
Accessibility links
- Skip to content
- Accessibility Help
KS2 History: Ancient Egypt - Gods and goddesses
BBC Teach > Primary Resources > History KS2 > Ancient Egypt
Exploring some of the many gods and goddesses of Ancient Egyptian civilisation and their significance within society.
This is a bronze hook from Ancient Egypt.
This object or artefact takes us back over three thousand years to the New Kingdom. In Ancient Egypt, when someone important died, their body was mummified to prepare them for burial.
To start with embalmers removed all moisture from the body, including the organs which they placed in special containers- called canopic jars - to dry.
That's where our artefact comes in: it was used to pull the brains out through the dead person's nose. Uh, yuck!
The heart was the only organ left in place and that's because the Ancient Egyptians believed the 'essence' or 'soul' of a person was in their heart.
The mummification process took seventy days to complete. It involved lots of different stages, including rubbing the body with oils and wrapping it in linen.
But why did they go to all that effort?
Well, that comes down to their religion which celebrated lots of different gods and goddesses each with their own role to play.
Ancient Egyptians believed they would be judged by their gods and goddesses to see if they could move on to the afterlife.
Mummification was just one step in preparing for the afterlife.
Osiris was chief god of the dead and one of the most popular gods.
He's usually shown as a mummified human wearing a white crown and holding two farming tools in his hands: the crook and the flail.
His skin is often green because he was also the god of vegetation growth and rebirth.
He's described as a judge in the 'Hall of Truth', where the heart of the dead person was weighed against a feather to see if they were good enough to pass on to the afterlife.
Osiris: Oh dear! No afterlife for you I'm afraid. Next! Oh excellent, welcome to the afterlife.
Nephthys, wife of Osiris, was known as friend of the dead because she looked after the souls of the dead in the afterlife.
She was one of the few goddesses, worshipped throughout the entire 3000 year period, so her image has been found by archaeologists at many tombs and temples, including the tomb of King Tutankhamun.
But the gods and goddesses that the Ancient Egyptians worshipped were about more than just the afterlife.
They controlled every part of nature and daily life.
Tawaret was a goddess of childbirth and a protector of women and children. She was thought to be a ferocious demon as well as a protective and caring goddess. Do you know anyone else like that?
Anyway, Tawaret had the body of a hippo, the legs of a lion and the tail of a crocodile. These were animals that were equally feared and respected by the Ancient Egyptians.
As well as the 'state gods' that everyone knew about, people had their own local gods and goddesses and those worshipped in one village can be very different from the next village.
Traveller 1: Who's that guy?
Traveller 2: Montu? Never heard of him!
If a particular person or city became the most powerful then their local gods became the 'state gods'.
This meant that a particular god or goddess could be popular for a few decades, then they would go out of fashion, the temple pulled down and the stone reused.
Around 1353 BC the Pharaoh Akhenaten tried to change the way gods were worshipped in Egypt.
Instead of having multiple gods and goddesses, each with different roles, he placed one god, the god Aten, above all others and introduced a Atenism .
This was not a popular decision, so after he died Akhenaten's monuments and statues were destroyed and hidden and his name was removed from the list of rulers.
Religious beliefs changed a lot during Ancient Egyptian history.
But what remained the same was the important role that gods and goddesses played in people's lives, their deaths and their journey onto the afterlife.
Gods and goddesses
Video summary.
This video gives pupils an introduction to the role of religion and gods / goddesses in Ancient Egyptian society.
It helps pupils to explore the process of mummification and how pharaohs were believed to become gods and goddesses after death.
We explore an artefact to help unearth the story of the past and find out more about how people lived and what they believed in.
The video explains the various roles that gods and goddesses had in Ancient Egyptian society and how each had a distinct purpose, with some of these being more important to the Ancient Egyptians than others.
It also explores how the roles of gods and goddesses changed over the years and how the beliefs and feelings of different pharaohs caused particular gods / goddesses to fall in or out of fashion.
Further resources

Some well-known Ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses
Click to display the image full-size
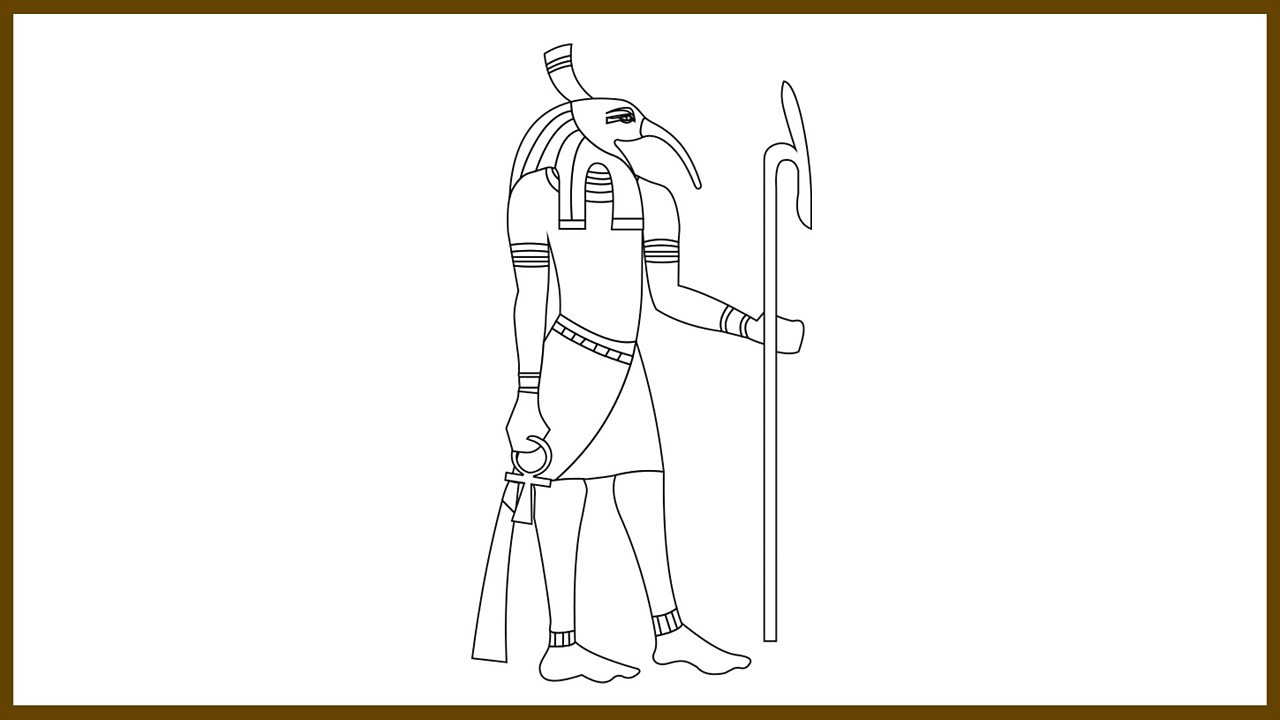
The god Thoth to colour in
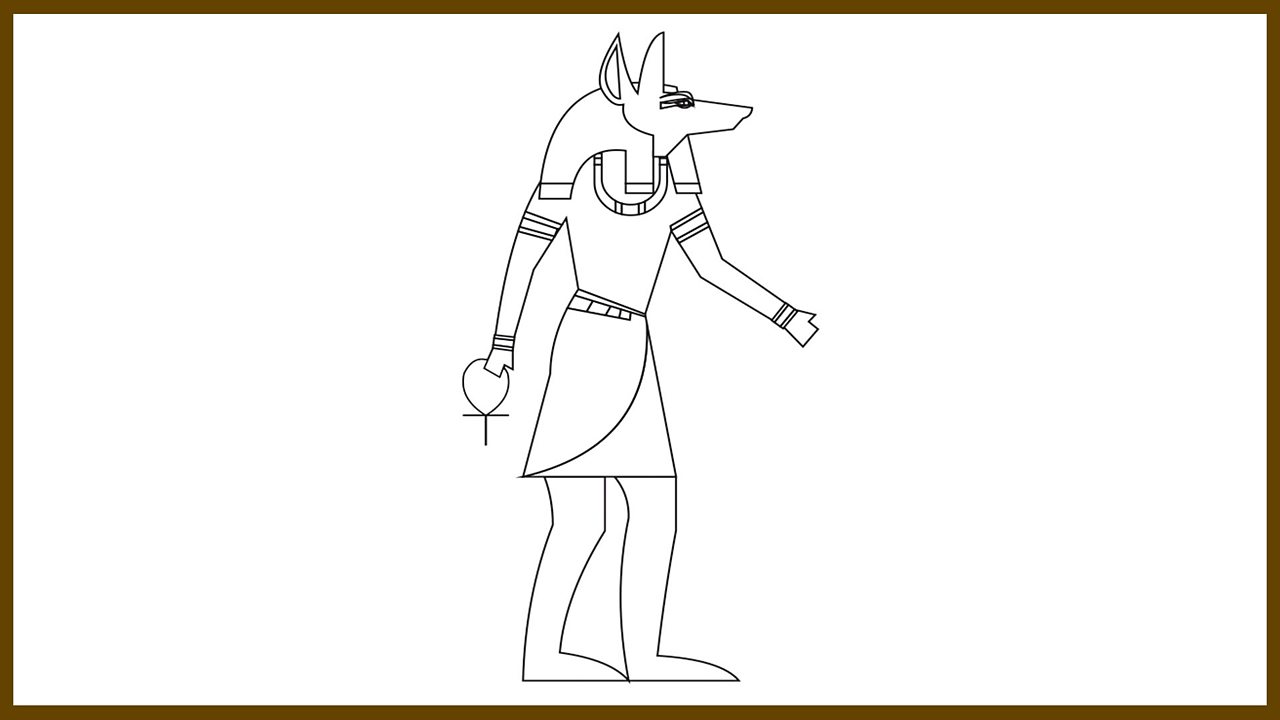
The god Anubis to colour in
Teacher's notes.
This animation gives a snapshot of Ancient Egypt and how important gods and goddesses were to the society and culture.
It provides a platform to discuss faith and belief and why gods and goddesses played such an important role in Ancient Egyptian life and death.
It can be used to help the pupils understand how we find out about the past and the role of sources or artefacts in this exploration.
We find out how the mummification process took place and in turn have an exciting platform for investigation in Science in relation to decomposition and decay.
The video provides an opportunity for pupils to discuss how Ancient Egyptian beliefs can be compared and contrasted with modern day beliefs and religions.
Points for discussion (History Linked)
- What is an artefact or source?
- What was the job of the artefact explored in the clip?
- Which types of people in Ancient Egypt became mummies?
- What happened during the process of mummification?
- Can you name any of the gods or goddesses and what they were believed to have done?
- What was a 'state' god?
- What was a 'local' god?
- Why did the Ancient Egyptians think their gods and goddesses were so important?
- What jobs did they believe they had in the afterlife?
Suggested Activities (Cross Curricular opportunities)
Qualities and beliefs – The Ancient Egyptians worshipped their many gods and goddesses due to the qualities and characteristics they believed that they brought to the afterlife. If the pupils were looking at qualities they think are important, how would they design their own Ancient Egyptian god or goddess?
Investigating decomposition? – The process of mummification took place to preserve the body of very important Ancient Egyptians. Pupils can explore ways to speed up decomposition. Using pieces of fruit and vegetables, can pupils create an environment where decomposition may happen faster, or an environment that it can happen more slowly? Using their scientific knowledge, pupils can make predictions and justify these.
Creating a mummy – The Ancient Egyptians found that the hot and dry conditions of the sand in Egypt helps dry out and preserve the bodies of the pharaohs. Can the pupils test this finding? Using two pieces of bread or home-made play dough, place one in an airtight container or bag alone and other in the same container but with sand. Leave the one with sand close to a radiator and the other away from a heat source. Watch and observe over time and see which begins to change as it rots first. Were the Ancient Egyptians onto something with their mummification process?
What is mummification? - Pupils to explore the process of mummification following watching the video. Pupils to explore what tools were needed and the order and timings of the process. Following research, pupils can write a set of instructions as to how to carry out the mummification process.
This film is relevant for teaching History at KS2 in England, Wales and Northern Ireland and 2nd Level in Scotland.
More from this series
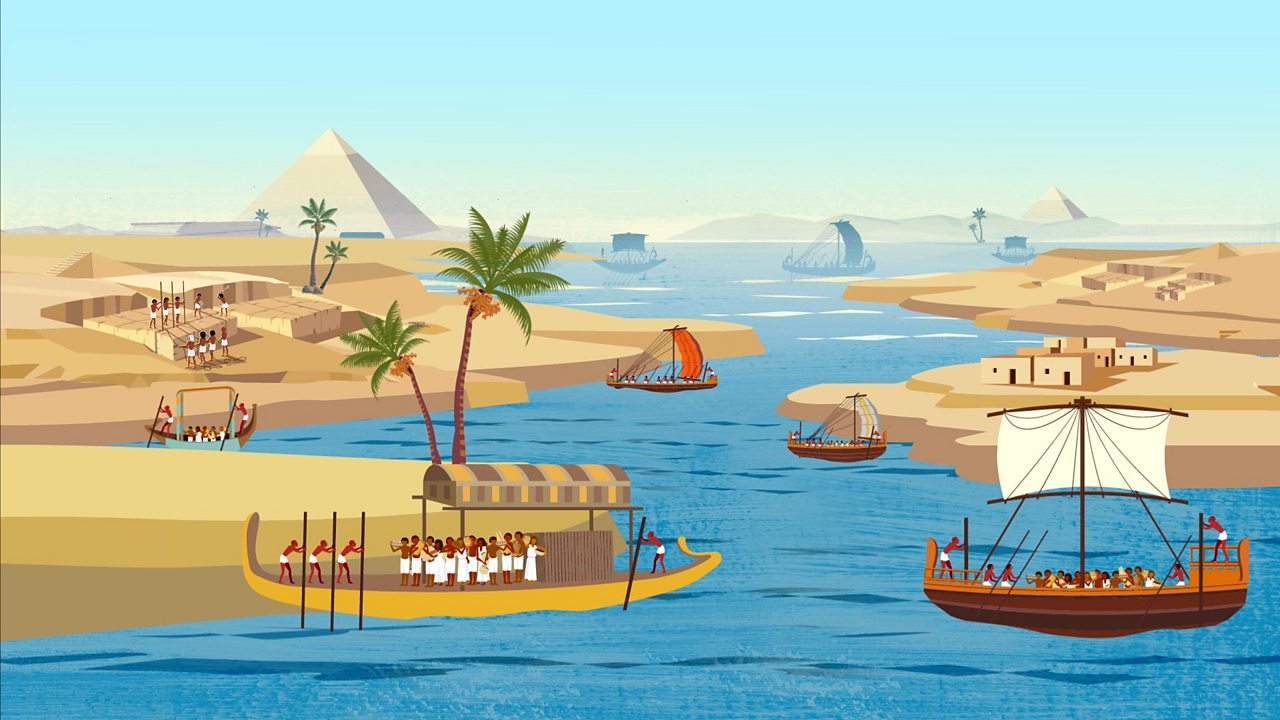

The River Nile
Understanding the key role of the River Nile in the establishment and success of Ancient Egypt.
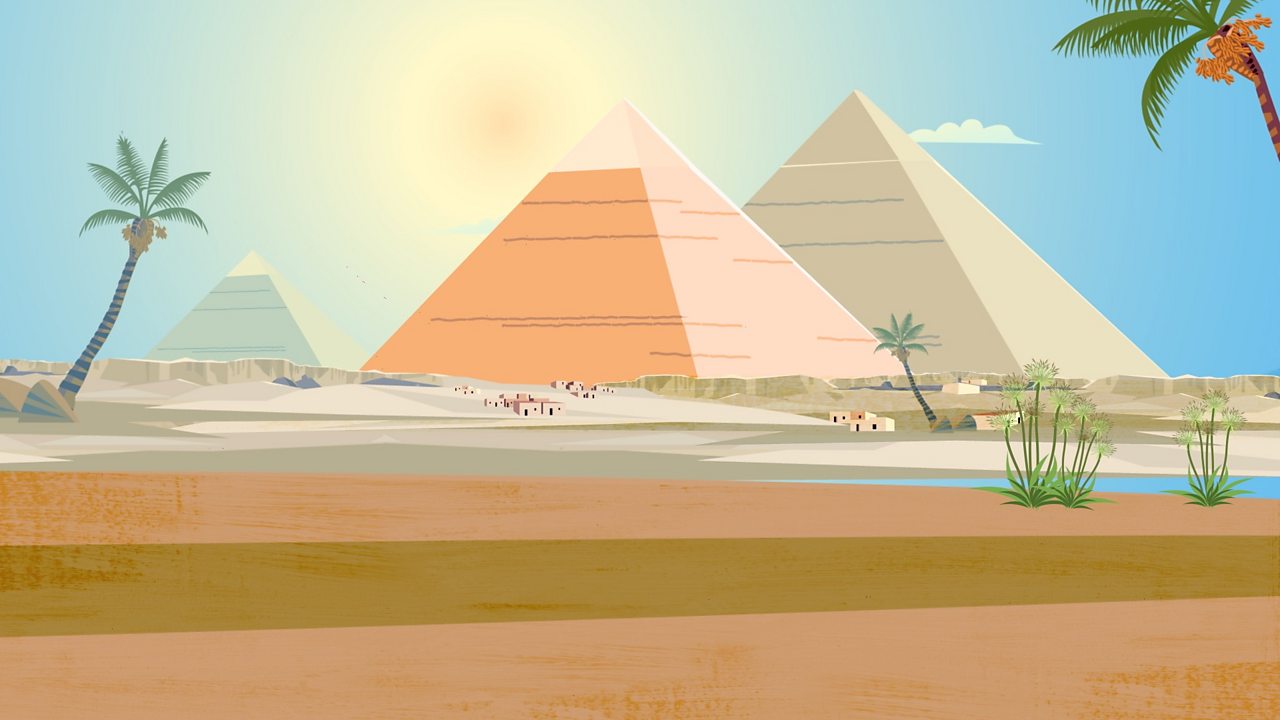

Exploring the different types of pyramids in Ancient Egypt - their construction and their purpose.

King Tutankhamun
Exploring the life and death of King Tutankhamun and the excavation of his tomb in 1922.
See also...

KS2 Music: Ancient Egypt
A collection of fun, catchy songs and activities to help you consolidate your study of Ancient Egypt.
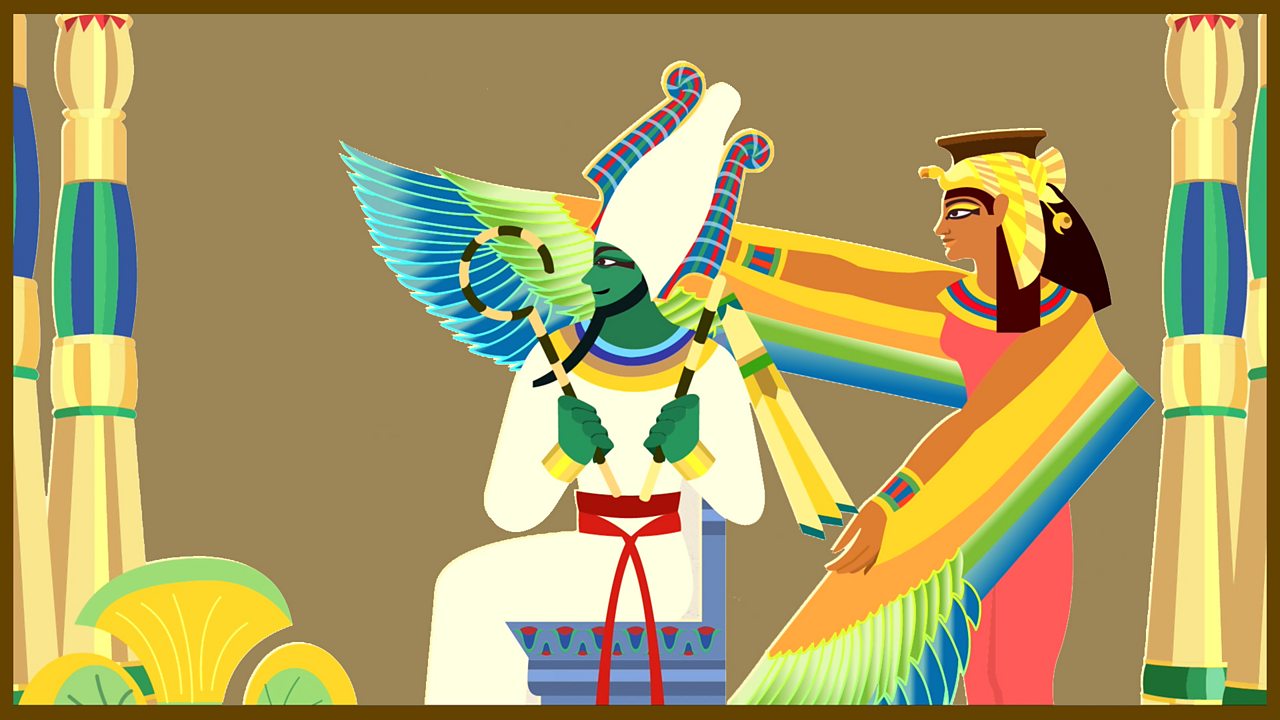

Song: 'So many gods and goddesses'
Join in with a song about some of the most important of the Ancient Egyptian gods.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Ancient Egyptian gods & goddesses Lesson
Subject: History
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
16 May 2022
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

A full lesson for KS2 exploring Ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses. The resource includes a detailed lesson plan, Powerpoint and pupil resource sheets.
Who were the Ancient Egyptian gods? In this lesson, pupils will play a game to learn about different gods and goddesses from Ancient Egypt, including how they were depicted and areas of responsibility. Pupils will create a set of fact files about three gods or goddesses. Then they will examine a series of historical sources and apply their new knowledge to work out which deity is depicted in each source.
Objectives:
- To compare different Ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses
- To look at some sources depicting Ancient Egyptian gods
The lesson plan includes differentiation ideas to adapt the activities for the needs of your class.
This lesson is part of the KS2History Ancient Egyptians Planning Pack for KS2.
This primary history resource is created by KS2History
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Get this resource as part of a bundle and save up to 63%
A bundle is a package of resources grouped together to teach a particular topic, or a series of lessons, in one place.
Ancient Egypt: Lessons
Download our popular Ancient Egypt lesson planning bundle containing 10 full lessons. This resource contains a bundle of history lessons that make up a complete unit covering the Ancient Egyptians topic. Each file contains a detailed lesson plan, Powerpoint slides and pupil resource sheets. The planning pack covers the following lessons: [Who were the Ancient Egyptians?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/ancient-egypt-12189369) [Why was Ancient Egypt the ‘Gift of the Nile’?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/river-nile-ancient-egypt-12162395) [Who were the Ancient Egyptian pharaohs?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/pharaohs-ancient-egypt-12189443) [Why did the Ancient Egyptians build the pyramids?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/pyramids-ancient-egypt-12162417) [What did the Ancient Egyptians do for fun?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/ancient-egypt-leisure-12162425) [What was mummification in Ancient Egypt?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/ancient-egypt-mummification-12162430) [Who were the Ancient Egyptian gods?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/ancient-egyptian-gods-and-goddesses-12162434) [What did Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics mean?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/hieroglyphics-12162436) [What was discovered inside Tutankhamun’s tomb?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/tutankhamun-s-tomb-12162441) [Who was Cleopatra and how is she remembered?](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/ancient-egypt-cleopatra-vii-12162460) These lessons are written for KS2 and are aligned to the National Curriculum in the UK but can be easily adapted to other curriculums too. The lesson plans include differentiation ideas to adapt the activities for the needs of your class. This bundle is brought to you by KS2History.com. You may also like our [Egyptian Cinderella Literacy Resource Pack](http://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/egyptian-cinderella-planning-egyptians-topic-11337937).
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

- DIGITAL MAGAZINE
MOST POPULAR
Ancient Egyptian life primary resource
Discover the customs and beliefs of the ancient egyptians.
This History primary resource introduces children to Ancient Egyptian life and culture. Discover the customs and beliefs of the Ancient Egyptians. Who were their rulers? How did they worship their Gods? Why was Ancient Egyptian medicine so advanced?
Pupils will learn about the lavish temples built to honour the pharaohs, the food that the workers and farmers ate, and the Great Pyramid at Giza in our National Geographic Kids’ Ancient Egyptians primary resource sheet.
The teaching resource can be used in study group tasks for understanding aspects of Ancient Egyptian life, as a printed handout for each pupil to review and annotate, or for display on the interactive whiteboard using the illustrations and short snippets of information for class discussion. The resource includes information on: Tutankhamun, Ancient Egyptian temples, mummification, pyramids, hieroglyphics, Cleopatra, Rameses II, Anubis, Egyptian gods and goddesses and Ancient Egyptian workers, farmers and pharaohs.
Activity: Ask children to choose one of the subheadings in the resource and use the information and their own research to create their own comic strip based on that topic, like The Land of the Pharaohs comic. They could also design their own temple decorations and designs, in the style of the photographs shown in the resource. Children could also complete the Hieroglyphic puzzle.
N.B. The following information for mapping the resource documents to the school curriculum is specifically tailored to the English National Curriculum and Scottish Curriculum for Excellence . We are currently working to bring specifically tailored curriculum resource links for our other territories; including South Africa , Australia and New Zealand . If you have any queries about our upcoming curriculum resource links, please email: [email protected]
This History primary resource assists with teaching the following History objectives from the National Curriculum :
- Know and understand significant aspects of the history of the wider world: the nature of ancient civilisations; the expansion and dissolution of empires; characteristic features of past non-European societies; achievements and follies of mankind.
National Curriculum Key Stage 2 History objective:
- Pupils should be taught about: the achievements of the earliest civilizations – an overview of where and when the first civilizations appeared and a depth study of one of the following: Ancient Sumer; The Indus Valley; Ancient Egypt; The Shang Dynasty of Ancient China
This History primary resource assists with teaching the following Social Studies First level objective from the Scottish Curriculum for Excellence :
- Having selected a significant individual from the past, I can contribute to a discussion on the influence of their actions, then and since
Scottish Curriculum for Excellence Second level Social Studies objective :
- I can discuss why people and events from a particular time in the past were important, placing them within a historical sequence.
Download primary resource
Leave a comment.
Your comment will be checked and approved shortly.

WELL DONE, YOUR COMMENT HAS BEEN ADDED!
Customize your avatar.

Check out The Royal Rabbits of London!
Your Amazing Brain!

Starfell: Willow Moss and the Forgotten tale

Sign up to our newsletter
Get uplifting news, exclusive offers, inspiring stories and activities to help you and your family explore and learn delivered straight to your inbox.
You will receive our UK newsletter. Change region
WHERE DO YOU LIVE?
COUNTRY * Australia Ireland New Zealand United Kingdom Other
By entering your email address you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy and will receive emails from us about news, offers, activities and partner offers.
You're all signed up! Back to subscription site
Type whatever you want to search
More Results

You’re leaving natgeokids.com to visit another website!
Ask a parent or guardian to check it out first and remember to stay safe online.

You're leaving our kids' pages to visit a page for grown-ups!
Be sure to check if your parent or guardian is okay with this first.
- Create new account
- Reset your password
Register and get FREE resources and activities
Ready to unlock all our resources?
Egyptian life and culture

Who were the Egyptians?
Egypt is a country in Africa. People have lived in that region for thousands and thousands of years. The Ancient Egyptians settled around the Nile River, and built pyramids that you can still see there today.
The Ancient Egyptians knew a lot about maths, medicine and farming. They also made their own paper out of reeds called papyrus, and wrote using pictures called hieroglyphics.
Top 10 facts
- The Egyptians settled in northeast Africa, and that’s where the country of Egypt is today.
- They lived in a very dry area, but they got water from the Nile River (the longest river in the world!) so they could grow crops.
- Farming techniques to water crops included using machines like the sakia and the shaduf – these are still used in Egypt today.
- The Egyptians created paper using reeds, called papyrus. They wrote using pictures called hieroglyphics that stood for different words.
- Only certain people studied how to write, and they worked as scribes.
- Scribes were ranked in the middle of the order of social groups in Egypt – the pharaoh was at the very top of this list, and slaves were at the very bottom.
- The Egyptians built pyramids as places to bury their kings and queens, who were called pharaohs.
- The Egyptians were very good at maths – they had to be, to work out how to build pyramids so perfectly!
- Both men and women wore make-up. The wealthier people were, the more make-up they’d wear.
- Egypt was conquered by Rome and became part of the Roman Empire .
Egyptian timeline
- c7500 BC People began to build homes and farm in the Nile Valley
- c3000 BC Hieroglyphics started to be used
- c2950 BC Upper and Lower Egypt were united into one kingdom by King Narmer (or Menes), and Memphis became the capital

- 2600-2150 BC The Old Kingdom
- 2181-2055 BC First Intermediate Period
- 2055-1650 BC Middle Kingdom
- 1650-1500 BC Second Intermediate Period
- 1500-1070 BC The New Kingdom
- 1473-1458 BC Queen Hatshepsut ruled

- 1279-1213 BC King Rameses II ruled
- 1069-664 BC Third Intermediate Period
- 669 BC Egypt was conquered by the Assyrians
- 664-332 BC Late Period
- 525 BC Egypt was conquered by the Persians
- 332 BC Alexander the Great from Greece conquered Egypt and founded Alexandria
- 196 BC The writings on the Rosetta Stone were carved
- 51-30 BC Cleopatra VII ruled; she was the last pharaoh

Boost Your Child's Maths & English Skills!
- Weekly resources delivered to your dashboard
- Keep your child's learning on track
Did you know?
- The Egyptians made paper from reeds called papyrus – it’s where we get the word ‘paper’ from! It took a long time to make papyrus, but it was easier than carrying around heavy clay tablets, which is what they did before.
- They wrote in pictures called hieroglyphics . Each picture means something so when you see a few different kinds of pictures in a row, you know what the writer is trying to say.
- The Egyptians used pictures for writing numbers too – different pictures stood for units, tens and hundreds.
- The Egyptians were very advanced at maths – they figured out how to work out tricky problems that helped other people after them understand more about maths. In fact, people who lived in other countries even knew that the Egyptians were the best at maths!
- The Egyptians made most of their clothes from linen, which is fabric that’s made from plants. They’d use different things to colour it, such as saffron to make it yellow and indigo to make it blue.
- Egyptians would shave their heads and wear wigs instead!
- Ancient Egyptians had a huge amount of respect for cats, and for a type of dog called a jackal. They also thought scarab beetles were very important; they represented rebirth and life after death.
- Egyptians loved perfume, and would wear it in solid cones on their head – the cones would melt during the day and keep them smelling nice when the weather was very hot.
- Both men and women wore make-up, black and green on their eyes and eyelashes, and red rouge for their cheeks.
Egyptian gallery:
- The Rosetta stone
- The Egyptian pharaoh Ramses
- An Egyptian tomb
- An image of the pharaoh Tutankhamen
- An engraving from the temple at Luxor
- The pyramid at Giza
- Amun-her-khepeshef, the son of Pharaoh Ramesses II and Queen Nefertari
- Hieroglyphs
- Illustrations of Egyptian figures
- Can you spot the Sphinx?
- Edfu Temple
- An Egyptian pharaoh design

The Egyptians were very good farmers . Over the centuries, they learned the best ways to grow crops in the dry land around the Nile River – but, they’d use different kinds of machines to get water from the river to their crops so the plants would grow. Some of the machines they used are:
- sakia – a type of water wheel that has buckets to scoop water out
- shaduf – a long stick that had a bucket on a rope on one end, and a heavy weight on the other; to water a field, the farmer would pull down on the weighted end so the bucket would come up, then swing the whole thing around to water a field next to the river.
Because farmers grew crops near the Nile, they had to schedule their growing season around times when the Nile flooded. This happened every year during June to September, so they’d plant new crops in October that would be ready to harvest in March. By the end of May, all of the crops would have been harvested in time for the Nile to flood again.
Egyptian farmers also had oxen pull ploughs through fields. We know about their farming techniques because of the paintings that archaeologists have found that the Egyptians made. The paintings show all sorts of things that the Egyptians did, such as tending livestock and harvesting the crops.
Make-up wasn’t always worn to dress up. Some make-up had practical uses as well, like black kohl used around the eyes. It shielded eyes from the sun, and it was also a kind of disinfectant that protected against eye diseases.
The papyrus that Egyptians made came from reeds that grew along the Nile River, which were called papyrus. To make paper, they would cut papyrus reeds into strips and spend quite a few days soaking them, rolling them out and repeating that process until the reeds were very thin. All of the thin reeds would be pounded together and clamped down to dry, then polished to smooth it out – the result was a thin yet very strong sheet that was ready to be written or drawn on.
The papyrus reeds were actually used for a lot of things besides paper. It was good for making mats to put on the floor, twisting into rope, plaiting together to make boats, and weaving to make baskets and sandals. The Egyptians also ate it, and used it to make different medicines.
The Egyptians made a lot of discoveries about medicine. We know this from reading what they wrote on papyrus, discovered later by archaeologists. They understood about heartbeats and listening for a healthy pulse, and knew how the body and organs worked because of the process of making mummies . They also learned about the ways that different plants healed different illnesses and injuries, such as aloe vera being good for healing burns.
Egyptian society was ranked into different classes, called a hierarchy. You couldn’t really move up the ranks, and people would usually stay around the rank that they were born into:
- Pharaoh – The pharaoh was at the top of the order, and thought to be a god.
- Vizier – Every pharaoh had a vizier; they were an advisor, they ran the pharaoh’s household, they acted as a judge, and they made sure that the Egyptians had enough food.
- Nobles and priests – Nobles included doctors, lawyers and military leaders. Priests were the ones who made sure the god in their temple was happy, and that they understood any messages the god was trying to say to them.
- Scribes and soldiers – Scribes were the only ones who were taught how to write; people in other professions (like priests) may have studied to be a scribe as well, but they could also have just hired someone to write things down for them. Being a soldier was a choice; they were given land to live on after they finished serving in the army.
- Craftsmen – This was a large group that included anyone who had a trade, such as potters, tailors, painters and blacksmiths.
- Farmers and slaves – The pharaoh and nobles hired farmers to work for them, and grow crops on their land; as payment, the farmers had a place to live, clothes to wear and food to eat. Slaves were people who were captured in battles with other civilisations, and they worked in the homes of the pharaoh and nobles or in temples.
Related Videos
Just for fun...
- Explore Ancient Egypt with an interactive exploration tool from the Children's University
- Walk around the Sphinx, clamber inside the Great Pyramid of Giza and seek out the pharaoh's burial chamber!
- Are you fit to rule as a pharaoh? Put your knowledge of Ancient Egypt to the test with a quiz !
- Take an Ancient Egyptian art lesson
- Use an interactive timeline of the Ancient Egyptian period
- Try some Ancient Egyptian number puzzles
- Write using a hieroglyphic typerwriter !
- Complete an Ancient Egypt online jigsaw puzzle
- Make your own Egyptian amulet , Egyptian mask and Egyptian costume with step-by-step guides from Hobbycraft
- Learn how to sound out your name in hieroglyphs , just like a scribe in Ancient Egypt
- Make a miniature cartonnage mummy case to discover how the Ancient Egyptians prepared for the journey to the afterlife
- Write your name in hieroglyphs in a cartouche and learn some Egyptian Maths with King Khasekhem
- Discover different aspects of life in Ancient Egypt with BBC Teach songs
Children's books about Ancient Egypt

See for yourself
- At the British Museum , you can see the Rosetta Stone and a statue of King Rameses II
- See Ancient Egyptian artefacts from the Art Institute Chicago's collection
- Browse through a huge collection of Egyptian artefacts at the Manchester Museum
- Look closely at Egyptian statues in the Brooklyn Museum
- See games from Ancient Egypt: a senet board game and a wooden toy cat
Find out more about Egyptian life and culture
- Watch BBC Bitesize animations about Ancient Egypt and new animations about life in Ancient Egypt on BBC Teach
- A DKfindout! children's introduction to Ancient Egypt , with lots of diagrams and illustrations
- Scan through an interactive timeline of Ancient Egypt
- Read some historical fiction for kids about Ancient Egypt
- Print out Ancient Egypt resources from the British Museum
- Find out more about Egyptian myths
- The history of papyrus paper
- Join historian Greg Jenner for a BBC Sounds kids' homeschool history lesson about Cleopatra or a homeschool history podcast about Ancient Egyptian religion
- Read about Ancient Egyptian inventions
- Understand more about Ancient Egyptian gods and see Egyptian gods' animal heads
- Explore the Ancient Egyptian number system and writing system (hieroglyphics)
- The Egyptians' society
- Find out about everyday life in Ancient Egypt
- Experience a day in the life of ordinary Egyptians

Give your child a headstart
- FREE articles & expert information
- FREE resources & activities
- FREE homework help
©Copyright Mandy Barrow 2013 primaryhomeworkhelp.com
Follow me on Twitter @mbarrow
I teach computers at The Granville School and St. John's Primary School in Sevenoaks Kent.
Woodlands Junior School, Hunt Road Tonbridge Kent TN10 4BB UK

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Some images of Ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses show them with a human body and the head of a bird or an animal. Animals were chosen to represent the powers of the god. Bastet was the Goddess of Protection of joy, love, pleasure and pregnant woman. In Egyptian mythology, the sacred cat is the animal incarnation of the goddess Bast or Bastet.
In about 3200 B. C. the pharaoh of the north conquered the south and Egypt became united. The pharaoh's name was King Narmer or Menes. Menes built a new capital city called Memphis. In the Greek language the word Memphis meant "Balance of the Two Lands." Ancient Egypt - Map of famous sites. Explore Ancient Egypt on an Interactive Map.
There were over 2000 Ancient Egyptian gods and Goddesses. Many took part-human, part-animal or part-bird forms. The animal was chosen for its power. Worshipping gods and goddesses was considered important to ensure life was good. Some Ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses were worshipped in temples by pharaohs, priests and people of high status.
A British Museum site exploring Egyptian daily life, religion, pyramids and other buildings, and mummification. Ancient Egyptian. Learn about the gods they worshiped, the Pharaohs they followed and the tombs and statues they left behind. Find out about famous people like Tutankhamun, the elaborate preparations they made for an eternal life.
This is known as a polytheistic religion. Some of the most important Egyptian gods include: Ra - God of the Sun. Anubis - God of the Dead. Osiris - God of the Underworld. Horus - God of the Sky. Isis - Goddess of Good Fortune and Protector of the Dead. Nut and Geb - God and Goddess of the Sky and Earth.
Pupils will learn about the famous pharaohs that ruled the land, the gods and goddesses they worshipped and how to decode Egyptian hieroglyphics in our National Geographic Kids' Ancient Egyptians primary resource sheet. The teaching resource can be used in study group tasks for examining different aspects of ancient civilisations, as a ...
The ancient Egyptians worshipped many thousands of gods and deities who ruled over all aspects of their lives. Learn about the Egyptian gods in this year 3/4 Bitesize History guide.
Video summary. This video gives pupils an introduction to the role of religion and gods / goddesses in Ancient Egyptian society. It helps pupils to explore the process of mummification and how ...
Amun - God of Air. Amun was the ancient Egyptian god of air. Initially, Amun was a local god of fertility in the city of Thebes (an ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile). However, over the years, he steadily grew in popularity. During the Eighteenth Dynasty, Amun became linked with Ra (god of the sun) and the two were fused to create ...
Hand-picked resources to support primary-aged pupils discover more about Ancient Egypt. Learning about the ancient Egyptians is usually one of the most memorable and exciting topics for primary children. From investigation into the discovery and lives of Egyptian pharaohs to exploring ancient religious practices and traditions such as ...
Egyptian Interactive Activites. The Magic Book Lesson. Learn how to build a pyramid, embalm a mummy and scribe in ancient hieroglyphic writing. BBC Pyramid challenge. Journey back four and a half thousand years to Egypt's Old Kingdom, to the Pyramid Age. As the vizier, or head of state, you undertake the most important project of your career ...
Ancient Egyptian gods & goddesses Lesson. Subject: History. Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Lesson (complete) File previews. pdf, 18.21 MB. ppt, 56.5 MB. A full lesson for KS2 exploring Ancient Egyptian gods and goddesses. The resource includes a detailed lesson plan, Powerpoint and pupil resource sheets.
The resource includes information on: Tutankhamun, Ancient Egyptian temples, mummification, pyramids, hieroglyphics, Cleopatra, Rameses II, Anubis, Egyptian gods and goddesses and Ancient Egyptian workers, farmers and pharaohs. Activity: Ask children to choose one of the subheadings in the resource and use the information and their own research ...
These worksheets will present new content and text on the series of different theme and concepts related to the ancient Egyptian civilization. We will explore the nature of their royalty and governing systems. We will also begin to tackle the reasoning and purpose behind the pyramids and sphinx. Students will examine their writing systems and ...
This period, the New Kingdom, was the age of empire. The once-peaceful Egyptians, having learned new techniques of warfare, embarked on foreign conquest on a large scale. The empire reached its peak under Thutmose III, one of the first great generals in history. He reigned from 1479 to 1426 bc, in the 18th dynasty.
Around 3000 B. C. the pharaoh of the north conquered the south and Egypt became united. The pharaoh's name was King Narmer (sometimes called Menes) . He founded the first capital of Egypt where the two lands met. It was called Memphis. ( Thebes became the next capital of Egypt and then Amarna was made the capital during the reign of King ...
Cleopatra was the last pharaoh of Egypt and is probably the most famous female pharaoh. Cleopatra was pharaoh until her brother stole the throne from her. After she and the Roman Emporer Julius Caesar fell in love, she won back her throne with the help of Rome's army. After Caeser's death, she fell in love with Marc Antony, a Roman leader and ...
Teach your children all about 10 of the most important Ancient Egyptian gods with the help of this interactive reading comprehension activity. Once downloaded, you'll have two pages featuring information about the Ancient Egyptian gods for children, along with an image of how each god was depicted. Then, your children will be challenged with answering a series of reading comprehension ...
Egypt is a country in Africa. People have lived in that region for thousands and thousands of years. The Ancient Egyptians settled around the Nile River, and built pyramids that you can still see there today. The Ancient Egyptians knew a lot about maths, medicine and farming. They also made their own paper out of reeds called papyrus, and wrote ...
The River Nile was important in terms of growing crops, protection, and transport. 2. Ra was the god of the sun. 3. Cats were believed to be sacred to the ancient Egyptians. 4. The pharaoh's hair would always be covered up. 5. The Egyptians believed that the afterlife was a paradise called the Field of Reeds.
By examining the objects (artifacts) and paintings in the tombs, we have been able to understand a lot more about life in Ancient Egypt. We can learn about how the Egyptians lived by looking at the objects stored in pyramids ready to be used in the afterlife. We can learn about how the Egyptians lived by looking at the walls of pyramids.