into account such as coordinating schedules and ensuring that all parties involved have adequate resources available.
Resources needed
It’s also critically important to consider what type of resources are necessary in order to conduct the research successfully. This includes physical materials such as lab equipment and chemicals but can also include intangible items like access to certain databases or software programs which may be necessary depending on the nature of your work. Additionally, if there are costs associated with obtaining these materials then this must also be factored into your evaluation process.
Potential risks
It’s important to consider the inherent potential risks for each potential research topic. These can include ethical risks (challenges getting ethical approval), data risks (not being able to access the data you’ll need), technical risks relating to the equipment you’ll use and funding risks (not securing the necessary financial back to undertake the research).
If you’re looking for more information about how to find, evaluate and select research topics for your dissertation or thesis, check out our free webinar here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1:1 help with the topic ideation process, consider our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Literature Searching

Characteristics of a good research question
The first step in a literature search is to construct a well-defined question. This helps in ensuring a comprehensive and efficient search of the available literature for relevant publications on your topic. The well-constructed research question provides guidance for determining search terms and search strategy parameters.
A good or well-constructed research question is:
- Original and of interest to the researcher and the outside world
- It is clear and focused: it provides enough specifics that it is easy to understand its purpose and it is narrow enough that it can be answered. If the question is too broad it may not be possible to answer it thoroughly. If it is too narrow you may not find enough resources or information to develop a strong argument or research hypothesis.
- The question concept is researchable in terms of time and access to a suitable amount of quality research resources.
- It is analytical rather than descriptive. The research question should allow you to produce an analysis of an issue or problem rather than a simple description of it. In other words, it is not answerable with a simple “yes” or “no” but requires a synthesis and analysis of ideas and sources.
- The results are potentially important and may change current ideas and/or practice
- And there is the potential to develop further projects with similar themes
The question you ask should be developed for the discipline you are studying. A question appropriate for Physical Therapy, for instance, is different from an appropriate one in Sociology, Political Science or Microbiology .
The well-constructed question provides guidance for determining search terms and search strategy parameters. The process of developing a good question to research involves taking your topic and breaking each aspect of it down into its component parts.
One well-established way that can be used both for creating research questions and developing strategies is known as PICO(T). The PICO framework was designed primarily for questions that include clinical interventions and comparisons, however other types of questions may also be able to follow its principles. If the PICO framework does not precisely fit your question, using its principles can help you to think about what you want to explore even if you do not end up with a true PICO question.
References/Additional Resources
Fandino W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian journal of anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611–616.
Vandenbroucke, J. P., & Pearce, N. (2018). From ideas to studies: how to get ideas and sharpen them into research questions . Clinical epidemiology , 10 , 253–264.
Ratan, S. K., Anand, T., & Ratan, J. (2019). Formulation of Research Question - Stepwise Approach . Journal of Indian Association of Pediatric Surgeons , 24 (1), 15–20.
Lipowski, E.E. (2008). Developing great research questions. American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, 65(17) , 1667–1670.
FINER Criteria
Another set of criteria for developing a research question was proposed by Hulley (2013) and is known as the FINER criteria.
FINER stands for:
Feasible – Writing a feasible research question means that it CAN be answered under objective aspects like time, scope, resources, expertise, or funding. Good questions must be amenable to the formulation of clear hypotheses.
Interesting – The question or topic should be of interest to the researcher and the outside world. It should have a clinical and/or educational significance – the “so what?” factor.
Novel – In scientific literature, novelty defines itself by being an answer to an existing gap in knowledge. Filling one of these gaps is highly rewarding for any researcher as it may represent a real difference in peoples’ lives.
Good research leads to new information. An investigation which simply reiterates what is previously proven is not worth the effort and cost. A question doesn’t have to be completely original. It may ask whether an earlier observation could be replicated, whether the results in one population also apply to others, or whether enhanced measurement methods can make clear the relationship between two variables.
Ethical – In empirical research, ethics is an absolute MUST. Make sure that safety and confidentiality measures are addressed, and according to the necessary IRB protocols.
Relevant – An idea that is considered relevant in the healthcare community has better chances to be discussed upon by a larger number of researchers and recognized experts, leading to innovation and rapid information dissemination.
The results could potentially be important and may change current ideas and/or practice.
Cummings, S.R., Browner, W.S., & Hulley, S.B. (2013). Conceiving the research question and developing the study plan. In: Designing clinical research (Hulley, S. R. Cummings, W. S. Browner, D. Grady, & T. B. Newman, Eds.; Fourth edition.). Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Pp. 14-22.
- << Previous: Major Steps in a Literature Search
- Next: Types of Research Questions >>
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
Formulating and Clarifying the Research Topic

1. How to cite: Chew, (2017)… 2. References on Harvard Referencing System Chew, B. C. 2017. Formulating and Clarifying the Research Topic. In: Borges, W. G. 2017. Business Research Methods. pp. 10-15. SJ Learning. Ch. 2.

RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.1: Key Attributes of a Research Design
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 26232

- Anol Bhattacherjee
- University of South Florida via Global Text Project
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
The quality of research designs can be defined in terms of four key design attributes: internal validity, external validity, construct validity, and statistical conclusion validity.
Internal validity , also called causality, examines whether the observed change in a dependent variable is indeed caused by a corresponding change in hypothesized independent variable, and not by variables extraneous to the research context. Causality requires three conditions: (1) covariation of cause and effect (i.e., if cause happens, then effect also happens; and if cause does not happen, effect does not happen), (2) temporal precedence: cause must precede effect in time, (3) no plausible alternative explanation (or spurious correlation). Certain research designs, such as laboratory experiments, are strong in internal validity by virtue of their ability to manipulate the independent variable (cause) via a treatment and observe the effect (dependent variable) of that treatment after a certain point in time, while controlling for the effects of extraneous variables. Other designs, such as field surveys, are poor in internal validity because of their inability to manipulate the independent variable (cause), and because cause and effect are measured at the same point in time which defeats temporal precedence making it equally likely that the expected effect might have influenced the expected cause rather than the reverse. Although higher in internal validity compared to other methods, laboratory experiments are, by no means, immune to threats of internal validity, and are susceptible to history, testing, instrumentation, regression, and other threats that are discussed later in the chapter on experimental designs. Nonetheless, different research designs vary considerably in their respective level of internal validity.
External validity or generalizability refers to whether the observed associations can be generalized from the sample to the population (population validity), or to other people, organizations, contexts, or time (ecological validity). For instance, can results drawn from a sample of financial firms in the United States be generalized to the population of financial firms (population validity) or to other firms within the United States (ecological validity)? Survey research, where data is sourced from a wide variety of individuals, firms, or other units of analysis, tends to have broader generalizability than laboratory experiments where artificially contrived treatments and strong control over extraneous variables render the findings less generalizable to real-life settings where treatments and extraneous variables cannot be controlled. The variation in internal and external validity for a wide range of research designs are shown in Figure 5.1.
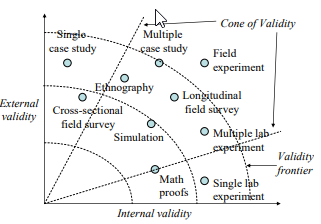
Some researchers claim that there is a tradeoff between internal and external validity: higher external validity can come only at the cost of internal validity and vice-versa. But this is not always the case. Research designs such as field experiments, longitudinal field surveys, and multiple case studies have higher degrees of both internal and external validities. Personally, I prefer research designs that have reasonable degrees of both internal and external validities, i.e., those that fall within the cone of validity shown in Figure 5.1. But this should not suggest that designs outside this cone are any less useful or valuable. Researchers’ choice of designs is ultimately a matter of their personal preference and competence, and the level of internal and external validity they desire.
Construct validity examines how well a given measurement scale is measuring the theoretical construct that it is expected to measure. Many constructs used in social science research such as empathy, resistance to change, and organizational learning are difficult to define, much less measure. For instance, construct validity must assure that a measure of empathy is indeed measuring empathy and not compassion, which may be difficult since these constructs are somewhat similar in meaning. Construct validity is assessed in positivist research based on correlational or factor analysis of pilot test data, as described in the next chapter.
Statistical conclusion validity examines the extent to which conclusions derived using a statistical procedure is valid. For example, it examines whether the right statistical method was used for hypotheses testing, whether the variables used meet the assumptions of that statistical test (such as sample size or distributional requirements), and so forth. Because interpretive research designs do not employ statistical test, statistical conclusion validity is not applicable for such analysis. The different kinds of validity and where they exist at the theoretical/empirical levels are illustrated in Figure 5.2.
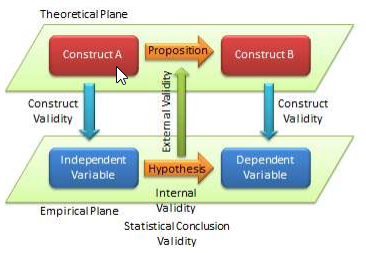

- Research Process
The Top 5 Qualities of Every Good Researcher
- 3 minute read
- 191.7K views
Table of Contents
What makes a good researcher? Is it some undefinable, innate genius, or is it something that we can practice and build upon? If it was just the former, then there would be far fewer innovations in the history of humankind than there have been. A careful look at researchers through the ages reveals that they all have certain attributes in common that have helped contribute to their success.
The characteristics of a good researcher:
1. curiosity.
They ask questions. An endless thirst for knowledge is what sets the best of the best apart from the others. Good researchers constantly strive to learn more, not just about their own field, but about other fields as well. The world around us is fascinating, be it the physics behind the way light refracts, or the anthropological constructions of our society. A good researcher keeps exploring the world and keeps searching for answers.
2. Analytical ability and foresight
They look for connections. Information is useless without interpretation. What drives research forward is finding meaning in our observations and data. Good researchers evaluate data from every angle and search for patterns. They explore cause and effect and untangle the tricky web that interconnects everyday phenomena. And then take it one step further to ask, ‘What is the bigger picture? How will the research develop in the future?’
3. Determination
They try, try, and try again. Research can be a frustrating experience. Experiments may not pan out how we expect them to. Even worse, sometimes experiments may run smoothly until they are 95% complete before failing. What sets an average researcher apart from a truly good one? The truly good researcher perseveres. They accept this disappointment, learn from the failure, reevaluate their experiment, and keep moving forward.
4. Collaboration
Teamwork makes the dream work. Contrary to the common perception of the solitary genius in their lab, research is an extremely collaborative process. There is simply too much to do for just one person to do it all. Moreover, research is becoming increasingly multidisciplinary. It is impossible for just one person to have expertise in all these fields. In general, research is conducted in teams , with each researcher having their individual roles and responsibilities. Being able to coordinate, communicate, and get along with team members is a major factor that can contribute to one’s success as a researcher.
5. Communication
They get their message across. Communication skills are an essential asset for every researcher. Not only do they have to communicate with their team members, but they also have to communicate with co-authors, journals, publishers, and funders. Whether it is writing a crisp and effective abstract, presenting at a conference, or writing a persuasive grant proposal to secure research funding, communication appears everywhere in a researcher’s life. The message in the old adage, ‘If a tree falls in the forest, but no one is around to hear it, does it make a sound?’ applies to research too. A discovery could be groundbreaking, but what is the use if the researcher can’t communicate this discovery to the rest of the world?
These are just a few of the skills required by researchers to make it to the top of their field. Other attributes like creativity and time management are also worth mentioning. Nevertheless, having one or more of these top five characteristics will make the research process smoother for you and increase the chances of positive results. Set yourself up for success by building up these skills, focusing on excellence, and asking for help when you need it. Elsevier Author Services is here to aid you at every step of the research journey. From translation services by experts in the field, to preparing your manuscript for publication, to helping you submit the best possible grant proposal, you can trust us to guide you in your journey to doing great research.

- Manuscript Preparation
What is the Background of a Study and How Should it be Written?

- Publication Process
Writing an Effective Cover Letter for Manuscript Resubmission
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

COMMENTS
In other words, it should be attractive, expressive and parsimonious. 3. A research topic should also be simple enough for your readers to understand. Keep in mind that you are writing to an audience that goes beyond your field of study. 4. Avoid abbreviation (s) in a research topic. A reader may find it difficult to know the full meaning of ...
Before diving into how to choose a research topic, it is important to think about what are some elements of a good research topic. Of course, this will depend specifically on your research project, but a good research topic will always: Relate to the assignment itself. Even when you have a choice for your research topic, you still want to make ...
Qualities of Good Research 1. Good research is anchored on a sound research question. A sound research question is one of the most important characteristics of good research. In fact, formulating one is embedded in the curricula of research-heavy programs like engineering and physics degrees and careers.In 2010, Farrugia et al. proposed that developing a research question is the most important ...
To recap, the "Big 5" assessment criteria include: Topic originality and novelty. Value and significance. Access to data and equipment. Time requirements. Ethical compliance. Be sure to grab a copy of our free research topic evaluator sheet here to fast-track your topic selection process.
In general, this includes all functions of business. The main areas include marketing, finance, human resources and strategy. Those of you on courses based on specific areas of business, e.g. a BA (Hons) in Marketing, will undoubtedly select a topic that is relevant to marketing. This might include.
Choosing a research idea video by Bunmi Malau-Aduli and Faith Alele, used under a CC BY NC ND 4.0 licence. Techniques for finding and choosing a research topic. There are two main approaches to finding and choosing a research topic- rational (logical) and creative (intuitive). 2,3 The creative approach requires techniques such as brainstorming, keeping a record of the ideas, using relevance ...
the research topic should clearly be discussed, be specific on the innovation to be added, the significance of your research (not more than a page), the objectives of ... Attributes of a Good Research Good research alone is of relevance in solving the problem under consideration.
The process of formulating a good research question can be challenging and frustrating. While a comprehensive literature review is compulsory, the researcher usually encounters methodological difficulties in the conduct of the study, particularly if the primary study question has not been adequately selected in accordance with the clinical dilemma that needs to be addressed.
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
A strong research topic comprises three important qualities: originality, value and feasibility.. Originality - a good topic explores an original area or takes a novel angle on an existing area of study.; Value - a strong research topic provides value and makes a contribution, either academically or practically.; Feasibility - a good research topic needs to be practical and manageable ...
A good research involves systematic planning and setting time-based, realistic objectives. It entails feasible research methods based upon a research methodology that best suits the nature of your research question. It is built upon sufficient relevant data and is reproducible and replicable. It is based on a suitable rationale and can suggest ...
It is builds on, but also offers something new to, previous research. It has the potential to suggest directions for future research. It is a purpose or question that the researcher is sincerely interested and/or invested in. It addresses directly or indirectly some real problem in the world. It takes ethical issues into consideration.
will outline and ex plain in detail the. characteristics of quality research, attributes of go od rese arch, research. ethics, step- by -step g uide to writing a. scientific article. This guide ...
Feasible - Writing a feasible research question means that it CAN be answered under objective aspects like time, scope, resources, expertise, or funding. Good questions must be amenable to the formulation of clear hypotheses. Interesting - The question or topic should be of interest to the researcher and the outside world. It should have a ...
Identify the attributes of a good research topic. 2. Generate solid research idea and explore techniques available. 3. Refine and evaluate your research idea. 10 | PART 1 Introduction to Business Research Methods INTRODUCTION When it comes to making decisions on a research topic, some students are stressed and others are excited.
Learn how to formulate a good research question for your academic project with tips and examples from George Mason University Library.
Characteristics of Good Research. 1. The purpose of the research should be clearly defined (aims and. objectives). 2. The need and significance of the topic of research must be stated. 3. Research ...
The characteristic of a good research. A researcher should understand and have a clear understanding of the different. types of research design and select the type which apply best for the study ...
113 Great Research Paper Topics. Posted by Christine Sarikas. General Education. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and ...
The quality of research designs can be defined in terms of four key design attributes: internal validity, external validity, construct validity, and statistical conclusion validity. Internal validity, also called causality, examines whether the observed change in a dependent variable is indeed caused by a corresponding change in hypothesized ...
2. Analytical ability and foresight. They look for connections. Information is useless without interpretation. What drives research forward is finding meaning in our observations and data. Good researchers evaluate data from every angle and search for patterns. They explore cause and effect and untangle the tricky web that interconnects ...
Becoming a good researcher requires time, dedication, key skills and attributes, and a lot of hard work! (Image by cookie_studio on Freepik) Year after year, people with different personalities and backgrounds step into the field of research eager to develop the key qualities of a good researcher, only to find themselves faced with anxiety and self-doubt.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A good research topic should: a. Pass the "so what?" test. b. Be specific. c. Capable of being answered by observable evidence. d. All of these are correct. e. None of these is correct., Which of the following is an attribute of a good research question? a. There should be many possible acceptable answers to it. b. It need NOT be ...