
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

How to write a speech that your audience remembers
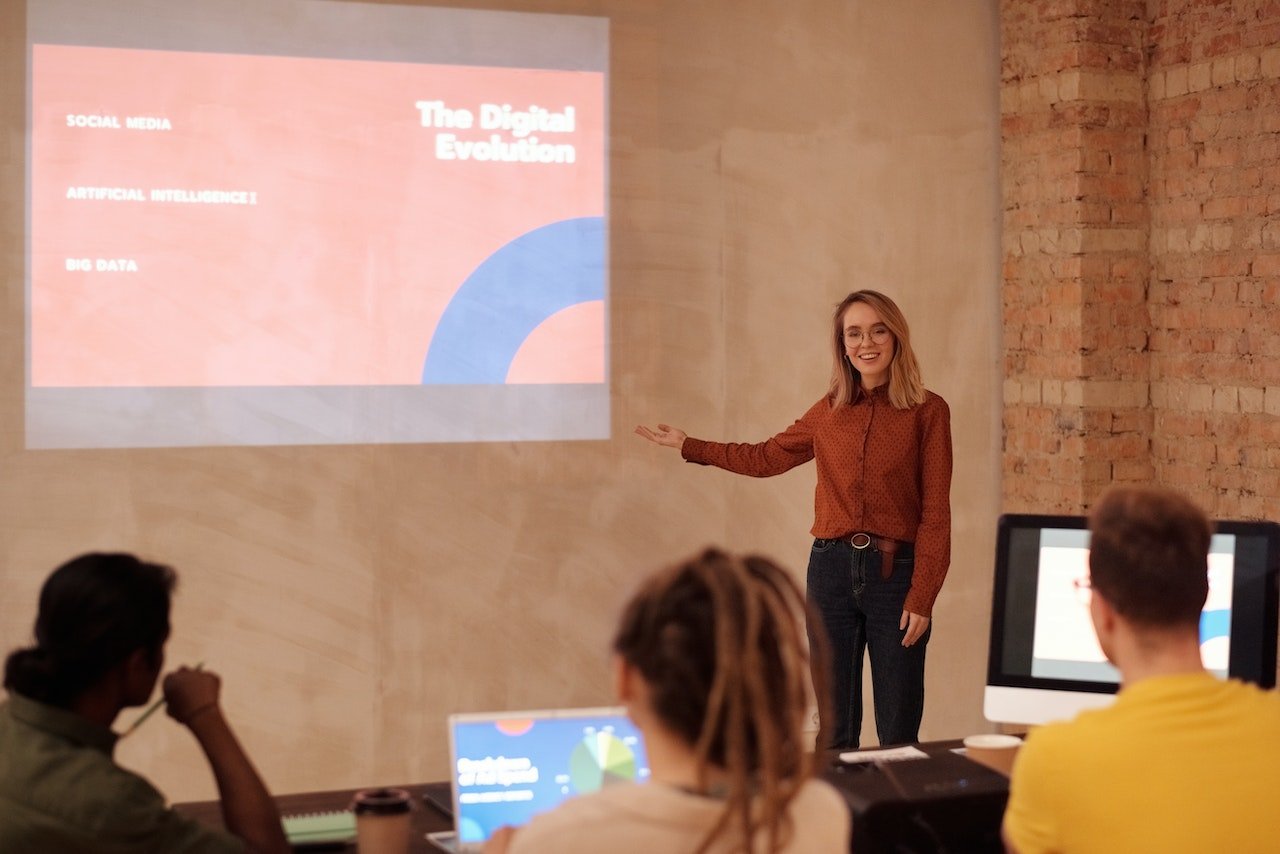

Whether in a work meeting or at an investor panel, you might give a speech at some point. And no matter how excited you are about the opportunity, the experience can be nerve-wracking .
But feeling butterflies doesn’t mean you can’t give a great speech. With the proper preparation and a clear outline, apprehensive public speakers and natural wordsmiths alike can write and present a compelling message. Here’s how to write a good speech you’ll be proud to deliver.
What is good speech writing?
Good speech writing is the art of crafting words and ideas into a compelling, coherent, and memorable message that resonates with the audience. Here are some key elements of great speech writing:
- It begins with clearly understanding the speech's purpose and the audience it seeks to engage.
- A well-written speech clearly conveys its central message, ensuring that the audience understands and retains the key points.
- It is structured thoughtfully, with a captivating opening, a well-organized body, and a conclusion that reinforces the main message.
- Good speech writing embraces the power of engaging content, weaving in stories, examples, and relatable anecdotes to connect with the audience on both intellectual and emotional levels.
Ultimately, it is the combination of these elements, along with the authenticity and delivery of the speaker , that transforms words on a page into a powerful and impactful spoken narrative.
What makes a good speech?
A great speech includes several key qualities, but three fundamental elements make a speech truly effective:
Clarity and purpose
Remembering the audience, cohesive structure.
While other important factors make a speech a home run, these three elements are essential for writing an effective speech.
The main elements of a good speech
The main elements of a speech typically include:
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your speech and grabs the audience's attention. It should include a hook or attention-grabbing opening, introduce the topic, and provide an overview of what will be covered.
- Opening/captivating statement: This is a strong statement that immediately engages the audience and creates curiosity about the speech topics.
- Thesis statement/central idea: The thesis statement or central idea is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of your speech. It serves as a roadmap for the audience to understand what your speech is about.
- Body: The body of the speech is where you elaborate on your main points or arguments. Each point is typically supported by evidence, examples, statistics, or anecdotes. The body should be organized logically and coherently, with smooth transitions between the main points.
- Supporting evidence: This includes facts, data, research findings, expert opinions, or personal stories that support and strengthen your main points. Well-chosen and credible evidence enhances the persuasive power of your speech.
- Transitions: Transitions are phrases or statements that connect different parts of your speech, guiding the audience from one idea to the next. Effective transitions signal the shifts in topics or ideas and help maintain a smooth flow throughout the speech.
- Counterarguments and rebuttals (if applicable): If your speech involves addressing opposing viewpoints or counterarguments, you should acknowledge and address them. Presenting counterarguments makes your speech more persuasive and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Conclusion: The conclusion is the final part of your speech and should bring your message to a satisfying close. Summarize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and leave the audience with a memorable closing thought or call to action.
- Closing statement: This is the final statement that leaves a lasting impression and reinforces the main message of your speech. It can be a call to action, a thought-provoking question, a powerful quote, or a memorable anecdote.
- Delivery and presentation: How you deliver your speech is also an essential element to consider. Pay attention to your tone, body language, eye contact , voice modulation, and timing. Practice and rehearse your speech, and try using the 7-38-55 rule to ensure confident and effective delivery.
While the order and emphasis of these elements may vary depending on the type of speech and audience, these elements provide a framework for organizing and delivering a successful speech.

How to structure a good speech
You know what message you want to transmit, who you’re delivering it to, and even how you want to say it. But you need to know how to start, develop, and close a speech before writing it.
Think of a speech like an essay. It should have an introduction, conclusion, and body sections in between. This places ideas in a logical order that the audience can better understand and follow them. Learning how to make a speech with an outline gives your storytelling the scaffolding it needs to get its point across.
Here’s a general speech structure to guide your writing process:
- Explanation 1
- Explanation 2
- Explanation 3
How to write a compelling speech opener
Some research shows that engaged audiences pay attention for only 15 to 20 minutes at a time. Other estimates are even lower, citing that people stop listening intently in fewer than 10 minutes . If you make a good first impression at the beginning of your speech, you have a better chance of interesting your audience through the middle when attention spans fade.
Implementing the INTRO model can help grab and keep your audience’s attention as soon as you start speaking. This acronym stands for interest, need, timing, roadmap, and objectives, and it represents the key points you should hit in an opening.
Here’s what to include for each of these points:
- Interest : Introduce yourself or your topic concisely and speak with confidence . Write a compelling opening statement using relevant data or an anecdote that the audience can relate to.
- Needs : The audience is listening to you because they have something to learn. If you’re pitching a new app idea to a panel of investors, those potential partners want to discover more about your product and what they can earn from it. Read the room and gently remind them of the purpose of your speech.
- Timing : When appropriate, let your audience know how long you’ll speak. This lets listeners set expectations and keep tabs on their own attention span. If a weary audience member knows you’ll talk for 40 minutes, they can better manage their energy as that time goes on.
- Routemap : Give a brief overview of the three main points you’ll cover in your speech. If an audience member’s attention starts to drop off and they miss a few sentences, they can more easily get their bearings if they know the general outline of the presentation.
- Objectives : Tell the audience what you hope to achieve, encouraging them to listen to the end for the payout.
Writing the middle of a speech
The body of your speech is the most information-dense section. Facts, visual aids, PowerPoints — all this information meets an audience with a waning attention span. Sticking to the speech structure gives your message focus and keeps you from going off track, making everything you say as useful as possible.
Limit the middle of your speech to three points, and support them with no more than three explanations. Following this model organizes your thoughts and prevents you from offering more information than the audience can retain.
Using this section of the speech to make your presentation interactive can add interest and engage your audience. Try including a video or demonstration to break the monotony. A quick poll or survey also keeps the audience on their toes.
Wrapping the speech up
To you, restating your points at the end can feel repetitive and dull. You’ve practiced countless times and heard it all before. But repetition aids memory and learning , helping your audience retain what you’ve told them. Use your speech’s conclusion to summarize the main points with a few short sentences.
Try to end on a memorable note, like posing a motivational quote or a thoughtful question the audience can contemplate once they leave. In proposal or pitch-style speeches, consider landing on a call to action (CTA) that invites your audience to take the next step.

How to write a good speech
If public speaking gives you the jitters, you’re not alone. Roughly 80% of the population feels nervous before giving a speech, and another 10% percent experiences intense anxiety and sometimes even panic.
The fear of failure can cause procrastination and can cause you to put off your speechwriting process until the last minute. Finding the right words takes time and preparation, and if you’re already feeling nervous, starting from a blank page might seem even harder.
But putting in the effort despite your stress is worth it. Presenting a speech you worked hard on fosters authenticity and connects you to the subject matter, which can help your audience understand your points better. Human connection is all about honesty and vulnerability, and if you want to connect to the people you’re speaking to, they should see that in you.
1. Identify your objectives and target audience
Before diving into the writing process, find healthy coping strategies to help you stop worrying . Then you can define your speech’s purpose, think about your target audience, and start identifying your objectives. Here are some questions to ask yourself and ground your thinking :
- What purpose do I want my speech to achieve?
- What would it mean to me if I achieved the speech’s purpose?
- What audience am I writing for?
- What do I know about my audience?
- What values do I want to transmit?
- If the audience remembers one take-home message, what should it be?
- What do I want my audience to feel, think, or do after I finish speaking?
- What parts of my message could be confusing and require further explanation?
2. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is crucial for tailoring your speech effectively. Consider the demographics of your audience, their interests, and their expectations. For instance, if you're addressing a group of healthcare professionals, you'll want to use medical terminology and data that resonate with them. Conversely, if your audience is a group of young students, you'd adjust your content to be more relatable to their experiences and interests.
3. Choose a clear message
Your message should be the central idea that you want your audience to take away from your speech. Let's say you're giving a speech on climate change. Your clear message might be something like, "Individual actions can make a significant impact on mitigating climate change." Throughout your speech, all your points and examples should support this central message, reinforcing it for your audience.
4. Structure your speech
Organizing your speech properly keeps your audience engaged and helps them follow your ideas. The introduction should grab your audience's attention and introduce the topic. For example, if you're discussing space exploration, you could start with a fascinating fact about a recent space mission. In the body, you'd present your main points logically, such as the history of space exploration, its scientific significance, and future prospects. Finally, in the conclusion, you'd summarize your key points and reiterate the importance of space exploration in advancing human knowledge.
5. Use engaging content for clarity
Engaging content includes stories, anecdotes, statistics, and examples that illustrate your main points. For instance, if you're giving a speech about the importance of reading, you might share a personal story about how a particular book changed your perspective. You could also include statistics on the benefits of reading, such as improved cognitive abilities and empathy.
6. Maintain clarity and simplicity
It's essential to communicate your ideas clearly. Avoid using overly technical jargon or complex language that might confuse your audience. For example, if you're discussing a medical breakthrough with a non-medical audience, explain complex terms in simple, understandable language.
7. Practice and rehearse
Practice is key to delivering a great speech. Rehearse multiple times to refine your delivery, timing, and tone. Consider using a mirror or recording yourself to observe your body language and gestures. For instance, if you're giving a motivational speech, practice your gestures and expressions to convey enthusiasm and confidence.
8. Consider nonverbal communication
Your body language, tone of voice, and gestures should align with your message . If you're delivering a speech on leadership, maintain strong eye contact to convey authority and connection with your audience. A steady pace and varied tone can also enhance your speech's impact.
9. Engage your audience
Engaging your audience keeps them interested and attentive. Encourage interaction by asking thought-provoking questions or sharing relatable anecdotes. If you're giving a speech on teamwork, ask the audience to recall a time when teamwork led to a successful outcome, fostering engagement and connection.
10. Prepare for Q&A
Anticipate potential questions or objections your audience might have and prepare concise, well-informed responses. If you're delivering a speech on a controversial topic, such as healthcare reform, be ready to address common concerns, like the impact on healthcare costs or access to services, during the Q&A session.
By following these steps and incorporating examples that align with your specific speech topic and purpose, you can craft and deliver a compelling and impactful speech that resonates with your audience.

Tools for writing a great speech
There are several helpful tools available for speechwriting, both technological and communication-related. Here are a few examples:
- Word processing software: Tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or other word processors provide a user-friendly environment for writing and editing speeches. They offer features like spell-checking, grammar correction, formatting options, and easy revision tracking.
- Presentation software: Software such as Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides is useful when creating visual aids to accompany your speech. These tools allow you to create engaging slideshows with text, images, charts, and videos to enhance your presentation.
- Speechwriting Templates: Online platforms or software offer pre-designed templates specifically for speechwriting. These templates provide guidance on structuring your speech and may include prompts for different sections like introductions, main points, and conclusions.
- Rhetorical devices and figures of speech: Rhetorical tools such as metaphors, similes, alliteration, and parallelism can add impact and persuasion to your speech. Resources like books, websites, or academic papers detailing various rhetorical devices can help you incorporate them effectively.
- Speechwriting apps: Mobile apps designed specifically for speechwriting can be helpful in organizing your thoughts, creating outlines, and composing a speech. These apps often provide features like voice recording, note-taking, and virtual prompts to keep you on track.
- Grammar and style checkers: Online tools or plugins like Grammarly or Hemingway Editor help improve the clarity and readability of your speech by checking for grammar, spelling, and style errors. They provide suggestions for sentence structure, word choice, and overall tone.
- Thesaurus and dictionary: Online or offline resources such as thesauruses and dictionaries help expand your vocabulary and find alternative words or phrases to express your ideas more effectively. They can also clarify meanings or provide context for unfamiliar terms.
- Online speechwriting communities: Joining online forums or communities focused on speechwriting can be beneficial for getting feedback, sharing ideas, and learning from experienced speechwriters. It's an opportunity to connect with like-minded individuals and improve your public speaking skills through collaboration.
Remember, while these tools can assist in the speechwriting process, it's essential to use them thoughtfully and adapt them to your specific needs and style. The most important aspect of speechwriting remains the creativity, authenticity, and connection with your audience that you bring to your speech.

5 tips for writing a speech
Behind every great speech is an excellent idea and a speaker who refined it. But a successful speech is about more than the initial words on the page, and there are a few more things you can do to help it land.
Here are five more tips for writing and practicing your speech:
1. Structure first, write second
If you start the writing process before organizing your thoughts, you may have to re-order, cut, and scrap the sentences you worked hard on. Save yourself some time by using a speech structure, like the one above, to order your talking points first. This can also help you identify unclear points or moments that disrupt your flow.
2. Do your homework
Data strengthens your argument with a scientific edge. Research your topic with an eye for attention-grabbing statistics, or look for findings you can use to support each point. If you’re pitching a product or service, pull information from company metrics that demonstrate past or potential successes.
Audience members will likely have questions, so learn all talking points inside and out. If you tell investors that your product will provide 12% returns, for example, come prepared with projections that support that statement.
3. Sound like yourself
Memorable speakers have distinct voices. Think of Martin Luther King Jr’s urgent, inspiring timbre or Oprah’s empathetic, personal tone . Establish your voice — one that aligns with your personality and values — and stick with it. If you’re a motivational speaker, keep your tone upbeat to inspire your audience . If you’re the CEO of a startup, try sounding assured but approachable.
4. Practice
As you practice a speech, you become more confident , gain a better handle on the material, and learn the outline so well that unexpected questions are less likely to trip you up. Practice in front of a colleague or friend for honest feedback about what you could change, and speak in front of the mirror to tweak your nonverbal communication and body language .
5. Remember to breathe
When you’re stressed, you breathe more rapidly . It can be challenging to talk normally when you can’t regulate your breath. Before your presentation, try some mindful breathing exercises so that when the day comes, you already have strategies that will calm you down and remain present . This can also help you control your voice and avoid speaking too quickly.
How to ghostwrite a great speech for someone else
Ghostwriting a speech requires a unique set of skills, as you're essentially writing a piece that will be delivered by someone else. Here are some tips on how to effectively ghostwrite a speech:
- Understand the speaker's voice and style : Begin by thoroughly understanding the speaker's personality, speaking style, and preferences. This includes their tone, humor, and any personal anecdotes they may want to include.
- Interview the speaker : Have a detailed conversation with the speaker to gather information about their speech's purpose, target audience, key messages, and any specific points they want to emphasize. Ask for personal stories or examples they may want to include.
- Research thoroughly : Research the topic to ensure you have a strong foundation of knowledge. This helps you craft a well-informed and credible speech.
- Create an outline : Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval.
- Write in the speaker's voice : While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style. Use language and phrasing that feel natural to them. If they have a particular way of expressing ideas, incorporate that into the speech.
- Craft a captivating opening : Begin the speech with a compelling opening that grabs the audience's attention. This could be a relevant quote, an interesting fact, a personal anecdote, or a thought-provoking question.
- Organize content logically : Ensure the speech flows logically, with each point building on the previous one. Use transitions to guide the audience from one idea to the next smoothly.
- Incorporate engaging stories and examples : Include anecdotes, stories, and real-life examples that illustrate key points and make the speech relatable and memorable.
- Edit and revise : Edit the speech carefully for clarity, grammar, and coherence. Ensure the speech is the right length and aligns with the speaker's time constraints.
- Seek feedback : Share drafts of the speech with the speaker for their feedback and revisions. They may have specific changes or additions they'd like to make.
- Practice delivery : If possible, work with the speaker on their delivery. Practice the speech together, allowing the speaker to become familiar with the content and your writing style.
- Maintain confidentiality : As a ghostwriter, it's essential to respect the confidentiality and anonymity of the work. Do not disclose that you wrote the speech unless you have the speaker's permission to do so.
- Be flexible : Be open to making changes and revisions as per the speaker's preferences. Your goal is to make them look good and effectively convey their message.
- Meet deadlines : Stick to agreed-upon deadlines for drafts and revisions. Punctuality and reliability are essential in ghostwriting.
- Provide support : Support the speaker during their preparation and rehearsal process. This can include helping with cue cards, speech notes, or any other materials they need.
Remember that successful ghostwriting is about capturing the essence of the speaker while delivering a well-structured and engaging speech. Collaboration, communication, and adaptability are key to achieving this.
Give your best speech yet
Learn how to make a speech that’ll hold an audience’s attention by structuring your thoughts and practicing frequently. Put the effort into writing and preparing your content, and aim to improve your breathing, eye contact , and body language as you practice. The more you work on your speech, the more confident you’ll become.
The energy you invest in writing an effective speech will help your audience remember and connect to every concept. Remember: some life-changing philosophies have come from good speeches, so give your words a chance to resonate with others. You might even change their thinking.
Elevate your communication skills
Unlock the power of clear and persuasive communication. Our coaches can guide you to build strong relationships and succeed in both personal and professional life.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
10 examples of principles that can guide your approach to work
Make the connection: 10 effective ways to connect with people, the 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills, 10+ interpersonal skills at work and ways to develop them, create a networking plan in 7 easy steps, how to write an impactful cover letter for a career change, what are analytical skills examples and how to level up, wondering how to change careers 12 steps to switch it up, self-management skills for a messy world, similar articles, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, how to disagree at work without being obnoxious, how to pitch ideas: 8 tips to captivate any audience, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, writing an elevator pitch about yourself: a how-to plus tips, 9 elevator pitch examples for making a strong first impression, 6 presentation skills and how to improve them, how to write a letter of recommendation (with examples), how to write a memo: 8 steps with examples, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

The 8 Key Elements of Highly Effective Speech
…and why your words barely matter.
Posted July 10, 2012 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan
I’d like you to take a moment to experience the following sentence, taken from a recent article exploring the nature of human consciousness: “Neuroplastic mechanisms relevant to the growing number of empirical studies of the capacity of directed attention and mental effort systematically alter brain function.”
Exciting? Hardly! In fact, most of the words you read barely register in your brain, and most of the words you speak barely register in the listener’s brain. In fact, research shows that words are the least important part of communication when you have face-to-face conversations with others. So before you utter another word to another person, memorize this list of the 8 key elements of highly effective speech:
- Gentle eye contact
- Kind facial expression
- Warm tone of voice
- Expressive hand and body gestures
- Relaxed disposition
- Slow speech rate
- The words themselves
Effective communication is based on trust, and if we don’t trust the speaker, we’re not going to listen to their words. Trust begins with eye contact because we need to see the person’s face to evaluate if they are being deceitful or not. In fact, when we are being watched, cooperation increases. [1] When we are not being watched, people tend to act more selfishly, with greater dishonesty. [2]
Gentle eye contact increases trustworthiness and encourages future cooperation, [3] and a happy gaze will increase emotional trust. [4] However, if we see the slightest bit of anger or fear on the speaker’s face, our trust will rapidly decrease. [5] But you can’t fake trustworthiness because the muscles around your mouth and eyes that reflect contentment and sincerity are involuntary. Solution: if you think about someone you love, or an event that brought you deep joy and satisfaction, a "Mona Lisa" smile will appear on your face and the muscles around your eyes will soften.
The tone of your voice is equally important when it comes to understanding what a person is really trying to say. If the facial expression expresses one emotion , but if the tone conveys a different one, neural dissonance takes place in the brain, causing the person confusion. [6] The result: trust erodes, suspicion increases, and cooperation decreases.
Researchers at the University of Amsterdam found that expressions of anger, contempt, disgust, fear, sadness, and surprise were better communicated through vocal tone than facial expression, whereas the face was more accurate for communicating expressions of joy, pride, and embarrassment . [7] And in business, a warm supportive voice is the sign of transformational leadership , generating more satisfaction, commitment, and cooperation between other members of the team. [8]
You can easily train your voice to convey more trust to others, and all you have to do is slow down and drop your pitch. This was tested at the University of Houston: when doctors reduced their speaking rate and pitch, especially when delivering bad news, the listener perceived them “as more caring and sympathetic.” [9] Harvard's Ted Kaptchuk also discovered that using a warm voice would double the healing power of a therapeutic treatment. [10]
If you want to express joy, your voice needs to become increasingly melodic, whereas sadness is spoken with a flat and monotonic voice. When we are angry, excited, or frightened, we raise the pitch and intensity of our voice, and there’s a lot of variability in both the speed and the tone. However, if the emotion is incongruent with the words you are using, it will create confusion for the listener. [11]
Gestures, and especially hand movements, are also important because they help orchestrate the language comprehension centers of your brain. [12] In fact, your brain needs to integrate both the sounds and body movements of the person who is speaking in order to accurately perceive what is meant. [13] From an evolutionary perspective, speech emerged from hand gestures and they both originate the same language area of the brain. [14] If our words and gestures are incongruent, it will create confusion in the listener’s brain. [15] Our suggestion: practice speaking in front of a mirror, consciously using your hands to “describe” the words you are speaking.

Your degree of relaxation is also reflected in your body language , facial expressions, and tone of voice, and any form of stress will convey a message of distrust . Why? Your stress tells the observer’s brain that there may be something wrong, and that stimulates defensive posturing in the listener. Research shows that even a one-minute relaxation exercise will increase activity in those parts of the brain that control language, communication, social awareness, mood-regulation, and decision-making . [16] Thus, a relaxed conversation allows for increased intimacy and empathy. Stress, however, causes us to talk too much because it hinders our ability to speak with clarity.
When you speak, slow down! Slow speech rates will increase the ability for the listener to comprehend what you are saying, and this is true for both young and older adults. [17] Slower speaking will also deepen that person’s respect for you, [18] Speaking slowly is not as natural as it may seem, and as children we automatically speak fast. But you can teach yourself, and your children to slow down by consciously cutting your speech rate in half. A slow voice has a calming effect on a person who is feeling anxious , whereas a loud fast voice will stimulate excitement, anger, or fear. [19]
Try this experiment: pair up with a partner and speak so slowly that … you … leave … 5 … seconds … of … silence … between … each … word. You’ll become aware of your negative inner speech that tells you that you should babble on endlessly and as fast as possible. It’s a trap, because the listener’s brain can only recall about 10 seconds of content! That’s why, when we train people in Compassionate Communication, we ask participants to speak only one sentence at a time, slowly, and then listen deeply as the other person speaks for ten seconds or less. This exercise will increase your overall consciousness about the importance of the first 7 elements of highly effective communication. Then, and only then, will you truly grasp the deeper meaning that is imparted by each word spoken by others.
But what about written communication, where you only have access to the words? When it comes to mutual comprehension, the written word pales in comparison to speech. To compensate, your brain imposes arbitrary meanings onto the words. You, the reader, give the words emotional impact that often differs from what the writer intended, which is why so many email correspondences get misinterpreted. And unless the writer fills in the blanks with specific emotional words and descriptive speech – storytelling – the reader will experience your writing as being flat, boring , dry, and probably more negative than you intended.
The solution: help the reader “paint a picture” in their mind with your words. Use concrete nouns and action verbs because they are easier for the reader’s brain to visualize. Words like “sunset” or “eat” are easy to see in the mind's eye, but words like “freedom” or “identify” force the brain to sort through too many conceptual frameworks. Instead, our lazy brain will skip over as many words as possible, especially the abstract ones. When this happens the deeper levels of meaning and feeling will be lost.
For more information on how to improve your speaking and listening skills, along with additional exercises to practice, see Words Can Change Your Brain: 12 Conversation Strategies for Building Trust, Reducing Conflict, and Increasing Intimacy (Newberg & Waldman, 2012, Hudson Street Press).
[1] Cues of being watched enhance cooperation in a real-world setting. Bateson M, Nettle D, Roberts G. Biol Lett. 2006 Sep 22;2(3):412-4.
[2] Effects of anonymity on antisocial behavior committed by individuals. Nogami T, Takai J. Psychol Rep. 2008 Feb;102(1):119-30.
[3] Eyes are on us, but nobody cares: are eye cues relevant for strong reciprocity? Fehr E, Schneider F. Proc Biol Sci. 2010 May 7;277(1686):1315-23.
[4] Evaluating faces on trustworthiness: an extension of systems for recognition of emotions signaling approach/avoidance behaviors. Todorov A. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008 Mar;1124:208-24.
[5] Common neural mechanisms for the evaluation of facial trustworthiness and emotional expressions as revealed by behavioral adaptation. Engell AD, Todorov A, Haxby JV. Perception. 2010;39(7):931-41.
[6] Use of affective prosody by young and older adults. Dupuis K, Pichora-Fuller MK. Psychol Aging. 2010 Mar;25(1):16-29.
[7] "Worth a thousand words": absolute and relative decoding of nonlinguistic affect vocalizations. Hawk ST, van Kleef GA, Fischer AH, van der Schalk J. Emotion. 2009 Jun;9(3):293-305.
[8] Leadership = Communication? The Relations of Leaders' Communication Styles with Leadership Styles, Knowledge Sharing and Leadership Outcomes. de Vries RE, Bakker-Pieper A, Oostenveld W. J Bus Psychol. 2010 Sep;25(3):367-380.
[9] Voice analysis during bad news discussion in oncology: reduced pitch, decreased speaking rate, and nonverbal communication of empathy. McHenry M, Parker PA, Baile WF, Lenzi R. Support Care Cancer. 2011 May 15.
[10] Components of placebo effect: randomised controlled trial in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Kaptchuk TJ, Kelley JM, Conboy LA, Davis RB, Kerr CE, Jacobson EE, Kirsch I, Schyner RN, Nam BH, Nguyen LT, Park M, Rivers AL, McManus C, Kokkotou E, Drossman DA, Goldman P, Lembo AJ. BMJ. 2008 May 3;336(7651):999-1003.
[11] Use of affective prosody by young and older adults. Dupuis K, Pichora-Fuller MK. Psychol Aging. 2010 Mar;25(1):16-29.
[12] Gestures orchestrate brain networks for language understanding. Skipper JI, Goldin-Meadow S, Nusbaum HC, Small SL. Curr Biol. 2009 Apr 28;19(8):661-7.
[13] When language meets action: the neural integration of gesture and speech. Willems RM, Ozyürek A, Hagoort P. Cereb Cortex. 2007 Oct;17(10):2322-33.
[14] When the hands speak. Gentilucci M, Dalla Volta R, Gianelli C. J Physiol Paris. 2008 Jan-May;102(1-3):21-30. Epub 2008 Mar 18.
[15] How symbolic gestures and words interact with each other. Barbieri F, Buonocore A,Volta RD, Gentilucci M. Brain Lang. 2009 Jul;110(1):1-11.
[16i] Short-term meditation training improves attention and self-regulation. Tang YY, Ma Y, Wang J, Fan Y, Feng S, Lu Q, Yu Q, Sui D, Rothbart MK, Fan M, Posner MI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 23;104(43):17152-6.
[17] Comprehension of speeded discourse by younger and older listeners. Gordon MS, Daneman M, Schneider BA. Exp Aging Res. 2009 Jul-Sep;35(3):277-96.
[18] Celerity and cajolery: rapid speech may promote or inhibit persuasion through its impact on message elaboration. Smith SM, Shaffer, DR. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 1991 Dec;17(6):663-669.
[19] Voices of fear and anxiety and sadness and depression: the effects of speech rate and loudness on fear and anxiety and sadness and depression. Siegman AW, Boyle S. J Abnorm Psychol. 1993 Aug;102(3):430-7. The angry voice: its effects on the experience of anger and cardiovascular reactivity. Siegman AW, Anderson RA, Berger T. Psychosom Med. 1990 Nov-Dec;52(6):631-43.

Andrew Newberg, M.D ., and Mark Robert Waldman are the authors of Words Can Change Your Brain .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
10 Tips for Improving Your Public Speaking Skills
Few are immune to the fear of public speaking. Marjorie North offers 10 tips for speakers to calm the nerves and deliverable memorable orations.
Marjorie North
Snakes? Fine. Flying? No problem. Public speaking? Yikes! Just thinking about public speaking — routinely described as one of the greatest (and most common) fears — can make your palms sweat. But there are many ways to tackle this anxiety and learn to deliver a memorable speech.
In part one of this series, Mastering the Basics of Communication , I shared strategies to improve how you communicate. In part two, How to Communicate More Effectively in the Workplace , I examined how to apply these techniques as you interact with colleagues and supervisors in the workplace. For the third and final part of this series, I’m providing you with public speaking tips that will help reduce your anxiety, dispel myths, and improve your performance.
Here Are My 10 Tips for Public Speaking:
1. nervousness is normal. practice and prepare.
All people feel some physiological reactions like pounding hearts and trembling hands. Do not associate these feelings with the sense that you will perform poorly or make a fool of yourself. Some nerves are good. The adrenaline rush that makes you sweat also makes you more alert and ready to give your best performance.
The best way to overcome anxiety is to prepare, prepare, and prepare some more. Take the time to go over your notes several times. Once you have become comfortable with the material, practice — a lot. Videotape yourself, or get a friend to critique your performance.
Communication Strategies: Presenting with Impact
Search all Communication programs.
2. Know Your Audience. Your Speech Is About Them, Not You.
Before you begin to craft your message, consider who the message is intended for. Learn as much about your listeners as you can. This will help you determine your choice of words, level of information, organization pattern, and motivational statement.
3. Organize Your Material in the Most Effective Manner to Attain Your Purpose.
Create the framework for your speech. Write down the topic, general purpose, specific purpose, central idea, and main points. Make sure to grab the audience’s attention in the first 30 seconds.
4. Watch for Feedback and Adapt to It.
Keep the focus on the audience. Gauge their reactions, adjust your message, and stay flexible. Delivering a canned speech will guarantee that you lose the attention of or confuse even the most devoted listeners.
5. Let Your Personality Come Through.
Be yourself, don’t become a talking head — in any type of communication. You will establish better credibility if your personality shines through, and your audience will trust what you have to say if they can see you as a real person.
6. Use Humor, Tell Stories, and Use Effective Language.
Inject a funny anecdote in your presentation, and you will certainly grab your audience’s attention. Audiences generally like a personal touch in a speech. A story can provide that.
7. Don’t Read Unless You Have to. Work from an Outline.
Reading from a script or slide fractures the interpersonal connection. By maintaining eye contact with the audience, you keep the focus on yourself and your message. A brief outline can serve to jog your memory and keep you on task.
8. Use Your Voice and Hands Effectively. Omit Nervous Gestures.
Nonverbal communication carries most of the message. Good delivery does not call attention to itself, but instead conveys the speaker’s ideas clearly and without distraction.
9. Grab Attention at the Beginning, and Close with a Dynamic End.
Do you enjoy hearing a speech start with “Today I’m going to talk to you about X”? Most people don’t. Instead, use a startling statistic, an interesting anecdote, or concise quotation. Conclude your speech with a summary and a strong statement that your audience is sure to remember.
10. Use Audiovisual Aids Wisely.
Too many can break the direct connection to the audience, so use them sparingly. They should enhance or clarify your content, or capture and maintain your audience’s attention.
Practice Does Not Make Perfect
Good communication is never perfect, and nobody expects you to be perfect. However, putting in the requisite time to prepare will help you deliver a better speech. You may not be able to shake your nerves entirely, but you can learn to minimize them.
Find related Communication programs.
Browse all Professional & Executive Development programs.
About the Author
North is a consultant for political candidates, physicians, and lawyers, and runs a private practice specializing in public speaking, and executive communication skills. Previously, she was the clinical director in the department of speech and language pathology and audiology at Northeastern University.
Why Gender Equity in the Workplace is Good for Business
Research indicates a correlation between gender equity and organizational success, yet it also points to obstacles for women in leadership.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

Rice Speechwriting
Examples of a good speech: learning from 10 famous speeches, 10 famous speeches with examples of a good speech.
Great speeches have the power to move people, to inspire and motivate, and to create lasting change. They have the ability to capture the attention of an audience and leave a lasting impact. In this blog post, we will be discussing the power of speeches and how they can influence personal growth. We will also be analyzing famous speeches from some of history’s most iconic figures, including Martin Luther King Jr., John F. Kennedy, Winston Churchill, Susan B. Anthony, Mahatma Gandhi, and Nelson Mandela. Through these analyses, we will gain insights into the art of public speaking such as ethos, logos, and pathos in speeches, storytelling techniques in speeches, pacing and pauses in effective speech delivery, etc. By understanding what makes these speeches so powerful, we can apply those lessons to our own lives and discover how to become better communicators ourselves.
The Power of Speeches
Speeches possess the ability to inspire, motivate, and persuade individuals, making them a potent tool for conveying viewpoints. Engaging speeches employ visual aids and storytelling to captivate the audience, emphasizing the significance of language and nonverbal cues in delivery. With the integration of NLP terms like ‘own speech’ and ‘student council,’ public speaking skills can be nurtured, contributing to personal and professional growth within the context of this blog.
Why are speeches influential?
Speeches have a powerful influence, shaping opinions and educating audiences. They connect through persuasion, vulnerability, sincerity, and imagery. A good speech addresses people’s interests, values, or concerns. Clear, concise points backed by evidence make speeches influential. They can evoke strong emotions and stimulate critical thinking.
Personal growth through speeches
Giving a speech can be a life-changing, confidence-boosting opportunity. The use of grammar, storytelling, and imagery in speeches can profoundly impact personal growth. Public speaking can cultivate various speech skills such as persuasion, entertainment, and impromptu delivery. When addressing an audience, consider employing short sentences, maintaining eye contact, or utilizing oratorical styles for different occasions. Overcoming speech anxiety or writer’s block can lead to personal growth and a successful speech.
Analysing Famous Speeches
Analysing renowned speeches offers valuable insights into the orator’s persuasive techniques and speech type. The context of a famous speech, whether a maid of honor speech, eulogy, or tribute, significantly impacts its effectiveness. Understanding the speech type, be it informative, persuasive, or demonstrative, is crucial for analysis. Effective speeches are distinguished by the use of imagery, vulnerability, sincerity, and persuasive speech examples. Critical thinking of the audience is influenced by grammar, storytelling, and nonverbal communication in speeches.
The context of famous speeches
The context of famous speeches significantly impacts their effectiveness and resonance with the audience. Whether it’s a birthday party, debate speech, or any special occasion, understanding the audience’s interests, values, and concerns is crucial. The type of speech, be it motivational or entertaining, also plays a pivotal role in shaping the main points and persuasion. Successful speeches take into account the specific context and adapt the content to resonate with the audience’s expectations and emotions.
The impact of famous speeches
Famous speeches, whether a farewell address or a special occasion presentation, leave a profound and enduring impact on the audience. The success of a speech is reflected in audience engagement, critical thinking, and persuasion. Influential speeches, such as a maid of honor’s address or an oratorical presentation, have the power to inspire and educate people. The use of imagery, storytelling, and vulnerability in a speech enhances its emotional and persuasive impact. Additionally, speech types, audience attention, and visual aids all contribute to the powerful impact of a speech.
Lessons from Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream”
Martin Luther King Jr.’s iconic speech exemplifies the persuasive use of imagery and sincerity, effectively conveying a powerful message of hope and equality. The emotional impact was amplified by the use of repetition and storytelling, captivating a wide audience with a motivational speech. Analyzing this renowned speech reveals powerful persuasion techniques, demonstrating the influential impact of oratorical speech types and visual aids in captivating an audience.
The power of imagery in speeches
Imagery in speeches creates immersive, sensory experiences that deeply resonate with the audience. Effective imagery, vulnerability, or storytelling evokes intense emotions and helps to visualize abstract concepts. A compelling speech, be it a student council address or one’s own blog, utilizes imagery and persuasion to engage and captivate the listeners. The usage of the right words, nonverbal communication, or oratorical speech type further enhances the impact of imagery in a speech, leaving a lasting impression on the audience.
The use of repetition for emphasis
Repetition serves as a potent tool, reinforcing key points, building momentum, and emphasizing critical ideas in a speech. Martin Luther King Jr.’s persuasive use of repetition, vulnerability, or sincerity magnified the impact of his speech. The right words, visual aids, or storytelling combined with repetition enhance a speech’s persuasive effect. Similarly, a maid of honor speech, best speech, or successful speech may benefit from skillful repetition for emphasis, strengthening its influence on the audience.
Insights from John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address
John F. Kennedy’s inaugural speech showcased persuasive delivery, captivating the audience through powerful imagery and sincerity. It serves as a valuable example for crafting impactful speeches. Analyzing his address provides insights into the influence of oratorical speech and nonverbal communication. Kennedy’s speech engagement is a testament to the art of persuasion and the use of inspirational language in public speaking, offering valuable lessons for student council members crafting their own speeches for a blog.
The art of persuasion in speeches
Influencing opinions through speeches is a powerful tool. Capturing the audience’s attention and swaying their point of view is essential for a good speech. The use of the right words, imagery, and nonverbal communication is critical in persuasive speeches. Vulnerability, sincerity, and storytelling play a significant role in persuasion. Oratorical speech, grammar, and powerful imagery add impact to persuasive speeches, enhancing their effectiveness in swaying opinions.
The role of inspirational language
In speeches, motivational and uplifting language has the power to inspire and encourage audiences. The use of concise sentences, impactful imagery, and visual aids contributes to the effectiveness of a speech. Examples of speeches from various special occasions, like birthdays or farewells, highlight how inspirational language can resonate with people. Understanding the different types of speeches, such as motivational or entertaining, is essential for crafting a speech with the right tone. Additionally, integrating persuasive speech examples and informative speech techniques adds depth and impact to one’s own speech.
Understanding Winston Churchill’s “We Shall Fight on the Beaches”
Analyzing Winston Churchill’s “We Shall Fight on the Beaches” demonstrates the adept usage of ethos, logos, and pathos. A formal address, it effectively captivated the audience. Supported by critical thinking, persuasion, and a compelling argument, Churchill’s speech serves as a formal example, inspiring public speaking skills. The speech exemplifies good speech techniques, making it a noteworthy example for students to study.
The importance of a strong delivery
A compelling speech relies on a potent, convincing, and inspiring presentation. Whether it’s a persuasive, formal, or impromptu speech, the ability to command a speech is key. From entertaining speeches to debate or maid of honor speeches, a strong delivery captures the audience. Be it an impromptu or a farewell speech, a powerful delivery leaves a lasting impression, emphasizing the significance of mastering the art of delivery in public speaking.
The use of emotion to connect with the audience
Connecting with the audience through sincerity, vulnerability, and imagery is crucial in a speech. The use of emotion is a powerful tool, evoking powerful storytelling and persuasive speech techniques. Emotional speeches, such as eulogies or tributes, require a genuine connection to resonate with the audience. When emotion is effectively utilized, a speech becomes memorable and impactful, creating a lasting impression on the audience.
Deconstructing Susan B. Anthony’s “On Women’s Right to Vote”
Analyzing Susan B. Anthony’s speech reveals the persuasive power of ethos, logos, and pathos, creating a compelling argument. Her speech serves as a valuable example, inspiring critical thinking and persuasive speech techniques. Great speeches like Anthony’s motivate public speaking and captivate audiences. The main points, supported by critical thinking and persuasion, make her speech a powerful tool for advocacy and change.
The role of ethos, logos, and pathos in speeches
Critical components of persuasive speeches are ethos, logos, and pathos, which contribute to a compelling argument. The usage of these elements is exemplified in various types of speeches, such as eulogies, farewell speeches, and motivational speeches. Ethical persuasion and the integration of ethos, logos, and pathos are powerful tools in crafting a speech that resonates with the audience, regardless of the speech’s purpose or context. Understanding the application of these elements is essential in delivering an impactful and persuasive speech.
The power of a compelling argument
Crafting a speech, like a debate speech, or an impromptu speech, involves anchoring a compelling argument supported by critical thinking and persuasion. Persuasive speech techniques serve as a powerful tool to captivate the audience’s attention and influence their point of view. Similar to a motivational speech or a farewell speech, a compelling argument resonates with the audience, making it a key element in delivering an impactful speech and connecting with the listeners.
Interpreting Mahatma Gandhi’s “Quit India”
Mahatma Gandhi’s “Quit India” speech exemplifies the cultural context, persuasion, and critical thinking in great speeches. It serves as a formal example, motivating public speaking, persuasive speech, or a successful speech. Gandhi’s speech demonstrates the power of critical thinking and persuasion, supporting the main points with a compelling argument. Understanding types of speeches, like informative or persuasive speech, involves applying critical thinking and persuasion, influencing the audience’s perspective.
The impact of cultural context on speeches
The tone, language, and persuasion techniques in speeches are heavily influenced by the cultural context and the type of speech. Whether it’s a formal speech, persuasive speech, or a great speech, cultural context plays a pivotal role in shaping the speech’s persuasive nature. It’s important to acknowledge the impact of cultural context when crafting different types of speeches, such as entertaining speeches or farewell speeches. Sample speeches, like formal speech examples or persuasive speech examples, vividly illustrate this influence.
The effectiveness of simple language
Incorporating plain language in speeches enhances audience understanding and fosters a stronger connection. Relatable simplicity effectively conveys complex ideas while maintaining audience engagement. By avoiding jargon and convoluted terminology, speakers can ensure that their message resonates with the audience. This approach not only promotes comprehension but also establishes a sense of inclusivity, making the speech accessible to diverse audiences.
Delving into Nelson Mandela’s “I am Prepared to Die”
Mandela’s “I am Prepared to Die” exemplifies potent storytelling, authentically impactful. His adept use of pacing and pauses held the audience in rapture, as personal experiences lent depth and sincerity. Captivating imagery painted a vivid picture, making the speech resonate profoundly. This speech is a prime example of how student council members can learn from their own speech and improve their oratory skills for public speaking competitions and blog writing.
The importance of authenticity in speeches
Authentic speeches deeply resonate with the audience, fostering trust and connection while creating a compelling emotional impact. Speakers, by embracing authenticity, can connect on a human level, establishing a strong rapport with the audience. Incorporating personal experiences into their own speech allows for genuine and influential communication, making their message more relatable and engaging for the student council. This authenticity adds depth and sincerity to the blog, enhancing its overall impact.
The power of personal experiences in public speaking
Incorporating personal experiences in public speaking adds a relatable dimension to speeches and evokes empathy from the audience. Sharing personal stories fosters a genuine, sincere connection and enhances the speaker’s vulnerability. Additionally, personal anecdotes create a memorable, impactful speech that resonates with the audience. By drawing from their own experiences, speakers can establish authenticity, fostering trust and connection with the audience.
Learning from Other Famous Speeches
Analyzing the composition and arrangement of a speech reveals its effectiveness. Observing the speaker’s intonation and presentation is crucial. Identifying rhetorical elements like repetition and metaphors enriches the understanding. Context and audience analysis provides valuable insights. Unveiling the central message and its alignment with the speaker’s objectives is imperative for learning from renowned speeches.
The art of storytelling in speeches
Crafting a compelling speech involves weaving vivid imagery and metaphors to captivate the audience. A powerful opening and closing set the tone and leave a lasting impact. Strategic repetition emphasizes key points, while personal connections foster engagement. Structuring the speech for maximum impact ensures coherence and resonance. Additionally, humor can lighten the mood and create a relaxed atmosphere, enhancing the overall delivery for an impactful student council, own speech, or blog.
The role of pacing and pauses in effective speeches
Effective speeches rely on the skillful use of pacing and pauses. These elements help to capture and maintain the audience’s attention, emphasizing key points and engaging listeners. By studying historical speeches, one can observe how impactful pacing and pauses contribute to the overall delivery. Practicing and mastering pacing and pausing is crucial for delivering an impactful speech that resonates with the audience.
How do these famous speeches influence modern public speaking?
The influence of these timeless speeches extends to modern public speaking practices, setting a high standard for persuasive communication. They serve as a powerful tool for studying speechwriting and delivery, inspiring speakers to draw inspiration from the techniques employed in these famous speeches.
In conclusion, famous speeches have a profound impact on individuals and society as a whole. They inspire change, ignite passion, and challenge societal norms. By analyzing and understanding these speeches, we can learn valuable lessons on the art of persuasion, the power of storytelling, and the importance of authenticity. From Martin Luther King Jr.’s powerful imagery to Susan B. Anthony’s compelling arguments, each speech offers unique insights into effective public speaking. By incorporating these lessons into our own communication, we can become more influential and effective in conveying our ideas and inspiring others. So, take the time to study and learn from these famous speeches, and let their wisdom guide you in your own journey as a speaker.
Unlocking the Secrets: Steps in Speech Writing Mastery
Expert tips for choosing good speech topics.

Popular Posts
How to write a retirement speech that wows: essential guide.
June 4, 2022
The Best Op Ed Format and Op Ed Examples: Hook, Teach, Ask (Part 2)
June 2, 2022
Inspiring Awards Ceremony Speech Examples
November 21, 2023
Mastering the Art of How to Give a Toast
Short award acceptance speech examples: inspiring examples, best giving an award speech examples.
November 22, 2023
Sentence Sense Newsletter
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
How to write a good speech in 7 steps
By: Susan Dugdale
- an easily followed format for writing a great speech
Did you know writing a speech doesn't have be an anxious, nail biting experience?
Unsure? Don't be.
You may have lived with the idea you were never good with words for a long time. Or perhaps giving speeches at school brought you out in cold sweats.
However learning how to write a speech is relatively straight forward when you learn to write out loud.
And that's the journey I am offering to take you on: step by step.
To learn quickly, go slow
Take all the time you need. This speech format has 7 steps, each building on the next.
Walk, rather than run, your way through all of them. Don't be tempted to rush. Familiarize yourself with the ideas. Try them out.
I know there are well-advertised short cuts and promises of 'write a speech in 5 minutes'. However in reality they only truly work for somebody who already has the basic foundations of speech writing in place.
The foundation of good speech writing
These steps are the backbone of sound speech preparation. Learn and follow them well at the outset and yes, given more experience and practice you could probably flick something together quickly. Like any skill, the more it's used, the easier it gets.
In the meantime...
Step 1: Begin with a speech overview or outline
Are you in a hurry? Without time to read a whole page? Grab ... The Quick How to Write a Speech Checklist And come back to get the details later.
- WHO you are writing your speech for (your target audience)
- WHY you are preparing this speech. What's the main purpose of your speech? Is it to inform or tell your audience about something? To teach them a new skill or demonstrate something? To persuade or to entertain? (See 4 types of speeches: informative, demonstrative, persuasive and special occasion or entertaining for more.) What do you want them to think, feel or do as a result of listening the speech?
- WHAT your speech is going to be about (its topic) - You'll want to have thought through your main points and have ranked them in order of importance. And have sorted the supporting research you need to make those points effectively.
- HOW much time you have for your speech eg. 3 minutes, 5 minutes... The amount of time you've been allocated dictates how much content you need. If you're unsure check this page: how many words per minute in a speech: a quick reference guide . You'll find estimates of the number of words required for 1 - 10 minute speeches by slow, medium and fast talkers.
Use an outline
The best way to make sure you deliver a perfect speech is to start by carefully completing a speech outline covering the essentials: WHO, WHY, WHAT and HOW.
Beginning to write without thinking your speech through is a bit like heading off on a journey not knowing why you're traveling or where you're going to end up. You can find yourself lost in a deep, dark, murky muddle of ideas very quickly!
Pulling together a speech overview or outline is a much safer option. It's the map you'll follow to get where you want to go.
Get a blank speech outline template to complete
Click the link to find out a whole lot more about preparing a speech outline . ☺ You'll also find a free printable blank speech outline template. I recommend using it!
Understanding speech construction
Before you begin to write, using your completed outline as a guide, let's briefly look at what you're aiming to prepare.
- an opening or introduction
- the body where the bulk of the information is given
- and an ending (or summary).
Imagine your speech as a sandwich

If you think of a speech as a sandwich you'll get the idea.
The opening and ending are the slices of bread holding the filling (the major points or the body of your speech) together.
You can build yourself a simple sandwich with one filling (one big idea) or you could go gourmet and add up to three or, even five. The choice is yours.
But whatever you choose to serve, as a good cook, you need to consider who is going to eat it! And that's your audience.
So let's find out who they are before we do anything else.
Step 2: Know who you are talking to
Understanding your audience.
Did you know a good speech is never written from the speaker's point of view? ( If you need to know more about why check out this page on building rapport .)
Begin with the most important idea/point on your outline.
Consider HOW you can explain (show, tell) that to your audience in the most effective way for them to easily understand it.
Writing from the audience's point of view

To help you write from an audience point of view, it's a good idea to identify either a real person or the type of person who is most likely to be listening to you.
Make sure you select someone who represents the "majority" of the people who will be in your audience. That is they are neither struggling to comprehend you at the bottom of your scale or light-years ahead at the top.
Now imagine they are sitting next to you eagerly waiting to hear what you're going to say. Give them a name, for example, Joe, to help make them real.
Ask yourself
- How do I need to tailor my information to meet Joe's needs? For example, do you tell personal stories to illustrate your main points? Absolutely! Yes. This is a very powerful technique. (Click storytelling in speeches to find out more.)
- What type or level of language is right for Joe as well as my topic? For example if I use jargon (activity, industry or profession specific vocabulary) will it be understood?
Step 3: Writing as you speak
Writing oral language.
Write down what you want to say about your first main point as if you were talking directly to Joe.
If it helps, say it all out loud before you write it down and/or record it.
Use the information below as a guide

(Click to download The Characteristics of Spoken Language as a pdf.)
You do not have to write absolutely everything you're going to say down * but you do need to write down, or outline, the sequence of ideas to ensure they are logical and easily followed.
Remember too, to explain or illustrate your point with examples from your research.
( * Tip: If this is your first speech the safety net of having everything written down could be just what you need. It's easier to recover from a patch of jitters when you have a word by word manuscript than if you have either none, or a bare outline. Your call!)
Step 4: Checking tone and language
The focus of this step is re-working what you've done in Step 2 and 3.
You identified who you were talking to (Step 2) and in Step 3, wrote up your first main point. Is it right? Have you made yourself clear? Check it.

How well you complete this step depends on how well you understand the needs of the people who are going to listen to your speech.
Please do not assume because you know what you're talking about the person (Joe) you've chosen to represent your audience will too. Joe is not a mind-reader!
How to check what you've prepared
- Check the "tone" of your language . Is it right for the occasion, subject matter and your audience?
- Check the length of your sentences. You need short sentences. If they're too long or complicated you risk losing your listeners.
Check for jargon too. These are industry, activity or group exclusive words.
For instance take the phrase: authentic learning . This comes from teaching and refers to connecting lessons to the daily life of students. Authentic learning is learning that is relevant and meaningful for students. If you're not a teacher you may not understand the phrase.
The use of any vocabulary requiring insider knowledge needs to be thought through from the audience perspective. Jargon can close people out.
- Read what you've written out loud. If it flows naturally, in a logical manner, continue the process with your next main idea. If it doesn't, rework.
We use whole sentences and part ones, and we mix them up with asides or appeals e.g. "Did you get that? Of course you did. Right...Let's move it along. I was saying ..."
Click for more about the differences between spoken and written language .
And now repeat the process
Repeat this process for the remainder of your main ideas.
Because you've done the first one carefully, the rest should follow fairly easily.
Step 5: Use transitions
Providing links or transitions between main ideas.
Between each of your main ideas you need to provide a bridge or pathway for your audience. The clearer the pathway or bridge, the easier it is for them to make the transition from one idea to the next.

If your speech contains more than three main ideas and each is building on the last, then consider using a "catch-up" or summary as part of your transitions.
Is your speech being evaluated? Find out exactly what aspects you're being assessed on using this standard speech evaluation form
Link/transition examples
A link can be as simple as:
"We've explored one scenario for the ending of Block Buster 111, but let's consider another. This time..."
What follows this transition is the introduction of Main Idea Two.
Here's a summarizing link/transition example:
"We've ended Blockbuster 111 four ways so far. In the first, everybody died. In the second, everybody died BUT their ghosts remained to haunt the area. In the third, one villain died. His partner reformed and after a fight-out with the hero, they both strode off into the sunset, friends forever. In the fourth, the hero dies in a major battle but is reborn sometime in the future.
And now what about one more? What if nobody died? The fifth possibility..."
Go back through your main ideas checking the links. Remember Joe as you go. Try each transition or link out loud and really listen to yourself. Is it obvious? Easily followed?
Keep them if they are clear and concise.
For more about transitions (with examples) see Andrew Dlugan's excellent article, Speech Transitions: Magical words and Phrases .
Step 6: The end of your speech
The ideal ending is highly memorable . You want it to live on in the minds of your listeners long after your speech is finished. Often it combines a call to action with a summary of major points.

Example speech endings
Example 1: The desired outcome of a speech persuading people to vote for you in an upcoming election is that they get out there on voting day and do so. You can help that outcome along by calling them to register their support by signing a prepared pledge statement as they leave.
"We're agreed we want change. You can help us give it to you by signing this pledge statement as you leave. Be part of the change you want to see!
Example 2: The desired outcome is increased sales figures. The call to action is made urgent with the introduction of time specific incentives.
"You have three weeks from the time you leave this hall to make that dream family holiday in New Zealand yours. Can you do it? Will you do it? The kids will love it. Your wife will love it. Do it now!"
How to figure out the right call to action
A clue for working out what the most appropriate call to action might be, is to go back to your original purpose for giving the speech.
- Was it to motivate or inspire?
- Was it to persuade to a particular point of view?
- Was it to share specialist information?
- Was it to celebrate a person, a place, time or event?
Ask yourself what you want people to do as a result of having listened to your speech.
For more about ending speeches
Visit this page for more about how to end a speech effectively . You'll find two additional types of speech endings with examples.
Write and test
Write your ending and test it out loud. Try it out on a friend, or two. Is it good? Does it work?
Step 7: The introduction
Once you've got the filling (main ideas) the linking and the ending in place, it's time to focus on the introduction.
The introduction comes last as it's the most important part of your speech. This is the bit that either has people sitting up alert or slumped and waiting for you to end. It's the tone setter!
What makes a great speech opening?
Ideally you want an opening that makes listening to you the only thing the 'Joes' in the audience want to do.
You want them to forget they're hungry or that their chair is hard or that their bills need paying.
The way to do that is to capture their interest straight away. You do this with a "hook".
Hooks to catch your audience's attention
Hooks come in as many forms as there are speeches and audiences. Your task is work out what specific hook is needed to catch your audience.

Go back to the purpose. Why are you giving this speech?
Once you have your answer, consider your call to action. What do you want the audience to do, and, or take away, as a result of listening to you?
Next think about the imaginary or real person you wrote for when you were focusing on your main ideas.
Choosing the best hook
- Is it humor?
- Would shock tactics work?
- Is it a rhetorical question?
- Is it formality or informality?
- Is it an outline or overview of what you're going to cover, including the call to action?
- Or is it a mix of all these elements?
A hook example
Here's an example from a fictional political speech. The speaker is lobbying for votes. His audience are predominately workers whose future's are not secure.
"How's your imagination this morning? Good? (Pause for response from audience) Great, I'm glad. Because we're going to put it to work starting right now.
I want you to see your future. What does it look like? Are you happy? Is everything as you want it to be? No? Let's change that. We could do it. And we could do it today.
At the end of this speech you're going to be given the opportunity to change your world, for a better one ...
No, I'm not a magician. Or a simpleton with big ideas and precious little commonsense. I'm an ordinary man, just like you. And I have a plan to share!"
And then our speaker is off into his main points supported by examples. The end, which he has already foreshadowed in his opening, is the call to vote for him.
Prepare several hooks
Experiment with several openings until you've found the one that serves your audience, your subject matter and your purpose best.
For many more examples of speech openings go to: how to write a speech introduction . You'll find 12 of the very best ways to start a speech.
That completes the initial seven steps towards writing your speech. If you've followed them all the way through, congratulations, you now have the text of your speech!
Although you might have the words, you're still a couple of steps away from being ready to deliver them. Both of them are essential if you want the very best outcome possible. They are below. Please take them.
Step 8: Checking content and timing
This step pulls everything together.
Check once, check twice, check three times & then once more!
Go through your speech really carefully.
On the first read through check you've got your main points in their correct order with supporting material, plus an effective introduction and ending.
On the second read through check the linking passages or transitions making sure they are clear and easily followed.
On the third reading check your sentence structure, language use and tone.
Double, triple check the timing
Now go though once more.
This time read it aloud slowly and time yourself.
If it's too long for the time allowance you've been given make the necessary cuts.
Start by looking at your examples rather than the main ideas themselves. If you've used several examples to illustrate one principal idea, cut the least important out.
Also look to see if you've repeated yourself unnecessarily or, gone off track. If it's not relevant, cut it.
Repeat the process, condensing until your speech fits the required length, preferably coming in just under your time limit.
You can also find out how approximately long it will take you to say the words you have by using this very handy words to minutes converter . It's an excellent tool, one I frequently use. While it can't give you a precise time, it does provide a reasonable estimate.

Step 9: Rehearsing your speech
And NOW you are finished with writing the speech, and are ready for REHEARSAL .

Please don't be tempted to skip this step. It is not an extra thrown in for good measure. It's essential.
The "not-so-secret" secret of successful speeches combines good writing with practice, practice and then, practicing some more.
Go to how to practice public speaking and you'll find rehearsal techniques and suggestions to boost your speech delivery from ordinary to extraordinary.
The Quick How to Write a Speech Checklist
Before you begin writing you need:.
- Your speech OUTLINE with your main ideas ranked in the order you're going to present them. (If you haven't done one complete this 4 step sample speech outline . It will make the writing process much easier.)
- Your RESEARCH
- You also need to know WHO you're speaking to, the PURPOSE of the speech and HOW long you're speaking for
The basic format
- the body where you present your main ideas
Split your time allowance so that you spend approximately 70% on the body and 15% each on the introduction and ending.
How to write the speech
- Write your main ideas out incorporating your examples and research
- Link them together making sure each flows in a smooth, logical progression
- Write your ending, summarizing your main ideas briefly and end with a call for action
- Write your introduction considering the 'hook' you're going to use to get your audience listening
- An often quoted saying to explain the process is: Tell them what you're going to tell them (Introduction) Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending)
TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing.

- Return to top
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 11 Tips for Giving a Great Speech
You might also enjoy…
- How to Survive Your First Academic Conference: 10 Vital Tips
- 6 Ways to Overcome Writer’s Block
Chances are you’ll be asked to give speeches or presentations in classes at school. If you get involved in volunteer groups, brief speeches to open events or thank participants are a must. Then there are the speeches at events such as weddings, as well as speeches that you might have to give in the workplace. That amounts to the average person being required to give quite a lot of speeches, even if they don’t get involved in an area such as politics where the ability to give a good speech becomes even more important. You might also have suffered through quite a number of bad speeches from other people – whether that’s at family events where the microphone squeaks the whole way through or a school presentation where the headteacher can’t quite make the jokes work. If you don’t want to inflict the same sort of experience on others, here are our top tips for giving a great speech.
1. Practise your microphone technique

2. Keep it short

Particularly at something like a party or a wedding, no one will be unhappy if your speech runs a little short; it’ll just give them more time to investigate the canapés. If you are giving a speech for a class in school, and it’ll be assessed, you need to prioritise keeping it within the required time limits. But even under these circumstances, if you’ve been tasked – say – with giving a 10-15 minute speech, it’s usually better to come in nearer the 10 than the 15 minute mark. Put simply, even if your speech is terrible, your audience can probably tolerate it for 10 minutes. Much longer, and they’ll be struggling. This shouldn’t limit what you can cover; in the film Up , the whole of Carl and Ellie’s heartbreaking love story is told in under 12 minutes. Do you really need longer to make your points? Achieve brevity by writing out the speech you would give if you had all the time in the world, and then cut anything that seems extraneous or boring.
3. Consider what your audience wants to hear
If you are giving a speech in class because it’s your assignment, what your audience wants to hear is likely to be “the bell ringing for lunch”; you can’t help them there. But under other circumstances, consider what your audience wants to hear and what you want to say, and strive for there to be as much overlap as possible. In the context of a political speech, for instance, what you want to say might be why your party should receive votes; what your audience wants to hear is what your party would do for them, if they won power. Hopefully it should be possible to write a speech that meets both sets of needs, rather than focusing solely on whatever it is that you want to say and leaving your audience disappointed.
4. Pick a theme and stick to it

Here’s a goal for giving a speech: someone sitting near the back, who’s messing around on their phone for at least two-thirds of it and focusing mainly on how long it will be until lunch, should nonetheless be able to give a reasonably accurate answer to the question, “what was it about?” If you’re supposed to be giving a speech in defence of the nuclear deterrent, for example, both the topic and your position on it should be clearly identifiable. This means – to stick with the nuclear deterrent example – not talking for a while about jobs, and then the wider economy, and then the North-South divide, and then Scottish independence, and then Ukraine with a brief digression into South Ossetia before rounding off by squeaking out “and that’s why we should renew Trident!” seconds before you run out of time – no matter how relevant that cornucopia of topics may feel (and they are all relevant, albeit tenuously). It means that even if you do have to take a while to explain a more complex idea, you need to be concise, and bring it back to your theme as quickly as you can.
5. Speak slowly
Most people speak more quickly than they realise when they’re on stage, especially if they’re nervous. But no one will be able to follow your speech if you’re jabbering it out. Thankfully, this one is easy to fix with a little effort and practise. First of all, figure out how quickly you’re actually speaking: do a word count for your speech and then time yourself saying it. A fast speaker will speak at maybe 160 words per minute, a slow speaker at 100 wpm and an average speaker at 130 wpm. For a formal speech, you want to be speaking on the slow side. While this will vary by culture and environment, 120 wpm is a reasonable target to aim for; slow enough that everyone should be able to understand you, and fast enough that you hopefully won’t be sending them to sleep.
6. Tell a couple of jokes

This is a tricky tip because there are lots of pitfalls in the world of telling jokes. For instance, there’s the temptation to include an in-joke that three of your friends will understand and find hilarious, that is utterly baffling to everyone else in the room. Avoid this – if you include any jokes, witty references or anything along those lines, make sure they are accessible to everyone present. All the same, if you can manage a joke or two, it can be a useful way to break up a speech and retain the audience’s interest. A little self-deprecation (not too much!) or the use of classic joke formats such as “the scene was chaotic; it looked as if a bomb had hit and we didn’t know where to start on repairs – but that’s enough about the hen party…” work nicely even if you’re not very confident. Don’t turn it into a stand-up comedy sketch if you’re not a comedian, don’t wait for ages for laughter that’s not showing up, and don’t make jokes at the expense of anyone who you don’t know for sure can take it.
7. Don’t be afraid to repeat yourself if you need to
If you follow US or UK politics at all, you’ve probably heard some of these phrases recently: take back control, make America great again, long-term economic plan, son of a bus driver. Three of these have already led the party or people they’re associated with to electoral victory; the fourth remains to be seen. To take the ‘son of a bus driver’ as an example, this refers to Sadiq Khan, now Mayor of London. There can be hardly anyone in London who doesn’t know what their Mayor’s dad did for a living. Meanwhile, many of them probably can’t remember his rival Zac Goldsmith’s name, let alone anything he said during the campaign. The point is that repetition works. In pursuit of point 4, if you want people to remember your key theme, you’re going to have to say it more than once. Don’t assume that everyone will have paid attention to everything you’ve said, unless you’re in a classroom setting where they’ll get told off if they don’t.
8. Only use the visual aids you need

This tip applies to two things: PowerPoints and notes. If you can do without either (and your assignment allows it), then do. Every time you’re glancing over your notes or up at the screen, fiddling with the laptop to get the slide to move on, fighting with a video that isn’t working or struggling to read your own handwriting, is time that you’re not spending engaging with your audience. A well-written, clear speech delivered without notes is always going to be better than someone awkwardly reading aloud the bullet points on their PowerPoint slides. If you must do a presentation – for instance, because there are photos that need to be included – have as little text on it as possible, preferably none. That way, if there are people at the back who can’t really see the screen through the sea of heads in front of them, they’ll still be able to follow what you’re saying.
9. Get a friend to check for awkward mannerisms
Mannerisms that are entirely fine in normal life become awkward and strange when you’re speaking in public. Perhaps you’re inclined to fiddle with your hair or your cuffs, you rock back and forth on the balls of your feet, or you have a habit of reaching your hand to your cheek when you’re talking. No one would notice in everyday conversation, but when you’re on a stage, it’ll become all they’ll see. Some of this is easily avoidable – for instance, if you have long hair that you’re inclined to twirl or otherwise fiddle with, tie it up. For other mannerisms, get the critical friend who helped you sort out your microphone technique to tell you what they are, and do your best to suppress the more annoying ones.
10. Look around the room

Talking about eye contact usually has the effect of making normal eye contact a lot harder, and so does giving a speech. All of a sudden, you’re up on stage, and you have no idea what a normal way to look at a group of people is. Some speakers deal with this by picking a point in the middle distance and speaking to it; others by picking a particular person near to the back and addressing their entire speech at them. This is obviously no fun for that person, who probably spends the whole thing feeling extremely uncomfortable, but it’s not too weird for everyone else. Better still, though, if you can manage it, is to look slowly and steadily around the room, trying to make eye contact with a decent range of people, before returning to the middle distance for a while, rinse and repeat. This needs to be slow and steady, or you give the impression that you’ve just smelled smoke and are casting about for a fire exit before the stampede beings.
11. Don’t be scared of a good reaction
If your speech is genuinely engaging, funny, inspiring or any of the other things you might hope it would be, your audience will react to it. There might be laughter, or applause, or even a bit of cheering depending on the setting. This can be daunting because when you’re practising your speech in front of your bedroom mirror, there’s no way to prepare for it. And it’s where even the best speakers can go wrong, by launching straight into what they were going to say next without waiting for the laughter or applause to stop, or by looking painfully awkward while it’s going on. It’s a pitfall that’s mostly solved by being aware it might happen. If your audience is applauding you or otherwise reacting well, it’s OK to smile, look up, wait for them to stop and then keep going with your speech – it’s as simple as that. You could even throw in a “thank you” before you continue in the knowledge that it’s all going well. Image credits: microphones ; audience ; boy with microphone ; clock ; winding road ; enjoy a joke ; sticky notes ;
- Personal Development
- Sales Training
- Business Training
- Time Management
- Leadership Training
- Book Writing
- Public Speaking
- Live Speaker Training With Brian
- See Brian Speak
- Coaching Programs
- Become a Coach
- Personal Success
- Sales Success
- Business Success
- Leadership Success
15 Ways to Start a Speech + Bonus Tips
You have heard the saying “First impressions are lasting; you never get a second chance to create a good first impression.”
The same is true when talking about how to start a speech…
The truth is, when you start your speech, you must focus everything on making a positive first impression on your audience members (especially if you are doing the presentation virtually ). The introduction is basically the formal greetings for speeches, so let’s be sure to get this right to really hook the audience.
Here are 15 different ways to start a speech as well as 2 extra BONUS tips at the end.
1) Thank the Organizers and Audience
You can start by thanking the audience for coming and thanking the organization for inviting you to speak.
Refer to the person who introduced you or to one or more of the senior people in the organization in the audience.
This compliments them, makes them feel proud and happy about your presence, and connects you to the audience like an electrical plug in a socket.
2) Start With a Positive Statement
A presentation tip at the start is to tell the audience members how much they will like and enjoy what you have to say.
For example, you might say:
“You’re really going to enjoy the time we spend together this evening. I’m going to share with you some of the most important ideas that have ever been discovered in this area.”
Remember that speaking is an art, so be an artist and take complete control of your performance,
3) Compliment the Audience
You can begin by complimenting the audience members sincerely and with great respect.
Smile as if you are really glad to see them as if they are all old friends of yours that you have not seen for quite a while.
You can tell them that it is a great honor for you to be here, that they are some of the most important people in this business or industry, and that you are looking forward to sharing some key ideas with them.
You could say something like:
“It is an honor to be here with you today. You are the elite, the top 10 percent of people in this industry. Only the very best people in any field will take the time and make the sacrifice to come so far for a conference like this.”
4) Start Your Speech By Referring to Current Events
Use a current event front-page news story to transition into your subject and to illustrate or prove your point. You can bring a copy of the newspaper and hold it up as you refer to it in your introduction.
This visual image of you holding the paper and reciting or reading a key point rivets the audience’s attention and causes people to lean forward to hear what you have to say.
5) Refer to a Historical Event
For many years, I studied military history…
Especially the lives and campaigns of the great generals and the decisive battles they won. One of my favorites was Alexander the Great.
One day, I was asked to give a talk on leadership principles to a roomful of managers for a Fortune 500 company.
I decided that the campaign of Alexander the Great against Darius of Persia would make an excellent story that would illustrate the leadership qualities of one of the great commanders in history.
I opened my talk with these words:
“Once upon a time there was a young man named Alex who grew up in a poor country. But Alex was a little bit ambitious. From an early age, he decided that he wanted to conquer the entire known world. But there was a small problem. Most of the known world was under the control of a huge multinational called the Persian Empire, headed by King Darius II. To fulfill his ambition, Alex was going to have to take the market share away from the market leader, who was very determined to hold on to it.
This is the same situation that exists between you and your major competitors in the market today. You are going to have to use all your leadership skills to win the great marketing battles of the future.”
6) Refer to a Well Known Person
You can start by quoting a well-known person or publication that recently made an important statement.
One of the subjects I touch upon regularly is the importance of continual personal development.
I will say something like:
“In the twenty-first century, knowledge and know-how are the keys to success. As basketball coach Pat Riley said, ‘If you are not getting better, you are getting worse.’”
7) Refer to a Recent Conversation
Start by telling a story about a recent conversation with someone in attendance.
For instance, I might say:
“A few minutes ago, I was talking with Tom Robinson in the lobby. He told me that this is one of the very best times to be working in this industry, and I agree.”
8) Make a Shocking Statement
You can start your talk by making a shocking statement of some kind.
For example, you might say something like:
“According to a recent study, there will be more change, more competition, and more opportunities in this industry in the next year than ever before. And 72 percent of the people in this room will be doing something different within two years if they do not rapidly adapt top these changes.”
Click here If you want to learn more techniques to wow your audience.
9) Quote From Recent Research
You can start by quoting a recent research report.
One example is:
“According to a story in a recent issue of Businessweek, there were almost 11 million millionaires in America in 2018, most of them self-made.”
10) Start Your Speech By Giving Them Hope
The French philosopher Gustav Le Bon once wrote, “The only religion of mankind is, and always has been hope.”
When you speak effectively, you give people hope of some kind.
Remember, the ultimate purpose of speaking is to inspire people to do things that they would not have done in the absence of your comments.
Everything you say should relate to the actions you want people to take and the reasons that they should take those actions.
11) Be Entertaining
Bill Gove used to walk onto the stage after his introduction if he had just finished talking to someone on the side and was breaking off to give his talk to the group.
The audience got the feeling that his entire talk was one continuous conversation, devoid of meaningless filler words .
Bill would often go to the edge of the stage and then drop his voice in a conspiratorial way, open his arms, and beckon the audience members to come a little closer.
He would say, “Come here, let me tell you something,” and then he would wave them forward as though he was about to tell a secret to the entire room.
The amazing thing was that everyone in the room would lean forward to hear this “secret” that he was about to share. People would all suddenly realize what they were doing and break out in laughter. It was a wonderful device to get the audience into the palm of his hands.
12) Ask a Question
You can open by making a positive statement and then ask a question requiring a show of hands.
Try something like this:
“This is a great time to be alive and in business in America. By the way how many people here are self-employed?”
Raise your hand to indicate what you want people to do. I have used this line, and after a number of hands go up, I then say to someone who raised their hand in the front, “How many people here are really self-employed?”
Invariably, someone will say, “We all are!”
I then compliment and affirm the answer: “You’re right! We are all self-employed, from the time we take our first jobs to the day that we retire; we all work for ourselves, no matter who signs our paychecks.”
13) Open With a Problem
You can start with a problem that must be solved. If it is a problem that almost everyone has in common, you will immediately have the audience’s complete and undivided attention.
For example, you could say:
“Fully 63 percent of baby boomers are moving toward retirement without enough money put aside to provide for themselves for as long as they are going to live. We must address this problem and take action immediately to ensure that each person who retires will be able to live comfortably for the rest of his or her natural life.”
14) Make a Strong Statement, Then Ask a Question
You can start by making a strong statement and then ask a question. You then follow with an answer and ask another question. This gets people immediately involved and listening to your every word.
Here’s an example:
“Twenty percent of the people in our society make 80 percent of the money. Are you a member of the top 20 percent? If not, would you like to join the top 20 percent or even the top 10 percent? Well, in the next few minutes, I am going to give you some ideas to help you become some of the highest-paid people in our society. Would that be a good goal for our time together today?”
15) Tell a Story
You can start your talk with a story. Some of the most powerful words grab the complete attention of the audience are, “Once upon a time…”
From infancy and early childhood, people love stories of any kind. When you start off with the words, “Once upon a time…” you tell the audience that a story is coming. People immediately settle down, become quiet, and lean forward like kids around a campfire.
When I conduct full-day seminars and I want to bring people back to their seats after a break, I will say loudly, “Once upon a time there was a man, right here in this city…”
As soon as I say these words, people hurry back to their seats and begin to listen attentively to the rest of the story.
The story technique is very effective.
In fact, its probably one of the best public speaking tips I’ve learned to this day.
Bonus Tip: Tell Them About Yourself
Very often, I will start a speech to a business, sales, or entrepreneurial group by saying:
“I started off without graduating from high school. My family had no money. Everything I accomplished in life I had to do on my own with very little help from anyone else.”
It is amazing how many people come up to me after a talk that began with those words and tells me that was their experience as well.
They tell me that they could immediately identify with me because they too had started with poor grades and limited funds, as most people do. As a result, they were open to the rest of my talk, even a full-day seminar, and felt that everything I said was more valid and authentic than if I had been a person who started off with a successful background.
Building a bridge like this is very helpful in bringing the audience onto your side.
Bonus Tip: Get Them Talking to One Another
You can ask people to turn to the person next to them to discuss a particular point.
For instance, you could say:
“Tell the person next to you what you would like to learn from this seminar.”
Whatever you ask your audience members to do, within reason, they will do it for you. Your commands and your thought leadership will easily influence them, as long as you ask them with confidence.
By following any one of these tips for starting your speech, you are sure to grab your audience’s attention every time. How do you start a speech? Let me know in the comments.
« Previous Post 9 Tips to End a Speech With a Bang Next Post » 15 Ways to Overcome Your Fears of Writing a Book
About Brian Tracy — Brian is recognized as the top sales training and personal success authority in the world today. He has authored more than 60 books and has produced more than 500 audio and video learning programs on sales, management, business success and personal development, including worldwide bestseller The Psychology of Achievement. Brian's goal is to help you achieve your personal and business goals faster and easier than you ever imagined. You can follow him on Twitter , Facebook , Pinterest , Linkedin and Youtube .
- Most Recent
- The Art of Business Success: A Blueprint for Entrepreneurs
- How to Develop a Habit That Will Last
- How to Write an Author Bio (Examples Included)
- Personal Development Plan Templates for Success
- How to Sell and Become a Master Salesperson
- Free Webinar: How To Write a Book and Become a Published Author
- Free Video Series: 3-Part Sales Mastery Training Series
- Free Assessment: The Confidence Factor
- Free Assessment: Discovering Your Talents
Browse Categories
- Financial Success
Follow Brian & Join the Discussion
- Free Resources
- Best Sellers
- Knowledge Base
- Shipping & Returns
- Privacy Policy
- About Brian
- Brian Recommends
Your Privacy is Guaranteed. We will never give, lease or sell your personal information. Period!
© Copyright 2001-2024 Brian Tracy International. All Rights Reserved.
Use Power Words in Your Speech to Persuade Your Audience

Average: 5 ( 1 vote)

"Words are the most powerful force available to humanity. They have energy and power with the ability to help, to heal, to hinder, to hurt, to harm, to humiliate, and to humble."
Why do you think this quote from Yehuda Berg, an international speaker and author, is so famous and used in so many articles about compelling writing and public speaking?
Firstly, because it’s true.
And secondly, because it sounds persuasive and argumentative , thanks to the power words the speaker uses. (Did you notice that every verb of the second sentence starts with "h"?)
Power words are words that evoke emotions and responses. Implementing them in your speech wherever appropriate can boost the audience's interest, transforming even lifeless arguments into persuasive messages that compel listeners to take action.
In this post, we'll reveal the nature of power words, their types, and ways to include them in your speech to motivate and persuade your audience.
What are power words?
As the author of Well Said! , a book about public speaking , Darlene Price rightly notes, "Whether it's inspiring a nation, launching a product, building a team, or mending a relationship, the right words spoken at the right time can change history."
Indeed, let's take the iconic speeches of Winston Churchill and Martin Luther King as examples. Both are full of carefully chosen power words drawing people from one emotion to another, inspiring them to act.
Churchill's speech abstract, with power words in red:

King's speech abstract, with power words in red:

Given the above, a good definition of power words is:
Power words are persuasive and descriptive lexical items that trigger a positive or negative emotional response. Spicing content with these words, an author influences the audience's reactions and compels them to take action.
How to know if a word is powerful?
It will fit into at least one of these five qualities:
Descriptive
Action-driven
Using power words in spoken, written, or video content is your chance to engage people and have them pay attention to your message, even in today's world of content shock and super-short attention spans .
It's critical to understand what words are responsible for the particular emotion you want to elicit with your speech. Also, it's essential to know how to layout your power words for them to do good, not harm.
Keep on reading for more details.

Power words are about action and emotion: They make the audience feel something and act accordingly. But emotions are varied.
To have your target audience feel specific emotions that motivate and persuade them to do what you plan, it's critical to choose words that trigger a particular response. Clearly, your speech will fail if you aim to build authority and trust but use vocabulary that engenders anger and greed.
It doesn't mean you shouldn't appeal to negative emotions. It means that you should avoid mixing mutually exclusive or conflicting power words in your speech.
Decide on what you want to evoke, and choose the best words for your public speech to achieve that. Here are some examples of what to evoke and words to use to do so:
Inspire curiosity
Curiosity is what motivates us to research, read, listen, and learn new things. It is probably a reason why you are reading this blog post right now. With the help of corresponding power words in your speech, you can hook your audience with what you're going to reveal.
Here are some examples of curiosity power words:
confidential
But make sure you do satisfy the evoked curiosity with your speech. Otherwise, you'll betray the audience's trust and your authority as a speaker.
Address their fears
Fear is the most powerful emotion to grab and keep people’s attention, and that's why news channels, newspapers, and marketers often appeal to it. We bet you've heard of FOMO, aka fear of missing out on something important: That's precisely how some copywriters and essay writers use fear to motivate consumers to act.
Fear power words examples:
disappointment
Obviously, you don't want your audience to fear for their lives or experience super negative emotions when listening to you. However, there are different levels of fear; evoking a little anxiety with power words, but then saying you also have a solution, can really grab the attention of your audience and influence their perceptions of your speech for the better.
Suggest safety
When using safety power words in your speech, you make the audience feel more secure dealing with you. They need to trust what you say and have confidence that you'll keep a promise. Make them feel as if you protect them from harm by providing actionable information.
Try these power words when appealing to safety:
bestselling
professional
trustworthy
Evoke greed
As well as fear, greed is a relatively negative emotion. We all are a little greedy, and that's why marketing copy is full of words appealing to this emotion: even when overused or cliche, they still work.
With targeted messages (what you want to tell or sell with your speech), consider using words that can help convince and convert your audience. Help them get what they want by suggesting exceptional value to them.
Appeal to greed with the following power words:
inexpensive
Establish your authority
As a speaker, you want to gain the audience's respect and trust. It's critical to exude authority when sharing presentation materials, and you can do that with words too.
A strong way to do this is to present third-party materials (statistics, research or study results, testimonials, and others) supporting your words. Prove that your data is relevant and critical enough for the audience to pay attention and listen to you.
Here are some power words to try to accomplish this:
unquestionable
Build trust
Trust goes hand in hand with authority in public speaking. It is more about building long-term relationships with the audience and convincing them that they can rely on you. Trust-related power words need to be consistent across your speech.
Here are some to try:
Lust is not just about romantic love. It can be about craving or longing for anything, whether an emotion or material possessions. Choose the correct power words in your speech to appeal to what your consumers long for, and satisfy those desires.
Some power words to try here are:
captivating
charismatic
fascinating
Use them together or by themselves to hook the audience and improve your speechwriting while you’re at it.
Make them feel powerful
This is your other weapon to gain the trust of your audience. Why do you think all those corny motivational speakers and internet marketing fraudsters are so popular with thousands of people? They make their audience members feel powerful. We’re not suggesting that you take advantage of, or are dishonest with your audience, but used in moderation, making them feel powerful will help get them on your side.
These are words you can use to boost your audience’s self-esteem:
accomplished
Encourage the audience
Let's face it, most people aren't that excited and motivated to listen to a speech on coaching platforms , conferences, or other events. There’s a good chance that they sat in front of you or their screens tired, bored, or even a bit depressed. Your challenge as a speaker is to wake them up and involve them in your communication.
The power words of encouragement can help. Here go some to consider in speech:
Additional tips for motivating and persuading the audience
Power words are numerous. Their biggest ambassador is Jon Morrow from Smart Blogger, continuously sharing and updating the list of power words on his blog. You can also find power word lists from copywriters, marketers, and bloggers. You can use these words in both headlines and copy, as well as your speeches. It’s a good idea to refer to such lists when looking for unique and action-driven words for your speech.
Together with power words, also consider these extra tips when trying to inspire and persuade your audience:
Use "you" more often than "I."
Call the audience and members by name when you can.
Practice using positive words and phrases: avoid "not" wherever possible.
Try using some literary devices to make your speech more compelling: Look into polysyndeton (extra conjunctions), chiasmus (reversal of structure), anaphora (word repetition at the beginning), or epistrophe (repetition at the end). Experiment with them and let us know the results.
Power words have nothing to do with psychological hacks or tricks to manipulate your audience. The use of power words is an instrument to engage people, grab their attention, and make them listen to your speech. Mix and match them whenever relevant to communicate your message and motivate your audience to take action.
Remember that certain words evoke specific emotions. Decide on what you want your audience to feel and choose your words carefully. Emotions overlap sometimes, so do your best to craft your public speech accordingly.
About the author:
Lesley Vos is a professional copywriter and guest contributor, currently blogging at Bid4Papers , a platform that helps students and authors with writing solutions. Specializing in data research, web text writing, and content promotion, she is in love with words, non-fiction literature, and jazz.

10 Keywords for Every Speaker

The 5-Minute Speech and How to Write One
Disclaimer: this article includes a paid product promotion..

How to Give Talks as a Software Developer: A Closer Look

How to Write an Informative Speech in 12 Easy Steps

3 Public Speaking Strategies for Environmental Conservationists

- Get an instant price to have your English document edited by professionals.
English Editing Blog
10 famous speeches in English and what you can learn from them
Speech is an essential element of language, one that we all employ in our daily lives. What about a speech ?
A speech is a formal address, delivered to an audience, that seeks to convince, persuade, inspire or inform. From historic moments to the present day, the English language has given us some extraordinary examples of the spoken word. A powerful tool in the right – or wrong – hands, spoken English can, and has, changed the world.
We’ve chosen ten of the most famous speeches in English. They range from celebrated, world-changing pieces of rhetoric to our personal favourites, but most importantly they still rouse our emotions when we hear them today. We’ve examined each for the tricks of the oratory trade. After each speech you’ll find some bullet points outlining its most distinctive rhetorical features, and why a speech writer would include them.
Remember these celebrated rhetoricians the next time you have to give a speech in public – be this at a wedding, award ceremony or business conference.
Scroll down to the end of this post for our essential tips on crafting speeches.
1. Martin Luther King I Have a Dream 1963
We couldn’t have an article about speeches without mentioning this one. Incredibly famous and iconic, Martin Luther King changed the character of speech making.
I have a dream that one day down in Alabama, with its vicious racists, with its governor having his lips dripping with the words of interposition and nullification – one day right there in Alabama little black boys and black girls will be able to join hands with little white boys and white girls as sisters and brothers. I have a dream today. I have a dream that one day every valley shall be exalted and every hill and mountain shall be made low, the rough places will be made plain, and the crooked places will be made straight, and the glory of the Lord shall be revealed and all flesh shall see it together.
What makes this a great speech?
– Abstract nouns like “ dream ” are incredibly emotional. Our dreams are an intimate part of our subconscious and express our strongest desires. Dreams belong to the realm of fantasy; of unworldly, soaring experiences. King’s repetition of the simple sentence “I have a dream” evokes a picture in our minds of a world where complete equality and freedom exist.
– It fuses simplicity of language with sincerity : something that all persuasive speeches seek to do!
– Use of tenses: King uses the future tense (“will be able”, “shall be”, “will be made””), which gives his a dream certainty and makes it seem immediate and real.
– Thanks to its highly biblical rhetoric , King’s speech reads like a sermon. The last paragraph we’ve quoted here is packed with biblical language and imagery .
2. King George VI Radio Address 1939
This speech was brought back to life recently thanks to the film, The King’s Speech (2010). While George VI will never go down in history as one of the world’s gifted orators, his speech will certainly be remembered.
In this grave hour, perhaps the most fateful in history, I send to every household of my peoples, both at home and overseas, this message, spoken with the same depth of feeling for each one of you as if I were able to cross your threshold and speak to you myself. For the second time in the lives of most of us, we are at war. Over and over again, we have tried to find a peaceful way out of the differences between ourselves and those who are now our enemies, but it has been in vain.
– At only 404 words long, the speech is impressively economical with language. Its short length means that every word is significant, and commands its audiences’ attention.
– This is a great example of how speechwriters use superlatives . George VI says that this moment is “the most fateful in history”. Nothing gets peoples’ attention like saying this is the “most important” or “best”.
– “ We ”, “ us ” and “ I ”: This is an extremely personal speech. George VI is using the first person, “I”, to reach out to each person listening to the speech. He also talks in the third person: “we are at war”, to unite British people against the common enemy: “them”, or Germany.
3. Winston Churchill We shall fight on the beaches 1940
Churchill is an icon of great speech making. All his life Churchill struggled with a stutter that caused him difficulty pronouncing the letter “s”. Nevertheless, with pronunciation and rehearsal he became one of the most famous orators in history.
…we shall defend our Island, whatever the cost may be, we shall fight on the beaches, we shall fight on the landing grounds, we shall fight in the fields and in the streets, we shall fight in the hills; we shall never surrender, and even if, which I do not for a moment believe, this Island or a large part of it were subjugated and starving, then our Empire beyond the seas, armed and guarded by the British Fleet, would carry on the struggle, until, in God’s good time, the New World, with all its power and might, steps forth to the rescue and the liberation of the old.
What makes it a powerful speech?
– Structural repetition of the simple phrase “we shall…”
– Active verbs like “defend” and “fight” are extremely motivational, rousing Churchill’s audience’s spirits.
– Very long sentences build the tension of the speech up to its climax “the rescue and the liberation of the old”, sweeping listeners along. A similar thing happens in musical pieces: the composition weaves a crescendo, which often induces emotion in its audience.
4. Elizabeth I Speech to the Troops 1588
The “Virgin Queen”, Elizabeth I, made this speech at a pivotal moment in English history. It is a remarkable speech in extraordinary circumstances: made by a woman, it deals with issues of gender, sovereignty and nationality.
I am come amongst you, as you see, at this time, not for my recreation and disport, but being resolved, in the midst and heat of the battle, to live and die amongst you all; to lay down for my God, and for my kingdom, and my people, my honour and my blood, even in the dust. I know I have the body but of a weak and feeble woman; but I have the heart and stomach of a king, and of a king of England too, and think foul scorn that Parma or Spain, or any prince of Europe, should dare to invade the borders of my realm; to which rather than any dishonour shall grow by me, I myself will take up arms, I myself will be your general, judge, and rewarder of every one of your virtues in the field.
– Elizabeth puts aside differences in social status and says she will “live and die amongst (her troops)”. This gives her speech a very inclusive message .
– She uses antithesis , or contrasting ideas. To offset the problem of her femininity – of being a “weak and feeble woman” – she swiftly emphasises her masculine qualities: that she has the “heart and stomach of a king”.
– Elizabeth takes on the role of a protector : there is much repetition of the pronoun “I”, and “I myself” to show how active she will be during the battle.
5. Chief Joseph Surrender Speech 1877
We’ve included this speech because there is something extremely raw and humbling about Chief Joseph’s surrender. Combining vulnerability with pride, this is an unusual speech and deserves attention.
Tell General Howard I know his heart. What he told me before, I have it in my heart. I am tired of fighting. Our Chiefs are killed; Looking Glass is dead, Ta Hool Hool Shute is dead. The old men are all dead. It is the young men who say yes or no. He who led on the young men is dead. It is cold, and we have no blankets; the little children are freezing to death. My people, some of them, have run away to the hills, and have no blankets, no food. No one knows where they are – perhaps freezing to death. I want to have time to look for my children, and see how many of them I can find. Maybe I shall find them among the dead. Hear me, my Chiefs! I am tired; my heart is sick and sad. From where the sun now stands I will fight no more forever.
What makes this a good speech?
– This speech is a perfect example of a how a non-native speaker can make the English language their own. Chief Joesph’s rhetoric retains the feels and culture of a Native American Indian speaker, and is all the more moving for this.
– Simple, short sentences.
– Declarative sentences such as “I know his heart” and “It is cold” present a listener with hard facts that are difficult to argue against.
6. Emmeline Pankhurst Freedom or Death 1913
Traditionally silent, women tend to have been left out of rhetoric. All that changed, however, with the advent of feminism. In her struggle for the vote, Pankhurst and her fellow protesters were compelled to find a voice.
You have left it to women in your land, the men of all civilised countries have left it to women, to work out their own salvation. That is the way in which we women of England are doing. Human life for us is sacred, but we say if any life is to be sacrificed it shall be ours; we won’t do it ourselves, but we will put the enemy in the position where they will have to choose between giving us freedom or giving us death.
– Direct acknowledgement of her audience through use of the pronoun you .
– Pankhurst uses stark, irreconcilable contrasts to emphasise the suffragettes’ seriousness. Binary concepts like men/women, salvation/damnation, freedom/imprisonment and life/death play an important role in her speech.
7. John F. Kennedy The Decision to go the Moon 19 61
Great moments require great speeches. The simplicity of Kennedy’s rhetoric preserves a sense of wonder at going beyond human capabilities, at this great event for science and technology.
We choose to go to the moon. We choose to go to the moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard, because that goal will serve to organize and measure the best of our energies and skills, because that challenge is one that we are willing to accept, one we are unwilling to postpone, and one which we intend to win, and the others, too.
– Simple sentence structures: “We choose to go to the moon” = Subject + Verb + Complement. The grammatical simplicity of the sentence allows an audience to reflect on important concepts, i.e. choice. Repetition emphasises this.
– Kennedy uses demonstrative (or pointing) pronouns e.g. “ this decade”, “ that goal” to create a sense of urgency; to convey how close to success the US is.
8. Shakespeare The Tempest Act 3 Scene 2 c.1610
Of course, any list of great speeches would be incomplete without a mention of the master of rhetoric, the Bard himself. If you caught the London Olympic Opening Ceremony you would have noticed that Kenneth Branagh delivered Caliban’s speech, from The Tempest .
Be not afeard; the isle is full of noises, Sounds and sweet airs, that give delight and hurt not. Sometimes a thousand twangling instruments Will hum about mine ears, and sometime voices That, if I then had waked after long sleep, Will make me sleep again: and then, in dreaming, The clouds methought would open and show riches Ready to drop upon me that, when I waked, I cried to dream again.
– It expresses a wonder and uncertainty of the world, and an inability to comprehend its mystery.
– It is highly alliterative , a rhetorical trick that makes speech memorable and powerful.
– Shakespeare uses onomatopoeia (e.g. “twangling”, “hum”: words whose sound is like they are describing) to make Caliban’s speech evocative.
9. Shakespeare Henry V Act 3 Scene 1, 1598
One of rhetoric’s most primal functions is to transform terrified men into bloodthirsty soldiers. “Once more unto the breach” is a speech that does just that. It is a perfect example of how poetry is an inextricable element of rhetoric.
Once more unto the breach, dear friends, once more; Or close the wall up with our English dead. In peace there’s nothing so becomes a man As modest stillness and humility: But when the blast of war blows in our ears, Then imitate the action of the tiger; Stiffen the sinews, summon up the blood, Disguise fair nature with hard-favour’d rage
What makes this such a great rousing battle speech?
-Shakespeare uses some fantastic imagery in King Henry’s speech. His “dear friends”, or soldiers, are tigers, commanded to block their enemies’ way with their dead comrades. This appeals to ideals of masculinity that men should be fierce and strong.
– Orders and imperative verbs give the speaker authority.
– Repetition of key phrases and units of sound: the vowel sounds in the repeated phrase “once more” are echoed by the words “or” and “our”. This makes it an extraordinarily powerful piece of rhetoric to hear spoken.
10. William Lyon Phelps The Pleasure of Books 1933
This speech was read a year before Nazis began their systematic destruction of books that didn’t match Nazi ideals. As major advocates of books at English Trackers, we’re naturally inclined to love speeches about their importance.
A borrowed book is like a guest in the house; it must be treated with punctiliousness, with a certain considerate formality. You must see that it sustains no damage; it must not suffer while under your roof. You cannot leave it carelessly, you cannot mark it, you cannot turn down the pages, you cannot use it familiarly. And then, some day, although this is seldom done, you really ought to return it.
– Phelps personifies books in this speech; that is, he gives books human characteristics – like the capacity to “suffer”. Comparing a book to a guest creates novelty , which engages and holds the interest of a listener.
– This speech uses both modal verbs (“must”, “ought”) and prohibitions (“you cannot”) to demonstrate both proper and improper behaviour.
Some tips to bear in mind when writing a speech
– KISS : the golden rule of Keep It Short and Simple really does apply. Keep your sentences short, your grammar simple. Not only is this more powerful than long rambling prose, but you’re more likely hold your audience’s attention – and be able to actually remember what you’re trying to say!
– Rule of 3 : another golden rule. The human brain responds magically to things that come in threes. Whether it’s a list of adjectives, a joke, or your main points, it’s most effective if you keep it to this structure.
– Imagery : Metaphors, similes and description will help an audience to understand you, and keep them entertained.
– Pronouns : Use “we” to create a sense of unity, “them” for a common enemy, “you” if you’re reaching out to your audience, and “I” / “me” if you want to take control.
– Poetry : Repetition, rhyme and alliteration are sound effects, used by poets and orators alike. They make a speech much more memorable. Remember to also structure pauses and parentheses into a speech. This will vary the flow of sound, helping you to hold your audience’s attention.
– Jokes : Humour is powerful. Use it to perk up a sleepy audience, as well as a rhetorical tool. Laughter is based on people having common, shared assumptions – and can therefore be used to persuade.
– Key words : “Every”, “improved”, “natural”, “pure”, “tested’ and “recommended” will, according to some surveys, press the right buttons and get a positive response from your listeners.
About the Author: This post comes to you from guest blogger, Natalie. Currently blogging, editing and based in London, Natalie previously worked with the English Trackers team.
Give me more!
Check out our post on Seven Ways to Seriously Improve your English
If you’re applying for a job, read our tips on English Resumes – How to Avoid Five Common Written Mistakes

30 Motivational Speeches To Get You Moving Forward Now
I like building and growing simple yet powerful products for the world and the worldwide web.
Published Date : October 29, 2021
Reading Time :
A sense of purpose in your professional and personal life is critical to success. It is useful advice for an impending deadline, an important presentation, or when clients rely on your performance.
Words can revitalize you on both a physical and emotional level. Motivational speeches may help you focus on your objectives and motivate your team. Having the right words to say the right thing at the right moment can transform and challenge your thinking.
You can use these motivational speeches to stay inspired and fulfilled no matter what life throws at you. These speeches will remind you why you do what you do and how much you enjoy doing it.
How Motivational Speeches Move People
People are propelled ahead by motivation. It rouses individuals from their complacency and opens their eyes to the thrilling possibilities . It is where motivational speeches help people to rise beyond the shackles of their ordinary existence.
Although motivation has a profound and even mystical effect on individuals, it is not as elusive as it first seems. The best motivational speeches are those that provoke thinking and meaning.
What Makes The Best Motivational Speeches
Best motivational speeches all have one thing in common: they’re filled with emotion . Emotions influence our decisions, behaviors, and viewpoints in every area of our lives. Motivational speeches are often filled with:
- Anecdotes about overcoming adversity
- Perseverance
- Achieving success
Speakers who use emotive topics and talking points that the audience can connect to are more likely to motivate the audience.
Plus, make them believe that they can overcome whatever obstacles stand in their way. The feeling of hope often sparks inspiration.
Qualities of Good Motivational Speakers
A few of the most effective motivational speakers share the characteristics listed below.
For more knowledge in delivering a motivational speech , here are some tips:
- Initiate mobility . Speakers begin with a speech , but concentrating the audience on various elements leads to a specific outcome.
- Straight to the point . Speakers convince the audience of their credibility while giving their speeches.
- Make it interesting . An effective motivational speaker knows that standing before an audience and blathering is never appreciated.
Practice your speech with Orai. Get feedback on your tone, tempo, confidence , and conciseness .
Motivational Speeches From Universities
Motivational speeches from well-known people are given during graduation each year to encourage students. Here are the best motivational speeches during the commencement exercises of different universities:
1. Denzel Washington – University of Pennsylvania
Denzel Washington’s motivational speech discusses the importance of taking chances in life and how. It is among the finest motivational speeches that are valid for business owners. He stated that when you fail, you should fall forward to his graduation address. Also, he encourages people to embrace failure and grow from it.
2. Steve Jobs – Stanford University
Definitely among the finest motivational speeches ever! His motivational speech discussed life’s setbacks, such as death, and how understanding death may help people make better life decisions. His comments to the graduating class on the value of learning and pursuing goals were the most valuable advice he could give them.
3. Jim Carrey – Maharishi University
At Maharishi University in Iowa, actor and comedian Jim Carrey delivered one of the most original graduation addresses ever. His takeaway from his motivational speech is: Never give up on your goals and never give up on yourself. Indeed, it is one of the best motivational speeches.
4. J.K. Rowling – Harvard University
Several publishers rejected J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series before it was finally accepted, as is well known. However, before she became successful, she was in a desperate position and was about to become bankrupt. In her Harvard address, she stressed the importance of not being afraid of failure and persisting in adversity.
5. Matthew McConaughey – University of Houston
Next on our list is Matthew McConaughey’s motivational speech . His speech has various excellent ideas. But, the one that stood out was when he said we should approach happiness constantly.
Ultimately, he discovered that everything came into place when he approached things step by step. After everything was said and done, Matthew McConaughey gave one of the best motivational speeches in recent years.
6. Michelle Obama – Eastern Kentucky University
Michelle Obama delivered a commencement speech to the Eastern Kentucky University class in 2013. She urged them to keep challenging their assumptions and find a way to make their flaws work for them. Her speech focused on giving the students motivation about life.
When it comes to defining moments in your life, it won’t be when you receive a promotion or have a breakthrough in your career.
7. Peter Dinklage – Bennington College
Game of Thrones actor Peter Dinklage is well-known for portraying Tyrion Lannister in the show. He delivered the Bennington College graduating speech in 2012. His message to the graduating class focused on perseverance and doing everything it takes to succeed.
8. John Roberts – Cardigan Mountain School
US Supreme Court Chief Justice John Roberts addressed his son’s graduating high school class in 2017. It’s not good luck; he wishes the grads in his address. He expresses his want for kids to experience loneliness, failure, and defeat from time to time.
9. Natalie Portman – Harvard University
Actress Natalie Portman addressed Harvard University’s 2015 graduating class during their graduation ceremony. She uses wide brushstrokes from all periods of her life to build a picture in her compelling speech . Also, she claims to have discovered that taking measured risks may result in life-altering benefits, as she has done it herself.
10. Meryl Streep – Barnard College
Meryl Streep is most recognized as a 16-time nominee and 2-time winner at the Academy Awards. While at Barnard College, she made a memorable graduating address in 2010 that inspired the audience. However, in her address, she emphasized the importance of her relationships with family and friends.
Become an excellent speaker with the perfect Motivational speech .
Download the Orai App to learn more
Motivational Speeches From Ted Talk
Reaffirming your confidence in humanity is one of the most powerful benefits of listening to motivational speeches. Next time you need a little additional energy, have this list handy.
1. Elizabeth Gilbert
Famous author and TED speaker Elizabeth Gilbert spoke about how we all have a “genius” that we may unleash. She is the author of the best-selling book Eat, Pray, Love. Gilbert’s motivational speech emphasized the importance of not being intimidated or scared of success.
2. Tony Robbins
One of the most well-known motivational speakers today is Tony Robbins. This TED lecture, in particular, profoundly affects the listener. It addresses two major issues in its title, “Why We Do What We Do.”
We learn about ourselves and others by asking these kinds of inquiries. What should you remember? You are the only person who can decide whether or not you succeed.
3. Richard St. John
Next on our list of motivational speeches is Richard St. John’s TED Talk from 2005, given by the author, marketer, and analyst. St. John’s address, which was based on his book “8 To Be Great,” gets to the point in a manner that most speeches don’t
The remainder of St. John’s discourse quickly transitions from one intriguing topic to the next without wasting time or words. There are also a few well-placed jokes in there. As a result, even though he covers a lot of subjects, his audience retains what he says.
4. Dan Pink
As a writer, Dan Pink’s reputation is supported by many “legs,” such as his writings and accolades. Also, in the late 1990s, he was the primary speechwriter for former US Vice President Al Gore.
Pink’s TED Talk is a role model for everyone who wants to convert a dull subject into motivating. He started his speech by examining how most economists see performance, stating, “If you want people to perform better, you reward them. Right? That’s how business works.”
5. Mel Robbins
Regarding speakers, Mel Robbins has a solid reputation for taking a direct and honest stance on even the most emotional subjects. Due to this, she’s not scared to speak her mind regarding difficult issues. She only chooses a person from her audience to underscore her speech ’s enormous chances of being born.
6. Simon Sinek
First seen in his 2009 TED Talk “How Great Leaders Inspire Action,” Simon Sinek is a best-selling author. Sinek proves he’s not just switching from one stereotyped issue to another. In addition, he encourages audiences to let go of their preconceived notions about the subject to approach it with a fresh perspective.
7. Tali Sharot
Dr. Tali Sharot is dedicated to helping people realize their personal and professional dreams. She works to increase awareness of the impact of emotions on our decisions and behavior. In this TED talk, she talks about how to motivate yourself to change your behavior.
8. Brene Brown
Brene Brown, a Texan with a penchant for ranting and raving, is an authority on shame and vulnerability. A key focus of Brown’s research is human connection. Over 16 million people have seen her motivational TED presentation in which she offers a profound discovery from her studies. It launched her on a personal mission to understand both herself and humankind.
9. Malcolm Gladwell
It wouldn’t be a list of motivational speeches without Malcolm Gladwell’s inclusion. Gladwell tells the tale of a guy who refused to believe in the existence of a ‘perfect’ spaghetti sauce. It contains important insights for executives who want to create work environments where their employees are pleased.
10. Sam Berns
It is one of the best motivational speeches you’ll ever see. A 17-year-old Sam became a public face for Progeria, a hereditary disorder with the evocative moniker aging sickness. While some claimed Sam would never transcend the constraints others had placed on him, he refused to let his illness define him.
He led the life he wanted, ignoring his disease and the things that set him apart in favor of his goals. It’s a remarkable heirloom left by a unique young man.
Best Motivational Speeches From Movies
While narrative and actors are important in movies, speeches leave an impression on audiences. So, here are the best motivational speeches from movies to help you out:
Given Sunday
To prepare for a rough day, hear this inspiring lecture from a well-known motivational speaker. It focuses on the importance of inches in American Football, even though we prefer to disregard them. He speaks about how his team may gain an inch on their competition by focusing on the little details of winning.
Irrespective of whether or not you saw the film, it provided cinemagoers with one of the most motivational speeches ever. You don’t have to yell or curse a lot. Depending on your personality, it may cause you to enter what we refer to as “the zone.” Speeches in earlier films have included theatrical components; this one does not.
3. Hoosiers
Even though we’re still in college, we’ve already gained enough life experience to realize that working hard doesn’t guarantee a W. Even if we give it our all, dozing off in the library at 3 a.m. on top of our books, that doesn’t guarantee an A. Isn’t it enough if you’re giving it your all?
4. Friday Night Lights
Is it possible for you to speak the truth to your friends while looking them in the eye? That you put out all of your efforts? In this film, Coach Gaines says that if you can accomplish it with love in your heart, you’ve achieved perfection. His message inspires honesty, camaraderie, and love among his team members in this scenario.
5. Rocky Balboa
Rocky Balboa reminds his kid that life isn’t fair in this scene since he is a father figure in the Rocky franchise. It is like boxing in that how hard you punch back is immaterial. According to him, what matters is how much you can absorb and how quickly you can advance.
6. The Pursuit of Happiness
It’s worth mentioning that the whole picture is moving since it depicts father-son relationships. In this speech , a father instructs his kid never to give up on his dreams, no matter how unlikely they may seem to others. If someone tells you you can’t attain your objectives, don’t believe them.
7. Wolf of Wall Street
The main hero’s speech in Wolf of Wall Street is encouraging because it takes achievement into account. Seeing examples of people who rose from poverty to riches might encourage others to take risks when an opportunity arises. Since his speech , having a decent standard of life has become more important.
8. Braveheart
In this scene, William Wallace gives a speech on the importance of freedom to a human being. For him, independence trumps the monotony of everyday existence. The speech can motivate listeners to take action instead of just producing food.
9. The Shawshank Redemption
Motivational speeches like this one demonstrate confidence in an optimistic future. You can still use it, even if you have to put in a lot of work to get there while another guy gives up. It would help if you always had an optimistic outlook on life’s prospects.
10. Independence Day
In this film, the president discusses the importance of humanism and goodwill among all countries. His message is motivational because he discusses uniting against common adversaries and preserving lives. If you’re considering international relations, this speech is a gold mine.
What event did Greta Thunberg speak at in 2019, and what was the focus of her speech?
In 2019, Greta Thunberg delivered a speech at the United Nations Climate Action Summit. The focus of her powerful address was to criticize world leaders for their inadequate actions toward addressing and combating climate change. Thunberg traveled by sailboat to the summit and accused these leaders of failing to take tangible steps to combat the global climate crisis.

Who is Greta Thunberg, and what is she known for?
Greta Thunberg is a prominent figure in the realm of environmental activism, hailing from Sweden. At the tender age of 20, she has gained international recognition for fearlessly challenging global leaders to address the urgent need for measures to counter the impacts of climate change. Thunberg’s passionate advocacy work centers around raising awareness about the climate crisis and urging policymakers to take concrete actions to combat it. Her inspiring efforts have made her synonymous with the fight against climate change on a global scale.
What insights were found through the analysis of Oprah Winfrey’s motivational speech?
Oprah Winfrey delivered a motivational speech without using any filler words, speaking at a conversational pace and maintaining positive body language . Her speech delivery was effective and can be an example for aspiring speakers. Yoodli is a tool that can help individuals improve their speech patterns and English proficiency.
What is the title and significance of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.’s famous speech 1963?
Dr. King’s “I Have a Dream” speech , delivered in 1963 at the height of the civil rights movement, remains iconic. Standing at the Lincoln Memorial, he addressed a massive crowd with a message of hope, equality, and justice. The speech ’s enduring power lies in its call to judge individuals by character, not skin color, inspiring generations to dream of a more just future.
Who gave the Nobel Peace Prize Lecture in 2014, and what was the content of the speech?
Malala Yousafzai, a young Pakistani champion for female education, delivered a powerful Nobel Peace Prize speech in 2014. Despite facing threats and violence, she expressed unwavering commitment to her cause, highlighting education’s role in achieving peace and leaving a lasting impact on the world.
What did Janelle Monáe discuss in her 2018 Trailblazer Award acceptance speech?
Janelle Monáe, a trailblazer, urged pushing boundaries and exploring oneself to create inclusive spaces. She highlighted self-discovery’s challenges and rewards, emphasizing authenticity’s power in empowering others.
Who is Janelle Monáe, and what awards has she received?
Janelle Monáe is a multi-talented pop artist who proudly identifies as queer and Black. Known for her powerful voice and dynamic performances, she has garnered recognition for her artistic contributions across various award ceremonies. Some of the awards and nominations she has received come from distinguished organizations such as BET, Billboard Music, ASCAP, and AICE. These accolades celebrate her exceptional talent and artistic achievements in the music industry.
Parting Words
That concludes our selection of the best motivational speeches to get you through the tough times ahead! Let’s take a look at some of the common themes that appear in all of these talks.
- It’s critical that you like your work.
- Even if you fail, that’s not the end of the world.
- It would be better if you aspired to it.
Now, consider the topics that will motivate your listeners to pay attention to your words. You may also use the Orai App to help you enhance your public speaking skills and capture your audience’s attention. Furthermore, take advantage of the free trial offer and start immediately.
Practice makes a man perfect. Start practicing and become a professional speaker.

You might also like

How Many Words is a 5-Minute Speech

Good Attention Getters for Speeches with 10+ Examples!
Quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
50 Speech Closing Lines (& How to Create Your Own) | The Ultimate Guide
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

While speech openings are definitely one of the most important components of a speech, something that is equally as important is the way you conclude your speech.
There are few worse ways to end your speech than with a terse ‘thank you’–no elaboration or addition whatsoever.
Speech endings are just as crucial to the success of your speech as speech openings, and you must spend just as much time picking the perfect ending as you do to determine your best possible speech opening.
The words you speak at the beginning and end of your speech are words that your audience will pay the most attention to, and remember longer than any other part of your speech.
Speech endings can put even the most experienced speaker in flux, and increase their anxiousness manifold as they sit there attempting to figure out the perfect way to end your speech.
If you’re someone who’s in flux about your speech ending too, don’t worry. We’ve got some amazing ways to conclude your speech with a bang!
1. Circling Back To The Beginning
The idea behind circling back to the beginning of your speech is to reinforce the idea of your speech being a complete whole. By circling back to the beginning and connecting it to your ending, you let the audience understand that the idea of your speech is complete & standalone.
Circling back to the beginning of your speech also acts as an excellent way of reinforcing the central idea of your speech in the audience’s mind, and makes it more likely that they will remember it after the speech ends.
Need more inspiration for speech opening lines? Check out our article on 15 Powerful Speech Opening Lines & Tips To Create Your Own.
How To Circle Back To The Beginning
The easiest way to do this is to set up your beginning for the conclusion of your speech. That is, if you’re saying something like, say, a story or joke in the beginning, then you can leave your audience in a cliffhanger until the ending arrives.
Another great way to circle back to the beginning is by simply restating something you said at the start. The added knowledge from attending the rest of your speech will help the audience see this piece of information in a new–and better–light.
1. Will Stephen
Ending Line: “I’d like you to think about what you heard in the beginning, and I want you to think about what you hear now. Because it was nothing & it’s still nothing.”
2. Canwen Xu
Speech Ending: My name is Canwen, my favorite color is purple and I play the piano but not so much the violin…
Think of a memorable moment from your life, and chances are you’ll realize that it involved a feeling of happiness–something that we can associate with smiling or laughter. And what better way to generate laughter than by incorporating the age-old strategy of good humor.
The happy and lighthearted feeling you associate with good memories is the kind of emotional reaction you want to create in your audience too. That’s what will make your speech stick in their memory.
Done incorrectly, humor can be a disaster. Done right, however, it can entirely transform a speech.
Humor doesn’t only mean slapstick comedy (although there’s nothing wrong with slapstick, either). Humor can come in many forms, including puns, jokes, a funny story…the list is endless.
How To Incorporate Humor In Your Speech Ending
The simplest way to incorporate humor into your speech ending is by telling a plain old joke–something that’s relevant to your topic, of course.
You can also tell them a short, funny anecdote–may be an unexpected conclusion to a story you set up in the beginning.
Another way would be by employing the power of repetition. You can do this by associating something funny with a word, and then repeating the word throughout your speech. During the end, simply say the word or phrase one last time, and it’s likely you’ll leave off your audience with a good chuckle.
1. Woody Roseland
Ending Line: “Why are balloons so expensive? Inflation.”
2. Andras Arato
Ending Line: “There are three rules to becoming famous. Unfortunately, nobody knows what they are.”
3. Hasan Minhaj
Ending Line: “And you want to know the scariest part? Pretty soon every country on the earth is going to have its own TLC show.”
4. Sophie Scott
Speech Ending: In other words, when it comes to laughter, you and me baby, ain’t nothing but mammals.
5. Tim Urban
Speech Ending: We need to stay away from the Instant Gratification Monkey. That’s a job for all of us. And because there’s not that many boxes on there. It’s a job that should probably start today. Well, maybe not today, but, you know, sometime soon.
6. Hasan Minhaj
Speech Ending: Showing my legs on TV is probably the scariest thing I’ve ever done. And keep in mind last week I went after the Prince of Saudi Arabia.
3. Question
The idea behind posing a question at the end of your speech is to get the wheels in your audience’s minds turning and to get them thinking of your speech long after it has ended. A question, if posed correctly, will make your audience re-think about crucial aspects of your speech, and is a great way to prompt discussion after your speech has ended.
How To Add Questions To Your Speech Ending
The best type of questions to add to your speech ending is rhetorical questions. That’s because, unlike a literal question, a rhetorical question will get the audience thinking and make them delve deeper into the topic at hand.
Make sure your question is central to the idea of your speech, and not something frivolous or extra. After all, the point of a question is to reinforce the central idea of your topic.
1. Lexie Alford
Speech Ending: Ask yourself: How uncomfortable are you willing to become in order to reach your fullest potential?
2. Apollo Robbins
Speech Ending: If you could control somebody’s attention, what would you do with it?
Quotes are concise, catchy phrases or sentences that are generally easy to remember and repeat.
Quotes are an age-old way to start–and conclude–a speech. And for good reason.
Quotes can reinforce your own ideas by providing a second voice to back them up. They can also provoke an audience’s mind & get them thinking. So, if you add your quote to the end of your speech, the audience will most likely be thinking about it for long after you have finished speaking.
How To Use Quotes In Your Speech Ending
While adding quotes to your speech ending, make sure that it’s relevant to your topic. Preferably, you want to pick a quote that summarizes your entire idea in a concise & memorable manner.
Make sure that your quote isn’t too long or complicated. Your audience should be able to repeat it as well as feel its impact themselves. They shouldn’t be puzzling over the semantics of your quote, but its intended meaning.
1. Edouard Jacqmin
Speech Ending: “Life is either a daring adventure or nothing at all.”
2. Chris Crowe
Speech Ending: “It’s more certain than death and taxes.”
3. Olivia Remes
Speech Ending: I’d like to leave you with a quote by Martin Luther King: “You don’ have to see the whole staircase. Just take the first step.”
4. Tomislav Perko
Speech Ending: Like that famous quote says, “In twenty years from now on, you’ll be more disappointed by the things you didn’t do than by the things you did do.
5. Diana Nyad
Speech Ending: To paraphrase the poet, Mary Oliver, she says, “So, what is it? What is it you’re doing with this one wild and precious life of yours?”
5. Piece Of Advice
The point of giving a piece of advice at the end of your speech is not to pull your audience down or to make them feel bad/inferior about themselves. Rather, the advice is added to motivate your audience to take steps to do something–something related to the topic at hand.
The key point to remember is that your advice is included to help your audience, not to discourage them.
How To Add Piece Of Advice To Your Speech Ending
To truly make your audience follow the advice you’re sharing, you must make sure it resonates with them. To do so, you need to inject emotions into your advice, and to present it in such a manner that your audience’s emotions are aroused when they hear it.
Your advice shouldn’t be something extra-complicated or seemingly impossible to achieve. This will act as a counter-agent. Remember that you want your audience to follow your advice, not to chuck it away as something impossible.
Our article, 15 Powerful Speech Ending Lines And Tips To Create Your Own , is another great repository for some inspiration.
1. Ricardo Lieuw On
Speech Ending: “Learn something new, or a new way of approaching something old because there are a few skills are valuable as the art of learning.”
2. Tomas Chamorro-Premuzic
Speech Ending: “If we want to improve the competence level of our leaders, then we should first improve our own competence for judging and selecting leaders.”
3. Sharique Samsudheen
Speech Ending: “Some people love money, some people hate money, some people crave money, some people even kill for money. But what they miss is they just need to learn how to manage money well, and that will give them financial freedom.”
4. Kate Simonds
Speech Ending: Teens, you need to believe in your voices and adults, you need to listen.
5. Melissa Butler
Speech Ending: When you go home today, see yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all your greatness that you embody, accept it, love it and finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn’t look like you.
6. Iskra Lawrence
Speech Ending: Speak to your body in a loving way. It’s the only one you got, it’s your home, and it deserves your respect. If you see anyone tearing themselves down, build them back up And watch your life positively grow when you give up the pursuit of perfection.
6. Contemplative Remark
As the name itself suggests, contemplative remarks are intended to make your audience contemplate or mull over something. The ‘something’ in question should be the idea central to your speech, or a key takeaway that you want them to return home with.
The idea is to get your audience thinking and to keep them thinking for a long, long time.
How To Add A Contemplative Remark To Your Speech Ending
To add a contemplative remark to your speech ending, you first need to figure out your key takeaway or main theme. Then, you want to arrange that as a question, and propose it to your audience at the end of your speech.
Remember that your question shouldn’t be something too wordy or complicated to understand. As with the quotes, you don’t want your audience stuck on the semantics. Rather, you want them to focus on the matter at hand.
1. Lisa Penney
Speech Ending: “So I invite you to pay more attention to your thoughts & consider the legacy you leave behind.”
2. Grant Sanderson
Speech Ending: “Some of the most useful math that you can find or teach has its origin in someone who was just looking for a good story.”
3. Greta Thunberg
Speech Ending: “We will not let you get away with this. Right here, right now is where we draw the line. The world is waking up & change is coming whether you like it or not.”
4. Bill Eckstrom
Speech Ending: Now, think about this: it’s not the complexity-triggering individuals or events you should fear the most, but it’s your own willingness to accept or seek discomfort that will dictate the growth of not just you, but our entire world.
5. Robert Hoge
Speech Ending: Choose to accept your face, choose to appreciate your face, don’t look away from the mirror so quickly; understand all the love, and the life, and the pain that is the part of your face, that is the art of your face. Tomorrow when you wake up, what will your choice be?
7. Personal Anecdote
Personal anecdotes, as the name suggests, are anecdotes that are personal to the speaker or instances from their life. Personal anecdotes are a great way to incorporate the magical powers of storytelling in your speech, as well as to make a personal connection with the audience. Using personal anecdotes, you can hit two birds with one stone!
How To Add Personal Anecdotes To Your Speech Ending
To add personal anecdotes to your speech ending, you need to filter through your life experiences to find out ones that directly relate to your topic at hand. You don’t want to include an anecdote, no matter how compelling it is, if it doesn’t relate to your topic.
Remember to not keep your anecdote too long. Your audience will most likely lose their attention if you do so.
1. Sheila Humphries
Speech Ending: “Why do you go work for these people?” My answer to them was, “If I could help one child make it in this world, it’ll be worth it all.”
8. Call To Action
A call-to-action is one of the absolute best ways to conclude a speech with a bang. A well-written speech should aim to alter the audience’s mind or belief system in some way and to make them take an action in that direction. One crucial way to assure your audience does this is by using a call to action.
How To Add A Call To Action To Your Speech Ending
A call to action comes right before the ending of your speech to provide your audience with a clear idea or set of instructions about what they’re supposed to do after your talk ends.
A call to action should provide a roadmap to the audience for their future steps, and to outline clearly what those future steps are going to be.
1. Armin Hamrah
Speech Ending: “So tonight, after you finish your Math homework & before you lay your head down on that fluffy pillow, bring a piece of paper and pen by your bedside…”
2. Graham Shaw
Speech Ending: “So I invite you to get your drawings out there & spread the word that when we draw, we remember more!”
3. Andy Puddicombe
Speech Ending: You don’t have to burn any incense, and you definitely don’t have to sit on the floor. All you need to do is to take out 10 minutes out a day to step back, familiarize yourself with the present moment so that you get to experience a greater sense of focus, calm, and clarity in your life.
4. Amy Cuddy
Speech Ending: Before you go into the next stressful evaluative situation, for two minutes, try doing this in the elevator…
5. Jia Jiang
Speech Ending: When you are facing the next obstacle or the next failure, consider the possibilities. Don’t run! If you just embrace them, they might become your gifts as well.
9. Motivational Remark
As the name clearly explains, a motivational remark motivates your audience to carry out a plan of action. It ruffles the audience’s mind and emotions and has a powerful impact on the steps that your audience will take after you’ve finished speaking.
How To Add A Motivational Remark To Your Speech Ending
The key to a good motivational remark is to inspire your audience. Your motivational remark should act as a ray of hope to your audience and positively inspire them to take a desired course of action.
Your motivational remark should not be negative in any way. You don’t want to guilt or coerce your audience into doing something or feeling a certain way. You want to leave them on a positive note to move forward with their life.
1. Khanh Vy Tran
Speech Ending: “No matter what you’re going through right now & no matter what the future holds for you, please don’t change yourself. Love yourself, accept yourself & then transform yourself.”
2. Mithila Palkar
Speech Ending: “Get a job, leave a job, dance, sing, fall in love. Carve your own niche. But most importantly: learn to love your own randomness.”
3. Andrew Tarvin
Speech Ending: “Anyone can learn to be funnier. And it all starts with a choice. A choice to try to find ways to use humor. A choice to be like my grandmother, to look at the world around you and say WTF–wow, that’s fun.”
4. Laura Vanderkam
Speech Ending: There is time. Even if we are busy, we have time for what matters. And when we focus on what matters, we can build the lives we want in the time we’ve got.
5. Julian Treasure
Speech Ending: Let’s get listening taught in schools, and transform the world in one generation into a conscious listening world, a world of connection, a world of understanding, and a world of peace.
6. Mariana Atencio
Speech Ending: Let’s celebrate those imperfections that make us special. I hope that it teaches you that nobody has a claim on the word ‘normal’. We are all different. We are all quirky and unique and that is what makes us wonderfully human.
10. Challenge
Much like a call to action, the aim of proposing a challenge at the end of your speech is to instigate your audience to take some desired course of action. A challenge should make an appeal to your audience’s emotion, and motivate them to meet it.
How To Add A Challenge To Your Speech Ending
To apply a challenge effectively to your speech ending, you need to make sure that it’s something relevant to your topic. Your challenge should drive the central topic of your speech forward, and make your audience engage in real-life steps to apply your idea in the real world.
While its always a good idea to set a high bar for your challenge, make sure its an achievable one too.
1. Jamak Golshani
Speech Ending: “I challenge you to open your heart to new possibilities, choose a career path that excites you & one that’s aligned to who you truly are.”
2. Ashley Clift-Jennings
Speech Ending: So, my challenge to you today is, “Do you know, would you even know how to recognize your soulmate?” If you are going out in the world right now, would you know what you are looking for?
11. Metaphor
Metaphors are commonly used as a short phrase that draws a comparison between two ideas in a non-literal sense. People use metaphors quite commonly in daily life to explain ideas that might be too difficult or confusing to understand otherwise. Metaphors are also great tools to be used in speech, as they can present your main idea in a simple and memorable way.
How To Add Metaphors To Your Speech Ending
To add a metaphor to your speech ending, you need to first decide on the main idea or takeaway of your speech. Your metaphor should then be organized in such a way that it simplifies your main idea and makes it easier for your audience to understand & remember it.
The key is to not make your metaphor overly complicated or difficult to retain and share. Remember that you’re trying to simplify your idea for the audience–not make them even more confused.
1. Ramona J. Smith
Speech Ending: “Stay in that ring. And even after you take a few hits, use what you learned from those previous fights, and at the end of the round, you’ll still remain standing.”
2. Shi Heng YI
Speech Ending: “If any of you chooses to climb that path to clarity, I will be very happy to meet you at the peak.”
3. Zifang “Sherrie” Su
Speech Ending: “Are you turning your back on your fear? Our life is like this stage, but what scares are now may bring you the most beautiful thing. Give it a chance.”
12. Storytelling
The idea behind using stories to end your speech is to leave your audience with a good memory to take away with them.
Stories are catchy, resonating & memorable ways to end any speech.
Human beings can easily relate to stories. This is because most people have grown up listening to stories of some kind or another, and thus a good story tends to evoke fond feelings in us.
How To Incorporate Stories In Your Speech Ending
A great way to incorporate stories in your speech ending is by setting up a story in the beginning and then concluding it during the end of your speech.
Another great way would be to tell a short & funny anecdote related to a personal experience or simply something related to the topic at hand.
However, remember that it’s the ending of your speech. Your audience is most likely at the end of their attention span. So, keep your story short & sweet.
1. Sameer Al Jaberi
Speech Ending: “I can still see that day when I came back from my honeymoon…”
2. Josephine Lee
Speech Ending: “At the end of dinner, Jenna turned to me and said…”
Facts are another excellent speech ending, and they are used quite often as openings as well. The point of adding a fact as your speech ending is to add shock value to your speech, and to get your audience thinking & discussing the fact even after your speech has ended.
How To Add Facts To Your Speech Ending
The key to adding facts to your speech ending is to pick a fact that thrusts forward your main idea in the most concise form possible. Your fact should also be something that adds shock value to the speech, and it should ideally be something that the audience hasn’t heard before.
Make sure that your fact is relevant to the topic at hand. No matter how interesting, a fact that doesn’t relate to your topic is going to be redundant.
1. David JP Phillips
Speech Ending: 3500 years ago, we started transfering knowledge from generation to generation through text. 28 years ago, PowerPoint was born. Which one do you think our brain is mostly adapted to?
14. Rhethoric Remark
Rhetoric remarks are another excellent way to get the wheels of your audience’s minds turning. Rhetoric remarks make your audience think of an imagined scenario, and to delve deeper into your topic. Rhetoric remarks or questioned don’t necessarily need to have a ‘right’ or one-shot answer, which means you can be as creative with them as possible!
How To Add Rhethoric Remarks To Your Speech Ending
Since rhetorical questions don’t need to have a definite answer, you have much freedom in determining the type of question or statement you wish to make. However, as with all other speech endings, a rhetorical question shouldn’t be asked just for the sake of it.
A rhetorical question should make your audience think about your topic in a new or more creative manner. It should get them thinking about the topic and maybe see it from an angle that they hadn’t before.
Rhetorical questions shouldn’t be too confusing. Use simple language & make sure it’s something that the audience can easily comprehend.
1. Mona Patel
Speech Ending: Pick your problem, ask “What if?” Come up with ideas. Bring them down. Then execute on them. Maybe you’re thinking, “What if we can’t?” I say to you, “What if we don’t?”
2. Lizzie Velasquez
Speech Ending: I want you to leave here and ask yourself what defines you. But remember: Brave starts here.
Another great way to end your speech with a literal bang is by using music! After all, if there’s something that can impact the human mind with just as much force as a few well-placed words, it’s the correct music.
How To Add Music To Your Speech Ending
To add music to your speech ending, you must make sure that the music has something to do with your speech theme. Remember that you’re not playing music in your concert. The piece of music that you choose must be relevant to your topic & work to have a contribution in your overall speech.
1. Tom Thum
Speech Ending: *ends the TED Talk with beat boxing*
16. Reitirate The Title
The title of your speech is its most important component. That’s why you need to pay careful attention to how you pick it, as it is something that your viewers will most likely remember the longest about your speech.
Your title will also act as a guiding hand towards how your audience forms an initial idea about your speech and is what they will associate your entire speech with.
By repeating your title at the end of your speech, you increase the chances that your audience will remember it–and your speech–for a long time.
How To Retierate The Title In Your Speech Ending
Your title is something that your audience associates your entire speech with. However, you don’t want to simply add the title in your speech end for the sake of adding it. Instead, make it flow naturally into your speech ending. This will make it seem less forced, and will also increase the chances of your audience remembering your entire speech ending and not just the title of your speech.
1. Ruairi Robertson
Speech Ending: I feel we can all contribute to this fight worth fighting for our own health, but more importantly, our future generations’ health by restoring the relationship between microbe and man. There is SOME FOOD FOR THOUGHT!
Need more inspiration for speech closing lines? Check out our article on 10 Of The Best Things To Say In Closing Remarks.
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
To sum up, speech endings are just as imperative to the success of your speech as speech openings, and you must spend just as much time picking the perfect ending as you do to determine your best possible speech opening. The words you speak at the beginning and end of your speech are words that your audience will pay the most attention to, and remember longer than any other part of your speech.
Still looking for inspiration? Check out this video we made on closing remarks:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

10 Hand Gestures That Will Make You More Confident and Efficient

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.
Oratory Club
Public Speaking Helpline

Speech Transitions: Words And Phrases to Connect Your Ideas
Speech transitions are important as they connect ideas and maintain a smooth flow. These transitions help guide the audience through the speech effectively.
Effective communication is crucial in delivering a compelling speech. To engage and captivate an audience, it is essential to connect ideas seamlessly. Speech transitions serve as connectors between different thoughts and ensure a logical progression of ideas. By employing suitable words and phrases, a speaker can enhance the flow of their speech and maintain the audience’s attention.
We will explore various words and phrases that can be used to connect ideas in a speech. These transitions play a vital role in conveying the message effectively and leaving a lasting impact on the listeners.

Credit: www.spanish.academy
Table of Contents
Why Are Speech Transitions Important In Public Speaking?
Speech transitions play a crucial role in public speaking by connecting ideas seamlessly. These words and phrases help maintain the flow of the speech and captivate the audience, ensuring a clear and coherent delivery.
Speech transitions play a significant role in public speaking. They serve as vital connectors that link together various ideas and concepts in a seamless manner. By using appropriate words and phrases to transition between different points, speakers can maintain the flow and coherence of their speech.
Here’s why speech transitions are important:
Benefits Of Using Speech Transitions:
- Enhance clarity: Transitions help speakers to clearly communicate their ideas and thoughts to the audience. By using transition words and phrases, they can guide the listeners through the different sections of their speech, making it easier to follow.
- Improve understanding: Effective transitions ensure that the audience can easily grasp the connections between ideas and concepts. This helps to prevent any confusion or misinterpretation of the speaker’s message.
- Increase engagement: Speech transitions prevent a monotonous or disjointed delivery, making the speech more engaging for the audience. By smoothly moving from one idea to another, the speaker captures the listeners’ attention and keeps them actively involved throughout the presentation.
- Highlight key points: Transitions can be used strategically to emphasize important information or key points. By signaling the significance of certain ideas, speakers can ensure that these points are understood and remembered by the audience.
Impact On Audience Engagement:
- Retention of information: With the help of effective speech transitions, speakers can enhance the audience’s ability to retain and recall the information presented. Logical connections created through transitions make it easier for listeners to process and remember the content.
- Focused attention: Well-placed transitions help to maintain the audience’s focus and prevent their minds from wandering. By smoothly transitioning between ideas, speakers keep the listeners engaged and attentive.
- Active participation: Speech transitions encourage the audience to actively participate in the speech. Clear connections between ideas enable listeners to anticipate the direction of the speech, allowing them to make connections and draw conclusions alongside the speaker.
- Emotionally connect: Transitions can also have an emotional impact on the audience. By using appropriate words and phrases, speakers can evoke specific feelings, making the speech more memorable and impactful.
Creating a smooth and coherent flow:
- Logical progression: Transitions facilitate a logical progression of ideas, enabling the speaker to present their thoughts in a structured manner. This ensures that the audience can easily follow the speaker’s intended flow of information.
- Seamless connection: Speech transitions act as bridges between different ideas or sections, creating a seamless connection between them. This helps to establish a sense of continuity in the speech, preventing any abrupt shifts in topic or subject matter.
- Professional delivery: The use of speech transitions demonstrates a speaker’s professionalism and command over their subject. It showcases their ability to present complex ideas in a clear and organized manner.
By recognizing the importance of speech transitions and incorporating them into public speaking, speakers can enhance the effectiveness of their presentations, captivate their audience, and ensure that their message is delivered with impact.
Types Of Speech Transitions
Discover various types of speech transitions that effectively connect ideas and thoughts in your speech. These words and phrases seamlessly guide the flow of your presentation, keeping your audience engaged and interested. Improve your public speaking skills with these powerful speech transition techniques.
Transition words and phrases play a crucial role in connecting your ideas and making your speech or presentation flow smoothly. By using these linguistic tools, you can create a cohesive and engaging narrative that keeps your listeners hooked. In this section, we will explore the different types of speech transitions, including transition words and phrases, verbal transitions, and nonverbal transitions.
Transition Words And Phrases:
- First and foremost, transition words and phrases serve as the glue that holds your speech together. They facilitate the logical progression of your ideas and help your audience follow along effortlessly.
- Additionally, transition words and phrases add clarity and coherence to your speech, ensuring that your message is easily understood.
- Moreover, they signal shifts in topic, introduce examples, emphasize crucial points, and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Furthermore, transition words and phrases enable you to create smooth transitions between different sections of your speech, which is essential for maintaining audience engagement.
Verbal Transitions:
- Verbal transitions involve the use of spoken words or phrases to guide your audience from one idea to another seamlessly.
- For instance, you can use phrases like “now, let’s move on to…”, “in relation to…”, or “on the other hand…” to smoothly transition between topics.
- Likewise, starting a sentence with phrases such as “in the same vein…”, “to illustrate my point…”, or “another key aspect is…” can effectively connect your ideas and make your speech more coherent.
- Furthermore, verbally signaling your intention to transition, using phrases like “now, let’s shift gears and discuss…”, “next up, we’ll explore…”, or “in light of this information…” can help your audience anticipate and comprehend your transitions better.
Nonverbal Transitions:
- Nonverbal transitions involve actions, gestures, or visuals that complement your verbal transitions, reinforcing the connections between your ideas.
- Use physical cues, such as changing your stance, moving to a different part of the stage, or making eye contact with a specific audience member, to signify a transition.
- Similarly, employing visual aids like slides, charts, or props can also assist in smoothly guiding your audience from one idea to the next.
- Additionally, adjusting your tone of voice, pausing strategically, or utilizing facial expressions can effectively emphasize the shift in ideas and engage your listeners.
Incorporating a variety of transition words and phrases, implementing verbal transitions, and utilizing nonverbal cues can greatly enhance the flow and impact of your speech. Integrating these techniques will help you maintain your audience’s attention and ensure that your ideas are communicated effectively.
So, let’s dive in and explore the world of speech transitions further!
Using Transition Words And Phrases
Discover the power of using speech transitions to seamlessly connect your ideas. By employing a variety of transition words and phrases, you can create a cohesive flow in your speech while keeping your audience engaged and interested. Swap repetitive terms for different expressions to ensure your content remains fresh and captivating.
Importance Of Strategic Placement:
- Transition words and phrases are essential in speech writing as they help to connect and smoothly organize ideas and thoughts.
- Strategic placement of transition words and phrases allows for a coherent flow of information, making it easier for the audience to follow the speaker’s train of thought.
- Proper use of transition words and phrases can enhance the overall impact of a speech by creating a logical progression of ideas and reinforcing key points.
- By strategically incorporating transition words and phrases, speakers can maintain the audience’s attention and prevent confusion or disengagement.
Commonly Used Transition Words:
- “furthermore”: Used to add another supporting point or to provide additional information.
- Example: Furthermore, research has shown that regular exercise improves overall mental health.
- “however”: Introduces a contrasting idea or viewpoint.
- Example: The study found that the new drug is effective; however, more research is needed to determine long-term effects.
- “meanwhile”: Shows a simultaneous action or event occurring.
- Example: The company was experiencing financial difficulties; meanwhile, their competitors were thriving.
- “moreover”: Indicates the addition of more information or evidence.
- Example: The data collected from the survey revealed alarming statistics; moreover, it highlighted the need for immediate action.
Connecting Ideas Within A Sentence:
- “similarly”: Demonstrates a likeness or similarity between two ideas.
- Example: The baby elephant walked with a wobble, similarly to a toddler taking their first steps.
- “in addition”: Introduces an additional piece of information or evidence.
- Example: The market research indicated a growing demand for organic products; in addition, consumer preferences were shifting towards sustainable packaging.
- “likewise”: Expresses similarity or agreement with a previous statement.
- Example: The new policy aims to increase employee satisfaction; likewise, it strives to improve overall productivity.
- “on the other hand”: Indicates a contrasting viewpoint or perspective.
- Example: The group was divided on the issue; on the other hand, some argued for immediate action while others preferred a more cautious approach.
Transition Phrases For Introducing New Points:
- “first and foremost”: Emphasizes the primary or most important point to be made.
- Example: First and foremost, it is crucial for individuals to prioritize their mental health.
- “another key point”: Introduces an additional significant idea or argument.
- Example: Another key point to consider is the impact of social media on mental well-being.
- “lastly”: Signals the final point or argument in a series or sequence.
- Example: Lastly, it is essential to provide accessible and affordable mental health services for all individuals.
Transition Words For Emphasizing Or Contrasting Ideas:
- “indeed”: Emphasizes and reinforces a previous point or statement.
- Example: The results of the study indeed highlight the need for further investigation.
- “contrarily”: Shows a contrasting or opposite perspective.
- Example: While some argue for stricter regulations, contrarily, others believe in the importance of personal freedoms.
- “in summary”: Provides a concise overview or recap of the main points discussed.
- Example: The research demonstrates the significant impact of early childhood education on future academic success.
Remember, incorporating these transition words and phrases into your speech can greatly enhance its overall effectiveness, making it more engaging and easy to follow. Use them strategically to guide your listeners through your ideas and ensure they stay connected and engaged with your message.
Incorporating Verbal Transitions
Discover the power of incorporating verbal transitions in your speech to effortlessly connect your ideas. Enhance your communication skills with carefully chosen phrases and words that keep your audience engaged and interested. Unlock the potential of seamless transitions for impactful speeches.
Establishing A Connection Between Ideas
- Incorporating verbal transitions is essential in speech delivery as it helps maintain a smooth flow of ideas. These transitions act as bridges between different thoughts, guiding the audience through your speech. By using the right words and phrases, you can establish clear connections between ideas, leaving a lasting impact on your listeners. Let’s explore some effective techniques for incorporating verbal transitions.
Using Clear Language And Cues
- Clear language and cues allow your audience to follow along effortlessly, ensuring that your ideas are effectively communicated. Consider the following strategies to enhance clarity in your speech:
- Signposting: The use of signposting phrases, such as “firstly,” “next,” or “” helps guide your audience through the structure of your speech, making it easier for them to follow your thought process.
- Repetition: Repeating key phrases or concepts throughout your speech can reinforce your ideas, making them more memorable for your audience.
- Pronouns: Utilize pronouns like “they,” “we,” or “you” to create a sense of inclusivity and engagement. This fosters a connection between you and your audience, encouraging active participation.
Examples Of Verbal Transition Techniques
- Here are some effective examples of verbal transition techniques to incorporate in your speech:
- Cause and effect: Use phrases like “as a result,” “consequently,” or “therefore” to highlight the cause and effect relationship between different ideas.
- Comparison and contrast: Employ phrases such as “similarly,” “on the other hand,” or “in contrast” to draw comparisons or highlight differences between ideas, helping your audience understand distinct concepts better.
- Time sequence: Signal the passage of time or progression of ideas with phrases like “before,” “afterward,” or “meanwhile.” This helps your audience follow the chronological order of events or thoughts.
Practice And Delivery Tips
- To improve your use of verbal transitions, consider these practice and delivery tips:
- Rehearse your speech: Practice delivering your speech multiple times, focusing on incorporating verbal transitions smoothly. This will help you become more comfortable and confident in your delivery.
- Record and review: Record yourself delivering the speech and take note of areas where verbal transitions can be improved. Analyzing your performance will enable you to refine your delivery and strengthen your speech.
- Seek feedback: Request constructive feedback or have a trusted person observe your speech. They can provide valuable insights on how to enhance your verbal transitions and overall impact.
Remember, incorporating verbal transitions in your speech not only enhances its coherence but also ensures that your ideas are effectively communicated and understood by your audience. By practicing and mastering these techniques, you’ll become a more engaging and persuasive speaker.
Keep honing your skills, and watch your speech captivate and inspire your listeners.
Leveraging Nonverbal Transitions
Discover the power of nonverbal transitions in connecting your ideas during speeches. Utilize effective words and phrases that enhance the flow of your presentation and engage your audience. Say goodbye to common speech transition pitfalls and captivate your listeners with seamless transitions.
In the realm of public speaking, effective speech transitions are crucial for connecting ideas and maintaining the attention of your audience. While verbal transitions are commonly employed, nonverbal cues can be just as powerful in conveying a seamless flow of thoughts.
This section will explore the various ways to leverage nonverbal transitions, including visual cues, body language, gestures and facial expressions, the importance of eye contact, and how to convey confidence and professionalism.
Visual Cues And Body Language:
- Visual cues play a vital role in indicating transitions and maintaining engagement during a speech.
- Use confident and purposeful body language to signify a change in topic or shift in ideas.
- Positioning yourself differently on stage or adjusting your stance can visually communicate a transition to your audience.
- Maintain an open and relaxed posture, which indicates a welcoming and inclusive environment.
Gestures And Facial Expressions:
- Utilize gestures and facial expressions to enhance the impact of your nonverbal transitions.
- Gesture with your hands to emphasize key points or signal a transition to a new idea.
- Employ facial expressions to convey enthusiasm, surprise, or seriousness, making your transitions more engaging and memorable.
Importance Of Eye Contact:
- Eye contact is a powerful nonverbal tool that establishes a connection with your audience and aids in smooth transitions.
- Engage with individuals in different parts of the room, ensuring that your eye contact is inclusive and not only focused on a single person or section.
- During transitions, maintain eye contact to signal that you are moving on to a new topic or idea.
- The use of eye contact can also help you gauge the audience’s reaction and adjust your delivery accordingly.
Conveying Confidence And Professionalism:
- Nonverbal transitions are instrumental in conveying confidence and professionalism throughout your speech.
- Maintain a calm and composed demeanor, which instills confidence in your audience.
- Avoid fidgeting or excessive movements that may distract from your message.
- By utilizing nonverbal cues effectively, you can create a sense of professionalism and competence, enhancing your overall speaker presence.
Incorporating nonverbal transitions into your speech can significantly improve its flow, captivate your audience, and reinforce your message. Visual cues, body language, gestures, facial expressions, eye contact, and conveying confidence and professionalism are all essential elements in creating a seamless and engaging speaking experience.
Practice and master these nonverbal techniques to elevate your speech to new heights.
Transitioning Between Different Sections Of A Speech
Transitioning between different sections of a speech is crucial for maintaining a coherent flow and engaging the audience. By utilizing effective speech transitions, you can seamlessly connect your ideas, avoiding clichés and repetitive terms, to ensure a captivating and impactful delivery.
Transitioning between different sections of a speech is crucial to maintain the flow and coherence of your ideas. To ensure a smooth transition, consider using the following techniques:
Introducing A New Topic Or Main Idea
- Pose a question: Start a new section by asking a thought-provoking question that introduces your audience to the upcoming topic. For example, “have you ever wondered how technology has revolutionized the way we communicate?”
- Provide a brief anecdote or story: Capture your audience’s attention by sharing a relevant story or anecdote that sets the stage for the new topic. This personal touch will engage your listeners from the start.
- Use a powerful quote: Begin your section with an impactful quote that relates to the subject matter. This will immediately draw your audience’s attention and create curiosity about the upcoming discussion.
Summarizing Key Points
- Highlight the main ideas: Summarize the key points you have discussed so far in a concise and clear manner. This allows your audience to understand the progress of your speech and reinforces the central ideas you want them to remember.
- Use transition words: Employ transition words and phrases such as “” “to summarize,” or “in conclusion” to signal that you are summarizing the main points. This helps the audience mentally prepare for the upcoming summary.
Shifting Focus Or Transitioning To A Conclusion
- Preview the provide a glimpse of what your conclusion will entail without delving into the details. This primes your audience for the upcoming ending, creating anticipation and signaling the shift in focus.
- Ask for the audience’s attention: Use phrases like “now, let’s turn to the final part of our discussion” to redirect the attention back to the conclusion. This helps maintain engagement and refocuses the audience’s thoughts on the closing remarks.
- Reinforce the central theme: Remind your listeners of the central theme or main message of your speech. This will ensure that the concluding remarks connect back to the core ideas you have been discussing.
Remember, effective transitions are like signposts that guide your audience through your speech. By utilizing these techniques, you can navigate between different sections smoothly and keep your audience fully engaged.
Tips For Effective Transitioning
Discover practical tips for effective transitioning in your speech through the use of appropriate words and phrases. Enhance the flow of your ideas by avoiding overused terms and incorporating a variety of expressions at the beginning of paragraphs. Keep your sentences concise and engaging to maintain the reader’s interest.
Preparing And Rehearsing Transitions:
- Craft a list of transitional words and phrases: To ensure smooth and seamless transitions between your ideas, compile a list of words and phrases that can serve as connectors. Examples include “however,” “in addition,” and “on the other hand.”
- Identify logical connections: Assess the flow of your speech and identify the logical connections between each point. This will help you determine the appropriate transitional words or phrases to use.
- Practice aloud: Once you have selected your transition words and phrases, practice incorporating them into your speech. Rehearse it several times to ensure that the transitions feel natural and help maintain the overall coherence of your ideas.
Using A Variety Of Transition Methods:
- Implement signposts: Signposts are words or phrases that indicate where you are in your speech and where you are going next. Examples include “firstly,” “next,” and “finally.” By using these signposts, you guide your audience through your speech, making it easier for them to follow along.
- Utilize parallel structure: Parallel structure involves using the same grammatical structure for each point in your speech. This creates a rhythm and consistency that facilitates smooth transitions. For example, instead of saying “i like hiking and to swim,” you would say “i like hiking and swimming.”
- Incorporate rhetorical questions: Asking a rhetorical question can help transition from one idea to the next seamlessly. It engages your audience and prompts them to reflect on the previous point before moving on to the next one.
- Use visual aids: Visual aids such as slides or props can serve as effective transition tools. By visually emphasizing the connection between ideas, you can make the transition more apparent to your audience.
- Provide summaries: Summarizing the main points of each section can be a powerful transition technique. It allows you to recap what has been discussed and prepare your audience for the upcoming topic.
Maintaining A Natural And Conversational Tone:
- Avoid using jargon: To keep your speech accessible and engaging, avoid using technical jargon or overly complicated language. Opt for words and phrases that your audience can easily understand.
- Vary sentence lengths: Using a mix of short and long sentences adds rhythm and variety to your speech. This prevents monotony and keeps your audience engaged.
- Practice active voice: Choosing active voice sentences instead of passive voice helps maintain a conversational tone. Active voice is more direct and engaging, making it easier for your audience to follow along.
- Engage with the audience: Encourage audience participation throughout your speech by asking for their thoughts or experiences related to your topic. This creates a more conversational and interactive atmosphere.
- Adjust your pace: Pay attention to your speaking pace and adjust it accordingly. Speaking too fast can make it difficult for your audience to process the information, while speaking too slowly can lead to disengagement. Aim for a rhythmic and natural pace.
Remember, effective transitioning is crucial for the cohesiveness and clarity of your speech. By preparing and rehearsing your transitions, utilizing a variety of transition methods, and maintaining a natural and conversational tone, you can ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and leave a lasting impact on your audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are speech transitions.
Speech transitions are words and phrases used to connect ideas and help the audience follow your presentation more smoothly. They create a logical flow and make it easier for listeners to understand and remember your key points.
Why Are Speech Transitions Important?
Speech transitions are important because they enhance the coherence and clarity of your speech. They help your audience navigate through your ideas and maintain their attention. Transitions also make your speech more engaging and polished, leaving a lasting impact on your listeners.
What Are Some Common Speech Transition Words And Phrases?
There are various speech transition words and phrases you can use, such as “in addition,” “however,” “on the other hand,” “moreover,” “as a result,” “to summarize,” and “finally. ” These transition words and phrases can help you transition between different ideas, compare and contrast points, and summarize information.
How Can Speech Transitions Improve My Public Speaking Skills?
Using speech transitions in your presentations enhances your public speaking skills by making your speech more organized, coherent, and impactful. With effective transitions, you can smoothly guide your audience through your ideas, keeping them engaged and helping them understand and remember your message.
To sum up, utilizing effective speech transitions is essential for seamless and coherent delivery. By incorporating appropriate words and phrases, you can effectively connect your ideas and guide your audience through your speech. Whether you are emphasizing a point, introducing a new topic, or providing examples, utilizing transitional words and phrases enhances the overall flow of your speech.
Moreover, these transitions help to maintain your audience’s engagement and comprehension. From using simple transitional words like “firstly” and “next,” to employing complex connectors such as “in contrast” and “similarly,” the right speech transitions can transform your speaking style. By following these guidelines and practicing your delivery, you can become a confident and compelling speaker.
Remember, speech transitions are powerful tools that can transform your speech from disjointed to cohesive, ensuring that your ideas are conveyed clearly and effectively. So, the next time you give a speech, make sure to incorporate these essential speech transitions and watch your message resonate with your audience.
Similar Posts

Who is the Maid of Honor to the Bride?
The Maid of Honor to the Bride is a close friend or relative who assists the bride throughout the wedding preparations and the ceremony. From helping with the wedding planning to standing by the bride’s side on the big day, the Maid of Honor plays a significant role in ensuring a smooth and memorable wedding…
Best Public Speaking Exercises
Public speaking exercises are a great way to improve your communication skills and boost your confidence in front of an audience. We will explore some of the best exercises that can help you become a more effective public speaker. Whether you are a novice or an experienced speaker, these exercises will provide you with valuable…
How to Become An Agile Lead?
So you’re interested in becoming an agile lead? That’s awesome! Being an agile lead means being able to guide a team to success in a fast-paced, ever-changing environment. It’s like being the captain of a sports team, making sure everyone is aligned and working together toward a common goal. But how do you become an…
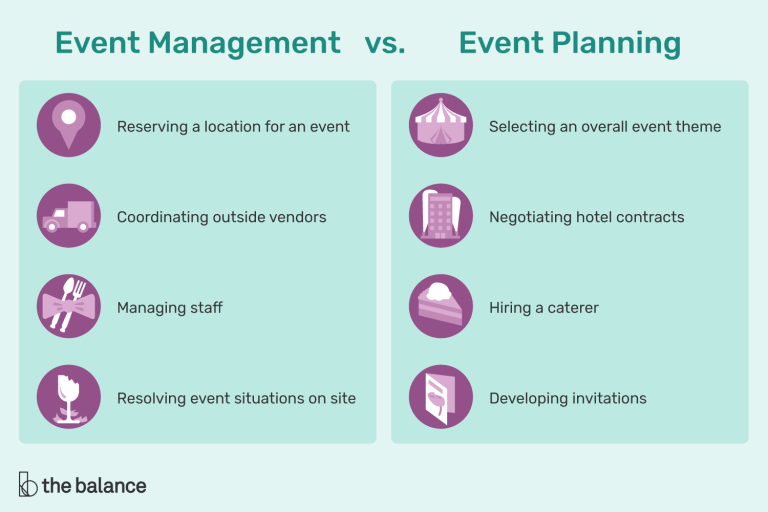
What Is Event Management?
Event Management is the process of planning and coordinating various activities to ensure the successful execution of an event. It involves organizing everything from venue selection and vendor management to logistics and on-site coordination. Event professionals oversee all aspects of an event to create a memorable experience for attendees. With meticulous attention to detail, event…
Crippling Anxiety Public Speaking
Imagine standing in front of a crowd, your heart pounding, your palms sweating. Crippling anxiety takes over as you’re about to deliver a speech or presentation. But hey, don’t worry, you’re not alone! Public speaking can be intimidating for many of us, especially when anxiety kicks in. Public speaking anxiety, also known as glossophobia, is…
The Best Public Speaking Books
The best public speaking books are a valuable resource for improving your communication skills. We will discuss some of the top books in this field that provide practical tips, techniques, and advice for becoming a better public speaker. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced speaker looking to refine your skills, these books offer…
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
13 Speeches in English for Listening and Speaking Practice
Giving a speech in front of a whole room of people can be pretty scary. Especially if you are giving a speech in English as a non-native speaker.
But you can learn from the best.
You can watch videos of famous, effective speeches in English to learn how to do it the right way .
In this post we will share 13 amazing speeches in English that you can use to become a more confident speaker yourself.
1. Speech on Kindness by a 10-year-old Girl
2. “the effects of lying” by georgia haukom, 3. “education for all” by cameron allen, 4. gender equality speech by emma watson, 5. “rocky balboa speech” by sylvester stallone, 6. 2008 presidential acceptance speech by president barack obama, 7. “this is water” speech by david foster wallace, 8. “the great dictator speech” by charlie chaplin, 9. 2018 golden globe speech by oprah winfrey, 10. “i have a dream” speech by martin luther king jr., 11. “the gettysburg address” by abraham lincoln, 12. “britain does owe reparations” by shashi tharoor, 13. mark antony’s speech by william shakespeare, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Level: Beginner
Do you think people should be kind to one another? This speaker sure does. And she knows how to convince you of the same.
This is a perfect informative speech for beginner English learners . The speaker is a child who is able to speak fluently but with simple words . She also uses her gestures and facial expressions to communicate her emotions with the audience.
This speech is perfect for listening practice . However, learners should be aware that her pauses are not perfect. Learners should focus more on her words and the content of the speech than her intonation or pacing while practicing.
Even though the speaker is a student in the fourth grade, her speech is one of the most interactive speeches I have seen. She starts with a game and is able to make her main point through the game itself.
English learners will enjoy her speech especially because the vocabulary she uses is simple and can be easily learned. But it does not feel like a beginner wrote this speech because she uses her words so well.
If you want to learn the art of making basic arguments while speaking, you should watch this speech. She is able to convince her audience because she is able to connect with them through games and stories.
She also uses scientific studies to back up (support) her main points.
Level: Intermediate
This is a short and simple speech about why everyone in the world should get an education. Because the speaker is a child, the speech does not have complex words or sentence structures.
This is also a classic example of an informative speech. The speaker presents the main argument and the facts simply and clearly . She also gives the basic definitions of important terms in the speech itself.
This speech is perfect for English listening and speaking practice because it is so short but also full of useful information. It is also a good example of the standard American English accent .
Emma Watson is a famous English actress who is best known for her role in the “Harry Potter” movie series as Hermione. She is also a United Nations Women Goodwill Ambassador .
In this speech, she is trying to both inform and convince the audience of why men should support feminism. Feminism is a movement that asks for equal rights and opportunities for women.
She mixes her formal tone with personal stories to do this. The speech is also a good example of British English .
This is a speech taken from the movie “Rocky Balboa.” In this scene, Rocky, played by Sylvester Stallone, is talking to his son.
His speech is a classic example of a motivational speech . In these kinds of speeches, a person tries to inspire someone else, especially when the listener feels hopeless or is full of shame.
The basic message of the speech is that no matter how strong a person is, he or she will always face difficulties. And even though the message does not sound positive, Stallone’s way of speaking still makes it inspiring.
Stallone is able to communicate his message with love, even though he is criticizing his son and telling him difficult facts about the world. Generally, this is called “tough love” in English.
Listeners should also notice how he uses gestures to make his point .
Compare this speech with the Oprah Winfrey and Martin Luther King speeches (later in this list). All of them inspire their audiences but have really different tones. Stallone’s speech is the most informal and personal while Martin Luther King’s speech is the most formal and written for a large audience. All these speeches are in American English.
Barack Obama was the first African American elected as president by U.S. citizens. He gave this speech after he won the election.
English learners can discover a lot from his speech. Obama talks about the most important issues Americans were facing back then and are still important to them. He also uses a kind of American English that is easy to understand . His speech is mainly about the values that he and Americans stand for.
Obama’s accent is a mixture of standard American English and the way of speaking commonly popular in African American communities. He is an expert in using pauses so that the audience can follow his words without breaking his rhythm.
As the speech is longer than most others on this list, you may want to listen to it in parts rather than beginning-to-end.
Level: Advanced
This speech is a perfect example of the mixture of casual and formal English . David Foster Wallace was an award-winning American writer who wrote about the culture of the U.S.
In this speech, he talks about the value of an education in liberal arts (general academic subjects, as opposed to technical/professional training). He believes that this kind of education teaches you how to think and think about others.
This is a good example of American English. Be aware that in some parts of the speech he also uses swear words (rude/offensive words) to create an emotional impact on the audience. This is very close to how people generally communicate with one another in daily life.
So, this speech is better for learning casual English even though it is a speech given at a university.
Level: Intermediate to Advanced
Charlie Chaplin is generally known for his gestures and facial expressions. In this movie, he proves that he can use speech as well to inspire and entertain the viewers.
The movie “The Great Dictator” is a satire about the rise of authoritarian governments in Europe. The word “authoritarian” means a person or a government that believes in controlling others and does not believe in freedom.
In this speech, Charlie Chaplin copies Adolf Hitler , but his message is exactly the opposite of Hitler’s ideas.
The interesting thing about the speech is how Chaplin uses short sentences for the most impact . There is also a lot of repetition that makes it easy for the audience to follow the speech.
Chaplin uses the tone, rhythm and pitch of his voice to make the speech interesting instead of using varied words. Chaplin’s speech can be categorized as inspirational or motivational. It does not use formal words but neither is it casual or informal.
Oprah Winfrey is an American talk show host and actor who is known around the world for her interviews. In the 2018 Golden Globe Awards, she was awarded the Cecil B. deMille award .
Her speech at the award show is about many different topics related to American society. She is the first African American woman to be awarded the prize . She talks about how watching an African American celebrity get another big entertainment award many years ago changed her life.
She also talks about sexual assault and the search for justice in American society. The MeToo movement is the main subject of the speech.
Even though the speech is in formal English , Oprah is able to make it emotional and personal .
Learners should focus on how she uses chunking in her sentences . Chunking is the technique of grouping words (called chunks) in a sentence with a slight pause between every chunk. It also helps with intonation and the rhythm of speaking.
This is one of the most well-known speeches of the last century . Martin Luther King Jr. was a leader of the civil rights movement in the U.S. The movement demanded that people of different races should be treated equally. This speech summarized the main vision of the movement using metaphors and repetition .
The speech begins by referring to the “Emancipation Proclamation.” The proclamation (official announcement) was an order by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863 that freed many slaves in the U.S. Martin Luther King talks about this because most of the slaves were African Americans and it was their first step towards freedom.
Advanced learners can learn about the history and cultural conflicts of America through this speech. It is also a perfect example of the use of formal English to convince other people .
Some of the words used in this speech are no longer common in American English. “Negro” is often regarded as an insult and learners should use words like “African American” instead.
This speech, delivered by the 16th president of the U.S. (Abraham Lincoln, whom we just discussed above) is considered to be one of the best speeches in English .
Lincoln delivered this in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania where many soldiers had died fighting a civil war. It was fought between Americans who wanted to ban slavery and people who did not. Lincoln was there to dedicate a graveyard to the soldiers.
In this speech, Lincoln reminds the people why this was an important war. He mentions that the U.S. was created on the values of liberty and equality. And this civil war was a test of whether a nation based on these values can last for long or not.
He honors the soldiers by saying that they have already “consecrated” the land for the people of America. (“To consecrate” means to make something sacred or holy.) He reminds the audience that they have to make sure that the idea of America as a nation of freedom continues so that the efforts of these soldiers are not wasted.
This is a very short speech . Learners can easily listen to it multiple times in a practice session. But only advanced learners can understand it since it has several difficult words in it. For instance, “score” is an outdated term used for the number 20. And when he mentions the word “fathers” in the first line he is actually referring to the leaders who had founded the country of America.
Even though Shashi Tharoor is not a native English speaker, his English is so fluent that he sounds like one. Learners from India will instantly recognize him because he is famous there for his English skills.
In this video, he is giving a speech as a part of a debate at Oxford University . He lists out arguments that support the idea that the U.K. should give reparations to its colonies. “Reparations” are payments to a country or community for some harm done to them. A colony is a region or a country that is controlled by another country by force.
Britain had a large number of colonies throughout the world between the 16th and 20th centuries. In this speech, Tharoor tries to convince his audience that the U.K. should give something for the damage they did to the countries they had colonized.
This is one of the finest examples of a formal speech in today’s English . Learners who want to go into academics can learn how to organize their arguments with evidence.
The speech is also great for vocabulary practice . Plus, Tharoor has deep knowledge of both the national history of the U.K. and the colonial history of India. Apart from the content of the speech, his way of speaking is also impressive and is similar to formal British English .
This speech is part of a play called “Julius Caesar” written by William Shakespeare. The play is based on the life and murder of Caesar who was a leader of the Roman Empire. The speech is considered to be one of the finest pieces of English literature .
It is also one of the best examples of the use of rhetoric (the art of speaking and persuasion).
Mark Antony makes this speech after Caesar is killed by other leaders of the Roman Empire. Antony was a close friend of Caesar’s and here he tries to remind the people of Rome that Caesar was actually a good man. He has to convince the people that his murderers like Brutus are actually criminals. But he has to do so without directly blaming the murderers.
Advanced learners should know this speech mainly because of its cultural value.
Many words in this speech have been replaced by other words in today’s English. “Hath” is the older form of “has” or “had.” “Thou” has also been replaced by the word “you.”
So rather than memorizing the vocabulary, learners should focus on how Damian Lewis delivers the speech instead. The intonation, tone, pitch and rhythm is similar to the formal English used today. He is also good at conveying emotions through pauses and expressions.
If you keep watching videos of native speakers talking, you’ll get used to hearing how different people talk in English. After watching these speeches, you could look for more speeches or interviews on YouTube.
FluentU takes authentic videos—like music videos, movie trailers, news and inspiring talks—and turns them into personalized language learning lessons.
You can try FluentU for free for 2 weeks. Check out the website or download the iOS app or Android app.
P.S. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Try FluentU for FREE!
The best way to learn the art of speaking is to first copy great speakers. Try to speak the same words in a style that is natural and comfortable to you. These speeches in English are the perfect material to master it!
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials , as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe


Words for Speaking: 30 Speech Verbs in English (With Audio)

Speaking is amazing, don’t you think?
Words and phrases come out of our mouths — they communicate meaning, and we humans understand each other (well, sometimes)!
But there are countless different ways of speaking.
Sometimes, we express ourselves by speaking quietly, loudly, angrily, unclearly or enthusiastically.
And sometimes, we can express ourselves really well without using any words at all — just sounds.
When we describe what someone said, of course we can say, “He said …” or “She said …”
But there are so many alternatives to “say” that describe the many different WAYS of speaking.
Here are some of the most common ones.
Words for talking loudly in English
Shout / yell / scream.
Sometimes you just need to say something LOUDLY!
Maybe you’re shouting at your kids to get off the climbing frame and come inside before the storm starts.
Or perhaps you’re just one of those people who just shout a lot of the time when you speak. And that’s fine. I’ve got a friend like that. He says it’s because he’s the youngest kid in a family full of brothers and sisters — he had to shout to make sure people heard him. And he still shouts.
Yelling is a bit different. When you yell, you’re probably angry or surprised or even in pain. Yelling is a bit shorter and more “in-the-moment.”
Screaming is similar but usually higher in pitch and full of fear or pain or total fury, like when you’ve just seen a ghost or when you’ve dropped a box of bricks on your foot.

“Stop yelling at me! I’m sorry! I made a mistake, but there’s no need to shout!”
Bark / Bellow / Roar
When I hear these words, I always imagine something like this:

These verbs all feel rather masculine, and you imagine them in a deep voice.
I always think of an army general walking around the room telling people what to do.
That’s probably why we have the phrase “to bark orders at someone,” which means to tell people what to do in an authoritative, loud and aggressive way.
“I can’t stand that William guy. He’s always barking orders at everyone!”
Shriek / Squeal / Screech
Ooooohhh …. These do not sound nice.
These are the sounds of a car stopping suddenly.
Or the sound a cat makes when you tread on her tail.
Or very overexcited kids at a birthday party after eating too much sugar.
These verbs are high pitched and sometimes painful to hear.
“When I heard her shriek , I ran to the kitchen to see what it was. Turned out it was just a mouse.”
“As soon as she opened the box and saw the present, she let out a squeal of delight!”
Wailing is also high pitched, but not so full of energy.
It’s usually full of sadness or even anger.
When I think of someone wailing, I imagine someone completely devastated — very sad — after losing someone they love.
You get a lot of wailing at funerals.
“It’s such a mess!” she wailed desperately. “It’ll take ages to clear up!”
Words for speaking quietly in English
When we talk about people speaking in quiet ways, for some reason, we often use words that we also use for animals.
In a way, this is useful, because we can immediately get a feel for the sound of the word.
This is the sound that snakes make.
Sometimes you want to be both quiet AND angry.
Maybe someone in the theatre is talking and you can’t hear what Hamlet’s saying, so you hiss at them to shut up.
Or maybe you’re hanging out with Barry and Naomi when Barry starts talking about Naomi’s husband, who she split up with last week.
Then you might want to hiss this information to Barry so that Naomi doesn’t hear.
But Naomi wasn’t listening anyway — she was miles away staring into the distance.
“You’ll regret this!” he hissed , pointing his finger in my face.
To be fair, this one’s a little complicated.
Whimpering is a kind of traumatised, uncomfortable sound.
If you think of a frightened animal, you might hear it make some kind of quiet, weak sound that shows it’s in pain or unhappy.
Or if you think of a kid who’s just been told she can’t have an ice cream.
Those sounds might be whimpers.
“Please! Don’t shoot me!” he whimpered , shielding his head with his arms.

Whispering is when you speak, but you bypass your vocal cords so that your words sound like wind.
In a way, it’s like you’re speaking air.
Which is a pretty cool way to look at it.
This is a really useful way of speaking if you’re into gossiping.
“Hey! What are you whispering about? Come on! Tell us! We’ll have no secrets here!”
Words for speaking negatively in English
Ranting means to speak at length about a particular topic.
However, there’s a bit more to it than that.
Ranting is lively, full of passion and usually about something important — at least important to the person speaking.
Sometimes it’s even quite angry.
We probably see rants most commonly on social media — especially by PEOPLE WHO LOVE USING CAPS LOCK AND LOTS OF EXCLAMATION MARKS!!!!!!
Ranting always sounds a little mad, whether you’re ranting about something reasonable, like the fact that there’s too much traffic in the city, or whether you’re ranting about something weird, like why the world is going to hell and it’s all because of people who like owning small, brown dogs.
“I tried to talk to George, but he just started ranting about the tax hike.”
“Did you see Jemima’s most recent Facebook rant ? All about how squirrels are trying to influence the election results with memes about Macaulay Culkin.”
Babble / Blabber / Blather / Drone / Prattle / Ramble

These words all have very similar meanings.
First of all, when someone babbles (or blabbers or blathers or drones or prattles or rambles), it means they are talking for a long time.
And probably not letting other people speak.
And, importantly, about nothing particularly interesting or important.
You know the type of person, right?
You run into a friend or someone you know.
All you do is ask, “How’s life?” and five minutes later, you’re still listening to them talking about their dog’s toilet problems.
They just ramble on about it for ages.
These verbs are often used with the preposition “on.”
That’s because “on” often means “continuously” in phrasal verbs .
So when someone “drones on,” it means they just talk for ages about nothing in particular.
“You’re meeting Aunt Thelma this evening? Oh, good luck! Have fun listening to her drone on and on about her horses.”
Groan / Grumble / Moan
These words simply mean “complain.”
There are some small differences, though.
When you groan , you probably don’t even say any words. Instead, you just complain with a sound.
When you grumble , you complain in a sort of angry or impatient way. It’s not a good way to get people to like you.
Finally, moaning is complaining, but without much direction.
You know the feeling, right?
Things are unfair, and stuff isn’t working, and it’s all making life more difficult than it should be.
We might not plan to do anything about it, but it definitely does feel good to just … complain about it.
Just to express your frustration about how unfair it all is and how you’ve been victimised and how you should be CEO by now and how you don’t get the respect you deserve and …
Well, you get the idea.
If you’re frustrated with things, maybe you just need to find a sympathetic ear and have a good moan.
“Pietor? He’s nice, but he does tend to grumble about the local kids playing football on the street.”
Words for speaking unclearly in English
Mumble / murmur / mutter.
These verbs are all very similar and describe speaking in a low and unclear way, almost like you’re speaking to yourself.
Have you ever been on the metro or the bus and seen someone in the corner just sitting and talking quietly and a little madly to themselves?
That’s mumbling (or murmuring or muttering).
What’s the difference?
Good question!
The differences are just in what type of quiet and unclear speaking you’re doing.
When someone’s mumbling , it means they’re difficult to understand. You might want to ask them to speak more clearly.
Murmuring is more neutral. It might be someone praying quietly to themselves, or you might even hear the murmur of voices behind a closed door.
Finally, muttering is usually quite passive-aggressive and has a feeling of complaining to it.
“I could hear him muttering under his breath after his mum told him off.”

How can you tell if someone’s been drinking too much booze (alcohol)?
Well, apart from the fact that they’re in the middle of trying to climb the traffic lights holding a traffic cone and wearing grass on their head, they’re also slurring — their words are all sort of sliding into each other. Like this .
This can also happen if you’re super tired.
“Get some sleep! You’re slurring your words.”
Stammer / Stutter
Th-th-th-this is wh-wh-when you try to g-g-g-get the words ou-ou-out, but it’s dif-dif-dif-difficu-… hard.
For some people, this is a speech disorder, and the person who’s doing it can’t help it.
If you’ve seen the 2010 film The King’s Speech , you’ll know what I’m talking about.
(Also you can let me know, was it good? I didn’t see it.)
This can also happen when you’re frightened or angry or really, really excited — and especially when you’re nervous.
That’s when you stammer your words.
“No … I mean, yeah … I mean no…” Wendy stammered .
Other words for speaking in English
If you drawl (or if you have a drawl), you speak in a slow way, maaakiiing the voowweeel sounds loooongeer thaan noormaal.
Some people think this sounds lazy, but I think it sounds kind of nice and relaxed.
Some regional accents, like Texan and some Australian accents, have a drawl to them.
“He was the first US President who spoke with that Texan drawl .”
“Welcome to cowboy country,” he drawled .
Grrrrrrrrrrrrrr!
That’s my impression of a dog there.
I was growling.
If you ever go cycling around remote Bulgarian villages, then you’re probably quite familiar with this sound.
There are dogs everywhere, and sometimes they just bark.
But sometimes, before barking, they growl — they make that low, threatening, throaty sound.
And it means “stay away.”
But people can growl, too, especially if they want to be threatening.
“‘Stay away from my family!’ he growled .”
Using speaking verbs as nouns
We can use these speaking verbs in the same way we use “say.”
For example, if someone says “Get out!” loudly, we can say:
“‘Get out!’ he shouted .”
However, most of the verbs we looked at today are also used as nouns. (You might have noticed in some of the examples.)
For example, if we want to focus on the fact that he was angry when he shouted, and not the words he used, we can say:
“He gave a shout of anger.”
We can use these nouns with various verbs, usually “ give ” or “ let out .”
“She gave a shout of surprise.”
“He let out a bellow of laughter.”
“I heard a faint murmur through the door.”
There you have it: 30 alternatives to “say.”
So next time you’re describing your favourite TV show or talking about the dramatic argument you saw the other day, you’ll be able to describe it more colourfully and expressively.
Did you like this post? Then be awesome and share by clicking the blue button below.
8 thoughts on “ Words for Speaking: 30 Speech Verbs in English (With Audio) ”
Always enlighten and fun.. thank you
Great job! Thank you so much for sharing with us. My students love your drawing and teaching very much. So do I of course.
Good news: I found more than 30 verbs for “speaking”. Bad news, only four of them were in your list. That is to say “Good news I’m only 50 I still have plenty of time to learn new things, bad news I’m already 50 and still have so much learn. Thanks for your posts, they’re so interesting and useful!
Excellent. Can I print it?
Thanks Iris.
And yes — Feel free to print it! 🙂
Thanks so much! It was very interesting and helpful❤
Great words, shouts and barks, Gabriel. I’m already writing them down, so I can practise with them bit by bit. Thanks for the lesson!
Thank you so much for sharing with us. .It is very useful
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Learn New Words 5 Times Faster
Subscribe to our newsletter to get the eBook free!


The Top Characteristics Of A Good Speech
“I tell my story, not because it is unique, but because it is not. It is the story of many…

“I tell my story, not because it is unique, but because it is not. It is the story of many girls… Though I appear as one girl, one person, who is 5ft 2in tall, if you include my high heels, I am not a lone voice, I am many. I am Shazia. I am Kainat Riaz. I am Kainat Somro. I am Mezon. I am Amina. I am those 66 million girls who are out of school.”
The youngest-ever Nobel Prize winner, Malala Yousafzai, then 17, uttered these evocative words at her acceptance speech in 2014.
A good speech such as this one is provocative, inspiring and personal. It is structured to present a clearly defined message and convey the speaker’s ideas and thoughts.
At work, you may be asked to speak at meetings, seminars and conferences. These are important events in your professional career that will help you establish your credibility, and build your personal brand and professional network.
Learning how to deliver a good speech will equip you for career success. Let’s look at the characteristics of a good speech to push you in the right direction.
Characteristics Of A Good Speech
If you want to make a good speech that leaves a lasting impression, focus on what you’re going to speak and how. A good speech isn’t only about your words but also how you present yourself. Body language and gestures play a critical role in transforming an average speech into a memorable one.
If you’re wondering what a good speech is, here are some of its qualities:
Clear Message And Key Ideas
A good speech always starts with a key idea and a well-defined message. Many people make the mistake of burying their ideas in the middle or at the end. That’s a mistake. The audience may get distracted halfway into your speech, and leave without even knowing what you’re talking about. If you want people to understand your big idea, present it right at the start. That will set the context for the rest of the speech.
Impactful Oral Delivery
Remember to consider every aspect of the speech. Your oral delivery—pitch, pause and pace—also influences the audience’s response. ( klonopin ) Modulate your voice and pace to keep your listeners interested in your words. You should be also prepared to make impromptu adjustments to your delivery if you sense the audience drifting away. For instance, if you’re talking about statistical data, make it interesting by asking questions or engaging in a dialogue with the audience. This way, you keep them involved.
Sprinkled With Personal Anecdotes
Don’t rely only on facts and figures. If you can support your claims with personal experiences, it’ll make it more interesting. Start with a personal anecdote that’s linked to your big idea and that your audience can relate to. Humor is also a fun way to break the ice and put everyone at ease.
Informative, But Not Repetitive
Your speech needs to be informative and packed with fresh and new information to have an impact. Be careful not to recycle old ideas packaged in fancy words. . Being original and sharing relevant, critical and helpful information will make your speech memorable. Edit your speech carefully to ensure there are no repetitions or data gaps. You can also add inspiring quotes for a good speech.
Powerful Nonverbal Cues
One of the most important qualities of a good speech is nonverbal communication . You may believe that your words do all the work. But your posture, facial expressions and gestures are equally, if not more, important. Imagine someone making a speech with a blank expression on their face or just reading their words off a page without emotion. That doesn’t make for a good speech. It’s about building tension, asking provoking questions and engaging with the audience. There’s power in using nonverbal cues, like making eye contact with someone in the audience. Using these cues well can greatly improve the quality of your speech.
There are many more characteristics of a good speech that you can incorporate. Harappa Education’s Speaking Effectively course is designed for professionals who want to improve their communication skills. You can use these skills for public speaking or formal workplace conversations, to connect and empathize with others. Build meaningful connections, share ideas effectively, and deliver memorable speeches with our high-impact online course.
Explore topics & skills such as Public Speaking , Verbal Communication , Oral Communication , Speaking Skills & Oratory Skills from Harappa Diaries and learn to express your ideas with confidence.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13 Transitions: Bridging Ideas for a Seamless Presentation

Good transitions can make a speech more important to the audience because they feel they are being taken to a positive conclusion without having to travel a bumpy road. – Joe Griffith
Transitions
The difference between a novice speaker and an advanced speaker is in how they bridge the gap between ideas. Learning to use transitions effectively will help take your speaking to the advanced level. Transitions can be one word, a phrase, or a full sentence.
The audience is dying to know the relationship between ideas. Their brains are hard-wired for that. It’s more important when you are speaking than when you are writing because the listeners can’t go back – they have to get it when it happens. If the brain is bored, or gets tired because it’s overwhelmed, or gets confused – it can’t stay in that place, so it daydreams, creating its own interest. Speech Coach Max Dixon, Westside Toastmasters.
So, let’s get started. I have included various transition types for you to consider. These do little good if you read them and do not use them. This list works best if you read it now and then revisit it every time you write a speech.
- Let’s begin with…
- First, I’d like to share with you…
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- Our first stop is…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
The Order of Things
- After that…
- Next…
- Second thing…
- Our next stop is…
- Let me tell you about your next step.
Steve Jobs Commencement to Stanford University
Steve Jobs clearly previews his main points, “Today I want to tell you three stories from my life. That’s it. No big deal. Just three stories.” He flows smoothly between points with clear transitions.
- “The first story is about connecting the dots.”
- “My second story is about love and loss.”
- “My third story is about death.”
Watch Steve Jobs Stanford Commencement Address
Between Similar Points
- In the same way…
- In addition…
- Likewise…
- Similarly…
Between Disagreeing Points
- Conversely…
- Despite this…
- The flip side of the issue…
- However…
- On the contrary…
- On the other hand…
- On the other side …
- Yet, we cannot ignore …
- The opposing argument …
- If we examine the opposite side, we see …
Introduce an example
- This is best illustrated by an example…
- For instance…
- Take the case of…
- For example…
- To understand this…
- Let me illustrate this by…
Introduce Research
- To make the point…
- As illustrated by…
- Case in point…
- To solidify this point…
- As researched by…
Cause and effect
- Therefore…
- Thus…
- Consequently…
- As a result…
- This is significant because…
- Hence…
- Resulting in…
- For that reason …
- The effect is…
Elaboration
- Also…
- Besides…
- What’s more…
- In addition/additionally…
- Moreover…
- Furthermore…
Transition to a Demonstration
- Let me show you how this works…
- Let me demonstrate this…
- Now that we’ve covered the theory, let’s see it in action …
- Next, I’d like to let you see this for yourselves…
Introducing Your Visual
- As you can see from this chart…
- I’d like you to notice that…
- The table indicates…
Questions as Transitions
- Now that you know the problem, what do you think will solve it?
- What do you think will solve this crisis?

Connective: A word or phrase that connects the ideas of a speech and indicates the relationship between them.
Transitions: A word or phrase that indicates when a speaker had finished one thought and it moving on to another.
Internal preview: A statement in the body of the speech that tells the audience what the speaker is going to discuss next.
Internal summary: A statement in the body of the speech that summarizes the speaker’s preceding point or points.
Signpost: A very brief statement that indicates where a speaker is in the speech or that focuses attention on key ideas.
From the Art of Public Speaking by Stephen Lucas
THOUGHTS FROM A FORMER STUDENT
One thing I learned in class that made me a better speechwriter was to pay attention to the transitions. In our outlines, there was space for our main points, but also our transitions between them. At the beginning of the semester, I thought this was a waste of time planning out my transition for a speech and that I would just wing it the day of, but I soon realized how important they were. Transitions are like the finishing touches that make everything fall together in a speech.
You may have some interesting points or facts to give to your audience, but without transitions, you have nothing to connect your points and create a narrative. An audience is much more interested in a talk if there is a continuing idea or theme, and transitions help create this. I found this out by watching the other students in my class as they learned to use transitions as well. I loved the speeches that were clearly organized and had a common idea with transitions.
Zoe Lawless, Honors Public Speaking, University of Arkansas

Movement as Transition
Many people don’t think about movement as a type of transition, but it can be a very powerful way to help your audience transition between ideas.
- Setting out a visual or putting it away signals a change in ideas.
- Some speakers will imagine a baseball diamond laid out on the floor and move to each base throughout the speech. Their opening comment is at home plate. Point one is delivered on first, point two on second, and point three on third. They stand back on their home plate to deliver the final closing statements.
- One speaker that I met said he always has a special place that is his big idea place. He may move around during his speech but when he wants the audience to know it is an important point, he stands in the big idea place.
Silence as a Transition
John Chappelear, speech consultant, suggests that the use of silence can be powerful. It is powerful, but it is not easy. Being able to stand silently in front of a large audience for 15-45 seconds requires practice. Sometimes you can use silence as a way to let the audience catch up and think deeply about what you just said.
Transitioning Between Slides
- As the next slide shows…
- As you can see…
- Next, I will show you…
Transitioning to Visuals
- I’d like to direct your attention to…
- This diagram compares…
- Now, I’d like to illustrate this with…
Signaling the End is Near
- In conclusion…
- To sum it up…
- Lastly…
- In a nutshell…
- To recap…
- I’d like to leave you with…
- Finally, I’d like to say…
- The takeaway from all of this is…
- To summarise…

Moving to the Next Speaker
- I told you about the most credible theories about climate change, now John will share with you some examples of what you can do.
- I’m going to turn it over to Malachi, who will take you through the next few points.
- Next, Angie will come up and talk about…
- To help us understand this topic better, we have Beatrice, who will talk us through…
- Look to the next speaker and motion towards them as they walk to the podium, Twila will tell you more…
Problems with Transitions
These are some of the most common problems with transitions:
- Not planning out transitions and just “winging it.”
- Using fancy phrases inconsistent with the rest of the speech.
- Saying, “I have five points” and then having only four or miscounting the points.
- Overusing the same transitional phrase.
- Long pauses before transitions as the speaker tries to figure out what to say next.
Tricks on Smoothly Presenting Transitions
Now you have a list of ideas to use when you write your next speech, let’s talk about how to use transitions effectively. Speakers typically struggle as they end one point and seek to move to the next idea. This usually happens because of poor planning, not enough practice, and poor note management. Let’s talk about these one at a time. First, poor planning happens because a speaker does not put enough time and effort into writing the speech. Second, not enough practice happened because even when a speech is practiced, it is practiced with regards to getting through the main points and not about moving smoothly between points. Finally, poor note management. Let me give you some tricks.
- Make your notes large-larger than you think you need.
- Give ample space between main ideas so you can look down and see the gap and know another point is coming.
- On your notecards, make each main idea a different color.
- I usually have a “T” in a circle to remind me that this is a transition statement.
- Practice your speech twice by just reading the transition statements and the next sentence.
- The night before your speech, visualize how you will manage the transitions.
Key Takeaways
Remember This!
- Using transitions will help your speech flow smoothly.
- Practice using your transitions.
- Plan transitions for impact.
Please share your feedback, suggestions, corrections, and ideas.
I want to hear from you.
Do you have an activity to include? Did you notice a typo that I should correct? Are you planning to use this as a resource and do you want me to know about it? Do you want to tell me something that really helped you?
Click here to share your feedback.
Allgood, E., & Ebersole, T. (Eds.). (2017). C OMM 2100 public speaking: A workbook for student success . Fountainhead Press.
Beqiri, G. (2018). Speech transitions: Words and phrases to connect your ideas. https://virtualspeech.com/blog/speech-transitions-words-phrases
Dugan, A. (2013, August 26). Speech transitions: Magical words and phrases. http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/speech-transitions/
Effective speech transitions, how to make your speech flow. https://franticallyspeaking.com/effective-speech-transitions-how-to-make-your-speech-flow/
Jobs, S. (2005). Steve Jobs commencement address to Stanford University. [Video]. YouTube. https://news.stanford.edu/2005/06/14/jobs-061505/ Standard YouTube License.
Lawless, Z. (2020). Honors Public Speaking, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville. Used with permission.
Lucas, S.E. (2009). The art of public speaking. McGraw Hill.
Pace, P. (n.d). Bridge the gap–Speech transitions. https://westsidetoastmasters.com/article_reference/bridge_the_gap-speech_transitions.html#:~:text=%22I%20think%20body%20movement%20is,carries%20the%20audience%20with%20him.
Media Attributions
- Sitting on bridge © Alex Azabache is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- karine-avetisyan-ipuiM-36tAg-unsplash © Karine Avetisyan is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- haniel-espinal-Oy9KX9NsDeU-unsplash © Haniel Espinal is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Panel_discussion_at_Wikipedia_Day_2019 © Eric Luth is licensed under a CC BY-SA (Attribution ShareAlike) license
Advanced Public Speaking Copyright © 2021 by Lynn Meade is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Speech transitions: words and phrases to connect your ideas
June 28, 2018 - Gini Beqiri
When delivering presentations it’s important for your words and ideas to flow so your audience can understand how everything links together and why it’s all relevant.
This can be done using speech transitions because these act as signposts to the audience – signalling the relationship between points and ideas. This article explores how to use speech transitions in presentations.
What are speech transitions?
Speech transitions are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified.
This makes it easier for the audience to understand your argument and without transitions the audience may be confused as to how one point relates to another and they may think you’re randomly jumping between points.
Types of transitions
Transitions can be one word, a phrase or a full sentence – there are many different types, here are a few:
Introduction
Introduce your topic:
- We will be looking at/identifying/investigating the effects of…
- Today I will be discussing…
Presentation outline
Inform the audience of the structure of your presentation:
- There are three key points I’ll be discussing…
- I want to begin by…, and then I’ll move on to…
- We’ll be covering… from two points of view…
- This presentation is divided into four parts…
Move from the introduction to the first point
Signify to the audience that you will now begin discussing the first main point:
- Now that you’re aware of the overview, let’s begin with…
- First, let’s begin with…
- I will first cover…
- My first point covers…
- To get started, let’s look at…
Shift between similar points
Move from one point to a similar one:
- In the same way…
- Likewise…
- Equally…
- This is similar to…
- Similarly…

Shift between disagreeing points
You may have to introduce conflicting ideas – bridging words and phrases are especially good for this:
- Conversely…
- Despite this…
- However…
- On the contrary…
- Now let’s consider…
- Even so…
- Nonetheless…
- We can’t ignore…
- On the other hand…
Transition to a significant issue
- Fundamentally…
- A major issue is…
- The crux of the matter…
- A significant concern is…
Referring to previous points
You may have to refer to something that you’ve already spoken about because, for example, there may have been a break or a fire alarm etc:
- Let’s return to…
- We briefly spoke about X earlier; let’s look at it in more depth now…
- Let’s revisit…
- Let’s go back to…
- Do you recall when I mentioned…
This can be also be useful to introduce a new point because adults learn better when new information builds on previously learned information.
Introducing an aside note
You may want to introduce a digression:
- I’d just like to mention…
- That reminds me…
- Incidentally…
Physical movement
You can move your body and your standing location when you transition to another point. The audience find it easier to follow your presentation and movement will increase their interest.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Emphasising importance
You need to ensure that the audience get the message by informing them why something is important:
- More importantly…
- This is essential…
- Primarily…
- Mainly…
Internal summaries
Internal summarising consists of summarising before moving on to the next point. You must inform the audience:
- What part of the presentation you covered – “In the first part of this speech we’ve covered…”
- What the key points were – “Precisely how…”
- How this links in with the overall presentation – “So that’s the context…”
- What you’re moving on to – “Now I’d like to move on to the second part of presentation which looks at…”

Cause and effect
You will have to transition to show relationships between factors:
- Therefore…
- Thus…
- Consequently…
- As a result…
- This is significant because…
- Hence…
Elaboration
- Also…
- Besides…
- What’s more…
- In addition/additionally…
- Moreover…
- Furthermore…
Point-by-point or steps of a process
- First/firstly/The first one is…
- Second/Secondly/The second one is…
- Third/Thirdly/The third one is…
- Last/Lastly/Finally/The fourth one is…
Introduce an example
- This is demonstrated by…
- For instance…
- Take the case of…
- For example…
- You may be asking whether this happens in X? The answer is yes…
- To show/illustrate/highlight this…
- Let me illustrate this by…
Transition to a demonstration
- Now that we’ve covered the theory, let’s practically apply it…
- I’ll conduct an experiment to show you this in action…
- Let me demonstrate this…
- I’ll now show you this…
Introducing a quotation
- X was a supporter of this thinking because he said…
- There is a lot of support for this, for example, X said…
Transition to another speaker
In a group presentation you must transition to other speakers:
- Briefly recap on what you covered in your section: “So that was a brief introduction on what health anxiety is and how it can affect somebody”
- Introduce the next speaker in the team and explain what they will discuss: “Now Gayle will talk about the prevalence of health anxiety.”
- Then end by looking at the next speaker, gesturing towards them and saying their name: “Gayle”.
- The next speaker should acknowledge this with a quick: “Thank you Simon.”
From these examples, you can see how the different sections of the presentations link which makes it easier for the audience to follow and remain engaged.
You can tell personal stories or share the experiences of others to introduce a point. Anecdotes are especially valuable for your introduction and between different sections of the presentation because they engage the audience. Ensure that you plan the stories thoroughly beforehand and that they are not too long.
Using questions
You can transition through your speech by asking questions and these questions also have the benefit of engaging your audience more. There are three different types of questions:
Direct questions require an answer: “What is the capital of Italy?” These are mentally stimulating for the audience.
Rhetorical questions do not require answers, they are often used to emphasises an idea or point: “Is the Pope catholic?
Loaded questions contain an unjustified assumption made to prompt the audience into providing a particular answer which you can then correct to support your point: You may ask “Why does your wonderful company have such a low incidence of mental health problems?”.
The audience will generally answer that they’re happy. After receiving the answers you could then say “Actually it’s because people are still unwilling and too embarrassed to seek help for mental health issues at work etc.”

Transition to a visual aid
If you are going to introduce a visual aid you must prepare the audience with what they’re going to see, for example, you might be leading into a diagram that supports your statement. Also, before you show the visual aid , explain why you’re going to show it, for example, “This graph is a significant piece of evidence supporting X”.
When the graphic is on display get the audience to focus on it:
- The table indicates…
- As you can see…
- I’d like to direct your attention to…
Explain what the visual is showing:
- You can see that there has been a reduction in…
- The diagram is comparing the…
Using a visual aid to transition
Visual aids can also be used as transitions and they have the benefit of being stimulating and breaking-up vocal transitions.
You might have a slide with just a picture on it to signify to the audience that you’re moving on to a new point – ensure that this image is relevant to the point. Many speakers like to use cartoons for this purpose but ensure its suitable for your audience.
Always summarise your key points first in the conclusion:
- Let’s recap on what we’ve spoken about today…
- Let me briefly summarise the main points…
And then conclude:
If you have a shorter speech you may choose to end your presentation with one statement:
- In short…
- To sum up…
- In a nutshell…
- To summarise…
- In conclusion…
However, using statements such as “To conclude” may cause the audience to stop listening. It’s better to say:
- I’d like to leave you with this…
- What you should take away from this is…
- Finally, I want to say…
Call to action
Requesting the audience to do something at the end of the presentation:
- You may be thinking how can I help in this matter? Well…
- My aim is to encourage you to go further and…
- What I’m requesting of you is…
Common mistakes
When transitions are used poorly you can annoy and confuse the audience. Avoid:
- Using transitions that are too short – transitions are a key part of ensuring the audience understands your presentation so spend sufficient time linking to your next idea.
- Too many tangents – any digressions should still be relevant to the topic and help the audience with their understanding, otherwise cut them out.
- Incompatible transitions – for example, if you’re about to introduce an example that supports your statement you wouldn’t introduce this by saying “but”. Use transitions that signify the relationship between points.
- Over-using the same transition because this is boring for the audience to hear repeatedly. Ensure that there is variety with your transitions, consider including visual transitions.
- Miscounting your transitions – for example, don’t say “first point”, “second point”, “next point” – refer to your points consistently.
Speech transitions are useful for unifying and connecting your presentation. The audience are more likely to remain engaged since they’ll be able to follow your points. But remember that it’s important to practice your transitions beforehand and not just the content of your arguments because you risk looking unprofessional and confusing the audience if the presentation does not flow smoothly.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Remarks by President Biden and Prime Minister Kishida Fumio of Japan at State Dinner
8:06 P.M. EDT
PRESIDENT BIDEN: Tonight, we celebrate the alliance between Japan and the United States.
And Jill and I are honored to have you all here, including so many members of the Japanese-American community. And we’d like to extend a particular welcome to President Clinton and Secretary Clinton, who’ve joined us this evening. (Applause.)
Mr. Prime Minister, Mrs. Kishida — Kishida, thank you for looking forward to this visit for a while. We’ve been anxious for you to come. I’m delighted you’re here. And, you know, even the cherry blossom bloomed early in anticipation of your — (laughter). Well, they did, by the way. They really did.
And all of us — as you all know, those blossoms are the first sign of spring has arrived, and they remind us that we can begin anew every year and tomorrow can be a better day than today. It’s a symbol of both our countries — what h- — what b- — what both our countries hold dear: new beginnings.
So, thank you, again, for being here.
And a few days after my inauguration over three years ago, I received a big, shiny, blue-and-red envelope covered with stickers on the envelope. It was a big envelope. And it was full of letters from an elementary school teacher in Japan who compiled them from her students. She teaches children who stutter, like I did as a child. And she wanted th- — me to know that when she told them — her class about — that I had a similar liability at the time, the kids lit up, smiling, and they said, “We’re the same. We’re the same.”
Well, we are the same, Japan and the United States. Many — we may be divided by distance, but the — generations after generation, we’ve been brought together — the same hopes, the same values, the same commitment to democracy and freedom and to dig- — dignity for all.
And today, without question, our alliance is literally stronger than it has even been. This was both not inevitable, but it was also — the fact is that both the Prime Minister and I came of age as our countries were — as they came together. We both remember the choices that were made to forge a friendship that were once only a devastating — a fight that existed before.
We both remember that hard work, what it has done to find healing, and where there was once such hardship. We both remember Japanese and American people who not only brought us together but who brought us forward, transforming our relationship for better — from bitter foes to the best friends we could be.
Tonight, we pledge to keep going. We stand at an inflection point where the decisions we make now are going to determine the course of the future for decades to come, a future that the kids of our two families and children in all of our two countries will remember.
But I also know that Japan and the United States stand together — and everyone should know that as well — committed to each other and committed to keeping — building a future worthy of the highest hopes and — that — of our predecessors and our people have dreamed of.
Ladies and gentlemen, so please join me in raising your glass — and I don’t have a glass. Neither do you. (Laughter.)
(An aide brings glasses for the President and Prime Minister.)
There you go. Do you have one for the Prime Minister?
PRIME MINISTER KISHIDA: Thank you.
PRESIDENT BIDEN: Join me in raising your glasses to our alliance, to our friendship, and, in the words of those young students in Japan, to the same future we share. Cheers.
(President Biden offers a toast.)
AUDIENCE: Cheers.
PRESIDENT BIDEN: I turn it over to you, Mr. Prime Minister.
Mr. Prime Minister.
PRIME MINISTER KISHIDA: Thank you.
Mr. President, Dr. Biden, distinguished guests, and ladies and gentlemen, I would like to express my heartfelt gratitude to you for hosting such a wonderful dinner and your warm welcome and hospitality.
Before I came here, my protocol staff told me that no one had ever complained that my speech was too short. (Laughter.) This is probably good advice. So, I’ll keep my speech short. (Laughter.)
First and foremost, to be honest, my breath is taken and I’m speechless in front of such a huge number of prominent American and Japanese guests. My wife, Yuko, also left breathless, just told me that it was hard to tell who the guest of honor is. (Laughter.) So, I was relieved when I was shown the seat right next to the President. (Laughter.)
Last year, President Biden and Dr. Biden visited my hometown of Hiroshima to attend the G7 summit meeting. It is a little-known fact that the largest number of Japanese immigrants to the United States came from Hiroshima. Many Hiroshimans headed to the United States to seek a new world, a better future, and greater heights.
Mr. President, I know that the late Senator Daniel Inouye was a good friend of yours.
PRESIDENT BIDEN: He was.
PRIME MINISTER KISHIDA: His mother was also from Hiroshima.
Looking back at the long history of Japan and the United States, our predecessors have carved out the path in various fields, such as business, academia, art, and sports, traveling back and forth between the two countries.
“The Pacific Ocean does not separate Japan and the United States. Rather, it unites us.” These were the words that President Kennedy sent to Prime Minister Ikeda, also hailing from Hiroshima, at the state luncheon held at the White House about 60 years ago.
I like this line. I — I use it so many times that my staff tried deleting it — (laughter) — whenever this phrase appeared on speech drafts. However, there is nothing that expresses our relationship as visibly as this. And never have these words been more relevant than today. Japan and the United States are united than ever before. (Applause.)
I believe that the Pacific Ocean has brought Japan and the United States together and so close because of the pioneering spirit of those who came before us and frontier spirit that we all have in common. The success of those standing on the frontier is not just because of their individual efforts but also the result of collective efforts as a team. This hol- — this holds true even between nations.
Our joint efforts are (inaudible) indispensable for our bright future and for the peace and stability of the world. We are now standing at a turning point in history, embarking on a new frontier and elevate this unshakable Japan-U.S. relationship to even greater heights and hand it to the next generation.
And, finally, let me conclude with the line from “Star Trek” — (laughter) — which you all know: “To boldly go where no one has gone before.” (Laughter and applause.)
By the way, George Takei, who played Hikaru Sulu, the helmsman of the USS Enterprise, also has roots in Hiroshima. (Laughter and applause.)
Mr. President, Dr. Biden, distinguished guests, and ladies and gentlemen, I would like to propose a toast to our voyage to the frontier of the Japan-U.S. relationship with this word: “boldly go.”
PRESIDENT BIDEN: Hear, hear.
PRIME MINISTER KISHIDA: And “boldly go.” Cheers.
(Prime Minister Kishida offers a toast.)
PRESIDENT BIDEN: Good job.
8:17 P.M. EDT
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
JFK, Dick Goodwin, and a speech that would be remembered in history
These words, “the city upon a hill,” delivered more than three centuries before, are how john kennedy’s farewell to massachusetts would be remembered in history..

The following is an excerpt from historian Doris Kearns Goodwin’s book, “ An Unfinished Love Story: A Personal History,” which will be published April 16. You can also hear Goodwin discuss her book on this week’s episode of “Say More with Shirley Leung.”
JAN. 9, 1961
John Kennedy’s first speech as president-elect was scheduled for the Boston State House 11 days before his Washington inauguration. Since Kennedy’s chief speechwriter, Ted Sorensen, was at work on the inaugural, Kennedy tasked his junior speechwriter (and my future husband) Dick Goodwin to begin drafting the Boston speech. By this point, having come through the primaries and the election, Dick had learned to decipher Kennedy’s manner of giving directives, however indirect or roundabout:
Advertisement
“I was always fond of [Abraham] Lincoln’s goodbye to his fellow townsmen in Springfield, Illinois,” Kennedy had remarked. “It’s from his heart, and it’s short. That’s important.”
“But, Dick,” he concluded with a nod and a smile, “less God.”

Dick set to work reading and rereading Lincoln’s adieu until he had committed it to memory. In the decades that followed, he would often recite Lincoln’s “Farewell Address,” along with choice passages from Shakespeare, Robert Service’s “The Cremation of Sam McGee,” Ralph Waldo Emerson’s “Concord Hymn” with its “shot heard round the world,” “Casey at the Bat,” Edward Lear’s “Owl and the Pussy-cat,” and countless others. Whenever he saw fit, Dick would draw from his wide and eclectic repertoire and declaim in his sonorous voice — whether at the ballpark, on walks with me, at our favorite bar, or simply waking up in our bedroom to greet the day.
“My friends,” Lincoln began from the train platform as he set forth on Feb. 11, 1861, for a 12-day journey to Washington. “No one, not in my situation, can appreciate my feeling of sadness at this parting. To this place, and the kindness of these people, I owe everything. Here I have lived a quarter of a century, and have passed from a young to an old man. Here my children have been born, and one is buried. I now leave, not knowing, when, or whether ever, I may return, with a task before me greater than that which rested upon Washington. Without the assistance of that Divine Being, who ever attended him, I cannot succeed. With that assistance I cannot fail.”
The historian Arthur Schlesinger had forwarded a memo to Kennedy suggesting an excerpt from John Winthrop’s sermon to his shipmates on the flagship “Arabella” as they landed in New England, facing the task of building a new government on a perilous new frontier. “We must always consider that we shall be a city upon a hill — the eyes of all people are upon us.” These words, “the city upon a hill,” delivered more than three centuries before, are how John Kennedy’s farewell to Massachusetts would be remembered in history.
It was an emotional speech to write. If it was a nostalgic farewell for Kennedy, it was a trip down memory lane for Dick as well. Massachusetts was Dick’s home, the place where he was born, the place he went to college and law school, the place where his mother and brother still lived. Kennedy had often joked with Dick that they were two Brookline boys. Both had deep emotional investments in Massachusetts.

The night before his address to the State House, Kennedy slept in his old apartment on Bowdoin Street where Dick had first met him during the spring of 1958. The tiny apartment — across from the State House and next to the Bellevue Hotel where local politicians gathered — had been Kennedy’s official Boston residence since his first run for Congress 12 years earlier. A kind of introductory interview had been arranged by Sumner Kaplan, the state representative from Brookline who had championed Dick’s first forays into politics during a rent control struggle and a fight to prevent discrimination in local fraternities and sororities.
A few days after this short Bowdoin Street encounter, Dick wrote his best college friend, George Cuomo:
“I recently had an interesting meeting with Senator Kennedy when he was in Boston. He intimated strongly that he would like to have me come to work for him next January after he finishes running for re-election for Senate.
“However, even if he wants me to work — and this is not at all certain — I am not sure. Work for him, no matter how interesting, is bound to be a sort of dead end for one so young.”
“I bet it didn’t seem such a dead end that morning of January 9th,” I remarked.
“Anything but,” Dick said. “I had changed a lot in those last two years and so had he.”
Despite the bitter cold morning, loud hurrahs and screams of hundreds of people greeted Kennedy as he emerged from his apartment at 10 a.m. before crossing the Charles River to attend a meeting of the Harvard Board of Overseers. There, an equally enthusiastic crowd trailed him through Harvard Yard. “Speech, speech,” they cried. Grinning as he climbed the steps to University Hall, Kennedy jested, “I am here to go over your grades with President Nathan Pusey, and I’ll protect your interests.” That touched off an explosion of applause. After lunch with the overseers, Kennedy spent the afternoon at Arthur Schlesinger’s house where he met with a small group of professors.

He then returned to the great domed Bulfinch building for his address to the joint session of the Legislature. Following ancient tradition, two sergeants-at-arms — in frock coats and top hats, carrying white and gold maces, were granted permission from the presiding officer to admit the president-elect. He had briefly addressed this body only once, 15 years before as a decorated Navy hero, accompanied by his grandfather and the former Boston mayor, John Francis Fitzgerald.
The president-elect was in “a nostalgic mood” as he began his speech. “For 14 years I have placed my confidence in the citizens of Massachusetts. … For 43 years — whether I was in London, Washington, the South Pacific, or elsewhere — this has been my home; and God willing, wherever I serve, this shall remain my home. It was here my grandparents were born — it is here I hope my grandchildren will be born.”
On the draft of the speech, Kennedy had made several annotations, crossing out and inserting new words. Those small changes revealed a huge shift in perspective. They delineate an astute distinction between the days before the election and the day after. No longer was he placing his confidence in the voters, as the draft had read, but rather in the citizens. He was not asking for votes. There were no sides now. We were all working together.
This tribute from a native son produced tumultuous applause in the packed chamber. His delivery barely resembled the clipped voice from the early primaries, and his leisurely pace was not that of the candidate who had raced through his talks as if he were a young student giving a report, anxious to get back to his seat. This was the president-elect returning to his home state, channeling Abraham Lincoln, promising that as he created his new administration, he would be guided by John Winthrop’s recognition that “we shall be as a city upon a hill — the eyes of all people are upon us.”
And then he turned to the future, to the hope that when “the high court of history” came to sit in judgment of his administration, it would note that he had surrounded himself with men of courage, judgment, integrity, and dedication.
“These are the qualities which, with God’s help, this son of Massachusetts hopes will characterize our government’s conduct in the four stormy years that lie ahead,” Kennedy concluded. “I ask for your help and your prayers, as I embark on this new and solemn journey.”
Abraham Lincoln never came back to live in Springfield. Nor would John Fitzgerald Kennedy return to reside in Boston.
Excerpted from “ An Unfinished Love Story: A Personal History ” by Doris Kearns Goodwin. © 2024 by Doris Kearns Goodwin. Reprinted by permission of Simon & Schuster, Inc. All Rights Reserved.

Globe Opinion
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.
How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
A mexican drug cartel is targeting seniors and their timeshares..
This transcript was created using speech recognition software. While it has been reviewed by human transcribers, it may contain errors. Please review the episode audio before quoting from this transcript and email [email protected] with any questions.
Hello, James.
Hey. How’s it going?
Yeah. I’m not having much luck. So the problem is funding. And all of my money is in Mexico, all of it.
From “The New York Times,” I’m Katrin Bennhold. This is “The Daily.” A massive scam targeting elderly Americans who own timeshare properties has resulted in hundreds of millions of dollars sent to Mexico.
Once you move forward and make your payment, if anything were to happen, he will directly pay you the full amount of what you’re entitled to, including the gains. He will pay you the full amount.
You’ve got all my money. It’s been sent. I sold a freaking house.
Listen to this. I sold a house that I grew up in so that I could come up with funds to send to Mexico.
I don’t even have anything from the sale, nothing.
My colleague Maria Abi-Habib on one victim who lost everything and the people on the other side of the phone.
That’s it. That’s it. There’s nothing —
You know what? That’s what has been said every freaking time. Every time, just pay this. That releases the funds.
But that’s why we won’t allow it to happen again. This is the last time, James.
It’s Friday, April 12.
Maria, you’ve been looking into this scam that’s targeting Americans. Where did your investigation start?
So several weeks ago, I received a phone call from a lawyer based in St. Petersburg, Florida, who had been contacted by a family who was very concerned that the father, this man named James, was in the middle of being scammed. He’d sent hundreds of thousands dollars to Mexico. And he was considering sending another $157,000 when his daughter decided to call up this law firm and try to get her father to stop, stop sending money to Mexico.
So I called him a few weeks ago as I was trying to understand what was going on.
Hi, James. How are you?
Good. Thank you.
He’s asked that his last name be withheld for privacy concerns because he’s quite embarrassed about the story that I’m about to tell you.
You’re retired now, but what were you doing for work? And if your wife was working, what was her job?
I was with the Highway Patrol.
James is a retired state trooper from California. And his wife Nikki is a former school nurse.
She was born in ‘51. So 71-ish.
Two. She’s just reminded me, 72.
And they’re both in their early 70s. And they own this timeshare that is in Lake Tahoe, California. And they bought it in the 1990s for about $8,000.
And for someone who did not grow up vacationing in a timeshare, remind me how exactly timeshares work.
Timeshares are essentially vacation properties. And they tend to be beach resorts. And multiple people can buy into this property. The ownership is a shared ownership. And this gives you the right to use the timeshare for one to two weeks out of every year.
And so James and Nikki used their timeshare every other year with their daughters. But as they hit retirement age and their daughters are growing up and starting their own families, they’re just not really using it that much anymore. And timeshares require the owners to pay off yearly maintenance fees. And so they’re starting to think about maybe letting go of their timeshare and selling it.
Then one day, in late 2022, James gets a phone call from a company that is purporting to be based out of Atlanta, Georgia called Worry Free Vacations.
Worry Free Vacations?
That sounds enticing.
Yeah. And they start off with a simple question, which is, do you want to buy a timeshare? And James says, I already have a timeshare. And then they say, great. Well, what about selling the timeshare? Do you want to sell? There’s this Mexican businessman, and he’s interested in your timeshare. And he’s willing to buy it for about $20,000.
So we figured, well, what the heck? If we can make a few bucks on it, we’ll go for it.
And James jumps at the opportunity.
And did he do anything to try and verify that this was real?
Yeah. So remember, James is former law enforcement. And he feels very confident in his abilities to sniff out untrustworthy people. So he goes online, and he googles this Mexican businessman and sees that, yeah, he is a real person.
He’s a very well-respected individual in Mexico, very well off. And —
And this makes James feel at ease, that he’s selling to a legitimate person, that Worry Free Vacations are who they claim to be and that he’s going to double his money overnight, essentially.
And what happens next?
Well, a couple of weeks after he makes the agreement with the buyer, he’s told that he needs to send a couple thousand dollars to facilitate the purchase.
What does that mean, facilitate?
[MUSIC PLAYING]
I can’t remember specifically whether it was supposed to be cross-border registration —
So he’s being told that there are these fees that are paid directly to the Mexican government.
Or SPID or some other fee that was Mexican government required or not.
A lot of these fees are the same types of fees that you would pay in the United States for a real estate transaction. So he begins wiring money to an account in Mexico.
After that —
— a few days later, we get a notification. Well, everything went well, except that we have to pay an additional fee.
Every time that he sends one fee, he’s being told that he’s got to send another fee right afterwards.
Does he get suspicious at any point?
His wife is suspicious. After the first couple of payments, she starts saying, this does not feel right.
But James is the former law enforcement officer, right? And he’s the one that basically handles the family finances. And he’s confident that all of this is going to work out because he’s being told that the buyer of the timeshare will reimburse James for all of these fees once the sale goes through.
Michael from the Worry Free Vacations was constantly reassuring me the money’s in that account. Check with the commercial escrow account. It’s there. It’s just these fees have to be paid, and you’re being reimbursed for all of this.
They’re sending James documents that show all of the reimbursements that he’s owed and how much money he’s going to get. And this just makes him feel like all of this is kosher.
We have this commercial escrow company that was involved out of New York. So there was an air of legitimacy that I was comfortable with.
Maybe OK, these guys just need one more fee and everything is going to finally be cleared.
But about a year in, James starts to get suspicious. He begins asking questions because he wants his money.
And every time I asked, hey, is there a way I can get a partial release of these funds, there was always no, these funds have to be paid from your account before they’re released.
But Worry Free Vacations, they pivot. And they tell him that, listen, there are all these complications. It’s going to be really hard to get your money out from this transaction.
I could pay about $30,000 and change to reinvest the $313,000 into an environmentally-conscious development in Loreto, Mexico.
Instead, we’ve got this other investment opportunity in Mexico.
And I’m sure you know where that is, over on the East Coast of Baja.
And that is going to make you a huge return, even more money than you had thought that you were going to make, much more than the $20,000.
I’m supposed to have 54 million pesos in a Mexican bank account.
So this is now no longer just about his timeshare. They are now partners in a real estate investment.
Right. And there’s this whole new round of fees and fines associated with that.
So how many payments would you say?
Quite a few. Couple dozen at least, maybe more.
When was your last payment?
It would have been 17 January.
Uh-huh. And what was that for?
Good question.
And all along, he believed it was necessary to pay these costs just to get the money that he’s owed.
The amount of money that I’ve sent to Mexico is just freaking exorbitant. And I mean, it is approaching $900,000 or more.
And at this point, he’s sent about $900,000 to Mexico over about a year and a half.
Nearly $1 million.
That was almost all the money that he and his wife had saved for their retirement.
It also included money from the sale of James’s childhood home and money that he had borrowed from his daughter and son-in-law, about $150,000 from them.
It’s awful. So they were completely cleaned out by these guys.
Yeah. And this is when his daughter asks a law firm to look into this, which is the point in the story when I meet James. And when we start talking, it was clear to me that he just did not know what to think, even after losing this much money.
So this started in 2022. When did it end?
We’re still in it.
And he’s still talking to the scammers.
And as a matter of fact, presently, there was a request for $157,000 and change to clear up this whole thing. It would clear the entire issue out. Now —
And James is even considering putting a second mortgage on his house to send that money that he’d been promised would finally clear all this up — one final payment of $157,000.
It really sounds like he’s still wanted to believe that this was somehow legit.
Yeah. It was pretty clear to me that he was being scammed. But I didn’t definitively know what was going on, so I asked him if he could start recording his phone calls with the scammers.
Would you be so kind as to do me a favor?
Would you be willing to give them a call and record them?
[LAUGHS]: I’ll let you in on a little secret. I’ve been recording them.
And it turns out he already had been.
Worry Free Vacations.
So he shared the recordings of these calls that he’d had with these scammers over the last year or so. And it was just remarkable. It gave me huge insight into how the scam worked and the way that it sounded over the phone.
Is this is Michael in? I think he’s trying to call me. I couldn’t get through pick up.
Yes, I believe he did try to call you, sir. Give me a second. I think he’s only going to be in for a couple of minutes. One second.
There are two main takeaways for me listening to these calls.
Good afternoon. Michael McCarthy.
Michael, I missed your call. I was trying to pick up.
Yeah, don’t worry. Yeah, I figured something was wrong with your phone. Everything OK?
The first is that these scammers had really gotten to know James so well, and they really made James believe that Worry Free was a company that was working for him.
That’s why we need to hurry up and get this money over to you. Because hey, I’m losing my mind too. I’m not even here to convince you, James. I’m not — I’m your broker, and —
One of the things they continuously say is, trust me.
Look, I’m doing everything I can in my power and will on my end. So James, just look — like I told you from the get-go, I’m going to resolve this. And we are doing it. I just need you to focus on the goal.
They would refocus the conversation on what James needed to do to get his money back.
Look, if you make your payment as a security deposit, right away they will release the funds to you. With these —
And the other thing —
I’ve been having so much trouble trying to reach you, and I have not been successful.
— is that the scammers had created this elaborate cast of characters.
Why don’t you answer my calls?
And some of them were really aggressive. James shared a recording of this one man who claimed to be an agent for the Mexican government. And he basically started yelling at James.
I don’t care if your wife is at the hospital. To be honest with you, I don’t give a damn! But you know where I do give a damn? It’s your money, and my name is written all over it! Do you understand?
And he even threatened James. If James didn’t pay off these fines, then he would lose all the money that he’d sent to Mexico already.
You could get the best lawyer you want. You could get whoever you want. And this is not a threat. This is facts. But anyways, who am I to convince you, right?
Well, thank you for the information. And — are you still there? Hello?
Wow. So these scammers were basically doing a good cop, bad cop routine to stop James from walking away and to squeeze every last penny out of him.
If you provide me your email, contact information, I will certainly be happy to forward all of the wire transfer information from my bank account to you so that you can see where those funds went.
Yeah, that would be great. I have your email.
James asks me, a reporter who’s based in Mexico, who speaks the language, if I could help him figure out where his money had gone to.
Thank you very much. I really appreciate your assistance.
I’m just doing my job. Thanks again, and we’ll talk soon.
And the only way that I could figure that out was to understand who was on the other side of the phone.
We’ll be right back.
So Maria, who was on the other side of that phone line?
So by the time that I’d met James, I’d already gotten a tip from US law enforcement agencies that they were seeing a new trend. Mexican drug cartels were getting involved in the timeshare scam industry.
Drug cartels?
Yeah. And not just any drug cartel. This is one of the most notorious, violent, bloody drug cartels that exists in Mexico and Latin America, the Jalisco New Generation cartel. And when I looked at James’s bank records, guess what? All the money that he was sending was going to various bank accounts that were all located in Jalisco state in Mexico.
Wow. So why would the drug cartels get into the timeshare scamming business?
It is a huge business. The FBI told me that it’s about $300 million in profits over the last five years.
But the thing is is that the potential for it to actually be multitudes more is huge. Because the FBI estimates that most of the scams are actually not even reported. In fact, only about 20 percent are. So that means the total timeshare scam business could actually be much larger than the $300 million that they have knowledge of over the last five years.
But wait. I thought the drug business was a pretty lucrative business in itself. So why get into the scamming of elderly people for their properties in Lake Tahoe?
Well, you have to remember that these drug cartels, they’re not just doing one thing. They’re doing multiple things. They’re essentially conglomerates. Because it’s really expensive to run a cartel. You need to pay off officials, both Mexican and American. You need to maintain basically an army in order to secure your routes up to the United States, ports of entry into Mexico from Colombia. And any big business, you need to diversify your income to make sure that you keep the money flowing. Because you never know when one business is going to be shut down by authorities or taken over by your rivals.
We’ve reported that they’re now in the avocado business and the construction business. And timeshare fraud is basically no different than any of those. So we’re seeing that the cartels have their fingers in many pies, the legitimate and the illegitimate economy here in Mexico.
It’s kind of fascinating to think of these drug cartels as like sprawling diversified business empires. But when did the cartels first get into the scamming business?
So Jalisco New Generation started about 15 years ago.
And when they started to consolidate their empire in Jalisco state, they found that there were all these scam timeshare call centers all over the state that were being run by various players, and that this was a huge, huge moneymaker. Because essentially, all you have to do is call up retired senior citizens in the US and Canada. It doesn’t take that much money to run that kind of a scheme. There’s no product you’re making.
So essentially, they conducted a hostile takeover of these call centers. They went in. They kicked down doors and dragged out the people who were managing these call centers by their hair and threatened to kill them unless they gave up the call centers or started handing over a cut of what they made. And slowly, slowly Jalisco New Generation cartel took over the entire timeshare fraud industry.
Interesting. Were you able to find any of these call centers?
So these call centers are pretty hard to find. They look like any other storefront. But I was able to visit two that were located in an upscale neighborhood in Guadalajara, which is the capital of Jalisco state. And it was just really perturbing because it was just so normal. Two villas about a mile away from each other outside. Outside of one villa, parents were walking by, holding their children’s hands as they did drop off at school.
It was right next to a park where people taking their morning exercise or their dogs for a walk. There was no real sign that the cartel was doing business there. But a few months before, Mexican law enforcement had found the bodies of eight young people who had used to work at one of these call centers and said that the Jalisco cartel had killed them.
Wow. What happened?
So I wasn’t able to talk directly to any of the victims’ families. They’re just too scared. But in general, this is usually how it starts.
The cartel seeks out English speakers to work for their call centers. Sometimes they don’t even tell them what exactly they are doing. They would tell the recruits that the job was adjacent to the hotel industry.
You have to remember, Jalisco is a huge, huge tourism magnet for Americans and Canadians and others. And the cartel would get their call lists from bribing hotel employees to give them the names of people who stayed at these hotels and also at the timeshare resorts. And the people who would work at the call centers are provided the names and a manual of what you need to do when you call, like a loose script of how to try to suck as much money as you can out of these people up North in Canada and the States.
So we don’t know for sure what exactly happened with the eight young Mexicans who were killed last year. But through an intermediary, one sibling told us that when their family member knew what their job actually was, they became extremely uncomfortable and tried to leave the call center and find another job maybe.
But the Jalisco New Generation cartel is known for being extremely brutal. They chop off heads, and they’ll put them on the gates of a playground, for instance. So that everybody in the neighborhood knows what went down. And in this case, it’s possible that they wanted to send a warning that there’s no defection from their timeshare call centers.
So basically making a very scary example of these guys, in case anyone else is thinking about quitting one of the call centers.
Exactly. And one man, who runs an organization who advocates for missing people and actually organizes search parties to comb the forests of Jalisco state looking for the missing, says that he knows of about 30 people who have disappeared from the call centers in Jalisco state since 2017. So while Americans and Canadians might be losing much of their life savings, in Mexico, this is actually deadly.
Are the authorities doing anything about this?
Not really, other than the fact that these two call centers were shut down. The authorities haven’t arrested others. They’re not putting pressure on Mexican banks, for instance, to look into these payments coming from senior citizens in the US or Canada. And you have to remember that people are really afraid. But you also have to remember that in Mexico things are not that clear. There is a lot of corruption and government collusion with organized crime and cartels.
And the tourism industry, it is huge in Mexico and particularly in Jalisco state. This is a multi-billion dollar industry. They don’t want Americans or Canadians or Europeans who are coming to Jalisco for its beautiful beaches and its mountains to hear about these stories regarding the cartels being involved in the tourism industry and think, I’m not going to send my family there for that beach vacation. It’s just simply too dangerous.
So everybody has an incentive to have the scam continue, whether because they’re too afraid and don’t want to speak out or because they’re in on it.
So in a way, local authorities have an interest in sweeping it under the carpet in order to just maintain this idea of a tourist destination.
Exactly. I mean, the spokeswoman for the prosecutor’s office was very responsive to me until I told her what I wanted to ask her questions about. And then she just simply never answered any of my texts or phone calls.
So Maria, based on everything you know, all the information you have, would you say that you’re confident that the cartels were the ones who scammed James?
Yes, 100 percent. Everything I’ve seen points in that direction.
What did James say when you told him this?
So it took him quite a while to really allow himself to believe it. On the advice of his lawyers, he stopped picking up the phone calls. And about a week ago, they stopped after the scammers kept trying to call him.
But you said he was in it for over a year. Why do you think it took him so long?
Can you tell me, after all of that had been presented to you, why do you think you weren’t willing to be entirely convinced?
Well, I actually asked him that question.
That’s a very good question. Why wasn’t I able to pick up on that right away? And I think in the back of my mind, I’m finding out that I’m a little more stubborn than I thought I was.
And for him, it was pretty complicated.
And I think that I didn’t want to believe that I had fallen for this. I didn’t feel I was that foolish and stupid when it came to this. You know? I guess I didn’t want to believe that I could be fooled.
To come to terms with the fact that he had lost so much money was to come to terms with the fact that he wasn’t the person that he thought that he was, that he wasn’t this kind of clever former law enforcement officer who was used to fighting the bad guys and winning.
I’m disappointed in myself. There’s a huge level of anger towards the perpetrators. And all of those things wrapped into one. And part of that, I think, contributes to not wanting to actually believe that I was wrong.
Hmm. Yeah, I hear you. I’m sorry. I can hear the pain in your voice.
[LAUGHS]: Yeah.
Some of it’s based on shame, right? That he lost all this money, everything that he’s worked for, and the fact that this was all supposed to be money that his children and his grandchildren were going to inherit. And now it’s gone.
And have you told your daughter that you think you’ve come to terms with the fact that this might have been a scam?
Oh, she’s been involved. Yeah. They know.
My daughter does.
I’m sorry. This is a tough time.
So I’ve got to make some sort of arrangement to compensate them for this on top of our regular debt. So yeah. It’s been a swell experience, all of it brought on by my — evidently, my stubbornness to believe that I couldn’t possibly be a victim.
How’s your wife doing throughout this whole process, with this new knowledge?
She’s not real happy, obviously, at all. I hear a lot of “I told you so.” And at this point, I’ve got no defense. She’s absolutely right. There’s no question about it.
Do you worry this is going to affect your marriage?
Yes, there has been an effect.
And do you think that at this point there’s any way for James and his family to get some kind of justice or at least find some kind of closure?
Ay. Justice? Unlikely.
At this point, I’m not necessarily expecting much in the way of restitution.
And as for closure, it’s a little bit too soon to tell. In a way, James has gone through several stages of acceptance for what happened. There’s fear. There’s shame. There’s resignation. And now he’s talking to me partly because he feels like it’s a public service, that he needs to be vocal so that other people don’t go through what he’s gone through and fall for the scam. And I think it also helps him feel a little bit empowered in a situation for over the last year and a half he was at the mercy of these people who were calling him multiple times a week.
I want to try to get as much information to as many of these official organizations as possible. I have a streak of anger through me now that I’ve developed to the point where I’m not going to let this go.
Well, Maria, thank you.
Thank you for having me.
Here’s what else you need to know today. OJ Simpson, the football star who was accused and later acquitted of murdering his former wife and her friend, died of cancer at his home in Las Vegas, his family said Thursday. He was 76.
Today’s episode was produced by Astha Chaturvedi and Will Reid, with help from Clare Toeniskoetter and Lindsay Garrison. It was edited by Brendan Klinkenberg and Michael Benoist, contains original music by Marion Lozano, Rowan Niemisto, Dan Powell, Pat McCusker, and Will Reid, and was engineered by Chris Wood. Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly.
[THEME MUSIC]
That’s it for “The Daily.” I’m Katrin Bennhold. See you on Monday.

- April 17, 2024 • 24:52 Are ‘Forever Chemicals’ a Forever Problem?
- April 16, 2024 • 29:29 A.I.’s Original Sin
- April 15, 2024 • 24:07 Iran’s Unprecedented Attack on Israel
- April 14, 2024 • 46:17 The Sunday Read: ‘What I Saw Working at The National Enquirer During Donald Trump’s Rise’
- April 12, 2024 • 34:23 How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
- April 11, 2024 • 28:39 The Staggering Success of Trump’s Trial Delay Tactics
- April 10, 2024 • 22:49 Trump’s Abortion Dilemma
- April 9, 2024 • 30:48 How Tesla Planted the Seeds for Its Own Potential Downfall
- April 8, 2024 • 30:28 The Eclipse Chaser
- April 7, 2024 The Sunday Read: ‘What Deathbed Visions Teach Us About Living’
- April 5, 2024 • 29:11 An Engineering Experiment to Cool the Earth
- April 4, 2024 • 32:37 Israel’s Deadly Airstrike on the World Central Kitchen
Hosted by Katrin Bennhold
Produced by Asthaa Chaturvedi and Will Reid
With Clare Toeniskoetter and Lynsea Garrison
Edited by Brendan Klinkenberg and Michael Benoist
Original music by Marion Lozano , Rowan Niemisto , Dan Powell , Pat McCusker and Will Reid
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
Warning: this episode contains descriptions of violence.
A massive scam targeting older Americans who own timeshare properties has resulted in hundreds of millions of dollars sent to Mexico.
Maria Abi-Habib, an investigative correspondent for The Times, tells the story of a victim who lost everything, and of the criminal group making the scam calls — Jalisco New Generation, one of Mexico’s most violent cartels.
On today’s episode

Maria Abi-Habib , an investigative correspondent for The New York Times based in Mexico City.

Background reading
How a brutal Mexican drug cartel came to target seniors and their timeshares .
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Katrin Bennhold is the Berlin bureau chief. A former Nieman fellow at Harvard University, she previously reported from London and Paris, covering a range of topics from the rise of populism to gender. More about Katrin Bennhold
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Whether you're writing an essay or speaking in front of a group, there are certain big words you can use to impress your audience. Dictionary Thesaurus Sentences Grammar ... Whether you're giving a rollicking good speech or writing the next great American novel, being effective comes down to using the right words. ...
Good speech writing embraces the power of engaging content, weaving in stories, examples, and relatable anecdotes to connect with the audience on both intellectual and emotional levels. Ultimately, it is the combination of these elements, along with the authenticity and delivery of the speaker , that transforms words on a page into a powerful ...
Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary. Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you. 4. Mohammed Qahtani.
So before you utter another word to another person, memorize this list of the 8 key elements of highly effective speech: Gentle eye contact. Kind facial expression. Warm tone of voice. Expressive ...
2. Know Your Audience. Your Speech Is About Them, Not You. Before you begin to craft your message, consider who the message is intended for. Learn as much about your listeners as you can. This will help you determine your choice of words, level of information, organization pattern, and motivational statement. 3.
Influencing opinions through speeches is a powerful tool. Capturing the audience's attention and swaying their point of view is essential for a good speech. The use of the right words, imagery, and nonverbal communication is critical in persuasive speeches. Vulnerability, sincerity, and storytelling play a significant role in persuasion.
Typical Patterns for Speech Openings. Get the audience's attention-called a hook or a grabber. Establish rapport and tell the audience why you care about the topic of why you are credible to speak on the topic. Introduce the speech thesis/preview/good idea. Tell the audience why they should care about this topic.
Step 3: Edit and polish what you've written until you have a cohesive first draft of your speech. Step 4: Practice, practice, practice. The more you practice your speech the more you'll discover which sections need reworked, which transitions should be improved, and which sentences are hard to say. You'll also find out how you're doing ...
Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending) TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing. Return to top. A step by step guide for writing a great speech.
11. Don't be scared of a good reaction. If your speech is genuinely engaging, funny, inspiring or any of the other things you might hope it would be, your audience will react to it. There might be laughter, or applause, or even a bit of cheering depending on the setting.
1) Thank the Organizers and Audience. You can start by thanking the audience for coming and thanking the organization for inviting you to speak. Refer to the person who introduced you or to one or more of the senior people in the organization in the audience. This compliments them, makes them feel proud and happy about your presence, and ...
The use of power words is an instrument to engage people, grab their attention, and make them listen to your speech. Mix and match them whenever relevant to communicate your message and motivate your audience to take action. Remember that certain words evoke specific emotions.
George VI is using the first person, "I", to reach out to each person listening to the speech. He also talks in the third person: "we are at war", to unite British people against the common enemy: "them", or Germany. 3. Winston Churchill We shall fight on the beaches 1940. Churchill is an icon of great speech making.
Also, he encourages people to embrace failure and grow from it. 2. Steve Jobs - Stanford University. Definitely among the finest motivational speeches ever! His motivational speechdiscussed life's setbacks, such as death, and how understanding death may help people make better life decisions.
Eulogy-Good Words. Lynn Meade. 26. Introducing a Speaker. Lynn Meade. 27. Tribute Speech: Celebrate the Occasion, the Person, or the Monument ... The point is for you to notice how he infuses speech, powerful visuals, and vivid words to persuade us to act and to help others to get clean water. If you watched the video, you saw a worm in the ...
5. Melissa Butler. Speech Ending: When you go home today, see yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all your greatness that you embody, accept it, love it and finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn't look like you. 6.
Craft a list of transitional words and phrases: To ensure smooth and seamless transitions between your ideas, compile a list of words and phrases that can serve as connectors. Examples include "however," "in addition," and "on the other hand.". Identify logical connections: Assess the flow of your speech and identify the logical ...
The speech is also a good example of British English. 5. "Rocky Balboa Speech" by Sylvester Stallone. Level: Intermediate. This is a speech taken from the movie "Rocky Balboa. ... Many words in this speech have been replaced by other words in today's English. "Hath" is the older form of "has" or "had." "Thou" has also ...
Transition words are transition phrases that are single words. Transition words are snappier, shorter, and quicker than transition phrases. They heighten the pace and intensity of a sentence in a ...
Babble / Blabber / Blather / Drone / Prattle / Ramble. These words all have very similar meanings. First of all, when someone babbles (or blabbers or blathers or drones or prattles or rambles), it means they are talking for a long time. Too long. And probably not letting other people speak.
A good speech isn't only about your words but also how you present yourself. Body language and gestures play a critical role in transforming an average speech into a memorable one. If you're wondering what a good speech is, here are some of its qualities: Clear Message And Key Ideas; A good speech always starts with a key idea and a well ...
A word or phrase that connects the ideas of a speech and indicates the relationship between them. Transitions: A word or phrase that indicates when a speaker had finished one thought and it moving on to another. Internal preview: A statement in the body of the speech that tells the audience what the speaker is going to discuss next.
Speech transitions are words and phrases that allow you to smoothly move from one point to another so that your speech flows and your presentation is unified. This makes it easier for the audience to understand your argument and without transitions the audience may be confused as to how one point relates to another and they may think you're ...
East Room. 8:06 P.M. EDT. PRESIDENT BIDEN: Tonight, we celebrate the alliance between Japan and the United States. And Jill and I are honored to have you all here, including so many members of the ...
OPINION JFK, Dick Goodwin, and a speech that would be remembered in history These words, "the city upon a hill," delivered more than three centuries before, are how John Kennedy's farewell ...
A Mexican drug cartel is targeting seniors and their timeshares. Hosted by Katrin Bennhold. Produced by Asthaa Chaturvedi and Will Reid. With Clare Toeniskoetter and Lynsea Garrison. Edited by ...