- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Affective Science
- Biological Foundations of Psychology
- Clinical Psychology: Disorders and Therapies
- Cognitive Psychology/Neuroscience
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational/School Psychology
- Forensic Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems of Psychology
- Individual Differences
- Methods and Approaches in Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational and Institutional Psychology
- Personality
- Psychology and Other Disciplines
- Social Psychology
- Sports Psychology
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter

Article contents
Work, stress, coping, and stress management.
- Sharon Glazer Sharon Glazer University of Baltimore
- and Cong Liu Cong Liu Hofstra University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190236557.013.30
- Published online: 26 April 2017
Work stress refers to the process of job stressors, or stimuli in the workplace, leading to strains, or negative responses or reactions. Organizational development refers to a process in which problems or opportunities in the work environment are identified, plans are made to remediate or capitalize on the stimuli, action is taken, and subsequently the results of the plans and actions are evaluated. When organizational development strategies are used to assess work stress in the workplace, the actions employed are various stress management interventions. Two key factors tying work stress and organizational development are the role of the person and the role of the environment. In order to cope with work-related stressors and manage strains, organizations must be able to identify and differentiate between factors in the environment that are potential sources of stressors and how individuals perceive those factors. Primary stress management interventions focus on preventing stressors from even presenting, such as by clearly articulating workers’ roles and providing necessary resources for employees to perform their job. Secondary stress management interventions focus on a person’s appraisal of job stressors as a threat or challenge, and the person’s ability to cope with the stressors (presuming sufficient internal resources, such as a sense of meaningfulness in life, or external resources, such as social support from a supervisor). When coping is not successful, strains may develop. Tertiary stress management interventions attempt to remediate strains, by addressing the consequence itself (e.g., diabetes management) and/or the source of the strain (e.g., reducing workload). The person and/or the organization may be the targets of the intervention. The ultimate goal of stress management interventions is to minimize problems in the work environment, intensify aspects of the work environment that create a sense of a quality work context, enable people to cope with stressors that might arise, and provide tools for employees and organizations to manage strains that might develop despite all best efforts to create a healthy workplace.
- stress management
- organization development
- organizational interventions
- stress theories and frameworks
Introduction
Work stress is a generic term that refers to work-related stimuli (aka job stressors) that may lead to physical, behavioral, or psychological consequences (i.e., strains) that affect both the health and well-being of the employee and the organization. Not all stressors lead to strains, but all strains are a result of stressors, actual or perceived. Common terms often used interchangeably with work stress are occupational stress, job stress, and work-related stress. Terms used interchangeably with job stressors include work stressors, and as the specificity of the type of stressor might include psychosocial stressor (referring to the psychological experience of work demands that have a social component, e.g., conflict between two people; Hauke, Flintrop, Brun, & Rugulies, 2011 ), hindrance stressor (i.e., a stressor that prevents goal attainment; Cavanaugh, Boswell, Roehling, & Boudreau, 2000 ), and challenge stressor (i.e., a stressor that is difficult, but attainable and possibly rewarding to attain; Cavanaugh et al., 2000 ).
Stress in the workplace continues to be a highly pervasive problem, having both direct negative effects on individuals experiencing it and companies paying for it, and indirect costs vis à vis lost productivity (Dopkeen & DuBois, 2014 ). For example, U.K. public civil servants’ work-related stress rose from 10.8% in 2006 to 22.4% in 2013 and about one-third of the workforce has taken more than 20 days of leave due to stress-related ill-health, while well over 50% are present at work when ill (French, 2015 ). These findings are consistent with a report by the International Labor Organization (ILO, 2012 ), whereby 50% to 60% of all workdays are lost due to absence attributed to factors associated with work stress.
The prevalence of work-related stress is not diminishing despite improvements in technology and employment rates. The sources of stress, such as workload, seem to exacerbate with improvements in technology (Coovert & Thompson, 2003 ). Moreover, accessibility through mobile technology and virtual computer terminals is linking people to their work more than ever before (ILO, 2012 ; Tarafdar, Tu, Ragu-Nathan, & Ragu-Nathan, 2007 ). Evidence of this kind of mobility and flexibility is further reinforced in a June 2007 survey of 4,025 email users (over 13 years of age); AOL reported that four in ten survey respondents reported planning their vacations around email accessibility and 83% checked their emails at least once a day while away (McMahon, 2007 ). Ironically, despite these mounting work-related stressors and clear financial and performance outcomes, some individuals are reporting they are less “stressed,” but only because “stress has become the new normal” (Jayson, 2012 , para. 4).
This new normal is likely the source of psychological and physiological illness. Siegrist ( 2010 ) contends that conditions in the workplace, particularly psychosocial stressors that are perceived as unfavorable relationships with others and self, and an increasingly sedentary lifestyle (reinforced with desk jobs) are increasingly contributing to cardiovascular disease. These factors together justify a need to continue on the path of helping individuals recognize and cope with deleterious stressors in the work environment and, equally important, to find ways to help organizations prevent harmful stressors over which they have control, as well as implement policies or mechanisms to help employees deal with these stressors and subsequent strains. Along with a greater focus on mitigating environmental constraints are interventions that can be used to prevent anxiety, poor attitudes toward the workplace conditions and arrangements, and subsequent cardiovascular illness, absenteeism, and poor job performance (Siegrist, 2010 ).
Even the ILO has presented guidance on how the workplace can help prevent harmful job stressors (aka hindrance stressors) or at least help workers cope with them. Consistent with the view that well-being is not the absence of stressors or strains and with the view that positive psychology offers a lens for proactively preventing stressors, the ILO promotes increasing preventative risk assessments, interventions to prevent and control stressors, transparent organizational communication, worker involvement in decision-making, networks and mechanisms for workplace social support, awareness of how working and living conditions interact, safety, health, and well-being in the organization (ILO, n.d. ). The field of industrial and organizational (IO) psychology supports the ILO’s recommendations.
IO psychology views work stress as the process of a person’s interaction with multiple aspects of the work environment, job design, and work conditions in the organization. Interventions to manage work stress, therefore, focus on the psychosocial factors of the person and his or her relationships with others and the socio-technical factors related to the work environment and work processes. Viewing work stress from the lens of the person and the environment stems from Kurt Lewin’s ( 1936 ) work that stipulates a person’s state of mental health and behaviors are a function of the person within a specific environment or situation. Aspects of the work environment that affect individuals’ mental states and behaviors include organizational hierarchy, organizational climate (including processes, policies, practices, and reward structures), resources to support a person’s ability to fulfill job duties, and management structure (including leadership). Job design refers to each contributor’s tasks and responsibilities for fulfilling goals associated with the work role. Finally, working conditions refers not only to the physical environment, but also the interpersonal relationships with other contributors.
Each of the conditions that are identified in the work environment may be perceived as potentially harmful or a threat to the person or as an opportunity. When a stressor is perceived as a threat to attaining desired goals or outcomes, the stressor may be labeled as a hindrance stressor (e.g., LePine, Podsakoff, & Lepine, 2005 ). When the stressor is perceived as an opportunity to attain a desired goal or end state, it may be labeled as a challenge stressor. According to LePine and colleagues’ ( 2005 ), both challenge (e.g., time urgency, workload) and hindrance (e.g., hassles, role ambiguity, role conflict) stressors could lead to strains (as measured by “anxiety, depersonalization, depression, emotional exhaustion, frustration, health complaints, hostility, illness, physical symptoms, and tension” [p. 767]). However, challenge stressors positively relate with motivation and performance, whereas hindrance stressors negatively relate with motivation and performance. Moreover, motivation and strains partially mediate the relationship between hindrance and challenge stressors with performance.
Figure 1. Organizational development frameworks to guide identification of work stress and interventions.
In order to (1) minimize any potential negative effects from stressors, (2) increase coping skills to deal with stressors, or (3) manage strains, organizational practitioners or consultants will devise organizational interventions geared toward prevention, coping, and/or stress management. Ultimately, toxic factors in the work environment can have deleterious effects on a person’s physical and psychological well-being, as well as on an organization’s total health. It behooves management to take stock of the organization’s health, which includes the health and well-being of its employees, if the organization wishes to thrive and be profitable. According to Page and Vella-Brodrick’s ( 2009 ) model of employee well-being, employee well-being results from subjective well-being (i.e., life satisfaction and general positive or negative affect), workplace well-being (composed of job satisfaction and work-specific positive or negative affect), and psychological well-being (e.g., self-acceptance, positive social relations, mastery, purpose in life). Job stressors that become unbearable are likely to negatively affect workplace well-being and thus overall employee well-being. Because work stress is a major organizational pain point and organizations often employ organizational consultants to help identify and remediate pain points, the focus here is on organizational development (OD) frameworks; several work stress frameworks are presented that together signal areas where organizations might focus efforts for change in employee behaviors, attitudes, and performance, as well as the organization’s performance and climate. Work stress, interventions, and several OD and stress frameworks are depicted in Figure 1 .
The goals are: (1) to conceptually define and clarify terms associated with stress and stress management, particularly focusing on organizational factors that contribute to stress and stress management, and (2) to present research that informs current knowledge and practices on workplace stress management strategies. Stressors and strains will be defined, leading OD and work stress frameworks that are used to organize and help organizations make sense of the work environment and the organization’s responsibility in stress management will be explored, and stress management will be explained as an overarching thematic label; an area of study and practice that focuses on prevention (primary) interventions, coping (secondary) interventions, and managing strains (tertiary) interventions; as well as the label typically used to denote tertiary interventions. Suggestions for future research and implications toward becoming a healthy organization are presented.
Defining Stressors and Strains
Work-related stressors or job stressors can lead to different kinds of strains individuals and organizations might experience. Various types of stress management interventions, guided by OD and work stress frameworks, may be employed to prevent or cope with job stressors and manage strains that develop(ed).
A job stressor is a stimulus external to an employee and a result of an employee’s work conditions. Example job stressors include organizational constraints, workplace mistreatments (such as abusive supervision, workplace ostracism, incivility, bullying), role stressors, workload, work-family conflicts, errors or mistakes, examinations and evaluations, and lack of structure (Jex & Beehr, 1991 ; Liu, Spector, & Shi, 2007 ; Narayanan, Menon, & Spector, 1999 ). Although stressors may be categorized as hindrances and challenges, there is not yet sufficient information to be able to propose which stress management interventions would better serve to reduce those hindrance stressors or to reduce strain-producing challenge stressors while reinforcing engagement-producing challenge stressors.
Organizational Constraints
Organizational constraints may be hindrance stressors as they prevent employees from translating their motivation and ability into high-level job performance (Peters & O’Connor, 1980 ). Peters and O’Connor ( 1988 ) defined 11 categories of organizational constraints: (1) job-related information, (2) budgetary support, (3) required support, (4) materials and supplies, (5) required services and help from others, (6) task preparation, (7) time availability, (8) the work environment, (9) scheduling of activities, (10) transportation, and (11) job-relevant authority. The inhibiting effect of organizational constraints may be due to the lack of, inadequacy of, or poor quality of these categories.
Workplace Mistreatment
Workplace mistreatment presents a cluster of interpersonal variables, such as interpersonal conflict, bullying, incivility, and workplace ostracism (Hershcovis, 2011 ; Tepper & Henle, 2011 ). Typical workplace mistreatment behaviors include gossiping, rude comments, showing favoritism, yelling, lying, and ignoring other people at work (Tepper & Henle, 2011 ). These variables relate to employees’ psychological well-being, physical well-being, work attitudes (e.g., job satisfaction and organizational commitment), and turnover intention (e.g., Hershcovis, 2011 ; Spector & Jex, 1998 ). Some researchers differentiated the source of mistreatment, such as mistreatment from one’s supervisor versus mistreatment from one’s coworker (e.g., Bruk-Lee & Spector, 2006 ; Frone, 2000 ; Liu, Liu, Spector, & Shi, 2011 ).
Role Stressors
Role stressors are demands, constraints, or opportunities a person perceives to be associated, and thus expected, with his or her work role(s) across various situations. Three commonly studied role stressors are role ambiguity, role conflict, and role overload (Glazer & Beehr, 2005 ; Kahn, Wolfe, Quinn, Snoek, & Rosenthal, 1964 ). Role ambiguity in the workplace occurs when an employee lacks clarity regarding what performance-related behaviors are expected of him or her. Role conflict refers to situations wherein an employee receives incompatible role requests from the same or different supervisors or the employee is asked to engage in work that impedes his or her performance in other work or nonwork roles or clashes with his or her values. Role overload refers to excessive demands and insufficient time (quantitative) or knowledge (qualitative) to complete the work. The construct is often used interchangeably with workload, though role overload focuses more on perceived expectations from others about one’s workload. These role stressors significantly relate to low job satisfaction, low organizational commitment, low job performance, high tension or anxiety, and high turnover intention (Abramis, 1994 ; Glazer & Beehr, 2005 ; Jackson & Schuler, 1985 ).
Excessive workload is one of the most salient stressors at work (e.g., Liu et al., 2007 ). There are two types of workload: quantitative and qualitative workload (LaRocco, Tetrick, & Meder, 1989 ; Parasuraman & Purohit, 2000 ). Quantitative workload refers to the excessive amount of work one has. In a summary of a Chartered Institute of Personnel & Development Report from 2006 , Dewe and Kompier ( 2008 ) noted that quantitative workload was one of the top three stressors workers experienced at work. Qualitative workload refers to the difficulty of work. Workload also differs by the type of the load. There are mental workload and physical workload (Dwyer & Ganster, 1991 ). Excessive physical workload may result in physical discomfort or illness. Excessive mental workload will cause psychological distress such as anxiety or frustration (Bowling & Kirkendall, 2012 ). Another factor affecting quantitative workload is interruptions (during the workday). Lin, Kain, and Fritz ( 2013 ) found that interruptions delay completion of job tasks, thus adding to the perception of workload.
Work-Family Conflict
Work-family conflict is a form of inter-role conflict in which demands from one’s work domain and one’s family domain are incompatible to some extent (Greenhaus & Beutell, 1985 ). Work can interfere with family (WIF) and/or family can interfere with work (FIW) due to time-related commitments to participating in one domain or another, incompatible behavioral expectations, or when strains in one domain carry over to the other (Greenhaus & Beutell, 1985 ). Work-family conflict significantly relates to work-related outcomes (e.g., job satisfaction, organizational commitment, turnover intention, burnout, absenteeism, job performance, job strains, career satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behaviors), family-related outcomes (e.g., marital satisfaction, family satisfaction, family-related performance, family-related strains), and domain-unspecific outcomes (e.g., life satisfaction, psychological strain, somatic or physical symptoms, depression, substance use or abuse, and anxiety; Amstad, Meier, Fasel, Elfering, & Semmer, 2011 ).
Individuals and organizations can experience work-related strains. Sometimes organizations will experience strains through the employee’s negative attitudes or strains, such as that a worker’s absence might yield lower production rates, which would roll up into an organizational metric of organizational performance. In the industrial and organizational (IO) psychology literature, organizational strains are mostly observed as macro-level indicators, such as health insurance costs, accident-free days, and pervasive problems with company morale. In contrast, individual strains, usually referred to as job strains, are internal to an employee. They are responses to work conditions and relate to health and well-being of employees. In other words, “job strains are adverse reactions employees have to job stressors” (Spector, Chen, & O’Connell, 2000 , p. 211). Job strains tend to fall into three categories: behavioral, physical, and psychological (Jex & Beehr, 1991 ).
Behavioral strains consist of actions that employees take in response to job stressors. Examples of behavioral strains include employees drinking alcohol in the workplace or intentionally calling in sick when they are not ill (Spector et al., 2000 ). Physical strains consist of health symptoms that are physiological in nature that employees contract in response to job stressors. Headaches and ulcers are examples of physical strains. Lastly, psychological strains are emotional reactions and attitudes that employees have in response to job stressors. Examples of psychological strains are job dissatisfaction, anxiety, and frustration (Spector et al., 2000 ). Interestingly, research studies that utilize self-report measures find that most job strains experienced by employees tend to be psychological strains (Spector et al., 2000 ).
Leading Frameworks
Organizations that are keen on identifying organizational pain points and remedying them through organizational campaigns or initiatives often discover the pain points are rooted in work-related stressors and strains and the initiatives have to focus on reducing workers’ stress and increasing a company’s profitability. Through organizational climate surveys, for example, companies discover that aspects of the organization’s environment, including its policies, practices, reward structures, procedures, and processes, as well as employees at all levels of the company, are contributing to the individual and organizational stress. Recent studies have even begun to examine team climates for eustress and distress assessed in terms of team members’ homogenous psychological experience of vigor, efficacy, dedication, and cynicism (e.g., Kożusznik, Rodriguez, & Peiro, 2015 ).
Each of the frameworks presented advances different aspects that need to be identified in order to understand the source and potential remedy for stressors and strains. In some models, the focus is on resources, in others on the interaction of the person and environment, and in still others on the role of the person in the workplace. Few frameworks directly examine the role of the organization, but the organization could use these frameworks to plan interventions that would minimize stressors, cope with existing stressors, and prevent and/or manage strains. One of the leading frameworks in work stress research that is used to guide organizational interventions is the person and environment (P-E) fit (French & Caplan, 1972 ). Its precursor is the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research’s (ISR) role stress model (Kahn, Wolfe, Quinn, Snoek, & Rosenthal, 1964 ) and Lewin’s Field Theory. Several other theories have since evolved from the P-E fit framework, including Karasek and Theorell’s ( 1990 ), Karasek ( 1979 ) Job Demands-Control Model (JD-C), the transactional framework (Lazarus & Folkman, 1984 ), Conservation of Resources (COR) theory (Hobfoll, 1989 ), and Siegrist’s ( 1996 ) Effort-Reward Imbalance (ERI) Model.
Field Theory
The premise of Kahn et al.’s ( 1964 ) role stress theory is Lewin’s ( 1997 ) Field Theory. Lewin purported that behavior and mental events are a dynamic function of the whole person, including a person’s beliefs, values, abilities, needs, thoughts, and feelings, within a given situation (field or environment), as well as the way a person represents his or her understanding of the field and behaves in that space. Lewin explains that work-related strains are a result of individuals’ subjective perceptions of objective factors, such as work roles, relationships with others in the workplace, as well as personality indicators, and can be used to predict people’s reactions, including illness. Thus, to make changes to an organizational system, it is necessary to understand a field and try to move that field from the current state to the desired state. Making this move necessitates identifying mechanisms influencing individuals.
Role Stress Theory
Role stress theory mostly isolates the perspective a person has about his or her work-related responsibilities and expectations to determine how those perceptions relate with a person’s work-related strains. However, those relationships have been met with somewhat varied results, which Glazer and Beehr ( 2005 ) concluded might be a function of differences in culture, an environmental factor often neglected in research. Kahn et al.’s ( 1964 ) role stress theory, coupled with Lewin’s ( 1936 ) Field Theory, serves as the foundation for the P-E fit theory. Lewin ( 1936 ) wrote, “Every psychological event depends upon the state of the person and at the same time on the environment” (p. 12). Researchers of IO psychology have narrowed the environment to the organization or work team. This narrowed view of the organizational environment is evident in French and Caplan’s ( 1972 ) P-E fit framework.
Person-Environment Fit Theory
The P-E fit framework focuses on the extent to which there is congruence between the person and a given environment, such as the organization (Caplan, 1987 ; Edwards, 2008 ). For example, does the person have the necessary skills and abilities to fulfill an organization’s demands, or does the environment support a person’s desire for autonomy (i.e., do the values align?) or fulfill a person’s needs (i.e., a person’s needs are rewarded). Theoretically and empirically, the greater the person-organization fit, the greater a person’s job satisfaction and organizational commitment, the less a person’s turnover intention and work-related stress (see meta-analyses by Assouline & Meir, 1987 ; Kristof-Brown, Zimmerman, & Johnson, 2005 ; Verquer, Beehr, & Wagner, 2003 ).
Job Demands-Control/Support (JD-C/S) and Job Demands-Resources (JD-R) Model
Focusing more closely on concrete aspects of work demands and the extent to which a person perceives he or she has control or decision latitude over those demands, Karasek ( 1979 ) developed the JD-C model. Karasek and Theorell ( 1990 ) posited that high job demands under conditions of little decision latitude or control yield high strains, which have varied implications on the health of an organization (e.g., in terms of high turnover, employee ill-health, poor organizational performance). This theory was modified slightly to address not only control, but also other resources that could protect a person from unruly job demands, including support (aka JD-C/S, Johnson & Hall, 1988 ; and JD-R, Bakker, van Veldhoven, & Xanthopoulou, 2010 ). Whether focusing on control or resources, both they and job demands are said to reflect workplace characteristics, while control and resources also represent coping strategies or tools (Siegrist, 2010 ).
Despite the glut of research testing the JD-C and JD-R, results are somewhat mixed. Testing the interaction between job demands and control, Beehr, Glaser, Canali, and Wallwey ( 2001 ) did not find empirical support for the JD-C theory. However, Dawson, O’Brien, and Beehr ( 2016 ) found that high control and high support buffered against the independent deleterious effects of interpersonal conflict, role conflict, and organizational politics (demands that were categorized as hindrance stressors) on anxiety, as well as the effects of interpersonal conflict and organizational politics on physiological symptoms, but control and support did not moderate the effects between challenge stressors and strains. Coupled with Bakker, Demerouti, and Sanz-Vergel’s ( 2014 ) note that excessive job demands are a source of strain, but increased job resources are a source of engagement, Dawson et al.’s results suggest that when an organization identifies that demands are hindrances, it can create strategies for primary (preventative) stress management interventions and attempt to remove or reduce such work demands. If the demands are challenging, though manageable, but latitude to control the challenging stressors and support are insufficient, the organization could modify practices and train employees on adopting better strategies for meeting or coping (secondary stress management intervention) with the demands. Finally, if the organization can neither afford to modify the demands or the level of control and support, it will be necessary for the organization to develop stress management (tertiary) interventions to deal with the inevitable strains.
Conservation of Resources Theory
The idea that job resources reinforce engagement in work has been propagated in Hobfoll’s ( 1989 ) Conservation of Resources (COR) theory. COR theory also draws on the foundational premise that people’s mental health is a function of the person and the environment, forwarding that how people interpret their environment (including the societal context) affects their stress levels. Hobfoll focuses on resources such as objects, personal characteristics, conditions, or energies as particularly instrumental to minimizing strains. He asserts that people do whatever they can to protect their valued resources. Thus, strains develop when resources are threatened to be taken away, actually taken away, or when additional resources are not attainable after investing in the possibility of gaining more resources (Hobfoll, 2001 ). By extension, organizations can invest in activities that would minimize resource loss and create opportunities for resource gains and thus have direct implications for devising primary and secondary stress management interventions.
Transactional Framework
Lazarus and Folkman ( 1984 ) developed the widely studied transactional framework of stress. This framework holds as a key component the cognitive appraisal process. When individuals perceive factors in the work environment as a threat (i.e., primary appraisal), they will scan the available resources (external or internal to himself or herself) to cope with the stressors (i.e., secondary appraisal). If the coping resources provide minimal relief, strains develop. Until recently, little attention has been given to the cognitive appraisal associated with different work stressors (Dewe & Kompier, 2008 ; Liu & Li, 2017 ). In a study of Polish and Spanish social care service providers, stressors appraised as a threat related positively to burnout and less engagement, but stressors perceived as challenges yielded greater engagement and less burnout (Kożusznik, Rodriguez, & Peiro, 2012 ). Similarly, Dawson et al. ( 2016 ) found that even with support and control resources, hindrance demands were more strain-producing than challenge demands, suggesting that appraisal of the stressor is important. In fact, “many people respond well to challenging work” (Beehr et al., 2001 , p. 126). Kożusznik et al. ( 2012 ) recommend training employees to change the way they view work demands in order to increase engagement, considering that part of the problem may be about how the person appraises his or her environment and, thus, copes with the stressors.
Effort-Reward Imbalance
Siegrist’s ( 1996 ) Model of Effort-Reward Imbalance (ERI) focuses on the notion of social reciprocity, such that a person fulfills required work tasks in exchange for desired rewards (Siegrist, 2010 ). ERI sheds light on how an imbalance in a person’s expectations of an organization’s rewards (e.g., pay, bonus, sense of advancement and development, job security) in exchange for a person’s efforts, that is a break in one’s work contract, leads to negative responses, including long-term ill-health (Siegrist, 2010 ; Siegrist et al., 2014 ). In fact, prolonged perception of a work contract imbalance leads to adverse health, including immunological problems and inflammation, which contribute to cardiovascular disease (Siegrist, 2010 ). The model resembles the relational and interactional psychological contract theory in that it describes an employee’s perception of the terms of the relationship between the person and the workplace, including expectations of performance, job security, training and development opportunities, career progression, salary, and bonuses (Thomas, Au, & Ravlin, 2003 ). The psychological contract, like the ERI model, focuses on social exchange. Furthermore, the psychological contract, like stress theories, are influenced by cultural factors that shape how people interpret their environments (Glazer, 2008 ; Thomas et al., 2003 ). Violations of the psychological contract will negatively affect a person’s attitudes toward the workplace and subsequent health and well-being (Siegrist, 2010 ). To remediate strain, Siegrist ( 2010 ) focuses on both the person and the environment, recognizing that the organization is particularly responsible for changing unfavorable work conditions and the person is responsible for modifying his or her reactions to such conditions.
Stress Management Interventions: Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary
Remediation of work stress and organizational development interventions are about realigning the employee’s experiences in the workplace with factors in the environment, as well as closing the gap between the current environment and the desired environment. Work stress develops when an employee perceives the work demands to exceed the person’s resources to cope and thus threatens employee well-being (Dewe & Kompier, 2008 ). Likewise, an organization’s need to change arises when forces in the environment are creating a need to change in order to survive (see Figure 1 ). Lewin’s ( 1951 ) Force Field Analysis, the foundations of which are in Field Theory, is one of the first organizational development intervention tools presented in the social science literature. The concept behind Force Field Analysis is that in order to survive, organizations must adapt to environmental forces driving a need for organizational change and remove restraining forces that create obstacles to organizational change. In order to do this, management needs to delineate the current field in which the organization is functioning, understand the driving forces for change, identify and dampen or eliminate the restraining forces against change. Several models for analyses may be applied, but most approaches are variations of organizational climate surveys.
Through organizational surveys, workers provide management with a snapshot view of how they perceive aspects of their work environment. Thus, the view of the health of an organization is a function of several factors, chief among them employees’ views (i.e., the climate) about the workplace (Lewin, 1951 ). Indeed, French and Kahn ( 1962 ) posited that well-being depends on the extent to which properties of the person and properties of the environment align in terms of what a person requires and the resources available in a given environment. Therefore, only when properties of the person and properties of the environment are sufficiently understood can plans for change be developed and implemented targeting the environment (e.g., change reporting structures to relieve, and thus prevent future, communication stressors) and/or the person (e.g., providing more autonomy, vacation days, training on new technology). In short, climate survey findings can guide consultants about the emphasis for organizational interventions: before a problem arises aka stress prevention, e.g., carefully crafting job roles), when a problem is present, but steps are taken to mitigate their consequences (aka coping, e.g., providing social support groups), and/or once strains develop (aka. stress management, e.g., healthcare management policies).
For each of the primary (prevention), secondary (coping), and tertiary (stress management) techniques the target for intervention can be the entire workforce, a subset of the workforce, or a specific person. Interventions that target the entire workforce may be considered organizational interventions, as they have direct implications on the health of all individuals and consequently the health of the organization. Several interventions categorized as primary and secondary interventions may also be implemented after strains have developed and after it has been discerned that a person or the organization did not do enough to mitigate stressors or strains (see Figure 1 ). The designation of many of the interventions as belonging to one category or another may be viewed as merely a suggestion.
Primary Interventions (Preventative Stress Management)
Before individuals begin to perceive work-related stressors, organizations engage in stress prevention strategies, such as providing people with resources (e.g., computers, printers, desk space, information about the job role, organizational reporting structures) to do their jobs. However, sometimes the institutional structures and resources are insufficient or ambiguous. Scholars and practitioners have identified several preventative stress management strategies that may be implemented.
Planning and Time Management
When employees feel quantitatively overloaded, sometimes the remedy is improving the employees’ abilities to plan and manage their time (Quick, Quick, Nelson, & Hurrell, 2003 ). Planning is a future-oriented activity that focuses on conceptual and comprehensive work goals. Time management is a behavior that focuses on organizing, prioritizing, and scheduling work activities to achieve short-term goals. Given the purpose of time management, it is considered a primary intervention, as engaging in time management helps to prevent work tasks from mounting and becoming unmanageable, which would subsequently lead to adverse outcomes. Time management comprises three fundamental components: (1) establishing goals, (2) identifying and prioritizing tasks to fulfill the goals, and (3) scheduling and monitoring progress toward goal achievement (Peeters & Rutte, 2005 ). Workers who employ time management have less role ambiguity (Macan, Shahani, Dipboye, & Philips, 1990 ), psychological stress or strain (Adams & Jex, 1999 ; Jex & Elaqua, 1999 ; Macan et al., 1990 ), and greater job satisfaction (Macan, 1994 ). However, Macan ( 1994 ) did not find a relationship between time management and performance. Still, Claessens, van Eerde, Rutte, and Roe ( 2004 ) found that perceived control of time partially mediated the relationships between planning behavior (an indicator of time management), job autonomy, and workload on one hand, and job strains, job satisfaction, and job performance on the other hand. Moreover, Peeters and Rutte ( 2005 ) observed that teachers with high work demands and low autonomy experienced more burnout when they had poor time management skills.
Person-Organization Fit
Just as it is important for organizations to find the right person for the job and organization, so is it the responsibility of a person to choose to work at the right organization—an organization that fulfills the person’s needs and upholds the values important to the individual, as much as the person fulfills the organization’s needs and adapts to its values. When people fit their employing organizations they are setting themselves up for experiencing less strain-producing stressors (Kristof-Brown et al., 2005 ). In a meta-analysis of 62 person-job fit studies and 110 person-organization fit studies, Kristof-Brown et al. ( 2005 ) found that person-job fit had a negative correlation with indicators of job strain. In fact, a primary intervention of career counseling can help to reduce stress levels (Firth-Cozens, 2003 ).
Job Redesign
The Job Demands-Control/Support (JD-C/S), Job Demands-Resources (JD-R), and transactional models all suggest that factors in the work context require modifications in order to reduce potential ill-health and poor organizational performance. Drawing on Hackman and Oldham’s ( 1980 ) Job Characteristics Model, it is possible to assess with the Job Diagnostics Survey (JDS) the current state of work characteristics related to skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback. Modifying those aspects would help create a sense of meaningfulness, sense of responsibility, and feeling of knowing how one is performing, which subsequently affects a person’s well-being as identified in assessments of motivation, satisfaction, improved performance, and reduced withdrawal intentions and behaviors. Extending this argument to the stress models, it can be deduced that reducing uncertainty or perceived unfairness that may be associated with a person’s perception of these work characteristics, as well as making changes to physical characteristics of the environment (e.g., lighting, seating, desk, air quality), nature of work (e.g., job responsibilities, roles, decision-making latitude), and organizational arrangements (e.g., reporting structure and feedback mechanisms), can help mitigate against numerous ill-health consequences and reduced organizational performance. In fact, Fried et al. ( 2013 ) showed that healthy patients of a medical clinic whose jobs were excessively low (i.e., monotonous) or excessively high (i.e., overstimulating) on job enrichment (as measured by the JDS) had greater abdominal obesity than those whose jobs were optimally enriched. By taking stock of employees’ perceptions of the current work situation, managers might think about ways to enhance employees’ coping toolkit, such as training on how to deal with difficult clients or creating stimulating opportunities when jobs have low levels of enrichment.
Participatory Action Research Interventions
Participatory action research (PAR) is an intervention wherein, through group discussions, employees help to identify and define problems in organizational structure, processes, policies, practices, and reward structures, as well as help to design, implement, and evaluate success of solutions. PAR is in itself an intervention, but its goal is to design interventions to eliminate or reduce work-related factors that are impeding performance and causing people to be unwell. An example of a successful primary intervention, utilizing principles of PAR and driven by the JD-C and JD-C/S stress frameworks is Health Circles (HCs; Aust & Ducki, 2004 ).
HCs, developed in Germany in the 1980s, were popular practices in industries, such as metal, steel, and chemical, and service. Similar to other problem-solving practices, such as quality circles, HCs were based on the assumptions that employees are the experts of their jobs. For this reason, to promote employee well-being, management and administrators solicited suggestions and ideas from the employees to improve occupational health, thereby increasing employees’ job control. HCs also promoted communication between managers and employees, which had a potential to increase social support. With more control and support, employees would experience less strains and better occupational well-being.
Employing the three-steps of (1) problem analysis (i.e., diagnosis or discovery through data generated from organizational records of absenteeism length, frequency, rate, and reason and employee survey), (2) HC meetings (6 to 10 meetings held over several months to brainstorm ideas to improve occupational safety and health concerns identified in the discovery phase), and (3) HC evaluation (to determine if desired changes were accomplished and if employees’ reports of stressors and strains changed after the course of 15 months), improvements were to be expected (Aust & Ducki, 2004 ). Aust and Ducki ( 2004 ) reviewed 11 studies presenting 81 health circles in 30 different organizations. Overall study participants had high satisfaction with the HCs practices. Most companies acted upon employees’ suggestions (e.g., improving driver’s seat and cab, reducing ticket sale during drive, team restructuring and job rotation to facilitate communication, hiring more employees during summer time, and supervisor training program to improve leadership and communication skills) to improve work conditions. Thus, HCs represent a successful theory-grounded intervention to routinely improve employees’ occupational health.
Physical Setting
The physical environment or physical workspace has an enormous impact on individuals’ well-being, attitudes, and interactions with others, as well as on the implications on innovation and well-being (Oksanen & Ståhle, 2013 ; Vischer, 2007 ). In a study of 74 new product development teams (total of 437 study respondents) in Western Europe, Chong, van Eerde, Rutte, and Chai ( 2012 ) found that when teams were faced with challenge time pressures, meaning the teams had a strong interest and desire in tackling complex, but engaging tasks, when they were working proximally close with one another, team communication improved. Chong et al. assert that their finding aligns with prior studies that have shown that physical proximity promotes increased awareness of other team members, greater tendency to initiate conversations, and greater team identification. However, they also found that when faced with hindrance time pressures, physical proximity related to low levels of team communication, but when hindrance time pressure was low, team proximity had an increasingly greater positive relationship with team communication.
In addition to considering the type of work demand teams must address, other physical workspace considerations include whether people need to work collaboratively and synchronously or independently and remotely (or a combination thereof). Consideration needs to be given to how company contributors would satisfy client needs through various modes of communication, such as email vs. telephone, and whether individuals who work by a window might need shading to block bright sunlight from glaring on their computer screens. Finally, people who have to use the telephone for extensive periods of time would benefit from earphones to prevent neck strains. Most physical stressors are rather simple to rectify. However, companies are often not aware of a problem until after a problem arises, such as when a person’s back is strained from trying to move heavy equipment. Companies then implement strategies to remediate the environmental stressor. With the help of human factors, and organizational and office design consultants, many of the physical barriers to optimal performance can be prevented (Rousseau & Aubé, 2010 ). In a study of 215 French-speaking Canadian healthcare employees, Rousseau and Aubé ( 2010 ) found that although supervisor instrumental support positively related with affective commitment to the organization, the relationship was even stronger for those who reported satisfaction with the ambient environment (i.e., temperature, lighting, sound, ventilation, and cleanliness).
Secondary Interventions (Coping)
Secondary interventions, also referred to as coping, focus on resources people can use to mitigate the risk of work-related illness or workplace injury. Resources may include properties related to social resources, behaviors, and cognitive structures. Each of these resource domains may be employed to cope with stressors. Monat and Lazarus ( 1991 ) summarize the definition of coping as “an individual’s efforts to master demands (or conditions of harm, threat, or challenge) that are appraised (or perceived) as exceeding or taxing his or her resources” (p. 5). To master demands requires use of the aforementioned resources. Secondary interventions help employees become aware of the psychological, physical, and behavioral responses that may occur from the stressors presented in their working environment. Secondary interventions help a person detect and attend to stressors and identify resources for and ways of mitigating job strains. Often, coping strategies are learned skills that have a cognitive foundation and serve important functions in improving people’s management of stressors (Lazarus & Folkman, 1991 ). Coping is effortful, but with practice it becomes easier to employ. This idea is the foundation for understanding the role of resilience in coping with stressors. However, “not all adaptive processes are coping. Coping is a subset of adaptational activities that involves effort and does not include everything that we do in relating to the environment” (Lazarus & Folkman, 1991 , p. 198). Furthermore, sometimes to cope with a stressor, a person may call upon social support sources to help with tangible materials or emotional comfort. People call upon support resources because they help to restructure how a person approaches or thinks about the stressor.
Most secondary interventions are aimed at helping the individual, though companies, as a policy, might require all employees to partake in training aimed at increasing employees’ awareness of and skills aimed at handling difficult situations vis à vis company channels (e.g., reporting on sexual harassment or discrimination). Furthermore, organizations might institute mentoring programs or work groups to address various work-related matters. These programs employ awareness-raising activities, stress-education, or skills training (cf., Bhagat, Segovis, & Nelson, 2012 ), which include development of skills in problem-solving, understanding emotion-focused coping, identifying and using social support, and enhancing capacity for resilience. The aim of these programs, therefore, is to help employees proactively review their perceptions of psychological, physical, and behavioral job-related strains, thereby extending their resilience, enabling them to form a personal plan to control stressors and practice coping skills (Cooper, Dewe, & O’Driscoll, 2011 ).
Often these stress management programs are instituted after an organization has observed excessive absenteeism and work-related performance problems and, therefore, are sometimes categorized as a tertiary stress management intervention or even a primary (prevention) intervention. However, the skills developed for coping with stressors also place the programs in secondary stress management interventions. Example programs that are categorized as tertiary or primary stress management interventions may also be secondary stress management interventions (see Figure 1 ), and these include lifestyle advice and planning, stress inoculation training, simple relaxation techniques, meditation, basic trainings in time management, anger management, problem-solving skills, and cognitive-behavioral therapy. Corporate wellness programs also fall under this category. In other words, some programs could be categorized as primary, secondary, or tertiary interventions depending upon when the employee (or organization) identifies the need to implement the program. For example, time management practices could be implemented as a means of preventing some stressors, as a way to cope with mounting stressors, or as a strategy to mitigate symptoms of excessive of stressors. Furthermore, these programs can be administered at the individual level or group level. As related to secondary interventions, these programs provide participants with opportunities to develop and practice skills to cognitively reappraise the stressor(s); to modify their perspectives about stressors; to take time out to breathe, stretch, meditate, relax, and/or exercise in an attempt to support better decision-making; to articulate concerns and call upon support resources; and to know how to say “no” to onslaughts of requests to complete tasks. Participants also learn how to proactively identify coping resources and solve problems.
According to Cooper, Dewe, and O’Driscoll ( 2001 ), secondary interventions are successful in helping employees modify or strengthen their ability to cope with the experience of stressors with the goal of mitigating the potential harm the job stressors may create. Secondary interventions focus on individuals’ transactions with the work environment and emphasize the fit between a person and his or her environment. However, researchers have pointed out that the underlying assumption of secondary interventions is that the responsibility for coping with the stressors of the environment lies within individuals (Quillian-Wolever & Wolever, 2003 ). If companies cannot prevent the stressors in the first place, then they are, in part, responsible for helping individuals develop coping strategies and informing employees about programs that would help them better cope with job stressors so that they are able to fulfill work assignments.
Stress management interventions that help people learn to cope with stressors focus mainly on the goals of enabling problem-resolution or expressing one’s emotions in a healthy manner. These goals are referred to as problem-focused coping and emotion-focused coping (Folkman & Lazarus, 1980 ; Pearlin & Schooler, 1978 ), and the person experiencing the stressors as potential threat is the agent for change and the recipient of the benefits of successful coping (Hobfoll, 1998 ). In addition to problem-focused and emotion-focused coping approaches, social support and resilience may be coping resources. There are many other sources for coping than there is room to present here (see e.g., Cartwright & Cooper, 2005 ); however, the current literature has primarily focused on these resources.
Problem-Focused Coping
Problem-focused or direct coping helps employees remove or reduce stressors in order to reduce their strain experiences (Bhagat et al., 2012 ). In problem-focused coping employees are responsible for working out a strategic plan in order to remove job stressors, such as setting up a set of goals and engaging in behaviors to meet these goals. Problem-focused coping is viewed as an adaptive response, though it can also be maladaptive if it creates more problems down the road, such as procrastinating getting work done or feigning illness to take time off from work. Adaptive problem-focused coping negatively relates to long-term job strains (Higgins & Endler, 1995 ). Discussion on problem-solving coping is framed from an adaptive perspective.
Problem-focused coping is featured as an extension of control, because engaging in problem-focused coping strategies requires a series of acts to keep job stressors under control (Bhagat et al., 2012 ). In the stress literature, there are generally two ways to categorize control: internal versus external locus of control, and primary versus secondary control. Locus of control refers to the extent to which people believe they have control over their own life (Rotter, 1966 ). People high in internal locus of control believe that they can control their own fate whereas people high in external locus of control believe that outside factors determine their life experience (Rotter, 1966 ). Generally, those with an external locus of control are less inclined to engage in problem-focused coping (Strentz & Auerbach, 1988 ). Primary control is the belief that people can directly influence their environment (Alloy & Abramson, 1979 ), and thus they are more likely to engage in problem-focused coping. However, when it is not feasible to exercise primary control, people search for secondary control, with which people try to adapt themselves into the objective environment (Rothbaum, Weisz, & Snyder, 1982 ).
Emotion-Focused Coping
Emotion-focused coping, sometimes referred to as palliative coping, helps employees reduce strains without the removal of job stressors. It involves cognitive or emotional efforts, such as talking about the stressor or distracting oneself from the stressor, in order to lessen emotional distress resulting from job stressors (Bhagat et al., 2012 ). Emotion-focused coping aims to reappraise and modify the perceptions of a situation or seek emotional support from friends or family. These methods do not include efforts to change the work situation or to remove the job stressors (Lazarus & Folkman, 1991 ). People tend to adopt emotion-focused coping strategies when they believe that little or nothing can be done to remove the threatening, harmful, and challenging stressors (Bhagat et al., 2012 ), such as when they are the only individuals to have the skills to get a project done or they are given increased responsibilities because of the unexpected departure of a colleague. Emotion-focused coping strategies include (1) reappraisal of the stressful situation, (2) talking to friends and receiving reassurance from them, (3) focusing on one’s strength rather than weakness, (4) optimistic comparison—comparing one’s situation to others’ or one’s past situation, (5) selective ignoring—paying less attention to the unpleasant aspects of one’s job and being more focused on the positive aspects of the job, (6) restrictive expectations—restricting one’s expectations on job satisfaction but paying more attention to monetary rewards, (7) avoidance coping—not thinking about the problem, leaving the situation, distracting oneself, or using alcohol or drugs (e.g., Billings & Moos, 1981 ).
Some emotion-focused coping strategies are maladaptive. For example, avoidance coping may lead to increased level of job strains in the long run (e.g., Parasuraman & Cleek, 1984 ). Furthermore, a person’s ability to cope with the imbalance of performing work to meet organizational expectations can take a toll on the person’s health, leading to physiological consequences such as cardiovascular disease, sleep disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, and diabetes (Fried et al., 2013 ; Siegrist, 2010 ; Toker, Shirom, Melamed, & Armon, 2012 ; Willert, Thulstrup, Hertz, & Bonde, 2010 ).
Comparing Coping Strategies across Cultures
Most coping research is conducted in individualistic, Western cultures wherein emotional control is emphasized and both problem-solving focused coping and primary control are preferred (Bhagat et al., 2010 ). However, in collectivistic cultures, emotion-focused coping and use of secondary control may be preferred and may not necessarily carry a negative evaluation (Bhagat et al., 2010 ). For example, African Americans are more likely to use emotion-focused coping than non–African Americans (Knight, Silverstein, McCallum, & Fox, 2000 ), and among women who experienced sexual harassment, Anglo American women were less likely to employ emotion focused coping (i.e., avoidance coping) than Turkish women and Hispanic American women, while Hispanic women used more denial than the other two groups (Wasti & Cortina, 2002 ).
Thus, whereas problem-focused coping is venerated in Western societies, emotion-focused coping may be more effective in reducing strains in collectivistic cultures, such as China, Japan, and India (Bhagat et al., 2010 ; Narayanan, Menon, & Spector, 1999 ; Selmer, 2002 ). Indeed, Swedish participants reported more problem-focused coping than did Chinese participants (Xiao, Ottosson, & Carlsson, 2013 ), American college students engaged in more problem-focused coping behaviors than did their Japanese counterparts (Ogawa, 2009 ), and Indian (vs. Canadian) students reported more emotion-focused coping, such as seeking social support and positive reappraisal (Sinha, Willson, & Watson, 2000 ). Moreover, Glazer, Stetz, and Izso ( 2004 ) found that internal locus of control was more predominant in individualistic cultures (United Kingdom and United States), whereas external locus of control was more predominant in communal cultures (Italy and Hungary). Also, internal locus of control was associated with less job stress, but more so for nurses in the United Kingdom and United States than Italy and Hungary. Taken together, adoption of coping strategies and their effectiveness differ significantly across cultures. The extent to which a coping strategy is perceived favorably and thus selected or not selected is not only a function of culture, but also a person’s sociocultural beliefs toward the coping strategy (Morimoto, Shimada, & Ozaki, 2013 ).
Social Support
Social support refers to the aid an entity gives to a person. The source of the support can be a single person, such as a supervisor, coworker, subordinate, family member, friend, or stranger, or an organization as represented by upper-level management representing organizational practices. The type of support can be instrumental or emotional. Instrumental support, including informational support, refers to that which is tangible, such as data to help someone make a decision or colleagues’ sick days so one does not lose vital pay while recovering from illness. Emotional support, including esteem support, refers to the psychological boost given to a person who needs to express emotions and feel empathy from others or to have his or her perspective validated. Beehr and Glazer ( 2001 ) present an overview of the role of social support on the stressor-strain relationship and arguments regarding the role of culture in shaping the utility of different sources and types of support.
Meaningfulness and Resilience
Meaningfulness reflects the extent to which people believe their lives are significant, purposeful, goal-directed, and fulfilling (Glazer, Kożusznik, Meyers, & Ganai, 2014 ). When faced with stressors, people who have a strong sense of meaning in life will also try to make sense of the stressors. Maintaining a positive outlook on life stressors helps to manage emotions, which is helpful in reducing strains, particularly when some stressors cannot be problem-solved (Lazarus & Folkman, 1991 ). Lazarus and Folkman ( 1991 ) emphasize that being able to reframe threatening situations can be just as important in an adaptation as efforts to control the stressors. Having a sense of meaningfulness motivates people to behave in ways that help them overcome stressors. Thus, meaningfulness is often used in the same breath as resilience, because people who are resilient are often protecting that which is meaningful.
Resilience is a personality state that can be fortified and enhanced through varied experiences. People who perceive their lives are meaningful are more likely to find ways to face adversity and are therefore more prone to intensifying their resiliency. When people demonstrate resilience to cope with noxious stressors, their ability to be resilient against other stressors strengthens because through the experience, they develop more competencies (Glazer et al., 2014 ). Thus, fitting with Hobfoll’s ( 1989 , 2001 ) COR theory, meaningfulness and resilience are psychological resources people attempt to conserve and protect, and employ when necessary for making sense of or coping with stressors.
Tertiary Interventions (Stress Management)
Stress management refers to interventions employed to treat and repair harmful repercussions of stressors that were not coped with sufficiently. As Lazarus and Folkman ( 1991 ) noted, not all stressors “are amenable to mastery” (p. 205). Stressors that are unmanageable and lead to strains require interventions to reverse or slow down those effects. Workplace interventions might focus on the person, the organization, or both. Unfortunately, instead of looking at the whole system to include the person and the workplace, most companies focus on the person. Such a focus should not be a surprise given the results of van der Klink, Blonk, Schene, and van Dijk’s ( 2001 ) meta-analysis of 48 experimental studies conducted between 1977 and 1996 . They found that of four types of tertiary interventions, the effect size for cognitive-behavioral interventions and multimodal programs (e.g., the combination of assertive training and time management) was moderate and the effect size for relaxation techniques was small in reducing psychological complaints, but not turnover intention related to work stress. However, the effects of (the five studies that used) organization-focused interventions were not significant. Similarly, Richardson and Rothstein’s ( 2008 ) meta-analytic study, including 36 experimental studies with 55 interventions, showed a larger effect size for cognitive-behavioral interventions than relaxation, organizational, multimodal, or alternative. However, like with van der Klink et al. ( 2001 ), Richardson and Rothstein ( 2008 ) cautioned that there were few organizational intervention studies included and the impact of interventions were determined on the basis of psychological outcomes and not physiological or organizational outcomes. Van der Klink et al. ( 2001 ) further expressed concern that organizational interventions target the workplace and that changes in the individual may take longer to observe than individual interventions aimed directly at the individual.
The long-term benefits of individual focused interventions are not yet clear either. Per Giga, Cooper, and Faragher ( 2003 ), the benefits of person-directed stress management programs will be short-lived if organizational factors to reduce stressors are not addressed too. Indeed, LaMontagne, Keegel, Louie, Ostry, and Landsbergis ( 2007 ), in their meta-analysis of 90 studies on stress management interventions published between 1990 and 2005 , revealed that in relation to interventions targeting organizations only, and interventions targeting individuals only, interventions targeting both organizations and individuals (i.e. the systems approach) had the most favorable positive effects on both the organizations and the individuals. Furthermore, the organization-level interventions were effective at both the individual and organization levels, but the individual-level interventions were effective only at the individual level.
Individual-Focused Stress Management
Individual-focused interventions concentrate on improving conditions for the individual, though counseling programs emphasize that the worker is in charge of reducing “stress,” whereas role-focused interventions emphasize activities that organizations can guide to actually reduce unnecessary noxious environmental factors.
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Employee Assistance Programs
When stress become sufficiently problematic (which is individually gauged or attended to by supportive others) in a worker’s life, employees may utilize the short-term counseling services or referral services Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) provide. People who utilize the counseling services may engage in cognitive behavioral therapy aimed at changing the way people think about the stressors (e.g., as challenge opportunity over threat) and manage strains. Example topics that may be covered in these therapy sessions include time management and goal setting (prioritization), career planning and development, cognitive restructuring and mindfulness, relaxation, and anger management. In a study of healthcare workers and teachers who participated in a 2-day to 2.5-day comprehensive stress management training program (including 26 topics on identifying, coping with, and managing stressors and strains), Siu, Cooper, and Phillips ( 2013 ) found psychological and physical improvements were self-reported among the healthcare workers (for which there was no control group). However, comparing an intervention group of teachers to a control group of teachers, the extent of change was not as visible, though teachers in the intervention group engaged in more mastery recovery experiences (i.e., they purposefully chose to engage in challenging activities after work).
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Mindfulness
A popular therapy today is to train people to be more mindful, which involves helping people live in the present, reduce negative judgement of current and past experiences, and practicing patience (Birnie, Speca, & Carlson, 2010 ). Mindfulness programs usually include training on relaxation exercises, gentle yoga, and awareness of the body’s senses. In one study offered through the continuing education program at a Canadian university, 104 study participants took part in an 8-week, 90 minute per group (15–20 participants per) session mindfulness program (Birnie et al., 2010 ). In addition to body scanning, they also listened to lectures on incorporating mindfulness into one’s daily life and received a take-home booklet and compact discs that guided participants through the exercises studied in person. Two weeks after completing the program, participants’ mindfulness attendance and general positive moods increased, while physical, psychological, and behavioral strains decreased. In another study on a sample of U.K. government employees, study participants receiving three sessions of 2.5 to 3 hours each training on mindfulness, with the first two sessions occurring in consecutive weeks and the third occurring about three months later, Flaxman and Bond ( 2010 ) found that compared to the control group, the intervention group showed a decrease in distress levels from Time 1 (baseline) to Time 2 (three months after first two training sessions) and Time 1 to Time 3 (after final training session). Moreover, of the mindfulness intervention study participants who were clinically distressed, 69% experienced clinical improvement in their psychological health.
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Biofeedback/Imagery/Meditation/Deep Breathing
Biofeedback uses electronic equipment to inform users about how their body is responding to tension. With guidance from a therapist, individuals then learn to change their physiological responses so that their pulse normalizes and muscles relax (Norris, Fahrion, & Oikawa, 2007 ). The therapist’s guidance might include reminders for imagery, meditation, body scan relaxation, and deep breathing. Saunders, Driskell, Johnston, and Salas’s ( 1996 ) meta-analysis of 37 studies found that imagery helped reduce state and performance anxiety. Once people have been trained to relax, reminder triggers may be sent through smartphone push notifications (Villani et al., 2013 ).
Smartphone technology can also be used to support weight loss programs, smoking cessation programs, and medication or disease (e.g., diabetes) management compliance (Heron & Smyth, 2010 ; Kannampallil, Waicekauskas, Morrow, Kopren, & Fu, 2013 ). For example, smartphones could remind a person to take medications or test blood sugar levels or send messages about healthy behaviors and positive affirmations.
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Sleep/Rest/Respite
Workers today sleep less per night than adults did nearly 30 years ago (Luckhaupt, Tak, & Calvert, 2010 ; National Sleep Foundation, 2005 , 2013 ). In order to combat problems, such as increased anxiety and cardiovascular artery disease, associated with sleep deprivation and insufficient rest, it is imperative that people disconnect from their work at least one day per week or preferably for several weeks so that they are able to restore psychological health (Etzion, Eden, & Lapidot, 1998 ; Ragsdale, Beehr, Grebner, & Han, 2011 ). When college students engaged in relaxation-type activities, such as reading or watching television, over the weekend, they experienced less emotional exhaustion and greater general well-being than students who engaged in resources-consuming activities, such as house cleaning (Ragsdale et al., 2011 ). Additional research and future directions for research are reviewed and identified in the work of Sonnentag ( 2012 ). For example, she asks whether lack of ability to detach from work is problematic for people who find their work meaningful. In other words, are negative health consequences only among those who do not take pleasure in their work? Sonnetag also asks how teleworkers detach from their work when engaging in work from the home. Ironically, one of the ways that companies are trying to help with the challenges of high workload or increased need to be available to colleagues, clients, or vendors around the globe is by offering flexible work arrangements, whereby employees who can work from home are given the opportunity to do so. Companies that require global interactions 24-hours per day often employ this strategy, but is the solution also a source of strain (Glazer, Kożusznik, & Shargo, 2012 )?
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Role Analysis
Role analysis or role clarification aims to redefine, expressly identify, and align employees’ roles and responsibilities with their work goals. Through role negotiation, involved parties begin to develop a new formal or informal contract about expectations and define resources needed to fulfill those expectations. Glazer has used this approach in organizational consulting and, with one memorable client engagement, found that not only were the individuals whose roles required deeper re-evaluation happier at work (six months later), but so were their subordinates. Subordinates who once characterized the two partners as hostile and akin to a couple going through a bad divorce, later referred to them as a blissful pair. Schaubroeck, Ganster, Sime, and Ditman ( 1993 ) also found in a three-wave study over a two-year period that university employees’ reports of role clarity and greater satisfaction with their supervisor increased after a role clarification exercise of top managers’ roles and subordinates’ roles. However, the intervention did not have any impact on reported physical symptoms, absenteeism, or psychological well-being. Role analysis is categorized under individual-focused stress management intervention because it is usually implemented after individuals or teams begin to demonstrate poor performance and because the intervention typically focuses on a few individuals rather than an entire organization or group. In other words, the intervention treats the person’s symptoms by redefining the role so as to eliminate the stimulant causing the problem.
Organization-Focused Stress Management
At the organizational level, companies that face major declines in productivity and profitability or increased costs related to healthcare and disability might be motivated to reassess organizational factors that might be impinging on employees’ health and well-being. After all, without healthy workers, it is not possible to have a healthy organization. Companies may choose to implement practices and policies that are expected to help not only the employees, but also the organization with reduced costs associated with employee ill-health, such as medical insurance, disability payments, and unused office space. Example practices and policies that may be implemented include flexible work arrangements to ensure that employees are not on the streets in the middle of the night for work that can be done from anywhere (such as the home), diversity programs to reduce stress-induced animosity and prejudice toward others, providing only healthy food choices in cafeterias, mandating that all employees have physicals in order to receive reduced prices for insurance, company-wide closures or mandatory paid time off, and changes in organizational visioning.
Organization-Focused Stress Management: Organizational-Level Occupational Health Interventions
As with job design interventions that are implemented to remediate work characteristics that were a source of unnecessary or excessive stressors, so are organizational-level occupational health (OLOH) interventions. As with many of the interventions, its placement as a primary or tertiary stress management intervention may seem arbitrary, but when considering the goal and target of change, it is clear that the intervention is implemented in response to some ailing organizational issues that need to be reversed or stopped, and because it brings in the entire organization’s workforce to address the problems, it has been placed in this category. There are several more case studies than empirical studies on the topic of whole system organizational change efforts (see example case studies presented by the United Kingdom’s Health and Safety Executive). It is possible that lack of published empirical work is not so much due to lack of attempting to gather and evaluate the data for publication, but rather because the OLOH interventions themselves never made it to the intervention stage, the interventions failed (Biron, Gatrell, & Cooper, 2010 ), or the level of evaluation was not rigorous enough to get into empirical peer-review journals. Fortunately, case studies provide some indication of the opportunities and problems associated with OLOH interventions.
One case study regarding Cardiff and Value University Health Board revealed that through focus group meetings with members of a steering group (including high-level managers and supported by top management) and facilitated by a neutral, non-judgemental organizational health consultant, ideas for change were posted on newsprint, discussed, and areas in the organization needing change were identified. The intervention for giving voice to people who initially had little already had a positive effect on the organization, as absence decreased by 2.09% and 6.9% merely 12 and 18 months, respectively, after the intervention. Translated in financial terms, the 6.9% change was equivalent to a quarterly savings of £80,000 (Health & Safety Executive, n.d. ). Thus, focusing on the context of change and how people will be involved in the change process probably helped the organization realize improvements (Biron et al., 2010 ). In a recent and rare empirical study, employing both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods, Sørensen and Holman ( 2014 ) utilized PAR in order to plan and implement an OLOH intervention over the course of 14 months. Their study aimed to examine the effectiveness of the PAR process in reducing workers’ work-related and social or interpersonal-related stressors that derive from the workplace and improving psychological, behavioral, and physiological well-being across six Danish organizations. Based on group dialogue, 30 proposals for change were proposed, all of which could be categorized as either interventions to focus on relational factors (e.g., management feedback improvement, engagement) or work processes (e.g., reduced interruptions, workload, reinforcing creativity). Of the interventions that were implemented, results showed improvements on manager relationship quality and reduced burnout, but no changes with respect to work processes (i.e., workload and work pace) perhaps because the employees already had sufficient task control and variety. These findings support Dewe and Kompier’s ( 2008 ) position that occupational health can be reinforced through organizational policies that reinforce quality jobs and work experiences.
Organization-Focused Stress Management: Flexible Work Arrangements
Dewe and Kompier ( 2008 ), citing the work of Isles ( 2005 ), noted that concern over losing one’s job is a reason for why 40% of survey respondents indicated they work more hours than formally required. In an attempt to create balance and perceived fairness in one’s compensation for putting in extra work hours, employees will sometimes be legitimately or illegitimately absent. As companies become increasingly global, many people with desk jobs are finding themselves communicating with colleagues who are halfway around the globe and at all hours of the day or night (Glazer et al., 2012 ). To help minimize the strains associated with these stressors, companies might devise flexible work arrangements (FWA), though the type of FWA needs to be tailored to the cultural environment (Masuda et al., 2012 ). FWAs give employees some leverage to decide what would be the optimal work arrangement for them (e.g., part-time, flexible work hours, compressed work week, telecommuting). In other words, FWA provides employees with the choice of when to work, where to work (on-site or off-site), and how many hours to work in a day, week, or pay period (Kossek, Thompson, & Lautsch, 2015 ). However, not all employees of an organization have equal access to or equitable use of FWAs; workers in low-wage, hourly jobs are often beholden to being physically present during specific hours (Swanberg McKechnie, Ojha, & James, 2011 ). In a study of over 1,300 full-time hourly retail employees in the United States, Swanberg et al. ( 2011 ) showed that employees who have control over their work schedules and over their work hours were satisfied with their work schedules, perceived support from the supervisor, and work engagement.
Unfortunately, not all FWAs yield successful results for the individual or the organization. Being able to work from home or part-time can have problems too, as a person finds himself or herself working more hours from home than required. Sometimes telecommuting creates work-family conflict too as a person struggles to balance work and family obligations while working from home. Other drawbacks include reduced face-to-face contact between work colleagues and stakeholders, challenges shaping one’s career growth due to limited contact, perceived inequity if some have more flexibility than others, and ambiguity about work role processes for interacting with employees utilizing the FWA (Kossek et al., 2015 ). Organizations that institute FWAs must carefully weigh the benefits and drawbacks the flexibility may have on the employees using it or the employees affected by others using it, as well as the implications on the organization, including the vendors who are serving and clients served by the organization.
Organization-Focused Stress Management: Diversity Programs
Employees in the workplace might experience strain due to feelings of discrimination or prejudice. Organizational climates that do not promote diversity (in terms of age, religion, physical abilities, ethnicity, nationality, sex, and other characteristics) are breeding grounds for undesirable attitudes toward the workplace, lower performance, and greater turnover intention (Bergman, Palmieri, Drasgow, & Ormerod, 2012 ; Velez, Moradi, & Brewster, 2013 ). Management is thus advised to implement programs that reinforce the value and importance of diversity, as well as manage diversity to reduce conflict and feelings of prejudice. In fact, managers who attended a leadership training program reported higher multicultural competence in dealing with stressful situations (Chrobot-Mason & Leslie, 2012 ), and managers who persevered through challenges were more dedicated to coping with difficult diversity issues (Cilliers, 2011 ). Thus, diversity programs can help to reduce strains by directly reducing stressors associated with conflict linked to diversity in the workplace and by building managers’ resilience.
Organization-Focused Stress Management: Healthcare Management Policies
Over the past few years, organizations have adopted insurance plans that implement wellness programs for the sake of managing the increasing cost of healthcare that is believed to be a result of individuals’ not managing their own health, with regular check-ups and treatment. The wellness programs require all insured employees to visit a primary care provider, complete a health risk assessment, and engage in disease management activities as specified by a physician (e.g., see frequently asked questions regarding the State of Maryland’s Wellness Program). Companies believe that requiring compliance will reduce health problems, although there is no proof that such programs save money or that people would comply. One study that does, however, boast success, was a 12-week workplace health promotion program aimed at reducing Houston airport workers’ weight (Ebunlomo, Hare-Everline, Weber, & Rich, 2015 ). The program, which included 235 volunteer participants, was deemed a success, as there was a total weight loss of 345 pounds (or 1.5 lbs per person). Given such results in Houston, it is clear why some people are also skeptical over the likely success of wellness programs, particularly as there is no clear method for evaluating their efficacy (Sinnott & Vatz, 2015 ).
Moreover, for some, such a program is too paternalistic and intrusive, as well as punishes anyone who chooses not to actively participate in disease management programs (Sinnott & Vatz, 2015 ). The programs put the onus of change on the person, though it is a response to the high costs of ill-health. The programs neglect to consider the role of the organization in reducing the barriers to healthy lifestyle, such as cloaking exempt employment as simply needing to get the work done, when it usually means working significantly more hours than a standard workweek. In fact, workplace health promotion programs did not reduce presenteeism (i.e., people going to work while unwell thereby reducing their job performance) among those who suffered from physical pain (Cancelliere, Cassidy, Ammendolia, & Côte, 2011 ). However, supervisor education, worksite exercise, lifestyle intervention through email, midday respite from repetitive work, a global stress management program, changes in lighting, and telephone interventions helped to reduce presenteeism. Thus, emphasis needs to be placed on psychosocial aspects of the organization’s structure, including managers and overall organizational climate for on-site presence, that reinforces such behavior (Cancelliere et al., 2011 ). Moreover, wellness programs are only as good as the interventions to reduce work-related stressors and improve organizational resources to enable workers to improve their overall psychological and physical health.
Concluding Remarks
Future research.
One of the areas requiring more theoretical and practical attention is that of the utility of stress frameworks to guide organizational development change interventions. Although it has been proposed that the foundation for work stress management interventions is in organizational development, and even though scholars and practitioners of organization development were also founders of research programs that focused on employee health and well-being or work stress, there are few studies or other theoretical works that link the two bodies of literature.
A second area that requires additional attention is the efficacy of stress management interventions across cultures. In examining secondary stress management interventions (i.e., coping), some cross-cultural differences in findings were described; however, there is still a dearth of literature from different countries on the utility of different prevention, coping, and stress management strategies.
A third area that has been blossoming since the start of the 21st century is the topic of hindrance and challenge stressors and the implications of both on workers’ well-being and performance. More research is needed on this topic in several areas. First, there is little consistency by which researchers label a stressor as a hindrance or a challenge. Researchers sometimes take liberties with labels, but it is not the researchers who should label a stressor but the study participants themselves who should indicate if a stressor is a source of strain. Rodríguez, Kozusznik, and Peiró ( 2013 ) developed a measure in which respondents indicate whether a stressor is a challenge or a hindrance. Just as some people may perceive demands to be challenges that they savor and that result in a psychological state of eustress (Nelson & Simmons, 2003 ), others find them to be constraints that impede goal fulfillment and thus might experience distress. Likewise, some people might perceive ambiguity as a challenge that can be overcome and others as a constraint over which he or she has little control and few or no resources with which to cope. More research on validating the measurement of challenge vs. hindrance stressors, as well as eustress vs. distress, and savoring vs. coping, is warranted. Second, at what point are challenge stressors harmful? Just because people experiencing challenge stressors continue to perform well, it does not necessarily mean that they are healthy people. A great deal of stressors are intellectually stimulating, but excessive stimulation can also take a toll on one’s physiological well-being, as evident by the droves of professionals experiencing different kinds of diseases not experienced as much a few decades ago, such as obesity (Fried et al., 2013 ). Third, which stress management interventions would better serve to reduce hindrance stressors or to reduce strain that may result from challenge stressors while reinforcing engagement-producing challenge stressors?
A fourth area that requires additional attention is that of the flexible work arrangements (FWAs). One of the reasons companies have been willing to permit employees to work from home is not so much out of concern for the employee, but out of the company’s need for the focal person to be able to communicate with a colleague working from a geographic region when it is night or early morning for the focal person. Glazer, Kożusznik, and Shargo ( 2012 ) presented several areas for future research on this topic, noting that by participating on global virtual teams, workers face additional stressors, even while given flexibility of workplace and work time. As noted earlier, more research needs to be done on the extent to which people who take advantage of FWAs are advantaged in terms of detachment from work. Can people working from home detach? Are those who find their work invigorating also likely to experience ill-health by not detaching from work?
A fifth area worthy of further research attention is workplace wellness programing. According to Page and Vella-Brodrick ( 2009 ), “subjective and psychological well-being [are] key criteria for employee mental health” (p. 442), whereby mental health focuses on wellness, rather than the absence of illness. They assert that by fostering employee mental health, organizations are supporting performance and retention. Employee well-being can be supported by ensuring that jobs are interesting and meaningful, goals are achievable, employees have control over their work, and skills are used to support organizational and individual goals (Dewe & Kompier, 2008 ). However, just as mental health is not the absence of illness, work stress is not indicative of an absence of psychological well-being. Given the perspective that employee well-being is a state of mind (Page & Vella-Brodrick, 2009 ), we suggest that employee well-being can be negatively affected by noxious job stressors that cannot be remediated, but when job stressors are preventable, employee well-being can serve to protect an employee who faces job stressors. Thus, wellness programs ought to focus on providing positive experiences by enhancing and promoting health, as well as building individual resources. These programs are termed “green cape” interventions (Pawelski, 2016 ). For example, with the growing interests in positive psychology, researchers and practitioners have suggested employing several positive psychology interventions, such as expressing gratitude, savoring experiences, and identifying one’s strengths (Tetrick & Winslow, 2015 ). Another stream of positive psychology is psychological capital, which includes four malleable functions of self-efficacy, optimism, hope, and resilience (Luthans, Youssef, & Avolio, 2007 ). Workplace interventions should include both “red cape” interventions (i.e., interventions to reduce negative experiences) and “green cape” interventions (i.e., workplace wellness programs; Polly, 2014 ).
A Healthy Organization’s Pledge
A healthy workplace requires healthy workers. Period. Among all organizations’ missions should be the focus on a healthy workforce. To maintain a healthy workforce, the company must routinely examine its own contributions in terms of how it structures itself; reinforces communications among employees, vendors, and clients; how it rewards and cares for its people (e.g., ensuring they get sufficient rest and can detach from work); and the extent to which people at the upper levels are truly connected with the people at the lower levels. As a matter of practice, management must recognize when employees are overworked, unwell, and poorly engaged. Management must also take stock of when it is doing well and right by its contributors’ and maintain and reinforce the good practices, norms, and procedures. People in the workplace make the rules; people in the workplace can change the rules. How management sees its employees and values their contribution will have a huge role in how a company takes stock of its own pain points. Providing employees with tools to manage their own reactions to work-related stressors and consequent strains is fine, but wouldn’t it be grand if organizations took better notice about what they could do to mitigate the strain-producing stressors in the first place and take ownership over how employees are treated?
- Abramis, D. J. (1994). Work role ambiguity, job satisfaction, and job performance: Meta-analyses and review. Psychological Report, 75 , 1411–1433.
- Adams, G. A. , & Jex, S. M. (1999). Relationships between time management, control, work–family conflict, and strain. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 1 , 72–77.
- Alloy, L. B. , & Abramson, L. Y. (1979). Judgment of contingency in depressed and nondepressed students: Sadder but wiser? Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 108 , 441–483.
- Amstad, F. T. , Meier, L. L. , Fasel, U. , Elfering, A. , & Semmer, N. K. (2011). A meta-analysis of work-family conflict and various outcomes with a special emphasis on cross-domain versus matching-domain relations. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 16 , 151–169.
- Assouline, M. , & Meir, E. I. (1987). Meta-analysis of the relationship between congruence and well-being measures. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 31 , 319–332.
- Aust, B. , & Ducki, A. (2004). Comprehensive health promotion interventions at the workplace: Experiences with health circles in Germany. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 9 , 258–270.
- Bakker, A. B. Demerouti, E. , Sanz-Vergel, A. I. (2014). Burnout and work engagement: The JD-R approach. Annual Review of Organizational Behavior, 1 , 389–411.
- Bakker, A. B. , van Veldhoven, M. J. P. M. , & Xanthopoulou, D. (2010). Beyond the demand-control model: Thriving on high job demands and resources. Journal of Personnel Psychology, 9 , 3–16.
- Beehr, T. A. , Glaser, K. M. , Canali, K. G. , & Wallwey, D. A. (2001). Back to basics: Re-examination of demand control theory of occupational stress. Work & Stress, 15 , 115–130.
- Beehr, T. A. , & Glazer, S. (2001). A cultural perspective of social support in relation to occupational stress. In P. Perrewé , D. C. Ganster , & J. Moran (Eds.), Research in occupational stress and well-being (pp. 97–142). Amsterdam: JAI Press.
- Bergman, M. E. , Palmieri, P. A. , Drasgow, F. , & Ormerod, A. J. (2012). Racial/ethnic harassment and discrimination, its antecedents, and its effect on job-related outcomes. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 17 , 65–78.
- Bhagat, R. S. , Krishnan, B. , Nelson, T. A. , Leonard, K. M. , Ford, D. J. , & Billing, T. K. (2010). Organizational stress, psychological strain, and work outcomes in six national contexts: A closer look at the moderating influences of coping styles and decision latitude . Cross Cultural Management, 17 , 10–29.
- Bhagat, R. S. , O’Driscoll, M. P. , Babakus, E. , Frey, L. , Chokkar, J. , Ninokumar, B. H , et al. (1994). Organizational stress and coping in seven national contexts: A cross-cultural investigation . In G. P. Keita & J. J. Hurrell (Eds.), Job stress in a changing workforce: Investigating gender, diversity, and family issues (pp. 93–105). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Bhagat, R. S. , Segovis, J. C. , & Nelson, T. A. (2012). Work stress and coping in the era of globalization . New York: Routledge.
- Billings, A. G. , & Moos, R. H. (1981). The role of coping responses and social resources in attenuating the stress of life events. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 4 , 139–157.
- Birnie, K. , Speca, M. , & Carlson, L. E. (2010). Exploring self-compassion and empathy in the context of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). Stress & Health, 26 , 359–371.
- Biron, C. , Gatrell, C. , & Cooper, C. L. (2010). Autopsy of a failure: Evaluating process and contextual issues in an organizational-level work stress intervention. International Journal of Stress Management, 17 , 135–158.
- Bowling, N. A. , & Kirkendall, C. (2012). Workload: A review of causes, consequences, and potential interventions. In J. Houdmont , S. Leka , & R. Sinclair (Eds.), Contemporary occupational health psychology (Vol. 2) (pp. 221–238). Chichester, U.K.: Wiley.
- Breaugh, J. A. , & Colihan, J. P. (1994). Measuring facets of job ambiguity: Construct validity evidence. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79 , 191–202.
- Bruk-Lee, V. , & Spector, P. E. (2006). The social stressors-counterproductive work behaviors link: Are conflicts with supervisors and coworkers the same? . Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 11 , 145–156.
- Cancelliere, C. , Cassidy, J. D. , Ammendolia, C. , & Côte, P. (2011). Are workplace health promotion programs effective at improving presenteeism in workers? A systematic review and best evidence synthesis of the literature. BMC Public Health, 11 , 395–406.
- Caplan, R. D. (1987). Person–environment fit in organizations: Theories, facts, and values. In A. W. Riley & S. J. Zaccaro (Eds.), Occupational stress and organizational effectiveness (pp. 103–140). New York: Praeger.
- Cartwright, S. , & Cooper, C. L. (2005). Individually targeted interventions. In J. Barling , E. K. Kelloway , & M. R. Frone (Eds.), Handbook of work stress (pp. 607–622). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Cavanaugh, M. A. , Boswell, W. R. , Roehling, M. V. , & Boudreau, J. W. (2000). An empirical examination of self-reported work stress among U.S. managers . Journal of Applied Psychology, 85 , 65–74.
- Chong, D. S. F. , van Eerde, W. , Rutte, C. G. , & Chai, K. H. (2012). Bringing employees closer: The effect of proximity on communication when teams function under time pressure. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 29 , 205–215.
- Chrobot-Mason, D. , & Leslie, J. B. (2012). The role of multicultural competence and emotional intelligence in managing diversity. Psychologist-Manager Journal, 15 , 219–236.
- Cilliers, F. (2011). Individual diversity management and salutogenic functioning. International Review of Psychiatry, 23 , 501–507.
- Claessens, B. C. , Van Eerde, W. , Rutte, C. G. , & Roe, R. A. (2004). Planning behavior and perceived control of time at work . Journal of Organizational Behavior, 25 , 937–950.
- Cooper, C. L. , Dewe, P. D. , & O’Driscoll, M. P. (2011). Employee assistance programs: Strengths, challenges, and future roles. In J. C. Quick , L. E. Tetrick , J. C. Quick , L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of occupational health psychology (2d ed.) (pp. 337–356). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Cooper, C. L. , Dewe, P. J. , & O’Driscoll, M. P. (2001). Organizational stress: A review and critique of theory, research, and applications . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Coovert, M. D. & Thompson, L. F. (2003). Technology and workplace health. In J. C. Quick & L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of occupational health psychology (pp. 221–241). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Dawson, K. M. , O’Brien, K. E. , & Beehr, T. A. (2016). The role of hindrance stressors in the job demand-control-support model of occupational stress: A proposed theory revision . Journal of Organizational Behavior, 37 (3), 397–415.
- Dewe, P. , & Kompier, M. (2008). Foresight mental capital and wellbeing project: Wellbeing and work: Future challenges . London: The Government Office for Science.
- Dopkeen, J. C. , & DuBois, R. (2014). Stress in the workplace: A policy synthesis on its dimensions and prevalence . White paper. University of Illinois Chicago, Center for Employee Health Studies, School of Public Health.
- Dwyer, D. J. , & Ganster, D. C. (1991). The effects of job demands and control on employee attendance and satisfaction. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 12 , 595–608.
- Ebunlomo, E. O. , Hare-Everline, N. , Weber, A. , & Rich, J. (2015). Development of a comprehensive 12-week health promotion program for Houston Airport System. Texas Public Health Journal, 67 (1), 11–13.
- Edwards, J. R. (2008). Person-environment fit in organizations: An assessment of theoretical progress. The Academy of Management Annals, 2 , 167–230.
- Etzion, D. , Eden, D. , & Lapidot, Y. (1998). Relief from job stressors and burnout: Reserve service as a respite. Journal of Applied Psychology, 83 , 577–585.
- Firth-Cozens, J. (2003). Doctors, their wellbeing, and their stress: It’s time to be proactive about stress—and prevent it. British Medical Journal, 326 , 670–671.
- Flaxman, P. E. , & Bond, F. W. (2010). Worksite stress management training: Moderated effects and clinical significance. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 15 , 347–358.
- Folkman, S. , & Lazarus, R. S. (1980). An analysis of coping in a middle-aged community sample . Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 21 , 219–239.
- French, J. R. P., Jr. , & Caplan, R. D. (1972). Organizational stress and individual strain. In A. Marrow (Ed.), The failure of success . New York: AMACOM.
- French, J. R. P., Jr. , & Kahn, R. L. (1962). A programmatic approach to studying the industrial environment and mental health. Journal of Social Issues, 18 , 1–48.
- French, S. (2015, May 27). PCS workload and work-life balance survey 2013 . London: Public and Commercial Services Union.
- Fried, Y. , Laurence, G. A. , Shirom, A. , Melamed, S. , Toker, S. , Berliner, S. , & Shapira, I. (2013). The relationship between job enrichment and abdominal obesity: A longitudinal field study of apparently healthy individuals. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 18 , 458–468.
- Frone, M. R. (2000). Interpersonal conflict at work and psychological outcomes: Testing a model among young workers. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 5 , 246–255.
- Giga, S. I. , Cooper, C. L. , & Faragher, B. (2003). The development of a framework for a comprehensive approach to stress management interventions at work. International Journal of Stress Management, 10 , 280–296.
- Glazer, S. (2008). Cross-cultural issues in stress and burnout. In J. R. B. Halbesleben (Ed.), Handbook of Stress and Burnout in Health Care (pp. 79–93). Huntington, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
- Glazer, S. , & Beehr, T. A. (2005). Consistency of the implications of three role stressors across four countries. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 26 , 467–487.
- Glazer, S. , Kożusznik, M. W. , Meyers, J. H. , & Ganai, O. (2014). Cultural implications of meaningfulness as a resource to mitigate work stress. In S. Leka & R. Sinclair (Eds.), Contemporary occupational health psychology: Global perspectives on research and practice (Vol. 3) (pp. 114–130). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
- Glazer, S. , Kożusznik, M. W. , & Shargo, I. A. (2012). Global virtual teams: A cure for- or a cause of- stress. In P. L. Perrewé , J. Halbesleben , & C. Rosen (Eds.), Research in occupational stress and well being: The role of the economic context on occupational stress and well being (Vol. 10, pp. 213–266). Bingley, U.K.: Emerald.
- Glazer, S. , Stetz, T. A. , & Izso, L. (2004). Effects of personality on subjective job stress: A cultural analysis. Personality and Individual Differences, 37 , 645–658.
- Greenhaus, J. H. , & Beutell, N. J. (1985). Sources of conflict between work and family roles. Academy of Management Review, 10 , 76–88.
- Hackman, J. R. , & Oldham, G. R. (1980). Work Redesign . Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- Hauke, A. , Flintrop, J. , Brun, E. , & Rugulies, R. (2011). The impact of work-related psychosocial stressors on the onset of musculoskeletal disorders in specific body regions: A review and meta-analysis of 54 longitudinal studies . Work & Stress, 25 , 243–256.
- Health & Safety Executive (n.d.). Cardiff and Value University Health Board—A stress case study .
- Heron, K. E. , & Smyth, J. M. (2010). Ecological momentary interventions: Incorporating mobile technology into psychosocial and health behaviour treatments. British Journal of Health Psychology, 15 , 1–39.
- Hershcovis, M. (2011). “Incivility, social undermining, bullying … oh my!”: A call to reconcile constructs within workplace aggression research . Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32 , 499–519.
- Higgins, J. E. , & Endler, N. S. (1995). Coping, life stress, and psychological and somatic distress . European Journal of Personality, 9 , 253–270.
- Hobfoll, S. E. (1989). Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist, 44 , 513–524.
- Hobfoll, S. E. (1998). Stress, culture, and community: The psychology and philosophy of stress . New York: Plenum Press.
- Hobfoll, S. E. (2001). The influence of culture, community, and the nested-self in the stress process: Advancing Conservation of Resources Theory. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 50 , 337–421.
- International Labor Organization (2012, July 5). Why stress at work matters . International Labor Organization.
- International Labor Organization (n.d.). Psychosocial risks and work-related stress . International Labor Organization.
- Jackson, S. E. , & Schuler, R. S. (1985). A meta-analysis and conceptual critique of research on role ambiguity and role conflict in work settings. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 36 , 16–78.
- Jayson, S. (2012, January 11). Yeah, we’re stressed but dealing with it; Americans report a decrease in stress for the first time in five years, maybe because it’s just the new normal . USA Today .
- Jex, S. M. , & Beehr, T. A. (1991). Emerging theoretical and methodological issues in the study of work-related stress. Research in Personnel and Human Resources Management, 9 , 311–365.
- Jex, S. M. , & Elaqua, T. C. (1999). Time management as a moderator of relations between stressors and employee strain. Work & Stress, 13 , 182–191.
- Johnson, J. V. , & Hall, E. M. (1988). Job strain, workplace social support, and cardiovascular disease: A cross-sectional study of a random sample of the Swedish working population. American Journal of Public Health, 78 , 1336–1342.
- Kahn, R. L. , Wolfe, D. M. , Quinn, R. P. , Snoek, J. D. , & Rosenthal, R. A. (1964). Organizational stress: Studies in role conflict and ambiguity . New York: Wiley.
- Kannampallil, T. G. , Waicekauskas, K. , Morrow, D. G. , Kopren, K. M. , & Fu, W. (2013). External tools for collaborative medication scheduling. Cognition, Technology & Work, 15 , 121–131.
- Karasek, R. A. (1979). Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: Implications for job redesign. Administrative Science Quarterly , 24 , 285–308.
- Karasek, R. A. , & Theorell, T. (1990). Healthy work: Stress, productivity, and the reconstruction of working life . New York: Basic Books.
- van der Klink, J. J. L. , Blonk, R. W. B. , Schene, A. H. , & van Dijk, F. J. H. (2001). The benefits of interventions for work-related stress. American Journal of Public Health, 91 , 270–276.
- Knight, B. G. , Silverstein, M. , McCallum, T. J. , & Fox, L. S. (2000). A sociocultural stress and coping model for mental health outcomes among African American caregivers in southern California . The Journals of Gerontology: Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 55B , 142–150.
- Kossek, E. E. , Thompson, R. J. , Lautsch, B. A. (2015). Balanced workplace flexibility: Avoiding the traps. California Management Review, 57 , 5–25.
- Kożusznik, M. , Rodriguez, I. , & Peiró, J. M. (2012). Cross-national outcomes of stress appraisal. Cross Cultural Management, 19 , 507–525.
- Kożusznik, M. , Rodriguez, I. , & Peiró, J. M. (2015). Eustress and distress climates in teams: Patterns and outcomes. International Journal of Stress Management, 22 , 1–23.
- Kristof-Brown, A. L. , Zimmerman, R. D. , & Johnson, E. C. (2005). Consequences of individuals’ fit at work: A meta-analysis of person-job, person-organization, person-group, and person-supervisor fit. Personnel Psychology, 58 , 281–342.
- LaMontagne, A. D. , Keegel, T. , Louie, A. M. , Ostry, A. , & Landsbergis, P. A. (2007). A systematic review of the job-stress intervention evaluation literature, 1990–2005. International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Health, 13 , 268–280.
- LaRocco, J. M. , Tetrick, L. E. , & Meder, D. (1989). Differences in perceptions of work environment conditions, job attitudes, and health beliefs among military physicians, dentists, and nurses. Military Psychology, 1 , 135–151.
- Lazarus, R. S. , & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, appraisal, and coping . New York: Springer.
- Lazarus, R. S. , & Folkman, S. (1991). The concept of coping. In A. Monat & R. S. Lazarus (Eds.), Stress and coping: An anthology (3d ed.) (pp. 189–206). New York: Columbia University Press.
- LePine, J. A. , Podsakoff, N. P. , & LePine, M. A. (2005). A meta-analytic test of the challenge stressor-hindrance stressor framework: An explanation for inconsistent relationships among stressors and performance. Academy of Management Journal, 48 , 764–775.
- Lewin, K. (1936). Principles of topological psychology . New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Lewin K. (1951). Field theory in social science . New York: Harper and Row.
- Lewin, K. (1997). Resolving social conflicts & Field theory in social science . Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. Previously published in 1948 and 1951.
- Lin, B. C. , Kain, J. M. , & Fritz, C. (2013). Don’t interrupt me! An examination of the relationship between intrusions at work and employee strain. International Journal of Stress Management, 20 , 77–94.
- Liu, C. , & Li, H. (2017) Stressor and stressor appraisals: The moderating effect of task efficacy . Journal of Business and Psychology , 1–14.
- Liu, C. , Liu, Y. , Spector, P. E. , Shi, L. (2011). The interaction of job autonomy and conflict with supervisor in China and the United States: A qualitative and quantitative comparison. International Journal of Stress Management, 18 , 222–245.
- Liu, C. , Spector, P. E. , & Shi, L. (2007). Cross-national job stress: A quantitative and qualitative study. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 28 , 209–239.
- Luckhaupt, S. E. , Tak, S. , Calvert, G. M. (2010). The prevalence of short sleep duration by industry and occupational in the National Health Interview Survey. Sleep, 33 , 149–159.
- Luthans, F. , Youssef, C. M. , & Avolio, B. J. (2007). Psychological capital: Developing the human competitive edge . New York: Oxford University Press.
- Macan, T. H. (1994). Time management: Test of a process model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79 , 381–391.
- Macan, T. H. , Shahani, C. , Dipboye, R. L. , & Philips, A. P. (1990). College students’ time management: Correlations with academic performance and stress. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82 , 760–768.
- Masuda, A. D. , Poelmans, S. A. Y. , Allen, T. D. , Spector, P. E. , Lapierre, L. M. , Cooper, C. L. , et al. (2012). Flexible work arrangements availability and their relationship with work-to-family conflict, job satisfaction, and turnover intentions: A comparison of three country clusters. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 61 , 1–29.
- McMahon, M. (2007). Think you might be addicted to email? You’re not alone . AOL.
- Monat, A. , & Lazarus, R. S. (Eds.). (1991). Stress and coping: An anthology (3d ed.). New York: Columbia University Press.
- Morimoto, H. , Shimada, H. , & Ozaki, K. (2013). Does stressor evaluation mediate sociocultural influence on coping selection? An investigation using Japanese employees. International Journal of Stress Management, 20 , 1–19.
- Narayanan, L. , Menon, S. , & Spector, P. E. (1999). A cross-cultural comparison of job stressors and reactions among employees holding comparable jobs in two countries. International Journal of Stress Management, 6 , 197–212.
- National Sleep Foundation (2005). Segment profiles . National Sleep Foundation.
- National Sleep Foundation (2013). How much sleep do adults need? . National Sleep Foundation.
- Nelson, D. L. , & Simmons, B. L. (2003). Health psychology and work stress: A more positive approach. In J. C. Quick & L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of Occupational Health Psychology (pp. 97–119). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Norris, P. A. , Fahrion, S. L. , & Oikawa, L. O. (2007). Autogenic biofeedback training in psychophysiological therapy and stress management. In P. M. Lehrer , R. L. Woolfolk , & W. E. Sime (Eds.), Principles and practices of stress management (3d ed., pp. 175–205). New York: Guilford.
- Ogawa, N. (2009). Stress, coping behavior, and social support in Japan and the United States. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A , 69 , 3802.
- Oksanen, K. , & Ståhle, P. (2013). Physical environment as a source for innovation: Investigating the attributes of innovative space. Journal of Knowledge Management, 17 , 815–827.
- Page, K. M. , & Vella-Brodrick, D. A. (2009). The “what,” “why” and “how” of employee well-being: A new model. Social Indicators Research, 90 , 441–458.
- Parasuraman, S. , & Cleek, M. A. (1984). Coping behaviors and managers’ affective reactions to role stressors . Journal of Vocational Behavior, 24 , 179–193.
- Parasuraman, S. , & Purohit, Y. S. (2000). Distress and boredom among orchestra musicians: The two faces of stress. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 5 , 74–83.
- Pawelski, J. O. (2016). Defining the “positive” in positive psychology: Part II. A normative analysis . Journal of Positive Psychology, 11 , 357–365.
- Pearlin, L. I. , & Schooler, C. (1978). The structure of coping . Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 19 , 2–21.
- Peeters, M. A. G. , & Rutte, C. G. (2005). Time management behavior as a moderator for the job demand-control interaction. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology , 1 , 64–75.
- Peters, L. H. , & O’Connor, E. J. (1980). Situational constraints and work outcomes: The influence of a frequently overlooked construct. Academy of Management Review , 5, 391–397.
- Peters, L. H. , & O’Connor, E. J. (1988). Measuring work obstacles: Procedures, issues, and implications. In F. D. Schoorman & B. Schneider (Eds.), Facilitating work effectiveness (pp. 105–123). Lexington, MA: Lexington Books.
- Polly, S. (2014, July 2). Workplace well-being is not an oxymoron . Positive Psychology News Daily .
- Quick, C. J. , Quick, J. D. , Nelson, D. L. , & Hurrell, J. J. (2003). Preventive stress management in organizations . Washington, DC: APA.
- Quillian-Wolever, R. E. , & Wolever, M. E. (2003). Stress management at work . In J. C. Quick & L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of occupational health psychology (pp. 355–375). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Ragsdale, J. M. , Beehr, T. A. , Grebner, S. , & Han, K. (2011). An integrated model of weekday stress and weekend recovery of students. International Journal of Stress Management, 18 , 153–180.
- Richardson, K. M. , & Rothstein, H. R. (2008). Effects of occupational stress management intervention programs: A meta-analysis. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 13 , 69–93.
- Rodríguez, I. , Kozusznik, M. W. , & Peiró, J. M. (2013). Development and validation of the Valencia Eustress-Distress Appraisal Scale. International Journal of Stress Management, 20 , 279–308.
- Rothbaum, F. , Weisz, J. R. , & Snyder, S. S. (1982). Changing the world and changing the self: A two-process model of perceived control. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 42 , 5–37.
- Rotter, J. B. (1966). Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychological Monographs, 80 , 609.
- Rousseau, V. , & Aubé, C. (2010). Social support at work and affective commitment to the organization: The moderating effect of job resource adequacy and ambient conditions. Journal of Social Psychology, 150 , 321–340.
- Saunders, T. , Driskell, J. E. , Johnston, J. , & Salas, E. (1996). The effect of stress inoculation training on anxiety and performance. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 1 , 170–186.
- Schaubroeck, J. , Ganster, D. C. , Sime, W. E. , & Ditman, D. (1993). A field experiment testing supervisory role clarification. Personnel Psychology, 46 , 1–25.
- Selmer, J. (2002). Coping strategies applied by Western vs overseas Chinese business expatriates in China. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 13 , 19–34.
- Siegrist, J. (1996). Adverse health effects of high effort/low reward conditions. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 1 , 27–41.
- Siegrist, J. (2010). Effort-reward imbalance at work and cardiovascular diseases. International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, 23 , 279–285.
- Siegrist, J. , Dragano, N. , Nyberg, S. T. , Lunau, T. , Alfredsson, L. , Erbel, R. , et al. (2014). Validating abbreviated measures of effort-reward imbalance at work in European cohort studies: The IPD-Work consortium. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 87 , 249–256.
- Sinha, B. K. , Willson, L. R. , & Watson, D. C. (2000). Stress and coping among students in India and Canada . Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue Canadienne Des Sciences Du Comportement , 32 (4), 218–225.
- Sinnott, J. , & Vatz, R. E. (2015, March 13). Maryland doesn’t trust state employees to manage their health . Baltimore Sun .
- Siu, O. L. , Cooper, C. L. , & Phillips, D. R. (2013, July 1). Intervention studies on enhancing work well-being, reducing burnout, and improving recovery experiences among Hong Kong health care workers and teachers . International Journal of Stress Management, 21 , 69–84.
- Sonnentag, S. (2012). Psychological detachment from work during leisure time: The benefits of mentally disengaging from work. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21 , 114–118.
- Sørensen, O. H. , & Holman, D. (2014). A participative intervention to improve employee well-being in knowledge work jobs: A mixed-methods evaluation study. Work & Stress, 28 , 67–86.
- Spector, P. E. , Chen, P. Y. , & O’Connell, B. J. (2000). A longitudinal study of relations between job stressors and job strains while controlling for prior negative affectivity and strains. Journal of Applied Psychology, 85 , 211–218.
- Spector, P. E. , & Jex, S. M. (1998). Development of four self-report measures of job stressors and strains: Interpersonal Conflict at Work Scale, Organizational Constraints Scale, Quantitative Workload Inventory, and Physical Symptoms Inventory. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 3 , 356–367.
- State of Maryland . (n.d.). Wellness program frequently asked questions . Maryland.gov.
- Strentz, T. , & Auerbach, S. M. (1988). Adjustment to the stress of simulated captivity: Effects of emotion-focused versus problem-focused preparation on hostages differing in locus of control . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55 , 652–660.
- Swanberg, J. E. , McKechnie, S. P. , Ojha, M. U. , & James, J. B. (2011). Schedule control, supervisor support and work engagement: A winning combination for workers in hourly jobs? Journal of Vocational Behavior, 79 , 613–624.
- Tarafdar, M. , Tu, Q. , Ragu-Nathan, B. S. , & Ragu-Nathan, T. , (2007). The impact of technostress on role stress and productivity. Journal of Management Information Systems, 24 , 301–328.
- Tepper, B. J. , & Henle, C. A. (2011). A case for recognizing distinctions among constructs that capture interpersonal mistreatment in work organizations . Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32 , 487–498.
- Tetrick, L. E. , & Winslow, C. J. (2015). Workplace stress management interventions and health promotion. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 2 , 583–603.
- Thomas, D. C. , Au, K. , & Ravlin, E. C. (2003). Cultural variation and the psychological contract. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 24 , 451–471.
- Toker, S. , Shirom, A. , Melamed, S. , & Armon, G. (2012). Work characteristics as predictors of diabetes incidence among apparently healthy employees. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 17 , 259–267.
- Velez, B. L. , Moradi, B. , & Brewster, M. E. (2013). Testing the tenets of minority stres theory in workplace contexts. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 60 , 532–542.
- Verquer, M. L. , Beehr, T. A. , & Wagner, S. H. (2003). A meta-analysis of relations between person–organization fit and work attitudes. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 63 , 473–489.
- Villani, D. , Grassi, A. , Cognetta, C. , Toniolo, D. , Cipresso, P. , & Riva, G. (2013). Self-help stress management training through mobile phones: An experience with oncology nurses. Psychological Services , 10 , 315–322.
- Vischer, J. C. (2007). The effects of the physical environment on job performance: Towards a theoretical model of workspace stress. Stress & Health, 23 , 175–184.
- Wasti, S. A. , & Cortina, L. M. (2002). Coping in context: Sociocultural determinants of responses to sexual harassment . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 83, 394–405.
- Willert, M. V. , Thulstrup, A. M. , Hertz, J. , & Bonde, J. P. (2010). Sleep and cognitive failures improved by a three-month stress management intervention . International Journal of Stress Management, 17 , 193–213.
- Xiao Q. , Ottosson I. , & Carlsson I. (2013). Stressors and coping strategies in Chinese and Swedish students at a Swedish university. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 21 , 309–312.
Related Articles
- Work and Family
- Organizational Climate and Culture
- Physical Activity and Stress Reactivity
- The Roles of Psychological Stress, Physical Activity, and Dietary Modifications on Cardiovascular Health Implications
- Inflammation as a Biomarker Method in Lifespan Developmental Methodology
- Stress and Coping Theory Across the Adult Lifespan
- Occupational Health Psychology
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Psychology. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 25 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.136]
- 81.177.182.136
Character limit 500 /500
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Stress management
- Health and behavioral science
- Health and wellness
Mentor Moment: Help Your Team Cope During Change
- August 12, 2018
Hijacked by Stress
- Harvard Business Publishing
Mindfulness in the Age of Complexity
- Ellen Langer
- Alison Beard
- From the March 2014 Issue

What to Do When You're Feeling Distracted at Work
- December 20, 2017
Yoga at Your Desk, Standing
- Jill Braverman

Pressure Doesn't Have to Turn into Stress
- Nicholas Petrie
- March 14, 2017
Why Are India’s Women So Stressed Out?
- Sylvia Ann Hewlett and Ripa Rashid
- August 29, 2011
Managing Your Energy to Maximize Performance
- Tony Schwartz
- September 22, 2017

The Ripple Effects of Parents Not Using Their Vacation Time
- Sarah Green Carmichael
- October 12, 2015
Conquer Your Nerves Before Your Presentation
- Nancy Duarte
- April 28, 2015

Surviving M&A
- Mitchell Lee Marks
- Philip Mirvis
- Ron Ashkenas
- From the March–April 2017 Issue
5 Work Stresses You Can Alleviate with Tech
- Alexandra Samuel
- August 25, 2015
Overwhelmed? Change How You Work
- Pablo Velez Jr.
- March 17, 2020

The Best Strategy for Reducing Stress
- Peter Bregman
- July 10, 2012
Living Through a Career Off Ramp
- April 24, 2012
Take Back Your Life in Ten Steps
- January 10, 2013

“Above All, Acknowledge the Pain”
- Adi Ignatius
- From the May–June 2017 Issue

Thriving in the Gig Economy
- Gianpiero Petriglieri
- Susan J. Ashford
- Amy Wrzesniewski
- From the March–April 2018 Issue

Mentoring During a Crisis
- David P Fessell
- Vineet Chopra MD
- Sanjay Saint MD
- October 29, 2020
Shape Serendipity, Understand Stress, Reignite Passion
- John Hagel III and John Seely Brown
- August 30, 2010

How Burnout Became Normal — and How to Push Back Against It
- Kandi Wiens
- April 23, 2024

Research: More People Use Mental Health Benefits When They Hear That Colleagues Use Them Too
- Laura M. Giurge
- Lauren C. Howe
- Zsofia Belovai
- Guusje Lindemann
- Sharon O’Connor
- April 22, 2024

5 Strategies for Improving Mental Health at Work
- Morra Aarons-Mele
- April 18, 2024

How to Fix Your Company’s Culture of Overwork
- Malissa Clark
- March 18, 2024

It’s Time to Reconceptualize What “Imposter Syndrome” Means for People of Color
- Kevin Cokley
- March 14, 2024

5 Ways to Deal with the Microstresses Draining Your Energy
- Karen Dillon
- Kevin Martin
- February 29, 2024

Do You Have a Phone Addiction?
- Alyson Meister
- February 12, 2024

The Restorative Power of Small Habits
- Francesca Giulia Mereu
- Jennifer Jordan
- February 09, 2024

3 Types of Overthinking — and How to Overcome Them
- Melody Wilding
- February 07, 2024

How to Stop Dwelling on Your Stress
- Jenny Taitz
- January 30, 2024
Work Through Challenging Feedback
- Cameron Conaway
- January 22, 2024

How to Sustain Your Empathy in Difficult Times
- From the January–February 2024 Issue

Is Your Curiosity Helping or Hurting Your Work?
- Elizabeth Grace Saunders
- November 14, 2023

Research: The Benefits of a Pet-Friendly Workplace
- Shawn X. Quan
- Kira Schabram
- November 13, 2023

The Perils of an Achievement Culture
- Ania G. Wieckowski
- From the November–December 2023 Issue

Research: Flexible Work Is Having a Mixed Impact on Employee Well-Being and Productivity
- Jeremie Brecheisen
- October 16, 2023

What’s Fueling Burnout in Your Organization?
- Martin Reeves
- October 04, 2023

Harvard’s Arthur C. Brooks on the Secrets to Happiness at Work
- September 01, 2023

Helping an Employee in Distress
- Kiran Bhatti
- Thomas Roulet
- From the September–October 2023 Issue

The Anxious Micromanager
- Julia DiGangi

Experience, Opportunity, and Developing Your Career (HBR Work Smart Series)
- Harvard Business Review
- Mimi Aboubaker
- Ruchika Tulshyan
- Tomas Chamorro-Premuzic
- Deborah Grayson Riegel
- May 14, 2024

Mental Health and the American Workplace
- John A. Quelch
- Carin-Isabel Knoop
- November 06, 2014

Order out of Chaos: Win Every Negotiation, Thrive in Adversity, and Become a World-Class Communicator
- Scott Walker
- March 26, 2024
Work and Job Search Related Stress
- Monica Higgins
- Stacy E. McManus
- Zibby Schwarzman
- July 07, 2004

Harvard ManageMentor: Change Management
- August 27, 2019

Total Leadership: Be a Better Leader, Have a Richer Life (With New Preface)
- Stewart D. Friedman
- October 07, 2014

Navigate Continual Change
- May 15, 2016

Doing It All as a Solo Parent (HBR Working Parents Series)
- Daisy Dowling
- Brigid Schulte
- Heidi Grant
- Shawn Achor
- March 08, 2022

5 Years of Must Reads from HBR: 2023 Edition (5 Books)
- May 30, 2023
HBR Guide to Managing Stress at Work
- January 14, 2014
Harvard ManageMentor v11, 44 topic
- November 01, 2014
Note on Why Leaders Lose Their Way
- William W. George
- March 31, 2004

HBR Emotional Intelligence Ultimate Boxed Set (14 Books) (HBR Emotional Intelligence Series)
- Daniel Goleman
- Annie McKee
- Bill George
- Herminia Ibarra
- December 17, 2019

HBR Working Parents Starter Set (5 Books)
- Bruce Feiler
- Alice Boyes
- August 02, 2022

Focus (HBR Emotional Intelligence Series)
- Rasmus Hougaard
- December 04, 2018

Two-Career Families (HBR Working Parents Series)
- Jennifer Petriglieri

Parents Who Lead: The Leadership Approach You Need to Parent with Purpose, Fuel Your Career, and Create a Richer Life
- Alyssa Westring
- March 10, 2020

Managing Teams in the Hybrid Age: The HBR Guides Collection (8 Books)
- June 13, 2023

HBR Guide to Navigating the Toxic Workplace
- January 16, 2024

Taking Charge of Your Career (HBR Women at Work Series)
- Dorie Clark
- Avivah Wittenberg-Cox
- Stacy Abrams
- Lara Hodgson
- December 13, 2022

There's No "Right" Way to Do Self-Care
- Alyssa F Westring
- April 20, 2021

HBR Special Issue: How to Overcome Impostor Syndrome
- May 15, 2023

How to Identify and Evaluate What's Stressing You Out
- November 28, 2017
Popular Topics
Partner center.
Advertisement
Stress and Well-Being: A Systematic Case Study of Adolescents’ Experiences in a Mindfulness-Based Program
- Original Paper
- Published: 28 November 2020
- Volume 30 , pages 431–446, ( 2021 )
Cite this article

- Deborah L. Schussler ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5970-4326 1 ,
- Yoonkyung Oh 2 ,
- Julia Mahfouz 3 ,
- Joseph Levitan 4 ,
- Jennifer L. Frank 1 ,
- Patricia C. Broderick 1 ,
- Joy L. Mitra 1 ,
- Elaine Berrena 1 ,
- Kimberly Kohler 1 &
- Mark T. Greenberg 1
2967 Accesses
11 Citations
13 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Research on mindfulness-based programs (MBPs) for adolescents suggests improvements in stress, emotion regulation, and ability to perform some cognitive tasks. However, there is little research examining the contextual factors impacting why specific students experience particular changes and the process by which these changes occur. Responding to the NIH call for “n-of-1 studies” that examine how individuals respond to interventions, we conducted a systematic case study, following an intervention trial (Learning to BREATHE), to investigate how individual students experienced an MBP. Specifically, we examined how students’ participation impacted their perceived stress and well-being and why students chose to implement practices in their daily lives. Students in health classes at two diverse high schools completed quantitative self-report measures (pre-, post-, follow-up), qualitative interviews, and open-ended survey questions. We analyzed self-report data to examine whether and to what extent student performance on measures of psychological functioning, stress, attention, and well-being changed before and after participation in an MBP. We analyzed qualitative data to investigate contextual information about why those changes may have occurred and why individuals chose to adopt or disregard mindfulness practices outside the classroom. Results suggest that, particularly for high-risk adolescents and those who integrated program practices into their daily lives, the intervention impacted internalizing symptoms, stress management, mindfulness, and emotion regulation. Mindful breathing was found to be a feasible practice easily incorporated into school routines. Contextual factors impacted practice uptake and program outcomes. Implications for practitioners aiming to help high school students manage stress are discussed.
Systematic case study provides nuanced data about how individuals respond to a mindfulness-based program (MBP).
High-risk adolescents received the most benefit from MBP participation.
Students who practiced were more likely to experience change across outcomes.
The MBP most impacted the way students responded to stress.
Mindful breathing may be the most accessible practice for students.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
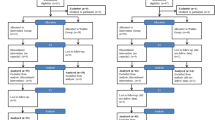
Exploring Mindfulness Benefits for Students and Teachers in Three German High Schools
Effects of Mindfulness Training on Daily Stress Response in College Students: Ecological Momentary Assessment of a Randomized Controlled Trial

Mindfulness and the College Transition: The Efficacy of an Adapted Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Intervention in Fostering Adjustment among First-Year Students
Benn, R., Akiva, T., Arel, S., & Roeser, R. W. (2012). Mindfulness training effects for parents and educators of children with special needs. Developmental Psychology , 48 (5), 1476–1487.
Article Google Scholar
Bergomi, C., Tschacher, W., & Kupper, Z. (2015). Meditation practice and self-reported mindfulness: a cross-sectional investigation of meditators and non-meditators using the Comprehensive Inventory of Mindfulness Experiences (CHIME). Mindfulness , 6 (6), 1411–1421.
Biegel, G. M., Brown, K. W., Shapiro, S. L., & Schubert, C. M. (2009). Mindfulness-based stress reduction for the treatment of adolescent psychiatric outpatients: a randomized clinical trial. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 77 (5), 855–866. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016241 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bluth, K., Campo, R. A., Pruteanu-Malinici, S., Reams, A., Mullarkey, M., & Broderick, P. C. (2016). A school-based mindfulness pilot study for ethnically diverse at-risk adolescents. Mindfulness , 7 (1), 90–104.
Bluth, K., & Eisenlohr-Moul, T. (2017). Response to a mindful self-compassion intervention in teens: A within-person association of mindfulness, self-compassion, and emotional well-being outcomes. Journal of Adolescence , 57 , 108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2017.04.001 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3 (2), 77–101.
Google Scholar
Broderick, P. C. (2013). Learning to BREATHE: A mindfulness curriculum for adolescents to cultivate emotion regulation, attention, and performance . New Harbinger Publications, Oakland, CA.
Byrne, D. G., Davenport, S. C., & Mazanov, J. (2007). Profiles of adolescent stress: the development of the adolescent stress questionnaire. Journal of Adolescence , 30 , 393–416.
Ciarrochi, J., Kashdan, T. B., Leeson, P., Heaven, P., & Jordan, C. (2011). On being aware andaccepting: A one-year longitudinal study into adolescent well-being. Journal of Adolescence , 34 (4), 695–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2010.09.003 .
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ.
Coleman, J. C., & Hendry, L. B. (1999). The nature of adolescence . Psychology Press, London, UK.
Creswell, J. W. (2015). Revisiting mixed methods and advancing scientific practices. In S. Hesse-Biber & R. B. Johnson (Eds.), Oxford handbook of multiple and mixed methods research . Oxford, New York, NY.
Dariotis, J. K., Mirabal-Beltran, R., Cluxton-Keller, F., Gould, L. F., Greenberg, M. T., & Mendelson, T. (2016). A qualitative evaluation of student learning and skills use in a school-based mindfulness and yoga program [journal article]. Mindfulness , 7 (1 Feb), 76–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-015-0463-y .
Dattilio, F. M., Edwards, D. J. A., & Fishman, D. B. (2010). Case studies within a mixed methods paradigm: toward a resolution of the alienation between researcher and practitioner in psychotherapy research. Psychotherapy Theory, Research, Practice, Training , 47 (4), 427–441.
Davidson, R. J., & Kaszniak, A. W. (2015). Conceptual and methodological issues in research on mindfulness and meditation. American Psychologist , 70 (7), 581–592.
Eberth, J., & Sedlmeier, P. (2012). The effects of mindfulness meditation: a meta-analysis. Mindfulness , 3 , 174–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-012-0101-x .
Elliott, R. (2002). Hermeneutic single-case efficacy design. Psychotherapy Research , 12 , 1–21.
Eva, A. L., & Thayer, N. M. (2017). Learning to BREATHE: a pilot study of a mindfulness-based intervention to support marginalized youth. Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine , 22 (4), 580–591. https://doi.org/10.1177/2156587217696928 .
Felver, J. C., Celis-de Hoyos, C. E., Tezanos, K., & Singh, N. (2016). A systematic review of mindfulness-based interventions for youth in school settings. Mindfulness , 7 (1), 34–45.
Felver, J. C., Clawson, A. J., Morton, M. L., Brier-Kennedy, E., Janack, P., & DiFlorio, R. A. (2018). School-based mindfulness intervention supports adolescent resiliency: a randomized controlled pilot study. International Journal of School & Educational Psychology . https://doi.org/10.1080/21683603.2018.1461722 .
Frank, J. L., Broderick, P. C., Oh, Y., Mitra, J., Kohler, K., Schussler, D. L., Geier, C., Roeser, R. W., Berrena, E., Mahfouz, J., Levitan, J., & Greenberg, M. T. (under review). The effectiveness of a teacher delivered mindfulness-based curriculum on adolescent social-emotional and executive functioning.
Fung, J., Guo, S., Jin, J., Bear, L., & Lau, A. (2016). A pilot randomized trial evaluating a school-based mindfulness intervention for ethnic minority youth [journal article]. Mindfulness , 7 (4 Aug), 819–828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-016-0519-7 .
Galla, B. M. (2016). Within-person changes in mindfulness and self-compassion predict enhanced emotional well-being in healthy, but stressed adolescents. Journal of Adolescence , 49 , 204–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.03.016 .
Gini, G., & Pozzoli, T. (2009). Association between bullying and psychosomatic problems: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics , 123 (3), 1059–1065. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2008-1215 .
Goodenow, C. (1993). Classroom belonging among early adolescent students: Relationship to motivation and achievement. Journal of Early Adolescense , 13 (1), 21–43.
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of psychopathology and behavioral assessment , 26 (1), 45–54.
Greco, L. A., Baer, R. A., & Smith, G. T. (2011). Assessing mindfulness in children and adolescents: development and validation of the child and adolescent mindfulness measure (CAMM). Psychological assessment , 23 (3), 606.
Greenberg, M. T., & Harris, A. R. (2012). Nurturing mindfulness in children and youth: current state of research. Child Development Perspectives , 6 (2), 161–166.
Grossman, P., Niemann, L., Schmidt, S., & Walach, H. (2004). Mindfulness-based stress reduction and health benefits: a meta-analysis. Journal of Psychosomatic Research , 57 (1), 35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00573-7 .
Hildebrandt, L. K., McCall, C., & Singer, T. (2017). Differential effects of attention-, compassion-, and socio-cognitively based mental practices on self-reports of mindfulness and compassion. Mindfulness , 8 , 1488–1512.
Huppert, F. A., & Johnson, D. M. (2010). A controlled trial of mindfulness training in schools: the importance of practice for an impact on well-being. Journal of Positive Psychology , 5 (4), 264–274.
Johnson, C., Burke, C., Brinkman, S., & Wade, T. (2017). A randomized controlled evaluation of a secondary school mindfulness program for early adolescents: Do we have the recipe right yet? Behaviour Research and Therapy , 99 , 37–46.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1990). Full catastrophe living: Using the wisdom of your body and mind to face stress, pain, and illness . Bantam Books, New York, NY.
Keng, S. L., Smoski, M. J., & Robins, C. J. (2011). Effects of mindfulness on psychological health: a review of empirical studies. Clinical Psychology Review , 31 , 1041–1056.
Kerrigan, D., Johnson, K., Stewart, M., Magyari, T., Hutton, N., Ellen, J. M., & Sibinga, E. M. S. (2011). Perceptions, experiences, and shifts in perspective occurring among urban youth participating in a mindfulness-based stress reduction program. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice , 17 (2), 96–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctcp.2010.08.003 .
Klingbeil, D. A., Renshaw, T. L., Willenbrink, J. B., Copek, R. A., Chan, K. T., Haddock, A., Yassine, J., & Clifton, J. (2017). Mindfulness-based interventions with youth: a comprehensive meta-analysis of group-design studies. Journal of School Psychology , 63 , 77–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2017.03.006 .
Kroenke, K., Strine, T. W., Spitzer, R. L., Williams, J. B. W., Berry, J. T., & Mokdad, A. H. (2009). The PHQ-8 as a measure of current depression in the general population. Journal of Affective Disorders , 114 (1), 163–173.
Lee, R. M., Draper, M., & Lee, S. (2001). Social connectedness, dysfunctional interpersonal behaviors, and psychological distress: testing a mediator model. Journal of counseling psychology , 48 (3), 310.
Lykins, E. L. B., & Baer, R. A. (2009). Psychological functioning in a sample of long term practitioners of mindfulness meditation. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy: An International Quarterly , 23 (3), 226–241.
Meiklejohn, J., Phillips, C., Freedman, M. L., Griffin, M. L., Biegel, G., Roach, A., Frank, J., Burke, C., Pinger, L., Soloway, G., Isberg, R., Sibinga, E., Grossman, L., & Saltzman, A. (2012). Integrating mindfulness training into K-12 education: fostering the resilience of teachers and students. Mindfulness , 3 (4), 291–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-012-0094-5 .
Metz, S. M., Frank, J. L., Riebel, D., Cantrell, T., Sanders, R., & Broderick, P. C. (2013). The effectiveness of the Learning to BREATHE program on adolescent emotion regulation. Research in Human Development , 10 (3), 252–272. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427609.2013.818488 .
Murphy, M. J., Mermelstein, L. C., Edwards, K. M., & Gidycz, C. A. (2012). The benefits of dispositional mindfulness in physical health: a longitudinal study of female college students. Journal of American College Health , 60 (5), 341–348. https://doi.org/10.1080/07448481.2011.629260 .
Osterman, K. (2000). Students’ need for belonging in the school community. Review of Educational Research , 70 (3), 323–368.
Parsons, C. E., Crane, C., Parsons, L. J., Fjorback, L. O., & Kuyken, W. (2017). Home practice in mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction: a systematic review and metaanalysis of participants’ mindfulness practice and its association with outcomes. Behaviour Research and Therapy , 95 , 29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2017.05.004 .
Raes, F., Pommier, E., Neff, K. D., & Van Gucht, D. (2011). Construction and factorial validation of a short form of the self-compassion scale. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapygrec , 18 (3), 250–255.
Ribeiro, L., Atchley, R. M., & Oken, B. S. (2018). Adherence to practice of mindfulness in novice meditators: Practices chosen, amount of time practiced, and long-term effects following a mindfulness-based intervention [journal article]. Mindfulness , 9 (2 Apr), 401–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-017-0781-3 .
Sapthiang, S., Van Gordon, W., & Shonin, E. (2019). Health school-based mindfulness interventions for improving mental health: a systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative studies. Journal of Child and Family Studies , 28 (10), 2650–2658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01482-w .
Schussler, D. L., Jennings, P. A., Sharp, J. E., & Frank, J. L. (2016). Improving teacher awareness and well-being through CARE: A qualitative analysis of the underlying mechanisms. Mindfulness , 7 (1), 130–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-015-0422-7 .
Schussler, D. L., DeWeese, A., Rasheed, D., DeMauro, A., Doyle, S. L., Brown, J. L., Greenberg, M. T., & Jennings, P. A. (2019). The relationship between adopting mindfulness practice and reperceiving: A qualitative investigation of CARE for teachers. Mindfulness , 10 , 2567–2582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-019-01228-1 .
Schwartz, S. J., Beyers, W., Luyckx, K., Soenens, B., Zamboanga, B. L., Forthun, L. F., Hardy, S. A., Vazsonyi, A. T., Ham, L. S., Kim, S. Y., Whitbourne, S. K., & Waterman, A. S. (2011). Examining the light and dark sides of emerging adults’ identity: a study of identity status differences in positive and negative psychosocial functioning. Journal of Youth and Adolescence , 40 (7), 839–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-010-9606-6 .
Sebastian, C., Burnett, S., & Blakemore, S. J. (2008). Development of the self-concept during adolescence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences , 12 (11), 441–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2008.07.008 .
Shapiro, S. L., Carlson, L. E., Astin, J. A., & Freedman, B. (2006). Mechanisms of mindfulness. Journal of Clinical Psychology , 62 (3), 373–386.
Sibinga, E. M. S., Kerrigan, D., Stewart, M., Johnson, K., Magyari, T., & M., E. J. (2011). Mindfulness-based stress reduction for urban youth. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine , 17 (3), 213–218. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2009.0605 .
Siegel, D. J. (2013). Brainstorm: The power and purpose of the teenage brain . The Penguin Group, New York, NY.
Spitzer, R. L., Williams, J. W., & Löwe, B. K. (2006). A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Archives of Internal Medicine , 166 , 1092–1097.
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1990). Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory procedures and techniques . Sage, Newbury Park, CA.
Tan, L. B. (2016). A critical review of adolescent mindfulness-based programmes. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 21 (2), 193–207.
Tang, Y.-Y., Ma, Y., Wang, J., Fan, Y., Feng, S., Lu, Q., et al. (2007). Short-term meditation training improves attention and self-regulation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104 (43), 17152–17156. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0707678104 .
Tottenham, N., & Galvan, A. (2016). Stress and the adolescent brain: amygdala-prefrontal cortex circuitry and ventral striatum as developmental targets. Neuroscientific Biobehavioral Review , 70 , 217–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.07.030 .
Trapnell, P. D., & Campbell, J. D. (1999). Private self-consciousness and the five-factor model of personality: distinguishing rumination from reflection. Journal of personality and social psychology , 76 (2), 284.
Van Ness, P. H., Murphy, T. E., & Ali, A. (2017). Attention to individuals: Mixed methods for n-of-1 health care interventions. Journal of Mixed Methods Research , 11 (3), 342–354.
Waters, L., Barsky, A., Ridd, A., & Allen, K. (2015). Contemplative education: a systematic, evidence-based review of the effect of meditation interventions in schools. Educational Psychology Review , 27 (1), 103–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-014-9258-2 .
Wolke, D., Copeland, W. E., Angold, A., & Costello, E. J. (2013). Impact of bullying in childhood on adult health, wealth, crime, and social outcomes. Psychological Science , 24 (10), 1958–1970.
Yoshikawa, H., Weisner, T. S., Kalil, A., & Way, N. (2008). Mixing qualitative and quantitative research in developmental science: Uses and methodological choices. Developmental Psychology , 44 (2), 344–354.
Zelazo, P. D., & Carlson, S. M. (2012). Hot and cool executive function in childhood and adolescence: development and plasticity. Child Development Perspectives , 6 (4), 354–360.
Zenner, C., Herrnleben-Kurz, S., & Walach, H. (2014). Mindfulness-based interventions in schools—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Frontiers in Psychology , 5 (603). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00603
Zoogman, S., Goldberg, S. B., Hoyt, W. T., & Miller, L. (2015). Mindfulness interventions with youth: a meta-analysis. Mindfulness , 6 (2), 290–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-013-0260-4 .
Download references
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Qualitative data collection and analysis were performed by D.L.S., J.M., and J.L. Quantitative analysis was performed by Y.O., while J.L.M., E.B., and K.K. led the quantitative data collection. The first draft of the manuscript was written by D.L.S. and Y.O., and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The project described was supported by Award Number R305A140113 from the Institute of Education Sciences (IES). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the Institute of Education Sciences or the U.S. Department of Education.

Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA
Deborah L. Schussler, Jennifer L. Frank, Patricia C. Broderick, Joy L. Mitra, Elaine Berrena, Kimberly Kohler & Mark T. Greenberg
University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX, USA
Yoonkyung Oh
University of Colorado, Denver, CO, USA
Julia Mahfouz
McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada
Joseph Levitan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Deborah L. Schussler .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
In accordance with ethical obligations, P.C.B., developer of Learning to Breathe, is reporting a financial interest that may be affected by the research reported in the enclosed paper.
Ethics Approval
This study was approved by the Human Research Ethics committee of Pennsylvania State University (Study 00000492; initial approval 2/24/2015).
Informed Consent
(1) Consent to Participate—Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Parents of minors provided passive consent to participate. (2) Consent to Publish—Participants provided informed consent for publication of their de-identified data.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Schussler, D.L., Oh, Y., Mahfouz, J. et al. Stress and Well-Being: A Systematic Case Study of Adolescents’ Experiences in a Mindfulness-Based Program. J Child Fam Stud 30 , 431–446 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-020-01864-5
Download citation
Accepted : 08 November 2020
Published : 28 November 2020
Issue Date : February 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-020-01864-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Emotion regulation
- Mindfulness
- Adolescents
- Systematic case study
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Exercises • 7 min read
Under Pressure: a Stress Management Case Study
Helping team members reflect on the symptoms of stress and how to alleviate it.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
This plausible case study will enable participants to recognize the symptoms of stress in themselves or in colleagues and take action to remedy the situation.

Participants will be able to …
- develop a higher level of awareness of stress in the workplace
- highlight the symptoms of stress and recognize them in themselves and in colleagues
- learn methods of dealing with stress in the workplace
Facilitator’s Guide
This straightforward case study requires little in the way of facilitation but mingle with the groups and be on hand to answer any questions or prompt discussion.
It could be used as part of a stress management workshop or stress awareness campaign. It would work best with groups of up to six participants. Allow just over an hour for completion.
Suggested Resources
- copy of task sheet per delegate
- white board or flipchart
What to Do (35 Minutes)
- Introduce the case study explaining its objectives to the participants.
- If you are dealing with a larger group, split them into sub–groups of five or six people.
- Distribute the task sheets amongst participants and allow 30 minutes for completion.
Review Activity (10 Minutes)
Bring the group(s) back to discuss their results. Possible answers to the questions could include the following:
1. What behavioral and psychological changes in Jen suggest that she may be stressed? Jen has become short–tempered, forgetful, intolerant, feels constantly anxious, her concentration is impaired and she is under–eating.
2. Can you list two other behavioral changes suggestive of stress? This could include any two of the following:
- aggressive behavior
- pessimistic and negative
- increased alcohol/drug use or smoking
- carelessness
- over–eating
- withdrawal and listlessness
3. What physical symptoms is Jen showing that suggest she may be stressed? Jen has decreased appetite, sleep disturbance, weight loss and she is susceptible to minor illnesses.
4. List five other physical symptoms or signs of stress. This could include any of the following:
- tightness of the chest, neck, jaw, face, abdomen, shoulder and back muscles
- hunched posture and clenched fists
- breathing becomes shallow and rapid
- irritable bowel symptoms such as diarrhea or constipation
- shaking hands
- chronic (long–term) pain
- facial expression shows tension – frown, tightened eyebrows, clenched jaw, pursed lips
5. If you were Ahmed, what would you do to help Jen? There are a number of approaches Ahmed could take to help Jen. Depending on his seniority, he may be able to take action in one of the following ways:
- arrange a meeting with Jen. Give her some notice, and outline why you want to meet her. You’re concerned about her health and you want to establish if it is work related. If so, establish what can be done to resolve these issues and to support Jen
- allow half a day, in private, perhaps away from the workplace, to explore your observations and Jen’s response in detail
- review the project objectives, timescales, resources, processes. Establish realistic goals and think creatively around overcoming the constraints. But, the constraints must be addressed
- assign another project manager to co–manage the project with Jen
- look at the hours that Jen is working and, if they are excessive, try to reduce them
- change the hours of Jen’s work week so that she is not traveling in rush-hour traffic
- offer Jen the opportunity to work from home where appropriate
In addition to the above, he could also:
- encourage Jen to take up a sport or a hobby
- suggest that she takes up yoga
- suggest that she speaks to her GP who may refer her on to a counselor or suggest other forms of treatment
- encourage her to investigate other methods of relaxation including aromatherapy, relaxation exercises and breathing exercises
It could be that Jen would find some of these options intrusive, others less so. Make sure that the group is aware of the sensitivities surrounding this.
This list is by no means exhaustive. There are positives and negatives surrounding each of these suggestions. Make sure that you cover all of these with the group.
Apply Learning (15 Minutes)
Ask participants to work individually for five minutes and either select a colleague they are concerned about, or themselves and list up to three:
- behavioral or psychological changes
- physical symptoms
Encourage them to select a learning partner if they wish and discuss what they can do to manage their own stress or how they can help/support their colleague.
Under Pressure – Task Sheet
Jen Breeze is a project manager for Techtron, a multinational IT consultancy. She has always enjoyed her work, but has recently found herself under increasing pressure in the workplace. Although when in her early 20s and 30s Jen ‘thrived on stress’ she feels that now, at 45, her work is taking a toll on both her health and her personal life.
Jen was recently assigned to work on her biggest project to date. As an experienced manager, she recognizes that both the budget and the timescale for the project are highly unrealistic. She has discussed her concerns with senior management, but her words fell on deaf ears. She knows that she is accountable for the success of the project and feels constantly uneasy. She has even found herself lying thinking about it in the early hours of the morning. On top of this, Jen has to drive 30 miles, each way, every day to reach work through rush-hour traffic.
A senior colleague, Ahmed Nazir, meets with Jen in the staff canteen for lunch on a regular basis, and has seen a gradual change in her over the last few months. She never seems to listen to him anymore and he has difficulty holding a sensible conversation with her. She looks tired and rarely eats much. He finds her forgetful and is concerned that this will have a knock-on effect on the quality of work that she is producing. He is, however, more worried about Jen and wants to help.
Jen herself is also worried, not only about the forthcoming project launch meeting, but about herself. Although Jen has a reputation for being approachable, she has found herself regularly ‘snapping’ without good reason at team members. At home too, she feels that she is short–tempered and intolerant of her husband. She feels ‘wound up’ all the time and can’t seem to relax. She knows that she has inadvertently lost a significant amount of weight. Her friends complain that they have not seen her in weeks, but she cannot face the simple task of phoning them. To make matters worse she has had a recurring cold for over three months and has been unable to shake it off. The thought of going into work each day fills her with dread and she is unsure how much longer she can go on functioning like this.
Task Consider the following questions:
- What behavioral and psychological changes in Jen suggest that she may be stressed?
- Can you list two other behavioral changes suggestive of stress?
- What physical symptoms is Jen showing that suggest she may be stressed?
- List five other physical symptoms or signs of stress.
- If you were Ahmed, what would you do to help Jen?
- If you were Jen what steps would you take to help yourself, and the project?
Join Mind Tools and get access to exclusive content.
This resource is only available to Mind Tools members.
Already a member? Please Login here

Try Mind Tools for FREE
Get unlimited access to all our career-boosting content and member benefits with our 7-day free trial.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Briefings

Onboarding With STEPS
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
New pain points podcast - perfectionism.
Why Am I Such a Perfectionist?
Pain Points Podcast - Building Trust
Developing and Strengthening Trust at Work
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
The one thing: the surprisingly simple truth behind extraordinary results.
Gary Keller, With Jay Papasan
Book Insights
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Click Here for Free Mind/Body Tools

Revealing the Hidden Consequences: Real-life Case Studies in Stress and Anxiety
In today's fast-paced world, stress and anxiety are part and parcel of everyday life. While they are natural reactions to challenging circumstances, persistent, poorly managed stress can result in serious health outcomes. The stress behind the development of these illnesses is often not seen or well-treated since it is invisible and doesn't show up on x-rays or lab tests.
Case Study 1: The Physical Toll of Chronic Stress and Anxiety
John, a middle-aged executive, experienced chronic stress due to work and family pressure, leading to a range of health issues. Having never learned good stress management skills, John overate, drank too much coffee in the daytime and alcohol in the evening, and made no time for exercise or relaxation in his overbusy days.
He didn’t complain or even recognize how stressed he was since all his colleagues and friends seemed to be dealing with the same issues. He didn't recognize the signs of stress but over a few years accumulated a number of medical diagnoses and medications to go with them.
- Eating on the run and too much coffee and alcohol gave him chronic heartburn, diagnosed as “GERD” (GastroEsophageal Reflux Disease) and treated with omeprazole and antacids
- John developed high blood pressure and high cholesterol, putting him at high risk for heart disease and stroke, so was given blood pressure medications and statin medication
- His increasingly poor sleep was treated with Trazodone, a medication that knocked him out but left him feeling groggy and starting his day with 2 or 3 large cups of coffee
- As he became increasingly exhausted and using more alcohol, he got crankier and more irritable, early signs of depression in men. His doctor started him on an antidepressant which helped his mood, but didn't help him change his lifestyle which was at the root of all these “diagnoses.”
Case Study 2: Mental and Emotional Consequences
Susan, a school teacher, faced constant anxiety due to high workload and financial problems. This prolonged exposure to unmanaged stress and anxiety led to:
- Emotional Burnout: Over time, Susan experienced emotional exhaustion leading to feelings of detachment, a condition often referred to as burnout.
- Cognitive Difficulties: Chronic stress and burnout affected her ability to concentrate, plan, and make good decisions.
- Depression: Eventually, persistent stress and anxiety triggered the onset of depression in Susan
Case Study 3: The Social Impact
Emma, a college student suffering from chronic stress, worry, and anxiety, exhibited changes in her social behavior:
- Isolation: She started withdrawing from her friends and social activities, leading to feelings of loneliness and even more stress.
- Conflict: Her stress made her irritable, leading to increased conflict in her personal relationships, worsening her isolation and loneliness.
Identifying these signs of too much stress is the first step towards recovery. None of these people had an illness or disease – they were overstressed and didn't have the tools or support to help them manage it. There are many techniques and tools that can help to keep stress and anxiety at manageable levels:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Techniques like these helped John stay focused on the present moment, reducing his stress levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise assisted Susan in reducing her stress. It served as a natural mood enhancer and distracted her from constant worry.
- Balanced Diet: Emma found that a healthy diet helped combat her stress. Certain foods even assisted in reducing stress, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin C.
- Guided Imagery: Upon recognizing the detrimental effects of stress and anxiety on their daily lives, John, Susan, and Emma decided to learn how to reduce stress and manage it better when it couldn’t be avoided. Either on their own or with the urging of a therapist, they discovered relaxation and guided imagery. The skills and practices they learned became a keystone of their healthy lifestyle, playing a significant role in alleviating their stress and anxiety and guiding them towards recovery.
Recognizing the signs of excessive stress and anxiety is the first step towards effectively managing them. Learning good elf-care stress and anxiety reduction skills is the second step. If you’re too overwhelmed or mired down in the stress, professional help you dig out of it. Remember, seeking help and making strides towards a healthier life is absolutely okay. Living a life free from the burden of constant worry is your right. The journey to that life begins now.
Videos To Help You
Products To Help You
The Worry Solution
The 3 Keys to Calmness
Change Password
Your password must have 6 characters or more:.
- a lower case character,
- an upper case character,
- a special character
Password Changed Successfully
Your password has been changed
Create your account
Forget yout password.
Enter your email address below and we will send you the reset instructions
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to reset your password
Forgot your Username?
Enter your email address below and we will send you your username
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to retrieve your username

- Spring 2024 | VOL. 22, NO. 2 Autism Across the Lifespan CURRENT ISSUE pp.147-262
- Winter 2024 | VOL. 22, NO. 1 Reproductive Psychiatry: Postpartum Depression is Only the Tip of the Iceberg pp.1-142
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) has updated its Privacy Policy and Terms of Use , including with new information specifically addressed to individuals in the European Economic Area. As described in the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use, this website utilizes cookies, including for the purpose of offering an optimal online experience and services tailored to your preferences.
Please read the entire Privacy Policy and Terms of Use. By closing this message, browsing this website, continuing the navigation, or otherwise continuing to use the APA's websites, you confirm that you understand and accept the terms of the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use, including the utilization of cookies.
Cognitive-Behavioral Treatments for Anxiety and Stress-Related Disorders
- Joshua E. Curtiss , Ph.D. ,
- Daniella S. Levine , B.A. ,
- Ilana Ander , B.A. ,
- Amanda W. Baker , Ph.D.
Search for more papers by this author
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a first-line, empirically supported intervention for anxiety disorders. CBT refers to a family of techniques that are designed to target maladaptive thoughts and behaviors that maintain anxiety over time. Several individual CBT protocols have been developed for individual presentations of anxiety. The article describes common and unique components of CBT interventions for the treatment of patients with anxiety and related disorders (i.e., panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, prolonged grief). Recent strategies for enhancing the efficacy of CBT protocols are highlighted as well.
Anxiety disorders are among the most prevalent of mental disorders and are associated with high societal burden ( 1 ). One of the most well-researched and efficacious treatments for anxiety disorders is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). At its core, CBT refers to a family of interventions and techniques that promote more adaptive thinking and behaviors in an effort to ameliorate distressing emotional experiences ( 2 ). CBT differs from other therapeutic orientations in that it is highly structured and often manualized. CBT sessions often occur weekly for a limited period (e.g., 12–16 weeks), and a small number of booster sessions are sometimes offered subsequently to reinforce independent use of skills. A cognitive-behavioral conceptualization of anxiety disorders includes identification of dysfunctional thinking patterns, distressing feelings or physiological experiences, and unproductive behaviors. When each of these three components interact and mutually reinforce one another, distressing and impairing levels of anxiety can be maintained over time. Although there are several CBT interventions for different types of anxiety, some common techniques and treatment goals form the basis of the CBT philosophy.
Cognitive Interventions
One of the primary CBT strategies is cognitive intervention. In brief, CBT holds that one’s emotional experience is dictated by one’s interpretation of the events and circumstances surrounding that experience ( 2 , 3 ). Anxiety disorders are associated with negatively biased cognitive distortions (e.g., “I think it’s 100% likely I will lose my job, and no one will ever hire me again”). The objective of cognitive interventions is to facilitate more adaptive thinking through cognitive restructuring and behavioral experiments. Cognitive restructuring promotes more adaptive and realistic interpretations of events by identifying the presence of thinking traps. These cognitive traps are patterns of biased thinking that contribute to overly negative appraisals. For example, “black-and-white thinking” describes the interpretation of circumstances as either all good or all bad, without recognition of interpretations between these two extremes, and “overgeneralization” describes the making of sweeping judgments on the basis of limited experiences). Through identification of thinking traps, cognitive restructuring can be used to promote more balanced thinking, encouraging patients to consider alternative interpretations of circumstances that are more helpful and less biased by anxiety (e.g., “Maybe thinking the chance of losing my job is 100% is overestimating the likelihood that it will actually happen. And, it’s not a forgone conclusion that even if I lose my job, I will never find another one for the rest of my life.”). Similarly, behavioral experiments can be used to facilitate cognitive change. Behavioral experiments involve encouraging patients to empirically test maladaptive beliefs to determine whether there is evidence supporting extreme thinking. For example, if a patient believes that he/she/they is romantically undesirable and that asking someone on a date will cause the other person to react with disgust and disdain, then the patient would be encouraged to test this belief by asking someone on a date. Some combination of cognitive restructuring and behavioral experiments are often implemented in CBT across all anxiety disorders.
Behavioral Interventions
There are several behavioral strategies in CBT for anxiety disorders, yet the central behavioral strategy is exposure therapy. Exposure techniques rely on learning theory to explain how prolonged fear is maintained over time. Specifically, heightened anxiety and fear prompt individuals to avoid experiences, events, and thoughts that they believe will lead to catastrophic outcomes. Continued avoidance of feared stimuli and events contributes to the maintenance of prolonged anxiety. Consistent with the premises underlying extinction learning, exposure exercises are designed to encourage a patient to confront a feared situation without engaging in avoidance or subtle safety behaviors (i.e., doing something to make an anxiety-inducing situation less distressing). After repeated exposures to a feared situation (e.g., heights) without engaging in avoidance or safety behaviors (e.g., closing one’s eyes to avoid looking down), the patient will learn that such a situation is less likely to be associated with disastrous outcomes, and new experiences of safety will be reinforced. Similar to the behavioral experiments described in the cognitive intervention section above, which test whether a faulty thought is true or false, exposure exercises offer the opportunity for patients to test their negative beliefs about the likelihood of a bad outcome by exposing themselves to whatever situations they have been avoiding. Thus, cognitive approaches and exposure exercises are complementary techniques that can benefit individuals with anxiety disorders. In the following sections, different aspects of CBT will be explored and emphasized insofar as they relate to specific presentations of anxiety.
CBT for Specific Disorders
Panic disorder.
Panic disorder, as defined by the DSM-5 , is characterized by recurrent, unexpected panic attacks accompanied by worry and behavioral changes in relation to future attacks. Panic attacks are marked by acute, intense discomfort, with symptoms including heart palpitations, sweating, and shortness of breath. Individuals with panic disorder exhibit cognitive and behavioral symptoms, such as catastrophic misinterpretations of their symptoms as dangerous (e.g., “my heart pounding means I will have a heart attack”) and avoidance of situations or sensations that induce panic ( 4 ). Cognitive-behavioral treatments thus target these symptoms. For example, cognitive restructuring is used to help patients reinterpret their maladaptive thoughts surrounding panic (e.g., “if I get dizzy, I will go crazy”) to be more flexible (e.g., “if I get dizzy, it may just mean that I spun around too fast”). Behavioral treatments for panic include exposure to the situations (i.e., in-vivo exposure, which might include driving in traffic or riding the subway) and bodily sensations (i.e., interoceptive exposure, which would include physical exercises to bring on physical symptoms) that trigger panic in order to reduce the fear and anticipatory anxiety that maintain the symptoms. The aim of these exposures is to illustrate that the situations and sensations are benign and not indicative of danger.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is characterized by excessive and uncontrollable worry about several life domains (e.g., finances, health, career, the future in general). Treatment for GAD involves a wholesale approach to target excessive worry with a combination of cognitive and behavioral strategies ( 5 ). Although cognitive restructuring exercises are indeed emphasized throughout the treatment to target dysfunctional thoughts, usually further cognitive treatments are included to address worry behavior in addition to thought content. Individuals with GAD rarely achieve complete remission after restructuring only one of their negative thoughts. The CBT conceptualization of worry describes worry as a mental behavior or process, characterized by repetitive negative thinking about catastrophic future outcomes. To target worrying as a process, cognitive techniques, such as mindfulness, are emphasized. Rather than targeting the content of worry (e.g., “I think I will definitely lose my job if I do not prepare for this meeting”), mindfulness exercises target the worry behavior by promoting the opposite of repetitive negative thinking (i.e., nonjudgmental and nonreactive present moment awareness), thereby facilitating greater psychological distance from negative thoughts. Exposure therapy is often implemented as imaginal exposures for GAD, because individuals with GAD rarely have an external object that is feared. Such imaginal exposures will encourage patients with GAD to write a detailed narrative of their worst-case scenario or catastrophic outcome and then imagine themselves undergoing such an experience without avoiding their emotions. Cognitive restructuring and imaginal exposure exercises can benefit patients with GAD by targeting their tendency to give catastrophic interpretations to their worries, whereas mindfulness can be helpful in targeting worry as a mental behavior itself ( 5 ).
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder involves a fear of negative evaluation in social situations and is accompanied by anxiety and avoidance of interpersonal interactions and performance in front of others. The primary treatment approach for social anxiety disorder consists of exposure exercises to feared social situations ( 6 ). Cognitive restructuring is used in conjunction with exposure exercises to reinforce the new learning and shift in perspective occurring through exposure therapy. Typically, exposure exercises for social anxiety disorder come in two stages ( 6 ). The first stage of exposures often targets patients’ overestimation that something bad will happen during a social interaction. For instance, patients with this disorder may fear that they will make many verbal faux pas (e.g., saying “uh” more than 30 times) during a conversation. An exposure exercise may consist of recording the patient having a 2-minute conversation and listening to the recording afterward to see whether the feared outcome actually occurred. The second stage of exposure exercises (i.e., social cost exposures) consists of having patients directly making their worst-case social anxiety scenario come true to determine how bad and intolerable it actually is. Such a social cost exposure might involve encouraging a patient to embarrass her- or himself on purpose by singing “Twinkle, Twinkle Little Star” in a crowded public street. After fully confronting a social situation that the patient predicted would be very embarrassing, the patient can then determine whether such a situation is as devastating and intolerable as predicted. After repeated social cost exposures, patients with social anxiety disorder experience less anxiety in embarrassing social situations and are more willing to adopt less catastrophic beliefs about the meaning of making mistakes in social situations.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is characterized by obsessions (i.e., unwanted thoughts or images that are intrusive in nature) and compulsions (i.e., actions or mental behaviors that are performed in a rule-like manner to neutralize the obsession). A CBT conceptualization of OCD considers compulsions as a form of emotional avoidance. Although both cognitive interventions and exposure exercises are helpful for individuals with OCD, the latter are often emphasized. The gold-standard CBT treatment for OCD is exposure and ritual prevention therapy ( 7 ). The primary idea underlying exposure and ritual prevention is to expose individuals with OCD to the feared circumstance associated with the obsession and prevent them from performing the compulsive ritual that gives them comfort through avoidance. For example, patients who experience frequent obsessions about whether their doors are locked or their appliances are off (e.g., “If my door is unlocked, then my house might be robbed or something bad might happen.”) will often feel compelled to perform a compulsion (e.g., ritualistic checking) to avoid the likelihood of having their obsession come true. Exposure and ritual prevention would be used to expose such patients to a feared situation, such as leaving their door unlocked on purpose, and resisting the compulsion to check the door or to lock it. During these exposures, the patients would be asked to embrace the uncertainty surrounding the possibility of the feared outcome coming true (i.e., someone entering the house). Repeated sessions of exposure and ritual prevention will facilitate corrective learning about the likelihood that feared outcomes will occur.
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
As defined by the DSM-5 , posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can arise after a traumatic event in which an individual directly experiences, witnesses, or learns about the actual or threatened death, serious injury, or sexual violence toward a loved one. After the traumatic stressor event, an individual with PTSD may experience intrusion symptoms (e.g., upsetting dreams or flashbacks of the event), avoidance of reminders of the event, changes in cognitions and affect (e.g., distorted beliefs about oneself, others, and the world), and changes in physiological arousal (e.g., jumpiness, irritability) ( 4 ). Gold-standard treatments for PTSD involve targeting the cognitive and behavioral symptoms that maintain the disorder ( 8 ). PTSD treatments target negative changes in cognition by restructuring the thoughts and beliefs surrounding the traumatic event. For example, evidence-based treatments alter persistent negative beliefs about the world (e.g., “I was assaulted; therefore, the world is dangerous”) to be more flexible (e.g., “even though I was assaulted, there are safe places for me to be”). In challenging these beliefs, the patient may be better able to foster flexible thinking, positive affect, trust, and control in their lives. PTSD treatments are also designed to help patients confront the upsetting memories and situations associated with the traumatic event. Through in-vivo exposures (i.e., approaching situations that are reminders of the trauma) and imaginal exposures (i.e., confronting upsetting memories of the trauma), the patient can begin to behaviorally approach, rather than avoid, reminders of the event to overcome their fears of the trauma and the associated symptoms.
Prolonged Grief Disorder
After losing a loved one, many individuals experience grief symptoms, such as thoughts (e.g., memories of the deceased, memories of the death), emotions (e.g., yearning, emotional pain), and behaviors (e.g., social withdrawal, avoidance of reminders). For most bereaved individuals, these symptoms decrease over time; however, some individuals experience a debilitating syndrome of persistent grief called prolonged grief disorder. This disorder is a direct consequence of the loss, thereby differentiating it from depression and PTSD. Evidence-based and efficacious treatment options for prolonged grief disorder draw from interpersonal therapy, CBT, and motivational interviewing, with additional psychoeducation components ( 9 ). These treatments aim to facilitate the natural bereavement process as individuals accept and integrate the loss. Strategies can be either loss-related or restoration-related. Specific loss-related strategies that draw from CBT include imaginal and situational revisiting (e.g., retelling the story of the loss, going to places that have been avoided since the loss) and a grief monitoring diary. Restoration-related strategies include short- and long-term planning, self-assessment and self-regulation, and rebuilding interpersonal connections.
Transdiagnostic Approaches to CBT for Anxiety Disorders
Throughout the past several decades, there has been a proliferation of CBT approaches that have been individualized to specific anxiety disorder presentations (e.g., panic disorder, specific phobias, social anxiety disorder). Each disorder-specific treatment manual is written to consider unique applications of CBT strategies for the presenting disorder. However, in recent years, there has been increased interest in considering transdiagnostic approaches to the treatment of anxiety and related disorders ( 10 ). The commonalities among individual anxiety disorders and the high levels of comorbidity have contributed to the rationale for a unified CBT approach that can target transdiagnostic mechanisms underlying all anxiety disorders. The Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders (UP) has been the most studied transdiagnostic treatment for anxiety disorders, and recent evidence ( 10 ) corroborates the equivalent efficacy of the UP relative to disorder-specific treatment protocols for individual anxiety disorders.
The UP consists of five core modules that target transdiagnostic mechanisms of emotional disorders, particularly neuroticism and emotional avoidance, underlying all anxiety disorders. Specifically, the modules are mindfulness of emotions, cognitive flexibility, identifying and preventing patterns of emotion avoidance, increasing tolerance of emotion-related physical sensations, and interoceptive and situational emotion-focused exposures ( 10 ). Each module may be used flexibly for individual patients. The first two modules are more cognitive in nature, whereas the latter modules are more behavioral and emphasize the treatment of avoidance. The first module emphasizes mindfulness of emotions, which consists of allowing oneself to fully and nonjudgmentally experience emotions and allow them to come and go while remaining focused on the present. The second module fosters cognitive flexibility by identifying thinking traps that lead to overly negative thoughts and interpretations and by teaching restructuring strategies to generate alternative interpretations of circumstances that are less biased and more adaptive. The third module promotes the identification of emotion-driven behaviors (i.e., actions that a given emotion compels a person to do, such as avoidance behaviors in response to fear) and the adoption of alternative actions (i.e., behaviors that are different from or the opposite of the emotion-driven behavior). For example, if social anxiety prompts an individual to avoid eye contact as an emotion-driven behavior, then an alternative action would be to intentionally maintain eye contact with another speaker to counteract this subtle form of avoidance. The final two modules consist of exposure exercises to develop better tolerance of unwanted physical symptoms produced by anxiety (e.g., increased heart rate) and to reduce fear in anxiety-provoking situations.
Because the UP contains many of the core components of disorder-specific protocols and has demonstrated equivalent efficacy, such a treatment approach may reduce the need for excessive reliance on disorder-specific protocols ( 10 ). Furthermore, the UP can be extended to other emotional disorders, such as depression.
Complementary Approaches for CBT
Mindfulness.
Mindfulness-based interventions function both as transdiagnostic adjunctive treatments to CBT for patients with anxiety and stress disorders as well as stand-alone treatments. Mindfulness is the practice of nonjudgmental awareness of the present moment experience. The aim of these interventions is to reduce emotional dysregulation and reactivity to stressors. Common mindfulness-based interventions include manualized group skills training programs called mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy ( 11 ). MBSR involves eight, 2–2.5-hour sessions with an instructor, in conjunction with a daylong retreat, weekly homework assignments, and practice sessions. Modules are designed to train participants in mindful meditation, interpersonal communication, sustained attention, and recognition of automatic stress reactivity. Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy has a structure similar to MBSR but includes cognitive therapy techniques to train participants to recognize and disengage from negative automatic thought patterns ( 12 ). These interventions omit aspects of traditional CBT (e.g., cognitive restructuring). Mindfulness-based interventions have been explored as both brief and Internet-delivered interventions and have been integrated into other evidence-based practices (e.g., dialectical behavior therapy and acceptance and commitment therapy).
Pharmacotherapy
There has been much interest in determining whether combination strategies of CBT and pharmacotherapy yield greater efficacy than either one alone for individuals with anxiety disorders. A comprehensive meta-analysis ( 13 ) examining this combination strategy suggested that adding pharmacotherapy to CBT may produce short-term benefit, yet such improvements diminished during 6-month follow-up. This combination strategy was more efficacious for individuals with panic disorder or GAD than for individuals with other presentations of anxiety. Moreover, the meta-analysis ( 13 ) indicated that the effect size for CBT combined with benzodiazepines was significantly greater than that for CBT combined with serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants. Another important consideration for pharmacotherapy in the treatment of individuals with anxiety disorders is to ensure that anxiolytic medications, such as benzodiazepines, are administered carefully in the context of exposure therapy. Anxiolytic medications taken to temporarily reduce anxiety may undermine quality exposure therapy sessions by preventing patients from fully learning whether they can tolerate fear without resorting to avoidance behaviors. Thus, although pharmacotherapy appears to improve outcomes in combination with CBT for patients with anxiety disorders, further research is needed to determine the durability of these effects.
D-Cycloserine in Conjunction With Exposures
One approach for improving patient outcomes is to target the extinction learning process underlying exposure exercises. There has been recent interest in cognitive enhancers, such as d-cycloserine (DCS) or methylene blue, as pharmacological adjuncts to exposure therapy ( 14 , 15 ). In preclinical studies, DCS has demonstrated evidence as a cognitive enhancer, consolidating new learning during extinction training. Specifically, the efficacy associated with DCS depends on the efficacy of the exposure exercise. For instance, during a successful exposure exercise, in which anxiety levels decrease substantially, the administration of DCS may confer additional benefit by consolidating this learning. However, if an exposure exercise was unsuccessful and fear levels never decreased, then DCS might consolidate the fear memory, thereby exacerbating the severity of the anxiety disorder ( 14 ). Recently, however, there has been evidence ( 16 ) suggesting that the efficacy of cognitive enhancers, such as DCS, has been declining, possibly because of changes in dose and dose timing. More research needs to be undertaken to understand under what circumstances (e.g., length of exposure session, amount of fear reduction, timing of dose) DCS would offer the greatest therapeutic effect in conjunction with exposure therapy.
Novel Delivery Methods
Internet-delivered CBT (I-CBT) is an alternative modality for the delivery of CBT for patients with anxiety and related disorders. I-CBT is a scalable alternative to in-person treatment, with the Internet used as an accessible and cost-effective method of delivery for evidence-based treatment. In I-CBT, CBT modules are delivered via computer or an application on a mobile device, with the support of a therapist or through a self-guided system. I-CBT has been shown ( 17 – 19 ) to be superior to waitlist and placebo conditions in the treatment of adults with a range of anxiety and trauma disorders, including anxiety and PTSD. Results ( 18 ) have indicated that I-CBT is similarly effective at reducing panic disorder symptoms as face-to-face CBT. The results of another trial ( 20 ) have indicated that I-CBT is also effective at reducing symptoms of OCD and social anxiety disorder.
In addition to Internet and mobile application platforms for CBT, virtual reality technology offers novel avenues to access cognitive-behavioral interventions ( 21 ). One key advantage is that recent advances in the sensory vividness of virtual reality platforms have facilitated more meaningful exposure exercises. For example, virtual reality flight simulators can be leveraged to expose a patient with flight phobia to several flight conditions with enhanced sensory detail (e.g., sounds of liftoff or landing, vibrations, images of clouds through a window, images of in-cabin atmosphere). This technology could obviate the need to purchase several expensive flights to participate in exposure exercises, thereby permitting more frequent exposure opportunities.
Conclusions
CBT is an effective, gold-standard treatment for anxiety and stress-related disorders. CBT uses specific techniques to target unhelpful thoughts, feelings, and behaviors shown to generate and maintain anxiety. CBT can be used as a stand-alone treatment, may be combined with standard medications for the treatment of patients with anxiety disorders (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), or used with novel interventions (e.g., mindfulness). Furthermore, this treatment is flexible in terms of who may benefit from it. Overall, whenever a patient is experiencing some form of emotional psychopathology (e.g., an anxiety or depression disorder) or distressing emotions that do not meet disorder threshold but cause distress or interference in daily activities, referral to a CBT provider is indicated to pursue a course of treatment to actively address such symptoms and problems.
The authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
1 Kessler RC , Petukhova M , Sampson NA , et al. : Twelve-month and lifetime prevalence and lifetime morbid risk of anxiety and mood disorders in the United States . Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 2012 ; 21 : 169 – 184 Crossref , Google Scholar
2 Hofmann SG , Asmundson GJ , Beck AT : The science of cognitive therapy . Behav Ther 2013 ; 44 : 199 – 212 Crossref , Google Scholar
3 Beck AT , Emery G , Greenberg RL : Anxiety Disorders and Phobias: A Cognitive Perspective . New York , Basic Books , 2005 Google Scholar
4 Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders , 5th ed . Washington, DC , American Psychiatric Association , 2013 Google Scholar
5 Hofmann SG , Carpenter J , Curtiss JE , et al. : The Anxiety Skills Workbook: Simple CBT and Mindfulness Strategies for Overcoming Anxiety, Fear, and Worry . Oakland, CA , New Harbinger , 2020 Google Scholar
6 Hofmann SG , Otto MW : Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Social Anxiety Disorder: Evidence-Based and Disorder Specific Treatment Techniques . New York , Routledge , 2017 Crossref , Google Scholar
7 Foa EB , Yadin E , Lichner TK : Exposure and Response (Ritual) Prevention for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Therapist Guide . New York , Oxford University Press , 2012 Crossref , Google Scholar
8 Resick PA , Nishith P , Weaver TL , et al. : A comparison of cognitive-processing therapy with prolonged exposure and a waiting condition for the treatment of chronic posttraumatic stress disorder in female rape victims . J Consult Clin Psychol 2002 ; 70 : 867 – 879 Crossref , Google Scholar
9 Shear MK : Complicated grief treatment: the theory, practice and outcomes . Bereave Care 2010 ; 29 : 10 – 14 Crossref , Google Scholar
10 Barlow DH , Farchione TJ , Bullis JR , et al. : The unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders compared with diagnosis-specific protocols for anxiety disorders: a randomized clinical trial . JAMA Psychiatry 2017 ; 74 : 875 – 884 Crossref , Google Scholar
11 Hofmann SG , Gómez AF : Mindfulness-based interventions for anxiety and depression . Psychiatr Clin North Am 2017 ; 40 : 739 – 749 Crossref , Google Scholar
12 Segal ZV , Williams JMG , Teasdale JD : Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy for Depression: A New Approach to Preventing Relapse . New York , Guilford , 2002 Google Scholar
13 Hofmann SG , Sawyer AT , Korte KJ , et al. : Is it beneficial to add pharmacotherapy to cognitive-behavioral therapy when treating anxiety disorders? A meta-analytic review . Int J Cogn Ther 2009 ; 2 : 160 – 175 Crossref , Google Scholar
14 Curtiss J , Carpenter J , Kind S , et al. : Incorporating Memory Enhancers into the Treatment of Anxiety and Related Disorders , 2nd ed . Oxford, UK , Elsevier , 2016 Google Scholar
15 Zoellner LA , Telch M , Foa EB , et al. : Enhancing extinction learning in posttraumatic stress disorder with brief daily imaginal exposure and methylene blue: a randomized controlled trial . J Clin Psychiatry 2017 ; 78 : e782 – e789 Crossref , Google Scholar
16 Rosenfield D , Smits JAJ , Hofmann SG , et al. : Changes in dosing and dose timing of D-cycloserine explain its apparent declining efficacy for augmenting exposure therapy for anxiety-related disorders: an individual participant-data meta-analysis . J Anxiety Disord 2019 ; 68 : 102149 Crossref , Google Scholar
17 Reger MAGG , Gahm GA : A meta-analysis of the effects of internet- and computer-based cognitive-behavioral treatments for anxiety . J Clin Psychol 2009 ; 65 : 53 – 75 Crossref , Google Scholar
18 Sijbrandij M , Kunovski I , Cuijpers P : Effectiveness of internet‐delivered cognitive behavioral therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder: a systematic review and meta‐analysis . Depress Anxiety 2016 ; 33 : 783 – 791 Crossref , Google Scholar
19 Stech EP , Lim J , Upton EL , et al. : Internet-delivered cognitive behavioral therapy for panic disorder with or without agoraphobia: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Cogn Behav Ther 2020 ; 49 : 270 – 293 Crossref , Google Scholar
20 Matsumoto K , Sutoh C , Asano K , et al. : Internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy with real-time therapist support via videoconference for patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder: pilot single-arm trial . J Med Internet Res 2018 ; 20 : e12091 Crossref , Google Scholar
21 Valmaggia LR , Latif L , Kempton MJ , et al. : Virtual reality in the psychological treatment for mental health problems: an systematic review of recent evidence . Psychiatry Res 2016 ; 236 : 189 – 195 Crossref , Google Scholar
- Efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy after the surgical treatment of women with endometriosis: A preliminary case-control study Medicine, Vol. 101, No. 51

- Anxiety and anxiety disorders
- Psychotherapy
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 15 April 2020
Practice of stress management behaviors and associated factors among undergraduate students of Mekelle University, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study
- Gebrezabher Niguse Hailu 1
BMC Psychiatry volume 20 , Article number: 162 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
31k Accesses
1 Citations
Metrics details
Stress is one of the top five threats to academic performance among college students globally. Consequently, students decrease in academic performance, learning ability and retention. However, no study has assessed the practice of stress management behaviors and associated factors among college students in Ethiopia. So the purpose of this study was to assess the practice of stress management behaviors and associated factors among undergraduate university students at Mekelle University, Tigray, Ethiopia, 2019.
A cross-sectional study was conducted on 633 study participants at Mekelle University from November 2018 to July 2019. Bivariate analysis was used to determine the association between the independent variable and the outcome variable at p < 0.25 significance level. Significant variables were selected for multivariate analysis.
The study found that the practice of stress management behaviors among undergraduate Mekelle university students was found as 367(58%) poor and 266(42%) good. The study also indicated that sex, year of education, monthly income, self-efficacy status, and social support status were significant predictors of stress management behaviors of college students.
This study found that the majority of the students had poor practice of stress management behaviors.
Peer Review reports
Stress is the physical and emotional adaptive response to an external situation that results in physical, psychological and behavioral deviations [ 1 ]. Stress can be roughly subdivided into the effects and mechanisms of chronic and acute stress [ 2 ]. Chronic psychological stress in early life and adulthood has been demonstrated to result in maladaptive changes in both the HPA-axis and the sympathetic nervous system. Acute and time-limited stressors seem to result in adaptive redistribution of all major leukocyte subpopulations [ 2 ].
Stress management behaviors are defined as behaviors people often use in the face of stress /or trauma to help manage painful or difficult emotions [ 3 ]. Stress management behaviors include sleeping 6–8 h each night, Make an effort to monitor emotional changes, Use adequate responses to unreasonable issues, Make schedules and set priorities, Make an effort to determine the source of each stress that occurs, Make an effort to spend time daily for muscle relaxation, Concentrate on pleasant thoughts at bedtime, Feel content and peace with yourself [ 4 ]. Practicing those behaviors are very important in helping people adjust to stressful events while helping them maintain their emotional wellbeing [ 3 ].
University students are a special group of people that are enduring a critical transitory period in which they are going from adolescence to adulthood and can be one of the most stressful times in a person’s life [ 5 ]. According to the American College Health Association’s National College Health Assessment, stress is one of the top five threats to academic performance among college students [ 6 ]. For instance, stress is a serious problem in college student populations across the United States [ 7 ].
I have searched literatures regarding stress among college students worldwide. For instance, among Malaysian university students, stress was observed among 36% of the respondents [ 8 ]. Another study reported that 43% of Hong Kong students were suffered from academic stress [ 9 ]. In western countries and other Middle Eastern countries, including 70% in Jordan [ 10 ], 83.9% in Australia [ 11 ]. Furthermore, based on a large nationally representative study the prevalence of stress among college students in Ethiopia was 40.9% [ 12 ].
Several studies have shown that socio-demographic characteristics and psychosocial factors like social support, health value and perceived self-efficacy were known to predict stress management behaviors [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ].
Although the prevalence of stress among college students is studied in many countries including Ethiopia, the practice of stress management behaviors which is very important in promoting the health of college students is not studied in Ethiopia. Therefore this study aimed to assess the practice of stress management behaviors and associated factors among undergraduate students at Mekelle University.
The study was conducted at Mekelle university colleges from November 2018 to July 2019 in Mekelle city, Tigray, Ethiopia. Mekelle University is a higher education and training public institution located in Mekelle city, Tigray at a distance of 783 Kilometers from the Ethiopian capital ( http://www.mu.edu.et/ ).
A cross-sectional study was conducted on 633 study participants. Students who were ill (unable to attend class due to illness), infield work and withdrawal were not included in the study.
The actual sample size (n) was computed by single population proportion formula [n = [(Za/2)2*P (1 − P)]/d2] by assuming 95% confidence level of Za/2 = 1.96, margin of error 5%, proportion (p) of 50% and the final sample size was estimated to be 633. A 1.5 design effect was used by considering the multistage sampling technique and assuming that there was no as such big variations among the students included in the study.
Multi-stage random sampling was used. Three colleges (College of health science, college of business and Economics and College of Natural and Computational Science) were selected from a total of the seven Colleges from Mekelle University using a simple random sampling technique in which proportional sample allocation was considered from each college.
Data were collected using a self-administered questionnaire by trained research assistants at the classes.
The questionnaire has three sections. The first section contained questions on demographic characteristics of the study participants. The second section contained questions to assess the practice of stress management of the students. The tool to assess the practice of stress management behaviors for college students was developed by Walker, Sechrist, and Pender [ 4 ]. The third section consisted of questions for factors associated with stress management of the students divided into four sub-domains, including health value used to assess the value participants place on their health [ 18 ]. The second subdomain is self-efficacy designed to assess optimistic self-beliefs to cope with a variety of difficult demands in life [ 19 ] and was adapted by Yesilay et al. [ 20 ]. The third subdomain is perceived social support measures three sources of support: family, friends, and significant others [ 21 ] and was adapted by Eker et al. [ 22 ]. The fourth subscale is perceived stress measures respondents’ evaluation of the stressfulness of situations in the past month of their lives [ 23 ] and was adapted by Örücü and Demir [ 24 ].
The entered data were edited, checked visually for its completeness and the response was coded and entered by Epi-data manager version 4.2 for windows and exported to SPSS version 21.0 for statistical analysis.
Bivariate analysis was used to determine the association between the independent variable and the outcome variable. Variables that were significant at p < 0.25 with the outcome variable were selected for multivariable analysis. And odds ratio with 95% confidence level was computed and p -value <= 0.05 was described as a significant association.
Operational definition
Good stress management behavior:.
Students score above or equal to the mean score.
Poor stress management behavior:
Students score below the mean score [ 4 ].
Seciodemographic characteristics
Among the total 633 study participants, 389(61.5%) were males, of those 204(32.2%) had poor stress management behavior. The Median age of the respondents was 20.00 (IQR = ±3). More ever, this result showed that 320(50.6%) of the students came from rural areas, 215(34%) of them had poor stress management behavior.
The result revealed that 363(57.35%) of the study participants were 2nd and 3rd year students, of them 195 (30.8%) had poor stress management.
This result indicated that 502 (79.3%) of the participants were in the monthly support category of > = 300 ETB with a median income of 300.00 ETB (IQR = ±500), from those, 273(43.1%) students had poor stress management behavior (Table 1 ).
Status of practice of stress management behaviors of under graduate students at Mekelle University, Ethiopia
Psychosocial factors
This result indicated that 352 (55.6%) of the students had a high health value status of them 215 (34%) had good stress management behavior. It also showed that 162 (25.6%) of the students had poor perceived self-efficacy, from those 31(4.9%) had a good practice of stress management behavior. Moreover, the result showed that 432(68.2%) of the study participants had poor social support status of them 116(18.3%) had a good practice of stress management behavior (Table 1 ).
Practice of stress management behaviors
The result showed that the majority (49.8%) of the students were sometimes made an effort to spend time daily for muscle relaxation. Whereas only 28(4.4%) students were routinely concentrated on pleasant thoughts at bedtime.
According to this result, only 169(26.7%) of the students were often made an effort to determine the source of stress that occurs. It also revealed that the majority (40.1%) of the students were never made an effort to monitor their emotional changes. Similarly, the result indicated that the majority (42.5%) of the students were never made schedules and set priorities.
The result revealed that only 68(10.7%) of the students routinely slept 6–8 h each night. More ever, the result showed that the majority (34.4%) of the students were sometimes used adequate responses to unreasonable issues (Table 2 ).
Status of the practice of stress management behaviors
The result revealed that the practice of stress management behaviors among regular undergraduate Mekelle university students was found as 367(58%) poor and 266(42%) good. (Fig 1 )
Factors associated with stress management behaviors
In the bivariate analysis sex, college, year of education, student’s monthly income’, perceived-self efficacy, perceived social support and perceived stress were significantly associated with stress management behavior at p < =0.25. Whereas in the multivariate analysis sex, year of education, student’s monthly income’, perceived-self efficacy and perceived social support were significantly associated with stress management behavior at p < =0.05.
Male students were 3.244 times more likely to have good practice stress management behaviors than female students (AOR: 3.244, CI: [1.934–5.439]). Students who were in the age category of less than 20 years were 70% less to have a good practice of stress management behaviors than students with the age of greater or equal to 20 year (AOR: 0.300, CI:[0.146–0.618]).
Students who had monthly income less than300 ETB were 64.4% less to have a good practice of stress management behaviors than students with monthly income greater or equal to 300 ETB (AOR: 0.356, CI:[0.187–0.678]).
Students who had poor self- efficacy status were 70.3% less to have a good practice of stress management behaviors than students with good self-efficacy status (AOR: 0.297, CI:[0.159–0.554]). Students who had poor social support were 70.5% less to have a good practice of stress management behaviors than students with good social support status (AOR: 0.295[0.155–0.560]) (Table 3 ).
The present study showed that the practice of stress management behaviors among regular undergraduate students was 367(58%) poor and 266(42%) good. The study indicated that sex, year of education, student’s monthly income, social support status, and perceived-self efficacy status were significant predictors of stress management behaviors of students.
The current study revealed that male students were more likely to have good practice of stress management behaviors than female students. This finding is contradictory with previous studies conducted in the USA [ 13 , 25 ], where female students were showed better practice of stress management behaviors than male students. This difference might be due to socioeconomic and measurement tool differences.
The current study indicated that students with monthly income less than 300 ETB were less likely to have good practice of stress management behaviors than students with monthly income greater than or equal to 300 ETB. This is congruent with the recently published book which argues a better understanding of our relationship with money (income). The book said “the people with more money are, on average, happier than the people with less money. They have less to worry about because they are not worried about where they are going to get food or money for their accommodation or whatever the following week, and this has a positive effect on their health” [ 26 ].
The present study found that first-year students were less likely to have good practice of stress management behaviors than senior students. This finding is similar to previous findings from Japan [ 27 ], China [ 28 ] and Ghana [ 29 ]. This might be because freshman students may encounter a multitude of stressors, some of which they may have dealt with in high school and others that may be a new experience for them. With so many new experiences, responsibilities, social settings, and demands on their time. As a first-time, incoming college freshman, experiencing life as an adult and acclimating to the numerous and varied types of demands placed on them can be a truly overwhelming experience. It can also lead to unhealthy amounts of stress. A report by the Anxiety and Depression Association of America found that 80% of freshman students frequently or sometimes experience daily stress [ 30 ].
The current study showed that students with poor self-efficacy status were less likely to have good practice of stress management behaviors. This is congruent with the previous study that has demonstrated quite convincingly that possessing high levels of self-efficacy acts to decrease people’s potential for experiencing negative stress feelings by increasing their sense of being in control of the situations they encounter [ 14 ]. More ever this study found that students with poor social support were less likely to have a good practice of stress management behaviors. This finding is similar to previous studies that found good social support, whether from a trusted group or valued individual, has shown to reduce the psychological and physiological consequences of stress, and may enhance immune function [ 15 , 16 , 17 ].
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethical clearance and approval obtained from the institutional review board of Mekelle University. Moreover, before conducting the study, the purpose and objective of the study were described to the study participants and written informed consent was obtained. The study participants were informed as they have full right to discontinue during the interview. Subject confidentiality and any special data security requirements were maintained and assured by not exposing the patient’s name and information.
Limitation of the study
There is limited literature regarding stress management behaviors and associated factors. There is no similar study done in Ethiopia previously. More ever, using a self-administered questionnaire, the respondents might not pay full attention to it/read it properly.
This study found that the majority of the students had poor practice of stress management behaviors. The study also found that sex, year of education, student’s monthly income, social support status, and perceived-self efficacy status were significant predictors of stress management behaviors of the students.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Adjusted Odd Ratio
College of Business& Economics
College of health sciences
Confidence interval
College of natural and computational sciences
Crud odds ratio
Ethiopian birr
Master of Sciences
United States of America
United kingdom
Figueroa-Romero C, Sadidi M, Feldman EL. Mechanisms of disease: the oxidative stress theory of diabetic neuropathy. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2008;9(4):301–14.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Lagraauw HM, Kuiper J, Bot I. Acute and chronic psychological stress as risk factors for cardiovascular disease: insights gained from epidemiological, clinical and experimental studies. Brain Behav Immun. 2015;50:18–30.
Article Google Scholar
Greenberg J. Comprehensive stress management: McGraw-Hill Education; 2012.
Walker SN, Sechrist KR, Pender NJ. The health-promoting lifestyle profile: development and psychometric characteristics. Nurs Res. 1987.
Buchanan JL. Prevention of depression in the college student population: a review of the literature. Arch Psychiatric Nurs. 2012;26(1):21–42.
Kisch J, Leino EV, Silverman MM. Aspects of suicidal behavior, depression, and treatment in college students: results from the spring 2000 National College Health Assessment Survey. Suicide Life Threat Behav. 2005;35(1):3–13.
Crandall KJ, Steward K, Warf TM. A mobile app for reducing perceived stress in college students. Am J Health Stud. 2016;31(2):68–73.
Google Scholar
Gan WY, Nasir MM, Zalilah MS, Hazizi AS. Disordered eating behaviors, depression, anxiety and stress among Malaysian university students. Coll Stud J. 2011;45(2):296–31.
Wong JG, Cheung EP, Chan KK, Ma KK, Wa TS. Web-based survey of depression, anxiety and stress in first-year tertiary education students in Hong Kong. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2006;40(9):777–82.
Abu-Ghazaleh SB, Rajab LD, Sonbol HN. Psychological stress among dental students at the University of Jordan. J Dent Educ. 2011;75(8):1107–14.
PubMed Google Scholar
McDermott BM, Cobham VE, Berry H, Stallman HM. Vulnerability factors for disaster-induced child post-traumatic stress disorder: the case for low family resilience and previous mental illness. Austr New Zeal J Psychiatry. 2010;44(4):384–9.
Dachew BA, Bisetegn TA, Gebremariam RB. Prevalence of mental distress and associated factors among undergraduate students of the University of Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia: a cross-sectional institutional based study. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0119464.
Matheny KB, Ashby JS, Cupp P. Gender differences in stress, coping, and illness among college students. J Individ Psychol. 2005;1:61(4).
Mills H, Reiss N, Dombeck M. Self-efficacy and the perception of control in stress reduction: Mental Help; 2008.
Morisky DE, DeMuth NM, Field-Fass M, Green LW, Levine DM. Evaluation of family health education to build social support for long-term control of high blood pressure. Health Educ Q. 1985;12(1):35–50.
Yilmaz FT, Sabancıogullari S, Aldemir K, Kumsar AK. Does social support affect development of cognitive dysfunction in individuals with diabetes mellitus? Saudi Med J. 2015;36(12):1425.
Barrera M Jr, Toobert DJ, Angell KL, Glasgow RE, MacKinnon DP. Social support and social-ecological resources as mediators of lifestyle intervention effects for type 2 diabetes. J Health Psychol. 2006;11(3):483–95.
Lau RR, Hartman KA, Ware JE. Health as a value: methodological and theoretical considerations. Health Psychol. 1986;5(1):25.
Zhang JX, Schwarzer R. Measuring optimistic self-beliefs: A Chinese adaptation of the General Self-Efficacy Scale. Psychologia. 1995.
Peker K, Bermek G. Predictors of health-promoting behaviors among freshman dental students at Istanbul University. J Dent Educ. 2011;75(3):413–20.
Zimet GD, Dahlem NW, Zimet SG, Farley GK. The multidimensional scale of perceived social support. J Pers Assess. 1988;52(1):30–41.
Eker D, Arkar H, Yaldiz H. Generality of support sources and psychometric properties of a scale of perceived social support in Turkey. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2000;35(5):228–33.
Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress. J Health Soc Behav. 1983;1:385–96.
Örücü MÇ, Demir A. Psychometric evaluation of perceived stress scale for Turkish university students. Stress Health. 2009;25(1):103–9.
Crockett LJ, Iturbide MI, Torres Stone RA, McGinley M, Raffaelli M, Carlo G. Acculturative stress, social support, and coping: relations to psychological adjustment among Mexican American college students. Cult Divers Ethn Minor Psychol. 2007;13(4):347.
Thaler RH, Sunstein CR. Nudge: Improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness: Penguin; 2009..
Wei CN, Harada K, Ueda K, Fukumoto K, Minamoto K, Ueda A. Assessment of health-promoting lifestyle profile in Japanese university students. Environ Health Prev Med. 2012;17(3):222.
Wang D, Ou CQ, Chen MY, Duan N. Health-promoting lifestyles of university students in mainland China. BMC Public Health. 2009;9(1):379.
Amponsah M, Owolabi HO. Perceived stress levels of fresh university students in Ghana: a case study. J Educ Soc Behav Sci. 2011;27:153–69.
Beiter R, Nash R, McCrady M, Rhoades D, Linscom BM, Clarahan M, Sammut S. The prevalence and correlates of depression, anxiety, and stress in a sample of college students. J Affect Disord. 2015;173:90–6.
Download references
Acknowledgments
Author thanks Mekelle University, data collectors, supervisors and study participants.
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of nursing, Mekelle University, Tigray, Ethiopia
Gebrezabher Niguse Hailu
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Make an interpretation of the data, make the analysis of the data, prepares and submits the manuscript. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gebrezabher Niguse Hailu .
Ethics declarations
Ethical clearance and approval obtained from the institutional review board of Mekelle University. Moreover, before conducting the study, the purpose and objective of the study were described to the study participants and written informed consent was obtained. The study participants were informed as they have full right to discontinue. Subject confidentiality and any special data security requirements were maintained and assured by not exposing patients’ names and information. Besides, the questionnaires and all other information were stored on a personal computer which is protected with a password.
Consent for publication
Not applicable as there is no image or other confidentiality related issues.
Competing interests
The author declares that he/she has no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hailu, G.N. Practice of stress management behaviors and associated factors among undergraduate students of Mekelle University, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 20 , 162 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-020-02574-4
Download citation
Received : 04 October 2019
Accepted : 30 March 2020
Published : 15 April 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-020-02574-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Stress management
- University students
BMC Psychiatry
ISSN: 1471-244X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Workplace stress: an occupational health case study
This case study on workplace stress shows how the evidence base for occupational health underpinned a successful intervention. Anne Donaldson and Anne Harriss explain.
Stress, anxiety or depression underpin much work-related ill health, accounting for 9.9 million days of sickness absence in 2014-15, with, on average, 23 days lost per person. It resulted in 35% of all days missed from work due to ill health. Industries reporting the highest prevalence of ill health from work-related stress included health and social care, teaching, public administration and defence (HSE, 2015).
The Mental Health Foundation claims 12 million adults consult their GP each year due to mental illness, much of it stress related; one in six of the population experiences anxiety (MHF, 2014).
The main causes of work-related stress reported to GPs (THOR – GP) were workload pressures, interpersonal relationships, including bullying, harassment and difficulty with superiors, and work changes, including responsibilities and reduction of resources (HSE, 2014). A YouGov survey (2012) found 48% of the British workforce said they were stressed most of the time and 47% cited performance issues as key reasons.
Impact of workplace stress on individuals and work colleagues
Stress wanes when stressors are reduced. Conversely, anxiety can persist without a clear cause to the individual.
Anxiety and stress are closely linked with similar signs and symptoms; anxiety may be associated with depression as the most common mood disorder seen in primary care (Kumar and Clark, 2012). People with low psychosocial resources are more likely to succumb to mood disturbance when stress levels increase despite experiencing few stressors (DeLongis et al, 1988).
Colleagues often undertake the work responsibilities of absent staff. This may lead to spiralling absences among co-workers, who are stressed because of the additional responsibility (HSE, 2014). This case study presents the assessment of an employee, Norman, in order to ensure his fitness to return to his role without impacting on his health (Palmer et al, 2013).
The objectives of the consultation were two-fold:
- evaluating whether work had adversely affected Norman’s health and whether it may continue to do so; and
- providing impartial advice to management regarding his sickness absence, suggesting modifications for their consideration in order to support a successful return to work.
Norman’s referral by management was precipitated by a four-week absence related to stress and anxiety. There had been four further single-day absences in the preceding six months attributed to gastrointestinal upsets.
The consultation
Norman, a 22-year-old part-time receptionist and administrative assistant, had been employed in this role for 10 months working 30 hours per week. He had been absent from work for a month on the day of the consultation and was preparing to return to work. On entering the department, his mobility difficulties and an obviously awkward gait and altered balance were noted. He disclosed treatment by his GP for stress, anxiety and depression.
He described previous short-term absences resulting from nausea and vomiting, relating these to his anxiety at attending work. In the previous five to six weeks, in addition to nausea he also referred to difficulty sleeping, restlessness, loss of appetite, palpitations and rumination on his low self-esteem. Rumination can be a negative effect of stress. Genet and Siemer (2012) claim that rumination moderates the relation between unpleasant daily effects and negative mood.
Although excessive rumination is maladaptive, McFarland et al (2007) agree that some limited self-focus can be beneficial. Norman felt anxious about returning to the same situation and was accessing counselling support to help anxiety management. Hunsley et al (2014) suggest that psychological treatments are of at least equal benefit to medication for common mental disorders.
He had been prescribed 75mg of Venlafaxine a day with good effect. Venlafaxine is a serotonin and noradrenaline re-uptake inhibitor used to treat depression or generalised anxiety disorder. His GP also prescribed 5mg of diazepam – a long-acting benzodiazepine anxiolytic – to be taken as required. Recently he had not taken this as he felt better.
Past health and social history
Norman had cerebral palsy and experienced difficulty walking during his early years. Achilles tendon surgery in childhood improved this, although surgery left him with residual lower leg discomfort if he walked too far or stood for sustained periods without resting. The orthopaedic team monitored him every 18 months.
Norman described excellent family support. A non-smoker and non-drinker of alcohol, he took no formal exercise but walked as much as he felt able. Increasing physical activity within his ability was advised as it is found to improve mental health (Crone & Guy, 2008; McArdle et al, 2012).
Work issues
Norman generally enjoyed his role, shared with an able-bodied colleague with whom he alternated his reception duties. He indicated the interface with the public could be challenging and stressful. His workload had increased in the previous four months following the resignation of a colleague who indicated that he too found this role stressful. Financial constraints resulted in this position remaining unfilled, increasing Norman’s responsibilities. Stress is recognised as contributing to high staff turnover and low morale (Wolever et al, 2012).
Although working primarily at the reception desk, Norman frequently got up from his chair to deal with customers and to undertake photocopying duties. On one occasion he spent an afternoon mostly standing, which resulted in leg discomfort. No workplace adjustments had been effected to support his disability.
On recruitment, his manager had enquired whether he required any adjustments. Norman declined this offer, not wanting to “make a fuss”. He had not disclosed his disability at pre-employment screening (PES) as he did not consider himself disabled.
Many of Norman’s perceived stressors are normal daily occurrences of reception duties, but his physical disability exacerbated this. As he had not requested adjustments, there was nothing in place to support him in relation to his mobility difficulties.
Although his disability had not been disclosed at PES, under s.2 of the Health and Safety at Work etc Act 1974, Norman’s employer has a duty of care to him. Withholding information at PES that later comes to light could lead to disciplinary action but Norman considered that declaring his disability may have precluded his employment.
Cerebral palsy describes a group of childhood syndromes, apparent from birth or early childhood, characterised by abnormalities in motor function and muscle tone caused by genetic, intrauterine or neonatal insults to brain development. Resulting disabilities, of varying degrees, may be physical and mental.
A full functional capability assessment should have been performed at the start of his employment, facilitating adjustments enabling him to function effectively (Palmer et al, 2013). This had not been undertaken.
Norman usually managed his leg discomforts but occasionally had been unable to rest them at work. A study of workers with rheumatoid arthritis suggested that the workers reported greater discomfort on the days when they experienced more undesirable work events or job “strain” (Fifield et al, 2004).
Although this study looked at rheumatoid arthritis, issues concerning chronic pain and discomfort are relevant in this case. Although ultimately a legal decision, Norman was likely to be covered under the Equality Act 2010 as he had a long-term disability.
Withholding information at PES was fundamental to the case of Cheltenham Borough Council v Laird (2009) . The council accused Laird of lying on her PES questionnaire by not disclosing her mental health history. She had been taking long-term antidepressants that kept her depression under control, but after some work problems her health deteriorated and she retired on health grounds. The judge confirmed there was no general duty of disclosure of information that was not specifically requested.
Thus, if a PES form does not directly ask about cerebral palsy, disclosure was not required. Kloss (2010) mentions these types of dilemmas are often only answered through the courts, but unless the employer is given information regarding disability, he cannot reasonably put adjustments in place. In the case of Hanlon v Kirklees Metropolitan Council and others , the employee declined to consent to the disclosure of medical records, arguing this would contravene his right to privacy, and subsequently lost his case of disability discrimination.
The Health and Safety Executive (HSE 2007) defines stress as: “The adverse reaction people have to excessive pressures or other types of demand placed on them at work.”
The stress response
Stressors initiate physiological responses, evolved to protect and preserve the individual in times of threat by ensuring a reaction (Alexander et al, 2006).
This response is triggered by the limbic system within the brain. This is a series of centres controlling emotions, reproductive and survival behaviours (Blows, 2011). When survival is threatened, the system is instantly triggered into action to protect the individual, regardless of the threat magnitude.
A chain reaction occurs: the hypothalamus mediates the autonomic nervous system (Alexander et al, 2006), resulting in a sequence of physiological changes. The initial reaction is very fast, and only when the information reaches the cerebrum can the urgency of the situation be determined and responses modified (Blows, 2011).
The initial flight-or-fight response acts on the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. Noradrenaline from the adrenal medulla immediately prepares the body for physical activity, mobilising glucose and oxygen to the heart, brain and skeletal muscles, preparing for flight or fight.
Non-essential functions, including digestion, are inhibited. Reduced bloodflow to the skin and kidneys promote the release of rennin, triggering the angiotensin – aldosterone pathway leading to fluid retention and hypertension. The resistance reaction results from corticotropin-releasing factor from the hypothalamus, stimulating the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone from the pituitary. This effects a release of cortisol from the adrenal cortex.
Cortisol effects are far-reaching, including lipolysis, gluconeogenesis and reducing inflammation. (Tortora and Grabowski, 2003). The body compensates for the effects of stress as long as possible. Three phases of stress are described as the general adaptation syndrome: alarm phase, resistance and exhaustion (Blows, 2011). The resistance and exhaustion phases may lead to immunosuppression and consequent disease (Tortora and Grabowski, 2003).
There is a reciprocal feedback link between the thalamus and amygdala. When the amygdala becomes overactive, fear and anxiety result. While adrenaline keeps the stress response active, endorphins protect the brain from the effects of fear (Blows, 2011). With so many physiological responses, there are numerous symptoms of stress that vary with each individual.
Significantly, stress causes muscle tension (HSE, 2007), exacerbating Norman’s discomfort, influencing his quality of life. As Kumar and Clark (2012) note, this is associated with depression.
The HSE (2007) management standards for work stress cover six main areas of primary work design that can contribute to stress if not properly managed. These include:
- Demands – including work patterns, workloads and work environment.
- Control – the extent of the worker’s job control.
- Support – provided by the organisation, management and colleagues.
- Role – understanding of their role and avoiding role-conflict.
- Change – management and communication of organisational change.
- Conflict – avoiding conflict, unacceptable behaviour and promoting positive working.
Fitness to work
The fitness-for-work assessment was based on a phenomenological appraisal as the effects of stress vary with each individual and their resilience (Alexander et al, 2006). A bio-psychosocial model informed the assessment. Norman stated that his condition was improving and he was ready to return to work. He no longer experienced symptoms that had taken him to the GP, but he was concerned at ending up in the same situation as before.
A patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9), providing an indication of depression, could have been used to assess Norman. Arroll et al (2010) found that the PHQ-9 is unreliable for diagnosing depression, whereas Manea et al (2012) refutes this assertion. At the time it seemed to be of limited value as he was making good progress.
Norman was advised to discuss his work concerns with his manager. With Norman’s consent, his manager was contacted and advised to carry out a comprehensive stress risk assessment as per the HSE management standards. It was suggested to Norman that he contact the organisation’s employee assistance programme and Access to Work, which offers grants for practical support for individuals with disabilities/health conditions to assist them with starting and staying at work. A phased return to work was formulated assisting Norman back into work and supporting him to stay at work. The following work regime was recommended:
- Week 1: Four hours on two days.
- Week 2: Four hours on four days.
- Week 3: Six hours on four days.
- Week 4: Full working week with the option of a review should Norman struggle.
Norman was to meet with his manager at the end of each week to review his progress, with the option to delay the next stage if this programme proved ineffective. In general, Norman had indicated that he had let his concerns take over without making any attempt to talk with his managers. He realised he should have discussed his work issues with his managers at an earlier stage. As Waddell and Burton (2006) note, early interventions are more effective at reducing long-term sickness absence and keeping workers at work.
Norman’s case illustrates how lack of control and apparent excessive demands and change can influence stress at work to negatively affect health. It reached a successful conclusion, but Norman’s case may have been prevented from requiring OH intervention had he been able to discuss his concerns and feelings with his manager in the first instance and a proactive approach, including the use of HSE stress management standards, been used at an earlier stage.
Anne Donaldson is an occupational health adviser. Anne Harriss is associate professor and course director, London South Bank University.
Alexander MF, Fawcett JN, and Runciman PJ (2006). Nursing Practice: Hospital and Home. 3rd edition. Edinburgh, Elsevier.
Arroll B, Goodyear-Smith F, Crengle S, Gunn J, Kerse N, Fishman T, Falloon K, and Hatcher S (2010). Validation of PHQ-2 and PHQ-9 to screen for major depression in the primary care population. Ann Fam Med. vol.8(4), pp.348-353. doi: 10.1370/afm.1139.
Blows W (2011). The biological basis of mental health nursing. 2nd edition. Abingdon, Oxon. Routledge.
Crone D, and Guy H (2008). “I know it is only exercise, but to me it is something that keeps me going: a qualitative approach to understanding mental health service users’ experiences of sports therapy”. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing, vol.17(3), pp.197-207.
DeLongis A, Folkman S, and Lazarus Richard S (1988). “The impact of daily stress on health and mood: psychological and social resources as mediators”. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, vol.54(3), pp.486-495. Available online. Accessed 19 April 2014.
Fifield J, McQuillan J, Armeli S, Tennen H, Reisne S, and Affleck G (2004). “Chronic strain, daily work stress and pain among workers with rheumatoid arthritis: does job stress make a bad day worse?” Work & Stress, vol.18(4), pp.275-291. Accessed 12 April 2014.
Genet JJ and Siemer M (2012). “Rumination moderates the effects of daily events on negative mood: results from a diary study”. Emotion, vol.12(6), pp.1,329-1,339.
Health and Safety Executive (2007). Managing the causes of work-related stress. A step-by-step approach using the management standards. 2nd edition HSE books. Available online. Accessed 12 April 2016.
Health and Safety Executive (2015). Stress-related and psychological disorders in Great Britain (2014). Available online. Accessed 22 April 2016.
Hunsley J, Elliott K, and Therrien Z (2014). “The efficacy and effectiveness of psychological treatments for mood, anxiety and related disorders”. Canadian Psychology/Psychologie Canadienne, vol.55(3), pp.161-176.
Kloss D (2010). Occupational Health Law, 5th edition, Oxford Wiley Blackwell.
Kumar P and Clark M (2012). Clinical Medicine, 8th edition, Edinburgh, Saunders Elsevier.
Manea L, Gilbody S, and McMillan D (2012). “Optimal cut-off score diagnosing depression with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9): a meta-analysis”. CMAJ, vol.184(3). doi: 10.1503/cmaj.110829.
McArdle S, McGale N, and Gaffney P (2012). “A qualitative exploration of men’s experiences of an integrated exercise/CBT mental health promotion programme”. International Journal Of Men’s Health, vol.11(3), pp.240-257. doi:10.3149/jmh.1103.240.
McFarland C, Buehler R, von Rüti R, Nguyen L, and Alvaro C (2007). “The impact of negative moods on self-enhancing cognitions: the role of reflective versus ruminative mood orientations”. Journal of Personality And Social Psychology, vol.93(5), pp.728-750.
Mental Health Foundation (2014). Mental Health Statistics Available online. Accessed 17 April 2016.
Palmer K, Brown I, and Hobson J (2013). Fitness for Work, 5th edition, Oxford University Press.
Tortora G and Grabowski S (2003). Principles of anatomy and physiology, 10th edition, Hoboken NJ, John Wiley & Sons.
Waddell G, Burton K, and Kendall N (2008). Vocational Rehabilitation, what works, for whom and when? London: TSO pdf. Available online. Accessed 19 April 2016.
Wolever RQ, Bobinet KJ, McCabe K, Mackenzie ER, Fekete E, Kusnick CA, and Baime M (2012). “Effective and viable mind-body stress reduction in the workplace: a randomized controlled trial”. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, vol.17(2), pp.246-258.
YouGov (2012). Stress Survey. Available online. Accessed 19 April 2016.
Cheltenham Borough Council v Laird [2009] IRLR 621.
Hanlon v Kirklees Metropolitan Council and others [2004] EAT 0119/04 (IDS Brief 767).
- 1 No poverty
- 2 Zero hunger
- 3 Good health and well-being
- 4 Quality education
- 5 Gender equality
- 6 Clean water and sanitation
- 7 Affordable and clean energy
- 8 Decent work and economic growth
- 9 Industry, innovation and infrastructure
- 10 Reduced inequalities
- 11 Sustainable cities and communities
- 12 Responsible consumption and production
- 13 Climate action
- 14 Life below water
- 15 Life on land
- 16 Peace, justice and strong institutions
- 17 Partnership for the goals
Related content
Quick reference.
- Tel: +44 20 7166 5500
- Email: [email protected]
- Terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Newsletter service
- Cookie Settings
All content on this site: Copyright © 2024 RELX plc. All rights, including for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies, are reserved. For all Open Access content, the Creative Commons licensing terms apply.

Stress: A Case Study
Read the story of a women who thought she was having a heart attack, but was instead diagnosed with panic disorder, panic attacks.

Although on the surface everything seemed fine, she felt that, "the wheels on my tricycle are about to fall off. I'm a mess." Over the past several months she had attacks of shortness of breath, heart palpitations, chest pains, dizziness, and tingling sensations in her fingers and toes. Filled with a sense of impending doom, she would become anxious to the point of panic. Every day she awoke with a dreaded feeling that an attack might strike without reason or warning.
On two occasions, she rushed to a nearby hospital emergency room fearing she was having a heart attack. The first episode followed an argument with her boyfriend about the future of their relationship. After studying her electrocardiogram, the emergency room doctor told her she was "just hyperventilating" and showed her how to breathe into a paper bag to handle the situation in the future. She felt foolish and went home embarrassed, angry and confused. She remained convinced that she had almost had a heart attack.
Her next severe attack occurred after a fight at work with her boss over a new marketing campaign. This time she insisted that she be hospitalized overnight for extensive diagnostic tests and that her internist be consulted. The results were the same--no heart attack. Her internist prescribed a tranquilizer to calm her down.
Convinced now that her own doctor was wrong, she sought the advice of a cardiologist, who conducted another battery of tests, again with no physical findings. The doctor concluded that stress was the primary cause of the panic attacks and "heart attack" symptoms. The doctor referred her to psychologist specializing in stress.
During her first visit, professionals administered stress tests and explained how stress could cause her physical symptoms. At her next visit, utilizing the tests results, they described to her the sources and nature of her health problems. The tests revealed that she was highly susceptible to stress, that she was enduring enormous stress from her family, her personal life, and her job, and that she was experiencing a number of stress-related symptoms in her emotional, sympathetic nervous, muscular and endocrine systems. She wasn't sleeping or eating well, didn't exercise, abused caffeine and alcohol, and lived on the edge financially.
The stress testing crystallized how susceptible she was to stress, what was causing her stress, and how stress was expressing itself in her "heart attack" and other symptoms. This newly found knowledge eliminated a lot of her confusion and separated her concerns into simpler, more manageable problems.
She realized that she was feeling tremendous pressure from her boyfriend, as well as her mother to settle down and get married; yet, she didn't feel ready. At the same time, work was overwhelming her as a new marketing campaign began. Any serious emotional incident--a quarrel with her boyfriend or her boss--sent her over the edge. Her body's response was hyperventilation, palpitations, chest pain, dizziness, anxiety, and a dreadful sense of doom. Stress, in short, was destroying her life.
Adapted from The Stress Solution by Lyle H. Miller, Ph.D., and Alma Dell Smith, Ph.D.
next: Terrorism Fear: What You Can Do To Alleviate It ~ anxiety-panic library articles ~ all anxiety disorders articles
APA Reference Staff, H. (2007, February 18). Stress: A Case Study, HealthyPlace. Retrieved on 2024, April 25 from https://www.healthyplace.com/anxiety-panic/articles/stress-a-case-study
Medically reviewed by Harry Croft, MD
Related Articles

Can You Cure Anxiety Attacks?
Treatment of anxiety disorders during pregnancy, anxiety - panic attack coping tips, video on social anxiety disorder, gaining control of your fear, conquering your panic, anxiety, and phobias, anxieties site homepage.
2024 HealthyPlace Inc. All Rights Reserved. Site last updated April 25, 2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Ann Occup Environ Med

Effectiveness of a Comprehensive Stress Management Program to Reduce Work-Related Stress in a Medium-Sized Enterprise
Shin-ae kim.
1 Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine & Institute of Environmental and Occupational Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University, 75, Bokji-ro, Busanjin-gu, Busan 633-165, Republic of Korea
Chunhui Suh
Mi-hee park.
2 Occupational Medical Examination Center, Good Morning Hospital, 110, Samsan-ro, Nam-gu, Ulsan 680-804, Republic of Korea
Kunhyung Kim
Chae-kwan lee, byung-chul son, jeong-ho kim, jong-tae lee, kuck-hyun woo.
3 Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Gumi Hospital, 179, Gongdan 1-dong, Gumi-si, Gyeongbuk 730-706, Republic of Korea
Kabsoon Kang
Hyunjin jung.
4 Education & Future Center, Hyunjin Materials. Co., Ltd, 1201-4, Jisa-dogn, Kangseo-gu, Busan 618-230, Republic of Korea
To assess the effectiveness of a comprehensive workplace stress management program consisting of participatory action-oriented training (PAOT) and individual management.
A comprehensive workplace stress management program was conducted in a medium-sized enterprise. The baseline survey was conducted in September 2011, using the Korean Occupational Stress Scale (KOSS) and Worker’s Stress Response Inventory (WSRI). After implementing both organizational and individual level interventions, the follow up evaluation was conducted in November 2011.
Most of the workers participated in the organizational level PAOT and made Team-based improvement plans. Based on the stress survey, 24 workers were interviewed by a researcher. After the organizational and individual level interventions, there was a reduction of several adverse psychosocial factors and stress responses. In the case of blue-collar workers, psychosocial factors such as the physical environment, job demands, organizational system, lack of rewards, and occupational climate were significantly improved; in the case of white-collar workers, the occupational climate was improved.
Conclusions
In light of these results, we concluded that the comprehensive stress management program was effective in reducing work-related stress in a short-term period. A persistent long-term follow up is necessary to determine whether the observed effects are maintained over time. Both team-based improvement activities and individual interviews have to be sustainable and complementary to each other under the long-term plan.
Introduction
Work-related stress can be defined as the harmful physical and emotional responses that occur when the requirements of the job do not match the capabilities, resources, or needs of the worker [ 1 ]. In the case of individual workers, work-relate distress can cause job dissatisfaction, absenteeism, accidents, voluntary unemployment, and finally lead to a decreased quality of life [ 2 ]. For employers, work-related stress has a significant effect on the risk of worker’s being injured in an occupational accident, which increases costs and lost productivity, and finally leads to a deterioration of management [ 3 ]. From the perspective of the nation and the community, these results have negative impacts such as competitive decline [ 4 ]. All workers can suffer from work-related stress, which has a huge social cost. Thus, work-related stress is not only an individual risk factor, but also a risk factor for employers, the community, and the country’s development.
In 27 countries of the European Union (EU) in 2005, 22.3% of the workers had symptoms caused by stress [ 5 ]. In the United Kingdom, estimates of work-related stress was 428,000 cases (40%) out of all work-related illnesses. This could be a factor responsible for the high number of lost work days, which reached 10.4 million in 2011/12 based on the Labour Force Survey data [ 6 ]. In a study conducted in Korea, 346 workers (22%) among 6,977 experienced critical levels of stress [ 7 ]; this was widely reported, particularly in small and mediumsized enterprises. Male white-collar workers with high job stress suffered from more depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms than workers with low job stress in an automobile company [ 8 ]. Depressive symptoms of male workers had a greater impact on work-related stress than the quality of sleep and fatigue in the case of a small manufacturing company [ 9 ]. The self-perceived fatigue of white-collar male workers had a greater impact on work-related stress than the psychosocial factors in the case of small and mediumsized enterprises [ 10 ].
In order to manage work-related stress, effective interventions applicable to the workplace are required. Internationally, various stress interventions in the workplace have been conducted on the basis of work-related stress research. Depending on whether the intervention focuses on an individual’s psychological resources (individual level) or occupational context (organizational level), there are two different approaches to managing work-related stress. At the individual level, relaxation and, cognitive-behavioral techniques have been applied to improve an individual’s psychological resources and responses. At the organizational level, job adjustment and workplace communication activation have been applied to improve the occupational context. In previous intervention studies at only the organization level, there was little impact on individual variables. Individual level interventions had more influence on psychosocial, physiological, and organisational aspects [ 11 ]. In a meta-analysis of workplace stress interventions, the cognitive-behavioral approach was found to be the most effective technique [ 12 , 13 ]. One year after the individual intervention, biofeedback and muscle relaxation showed reduced absenteeism. In the following year, however, the effects of the intervention disappeared and the variables returned to their previous status [ 14 ]. In a similar study, individual level interventions showed only short-term effects [ 15 ]. Secondary or tertiary prevention, which was usually applied to the individual level intervention, strengthened coping with stress that had already occurred, but primary prevention, which was usually applied as an organizational level intervention, reduced the cause of stress. Therefore, only secondary or tertiary prevention without primary prevention seemed to have a limited effect on the reduction of work-related stress. In previous reports, both individual and organizational management for improving workplace mental health were important to manage the causes of stress in the workplace [ 12 ]. The improvement of the psychosocial work environment is helpful to the improvement of the mental health of workers [ 16 ], and mental health is closely related to productivity improvement [ 17 ]. If intervention measures are not mutually exclusive but complementary, an even greater effect can be observed. Therefore, comprehensive stress management should be emphasized [ 18 ].
Participation in workplace health promotion has increased significantly [ 19 , 20 ]. Involvement of the participants can enhance autonomy, justice, and social support, which are the basic components of work-related stress [ 21 ]. Participatory action-oriented training (PAOT) is one of the methods for engaging employees in workplace interventions. Workers who participate in this workshop discover the problems caused by their own work environment. The program suggests appropriate solutions to workplace problems and improves the work environment [ 20 ]. This participatory approach to reducing work-related stress in the work environment reduces psychosocial stressors. It also reinforces the buffer elements against stress [ 22 ]. The application of both participatory approach methods and psychosocial stress reduction methods has been effective in improving a worker’s mental health and productivity [ 23 ].
In this study, a comprehensive stress management program was applied to a medium-sized enterprise that experienced an increase in work-related stress due to rapid growth. The comprehensive stress management program was composed of both participatory organizational intervention for improving the work environment and individual interventions for reinforcing the coping skills against stress. Further, we implemented the stress management program and evaluated its effects.
Materials and methods
Setting and subjects.
This study was conducted in a mediumsized metal forging company that manufactures large parts for marine engines, wind power components, and crank engines. From 2005 to 2011, the company’s annual revenue increased up to 70.4% and the number of employeesincreased by three times. However, problems occurred with the rapid growth of the scale of the company and changes in the organizational structure. Since 2007, to solve this problem, the company has run a variety of projects. An internal evaluation revealed that work-related stress was high due to a change in the organizational culture. Therefore, a workplace stress management program was conducted from September 5 to November 25, 2011. This company had 19 teams of white-collar workers and 12 teams of blue-collar workers, and the total number of employees was 295. The white-collar workers engaged in quality assurance, management support, domestic sales, international sales, production management, technology research, financial strategy, integrated purchasing and trade, quality management, and financial planning. The blue-collar workers engaged in pressing, heat treatment, support, cutting, and maintenance. Seven teams were excluded due to distance of another location or the continuous operation of their machinery. The participants were 123 white-collar workers comprising 13 teams and 129 blue-collar workers comprising 11 teams. Four workers could not respond to the pre-stress survey for reasons such as sick leave and external training. During the study period, 13 workers retired. Five workers could not respond to the post-stress survey for reasons such as sick leave and vacation. There were anonymous responses by 8 workers in the pre- and 16 workers in the post-stress survey; therefore, we could not perform the paired analysis for them. Finally, 91 white-collar workers and 120 blue-collar workers were analyzed in the paired analysis. An outline of the comprehensive stress management program is illustrated in Figure 1 .

Outline of comprehensive stress management program. *Korean Occupational Stress Scale, † Worker’s Stress Response Inventory, ‡ Participatory action-oriented training, ∮ Mental Health Action Checklist ∥Simple, inexpensive, clever.
Stress survey
All of the workers were asked to fill out self-reported questionnaires on September 19–22 and November 28–30, 2011. The same questionnaires were administered in the pre- and post-stress surveys. The questionnaires included general questions related to gender, age, educational level, and position. To compare the before- and after-program effects, we used the Korean Occupational Stress Scale (KOSS) and Worker’s Stress Response Inventory (WSRI). The questionnaires were distributed and collected in sealed envelopes by the company’s human resources department. The collected questionnaires were submitted to the researchers for analysis. The participants were clearly told that their responses would be kept confidential from the company before we carried out the survey as described above.
The KOSS was used to evaluate work-related stressors to reflect the domestic work environment. The KOSS includes eight subscales with 43 items, including the physical environment, job demands, insufficient job control, interpersonal conflicts, job insecurity, organizational system, lack of rewards, and organizational climate [ 24 ]. The WSRI was used to measure stress-related symptoms associated with the job [ 25 ]. The WSRI was a combination of two tools. One was a short-form questionnaire based on the stress response scale developed by Koh [ 26 ], and the other was derived as a subscale of the Korean Version of the Occupational Stress Inventory (K-OSI). WSRI included four subscales with 26 items, namely depressive symptoms, physical symptoms, anger symptoms, and work-related symptoms.
Intervention
Organizational level.
The PAOT was performed using a mental health action checklist focused on improving the work environment [ 27 ] from September 29 to November 25, 2011. The intervention attempted to solve the problems on a team-based approach. Improving the workplace environment was focused on the reduction of work-related stress through the participation of workers. The PAOT emphasized a voluntary initiative of the workers rather than the traditional rule-based approach [ 20 ]. Facilitator workshops were performed first, followed by team-based participatory workshops. One month after the workshops, improved activity checks were conducted by the stress management team. Finally, a simple, inexpensive, clever (SIC) contest was held for determining the recipients of the achievement awards, and the improved activities were announced.
Stress management team
The stress management team was involved in the overall program planning, implementation, follow up, and evaluation. The team consisted of occupational and environmental medicine (OEM) specialists, residents, and occupational health nurses. Two OEM specialists who had been trained on PAOT educated one specialist, two residents, and nine occupational health nurses. The stress management team selected the Mental Health Action Checklist (MHACL) [ 27 ] to evaluate workplace stress voluntarily and to facilitate the improvement brought about by the workers. Meetings with the human resources department were held to discuss the workplace situation and to encourage workers to participate in the stress management program in the preparation phase.
The MHACL focused on the improvement of the work environment
This study used the Korean version [ 27 ] of the Japanese MHACL [ 28 ], which was translated by Park to fit domestic conditions. The MHACL is a useful guide for work-related stress assessment and provides the available options of feasible improvement in various sectors. MHACL consists of 24 good practices in six areas: (1) participation in work planning, (2) working time and organization, (3) ergonomic work methods, (4) workplace environment, (5) mutual support in the workplace, and (6) preparedness and care [ 28 ]. The checklist was developed to facilitate improvement activities. Participants can discuss work-related stress or the work environment effectively using the MHACL, and find ways to improve their work environment followed by reducing work-related stress.
PAOT workshop implementation
Facilitator workshop
The facilitator workshop targeted 24 team leaders and was conducted twice, once on September 29 and next on October 5, at the company’s auditorium. The first workshop lasted 2 hours. The stress management team explained the stress survey results and introduced the PAOT concepts and the MHACL. The second workshop lasted 4 hours and was focused on the interactive learning of how to run a PAOT in detail and a good practice photograph contest. The good practice photographs collected in previous PAOT workshops at other workplaces were exhibited, and each participant selected three pictures that were thought to fit their workplace well. It enabled participants to learn good practices by knowing the reason for their selection, helped them to understand the MHACL on the basis of the good practices, and motivated them to improve their work environment. After the photograph contest, the participants created their own MHACL from the original MHACL by selecting items that fit their work environment (checklist redesign). The participants conducted a walk-through of their workplace to practice the redesigned MHACL. The “good practices” and “practices to be improved” were discussed in the group meetings and presentations.
Team-based participatory workshop
The team-based participatory workshop was conducted with 86 white-collar workers in 13 teams and 108 blue-collar workers in 11 teams. The workshops lasted 2 hours for each team and were conducted on October 7, 10, and 11 in 2011. The stress management team explained the concepts of work-related stress and mental health in the workplace, and introduced PAOT concepts and MHACL. The participants of each team discussed the items of the MHACL and selected three good practices and three practices to be improved. Short- and long-term action plans for the practices to be improved were developed. The facilitators participated in the discussion of each team, encouraged workers to make an active commitment, and if necessary, answered and provided advice on the questions. At the end of the workshop, each team announced the results of the discussion: good practices, practices to be improved, and short-term and long-term action plans.
Improvement activity checks
The researchers summarized the results of the team-based participatory workshop. The human resources department circulated the document of action plans in each team for the purpose of the reconfirmation and stimulation improvement activity on October 31, 2011. The intermediate improvement activities were collected until November 4, 2011. The researchers monitored the implementation of the action plans. If the action plans did not run appropriately, the researchers investigated the problems and provided relevant advice.
Simple, inexpensive, clever (SIC) contest
The SIC contest was held with team leaders who participated in the facilitator workshop. The implementation of action plans was evaluated. Team leaders presented their improvement activities. Good practices to reduce work-related stress were shared. The most simple, inexpensive, and clever improvement practices were chosen by a vote and awarded.
Individual level
Personal interviews.
The interview subjects were selected: 9 workers above 31 points on the WSRI and 9 workers above 22 points on the sleep questionnaire. Among them, 15 workers were interviewed; of the 3 not considered, 1 had retired and 2 were redundant. Finally, 24 workers were interviewed, including 9 voluntary applicants who wanted to be interviewed. The interviews were conducted five times every Tuesday afternoon from October 18 to November 22, 2011.
The occupational and environmental medicine (OEM) specialist interviewed subjects in a separate room. Brief descriptions of subjective stressors, responses, and coping methods for work-related stress were provided on paper before the interview. The coping part of the K-OSI [ 29 ] composed of recreational activities, self-care, social support, and rational and cognitive coping was also completed, and the OEM specialist evaluated the coping skills of individual workers. The interview began with the individual results of the KOSS and WSRI. The OEM specialist encouraged the workers to speak freely about the stress caused by their work. Based on these data, the OEM specialist helped workers to identify their work-related stressors and strengthen their coping skills.
Disseminating stress management information
Information about work-related stressors and coping skills were distributed seven times through the company’s computer network, every Tuesday from October 11 to November 22, 2011. This information included details regarding the following: identification of the stressors, goal setting for stress management, cognitive-behavioral therapy, anger management training, how to induce sleep, abdominal breathing techniques, and muscle relaxation techniques.
Statistical analysis
A chi-squared test was used to analyze general characteristics and work-related characteristics. The descriptive statistics were expressed in terms of frequency and percentage. In order to confirm the effect of the comprehensive stress management programs, a paired t-test was used to compare the pre- and the post-stress surveys, which included the KOSS and WSRI. Reliability was determined by the value of Cronbach’s alpha. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 18, and the significance level was fixed at 0.05.
General characteristics
A total of 211 workers were eligible for the study. There were 120 (56.9%) blue-collar and 91 (43.1%) white-collar workers. The blue-collar worker group was composed only of male workers, and the white-collar worker group had 73 (80.2%) male workers. Most of the blue-collar and white-collar workers considered in this study were in their thirties. With respect to the education level, the group of “high school or less” had 70 blue-collar workers (58.8%) and the group of “college graduates” had 49 blue-collar workers (41.2%). The group of white-collar workers was composed mostly of college graduates, 89 (98.9%). With respect to the employment status, 72 blue-collar workers (60.0%) belonged to the “general” group. In contrast, 46 white-collar workers (51.1%) belonged to the “general” group, in which the general and supervisor’s rate was relatively evenly distributed (Table 1 ).
General characteristics of blue-collar workers and white-collar workers
*p-value by chi-squared test.
† “general” means mere clerk.
‡ “supervisor” means higher position than mere clerk such as section chief or director.
Action plans
The three action plans that were mentioned the most were as follows: First, in the case of blue-collar workers, the short-term action plans were to wear safety protective equipment and respiratory protective masks, to clean the workplace, and to adjust holidays considering the work and individual schedule. The long-term action plans were to improve ventilation, lighting, and noise; to allocate flexible work hours considering the personal needs of workers; and to increase the blue-collar workforce. Second, in the case of white-collar workers, the short-term action plans were to change and clean the lighting, to hold a brief meeting before work, and to change the atmosphere of team dinners such as conversing without alcohol or watching a movie, baseball game, etc. The long-term action plans were to improve ventilation, lighting, and noise; to provide hygienic toilets and resting facilities; and to organize informal social gatherings and recreational activities (Table 2 ).
Action plans presented at the workshop
Comparison of the KOSS score before and after the program
Table 3 shows the changes in the mean subscale scores of the KOSS obtained through the pre- and post-stress surveys. The blue-collar workers exhibited a statistically significant intervention effect in the case of physical environment (p = 0.003), job demands (p = 0.001), organizational system (p = 0.001), lack of rewards (p = 0.035), organizational climate (p = 0.048), and total score (p < 0.001). The white-collar workers exhibited a statistically significant intervention effect in the case of the organizational climate (p = 0.011). Although not statistically significant, the subscales of insufficient job control, interpersonal conflicts, and job insecurity were improved in the case of blue-collar workers. Although not statistically significant, the subscales of job demands, insufficient job control, interpersonal conflicts, organizational system, lack of rewards, and total score were improved in the case of white-collar workers (Table 3 ). The value of Cronbach’s alpha was in the range of 0.706 to 0.880.
Comparison of the KOSS scores obtained through the pre- and post-stress surveys
*p-value by paired t-test.
KOSS: Korean Occupational Stress Scale, SD: Standard deviation, CB α: Cronbach’s alpha.
Comparison of the WSRI score before and after the program
Table 4 shows the changes in the mean subscale scores of the WSRI obtained through the pre- and post-stress surveys. Although not statistically significant, the subscales of somatic symptoms, depressive symptoms, work-related symptoms, and total score were improved in the case of both blue- and white-collar workers. The value of Cronbach’s alpha was in the range of 0.747 to 0.877.
Comparison of WSRI scores obtained through the pre- and post-stress surveys
WSRI: Worker’s Stress Response Inventory, SD: Standard deviation, CB α: Cronbach’s alpha.
The comprehensive stress management program, which was composed of the organizational and the individual level intervention, was conducted to reduce work-related stress in a medium-sized enterprise. Work-related stress management has usually been focused on individual management corresponding to secondary and tertiary prevention [ 12 ]. Thus, the occupational context including physical, environmental factors that caused stress tended to be overlooked. By changing the demands of the work environment and emphasizing organizational support and responsibility, the comprehensive stress management which encompasses primary, secondary and tertiary prevention is emerging as important [ 18 , 30 - 32 ].
To reduce work-related stress, workers carried out a risk assessment of their workplace and created ready-to-run action plans by participating in a PAOT. The PAOT using the MHACL has shown a reduction in work-related stress in previous studies, similar to our findings. In a manufacturing company, female white-collar workers showed improvement in job skills, mutual support, and psychological stress [ 33 ]. In an electronic components factory, blue-collar workers exhibited an improvement in mental health and job skills [ 34 ].
The MHACL helped the participants to efficiently discuss issues related to the reduction of work-related stress through improvements in the work environment. The MHACL encompasses a variety of areas from the physical to psychosocial work environment; therefore, it can be applied to various types of workplaces [ 28 ]. In this study, the MHACL was applied to establish and implement action plans in each team. Based on the practices to be improved as determined through a discussion, each team prepared three short-term and long-term action plans. In previous studies, the MHACL was useful guidance for work-related risks and facilitated workers to set immediate goals and to plan local feasible improvements activities [ 20 , 35 ]. In this study, the examples of improvement activities were as follows: spraying water in order to prevent dust, adjusting work hours considering individual circumstances, and arranging regular meetings to share information. Improvement plans were made to remove obstacles causing work-related stress. Plans were made to be feasible, and improvements have been made in the desirable direction.
A comparison of KOSS scores obtained through pre- and post-stress surveys was used for evaluating the intervention effect. Blue-collar workers exhibited significant effects in the case of the subscales for the physical environment, job demands, organizational system, lack of rewards, and organizational climate. Work-related stress was reduced in the process of discovering the practices to be improved, discussing action plans with team members, and implementing improvement activities. In a previous study on the development of action plans by workers for resolving problems in the workplace, desired effects were also shown through a process of recognition and intervention [ 36 ]. In order to reduce workplace stressors and improve business efficiency and productivity, an agreement among various departments with respect to preparation for unexpected work and an understanding of task progress should be reached. White-collar workers exhibited significant effects in the case of organizational climate. Although not statistically significant, the subscales of job demands, insufficient job control, interpersonal conflicts, organizational system, and lack of rewards were improved. In the case of white-collar workers, work-related stress was induced by unreasonable communication and relationship conflicts. They felt the burden of close deadlines, work interruption due to other work, increased workload, and excessive responsibility. Work-related stress was reduced after carrying out the suggested improvements. These results were similar to those of training programs on social motivation and interpersonal conflict mediation [ 37 ]. A comparison of WSRI scores obtained through the pre- and post-stress surveys was used for evaluating the intervention effect. Although not statistically significant, the subscales of somatic symptoms, depressive symptoms, and work-related symptoms were improved. In a previous workplace-based participative intervention study, there was significant reduction in sleeping problems in hospital workers. Although not statistically significant, psychological distress, which includes anxiety, depression, aggressiveness, and cognitive problems, was also reduced after an intervention, as found in our study [ 39 ].
In the case of workplace health promotion, it is essential to promote voluntary initiatives and participation of workers throughout the entire intervention process: planning, implementation, and review [ 20 ]. In various sectors, the participatory approach has been proven to be effective in workplace stress management [ 33 , 34 , 38 , 39 ]. Encouragement and active participation of employees in risk assessment and control could be incorporated into the management system, followed by facilitating organizational change. In our study, most of the employees participated in the organizational level intervention. During workshops, inter- and intra-departmental communication was activated, and this effect was sustained throughout the execution of the improvement activities. Good communication helped to alleviate the problems caused by work-related stressors such as interpersonal conflicts, adverse effects to the organizational system, and deterioration of the organizational climate. These achievements would be impossible without good communication and cooperation among the departments. Assuming that the entire company was one organism made of a number of departments, it was not sufficient to enhance the individual’s coping resources with a random selection for dealing with stressors that occurred in a relationship between departments or in an organizational context. Thus, primary prevention that emphasizes worker participation has attracted attention [ 18 ].
Individual level intervention included personal interviews and the dissemination of stress management information. The interviews began with a discussion of the interviewees’ own work-related stressors and stress responses, and enhanced or supported their coping strategies against stress. Before the interview, the interviewer checked the good practices and practices to be improved for the department to which the interviewee belonged, through a team-based participatory workshop. This information helped the interviewer and the interviewee to communicate efficiently about stressors and coping methods. In addition, sensitive organizational level stressors that were difficult to describe in a public workshop were revealed in the personal interview, and feedback could be provided through improvement activity checks or SIC contest.
As this study did not apply blinding, a possible Hawthorne effect could have produced the favorable results, as workers already knew they were under the intervention. Further, this study did not include a control group; therefore, the interpretation of the results is limited. However, considering the characteristics of the workplace intervention study, the control group in the same workplace was likely to be affected by the intervention group, and the intervention effect could thereby decrease. In addition, a number of previous studies have already proven the effects of work-related stress interventions; thus, the need to select a control group is relatively low. In this study, the stress surveys relied on self-reported questionnaires; hence, an information bias could have originated from the subjective tendency to remember work-related stress. The KOSS and WSRI, as domestic evaluation scales, have certain limitations as compared to international evaluation scales. However, they provide a national reference level and have proven reliability to make an accurate assessment. Our study evaluated only the short-term effects of a comprehensive stress management program; a continuous assessment is required.
Despite these limitations, this study has great significance in terms of workplace stress intervention considering that previous stress studies in the workplace were confined to epidemiological observation in Korea. The comprehensive stress management program was conducted on the basis of stress surveys. Both organizational level interventions through participatory improvement activities and individual level interventions through interviews and information dissemination were performed. This study suggests that a comprehensive stress management program can improve the mental health of workers.
Competing interests
Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
SAK, CS, MHP, JTL, KHW, and HJ conceived of the study and participated its design. MHP, CS, KHW, KK, and HJ participated in the intervention and the acquisition of data. SAK, CS, KK, CKL, BCS, JHK, and JTL performed the statistical analysis and interpretation. SAK and MHP drafted and revised the manuscript. CS coordinated the study and helped to draft and revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all workers who participated in stress management program, and managerial staffs. This work was supported by grant from Inje University, 2011 and Busan Regional Center of the Korean Occupational Safety and Health Agency, 2011.
- Sauter S, Murphy L, Colligan M, Swanson N, Hurrell J, Scharf F, Sinclair R, Grubb P, Goldenhar L, Alterman T, Johnston J, Hamilton A, Tisdale J. Stress at work. Cincinnati: DHHS (NIOSH) Pub; 1999. pp. 1–25. No. 99–101. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shigemi J, Mino Y, Ohtus T, Tsuda T. Effects of perceived job stress on mental health. A longitudinal survey in a Japanese electronics company. Eur J Epidemiol. 2000; 26 (4):371–376. doi: 10.1023/A:1007646323031. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Swaen GM, van Amelsvoort LG, Bultmann U, Slangen JJ, Kant IJ. Psychosocial work characteristics as risk factors for being injured in an occupational accident. J Occup Environ Med. 2004; 26 :521–527. doi: 10.1097/01.jom.0000128150.94272.12. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Henderson M, Glozier N, Holland Elliott K. Long term sickness absence. BMJ. 2005; 26 (7495):802–803. doi: 10.1136/bmj.330.7495.802. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Parent-Thirion A, Maci’as EF, Hurley J, Vermeylen G. Fourth European Working Conditions Survey. Doublin: European Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working Conditions; 2007. pp. 61–62. [ Google Scholar ]
- Health and Safety Executive. Stress-related and psychological disorders in Great Britain. Available: http://www.hse.gov.uk/statistics/causdis/stress [cited 26 July 2013]
- Chang SJ, Koh SB, Kang MG, Cha BS, Park JK, Hyun SJ, Park JH, Kim SA, Kang DM, Chang SS, Lee KJ, Ha EH, Ha MN, Woo JM, Cho JJ, Kim HS, Park JS. Epidemiology of psychological distress in Korean employees. J Prev Med Public Health. 2005; 26 (1):25–37. Korean. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Park KC, Lee KJ, Park JB, Min KB, Lee KW. Association between occupational stress and depression, anxiety, and stress symptoms among white-collar male workers in an automotive company. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2008; 26 (3):215–24. Korean. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee KS, Lee DB, Kwon IS, Cho YC. Depressive symptoms and their association with sleep quality, occupational stress and fatigue among small-scaled manufacturing male workers. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2011; 26 (2):99–111. Korean. [ Google Scholar ]
- Park SP, Lee DB, Kwon IS, Cho YC. Analysis of the influence of job stress and psychosocial factors on self perceived fatigue in white collar male workers using the structural equation model. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2010; 26 (1):48–57. Korean. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim JH. A meta-analysis of effects of job stress management interventions (SMIs) J Korean Acad Nur. 2007; 26 (4):529–39. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Czabała C, Charzyńska K, Mroziak B. Psychosocial interventions in workplace mental health promotion: an overview. Health Promot Int. 2011; 26 (1):70–84. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Van der Klink JJ, Blonk RW, Schene AH, Van Dijk FJ. The benefits of interventions for work-related stress. Am J Public Health. 2001; 26 (2):270–6. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murphy LR, Sorenson S. Employee behaviors before and after stress management. Jr Organizational Behavior. 1988; 26 (2):173–82. doi: 10.1002/job.4030090208. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reynolds S. Interventions: what works, what doesn’t? Occup Med. 2000; 26 (5):315–9. doi: 10.1093/occmed/50.5.315. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stansfeld S, Candy B. Psychosocial work environment and mental health-a meta analytic review. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2006; 26 :443–62. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.1050. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kalia M. Assessing the economic impact of stress-the modern day hidden epidemic. Metabolism. 2002; 26 (6suppl1):49–53. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- La Montagne AD, Keegel T, Louie AM, Ostry A, Landsbergis PA. A systematic review of the job-stress intervention evaluation literature, 1990–2005. Int J Occup Environmen Health. 2007; 26 (3):268–80. doi: 10.1179/oeh.2007.13.3.268. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- World health organization regional office for the western pacific. Regional Guidelines for the Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific. Regional Guidelines for the Development of Healthy Workplaces (1999) Available: http://www.who.int/occupational_health/regions/en/oehwproguidelines.pdf [cited 26 July 2013]
- Kogi K. Roles of participatory action-oriented programs in promoting safety and health at work. Safety Health Work. 2012; 26 (3):155–165. doi: 10.5491/SHAW.2012.3.3.155. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karasek R. An analysis of 19 international case studies of stress prevention through work reorganization using the demand/control model. Bull Sci Technol. 2004; 26 :446–56. doi: 10.1177/0270467604269583. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Murphy LR. Stress management in work settings: a critical review of the health effects. Am J Health Promot. 1996; 26 (2):112–35. doi: 10.4278/0890-1171-11.2.112. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anderzén I, Arnetz BB. The impact of a prospective survey-based workplace intervention program onemployee health, biologic stress markers, and organizational productivity. J Occup Environ Med. 2005; 26 :671–82. doi: 10.1097/01.jom.0000167259.03247.1e. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chang SJ, Koh SB, Kang DM, Kim SA, Kang MG, Lee CG, Chung JJ, Cho JJ, Son M, Chae CH, Kim JW, Kim JI, Kim HS, Roh SC, Park JB, Woo JM, Kim SY, Kim JY, Ha M, Park JS, Rhee KY, Kim HR, Kong JO, Kim IA, Kim JS, Park JH, Huyun SJ, Son DK. Developing an occupational stress scale for Korean employees. Korean J Occup Environ Med. 2005; 26 (4):297–317. Korean. [ Google Scholar ]
- Woo JM. Job stress of shift workers. In Proceedings of the Second Korea Institute of Occupational Stress Education and Winter Conference Kit. Seoul; 2004. pp. 127–45. [ Google Scholar ]
- Koh KB, Park JK, Kim CH, Cho SH. Development of the stress response inventory and its application in clinical practice. Psychosom Med. 2001; 26 (4):668–78. doi: 10.1097/00006842-200107000-00020. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Park JS, Korean Occupational Safety and Health Research Institute. Checklist of Measures for Promotion of Mental Health at Work. (Translated by Kim SA) Incheon (Korean): KOSHA; 2006. pp. 70–73. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yoshikawa T, Kawakami N, Kogi K, Tsutsumi A, Shimazu M, Shimazu A. Development of a mental health action checklist for improving workplace environment as means of job stress prevention. San Eishi. 2007; 26 (4):127–42. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee DS, Kim JH, Han WS, Woo JM, Kang DW, Ko YG, Yeon BG, Kim YY. A study of development and standardization to measure job stress inventory (K-OSI) Jr Kor Neuropsychiatric Asso. 1999; 26 (5):1026–37. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim JH. Case Study (Chapter 5) on the Health Conditions of the Stress. (Translated by Kim SA) Incheon: KOSHA; 2003. pp. 109–144. Korean. [ Google Scholar ]
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) Stress at Work. Available: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/99-101 [cited 26 July 2013]
- Landsbergis PA, Cahill J. Labor union programs to reduce or prevent occupational stress in the united states. Int J Health Serv. 1994; 26 (1):105–29. doi: 10.2190/501D-4E1P-260K-2500. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kobayashi Y, Kaneyoshi A, Yokota A, Kawakami N. Effects of a worker participatory program for improving work environments on job stressors and mental health among workers: a controlled trial. J Occup Health. 2008; 26 (6):455–70. doi: 10.1539/joh.L7166. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tsutsumi A, Nagami M, Yoshikawa T, Kogi K, Kawakami N. Participatory intervention for workplace improvements on mental health and Job performance among blue-collar workers: a cluster randomized controlled trial. J Occup Health. 2009; 26 (5):554–63. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shimazu M. A practical case of a comprehensive stress management program using both individual and organizational approaches. Job Stress Res. 2005; 26 :329–35. [ Google Scholar ]
- Park KO, Schaffer BS, Griffin-Blake CS, Dejoy DM, Wilson MG, Vandenberg RJ. Effectiveness of a healthy work organization intervention: ethnic group differences. J Occup Environ Med. 2004; 26 :23–34. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dupuis R, Struthers CW. The effects of social motivational training following perceived and actual interpersonal offenses at work. J Applied Social Psychology. 2007; 26 (2):426–56. doi: 10.1111/j.0021-9029.2007.00167.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bourbonnais R, Brisson C, Vinet A, Vézina M, Abdous B, Gaudet M. Effectiveness of a participative intervention on psychosocial work factors to prevent mental health problems in a hospital setting. Occup Environ Med. 2006; 26 (5):335–42. doi: 10.1136/oem.2004.018077. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elo AL, Ervasti J, Kuosma E, Mattila P. Evaluation of an organizational stress management program in a municipal public works organization. J Occup Health Psychology. 2008; 26 (1):10–23. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Case Study on Stress Management Coaching: Transformative Coaching Approach
- Published: 18 Jul '23
- Updated: 08 Mar '24

Table of Contents
I received a call from Heena (name changed), she mentioned that she was experiencing increased feelings of being stressed, overwhelmed and weighed down by her commitments in life. She has been particularly concerned about her negative thoughts which she always ruminates and overthink about.
After having an initial conversation over the phone, we scheduled an online consultation session.
Stress Management Coaching – Complete Session Flow
Initial consultation.

When asked to mention the problem that Heena is facing currently, she mentioned,
She is a single parent of a five years old daughter. She has a full time help to take care of her daughter and household during her office hours. She has also been studying part time to upgrade her skills.
Heena states that she enjoys her job but it can be demanding and physically tiring at times. She has previously enjoyed her studies but is now finding it difficult to tackle the work and studies with the responsibilities of a small baby.
She has often found herself to be snappy, irritable, exhausted and demotivated at home and at work. Her mother visits her from time to time to support and to take care of the baby and her house but she often gets irritated by her presence.
Heena recently went to the doctor complaining of an itchy rash covering her neck and throbbing headaches at night and in the morning. She stated that medical tests revealed no physical reason for these complaints and her doctor suggested that working through some of the demands and pressures she had in her life may relieve the symptoms, as they may be directly related to stress and tension.
After hearing Heena’s challenges, I began by psycho-educating her about the core concepts behind the process and the frame work of SOFTSEA that we follow.
Session 1: Defining Challenge and Desired Outcome

In the first session of stress management coaching, I used the SOFT SEA Coaching Framework in combination with Meta Model Question for helping Heena define her current situation and desired outcome
I asked her what she felt was the most important issue requiring attention. She identified this as her negative thought patterns and pessimistic way of looking at each day in the morning.
I asked Heena to summarise the current challenge she was facing and wanted to overcome via stress management coaching in her own words.
Heena expressed the feelings of being stressed, overwhelmed and weighed down by my commitments in life. She was particularly concerned about the negative thoughts and attitude at work and at home and would like to change this.
I asked Heena to reframe her problem statement using the following format:
I feel ………… about ………… when …………
I feel overwhelmed and stressed about my negative thoughts and attitude in life.
I asked her to read the statement a couple of times and tell me what was the desired outcome that she wanted to achieve at the end of these sessions in the format
I wish…………………………………..
She couldn’t come up with the outcome but the Transformation Metaphor revealed everything she wanted. Her I wish statement says:
Heena: I wish to be able to feel energetic and excited about my ability to manage and complete the things that I need to do in my life.
Session 2: Defining Future
I asked Heena to describe the dream future that she would love to work towards?
Heena said that she has never thought about the future in detail. She again felt the headache, so I did Release Metaphor with her.
I again asked her to think about how her dream future looks like, feels like and sounds like. I ask her Imagine/pretend that she has acheived her outcome and is energetic and excited about her life each day and how will she describe what that would be like.
With some resistance she began describing the desired future. In Heena’s description, there was more reference to what he would not want or the problems that he wouldn’t have.
For each such reference, I asked Heena, if not this then what?
Gradually Heena was able to describe the desired future a bit more clearly and with more specific observable details. She also mentioned about the reaction of the people around her, the compliments that she is now receiving from her colleagues and also her mother.
I helped Heena understanding the importance of future writing. I now asked Heena to list down all the triggers where she start feeling these negative thoughts in her mind and ask her to narrate all the negative thoughts that comes to her mind during the week and also to complete her future in elaborated way as her assignment for the week.

Session 3: Working with Task List and Hindrances
I began session 3 of stress management coaching by asking her about the week and any changes that she noticed in her behaviours, thoughts, or emotions. Heena mentioned that while she was writing about the future, she actually felt little energetic and hopeful about herself. She felt quite motivated but the negative thought patterns and pessimistic way of looking at each day in the morning is still there.
As I had asked her to do some homework, I was going through it wherein she described that her negative thought patterns and pessimistic way of looking at each day in the morning is still bothering a lot.
I used Thought restructuring with her to help her change her thoughts associated with the identified triggers.
Trigger – Alarm rings every morning at 6 am
Current Thought: Self Talk “I hate my job. This is going to be another horrible day”
Current Emotion: Sense of despair
New Emotion: Excitement
New Thought: “I can do this. Every day is a new day. I will work well today”
When-Then: When Alarm rings every morning at 7am then I realise every day is a new day, I will work well today and i can do this.
I asked to practice the thought restructuring technique daily to make the new thoughts more automatic.
Further, I asked Heena to make a list of actionable task plan.
Once Heena listed all the activities (tasks), I asked her to prioritise and schedule each of these activities. We broke each steps down into mini actionable steps that she could take, one at a time. She instantly felt a boost when she realise that how a huge task can be chunk done in small steps.
I also asked him to identify the specific thoughts and beliefs that were stopping her (or could stop her in future) from taking consistent action towards her task list.
Session 4: Working with Task List and Hindrances Cont…
In the fourth session, Heena reported that she had started feeling better in the past week. I said she realised that making a list and prioritising all her work made her more efficient.

As I was going through her home assignment, Heena had made a complete list of all the tasks that she needs to do for her smooth work life balance.
While we were listing down all the thoughts and emotions that she felt with respect to each of these tasks, I observed that the most frequent emotion that Heena wanted to feel was Energetic.
I asked her to tell me 1 situation from the past where she felt most energetic and pick up 3 situations from the list where she would like to immediately feel energetic.
Once Heena told me the 3 future situations, I did the NLP anchoring technique with her. At the end of the session, Heena looked quite satisfied and joyful.
Session 5: Induction Process
In the fifth session, Heena told me she actually started feeling energetic and excited about her ability to manage her daughter and about her work life.
I did the complete induction process with her as I took Heena into a deep relaxed state and narrated her complete future with when-then statements.
In the next 2 sessions, She was able to restructure limiting beliefs about her own ability and get rid of her past experiences with respect to her ex-husband. Heena took 8 sessions and this coaching helped her not only overcome the negative thoughts but also instilled a newfound enthusiasm to live life to the fullest. She becomes more resilient as a parent of a young child and find a new energy at her work place.
My Observation about this stress management coaching
After talking to a week post her session completion…..
Heena Had been able to successfully upskilled herself and also got promotion in her job for exceeding the turnover target of her organisation. She was now excited about looking forward to future. After the sessions ,she is now able to spend more mindful time with her daughter and mother and is open to a new relationship in her life.
References of techniques used for helping clients manage stress
The techniques employed in this case study draw from various methodologies, including :
- SOFT SEA Coaching Model
- Thought Restructuring
These approaches have been integrated to create a comprehensive and effective stress management coaching process.
The concepts and techniques discussed during this case study are based on the topics covered during the Cognitive Hypnotic Coaching® Diploma and the Cognitive Hypnotic Psychotherapy® Diploma
By applying these evidence-based techniques and building upon a solid theoretical framework, counsellors can effectively support their clients’ progress and help them achieve their desired outcomes.
- Category: Psychotherapy & Coaching
- Tags: Case Studies , Coaching , For Therapists

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Stress Management - A Case Study. Dr. Radhika Kapur. Abstract. Stress is considered to be an integral part of ones life; stress can be any kind of worry, anxiety, hassle, trauma, tension, pain ...
Secondary stress management interventions focus on a person's appraisal of job stressors as a threat or challenge, and the person's ability to cope with the stressors (presuming sufficient internal resources, such as a sense of meaningfulness in life, or external resources, such as social support from a supervisor). ... One case study ...
Laura M. Giurge. Lauren C. Howe. Zsofia Belovai. Guusje Lindemann. Sharon O'Connor. A study of 2,400 Novartis employees around the world found that simply hearing about others' struggles can ...
Stress management application development for wearable smart devices is a growing market. The use of wearable smart devices and biofeedback for individualized real-life stress reduction interventions has received less attention. ... Algorithmic Programming Contest Case Study. Sensors. 2019; 19:1849. doi: 10.3390/s19081849. [PMC free article ...
Research on mindfulness-based programs (MBPs) for adolescents suggests improvements in stress, emotion regulation, and ability to perform some cognitive tasks. However, there is little research examining the contextual factors impacting why specific students experience particular changes and the process by which these changes occur. Responding to the NIH call for "n-of-1 studies" that ...
Stress management policies and procedures are then explained and specified for each significant type of a stressor. This is done using a practical case study of an organization, where it shows how this firm deals with each kind of different stressors. Keywords: stress, productivity, time management, conflict management, workplace diversity. 1.
This study attempts to understand the gender differences between how using exercise as a stress management technique predicts perceived stress levels during the COVID-19 pandemic. Students completed an online survey to self-report their stress management techniques, perceived stress (PSS-10), grade point average (GPA) and demographics (age ...
This straightforward case study requires little in the way of facilitation but mingle with the groups and be on hand to answer any questions or prompt discussion. It could be used as part of a stress management workshop or stress awareness campaign. It would work best with groups of up to six participants. Allow just over an hour for completion.
Case Study 1: The Physical Toll of Chronic Stress and Anxiety John, a middle-aged executive, experienced chronic stress due to work and family pressure, leading to a range of health issues. Having never learned good stress management skills, John overate, drank too much coffee in the daytime and alcohol in the evening, and made no time for ...
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a first-line, empirically supported intervention for anxiety disorders. CBT refers to a family of techniques that are designed to target maladaptive thoughts and behaviors that maintain anxiety over time. Several individual CBT protocols have been developed for individual presentations of anxiety. The article describes common and unique components of CBT ...
Stress is one of the top five threats to academic performance among college students globally. Consequently, students decrease in academic performance, learning ability and retention. However, no study has assessed the practice of stress management behaviors and associated factors among college students in Ethiopia. So the purpose of this study was to assess the practice of stress management ...
Methods. In a randomized controlled multicenter trial participants with a self-assessed subjective stress level ≥ 40 mm on a visual analogue scale (0-100 mm; VAS) for the previous week and a stable state of health were randomized to either 5 weekly sessions of 120-min duration of a hypnotherapeutic group program for stress reduction and improved stress coping plus 5 hypnosis audiorecords ...
Stress is a deadly poison. It can disturb any one's physical, mental, emotional and behavioral balance. Stress can damage different parts of human body from muscles and tissues to organs and blood vessels. It can speed up pulse rate and respiration. It can raise blood pressure and body temperature.
This case study looks at the impact of stress on a part-time worker with celebral palsy, and its effect on their well-being. The study shows how using a proactive approach, including the use of HSE stress management standards, can help to avoid negative outcomes for the employee. Stress management in the workplace contributes to the advancement of SDG 3.4 to prevent and treat mental health ...
This case is ideally suited for an undergraduate or graduate course in Business Law and/or Employment Law. It may also have application in Business and Society, Human Resource. Management and Business Policy courses. This case can be used to demonstrate the legal implications of workplace stress.
Stress: A Case Study. Read the story of a women who thought she was having a heart attack, but was instead diagnosed with panic disorder, panic attacks. A young woman sought psychological services after her cardiologist referred her for stress management and treatment of "heart attack" symptoms. This 36 year old woman had the world by the tail.
An analysis of 19 international case studies of stress prevention through work reorganization using the demand/control model. Bull Sci Technol. 2004; 26:446-56. doi: ... Shimazu M. A practical case of a comprehensive stress management program using both individual and organizational approaches. Job Stress Res. 2005; 26:329-35.
Stress management in patient care is a very important aspect of nursing care. A case study is provided with cues to identify and nursing interventions for assessing stress in a patient.
References of techniques used for helping clients manage stress. The techniques employed in this case study draw from various methodologies, including : SOFT SEA Coaching Model; Meta Model; Thought Restructuring; Anchoring; Hypnosis; These approaches have been integrated to create a comprehensive and effective stress management coaching process.
Stress Management at Work Place - A Case Study on Wipro - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Stress Management