

Project Final Report

Project management is a difficult task to accomplish as you have to take a lot of aspects into consideration. After finishing a project, it’s also required to prepare a detailed project report. A Project Report must contain a summary of all the points that were taken into consideration while working on a particular project. It must covey the usage and viability of the project and the benefit of the project to the concerned parties. Here is a list of 19+ project final report examples and templates.
Project Final Report Examples & Templates
1. free final project handover report.

- Editable PDF
Size: A4 & US
A final report must contain a just of the important information about the project. This template can be used to prepare a final project handover report with signatures of the receiver and provider to keep a record.
2. Project Design Final Report

Size: 266 KB
Engineering students need to work on a project and submit at the end of the semester. This templates is an instruction list that can be used by an engineering student to prepare a final report for their project as it contains the guidelines for the final report .
3. Project Final Report Example

This template is a sample of a final project report of a scientific research project. It describes the objectives of the project conducted and also achieved outcomes of the project. It can be used by companies in the food industry to get an overview of the market.
4. Project Final Report in PDF

Size: 87 KB
This template is a sample of guidelines provided by a nursing foundation (FoNS) for the preparation of a final project report. It contains a list of topics and subtopics which are required to be mentioned to prepare a final report on any of their projects.
5. Sample Project Final Report

Size: 184 KB
This template is a sample of a project final report which has been prepared in two parts. The first part provides achievements and the feedback on the project’s implementation and the second part provides technical support to co-operation programs through a pilot scheme based on the achievements, and problems that the first part has undergone. It is primarily aimed at financially viable research startups.
6. Basic Project Final Report Example
Preparing a project final report is a long process. This template explains and guides you through the steps of creating a project final report through the use of an energy expenditure plan online, which is specifically designed for the benefit of Local Educational Agencies of the concerning area.
7. Project Final Report Format

If you are a professor and are required to manage several projects of students on software development, then this template can be useful to you to suggest a similar solution to your university as it will help manage the projects in an automated manner and will give a summary of project final reports very easily.
8. Sample Project Final Report Example
Size: 532 KB
This template is a sample of a RiCORE project final report. This template will provide you with the risk profile of the project and also explain the list of different phases of projects they have worked on to ensure the environmental impact is within manageable limits, and that the standards are acceptable to all member countries of the forum.
9. Basic Project Final Report

Size: 964 KB
Some organizations provide grants for the success of a project. This template provides a guide on the requirement of information that the organization wants in the final report before payment of the grant money.
10. Standard Project Final Report

This template is a standard final report of a project on an understanding of eco-innovation by MEI. This final report gives complete information about the eco-innovation drive that has been launched and also measures the competitiveness of eco-innovation for the benefit of the ecology.
11. Simple Project Final Report Example

Size: 264 KB
This template is a simple project final report on European educational research quality indicators. This template explains the research quality measurement and the new innovative methods introduced in the last few years in this arena.
12. Standard Project Final Report Sample

This template is a standard project final report of a study of conflict among the diverse societies in North Eastern India, and how can the conflicts be reduced. A grant is provided to the researchers for completing the project. This sample final report is to be submitted to avail the grant.
13. Formal Project Final Report

This template is a sample of a formal scientific project final report. This project was done in collaboration and the report discusses the ways to improve the long term safety assessment for a geological disposal facility.
14. Project Research Final Report

This template is a project research final report. While working on a project the members have to visit a lot of places. This final report includes the expenditure the members incurred while working on the project to submit to UGC for the sanctioned grant and also contains the research study matter.
15. Project Year Final Report

Size: 26 MB
This template is a final report of a canal lining demonstration project. In a large project, the workers have to take care of several aspects to make sure that everything is on track. This template gives detailed information about those aspects of the project.
16. Sample Project Final Report in PDF

This template shows goals, management practices and the monitoring results of the project and is a guide for others participating similar government irrigation projects.
17. Professional Project Final Report Example

Size: 877 KB
This template is a professional project final report of the Enewetak radiological support project by the United States Department of Nuclear Energy. It explains the usage of nuclear energy and its effects on the test area and how the reclamation work has been implemented for restoring the ecological balance, along with defense benefits due to nuclear energy.
18. Formal Project Final Report Example

This Project Analysis Example is a sample of project report of real-time monitoring and optimization of resource efficiency in integrated processing plants. This template discusses the main result, impact, analysis and the use of the project.
19. Professional Project Final Report

This is a sample of a project final report of business model innovation for high-performance buildings supported by whole life optimization. The project aims at creating innovative buildings that are optimized to conserve energy.
20. Project Final Report Template

If you are an electrical engineering student, then this template can be of great help to you. This template will guide you through the different aspects of the innovative project.
Report Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.
Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Simon Fraser University Engaging the World
- A-Z directory
Guide to Completing Your Final Report
Purposes of a Final Report
How we evaluate final reports
Part I of the final report template: Report of findings
Parts II to V: Changes & Implications; Sharing & Dissemination; Keywords & Student Involvement
- Guide to Completing Your Final Report (PDF)
Useful links:
- Final report template (DOCX)
- Final report exemplars
- Excel graph templates (XLSX)
The ISTLD sometimes receives requests from project teams for either examples of project final reports or advice on how to write them. It is challenging to respond with generic advice as all the projects are very different from one another and faculty bring a wide-range of research tools and perspectives to the task of doing their projects. As a result, each project can have unique reporting needs. This document provides a general outline of how to proceed, but we encourage faculty who feel they might need advice on analysis, data display or reporting to contact the ISTLD to talk through their concerns and get some advice.
- The project PI is accountable to ISTLD for completion of the work
- In turn, the ISTLD is accountable to the VPA and must demonstrate the project funding has been well-spent
- The reports are made public on the ISTLD website
- We provide links to final reports to other faculty developing related project proposals
- We often provide links to final reports for faculty conducting projects or writing up their own reports
- Evidence of project impact on student learning and experience
- Evidence of project impact on instructor learning and growth
- Evidence of project impact beyond it original intent (that is, “ripple effects”)
Because of the accountability role final reports serve, faculty who do not turn in final reports or do not make requested edits are ineligible for future funding from the ISTLD.
For about 40% of the final reports turned in, we do ask for some edits. We do our best to minimize such requests and most are for minor changes to improve clarity. We look for the following in the reports:
- Did you do what you said you were going to do?
- Can we understand what you did? Will other faculty understand what you did?
- Can we understand what you learned? Will other faculty understand what you learned?
- Did you complete all the sections of the final report template?
To get started: Re-read your proposal, especially the section titled, “ Contents of the Final Report ”
This is the bulk of your final report. We want you to organize it in a way that makes sense to you and write in a reporting style that feels comfortable given your disciplinary training. It does not have to have a formal style like that used in a journal article, but it does need to be clear, organized and understandable by other faculty at SFU. (See Proposal and Final Report Exemplars , for several final reports of very different kinds that do a good job of meeting our core criteria: http://www.sfu.ca/istld/faculty/resources/exemplars.html )
Some faculty members write, “see attached,” for this section and append a technical report or draft manuscript to the end of the final report template, or as a separate document. This strategy is fine.
We have been asked at times to “not post” this section of the final report if either (a) it is a draft manuscript under review or (b) contains sensitive information or (c) contains policy recommendations that need approval by departments or administration. We request under these circumstances that you include a 1-2 page summary of your main findings and conclusions (essentially an extended abstract). We still want other faculty to learn from your project and they can’t do so if your findings aren’t available at all. Manuscript review can take a long time and in the meantime, the summary will do. We will make arrangements to check back with you regarding when the full final report can be posted on our website.
As you write the report of findings section, keep in mind the following:
- It should cover everything mentioned in the section of your proposal titled, “ Contents of the Final Report .”
- Think of other faculty at SFU as your audience .
- Include a brief description of the intent of your project (the problem you were trying to address or the question you were trying to explore) so that those reading the report have some context. It may help to start with the introduction from your proposal and edit that.
- Describe any changes of instruction , class structure, or teaching techniques that were the objects of study well enough that other faculty could see what you did and might be able to try it themselves.
- Describe the data you collected and your analysis methods . This description may be brief in nature, but as with a typical research report in your field, it should be clear what your data sources are and you should give your readers a basic understanding of the way you went about looking at your data. Please name and give citation information for published instruments (surveys, observation protocols, etc.) you have used or adapted. Include in an appendix those you have personally developed. For those working with kinds of data and analysis they’ve not done before, we offer advice on data analysis.
- Display your data and findings clearly. Make sure your data is understandable to others. If you use tables and graphs make sure they are clearly labeled. If you use a more narrative means of describing data and findings, make clear the breadth of the data you’re calling upon to support your story. If you or your RA are new to the kind of data you are representing, we can provide advice on data display. (See Excel Graph Templates )
- Describe your experiences and/or results : How did your changes go? What was their impact? What went well? What did not? What did you learn?
- Provide your conclusions and recommendations based on your findings . What would you do again? What do you plan to change? What are the implications of what you learned?
This section of the final report template mostly provides accountability, evaluation and research data for ISTLD. We do publish lists of project-related papers and publications, and trace the impact the projects have on students, faculty and (where applicable) SFU’s programs and structures. It typically takes only 10-15 minutes to complete.
- Complete all segments of this part of the template. If you have no response for a particular section, please write “no” or “not applicable.”
- Your response can be short and to the point for each of the questions in this section.
- If there were changes made to your project so that it differs from your original proposal, they should be described here. As long as these are relatively small and well justified they are okay. (If you encounter the need to make major changes during the conduct of your project, it is best to contact ISTLD and revise your proposal accordingly at the time the need arises.)
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
Research reports
This resource will help you identify the common elements and basic format of a research report.
Research reports generally follow a similar structure and have common elements, each with a particular purpose. Learn more about each of these elements below.
Common elements of reports
Your title should be brief, topic-specific, and informative, clearly indicating the purpose and scope of your study. Include key words in your title so that search engines can easily access your work. For example: Measurement of water around Station Pier.
An abstract is a concise summary that helps readers to quickly assess the content and direction of your paper. It should be brief, written in a single paragraph and cover: the scope and purpose of your report; an overview of methodology; a summary of the main findings or results; principal conclusions or significance of the findings; and recommendations made.
The information in the abstract must be presented in the same order as it is in your report. The abstract is usually written last when you have developed your arguments and synthesised the results.
The introduction creates the context for your research. It should provide sufficient background to allow the reader to understand and evaluate your study without needing to refer to previous publications. After reading the introduction your reader should understand exactly what your research is about, what you plan to do, why you are undertaking this research and which methods you have used. Introductions generally include:
- The rationale for the present study. Why are you interested in this topic? Why is this topic worth investigating?
- Key terms and definitions.
- An outline of the research questions and hypotheses; the assumptions or propositions that your research will test.
Not all research reports have a separate literature review section. In shorter research reports, the review is usually part of the Introduction.
A literature review is a critical survey of recent relevant research in a particular field. The review should be a selection of carefully organised, focused and relevant literature that develops a narrative ‘story’ about your topic. Your review should answer key questions about the literature:
- What is the current state of knowledge on the topic?
- What differences in approaches / methodologies are there?
- Where are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
- What further research is needed? The review may identify a gap in the literature which provides a rationale for your study and supports your research questions and methodology.
The review is not just a summary of all you have read. Rather, it must develop an argument or a point of view that supports your chosen methodology and research questions.
The purpose of this section is to detail how you conducted your research so that others can understand and replicate your approach.
You need to briefly describe the subjects (if appropriate), any equipment or materials used and the approach taken. If the research method or method of data analysis is commonly used within your field of study, then simply reference the procedure. If, however, your methods are new or controversial then you need to describe them in more detail and provide a rationale for your approach. The methodology is written in the past tense and should be as concise as possible.
This section is a concise, factual summary of your findings, listed under headings appropriate to your research questions. It’s common to use tables and graphics. Raw data or details about the method of statistical analysis used should be included in the Appendices.
Present your results in a consistent manner. For example, if you present the first group of results as percentages, it will be confusing for the reader and difficult to make comparisons of data if later results are presented as fractions or as decimal values.
In general, you won’t discuss your results here. Any analysis of your results usually occurs in the Discussion section.
Notes on visual data representation:
- Graphs and tables may be used to reveal trends in your data, but they must be explained and referred to in adjacent accompanying text.
- Figures and tables do not simply repeat information given in the text: they summarise, amplify or complement it.
- Graphs are always referred to as ‘Figures’, and both axes must be clearly labelled.
- Tables must be numbered, and they must be able to stand-alone or make sense without your reader needing to read all of the accompanying text.
The Discussion responds to the hypothesis or research question. This section is where you interpret your results, account for your findings and explain their significance within the context of other research. Consider the adequacy of your sampling techniques, the scope and long-term implications of your study, any problems with data collection or analysis and any assumptions on which your study was based. This is also the place to discuss any disappointing results and address limitations.
Checklist for the discussion
- To what extent was each hypothesis supported?
- To what extent are your findings validated or supported by other research?
- Were there unexpected variables that affected your results?
- On reflection, was your research method appropriate?
- Can you account for any differences between your results and other studies?
Conclusions in research reports are generally fairly short and should follow on naturally from points raised in the Discussion. In this section you should discuss the significance of your findings. To what extent and in what ways are your findings useful or conclusive? Is further research required? If so, based on your research experience, what suggestions could you make about improvements to the scope or methodology of future studies?
Also, consider the practical implications of your results and any recommendations you could make. For example, if your research is on reading strategies in the primary school classroom, what are the implications of your results for the classroom teacher? What recommendations could you make for teachers?
A Reference List contains all the resources you have cited in your work, while a Bibliography is a wider list containing all the resources you have consulted (but not necessarily cited) in the preparation of your work. It is important to check which of these is required, and the preferred format, style of references and presentation requirements of your own department.
Appendices (singular ‘Appendix’) provide supporting material to your project. Examples of such materials include:
- Relevant letters to participants and organisations (e.g. regarding the ethics or conduct of the project).
- Background reports.
- Detailed calculations.
Different types of data are presented in separate appendices. Each appendix must be titled, labelled with a number or letter, and referred to in the body of the report.
Appendices are placed at the end of a report, and the contents are generally not included in the word count.
Fi nal ti p
While there are many common elements to research reports, it’s always best to double check the exact requirements for your task. You may find that you don’t need some sections, can combine others or have specific requirements about referencing, formatting or word limits.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments
Filter by Keywords
Project Management
How to write a project report (with steps & templates).
March 21, 2024
Juggling all the different components of a project can be quite a challenge. If that weren’t enough, you also have to write a project status report to update key stakeholders on the project’s progress. The struggle is real.
So where do you start? Fortunately, we have the answer. And that’s precisely why we put together this guide—to walk you through the process so you have a clear path from start to finish.
Learn more about creating project reports and different types of project status reports. Plus, you’ll walk away with five free project report templates, carefully crafted to streamline your project management workflow, save you time, and impress your stakeholders. 🤩
What is a Project Report?
How to write a project report, 1. project status report, 2. project progress report, 3. project cost benefit analysis report, 4. project time tracking report, 5. project resource report, 6. project risk report, 7. project variance report, 8. project performance report, 9. project completion report, why is project reporting important, 1. final project report template, 2. project status report template, 3. digital marketing report template, 4. employee daily activity report template, 5. campaign report template, create professional project reports in less time with clickup.
A project report is a document offering a comprehensive overview of a project’s objectives, progress, team performance, and milestone accomplishments. It also gives an account of the challenges faced during a project’s execution , solutions devised to tackle them, and the lessons learned during the process.
Project managers create these reports to communicate with other project stakeholders—including team members, sponsors, clients, and other interested parties—to ensure everyone’s on the same page. The document also serves as a foundation for further evaluation and analysis to ensure the project says on track and achieves its goals. 🎯

Creating a project report doesn’t have to be a daunting task. Follow these three simple steps to create your first project report with ease.
Understand the purpose of the report
Before you create a project report, you need to understand the purpose of the report (the “why”) and know your target audience (the “who”). This will guide the content, structure, and tone of your project report.
Gather and organize the relevant information
At this point, you need to gather project information relevant to your project report. Make sure your data is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date. Organize the gathered information in a logical and structured manner.
- Executive summary : As its name suggests, this project summary gives readers a quick overview of the whole report. It’s a snapshot that highlights the most important parts of the project. While it’s placed at the start of the report, it’s often written last. It covers the project’s objectives, methodology, major outcomes, and conclusions.
- Introduction: This sets the context and expectations of the entire report. It includes the project’s purpose and scope, project schedule, the problems it aims to address, and the methodologies to get there. It also outlines the structure and organization of the rest of the report.
- Body: Typically, this is the longest part of project management reports because it dives into in-depth details, including project progress, data collection, analysis reports, constraints, and limitations. Remember that whatever you include here should reflect the purpose of your project report and the preferences of your target audience.
- Conclusions & Recommendations: Based on your findings and analysis, identify opportunities for improvement, suggest strategies for addressing them, or propose avenues for future research.
Format and proofread the report
Ensure that your project report follows a consistent formatting style—headings, subheadings, and bullet points will make it easier to read. In addition, scan your report for spelling or grammar errors and typos.
Types of Project Reports
Project reports come in diverse formats, with each serving different use cases. Here are nine of the most commonly used types of project reports.
A project status report is a document that gives a snapshot of where your project stands at any given moment. It’s like answering the question, “How’s the project doing?”
But instead of just saying “The project is fine,” you actually dive into the project goals, tasks completed, milestones achieved, challenges faced, lessons learned, potential roadblocks, and next steps.
Whether it’s a weekly project status report or a monthly status report, this documentation eliminates the need for status meetings while giving stakeholders the most recent status of the project.
A project progress report is slightly similar to a status update report, as they both discuss task progress. However, the progress report is more quantitative and zooms in on individual tasks and project milestones .
It’s like taking a magnifying glass and examining the progress of each task, one by one. For example, it could include in-depth information on the percentage of completion and current status of each task (completed, on track, delayed, etc.).
The cost-benefit analysis report is usually prepared before a project is put into motion. Of the various project reports, this one aims to answer a simple question: “Is it worth pursuing this project?”
To answer this question, the report first assesses all project costs like operational expenses, materials, salaries, equipment, and potential risks.
It then considers the projected benefits, such as increased profit margins, cost savings, improved efficiency, or happier customers. Finally, the report compares the costs to the benefits to determine if it’s time to move forward or explore other options.
A project time-tracking report is a document that records and summarizes time spent on project activities. Each project team member contributes to writing this report—they track and record the amount of time they’ve spent on tasks and submit it to the project manager. ⏰
Thankfully, the rise of project management tools has eliminated the need for paper-based time-tracking submissions. They make it easy for team members to submit accurate and detailed time reports to the project manager—while reducing the administrative burden of manual report compilation.
Project managers can see how time is spent and the overall productivity of team members. As a result, they’re able to make informed decisions, such as redistributing workload (aka workload management ), reassigning tasks, and providing feedback and support to team members.
A project resource dashboard offers a bird’s-eye view of how resources (e.g., labor, equipment, materials, budget, etc.) are allocated in a project. Think of it as a comprehensive resource inventory, listing every project task, the responsible party, and the resources being used.
Project reports like this help project managers keep track of resource availability, identify potential resource constraints or shortages, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and optimization.
A project risk report offers a comprehensive analysis of potential risks, their likelihood of occurrence, their potential impact on the project, and recommended mitigation strategies.
Rather than waiting for future events to derail the project, project reports like this one allow project managers to take a more proactive approach to risk management—thereby boosting the chances of overall project success.
A project variance report reveals the gaps or deviations between project plans and the actual performance or results achieved. It compares various factors—like budget, time, resources, and scope—and their planned values with their actual values, then computes the differences (or variances).
By analyzing these variances, project managers and stakeholders can discuss the possible reasons behind them, identify areas that need attention, and take corrective actions where necessary.
A project performance report evaluates the overall performance and achievements of a project against predetermined metrics and objectives. It includes information on project deliverables, key performance indicators (KPIs) , and stakeholder satisfaction.
This report helps project managers assess project success, identify areas for improvement, and communicate the project’s performance to stakeholders.
A project completion report marks the end of a project journey. It summarizes the entire project lifecycle, from initiation to closure. This report contains an overview of the project’s objectives, deliverables, milestones, challenges, and recommendations for future projects.
Writing project reports may initially seem redundant and time-consuming. However, it plays a crucial role in achieving project success. While a few benefits were hinted at earlier, let’s get a better picture of why project reports should not be overlooked.
More clarity
Creating a project report allows you to step back and reflect on the project’s progress. As you record the milestones, successes, and challenges, a wealth of insights begin to unfold—strengths, weaknesses, and areas that need attention.
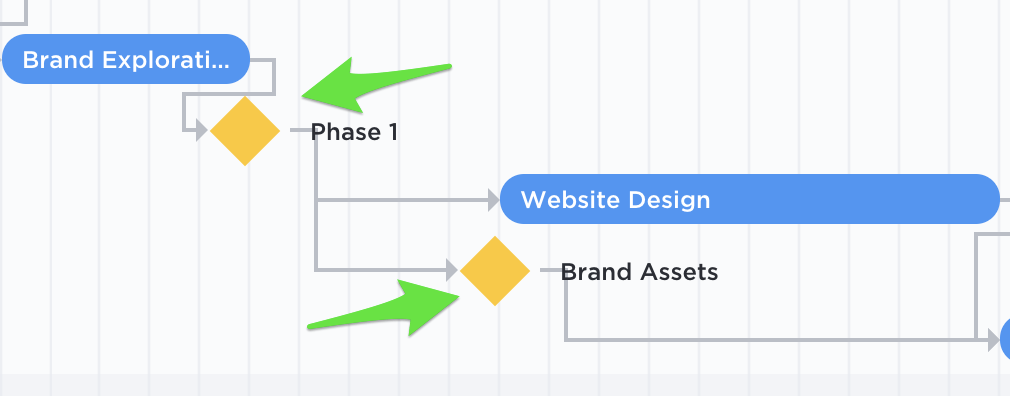
This holistic view of the project’s health helps you steer it toward the desired outcomes and ensure it stays on track.
Encourages evaluation and analysis
Project reports allow you to evaluate and analyze the different aspects of a project in a systematic way—gathering relevant data, analyzing them, and evaluating their significance. By giving your project a critical analysis, you can uncover valuable insights, identify patterns, draw meaningful conclusions, and take strategic action. 🛠️
Enhances communication and collaboration
Creating a project report challenges you to present the project’s progress and results to stakeholders in a clear and coherent manner. A well-written report promotes project transparency and ensures everyone is on the same page.
It also facilitates collaboration by providing a common reference point for discussions, feedback, and decision-making.
Boosts professionalism and credibility
When you present a comprehensive and well-structured report, it shows that you have conducted thorough research, followed a methodical approach, and can effectively communicate complex information. This, in turn, boosts your reputation, enhances your credibility, and showcases your expertise among peers, colleagues, and potential employers.
Knowledge preservation
A project report serves as a valuable reference for future research or projects. By documenting your process, methodologies, challenges, lessons, and results, you create a resource that can be consulted and built upon by others.
This contributes to the cumulative knowledge in your field and fosters a culture of collaboration and innovation.
Improves Team Alignment
Project reports are instrumental in enhancing team alignment. They provide a clear, concise snapshot of progress, identifying accomplishments, challenges, and next steps. This enables all team members to understand the project’s current status and their respective roles in achieving the overall objectives.
Check out these project report templates for teams:
- Nonprofit Organizations Project Report
- Operations Teams Project Report
- Finance Teams Project Report
- DevOps Teams Project Report
- Agile Teams Project Report
- Sales Teams Project Report
5 Project Report Examples & Templates
Sure, you could write project reports from scratch and spend countless hours formatting and structuring them. But why would you when you can use free project report templates? They provide a structure and format for your report so you can simply plug in your data and customize the design to fit your needs. Not only do project report templates speed up the report creation process, but they also enhance the overall quality of your reports.
Let’s jump right in to explore our top five project report templates. 📈
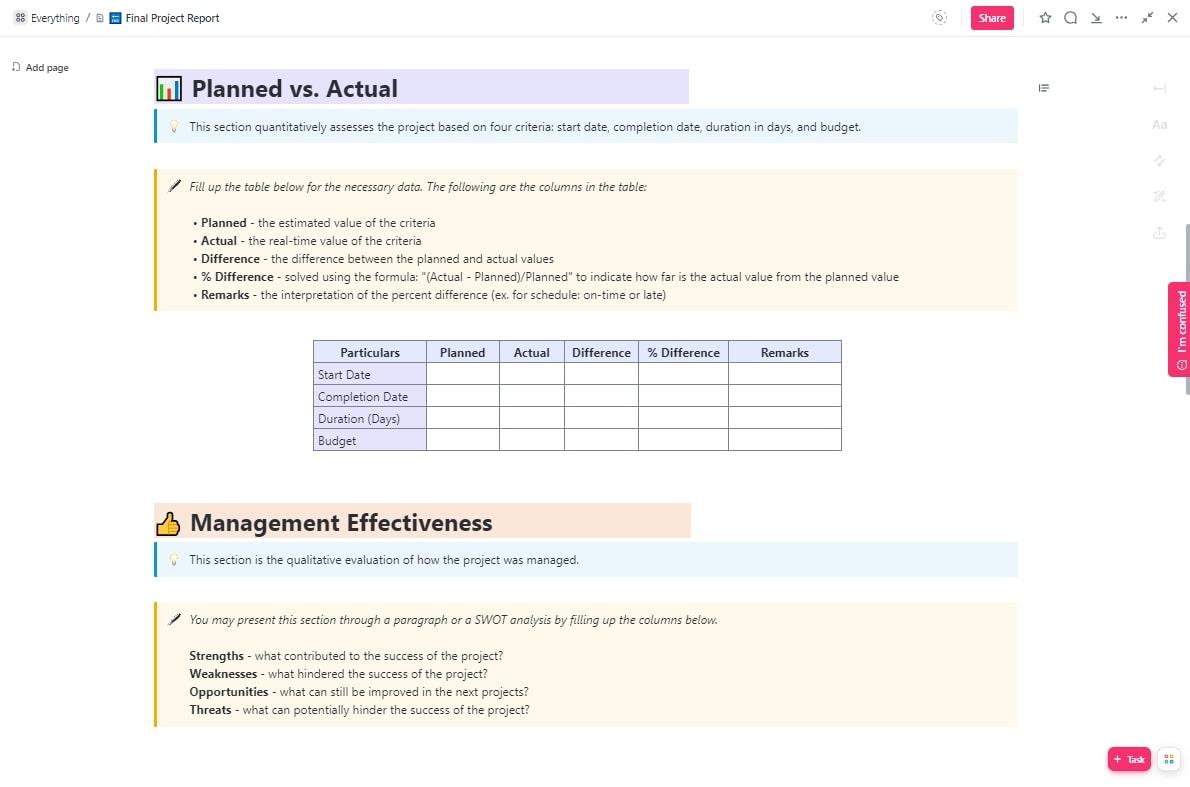
A final project report is the perfect finishing touch to conclude a project and highlight its achievements. ClickUp’s Final Project Report Template provides a solid structure to help you put it together with the following key sections:
- Planned vs. Actual: A quantitative breakdown of how the project deviated from the original plan with regard to its start date, completion date, duration, and budget
- Management Effectiveness: A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis evaluating how the project was managed
- Project Learnings : Share the important project lessons learned by the team throughout the lifespan of the project
- Contract Terms Checklist : A simple table listing the various contract terms, whether they were completed, and any remarks you have
- Overall Performance rating: A 1 out of 5 rating of the different aspects of the project, from planning and execution to leadership and communication
This template is built in ClickUp Docs , which means you have unlimited flexibility for customization—add extra sections and tweak the appearance to suit your taste. And guess what? The table of content updates in real-time as you add, edit, or delete multiple headers.
If you want to wow your team and clients, this project status report template will help you get the job done.
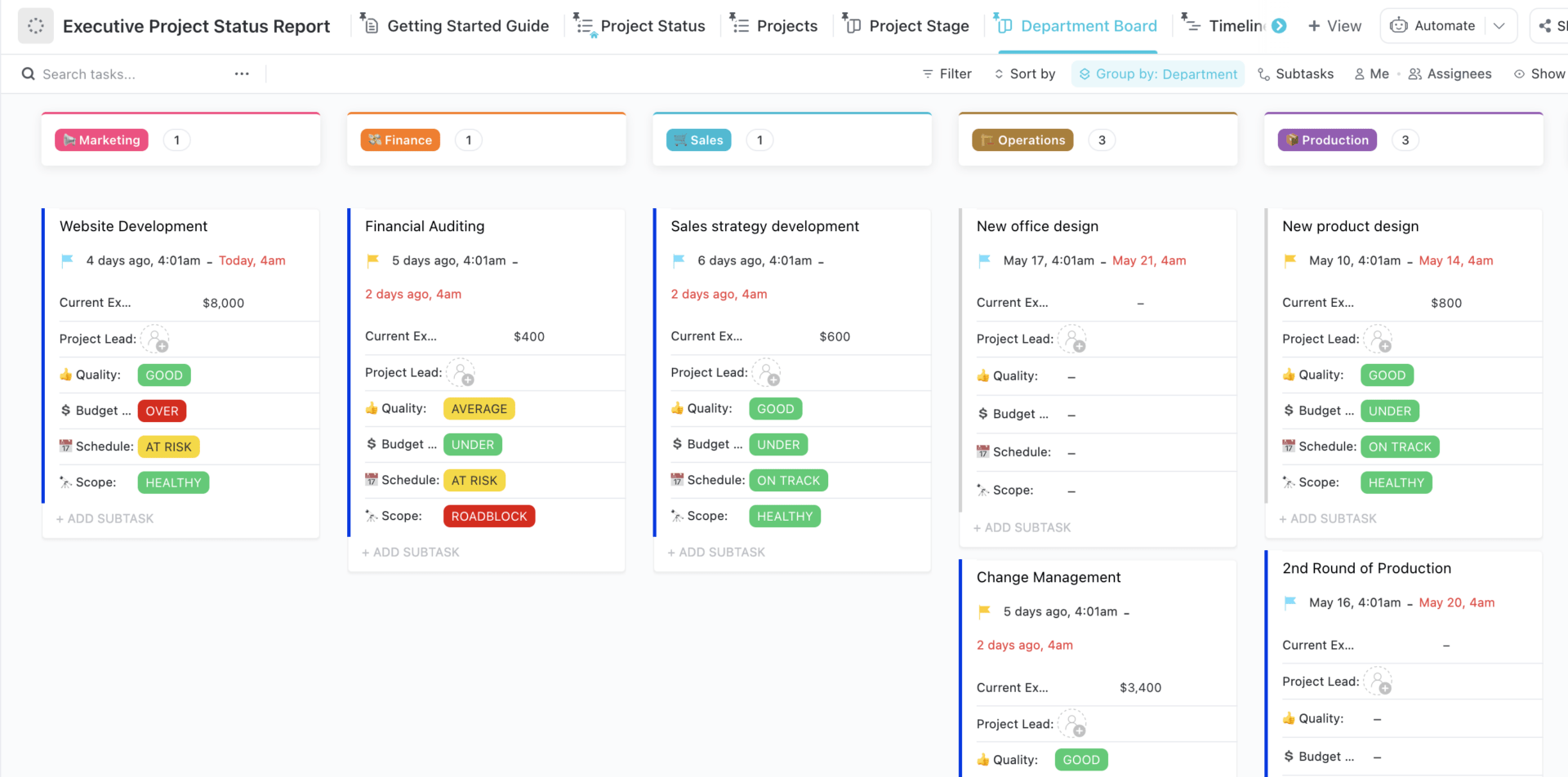
Writing a project status report is fairly straightforward. But staring at a blank document and worrying about crafting perfectly manicured sentences can make this process last a lot longer than it should.
Thankfully, ClickUp’s Project Status Report Template is here to save the day! Built inside ClickUp Whiteboards, this template provides a hassle-free method to quickly capture key project details in a visually engaging way.
- General information: Cover general project details (e.g., project name, objectives, project timeline , reporting period, etc.) which you’ll need to fill in only once
- Progress details: Use color-coding to share in-progress, at-risk, delayed, and completed tasks
- Support and resources: List out assets (e.g., labor, money, etc.) needed for a smooth operation
- Highlights and takeaways: Share key lessons learned and other noteworthy highlights
- What went well/What needs improvement: Use this opportunity to reflect on the project’s progress and share the areas that performed well and what needs attention
- Next steps: Highlight the key action items that need to get done to keep the project on track
Enter the details under each of these sections onto sticky notes, which’ll help you quickly pour down your thoughts without worrying about writing perfect sentences. It’s also very helpful for stakeholders as the information on sticky notes is short and straight to the point.
This template removes the pressure of creating a status report and saves valuable time—all while keeping key stakeholders informed and up to date.
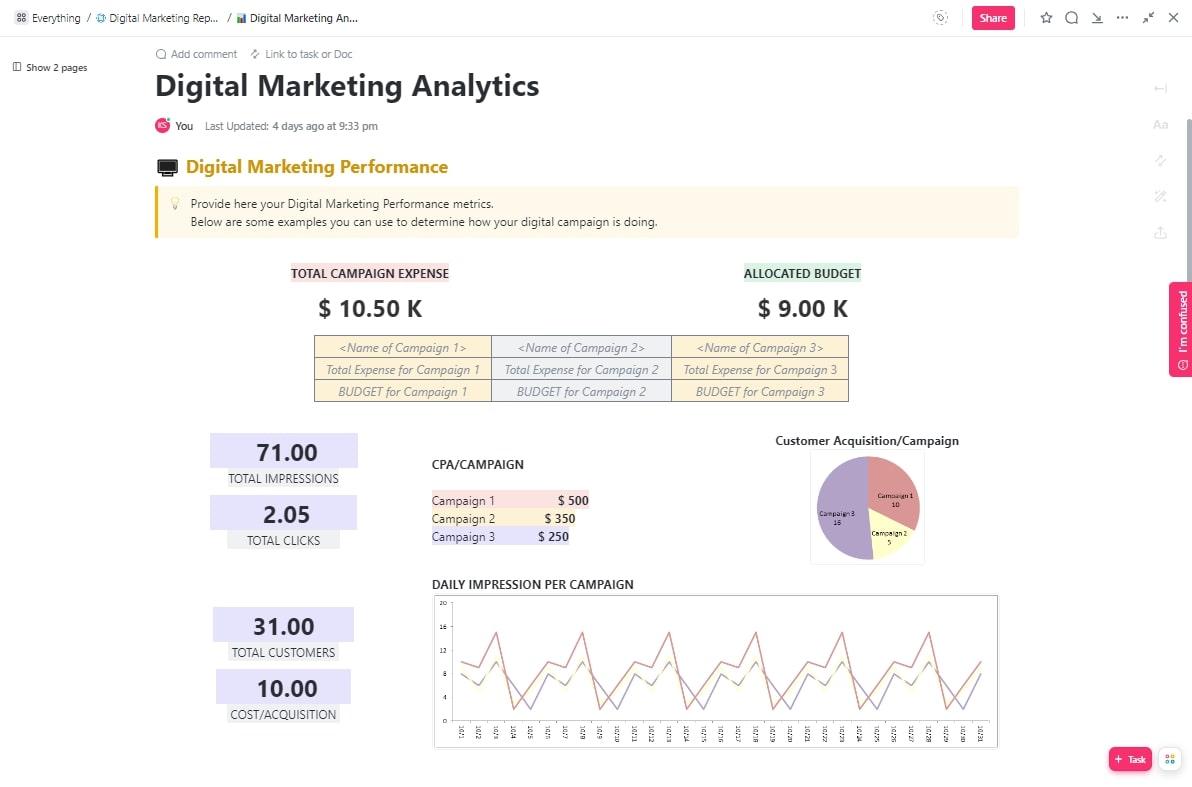
After running a digital marketing campaign project, you need to gather key metrics from the campaign and present it to key stakeholders for evaluation, performance analysis, and notes for future improvements.
Sharing this info across multiple digital channels can get overwhelming but there’s no need to worry. ClickUp’s Digital Marketing Report Template has you covered with everything you need. Plus, it’s neatly broken down into the following sections:
- Digital Marketing Performance: This section lets you summarize the overall performance of your campaign by capturing key details like project budget allocations, actual expenses, cost per acquisition, total impressions, and total clicks across multiple campaigns
- Web Analytics Report: This section analyzes website performance during and after the project’s completion. It captures metrics like page views, bounce rate, traffic sources, and overall conversion rate
- Social Media Campaign Performance: This section analyzes social media performance by measuring metrics like impressions, followers, and engagement rate—all in a simple table for each social media platform
Use this template to present the performance of your digital marketing project in a simple and visually engaging way. This makes it easy to identify trends, analyze the impact of your campaign, and make informed decisions regarding future marketing initiatives.
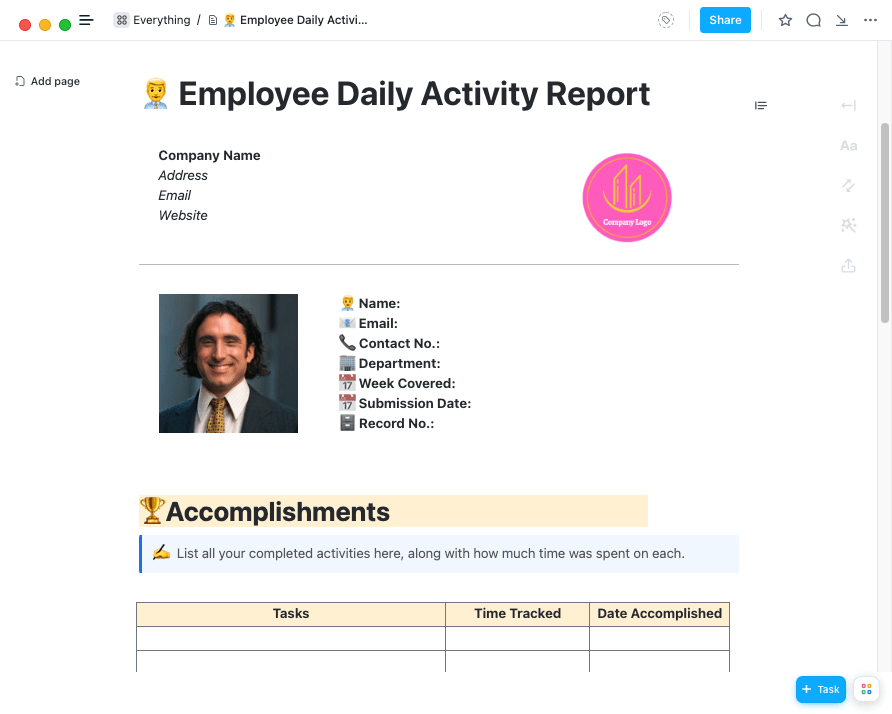
A key way to stay on track and guarantee overall project success is to engage team members in the process.
The Employee Daily Activity Report Template by ClickUp has a simple tabular layout that makes it easy for team members to record and keep track of:
- Completed tasks and the time spent on each
- Ongoing tasks and their due dates
- Upcoming tasks and any support they’ll need
This template encourages each team member to get work done and ask for support when needed—while allowing you to keep the project on track by providing support and maximizing team performance.

Remember the Digital Marketing Report Template we looked at earlier? You can choose to further analyze the marketing performance section, with elements from this Campaign Report Template by ClickUp .
Dive deeper into how each marketing channel contributed to overall ad cost, ad revenue, and ad conversion rate. You can further break down each channel’s performance by analyzing the metrics from each individual campaign on that channel.
There you have it—your secret sauce for creating an effective project report in a fraction of the time. And that’s only scratching the surface … working inside ClickUp unlocks a lot more perks.
Not only does ClickUp make project reporting easy and quick, but it also gives you access to free project management templates to enhance your workflow. Quickly assign tasks to your team, keep track of progress, discuss updates, and collaborate on documents and whiteboards—all in one place. ✨
Did we mention the integrations? ClickUp plays nicely with other apps, allowing you to seamlessly connect your favorite tools to supercharge your team’s productivity. And let’s not forget about the time you’ll save using ClickUp’s automations—a feature that lets you breeze through repetitive tasks that used to eat up valuable time across project management reports.
Just imagine what you can do with those extra hours—maybe enjoy a cup of coffee or catch up with your team about how best you can support them. Make project reporting a blast with ClickUp and boost your chances of a successful project.
Get started by signing up for free on ClickUp today … Ready? Set? Report!
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

Final Report

All students are required to complete a final paper by the due date set by each program. Future SFP applications, recommendations, or acknowledgement of the award on Caltech transcripts will be jeopardized by not completing this requirement in a timely fashion. Please read all instructions below!
Final Report Writing Requirements Final reports should be clear, concise, and written for a broad scientific audience. Consult with your mentor to determine a style usually used in their discipline.
Use clear, significant words when writing your paper and avoid using jargon or specialized terms whenever possible. It is often useful for authors to have students in other disciplines read their papers to improve clarity. Work with your mentor and co-mentor to edit your paper.
Final Report Format:
Instructions for Uploading Final Paper Students must upload a draft of the final paper by their program due date:
JPL Students
- CSU STAR Students: September 1
- All Other JPL Students: Monday of student's final week.
All other students: Fourth Friday in September.
The paper must be in PDF format, and must not exceed 10MB. (If you absolutely can't make your paper smaller than 10MB, please contact [email protected] for instructions.) Once the paper is uploaded it will be locked in the system, and your mentor will be sent a message containing instructions for accessing your paper online. Your mentor then has two options:
- Approve your paper as is. You will receive confirmation of this action via e-mail.
- Return your paper and give suggestions for improvements. You will receive confirmation of this action via e-mail along with your mentor's comments. When your paper is returned, it is unlocked in the system. This allows you to incorporate your mentor's suggestions, go online to delete your previous paper, and then upload the new version. Your mentor will again receive instructions for accessing your paper and the whole process starts again. This can continue as many times as necessary until your mentor gives final approval of your paper.
Once your paper is approved, your paper will remain locked. If you would like to submit a revised version of your paper after a previous version has been approved, e-mail your revised paper to [email protected] and we will replace your old paper with the new version.
Mentors must approve the final paper no later than November 1.
Submissions to CURJ Students may submit any paper that follows the SFP final report guidelines to the Caltech Undergraduate Research Journal (CURJ). CURJ editors will work with authors to prepare their articles for publication, if selected.
A publication release signed by the head of the laboratory (not a graduate student or postdoc) will also be required. This document is legally binding. You and your mentor are advised to consult with the appropriate journals and must resolve any copyright issues before submission. Once your paper is accepted, it cannot be withdrawn.
Additional Publishing Opportunities Students are encouraged to further develop their scientific writing skills and to share their research. The Council on Undergraduate Research keeps a list of undergraduate research journals where students can submit their work. Please note, it is important to consult with your mentor before sharing your research at a conference or in a publication.

How to Write a Project Report: Step-By-Step Guide [+ 4 Free Templates]
By archtc on December 26, 2017 — 21 minutes to read
- How to Write a Project Report: Step-By-Step Guide Part 1
- Project Report Templates: Free Download Part 2
- Additional Resources Part 3
- How to Dramatically Reduce Time You Spend Creating Reports Part 4
At some point during the implementation of a project, a project report has to be generated in order to paint a mental image of the whole project. Ultimately, a project report must maximize the insight gained with minimal effort from the reader. Apart from describing its results, it must also explain the implications of those results to the organization and its business operations.
How to Write a Project Status Report:
The most common type of project report, a project status report provides a general state of the project to its stakeholders. It quantifies work performed and completed in measurable terms. It compares this with an established baseline to see if the project is on track or; if adjustments have to be made if the project is behind its schedule. It keeps everyone on the same page and manages each other’s expectations.
Project status reports are accomplished to serve the following purposes;
- to keep an updated flow of information in relation to the project’s progress
- to immediately address issues and concerns that may come up at any point of the project’s implementation or duration
- to document reasons for changes and adjustments made to the original plan for the project
- to monitor fund utilization and to ensure that the project expenses are still within the budget
- to serve as a basis for decision-making and addressing problems
- to keep track of the team’s performance and individual contributions
- to act as a uniform procedure for communicating project development to the stakeholders.
Status reports are most effective when they follow a standard form with predefined fields that need to be regularly updated. Doing so will save time and provide consistency and predictability of the information the stakeholders will receive about the status of the project.
WHAT TO INCLUDE
For a status report to be comprehensive, it must include the following elements:
Summary/overall health of the project, facts on the project progress, target vs. actual accomplishments, action(s) taken, risks and issues, keys to an effective project status report.
- Submit the report on time . A status report is time sensitive and sending it late defeats the purpose of such a report.
- Giving complete but inaccurate information is just as bad as giving accurate but incomplete information . Since stakeholders rely on the status report for a heads-up on the project, and its content is used as the basis for decision-making, it is critical that the report provides both complete and accurate information.
- Do not cover up bad news or adverse reports as these are all part of the transparency of the status report . Keep in mind that being open with the stakeholders, whether the project is sailing smoothly or not, will benefit both the team and the client, since any problems there are will be immediately given attention and solved.
- Be proud of the team’s accomplishments, after all, this is what the clients and the stakeholders will want to know about .
- Anticipate questions from the clients or stakeholders and be prepared to answer them .
- Be familiar with the culture of the organization and respect the information hierarchy they observe . There are instances when the CEO wants to be the first to know about the contents of these reports before cascading it to his downlines. On the other hand, middle managers will want a head start on these reports so they can also anticipate and prepare for any reaction from the top executives.
- Craft the status report in such a way that there will be no information overload . It should contain necessary information that the stakeholders need to know. Lengthy reports will consume not only the writer’s time but also that of the reader. Too many details also give an impression of micro management.
Risk Registers
All projects, or any activities of business, face risks. It is just a matter of how an organization identifies, assesses, analyzes, and monitors these risks. With a Risk Register, an organization is equipped with a tool to better respond to problems that may arise because of these risks. It helps in the decision-making process and enables the stakeholders to take care of the threats in the best way possible.
A Risk Register, also called an Issue Log, is iterative because it will be updated periodically depending on how often the team identifies a potential risk. It may also be updated if the characteristics of the existing potential risks change as the project progresses.
The Risk Register document contains information about the following:
Risk Identification
- Risk Category: Grouping these risks under different categories is helpful. Doing so will provide a way to make a plan of action that will address most, if not all of the risks falling under the same category, saving time, effort, and resources.
- Risk Description: Provide a brief explanation of the identified potential risk. The description can be done in a variety of ways depending on the level of detail. A general description can be difficult to address while giving too much detail about the risk may entail a significant amount of work. Three factors to consider when making a risk description are: the way these risks are going to be managed, who will handle them, and the reporting requirements of the person receiving the risk register.
- Risk ID: Assign a unique identification code to each risk identified to track it in the risk register easily. Create a system of coding in such a way that the category to which the said risk belongs is easily identifiable.
Risk Analysis
- Project Impact: Indicate the potential effect of the assumed risk on different aspects of the project such as budget, timelines, quality, and performance.
- Likelihood: Referring to the possibility of the risk occurring, the likelihood can be expressed qualitatively—high, medium, low—or quantitatively, if there is enough information available. Whatever criteria are to be used, assign a number—with the highest value corresponding to that which is most likely to occur.
Risk Evaluation
Using the table above, the identified risk can be ranked this way:
- Risk Trigger: These are the potential risk events that will trigger the implementation of a contingency plan based on the risk management plan. This plan should have been prepared prior to the development of a risk register.
Risk Treatment
- Prevention Plan: This enumerates the steps or action to be taken to prevent the risks from occurring.
- Contingency Plan: On the other hand, the contingency plan determines the steps or action to be taken once the risk events have occurred. This program also contains the measures to be taken to reduce the impact of such risks to the project.
- Risk Owner: The person responsible for managing risk, and the implementation of the prevention and contingency plans, it can be anyone among the stakeholders—members of the team, a project manager, or project sponsors.
- Residual Risk: Sometimes, a risk cannot be entirely eliminated after treatment. Part of it may linger throughout the duration of the project, but once it has been treated, it can be considered as a low-level risk.
Keys to an Effective Risk Register
- The first risk register must be created as soon as the project plan and the risk management plan has been approved . This initial risk register must be integrated into the project plan.
- Active risks during a particular period must also be included in the project status report .
- Risk management is an iterative process which is why the risk register must also be updated from time to time . Updates can be made when new risks are identified or there have been changes in the risks already in the register.
- The numerical value assigned to the likelihood and severity levels must remain constant throughout the duration of the whole project .
- Likewise, any terms used must be defined, and this definition must be utilized consistently .
Project Closure Report
As the end of a project, a Project Closure Report signals its culmination. Its submission officially concludes a project and implies that funds and resources will no longer be needed, and everything will go back to its status prior to the implementation of the project.
This process is critical as it will officially tie up all loose ends and prevent confusion among stakeholders.
This particular type of project report summarizes information on the project results, the criteria used to measure the effectiveness of the project delivery process, and the feedback from the stakeholders. Each performance metric includes an assessment and a narration of how the team performed on such metrics.
This performance metric describes how the team utilized the budget in carrying out the project effectively. Under this performance metric, the following aspects are measured:
Component Breakdown
Budget variance, explanations for key variances.
Describe how the team implemented the project within the expected time frame and schedule.
Overall Project Duration
Schedule variance, the explanations for key variances, change management.
This metric refers to the team’s ability to handle and manage changes throughout the project’s implementation effectively. It is measured through the following:
Total Number of Changes
The impact of the changes, the highlight of changes, quality management.
This particular metric refers to the team’s ability to observe and comply with quality standards during the project’s implementation.
Total Number of Defects Identified
The explanation for resolved defects, risk and issue management.
This metric deals with how risks and matters that occurred during project implementation were handled and resolved by the team. Key points to include are the following:
The impact of the Risks and Issues to the Project
Human resource management.
This refers to the team’s ability to carry out the project effectively.
Project Organization Structure
This metric looks at how the stakeholders participated in the project.
Decision-makers
Communication management.
Under this metric, communication throughout the duration of the project is assessed.
Communication Management Plan
- Summarize essential feedback collected . Describe the method by which these comments were gathered and who was solicited for feedback. Also include how they responded to each question and briefly discuss which items received great responses from the participants and which ones got few answers.
- Take note of common themes or trends of feedback gathered .
- From the feedback gathered, also take note of any opportunities from this feedback and discuss how these opportunities can be applied to future projects, or in the organization itself .
Lesson Learned
- Give a brief discussion of what the team learned when carrying out the project . Among these learnings, discuss which ones can be applied to future projects and how it will impact not only those future projects but also the whole organization.

Other Metrics
Other points of interest may not have been captured in the Project Status Report and may be included in the Project Closeout Report. Some of these factors include:
Duration and Effort by Project Phase
Benefits realized, benchmark comparisons, keys to an effective project closure report.
- The closure report is mostly a summary of all efforts related to the project . It is important to ensure that all highlights of the project have been properly documented so that retrieval of these reports is easier and all efforts will be acknowledged.
- Emphasize the high points the project delivered, how efficiently it was done, and what has been learned from the process.
- If there are notable variances during the project implementation, make sure to provide a fact-based explanation on it . In addition, the impact of this difference must also be described.
- A critical point in a project closure report is establishing the link between the project performance, the lessons learned, and the steps that will be taken by the organization for its continuous improvement . Aside from the project deliverables, another valuable output of a project is the learnings derived from the process and how it will be translated into concrete concepts applicable to the business processes of the organization.
Executive Summary
A little bit different from the types of project reports previously mentioned, an Executive Summary is a distinct kind of report which uses different language. It is a high-level report which aims to provide a bigger and deeper understanding of the project—how it will benefit the organization and how it will fit into future business strategies. It is written with a busy executive in mind, someone who has a lot of important things to do and may find reading a lengthy piece of prose a waste of precious time. Factual and objective, this particular type of project report must be able to provide a realistic status of the project, as business executives understand that everything may not go according to the plan.
Some may confuse an executive summary with an abstract but, in reality, they are clearly distinct from one another and serve a different purpose.
An abstract is usually written for academic or scientific papers. It is written with a topic sentence which, generally, gives an overview of what the article is about. It is, then, supported by two or three supporting sentences which support the main idea of the topic sentence.
An executive summary, on the other hand, is composed of different sections discussing almost every significant aspect of an undertaking. It consists of sequentially arranged key points supported by conclusions and recommendations. Check our in-depth article on how to write an effective executive summary .
Things to Remember in Writing Project Reports
Here are some of the principles that need to be observed in writing an effective project report;
Write for the reader
The report should have a structure, ensure that the report is evidence-based and is supported by data, make it as objective as possible.
There is a clear distinction between facts and opinions . These should never be used together, especially if the report is dwelling on a failed project. The report becomes subjective if it reflects personal opinions of the writer. Make it objective by eliminating all parts which are not based on facts and real events. If it is really necessary to include a personal view or opinion, make sure to explicitly identify it as such. A separate section of the project report may be devoted to the writer’s personal opinion to keep the rest of the report unbiased.
There are a number of ways project reporting helps an organization, a team, and even the project itself and here are some of them:
It tracks the progress of the project
It helps identify risks, it helps manage project cost, it gives stakeholders an insight on how the project is performing, project report template: free download.
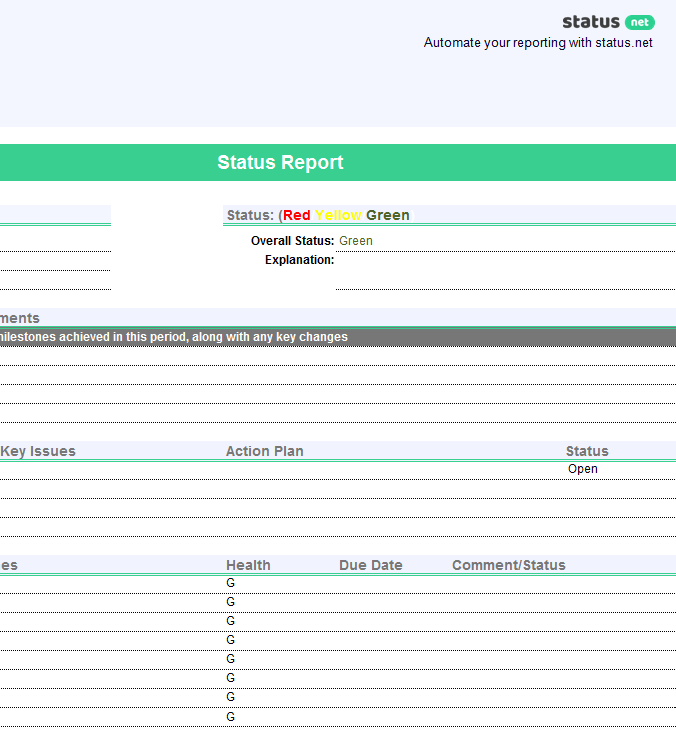
Click Here to Download Project Status Report XLSX

Click Here to Download Project Update Report DOC

Click Here to Download Project Update Report 2 DOCX
Click Here to Download General Project Report DOCX
—————————————————————————-
Templates on ProsperForms:
Edit and use this template
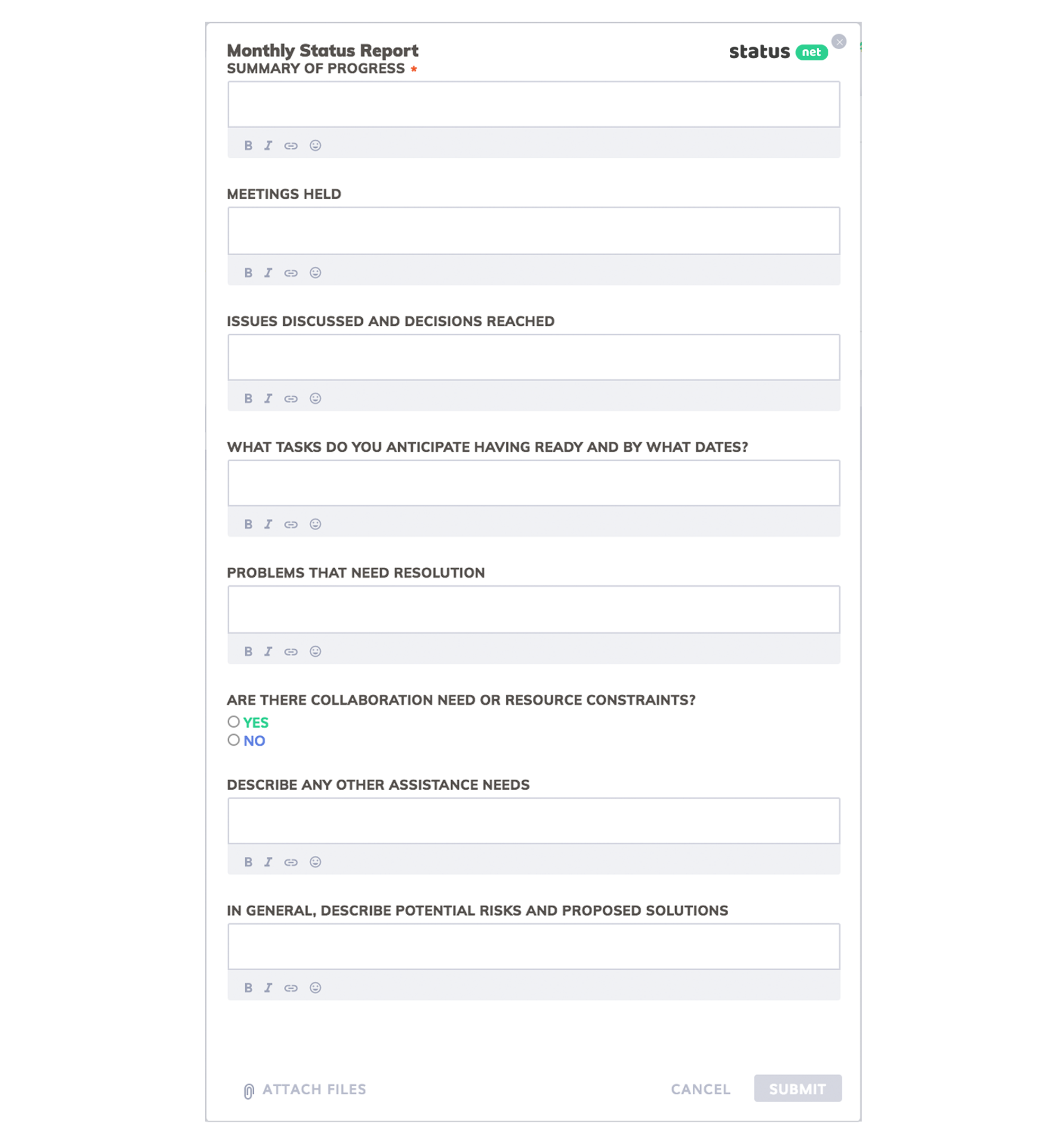
Additional Sources
- How to Write an Outstanding Weekly Report + Free Template Download
- Project Status Dashboard and Project Tracking
- How to Create a Project Meeting Template + Free Download
About Project Reports
NSF requires that NSF-funded researchers regularly report on the progress of supported projects and the way funds are used.
- Only Principal Investigators (PIs) and co-PIs can create, edit and submit project reports
- Sponsored Projects Office (SPO) staff and administrative users with read-only access can view project reports
Sign In to create, edit and submit reports Find project outcomes reports
The 4 types of project reports are:
- Annual report
- Interim report
- Final report
- Project outcomes report
Annual, Interim and Final Reports Annual project reports are required for all standard and continuing grants and cooperative agreements. Final reports are required for all standard and continuing grants, cooperative agreements and fellowships. Interim project reports are not required and are used to update the progress of a project any time during or before the award period expires
All submitted annual and final reports must be approved by an NSF Program Officer to meet the submission requirements.
Key features of Project Reporting System in Research.gov:
- A consolidated project reporting dashboard that includes annual, final, interim, and project outcomes report
- Ability to deposit published journal articles and juried conference papers in NSF Public Access Repository to be compliant with the Public Access requirement. PIs and co-PIs can also submit publications in the NSF’s Public Access repository through their project reports and comply with the Public Access requirement.Refer to Public Access page for additional information
- Upload multiple Products via BibTex upload feature
Project Outcome Reports (for general public) The Project Outcomes Report is a report written for new and existing awards, specifically for the public, that provides insight into the outcomes of NSF-funded research. Project Outcome Reports can be viewed through Research.gov’s Research Spending & Results search service.
Note: Project Outcome Reports are not reviewed or approved by NSF
More Information
- About Public Access
- Example Project Reports (Demo site)
Project Report Screenshots and Instructions
Project reports template
Project Reporting Getting Started Guide
Project Reporting FAQ's
Project Reports and Reminder Email Schedule Tip Sheet
For additional information on Project Reports, please visit the Help section .
The Top 17 Free Project Report Templates For Effective Project Management
By Kate Eby | August 5, 2019 (updated August 7, 2023)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll find a comprehensive list of project report templates to support your project management efforts. These pre-built templates are free to download in a variety of formats, including Excel, Word, PowerPoint, PDF, and Google Docs.
Included on this page, you'll find many free, downloadable templates for your next project, including a project status report template , a daily project progress report template , a business project report template , and many more.
Project Status Report Template
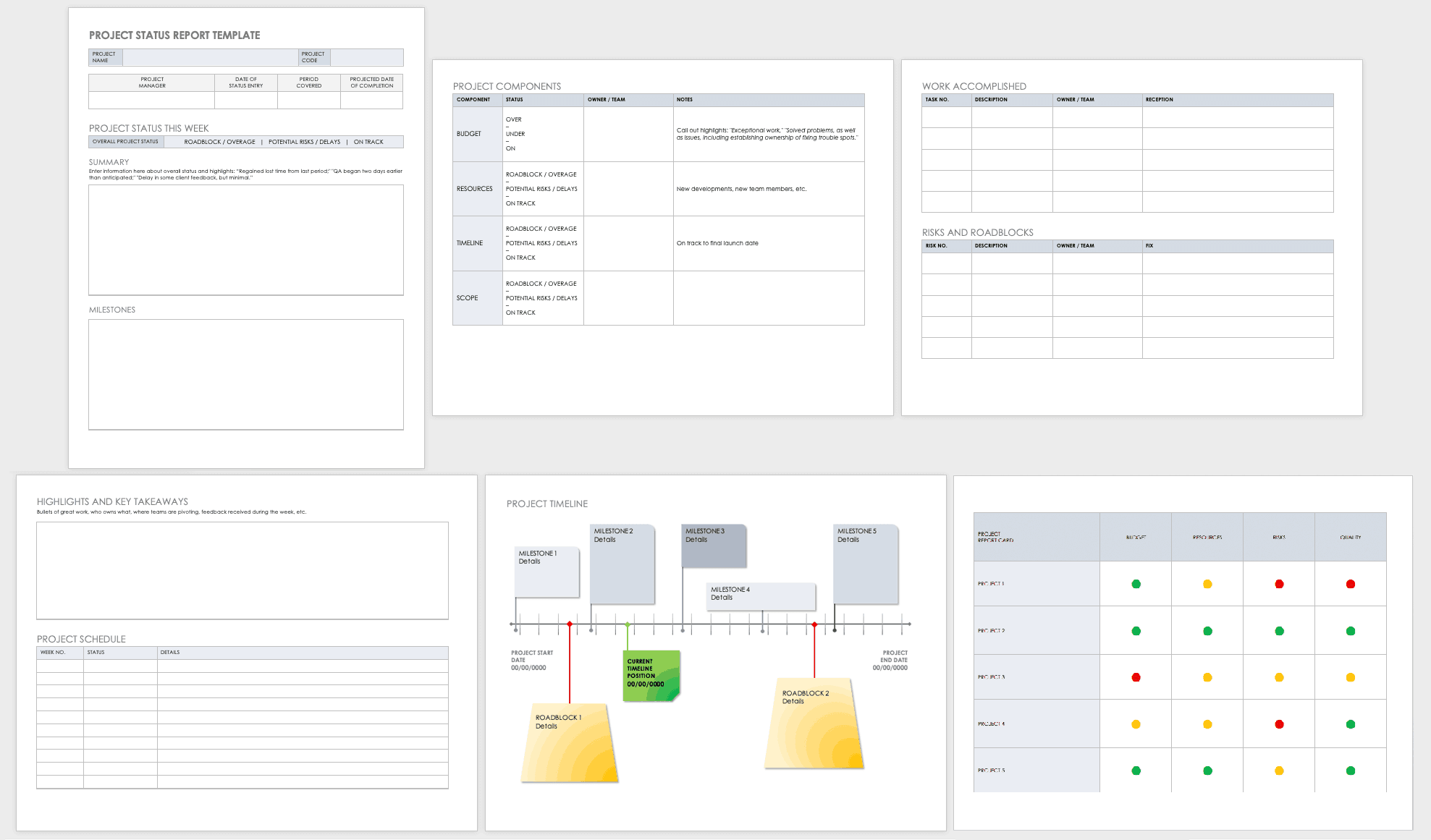
Download Project Status Report Template
Word | PowerPoint | Smartsheet
Consistent and thorough status reporting is an essential component of effective project management. Ensure you meet project objectives by utilizing this customizable project status report template. This template provides space to summarize the project and track risks, roadblocks, milestones, accomplishments, and key takeaways. It also includes a visual project timeline to give you easy visibility into major project events.
One-Page Project Status Report Template
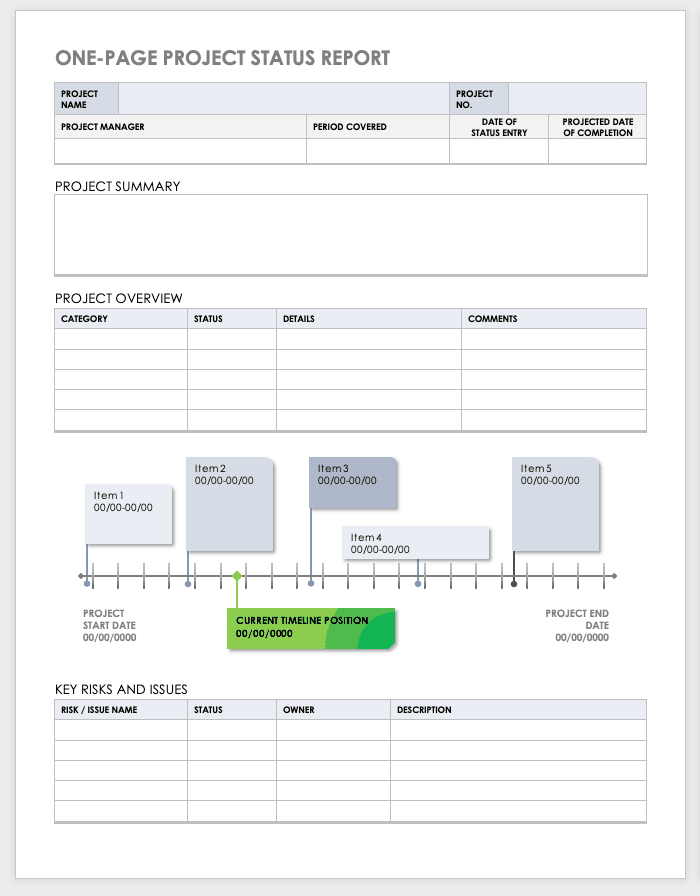
Download One-Page Project Status Report Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
This template covers all the primary elements of the project status report in a convenient one-page format. The pre-built status report provides an overview of project status by category (i.e., budget, scope, etc.), project timeline, key risks and issues, as well as issue ownership to ensure that you account for and complete all project action items on schedule. Learn how to create an effective project status report in this article .
Project Report Dashboard Template
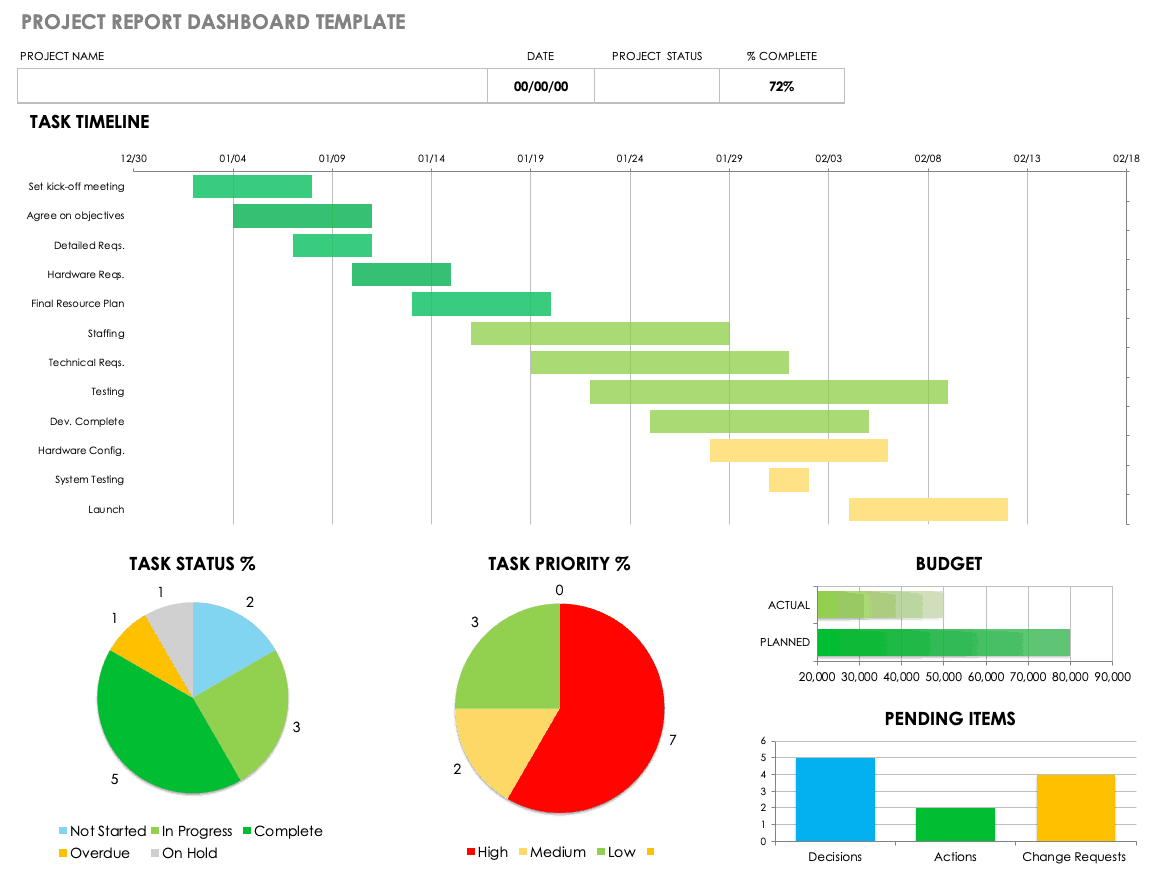
Download Project Report Dashboard Template - Excel
Having a clear visual of a project’s high-level metrics and overall performance enables a project manager to identify and home in on problem areas that need further attention. Download this project report dashboard template to track the status of key components of a project, including tasks, costs, and pending action items. This template also helps you support the decisions you make for future project initiatives. Check out this article to find more free Excel dashboard templates for all of your business needs .
Daily Project Progress Report Template
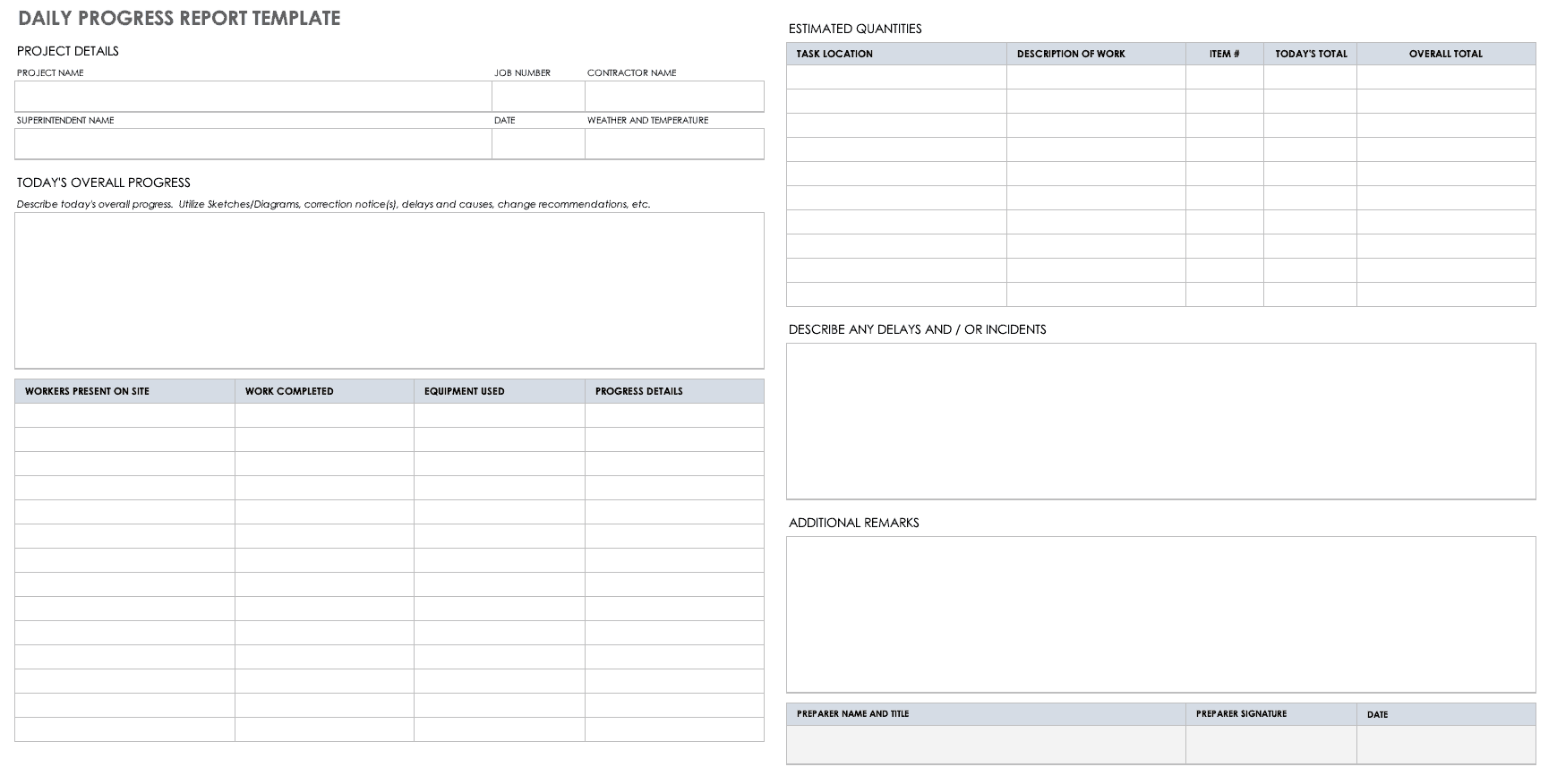
Download Daily Project Progress Report Template
Excel | Word | PDF
Provide stakeholders with insight into a project’s daily development using this progress report template. This template provides space to outline progression details, work completed, equipment used, workers on site, task locations, delays, incidents, and more. This report allows you to compare activity progress with the project plan to effectively maintain governance.
Performance Project Report Template
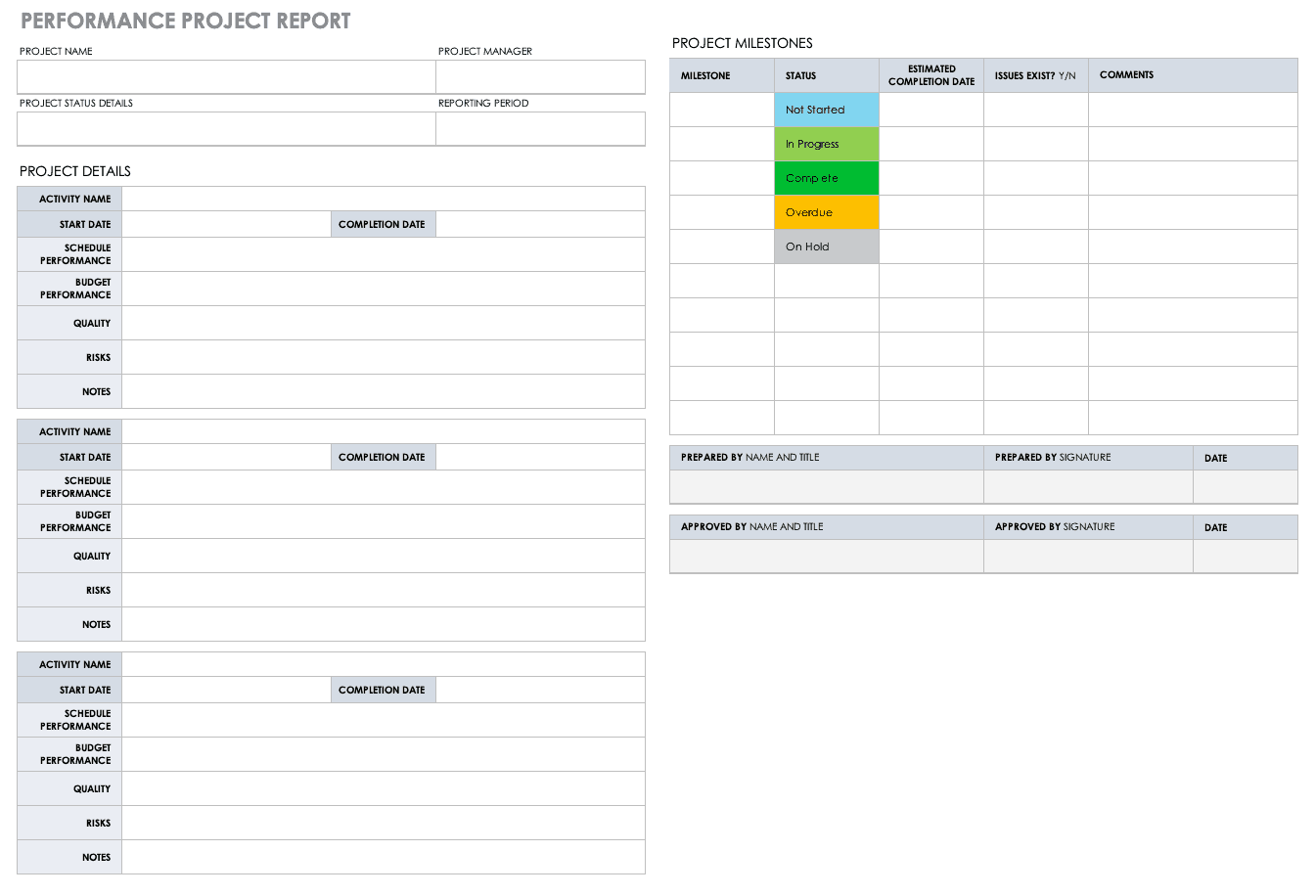
Download Performance Project Report Template
Communicate the performance of key project elements using this customizable project performance report template. Detail key activities, deadlines, work quality, risks, budgeting performance, and more to ensure you carry out major project deliverables on schedule and according to plan.
Project Summary Report Template
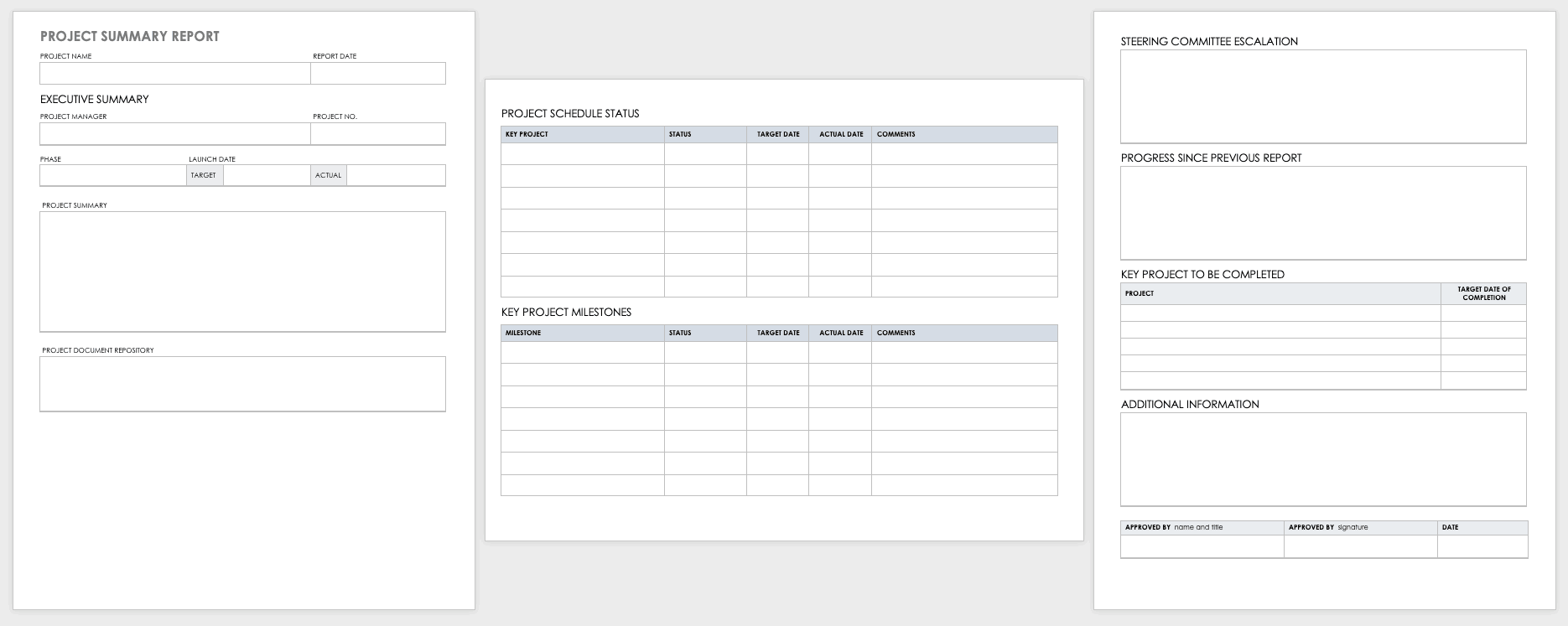
Download Project Summary Report Template
Effective project management requires that you keep lines of communication open (between the team and client) and ensure that the information you present is accurate and up to date. Provide all stakeholders with the current status of key projects, milestones, steering committee escalations, progress, and upcoming events using this pre-built project summary report template.
Weekly Project Status Report Template

Download Weekly Project Status Report Template
Excel | Word | Smartsheet
This customizable project status report template provides a snapshot of a project’s health on any given week. Track overall project performance and the status of each project component, including budget, resources, scope, milestones, work accomplished, roadblocks, highlights, and more. This template also comes with a pre-built visual timeline to display major project details at a glance.
Monthly Project Status Report Template
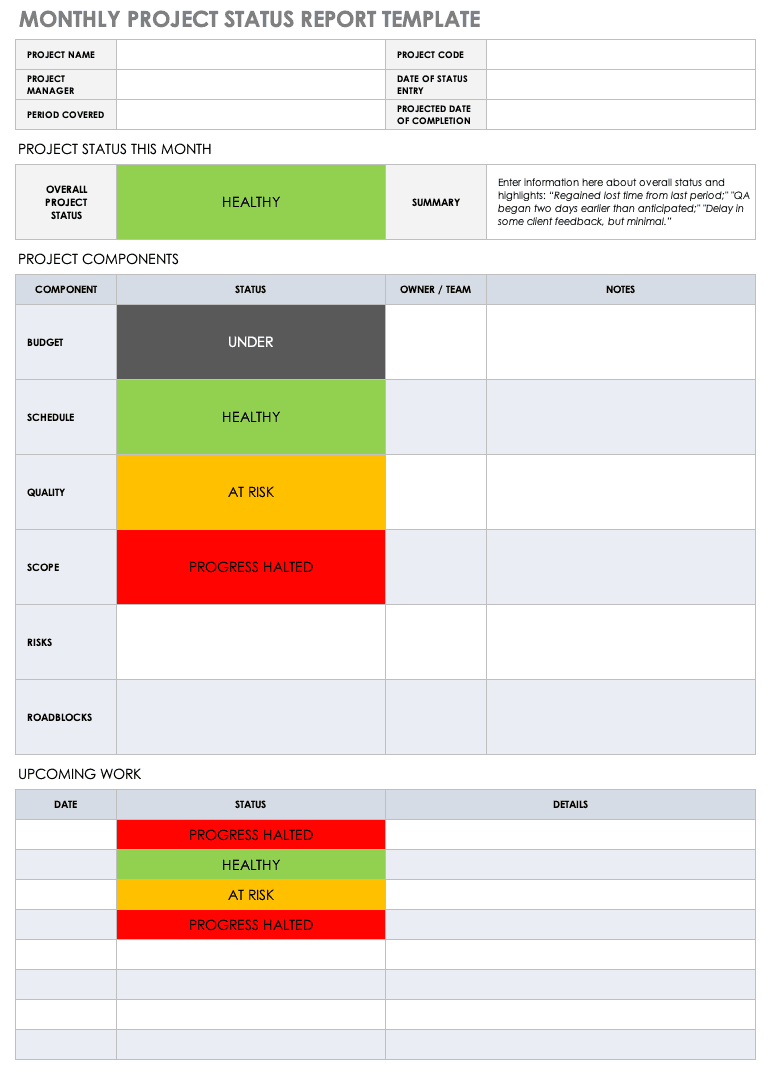
Download Monthly Project Status Report Template
Excel | Word
This project status report template captures the status of key project elements at a monthly view. Use this downloadable template to track notable project components that are complete, in progress, on hold, or at risk and outline deadlines and details for upcoming work.
Stoplight Project Status Report Template
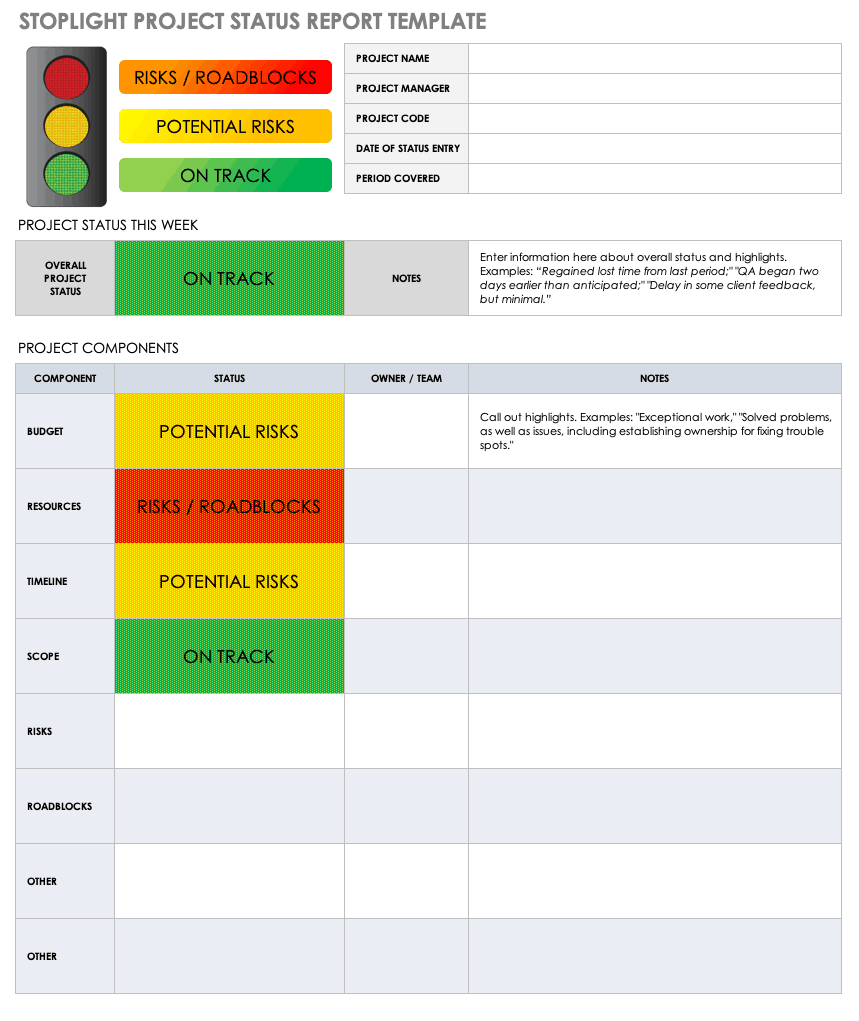
Download Stoplight Project Status Report Template
Stoplight project status reports are an effective way to visualize project items that require immediate attention and additional planning. Use the stoplight key to define the parameters of what constitutes a red, yellow, or green status and ensure that the client and team members are on the same page regarding these conditions. This template will help keep the process streamlined.
Business Project Report Template
Download Business Project Report Template
Word | Google Docs
A business project report is a detailed document that serves as a roadmap for a proposed project or business venture. This business project report template provides a solid basis to expand upon according to your needs. It includes space for a table of contents, an executive summary, key project activities, a marketing analysis, a SWOT analysis, recommendations, appendices, and more.
IT Project Status Report Template
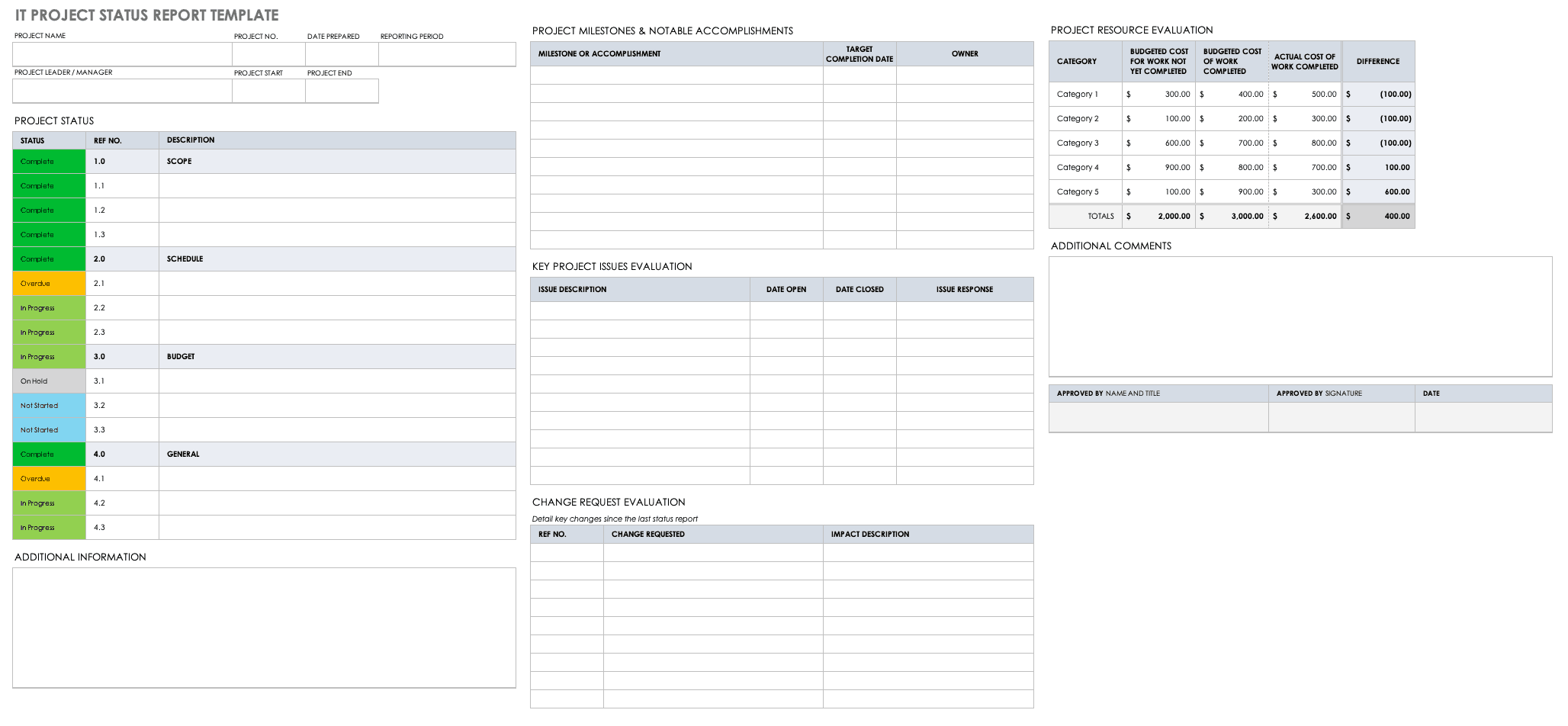
Download IT Project Status Report Template
Information technology project management and operations can be complex and involve many moving parts. Between balancing the budget, making adjustments mid-project, and meeting the needs of project stakeholders, this pre-built IT project status report template will help ensure that you track and account for all the key components of your project. This template provides room for project milestones, open and closed issues, change requests, resource evaluation, and the current status of all major project categories. Learn the essential tips for successful IT project management by checking out this article .
Construction Project Report Template

Download Construction Project Report Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Google Docs
Effective reporting is a key factor in the overall success of a construction project. This pre-built construction project report template includes all major day-to-day project details, like daily progress, materials and equipment used, number of workers and work hours performed on site, progress obstructions, and official visitors. Additionally, the template includes space for the inspector to sign off on the report in order to ensure overall project compliance. For a wide variety of free construction management templates to download, visit this page .
Executive Project Report Template

Download Executive Project Report Template
An executive project report is a high-level view of the project that highlights progress, without getting into the granular details of the project. Use this customizable executive project report template to communicate the essential elements of the project, including key milestones, accomplishments, risks, issues, financial overview, and project requirements.
Final Project Report Template
Download Final Project Report Template
The purpose of the final project report is to briefly and clearly summarize the outcomes of a completed project. This final project report template contains a table of contents, as well as space for names and roles of team members, project summary, scope, costs, risks, communication strategies, learning outcomes, top-level project performance details, and more.
Project Report Template for Teams or Departments
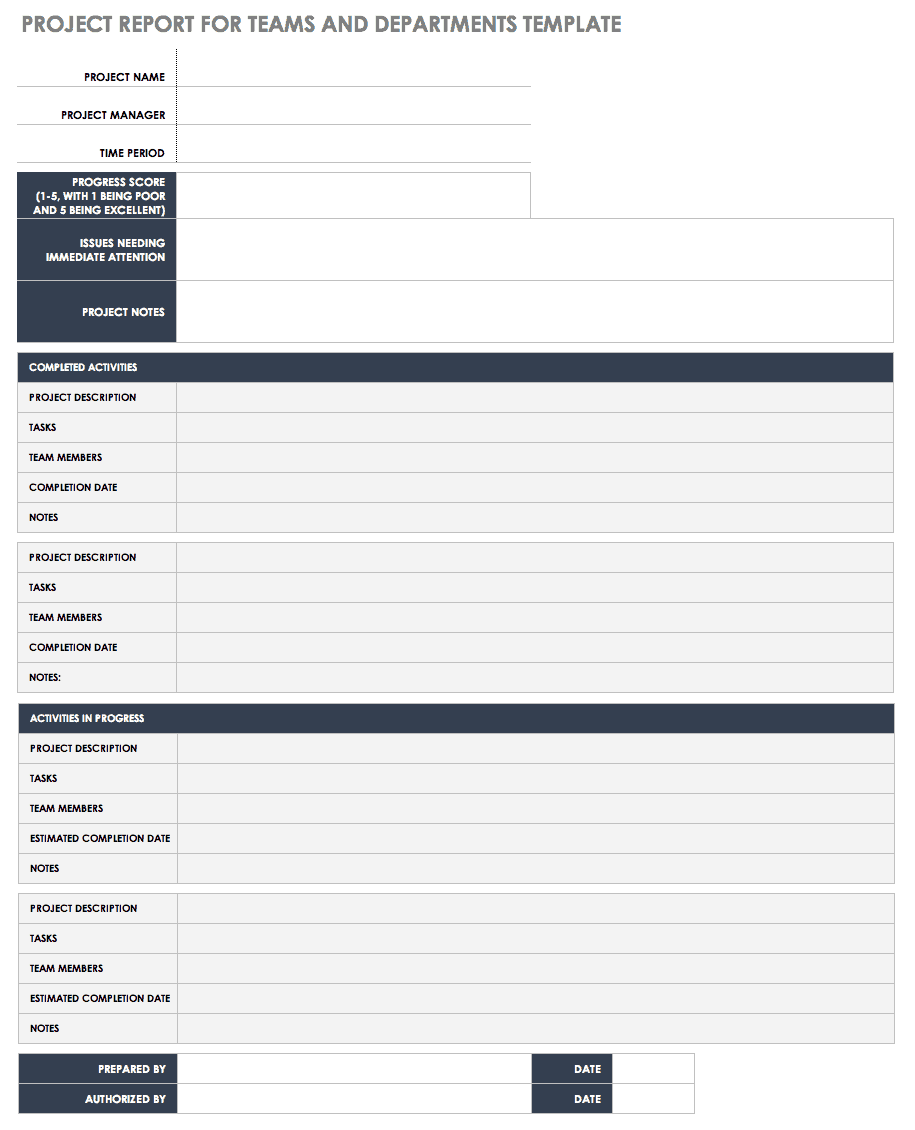
Download Project Report Template for Teams or Departments
Teams or departments can use this project report to communicate the status of project activities: That is, they can indicate whether they have completed an activity or whether an activity is still in progress. Use this template to track key tasks, team members involved, deadlines, progress scores, issues needing attention, and other project developments to ensure teams or departments account for and complete assignments on schedule.
Project Report for Stakeholders and Partners
Download Project Report for Stakeholders and Partners
Use this project report is to provide key stakeholders and partners with high-level visibility into a project’s overall performance. Briefly summarize progress, project deliverables, start and end dates, outputs, and other major project details to keep stakeholders up to date on current project happenings.
Project Postmortem Report Template
Download Project Post-Mortem Report Template
This customizable project postmortem report template should be completed as a workshop comprised of key team members within a week of concluding the project work. This report highlights project details, such as accomplishments, problem areas, lessons learned, and more to facilitate the process of analyzing the performance of all the project’s elements. Once you’ve completed this template, the project sponsor should sign off on it to formally close out the project.
Tips on Writing a Project Report
When writing a project report, stick to the facts and back up your claims with data. Consider using a template to give structure to your report, and tailor the report to your audience. We’ve outlined top report-writing tips below:
- Know Your Audience: The type and depth of information you communicate in a report will depend on the nature of your audience. For instance, managers and clients may have a better understanding of the concepts and terminology involved in a project than do stakeholders and other personnel. Effective project reporting, therefore, requires using the appropriate tone and phraseology and knowing when to share high-level versus granular project details. Your audience may also care about different details when viewing a year-end report versus a project status report .
- Give Structure to Your Report: Once you’ve identified your audience and which components of the project to communicate, organize the segments of the report so the information makes sense and is helpful to the reader. For example, you should place project identification and background details near the beginning of the report; place summarizing details near the end.
- Only Provide Facts: The report should remain objective and free from personal bias, regardless of whether the project is failing or performing successfully. If an opinion is needed, it should be labeled clearly and placed in a separate segment of the report. Additionally, the charts, metrics, and other performance data you present in the report should be accurate and up to date so that such information is credible and meaningful to the reader.
- Use a Template: Save time building out your report by using a customizable template to get you started. Templates are beneficial for standardizing processes, and you can easily adapt them to fit your needs. Use the free templates provided above for your reporting needs, and then check out this article for more project management templates .
- Use an Online Reporting Tool: Keeping a project’s development aligned with business goals is the basis of project management, and the success or failure of a project can greatly depend on the tools you use. Employ an online tool that displays data in different ways (e.g., Kanban boards, Gantt views, and dashboards), shows the real-time status of multiple projects, provides various permission levels, and allows you to set up recurring reports (such tools can automatically email these recurring reports at a set frequency to designated stakeholders, which allows project managers to shift their focus to other critical project matters). These online tools provide increased visibility into project processes and status.
Improve Project Reporting with Smartsheet for Project Management
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Our Privacy Notice describes how we process your personal data.
Looking for more
Free 30-day trial
Enable everyone to work better, at scale, with Smartsheet.
Get started for free

Free Smartsheet templates
Get free templates

Free ebook: Project & Portfolio Management 101
Get the most out of your PPM efforts with our secrets for success.
Get the free ebook
Recommended Articles

Future of Work Management Report 2023
Project Management Guide

Free Project Management Plan Templates
Improve project reporting with instant visibility and real-time collaboration in smartsheet..
All Formats
Table of Contents
Report template bundle, free 10+ research project report templates in pdf | ms word, 1. marketing research project report, 2. sample research project report, 3. basic research project report, 4. action research project report, 5. minor research project final report, 6. equity research project report, 7. simple research project report, 8. major research project final report, 9. annual research project report, 10. standard research project report, 11. research project report example, what are the components in a research project report, how to write a research project report, tips to write a research project report:, faq’s, where is a research project report used, what is research report summary, report templates.
Generally, a research project report is displayed in a composed structure. The down to earth utility of the research study relies intensely upon how it is exhibited to the individuals who are required to follow up based on look into discoveries. The research report is a composed archive containing key parts of a research venture.

- Google Docs

Research Introduction
Research methodology, research results, research discussion, research references and conclusion, have a reasonable research objective, set up a working model.
- Assemble all the data about the examination theme. Who are the contenders of our clients? Converse with different analysts who have examined the subject of research, know the language of the business. Abuse of the terms can debilitate the per users of research reports from perusing further.
- Examine just the critical disclosures. On the off chance that a few information is not so much noteworthy, don’t refer to them. Recall that not all things are genuinely significant or basic inside research reports.
- Attempt and adhere to the study questions. For instance, don’t state that the individuals reviewed “were stressed” about an issue, when there are various degrees of concern.
- The charts must be sufficiently clear with the goal that they get themselves. Try not to let diagrams lead the per user to commit errors: give them a title, incorporate the signs, the size of the example, and the right wording of the inquiry.
- Be clear with messages. A scientist ought to consistently compose each area of the report with an exactness of subtleties and language.
- Be innovative with titles–Particularly in division examines pick names “that offer life to inquire about”. Such names can make due for quite a while after the underlying examination.
- Make a powerful end: The end in the examination reports is the hardest to compose, however, it is an unbelievable chance to exceed expectations. Make an exact synopsis.
- At times it assists with beginning the end with something explicit, at that point, it portrays the most significant piece of the investigation, lastly, it gives the ramifications of the ends.
- Get a couple more pairs of eyes to peruse the report. Essayists experience difficulty distinguishing their slip-ups. Be that as it may, they are answerable for what is introduced. Guarantee it has been endorsed by associates or companions before sending the discover draft out.
More in Report Templates
Research project flowchart template, research project report template, cost estimate for a research project template, project research template, research project plan template, research project annotated bibliography template, research project communication plan template, research project mind map template, research project budget template.
- How to Create a Financial Audit Report [10+ Templates to Download]
- 40+ Monthly Management Report Templates in PDF | Google Docs | Excel | Apple Pages
- 25+ Non Conformance Report Templates – PDF, Docs, Word, Pages
- 19+ Event Report Templates – Word, PDF, Docs, Pages
- 34+ Report Card Templates- Word, Docs, PDF, Pages
- 23+ Sample Inspection Report Templates- Docs, Word, Pages
- 36+ Weekly Activity Report Templates – PDF, Docs
- 10+ Free Audit Findings Report Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Audit Exception Report Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 11+ Audit Committee Report Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 6+ Logistics Audit Report Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 11+ Logistic Report Templates in PDF
- 8+ Logistics Monthly Report Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 17+ Internship Student Report Templates
- 64+ Monthly Report Samples
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
50+ SAMPLE Research Project Report in PDF | MS Word

Research Project Report | MS Word
50+ sample research project report, what is a research project report, components of a research project report, how to write a research project report, what are the five parts of a research paper, what are the types of research report, what makes a good research report.

Research Project Report Template

Research Short Term Project Report
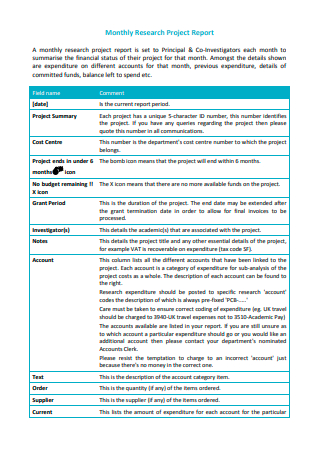
Monthly Research Project Report

Class Research Project Report Form

Research Project Written Report

Kindergarten Expanded Research Project Report

Research Project Final Report

Preliminary Research Project Report
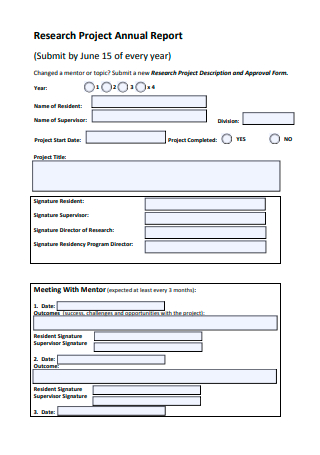
Research Project Annual Report

Research Project Report in PDF

Research Project Report and Masters Thesis

Research Progress Grant Project Report

Printable Research Project Report

Tree Regulations Research Project Final Report

Distributed Ledger Research Project Report

Research Project Grants Report

Science Research Project Progress Report

Equity Research Project Report

Research Project Report Example

Simple Research Project Report

Mall Research Project Report

Research Foundation Project Report Form
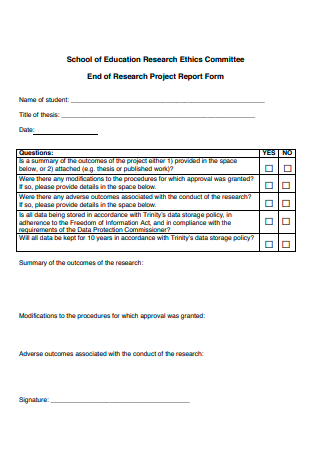
End of Research Project Report Form

Research Home For Project Reporting

Research Clinical Investigation Project Report
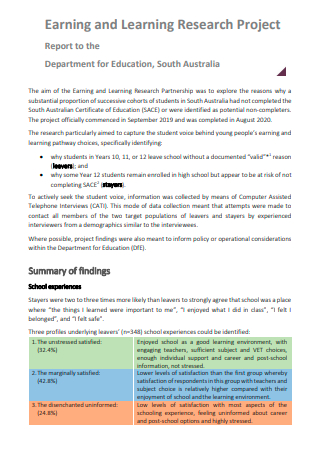
Earning and Learning Research Project Report

Undergraduate Resilience Research Project Report
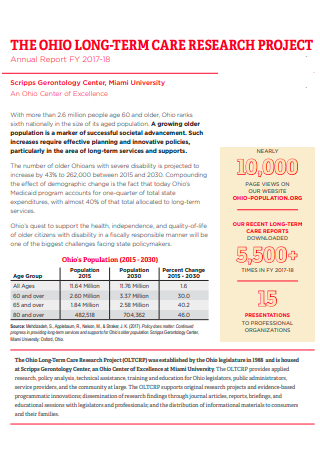
Long Term Care Research Project Annual Report

Standard Research Project Final Report

Research Project Report Outline

Research Paper Project Report

Major Research Project Report

Research Participants Project Report
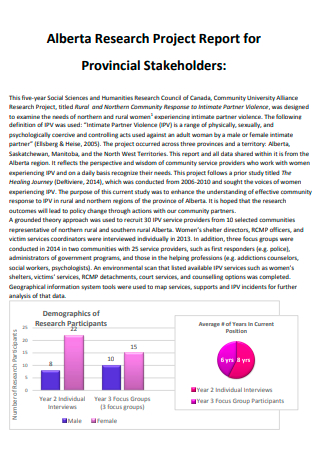
Research Project Report For Provincial Stakeholders
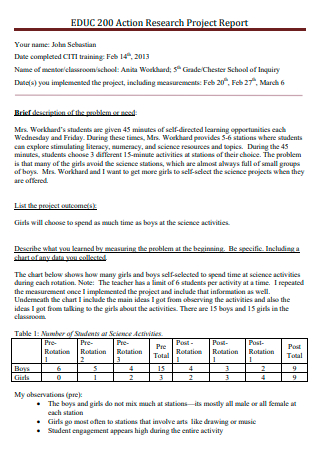
Action Research Project Report

Basic Research Project Report

Teacher Education Research Project Final Report

Participatory Research Project Report

Rural Outreach Research Project Report

Initial Research Project Report

Interagency Science and Research Strategy Final Project Report

Funded Volunteer Research Project Report

Research Management Trust Project Report

Removal Research Project Report

Pictorial Research Project Report
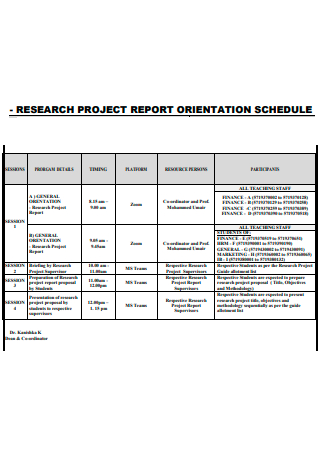
Research Project Report Orientation Schedule
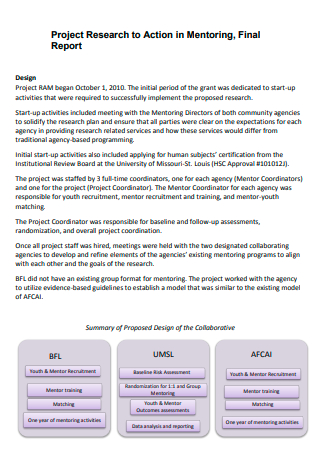
Project Research to Action in Mentoring Final Report

Formal Research Project Report

Community Child Care Research Project Final Report
Research Project Review and Progress Report

Research Project Progress Report
1. perform a task analysis before research, 2. develop a rough research plan, 3. conduct the research plan, 4. draft the body of the report, 5. draft supplementary and preliminary materials, 6. polish and proofread the research report, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 12+ sample construction daily report in ms word | pdf.
Introducing our comprehensive sample Construction Daily Report the cornerstone of effective project management in the construction industry. With this easy-to-use report, you'll gain valuable insights into daily activities report,…
25+ SAMPLE Food Safety Reports in PDF | MS Word

Proper food handling ensures that the food we intake is clean and safe. If not, then we expose ourselves to illnesses and food poisoning. Which is why a thorough…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
the component parts of a research report, starting from the preliminary pages, the major chapters and sub-headings, and the explanation of how to conduct a research project. Part two outlines the format of writing and presenting a research report. The entire booklet Manual captures the essence of writing a good research report as well as other ...
Size: 1 MB. Download. This template is a standard project final report of a study of conflict among the diverse societies in North Eastern India, and how can the conflicts be reduced. A grant is provided to the researchers for completing the project. This sample final report is to be submitted to avail the grant. 13.
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree, although it can also ...
Use the section headings (outlined above) to assist with your rough plan. Write a thesis statement that clarifies the overall purpose of your report. Jot down anything you already know about the topic in the relevant sections. 3 Do the Research. Steps 1 and 2 will guide your research for this report.
Writing a Research Report: Presentation. Tables, Diagrams, Photos, and Maps. - Use when relevant and refer to them in the text. - Redraw diagrams rather than copying them directly. - Place at appropriate points in the text. - Select the most appropriate device. - List in contents at beginning of the report.
Guide to Completing Your Final Report (PDF) Useful links: Final report template (DOCX) Final report exemplars. Excel graph templates (XLSX) The ISTLD sometimes receives requests from project teams for either examples of project final reports or advice on how to write them. It is challenging to respond with generic advice as all the projects are ...
An outline of the research questions and hypotheses; the assumptions or propositions that your research will test. Literature Review. Not all research reports have a separate literature review section. In shorter research reports, the review is usually part of the Introduction. A literature review is a critical survey of recent relevant ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
4. Project Time Tracking Report. A project time-tracking report is a document that records and summarizes time spent on project activities. Each project team member contributes to writing this report—they track and record the amount of time they've spent on tasks and submit it to the project manager. ⏰.
At the end of the time period allotted for completing the research, the investigator needs to prepare the final report on the project. To be accepted by the Program, the final report must be presented in the form of a scientific article. The completed manuscript should not exceed 20 pages (either letter-size or A4). The pages should be typed on ...
Project reports—dissertations, theses, and technical reports, which are typically written in chapters, sections, and subsections, have three sub-divisions—preliminary pages, the main text, and supplementary pages.The project report writing is the final stage of any research and communication process where its predominant objective is to present or disseminate the research project and its ...
Final Report Format: Title Author Faculty Mentor (and Co-Mentor if applicable) Abstract. The abstract is a succinct outline of the research project. For experimental projects, it presents the principal objective and scope of the project, describes the methodology, summarizes the results, and states the principal conclusions. ...
Formatting a Chicago paper. The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Use 1 inch margins or larger. Apply double line spacing. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch. Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
Part I - General Information. These guidelines are for the preparation of research project reports prepared by or for the Georgia Department of Transportation (GDOT). The information contained herein is provided to uni-formity in research reports and to ensure that applicable GDOT and Federal Highway Admin-istration (FHWA) regulations are ...
How to Write a Project Report: Step-By-Step GuidePart 1. Project Report Templates: Free DownloadPart 2. Additional ResourcesPart 3. How to Dramatically Reduce Time You Spend Creating ReportsPart 4. At some point during the implementation of a project, a project report has to be generated in order to paint a mental image of the whole project.
The Project Outcomes Report is a report written for new and existing awards, specifically for the public, that provides insight into the outcomes of NSF-funded research. Project Outcome Reports can be viewed through Research.gov's Research Spending & Results search service. Note: Project Outcome Reports are not reviewed or approved by NSF.
Project Final Report Page 2 of 2 PROJECT SUMMARY Provide a succinct summary of the project, including the objectives and the research activities that were undertaken to address the research need and achieve the project objectives. OUTPUTS & IMPACTS State the key outputs/results of the research project and their impacts what did the project find ...
Download this project report dashboard template to track the status of key components of a project, including tasks, costs, and pending action items. This template also helps you support the decisions you make for future project initiatives. Check out this article to find more free Excel dashboard templates for all of your business needs.
Action research. Study of an attempt by you to actively solve a problem and/or change a situation. To gain a greater understanding and improvement of practice over a period of time. Case study. In-depth exploration of one situation. Investigation of a particular situation, problem, company or group of companies.
Final report of project, highlighting methodologies and techniques adopted to achieve the desired results. Discover the world's research. 25+ million members; 160+ million publication pages;
Final report from the research project. Discover the world's research. 25+ million members; 160+ million publication pages; 2.3+ billion citations; Join for free. Public Full-text 1.
Minor Research Project Final Report. bhu.ac.in. Details. File Format. PDF; Size: 929.7 KB ... The research project report is a medium to convey look into work with significant individuals. It is likewise a decent wellspring of conservation of research work for the future reference. ... Research Project Report Template. Cost Estimate for a ...
6. Polish and Proofread the Research Report. The final step of writing the research project report is to guarantee that the researcher follows all the rules and regulations as stated in the course outline. Before publishing the report, conduct another thorough read to authenticate all the information and check for grammatical and spelling ...