- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans

How To Write the Management Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Ownership Structure
Internal management team, external management resources, human resources, frequently asked questions (faqs).
When developing a business plan , the 'management section' describes your management team, staff, resources, and how your business ownership is structured. This section should not only describe who's on your management team but how each person's skill set will contribute to your bottom line. In this article, we will detail exactly how to compose and best highlight your management team.
Key Takeaways
- The management section of a business plan helps show how your management team and company are structured.
- The first section shows the ownership structure, which might be a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation.
- The internal management section shows the department heads, including sales, marketing, administration, and production.
- The external management resources help back up your internal management and include an advisory board and consultants.
- The human resources section contains staffing requirements—part-time or full-time—skills needed for employees and the costs.
This section outlines the legal structure of your business. It may only be a single sentence if your business is a sole proprietorship. If your business is a partnership or a corporation, it can be longer. You want to be sure you explain who holds what percentage of ownership in the company.
The internal management section should describe the business management categories relevant to your business, identify who will have responsibility for each category, and then include a short profile highlighting each person's skills.
The primary business categories of sales, marketing , administration, and production usually work for many small businesses. If your business has employees, you will also need a human resources section. You may also find that your company needs additional management categories to fit your unique circumstances.
It's not necessary to have a different person in charge of each category; some key management people often fill more than one role. Identify the key managers in your business and explain what functions and experience each team member will serve. You may wish to present this as an organizational chart in your business plan, although the list format is also appropriate.
Along with this section, you should include the complete resumés of each management team member (including your own). Follow this with an explanation of how each member will be compensated and their benefits package, and describe any profit-sharing plans that may apply.
If there are any contracts that relate directly to your management team members, such as work contracts or non-competition agreements, you should include them in an Appendix to your business plan.
While external management resources are often overlooked when writing a business plan , using these resources effectively can make the difference between the success or failure of your managers. Think of these external resources as your internal management team's backup. They give your business credibility and an additional pool of expertise.
Advisory Board
An Advisory Board can increase consumer and investor confidence, attract talented employees by showing a commitment to company growth and bring a diversity of contributions. If you choose to have an Advisory Board , list all the board members in this section, and include a bio and all relevant specializations. If you choose your board members carefully, the group can compensate for the niche forms of expertise that your internal managers lack.
When selecting your board members, look for people who are genuinely interested in seeing your business do well and have the patience and time to provide sound advice.
Recently retired executives or managers, other successful entrepreneurs, and/or vendors would be good choices for an Advisory Board.
Professional Services
Professional Services should also be highlighted in the external management resources section. Describe all the external professional advisors that your business will use, such as accountants, bankers, lawyers, IT consultants, business consultants, and/or business coaches. These professionals provide a web of advice and support outside your internal management team that can be invaluable in making management decisions and your new business a success .
The last point you should address in the management section of your business plan is your human resources needs. The trick to writing about human resources is to be specific. To simply write, "We'll need more people once we get up and running," isn't sufficient. Follow this list:
- Detail how many employees your business will need at each stage and what they will cost.
- Describe exactly how your business's human resources needs can be met. Will it be best to have employees, or should you operate with contract workers or freelancers ? Do you need full-time or part-time staff or a mix of both?
- Outline your staffing requirements, including a description of the specific skills that the people working for you will need to possess.
- Calculate your labor costs. Decide the number of employees you will need and how many customers each employee can serve. For example, if it takes one employee to serve 150 customers, and you forecast 1,500 customers in your first year, your business will need 10 employees.
- Determine how much each employee will receive and total the salary cost for all your employees.
- Add to this the cost of Workers' Compensation Insurance (mandatory for most businesses) and the cost of any other employee benefits, such as company-sponsored medical and dental plans.
After you've listed the points above, describe how you will find the staff your business needs and how you will train them. Your description of staff recruitment should explain whether or not sufficient local labor is available and how you will recruit staff.
When you're writing about staff training, you'll want to include as many specifics as possible. What specific training will your staff undergo? What ongoing training opportunities will you provide your employees?
Even if the plan for your business is to start as a sole proprietorship, you should include a section on potential human resources demands as a way to demonstrate that you've thought about the staffing your business may require as it grows.
Business plans are about the future and the hypothetical challenges and successes that await. It's worth visualizing and documenting the details of your business so that the materials and network around your dream can begin to take shape.
What is the management section of a business plan?
The 'management section' describes your management team, staff, resources, and how your business ownership is structured.
What are the 5 sections of a business plan?
A business plan provides a road map showing your company's goals and how you'll achieve them. The five sections of a business plan are as follows:
- The market analysis outlines the demand for your product or service.
- The competitive analysis section shows your competition's strengths and weaknesses and your strategy for gaining market share.
- The management plan outlines your ownership structure, the management team, and staffing requirements.
- The operating plan details your business location and the facilities, equipment, and supplies needed to operate.
- The financial plan shows the map to financial success and the sources of funding, such as bank loans or investors.
SCORE. " Why Small Businesses Should Consider Workers’ Comp Insurance ."

How to Write the Management Team Section of a Business Plan + Examples
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the last 20+ years, we’ve written business plans for over 4,000 companies and hundreds of thousands of others have used our business plan template and other business planning materials.
From this vast experience, we’ve gained valuable insights on how to write a business plan effectively , specifically in the management section.
What is a Management Team Business Plan?
A management team business plan is a section in a comprehensive business plan that introduces and highlights the key members of the company’s management team. This part provides essential details about the individuals responsible for leading and running the business, including their backgrounds, skills, and experience.
It’s crucial for potential investors and stakeholders to evaluate the management team’s competence and qualifications, as a strong team can instill confidence in the company’s ability to succeed.
Why is the Management Team Section of a Business Plan Important?
Your management team plan has 3 goals:
- To prove to you that you have the right team to execute on the opportunity you have defined, and if not, to identify who you must hire to round out your current team
- To convince lenders and investors (e.g., angel investors, venture capitalists) to fund your company (if needed)
- To document how your Board (if applicable) can best help your team succeed
What to Include in Your Management Team Section
There are two key elements to include in your management team business plan as follows:
Management Team Members
For each key member of your team, document their name, title, and background.
Their backgrounds are most important in telling you and investors they are qualified to execute. Describe what positions each member has held in the past and what they accomplished in those positions. For example, if your VP of Sales was formerly the VP of Sales for another company in which they grew sales from zero to $10 million, that would be an important and compelling accomplishment to document.
Importantly, try to relate your team members’ past job experience with what you need them to accomplish at your company. For example, if a former high school principal was on your team, you could state that their vast experience working with both teenagers and their parents will help them succeed in their current position (particularly if the current position required them to work with both customer segments).
This is true for a management team for a small business, a medium-sized or large business.
Management Team Gaps
In this section, detail if your management team currently has any gaps or missing individuals. Not having a complete team at the time you develop your business plan. But, you must show your plan to complete your team.
As such, describe what positions are missing and who will fill the positions. For example, if you know you need to hire a VP of Marketing, state this. Further, state the job description of this person. For example, you might say that this hire will have 10 years of experience managing a marketing team, establishing new accounts, working with social media marketing, have startup experience, etc.
To give you a “checklist” of the employees you might want to include in your Management Team Members and/or Gaps sections, below are the most common management titles at a growing startup (note that many are specific to tech startups):
- Founder, CEO, and/or President
- Chief Operating Officer
- Chief Financial Officer
- VP of Sales
- VP of Marketing
- VP of Web Development and/or Engineering
- UX Designer/Manager
- Product Manager
- Digital Marketing Manager
- Business Development Manager
- Account Management/Customer Service Manager
- Sales Managers/Sales Staff
- Board Members
If you have a Board of Directors or Board of Advisors, you would include the bios of the members of your board in this section.
A Board of Directors is a paid group of individuals who help guide your company. Typically startups do not have such a board until they raise VC funding.
If your company is not at this stage, consider forming a Board of Advisors. Such a board is ideal particularly if your team is missing expertise and/or experience in certain areas. An advisory board includes 2 to 8 individuals who act as mentors to your business. Usually, you meet with them monthly or quarterly and they help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. You typically do not pay advisory board members with cash, but offering them options in your company is a best practice as it allows you to attract better board members and better motivate them.
Management Team Business Plan Example
Below are examples of how to include your management section in your business plan.
Key Team Members
Jim Smith, Founder & CEO
Jim has 15 years of experience in online software development, having co-founded two previous successful online businesses. His first company specialized in developing workflow automation software for government agencies and was sold to a public company in 2003. Jim’s second company developed a mobile app for parents to manage their children’s activities, which was sold to a large public company in 2014. Jim has a B.S. in computer science from MIT and an M.B.A from the University of Chicago
Bill Jones, COO
Bill has 20 years of sales and business development experience from working with several startups that he helped grow into large businesses. He has a B.S. in mechanical engineering from M.I.T., where he also played Division I lacrosse for four years.
We currently have no gaps in our management team, but we plan to expand our team by hiring a Vice President of Marketing to be responsible for all digital marketing efforts.
Vance Williamson, Founder & CEO
Prior to founding GoDoIt, Vance was the CIO of a major corporation with more than 100 retail locations. He oversaw all IT initiatives including software development, sales technology, mobile apps for customers and employees, security systems, customer databases/CRM platforms, etc. He has a B.S in computer science and an MBA in operations management from UCLA.
We currently have two gaps in our Management Team:
A VP of Sales with 10 years of experience managing sales teams, overseeing sales processes, working with manufacturers, establishing new accounts, working with digital marketing/advertising agencies to build brand awareness, etc.
In addition, we need to hire a VP of Marketing with experience creating online marketing campaigns that attract new customers to our site.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Executive Summary
- How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
- The Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
- Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
- Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan
- How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan
- Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix
- Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


Business Plan Organization and Management: How to Write Guide .
Sep 17, 2023 | Business Consulting , Business Plan , Organization and Management , Organizational Development , Strategy

Writing the Business Plan Organization and Management Section
It provides critical information for those looking for evidence that your staff has the necessary experience, skills, and pedigree to realize the objectives detailed in the rest of your business plan.
What Is the Organization and Management Section in a Business Plan?
The organization and management section of your business plan should provide details about your business structure and team. This section typically comes after the executive summary. However, some people have it further in the document after the market analysis section.
This section generally is separated into two parts. The first concerns the organization as a whole. It gives readers an overview of the company structure, which is an excellent opportunity for the reader to lift the roof off your office and peer into its inner workings. For your legal design, you may set up as a limited liability company (LLC) or nonprofit/ charity or form a partnership. It’s crucial to include this section. However, suppose you’re starting a home business or have an already operating business where you’re the only person involved. In that case, you can skip this section or show the company registration details from either the company’s house or the awarding .gov.
The second part focuses specifically on your management team and introduces readers to each member — your chance to impress them with the many accomplishments pinned to your organization’s management team.
This section may seem less important than some of the other parts of your business plan, but the truth is that your people are your business. If they’re highly competent and accomplished, the implication is that so is your business.
Of course, if you’re a sole proprietor with no management structure or any employees, this section is unnecessary other than to talk about yourself and your achievements.

The section on organization and management should outline the hierarchy, individual roles, and corresponding responsibilities. It should also highlight each person’s strengths and qualifications for their positions.
Business Plan Organization Section
The organizational section of your business plan outlines the hierarchy of individuals involved in your business, typically in a chart format. This section identifies the President or CEO, CFO, Director of Marketing, and other roles for partnerships or multi-member LLCs. If you’re a single-person home business, this section is straightforward as you are the only person on the chart.
Although this section primarily focuses on owner members, you can include outsourced workers or virtual assistants if you plan to hire them. For example, you may have a freelance web admin, marketing assistant, or copywriter. You may even have a virtual assistant who coordinates with your other freelancers. While these individuals are not owners, they hold significant responsibilities in your business.
There are various business structures, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, LLCs, and corporations.
Detail the Legal Structure within the Business Plan Organization and Management Section
Here is an indicative list of business structures. It would help if you talked to your accountant and legal advisors to determine which legal form is the best for your business proposition.
Sole Proprietorship
When embarking on a business venture, it’s essential to consider the various structures available. A sole proprietorship is a structure whereby the business is not regarded as separate from its owner’s finances. The owner retains complete control and responsibility for the company. However, they are unable to sell stocks or bring in new owners. The business becomes a sole proprietorship if not registered under any other structure.
Partnership
When forming a partnership, it can either be a limited partnership (LP) or a limited liability partnership (LLP). One partner assumes most liability in a limited partnership (LP). In contrast, the other partners have limited liability and control over the business. Alternatively, in a limited liability partnership (LLP), all partners have limited liability from debts and actions of other partners, and there is no general partner.
Limited Liability Company
A limited company (LTD) or limited liability company (LLC) is a mixture of business structures that mixes aspects of partnerships and corporations. It offers limited personal liability to the owner and passes profits through to their tax returns.
Corporation
There are various types of corporate structures. A C-corporation enables the issuance of stock shares, pays corporate taxes instead of personal returns, and provides the highest level of personal protection from business activities. On the other hand, nonprofit corporations are similar to C corporations. However, they do not aim to make profits and are exempt from state or federal income taxes.
More information on company legal structures is available on UK.Gov and USA.SBA websites.
Describe Your Company’s Organizational Structure
This first step illustrates the positions in your organization’s employee hierarchy and how they all relate to each other.
This is usually done graphically as a guide, using an organizational chart, or “org chart” for short. People use a Microsoft tool, i.e., PowerPoint or Excel, to help.
Organization Charts typically follow a top-down hierarchy, starting with your CEO/ Managing Director in the top box at the top of the page. Lines extend down from that person’s name to boxes containing the terms of the CEO’s direct reports.
We have included an example organizational chart below for guidelines only.
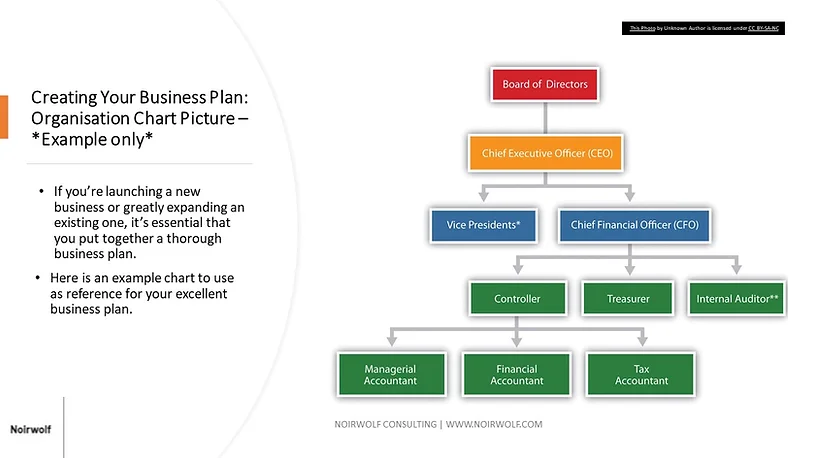
Identify your business organization structure and list your team members’ strengths and skills.
Those managers then have lines extending to those who report to them, and so on, down to your lowest staff positions.
This section will give your readers a quick understanding of your management and governance structure, the size of your organization, and your lines of control and communication.
Describe your Team in your Business Plan Organization and Management Section
In your business plan’s Organization and Management section, please provide a detailed description of your team. Y ou will discuss the company’s management team, starting with the owners.
This section highlights who is involved in the running of your business and who are the support professionals. It also includes the roles and responsibilities of managers.
Suppose the company structure is a multi-owner arrangement or some other multi-owner arrangement. In that case, you’ll want to include information for every member and their percentage of ownership and ongoing involvement in the company.
It’s important to discuss how ownership interests are split, their responsibilities, what they did before securing their current position, and how they came to be involved with the company.
Here, it would help if you talked about some of your critical team members. These people are directly responsible for large portions of your business operations.
Owner/Manager/Members
Within your business o rganization and management section, y ou should introduce the team and talk about their experience, qualifications, previous companies and achievements, role in the company, and any special skills they bring with them. Please provide the following details for each owner, manager, or member of the business within your business plan:
- Percentage of ownership (if applicable)
- Level of involvement (active or silent partner)
- Type of ownership (e.g., stock options, general partner)
- Position in the company (CEO, CFO, etc.)
- Responsibilities and Duties
- Educational background
- Relevant experience and skills
- Previous employment history
- Skills that will benefit the business
- Awards or recognition received
- Compensation structure
- How each individual’s skills and experience will complement and contribute to the business’s success
Perhaps they’re an entrepreneur, business coach, exclusive advisor, or industry specialist to help you grow.
This is an ideal opportunity for companies with an Executive Board of Directors, Governance Structure, or Advisory Board to introduce them to your readers.
Executive Board
Having a board of directors is essential for your management team. Without one, you may be missing out on crucial information. This section includes details similar to those found in the ownership and management team sub-section, such as the names, areas of expertise, positions (if applicable), and involvement with the company of each board member.
Strategic Advisors
Suppose you’re looking for funding for your business or to fill a gap in your knowledge, or you may not have the funds to hire an executive board. In that case, you must inform potential partners and investors that you have a team of professionals assisting you. This includes lawyers, accountants, and any freelancers or contractors you may be working with. When listing these individuals, include their name, title, educational background, certifications, services they provide to your business, and their relationship with you (i.e., hourly rates, projects, retainer, as-needed, regular). Additionally, highlight their skills and experience that make them an asset to your team you need
Does anything else make them stand out as quality professionals (awards, past working with credible brands)?
Spotlight on the Wider Team Structure
Now, you’ve showcased the management team in its entirety. You can provide brief bios for hiring team needs or secondary members and talk at length about how the team’s combined skills complement each other and how they amplify the team’s effectiveness.
It’s also important to point out any gaps in the knowledge your team is currently suffering. Your readers will likely be savvy enough to pick up on existing holes.
Therefore, you’ll want to get ahead of these criticisms and demonstrate that you’re already aware of the positions and complementary skill sets your management team still requires and how you plan to address the knowledge gaps with future hires.
Do you need help writing your business plan o rganization and management section ?
Every successful business plan should include the organization and management section, helping you communicate your legal structure and team.
Writing a business plan can seem overwhelming, especially when starting a small, one-person business. However, it can be a reasonably simple task. This section of the plan should be updated if there are any changes to the organization structure or team members, such as additional training, awards, or other resume changes that benefit the business.
Creating your comprehensive business plan takes planning, research, time, and a herculean effort. If, at any point, the work becomes too much to handle, we can step in to assist.
Do you want an expert “second opinion” before creating your business plan or financial forecasts? Let’s talk !
Get in Touch
Are you looking to grow your business but unsure where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We’ll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free 30-minute consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let’s get started!
Contact Noirwolf Consulting today using the website contact form or by emailing [email protected] or call us at +44 113 328 0868.
Recent posts .

What is Program Management?
Apr 2, 2024
Program management is a vital component of organizational success, as it enables the coordinated execution of interdependent projects that yield benefits beyond the scope of individual project management. It involves the judicious application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet specific program requirements. Our experience has demonstrated that organizations with well-developed program management and program management offices (PMOs) consistently outperform those that lack such structures. Therefore, it is imperative that organizations prioritize the establishment of robust program management frameworks to achieve their strategic objectives.

Business Transformation Strategy: A 10-Step Strategy Guide
Mar 4, 2024
Business transformation strategy is a complex and dynamic process that fundamentally restructures an organization’s strategy, processes, and systems. Though each business transformation is unique, several critical steps remain foundational to a successful change management plan. A comprehensive business transformation framework ensures a smooth and practical transformation. This framework should encompass various elements, such as defining the vision and aims of the transformation, assessing the current state of the business, identifying gaps and areas of improvement, developing a roadmap and action plan, implementing the changes, monitoring and measuring progress, and continuously refining the transformation approach as needed.

What is the Change Management Process?
Feb 2, 2024
Change is the only constant in today’s fast-paced world, and organizations must adapt to stay ahead. Fortunately, change management provides a structured and coordinated approach that enables businesses to move from their current state to a future desirable state. To deliver business value, organizations introduce change through projects, programs, and portfolios. However, introducing change is just the beginning! The real challenge is to embed the change and make it a new normal state for the organization. This calls for implementing the main principles of change management, which we will discuss in this article. Get ready to transform your organization and achieve your desired outcomes by mastering the art of change management!
Happy clients .
Trevor mcomber, us.
I recently worked with Zoe@Noirwolf, who provided me with an outstanding 5-year business plan. The expertise in financial planning, market research, SWOT analysis, and consulting was exceptional. Zoe provided me with a comprehensive and well-researched plan tailored to my business. The entire process was professional, timely, and communicative.
Bill Walton, Leeds
Zoe provided first-rate work and is an excellent business consultant. I was trying to figure out my cash flow forecast for my startup. Zoe gave me an interactive consultation session over MS teams, which was valuable and saved me a lot of time. She is super quick in excel and knowledgeable about what to include in your estimates. She was able to offer me ideas & choices that I hadn't considered. Highly recommended.
Jeendanie Lorthe, US
Warren kim, us, oscar sinclair, london, get in touch ..
Looking to grow your business but feeling unsure about where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We'll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free one-hour consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let's get started!
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning
Tips on Writing the Management Team Section of a Business Plan

Free Ultimate Guide On Writing A Business Plan
- December 21, 2023
10 Min Read

A business is as efficient as its team and its management. It, therefore, becomes important for business owners to build a structured management team that achieves the objectives and goals set by the organization. Thus, making the management section of a business plan the most essential component.
Andrew Carnegie , an American steel magnate, beautifully summarized it –
Teamwork is the ability to work together toward a common vision. The ability to direct individual accomplishments toward organizational objectives. It is the fuel that allows common people to attain uncommon results.
A business management plan helps build an efficient team and formalize business operations . This helps businesses streamline strategies to achieve their goals.
It, therefore, becomes imperative that business owners pay utmost importance while writing the management section of a business plan.
So, if you are a business owner who is looking to formalize their business structure and write the management team section in their business plan , this guide is for you.
Here’s a sneak peek into what you’ll learn:
Table of Contents
- What Is the Management Section?
- Importance of the Management Section
- What to Include in the Management Section?
- Example of a Management Section Plan
- Ensure That the Management Section Is Fool-proof?
Sounds good? Let’s dive in.
What Is The Management Section Of A Business Plan?
The management section of a business plan is an in-depth description of a business’s team, its structure, and the ownership of a business.
The section discusses in detail who is on the management team – internal and external- their skill sets, experiences, and how meaningfully they would contribute to an organization’s goals and outcomes.
Now that we have defined what is the management section of a business plan, let’s understand why it is so important.
The Importance Of The Management Section Of A Business Plan
The management section helps you to:
1. Convince your investors (banks and government agencies) to disburse loans and grants for your business idea
2. Prove that your management team can execute your idea and if not, help hire the right fit for a position
3. Share how your advisory board can help your team succeed
What To Include In the Management Section Of A Business Plan?
The management section of a business plan helps in formalizing and structuring the management team plan and is comprised of
- The Management Team
- The Management Team Gaps
- The Management Structure
Let’s understand them in detail.
1. The Management Team
An organization’s entire management team can be divided into parts – the internal team and the external team.
The Internal Management Team
A business team consists of several departments. The most common departments are – Marketing, Sales, IT, Customer Service, Operations, Finance, and HR.
These departments may or may not be required. It purely depends on the nature and functioning of your business. For example, a dental clinic may not require a sales department per se.
The entire management team is compartmentalized according to their responsibility. This helps the business owners and investors be aware of the roles, benefits, ESOPs (if applicable), profit sharing (for sales), work contracts, NDAs (Non-Disclosure Agreements), and Non-Competition Agreements of the entire team.
It is recommended that business owners collect and document the following information about their team:
- Educational Background
- Work Experience
- Accomplishments
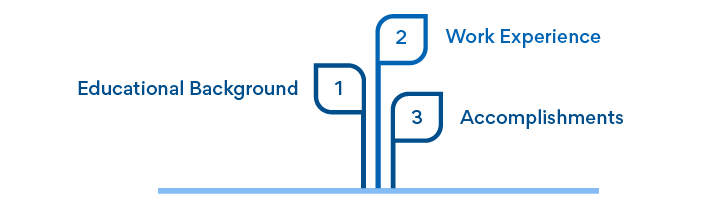
For example, your present VP of Marketing helped their previous company grow its bottom line from $3 million to $10 million over 18 months.
The External Management Team
The external management team is usually composed of – Advisory Board Members and Professional Services.
Advisory board members help by :
- Establishing trust, showing results, and experiencing the table.
- Increasing the confidence of investors and consumers.
This helps attract talented employees to the team. Credible advisory board members show great commitment to a company’s growth. Therefore, it becomes important to document their experience and specialization in the business management plan. The advisory board members can help give valuable advice that internal team members need or lack.
If your business has not or will not have VC funding, you may not require board members on your team.
Usually, board members meet quarterly or monthly to provide strategic guidance in place of stock options in your company. This helps attract the best advisors and motivates them to invest in your business.
For example, founders and business owners coming to raise funds in Shark Tank , a business television series, are looking for advisory members who would invest money and provide guidance on necessary steps.
On the other hand, Professional Service helps by
- Offering highly specialized advice and sharing knowledge.
- Business owners make key strategic management decisions.
Such services help businesses leverage skills that would be difficult to build and acquire over a short period.
Examples of such professional services are
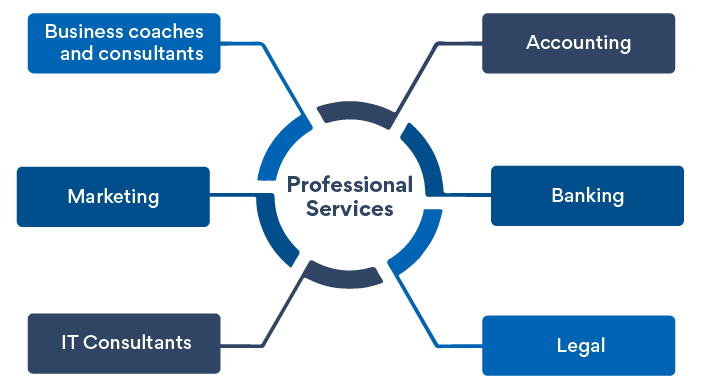
- IT Consultants
- Business coaches and consultants
After a brief overview of the Management Team of an organization, let’s dive into what to include in Management Team Gaps.
2. The Management Team Gaps
The management team gap is an important part of the management section. Primarily because it helps document if your management team currently has gaps or missing skills. Your team may lack a few required skills while starting. The management team gaps help you to be aware and make efforts to close this gap.
As a business owner, you must document what positions are missing and who ought to fill that positions or take responsibility.
For example, if you need a VP of Sales, clearly document this in the section.
Also, write down the job description and key responsibilities to be undertaken,
Example – You might mention that role required 10 years of experience in the sales domain. The applicant must have experience handling a sales team, closing new accounts, working in tandem with the marketing team, and having relevant startup experience.
Be as detailed as possible. This will help you build a checklist while interviewing the right candidate and also win investor confidence in your managerial skills.
Following are a few key positions you would want to include in your management team:
- Founder and/or, CEO
- Chief Technical Officer (CTO)
- Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
- Chief Operating Officer (COO)
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
- Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO)
- Head of Product Management (PM)
- VP of Sales
- VP of Marketing
- UX Designer
- Digital Marketing Manager
- Business Development Manager
- Customer Service Manager
- Customer Success Manager
- Sales Managers/Sales Staff
- Advisory Board Members
Let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of the management structure.
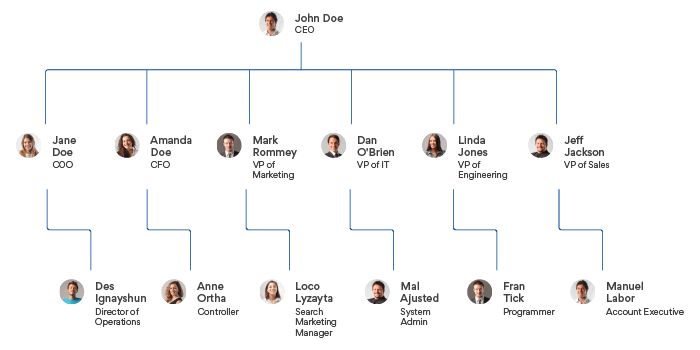
3. The Management Structure
The management structure defines how a business organizes its management hierarchy. A hierarchy helps determine the roles, positions, power, and responsibilities of all team members.
The management structure also depends upon the type of business ownership. Business ownership can be – a sole proprietorship, partnership, or simply an LLC.
Following is a sample management structure of an organization.
Now that we understand what details we need to document in the business management plan, let’s look at a few examples of the management plan.

Example Of A Management Section Plan
[management section of a hotel], [management team], internal team members.
Name: Charles Fargo Role: Owner Responsibility: Formulating key strategies, defining budgets, and building a business plan Experience: 35 years of owning multiple hotels in Las Vegas Educational Background: B.Sc in Hospitality Management from South Dakota State University.
Name: Michael Clark Role: General Manager Responsibility: Overall hotel operations – guest interactions, revenue management, brand ambassador of the hotel, customer satisfaction, and experience, leadership to all departments Experience: 25 years working with several technology hotels as the general manager. Educational Background: MBA from Wharton School
Name: George Trump Role: Department Manager Responsibility: Manage employees, smooth coordination amongst employees, plan daily affairs of the department, strategize, prepare reports, and deal with complaints and suggestions. Lead team members to function as a team Experience: 15 years working as a department manager Educational Background: BSc in Hotel Management from Texas University
Note: There can be multiple Department Managers depending on the nature of your business. In the case of hotels, departments can include – housekeeping, logistics, security, food, and banquets.
Name: Donald Clooney Role: Marketing and Sales Manager Responsibility: Increase occupancy and generate revenue. Position the hotel as an option for leisure activities, relaxation, and holidays. Experience: 11 years working as the marketing and sales manager for hotels Educational Background: MBA in Tourism and Hospitality from Midway University
External Team Members
Advisory Board Member
#1 Richard Branson Responsibility: Strategic advisory for sustainable growth and expansion Experience: Founder of Virgin Group
Professional Services
[management structure].
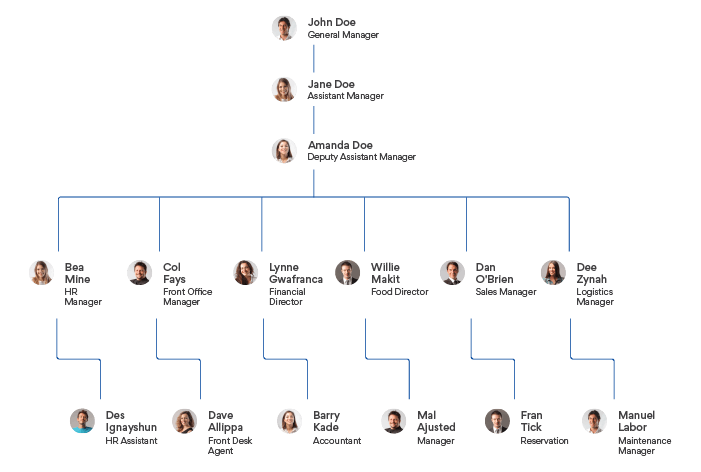
There is a gap in one key position in our startup.
#1 Chief Finance Officer (CFO) Responsibilities: Finance, Accounting, Tracking Profit and Loss, and overseeing FP&A (Financial Planning and Analysis)
How To Ensure That The Management Section Of Your Business Plan Is Fool-Proof?
“In preparing for battle I have always found that plans are useless, but planning is indispensable.” ― Dwight D. Eisenhower
By building a fool-proof management plan and ensuring that all the intricate details are accounted for, we can ensure that your business has a greater chance of succeeding.
Business planning software like Upmetrics ensures that business owners, like you, get the management section planning correct on the first attempt itself.
You can also get started with a free demo today to discover how Upmetrics can help you plan your business in a breeze.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Related Articles

How to Write an Operations Plan Section of your Business Plan

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix Section

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information you need to cover in a business plan sometimes isn’t quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
If you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template to get you started, download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

4 Min. Read
10 Business Plan Myths That Hurt Your Business

How to Write About Sourcing and Fulfillment in Your Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Business Skills
- Business Writing
How to Write a Management Plan
Last Updated: September 18, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Madison Boehm . Madison Boehm is a Business Advisor and the Co-Founder of Jaxson Maximus, a men’s salon and custom clothiers based in southern Florida. She specializes in business development, operations, and finance. Additionally, she has experience in the salon, clothing, and retail sectors. Madison holds a BBA in Entrepreneurship and Marketing from The University of Houston. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 235,725 times.
A management plan describes how an organization or business is run. Writing a management plan allows you to formalize your management structure and operations. It also ensures that everyone is on the same page and that your goals will be accomplished. You can easily write your own management plan with a few simple steps.
Management Plan Outline and Example

Starting Your Management Plan

- Defining roles also creates accountability by making it clear who's fault it was that something did or did not happen. [3] X Trustworthy Source Kansas University Center for Community Health and Development Community-based research center focused on supporting public health development and education Go to source

- A section detailing management members and their responsibilities and authorities.
- A chart of section detailing interactions between and responsibilities of each level of the organization.
- A section explaining different aspects of your organization being managed and the policies and procedures of that management.
- A schedule for updating, enhancing, and growing management and the management plan. [6] X Research source

Describing Ownership and Management

- Include a copy of board policies, including election policies, term length, responsibility, authority, and conflict resolution. This information should already be stated in your operating agreement or other founding documents.

- List past positions and duties of each member that apply to their current management obligations. Explain how these obligations highlight applicable skills and strengthen the management positions.
- Highlight all relevant educational backgrounds for each of the managers. Explain how their training will benefit the company. Only include the education that is relevant to the positions that they currently hold.
- If you are the only employee in your business, be sure to include your own experience and strengths.

- Accountants.
- Insurance brokers.
- Consultants.

- For example, “Our team, with its diverse array of skills, have a combined forty years of experience in this field. With our coordinated democratic structure, they can work together effectively to produce results. With this team, we are confident that our business will become profitable in two years.”

Writing Out Policies and Procedures

- For example, a policy might be using and selling only green materials and products. The procedures to support that policy might be shopping from approved green vendors or checking the environmental impact of each material or product used.

Revising Your Plan

- When they approve, have all owners sign the plan before you submit it to your investors, bank, or fundraising bodies.

- Make sure there is a way for all management and employees to submit their feedback regarding the plan.
- Then, create a method by which changes to the plan can be approved and instituted. [20] X Trustworthy Source Kansas University Center for Community Health and Development Community-based research center focused on supporting public health development and education Go to source
Expert Q&A

- Many investors will read the management section of your business plan before any other section, including marketing and finances, so you want to make sure that you have the best proposal possible. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Do not neglect your management plan in favor of your financial plans. Both are equally important to a business plan. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Madison Boehm. Business Advisor, Jaxson Maximus. Expert Interview. 24 August 2021.
- ↑ http://ctb.ku.edu/en/table-of-contents/leadership/effective-manager/management-plan/main
- ↑ https://www.brown.edu/research/conducting-research-brown/preparing-proposal/proposal-development-services/writing-management-plan
- ↑ https://www.thebalance.com/how-to-write-the-management-summary-2951561
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/humanresourcemanagement/chapter/4-1-the-recruitment-process/
- ↑ https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/241072
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/4533-business-plan-outline.html
About This Article

The best way to write a management report is to describe the company’s management structure in 10 to 20 pages. Name the board members and explain the company’s ownership policies. Introduce all management members and present the strengths of each team member. Then, write out workplace policies and procedures. Send the management report to the company’s bank, investors, or fundraising bodies. For more tips from our Financial Reviewer, like how to outline, format, and revise your plan, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Moshakge Molokwane
Apr 12, 2017
Did this article help you?
Mar 14, 2019
Jamie Willacy
Feb 1, 2023

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Business Plan Section 3: Organization and Management
This section explains how your business runs and who’s on your team. Learn how to present the information in this section of your business plan.

This section of your business plan, Organization and Management, is where you’ll explain exactly how you’re set up to make your ideas happen, plus you’ll introduce the players on your team.
As always, remember your audience. If this is a plan for your internal use, you can be a little more general than if you’ll be presenting it to a potential lender or investor. No matter what its purpose, you’ll want to break the organization and management section into two segments: one describing the way you’ve set up the company to run (its organizational structure), and the other introducing the people involved (its management).
Business Organization
Having a solid plan for how your business will run is a key component of its smooth and successful operation. Of course, you need to surround yourself with good people, but you have to set things up to enable them to work well with each other and on their own.
It’s important to define the positions in the company, which job is responsible for what, and to whom everyone will report. Over time, the structure may grow and change and you can certainly keep tweaking it as you go along, but you need to have an initial plan.
If you’re applying for funding to start a business or expand one, you may not even have employees to fit all the roles in the organization. However, you can still list them in your plan for how the company will ideally operate once you have the ability to do so.
Obviously, for small businesses, the organization will be far more streamlined and less complicated than it is for larger ones, but your business plan still needs to demonstrate an understanding of how you’ll handle the workflow. At the very least, you’ll need to touch on sales and marketing, administration, and the production and distribution of your product or the execution of your service.
For larger companies, an organizational plan with well-thought-out procedures is even more important. This is the best way to make sure you’re not wasting time duplicating efforts or dealing with internal confusion about responsibilities. A smooth-running operation runs far more efficiently and cost-effectively than one flying by the seat of its pants, and this section of your business plan will be another indication that you know what you’re doing. A large company is also likely to need additional operational categories such as human resources and possibly research and development.
One way to explain your organizational structure in the business plan is graphically. A simple diagram or flowchart can easily demonstrate levels of management and the positions within them, clearly illustrating who reports to whom, and how different divisions of the company (such as sales and marketing) relate to each other.
Here is where you can also talk about the other levels of employees in your company. Your lower-level staff will carry out the day-to-day work, so it’s important to recognize the types of people you’ll need, how many, what their qualifications should be, where you’ll find them, and what they’ll cost.
If the business will use outside consultants, freelancers, or independent contractors, mention it here as well. And talk about positions you’d want to add in the future if you’re successful enough to expand.
Business Management
Now that we understand the structure of your business, we need to meet the people who’ll be running it. Who does what, and why are they onboard? This section is important even for a single practitioner or sole proprietorship, as it will introduce you and your qualifications to the readers of your plan.
Start at the top with the legal structure and ownership of the business. If you are incorporated, say so, and detail whether you are a C or S corporation. If you haven’t yet incorporated, make sure to discuss this with your attorney and tax advisor to figure out which way to go. Whether you’re in a partnership or are a sole owner, this is where to mention it.
List the names of the owners of the business, what percent of the company each of them owns, the form of ownership (common or preferred stock, general or limited partner), and what kind of involvement they’ll have with day-to-day operations; for example, if they’re an active or silent partner.
Here’s where you’ll list the names and profiles of your management team, along with what their responsibilities are. Especially if you’re looking for funding, make sure to highlight the proven track record of these key employees. Lenders and investors will be keenly interested in their previous successes, particularly in how they relate to this current venture.
Include each person’s name and position, along with a short description of what the individual’s main duties will be. Detail his or her education, and any unique skills or experience, especially if they’re relevant to the job at hand. Mention previous employment and any industry awards or recognition related to it, along with involvement with charities or other non-profit organizations.
Think of this section as a resume-in-a-nutshell, recapping the highlights and achievements of the people you’ve chosen to surround yourself with. Actual detailed resumes for you and your management team should go in the plan’s appendix, and you can cross-reference them here. You want your readers to feel like your top staff complements you and supplements your own particular skill set. You also want readers to understand why these people are so qualified to help make your business a success.
This section will spell out the compensation for management team members, such as salary, benefits, and any profit-sharing you might be offering. If any of the team will be under contract or bound by non-compete agreements, you would mention that here, as well.
If your company will have a Board of Directors, its members also need to be listed in the business plan. Introduce each person by name and the position they’ll hold on the board. Talk about how each might be involved with the business (in addition to board meetings.
Similar to what you did for your management team, give each member’s background information, including education, experience, special skills, etc., along with any contributions they may already have had to the success of the business. Include the full resumes for your board members in the appendix.
Alternately, if you don’t have a Board of Directors, include information about an Advisory Board you’ve put together, or a panel of experts you’ve convened to help you along the way. Having either of these, by the way, is something your company might want to consider whether or not you’re putting together the organization and management section or your business plan.
NEXT ARTICLE > Business Plan Section 4: Products and Services
Apply for a loan, get started.
Loans from $5,000 - $100,000 with transparent terms and no prepayment penalty. Tell us a little about yourself, your business and receive your quote in minutes without impacting your credit score.
Thanks for applying!
Loans are originated and funded through our lending arm, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development. By clicking “Continue to Application,” you consent to, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development’s Terms of Use and Privacy Policy ; and to receive emails, calls and texts , potentially for marketing purposes, including autodialed or pre-recorded calls. You may opt out of receiving certain communications as provided in our Privacy Policy .
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Operations and Management Business Plan (+Sample in PDF)
AUG.03, 2023

1. What Is a Management and Operations Plan?
RephraseA management and operations plan is a crucial document that outlines the direction and management of an organization or enterprise. Typically created with a specific objective in mind, such as achieving company growth, expanding operations, or launching new products, this plan details the organization’s goals and objectives. It provides a roadmap for achieving these goals, serves as a reference for monitoring progress, and allows for necessary adjustments along the way.
The plan provides a comprehensive outline of the roles and responsibilities of every manager and staff member within the organization. This crucial information ensures effective coordination among the management team and helps facilitate goal attainment. Additionally, a well-developed management and operations plan plays a significant role in attracting and retaining investors and customers.

2. Management and operations business plan Sample
The following management and operations business plan will be based on the successful startup of a new facility management business. Professional Business Planning service is focused on creating a sustainable facility management business that prioritizes delivering a unique customer experience through comprehensive services and cost-effective solutions.
Facility Management
The main focus will be on providing tailored Facility Management services to our clients. These services may include facilities maintenance, energy management, environmental compliance, landscaping, housekeeping, and security. We also offer after-hours support and maintenance to ensure all client needs are met professionally and in a timely manner.
The strategic and business plan operations management will maintain a comprehensive inventory of facility management supplies, crisis management, and equipment, including tools, cleaning and janitorial supplies, and appliance parts. The business will also keep inventory of safety supplies, including non-slip mats, fire extinguishers, and first-aid kits.
Objectives and Goals
The best business plans to launch its facility management services no later than six months after beginning operations. Initially, the business plan management operation and organization will focus on acquiring new clients and establishing a quality service process. After this initial stage, the business will aim to grow its services and customer reach by targeting nearby communities and neighboring businesses.
Employees and Organizational Structure
The management and operations in the business plan will employ a full-time staff of three and three part-time employees. The staff will have several key responsibilities, including scheduling services, addressing customer inquiries, managing facilities, and keeping track of inventory. They will also undergo comprehensive training to ensure excellent customer service. The business will also have a dedicated service technician available on-call and an administrative assistant to handle customer inquiries and scheduling.
3. Operations and management business plan examples
When developing a business plan for operations and management, it’s crucial to carefully consider the unique goals and objectives of the business. For instance, if you’re starting a restaurant, you need to give careful thought to aspects such as menu options, operating hours, staffing requirements, and other factors that are vital for ensuring the success of your establishment. The same consideration must be given when starting a salon, home care business, or law firm. Running different types of establishments requires a tailored approach, including specific staffing and policies. Creating a successful operations and management business plan involves taking a holistic view of the business while keeping the customer front and center.
For a restaurant, an operations and management business plan examples should include key elements like the types of foods they will serve, pricing, and a detailed schedule for opening and closing by Professional Business Plan Writers . The Restaurant Business Plan should also include plans for hiring and managing staff and the necessary systems and procedures to ensure the restaurant runs smoothly. A salon will also have to consider how they will attract customers, manage services, and care for client safety and satisfaction. Home care and law firms should include detailed plans for recruiting, selecting, and training staff; organization policies; service offerings; and customer service processes.
Overall, management and operations in a business plan for service should outline all operational processes, personnel management, customer service, and marketing tactics for the business to succeed. From food offerings to staff selection, business owners should clearly outline their plan of action and adhere to their operations and management business plan for success.
4. Unlock the Path to Growth and Profit with OGS Capital: The ‘Go-To’ Management Plan Experts
At OGS Capital, we are experts in operations and management business plan consulting. With over 15 years of experience, our team of skilled business and operations strategists is dedicated to helping businesses like yours achieve growth and profitability. We have a deep understanding of the intricacies involved in developing effective operations and management business plans and specialize in creating personalized strategies that address each client’s unique needs.
We provide Professional Business Planning Services, starting with our thorough business assessment services. Our consultants offer personalized guidance based on their extensive industry expertise.
At our company, we prioritize strategic customer targeting in our operations and management business plan development services. Our expertise lies in creating accurate customer segmentation models and impactful market positioning plans. These plans enable you to effectively identify the most suitable customers for your products and services, maximizing your chances of capturing your target market.
With OGS Capital by your side every step of the way, you can be confident that your plan will be completed to the highest quality and efficacy standards. Contact us today to unlock your path to success.

Q.How do you write management and operations in a business plan?
In the management and operations section of a business plan, it is crucial to provide details about the various tasks required to run your business and the roles and responsibilities of each team member. This section should address important questions such as who makes decisions, who handles daily operations, and how the staff hierarchy is structured. Additionally, you should include information on how the business acquires resources and manages finances.
Q.What is an example of an operation management plan?
An example of an operational management plan is a comprehensive blueprint that outlines strategies and steps to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of producing and delivering goods and services. This plan includes specific details about procedures for improving processes, selecting equipment, allocating labor resources, managing inventory, and ensuring quality control. It also encompasses provisions for monitoring, evaluating, and making adjustments to operational changes. Furthermore, the plan identifies potential risks and provides strategies to mitigate them effectively.
Download Operations and Management Business Plan in PDF
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:

Management Summary Business Plan Sample
Each business plan has a management summary which describes the structure of the business and names the people involved. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
How do you create a management summary business plan sample? Each business plan has a management summary which describes the structure of the business and names the people involved. It offers important information on the company management and how these people manage the company, along with outside resources that the business uses.
Management Summary in a Business Plan
- This summary is important to a business plan because it describes the team's competencies and shows their experience which is important to achieve the company's goals. Shareholders and investors are more than likely going to be interested in this kind of information.
- Once you decide to create a business plan, you have to also think about writing the management summary for the business. Many investors will make a decision based solely on the strengths of the management.
- Management summaries should have names and titles of the management and those who will join in the future, their pay, consultants that are going to be hired, and management style and structure.
- The summary begins with the founder and then the managers who will run everyday operations. Keep the summary limited to about five or six who will be responsible for the business goals.
Key Elements Included in a Management Summary
Team leader - This person is responsible for putting together the team. Everything about this person should be written down including their background, credentials and vision. A business plan's summary will show off the owner's experience in the industry. It's a summary of the owner's resume as experiences that aren't important to the business plan don't have to be listed. The important thing is to specify positions, successes, and responsibilities.
Structure of business - Describe the type of structure for your business. Whether it's a corporation, partnership, LLC or sole proprietorship. Is it top-down where information is in one to two sources or horizontal, where employees have more responsibilities? Motivated employees can work better when they have access to information. Smaller business work better with a hierarchy where the information is controlled.
Team - Describe the team that will manage the business. Their skills and business background should be written. Make sure to describe the following:
- Education - write what is important to the position held.
- Work experience - write past and present work positions.
- Competencies - write what's relevant to the present position.
- Accomplishments - write what has been accomplished while working for the company.
- Personal data - include details like residency and age. Their motivation is also important to note.
List the titles of the managers even if this hasn't been finalized. This makes the company seem very organized and when investors read this and feel better about investing in the business.
Board - If the business has a board of directors make sure to write their names in the management summary. Describe why each was chosen to be part of the board. Consultants can also help with the management structure. They can do the work of an employee without the same expenses.
A person who's part of the company with a great track record is a good addition to the summary. Board of directors are often people who invested in the company and want a certain control over the direction of the business. They can help bring insight with their business experience.
Outside professionals - Each business uses outside professionals who help the company's goals. They have a stake in the company and should be in the management summary. Write down their main responsibilities in helping your company's goals.
Include any management that will be hired in the future as well. If you know your company will need a certain position then include this in the business plans. If a lender realizes the company is not running well without a certain person, and you didn't state it in the summary then the business will look weak. It's important to not underestimate investor scrutiny and give your business all the advantages possible.
If you also know how much the manager pay will be, then include this as well. Make sure you mention your management style and who has authority over the others.
If you need help with a management summary business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- How to Write An Executive Summary for a Business Plan
- Example of a Good Executive Summary for Business Plan
- Creating a Business Plan
- Business Plan Management Structure: What You Need to Know
- Business Plan Executive Summary Example Startup
- Business Plan Format: Everything you Need to Know
- Management Plan in a Business Plan
- Business Description Outline
- Management Contracts
- Business Plan
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
This is the ultimate guide to creating a comprehensive and effective plan to start a business . In today’s dynamic business landscape, having a well-crafted business plan is an important first step to securing funding, attracting partners, and navigating the challenges of entrepreneurship.
This guide has been designed to help you create a winning plan that stands out in the ever-evolving marketplace. U sing real-world examples and a free downloadable template, it will walk you through each step of the process.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Embarking on the journey of creating a successful business requires a solid foundation, and a well-crafted business plan is the cornerstone. Here is the process of writing a comprehensive business plan and the main parts of a winning business plan . From setting objectives to conducting market research, this guide will have everything you need.
Executive Summary

The Executive Summary serves as the gateway to your business plan, offering a snapshot of your venture’s core aspects. This section should captivate and inform, succinctly summarizing the essence of your plan.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Think of it as an elevator pitch in written form: it should be compelling enough to engage potential investors or stakeholders and provide them with a clear understanding of what your business is about, its goals, and why it’s a promising investment.
Example: EcoTech is a technology company specializing in eco-friendly and sustainable products designed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste. Our mission is to create innovative solutions that contribute to a cleaner, greener environment.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives

In the Overview and Business Objectives section, outline your business’s core goals and the strategic approaches you plan to use to achieve them. This section should set forth clear, specific objectives that are attainable and time-bound, providing a roadmap for your business’s growth and success.
It’s important to detail how these objectives align with your company’s overall mission and vision. Discuss the milestones you aim to achieve and the timeframe you’ve set for these accomplishments.
This part of the plan demonstrates to investors and stakeholders your vision for growth and the practical steps you’ll take to get there.
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
- Introducing three new products within the first two years of operation.
- Achieving annual revenue growth of 30%.
- Expanding our customer base to over 10,000 clients by the end of the third year.
Company Description

The Company Description section is your opportunity to delve into the details of your business. Provide a comprehensive overview that includes your company’s history, its mission statement, and its vision for the future.
Highlight your unique selling proposition (USP) – what makes your business stand out in the market. Explain the problems your company solves and how it benefits your customers.
Include information about the company’s founders, their expertise, and why they are suited to lead the business to success. This section should paint a vivid picture of your business, its values, and its place in the industry.
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market

Defining Your Target Market is critical for tailoring your business strategy effectively. This section should describe your ideal customer base in detail, including demographic information (such as age, gender, income level, and location) and psychographic data (like interests, values, and lifestyle).
Elucidate on the specific needs or pain points of your target audience and how your product or service addresses these. This information will help you know your target market and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Example: Our target market comprises environmentally conscious consumers and businesses looking for innovative solutions to reduce their carbon footprint. Our ideal customers are those who prioritize sustainability and are willing to invest in eco-friendly products.
Market Analysis

The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
This analysis will enable you to spot market opportunities and anticipate potential challenges. Include data and statistics to back up your claims, and use graphs or charts to illustrate market trends.
This section should demonstrate that you have a deep understanding of the market in which you operate and that your business is well-positioned to capitalize on its opportunities.
Example: The market for eco-friendly technology products has experienced significant growth in recent years, with an estimated annual growth rate of 10%. As consumers become increasingly aware of environmental issues, the demand for sustainable solutions continues to rise.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis

A SWOT analysis in your business plan offers a comprehensive examination of your company’s internal and external factors. By assessing Strengths, you showcase what your business does best and where your capabilities lie.
Weaknesses involve an honest introspection of areas where your business may be lacking or could improve. Opportunities can be external factors that your business could capitalize on, such as market gaps or emerging trends.
Threats include external challenges your business may face, like competition or market changes. This analysis is crucial for strategic planning, as it helps in recognizing and leveraging your strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and preparing for potential threats.
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
- Innovative and eco-friendly product offerings.
- Strong commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.
- Skilled and experienced team with expertise in technology and sustainability.
Weaknesses:
- Limited brand recognition compared to established competitors.
- Reliance on third-party manufacturers for product development.
Opportunities:
- Growing consumer interest in sustainable products.
- Partnerships with environmentally-focused organizations and influencers.
- Expansion into international markets.
- Intense competition from established technology companies.
- Regulatory changes could impact the sustainable technology market.
Competitive Analysis

In this section, you’ll analyze your competitors in-depth, examining their products, services, market positioning, and pricing strategies. Understanding your competition allows you to identify gaps in the market and tailor your offerings to outperform them.
By conducting a thorough competitive analysis, you can gain insights into your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to develop strategies to differentiate your business and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Example: Key competitors include:
GreenTech: A well-known brand offering eco-friendly technology products, but with a narrower focus on energy-saving devices.
EarthSolutions: A direct competitor specializing in sustainable technology, but with a limited product range and higher prices.
By offering a diverse product portfolio, competitive pricing, and continuous innovation, we believe we can capture a significant share of the growing sustainable technology market.
Organization and Management Team

Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Showcasing your team’s background, skills, and accomplishments instills confidence in investors and other stakeholders, proving that your business has the leadership and talent necessary to achieve its objectives and manage growth effectively.
Example: EcoTech’s organizational structure comprises the following key roles: CEO, CTO, CFO, Sales Director, Marketing Director, and R&D Manager. Our management team has extensive experience in technology, sustainability, and business development, ensuring that we are well-equipped to execute our business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered

Describe the products or services your business offers, focusing on their unique features and benefits. Explain how your offerings solve customer pain points and why they will choose your products or services over the competition.
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Example: EcoTech offers a range of eco-friendly technology products, including energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers, and smart home devices that optimize energy usage. Our products are designed to help customers reduce energy consumption, minimize waste, and contribute to a cleaner environment.
Marketing and Sales Strategy

In this section, articulate your comprehensive strategy for reaching your target market and driving sales. Detail the specific marketing channels you plan to use, such as social media, email marketing, SEO, or traditional advertising.
Describe the nature of your advertising campaigns and promotional activities, explaining how they will capture the attention of your target audience and convey the value of your products or services. Outline your sales strategy, including your sales process, team structure, and sales targets.
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
This section is critical to convey to investors and stakeholders that you have a well-thought-out approach to market your business effectively and drive sales growth.
Example: Our marketing strategy includes digital advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, and influencer partnerships. We will also attend trade shows and conferences to showcase our products and connect with potential clients. Our sales strategy involves both direct sales and partnerships with retail stores, as well as online sales through our website and e-commerce platforms.
Logistics and Operations Plan

The Logistics and Operations Plan is a critical component that outlines the inner workings of your business. It encompasses the management of your supply chain, detailing how you acquire raw materials and manage vendor relationships.
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
Quality control measures are essential to maintain product standards and customer satisfaction. This plan assures investors and stakeholders of your operational competency and readiness to meet business demands.
Highlighting your commitment to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction underlines your business’s capability to maintain smooth, effective operations even as it scales.
Example: EcoTech partners with reliable third-party manufacturers to produce our eco-friendly technology products. Our operations involve maintaining strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring quality control, and managing inventory.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan

In the Financial Projections Plan, lay out a clear and realistic financial future for your business. This should include detailed projections for revenue, costs, and profitability over the next three to five years.
Ground these projections in solid assumptions based on your market analysis, industry benchmarks, and realistic growth scenarios. Break down revenue streams and include an analysis of the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and potential investments.
This section should also discuss your break-even analysis, cash flow projections, and any assumptions about external funding requirements.
By presenting a thorough and data-backed financial forecast, you instill confidence in potential investors and lenders, showcasing your business’s potential for profitability and financial stability.
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Example: Over the next three years, we expect to see significant growth in revenue, driven by new product launches and market expansion. Our financial projections include:
- Year 1: $1.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $200,000.
- Year 2: $3 million in revenue, with a net profit of $500,000.
- Year 3: $4.5 million in revenue, with a net profit of $1 million.
These projections are based on realistic market analysis, growth rates, and product pricing.
Income Statement

The income statement , also known as the profit and loss statement, provides a summary of your company’s revenues and expenses over a specified period. It helps you track your business’s financial performance and identify trends, ensuring you stay on track to achieve your financial goals.
Regularly reviewing and analyzing your income statement allows you to monitor the health of your business, evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
Example: The income statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
- Revenue: $1,500,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $800,000
- Gross Profit: $700,000
- Operating Expenses: $450,000
- Net Income: $250,000
This statement highlights our company’s profitability and overall financial health during the first year of operation.
Cash Flow Statement

A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
By including a cash flow statement in your business plan, you demonstrate your ability to manage your company’s finances effectively.
Example: The cash flow statement for EcoTech’s first year of operation is as follows:
Operating Activities:
- Depreciation: $10,000
- Changes in Working Capital: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Operating Activities: $210,000
Investing Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: -$100,000
- Net Cash from Investing Activities: -$100,000
Financing Activities:
- Proceeds from Loans: $150,000
- Loan Repayments: -$50,000
- Net Cash from Financing Activities: $100,000
- Net Increase in Cash: $210,000
This statement demonstrates EcoTech’s ability to generate positive cash flow from operations, maintain sufficient liquidity, and invest in growth opportunities.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan

1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively.
2. Conduct thorough research: Before writing your business plan, gather as much information as possible about your industry, competitors, and target market. Use reliable sources and industry reports to inform your analysis and make data-driven decisions.
3. Set realistic goals: Your business plan should outline achievable objectives that are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting realistic goals demonstrates your understanding of the market and increases the likelihood of success.
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
5. Be flexible and adaptable: A business plan is a living document that should evolve as your business grows and changes. Be prepared to update and revise your plan as you gather new information and learn from your experiences.
6. Use visuals to enhance understanding: Include charts, graphs, and other visuals to help convey complex data and ideas. Visuals can make your business plan more engaging and easier to digest, especially for those who prefer visual learning.
7. Seek feedback from trusted sources: Share your business plan with mentors, industry experts, or colleagues and ask for their feedback. Their insights can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your plan before presenting it to potential investors or partners.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
The template is divided into the following sections:
- Mission statement
- Business Overview
- Key products or services
- Target market
- Financial highlights
- Company goals
- Strategies to achieve goals
- Measurable, time-bound objectives
- Company History
- Mission and vision
- Unique selling proposition
- Demographics
- Psychographics
- Pain points
- Industry trends
- Customer needs
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Competitor products and services
- Market positioning
- Pricing strategies
- Organizational structure
- Key roles and responsibilities
- Management team backgrounds
- Product or service features
- Competitive advantages
- Marketing channels
- Advertising campaigns
- Promotional activities
- Sales strategies
- Supply chain management
- Inventory control
- Production processes
- Quality control measures
- Projected revenue
- Assumptions
- Cash inflows
- Cash outflows
- Net cash flow
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document that outlines an organization’s goals, objectives, and the steps required to achieve them. It serves as a roadmap as you start a business , guiding the company’s direction and growth while identifying potential obstacles and opportunities.
Typically, a business plan covers areas such as market analysis, financial projections, marketing strategies, and organizational structure. It not only helps in securing funding from investors and lenders but also provides clarity and focus to the management team.
A well-crafted business plan is a very important part of your business startup checklist because it fosters informed decision-making and long-term success.

Why You Should Write a Business Plan
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
- Attract Investors and Secure Funding : A well-written business plan demonstrates your venture’s potential and profitability, making it easier to attract investors and secure the necessary funding for growth and development. It provides a detailed overview of your business model, target market, financial projections, and growth strategies, instilling confidence in potential investors and lenders that your company is a worthy investment.
- Clarify Business Objectives and Strategies : Crafting a business plan forces you to think critically about your goals and the strategies you’ll employ to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for success. This process helps you refine your vision and prioritize the most critical objectives, ensuring that your efforts are focused on achieving the desired results.
- Identify Potential Risks and Opportunities : Analyzing the market, competition, and industry trends within your business plan helps identify potential risks and uncover untapped opportunities for growth and expansion. This insight enables you to develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities, positioning your business for long-term success.
- Improve Decision-Making : A business plan serves as a reference point so you can make informed decisions that align with your company’s overall objectives and long-term vision. By consistently referring to your plan and adjusting it as needed, you can ensure that your business remains on track and adapts to changes in the market, industry, or internal operations.
- Foster Team Alignment and Communication : A shared business plan helps ensure that all team members are on the same page, promoting clear communication, collaboration, and a unified approach to achieving the company’s goals. By involving your team in the planning process and regularly reviewing the plan together, you can foster a sense of ownership, commitment, and accountability that drives success.
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
In today’s fast-paced business world, having a well-structured roadmap is more important than ever. A traditional business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your company’s goals and strategies, helping you make informed decisions and achieve long-term success. There are various types of business plans, each designed to suit different needs and purposes. Let’s explore the main types:
- Startup Business Plan: Tailored for new ventures, a startup business plan outlines the company’s mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. It helps entrepreneurs clarify their vision, secure funding from investors, and create a roadmap for their business’s future. Additionally, this plan identifies potential challenges and opportunities, which are crucial for making informed decisions and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Internal Business Plan: This type of plan is intended for internal use, focusing on strategies, milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation. It serves as a management tool for guiding the company’s growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. The internal business plan also helps identify areas of improvement, fosters collaboration among team members, and provides a reference point for measuring performance.
- Strategic Business Plan: A strategic business plan outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them, providing a clear roadmap for the company’s direction. It typically includes a SWOT analysis, market research, and competitive analysis. This plan allows businesses to align their resources with their objectives, anticipate changes in the market, and develop contingency plans. By focusing on the big picture, a strategic business plan fosters long-term success and stability.
- Feasibility Business Plan: This plan is designed to assess the viability of a business idea, examining factors such as market demand, competition, and financial projections. It is often used to decide whether or not to pursue a particular venture. By conducting a thorough feasibility analysis, entrepreneurs can avoid investing time and resources into an unviable business concept. This plan also helps refine the business idea, identify potential obstacles, and determine the necessary resources for success.
- Growth Business Plan: Also known as an expansion plan, a growth business plan focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. It includes market analysis, new product or service offerings, and financial projections to support expansion plans. This type of plan is essential for businesses looking to enter new markets, increase their customer base, or launch new products or services. By outlining clear growth strategies, the plan helps ensure that expansion efforts are well-coordinated and sustainable.
- Operational Business Plan: This type of plan outlines the company’s day-to-day operations, detailing the processes, procedures, and organizational structure. It is an essential tool for managing resources, streamlining workflows, and ensuring smooth operations. The operational business plan also helps identify inefficiencies, implement best practices, and establish a strong foundation for future growth. By providing a clear understanding of daily operations, this plan enables businesses to optimize their resources and enhance productivity.
- Lean Business Plan: A lean business plan is a simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements such as value proposition, customer segments, revenue streams, and cost structure. It is perfect for startups looking for a flexible, adaptable planning approach. The lean business plan allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement, enabling businesses to pivot and adapt to changing market conditions. This streamlined approach is particularly beneficial for businesses in fast-paced or uncertain industries.
- One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, a one-page business plan is a concise summary of your company’s key objectives, strategies, and milestones. It serves as a quick reference guide and is ideal for pitching to potential investors or partners. This plan helps keep teams focused on essential goals and priorities, fosters clear communication, and provides a snapshot of the company’s progress. While not as comprehensive as other plans, a one-page business plan is an effective tool for maintaining clarity and direction.
- Nonprofit Business Plan: Specifically designed for nonprofit organizations, this plan outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation. It helps secure grants and donations while ensuring the organization stays on track with its objectives. The nonprofit business plan also helps attract volunteers, board members, and community support. By demonstrating the organization’s impact and plans for the future, this plan is essential for maintaining transparency, accountability, and long-term sustainability within the nonprofit sector.
- Franchise Business Plan: For entrepreneurs seeking to open a franchise, this type of plan focuses on the franchisor’s requirements, as well as the franchisee’s goals, strategies, and financial projections. It is crucial for securing a franchise agreement and ensuring the business’s success within the franchise system. This plan outlines the franchisee’s commitment to brand standards, marketing efforts, and operational procedures, while also addressing local market conditions and opportunities. By creating a solid franchise business plan, entrepreneurs can demonstrate their ability to effectively manage and grow their franchise, increasing the likelihood of a successful partnership with the franchisor.
Using Business Plan Software

Creating a comprehensive business plan can be intimidating, but business plan software can streamline the process and help you produce a professional document. These tools offer a number of benefits, including guided step-by-step instructions, financial projections, and industry-specific templates. Here are the top 5 business plan software options available to help you craft a great business plan.
1. LivePlan
LivePlan is a popular choice for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive features. It offers over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, and the ability to track your progress against key performance indicators. With LivePlan, you can create visually appealing, professional business plans that will impress investors and stakeholders.
2. Upmetrics
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
Bizplan is designed to simplify the business planning process with a drag-and-drop builder and modular sections. It offers financial forecasting tools, progress tracking, and a visually appealing interface. With Bizplan, you can create a business plan that is both easy to understand and visually engaging.
Enloop is a robust business plan software that automatically generates a tailored plan based on your inputs. It provides industry-specific templates, financial forecasting, and a unique performance score that updates as you make changes to your plan. Enloop also offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget.
5. Tarkenton GoSmallBiz
Developed by NFL Hall of Famer Fran Tarkenton, GoSmallBiz is tailored for small businesses and startups. It features a guided business plan builder, customizable templates, and financial projection tools. GoSmallBiz also offers additional resources, such as CRM tools and legal document templates, to support your business beyond the planning stage.
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
The three main purposes of a business plan are to guide the company’s strategy, attract investment, and evaluate performance against objectives. Here’s a closer look at each of these:
- It outlines the company’s purpose and core values to ensure that all activities align with its mission and vision.
- It provides an in-depth analysis of the market, including trends, customer needs, and competition, helping the company tailor its products and services to meet market demands.
- It defines the company’s marketing and sales strategies, guiding how the company will attract and retain customers.
- It describes the company’s organizational structure and management team, outlining roles and responsibilities to ensure effective operation and leadership.
- It sets measurable, time-bound objectives, allowing the company to plan its activities effectively and make strategic decisions to achieve these goals.
- It provides a comprehensive overview of the company and its business model, demonstrating its uniqueness and potential for success.
- It presents the company’s financial projections, showing its potential for profitability and return on investment.
- It demonstrates the company’s understanding of the market, including its target customers and competition, convincing investors that the company is capable of gaining a significant market share.
- It showcases the management team’s expertise and experience, instilling confidence in investors that the team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
- It establishes clear, measurable objectives that serve as performance benchmarks.
- It provides a basis for regular performance reviews, allowing the company to monitor its progress and identify areas for improvement.
- It enables the company to assess the effectiveness of its strategies and make adjustments as needed to achieve its objectives.
- It helps the company identify potential risks and challenges, enabling it to develop contingency plans and manage risks effectively.
- It provides a mechanism for evaluating the company’s financial performance, including revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow.
Can I write a business plan by myself?
Yes, you can write a business plan by yourself, but it can be helpful to consult with mentors, colleagues, or industry experts to gather feedback and insights. There are also many creative business plan templates and business plan examples available online, including those above.
We also have examples for specific industries, including a using food truck business plan , salon business plan , farm business plan , daycare business plan , and restaurant business plan .
Is it possible to create a one-page business plan?
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
A typical business plan ranges from 20 to 50 pages, but the length may vary depending on the complexity and needs of the business.
What is a business plan outline?
A business plan outline is a structured framework that organizes the content of a business plan into sections, such as the executive summary, company description, market analysis, and financial projections.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
The five most common business plan mistakes include inadequate research, unrealistic financial projections, lack of focus on the unique selling proposition, poor organization and structure, and failure to update the plan as circumstances change.
What questions should be asked in a business plan?
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan focuses on the overall vision, goals, and tactics of a company, while a strategic plan outlines the specific strategies, action steps, and performance measures necessary to achieve the company’s objectives.
How is business planning for a nonprofit different?
Nonprofit business planning focuses on the organization’s mission, social impact, and resource management, rather than profit generation. The financial section typically includes funding sources, expenses, and projected budgets for programs and operations.
Image: Envato Elements

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
© Copyright 2003 - 2024, Small Business Trends LLC. All rights reserved. "Small Business Trends" is a registered trademark.
Business Plan Management Team Section
An overview of your founders, key employees, and advisors, management team.
The purpose of including the management team in a business plan is that it provides an overview of your founders and key employees. Yet, in the beginning, that might be just one person. You can increase your plan’s credibility by establishing a supporting cast of key mentors and advisors and including them in this section.
This article provides information about how to present your management team, including examples and a management team template you can use for your business plan.
Important Considerations for Presenting Your Management Team
Venture capitalists will often say, “We don’t invest in ideas. We invest in people.” Their rationale is that, over time, the idea will have to evolve. The right team will develop the idea into a winner. But the wrong team can ruin even what was initially an outstanding idea. So the question to be answered by this section is, “What experience and achievements in this team’s past demonstrate that they will succeed in this new business?”
Business Plan Outline for your Management Team:
The structure for the management team section of your business plan is straightforward. For each bullet point item below, expand on the experience and value brought to your company by their participation. The following sections will recommend best practices for presenting your management team in a way that investors and lenders will appreciate.
- Key Employees
Hiring Plans
Board members.
- Professional Advisors
Founders and CEOs
Most startup businesses will be led by the founder as the Chief Executive Officer or CEO. For a startup, the title of President is equally suitable.
If Your Founder is also the CEO
Assuming your President or CEO is also the founder, begin your Management Team section with a description of the individual who will be the CEO or senior person in charge of running the company.
Under the heading of Founder and CEO, include a mini-bio relevant to the credibility of this person leading the firm to success. A lender or investor will go to LinkedIn to get the full bio, so stick to the essential elements.
The best thing you can say about the founder is that he or she has CEO-level experience running a similar business or one in a similar space. Realistically, you’re only sometimes going to be able to say that. What can you say?
First, present the most relevant experience that makes the CEO “investable.” That could be technical expertise, sales experience, or management skills from another company. By stating the most relevant experience to the new business right up front, you’ll help the reader see the transferable skills. If there is no CEO experience, don’t worry. In the following sections, we’ll show you how to build a bridge of confidence to cover that gap.
If Your Founder is not the CEO
If the founder is not the CEO, two questions must be answered in this lead-off sub-section of your business plan management team. First, why is the founder not leading the company as its CEO? Next, what role will the founder play in the business?
Hopefully, the first question answers itself by presenting the outstanding qualifications of the CEO, such that the reader would be impressed by the fact that you were able to get this person to come on board to grow your business. A simple example would be:
Robert Nelson has 20 years of experience in our industry, 10 of that as a CEO. Robert will lead MyCo as our CEO. Robert is known and respected in the field and will surely accelerate our growth.
Dana Elders, our founder, worked under Robert as the head of sales, where he flourished. Dana will be MyCo’s President and will also be responsible for driving revenue.
Whatever the circumstances are that led to your founder not being the CEO, one would expect that there is an advantage with an upside. Otherwise, why would the founder abdicate this role? Be sure to identify the upside in your business plan.
Key Management Team Members
Highlight the relevant experience and accomplishments your team brings to the table. You can include the resumes of your key management team members as appendices in your business plan and refer to them in this section.
Whom should you include?
Include as many of the following roles in your management team as you have filled. Adapt these to align more closely with the important roles in your industry.
- Any VP-level person
- Chief Operating Officer
- Chief Financial Officer
- Chief Product Officer
- Chief Technology Officer
- Head of Sales
- Head of Marketing
- Head of Operations
- Any outstanding contributor with experience that will obviously contribute to the success of your business.
What to Say about Each Person on Your Management Team
For each individual you list, include their relevant experience, transferable skills, and key accomplishments, emphasizing factors that will contribute to your business’ success. Avoid making readers “connect the dots” on their own. Rather, make the connection for them.
For example:
Jose Rodero, VP of Product and Marketing.
In Jose’s previous role as Chief Product Officer of LikeMine Company, he expanded into new markets and tripled the size of the business in three years. This experience is ideal for MyCo as we move beyond a single market to expand into adjacent markets.
Highlight Relevant Accomplishments
For each person you list in the key management section, it’s helpful to convey a pattern of accomplishments, such as, “At her last company, Ms. Johnson was named Employee of the Year for the past two years. During that time, she was twice promoted. First to VP of Sales and then to COO.
Leave out admirable but “sideline” accolades such as, “Ms. Johnson is a two-time winner of the La Jolla Triathlon.” Unless an accolade relates to the success of your business, you’re better off mentioning it in the biography (included as an appendix) or leaving it out altogether.
At the early stages of your company, you might be missing some key people on your management team—this is normal and acceptable. Usually, this has a lot to do with why you are seeking funding. If you haven’t yet hired all your key people, you can address this in your business plan in two ways.
First, if you have lined up some individuals who will come on board when you bring in your funding, you can identify them in your business plan. If this information is not ready to be disclosed, you can allude to it in generalized terms without divulging the person’s name or current company.
“We have identified an individual with ten years of experience in a similar company to fill the Director of Marketing role. Pending the timing of our funding, we expect this person to join our team.
Next, address any gaps in your management team that need to be filled. Identify key hires that remain and the order in which you expect to fill the positions. Doing so shows that you’re thinking ahead and shields you from any criticism about holes in your current team.
While you may think these gaps are a weakness in your plan, your potential investors or lenders become a source of free candidate referrals!
Board of Directors versus Board of Advisors
There are two types of boards: a board of directors and a board of advisors, sometimes called an advisory board. A board of directors can have specific legal responsibilities and authority. For that reason, some individuals would prefer to join a board of advisors.
A board of advisors generally has fewer or no formal responsibilities but can be just as beneficial to the company through the guidance they provide. It’s never too early, and your business is never too small to have a board of advisors.
Whether it’s a board of directors or a board of advisors, it is important to surround yourself with experienced advisors who will provide sound advice that you will be willing to follow. Anything less will waste your time and theirs.
One founder we met with had this to say about a particular board member:
“I selected him to be on the board of my first company because he was strongly recommended by two successful business people I knew. I found him to be someone who pushed back on many of my ideas, asked lots of tough questions, and always held me to task on everything I said we would accomplish. We were not friends outside of the business.
When I started my next business, and we needed to set up a board–he was the first person I called.”
Your best board members may not be your best friends, and hopefully, they won’t be people who think just like you. A board brings a diversity of thought and critical thinking. They help you be a better version of yourself.
Having a board of directors or board of advisors tells lenders and investors that you value the input of outside thinking and have the skills to build relationships with people who can help your business succeed. That bodes well for the future success of your business!
Board of Directors
Your initial board of directors will almost certainly be led by the founder as its Chair. Typically, a co-founder, angel investor, or key employee with very senior executive experience might also be on the board. A small board of directors is fine, especially if you’ll be adding a board of advisors.
Depending on the state where you start your business and your corporate structure, a minimum number of board members may be prescribed.
Advisory Board
If you still need to get a board of directors beyond the minimum required roles, consider putting together a board of advisors. Chances are you have mentors and people with relevant experience who are giving you input on your business idea. Perhaps one of them is even a customer or potential customer.
Consider asking these people to agree to be on your board of advisors, a group that would meet quarterly to hear updates on your business and to provide input. With their consent, you can list members of your board of advisors in your business plan. You’ll find that accomplished people are often happy to join your board of advisors for little or no compensation.
What to Show in Your Business Plan for Board Members (Directors and Advisors)
For each board member in your board of directors and board of advisors, list their name, current or most recent position, and company. If members have special experience that pertains strongly to your business, naturally, you would also want to include that information. Include up to two or three sentences of narrative about each board member.
Using the format above, first list your Board of Directors and then your Board of Advisors.
Professional Services Advisors
If you have worked with an attorney to establish your business, an accountant to help prepare your financial forecasts, or an advertising or PR firm to help prepare some promotional materials—include these organizations in your business plan’s management section under the heading “Professional Advisors.”
Bankers and investors are often well-connected to area professional service providers. Knowing that you are working with recognized names in the business community can boost your credibility. It also tells the reader that you’re being advised by professionals.
Be sure to let your advisors know in advance that you’ve listed them in your business plan since oftentimes, they’ll get a phone call asking for their impressions of the business. Better still, seek and obtain their permission.
In this section, include the type of services provided, the name of the firm, and your primary contact.
Legal Advisors: Dewey and Howe. Jerry Mander, Partner.
Management Team Example Summary
Most startup businesses have a lean management team. A savvy founder will find a way to surround him or herself with individuals who will help the business get started, grow and thrive as non-executive contributors.
Use our provided information and management team examples to present a well-rounded management team section in your business plan.
If you still need to get some of the ancillary advisors we’ve recommended, now is the time to expand your influence circle. You’ll find that there are highly qualified individuals who are willing and even enthusiastic to be a part of your success.
Ready to complete your business plan in just 1 day?
Click GET STARTED to learn more about our fill-in-the-blank business plan template. We’ll step you through all the details you need to develop a professional business plan in just one day!
Successfully used by thousands of people starting a business and writing a business plan. It will work for you too!
Management plan 101: How to create a comprehensive plan
Last updated
31 January 2024
Reviewed by
Shawnna Johnson
A company's success begins with a comprehensive management plan. This plan becomes the North Star for the team and maintains operations integrity when problems arise.
A management plan is the framework a company needs to achieve its goals and acquire new market share. Let's explore the concept of a management plan and discuss essential strategies.
- What is a management plan?
A management plan is a document that describes how to execute, monitor, and control a project, program, business, or organization. The size and complexity of the plan depend on the scope.
The management plan's goal is to guide the team, build consistency, and help meet deadlines. Since each project involves simultaneous processes, it's easy to get off track without a plan.
A well-designed management plan can help business owners manage resources, meet goals, and plan future operations. It contains a strategy for meeting short- and long-term goals.
Management plans aren't set in stone. They are flexible enough to introduce changes according to the project's progress, economic downturns, market fluctuations, and other variables.
- Benefits of a management plan
A business can benefit from a management plan regardless of its size. Even if you have a small team, a comprehensive plan can become integral to successful operations.
No matter how many tasks you have to manage to achieve your goals, a transparent framework can maximize operational efficiency.
Resource management
Juggling numerous resources is one of the toughest tasks a company faces when executing a project. From financial to human, companies often waste these resources due to the lack of structure.
A management plan outlines the resources an organization needs for each project, allowing you to control available assets and avoid waste.
Imagine a software development firm lands a large one-time government project. A management plan can help the company see how many developers it can spare while considering ongoing work.
Goal alignment
A management plan doesn't just serve as a robust operation framework. It helps the company to set clear goals. In fact, without setting SMART goals , it can be nearly impossible to design an effective plan.
Goal clarity helps allocate resources and delegate tasks to team members. It also shows your employees how their work contributes to business success, increasing engagement and boosting productivity.
Risk mitigation
No matter how strong your business is, unexpected issues arise with internal operations and the external environment. From local security breaches to economic crises, each disruption can cause downtime and lost market share.
A management plan accounts for risks and gives your team guidelines to counter them. Your plan can minimize the impact of risk by proactively assessing and preparing for it.
Decision-making
A management plan can make your decision-making process more strategic. A robust framework ensures decision-makers have an easier time considering risks, evaluating options, and selecting the most suitable course of action.
With a management plan, there is less uncertainty for the future and more opportunities for making data-driven decisions. This is especially valuable during crises.
Performance measurement
A robust management plan establishes key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to evaluate the project’s progress. This simplifies ongoing monitoring and allows for timely adjustments.
Higher-level management can use the performance management instruments outlined in the plan to prioritize activities when directing the team. It simplifies the process of making adjustments and staying on track to achieving the goal.
Communication
A management plan should define communication channels at the project planning stage. It must outline exactly how all team members communicate and the reporting hierarchy. This can ensure proper accountability for each employee.
With the right approach to communication planning, you can minimize misunderstandings, waste, and duplicate work.
- How to create an effective management plan
While complex plans may require extensive blueprints, the effort you invest in creating an effective management plan can have an impressive ROI. Each step of a management plan simplifies business operations and risk mitigation.
Step 1: Outline vision and mission statements
Regardless of the project you’re working on, you must ensure it aligns with your vision and mission. This is especially important when creating a general management plan for your company's operations.
These statements guide your team when setting goals, prioritizing, and outlining key steps to achieve milestones. Ensure you’re clear on the purpose of your business, its underlying philosophy and values, and your target audience.
Step 2: Set goals
Whether you’re creating a long-term business management plan or a short-term project management plan, you need to identify goals. Even plans for short-term projects should still be part of long-term business objectives.
Ideally, you should be creating SMART goals from the start. If your current objectives are vague, consider breaking them down into smaller parts.
Since goal clarity is the power behind an effective plan, try to provide as many details as possible. Make sure all goals align with the company's mission, values, and philosophy.
While setting goals, consider focusing on negative goals as well. Outline exactly what you don't want the project to focus on. These boundaries can keep your team on track.
Step 3: Allocate resources
The next step is to outline the finances, time, people, and equipment you need to achieve the goals. How much time can you spare for this particular project? This step has a direct effect on the scope of your operations. It may also help you adjust the initial goals.
The money and workforce you can dedicate to the project must be realistic. Rely on historical company data to understand how much you can invest. If you couldn’t complete similar projects in the past, make relevant adjustments to resource distribution.
At this step, you should also plan for unexpected factors. The project's budget should include a force majeure allocation. Meanwhile, you should have a backup plan for bringing in more team players if necessary.
Step 4: Define roles
At this stage, focus on delegating project elements to team members. Clarity and detail are essential to avoid confusion.
You can create a team chart that demonstrates who is involved in the project and what activities they’re responsible for. Simplify collaboration by mentioning who each person reports to and adding contact options.
Each team member must know who to turn to for advice and information. Otherwise, you won't be able to handle any emergencies effectively.
Step 5: Create a timeline
If you have a time-bound goal, create a timeline to help your team stay on track for deadlines. A transparent schedule will also help with allocating resources.
Imagine you’re planning a rebranding. A key question is how long it will take. Without a defined timeline, this sizable project could continue indefinitely, hurting your business and affecting employee engagement.
Your goal is to make sure everyone knows when they have to deliver. Outlining this in a plan creates a North Star for the team.
Step 6: Conduct a situational analysis
To mitigate risks and support operations, you need to assess the internal and external factors that can impact your business and its projects. A SWOT analysis covers everything, including analyzing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
During the threat analysis, you need to identify:
Problems with the potential to disrupt the project or business operations
Any point in a timeline where risks are likely
The chance of risks and disasters
Risk triggers
Next, you need to figure out a strategy for addressing the possible risks and avoiding triggers.
Understanding what outcomes to expect if a disaster happens mitigates the negative elements, keeping the business on track.
Step 7: Share your management plan
Communicating your management plan to all the stakeholders brings everyone on board.
Share the plan with employees, managers, and investors in the most digestible way possible. For some, this plan becomes an essential tool for team management. For others, it's proof of your business' stability and potential.
Educate your team members about the elements of the management plan and teach them how to use it for their benefit. Explain how this guidance can help them achieve business goals.
Step 8: Create an executive summary
An executive summary is a concise overview of the key plan elements and highlights. It provides a high-level summary of your business's goals, strategies, and action plans.
This summary provides busy executives, stakeholders, or decision-makers with a quick understanding of the management plan without reading the entire document.
Your summary should include:
Brief business description
Mission and vision
Key objectives
Execution strategies
Major initiatives
Expected outcomes
In short, the executive summary should capture the essence of the management plan and invite the reader to explore details where necessary.
Step 9: Review and update your plan
Management plans require continuous monitoring, reviewing, and updating. As the market, economy, or internal situation changes, you may need to adjust the plan.
Make sure the plan stays relevant to your business goals and external factors. Otherwise, even the most robust risk mitigation strategy won't be able to keep the business running smoothly.
- Project management plan template
An example of a project management plan is:
Project scope:
Project goals, objectives, and deliverables
Key stakeholders and their roles and responsibilities
Project timelines and milestones
Team organization:
A project team with the required skills and expertise
Roles and responsibilities of each team member
Communication channels and reporting structures
Risk management:
Potential risks and uncertainties that could impact the project
Risk mitigation plan to address and minimize the impact of these risks
Resource allocation
Identification of available resources (staffing, equipment, budget)
Resource allocation according to the project needs and schedule
Communication plan:
Team and stakeholder communication channels
Frequency and methods of project communication (meetings, reports, emails, etc.)
Change management:
Process for managing changes to the project scope, requirements, or timeline
Roles and responsibilities for change control
Project monitoring and control:
A system to track progress, including key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics
Corrective actions for deviations
Documentation and reporting:
A documentation plan to ensure all project-related documents are properly maintained
Reporting schedule and format for project updates
While this example works for most cases, you should tailor your management plan to the specific needs of your project and business.
- Leveraging management plans for business improvement
Business and project management plans can streamline your business operations. They give you the blueprint for achieving goals and guide the team to stay on track.
A successful management plan requires in-depth research and a full evaluation of the company's capabilities. The more you analyze historical data, the easier it will be to create a realistic plan.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 3 October 2023
Last updated: 16 September 2023
Last updated: 21 March 2024
Last updated: 29 November 2023
Last updated: 23 November 2023
Last updated: 18 July 2023
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Last updated: 29 June 2023
Last updated: 8 December 2023
Last updated: 14 November 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Sample Business Plan
Following is a business plan written by The Business Plan Store. It is posted here with the express permission of the client (Executive names are fictitious)
We write business plans! To get started on yours, contact us here .
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach to managing and streamlining business processes . BPM is intended to help improve the efficiency of existing processes, with the goal of increasing productivity and overall business performance.
BPM is often confused with other seemingly similar initiatives. For example, BPM is smaller in scale than business process reengineering (BPR), which radically overhauls or replaces processes. Conversely, it has a larger scope than task management, which deals with individual tasks, and project management, which handles one-time initiatives. And while enterprise resource planning (ERP) integrates and manages all aspects of a business, BPM focuses on its individual functions—optimizing the organization’s existing, repeatable processes end-to-end.
An effective BPM project employs structured processes, uses appropriate technologies and fosters collaboration among team members. It enables organizations to streamline project workflows, enhance productivity and consistently deliver value to stakeholders. Ultimately, the successful implementation of BPM tools can lead to increased customer satisfaction, competitive advantage and improved business outcomes.
3 main types of business process management
Integration-centric BPM focuses on processes that don’t require much human involvement. These include connecting different systems and software to streamline processes and improve data flow across the organization, for example human resource management (HRM) or customer relationship management (CRM)
Human-centric BPM centers around human involvement, often where an approval process is required. Human-centric BPM prioritizes the designing of intuitive processes with drag and drop features that are easy for people to use and understand, aiming to enhance productivity and collaboration among employees.
Document-centric BPM is for efficiently managing documents and content—such as contracts—within processes. A purchasing agreement between a client and vendor, for example, needs to evolve and go through different rounds of approval and be organized, accessible and compliant with regulations.
Business process management examples
BPM can help improve overall business operations by optimizing various business processes. Here are some BPM examples that outline the use cases and benefits of BPM methodology:
Business strategy
BPM serves as a strategic tool for aligning business processes with organizational goals and objectives. By connecting workflow management, centralizing data management , and fostering collaboration and communication, BPM enables organizations to remain competitive by providing access to accurate and timely data. This ensures that strategic decisions are based on reliable insights.
Through BPM, disparate data sources—including spend data, internal performance metrics and external market research—can be connected. This can uncover internal process improvements, strategic partnership opportunities and potential cost-saving initiatives. BPM also provides the foundation for making refinements and enhancements that lead to continuous improvement.
- Enhanced decision-making
- Efficient optimization
- Continuous improvement
Claims management
BPM can be used to standardize and optimize the claims process from start to finish. BPM software can automate repetitive tasks such as claim intake, validation, assessment, and payment processing—using technology such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA ). By establishing standardized workflows and decision rules, BPM streamlines the claims process by reducing processing times and minimizing errors. BPM can also provide real-time visibility into claim status and performance metrics. This enables proactive decision-making, ensures consistency and improves operational efficiency.
- Automated claim processing
- Reduced processing times
- Enhanced visibility
Compliance and risk management
By automating routine tasks and implementing predefined rules, BPM enables timely compliance with regulatory requirements and internal policies. Processes such as compliance checks, risk evaluations and audit trails can be automated by using business process management software, and organizations can establish standardized workflows for identifying, assessing, and mitigating compliance risks. Also, BPM provides real-time insights into compliance metrics and risk exposure, enabling proactive risk management and regulatory reporting.
- Automated compliance checks
- Real-time insights into risk exposure
- Enhanced regulatory compliance
Contract management
Contract turnaround times can be accelerated, and administrative work can be reduced by automating tasks such as document routing, approval workflows and compliance checks. Processes such as contract drafting, negotiation, approval, and execution can also be digitized and automated. Standardized workflows can be created that guide contracts through each stage of the lifecycle. This ensures consistency and reduces inefficiency. Real-time visibility into contract status improves overall contract management.
- Accelerated contract turnaround times
- Real-time visibility into contract status
- Strengthened business relationships
Customer service
BPM transforms customer service operations by automating service request handling, tracking customer interactions, and facilitating resolution workflows. Through BPM, organizations can streamline customer support processes across multiple channels, including phone, email, chat, and social media. With BPM, routine tasks such as ticket routing and escalation are automated. Notifications can be generated to update customers about the status of their requests. This reduces response times and improves customer experience by making service more consistent. BPM also provides agents with access to a centralized knowledge base and customer history, enabling them to resolve inquiries more efficiently and effectively.
- Streamlined service request handling
- Centralized knowledge base access
- Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty
Financial management
BPM is used to streamline financial processes such as budgeting, forecasting, expense management, and financial reporting. It ensures consistency and accuracy in financial processes by establishing standardized workflows and decision rules, reducing the risk of human errors and improving regulatory compliance. BPM uses workflow automation to automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, reconciliation and report generation. Real-time visibility into financial data enables organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Increased operational efficiency
- Instant insights for informed decision-making
- Enhanced compliance with regulations and policies
Human resources
Using BPM, organizations can implement standardized HR workflows that guide employees through each stage of their employment experience, from recruitment to retirement . The new employee onboarding process and performance evaluations can be digitized, which reduces administrative work and allows team members to focus on strategic initiatives such as talent development and workforce planning. Real-time tracking of HR metrics provides insights into employee engagement, retention rates, and the use and effectiveness of training.
- Reduced administrative work
- Real-time tracking of HR metrics
- Enhanced employee experience
Logistics management
BPM optimizes logistics management by automating processes such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and shipment tracking, including those within the supply chain. Workflows can be established that govern the movement of goods from supplier to customer. Automating specific tasks such as order processing, picking, packing and shipping reduces cycle times and improves order accuracy. BPM can also provide real-time data for inventory levels and shipment status, which enables proactive decision-making and exception management.
- Streamlined order processing and fulfillment
- Real-time visibility into inventory and shipments
- Enhanced customer satisfaction and cost savings
Order management
BPM streamlines processes such as order processing, tracking, and fulfillment. BPM facilitates business process automation —the automation of routine tasks such as order entry, inventory management, and shipping, reducing processing times and improving order accuracy. By establishing standardized workflows and rules, BPM ensures consistency and efficiency throughout the order lifecycle. Increased visibility of order status and inventory levels enables proactive decision-making and exception management.
- Automated order processing
- Real-time visibility into order status
- Improved customer satisfaction
Procurement management
BPM revolutionizes procurement management through the digital transformation and automation of processes such as vendor selection, purchase requisition, contract management, and pricing negotiations. Workflows can be established that govern each stage of the procurement lifecycle, from sourcing to payment. By automating tasks such as supplier qualification, RFx management, and purchase order processing, BPM reduces cycle times and improves efficiency. Also, with real-time metrics such as spend analysis, supplier performance, and contract compliance, BPM enables business process improvement by providing insights into areas suitable for optimization.
- Standardized procurement workflows
- Real-time insights into procurement metrics
- Cost savings and improved supplier relationships
Product lifecycle management
BPM revolutionizes product lifecycle management by digitizing and automating processes such as product design, development, launch, and maintenance. Workflows that govern each stage of the product lifecycle, from ideation to retirement can be standardized. Requirements gathering, design reviews, and change management , can be automated. This accelerates time-to-market and reduces development costs. BPM can also encourage cross-functional collaboration among product development teams, which ensures alignment and transparency throughout the process.
- Accelerated time-to-market
- Reduced development costs
- Enhanced cross-functional collaboration
Project management
In the beginning of this page, we noted that BPM is larger in scale than project management. In fact, BPM can be used to improve the project management process. Business process management tools can assign tasks, track progress, identify bottlenecks and allocate resources. Business process modeling helps in visualizing and designing new workflows to guide projects through each stage of the BPM lifecycle. This ensures consistency and alignment with project objectives. Tasks assignments, scheduling, and progress monitoring can be automated, which reduces administrative burden and improves efficiency. Also, resource utilization and project performance can be monitored in real time to make sure resources are being used efficiently and effectively.
- Streamlined project workflows
- Real-time insights into project performance
- Enhanced stakeholder satisfaction
Quality assurance management
BPM facilitates the automation of processes such as quality control, testing, and defect tracking, while also providing insights into KPIs such as defect rates and customer satisfaction scores. Quality assurance (QA) process steps are guided by using standardized workflows to ensure consistency and compliance with quality standards. Metrics and process performance can be tracked in real time to enable proactive quality management. Process-mapping tools can also help identify inefficiencies, thereby fostering continuous improvement and QA process optimization.
- Automated quality control processes
- Real-time visibility into quality metrics
Business process management examples: Case studies
Improving procure-to-pay in state government.
In 2020, one of America’s largest state governments found itself in search of a new process analysis solution . The state had integrated a second management system into its procurement process, which required the two systems, SAP SRM and SAP ECC, to exchange data in real time. With no way to analyze the collected data, the state couldn’t monitor the impact of its newly integrated SAP SRM system, nor detect deviations during the procurement process. This created an expensive problem.
The state used IBM Process Mining to map out its current workflow and track the progress of the SAP SRM system integration. Using the software’s discovery tool, data from both management systems was optimized to create a single, comprehensive process model. With the end-to-end process mapped out, the state was able to monitor all its process activities and review the performance of specific agencies.
Streamlining HR at Anheuser-Busch
AB InBev wanted to streamline its complicated HR landscape by implementing a singular global solution to support employees and improve their experience, and it selected workday as its human capital management (HCM) software. Working with a team from IBM® Workday consulting services , part of IBM Consulting™, AB InBev worked with IBM to remediate the integration between the legacy HR apps and the HCM software.
What was once a multi-system tool with unorganized data has become a single source of truth, enabling AB InBev to run analytics for initiatives like examining employee turnover at a local scale. Workday provides AB InBev with a streamlined path for managing and analyzing data, ultimately helping the company improve HR processes and reach business goals.
Business process management and IBM
Effective business process management (BPM) is crucial for organizations to achieve more streamlined operations and enhance efficiency. By optimizing processes, businesses can drive growth, stay competitive and realize sustainable success.
IBM Consulting offers a range of solutions to make your process transformation journey predictable and rewarding.
- Traditional AI and generative AI-enabled Process Excellence practice uses the leading process mining tools across the IBM ecosystem and partners.
- Our patented IBM PEX Value Triangle includes industry standards, benchmarks, and KPIs and is used to quickly identify process performance issues and assess where and how our clients can optimize and automate everywhere possible.
- IBM Automation Quotient Framework and Digital Center of Excellence (COE) platform prioritized and speeds up automation opportunities, ultimately establishing a Process Excellence COE for continuous value orchestration and governance across your organization.
Key improvements might include 60-70% faster procurement, faster loan booking, and reduced finance rework rate, along with risk avoidance, and increased customer and employee satisfaction.
With principles grounded in open innovation, collaboration and trust, IBM Consulting doesn’t just advise clients. We work side by side to design, build, and operate high-performing businesses—together with our clients and partners.
More from Business transformation
Using generative ai to accelerate product innovation.
3 min read - Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) can be a powerful tool for driving product innovation, if used in the right ways. We’ll discuss select high-impact product use cases that demonstrate the potential of AI to revolutionize the way we develop, market and deliver products to customers. Stacking strong data management, predictive analytics and GenAI is foundational to taking your product organization to the next level. 1. Addressing customer inquiries with an AI-driven chatbot ChatGPT distinguished itself as the first publicly accessible GenAI-powered…
Integrating AI into Asset Performance Management: It’s all about the data
3 min read - Imagine a future where artificial intelligence (AI) seamlessly collaborates with existing supply chain solutions, redefining how organizations manage their assets. If you’re currently using traditional AI, advanced analytics, and intelligent automation, aren’t you already getting deep insights into asset performance? Undoubtedly. But what if you could optimize even further? That’s the transformative promise of generative AI, which is beginning to revolutionize business operations in game-changing ways. It may be the solution that finally breaks through dysfunctional silos of business units,…
Create a lasting customer retention strategy
6 min read - Customer retention must be a top priority for leaders of any company wanting to remain competitive. An effective customer retention strategy should support the company to maintain a healthy stable of loyal customers and bring in new customers. Generating repeat business is critical: McKinsey’s report on customer acquisition states (link resides outside of ibm.com) that companies need to acquire three new customers to make up the business value of losing one existing customer. Customer retention has become more difficult in…
IBM Newsletters
Portal login
Cyber Security Incident Response Plan

Content written for
Attachments.
- Cyber Incident Response Plan - Guidance - July 2022 1.98MB .pdf
- Cyber Incident Response Readiness Checklist - July 2022 1.18MB .pdf
- Cyber Security Incident Response Plan - Template 1.31MB .docx
The Australian Signals Directorate's Australian Cyber Security Centre (ASD's ACSC) defines a cyber security incident as an unwanted or unexpected cyber security event, or a series of such events, that have a significant probability of compromising business operations.
Australian organisations are frequently targeted by malicious cyber adversaries. ASD's ACSC assessed that malicious cyber activity against Australia’s national and economic interests is increasing in frequency, scale, and sophistication. As adversaries become more adept, the likelihood and severity of cyber attacks is also increasing due to the inter-connectivity and availability of information technology platforms, devices and systems exposed to the internet.
To illustrate the volume of cyber security incidents occurring in Australia, ASD's ACSC responded to over 1500 cyber security incidents between 1 July 2020 and 30 June 2021. While many of the incidents reported to the ASD's ACSC could have been avoided or mitigated by good cyber security practices, such as implementation of ASD’s Essential Eight security controls, risks will still remain when organisations operate online.
All organisations should have a cyber security incident response plan to ensure an effective response and prompt recovery in the event security controls don’t prevent an incident occurring. This plan should be tested and regularly reviewed.
To be effective, a cyber security incident response plan should align with the organisation’s incident, emergency, crisis and business continuity arrangements, as well as jurisdictional and national cyber and emergency arrangements. It should support personnel to fulfill their roles by outlining their responsibilities and all legal and regulatory obligations.
For more information download the Cyber Security Incident Response Plan - Guidance & Template and the Cyber Security Incident Response Readiness Checklist .
Thanks for your feedback!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The management section of a business plan helps show how your management team and company are structured. The first section shows the ownership structure, which might be a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. The internal management section shows the department heads, including sales, marketing, administration, and production.
Examples of management plans for a business plan. Performance & Compensation A description of your performance management and compensation processes, practices and policies. The goal is to show a degree of organizational maturity in tying compensation to performance whereby a formal performance review process occurs and this is visible to your governance structures.
Management Team Business Plan Example. Below are examples of how to include your management section in your business plan. Example #1. Key Team Members. Jim Smith, Founder & CEO. Jim has 15 years of experience in online software development, having co-founded two previous successful online businesses. His first company specialized in developing ...
The management plan is all about employees and operations. Employees are one of the most important parts of any new venture. Good employees can make your life much easier, while bad employees can distract you and be a detriment to your success. Operational structure can be the difference between a successful venture and a failure.
The organization and management section of your business plan should provide details about your business structure and team. This section typically comes after the executive summary. However, some people have it further in the document after the market analysis section. ... We have included an example organizational chart below for guidelines only.
2. Prove that your management team can execute your idea and if not, help hire the right fit for a position. 3. Share how your advisory board can help your team succeed. Your business plan readers are usually investors. They are interested in how trustworthy and experienced your management team is.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
For example, ownership might be divided in a partnership agreement or to holders of stock in the company. 2. Name your board members. If your business has a board, you should clearly identify its members. Write a brief summary of their leadership capabilities, past experiences, strengths, and weaknesses.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
This section of your business plan, Organization and Management, is where you'll explain exactly how you're set up to make your ideas happen, plus you'll introduce the players on your team. As always, remember your audience. If this is a plan for your internal use, you can be a little more general than if you'll be presenting it to a ...
A management plan is a document that outlines how a management team will direct resources to achieve objectives. These can be used to manage missions, teams, programs, projects and initiatives. The following are examples of sections that can be included in a management plan as required. ... 5 Examples of a Management Plan for a Business Plan »
The management and operations in the business plan will employ a full-time staff of three and three part-time employees. The staff will have several key responsibilities, including scheduling services, addressing customer inquiries, managing facilities, and keeping track of inventory. They will also undergo comprehensive training to ...
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
Consider following these instructions to create an impressive team business plan: 1. Collect resumes from each manager. Resumes typically discuss a professional's credentials, including education, work experience and soft and technical skills. You can use your management team's resumes to guide you into creating content for your business plan.
Every business plan has key sections such as management and marketing. It should also have an executive summary, which is a synopsis of each of the plan sections in a one- to two-page overview.
Business Planning. Planning by business, marketing and sales units that are responsible for revenue. Business development strategy. Product management strategy. Product development planning. Go-to-market strategy. Marketing strategy. Sales strategy. Sales forecasting.
Management Summary in a Business Plan. This summary is important to a business plan because it describes the team's competencies and shows their experience which is important to achieve the company's goals. Shareholders and investors are more than likely going to be interested in this kind of information. Once you decide to create a business ...
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
Management Team. The purpose of including the management team in a business plan is that it provides an overview of your founders and key employees. Yet, in the beginning, that might be just one person. You can increase your plan's credibility by establishing a supporting cast of key mentors and advisors and including them in this section.
A management plan is a document that describes how to execute, monitor, and control a project, program, business, or organization. The size and complexity of the plan depend on the scope. The management plan's goal is to guide the team, build consistency, and help meet deadlines. Since each project involves simultaneous processes, it's easy to ...
Sample Business Plan. Following is a business plan written by The Business Plan Store. It is posted here with the express permission of the client. (Executive names are fictitious) Management Summary. Our management team is comprised of people with many years of experience in the long-term care provider and software development industries.
1. Regular reviews and updates. Markets shift, consumer behavior changes, and your business will grow. Your plan must evolve with these factors, which makes regular reviews and updates a must-do ...
BPM is intended to help improve the efficiency of existing processes, with the goal of increasing productivity and overall business performance. BPM is often confused with other seemingly similar initiatives. For example, BPM is smaller in scale than business process reengineering (BPR), which radically overhauls or replaces processes.
To be effective, a cyber security incident response plan should align with the organisation's incident, emergency, crisis and business continuity arrangements, as well as jurisdictional and national cyber and emergency arrangements. It should support personnel to fulfill their roles by outlining their responsibilities and all legal and ...