Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples

Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
Published on March 8, 2021 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different treatment groups using randomization.
With simple random assignment, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group. Studies that use simple random assignment are also called completely randomized designs .
Random assignment is a key part of experimental design . It helps you ensure that all groups are comparable at the start of a study: any differences between them are due to random factors, not research biases like sampling bias or selection bias .
Table of contents
Why does random assignment matter, random sampling vs random assignment, how do you use random assignment, when is random assignment not used, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about random assignment.
Random assignment is an important part of control in experimental research, because it helps strengthen the internal validity of an experiment and avoid biases.
In experiments, researchers manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables. To do so, they often use different levels of an independent variable for different groups of participants.
This is called a between-groups or independent measures design.
You use three groups of participants that are each given a different level of the independent variable:
- a control group that’s given a placebo (no dosage, to control for a placebo effect ),
- an experimental group that’s given a low dosage,
- a second experimental group that’s given a high dosage.
Random assignment to helps you make sure that the treatment groups don’t differ in systematic ways at the start of the experiment, as this can seriously affect (and even invalidate) your work.
If you don’t use random assignment, you may not be able to rule out alternative explanations for your results.
- participants recruited from cafes are placed in the control group ,
- participants recruited from local community centers are placed in the low dosage experimental group,
- participants recruited from gyms are placed in the high dosage group.
With this type of assignment, it’s hard to tell whether the participant characteristics are the same across all groups at the start of the study. Gym-users may tend to engage in more healthy behaviors than people who frequent cafes or community centers, and this would introduce a healthy user bias in your study.
Although random assignment helps even out baseline differences between groups, it doesn’t always make them completely equivalent. There may still be extraneous variables that differ between groups, and there will always be some group differences that arise from chance.
Most of the time, the random variation between groups is low, and, therefore, it’s acceptable for further analysis. This is especially true when you have a large sample. In general, you should always use random assignment in experiments when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

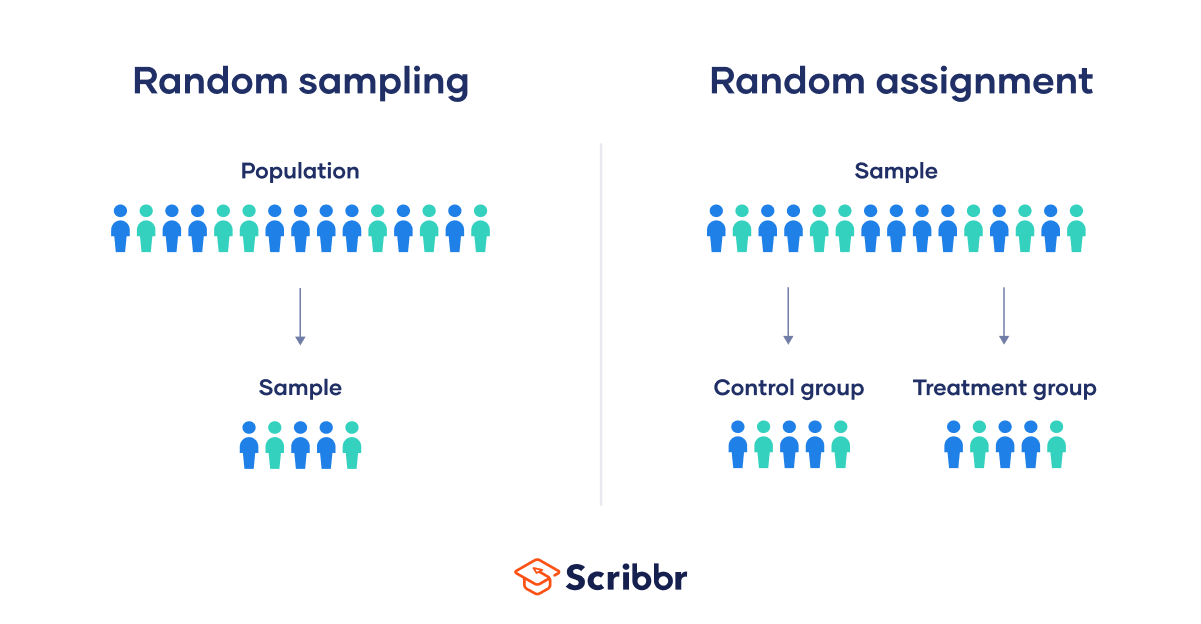
Random sampling and random assignment are both important concepts in research, but it’s important to understand the difference between them.
Random sampling (also called probability sampling or random selection) is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups.
While random sampling is used in many types of studies, random assignment is only used in between-subjects experimental designs.
Some studies use both random sampling and random assignment, while others use only one or the other.
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalizability of your results, because it helps ensure that your sample is unbiased and representative of the whole population. This allows you to make stronger statistical inferences .
You use a simple random sample to collect data. Because you have access to the whole population (all employees), you can assign all 8000 employees a number and use a random number generator to select 300 employees. These 300 employees are your full sample.
Random assignment enhances the internal validity of the study, because it ensures that there are no systematic differences between the participants in each group. This helps you conclude that the outcomes can be attributed to the independent variable .
- a control group that receives no intervention.
- an experimental group that has a remote team-building intervention every week for a month.
You use random assignment to place participants into the control or experimental group. To do so, you take your list of participants and assign each participant a number. Again, you use a random number generator to place each participant in one of the two groups.
To use simple random assignment, you start by giving every member of the sample a unique number. Then, you can use computer programs or manual methods to randomly assign each participant to a group.
- Random number generator: Use a computer program to generate random numbers from the list for each group.
- Lottery method: Place all numbers individually in a hat or a bucket, and draw numbers at random for each group.
- Flip a coin: When you only have two groups, for each number on the list, flip a coin to decide if they’ll be in the control or the experimental group.
- Use a dice: When you have three groups, for each number on the list, roll a dice to decide which of the groups they will be in. For example, assume that rolling 1 or 2 lands them in a control group; 3 or 4 in an experimental group; and 5 or 6 in a second control or experimental group.
This type of random assignment is the most powerful method of placing participants in conditions, because each individual has an equal chance of being placed in any one of your treatment groups.
Random assignment in block designs
In more complicated experimental designs, random assignment is only used after participants are grouped into blocks based on some characteristic (e.g., test score or demographic variable). These groupings mean that you need a larger sample to achieve high statistical power .
For example, a randomized block design involves placing participants into blocks based on a shared characteristic (e.g., college students versus graduates), and then using random assignment within each block to assign participants to every treatment condition. This helps you assess whether the characteristic affects the outcomes of your treatment.
In an experimental matched design , you use blocking and then match up individual participants from each block based on specific characteristics. Within each matched pair or group, you randomly assign each participant to one of the conditions in the experiment and compare their outcomes.
Sometimes, it’s not relevant or ethical to use simple random assignment, so groups are assigned in a different way.
When comparing different groups
Sometimes, differences between participants are the main focus of a study, for example, when comparing men and women or people with and without health conditions. Participants are not randomly assigned to different groups, but instead assigned based on their characteristics.
In this type of study, the characteristic of interest (e.g., gender) is an independent variable, and the groups differ based on the different levels (e.g., men, women, etc.). All participants are tested the same way, and then their group-level outcomes are compared.
When it’s not ethically permissible
When studying unhealthy or dangerous behaviors, it’s not possible to use random assignment. For example, if you’re studying heavy drinkers and social drinkers, it’s unethical to randomly assign participants to one of the two groups and ask them to drink large amounts of alcohol for your experiment.
When you can’t assign participants to groups, you can also conduct a quasi-experimental study . In a quasi-experiment, you study the outcomes of pre-existing groups who receive treatments that you may not have any control over (e.g., heavy drinkers and social drinkers). These groups aren’t randomly assigned, but may be considered comparable when some other variables (e.g., age or socioeconomic status) are controlled for.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different groups using randomization. With this method, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group.
Random selection, or random sampling , is a way of selecting members of a population for your study’s sample.
In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample into control and experimental groups.
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalizability of your results, while random assignment improves the internal validity of your study.
Random assignment is used in experiments with a between-groups or independent measures design. In this research design, there’s usually a control group and one or more experimental groups. Random assignment helps ensure that the groups are comparable.
In general, you should always use random assignment in this type of experimental design when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic.
To implement random assignment , assign a unique number to every member of your study’s sample .
Then, you can use a random number generator or a lottery method to randomly assign each number to a control or experimental group. You can also do so manually, by flipping a coin or rolling a dice to randomly assign participants to groups.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/random-assignment/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, confounding variables | definition, examples & controls, control groups and treatment groups | uses & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Definition of Random Assignment According to Psychology
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Materio / Getty Images
Random assignment refers to the use of chance procedures in psychology experiments to ensure that each participant has the same opportunity to be assigned to any given group in a study to eliminate any potential bias in the experiment at the outset. Participants are randomly assigned to different groups, such as the treatment group versus the control group. In clinical research, randomized clinical trials are known as the gold standard for meaningful results.
Simple random assignment techniques might involve tactics such as flipping a coin, drawing names out of a hat, rolling dice, or assigning random numbers to a list of participants. It is important to note that random assignment differs from random selection .
While random selection refers to how participants are randomly chosen from a target population as representatives of that population, random assignment refers to how those chosen participants are then assigned to experimental groups.
Random Assignment In Research
To determine if changes in one variable will cause changes in another variable, psychologists must perform an experiment. Random assignment is a critical part of the experimental design that helps ensure the reliability of the study outcomes.
Researchers often begin by forming a testable hypothesis predicting that one variable of interest will have some predictable impact on another variable.
The variable that the experimenters will manipulate in the experiment is known as the independent variable , while the variable that they will then measure for different outcomes is known as the dependent variable. While there are different ways to look at relationships between variables, an experiment is the best way to get a clear idea if there is a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables.
Once researchers have formulated a hypothesis, conducted background research, and chosen an experimental design, it is time to find participants for their experiment. How exactly do researchers decide who will be part of an experiment? As mentioned previously, this is often accomplished through something known as random selection.
Random Selection
In order to generalize the results of an experiment to a larger group, it is important to choose a sample that is representative of the qualities found in that population. For example, if the total population is 60% female and 40% male, then the sample should reflect those same percentages.
Choosing a representative sample is often accomplished by randomly picking people from the population to be participants in a study. Random selection means that everyone in the group stands an equal chance of being chosen to minimize any bias. Once a pool of participants has been selected, it is time to assign them to groups.
By randomly assigning the participants into groups, the experimenters can be fairly sure that each group will have the same characteristics before the independent variable is applied.
Participants might be randomly assigned to the control group , which does not receive the treatment in question. The control group may receive a placebo or receive the standard treatment. Participants may also be randomly assigned to the experimental group , which receives the treatment of interest. In larger studies, there can be multiple treatment groups for comparison.
There are simple methods of random assignment, like rolling the die. However, there are more complex techniques that involve random number generators to remove any human error.
There can also be random assignment to groups with pre-established rules or parameters. For example, if you want to have an equal number of men and women in each of your study groups, you might separate your sample into two groups (by sex) before randomly assigning each of those groups into the treatment group and control group.
Random assignment is essential because it increases the likelihood that the groups are the same at the outset. With all characteristics being equal between groups, other than the application of the independent variable, any differences found between group outcomes can be more confidently attributed to the effect of the intervention.
Example of Random Assignment
Imagine that a researcher is interested in learning whether or not drinking caffeinated beverages prior to an exam will improve test performance. After randomly selecting a pool of participants, each person is randomly assigned to either the control group or the experimental group.
The participants in the control group consume a placebo drink prior to the exam that does not contain any caffeine. Those in the experimental group, on the other hand, consume a caffeinated beverage before taking the test.
Participants in both groups then take the test, and the researcher compares the results to determine if the caffeinated beverage had any impact on test performance.
A Word From Verywell
Random assignment plays an important role in the psychology research process. Not only does this process help eliminate possible sources of bias, but it also makes it easier to generalize the results of a tested sample of participants to a larger population.
Random assignment helps ensure that members of each group in the experiment are the same, which means that the groups are also likely more representative of what is present in the larger population of interest. Through the use of this technique, psychology researchers are able to study complex phenomena and contribute to our understanding of the human mind and behavior.
Lin Y, Zhu M, Su Z. The pursuit of balance: An overview of covariate-adaptive randomization techniques in clinical trials . Contemp Clin Trials. 2015;45(Pt A):21-25. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2015.07.011
Sullivan L. Random assignment versus random selection . In: The SAGE Glossary of the Social and Behavioral Sciences. SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2009. doi:10.4135/9781412972024.n2108
Alferes VR. Methods of Randomization in Experimental Design . SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2012. doi:10.4135/9781452270012
Nestor PG, Schutt RK. Research Methods in Psychology: Investigating Human Behavior. (2nd Ed.). SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2015.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
As previously mentioned, one of the characteristics of a true experiment is that researchers use a random process to decide which participants are tested under which conditions. Random assignation is a powerful research technique that addresses the assumption of pre-test equivalence – that the experimental and control group are equal in all respects before the administration of the independent variable (Palys & Atchison, 2014).
Random assignation is the primary way that researchers attempt to control extraneous variables across conditions. Random assignation is associated with experimental research methods. In its strictest sense, random assignment should meet two criteria. One is that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to each condition (e.g., a 50% chance of being assigned to each of two conditions). The second is that each participant is assigned to a condition independently of other participants. Thus, one way to assign participants to two conditions would be to flip a coin for each one. If the coin lands on the heads side, the participant is assigned to Condition A, and if it lands on the tails side, the participant is assigned to Condition B. For three conditions, one could use a computer to generate a random integer from 1 to 3 for each participant. If the integer is 1, the participant is assigned to Condition A; if it is 2, the participant is assigned to Condition B; and, if it is 3, the participant is assigned to Condition C. In practice, a full sequence of conditions—one for each participant expected to be in the experiment—is usually created ahead of time, and each new participant is assigned to the next condition in the sequence as he or she is tested.
However, one problem with coin flipping and other strict procedures for random assignment is that they are likely to result in unequal sample sizes in the different conditions. Unequal sample sizes are generally not a serious problem, and you should never throw away data you have already collected to achieve equal sample sizes. However, for a fixed number of participants, it is statistically most efficient to divide them into equal-sized groups. It is standard practice, therefore, to use a kind of modified random assignment that keeps the number of participants in each group as similar as possible.
One approach is block randomization. In block randomization, all the conditions occur once in the sequence before any of them is repeated. Then they all occur again before any of them is repeated again. Within each of these “blocks,” the conditions occur in a random order. Again, the sequence of conditions is usually generated before any participants are tested, and each new participant is assigned to the next condition in the sequence. When the procedure is computerized, the computer program often handles the random assignment, which is obviously much easier. You can also find programs online to help you randomize your random assignation. For example, the Research Randomizer website will generate block randomization sequences for any number of participants and conditions ( Research Randomizer ).
Random assignation is not guaranteed to control all extraneous variables across conditions. It is always possible that, just by chance, the participants in one condition might turn out to be substantially older, less tired, more motivated, or less depressed on average than the participants in another condition. However, there are some reasons that this may not be a major concern. One is that random assignment works better than one might expect, especially for large samples. Another is that the inferential statistics that researchers use to decide whether a difference between groups reflects a difference in the population take the “fallibility” of random assignment into account. Yet another reason is that even if random assignment does result in a confounding variable and therefore produces misleading results, this confound is likely to be detected when the experiment is replicated. The upshot is that random assignment to conditions—although not infallible in terms of controlling extraneous variables—is always considered a strength of a research design. Note: Do not confuse random assignation with random sampling. Random sampling is a method for selecting a sample from a population; we will talk about this in Chapter 7.
Research Methods, Data Collection and Ethics Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
5.2 Experimental Design
Learning objectives.
- Explain the difference between between-subjects and within-subjects experiments, list some of the pros and cons of each approach, and decide which approach to use to answer a particular research question.
- Define random assignment, distinguish it from random sampling, explain its purpose in experimental research, and use some simple strategies to implement it
- Define several types of carryover effect, give examples of each, and explain how counterbalancing helps to deal with them.
In this section, we look at some different ways to design an experiment. The primary distinction we will make is between approaches in which each participant experiences one level of the independent variable and approaches in which each participant experiences all levels of the independent variable. The former are called between-subjects experiments and the latter are called within-subjects experiments.
Between-Subjects Experiments
In a between-subjects experiment , each participant is tested in only one condition. For example, a researcher with a sample of 100 university students might assign half of them to write about a traumatic event and the other half write about a neutral event. Or a researcher with a sample of 60 people with severe agoraphobia (fear of open spaces) might assign 20 of them to receive each of three different treatments for that disorder. It is essential in a between-subjects experiment that the researcher assigns participants to conditions so that the different groups are, on average, highly similar to each other. Those in a trauma condition and a neutral condition, for example, should include a similar proportion of men and women, and they should have similar average intelligence quotients (IQs), similar average levels of motivation, similar average numbers of health problems, and so on. This matching is a matter of controlling these extraneous participant variables across conditions so that they do not become confounding variables.
Random Assignment
The primary way that researchers accomplish this kind of control of extraneous variables across conditions is called random assignment , which means using a random process to decide which participants are tested in which conditions. Do not confuse random assignment with random sampling. Random sampling is a method for selecting a sample from a population, and it is rarely used in psychological research. Random assignment is a method for assigning participants in a sample to the different conditions, and it is an important element of all experimental research in psychology and other fields too.
In its strictest sense, random assignment should meet two criteria. One is that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to each condition (e.g., a 50% chance of being assigned to each of two conditions). The second is that each participant is assigned to a condition independently of other participants. Thus one way to assign participants to two conditions would be to flip a coin for each one. If the coin lands heads, the participant is assigned to Condition A, and if it lands tails, the participant is assigned to Condition B. For three conditions, one could use a computer to generate a random integer from 1 to 3 for each participant. If the integer is 1, the participant is assigned to Condition A; if it is 2, the participant is assigned to Condition B; and if it is 3, the participant is assigned to Condition C. In practice, a full sequence of conditions—one for each participant expected to be in the experiment—is usually created ahead of time, and each new participant is assigned to the next condition in the sequence as he or she is tested. When the procedure is computerized, the computer program often handles the random assignment.
One problem with coin flipping and other strict procedures for random assignment is that they are likely to result in unequal sample sizes in the different conditions. Unequal sample sizes are generally not a serious problem, and you should never throw away data you have already collected to achieve equal sample sizes. However, for a fixed number of participants, it is statistically most efficient to divide them into equal-sized groups. It is standard practice, therefore, to use a kind of modified random assignment that keeps the number of participants in each group as similar as possible. One approach is block randomization . In block randomization, all the conditions occur once in the sequence before any of them is repeated. Then they all occur again before any of them is repeated again. Within each of these “blocks,” the conditions occur in a random order. Again, the sequence of conditions is usually generated before any participants are tested, and each new participant is assigned to the next condition in the sequence. Table 5.2 shows such a sequence for assigning nine participants to three conditions. The Research Randomizer website ( http://www.randomizer.org ) will generate block randomization sequences for any number of participants and conditions. Again, when the procedure is computerized, the computer program often handles the block randomization.
Random assignment is not guaranteed to control all extraneous variables across conditions. The process is random, so it is always possible that just by chance, the participants in one condition might turn out to be substantially older, less tired, more motivated, or less depressed on average than the participants in another condition. However, there are some reasons that this possibility is not a major concern. One is that random assignment works better than one might expect, especially for large samples. Another is that the inferential statistics that researchers use to decide whether a difference between groups reflects a difference in the population takes the “fallibility” of random assignment into account. Yet another reason is that even if random assignment does result in a confounding variable and therefore produces misleading results, this confound is likely to be detected when the experiment is replicated. The upshot is that random assignment to conditions—although not infallible in terms of controlling extraneous variables—is always considered a strength of a research design.
Matched Groups
An alternative to simple random assignment of participants to conditions is the use of a matched-groups design . Using this design, participants in the various conditions are matched on the dependent variable or on some extraneous variable(s) prior the manipulation of the independent variable. This guarantees that these variables will not be confounded across the experimental conditions. For instance, if we want to determine whether expressive writing affects people’s health then we could start by measuring various health-related variables in our prospective research participants. We could then use that information to rank-order participants according to how healthy or unhealthy they are. Next, the two healthiest participants would be randomly assigned to complete different conditions (one would be randomly assigned to the traumatic experiences writing condition and the other to the neutral writing condition). The next two healthiest participants would then be randomly assigned to complete different conditions, and so on until the two least healthy participants. This method would ensure that participants in the traumatic experiences writing condition are matched to participants in the neutral writing condition with respect to health at the beginning of the study. If at the end of the experiment, a difference in health was detected across the two conditions, then we would know that it is due to the writing manipulation and not to pre-existing differences in health.
Within-Subjects Experiments
In a within-subjects experiment , each participant is tested under all conditions. Consider an experiment on the effect of a defendant’s physical attractiveness on judgments of his guilt. Again, in a between-subjects experiment, one group of participants would be shown an attractive defendant and asked to judge his guilt, and another group of participants would be shown an unattractive defendant and asked to judge his guilt. In a within-subjects experiment, however, the same group of participants would judge the guilt of both an attractive and an unattractive defendant.
The primary advantage of this approach is that it provides maximum control of extraneous participant variables. Participants in all conditions have the same mean IQ, same socioeconomic status, same number of siblings, and so on—because they are the very same people. Within-subjects experiments also make it possible to use statistical procedures that remove the effect of these extraneous participant variables on the dependent variable and therefore make the data less “noisy” and the effect of the independent variable easier to detect. We will look more closely at this idea later in the book . However, not all experiments can use a within-subjects design nor would it be desirable to do so.
One disadvantage of within-subjects experiments is that they make it easier for participants to guess the hypothesis. For example, a participant who is asked to judge the guilt of an attractive defendant and then is asked to judge the guilt of an unattractive defendant is likely to guess that the hypothesis is that defendant attractiveness affects judgments of guilt. This knowledge could lead the participant to judge the unattractive defendant more harshly because he thinks this is what he is expected to do. Or it could make participants judge the two defendants similarly in an effort to be “fair.”
Carryover Effects and Counterbalancing
The primary disadvantage of within-subjects designs is that they can result in order effects. An order effect occurs when participants’ responses in the various conditions are affected by the order of conditions to which they were exposed. One type of order effect is a carryover effect. A carryover effect is an effect of being tested in one condition on participants’ behavior in later conditions. One type of carryover effect is a practice effect , where participants perform a task better in later conditions because they have had a chance to practice it. Another type is a fatigue effect , where participants perform a task worse in later conditions because they become tired or bored. Being tested in one condition can also change how participants perceive stimuli or interpret their task in later conditions. This type of effect is called a context effect (or contrast effect) . For example, an average-looking defendant might be judged more harshly when participants have just judged an attractive defendant than when they have just judged an unattractive defendant. Within-subjects experiments also make it easier for participants to guess the hypothesis. For example, a participant who is asked to judge the guilt of an attractive defendant and then is asked to judge the guilt of an unattractive defendant is likely to guess that the hypothesis is that defendant attractiveness affects judgments of guilt.
Carryover effects can be interesting in their own right. (Does the attractiveness of one person depend on the attractiveness of other people that we have seen recently?) But when they are not the focus of the research, carryover effects can be problematic. Imagine, for example, that participants judge the guilt of an attractive defendant and then judge the guilt of an unattractive defendant. If they judge the unattractive defendant more harshly, this might be because of his unattractiveness. But it could be instead that they judge him more harshly because they are becoming bored or tired. In other words, the order of the conditions is a confounding variable. The attractive condition is always the first condition and the unattractive condition the second. Thus any difference between the conditions in terms of the dependent variable could be caused by the order of the conditions and not the independent variable itself.
There is a solution to the problem of order effects, however, that can be used in many situations. It is counterbalancing , which means testing different participants in different orders. The best method of counterbalancing is complete counterbalancing in which an equal number of participants complete each possible order of conditions. For example, half of the participants would be tested in the attractive defendant condition followed by the unattractive defendant condition, and others half would be tested in the unattractive condition followed by the attractive condition. With three conditions, there would be six different orders (ABC, ACB, BAC, BCA, CAB, and CBA), so some participants would be tested in each of the six orders. With four conditions, there would be 24 different orders; with five conditions there would be 120 possible orders. With counterbalancing, participants are assigned to orders randomly, using the techniques we have already discussed. Thus, random assignment plays an important role in within-subjects designs just as in between-subjects designs. Here, instead of randomly assigning to conditions, they are randomly assigned to different orders of conditions. In fact, it can safely be said that if a study does not involve random assignment in one form or another, it is not an experiment.
A more efficient way of counterbalancing is through a Latin square design which randomizes through having equal rows and columns. For example, if you have four treatments, you must have four versions. Like a Sudoku puzzle, no treatment can repeat in a row or column. For four versions of four treatments, the Latin square design would look like:
You can see in the diagram above that the square has been constructed to ensure that each condition appears at each ordinal position (A appears first once, second once, third once, and fourth once) and each condition preceded and follows each other condition one time. A Latin square for an experiment with 6 conditions would by 6 x 6 in dimension, one for an experiment with 8 conditions would be 8 x 8 in dimension, and so on. So while complete counterbalancing of 6 conditions would require 720 orders, a Latin square would only require 6 orders.
Finally, when the number of conditions is large experiments can use random counterbalancing in which the order of the conditions is randomly determined for each participant. Using this technique every possible order of conditions is determined and then one of these orders is randomly selected for each participant. This is not as powerful a technique as complete counterbalancing or partial counterbalancing using a Latin squares design. Use of random counterbalancing will result in more random error, but if order effects are likely to be small and the number of conditions is large, this is an option available to researchers.
There are two ways to think about what counterbalancing accomplishes. One is that it controls the order of conditions so that it is no longer a confounding variable. Instead of the attractive condition always being first and the unattractive condition always being second, the attractive condition comes first for some participants and second for others. Likewise, the unattractive condition comes first for some participants and second for others. Thus any overall difference in the dependent variable between the two conditions cannot have been caused by the order of conditions. A second way to think about what counterbalancing accomplishes is that if there are carryover effects, it makes it possible to detect them. One can analyze the data separately for each order to see whether it had an effect.
When 9 Is “Larger” Than 221
Researcher Michael Birnbaum has argued that the lack of context provided by between-subjects designs is often a bigger problem than the context effects created by within-subjects designs. To demonstrate this problem, he asked participants to rate two numbers on how large they were on a scale of 1-to-10 where 1 was “very very small” and 10 was “very very large”. One group of participants were asked to rate the number 9 and another group was asked to rate the number 221 (Birnbaum, 1999) [1] . Participants in this between-subjects design gave the number 9 a mean rating of 5.13 and the number 221 a mean rating of 3.10. In other words, they rated 9 as larger than 221! According to Birnbaum, this difference is because participants spontaneously compared 9 with other one-digit numbers (in which case it is relatively large) and compared 221 with other three-digit numbers (in which case it is relatively small).
Simultaneous Within-Subjects Designs
So far, we have discussed an approach to within-subjects designs in which participants are tested in one condition at a time. There is another approach, however, that is often used when participants make multiple responses in each condition. Imagine, for example, that participants judge the guilt of 10 attractive defendants and 10 unattractive defendants. Instead of having people make judgments about all 10 defendants of one type followed by all 10 defendants of the other type, the researcher could present all 20 defendants in a sequence that mixed the two types. The researcher could then compute each participant’s mean rating for each type of defendant. Or imagine an experiment designed to see whether people with social anxiety disorder remember negative adjectives (e.g., “stupid,” “incompetent”) better than positive ones (e.g., “happy,” “productive”). The researcher could have participants study a single list that includes both kinds of words and then have them try to recall as many words as possible. The researcher could then count the number of each type of word that was recalled.
Between-Subjects or Within-Subjects?
Almost every experiment can be conducted using either a between-subjects design or a within-subjects design. This possibility means that researchers must choose between the two approaches based on their relative merits for the particular situation.
Between-subjects experiments have the advantage of being conceptually simpler and requiring less testing time per participant. They also avoid carryover effects without the need for counterbalancing. Within-subjects experiments have the advantage of controlling extraneous participant variables, which generally reduces noise in the data and makes it easier to detect a relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
A good rule of thumb, then, is that if it is possible to conduct a within-subjects experiment (with proper counterbalancing) in the time that is available per participant—and you have no serious concerns about carryover effects—this design is probably the best option. If a within-subjects design would be difficult or impossible to carry out, then you should consider a between-subjects design instead. For example, if you were testing participants in a doctor’s waiting room or shoppers in line at a grocery store, you might not have enough time to test each participant in all conditions and therefore would opt for a between-subjects design. Or imagine you were trying to reduce people’s level of prejudice by having them interact with someone of another race. A within-subjects design with counterbalancing would require testing some participants in the treatment condition first and then in a control condition. But if the treatment works and reduces people’s level of prejudice, then they would no longer be suitable for testing in the control condition. This difficulty is true for many designs that involve a treatment meant to produce long-term change in participants’ behavior (e.g., studies testing the effectiveness of psychotherapy). Clearly, a between-subjects design would be necessary here.
Remember also that using one type of design does not preclude using the other type in a different study. There is no reason that a researcher could not use both a between-subjects design and a within-subjects design to answer the same research question. In fact, professional researchers often take exactly this type of mixed methods approach.
Key Takeaways
- Experiments can be conducted using either between-subjects or within-subjects designs. Deciding which to use in a particular situation requires careful consideration of the pros and cons of each approach.
- Random assignment to conditions in between-subjects experiments or counterbalancing of orders of conditions in within-subjects experiments is a fundamental element of experimental research. The purpose of these techniques is to control extraneous variables so that they do not become confounding variables.
- You want to test the relative effectiveness of two training programs for running a marathon.
- Using photographs of people as stimuli, you want to see if smiling people are perceived as more intelligent than people who are not smiling.
- In a field experiment, you want to see if the way a panhandler is dressed (neatly vs. sloppily) affects whether or not passersby give him any money.
- You want to see if concrete nouns (e.g., dog ) are recalled better than abstract nouns (e.g., truth).
- Birnbaum, M.H. (1999). How to show that 9>221: Collect judgments in a between-subjects design. Psychological Methods, 4 (3), 243-249. ↵

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size

What Is Random Assignment in Psychology?
Categories Research Methods

Sharing is caring!
Random assignment means that every participant has the same chance of being chosen for the experimental or control group. It involves using procedures that rely on chance to assign participants to groups. Doing this means that every participant in a study has an equal opportunity to be assigned to any group.
For example, in a psychology experiment, participants might be assigned to either a control or experimental group. Some experiments might only have one experimental group, while others may have several treatment variations.
Using random assignment means that each participant has the same chance of being assigned to any of these groups.
Table of Contents
How to Use Random Assignment
So what type of procedures might psychologists utilize for random assignment? Strategies can include:
- Flipping a coin
- Assigning random numbers
- Rolling dice
- Drawing names out of a hat
How Does Random Assignment Work?
A psychology experiment aims to determine if changes in one variable lead to changes in another variable. Researchers will first begin by coming up with a hypothesis. Once researchers have an idea of what they think they might find in a population, they will come up with an experimental design and then recruit participants for their study.
Once they have a pool of participants representative of the population they are interested in looking at, they will randomly assign the participants to their groups.
- Control group : Some participants will end up in the control group, which serves as a baseline and does not receive the independent variables.
- Experimental group : Other participants will end up in the experimental groups that receive some form of the independent variables.
By using random assignment, the researchers make it more likely that the groups are equal at the start of the experiment. Since the groups are the same on other variables, it can be assumed that any changes that occur are the result of varying the independent variables.
After a treatment has been administered, the researchers will then collect data in order to determine if the independent variable had any impact on the dependent variable.
Random Assignment vs. Random Selection
It is important to remember that random assignment is not the same thing as random selection , also known as random sampling.
Random selection instead involves how people are chosen to be in a study. Using random selection, every member of a population stands an equal chance of being chosen for a study or experiment.
So random sampling affects how participants are chosen for a study, while random assignment affects how participants are then assigned to groups.
Examples of Random Assignment
Imagine that a psychology researcher is conducting an experiment to determine if getting adequate sleep the night before an exam results in better test scores.
Forming a Hypothesis
They hypothesize that participants who get 8 hours of sleep will do better on a math exam than participants who only get 4 hours of sleep.
Obtaining Participants
The researcher starts by obtaining a pool of participants. They find 100 participants from a local university. Half of the participants are female, and half are male.
Randomly Assign Participants to Groups
The researcher then assigns random numbers to each participant and uses a random number generator to randomly assign each number to either the 4-hour or 8-hour sleep groups.
Conduct the Experiment
Those in the 8-hour sleep group agree to sleep for 8 hours that night, while those in the 4-hour group agree to wake up after only 4 hours. The following day, all of the participants meet in a classroom.
Collect and Analyze Data
Everyone takes the same math test. The test scores are then compared to see if the amount of sleep the night before had any impact on test scores.
Why Is Random Assignment Important in Psychology Research?
Random assignment is important in psychology research because it helps improve a study’s internal validity. This means that the researchers are sure that the study demonstrates a cause-and-effect relationship between an independent and dependent variable.
Random assignment improves the internal validity by minimizing the risk that there are systematic differences in the participants who are in each group.
Key Points to Remember About Random Assignment
- Random assignment in psychology involves each participant having an equal chance of being chosen for any of the groups, including the control and experimental groups.
- It helps control for potential confounding variables, reducing the likelihood of pre-existing differences between groups.
- This method enhances the internal validity of experiments, allowing researchers to draw more reliable conclusions about cause-and-effect relationships.
- Random assignment is crucial for creating comparable groups and increasing the scientific rigor of psychological studies.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Statistics
Course: ap®︎/college statistics > unit 6.
- Statistical significance of experiment
Random sampling vs. random assignment (scope of inference)
- Conclusions in observational studies versus experiments
- Finding errors in study conclusions
- (Choice A) Just the residents involved in Hilary's study. A Just the residents involved in Hilary's study.
- (Choice B) All residents in Hilary's town. B All residents in Hilary's town.
- (Choice C) All residents in Hilary's country. C All residents in Hilary's country.
- (Choice A) Yes A Yes
- (Choice B) No B No
- (Choice A) Just the residents in Hilary's study. A Just the residents in Hilary's study.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

- Yale Directories
Institution for Social and Policy Studies
Advancing research • shaping policy • developing leaders, why randomize.
About Randomized Field Experiments Randomized field experiments allow researchers to scientifically measure the impact of an intervention on a particular outcome of interest.
What is a randomized field experiment? In a randomized experiment, a study sample is divided into one group that will receive the intervention being studied (the treatment group) and another group that will not receive the intervention (the control group). For instance, a study sample might consist of all registered voters in a particular city. This sample will then be randomly divided into treatment and control groups. Perhaps 40% of the sample will be on a campaign’s Get-Out-the-Vote (GOTV) mailing list and the other 60% of the sample will not receive the GOTV mailings. The outcome measured –voter turnout– can then be compared in the two groups. The difference in turnout will reflect the effectiveness of the intervention.
What does random assignment mean? The key to randomized experimental research design is in the random assignment of study subjects – for example, individual voters, precincts, media markets or some other group – into treatment or control groups. Randomization has a very specific meaning in this context. It does not refer to haphazard or casual choosing of some and not others. Randomization in this context means that care is taken to ensure that no pattern exists between the assignment of subjects into groups and any characteristics of those subjects. Every subject is as likely as any other to be assigned to the treatment (or control) group. Randomization is generally achieved by employing a computer program containing a random number generator. Randomization procedures differ based upon the research design of the experiment. Individuals or groups may be randomly assigned to treatment or control groups. Some research designs stratify subjects by geographic, demographic or other factors prior to random assignment in order to maximize the statistical power of the estimated effect of the treatment (e.g., GOTV intervention). Information about the randomization procedure is included in each experiment summary on the site.
What are the advantages of randomized experimental designs? Randomized experimental design yields the most accurate analysis of the effect of an intervention (e.g., a voter mobilization phone drive or a visit from a GOTV canvasser, on voter behavior). By randomly assigning subjects to be in the group that receives the treatment or to be in the control group, researchers can measure the effect of the mobilization method regardless of other factors that may make some people or groups more likely to participate in the political process. To provide a simple example, say we are testing the effectiveness of a voter education program on high school seniors. If we allow students from the class to volunteer to participate in the program, and we then compare the volunteers’ voting behavior against those who did not participate, our results will reflect something other than the effects of the voter education intervention. This is because there are, no doubt, qualities about those volunteers that make them different from students who do not volunteer. And, most important for our work, those differences may very well correlate with propensity to vote. Instead of letting students self-select, or even letting teachers select students (as teachers may have biases in who they choose), we could randomly assign all students in a given class to be in either a treatment or control group. This would ensure that those in the treatment and control groups differ solely due to chance. The value of randomization may also be seen in the use of walk lists for door-to-door canvassers. If canvassers choose which houses they will go to and which they will skip, they may choose houses that seem more inviting or they may choose houses that are placed closely together rather than those that are more spread out. These differences could conceivably correlate with voter turnout. Or if house numbers are chosen by selecting those on the first half of a ten page list, they may be clustered in neighborhoods that differ in important ways from neighborhoods in the second half of the list. Random assignment controls for both known and unknown variables that can creep in with other selection processes to confound analyses. Randomized experimental design is a powerful tool for drawing valid inferences about cause and effect. The use of randomized experimental design should allow a degree of certainty that the research findings cited in studies that employ this methodology reflect the effects of the interventions being measured and not some other underlying variable or variables.
What is a Randomized Control Trial (RCT)?
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A randomized control trial (RCT) is a type of study design that involves randomly assigning participants to either an experimental group or a control group to measure the effectiveness of an intervention or treatment.
Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) are considered the “gold standard” in medical and health research due to their rigorous design.
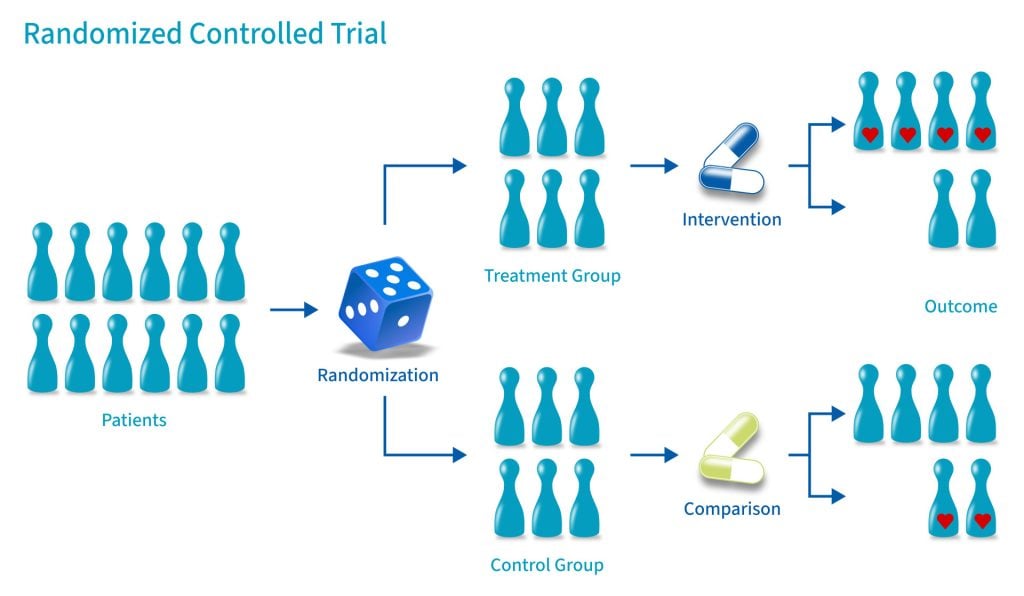
Control Group
A control group consists of participants who do not receive any treatment or intervention but a placebo or reference treatment. The control participants serve as a comparison group.
The control group is matched as closely as possible to the experimental group, including age, gender, social class, ethnicity, etc.
Because the participants are randomly assigned, the characteristics between the two groups should be balanced, enabling researchers to attribute any differences in outcome to the study intervention.
Since researchers can be confident that any differences between the control and treatment groups are due solely to the effects of the treatments, scientists view RCTs as the gold standard for clinical trials.
Random Allocation
Random allocation and random assignment are terms used interchangeably in the context of a randomized controlled trial (RCT).
Both refer to assigning participants to different groups in a study (such as a treatment group or a control group) in a way that is completely determined by chance.
The process of random assignment controls for confounding variables , ensuring differences between groups are due to chance alone.
Without randomization, researchers might consciously or subconsciously assign patients to a particular group for various reasons.
Several methods can be used for randomization in a Randomized Control Trial (RCT). Here are a few examples:
- Simple Randomization: This is the simplest method, like flipping a coin. Each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group. This can be achieved using random number tables, computerized random number generators, or drawing lots or envelopes.
- Block Randomization: In this method, participants are randomized within blocks, ensuring that each block has an equal number of participants in each group. This helps to balance the number of participants in each group at any given time during the study.
- Stratified Randomization: This method is used when researchers want to ensure that certain subgroups of participants are equally represented in each group. Participants are divided into strata, or subgroups, based on characteristics like age or disease severity, and then randomized within these strata.
- Cluster Randomization: In this method, groups of participants (like families or entire communities), rather than individuals, are randomized.
- Adaptive Randomization: In this method, the probability of being assigned to each group changes based on the participants already assigned to each group. For example, if more participants have been assigned to the control group, new participants will have a higher probability of being assigned to the experimental group.
Computer software can generate random numbers or sequences that can be used to assign participants to groups in a simple randomization process.
For more complex methods like block, stratified, or adaptive randomization, computer algorithms can be used to consider the additional parameters and ensure that participants are assigned to groups appropriately.
Using a computerized system can also help to maintain the integrity of the randomization process by preventing researchers from knowing in advance which group a participant will be assigned to (a principle known as allocation concealment). This can help to prevent selection bias and ensure the validity of the study results .
Allocation Concealment
Allocation concealment is a technique to ensure the random allocation process is truly random and unbiased.
RCTs use allocation concealment to decide which patients get the real medicine and which get a placebo (a fake medicine)
It involves keeping the sequence of group assignments (i.e., who gets assigned to the treatment group and who gets assigned to the control group next) hidden from the researchers before a participant has enrolled in the study.
This helps to prevent the researchers from consciously or unconsciously selecting certain participants for one group or the other based on their knowledge of which group is next in the sequence.
Allocation concealment ensures that the investigator does not know in advance which treatment the next person will get, thus maintaining the integrity of the randomization process.
Blinding (Masking)
Binding, or masking, refers to withholding information regarding the group assignments (who is in the treatment group and who is in the control group) from the participants, the researchers, or both during the study .
A blinded study prevents the participants from knowing about their treatment to avoid bias in the research. Any information that can influence the subjects is withheld until the completion of the research.
Blinding can be imposed on any participant in an experiment, including researchers, data collectors, evaluators, technicians, and data analysts.
Good blinding can eliminate experimental biases arising from the subjects’ expectations, observer bias, confirmation bias, researcher bias, observer’s effect on the participants, and other biases that may occur in a research test.
In a double-blind study , neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving the drug or the placebo. When a participant is enrolled, they are randomly assigned to one of the two groups. The medication they receive looks identical whether it’s the drug or the placebo.
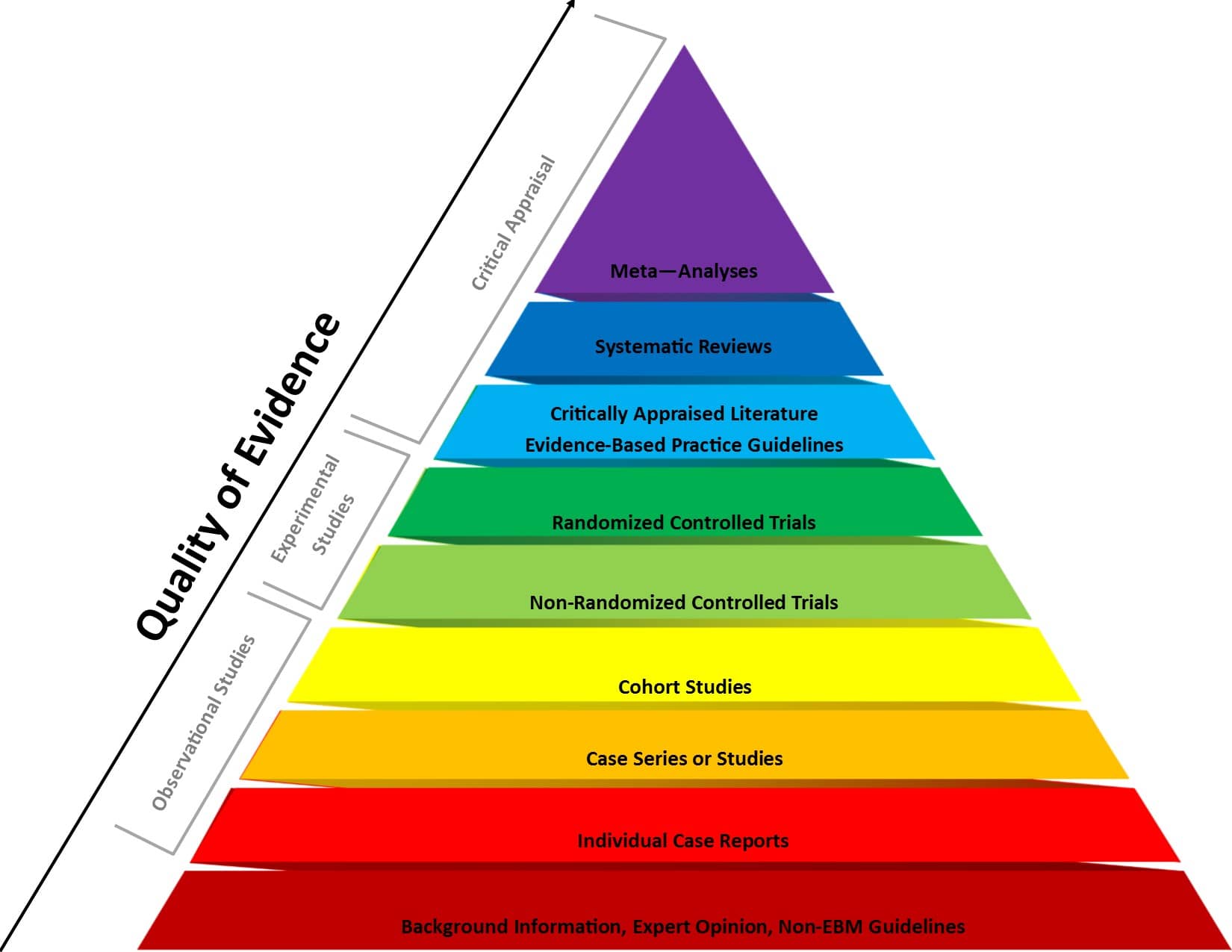
Figure 1 . Evidence-based medicine pyramid. The levels of evidence are appropriately represented by a pyramid as each level, from bottom to top, reflects the quality of research designs (increasing) and quantity (decreasing) of each study design in the body of published literature. For example, randomized control trials are higher quality and more labor intensive to conduct, so there is a lower quantity published.
Prevents bias
In randomized control trials, participants must be randomly assigned to either the intervention group or the control group, such that each individual has an equal chance of being placed in either group.
This is meant to prevent selection bias and allocation bias and achieve control over any confounding variables to provide an accurate comparison of the treatment being studied.
Because the distribution of characteristics of patients that could influence the outcome is randomly assigned between groups, any differences in outcome can be explained only by the treatment.
High statistical power
Because the participants are randomized and the characteristics between the two groups are balanced, researchers can assume that if there are significant differences in the primary outcome between the two groups, the differences are likely to be due to the intervention.
This warrants researchers to be confident that randomized control trials will have high statistical power compared to other types of study designs.
Since the focus of conducting a randomized control trial is eliminating bias, blinded RCTs can help minimize any unconscious information bias.
In a blinded RCT, the participants do not know which group they are assigned to or which intervention is received. This blinding procedure should also apply to researchers, health care professionals, assessors, and investigators when possible.
“Single-blind” refers to an RCT where participants do not know the details of the treatment, but the researchers do.
“ Double-blind ” refers to an RCT where both participants and data collectors are masked of the assigned treatment.
Limitations
Costly and timely.
Some interventions require years or even decades to evaluate, rendering them expensive and time-consuming.
It might take an extended period of time before researchers can identify a drug’s effects or discover significant results.
Requires large sample size
There must be enough participants in each group of a randomized control trial so researchers can detect any true differences or effects in outcomes between the groups.
Researchers cannot detect clinically important results if the sample size is too small.
Change in population over time
Because randomized control trials are longitudinal in nature, it is almost inevitable that some participants will not complete the study, whether due to death, migration, non-compliance, or loss of interest in the study.
This tendency is known as selective attrition and can threaten the statistical power of an experiment.
Randomized control trials are not always practical or ethical, and such limitations can prevent researchers from conducting their studies.
For example, a treatment could be too invasive, or administering a placebo instead of an actual drug during a trial for treating a serious illness could deny a participant’s normal course of treatment. Without ethical approval, a randomized control trial cannot proceed.
Fictitious Example
An example of an RCT would be a clinical trial comparing a drug’s effect or a new treatment on a select population.
The researchers would randomly assign participants to either the experimental group or the control group and compare the differences in outcomes between those who receive the drug or treatment and those who do not.
Real-life Examples
- Preventing illicit drug use in adolescents: Long-term follow-up data from a randomized control trial of a school population (Botvin et al., 2000).
- A prospective randomized control trial comparing medical and surgical treatment for early pregnancy failure (Demetroulis et al., 2001).
- A randomized control trial to evaluate a paging system for people with traumatic brain injury (Wilson et al., 2009).
- Prehabilitation versus Rehabilitation: A Randomized Control Trial in Patients Undergoing Colorectal Resection for Cancer (Gillis et al., 2014).
- A Randomized Control Trial of Right-Heart Catheterization in Critically Ill Patients (Guyatt, 1991).
- Berry, R. B., Kryger, M. H., & Massie, C. A. (2011). A novel nasal excitatory positive airway pressure (EPAP) device for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized controlled trial. Sleep , 34, 479–485.
- Gloy, V. L., Briel, M., Bhatt, D. L., Kashyap, S. R., Schauer, P. R., Mingrone, G., . . . Nordmann, A. J. (2013, October 22). Bariatric surgery versus non-surgical treatment for obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMJ , 347.
- Streeton, C., & Whelan, G. (2001). Naltrexone, a relapse prevention maintenance treatment of alcohol dependence: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 36 (6), 544–552.
How Should an RCT be Reported?
Reporting of a Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) should be done in a clear, transparent, and comprehensive manner to allow readers to understand the design, conduct, analysis, and interpretation of the trial.
The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials ( CONSORT ) statement is a widely accepted guideline for reporting RCTs.
Further Information
- Cocks, K., & Torgerson, D. J. (2013). Sample size calculations for pilot randomized trials: a confidence interval approach. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 66(2), 197-201.
- Kendall, J. (2003). Designing a research project: randomised controlled trials and their principles. Emergency medicine journal: EMJ, 20(2), 164.
Akobeng, A.K., Understanding randomized controlled trials. Archives of Disease in Childhood , 2005; 90: 840-844.
Bell, C. C., Gibbons, R., & McKay, M. M. (2008). Building protective factors to offset sexually risky behaviors among black youths: a randomized control trial. Journal of the National Medical Association, 100 (8), 936-944.
Bhide, A., Shah, P. S., & Acharya, G. (2018). A simplified guide to randomized controlled trials. Acta obstetricia et gynecologica Scandinavica, 97 (4), 380-387.
Botvin, G. J., Griffin, K. W., Diaz, T., Scheier, L. M., Williams, C., & Epstein, J. A. (2000). Preventing illicit drug use in adolescents: Long-term follow-up data from a randomized control trial of a school population. Addictive Behaviors, 25 (5), 769-774.
Demetroulis, C., Saridogan, E., Kunde, D., & Naftalin, A. A. (2001). A prospective randomized control trial comparing medical and surgical treatment for early pregnancy failure. Human Reproduction, 16 (2), 365-369.
Gillis, C., Li, C., Lee, L., Awasthi, R., Augustin, B., Gamsa, A., … & Carli, F. (2014). Prehabilitation versus rehabilitation: a randomized control trial in patients undergoing colorectal resection for cancer. Anesthesiology, 121 (5), 937-947.
Globas, C., Becker, C., Cerny, J., Lam, J. M., Lindemann, U., Forrester, L. W., … & Luft, A. R. (2012). Chronic stroke survivors benefit from high-intensity aerobic treadmill exercise: a randomized control trial. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, 26 (1), 85-95.
Guyatt, G. (1991). A randomized control trial of right-heart catheterization in critically ill patients. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine, 6 (2), 91-95.
MediLexicon International. (n.d.). Randomized controlled trials: Overview, benefits, and limitations. Medical News Today. Retrieved from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/280574#what-is-a-randomized-controlled-trial
Wilson, B. A., Emslie, H., Quirk, K., Evans, J., & Watson, P. (2005). A randomized control trial to evaluate a paging system for people with traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 19 (11), 891-894.
Random Assignment in Psychology (Intro for Students)
Random assignment is a research procedure used to randomly assign participants to different experimental conditions (or ‘groups’). This introduces the element of chance, ensuring that each participant has an equal likelihood of being placed in any condition group for the study.
It is absolutely essential that the treatment condition and the control condition are the same in all ways except for the variable being manipulated.
Using random assignment to place participants in different conditions helps to achieve this.
It ensures that those conditions are the same in regards to all potential confounding variables and extraneous factors .
Why Researchers Use Random Assignment
Researchers use random assignment to control for confounds in research.
Confounds refer to unwanted and often unaccounted-for variables that might affect the outcome of a study. These confounding variables can skew the results, rendering the experiment unreliable.
For example, below is a study with two groups. Note how there are more ‘red’ individuals in the first group than the second:
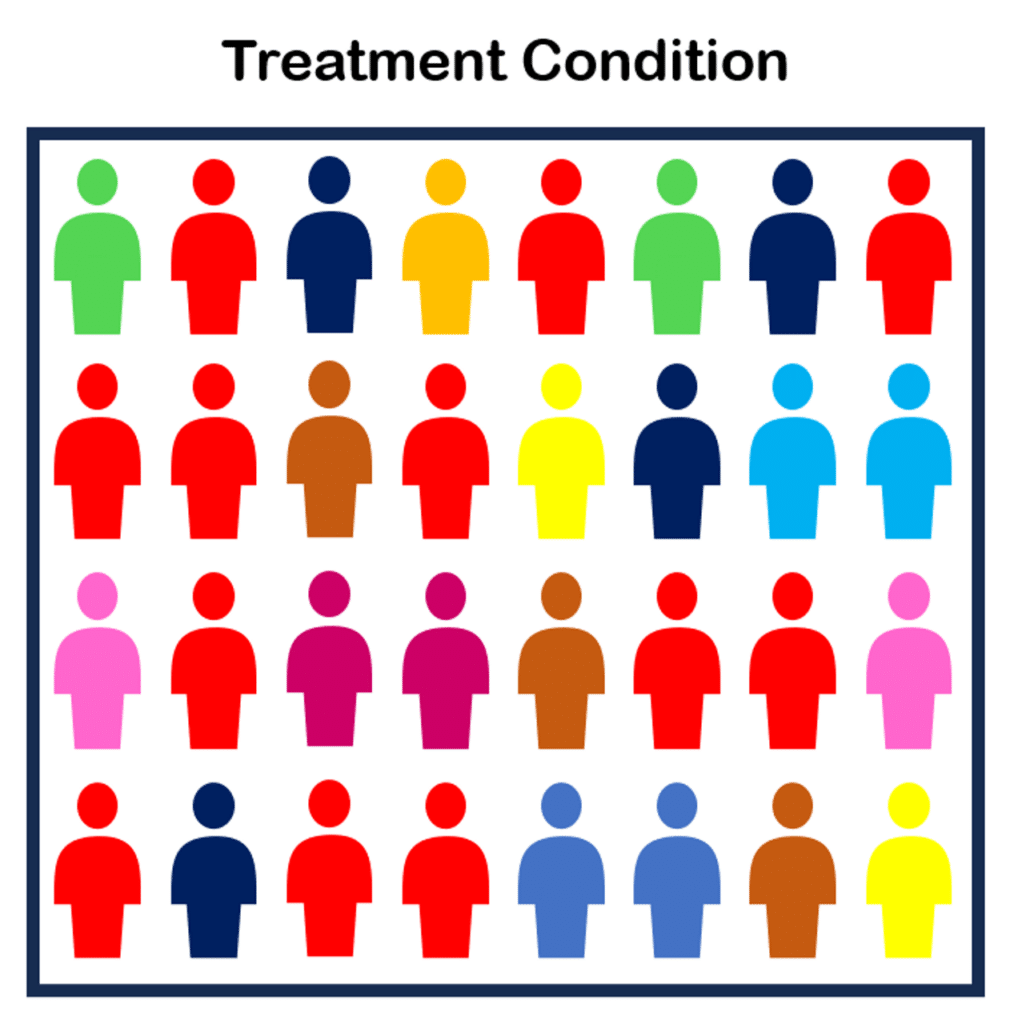
There is likely a confounding variable in this experiment explaining why more red people ended up in the treatment condition and less in the control condition. The red people might have self-selected, for example, leading to a skew of them in one group over the other.
Ideally, we’d want a more even distribution, like below:
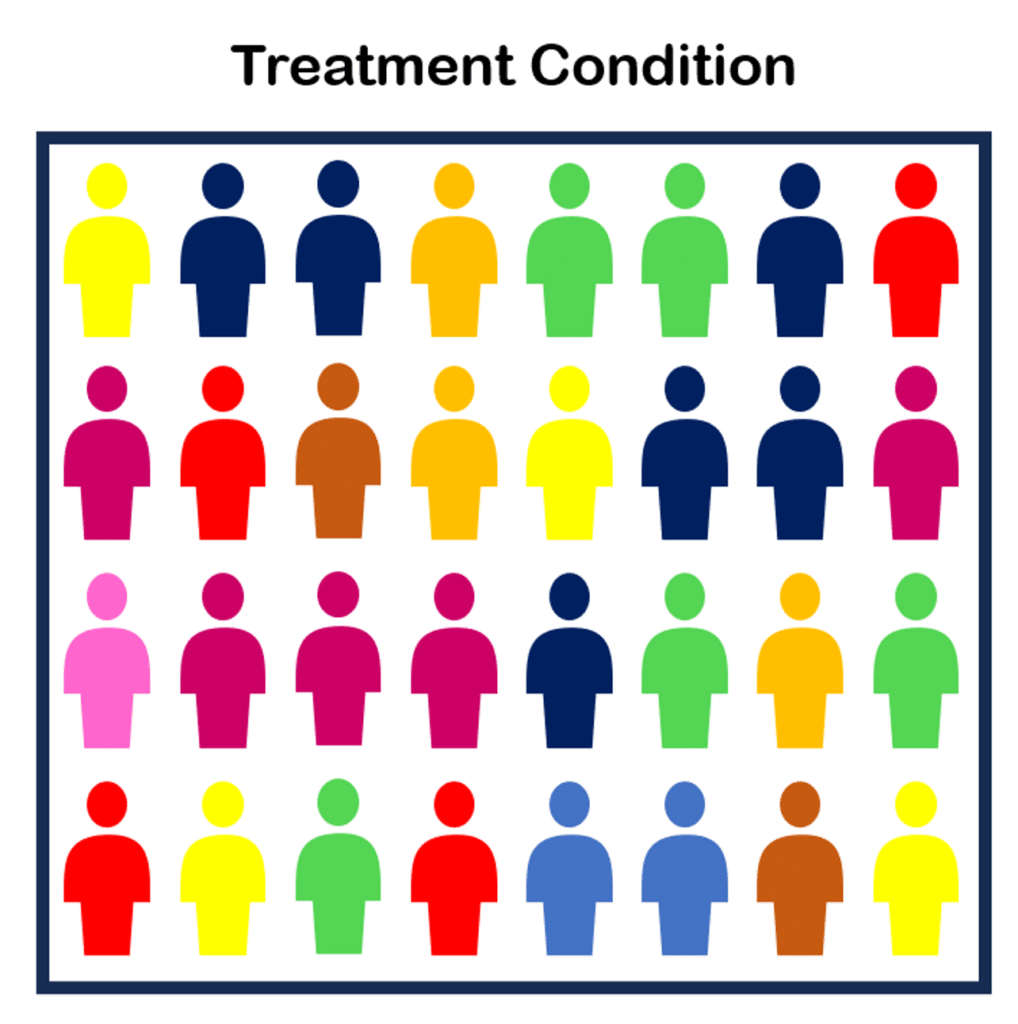
To achieve better balance in our two conditions, we use randomized sampling.
Fact File: Experiments 101
Random assignment is used in the type of research called the experiment.
An experiment involves manipulating the level of one variable and examining how it affects another variable. These are the independent and dependent variables :
- Independent Variable: The variable manipulated is called the independent variable (IV)
- Dependent Variable: The variable that it is expected to affect is called the dependent variable (DV).
The most basic form of the experiment involves two conditions: the treatment and the control .
- The Treatment Condition: The treatment condition involves the participants being exposed to the IV.
- The Control Condition: The control condition involves the absence of the IV. Therefore, the IV has two levels: zero and some quantity.
Researchers utilize random assignment to determine which participants go into which conditions.
Methods of Random Assignment
There are several procedures that researchers can use to randomly assign participants to different conditions.
1. Random number generator
There are several websites that offer computer-generated random numbers. Simply indicate how many conditions are in the experiment and then click. If there are 4 conditions, the program will randomly generate a number between 1 and 4 each time it is clicked.
2. Flipping a coin
If there are two conditions in an experiment, then the simplest way to implement random assignment is to flip a coin for each participant. Heads means being assigned to the treatment and tails means being assigned to the control (or vice versa).
3. Rolling a die
Rolling a single die is another way to randomly assign participants. If the experiment has three conditions, then numbers 1 and 2 mean being assigned to the control; numbers 3 and 4 mean treatment condition one; and numbers 5 and 6 mean treatment condition two.
4. Condition names in a hat
In some studies, the researcher will write the name of the treatment condition(s) or control on slips of paper and place them in a hat. If there are 4 conditions and 1 control, then there are 5 slips of paper.
The researcher closes their eyes and selects one slip for each participant. That person is then assigned to one of the conditions in the study and that slip of paper is placed back in the hat. Repeat as necessary.
There are other ways of trying to ensure that the groups of participants are equal in all ways with the exception of the IV. However, random assignment is the most often used because it is so effective at reducing confounds.
Read About More Methods and Examples of Random Assignment Here
Potential Confounding Effects
Random assignment is all about minimizing confounding effects.
Here are six types of confounds that can be controlled for using random assignment:
- Individual Differences: Participants in a study will naturally vary in terms of personality, intelligence, mood, prior knowledge, and many other characteristics. If one group happens to have more people with a particular characteristic, this could affect the results. Random assignment ensures that these individual differences are spread out equally among the experimental groups, making it less likely that they will unduly influence the outcome.
- Temporal or Time-Related Confounds: Events or situations that occur at a particular time can influence the outcome of an experiment. For example, a participant might be tested after a stressful event, while another might be tested after a relaxing weekend. Random assignment ensures that such effects are equally distributed among groups, thus controlling for their potential influence.
- Order Effects: If participants are exposed to multiple treatments or tests, the order in which they experience them can influence their responses. Randomly assigning the order of treatments for different participants helps control for this.
- Location or Environmental Confounds: The environment in which the study is conducted can influence the results. One group might be tested in a noisy room, while another might be in a quiet room. Randomly assigning participants to different locations can control for these effects.
- Instrumentation Confounds: These occur when there are variations in the calibration or functioning of measurement instruments across conditions. If one group’s responses are being measured using a slightly different tool or scale, it can introduce a confound. Random assignment can ensure that any such potential inconsistencies in instrumentation are equally distributed among groups.
- Experimenter Effects: Sometimes, the behavior or expectations of the person administering the experiment can unintentionally influence the participants’ behavior or responses. For instance, if an experimenter believes one treatment is superior, they might unconsciously communicate this belief to participants. Randomly assigning experimenters or using a double-blind procedure (where neither the participant nor the experimenter knows the treatment being given) can help control for this.
Random assignment helps balance out these and other potential confounds across groups, ensuring that any observed differences are more likely due to the manipulated independent variable rather than some extraneous factor.
Limitations of the Random Assignment Procedure
Although random assignment is extremely effective at eliminating the presence of participant-related confounds, there are several scenarios in which it cannot be used.
- Ethics: The most obvious scenario is when it would be unethical. For example, if wanting to investigate the effects of emotional abuse on children, it would be unethical to randomly assign children to either received abuse or not. Even if a researcher were to propose such a study, it would not receive approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) which oversees research by university faculty.
- Practicality: Other scenarios involve matters of practicality. For example, randomly assigning people to specific types of diet over a 10-year period would be interesting, but it would be highly unlikely that participants would be diligent enough to make the study valid. This is why examining these types of subjects has to be carried out through observational studies . The data is correlational, which is informative, but falls short of the scientist’s ultimate goal of identifying causality.
- Small Sample Size: The smaller the sample size being assigned to conditions, the more likely it is that the two groups will be unequal. For example, if you flip a coin many times in a row then you will notice that sometimes there will be a string of heads or tails that come up consecutively. This means that one condition may have a build-up of participants that share the same characteristics. However, if you continue flipping the coin, over the long-term, there will be a balance of heads and tails. Unfortunately, how large a sample size is necessary has been the subject of considerable debate (Bloom, 2006; Shadish et al., 2002).
“It is well known that larger sample sizes reduce the probability that random assignment will result in conditions that are unequal” (Goldberg, 2019, p. 2).
Applications of Random Assignment
The importance of random assignment has been recognized in a wide range of scientific and applied disciplines (Bloom, 2006).
Random assignment began as a tool in agricultural research by Fisher (1925, 1935). After WWII, it became extensively used in medical research to test the effectiveness of new treatments and pharmaceuticals (Marks, 1997).
Today it is widely used in industrial engineering (Box, Hunter, and Hunter, 2005), educational research (Lindquist, 1953; Ong-Dean et al., 2011)), psychology (Myers, 1972), and social policy studies (Boruch, 1998; Orr, 1999).
One of the biggest obstacles to the validity of an experiment is the confound. If the group of participants in the treatment condition are substantially different from the group in the control condition, then it is impossible to determine if the IV has an affect or if the confound has an effect.
Thankfully, random assignment is highly effective at eliminating confounds that are known and unknown. Because each participant has an equal chance of being placed in each condition, they are equally distributed.
There are several ways of implementing random assignment, including flipping a coin or using a random number generator.
Random assignment has become an essential procedure in research in a wide range of subjects such as psychology, education, and social policy.
Alferes, V. R. (2012). Methods of randomization in experimental design . Sage Publications.
Bloom, H. S. (2008). The core analytics of randomized experiments for social research. The SAGE Handbook of Social Research Methods , 115-133.
Boruch, R. F. (1998). Randomized controlled experiments for evaluation and planning. Handbook of applied social research methods , 161-191.
Box, G. E., Hunter, W. G., & Hunter, J. S. (2005). Design of experiments: Statistics for Experimenters: Design, Innovation and Discovery.
Dehue, T. (1997). Deception, efficiency, and random groups: Psychology and the gradual origination of the random group design. Isis , 88 (4), 653-673.
Fisher, R.A. (1925). Statistical methods for research workers (11th ed. rev.). Oliver and Boyd: Edinburgh.
Fisher, R. A. (1935). The Design of Experiments. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd.
Goldberg, M. H. (2019). How often does random assignment fail? Estimates and recommendations. Journal of Environmental Psychology , 66 , 101351.
Jamison, J. C. (2019). The entry of randomized assignment into the social sciences. Journal of Causal Inference , 7 (1), 20170025.
Lindquist, E. F. (1953). Design and analysis of experiments in psychology and education . Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Marks, H. M. (1997). The progress of experiment: Science and therapeutic reform in the United States, 1900-1990 . Cambridge University Press.
Myers, J. L. (1972). Fundamentals of experimental design (2nd ed.). Allyn & Bacon.
Ong-Dean, C., Huie Hofstetter, C., & Strick, B. R. (2011). Challenges and dilemmas in implementing random assignment in educational research. American Journal of Evaluation , 32 (1), 29-49.
Orr, L. L. (1999). Social experiments: Evaluating public programs with experimental methods . Sage.
Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Quasi-experiments: interrupted time-series designs. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference , 171-205.
Stigler, S. M. (1992). A historical view of statistical concepts in psychology and educational research. American Journal of Education , 101 (1), 60-70.

Dave Cornell (PhD)
Dr. Cornell has worked in education for more than 20 years. His work has involved designing teacher certification for Trinity College in London and in-service training for state governments in the United States. He has trained kindergarten teachers in 8 countries and helped businessmen and women open baby centers and kindergartens in 3 countries.
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Random Assignment in Psychology (Definition + 40 Examples)

Have you ever wondered how researchers discover new ways to help people learn, make decisions, or overcome challenges? A hidden hero in this adventure of discovery is a method called random assignment, a cornerstone in psychological research that helps scientists uncover the truths about the human mind and behavior.
Random Assignment is a process used in research where each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group within the study. This technique is essential in experiments as it helps to eliminate biases, ensuring that the different groups being compared are similar in all important aspects.
By doing so, researchers can be confident that any differences observed are likely due to the variable being tested, rather than other factors.
In this article, we’ll explore the intriguing world of random assignment, diving into its history, principles, real-world examples, and the impact it has had on the field of psychology.
History of Random Assignment
Stepping back in time, we delve into the origins of random assignment, which finds its roots in the early 20th century.
The pioneering mind behind this innovative technique was Sir Ronald A. Fisher , a British statistician and biologist. Fisher introduced the concept of random assignment in the 1920s, aiming to improve the quality and reliability of experimental research .
His contributions laid the groundwork for the method's evolution and its widespread adoption in various fields, particularly in psychology.
Fisher’s groundbreaking work on random assignment was motivated by his desire to control for confounding variables – those pesky factors that could muddy the waters of research findings.
By assigning participants to different groups purely by chance, he realized that the influence of these confounding variables could be minimized, paving the way for more accurate and trustworthy results.
Early Studies Utilizing Random Assignment
Following Fisher's initial development, random assignment started to gain traction in the research community. Early studies adopting this methodology focused on a variety of topics, from agriculture (which was Fisher’s primary field of interest) to medicine and psychology.
The approach allowed researchers to draw stronger conclusions from their experiments, bolstering the development of new theories and practices.
One notable early study utilizing random assignment was conducted in the field of educational psychology. Researchers were keen to understand the impact of different teaching methods on student outcomes.
By randomly assigning students to various instructional approaches, they were able to isolate the effects of the teaching methods, leading to valuable insights and recommendations for educators.
Evolution of the Methodology
As the decades rolled on, random assignment continued to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of research.
Advances in technology introduced new tools and techniques for implementing randomization, such as computerized random number generators, which offered greater precision and ease of use.
The application of random assignment expanded beyond the confines of the laboratory, finding its way into field studies and large-scale surveys.
Researchers across diverse disciplines embraced the methodology, recognizing its potential to enhance the validity of their findings and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
From its humble beginnings in the early 20th century to its widespread use today, random assignment has proven to be a cornerstone of scientific inquiry.
Its development and evolution have played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of psychological research, driving discoveries that have improved lives and deepened our understanding of the human experience.
Principles of Random Assignment
Delving into the heart of random assignment, we uncover the theories and principles that form its foundation.
The method is steeped in the basics of probability theory and statistical inference, ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group, thus fostering fair and unbiased results.

Basic Principles of Random Assignment
Understanding the core principles of random assignment is key to grasping its significance in research. There are three principles: equal probability of selection, reduction of bias, and ensuring representativeness.
The first principle, equal probability of selection , ensures that every participant has an identical chance of being assigned to any group in the study. This randomness is crucial as it mitigates the risk of bias and establishes a level playing field.
The second principle focuses on the reduction of bias . Random assignment acts as a safeguard, ensuring that the groups being compared are alike in all essential aspects before the experiment begins.
This similarity between groups allows researchers to attribute any differences observed in the outcomes directly to the independent variable being studied.
Lastly, ensuring representativeness is a vital principle. When participants are assigned randomly, the resulting groups are more likely to be representative of the larger population.
This characteristic is crucial for the generalizability of the study’s findings, allowing researchers to apply their insights broadly.
Theoretical Foundation
The theoretical foundation of random assignment lies in probability theory and statistical inference .
Probability theory deals with the likelihood of different outcomes, providing a mathematical framework for analyzing random phenomena. In the context of random assignment, it helps in ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group.
Statistical inference, on the other hand, allows researchers to draw conclusions about a population based on a sample of data drawn from that population. It is the mechanism through which the results of a study can be generalized to a broader context.
Random assignment enhances the reliability of statistical inferences by reducing biases and ensuring that the sample is representative.
Differentiating Random Assignment from Random Selection
It’s essential to distinguish between random assignment and random selection, as the two terms, while related, have distinct meanings in the realm of research.
Random assignment refers to how participants are placed into different groups in an experiment, aiming to control for confounding variables and help determine causes.
In contrast, random selection pertains to how individuals are chosen to participate in a study. This method is used to ensure that the sample of participants is representative of the larger population, which is vital for the external validity of the research.
While both methods are rooted in randomness and probability, they serve different purposes in the research process.
Understanding the theories, principles, and distinctions of random assignment illuminates its pivotal role in psychological research.
This method, anchored in probability theory and statistical inference, serves as a beacon of reliability, guiding researchers in their quest for knowledge and ensuring that their findings stand the test of validity and applicability.
Methodology of Random Assignment
Implementing random assignment in a study is a meticulous process that involves several crucial steps.
The initial step is participant selection, where individuals are chosen to partake in the study. This stage is critical to ensure that the pool of participants is diverse and representative of the population the study aims to generalize to.
Once the pool of participants has been established, the actual assignment process begins. In this step, each participant is allocated randomly to one of the groups in the study.
Researchers use various tools, such as random number generators or computerized methods, to ensure that this assignment is genuinely random and free from biases.
Monitoring and adjusting form the final step in the implementation of random assignment. Researchers need to continuously observe the groups to ensure that they remain comparable in all essential aspects throughout the study.
If any significant discrepancies arise, adjustments might be necessary to maintain the study’s integrity and validity.
Tools and Techniques Used
The evolution of technology has introduced a variety of tools and techniques to facilitate random assignment.
Random number generators, both manual and computerized, are commonly used to assign participants to different groups. These generators ensure that each individual has an equal chance of being placed in any group, upholding the principle of equal probability of selection.
In addition to random number generators, researchers often use specialized computer software designed for statistical analysis and experimental design.
These software programs offer advanced features that allow for precise and efficient random assignment, minimizing the risk of human error and enhancing the study’s reliability.
Ethical Considerations
The implementation of random assignment is not devoid of ethical considerations. Informed consent is a fundamental ethical principle that researchers must uphold.
Informed consent means that every participant should be fully informed about the nature of the study, the procedures involved, and any potential risks or benefits, ensuring that they voluntarily agree to participate.
Beyond informed consent, researchers must conduct a thorough risk and benefit analysis. The potential benefits of the study should outweigh any risks or harms to the participants.
Safeguarding the well-being of participants is paramount, and any study employing random assignment must adhere to established ethical guidelines and standards.
Conclusion of Methodology
The methodology of random assignment, while seemingly straightforward, is a multifaceted process that demands precision, fairness, and ethical integrity. From participant selection to assignment and monitoring, each step is crucial to ensure the validity of the study’s findings.
The tools and techniques employed, coupled with a steadfast commitment to ethical principles, underscore the significance of random assignment as a cornerstone of robust psychological research.
Benefits of Random Assignment in Psychological Research
The impact and importance of random assignment in psychological research cannot be overstated. It is fundamental for ensuring the study is accurate, allowing the researchers to determine if their study actually caused the results they saw, and making sure the findings can be applied to the real world.
Facilitating Causal Inferences
When participants are randomly assigned to different groups, researchers can be more confident that the observed effects are due to the independent variable being changed, and not other factors.
This ability to determine the cause is called causal inference .
This confidence allows for the drawing of causal relationships, which are foundational for theory development and application in psychology.
Ensuring Internal Validity
One of the foremost impacts of random assignment is its ability to enhance the internal validity of an experiment.
Internal validity refers to the extent to which a researcher can assert that changes in the dependent variable are solely due to manipulations of the independent variable , and not due to confounding variables.
By ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being in any condition of the experiment, random assignment helps control for participant characteristics that could otherwise complicate the results.
Enhancing Generalizability
Beyond internal validity, random assignment also plays a crucial role in enhancing the generalizability of research findings.
When done correctly, it ensures that the sample groups are representative of the larger population, so can allow researchers to apply their findings more broadly.
This representative nature is essential for the practical application of research, impacting policy, interventions, and psychological therapies.
Limitations of Random Assignment
Potential for implementation issues.
While the principles of random assignment are robust, the method can face implementation issues.
One of the most common problems is logistical constraints. Some studies, due to their nature or the specific population being studied, find it challenging to implement random assignment effectively.
For instance, in educational settings, logistical issues such as class schedules and school policies might stop the random allocation of students to different teaching methods .
Ethical Dilemmas
Random assignment, while methodologically sound, can also present ethical dilemmas.
In some cases, withholding a potentially beneficial treatment from one of the groups of participants can raise serious ethical questions, especially in medical or clinical research where participants' well-being might be directly affected.
Researchers must navigate these ethical waters carefully, balancing the pursuit of knowledge with the well-being of participants.
Generalizability Concerns
Even when implemented correctly, random assignment does not always guarantee generalizable results.
The types of people in the participant pool, the specific context of the study, and the nature of the variables being studied can all influence the extent to which the findings can be applied to the broader population.
Researchers must be cautious in making broad generalizations from studies, even those employing strict random assignment.
Practical and Real-World Limitations
In the real world, many variables cannot be manipulated for ethical or practical reasons, limiting the applicability of random assignment.
For instance, researchers cannot randomly assign individuals to different levels of intelligence, socioeconomic status, or cultural backgrounds.
This limitation necessitates the use of other research designs, such as correlational or observational studies , when exploring relationships involving such variables.
Response to Critiques
In response to these critiques, people in favor of random assignment argue that the method, despite its limitations, remains one of the most reliable ways to establish cause and effect in experimental research.
They acknowledge the challenges and ethical considerations but emphasize the rigorous frameworks in place to address them.
The ongoing discussion around the limitations and critiques of random assignment contributes to the evolution of the method, making sure it is continuously relevant and applicable in psychological research.
While random assignment is a powerful tool in experimental research, it is not without its critiques and limitations. Implementation issues, ethical dilemmas, generalizability concerns, and real-world limitations can pose significant challenges.
However, the continued discourse and refinement around these issues underline the method's enduring significance in the pursuit of knowledge in psychology.
By being careful with how we do things and doing what's right, random assignment stays a really important part of studying how people act and think.
Real-World Applications and Examples

Random assignment has been employed in many studies across various fields of psychology, leading to significant discoveries and advancements.
Here are some real-world applications and examples illustrating the diversity and impact of this method:
- Medicine and Health Psychology: Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) are the gold standard in medical research. In these studies, participants are randomly assigned to either the treatment or control group to test the efficacy of new medications or interventions.
- Educational Psychology: Studies in this field have used random assignment to explore the effects of different teaching methods, classroom environments, and educational technologies on student learning and outcomes.
- Cognitive Psychology: Researchers have employed random assignment to investigate various aspects of human cognition, including memory, attention, and problem-solving, leading to a deeper understanding of how the mind works.
- Social Psychology: Random assignment has been instrumental in studying social phenomena, such as conformity, aggression, and prosocial behavior, shedding light on the intricate dynamics of human interaction.
Let's get into some specific examples. You'll need to know one term though, and that is "control group." A control group is a set of participants in a study who do not receive the treatment or intervention being tested , serving as a baseline to compare with the group that does, in order to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Smoking Cessation Study: Researchers used random assignment to put participants into two groups. One group received a new anti-smoking program, while the other did not. This helped determine if the program was effective in helping people quit smoking.
- Math Tutoring Program: A study on students used random assignment to place them into two groups. One group received additional math tutoring, while the other continued with regular classes, to see if the extra help improved their grades.
- Exercise and Mental Health: Adults were randomly assigned to either an exercise group or a control group to study the impact of physical activity on mental health and mood.
- Diet and Weight Loss: A study randomly assigned participants to different diet plans to compare their effectiveness in promoting weight loss and improving health markers.
- Sleep and Learning: Researchers randomly assigned students to either a sleep extension group or a regular sleep group to study the impact of sleep on learning and memory.
- Classroom Seating Arrangement: Teachers used random assignment to place students in different seating arrangements to examine the effect on focus and academic performance.
- Music and Productivity: Employees were randomly assigned to listen to music or work in silence to investigate the effect of music on workplace productivity.
- Medication for ADHD: Children with ADHD were randomly assigned to receive either medication, behavioral therapy, or a placebo to compare treatment effectiveness.
- Mindfulness Meditation for Stress: Adults were randomly assigned to a mindfulness meditation group or a waitlist control group to study the impact on stress levels.
- Video Games and Aggression: A study randomly assigned participants to play either violent or non-violent video games and then measured their aggression levels.
- Online Learning Platforms: Students were randomly assigned to use different online learning platforms to evaluate their effectiveness in enhancing learning outcomes.
- Hand Sanitizers in Schools: Schools were randomly assigned to use hand sanitizers or not to study the impact on student illness and absenteeism.
- Caffeine and Alertness: Participants were randomly assigned to consume caffeinated or decaffeinated beverages to measure the effects on alertness and cognitive performance.
- Green Spaces and Well-being: Neighborhoods were randomly assigned to receive green space interventions to study the impact on residents’ well-being and community connections.
- Pet Therapy for Hospital Patients: Patients were randomly assigned to receive pet therapy or standard care to assess the impact on recovery and mood.
- Yoga for Chronic Pain: Individuals with chronic pain were randomly assigned to a yoga intervention group or a control group to study the effect on pain levels and quality of life.
- Flu Vaccines Effectiveness: Different groups of people were randomly assigned to receive either the flu vaccine or a placebo to determine the vaccine’s effectiveness.
- Reading Strategies for Dyslexia: Children with dyslexia were randomly assigned to different reading intervention strategies to compare their effectiveness.
- Physical Environment and Creativity: Participants were randomly assigned to different room setups to study the impact of physical environment on creative thinking.
- Laughter Therapy for Depression: Individuals with depression were randomly assigned to laughter therapy sessions or control groups to assess the impact on mood.
- Financial Incentives for Exercise: Participants were randomly assigned to receive financial incentives for exercising to study the impact on physical activity levels.
- Art Therapy for Anxiety: Individuals with anxiety were randomly assigned to art therapy sessions or a waitlist control group to measure the effect on anxiety levels.
- Natural Light in Offices: Employees were randomly assigned to workspaces with natural or artificial light to study the impact on productivity and job satisfaction.
- School Start Times and Academic Performance: Schools were randomly assigned different start times to study the effect on student academic performance and well-being.
- Horticulture Therapy for Seniors: Older adults were randomly assigned to participate in horticulture therapy or traditional activities to study the impact on cognitive function and life satisfaction.
- Hydration and Cognitive Function: Participants were randomly assigned to different hydration levels to measure the impact on cognitive function and alertness.
- Intergenerational Programs: Seniors and young people were randomly assigned to intergenerational programs to study the effects on well-being and cross-generational understanding.
- Therapeutic Horseback Riding for Autism: Children with autism were randomly assigned to therapeutic horseback riding or traditional therapy to study the impact on social communication skills.
- Active Commuting and Health: Employees were randomly assigned to active commuting (cycling, walking) or passive commuting to study the effect on physical health.
- Mindful Eating for Weight Management: Individuals were randomly assigned to mindful eating workshops or control groups to study the impact on weight management and eating habits.
- Noise Levels and Learning: Students were randomly assigned to classrooms with different noise levels to study the effect on learning and concentration.
- Bilingual Education Methods: Schools were randomly assigned different bilingual education methods to compare their effectiveness in language acquisition.
- Outdoor Play and Child Development: Children were randomly assigned to different amounts of outdoor playtime to study the impact on physical and cognitive development.
- Social Media Detox: Participants were randomly assigned to a social media detox or regular usage to study the impact on mental health and well-being.
- Therapeutic Writing for Trauma Survivors: Individuals who experienced trauma were randomly assigned to therapeutic writing sessions or control groups to study the impact on psychological well-being.
- Mentoring Programs for At-risk Youth: At-risk youth were randomly assigned to mentoring programs or control groups to assess the impact on academic achievement and behavior.
- Dance Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: Individuals with Parkinson’s disease were randomly assigned to dance therapy or traditional exercise to study the effect on motor function and quality of life.
- Aquaponics in Schools: Schools were randomly assigned to implement aquaponics programs to study the impact on student engagement and environmental awareness.
- Virtual Reality for Phobia Treatment: Individuals with phobias were randomly assigned to virtual reality exposure therapy or traditional therapy to compare effectiveness.
- Gardening and Mental Health: Participants were randomly assigned to engage in gardening or other leisure activities to study the impact on mental health and stress reduction.
Each of these studies exemplifies how random assignment is utilized in various fields and settings, shedding light on the multitude of ways it can be applied to glean valuable insights and knowledge.
Real-world Impact of Random Assignment

Random assignment is like a key tool in the world of learning about people's minds and behaviors. It’s super important and helps in many different areas of our everyday lives. It helps make better rules, creates new ways to help people, and is used in lots of different fields.
Health and Medicine
In health and medicine, random assignment has helped doctors and scientists make lots of discoveries. It’s a big part of tests that help create new medicines and treatments.
By putting people into different groups by chance, scientists can really see if a medicine works.
This has led to new ways to help people with all sorts of health problems, like diabetes, heart disease, and mental health issues like depression and anxiety.
Schools and education have also learned a lot from random assignment. Researchers have used it to look at different ways of teaching, what kind of classrooms are best, and how technology can help learning.
This knowledge has helped make better school rules, develop what we learn in school, and find the best ways to teach students of all ages and backgrounds.
Workplace and Organizational Behavior
Random assignment helps us understand how people act at work and what makes a workplace good or bad.
Studies have looked at different kinds of workplaces, how bosses should act, and how teams should be put together. This has helped companies make better rules and create places to work that are helpful and make people happy.
Environmental and Social Changes
Random assignment is also used to see how changes in the community and environment affect people. Studies have looked at community projects, changes to the environment, and social programs to see how they help or hurt people’s well-being.
This has led to better community projects, efforts to protect the environment, and programs to help people in society.
Technology and Human Interaction
In our world where technology is always changing, studies with random assignment help us see how tech like social media, virtual reality, and online stuff affect how we act and feel.
This has helped make better and safer technology and rules about using it so that everyone can benefit.
The effects of random assignment go far and wide, way beyond just a science lab. It helps us understand lots of different things, leads to new and improved ways to do things, and really makes a difference in the world around us.
From making healthcare and schools better to creating positive changes in communities and the environment, the real-world impact of random assignment shows just how important it is in helping us learn and make the world a better place.
So, what have we learned? Random assignment is like a super tool in learning about how people think and act. It's like a detective helping us find clues and solve mysteries in many parts of our lives.
From creating new medicines to helping kids learn better in school, and from making workplaces happier to protecting the environment, it’s got a big job!
This method isn’t just something scientists use in labs; it reaches out and touches our everyday lives. It helps make positive changes and teaches us valuable lessons.
Whether we are talking about technology, health, education, or the environment, random assignment is there, working behind the scenes, making things better and safer for all of us.
In the end, the simple act of putting people into groups by chance helps us make big discoveries and improvements. It’s like throwing a small stone into a pond and watching the ripples spread out far and wide.
Thanks to random assignment, we are always learning, growing, and finding new ways to make our world a happier and healthier place for everyone!
Related posts:
- 19+ Experimental Design Examples (Methods + Types)
- Cluster Sampling vs Stratified Sampling
- 41+ White Collar Job Examples (Salary + Path)
- 47+ Blue Collar Job Examples (Salary + Path)
- McDonaldization of Society (Definition + Examples)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test

Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
Random Assignment
- First Online: 17 May 2019
Cite this chapter

- Gideon J. Mellenbergh 2
483 Accesses
A substantial part of behavioral research is aimed at the testing of substantive hypotheses. In general, a hypothesis testing study investigates the causal influence of an independent variable (IV) on a dependent variable (DV) . The discussion is restricted to IVs that can be manipulated by the researcher, such as, experimental (E- ) and control (C- ) conditions. Association between IV and DV does not imply that the IV has a causal influence on the DV . The association can be spurious because it is caused by an other variable (OV). OVs that cause spurious associations come from the (1) participant, (2) research situation, and (3) reactions of the participants to the research situation. If participants select their own (E- or C- ) condition or others select a condition for them, the assignment to conditions is usually biased (e.g., males prefer the E-condition and females the C-condition), and participant variables (e.g., participants’ sex) may cause a spurious association between the IV and DV . This selection bias is a systematic error of a design. It is counteracted by random assignment of participants to conditions. Random assignment guarantees that all participant variables are related to the IV by chance, and turns systematic error into random error. Random errors decrease the precision of parameter estimates. Random error variance is reduced by including auxiliary variables into the randomized design. A randomized block design includes an auxiliary variable to divide the participants into relatively homogeneous blocks, and randomly assigns participants to the conditions per block. A covariate is an auxiliary variable that is used in the statistical analysis of the data to reduce the error variance. Cluster randomization randomly assigns clusters (e.g., classes of students) to conditions, which yields specific problems. Random assignment should not be confused with random selection. Random assignment controls for selection bias , whereas random selection makes possible to generalize study results of a sample to the population.
- Cluster randomization
- Cross-over design
- Independent and dependent variables
- Random assignment and random selection
- Randomized block design
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Cox, D. R. (2006). Principles of statistical inference . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Google Scholar
Hox, J. (2002). Multilevel analysis: Techniques and applications . Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Lai, K., & Kelley, K. (2012). Accuracy in parameter estimation for ANCOVA and ANOVA contrasts: Sample size planning via narrow confidence intervals. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 65, 350–370.
PubMed Google Scholar
McNeish, D., Stapleton, L. M., & Silverman, R. D. (2017). On the unnecessary ubiquity of hierarchical linear modelling. Psychological Methods, 22, 114–140.
Murray, D. M., Varnell, S. P., & Blitstein, J. L. (2004). Design and analysis of group-randomized trials: A review of recent methodological developments. American Journal of Public Health, 94, 423–432.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Snijders, T. A. B., & Bosker, R. J. (1999). Multilevel analysis . London, UK: Sage.
van Belle, G. (2002). Statistical rules of thumb . New York, NY: Wiley.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Emeritus Professor Psychological Methods, Department of Psychology, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Gideon J. Mellenbergh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gideon J. Mellenbergh .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Mellenbergh, G.J. (2019). Random Assignment. In: Counteracting Methodological Errors in Behavioral Research. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12272-0_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12272-0_4
Published : 17 May 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-74352-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-12272-0
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Statistical Thinking: A Simulation Approach to Modeling Uncertainty (UM STAT 216 edition)
3.6 causation and random assignment.
Medical researchers may be interested in showing that a drug helps improve people’s health (the cause of improvement is the drug), while educational researchers may be interested in showing a curricular innovation improves students’ learning (the curricular innovation causes improved learning).
To attribute a causal relationship, there are three criteria a researcher needs to establish:
- Association of the Cause and Effect: There needs to be a association between the cause and effect.
- Timing: The cause needs to happen BEFORE the effect.
- No Plausible Alternative Explanations: ALL other possible explanations for the effect need to be ruled out.
Please read more about each of these criteria at the Web Center for Social Research Methods .
The third criterion can be quite difficult to meet. To rule out ALL other possible explanations for the effect, we want to compare the world with the cause applied to the world without the cause. In practice, we do this by comparing two different groups: a “treatment” group that gets the cause applied to them, and a “control” group that does not. To rule out alternative explanations, the groups need to be “identical” with respect to every possible characteristic (aside from the treatment) that could explain differences. This way the only characteristic that will be different is that the treatment group gets the treatment and the control group doesn’t. If there are differences in the outcome, then it must be attributable to the treatment, because the other possible explanations are ruled out.
So, the key is to make the control and treatment groups “identical” when you are forming them. One thing that makes this task (slightly) easier is that they don’t have to be exactly identical, only probabilistically equivalent . This means, for example, that if you were matching groups on age that you don’t need the two groups to have identical age distributions; they would only need to have roughly the same AVERAGE age. Here roughly means “the average ages should be the same within what we expect because of sampling error.”
Now we just need to create the groups so that they have, on average, the same characteristics … for EVERY POSSIBLE CHARCTERISTIC that could explain differences in the outcome.
It turns out that creating probabilistically equivalent groups is a really difficult problem. One method that works pretty well for doing this is to randomly assign participants to the groups. This works best when you have large sample sizes, but even with small sample sizes random assignment has the advantage of at least removing the systematic bias between the two groups (any differences are due to chance and will probably even out between the groups). As Wikipedia’s page on random assignment points out,
Random assignment of participants helps to ensure that any differences between and within the groups are not systematic at the outset of the experiment. Thus, any differences between groups recorded at the end of the experiment can be more confidently attributed to the experimental procedures or treatment. … Random assignment does not guarantee that the groups are matched or equivalent. The groups may still differ on some preexisting attribute due to chance. The use of random assignment cannot eliminate this possibility, but it greatly reduces it.
We use the term internal validity to describe the degree to which cause-and-effect inferences are accurate and meaningful. Causal attribution is the goal for many researchers. Thus, by using random assignment we have a pretty high degree of evidence for internal validity; we have a much higher belief in causal inferences. Much like evidence used in a court of law, it is useful to think about validity evidence on a continuum. For example, a visualization of the internal validity evidence for a study that employed random assignment in the design might be:

The degree of internal validity evidence is high (in the upper-third). How high depends on other factors such as sample size.
To learn more about random assignment, you can read the following:
- The research report, Random Assignment Evaluation Studies: A Guide for Out-of-School Time Program Practitioners
3.6.1 Example: Does sleep deprivation cause an decrease in performance?
Let’s consider the criteria with respect to the sleep deprivation study we explored in class.
3.6.1.1 Association of cause and effect
First, we ask, Is there an association between the cause and the effect? In the sleep deprivation study, we would ask, “Is sleep deprivation associated with an decrease in performance?”
This is what a hypothesis test helps us answer! If the result is statistically significant , then we have an association between the cause and the effect. If the result is not statistically significant, then there is not sufficient evidence for an association between cause and effect.
In the case of the sleep deprivation experiment, the result was statistically significant, so we can say that sleep deprivation is associated with a decrease in performance.
3.6.1.2 Timing
Second, we ask, Did the cause come before the effect? In the sleep deprivation study, the answer is yes. The participants were sleep deprived before their performance was tested. It may seem like this is a silly question to ask, but as the link above describes, it is not always so clear to establish the timing. Thus, it is important to consider this question any time we are interested in establishing causality.
3.6.1.3 No plausible alternative explanations
Finally, we ask Are there any plausible alternative explanations for the observed effect? In the sleep deprivation study, we would ask, “Are there plausible alternative explanations for the observed difference between the groups, other than sleep deprivation?” Because this is a question about plausibility, human judgment comes into play. Researchers must make an argument about why there are no plausible alternatives. As described above, a strong study design can help to strengthen the argument.
At first, it may seem like there are a lot of plausible alternative explanations for the difference in performance. There are a lot of things that might affect someone’s performance on a visual task! Sleep deprivation is just one of them! For example, artists may be more adept at visual discrimination than other people. This is an example of a potential confounding variable. A confounding variable is a variable that might affect the results, other than the causal variable that we are interested in.
Here’s the thing though. We are not interested in figuring out why any particular person got the score that they did. Instead, we are interested in determining why one group was different from another group. In the sleep deprivation study, the participants were randomly assigned. This means that the there is no systematic difference between the groups, with respect to any confounding variables. Yes—artistic experience is a possible confounding variable, and it may be the reason why two people score differently. BUT: There is no systematic difference between the groups with respect to artistic experience, and so artistic experience is not a plausible explanation as to why the groups would be different. The same can be said for any possible confounding variable. Because the groups were randomly assigned, it is not plausible to say that the groups are different with respect to any confounding variable. Random assignment helps us rule out plausible alternatives.
3.6.1.4 Making a causal claim
Now, let’s see about make a causal claim for the sleep deprivation study:
- Association: There is a statistically significant result, so the cause is associated with the effect
- Timing: The participants were sleep deprived before their performance was measured, so the cause came before the effect
- Plausible alternative explanations: The participants were randomly assigned, so the groups are not systematically different on any confounding variable. The only systematic difference between the groups was sleep deprivation. Thus, there are no plausible alternative explanations for the difference between the groups, other than sleep deprivation
Thus, the internal validity evidence for this study is high, and we can make a causal claim. For the participants in this study, we can say that sleep deprivation caused a decrease in performance.
Key points: Causation and internal validity
To make a cause-and-effect inference, you need to consider three criteria:
- Association of the Cause and Effect: There needs to be a association between the cause and effect. This can be established by a hypothesis test.
Random assignment removes any systematic differences between the groups (other than the treatment), and thus helps to rule out plausible alternative explanations.
Internal validity describes the degree to which cause-and-effect inferences are accurate and meaningful.
Confounding variables are variables that might affect the results, other than the causal variable that we are interested in.
Probabilistic equivalence means that there is not a systematic difference between groups. The groups are the same on average.
How can we make "equivalent" experimental groups?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 13 February 2023.
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different treatment groups using randomisation.
With simple random assignment, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group. Studies that use simple random assignment are also called completely randomised designs .
Random assignment is a key part of experimental design . It helps you ensure that all groups are comparable at the start of a study: any differences between them are due to random factors.
Table of contents
Why does random assignment matter, random sampling vs random assignment, how do you use random assignment, when is random assignment not used, frequently asked questions about random assignment.
Random assignment is an important part of control in experimental research, because it helps strengthen the internal validity of an experiment.
In experiments, researchers manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables. To do so, they often use different levels of an independent variable for different groups of participants.
This is called a between-groups or independent measures design.
You use three groups of participants that are each given a different level of the independent variable:
- A control group that’s given a placebo (no dosage)
- An experimental group that’s given a low dosage
- A second experimental group that’s given a high dosage
Random assignment to helps you make sure that the treatment groups don’t differ in systematic or biased ways at the start of the experiment.
If you don’t use random assignment, you may not be able to rule out alternative explanations for your results.
- Participants recruited from pubs are placed in the control group
- Participants recruited from local community centres are placed in the low-dosage experimental group
- Participants recruited from gyms are placed in the high-dosage group
With this type of assignment, it’s hard to tell whether the participant characteristics are the same across all groups at the start of the study. Gym users may tend to engage in more healthy behaviours than people who frequent pubs or community centres, and this would introduce a healthy user bias in your study.
Although random assignment helps even out baseline differences between groups, it doesn’t always make them completely equivalent. There may still be extraneous variables that differ between groups, and there will always be some group differences that arise from chance.
Most of the time, the random variation between groups is low, and, therefore, it’s acceptable for further analysis. This is especially true when you have a large sample. In general, you should always use random assignment in experiments when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Random sampling and random assignment are both important concepts in research, but it’s important to understand the difference between them.
Random sampling (also called probability sampling or random selection) is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups.
While random sampling is used in many types of studies, random assignment is only used in between-subjects experimental designs.
Some studies use both random sampling and random assignment, while others use only one or the other.
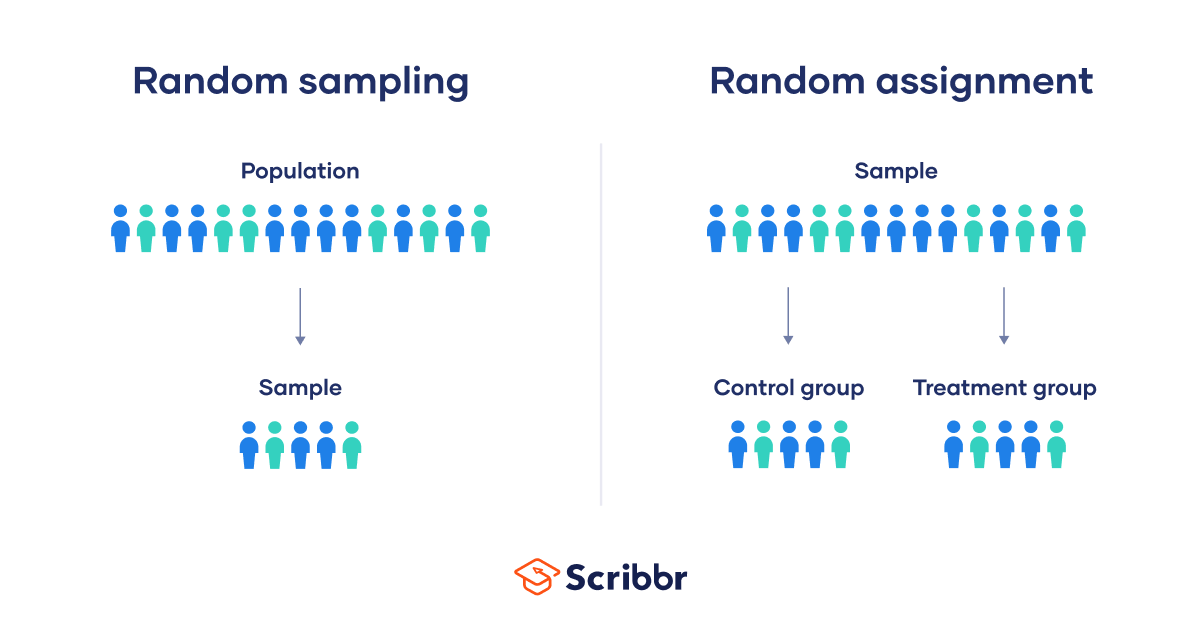
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalisability of your results, because it helps to ensure that your sample is unbiased and representative of the whole population. This allows you to make stronger statistical inferences .
You use a simple random sample to collect data. Because you have access to the whole population (all employees), you can assign all 8,000 employees a number and use a random number generator to select 300 employees. These 300 employees are your full sample.
Random assignment enhances the internal validity of the study, because it ensures that there are no systematic differences between the participants in each group. This helps you conclude that the outcomes can be attributed to the independent variable .
- A control group that receives no intervention
- An experimental group that has a remote team-building intervention every week for a month
You use random assignment to place participants into the control or experimental group. To do so, you take your list of participants and assign each participant a number. Again, you use a random number generator to place each participant in one of the two groups.
To use simple random assignment, you start by giving every member of the sample a unique number. Then, you can use computer programs or manual methods to randomly assign each participant to a group.
- Random number generator: Use a computer program to generate random numbers from the list for each group.
- Lottery method: Place all numbers individually into a hat or a bucket, and draw numbers at random for each group.
- Flip a coin: When you only have two groups, for each number on the list, flip a coin to decide if they’ll be in the control or the experimental group.
- Use a dice: When you have three groups, for each number on the list, roll a die to decide which of the groups they will be in. For example, assume that rolling 1 or 2 lands them in a control group; 3 or 4 in an experimental group; and 5 or 6 in a second control or experimental group.
This type of random assignment is the most powerful method of placing participants in conditions, because each individual has an equal chance of being placed in any one of your treatment groups.
Random assignment in block designs
In more complicated experimental designs, random assignment is only used after participants are grouped into blocks based on some characteristic (e.g., test score or demographic variable). These groupings mean that you need a larger sample to achieve high statistical power .
For example, a randomised block design involves placing participants into blocks based on a shared characteristic (e.g., college students vs graduates), and then using random assignment within each block to assign participants to every treatment condition. This helps you assess whether the characteristic affects the outcomes of your treatment.
In an experimental matched design , you use blocking and then match up individual participants from each block based on specific characteristics. Within each matched pair or group, you randomly assign each participant to one of the conditions in the experiment and compare their outcomes.
Sometimes, it’s not relevant or ethical to use simple random assignment, so groups are assigned in a different way.
When comparing different groups
Sometimes, differences between participants are the main focus of a study, for example, when comparing children and adults or people with and without health conditions. Participants are not randomly assigned to different groups, but instead assigned based on their characteristics.
In this type of study, the characteristic of interest (e.g., gender) is an independent variable, and the groups differ based on the different levels (e.g., men, women). All participants are tested the same way, and then their group-level outcomes are compared.
When it’s not ethically permissible
When studying unhealthy or dangerous behaviours, it’s not possible to use random assignment. For example, if you’re studying heavy drinkers and social drinkers, it’s unethical to randomly assign participants to one of the two groups and ask them to drink large amounts of alcohol for your experiment.
When you can’t assign participants to groups, you can also conduct a quasi-experimental study . In a quasi-experiment, you study the outcomes of pre-existing groups who receive treatments that you may not have any control over (e.g., heavy drinkers and social drinkers).
These groups aren’t randomly assigned, but may be considered comparable when some other variables (e.g., age or socioeconomic status) are controlled for.
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different groups using randomisation. With this method, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group.
Random selection, or random sampling , is a way of selecting members of a population for your study’s sample.
In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample into control and experimental groups.
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalisability of your results, while random assignment improves the internal validity of your study.
Random assignment is used in experiments with a between-groups or independent measures design. In this research design, there’s usually a control group and one or more experimental groups. Random assignment helps ensure that the groups are comparable.
In general, you should always use random assignment in this type of experimental design when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic.
To implement random assignment , assign a unique number to every member of your study’s sample .
Then, you can use a random number generator or a lottery method to randomly assign each number to a control or experimental group. You can also do so manually, by flipping a coin or rolling a die to randomly assign participants to groups.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, February 13). Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/random-assignment-experiments/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, controlled experiments | methods & examples of control, control groups and treatment groups | uses & examples.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.3(6); 2006 Jun

Does Random Treatment Assignment Cause Harm to Research Participants?
Cary p gross.
1 Section of General Internal Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, United States of America,
3 Robert Wood Johnson Clinical Scholars Program, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, United States of America,
Harlan M Krumholz
2 Section of General Internal Medicine and Yale Cancer Center, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, United States of America,
4 Section of Health Policy and Administration, Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, United States of America,
Gretchen Van Wye
5 Section of Chronic Disease Epidemiology, Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, United States of America,
Ezekiel J Emanuel
6 Department of Clinical Bioethics, Warren G. Magnuson Clinical Center, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, United States of America
David Wendler
Associated data.
Some argue that by precluding individualized treatment, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) provide substandard medical care, while others claim that participation in clinical research is associated with improved patient outcomes. However, there are few data to assess the impact of random treatment assignment on RCT participants. We therefore performed a systematic review to quantify the differences in health outcomes between randomized trial participants and eligible non-participants.
Methods and Findings
Studies were identified by searching Medline, the Web of Science citation database, and manuscript references. Studies were eligible if they documented baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes of RCT participants and eligible non-participants, and allowed non-participants access to the same interventions available to trial participants. Primary study outcomes according to patient group (randomized trial participants versus eligible non-participants) were extracted from all eligible manuscripts. For 22 of the 25 studies (88%) meeting eligibility criteria, there were no significant differences in clinical outcomes between patients who received random assignment of treatment (RCT participants) and those who received individualized treatment assignment (eligible non-participants). In addition, there was no relation between random treatment assignment and clinical outcome in 15 of the 17 studies (88%) in which randomized and nonrandomized patients had similar health status at baseline.
Conclusions
These findings suggest that randomized treatment assignment as part of a clinical trial does not harm research participants.
A search was conducted for RCTs where information was recorded on outcomes for participants and those who did not enter the trial, but still had access to the same treatments. No significant difference was found between randomised and non-randomised patients.
Introduction
Despite widespread reliance on randomized clinical trials (RCTs), and claims that they represent the “gold standard” for assessing treatment efficacy, ethical concern has been raised about the impact of RCTs on participants [ 1 – 4 ]. Specifically, there is a perception that individual patients are likely to have better outcomes when treatment decisions are based on physicians' clinical judgment, rather than random assignment [ 1 , 2 ]. It has been claimed that by foregoing individualized treatment assignment, the process of choosing research participants' treatments by random assignment leads to an “inevitable compromise of personal care in the service of obtaining valid research results” [ 1 ]. Further, physician and patient concerns about random treatment assignment are among the most frequently cited reasons for refusal to enroll in RCTs [ 5 – 8 ].
While some commentators focus on the specific impact of random treatment assignment, others have investigated the broader topic of differences in clinical outcomes between research participants and “real” patients in the community setting. Some studies have suggested that research participation may be associated with improved clinical outcomes [ 9 – 14 ]. These data have led some to recommend trial participation as a means to better treatment [ 15 ]. For instance, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network's clinical practice guidelines in oncology state that “the best management for any cancer patient is in a clinical trial” [ 15 ]. Yet these conclusions are not based on strong evidence [ 16 ]. In particular, comparisons of research participants versus non-participants often include non-participants who do not meet trial eligibility criteria [ 16 ]. Because of stringent eligibility criteria, trial participants tend to be younger and healthier than non-participants in the community [ 16 – 18 ]. Trial participation may also be the only means of access to some therapies: if the investigational therapy is available only in the research setting and turns out to be superior to existing therapies, trial participants who were allocated to the newer agent would be more likely to benefit. Further, the supportive clinical care that participants receive as part of research in resource-rich settings associated with some clinical trials may also be associated with superior outcomes. Recognizing these flaws in the existing data, a recent review of the literature called for more studies that assess the impact of participation in clinical research on patient outcomes in a methodologically rigorous manner [ 16 ].
It is particularly timely to disentangle the issues surrounding the effect of research participation on patients. There has recently been increased emphasis on designing trials that compare commercially available, clinically relevant alternatives [ 19 – 21 ]. Some authors have advocated substantial increases in funding of “pragmatic” trials enrolling large numbers of patients in community practice settings [ 19 ]. Additionally, Medicare's policy has recently been modified so as to provide reimbursement for some new therapies only if patients receive them in the setting of a clinical trial [ 22 ]. Unlike in the previous paradigm, which viewed randomized trials as a tool to evaluate the efficacy of novel therapeutic agents, these innovations will likely result in many more patients encountering the decision of trial enrollment in the setting of routine clinical care. Prospective participants who are asked to participate in these pragmatic trials will have to decide whether to receive therapy that was selected via randomization or to select treatment with the input of their clinician.
Given the increased emphasis on recruiting large numbers of patients into trials, it is important to consider the question of enrollment from the perspective of patients who meet all eligibility criteria and are asked to enroll. If they agree to have their treatment selected at random, rather than by their clinicians or themselves, will they be more likely to experience adverse outcomes? We sought to answer this question by examining the potential risks associated with random treatment allocation, rather than delineating differences between trial participants and non-participants [ 16 , 18 ]. While numerous studies have demonstrated the differences between trial participants and their counterparts in the community, few have focused specifically on the impact of random treatment assignment. Specifically, we were interested in the group of patients who were eligible for participation in an RCT but could also receive either of the therapies offered in the RCT even if they refused to enroll. We conducted a systematic review of published randomized controlled trials to compare the clinical outcomes of randomized patients and nonrandomized patients who were eligible for the same trial, were cared for in the same clinical setting, and received the same agents available to trial participants.
Selection of Studies
We conducted a Medline search to identify studies that (1) included only patients who were eligible for trial participation, (2) included only patients who were cared for at the same institutions and at the same time in which the randomized trial was recruiting, (3) allowed non-participants access to the agents used in the trial, (4) provided outcome data for both trial participants and eligible non-participants, and (5) recruited all participants in a similar manner.
The Medline search employed 23 unique combinations of terms and strings of terms (see Protocol S1 ). We focused a significant portion of our Medline search on identifying studies that met our definition of comprehensive cohort study design (see Protocol S1 for terms and phrases). The comprehensive cohort study design, also called the partially randomized patient preference trial design, offers eligible research participants the chance to refuse randomization but receive either the study intervention or the control intervention per study protocol [ 23 ]. In addition, we used the references of relevant manuscripts, authors' own bibliographic libraries, and Web of Science to identify frequently cited researchers and papers.
The Medline search identified 1,505 studies; the Web of Science search identified 371 studies. Of these 1,876 studies, the titles of 1,555 were identified by the two reviewers as potentially appropriate for inclusion in the current analysis. The abstracts of these 1,555 studies were assessed by two authors for appropriate content and relevant methodology. The full texts of 48 potentially suitable manuscripts were retrieved and assessed. Of these, 25 studies met the eligibility criteria.
Data Analysis
An explicit abstraction instrument was used to obtain baseline characteristics of the RCT participants and eligible non-participants and primary clinical outcomes. Outcomes were restricted to the primary outcome listed in each manuscript; if more than one primary outcome was specified, the first one listed was used. To compare outcomes across studies, all study outcomes were standardized to “adverse” outcomes, e.g., for studies that reported survival, we converted probability of survival to probability of death. Most of the studies had dichotomous outcomes that enabled the calculation of odds ratios; those that did not were analyzed separately. In the two studies in which outcomes were expressed only as rates rather than as frequency counts, the stated proportion of people in each group who experienced the study outcome was multiplied by the number at baseline to estimate the frequency [ 24 , 25 ]. In one study, non-participants were able to select from three treatment options, only two of which were part of the RCT. For this study, we included data only from non-participants who received one of the two treatments that were part of the RCT [ 25 ].
Because the relation between trial participation and clinical outcomes might be confounded by differences in baseline health status, we categorized the studies into three mutually exclusive groups: those in which the RCT participants were, overall, less healthy than eligible non-participants at baseline, those in which there was no clear difference in baseline health status, and those in which RCT participants were, overall, healthier at baseline. Two clinicians, using an implicit schema involving examination of baseline clinical and demographic characteristics of randomized and nonrandomized patients, independently categorized each study according to whether there was a balance of important prognostic factors between groups. Disagreements were resolved by consensus.
The odds ratios of experiencing the primary clinical outcome for RCT participants versus eligible non-participants were calculated using SAS 8.1 [ 26 ]. A Breslow–Day chi-square statistic indicated that it would be inappropriate to aggregate the results of studies with dichotomous outcomes because of heterogeneity. Thus, the outcomes are presented simply by study, according to baseline differences.
A total of 25 articles met the inclusion criteria and were selected for data abstraction. The dates of publication ranged from 1984 to 2002; the majority (80%) were published in 1990 or later. There was a broad range of conditions under investigation, and types of studies, including surgical trials, drug trials, and trials of counseling. The most common specialties represented were oncology (six studies), cardiovascular disease (five studies), and obstetrics/gynecology (five studies). The total number of eligible patients across all studies was 17,934 (range: 79 to 3,610); the proportion of eligible patients who agreed to be randomized ranged from 29% to 89% (average: 45 %; median: 47 %). The primary outcomes of interest varied across studies; the most common were mortality (9/25), acceptability of treatment (5/25), and proportion of time or number of days with a given condition (2/25).
Baseline Characteristics
Table 1 shows the study intervention and enrollment data for all 25 studies, categorized according to baseline clinical and sociodemographic characteristics. There were no clear differences in baseline health status between RCT participants and eligible non-participants in 17 studies. In one study, RCT participants were healthier than eligible non-participants at baseline, and in seven studies RCT participants were less healthy at baseline than eligible non-participants. There was no significant relation between the proportion of eligible patients who agreed to be randomized and the occurrence of differences in baseline health status of randomized versus nonrandomized patients. The mean proportion of eligible patients who agreed to be randomized in the seven studies categorized as “RCT patients less healthy” was 48.9%, while the mean in the 17 studies with no baseline differences was 43.5% ( p = 0.61).
Study Characteristics

Differences in clinical sociodemographic characteristics between groups also varied in magnitude and significance. For instance, in the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation of angioplasty versus coronary artery bypass graft, RCT participants were significantly more likely than non-participants to have a history of myocardial infarction (55% versus 51%), heart failure (9% versus 5%), or diabetes (19% versus 17%) [ 24 ]. Significant differences in race were found in two studies: the study by Marcus and colleagues included more non-whites in the eligible, nonrandomized group (10% versus 24%; p = 0.008), and the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation included more non-whites in the RCT group (10% versus 6%, p < 0.001) [ 24 , 27 , 28 ].
In 22 of the 25 studies (88%), there were no significant differences in clinical outcomes between patients whose treatment was selected by randomized allocation and those whose treatment was selected on the basis of clinical judgment and/or patient preferences ( Table 2 ; Figure 1 ). There were no significant differences in clinical outcomes between randomized and nonrandomized patients in 15 of the 17 studies (88%) in which there were no clear baseline differences in health or sociodemographic status. Similarly, there were no significant differences in clinical outcomes between randomized and nonrandomized patients in six of the seven studies in which RCT participants were sicker than non-participants at baseline (86%; chi-square test, p > 0.05 for comparison with the “no clear baseline differences” group).
Clinical Outcome in Randomized and Nonrandomized Patients

Asterisks indicate statistical significance. The relevant references for the studies listed along the x- axis are as follows: AVID [ 50 , 68 ], EAST [ 51 ], Cooper [ 52 ], BARI [ 24 ], Chilvers [ 53 ], Bain [ 54 ], CASS [ 55 ], Link [ 57 ], Blichert-Toft [ 30 ], Henshaw [ 58 ], Nicolaides [ 59 ], SMASH [ 63 ], Mosekilde [ 64 ], Kerry [ 67 ], Bijker [ 25 ], Melchart [ 29 ], and Antman [ 31 ].
In Feit et al.'s analysis of the data from the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation [ 24 ], randomized patients were more likely to have risk factors for adverse outcomes at baseline: they were more likely to have congestive heart failure, prior myocardial infarction, or diabetes, and were more likely to be non-white and less educated. The 7-y mortality in the randomized group was 17.3%, compared with 14.5% in the nonrandomized group (relative risk: 1.19; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.03, 1.39) [ 24 ]. In Melchart et al.'s study of acupuncture versus midazolam as pretreatment for gastroscopy [ 29 ], there were no significant differences in baseline health status between randomized and nonrandomized groups. Randomized patients were more likely than nonrandomized patients to state that they would not undergo the same treatment again (34.6% versus 15.3%; relative risk: 2.27; 95% CI: 1.06, 4.84). Similarly, in Blichert-Toft's study of mastectomy versus breast-conserving surgery for breast cancer [ 30 ], randomized patients were more likely than nonrandomized patients to experience the outcome of cancer recurrence (13.7% versus 6.6%), although the difference was of borderline significance (relative risk: 2.08; 95% CI: 1.07, 4.02).
In the single study in which randomized patients were categorized as having a better baseline health status than nonrandomized patients, there was a nonsignificant trend towards the randomized patients being less likely to experience disease recurrence or death (odds ratio for randomized versus nonrandomized: 0.35; 95% CI: 0.12, 1.01) [ 31 ].
When there are several treatment options available, and there is uncertainty about which one is superior, it is assumed that individualized treatment assignment—in which clinicians consider the health status and preferences of each patient and incorporate them into a recommendation—is more likely to yield desirable outcomes. This is why doctors don't flip coins, and this is also why some may assume that randomization as part of a trial is harmful. In 23 of the 25 published clinical trials that met inclusion criteria, there were no significant differences in the likelihood of experiencing the primary study outcomes between patients whose treatment was determined by random allocation versus those whose treatment was selected on the basis of clinical judgment and/or patient preferences. More importantly, in 15 of the 17 studies in which randomized and nonrandomized patients were classified as having similar health status at baseline, there were no significant differences between these groups in clinical outcomes. These data contradict the perception that random treatment assignment as part of a clinical trial is harmful to research participants.
The finding that randomized research participants and non-participants tend to achieve similar clinical outcomes also contradicts prior studies suggesting that trial participation may be associated with superior clinical outcomes [ 9 – 14 ]. Many of the previous studies that reported such a difference failed to account for the numerous differences between clinical care and clinical research that may influence patient outcomes, including the fact that research participants are often younger, healthier, and treated by clinicians with more experience in treating patients with the condition of interest. Specifically, we restricted the present analysis to studies that included only patients who were eligible for RCT participation and had access to similar treatments whether or not they chose to enroll in the RCT. Hence, while our study sample was therefore restricted to a relatively small subset of RCTs, our findings suggest that the purported benefit of trial participation is probably due to baseline differences between participants and non-participants, or to differences in treatments received.
All of the studies included in the present analysis allowed access to the experimental therapies to patients who refused trial enrollment. It is unclear whether our results can be generalized to randomized trials that include newer, and potentially more efficacious, therapies that are not available outside the research setting. However, a recent analysis found that only 36% of trials presented at an annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology yielded “positive” results [ 32 ]. These findings contradict the widespread assumption that access to experimental therapies is beneficial [ 33 – 38 ]. Future work should explore whether participation in randomized trials of otherwise unavailable agents is associated with superior clinical outcomes.
While our comprehensive and systematic search identified far more manuscripts than prior reviews of this topic that we are aware of, our final sample size is small relative to the number of RCTs conducted annually [ 39 ]. As a result, although our findings were consistent across disease entities and different types of intervention, they may not be generalizable. As noted in prior reviews, many of the primary studies did not control for differences in baseline health characteristics [ 16 , 39 ]. We used an implicit, dual review approach to account for this potential bias, stratifying manuscripts according to baseline differences between trial participants and non-participants. Ideally, future work employing primary data would enable multivariate analysis of patient-level information, to account for important patient characteristics that may affect patient outcomes. The increasing use of electronic medical records represents a tremendous opportunity for establishing longitudinal registry databases to facilitate follow-up of patients who are offered trial enrollment, yet decline.
Our results should be interpreted with several considerations in mind. We restricted our analysis to the primary outcomes assessed in the included studies. In particular, many studies assessed the outcome of mortality, and there may have been differences in the probability of other adverse events, satisfaction, or quality of life between RCT participants and non-participants. Similarly, clinical trials may include additional research procedures, such as blood draws and lumbar punctures that do not affect patient outcomes but that pose burdens to participants. Additionally, random assignment refers only to the investigational agent. Even among RCT participants, clinician-investigators generally have some latitude regarding other aspects of care that are administered to their patients and can therefore provide individualized care that consists of interventions that are distinct from the investigational agent. Similarly, clinicians may halt existing treatment for patients who are offered a choice of enrolling in a study. In these instances, if a patient is provided one of the treatment interventions offered in the study—whether selected with randomization or by patient choice—it is possible that the initial treatment may have been superior to either of the treatments under investigation. Further, publication bias might have yielded underestimates of differences between RCT participants and eligible non-participants, as investigators may have been reluctant to report data from the non-participants in their registries if they did not support the generalizability of their RCTs. Finally, there may have been important differences in health status between randomized and nonrandomized patients that were not reported by the investigators. However, given that the vast majority of the study samples in our sample found no difference in health outcome between groups, one would have to invoke a systematic over- or underestimation of health status in the randomized groups across multiple studies in order to instill bias in this synthesis.
Numerous studies indicate that RCT participants often fail to understand that their treatments will be determined by random assignment [ 18 , 40 – 42 ]. For example, a recent analysis found that half of parents who decided whether to enroll their children in a leukemia trial did not understand that treatment allocation would be determined by chance [ 18 ]. The failure to understand randomization is often regarded as part of a broader phenomenon, termed the “therapeutic misconception,” according to which individuals assume that research treatments are based on physicians' decisions regarding what is best for them [ 1 , 43 ]. In this context, our findings have important implications for the informed consent process. In addition to explaining randomization, investigators should also explain that, in general, there is little evidence to support that participating in randomized trials is either helpful or harmful.
What do our findings say about the impact of clinical judgment and patient preferences on clinical outcomes? Although clinicians and patients may be reluctant to forego clinical decision-making, our data suggest that undergoing randomization, rather than individualized treatment recommendations by clinicians, is not harmful. This conclusion calls into question clinicians' ability to determine which therapy is superior for their patients in the setting of clinical equipoise, i.e., when there is uncertainty in the expert community about which treatment is superior for patients in general [ 44 ]. It has also been suggested that some patients who are not randomly assigned to a treatment may achieve a better outcome not because of an objective therapeutic effect, but because they were assigned to the treatment arm they preferred—a logical extension of the placebo effect [ 45 ]. To account for this possible “preference effect,” some have called for incorporating patient treatment preferences into the analysis phase of RCTs [ 45 ]. Our data provide preliminary evidence that this preference effect does not bias the outcomes of RCTs: patients who received a treatment preferred by themselves or their clinicians did not experience superior outcomes. These findings are consistent with the result of a recent review in which the authors stratified patients according to treatment received and then compared the outcome of patients who were randomized versus those who selected each therapy [ 46 ].
A critical barrier to enrolling patients in research studies is the fact that many patients are not even asked to participate [ 47 ]. One reason why physicians are reluctant to recruit their own patients is their reluctance to forego individualized treatment decisions for their patients [ 7 , 48 ]. This reluctance is especially important because physician recommendations are among the strongest predictors of trial enrollment [ 49 ]. The current findings suggest that in the setting of clinical equipoise, randomized treatment allocation as part of an RCT is unlikely to be harmful This does not imply that all research is not risky, as the risks and benefits of experimental treatment may vary substantially between studies. However, in the situation in which patients will have access to the treatments that are used in the study setting regardless of whether the patient enrolls, prospective participants and their referring physicians should be reassured: there is no evidence that random treatment assignment leads to worse clinical outcomes. Furthermore, patients who do participate in such research can contribute to the important objective of improving health and well-being for all patients.
Supporting Information
Protocol s1.
(67 KB DOC)
Editors' Summary
Background..
When researchers test a new treatment, they give it to a group of patients. If the test is to be fair and provide useful results, there should also be a control group of patients who are studied in parallel. The patients in the control group receive either a different treatment, a pretend treatment (“a placebo”), or no treatment at all. But how do researchers decide who should be in the treatment group and who should be in the control group? This is an important question because the test would not be fair if, for example, all the individuals in the treatment group were elderly men and the controls were all young women, or if everyone in the treatment group received their treatment in a well-equipped specialist hospital and the controls received care in a local general hospital. Statisticians would say that the results from such studies were “confounded” by the differences between the two groups. Instead, patients should be allocated to treatment or control groups at random. Randomization also has the advantage that it can conceal from the researchers, and from the patients, whether the treatment being given is the new one or an old one or a placebo. This is important because—again for example—researchers might hold strong beliefs about the effectiveness of a new treatment and this bias in its favor might lead them, perhaps only subconsciously, to allocate younger, stronger patients to the treatment group. For these and other reasons, randomized clinical trials (RCTs) are regarded as the “gold standard” in assessing the effectiveness of treatments.
Why Was This Study Done?
Doctors normally decide on the “best” treatment for an individual patient based on their knowledge and experience. However, if a patient has agreed to be part of an RCT, then their treatment will instead be chosen at random. Some people worry that patients who participate in RCTs may, because their treatment is less “personalized,” have a lower chance of recovery from their illness than similar patients who are not in trials. In contrast, other argue that, particularly if the trial is part of an important research program, being in an RCT is to the patient's advantage. This study aimed to find out whether either of these possibilities is true.
What Did the Researchers Do and Find?
The researchers conducted a thorough electronic search of medical journals in order to find published RCTs for which information—both before and after treatment—had been recorded not only about the patients who were enrolled in the trials, but also about other patients whose condition made them eligible to participate but who were not actually enrolled. The researchers also decided in advance that they were only interested in such RCTs if the non-enrolled patients had access to the same treatment or treatments that were given to the trial participants. Only 25 RCTs were found that met these requirements. There were nearly 18,000 patients in these studies; overall 45% had received treatment after randomization and 55% had not been randomized. Most of the RCTs were for treatments for cancer, problems of the heart and circulation, and obstetric and gynecological issues. The “clinical outcomes” recorded in the trials varied and included, for example, death/survival, recurrence of cancer, and improvement of hearing. In 22 of these trials, there were no statistically significant differences in clinical outcomes between patients who received random assignment of treatment (i.e., the RCT participants) and those who received individualized treatment assignment (eligible non-participants). In one trial the randomized patients fared better, and in the remaining two the nonrandomized patients had the better outcomes.
What Do These Findings Mean?
These findings suggest that randomized treatment assignment as part of a clinical trial does not harm research participants, nor does there appear to be an advantage to being randomized in a trial.
Additional Information
Please access these Web sites via the online version of this summary at http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0030188 .
•The James Lind Library has been created to help patients and researchers understand fair tests of treatments in health care by illustrating how fair tests have developed over the centuries
• Wikipedia , a free Internet encyclopedia that anyone can edit, has pages on RCTs
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Drs. Frank Miller and Stephen Straus for their thoughtful comments. The views expressed are the authors' own. They do not represent the position or policy of the National Institutes of Health or the Department of Health and Human Services.
Author contributions. CPG, EJE, and DW designed the study. GVW abstracted data from articles. CPG, GVW, EJE, and DW analyzed the data. CPG, HMK, GVW, EJE, and DW contributed to writing the paper.
Abbreviations
Citation: Gross CP, Krumholz HM, Van Wye G, Emanuel EJ, Wendler D (2006) Does random treatment assignment cause harm to research participants? PLoS Med 3(6): e188. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030188
Funding: This work was funded with a contract from the Department of Clinical Bioethics, National Institutes of Health. CPG's efforts were supported by a Cancer Prevention, Control, and Population Sciences Career Development Award (1K07CA-90402) and the Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center at Yale (P30AG21342). The study sponsors played no role in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
- Appelbaum PS, Roth LH, Lidz CW, Benson P, Winslade W. False hopes and best data: Consent to research and the therapeutic misconception. Hastings Cent Rep. 1987; 17 :20–24. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor KM, Margolese RG, Soskolne CL. Physicians' reasons for not entering eligible patients in a randomized clinical trial of surgery for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1984; 310 :1363–1367. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feinstein AR. Current problems and future challenges in randomized clinical trials. Circulation. 1984; 70 :767–774. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Abel U, Koch A. The role of randomization in clinical studies: Myths and beliefs. J Clin Epidemiol. 1999; 52 :487–497. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kemeny MM, Peterson BL, Kornblith AB, Muss HB, Wheeler J, et al. Barriers to clinical trial participation by older women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21 :2268–2275. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jenkins V, Fallowfield L. Reasons for accepting or declining to participate in randomized clinical trials for cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 2000; 82 :1783–1788. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fallowfield L, Ratcliffe D, Souhami R. Clinicians' attitudes to clinical trials of cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer. 1997; 33 :2221–2229. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor K, Feldstein M, Skeel R, Pandya K, Carbone P. Fundamental dilemmas of the randomized clinical trial process: Results of a survey of 1737 Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group investigators. J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12 :1796–1805. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Daugherty C, Ratain MJ, Grochowski E, Stocking C, Kodish E, et al. Perceptions of cancer patients and their physicians involved in phase I trials. J Clin Oncol. 1995; 13 :1062–1072. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Joffe S, Weeks JC. Views of American oncologists about the purposes of clinical trials. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002; 94 :1847–1853. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yuval R, Halon DA, Merdler A, Khader N, Karkabi B, et al. Patient comprehension and reaction to participating in a double-blind randomized clinical trial (ISIS-4) in acute myocardial infarction. Arch Intern Med. 2000; 160 :1142–1146. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Karjalainen S, Palva I. Do treatment protocols improve end results? A study of survival of patients with multiple myeloma in Finland. BMJ. 1989; 299 :1069–1072. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davis S, Wright P, Schulman S, Hill L, Pikham R, et al. Participants in prospective randomized clinical trials for resected non-small lung cancer have improved survival compared with non-participants in such trials. Cancer. 1985; 56 :1710–1718. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marubini E, Mariani L, Salvadori B, Veronesi U, Saccozzi R, et al. Results of a breast-cancer-surgery trial compared with observational data from routine practice. Lancet. 1996; 347 :1000–1003. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Jenkintown (Pennsylvania): National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2006. Available: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/f_guidelines.asp . Accessed 4 April 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Peppercorn J, Weeks JC, Cook EF, Joffe S. Comparison of outcomes in cancer patients treated within and outside clinical trials: Conceptual framework and structured review. Lancet. 2004; 363 :263–270. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heiat A, Gross CP, Krumholz HM. Representation of the elderly, women, and minorities in heart failure clinical trials. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162 :1682–1688. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kodish E, Eder M, Noll RB, Ruccione K, Lange B, et al. Communication of Randomization in Childhood Leukemia Trials. JAMA. 2004; 291 :470–475. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tunis SR, Stryer DB, Clancy CM. Practical clinical trials: Increasing the value of clinical research for decision making in clinical and health policy. JAMA. 2003; 290 :1624–1632. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- ALLHAT Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic: The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) JAMA. 2002; 288 :2981–2997. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cannon CP, McCabe CH, Belder R, Breen J, Braunwald E. Design of the Pravastatin or Atorvastatin Evaluation and Infection Therapy (PROVE IT)-TIMI 22 trial. Am J Cardiol. 2002; 89 :860–861. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kolata G. Medicare covering new treatments, but with a catch. New York Times; Sect A: 1; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Olschewski M, Scheurlen H. Comprehensive cohort study: An alternative to randomised consent. Methods Inf Med. 1985; 24 :131–134. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feit F, Brooks M, Sopko G, Keller N, Rosen A, et al. Long-term clinical outcome in the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation Registry. Circulation. 2000; 101 :2795–2802. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bijker N, Peterse JL, Fentiman IS, Julien JP, Hart AA, et al. Effects of patient selection on the applicability of results from a randomised clinical trial (EORTC 10853) investigating breast-conserving therapy for DCIS. Br J Cancer. 2002; 87 :615–620. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- SAS Institute. SAS/STAT, version 8.1 [computer program] Cary (North Carolina): SAS Institute; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marcus S. Assessing non-consent bias with parallel randomized and nonrandomized clinical trials. J Clin Epidemiol. 1997; 50 :823–828. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paradise JL, Bluestone CD, Rogers KD, Taylor FH, Colborn DK, et al. Efficacy of adenoidectomy for recurrent otitis media in children previously treated with tympanostomy-tube placement. Results of parallel randomized and nonrandomized trials. JAMA. 1990; 263 :2066–2073. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Melchart D, Steger HG, Linde K, Makarian K, Hatahet Z, et al. Integrating patient preferences in clinical trials: A pilot study of acupuncture versus midazolam for gastroscopy. J Altern Complement Med. 2002; 8 :265–274. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blichert-Toft M, Brincker H, Andersen JA, Andersen KW, Axelsson CK, et al. A Danish randomized trial comparing breast-preserving therapy with mastectomy in mammary carcinoma. Preliminary results. Acta Oncol. 1988; 27 :671–677. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Antman K, Amato D, Wood W, Carson J, Suit H, et al. Selection bias in clinical trials. J Clin Oncol. 1985; 3 :1142–1147. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krzyzanowska MK, Pintilie M, Tannock IF. Factors associated with failure to publish large randomized trials presented at an oncology meeting. JAMA. 2003; 290 :495–501. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Weijer C. Selecting subjects for participation in clinical research: One sphere of justice. J Med Ethics. 1999; 25 :31–36. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- United States Public Law 103–43. NIH Revitalization Act of 1993, Subtitle B, Section. 1993 Jun 10;:131–133. [ Google Scholar ]
- National Cancer Institute. Age alone should not prevent older patients from enrolling in clinical trials. Bethesda (Maryland): National Cancer Institute; 2003. Available: http://www.cancer.gov/clinicaltrials/developments/age-as-barrier1005 . Accessed 20 April 2006 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Stallings FL, Ford ME, Simpson NK, Fouad M, Jernigan JC, et al. Black participation in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian (PLCO) Cancer Screening Trial. Control Clin Trials. 2000; 21 :379S–389S. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kolata G, Eichenwald. Group of insurers to pay for experimental cancer therapy. New York Times; Sect C: 1, 9; 1999. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- ECRI. Should I enter a clinical trial? A patient reference guide for adults with a serious or life-threatening illness. Plymouth Meeting (Pennsylvania): ECRI; 2002. Feb, Available: http://www.ecri.org/Patient_Information/Patient_Reference_Guide/prg.pdf . Accessed 4 April 2006 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Braunholtz DA, Edwards SJ, Lilford RJ. Are randomized clinical trials good for us (in the short term)? Evidence for a “trial effect” J Clin Epidemiol. 2001; 54 :217–224. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Joffe S, Cook EF, Cleary PD, Clark JW, Weeks JC. Quality of informed consent in cancer clinical trials: A cross-sectional survey. Lancet. 2001; 358 :1772–1777. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taub HA, Baker MT, Sturr JF. Informed consent for research. Effects of readability, patient age, and education. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1986; 34 :601–606. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dunn LB, Lindamer LA, Palmer BW, Golshan S, Schneiderman LJ, et al. Improving understanding of research consent in middle-aged and elderly patients with psychotic disorders. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2002; 10 :142–150. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lidz CW, Appelbaum PS, Grisso T, Renaud M. Therapeutic misconception and the appreciation of risks in clinical trials. Soc Sci Med. 2004; 58 :1689–1697. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sreenivasan G. Does informed consent to research require comprehension? Lancet. 2003; 362 :2016–2018. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McPherson K, Britton A. The impact of patient preferences on the interpretation of randomised controlled trials. Eur J Cancer. 1999; 35 :1598–1602. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King M, Nazareth I, Lampe F, Bower P, Chandler M, et al. Impact of participant and physician intervention preferences on randomized trials: A systematic review. JAMA. 2005; 293 :1089–1099. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wendler D, Kington R, Madans J, Wye GV, Christ-Schmidt H, et al. Are racial and ethnic minorities less willing to participate in health research? PLoS Med. 2006; 3 :e19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030019. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fleming I. Clinical trials for cancer patients: The community practicing physician's perspective. Cancer. 1990; 65 :2388–2390. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Foley J, Moertel C. Improving accrual into cancer clinical trials. J Cancer Educ. 1991; 6 :165–173. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hallstrom A, Friedman L, Denes P, Rizo-Patron C, Morris M. Do arrhythmia patients improve survival by participating in randomized clinical trials? Observations from the Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST) and the Antiarrhythmics Versus Implantable Defibrillators Trial (AVID) Control Clin Trials. 2003; 24 :341–352. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King SB, Barnhart HX, Kosinski AS, Weintraub WS, Lembo NJ, et al. Angioplasty or surgery for multivessel coronary artery disease: Comparison of eligible registry and randomized patients in the EAST trial and influence of treatment selection on outcomes. Am J Cardiol. 1997; 79 :1453–1459. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper KG, Grant AM, Garratt AM. The impact of using a partially randomised patient preference design when evaluating alternative managements for heavy menstrual bleeding. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997; 104 :1367–1373. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chilvers C, Dewey M, Fielding K, Gretton V, Miller P, et al. Antidepressant drugs and generic counselling for treatment of major depression in primary care: Randomised trial with patient preference arms. BMJ. 2001; 322 :772–775. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bain C, Cooper KG, Parkin DE. A partially randomized patient preference trial of microwave endometrial ablation using local anaesthesia and intravenous sedation or general anaesthesia: A pilot study. Gynaecol Endosc. 2001; 10 :223–228. [ Google Scholar ]
- CASS Principal Investigators and their associates. Coronary Artery Surgery Study (CASS): A randomized trial of coronary artery bypass surgery. Comparability of entry characteristics and survival in randomized patients and nonrandomized patients meeting randomization criteria. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984; 3 :114–128. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Paradise JL, Bluestone CD, Bachman RZ, Colborn DK, Bernard BS, et al. Efficacy of tonsillectomy for recurrent throat infection in severely affected children. Results of parallel randomized and nonrandomized clinical trials. N Engl J Med. 1984; 310 :674–683. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Link MP, Goorin AM, Miser AW, Green AA, Pratt CB, et al. The effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse-free survival in patients with osteosarcoma of the extremity. N Engl J Med. 1986; 314 :1600–1606. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Henshaw RC, Naji SA, Russell IT, Templeton AA. Comparison of medical abortion with surgical vacuum aspiration: Women's preferences and acceptability of treatment. BMJ. 1993; 307 :714–717. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nicolaides K, Brizot Mde L, Patel F, Snijders R. Comparison of chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis for fetal karyotyping at 10–13 weeks' gestation. Lancet. 1994; 344 :435–439. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McKay JR, Alterman AI, McLellan AT, Snider EC, O'Brien CP. Effect of random versus nonrandom assignment in a comparison of inpatient and day hospital rehabilitation for male alcoholics. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1995; 63 :70–78. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schmoor C, Olschewski M, Schumacher M. Randomized and non-randomized patients in clinical trials: Experiences with comprehensive cohort studies. Stat Med. 1996; 15 :263–271. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- de C Williams AC, Nicholas MK, Richardson PH, Pither CE, Fernandes J. Generalizing from a controlled trial: The effects of patient preference versus randomization on the outcome of inpatient versus outpatient chronic pain management. Pain. 1999; 83 :57–65. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Urban P, Stauffer JC, Bleed D, Khatchatrian N, Amann W, et al. A randomized evaluation of early revascularization to treat shock complicating acute myocardial infarction. The (Swiss) Multicenter Trial of Angioplasty for Shock—(S)MASH. Eur Heart J. 1999; 20 :1030–1038. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mosekilde L, Beck-Nielsen H, Sorensen OH, Nielsen SP, Charles P, et al. Hormonal replacement therapy reduces forearm fracture incidence in recent postmenopausal women—Results of the Danish Osteoporosis Prevention Study. Maturitas. 2000; 36 :181–193. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rovers MM, Straatman H, Ingels K, van der Wilt GJ, van den Broek P, et al. Generalizability of trial results based on randomized versus nonrandomized allocation of OME infants to ventilation tubes or watchful waiting. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001; 54 :789–794. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wieringa–de Waard M, Vos J, Bonsel GJ, Bindels PJ, Ankum WM. Management of miscarriage: A randomized controlled trial of expectant management versus surgical evacuation. Hum Reprod. 2002; 17 :2445–2450. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kerry S, Hilton S, Dundas D, Rink E, Oakeshott P. Radiography for low back pain: A randomised controlled trial and observational study in primary care. Bri J Gen Pract. 2002; 52 :469–474. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kim SG, Hallstrom A, Love JC, Rosenberg Y, Powell J, et al. Comparison of clinical characteristics and frequency of implantable defibrillator use between randomized patients in the Antiarrhythmics Vs Implantable Defibrillators (AVID) trial and nonrandomized registry patients. Am J Cardiol. 1997; 80 :454–457. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Random sampling (also called probability sampling or random selection) is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups. While random sampling is used in many types of studies, random assignment is only used ...
Random selection (also called probability sampling or random sampling) is a way of randomly selecting members of a population to be included in your study. On the other hand, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and treatment groups. Random selection ensures that everyone in the population has an equal ...
Random assignment or random placement is an experimental technique for assigning human participants or animal subjects to different groups in an experiment (e.g., a treatment group versus a control group) using randomization, such as by a chance procedure (e.g., flipping a coin) or a random number generator. This ensures that each participant or subject has an equal chance of being placed in ...
Random assignment refers to the use of chance procedures in psychology experiments to ensure that each participant has the same opportunity to be assigned to any given group in a study to eliminate any potential bias in the experiment at the outset. Participants are randomly assigned to different groups, such as the treatment group versus the ...
Random sampling is a process for obtaining a sample that accurately represents a population. Random assignment uses a chance process to assign subjects to experimental groups. Using random assignment requires that the experimenters can control the group assignment for all study subjects. For our study, we must be able to assign our participants ...
Elements of Research. Random assignment. Random assignment is a procedure used in experiments to create multiple study groups that include participants with similar characteristics so that the groups are equivalent at the beginning of the study. The procedure involves assigning individuals to an experimental treatment or program at random, or ...
Random assignation is associated with experimental research methods. In its strictest sense, random assignment should meet two criteria. One is that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to each condition (e.g., a 50% chance of being assigned to each of two conditions). The second is that each participant is assigned to a ...
Random selection is thus essential to external validity, or the extent to which the researcher can use the results of the study to generalize to the larger population. Random assignment is central to internal validity, which allows the researcher to make causal claims about the effect of the treatment. Nonrandom assignment often leads to non ...
Random assignment is a method for assigning participants in a sample to the different conditions, and it is an important element of all experimental research in psychology and other fields too. In its strictest sense, random assignment should meet two criteria. One is that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to each condition ...
Random assignment in psychology involves each participant having an equal chance of being chosen for any of the groups, including the control and experimental groups. It helps control for potential confounding variables, reducing the likelihood of pre-existing differences between groups. This method enhances the internal validity of experiments ...
Random sampling vs. random assignment (scope of inference) Hilary wants to determine if any relationship exists between Vitamin D and blood pressure. She is considering using one of a few different designs for her study. Determine what type of conclusions can be drawn from each study design.
What does random assignment mean? The key to randomized experimental research design is in the random assignment of study subjects - for example, individual voters, precincts, media markets or some other group - into treatment or control groups. Randomization has a very specific meaning in this context.
A randomized control trial (RCT) is a type of study design that involves randomly assigning participants to either an experimental group or a control group to measure the effectiveness of an intervention or treatment. Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) are considered the "gold standard" in medical and health research due to their rigorous ...
Random assignment is a research procedure used to randomly assign participants to different experimental conditions (or 'groups'). This introduces the element of chance, ensuring that each participant has an equal likelihood of being placed in any condition group for the study. It is absolutely essential that the treatment condition and the ...
What is random assignment? In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different groups using randomisation. With this method, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group.
Random Assignment is a process used in research where each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group within the study. This technique is essential in experiments as it helps to eliminate biases, ensuring that the different groups being compared are similar in all important aspects.
Random assignment should not be confused with random selection. Random assignment controls for selection bias , whereas random selection makes possible to generalize study results of a sample to the population. Keywords. Cluster randomization; Covariate; Cross-over design; Independent and dependent variables; Random assignment and random selection
Random assignment of participants helps to ensure that any differences between and within the groups are not systematic at the outset of the experiment. Thus, any differences between groups recorded at the end of the experiment can be more confidently attributed to the experimental procedures or treatment. … Random assignment does not ...
Random sampling (also called probability sampling or random selection) is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups. While random sampling is used in many types of studies, random assignment is only used ...
Simple random allocation is the easiest and most basic approach that provides unpredictability of treatment assignment. In simple random allocation, treatment assignment is made by chance without regard to prior allocation (that is, it bears no relation to past allocations and it is not discoverable ahead of time).
In the language of social science research, random assignment to conditions is when a random process (e.g., a random number generator, the flip of a coin, choosing from a shuffled deck of cards) is used to assign participants to experimental conditions, giving all participants an equal chance of being assigned to either condition. Fisher (1937; p.
Conclusions. These findings suggest that randomized treatment assignment as part of a clinical trial does not harm research participants. A search was conducted for RCTs where information was recorded on outcomes for participants and those who did not enter the trial, but still had access to the same treatments.
THE CONTEXT AND APPLICATION OF SCRIPTURE: Bro., Dr. James Michael Crusoe, Arlington Rd Church of Christ, Hopewell, VA