- français
- español
- português

Related Links
Drug utilization studies: methods and uses.

View Statistics
Description, document number, collections.
- Publications
Show Statistical Information
- 5. Regional Office for Europe
Advertisement
Assessment of antibacterial drug utilization patterns and antibiogram in infectious diseases: a prospective cross-sectional study
- Published: 14 August 2023
- Volume 397 , pages 1053–1059, ( 2024 )
Cite this article

- Solanki Nilay ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1845-4740 1 ,
- Patel Shreya 1 &
- Siddhpura Vivek 2
178 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Antibacterial drugs are successful in combating most types of infections. Irrational use and higher consumption of these drugs can give rise to the antibiotic resistance globally.
To evaluate antibacterial drug prescribing patterns and antibiogram in infectious disease cases admitted to the hospital.
A cross-sectional, observational study was conducted from September 2019 to February 2020 among inpatients ward at the hospital after ethical approval. All the data was analysed by the mean and percentage values using Microsoft excel.
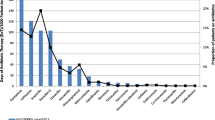
Out of 250 admitted patients, males and females were 156 (62%) and 94 (38%) respectively. The majority of patients 79 (32%) belonged to the age group of 20–40 years. The majority of prescriptions reported were for viral fever 48 (19%), lower respiratory tract infections 40 (16%) and dengue 33 (13%). Antibacterial drugs administered through the intravenous route and the oral route were 301 (83%) and 63 (17%) respectively. The most frequently utilized antibacterial drugs were beta-lactam class ceftriaxone 149 (60%) and the fixed-dose combination, amoxicillin plus clavulanic acid 65 (26%). Further highly prescribed antibacterial drugs were metronidazole 52 (21%), azithromycin 36 (15%), and levofloxacin 24 (10%). In Gram-negative bacteria, Escherichia coli 6 (30%) contributed majorly, while in Gram-positive coagulase-negative, Staphylococci 6 (30%) contributed the highest growth of bacteria for the specific infections in the admitted cases.
Ceftriaxone and the amoxicillin-clavulanic acid combination were highly prescribed among all antibacterial drugs, followed by metronidazole and azithromycin. The current study showed that in the antibiogram pattern, Escherichia coli and coagulase-negative Staphylococci contributed significantly as causative organisms for infectious disease cases. The present study highlighted demographic distribution, infectious diseases with their antibacterial drug utilization patterns and antibiogram assessment in the admitted patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Assessing the Prescription Pattern of Antimicrobial Agents in Intensive Care Unit at Tertiary Care Hospital
Pattern of inappropriate antibiotic use among hospitalized patients in pakistan: a longitudinal surveillance and implications.
Antibiotic use on paediatric inpatients in a teaching hospital in the Gambia, a retrospective study
Data availability.
All the data with respect to study presented in the manuscript only.
Ali AK, Hartzema AG (2018) Post-authorization Safety studies of medicinal products: The PASS Book. 107–163. Academic Press
Al Shimemeri A, Al Ghadeer H, Memish Z (2011) Antibiotic utilization pattern in a general medical ward of a tertiary medical center in Saudi Arabia. Avicenna J Med 1(1):8
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Amaha ND, Berhe YH, Kaushik A (2018) Assessment of inpatient antibiotic use in Halibet National Referral Hospital using WHO indicators: a retrospective study. BMC Res Notes 11(1):1–5
Article Google Scholar
Charles MP, Kali A, Easow JM, Joseph NM, Ravishankar M, Srinivasan S, Kumar S, Umadevi S (2014) Ventilator-associated pneumonia. Australas Med J 7(8):334–344. https://doi.org/10.4066/AMJ.2014.2105
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Delgado-Valverde M, Conejo MD, Serrano L, Fernández-Cuenca F, Pascual A (2020) Activity of cefiderocol against high-risk clones of multidrug-resistant Enterobacterales, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Antimicrob Chemother 75(7):1840–1849
Demoz GT, Kasahun GG, Hagazy K, Woldu G, Wahdey S, Tadesse DB et al (2020) Prescribing pattern of antibiotics using who prescribing indicators among inpatients in Ethiopia: a need for antibiotic stewardship program. Infect Drug Resist 13:2783–2794
Fridkin S, Baggs J, Fagan R, Magill S, Pollack LA, Malpiedi P, Slayton R, Khader K, Rubin MA, Jones M, Samore MH (2014) Vital signs: improving antibiotic use among hospitalized patients. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 63(9):194
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Friedman ND, Temkin E, Carmeli Y (2016) The negative impact of antibiotic resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect 22(5):416–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2015.12.002
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Gajic I, Kabic J, Kekic D, Jovicevic M, Milenkovic M, MiticCulafic D, Trudic A, Ranin L, Opavski N (2022) Antimicrobial susceptibility testing: a comprehensive review of currently used methods. Antibiotics (basel) 11(4):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11040427
International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision. The global standard for diagnostic health information. https://icd.who.int/en (referred on 1st July, 2023)
Joshi S (2010) Hospital antibiogram: a necessity. Indian J Med Microbiol 28(4):277–280. https://doi.org/10.4103/0255-0857.71802
Luyt CE, Bréchot N, Trouillet JL, Chastre J (2014) Antibiotic stewardship in the intensive care unit. Crit Care 18(5):1–12
Meena VK, Atray M, Agrawal A (2016) Evaluation of drug utilization pattern in indoor patients of medicine department at tertiary care teaching hospital in Southern Rajasthan. Int J Pharm Sci Res 7(9):3835
Google Scholar
Meher BR, Mukharjee D, Shankar U (2014) A study on antibiotic utilization pattern in a general medicine ward of a tertiary care teaching hospital. J Chem Pharm Res. 6:1847–9
Moehring RW, Hazen KC, Hawkins MR, Drew RH, Sexton DJ, Anderson DJ (2015) Challenges in preparation of cumulative antibiogram reports for community hospitals. J Clin Microbiol 53(9):2977–2982. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01077-15
Nagvekar V, Sawant S, Amey S (2020) Prevalence of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria cases at admission in a multispeciality hospital. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 22:457–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgar.2020.02.030
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Parthasarathi G, Nyfort Hansen K, Nahan MC (2012) A text book of clinical pharmacy practice: essential concepts and skills. Orient Blackswan edition
Pottegård A, Broe A, Aabenhus R, Bjerrum L, Hallas J, Damkier P (2015) Use of antibiotics in children: a Danish nationwide drug utilization study. Pediatr Infect Dis J 34(2):e16-22. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000000519
Rangdal K, Kanaki A, Patil K (2019) Drug utilization study of antibiotics in infectious diseases in a tertiary care hospital. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol 8(3):469
Sawant PM, Padwal LS, Kale SA, Pise NH, Shinde MR (2017) Study of drug prescription pattern among COPD patients admitted to medicine in-patient department of tertiary care hospital. IJBCP 6(9):2228–32. https://doi.org/10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20173750
Seifert R, Schirmer B (2021) Problems associated with the use of the term “antibiotics.” Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 394(11):2153–2166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02144-9
Sharma S (2018) Tools for assessing and monitoring medicine use. In Pharmaceutical Medicine and Translational Clinical Research, 445–463. Academic Press
Singha J, Chowdhury D, Hazarika H, Krishnatreyya H (2020) Pharmacy practice & drug research https://doi.org/10.21276/ijppdr.2018.8.1.7
Solanki ND, Patel P (2017) Drug utilization pattern and pharmacoeconomic analysis of antihypertensive drugs prescribed in secondary care hospital in Gujarat India. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 10(3):120–4. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2017.v10i3.15537
Article CAS Google Scholar
Solanki N, Patel Y (2019) Drug utilization pattern and drug interaction study of antibiotics prescribed to orthopedic patients in private hospital. Arch Pharm Pract 10(4):114–117
Solanki N, Patel V, Patel R (2019) Prescribing trends in cardiovascular conditions: a prospective cross-sectional study. J Basic Clin Pharma 10:23–26
Solanki N, Pandit D, Desai S (2021) Effectiveness and safety assessment of beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers in hypertensive patients: a prospective study. Am J Cardiovasc Dis 11(5):601
PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Solanki N, Champaneri I, Patel V (2023) Assessing drug utilization and drug–drug interactions in the management of epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease and migraine. J Pharm Health Serv Res rmad034. https://doi.org/10.1093/jphsr/rmad034
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Ramanbhai Patel College of Pharmacy, Charotar University of Science and Technology and CHARUSAT Hospital, Changa, Gujarat, for providing the necessary facilities and support during the course of the study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pharmacology, Ramanbhai Patel College of Pharmacy, Charotar University of Science and Technology, CHARUSAT Campus, Changa, 388421, Gujarat, India
Solanki Nilay & Patel Shreya
CHARUSAT Hospital, CHARUSAT Health Care Campus, Changa, 388421, Gujarat, India
Siddhpura Vivek
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Solanki Nilay .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
The Institutional Ethics Committee for Human Research of the University ethically approved this study with reference number RPCP/IECHR/2/2019-20/PG/R-02, and permission was obtained from participants for the study and publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Nilay, S., Shreya, P. & Vivek, S. Assessment of antibacterial drug utilization patterns and antibiogram in infectious diseases: a prospective cross-sectional study. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397 , 1053–1059 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02659-3
Download citation
Received : 08 July 2023
Accepted : 01 August 2023
Published : 14 August 2023
Issue Date : February 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02659-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bacterial infection
- Viral fever
- Lower respiratory tract infection
- Beta lactam
- Ceftriaxone
- Antibiogram
- Escherichia coli
- Staphylococci
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Evaluation of drug utilization in cardiovascular disease at a teaching and referral hospital in Northern Telangana
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kakatiya University, Warangal, Telangana, India.
- 2 Department of General Medicine, Kakatiya Medical College, Mahatma Gandhi Memorial Hospital, Warangal, Telangana, India.
- 3 National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Mohali, Punjab, India.
- PMID: 31831921
- PMCID: PMC6892011
- DOI: 10.4103/ijp.IJP_743_17
Objectives: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the primary cause of death globally despite the advanced health-care facilities. Extensive disparity exists in pharmacotherapy pattern among CVD patients where rational drug use plays a pivotal role in promoting safety and efficacy. The study focused to evaluate drug utilization using the World Health Organization (WHO) prescribing indicators and defined daily dose (DDD) in patients admitted to a teaching/referral hospital in Northern Telangana.
Materials and methods: A total of 1120 medical records were analyzed for drug utilization for a period of 7 months. Prescription pattern was assessed using the WHO prescribing indicators and DDD to measure individual drug utilization categorized under anatomical-therapeutic-chemical classification.
Results: Of the total admissions, 58.57% (55.19 ± 15.19 years) were male and 41.43% (56.64 ± 15.28 years) were female where coronary artery disease was the most common cause of admission followed by cardiomyopathy. Among prescribing indicators, percentage of drugs with generic names was least accounted with 26.86% and 18.95% during hospitalization and discharge, respectively. A mean of 11.55 (hospitalization) and 6.55 (discharge) drugs were prescribed per prescription. Antiplatelet (72.86%) and statin (80.62%) use was predominate during complete therapy. The DDD of furosemide (109.33) was found to be high, followed by atorvastatin (64.6), enalapril (58.44), aspirin (58.14) and clopidogrel (53.2).
Conclusion: Polypharmacy and least use of generic name were observed in the study which may affect the rationality. The use of antiplatelets, statins, and angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitors was appropriate, but furosemide overuse is of major concern. Therefore, appropriate prescription writing improvises treatment compliance in the patients, which results in rationality.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; defined daily dose; prescribing indicators; rational drug use.
Copyright: © 2019 Indian Journal of Pharmacology.
Publication types
- Observational Study
- Cardiovascular Agents / therapeutic use*
- Cardiovascular Diseases / drug therapy*
- Cardiovascular Diseases / physiopathology
- Drugs, Generic / therapeutic use*
- Hospitals, Teaching
- Middle Aged
- Polypharmacy*
- Practice Patterns, Physicians' / statistics & numerical data*
- Prospective Studies
- Cardiovascular Agents
- Drugs, Generic
Maintenance work is planned for Wednesday 1st May 2024 from 9:00am to 11:00am (BST).
During this time, the performance of our website may be affected - searches may run slowly and some pages may be temporarily unavailable. If this happens, please try refreshing your web browser or try waiting two to three minutes before trying again.
We apologise for any inconvenience this might cause and thank you for your patience.

RSC Advances
Advancements in application of chitosan and cyclodextrins in biomedicine and pharmaceutics: recent progress and future trends.

* Corresponding authors
a Nutrition Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
b Pharmaceutical Analysis Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran E-mail: [email protected]
c Food and Drug Safety Research Center, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran
d Department of Nanotechnology, Faculty of Chemistry, Urmia University, Urmia, Iran
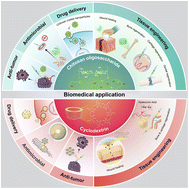
The global community is faced with numerous health concerns such as cancer, cardiovascular and neurological diseases, diabetes, joint pain, osteoporosis, among others. With the advancement of research in the fields of materials chemistry and medicine, pharmaceutical technology and biomedical analysis have entered a new stage of development. The utilization of natural oligosaccharides and polysaccharides in pharmaceutical/biomedical studies has gained significant attention. Over the past decade, several studies have shown that chitosan and cyclodextrin have promising biomedical implications in background analysis, ongoing development, and critical applications in biomedical and pharmaceutical research fields. This review introduces different types of saccharides/natural biopolymers such as chitosan and cyclodextrin and discusses their wide-ranging applications in the biomedical/pharmaceutical research area. Recent research advances in pharmaceutics and drug delivery based on cyclodextrin, and their response to smart stimuli, as well as the biological functions of cyclodextrin and chitosan, such as the immunomodulatory effects, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties, have also been discussed, along with their applications in tissue engineering, wound dressing, and drug delivery systems. Finally, the innovative applications of chitosan and cyclodextrin in the pharmaceutical/biomedicine were reviewed, and current challenges, research/technological gaps, and future development opportunities were surveyed.
Article information
Download Citation
Permissions.
F. Bahavarnia, M. Hasanzadeh, P. Bahavarnia and N. Shadjou, RSC Adv. , 2024, 14 , 13384 DOI: 10.1039/D4RA01370K
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence . You can use material from this article in other publications, without requesting further permission from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given and it is not used for commercial purposes.
To request permission to reproduce material from this article in a commercial publication , please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party commercial publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author, advertisements.
- Washington State University
- Go to wsu twitter
- Go to wsu facebook
- Go to wsu linkedin
Voiland College names 2024 outstanding students

Washington State University Voiland College of Engineering and Architecture recognized outstanding students at its annual convocation ceremony on April 11. The event was sponsored by the Boeing Company. Honored award winners included:
- Outstanding Sophomore: Rylee Gannon A chemical engineering major with a 3.8 GPA, Rylee Gannon is a research assistant for Professor Steve Saunders, where she synthesizes and characterizes nanomaterials for use as catalysts in oxidation reactions Gannon also works in the Frank Innovation Zone and is an active member of the Society of Women Engineers.
- Outstanding Junior: Ethan Villalovoz Ethan Villalovoz is a computer science student with a GPA of 3.99, specializing in data mining, machine learning, and data science. Some of his more notable achievements include being a CS Research Mentorship Program Scholar, a Generation Google Scholarship Recipient, and a Hispanic Scholarship Fund Scholar. He has also engaged in extensive extracurricular activities, including internships at Google and a research position at Carnegie Mellon University.
- Outstanding Senior: Katy Ayers A Fulbright Fellowship Award and Marshall Scholarship Semifinalist, Katy Ayers is the first WSU student to win the Udall Scholar in Environment award. Her thirst for knowledge has given her robust research experience around the country and the world. One of Ayers’ nominators said, “Although I have worked with many outstanding students in my 20 years of teaching at the undergraduate level, I don’t think I have met anyone with Katy’s experiences, accomplishments and passion. She is motivated, demonstrates curiosity and critical thinking and communicates incredibly well.”
- Outstanding Teaching Assistant for grading/office hours: Kutay Sesli Kutay Sesli’s nominators were impressed by his innovative approaches and genuine care for students this past year. Kutay recognized that that conventional ways to grade assignments might not provide a full picture of where students need improvement, so he took the initiative to develop an innovative, consistent, fair, and detailed grading system that helped students develop trust in the grading process and a better understanding of how to improve their performance throughout the semester. He approaches each task with the mindset of a true engineer, and the results left no doubt that his grading was done with meticulous attention to detail and with the best outcomes for students in mind. Among the feedback students have given include: “Kutay is the best TA all semester, excellent job!” and “Kutay is dope!”
- Outstanding Teaching Assistant — Teaching/Instruction: Chris Pereyda Chris Pereyda has served as teaching assistant in several courses, including Introduction to Computer Programming. In one of his courses there were more than 500 students. One of those students said of Chris: “He is one of the best TAs I have ever had the pleasure of learning from. Being a Computer Science student can be difficult, but his explanations and knowledge of the source material helped me grasp some of the concepts better and persevere.” One of his faculty members said, “Chris was one of my most reliable, impactful, and effective TAs during my twenty years of teaching at WSU. Chris is the ideal example of a lead teaching assistant. He is knowledgeable in the area, patient with TAs and students, flexible and adaptive to different TAs’ and students’ styles and paces. There is not a better example of a TA than Chris.
- Outstanding Research Assistant: Ali Mahmoodigahrouei As a PhD candidate at WSU, Ali Mahmoodigahrouei has shown an exceptional academic record and research skills. Since joining WSU in 2022, he has published 14 impactful papers with over 300 citations, earning several prestigious awards, including the David C. Goss Scholarship and the “UTC Outstanding Student of the Year Award.” His nominators feel he consistently goes above and beyond expectations, managing multiple projects simultaneously and with great success. He also excels as a mentor, effectively supervising undergraduate students while providing valuable assistance to other PhD students in his research group.
- Outstanding Dissertation: Lin Shao Lin Shao’s nominators say that he is a truly exceptional graduate student and has done excellent research on chemical recycling of plastic waste by aminolysis and utilization of the recycled compounds for preparation of new polymer materials. His thesis research has received a broad interest from researchers around the world. Shao, as one of guest speakers, was invited to give a seminar at the Royal Society of Chemistry and Chemistry World. His research was also featured by “The Voice of America.”

Exhibit explores queer experience on the Palouse
Recent news.

Phyllis J. Campbell endows deanship at WSU’s Carson College of Business


Spanish, bilingual course from WSU Extension creates climate ambassadors

VR can motivate people to donate to refugee crises regardless of politics
Todd butler resigns as college of arts and sciences dean.

Tri-state team releases calendar guide for more productive, sustainable pastures

WSU to study effect of controversial drug on racehorses
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Clin Diagn Res
- v.10(2); 2016 Feb
Study of Drug Utilization Pattern for Skin Diseases in Dermatology OPD of an Indian Tertiary Care Hospital - A Prescription Survey
Anuj kumar pathak.
1 Senior Resident, Department of Pharmacology, IGIMS, Sheikhpura, Patna, Bihar, India.
Subodh Kumar
2 Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology SRMSIMS, Bareilly, UP, India.
Manish Kumar
3 Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology, IGIMS, Sheikhpura, Patna, Bihar, India.
Lalit Mohan
4 Associate Professor, Department of Pharmacology, IGIMS, Sheikhpura, Patna, Bihar, India.
Harihar Dikshit
5 Professor, Department of Pharmacology, IGIMS, Sheikhpura, Patna, Bihar, India.
Introduction
Skin diseases are the major contributors of disease burden in society. It affects individuals of all ages, neonates to elderly. Owing to its chronic nature, it causes serious impact on quality of life and financial status of the sufferer and his family. The problem gets compounded with the inappropriate and irrational use of medicines. Periodic prescription audit in form of drug utilization study is a way to improve the quality of prescription and curb the menace of irrational prescribing which has become a global phenomenon.
This study aims to determine the drug utilization pattern and assess the economic burden of the patient with skin disease.
Materials and Methods
It was a prospective, cross-sectional study conducted over a period of three months from January to March 2015 in newly diagnosed cases attending outpatient department of Skin and VD, IGIMS, Patna. The prescriptions were analysed with the help of descriptive statistics and results were expressed in percentage.
Total 752 prescriptions were analysed during the study. Male patients were lesser as compared to female as male to female ratio was 0.88. Over 50% of patients were in adolescent age group i.e. 21-40 years. Acne (17.95%) was most common disease in the study population followed by eczema and Dermatophytosis. Among the drugs, antihistaminics (24.13%) were prescribed most frequently followed by antifungals and antibiotics. Topical agents constituted almost 60% of the total prescription and average number of drugs per prescription was 5.13, irrespective of the dosage forms prescribed.
This drug utilization study provides an insight to the prescriber regarding various issues related to polypharmacy, cost analysis and prevalent disease pattern in the region. This study also suggests periodic evaluation of prescription pattern to monitor and improve quality of prescription in other departments of the hospital.
Skin is the part of integumentary system that constitutes the largest organ of human body and thus it is exposed to injury by various extrinsic factors such as environmental, chemical, infectious agents as well as intrinsic factors such as metabolic, genetic and immunological. In addition to this, many systemic diseases are also identified by their dermatological manifestations thus it is said metaphorically as a mirror to various internal diseases [ 1 , 2 ].
Skin diseases are common and cause a huge disease burden globally. Collectively skin is the 18 th leading cause of health burden worldwide and it was 4 th leading cause of nonfatal health burden in 2010 globally [ 3 ]. The skin disorders constitute 2% of total Out Patient Department (OPD) consultations worldwide [ 4 ]. However no such data is available from India but still skin disorders in India are common and include pyoderma, acne, urticaria, dermatitis, scabies fungal skin infections and alopecia etc [ 5 ].
The skin disorders have serious detrimental effect on quality of life of the general population by increasing the suffering in terms of physical, social, psychological as well as it increases financial burden as most of the skin diseases are chronic and requires longer duration of treatment [ 6 ].
In India, there are various problems in prescription pattern of drugs like irrational drug combinations, overuse of multivitamins, unnecessary use of antibacterial in fungal conditions and prescribing drugs from same class [ 7 , 8 ]. It contributes to the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. Dermatologists account for almost 5% of antibiotic prescriptions worldwide and most of the conditions require prolonged treatment [ 9 , 10 ]. Further, the skin conditions are wrongly diagnosed and treated. Thus continuous monitoring is needed to evaluate pattern of drug use to detect any changes from contemporary practices or available guidelines. Hence in order to generate data, drug utilization studies are need of the hour.
As per WHO, Drug utilization studies or research are tools that deals with the marketing, distribution and prescription pattern of drugs and helps to assess the subsequent impact of these on medical and socioeconomic status of patients [ 11 ]. Thus drug utilization studies helps in the understanding of prescription pattern as well as the quality of prescription in terms of rationality, drug interactions and financial burden of disease to the individual. These studies have a favourable impact on improving the standards of treatment and identify the problems related to polypharmacy, drug-drug interaction and adverse drug reactions. Periodic auditing of prescriptions in form of drug utilization studies are important tool to enhance the therapeutic efficacy, to minimize the adverse effect, to optimize the cost of the treatment and to provide useful feedback to the clinician [ 12 , 13 ]. Previous studies conducted in Australia suggest that academic detailing improves the quality of prescription and increases the adherence of clinician to standard treatment guidelines [ 14 ]. The data regarding pattern of drug used in India, particularly in dermatology departments are very limited.
Considering these facts the present study was done to assess the drug use pattern for common skin condition and to analyse the cost of individual prescription in outpatient department of Skin and VD at IGIMS, Patna, Bihar, India.
To study the drug utilization pattern in dermatology outpatient department and cost analysis of the prescriptions obtained.
The permission to conduct the study was taken from Institutional ethics sub-committee prior to the study. The present study was conducted in Department of Skin and VD in IGIMS Patna. It was a prospective cross-sectional study conducted over a period of three months. A Performa was designed on which the data were compiled and later on analysed through extensive data mining. Prescriptions were collected on three alternate days in a week for a period of three months from January to March 2015. Total 752 prescriptions were collected during the study period, satisfying the WHO criteria for sample size which suggests to include at least 600 encounters in a cross-sectional survey to describe the current prescribing practices, with a greater number, if possible [ 15 ]. The inclusion criteria for the study included only OPD patients, first time visitors and newly diagnosed patients. For this prescriptions were collected from outpatient departments and also the help of hospital medical record department (MRD) section were taken to collect the data in days when prescriptions could not be collected from OPD due to some unavoidable reasons.
After extensive data mining, various relevant data were derived from the collected prescriptions that included demographic profiles, diagnosis or pattern of skin disease, classes of drug prescribed with their frequency and dosage form. Also, average number of drug prescribed per prescription and cost analysis of prescriptions were done. To calculate the number of drugs per prescription all the drugs in prescription were taken into consideration and divided by total number of prescriptions (n=752). In case of fixed dose combinations (FDC) all the component of FDC were taken separately to calculate the number of drugs.
[ Table/Fig-1 ] illustrates the contribution of skin and VD OPD in total new patients of hospital during the study period of three months from January to March 2015. Total 34672 new patients attended the outpatient department in IGIMS Patna amongst which 1057 (3.04%) patients attended the skin and VD OPD. Of these prescriptions 752(n) prescriptions were found to satisfy the inclusion criteria for the study and were included for analysis.
[Table/Fig-1]:
Hospital OPD Data.
Demographic data
[ Table/Fig-2 ] shows that in this study number of male patients was 354 (47.07%) while number of female patients was 398 (52.93%) thus female patients outnumbered the males in this regard and male to female ratio was 0.88.
[Table/Fig-2]:
Total prescriptions collected = 752(n).
[ Table/Fig-3 ] represents the age distribution of the study population where more than 50% of the patient were in the age group of 21 to 40 years and of them highest no. of patient were in the age group of 31-40 years (26.99%), followed by 21-30 year age group (23.94%). No of patients at two extreme of ages were very less i.e. above 61 years only 3.06% followed by 6.91% at 0-10 years. It was found that there was progressive increase in number of patients as the age of the patient increases, till 40 years and then there was a decrease in number of patient.
[Table/Fig-3]:
Age distribution.
Data on disease distribution
As in [ Table/Fig-4 ], acne with (17.95%) was most common dermatological disorder closely followed by eczema (16.62%) and dermatophytosis (14.89%). Very small percentage of patients had scabies (7.57%) especially in paediatric age group. Alopecia (4.12%) and psoriasis (3.06%) were other disease but these were relatively uncommon. Pigmentation disorders including both hyper and hypo-pigmentation were 3.47%.

Disease distribution (%).
Data related to drug use
As shown in [ Table/Fig-5 ], antihistaminics were the most common drugs prescribed (24.13%). Among antihistaminic second generation antihistaminics levocetrizine (41.22%) and cetrizine (19.17%) and fexofenadine (17.85%) were common while highly sedative hydroxyzine (11.77%) was used less commonly.

Drugs used (%).
Antifungal (21.02%) was the second most common prescribed drug class. Among oral antifungals, fluconazole (53.12%), itracnazole (21.73%) were used and among topical agents clotrimazole, ketoconazole were used in form of powder, shampoo and soaps. Terbinafine (15.2%) was also used in both oral as well as in cream form for dermatophytosis treatment.
Antibiotic (15.91%) were used in both oral (39.27%) as well as topical (60.73%) route. Among oral antibiotics, azithromycin, amoxicillin-clavulinic acid and cefadroxil was used and among topical antibiotics, clindamycin for acne treatment was very common, other than this mupirocin and fusidic acid and other fixed dose combinations of two or more antibiotics or along with steroids were used very frequently.
Topical steroids and their combinations were prescribed more frequently than oral or parenteral forms of steroids. This may be attributed to various systemic side effects of oral or parenteral steroid.
Ranitidine and pantoprazole were the two antacids prescribed frequently. Among antiparasites permethrin, ivermectin for scabies and albendazole and mebendazole as anthelmintics were prescribed in very few cases. Other drugs used in the treatment of skin diseases were some anti- herpes drugs, some antimetabolites like methotrexate, keratolytic, emollients and antileprotic agents etc. As the number of new cases with these diseases were very less so we grouped all these drugs as other drugs and these constituted 5.91% of the prescriptions.
Dosage forms of the drugs
[ Table/Fig-6 ] represents the drugs used in various dosage forms and route of administration for treatment of skin disease. It included oral form i.e. tablets (47.11%), parenteral i.e. intections (0.96%) and various topical (51.93%) route of administration. Use of parenteral forms were very much limited and usually given for severe forms of infections resistant to oral antibiotics, intralesional corticosteroids, and systemic fungal infections. Various anti-bacterial and antifungal agents were prescribed in topical dosage forms as clotrimazole powder, ketoconazole shampoo, mupirocin ointment, fusidic acid ointment lotions gel, cream. Also, various corticosteroid and their combinations in ointment and gel forms were also available and prescribed. Tablet was prescribed most commonly (35.04%) that included various antihisaminics, antifungal and antacids preparations. Some antacids, antibacterial and multivitamins were prescribed in capsule form (4.07%) also. In topical agents, ointment was the most common dosage form prescribed (21.00%) with different compositions of steroid and their combinations, some antifungal and antibacterial drugs. This was followed by lotion (13.01%), as zinc calamine lotion for soothing, astringent, antipruritic effect and gel preparations (10.94%) as for antiacne and antibacterial preparations. Powder forms were prescribed for external use in (5.21%) of cases and it was mostly antifungal preparation and dusting powder and boric acid. Other dosage forms included shampoo for seborrheic dermatitis, antihistaminic and antibiotic syrups to children and some liquid antacids preparation to adults, etc.

Dosage forms (%).
Number of drugs per prescription
Total number of drugs prescribed in 752 prescriptions were 3858. Thus average number of drugs per prescription in this study comes to 5.13. However, it had a large variation depending on type of disease and its severity. Most of the prescription had 4 to 5 drugs while very few prescriptions with disease of lesser severity were treated with only one or two drugs. Some other patients with very extensive lesions required 6 or more drugs of different classes including systemic as well as topical agents.
Cost per prescription
Average total cost per prescription was found to be INR 487.50 with minimum prescription cost of INR 57 and maximum prescription cost of INR 1783 for 7 days treatment. In majority of the prescriptions, the cost of one week treatment was within the range of INR 200-300. However, small number of prescriptions reported very high cost per prescription that was attributed to some high cost drugs such as immunomodulators (tacrolimus), antifungals (itraconazole). This shifted the average cost per prescription to higher values. Polypharmacy also factored in inflating the average cost per prescription.
Prescription is a written instruction given by a qualified medical practitioner with the intent to provide medicine or treatment for the benefit of the patient. Thus the prescription in other words reflects the doctors knowledge and his attitude to treat the patient with due consideration of the patient’s condition physically as well as financially [ 16 ]. Availability and affordability are the two major determinants of a prescription and various other very important parameters are quality, rationality, completeness and cost per prescription. And one study that incorporates all these components is the drug utilization study. Till now very few drug utilization studies have been conducted in our institute and thus we did not have any comparable data of other studies from our institute. Thus ultimate aim of the study was to help the dermatology prescriber in achieving rational and affordable treatment to their patients in terms of cost. This will also help in the mission of providing “Health care to all” [ 17 ].
Patient related data
In our study the total no of new patients attending skin OPD was 3.04% of the total OPD attendance. These included new as well as follow up patients. Of the 752 prescription collected, no. of females were more than the no. of male that was in line with the study of Manjusha Sajith et al., and differs slightly from the study of Bijoy KP et al., [ 18 , 19 ]. In this study, more than 50% of the patients were adult in the age group 21-40 years, this was higher than the study conducted by Bijoy KP et al., and Sarkar et al., [ 19 , 20 ].
Disease distribution
Our study findings suggested that acne was most common disease of skin at our institute in the study duration. This was more common in females, involving face and in some cases on chest and back, mostly these were mild and non scarring. In this study the age group most commonly affected by acne was adolescents group this may be due to androgen induced increased sebum production, formation of comedone by excessive keratin deposition, follicle colonization by Propionibacterium acnes bacteria leading to inflammation and release of pro-inflammatory mediators in the skin [ 21 ]. In a study by Sarkar et al., cutaneous infections (40%) were the most common dermatologic condition followed by eczema (31%) [ 20 ]. In our study eczema with a myriad aetiologies was next in order. Atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, seborrhoeic dermatitis was three common types encountered. The common fungal infections were dermatophytosis e.g. tinea cruris (ring worm), tinea capitis, tinea corporis and candidiasis. This may be due to sweating, high humidity and poor personal hygiene. Other disorders like psoriasis, leprosy and pigmentary disorders were very less in number.
Number of drug per prescription
Average number of drugs per prescription in our study was 5.13, which was very high as compared to studies by Sarkar C et al., and Narwane SP et al., where average number of drugs prescribed were lesser than 3 drugs per prescription i.e., 2.42 and 2.7/prescription respectively [ 20 , 22 ]. Polypharmacy promotes undesirable drug interactions and irrational drug prescribing. Unnecessary prescription of drugs increases the incidence of side effects and increases the economic burden to patients. So this was the issue of concern in our institute and we need to improve this.
Pattern of drug use
Our study finding showed antihistaminics as the most commonly prescribed drug class followed by antifungals and antibiotics which was similar to the study carried out by Narwane SP et al., showing antiallergics as the most commonly prescribed drug followed by antifungal and antibiotic [ 22 ]. This is expected as pruritus is one of the major complaints associated with majority of skin diseases and it is very troublesome and socially annoying to patient [ 23 ]. Antihistaminics are the mainstay for treatment of pruritus, and it is also prescribed other allergic conditions. Among these, second generation antihistaminics, that are nonsedative bears the major part of all the prescriptions. Levocetrizine, cetrizine, fexofenadine and loratidine are the main drugs in this group. These were prescribed mainly at the day time and patients were advised to avoid driving after taking medicines [ 24 ]. Highly sedative antihistaminics like hydroxyzine was prescribed for severe cases of urticaria, intractable pruritus, eczema etc and patients were usually prescribed to take them at bedtime. Antifungal drugs were the second most widely prescribed class in our study which was less prescribed as compared to the study conducted by Yuwante AH et al., in which it was 33.5% of the total drug used [ 25 ]. In our study topical antifungal e.g. clotrimazole, ketoconazole, terbinafine etc. were prescribed more frequently (82.12%) than the oral antifungals like fluconazole and itraconazole. Further fluconazole was most common in oral antifungal group this may be due to its cost effectiveness and once in a week dosing. Antibiotics including antisceptics constitute (16%) of prescription which was almost equal to the study conducted by Yuwante AH et al., [ 25 ]. Steroids and their various FDC contributed (13.05%) of total prescriptions. Here also topical agents were prescribed in maximum number of patients. This may be due to various side effects associated with systemic steroid therapy as well as its site specific action, less systemic absorption resulting in less side effects and convenient for patient use. This finding was comparable with studies by Sarkar C et al., and Khan NA et al., that showed steroid and antibiotics were most commonly prescribed topically [ 20 , 26 ]. Topical corticosteroids are mainly used for non-infective dermatologic disorders such as atopic dermatitis and contact dermatitis, lichen planus, psoriasis etc., Ranitidine and pantoprazole among antacids was prescribed in good number of cases. Here pantoprazole had upper hand due to its one time dosing and better patient compliance. Beyond this a large number of drugs e.g. multivitamins, retinoids, immunosuppressants, paraciticides etc were also prescribed in our study for the treatment of particular disease but individually these contributed to very small percentage of cases.
Frequency, duration of administration, dose/strength and diagnosis was specified in majority of prescriptions (95%) in our study which shows rational prescribing also majority of prescriptions were complete with respect to patient related data and doctors initial. All the OPD prescriptions card had the message and toll free number over their footnote for spontaneous reporting of adverse drug reactions and patient were educated by the prescriber regarding this facility.
Cost analysis of the prescription
In our study average cost per prescription was INR 487.50 this was high as compared to the study by Narwane et al., [ 22 ]. This high cost may be attributed to the polypharmacy, absence of generic drugs in prescription as well as high cost of the dermatological products. In a similar study where generic drugs were prescribed, cost was merely 19.40 INR [ 22 ]. As majority of patients in our hospital belongs to the poor socio-economic strata, the cost of treatment was major determinant for drug compliance [ 27 ]. This cost excluded the amount spent by patient on other expenditures such as cost of diagnosis, cost of travel loss of wages etc. So use of generic drugs should be promoted to improve the compliance and reduce the economic burden of the disease.
Irrational drug prescription is a global problem among the physicians and solution has to come from the physicians himself as well as locally in form of appropriate policies and guidelines in accordance with WHO guidelines. In light of the finding of this survey, following recommendation can be given to minimize the irrational prescribing and the risk associated with it. It includes-
- Formulation of policies related to appropriate use of medicines
- Making a hospital based formulary
- Continuous supervision, audit and monitoring of prescription and feedback
- Continuing education of involved health care provider
Drug utilization study is an effective tool to promote rational and cost-effective drug prescribing. Despite all the limitations such as small sample size, shorter study duration, and single study centre etc the study may prove to be an eye opener for the healthcare provider. This study suggests the prescribers to consider factors as polypharmacy, rationality of prescription and cost benefit analysis before writing any prescription. Hospital authority should also take concrete steps to ensure generic prescribing to reduce the cost of treatment and to sensitize the physicians regularly regarding the need of rational prescribing by conducting continuing medical education.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere thanks and gratitude to Dr. K C Jaykar, Assistant Professor, Department of SKIN & VD and 3rd semester undergraduate students of IGIMS Patna for their valuable support to carry out the study and collect data.
Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee
Financial or Other Competing Interests

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The present observational study was conducted to generate data on drug utilization in inpatients of our tertiary care hospital to identify potential targets for improving drug prescribing patterns. Data was collected retrospectively from randomly selected 231 medical records of patients admitted in various wards of the hospital. WHO Anatomical ...
drug use including prescribing, patient care, facility, complementary drug use indicators may also be used to calculate rationality and utilization trends of medicines (Henry, 2006; Mohanraj et al., 2015; WHO,2003). Therefore, current study was planned to investigate the prescribing trends and aptness of antibiotics utilization in
The drug utilization pattern analysis in the geriatric patients reveals deviation of the average number of drugs per prescription from the WHO standard recommendation. The most common comorbid condition among the geriatric patients was diabetes mellitus. Among the drugs prescribed, alimentary tract and metabolism class of drugs were the most ...
This book presents a survey of instruments and methods developed to investigate patterns of drug consumption and to answer fundamental questions about prescribing practices, therapeutic value and safety. By reviewing the state-of-the-art in research methodology, it also aims to show how drug utilization studies can contribute to national health ...
ISBN 978-1-118-94978-8. Hardcover, 536 pages. $191.95. Drug utilization research has evolved over the years to become a cross-disciplinary science that explores the medical, social, and economic consequences of drug utilization. The European Drug Utilization Research Group and the International Society for Pharmacoepidemiology's Special ...
Overview. The ultimate goal of drug utilization research must be to assess whether drug therapy is rational or not. History has taught us that successful research in drug utilization requires multidisciplinary collaboration between clinicians, clinical pharmacologists, pharmacists and epidemiologists. Without the support of the prescribers ...
health care databases (HCDs) 400. health care providers-reported data 30-31. Index 501. health care service delivery 200. health care system drug management. 222-223, 230. demand-side measures 223-225. policy case histories. enhanced generic utilization 227-229.
Conclusions—Comparing drug utilization patterns in a pediatric population using observational data, we found similar rates of retention and therapeutic changes. These findings are consistent Corresponding Author: Florence T Bourgeois MD, MPH, Division of Emergency Medicine, Boston Children's Hospital, 300
Drug utilization research can be defined as "an eclectic collection of descriptive and analytic methods for the quantification, understanding and evaluation of the processes of prescribing, dispensing, and consumption of medicines and for the testing of interventions to enhance the quality of these processes.".
Background Antibacterial drugs are successful in combating most types of infections. Irrational use and higher consumption of these drugs can give rise to the antibiotic resistance globally. Objective To evaluate antibacterial drug prescribing patterns and antibiogram in infectious disease cases admitted to the hospital. Methods A cross-sectional, observational study was conducted from ...
importance of drug utilization studies in pharmacoepidemiology has been increasing due to their close association to other areas like public health, pharmacovigilance, pharmacoeconomics and pharmacogenetics. In recent years studies on drug utilization have become a potential tool to be used in the evaluation of health systems. Studies on the process of drug utilization focus on factors related ...
with healthcare professionals and utilization of healthcare that may affect drug utilization. Study I was an observational cross-sectional study using data from the Swedish Prescribed Drug Register (SPDR) analyzing differences between men and women in drug utilization, overall and within different pharmacological groups in Sweden 2010.
The study focused to evaluate drug utilization using the World Health Organization (WHO) prescribing indicators and defined daily dose (DDD) in patients admitted to a teaching/referral hospital in Northern Telangana. Materials and methods: A total of 1120 medical records were analyzed for drug utilization for a period of 7 months. Prescription ...
are studies documenting an increase in Medicaid paid prescription drug utilization (Mulcahy et al. 2016; Ghosh et al. 2017), but relatively few studies examine the utilization of SUD treatment. Wen et al. (2017) employ the Medicaid State Drug Utilization Data to examine the changes in use of buprenorphine between
Drug utilization study of anti-diabetic drugs in a tertiary care hospital Dr. Naseem Begum, Dr. S Ramesh, Dr. B Prahlad and Dr. G Bhawani Abstract Background: Diabetes mellitus is a major non-communicable disease and a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. The anti-diabetic drugs used for its management constitute a significant portion
Drug utilization studies are often focused on examining one of the key stages in the medicines-use chain, such as (World Health Organization, 2003a):. the systems and structures regarding medicines use (e.g., how medicines are ordered, delivered, and administered in a hospital or health care facility).. the processes of medicines use (e.g., what medicines are used and the manner of use ...
Inappropriate use of drugs can lead to various problems such as cost burden, prolonged hospital stays, development of microbial resistance, adverse effects and mortality[1]. However variations in selection and use of drugs are routinely practiced. Drug utilization studies will be helpful to evaluate and analyse drug therapy from time to time.
Hence, this study was planned to evaluate drug utilization patterns and generate pharmacoeconomic data on immunosuppressant drugs in patients with skin disorders in a tertiary care hospital in eastern India. The objective was to determine and compare the drug utilization pattern, prescribed daily dose/defined daily dose (PDD/DDD) defined by the ...
utilization of drugs and to spot the factors that contribute to the pediatric. pneumonia patients at tertiary care teaching hospitals. Material and. methods: A prospective, observational study was ...
Objective: This study attempts to get an insight into the utilization pattern of anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) and their drug interactions in cases collected from the neurology department in a ...
Drug Utilization Studies (DUS) are essential for determining the level of drug use, spotting variations between or within regions, and creating interventions to promote sensible drug use[1]. DUS are therefore seen as an important instrument for assessing the health-care systemright now [2]. DUS are more crucially needed in nations like ours ...
Drug utilization study is important in clinical practice because it serves as the foundation for implementing changes to drug dispensing policies at the local and national levels. Also, since it helps in developing strategies to utilize health resources most efficiently, it is particularly needed in a developing economy like India where 72% of ...
Recent research advances in pharmaceutics and drug delivery based on cyclodextrin, and their response to smart stimuli, as well as the biological functions of cyclodextrin and chitosan, such as the immunomodulatory effects, antioxidant, and antibacterial properties, have also been discussed, along with their applications in tissue engineering ...
Lin Shao's nominators say that he is a truly exceptional graduate student and has done excellent research on chemical recycling of plastic waste by aminolysis and utilization of the recycled compounds for preparation of new polymer materials. His thesis research has received a broad interest from researchers around the world.
Drug utilization study is an effective tool to promote rational and cost-effective drug prescribing. Despite all the limitations such as small sample size, shorter study duration, and single study centre etc the study may prove to be an eye opener for the healthcare provider. This study suggests the prescribers to consider factors as ...