
20 Common Researcher Interview Questions and Answers
Common Researcher interview questions, how to answer them, and sample answers from a certified career coach.

You’ve been invited to interview for a research position—congratulations! You know you have the skills and experience, but now it’s time to prove it.
The key to success? Being prepared. To help make sure you shine in your upcoming interview, we’ve compiled some of the most common questions asked during research interviews. Read on, get familiar with them, and practice your answers so you can ace that job interview like a pro.
- What research methods do you use to collect data?
- How do you ensure the accuracy and validity of your research results?
- Describe a time when you had to analyze complex data sets and draw meaningful conclusions from them.
- Explain how you would go about designing an experiment or survey to answer a specific research question.
- Are you familiar with any statistical software programs? If so, which ones?
- What strategies do you use to stay organized while conducting research?
- How do you handle ethical considerations when conducting research?
- Have you ever encountered a situation where you had to adjust your research methodology due to unexpected circumstances?
- Describe a time when you had to present your research findings in a clear and concise manner.
- Do you have experience working with large datasets?
- What challenges have you faced when collecting primary data for a research project?
- How do you approach writing up a research paper or report?
- What techniques do you use to identify potential sources of bias in your research?
- How do you evaluate the quality of secondary sources used in your research?
- What strategies do you use to keep track of changes in the field of research you are studying?
- How do you decide which research questions to pursue?
- What is your experience with peer review processes?
- How do you manage competing demands on your time when conducting research?
- What strategies do you use to ensure that your research remains relevant and up-to-date?
- How do you ensure that your research meets the highest standards of academic integrity?
1. What research methods do you use to collect data?
Research methods are the core of any researcher’s job. You’ll need to be familiar with a variety of different methods, such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and experiments, and be able to explain how you use each one in your work. This will help the interviewer understand your process and how you can contribute to their organization.
How to Answer:
You should be prepared to explain the research methods you have used in your past work. Talk about how you use surveys, interviews, focus groups, and experiments to collect data, as well as any other methods you may have experience with. If you’re just starting out, then talk through the steps you would take to select a method for each project. You can also mention any specialized methods or software that you are familiar with.
Example: “I use a variety of research methods to collect data, depending on the project. I often use surveys and interviews as primary sources of information, but I also have experience with focus groups, experiments, and software tools like Qualtrics for collecting quantitative data. I’m familiar with specialized methods such as content analysis and ethnography when appropriate. My goal is always to select the method that will provide the most accurate and reliable data for each project.”
2. How do you ensure the accuracy and validity of your research results?
Research requires a level of precision that goes beyond the normal workplace. Good researchers are able to identify what data is relevant and how to collect it in order to make reliable conclusions. Interviewers will want to know that you have the skills and knowledge to conduct research that is both accurate and valid. They’ll also want to know if you use any specific methods or tools to ensure accuracy and validity.
You should be prepared to explain what methods you use to ensure accuracy and validity of your research. This could include double-checking sources, using multiple data points, or triangulating information from different sources to verify results. You can also mention any specific tools or techniques you use, such as conducting surveys or interviews with experts in the field. Be sure to emphasize how important it is for you to make sure that your research is accurate and valid before drawing conclusions.
Example: “When I was working on a research project for ABC Corporation, I had to analyze the data from three different sources. My approach was to use statistical analysis techniques and software tools to cross-reference the data sets and identify any potential discrepancies or outliers. After analyzing the results, I identified a number of key trends that allowed us to draw meaningful conclusions about the company’s operations. The insights gained from this research ultimately led to improvements in the organization’s processes, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity.”
3. Describe a time when you had to analyze complex data sets and draw meaningful conclusions from them.
Research projects often involve a lot of data analysis and interpretation. Knowing how to take large amounts of data and make it into something meaningful is a valuable skill for any researcher. This question is a way for the interviewer to gauge your ability to work with data and draw meaningful conclusions from it.
You should be prepared to provide a specific example of when you had to analyze complex data sets and draw meaningful conclusions from them. Talk about the project, your approach to analyzing the data, and any insights or conclusions that you drew from it. Be sure to emphasize the impact of your findings on the project or organization as well.
Example: “I recently worked on a project for my previous employer in which I had to analyze a large and complex data set. My approach was to break down the data into smaller, more manageable chunks and then look for patterns or correlations between different variables. After doing this, I was able to identify a few key trends that were relevant to the project goals. This allowed us to make better decisions about how to allocate resources and focus our efforts, resulting in a successful outcome.”
4. Explain how you would go about designing an experiment or survey to answer a specific research question.
This question is designed to determine if you have the skills necessary to design and implement valid research experiments. The interviewer wants to know if you understand the fundamentals of research design, such as how to select a sample, how to develop a hypothesis, and how to determine the validity of a study. They also want to know if you can explain the process in a clear and concise manner.
Start by explaining the steps you would take to design an experiment or survey. You should include the following: defining the research question, selecting a sample, developing a hypothesis, creating a data collection plan, and determining how to analyze the results. Be sure to explain any specific techniques you might use in each step, such as random sampling or stratified sampling for your sample selection process. Finally, emphasize the importance of validating the results to ensure they are accurate and reliable.
Example: “When designing an experiment or survey, the first step is to define the research question. Once the research question has been identified, I would then select a sample that is representative of the population being studied. I would also develop a hypothesis based on my understanding of the research question and the available data. After that, I would create a data collection plan that outlines how the data will be collected, such as using surveys, interviews, or focus groups. Finally, I would determine the best method for analyzing the results in order to draw valid conclusions from the research. In all cases, it’s important to validate the results to ensure they are accurate and reliable.”
5. Are you familiar with any statistical software programs? If so, which ones?
Researchers often have to analyze data and present it in a meaningful way. This requires familiarity with statistical software programs like SPSS, SAS, or R. Knowing how to use these programs is a critical part of being a successful researcher, so this question is meant to gauge your level of expertise.
If you are familiar with any of the programs mentioned above, be sure to mention that and explain how you have used them in past research projects. If you are not familiar with these programs, it is still important to emphasize your ability to learn new software quickly. Explain how you approach learning new technologies and provide examples of times when you have successfully done so in the past.
Example: “I have used SPSS and SAS in my previous research projects. I am also comfortable with learning new statistical software programs, as I have done so on multiple occasions in the past. For example, when starting a new project at my last job, I was asked to learn R quickly in order to analyze data. Within two weeks, I had become proficient enough to use it for all of our research needs.”
6. What strategies do you use to stay organized while conducting research?
Research can be a long and complex process, with lots of data to sift through, organize, and analyze. It’s important to show the interviewer that you have a system in place to stay organized throughout the research process, from the initial research plan to the final report. This will demonstrate that you can effectively manage your time and resources, as well as prioritize tasks and remain focused on the task at hand.
You can answer this question by talking about the strategies you use to stay organized while conducting research. You could mention that you create detailed research plans, break down large tasks into smaller ones, and prioritize tasks based on importance and deadlines. Additionally, you could talk about how you utilize organizational tools such as spreadsheets and databases to store data, track progress, and easily access information when needed. Finally, you might also discuss how you take notes during your research process in order to keep track of important ideas or findings.
Example: “I use a variety of strategies to stay organized while conducting research. I always start by creating a detailed research plan that outlines the scope of my work and any deadlines associated with it. From there, I break down large tasks into smaller ones in order to tackle them more efficiently. Additionally, I prioritize tasks based on importance and deadlines in order to remain focused on the task at hand. To help store data, track progress, and access information quickly, I also utilize organizational tools such as spreadsheets and databases. Finally, I take notes during my research process in order to keep track of important ideas or findings.”
7. How do you handle ethical considerations when conducting research?
Research often involves collecting personal data, and it’s important that researchers understand how to approach these situations with respect and integrity. Interviewers want to know that you are aware of ethical considerations and that you are capable of adhering to them. This question is likely to be asked to all potential researchers, as it is an important part of the job.
Talk about the ethical considerations you take into account when conducting research. These can include obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring confidentiality and anonymity of data, respecting privacy laws, protecting vulnerable populations, and considering potential biases that may arise in your research. You should also mention any processes or protocols you have implemented to ensure ethical compliance with research projects. Finally, emphasize how important it is for researchers to adhere to ethical standards and how seriously you take them.
Example: “I understand the importance of adhering to ethical standards when conducting research, and I take this responsibility very seriously. In my current position as a researcher at ABC University, I follow a strict protocol for obtaining informed consent from participants and ensuring that data is kept confidential and anonymous. I also make sure to consider any potential biases in our research before collecting data and am familiar with applicable privacy laws. Lastly, I always strive to protect vulnerable populations, such as children or those with disabilities, when conducting research.”
8. Have you ever encountered a situation where you had to adjust your research methodology due to unexpected circumstances?
Research is a dynamic process and researchers must be prepared to adjust their methods as needed. This question is designed to assess the flexibility of potential candidates and their ability to think on their feet. It also provides insight into how well a candidate understands the research process, including how to identify and address potential problems.
To answer this question, provide an example of a situation where you had to adjust your research methodology due to unexpected circumstances. Explain how you identified the problem and how you adjusted your methods in order to successfully complete the project. Be sure to emphasize any creative solutions you implemented and the positive outcome that resulted from your adjustment.
Example: “I recently encountered a situation where I had to adjust my research methodology due to unexpected circumstances. I was conducting a survey to analyze consumer behavior in relation to a new product launch. After collecting the first round of data, I noticed a discrepancy in the results that could not be explained. After further investigation, I realized that the sample size I was using was not large enough to accurately capture the data. I quickly adjusted my methodology by increasing the sample size and collecting more data, which ultimately allowed me to identify the discrepancy and provide an accurate analysis of consumer behavior.”
9. Describe a time when you had to present your research findings in a clear and concise manner.
Researchers often have to communicate their findings to colleagues, stakeholders, and the public. The ability to communicate complex research findings in an understandable way is a key skill for someone in this role. This question allows the interviewer to gauge your ability to explain complex concepts in a clear and concise manner.
You should come prepared with an example of a time when you had to present your research findings. Talk about the project, what the goal was, and how you went about presenting it. If possible, provide specific details such as the type of presentation (oral, written, etc.), who you presented to, and the feedback you received. You should also explain the strategies that you used to make sure that the audience understood your message. This could include using visual aids, breaking down complex concepts into simpler terms, or providing examples to illustrate your points.
Example: “My most recent research project focused on the long-term effects of climate change on agricultural production. I knew that it was important to make sure that the findings were presented in a way that was easy to understand and digest. I created a PowerPoint presentation that included visuals and graphs to illustrate my points, as well as a written report that provided a detailed breakdown of the findings. I then presented my findings to a group of stakeholders and received positive feedback. They appreciated my ability to take complex concepts and explain them in a way that was easy to understand.”
10. Do you have experience working with large datasets?
Many research roles require the ability to work with large datasets and analyze the information within them. This question helps employers understand how comfortable you are with such tasks, and it also serves as a way to gauge your technical skills. To answer this question, talk about how you’ve used various tools and techniques to analyze data and how you’ve been able to draw meaningful insights from it.
Start by talking about the types of datasets you’ve worked with, such as structured or unstructured data, and explain how you’ve gone about analyzing them. Then, provide a few examples of projects you’ve completed that involved working with large datasets. Finally, discuss any tools or techniques you’ve used to work with the data, such as statistical software, data visualization tools, machine learning algorithms, etc. Be sure to emphasize your ability to draw meaningful insights from the data and how those insights have helped inform decisions.
Example: “I have experience working with large datasets in both structured and unstructured formats. I have utilized various tools and techniques to analyze the data, such as statistical software and data visualization tools. I’ve also employed machine learning algorithms to uncover patterns and trends from the data. For example, in my most recent project I utilized a variety of data sources to identify potential new markets for our company. Through analyzing the data, I was able to identify key demographic, geographic, and psychographic trends that we could use to target our new customers. This analysis provided valuable insights that informed our marketing strategy and ultimately led to increased sales.”
11. What challenges have you faced when collecting primary data for a research project?
Research often involves gathering primary data from sources such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observations. It’s important to determine whether the candidate has the skills necessary to design and implement a research project in order to successfully collect data. This question helps the interviewer understand the candidate’s ability to handle the logistics and challenges of primary data collection.
When answering this question, it’s important to provide specific examples of challenges you have faced and how you overcame them. For example, you could talk about the challenge of finding participants for a survey or focus group, or the difficulty in scheduling interviews with busy professionals. You can also discuss any logistical issues that arose during data collection, such as having unreliable equipment or dealing with uncooperative participants. Be sure to emphasize your problem-solving skills and ability to think on your feet when facing unexpected obstacles.
Example: “I’ve encountered a few challenges when gathering primary data for research projects. For example, when I was working on a survey project for a university, it took me several weeks to find participants willing to answer the survey. I had to be creative in my approach and reach out to different groups, such as student organizations, to recruit participants. I also encountered a few logistical issues, such as having unreliable equipment or dealing with uncooperative participants. I was able to quickly come up with solutions to these issues, such as having backup equipment and developing strategies to engage the participants. Overall, I was able to successfully gather the data I needed and produce valuable research findings.”
12. How do you approach writing up a research paper or report?
Research is a process that requires both creativity and structure. As a researcher, you must be able to synthesize information from a variety of sources, develop strong arguments, and communicate those arguments clearly and concisely in written form. Being able to articulate your approach to researching and writing up a paper will demonstrate your ability to think critically and logically.
Your answer should include the steps you take when writing up a research paper or report. This could include outlining your topic, researching relevant sources, organizing and synthesizing data, developing an argument, drafting and revising the paper, and proofreading for accuracy. It is also important to emphasize how you use critical thinking skills to develop strong arguments and draw meaningful conclusions from your research. Finally, make sure to mention any specific techniques or strategies that you have used successfully in the past.
Example: “When writing up a research paper or report, I approach the task systematically. I begin by outlining my topic and any relevant research questions. I then conduct research to find relevant sources, both primary and secondary. I carefully review and analyze the information I find, and use it to develop my argument. After that, I draft and revise the paper, making sure to include evidence to support my points. Finally, I proofread for accuracy and clarity. Throughout the process, I strive to use critical thinking skills to ensure that my arguments are sound and my conclusions are meaningful.”
13. What techniques do you use to identify potential sources of bias in your research?
Researchers need to be able to identify potential sources of bias in their work, such as selection bias or confirmation bias, in order to ensure the accuracy of their data and the validity of their results. By asking this question, the interviewer is gauging your ability to identify potential sources of bias and how you handle them.
To answer this question, you should discuss the techniques you use to identify potential sources of bias in your research. This could include methods such as double-checking data for accuracy and completeness, using multiple sources of information, or conducting blind studies. Additionally, you can talk about how you handle any biases you may find, such as adjusting your research design or changing your methodology. Be sure to emphasize that accuracy and validity are important to you and that you take steps to ensure they remain a priority.
Example: “I understand the importance of accuracy and validity in research, so I always strive to identify and address any potential sources of bias. I use several techniques to identify bias, such as double-checking my data for accuracy and completeness, using multiple sources of information, and conducting blind studies. When I do identify a potential source of bias, I adjust my research design or change my methodology to address it. I also make sure to communicate any changes to my team and stakeholders to ensure that we’re all on the same page.”
14. How do you evaluate the quality of secondary sources used in your research?
One of the most important skills of a researcher is being able to evaluate the quality of sources used in research. This question allows the interviewer to get a better understanding of your research process and your ability to critically evaluate sources. It also allows them to gauge your level of experience in the field and your knowledge of the research landscape.
To answer this question, you should explain your process for evaluating secondary sources. You can talk about the criteria that you use to evaluate a source’s credibility such as its author or publisher, the date of publication, and any peer reviews that have been conducted on the source. Additionally, you can mention any methods you use to assess the accuracy of information in the source such as cross-referencing with other sources or conducting additional research on the topic. Finally, you should discuss how you use these evaluations to inform your own research.
Example: “When evaluating the quality of secondary sources I use in my research, I consider a few key factors. I always look at the author or publisher of the source, the date of publication, and any peer reviews that have been conducted. I also use a variety of methods to assess the accuracy of the information in the source, such as cross-referencing with other sources and conducting additional research. From there, I use my evaluations to inform my own research and determine how best to use the source. This helps me ensure that I’m using the most reliable and up-to-date sources in my research.”
15. What strategies do you use to keep track of changes in the field of research you are studying?
Research is an ever-evolving field and keeping up with changes in the field is essential to remain relevant and up to date. Interviewers want to know that you have the skills and strategies to stay on top of the latest research, trends, and developments in the field. They’ll be looking for evidence that you have the self-discipline and organizational skills to stay on top of your work and be able to provide timely, accurate research.
You should be prepared to discuss the strategies and tools you use to stay up-to-date on changes in your field. Talk about how you keep track of new research articles, publications, conferences, and other sources of information that are relevant to your work. You can also talk about how you use technology such as RSS feeds, social media, or email alerts to ensure that you’re aware of any news or updates related to your research. Additionally, mention any methods you have for organizing and cataloging the information you collect so it is easily accessible when needed.
Example: “To stay on top of changes in my field, I use a variety of strategies and tools. I subscribe to relevant RSS feeds and email alerts to ensure I’m aware of any new research articles or publications. I also use social media to follow industry leaders and experts in the field and get updates on their work. I also keep an organized library of research material that I have collected over the years. I use a combination of software tools and physical filing systems to keep track of all the information I need. This allows me to quickly access any information I need, when I need it.”
16. How do you decide which research questions to pursue?
Being a researcher requires the ability to prioritize and select the best questions to pursue in order to achieve the desired outcome. This question helps the interviewer get a sense of your process and how you approach problem solving. It also gives them an insight into your critical thinking skills, as well as your ability to analyze data and make meaningful conclusions.
The best way to answer this question is to provide a step-by-step approach of how you decide which research questions to pursue. Start by explaining the research process you go through, such as collecting data, analyzing it and forming hypotheses. Then explain how you prioritize certain questions based on their importance and relevance to the project at hand. Finally, discuss how you use your findings to make informed decisions about which questions are worth pursuing further.
Example: “When I’m deciding which research questions to pursue, I start by gathering all the available data related to the project. From there, I analyze the data to form hypotheses and then prioritize the questions based on their importance and relevance to the project. I also consider the impact each question could have on the overall outcome of the research. Once I have a list of the most important questions, I evaluate the data and use my findings to make informed decisions about which questions are worth pursuing further. Ultimately, my goal is to select the best questions that will yield the most meaningful results.”
17. What is your experience with peer review processes?
Peer review is a critical part of the research process. It requires that researchers review and critique each other’s work in order to ensure that the research is unbiased and credible. This question is a way for the interviewer to assess your knowledge of the research process and your ability to work with other researchers.
To answer this question, you should provide specific examples of your experience with peer review processes. Talk about how you have worked with other researchers to review and critique their work, as well as how you have incorporated feedback from peers into your own research. You can also discuss any challenges or successes you had during the process. Finally, emphasize your understanding of the importance of peer review in the research process and why it is necessary for producing high-quality results.
Example: “I have extensive experience with peer review processes, both as a reviewer and as an author. I have worked with other researchers to review their work and provide constructive feedback, as well as incorporating feedback from peers into my own research. I understand the importance of peer review in the research process and am committed to producing high-quality results. I have also had success in resolving disagreements between reviewers and authors when needed, and I have a strong track record of producing quality research that has been accepted for publication.”
18. How do you manage competing demands on your time when conducting research?
Research can be a demanding job, with a lot of deadlines, competing agendas, and complex data sets to analyze. The interviewer wants to make sure you can prioritize tasks, keep track of multiple projects, and adjust when needed. Your ability to manage competing demands on your time is a key indicator of how successful you will be at the job.
To answer this question, you should focus on how you prioritize tasks and manage deadlines. Talk about the strategies you use to stay organized, such as setting up a calendar or using task management tools. Also discuss any techniques you have for staying focused when there are multiple demands on your time. Finally, emphasize your ability to adjust your plans when needed, such as if an unexpected project comes in or a deadline needs to be moved up.
Example: “I have a few strategies for managing competing demands on my time when conducting research. I prioritize tasks by breaking them down into smaller, manageable chunks and then assigning deadlines to each one. I also use task management tools to keep track of what I need to do and stay organized. And I make sure to take regular breaks to stay focused and energized. When I need to adjust my plans due to unexpected events, I’m able to reassess and re-prioritize my tasks accordingly. I’m confident in my ability to manage competing demands on my time and stay organized when conducting research.”
19. What strategies do you use to ensure that your research remains relevant and up-to-date?
Research is a dynamic field, and the best researchers know that they need to stay informed of the latest developments and trends in order to remain relevant. This question allows your interviewer to assess your knowledge of the field and your commitment to keeping up with the latest research. It shows that you are aware of the need to stay ahead of the curve and that you have the skills to do so.
To answer this question, you should start by discussing the strategies that you use to stay informed. You can talk about how you read industry publications, attend conferences and seminars, or network with other researchers in your field. You should also mention any specific platforms or tools that you use to keep up-to-date on the latest research. Finally, you should explain why staying informed is important to you and how it helps you do better work.
Example: “I use a variety of strategies to ensure that my research remains relevant and up-to-date. I read industry publications, attend conferences and seminars, and network with other researchers to stay informed. I also use specific tools like Google Scholar and ResearchGate to keep track of new developments in my field. It’s important to me to stay ahead of the curve and make sure that my research is as current and relevant as possible. Doing so not only helps me do better work, but it also helps me to provide more value to my employer and contribute to the success of their projects.”
20. How do you ensure that your research meets the highest standards of academic integrity?
Research is the backbone of any organization, and it is crucial for a researcher to maintain the highest standards of academic integrity. Employers want to know that you understand the importance of being thorough and accurate, as well as ethical in your research. They may also want to know how you go about verifying the accuracy of your data and sources, and how you ensure that your research meets the standards expected in the field.
Start off by detailing the steps you take to ensure that your research meets academic integrity standards. For example, you can mention how you always double-check sources and data for accuracy and reliability, or how you use peer review processes to vet your work. Additionally, be sure to emphasize any specific techniques or methods you have used in the past to verify the validity of your findings. Finally, explain why it is important to you to maintain the highest level of academic integrity in your research.
Example: “I understand the importance of academic integrity and take it very seriously in my research. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy, I always double-check my sources and data, and use peer review processes to vet my work. Additionally, I frequently use replication studies to verify the validity of my findings. To me, it is essential to ensure that my research meets the highest standards of academic integrity, as it is the foundation of any successful research project.”
20 Interview Questions Every Data Center Engineer Must Be Able To Answer
20 help desk interview questions and answers, you may also be interested in..., 30 quality leader interview questions and answers, 30 community specialist interview questions and answers, 20 medical coordinator interview questions and answers, 30 corporate security officer interview questions and answers.
Qualitative Research 101: Interviewing
5 Common Mistakes To Avoid When Undertaking Interviews
By: David Phair (PhD) and Kerryn Warren (PhD) | March 2022
Undertaking interviews is potentially the most important step in the qualitative research process. If you don’t collect useful, useable data in your interviews, you’ll struggle through the rest of your dissertation or thesis. Having helped numerous students with their research over the years, we’ve noticed some common interviewing mistakes that first-time researchers make. In this post, we’ll discuss five costly interview-related mistakes and outline useful strategies to avoid making these.
Overview: 5 Interviewing Mistakes
- Not having a clear interview strategy /plan
- Not having good interview techniques /skills
- Not securing a suitable location and equipment
- Not having a basic risk management plan
- Not keeping your “ golden thread ” front of mind
1. Not having a clear interview strategy
The first common mistake that we’ll look at is that of starting the interviewing process without having first come up with a clear interview strategy or plan of action. While it’s natural to be keen to get started engaging with your interviewees, a lack of planning can result in a mess of data and inconsistency between interviews.
There are several design choices to decide on and plan for before you start interviewing anyone. Some of the most important questions you need to ask yourself before conducting interviews include:
- What are the guiding research aims and research questions of my study?
- Will I use a structured, semi-structured or unstructured interview approach?
- How will I record the interviews (audio or video)?
- Who will be interviewed and by whom ?
- What ethics and data law considerations do I need to adhere to?
- How will I analyze my data?
Let’s take a quick look at some of these.
The core objective of the interviewing process is to generate useful data that will help you address your overall research aims. Therefore, your interviews need to be conducted in a way that directly links to your research aims, objectives and research questions (i.e. your “golden thread”). This means that you need to carefully consider the questions you’ll ask to ensure that they align with and feed into your golden thread. If any question doesn’t align with this, you may want to consider scrapping it.
Another important design choice is whether you’ll use an unstructured, semi-structured or structured interview approach . For semi-structured interviews, you will have a list of questions that you plan to ask and these questions will be open-ended in nature. You’ll also allow the discussion to digress from the core question set if something interesting comes up. This means that the type of information generated might differ a fair amount between interviews.
Contrasted to this, a structured approach to interviews is more rigid, where a specific set of closed questions is developed and asked for each interviewee in exactly the same order. Closed questions have a limited set of answers, that are often single-word answers. Therefore, you need to think about what you’re trying to achieve with your research project (i.e. your research aims) and decided on which approach would be best suited in your case.
It is also important to plan ahead with regards to who will be interviewed and how. You need to think about how you will approach the possible interviewees to get their cooperation, who will conduct the interviews, when to conduct the interviews and how to record the interviews. For each of these decisions, it’s also essential to make sure that all ethical considerations and data protection laws are taken into account.
Finally, you should think through how you plan to analyze the data (i.e., your qualitative analysis method) generated by the interviews. Different types of analysis rely on different types of data, so you need to ensure you’re asking the right types of questions and correctly guiding your respondents.
Simply put, you need to have a plan of action regarding the specifics of your interview approach before you start collecting data. If not, you’ll end up drifting in your approach from interview to interview, which will result in inconsistent, unusable data.

2. Not having good interview technique
While you’re generally not expected to become you to be an expert interviewer for a dissertation or thesis, it is important to practice good interview technique and develop basic interviewing skills .
Let’s go through some basics that will help the process along.
Firstly, before the interview , make sure you know your interview questions well and have a clear idea of what you want from the interview. Naturally, the specificity of your questions will depend on whether you’re taking a structured, semi-structured or unstructured approach, but you still need a consistent starting point . Ideally, you should develop an interview guide beforehand (more on this later) that details your core question and links these to the research aims, objectives and research questions.
Before you undertake any interviews, it’s a good idea to do a few mock interviews with friends or family members. This will help you get comfortable with the interviewer role, prepare for potentially unexpected answers and give you a good idea of how long the interview will take to conduct. In the interviewing process, you’re likely to encounter two kinds of challenging interviewees ; the two-word respondent and the respondent who meanders and babbles. Therefore, you should prepare yourself for both and come up with a plan to respond to each in a way that will allow the interview to continue productively.
To begin the formal interview , provide the person you are interviewing with an overview of your research. This will help to calm their nerves (and yours) and contextualize the interaction. Ultimately, you want the interviewee to feel comfortable and be willing to be open and honest with you, so it’s useful to start in a more casual, relaxed fashion and allow them to ask any questions they may have. From there, you can ease them into the rest of the questions.
As the interview progresses , avoid asking leading questions (i.e., questions that assume something about the interviewee or their response). Make sure that you speak clearly and slowly , using plain language and being ready to paraphrase questions if the person you are interviewing misunderstands. Be particularly careful with interviewing English second language speakers to ensure that you’re both on the same page.
Engage with the interviewee by listening to them carefully and acknowledging that you are listening to them by smiling or nodding. Show them that you’re interested in what they’re saying and thank them for their openness as appropriate. This will also encourage your interviewee to respond openly.
Need a helping hand?
3. Not securing a suitable location and quality equipment
Where you conduct your interviews and the equipment you use to record them both play an important role in how the process unfolds. Therefore, you need to think carefully about each of these variables before you start interviewing.
Poor location: A bad location can result in the quality of your interviews being compromised, interrupted, or cancelled. If you are conducting physical interviews, you’ll need a location that is quiet, safe, and welcoming . It’s very important that your location of choice is not prone to interruptions (the workplace office is generally problematic, for example) and has suitable facilities (such as water, a bathroom, and snacks).
If you are conducting online interviews , you need to consider a few other factors. Importantly, you need to make sure that both you and your respondent have access to a good, stable internet connection and electricity. Always check before the time that both of you know how to use the relevant software and it’s accessible (sometimes meeting platforms are blocked by workplace policies or firewalls). It’s also good to have alternatives in place (such as WhatsApp, Zoom, or Teams) to cater for these types of issues.
Poor equipment: Using poor-quality recording equipment or using equipment incorrectly means that you will have trouble transcribing, coding, and analyzing your interviews. This can be a major issue , as some of your interview data may go completely to waste if not recorded well. So, make sure that you use good-quality recording equipment and that you know how to use it correctly.
To avoid issues, you should always conduct test recordings before every interview to ensure that you can use the relevant equipment properly. It’s also a good idea to spot check each recording afterwards, just to make sure it was recorded as planned. If your equipment uses batteries, be sure to always carry a spare set.

4. Not having a basic risk management plan
Many possible issues can arise during the interview process. Not planning for these issues can mean that you are left with compromised data that might not be useful to you. Therefore, it’s important to map out some sort of risk management plan ahead of time, considering the potential risks, how you’ll minimize their probability and how you’ll manage them if they materialize.
Common potential issues related to the actual interview include cancellations (people pulling out), delays (such as getting stuck in traffic), language and accent differences (especially in the case of poor internet connections), issues with internet connections and power supply. Other issues can also occur in the interview itself. For example, the interviewee could drift off-topic, or you might encounter an interviewee who does not say much at all.
You can prepare for these potential issues by considering possible worst-case scenarios and preparing a response for each scenario. For instance, it is important to plan a backup date just in case your interviewee cannot make it to the first meeting you scheduled with them. It’s also a good idea to factor in a 30-minute gap between your interviews for the instances where someone might be late, or an interview runs overtime for other reasons. Make sure that you also plan backup questions that could be used to bring a respondent back on topic if they start rambling, or questions to encourage those who are saying too little.
In general, it’s best practice to plan to conduct more interviews than you think you need (this is called oversampling ). Doing so will allow you some room for error if there are interviews that don’t go as planned, or if some interviewees withdraw. If you need 10 interviews, it is a good idea to plan for 15. Likely, a few will cancel , delay, or not produce useful data.

5. Not keeping your golden thread front of mind
We touched on this a little earlier, but it is a key point that should be central to your entire research process. You don’t want to end up with pages and pages of data after conducting your interviews and realize that it is not useful to your research aims . Your research aims, objectives and research questions – i.e., your golden thread – should influence every design decision and should guide the interview process at all times.
A useful way to avoid this mistake is by developing an interview guide before you begin interviewing your respondents. An interview guide is a document that contains all of your questions with notes on how each of the interview questions is linked to the research question(s) of your study. You can also include your research aims and objectives here for a more comprehensive linkage.
You can easily create an interview guide by drawing up a table with one column containing your core interview questions . Then add another column with your research questions , another with expectations that you may have in light of the relevant literature and another with backup or follow-up questions . As mentioned, you can also bring in your research aims and objectives to help you connect them all together. If you’d like, you can download a copy of our free interview guide here .
Recap: Qualitative Interview Mistakes
In this post, we’ve discussed 5 common costly mistakes that are easy to make in the process of planning and conducting qualitative interviews.
To recap, these include:
If you have any questions about these interviewing mistakes, drop a comment below. Alternatively, if you’re interested in getting 1-on-1 help with your thesis or dissertation , check out our dissertation coaching service or book a free initial consultation with one of our friendly Grad Coaches.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research Interviews
Try Qualtrics for free
How to carry out great interviews in qualitative research.
11 min read An interview is one of the most versatile methods used in qualitative research. Here’s what you need to know about conducting great qualitative interviews.
What is a qualitative research interview?
Qualitative research interviews are a mainstay among q ualitative research techniques, and have been in use for decades either as a primary data collection method or as an adjunct to a wider research process. A qualitative research interview is a one-to-one data collection session between a researcher and a participant. Interviews may be carried out face-to-face, over the phone or via video call using a service like Skype or Zoom.
There are three main types of qualitative research interview – structured, unstructured or semi-structured.
- Structured interviews Structured interviews are based around a schedule of predetermined questions and talking points that the researcher has developed. At their most rigid, structured interviews may have a precise wording and question order, meaning that they can be replicated across many different interviewers and participants with relatively consistent results.
- Unstructured interviews Unstructured interviews have no predetermined format, although that doesn’t mean they’re ad hoc or unplanned. An unstructured interview may outwardly resemble a normal conversation, but the interviewer will in fact be working carefully to make sure the right topics are addressed during the interaction while putting the participant at ease with a natural manner.
- Semi-structured interviews Semi-structured interviews are the most common type of qualitative research interview, combining the informality and rapport of an unstructured interview with the consistency and replicability of a structured interview. The researcher will come prepared with questions and topics, but will not need to stick to precise wording. This blended approach can work well for in-depth interviews.
Free eBook: The qualitative research design handbook
What are the pros and cons of interviews in qualitative research?
As a qualitative research method interviewing is hard to beat, with applications in social research, market research, and even basic and clinical pharmacy. But like any aspect of the research process, it’s not without its limitations. Before choosing qualitative interviewing as your research method, it’s worth weighing up the pros and cons.
Pros of qualitative interviews:
- provide in-depth information and context
- can be used effectively when their are low numbers of participants
- provide an opportunity to discuss and explain questions
- useful for complex topics
- rich in data – in the case of in-person or video interviews , the researcher can observe body language and facial expression as well as the answers to questions
Cons of qualitative interviews:
- can be time-consuming to carry out
- costly when compared to some other research methods
- because of time and cost constraints, they often limit you to a small number of participants
- difficult to standardize your data across different researchers and participants unless the interviews are very tightly structured
- As the Open University of Hong Kong notes, qualitative interviews may take an emotional toll on interviewers
Qualitative interview guides
Semi-structured interviews are based on a qualitative interview guide, which acts as a road map for the researcher. While conducting interviews, the researcher can use the interview guide to help them stay focused on their research questions and make sure they cover all the topics they intend to.
An interview guide may include a list of questions written out in full, or it may be a set of bullet points grouped around particular topics. It can prompt the interviewer to dig deeper and ask probing questions during the interview if appropriate.
Consider writing out the project’s research question at the top of your interview guide, ahead of the interview questions. This may help you steer the interview in the right direction if it threatens to head off on a tangent.
Avoid bias in qualitative research interviews
According to Duke University , bias can create significant problems in your qualitative interview.
- Acquiescence bias is common to many qualitative methods, including focus groups. It occurs when the participant feels obliged to say what they think the researcher wants to hear. This can be especially problematic when there is a perceived power imbalance between participant and interviewer. To counteract this, Duke University’s experts recommend emphasizing the participant’s expertise in the subject being discussed, and the value of their contributions.
- Interviewer bias is when the interviewer’s own feelings about the topic come to light through hand gestures, facial expressions or turns of phrase. Duke’s recommendation is to stick to scripted phrases where this is an issue, and to make sure researchers become very familiar with the interview guide or script before conducting interviews, so that they can hone their delivery.
What kinds of questions should you ask in a qualitative interview?
The interview questions you ask need to be carefully considered both before and during the data collection process. As well as considering the topics you’ll cover, you will need to think carefully about the way you ask questions.
Open-ended interview questions – which cannot be answered with a ‘yes’ ‘no’ or ‘maybe’ – are recommended by many researchers as a way to pursue in depth information.
An example of an open-ended question is “What made you want to move to the East Coast?” This will prompt the participant to consider different factors and select at least one. Having thought about it carefully, they may give you more detailed information about their reasoning.
A closed-ended question , such as “Would you recommend your neighborhood to a friend?” can be answered without too much deliberation, and without giving much information about personal thoughts, opinions and feelings.
Follow-up questions can be used to delve deeper into the research topic and to get more detail from open-ended questions. Examples of follow-up questions include:
- What makes you say that?
- What do you mean by that?
- Can you tell me more about X?
- What did/does that mean to you?
As well as avoiding closed-ended questions, be wary of leading questions. As with other qualitative research techniques such as surveys or focus groups, these can introduce bias in your data. Leading questions presume a certain point of view shared by the interviewer and participant, and may even suggest a foregone conclusion.
An example of a leading question might be: “You moved to New York in 1990, didn’t you?” In answering the question, the participant is much more likely to agree than disagree. This may be down to acquiescence bias or a belief that the interviewer has checked the information and already knows the correct answer.
Other leading questions involve adjectival phrases or other wording that introduces negative or positive connotations about a particular topic. An example of this kind of leading question is: “Many employees dislike wearing masks to work. How do you feel about this?” It presumes a positive opinion and the participant may be swayed by it, or not want to contradict the interviewer.
Harvard University’s guidelines for qualitative interview research add that you shouldn’t be afraid to ask embarrassing questions – “if you don’t ask, they won’t tell.” Bear in mind though that too much probing around sensitive topics may cause the interview participant to withdraw. The Harvard guidelines recommend leaving sensitive questions til the later stages of the interview when a rapport has been established.
More tips for conducting qualitative interviews
Observing a participant’s body language can give you important data about their thoughts and feelings. It can also help you decide when to broach a topic, and whether to use a follow-up question or return to the subject later in the interview.
Be conscious that the participant may regard you as the expert, not themselves. In order to make sure they express their opinions openly, use active listening skills like verbal encouragement and paraphrasing and clarifying their meaning to show how much you value what they are saying.
Remember that part of the goal is to leave the interview participant feeling good about volunteering their time and their thought process to your research. Aim to make them feel empowered , respected and heard.
Unstructured interviews can demand a lot of a researcher, both cognitively and emotionally. Be sure to leave time in between in-depth interviews when scheduling your data collection to make sure you maintain the quality of your data, as well as your own well-being .
Recording and transcribing interviews
Historically, recording qualitative research interviews and then transcribing the conversation manually would have represented a significant part of the cost and time involved in research projects that collect qualitative data.
Fortunately, researchers now have access to digital recording tools, and even speech-to-text technology that can automatically transcribe interview data using AI and machine learning. This type of tool can also be used to capture qualitative data from qualitative research (focus groups,ect.) making this kind of social research or market research much less time consuming.
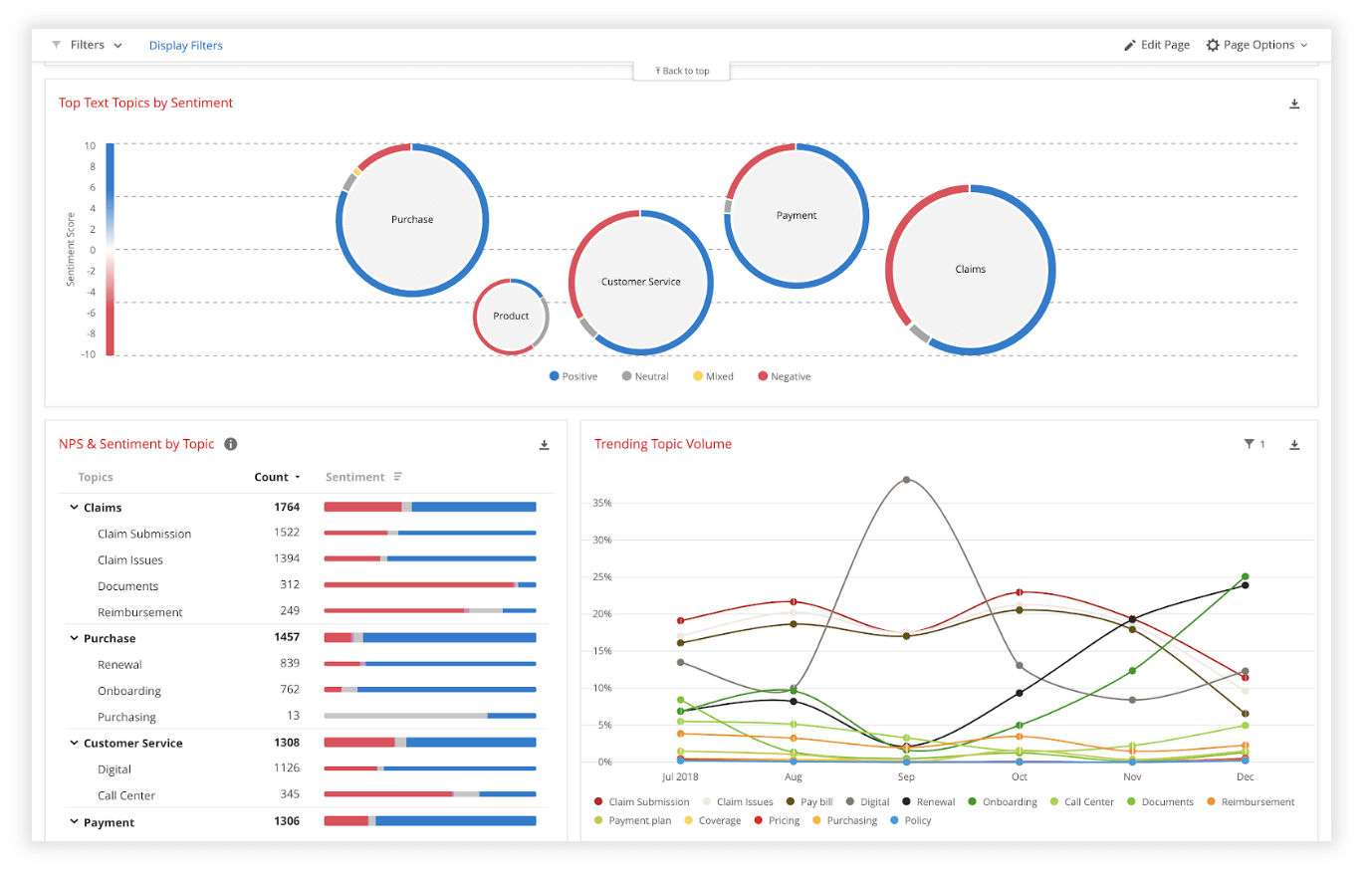
Data analysis
Qualitative interview data is unstructured, rich in content and difficult to analyze without the appropriate tools. Fortunately, machine learning and AI can once again make things faster and easier when you use qualitative methods like the research interview.
Text analysis tools and natural language processing software can ‘read’ your transcripts and voice data and identify patterns and trends across large volumes of text or speech. They can also perform khttps://www.qualtrics.com/experience-management/research/sentiment-analysis/
which assesses overall trends in opinion and provides an unbiased overall summary of how participants are feeling.
Another feature of text analysis tools is their ability to categorize information by topic, sorting it into groupings that help you organize your data according to the topic discussed.
All in all, interviews are a valuable technique for qualitative research in business, yielding rich and detailed unstructured data. Historically, they have only been limited by the human capacity to interpret and communicate results and conclusions, which demands considerable time and skill.
When you combine this data with AI tools that can interpret it quickly and automatically, it becomes easy to analyze and structure, dovetailing perfectly with your other business data. An additional benefit of natural language analysis tools is that they are free of subjective biases, and can replicate the same approach across as much data as you choose. By combining human research skills with machine analysis, qualitative research methods such as interviews are more valuable than ever to your business.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Topic Guides
- Research Methods Guide
- Interview Research
Research Methods Guide: Interview Research
- Introduction
- Research Design & Method
- Survey Research
- Data Analysis
- Resources & Consultation
Tutorial Videos: Interview Method
Interview as a Method for Qualitative Research

Goals of Interview Research
- Preferences
- They help you explain, better understand, and explore research subjects' opinions, behavior, experiences, phenomenon, etc.
- Interview questions are usually open-ended questions so that in-depth information will be collected.
Mode of Data Collection
There are several types of interviews, including:
- Face-to-Face
- Online (e.g. Skype, Googlehangout, etc)
FAQ: Conducting Interview Research
What are the important steps involved in interviews?
- Think about who you will interview
- Think about what kind of information you want to obtain from interviews
- Think about why you want to pursue in-depth information around your research topic
- Introduce yourself and explain the aim of the interview
- Devise your questions so interviewees can help answer your research question
- Have a sequence to your questions / topics by grouping them in themes
- Make sure you can easily move back and forth between questions / topics
- Make sure your questions are clear and easy to understand
- Do not ask leading questions
- Do you want to bring a second interviewer with you?
- Do you want to bring a notetaker?
- Do you want to record interviews? If so, do you have time to transcribe interview recordings?
- Where will you interview people? Where is the setting with the least distraction?
- How long will each interview take?
- Do you need to address terms of confidentiality?
Do I have to choose either a survey or interviewing method?
No. In fact, many researchers use a mixed method - interviews can be useful as follow-up to certain respondents to surveys, e.g., to further investigate their responses.
Is training an interviewer important?
Yes, since the interviewer can control the quality of the result, training the interviewer becomes crucial. If more than one interviewers are involved in your study, it is important to have every interviewer understand the interviewing procedure and rehearse the interviewing process before beginning the formal study.
- << Previous: Survey Research
- Next: Data Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 10:42 AM

Research Interviews: An effective and insightful way of data collection
Research interviews play a pivotal role in collecting data for various academic, scientific, and professional endeavors. They provide researchers with an opportunity to delve deep into the thoughts, experiences, and perspectives of an individual, thus enabling a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena. It is important for researchers to design an effective and insightful method of data collection on a particular topic. A research interview is typically a two-person meeting conducted to collect information on a certain topic. It is a qualitative data collection method to gain primary information.
The three key features of a research interview are as follows:
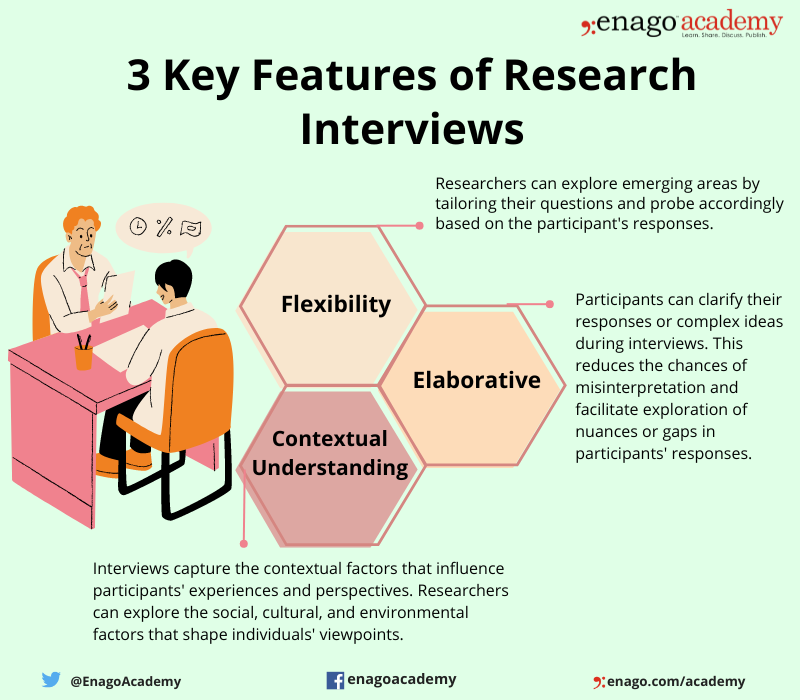
Table of Contents
The Significance of Research Interviews in Gathering Primary Data
The role of research interviews in gathering first-hand information is invaluable. Additionally, they allow researchers to interact directly with participants, enabling them to collect unfiltered primary data.
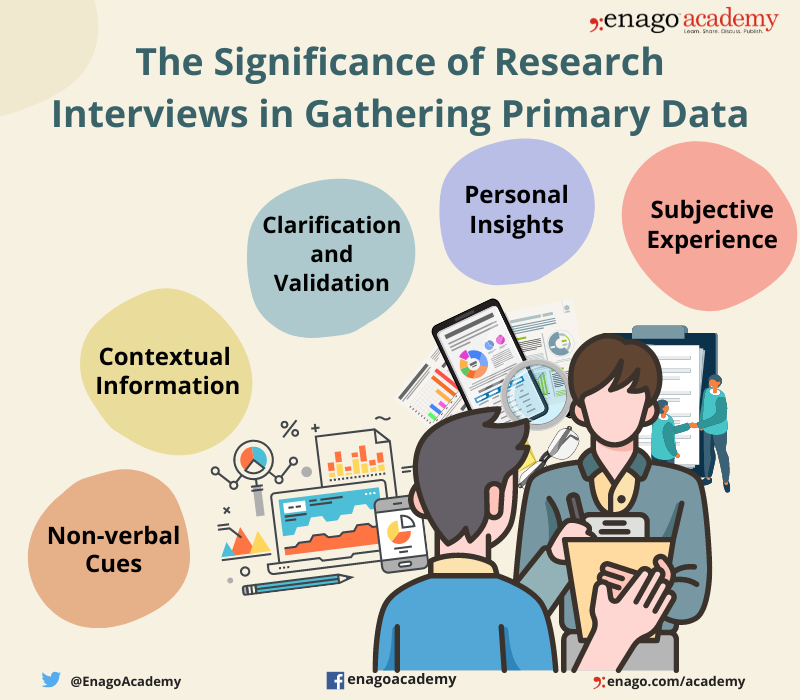
1. Subjective Experience
Research interviews facilitate in-depth exploration of a research topic. Thus, by engaging in one-to-one conversation with participants, researchers can delve into the nuances and complexities of their experiences, perspectives, and opinions. This allows comprehensive understanding of the research subject that may not be possible through other methods. Also, research interviews offer the unique advantage of capturing subjective experiences through personal narratives. Moreover, participants can express their thoughts, feelings, and beliefs, which add depth to the findings.
2. Personal Insights
Research interviews offer an opportunity for participants to share their views and opinions on the objective they are being interviewed for. Furthermore, participants can express their thoughts and experiences, providing rich qualitative data . Consequently, these personal narratives add a human element to the research, thus enhancing the understanding of the topic from the participants’ perspectives. Research interviews offer the opportunity to uncover unanticipated insights or emerging themes. Additionally, open-ended questions and active listening can help the researchers to identify new perspectives, ideas, or patterns that may not have been initially considered. As a result, these factors can lead to new avenues for exploration.
3. Clarification and Validation
Researchers can clarify participants’ responses and validate their understanding during an interview. This ensures accurate data collection and interpretation. Additionally, researchers can probe deeper into participants’ statements and seek clarification on any ambiguity in the information.
4. Contextual Information
Research interviews allow researchers to gather contextual information that offers a comprehensive understanding of the research topic. Additionally, participants can provide insights into the social, cultural, or environmental factors that shape their experiences, behaviors, and beliefs. This contextual information helps researchers place the data in a broader context and facilitates a more nuanced analysis.
5. Non-verbal Cues
In addition to verbal responses, research interviews allow researchers to observe non-verbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. Additionally, non-verbal cues can convey information, such as emotions, attitudes, or levels of comfort. Furthermore, integrating non-verbal cues with verbal responses provides a more holistic understanding of participants’ experiences and enriches the data collection process.
Research interviews offer several advantages, making them a reliable tool for collecting information. However, choosing the right type of research interview is essential for collecting useful data.
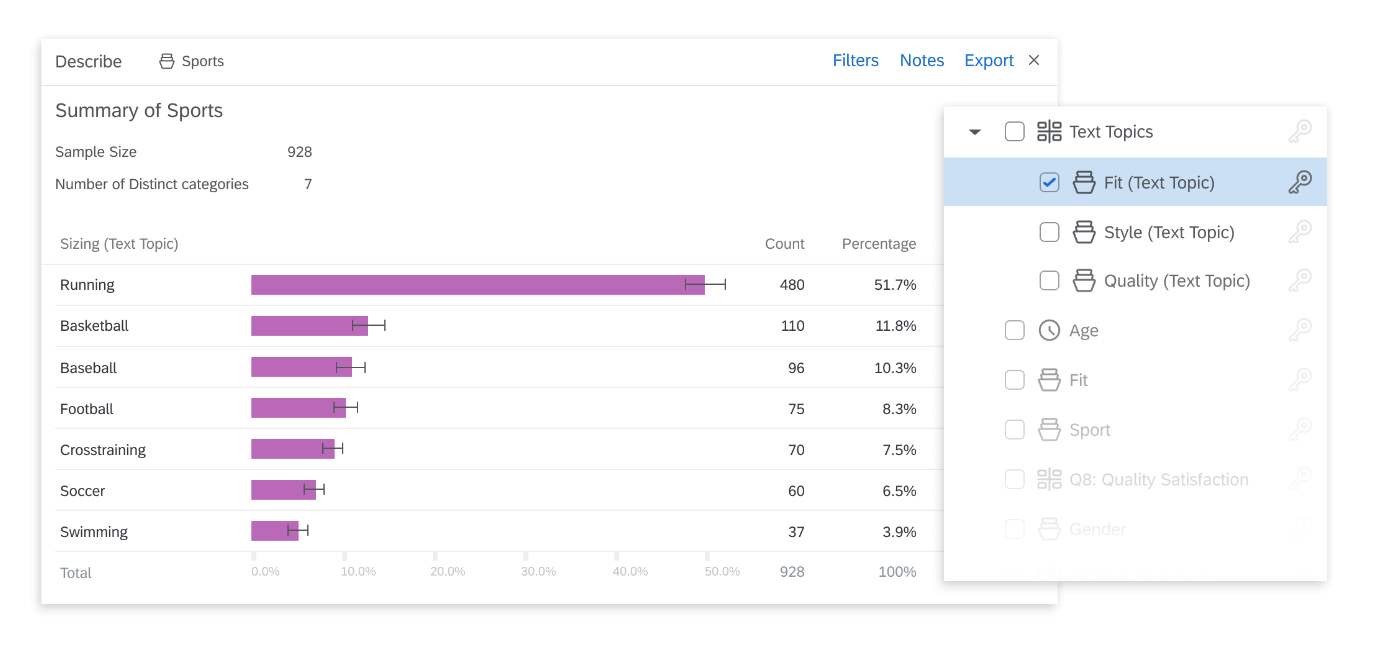
Types of Research Interviews
There are several types of research interviews that researchers can use based on their research goals , the nature of their study, and the data they aim to collect. Here are some common types of research interviews:
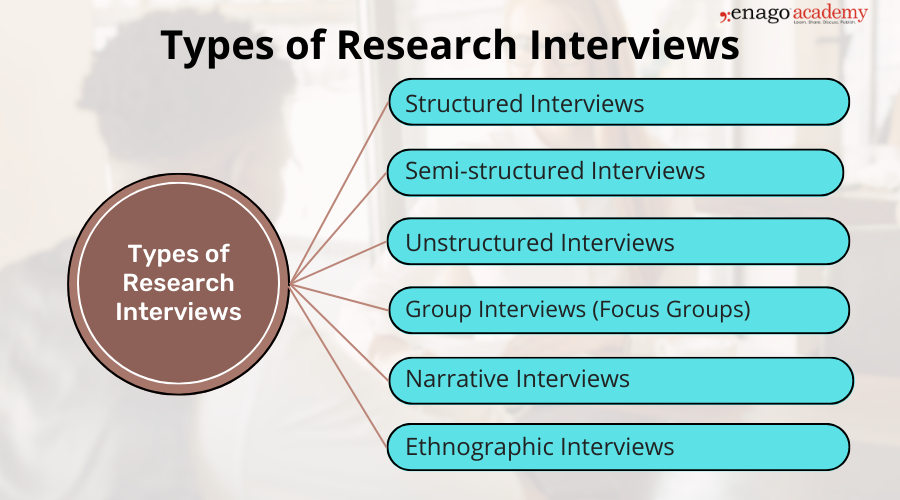
1. Structured Interviews
- Structured interviews are standardized and follow a fixed format.
- Therefore, these interviews have a pre-determined set of questions.
- All the participants are asked the same set of questions in the same order.
- Therefore, this type of interview facilitates standardization and allows easy comparison and quantitative analysis of responses.
- As a result, structured interviews are used in surveys or studies which aims for a high level of standardization and comparability.
2. Semi-structured Interviews
- Semi-structured interviews offer a flexible framework by combining pre-determined questions.
- So, this gives an opportunity for follow-up questions and open-ended discussions.
- Researchers have a list of core questions but can adapt the interview depending on the participant’s responses.
- Consequently, this allows for in-depth exploration while maintaining some level of consistency across interviews.
- As a result, semi-structured interviews are widely used in qualitative research, where content-rich data is desired.
3. Unstructured Interviews
- Unstructured interviews provide the greatest flexibility and freedom in the interview process.
- This type do not have a pre-determined set of questions.
- Thus, the conversation flows naturally based on the participant’s responses and the researcher’s interests.
- Moreover, this type of interview allows for open-ended exploration and encourages participants to share their experiences, thoughts, and perspectives freely.
- Unstructured interviews useful to explore new or complex research topics, with limited preconceived questions.
4. Group Interviews (Focus Groups)
- Group interviews involve multiple participants who engage in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic.
- This format allows the interaction and exchange of ideas among participants, generating a group dynamic.
- Therefore, group interviews are beneficial for capturing diverse perspectives, and generating collective insights.
- They are often used in market research, social sciences, or studies demanding shared experiences.
5. Narrative Interviews
- Narrative interviews focus on eliciting participants’ personal stories, views, experiences, and narratives. Researchers aim to look into the individual’s life journey.
- As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data.
- Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews.
6. Ethnographic Interviews
- Ethnographic interviews are conducted within the context of ethnographic research, where researchers immerse themselves in a specific social or cultural setting.
- These interviews aim to understand participants’ experiences, beliefs, and practices within their cultural context, thereby understanding diversity in different ethnic groups.
- Furthermore, ethnographic interviews involve building rapport, observing the participants’ daily lives, and engaging in conversations that capture the nuances of the culture under study.
It must be noted that these interview types are not mutually exclusive. Therefore, researchers often employ a combination of approaches to gather the most comprehensive data for their research. The choice of interview type depends on the research objectives and the nature of the research topic.
Steps of Conducting a Research Interview
Research interviews offer several benefits, and thus careful planning and execution of the entire process are important to gather in-depth information from the participants. While conducting an interview, it is essential to know the necessary steps to follow for ensuring success. The steps to conduct a research interview are as follows:
- Identify the objectives and understand the goals
- Select an appropriate interview format
- Organize the necessary materials for the interview
- Understand the questions to be addressed
- Analyze the demographics of interviewees
- Select the interviewees
- Design the interview questions to gather sufficient information
- Schedule the interview
- Explain the purpose of the interview
- Analyze the interviewee based on his/her responses
Considerations for Research Interviews
Since the flexible nature of research interviews makes them an invaluable tool for data collection, researchers must consider certain factors to make the process effective. They should avoid bias and preconceived notion against the participants. Furthermore, researchers must comply with ethical considerations and respect the cultural differences between them and the participants. Also, they should ensure careful tailoring of the questions to avoid making them offensive or derogatory. The interviewers must respect the privacy of the participants and ensure the confidentiality of their details.

By ensuring due diligence of these considerations associated with research interviews, researchers can maximize the validity and reliability of the collected data, leading to robust and meaningful research outcomes.
Have you ever conducted a research interview? What was your experience? What factors did you consider when conducting a research interview? Share it with researchers worldwide by submitting your thought piece on Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform .
Frequently Asked Questions
• Identify the objectives of the interview • State and explain the purpose of the interview • Select an appropriate interview format • Organize the necessary materials for the Interview • Check the demographics of the participants • Select the Interviewees or the participants • Prepare the list of questions to gather maximum useful data from the participants • Schedule the Interview • Analyze the participant based on his/ her Responses
Interviews are important in research as it helps to gather elaborative first-hand information. It helps to draw conclusions from the non-verbal views and personal experiences. It reduces the ambiguity of data through detailed discussions.
The advantages of research interviews are: • It offers first-hand information • Offers detailed assessment which can result in elaborate conclusions • It is easy to conduct • Provides non-verbal cues The disadvantages of research interviews are: • There is a risk of personal bias • It can be time consuming • The outcomes might be unpredictable
The difference between structured and unstructured interview are: • Structured interviews have well-structured questions in a pre-determined order; while unstructured interviews are flexible and do not have a pre-planned set of questions. • Structured interview is more detailed; while unstructured interviews are exploratory in nature. • Structured interview is easier to replicate as compared to unstructured interview.
Focus groups is a group of multiple participants engaging in a facilitated discussion on a specific topic. This format allows for interaction and exchange of ideas among participants.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now
Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Science under Surveillance: Journals adopt advanced AI to uncover image manipulation
Journals are increasingly turning to cutting-edge AI tools to uncover deceitful images published in manuscripts.…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
18 Researcher Interview Questions (With Example Answers)
It's important to prepare for an interview in order to improve your chances of getting the job. Researching questions beforehand can help you give better answers during the interview. Most interviews will include questions about your personality, qualifications, experience and how well you would fit the job. In this article, we review examples of various researcher interview questions and sample answers to some of the most common questions.

or download as PDF
Common Researcher Interview Questions
What inspired you to pursue a career in research, what do you think sets research apart from other disciplines, what do you think is the most important skill for a researcher, what do you think is the most exciting thing about research, what do you think is the best thing about being a researcher, what do you think is the worst thing about being a researcher, what do you think is the most challenging thing about research, what do you think is the best thing about conducting research, what do you think is the worst thing about conducting research, what do you think is the most important thing to remember when conducting research, what do you think is the best way to approach research, what do you think is the worst way to approach research, what do you think is the most important thing to keep in mind when writing a research paper, what do you think is the best way to format a research paper, what do you think is the worst way to format a research paper, what do you think is the most important thing to consider when choosing a topic for a research paper, what do you think is the best way to go about finding sources for a research paper, what do you think is the worst way to go about finding sources for a research paper.
There are many reasons why someone might be inspired to pursue a career in research. For example, they may be inspired by the opportunity to make new discoveries that could improve the lives of people around the world. Or, they may be motivated by the challenge of solving complex problems and pushing the boundaries of knowledge.
It is important for interviewers to ask this question because it can help them to understand a candidate's motivation for pursuing a career in research. This can be helpful in assessing whether the candidate is likely to be successful in their role and whether they will be a good fit for the organisation.
Example: “ I have always been fascinated by the process of discovery and the role that research plays in advancing our understanding of the world around us. Pursuing a career in research allows me to contribute to this process and to make a difference in the world. ”
There are a few reasons why an interviewer might ask this question. First, they may be trying to gauge your level of experience and expertise in research. Second, they may be trying to understand your research process and methods. Finally, they may be trying to assess your ability to communicate and collaborate with other researchers.
This question is important because it can help the interviewer understand your level of experience and expertise in research. Additionally, it can help them understand your research process and methods. Finally, it can help them assess your ability to communicate and collaborate with other researchers.
Example: “ There are a few key things that set research apart from other disciplines: 1. The scientific method: In order to be considered research, an investigation must follow the scientific method, which is a systematic process for gathering and testing evidence. This ensures that research is as objective and unbiased as possible. 2. Peer review: Another key element of research is peer review, which is the process by which experts in a field check each other's work to ensure its quality. This helps to ensure that only the best and most reliable research is published. 3. Replication: Research is also designed to be replicated, or repeated, in order to verify its findings. This helps to ensure that the results are not simply due to chance or error. ”
There are many important skills for researchers, but some skills are more important than others. The most important skill for researchers is the ability to think critically. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze data and information and make decisions based on that analysis. It is important because it allows researchers to understand complex problems and find solutions to those problems.
Example: “ There are many important skills for a researcher, but some of the most important include: -The ability to ask clear and concise research questions -The ability to design effective research studies -The ability to collect high-quality data -The ability to analyze data effectively -The ability to communicate research findings clearly and effectively ”
There are many possible reasons an interviewer might ask this question to a researcher. They may be trying to gauge the level of enthusiasm the researcher has for their work, or they may be trying to assess how well the researcher understands the implications of their research. Additionally, the interviewer may be trying to determine if the researcher is able to articulate the significance of their work in a way that is understandable and relatable to a lay audience. Ultimately, it is important for the interviewer to gain a better understanding of the researcher's motivations and perspective on their work in order to get a sense of how well they will be able to communicate their findings to the public.
Example: “ There are many exciting things about research, but one of the most exciting things is the opportunity to make new discoveries. Every day, researchers are uncovering new information about the world around us and the universe we live in. This constantly expanding body of knowledge provides us with a greater understanding of our place in the world and how we can improve our lives. ”
There could be several reasons why an interviewer might ask this question. They may be trying to gauge the researcher's level of commitment to their work, or they may be trying to identify what motivates the researcher to do their job. Additionally, the interviewer may be trying to assess the researcher's ability to reflect on their work and identify areas of improvement. Ultimately, it is important for the interviewer to understand what the researcher finds most rewarding about their work in order to determine whether or not the researcher is a good fit for the position.
Example: “ There are many great things about being a researcher. One of the best things is that researchers get to learn new things all the time. They also get to help other people learn new things by sharing their findings with them. Researchers also get to travel to different places to conduct their research, which can be very exciting. ”
The interviewer is trying to gauge the researcher's self-awareness and ability to reflect on their work. This is important because it shows that the researcher is able to identify areas for improvement and is committed to professional development.
Example: “ There are a few potential drawbacks to being a researcher. First, the job can be quite isolating. Researchers often work alone in their labs or offices, and they may not have much interaction with other people on a daily basis. This can be lonely and frustrating for some people. Second, research can be slow and tedious. It can take years to complete a study, and the results may not be immediately apparent. This can be frustrating for people who want to see quick results. Finally, research can be expensive. Funding for research projects is often limited, so researchers may have to make do with less money than they would like. This can make it difficult to conduct high-quality research. ”
There are many potential challenges that come with research, such as finding accurate and reliable sources, developing a hypothesis, conducting experiments or surveys, and analyzing data. The most challenging thing about research can vary depending on the project and the researcher's individual skills and experience. By asking this question, the interviewer is trying to understand what the researcher feels is the most difficult part of the research process and why they feel that way. This information can help the interviewer determine if the researcher is a good fit for the project and if they will be able to overcome any challenges they may face.
Example: “ There are many challenges that come with research, but I think the most challenging thing is trying to find accurate and reliable information. With so much information available online, it can be difficult to know what is true and what is not. This can make it challenging to find the right data and resources to use for your research. ”
There are many reasons why an interviewer might ask a researcher what they think is the best thing about conducting research. It is important to remember that research is a process of inquiry that is used to uncover new knowledge or to confirm existing knowledge. The best thing about conducting research is that it allows us to constantly learn new things and to deepen our understanding of the world around us.
Example: “ There are many great things about conducting research, but one of the best things is that it allows you to explore new ideas and discover new knowledge. It can be very exciting to be on the cutting edge of new discoveries, and research allows you to do just that. Additionally, research is a great way to learn more about a specific topic or subject that you are interested in. Conducting research can help you gain a deeper understanding of the world around you and how it works. ”
The interviewer is trying to gauge the researcher's ability to reflect on their work and identify areas for improvement. This is important because it shows that the researcher is constantly trying to improve their methods and is willing to listen to criticism.
Example: “ There are a few potential worst things about conducting research, depending on the individual researcher's perspective. One worst thing could be the amount of time and effort required to produce high-quality research results. This can be especially true in fields where data is difficult to collect or analyze, or where experiments are expensive or time-consuming to carry out. Another worst thing about conducting research could be the pressure to publish results in prestigious journals, which can lead to cut corners being taken in the research process. Additionally, some researchers may find the constant criticism and peer review process to be frustrating and demoralizing. ”
An interviewer would ask this question in order to gauge the respondent's understanding of the research process and their ability to identify key components of a successful research project. It is important for researchers to be able to identify the most important aspects of their work in order to ensure that they are able to effectively communicate their findings to others. Additionally, this question can help to reveal areas where the respondent may need further training or education in order to improve their research skills.
Example: “ There are a few things that are important to remember when conducting research: 1. Make sure you have a clear research question that you want to answer. This will help guide your research and keep you focused. 2. Do your background research and make sure you understand the topic area you are researching. This will help ensure that your research is accurate and complete. 3. Be sure to use reliable and credible sources for your research. This will help ensure that your findings are trustworthy. 4. Be organized and keep track of your data and findings. This will help you to see patterns and trends in your data, and make it easier to write up your results. 5. Be critical of your data and findings, and try to identify any potential biases or errors. This will help you to produce more accurate results. ”
The interviewer is likely looking for qualities that the researcher has that make them successful at their job. This might include qualities such as being able to effectively plan and execute research projects, being able to troubleshoot problems that arise, and being able to communicate findings to others. It is important for the interviewer to gauge the researcher's self-awareness and ability to reflect on their own work in order to get a sense of how they might approach future projects.
Example: “ There is no one answer to this question as different researchers will have different opinions on the best way to approach research. However, some general tips that may be useful include: developing a clear research question or hypothesis, reviewing the relevant literature, designing an appropriate study methodology, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. It is also important to communicate the results of one's research in a clear and concise manner. ”
There are a few reasons why an interviewer might ask this question. First, they want to see if the researcher is familiar with different research approaches and can identify which ones are less effective. Second, the interviewer wants to gauge the researcher's critical thinking skills and ability to identify flaws in research methods. Finally, this question allows the interviewer to get a sense of the researcher's opinion on the best way to conduct research.
This question is important because it allows the interviewer to assess the researcher's knowledge of research methods, critical thinking skills, and opinion on the best way to conduct research. By understanding the researcher's thoughts on this topic, the interviewer can get a better sense of their thought process and whether they would be a good fit for the position.
Example: “ There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question, as the worst way to approach research depends on the specific research question and context. However, some general approaches that could be considered bad ways to approach research include: 1. Not Defining the Research Question Clearly If the research question is not clearly defined from the outset, it can be difficult to know what direction to take the research in and what data to collect. This can lead to a lot of wasted time and effort, as well as potentially biased or irrelevant results. 2. Relying Too Much on Secondary Data While secondary data can be a valuable resource, it should not be relied upon too heavily. This is because secondary data may not be relevant to the specific research question or context, and it may also be out of date. In addition, secondary data cannot be controlled by the researcher, so it may not be possible to obtain the level of detail required for the research. 3. Collecting Data Without a Plan It is important to have a plan for how data will be collected before starting to collect it. This plan should specify what type of data will be collected, how it will be collected, and who will be responsible for collecting ”
The interviewer is likely trying to gauge the researcher's writing ability and whether they are able to produce a well-thought-out, comprehensive research paper. The most important thing to keep in mind when writing a research paper is to make sure that all of the information is accurate and that the sources are reliable. The paper should also be clear and concise so that the reader can easily follow the argument.
Example: “ There are a few things to keep in mind when writing a research paper that will help ensure your paper is well-received by your audience. First, make sure to choose a topic that is interesting and relevant to your audience. Second, take the time to thoroughly research your topic and provide well-supported arguments for your position. Third, be sure to edit and proofread your paper before submitting it for review. By following these simple tips, you can increase the chances that your research paper will be well-received by your intended audience. ”
The best way to format a research paper may vary depending on the discipline, but there are some general guidelines that can help a researcher ensure their paper is well-formatted and easy to read. Some important considerations for formatting a research paper include margins, font size and type, line spacing, and page numbers. Proper formatting can help make a research paper more accessible and easier to read, which can ultimately lead to more impactful research.
Example: “ There is no one correct answer to this question. Different researchers have different preferences for how to format a research paper. Some common elements that are typically included in a research paper are an abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and discussion. ”
There is no one answer to this question, as it depends on the specific field of research and the preferences of the journal or conference. However, some elements that could make a research paper poorly formatted include using an incorrect citation style, not following the required page layout, or using too many graphics and images. Poorly formatted papers can be difficult to read and may be less likely to be accepted for publication.
Example: “ There is no one "worst" way to format a research paper. However, there are several common formatting errors that can make a paper difficult to read and understand. These include: • Not using proper headings and subheadings to organize the paper. • Not using clear and concise sentences. • Not using proper grammar and punctuation. • Not citing sources properly. ”
There are many things to consider when choosing a topic for a research paper, but the most important thing is to choose a topic that is interesting and relevant to the researcher. The topic should also be something that the researcher is familiar with and has some knowledge about. Additionally, the topic should be something that is not too narrow or too broad, and it should be something that has been researched before.
Example: “ There are many things to consider when choosing a topic for a research paper. The most important thing is to choose a topic that is interesting and relevant to you. It is also important to choose a topic that is narrow enough to be covered in a single research paper. Additionally, it is important to consider the resources available to you when choosing a topic. Finally, it is also important to consider the audience you are writing for when choosing a topic. ”
One of the most important aspects of research is finding reliable sources. Without sources that can be verified and relied upon, the researcher's findings will not be credible. Therefore, it is important for the interviewer to ask how the researcher plans to find sources for their paper in order to ensure that the research is of high quality.
Example: “ There is no one answer to this question as it depends on the topic of the research paper and the type of sources required. However, some tips on finding sources for a research paper include using online search engines such as Google Scholar, looking through bibliographies of relevant books and articles, and searching for open access journals that cover the topic. Additionally, contacting experts in the field and asking for recommendations can be helpful. ”
The interviewer is trying to gauge the researcher's ability to find reliable sources of information. This is important because research papers are only as good as the sources they are based on. If a researcher cannot find reliable sources, then their paper will not be credible.
Example: “ There are a few ways that researchers can go about finding sources for their papers that are considered to be less than ideal. One way is to simply do a Google search on the topic and hope that relevant sources come up. This is often not very effective, as much of the information that comes up in a general search may not be relevant or reliable. Another way is to ask friends or colleagues for recommendations. This can be somewhat helpful, but it is often limited to the resources that those individuals are aware of. A better way to find sources is to use a database or search engine specifically designed for academic research. These tools will allow you to narrow your search to more reputable and relevant sources. ”
Related Interview Questions
- Market Researcher
- Survey Researcher
- Clinical Researcher
- User Experience Researcher
Skip to content. | Skip to navigation
Personal tools
- Log in/Register Register

https://www.vitae.ac.uk/researcher-careers/pursuing-an-academic-career/applying-for-academic-jobs/commonly-asked-questions-in-academic-interviews
This page has been reproduced from the Vitae website (www.vitae.ac.uk). Vitae is dedicated to realising the potential of researchers through transforming their professional and career development.
- Vitae members' area
Commonly asked questions in academic interviews
Be prepared to answer the sort of questions in this list (which will be tailored to your research area) in addition to general interview questions. It is a good idea to prepare and even rehearse your answers. If you are confident in answering all of these you will be well-prepared.
About your research General research questions About you and your capabilities About your ability to gain funding About your proposed research About your role as supervisor/teacher About your ‘fit’ with the department
About your research
- What is innovative about your research ?
- How is your work distinct from your supervisor’s/principal investigator’s? How intellectually independent are you?
- What influences have you been exposed to? Do you think you have enough breadth of experience?
- Who has influenced you the most?
- What has been your role so far in developing research ideas and carrying them forward?
- What do you think are your most significant research accomplishments?
- What do you consider to be your best paper/work and why? What did it change about the way people approach the field?
- What are your most important publications?
- What has been the impact of your research?
- What papers do you have coming through in the next year?
- If we gave you the position what might go wrong? How will you manage the risks
General research questions
- What do you see yourself doing in ten years' time? What are your professional goals in the next five, and ten years?
- How will this job help you achieve your long term career plans?
- What would you do on the first day of the job?
- What are the big issues in your research area?
- Who are the key researchers in your area? How does your work compare with theirs?
- Who are your main competitors? What are they doing? How will you compete with them?
- Why would someone come to work for you and not for your competitors?
- How does your work align with contemporary trends or funding priorities?
- How would you bridge the gap from your research to research users?
- The university is keen to serve the wider community and economy. Does your planned research have any potential in these areas?
- How do you feel about translating your research into innovation or spin-outs? Can you give an example of when you have been enterprising?
- Describe in layman’s terms why your research project is interesting in two minutes.
About you and your capabilities
- How have you managed your research project?
- How do you balance your time? If several challenges came up at the same time (grant deadline, pastoral care for a student, teaching commitments) how would you prioritise?
- If you were starting your project again today, what would you do differently?
- Describe a research problem you have faced. What did you learn?
- What has been the most productive period in your research career and why?
- Why do you think you are ready for this position?
- If you get this position how will you run your research project?
- Why do you think you are the right person for this position?
About your ability to gain funding
- What experience do you have of attracting funding?
- Previously, you have only brought in small amounts of funding: how can you convince us you will be able to bring in larger amounts?
- Where will you apply for grants? If your funding applications are unsuccessful, what alternatives do you have in mind? (looking for knowledge of the funding infrastructure)
- How would you convince a funding body that they should fund your research rather than one of the other hundreds of proposals they receive?
- Who are you currently funded by, and why do you think they were interested in funding your project?
About your proposed research
- What will be your major focus as an independent researcher?
- In one sentence, what is the most important question you want to address?
- How does the work you propose follow on from what you are already doing?
- What will you focus on and what gives you a competitive edge in this area?
- What is the overall importance of this project? How do you see this work impacting the field?
- What will you do if your hypothesis is proved wrong? Can you see any of your research proposal failing?
- Why is the technique you have chosen more likely to succeed than other approaches?
- Have you already done anything to test the feasibility of your project?
- If you could only do one aspect of this project, which one do you think is key?
- If we gave you unlimited resources, what would you do with them?
- If we gave you X amount of money, what would you do with it?
- What resources will you need?
- How would you deal with the more limited resources or facilities compared to what you anticipate for the project?
- How do you plan to manage this project on a day-to-day level?
About your role as supervisor/ teacher
- Describe your teaching experience. How do you feel about teaching? What is your teaching philosophy?
- Do you have any experience in curriculum development?
- Have you supervised doctoral candidates, and how did you find this experience? How did you manage them?
- What advice would you give to a new researcher about supervising undergraduate or masters students?
- How would you go about interviewing a prospective postgraduate researcher?
- How would you induce a new doctoral candidate into their research project?
- How would you go about motivating a researcher who is going through a low point?
- How would you deal with a weak researcher?
- How would you deal with any conflict/disagreement within the research group? Do you have an example of when you have had to deal with a disagreement?
- Do you anticipate building a research group? How many people would you like for it to be optimal?
About your ‘fit’ with the department
- Why do you want to come here?
- What will you bring to the institution?
- We are keen to develop collaborations between departments. What opportunities for multi-disciplinary work does your research offer?
- How would you fit with the existing activities in the department? Who do would you expect to collaborate with in the institution? Why do you want to collaborate with them?
- What committee work have you done and what challenges has it presented?
- In what ways, other than research and teaching could you contribute to this department?
Bookmark & Share
- Recently Active
- Top Discussions
- Best Content
By Industry
- Investment Banking
- Private Equity
- Hedge Funds
- Real Estate
- Venture Capital
- Asset Management
- Equity Research
- Investing, Markets Forum
- Business School
- Fashion Advice
- Interview Questions
Equity Research Interview Questions and Answers (40 Samples)
40 common equity research interview questions. Examples include technical, transactional, behavioral, and logical tests with sample answers

Prior to becoming a Founder for Curiocity, Hassan worked for Houlihan Lokey as an Investment Banking Analyst focusing on sellside and buyside M&A , restructurings, financings and strategic advisory engagements across industry groups.
Hassan holds a BS from the University of Pennsylvania in Economics.

Mr. Arora is an experienced private equity investment professional, with experience working across multiple markets. Rohan has a focus in particular on consumer and business services transactions and operational growth. Rohan has also worked at Evercore, where he also spent time in private equity advisory.
Rohan holds a BA (Hons., Scholar) in Economics and Management from Oxford University.

Common First Equity Research Interview Questions
15 common equity research technical questions.
- WSO Bonus Technical Question
8 Fund-Specific Hard Technical Questions
- 5 Most Common Equity Research Behavioral/Fit Questions
5 Firm-Specific Behavioral/Fit Questions
5 logical puzzles - interview brain teasers, full wso hedge fund prep guide & additional resources, list of hedge funds.
Equity Research (ER) attracts seasoned professionals and new hires with a variety of talents and diversified skill sets across the world for a fulfilling career. New hires starting right out of school will start as research associates and move up the chain to becoming research analysts after gaining experience in the industry.

Given the limited number of positions for a tremendous amount of applicants, it is no surprise that the interview process is designed to be incredibly competitive .
Consequently, answering the technical and behavioral questions confidently and consistently is key to converting an interview into an offer . Therefore, the best way to prepare for these interviews is to follow the markers, learn to answer the common questions asked (covered below!), and practice tirelessly.
The following free WSO ER interview guide is a comprehensive tool designed to cover every single aspect of the ER interview process, walking you through step by step from the beginning to the end of the interview. This interview guide will drastically improve your chances of securing an offer with your dream job.
Our guide covers a total of 40 of the most common behavioral, technical, and logical questions, along with proven sample answers , that are asked by hedge funds professionals to candidates during the hiring process.
We strongly believe it’s a great place to start your preparation before investing in our more comprehensive Hedge Fund Interview Course .
This resource features 13 firm-specific questions from leading hedge funds ( Citadel , Bridgewater Associates , etc.) and proven sample answers to them.

Successful professionals within the equity research industry can present themselves as the ideal candidate for the position by highlighting their genuine interest in finance and strong work ethic. A candidate’s presentation of themself occurs at the beginning of the interview, often through these two questions. Regardless of the firm, the position, or the location, we can guarantee that these industry standard questions will be asked.
Anticipating both of these questions before walking into the interview, being well-practiced in crafting a compelling narrative around them, and selling yourself will make you stand out from amongst the pool of potential candidates.
Walk me through your background/resume
We recommend you dial in a cohesive 90-second resume walkthrough that highlights as well as explains all the on the positive and motivating factors behind every transition on your resume (school to job, job to better job, most recent position to grad school).
A good example highlighting this is as follows,
I initially went to school to learn how to design cars, but after my first internship in the field, I realized that I loved interacting with clients directly and decided to pursue full-time roles in B2B sales. In these sales roles, I learned and developed solid selling skills as well as gained direct exposure to A, B, and C. Since I wanted to continue refining that skill set and branch out to focus on X, Y, and Z, I am looking for a new role/promotion which provides that opportunity…
Be deliberate with your delivery. Every decision you made should have a purpose (preferably that you initiated). Don't be negative with your answers. It's important to never say you left because you were bored or "wanted to try something new."

Moving on from there, have a few backup stories prepared. These stories should effectively portray you as a good ER candidate involve highlighting your abilities as a go-getter with a genuine interest in financial markets . Have these stories prepped and use them to answer whatever the interviewer is asking you. Tell these stories with confidence, clarity, and relevance, and you’ll be putting yourself in good territory. Again, it is key to ensure your resume lines up and supports your stories.
WSO has published its very own Equity Research sample resume template and provides guidelines on crafting a successful ER resume. Check it out at WSO’s official Equity Research Resume Guidelines page.
Why equity research?
Given the wide variety of professional backgrounds that candidates come from, WSO has created a dedicated page to answer this question. WSO’s “Why Equity Research?” page covers a variety of sample answers tailored for students and professionals looking to break into equity research.
Free Interview Training
Sign up to our FREE 5-Day Interview Training to kickstart your interview prep.
Technical questions are a cruical component of almost every equity research recruiting process. Therefore, your interviewers will expect accurate and detailed responses to commonly asked technical questions. It's important that and your answers must demonstrate in-depth knowledge and expertise of the topics at hand. The following section features 15 common ER interview questions , and sample answers have been provided for every question.
At the end of these 15 questions, we have also provided you with eight exclusive firm-specific technical questions to jumpstart your mock interview training.

The 15 technical questions covered below are exclusive to the equity research industry. However, equity research interviews often overlap with investment banking and hedge fund interviews as general finance/accounting questions can also be asked. To check out an additional 45 technical questions with sample answers, check out WSO’s free 101 Investment Banking Interview Questions and Answers and Hedge Fund Interview Questions pages.
1. What is EBITDA?
EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization . It is a general metric for evaluating a company’s cash profitability. In addition, it is sometimes used as a proxy for free cash flow because it will allow you to gauge how much cash is available from operations to pay financing costs like interest, capital expenditures, etc. This is one of the most important single items someone will look at in evaluating a Company.
EBITDA = Revenues - Expenses (excluding non-cash and non-operational items like interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization)
Sample Answer:
EBITDA is an acronym for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It’s an excellent high-level indicator of a company’s financial performance .
Since it removes the effects of financing and accounting decisions such as interest and depreciation, it is a much better metric than revenue or net profit for comparing different companies. As a result, it serves as a rough estimate of free cash flow and is used in the EV/EBITDA multiple to establish a company’s high-level valuation quickly .
2. What is enterprise value?
Enterprise Value is the value of an entire firm. It accounts for the debt and equity in a business and is calculated using the equation below. This is the price that would be paid for a company in the event of an acquisition, where the acquirer takes on all the debt and equity of the acquiree .
Simplified Enterprise Value Formula :
Enterprise Value = Market Value of Equity + Debt + Preferred Stock + Minority Interest - Cash
Enterprise Value is the value of a firm as a whole from the perspective of its owners, including both debt and equity holders. In its simplest form, you calculate an Enterprise Value by taking the market value of equity (aka the company’s market cap ), adding the debt and the value of the outstanding preferred stock. Then you add the value of any minority interests the company owns and then subtract the cash the company currently holds.
3. What is the difference between enterprise value and equity value?
Equity Value represents residual value for common shareholders after the company satisfies its outstanding obligations (net debt, preferred stock, which is senior to common equity). In contrast, enterprise value represents the value available to both equity and debt holders.

4. How do you value a private company?
- You cannot use a straight market valuation since the company is not publicly traded.
- A DCF can be complicated by the absence of an equity beta, making calculating WACC difficult. In this case, you have to use the equity beta of a close comp in your WACC calculation.
- Financial information for private companies is more difficult to find because they are not required to make public online filings.
- An analyst may apply a discount on a comparable company’s valuation if the comps are publicly held because a public company will demand a 10-15% premium for the liquidity an investor enjoys when investing in a public company.
5. Why might there be multiple valuations of a single company?
Each valuation method will generate a different value because it is based on various assumptions, multiples, or comparable companies and/or transactions.
Typically, the precedent transaction methodology and discounted cash flow method result in a higher valuation than the result of a comparable companies' analysis or market valuation. In addition, the precedent transaction result may be higher because the approach usually includes a “ control premium ” while calculating the company’s market value. This premium exists to entice shareholders to sell and will account for the “synergies” that are expected from the merger .
The DCF approach typically produces higher valuations because analysts’ projections and assumptions are usually somewhat optimistic.
You can value a private company with many of the same techniques one may use for a public company valuation. However, there are a few differences. There will be difficulty in obtaining the right inputs as financial information will likely be harder to find, potentially less complete, and less reliable. Further, you can’t simply use a straight market valuation for a company that isn’t publicly traded. On top of this, a DCF can be problematic because a private company will not have an equity beta to use in the usual WACC calculation. Finally, if you are doing a comps analysis using publicly traded companies, a 10-15% discount may be required in the calculations as a 10-15% premium is typically paid for the public company’s relative liquidity.

6. How do you calculate a firm’s terminal value?
Terminal Value = ( FCF t (1+g)) / (WACC - g)
- To establish a terminal value, you can either use the formula above, which is the perpetual growth methodology, or the multiples method.
- In the multiples method, you assign a valuation multiple (such as EV/EBITDA) to the final year’s projection and use that as the “terminal value” of the firm.
- In either case, you must remember to discount this “cash flow” back to year zero as you have with all other cash flows in the DCF model .
There are two ways to calculate terminal values. The first is the multiples method. In order to use this method, you choose an operation metric (most commonly EBITDA) and apply a comparable company’s multiple to that number from the final year of projections.
The second method is the perpetual growth method, where you select a modest growth rate, typically just a little bit higher than the inflation rate and lower than the GDP growth rate , and assume that the company can grow at this rate infinitely. Then you multiply the FCF from the final year by 1 plus the growth rate and divide that number by the discount rate (WACC) minus the assumed growth rate.

7. What is beta?
- It represents the relative volatility or risk of a given investment with respect to the market.
- Beta is a measure of the volatility of an investment compared with the market as a whole. The market has a beta of 1, while investments that are more volatile than the market have a beta greater than 1, and those that are less volatile have a beta less than 1.
- β < 1 means less volatile than the market (lower risk, lower reward).
- β > 1 means more volatile than the market (higher risk, higher reward).
- A beta of 1.2 means that an investment theoretically will be 20% more volatile than the market. For example, if the market goes up 10%, that investment should increase by 12%.
8. What is the market risk premium?
The market risk premium is the excess return that investors require for choosing to purchase stocks over “risk-free” securities. It is calculated as the average return on the market (usually the S&P 500, typically around 10-12%) minus the risk-free rate (current yield on a 10-year Treasury).
9. When should an investor buy preferred stock?
- Preferred stock could be looked at as a cross between debt and equity. It will generally provide investors with a fixed dividend rate (like a bond), but also allow for some capital appreciation (like a stock). Preferred stock may also have a conversion feature that allows shareholders to convert their preferred stock into common stock .
- It typically does not have voting rights like those of common stock.
- It is senior to common stock within the company’s capital structure .
An investor should buy preferred stock for the upside potential of equity while limiting risk and assuring stability of current income in the form of a dividend. In addition, preferred stock’s dividends are more secure than those from common stock. Owners of preferred stock also enjoy a superior right to the company’s assets, though inferior to those of debt holders, should the company go bankrupt.
10. When should a company buy back stock?
A company should buy back its own stock if it believes the stock is undervalued when it has extra cash. However, if it believes it can make money by investing in its own operations, or if it wants to increase its stock price by increasing its EPS by reducing shares outstanding or sending a positive signal to the market. Also, a stock buyback is the best way to return money to shareholders, as they are tax-efficient when compared to dividends.

11. What might a shareholder analysis tell you about an equity deal?
- For an existing public company, a shareholder analysis compares current institutional investors to ones that the company might target in a new equity offering.
- You could also use this analysis to find institutional investors with similar industry holdings that have not yet invested in your client and target them in the offering.
12. Suppose you hold a put option on Microsoft stock with an exercise price of $60. The expiration date is today, and Microsoft is trading at $50. How much is your put worth, and why?
This put is worth $10. It gives you the option to sell your shares at $60, and you can buy them in the open market at $50. You therefore would buy shares of Microsoft at $50 per share and immediately sell them for $60, making a profit of $10 per share.
13. Where did the S&P 500/Dow Jones Industrial Average/NASDAQ close yesterday?
- This question is used to gauge your general interest in the financial markets . You probably will not be expected to know the number to the penny, but knowing the levels of the three major exchanges/indices, as well as whether they were up or down and why will show your interviewer that you keep track of what is going on in the world of finance.
- You should know how the market moved (up or down) the previous day and why it moved. You can find this information by watching CNBC , reading the WSJ, or just by using Google.
- Yesterday the XXXX closed at XXXX, up/down XXX from the open. I also noticed that it was up XXX from the day before due to …
- It would also be a good demonstration of market interest to know the overall valuation levels of the three major indices. The P/E ratios for the overall Dow, S&P 500, and Nasdaq are publicly available on major financial news publications.
14. Where do you believe the stock market will be in future, say 3/6/12 months from now?
- This question can show your interest in the markets. There’s no right/wrong answer as everyone has different opinions on where the market is going.
- You need to have an opinion and well-thought-out reasoning for that opinion.
- If you think the market will drop in the next three months, hit bottom, and then begin to bounce back, have a reason to explain why you think it is going to drop, why it is going to bottom out, and why it is going to bottom out will begin to rise.
- It is more important to display logical reasoning than to be correct.
- Do some research before your interview. Read what writers for major newspapers are predicting and saying, and then implement some of their reasons in your own explanation.
- Also, be sure to stick to your reasoning. Your interviewer may challenge your position and question your reasoning. If you have to come up with a solid theory behind your response, be confident in your position and try to explain your rationale. If your logic and thought process makes sense, don’t change your opinion just to agree with your interviewer.
15. Is 15 a high P/E (Price to Earnings) ratio?
This is not just a yes or no question. A firm’s P/E ratio is essential compared to other companies in its industry. P/E can be thought of as how many dollars an investor is willing to pay for one dollar of earnings.
A high P/E represents high anticipated growth in earnings. In high-growth industries, such as technology, a P/E ratio of 15 may be considered relatively low. This is because the company is expected to grow its earnings at a high rate and therefore deserves a higher valuation relative to its present earnings.
However, a P/E of 15 may be considered high for a large pharmaceutical company since earnings growth may be expected to be slow but steady in future years.
It depends on the industry. For example, a P/E ratio of 15 in an industry like financial institutions may be considered a bit high, but if the company is a high-growth tech company, 15 may be considered relatively low.
WSO Bonus Technical Question:
"pitch me a stock".
The stock pitch is arguably the most crucial and most common question you will be asked during the interview process. Ideally, you want to have 2-4 stocks in mind that you can pitch , i.e. large-cap, small-cap, stock to short. We advise spending 30 minutes to a couple of hours finding a stock you like and listing out the reasons why. Even if your interviewer doesn't ask you, it's always better to be prepared for these interviews. Here's a good explanation of how to answer this question.

They are trying to figure out whether you understand the underlying concept of what drives a business. Some questions to help figure this out are:
- What are the key drivers of the company (both revenue and cost)?
- Why is it a good investment?
- What are the potential opportunities available?
- What' s their competitive advantage ?
- What are the primary risks?
Here's a sample stock pitch, courtesy of [esbanker] , a private equity associate. The post has been edited and formatted.
Well, I've recently been following Copa Airlines, a Panamanian airline company, currently trading at $xx per share. Recently, the airline industry has been underperforming the markets for several reasons: compressed margins from the volatility in oil this year increased competition from low-cost carriers, and over-leverage by most airlines (think American or Air Canada). While many airline companies are in desperate need of restructuring, Copa airlines have seen their revenues - now at $1.4 billion - growing at a robust 10% compounded over the last 5 years. Copa boasts an EBITDA of approx. $350 MM, Net Income of around $240MM, which translates to roughly 18%. Margins have remained stable over the last few years and are significantly greater than other airlines. After running a basic DCF (5-year projections), Copa has an implied price per share of $xxx. In terms of comps, Copa is trading at an EV/ EBITDAR of 7.7x, which is slightly less than the industry median of 10.3 x, and a PE ratio of 12.9 x relative to an industry median of 14.1 x. Given Copa's strategic positioning in Latin America, its strong operating and financial performance of late, and its relatively low share price, I would strongly recommend buying Copa Airlines.
Some of the numbers are out of date - this is from an early 2011 model.

Walking into the interview with an in-depth understanding of the above-covered 15 technical questions will undoubtedly make you stand out in the applicant pool. However, to achieve complete technical mastery, you must expect technical questions that are specific to different hedge funds.
The following section features eight exclusive interview questions that actual interviewers asked potential candidates at some of the world’s largest hedge funds during equity research interviews.
The following questions are from WSO’s company database , which is sourced from the detailed personal experiences of more than 30,000 people with hedge funds interviews. The Hedge Fund Interview Course includes access to over 800 questions across 165 hedge funds (no other resource comes close).
Point72 Technical Questions

- In order to value a company with no revenue, such as a start-up, you must project the company’s cash flows for future years and then construct a discounted cash flow model of those cash flows using an appropriate discount rate .
- Alternatively, you could also use other operating metrics to value the company. If you took a start-up website with 50,000 subscribers, but no revenue, you could look at a similar website’s value per subscriber and apply that multiple to the website you are valuing.
- Valuing a company with no revenue comes down to determining the market opportunity for a company and assigning a value per user, customer, or subscriber, and then discounting that back at an appropriate rate that accounts for the inherent execution and market risk .
A sample general approach to modeling and research could involve the following 6-step process:
- Formation of assumption/hypothesis
- Collection of relevant data
- Analysis of markets
- Creation of forecast
- Simulation/test-run
- Release and monitoring of model
- The profits generated on the Income Statement after any payment of dividends are added to shareholder ’s equity on the Balance Sheet under retained earnings .
- Debt on the Balance Sheet is used to calculate interest expense on the Income Statement .
- Property, plant, and equipment, on the Balance Sheet , are used to calculate depreciation expenses on the Income Statement.
There are many other links, but the above are some of the primary connections frequently analyzed as part of accompanying schedules in financial modeling .
There are many links between the Balance Sheet and the Income Statement. The central link is that any net income from the Income Statement, after the payment of any dividends, is added to retained earnings. In addition, debt on the Balance Sheet is used to calculate the interest expense on the Income Statement, and property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) are used to calculate any depreciation expense .
Citadel Investment Group Technical Questions

The exchange ratio is the relative number of new shares given to existing shareholders of a company that has been acquired or merged with another. It is used by companies looking to offer a full or part equity offer for an acquisition transaction.
It is best to go prepared with one long idea and one short idea. Being able to demonstrate that you understand the many nuances of shorting is a fantastic way to differentiate yourself from other possible candidates.
If you are interviewing for a specific sector/industry, then select a business from that industry to pitch . While your interviewer will likely know more about the industry and/or company, but as long as you stick to stating this, you should be in the clear.
Using a pitch structure such as the one below gives the best results:
- Industry : Why is the industry attractive? [Use a quantitative metric to show you did your homework here, such as, "ABC Industry has the ability to grow xyz% in the next 3-5 years. This is also a good place to highlight changing competitive dynamics, etc.]
- Company : Why is the company attractive? ["The business has sales of $30 in a $3,000 industry representing a 3% market share despite being recognized as the product leader and having an exceptional management team" is an example of one of the best way to address this]
- Catalyst : Why is the market wrong and how will the market realize the intrinsic value of the business? [This is the most critical part of the pitch. For example, "ABC is currently valued at 10x [insert multiple] but is being unfairly discounted because of the incompetency of the prior management team. Since the current management team has taken over [insert metric] XYZ has improved. As of right now, the market has not recognized the improvement in XYZ or the overall business, but I expect that [insert catalyst] will demonstrate ABC's true value to the market within [insert time frame]."
- Valuation : What is the intrinsic value of the business? ["If my assumptions [discuss them here] about the effect of [insert catalyst] prove true, then the market will realize ABC's intrinsic value of [insert valuation]." You can then speak about contingency valuations, etc.]
Try to keep your pitches as short as possible and as high-level as possible. This helps to minimize the chances of putting your foot in your mouth and allows the interviewer to ask more in-depth questions where they feel necessary. Of course, you also need to be prepared to answer in-depth questions about anything pertaining to your pitch. This includes topics ranging from the industry, competitors, or the company.
Note: The above extract was taken and paraphrased from WSO User @Simple As…’s post, “ The Asymmetric Risk Profile: Preparing For The Hedge Fund Interview ”
We assume that the entire Net Operating Balance ( NOL ) goes to $0 in an M&A transaction, and therefore we write down the existing Deferred Tax Asset by this NOL write -down.
Bridgewater Associates Technical Question

It could be beneficial to increase the volume of software sold and increase the price of pens, as the incremental cost of each additional software license sold is relatively low, and almost all of the additional revenue would flow directly to margins, not to mention its scalability. Increasing the price of pens has more advantages from a financial standpoint as they have a higher incremental cost (cost of producing a pen scales with quantity sold).
D.E. Shaw Group Technical Question

During the Covid-19 pandemic, the Fed lowered interest rates to accommodate the lack of demand due to the uncertainty caused by the pandemic. This led to massive inflation, the effects of which are now being realized. Looking at the treasury curve and comments by Mr. Powell (who mentioned that inflation is not transitionary), it is evident that the rates will increase by mid-2022. This is to ensure that inflation is curbed and the economy moves towards normalization post-Covid.
5 Most Common Equity Research behavioral/Fit Questions
Fit or “behavioral” questions are used to gauge whether or not you have the right work ethic, attitude, personality, and values to fit in with a Hedge Fund’s equity research department. Many Hedge Funds take this process extremely seriously because most firms typically have only a handful of investment professionals who must collaborate on projects over long hours and under tight deadlines.

For example, Bridgewater Associates is known for its intense corporate culture of radical truth and radical transparency . Therefore, its interviews consist mainly of ethical and moral questions.
The following section walks you through 5 of the most common types of fit questions and suggests approaches for answering them. The proposed strategies and sample answers are meant to be illustrative. Always remember, you need to adapt your responses to be true to yourself and your own words.
1. What do you consider to be your greatest accomplishment?
- If you want your answer to be related to your education, talk about how you worked on an assigned project that you didn’t understand at first, struggled through understanding it, and eventually received an A for your hard work.
- If you want to relate it to your personal life, talk about something you are proud of in your family life. You can even connect it to athletic success, community service, or recovery from illness.
- You can use this question to reveal the balance in your life. This can be especially useful if your resume is short on classroom excellence. Be sure to explain that you are extremely proud of your less-than-perfect GPA because it allowed you to accomplish other activities at school (as long as you have a solid list of extracurricular activities).
- Whatever approach you choose to answer this question, be sure you spin it to demonstrate how one or more of the qualities valued in finance, such as positive attitude, willingness to learn, drive, and determination lead you to success.
I consider one of my most significant accomplishments to be the work-life balance I have achieved between keeping my grades up while serving as the captain of my hockey team. As a result of this, I gained greater leadership skills as I led our varsity team through the entire season as well as structured our fall and spring workouts. This leadership role required me to polish my time management skills which were invaluable. I also wouldn’t trade the friendships and connections I made during my time on the hockey team I made for anything else in the world.

2. Coming out of this interview, what are three things about you that I should take with me?
Choose three traits you have that demonstrate your natural abilities at equity research and reveal that you are memorable and unique compared to other potential candidates.
The three things that I would like you to take from this interview are,
- To start, I want you to know that I am extremely hard working and will bust my tail every day to ensure that the job gets done
- That I have excellent communication skills and a positive attitude; and
- Your firm is my top choice, and I would be ecstatic to come to work here every day. I’ve already spoken to X, Y, and Z people and I believe that I’ll make a great fit with the other team members.
3. Describe your ideal work environment?
- The most important things about your work environment, especially in finance where people spend many hours together, are the people you work with every day.
- Talk about the fact that you want to be in a work environment with others who are all as driven, dedicated, and hard-working as you are, where everyone can rely on one another to get tasks done efficiently.
- Talk about your ideal environment as one that allows you to excel due to great teamwork and communication, one that allows you to grow intellectually and professionally, where your performance evaluations are directly correlated to your rewards.
In my mind, at least in finance, the most crucial aspect of the working environment is the people you are working with on a daily basis. Suppose you do not enjoy the company of your colleagues or teammates. In that case, the environment will be especially challenging because you’ll often be working countless hours per week, over multiple years, with these same people.
My ideal workplace is one where everyone works hard, communicates well, and trusts each other to get the job done right and on time. As a result, the team is then rewarded and evaluated based on our performance.

4. What would your last boss tell me about you?/Tell a story about a time when your boss praised you for a job you performed exceptionally well.
- highly motivated
- hard-working
- strong analytical and quantitative skills
- a good team player
- Be sure to talk about a quality your boss observed that may not be clearly listed on your resume. For example, your ability to put clients at ease upon meeting them or that you’re a great leader who sees the best in every team member.
My boss from last summer’s internship would say I worked extremely hard with maximum dedication and minimal supervision. On one occasion, he actually tell me to go home when it was getting late and I was still at my desk. He even reminded me it was just a summer internship .
Since I really strived to get the most out of my time with the internship, I guess I just didn’t want to leave any task unfinished, even if it would have been OK with my boss. At the end of the summer, my boss telling me how dedicated I was to the position was one of the biggest compliments he had to have given me.
5. What makes you think you can put up with the stress, pressure, and long hours of a career in finance?
Talk about a time in your life when you worked long hours and managed many different tasks.
The story can be from work, school, home, or a combination of all of them. For example, maybe during finals week, you had to study for two exams, finalize the school newspaper, write three papers, and still go to soccer practice.
It’s vital to ensure that you explain that while your past experience has not been as intensive as working full time as a finance professional, you are still 100% dedicated to succeeding, you feel as well prepared as anyone, and you’re willing to do whatever it takes to get the job done.
I am as prepared as anyone else coming out of college to handle the long hours of working in finance. In fact, when you add up all the time I spent doing all my extracurricular activities, my school hours were almost as long as a full-time position. Every day I was up at 7:30 for classes that ran from 8:15 until 1:00. Then, after class, I would grab lunch and then go to soccer practice, which means I didn’t get back until 5:00.
Then I would grab dinner and work in either the library or my room until I was done. This would typically go pretty late at night or into the morning. So while I know it isn’t the same time commitment and stress as working in finance, I feel my experience has left me well prepared for this career.

Knowing the culture of each hedge fund before walking into an interview is one of the secrets to connecting with the interviewer and walking out with an offer.
The following section features 5 exclusive questions that interviewers have asked in the world’s biggest hedge funds (Point72, Bridgewater Associates, Millennium Partners , etc.) during interviews. These should give you a jumpstart to help with your training for the respective hedge funds interviewing you.
- What roles are you applying for right now? What types of firms?
- What do you consider your greatest failure?
- What is your strength?
- What feedback did you receive from your last job/internship?
- What motivates you?
WSO Free Resource:
To view WSO’s sample answers and walkthroughs for the above-mentioned exclusive fund-specific behavioral questions, check out WSO’s free Hedge Fund Interview Questions page.

Logical puzzles, brainteasers , and riddles are typically used in the interview process to gauge the candidate's critical thinking abilities.
In this part of the interview, your interviewers aren’t focused on whether you can answer the riddles correctly or not. Instead, they are really focused on trying to figure out your thought process and how you arrive at your answer when solving the riddles presented before you.
Given this, it is critical to walk your interviewer through your thinking as you progress through the riddle. They may even probe you with questions to assist you or test your logic. By occasionally asking if you’re headed in the right direction and giving them a rundown of your thoughts demonstrates your ability to reflect and approach a problem with composure.
However, it is still beneficial to foresee these brainteasers in order to avoid being put in an awkward position and caught off guard in the interview. The next section has 5 commonly asked logical puzzles that you can practice beforehand to impress your interviewer.
1. How many NYSE-Listed companies have 1 letter ticker symbols?
It could be 26 as that’s how many letters are in the English alphabet, but in this case it is only 24 because I & M are already saved for Microsoft and Intel, in case they change their minds.
2. A stock is trading at 10 and 1/16. There are 1 million shares outstanding. What is the stock’s market cap?
This question is just a test of your mental math abilities.
- If a fourth is 0.25
- An eighth is 0.125
- A sixteenth is 0.0625
As a result, the stock price is 10.0625 and the Market Cap is 10.0625 million.
3. What is the probability that the first business day of a month is a Monday?
Each day has a 1 in 7 chance of being the first day of the month. However, if the month starts on a Saturday or a Sunday, the first business day of the month will be a Monday. Therefore, the chances of the first business day being a Monday is 3 in 7 since if the month starts on Saturday, Sunday, or Monday, the first business day is a Monday.
4. You have 10 black marbles, 10 white marbles, and 2 buckets. I am going to pick one of the two buckets at random and select one marble from it at random. How would you fill the two buckets with marbles to maximize the odds that I select a white marble?
For this scenario, you want to put one white marble in one bucket and put the other 19 marbles in the other bucket. Due to this setup, the bucket with the lone white marble will be chosen nearly 50% of the time. When the alternative bucket is selected, the odds that a white marble is pulled are still nearly 50%. Setting up the situation this way makes the overall odds of a white marble selection almost 75%.
5. A 10x10 Rubik's Cube is dropped into a bucket of paint. How many of the individual cubes have paint on them?
The trick is to realize that cubes on the edge of any one of the 6 faces have a side on two faces (3 faces for corner cubes). This prevents you from simply calculating the number of cubes on a single face and multiplying by the number of faces. One of the most intuitive ways to solve this problem is to calculate the total number of individual cubes in a 10x10x10 Rubik’s cube. Once you have that you want to subtract the number of all internal cubes with no facings on the outside. There are 10x10x10 total individual cubes on this Rubik's cube. On the inside of a 10x10x10 cube, is an 8x8x8 cube with no outside facings. The 8x8x8 cube contains 512 individual cubes. Therefore, there are 1,000 - 512 = 488 cubes on the outside of the Rubik’s cube with paint on them.
The majority of questions and sample answers covered in this free guide were obtained directly from WSO’s very own Hedge Fund Interview Course , which features:
- 814 questions across 165 hedge funds
- 10+ exclusive case videos with detailed pitches
- Long, short, equity, credit, event-driven, macro+ questions
Think about it - if this page alone can set you miles ahead of the competition, imagine what our complete course can do for you. The WSO Hedge Fund Interview Prep Course will guide you through each step of the interview process and ensure you're in the strongest position to land the job at a hedge fund. Click the button below to check it out!

Everything You Need To Break into Hedge Funds
Sign Up to The Insider's Guide on How to Land the Most Prestigious Buyside Roles on Wall Street.
The following are additional resources as forum posts posted by WSO and WSO’s users alike over the last 15 years and are recommended by WSO for taking a look at.
- Equity Research Resume Guidelines
- Overview Of The Equity Research Industry
- Hedge Fund Careers: Getting A Hedge Fund Job Out Of Undergrad And Beyond
- Anatomy Of The 10-K
- WSO Financial Dictionary
The following are some of the biggest of the 750+ hedge funds firms WSO has data on in its company database :
Bridgewater Associates | Bridgewater Associates Overview | Bridgewater Associates Site The Tudor Group | The Tudor Group Overview | The Tudor Group Site Brandes Investment Partners | Brandes Investment Partners Overview | Brandes Investment Partners Site Renaissance Capital | Renaissance Capital Overview | Renaissance Capital Site Millennium Partners Group | Millennium Partners Overview | Millennium Partners Site Alpine Woods | Alpine Woods Overview | Alpine Woods Site Carlson Capital | Carlson Capital Overview | Carlson Capital Site 360 Global Capital | 360 Global Capital Overview | 360 Global Capital Site GSO Capital Partners | GSO Capital Partners Overview | GSO Capital Partners Site
Additional interview resources
To learn more about interviews and the questions asked, please check out the additional interview resources below:
- Investment Banking Interview Questions and Answers
- Private Equity Interview Questions and Answers
- Hedge Funds Interview Questions and Answers
- Finance Interview Questions and Answers
- Accounting Interview Questions and Answers

Get instant access to lessons taught by experienced private equity pros and bulge bracket investment bankers including financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel Modeling.
or Want to Sign up with your social account?
- Find a Course
- For Business
- For Educators
- Product News
Interview prep: Questions you should ask
April 30, 2024

Picture it: You’ve made it to the end of your interview for your dream job. You sailed through your reasons for applying and answered every behavioral and situational question with ease (thanks, STAR method !). You’re down to the final question: “ Do you have any questions for me? ”
No sweat. You knew they’d ask this question—they always do!—so you came prepared. Not only did you engage your interviewer, but you are also leaving the interview feeling even more confident that this is the career path for you.
So, what did you ask?
Questions to ask at the end of an interview
An interview is an important time to discuss your experience, skills, and interest in a position—but it’s also a conversation. You’re interviewing the company as much as the company is interviewing you.
Asking thoughtful questions during an interview can achieve a lot. For starters, it signals to the hiring manager that you’re a conscientious job-seeker who’s interested in the role. It’s also how you can figure out if you actually want to work there. Just as your interviewer is deciding whether you’ll be a good fit for their company, this is your opportunity to determine whether this company and this role are going to help you achieve your goals .
Think about what you expect this role to be like, if you get it. Are there any gray areas that your interviewer could clarify for you? Some common things to ask about may be:
- The role and daily responsibilities: “What might a typical day in this role involve?”
- How your performance will be measured: “How do you measure success?”
- Future growth opportunities you’d be moving toward: “How do you help employees grow as professionals?”
- Your potential manager and team structure: “What kind of feedback and support would I receive?”
- The company culture: “What do you love about working at this company?”
Before an interview, take a moment to write down some questions—around five is a good start, but some people feel more comfortable preparing closer to 10 questions. This way, if any of your questions come up during the interview, you can ask them mid-conversation and still have more on hand to ask at the end of the interview.
As you move through the interview process and get answers to your questions, you might want to ask different interviewers similar questions to compare answers—or find new ones to ask.
Want more questions? Here’s a list of 30 questions to ask and tips for choosing the best questions for your needs.
Keep practicing
Remember: If you’ve made it to the interview, you’ve already demonstrated that you have the skills and experience your interviewer is looking for. Now, it’s time to show your personality. Here are some courses to help guide your interview prep:
- To feel like a more confident speaker, try the University of London’s Finding Your Professional Voice: Confidence & Impact . This course is available for free and only takes about nine hours to complete.
- For an overview of the interview process, try Big Interview’s The Art of the Job Interview . You’ll explore common interview questions and learn how to answer them in a single course.
- For an in-depth exploration of the interview process, try the University of Maryland’s Interviewing and Resume Writing in English Specialization . Here, you’ll spend more time examining interview preparation , successful interviewing tips , and how to answer common questions .
With that, our interview series ends. If you have any more questions, feel free to leave them in the comments.
Keep reading
- Top skill alert: Open doors with spreadsheets
- How to Ask Your Employer to Pay for Your Degree
- How to answer interview questions with the STAR method
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
I've Been Offered Every Job I've Interviewed For. Here Are 5 Questions I Ask Interviewers. Career consultant Kendal Lindstrom says these five questions are the winning formula for landing the role.
By Tim Paradis • May 9, 2024
Key Takeaways
- Kendal Lindstrom started a career-change consultancy after struggling to change jobs.
- She shared her strategy for acing job interviews, which includes having five key questions ready.
- They focus on areas such as company culture, team dynamics, and the employer's long-term plans.
This article originally appeared on Business Insider .
This as-told-to essay is based on a conversation with Kendal Lindstrom, 25, who lives in Scottsdale, Arizona. She runs a career-change consulting firm named Doux and works in tech. She recently posted a TikTok about five questions she has ready for a job interview. Lindstrom says she believes asking at least some of these questions is why she's always landed a role she interviewed for. The following has been edited for brevity and clarity.
I started Doux because I never liked to be put in a box in terms of my career. Coming out of college, I thought, "I just want to be known as the girl in fashion." I was so wrong. But I didn't know how to pivot into a new industry . It took me two years of connecting, trying, and failing. I found the framework of what Doux is now by failing.
After working in fashion, I got myself into medical sales. I then switched to tech because that's where my passions lie. It took me two years to go from fashion to medical sales. But from the day I decided I wanted to be a tech consultant, it only took me three weeks to get my offer letter.
The difference was I knew how to write my résumé. I knew how to become the candidate that they needed.
My formula is to map your résumé to the career you're going to, not the career you've been in. To get to my current job, I created a résumé that was unstoppable.
Usually, I tell my clients to reach out to the hiring manager. In this case, the hiring manager got to me within minutes of me submitting my résumé. The interview process was extensive, but, like I always tell my clients, it's about follow-ups.
I followed up three times because they had great candidates. But I needed to stay in front, and I needed to be the person they chose.
I had the drive
It's funny when I look back and talk to the executives who hired me. They're like: "You had no business being in tech. You had nothing on your résumé that told us that you would do a good job in this. But the way you presented yourself, it was a no-brainer to hire you because we knew you would get it." So, it's often more how you're presenting yourself in a professional realm rather than what you're saying to answer the questions.
I had drive, and that's what they were looking for. They were looking for someone young to grow with the company. If they wanted someone young, they weren't going to get all the experience in the software that they needed. But I was eager to learn, and however many hours outside work that took, I was willing to do it. I really drove home that it doesn't stop at 5 p.m. My job stops when my job is done.
Each day after work, I spent 30 minutes reading a training book my company had given me. Then, I tried to apply the knowledge for 30 minutes. The next day, I would get time on my boss's calendar and say: "This is what I learned yesterday. Tell me how you have seen this applied in scenarios with a client."
It took me about a year to really digest everything. It was tough, but it came down to whether I was willing to ask questions when I needed help rather than having too much pride and not asking anyone.
I've done a lot of interviews for my age because I kept my options open no matter where I was in my career. I've never wanted to be stagnant. So I have done upwards of 10 or 11 interviews, and I've never been told no because my goal was to make an employer feel like I had their best interests at heart and I wanted to be part of their company, which meant I needed to sell myself as a solution. And it's more about the questions you ask than the answers you get.
I have pretty thick skin
When I worked in medical sales — or even with some of the comments on my TikTok — so much was about my image. I was like, "What does my blonde hair have to do with the knowledge that I have?" Not that it ever hurt my feelings because I have pretty thick skin. In any industry, there will be people who would want to discredit someone's abilities because of how they look. But at the end of the day, I can use my brain to where people are like, "We need to listen to you."
@kendallindstrom it's more about the questions you ask than the answers you get. people want to talk about themselves. #interviewquestions #jobinterview #resume #careerchange #womeninbusines ♬ original sound - DOUX | CAREER CHANGE MGMT
Some of the comments on my TikTok have been so far off the mark. At the time of my interviews for my current job, I didn't have a website, and my social media wasn't publicly available. So, I got the job because of the things I said and the questions I asked, and not because of my appearance.
These are my five key questions:
What's the company culture like?
The first thing I tell people to ask is about company culture. That's a big one. It's such a make-it-or-break-it for enjoying your job. I wanted my audience to know that asking about it is so important because if you're miserable in your job, you're only setting yourself up to fail.
What's the lowdown on my predecessor?
The second one is, "What did the person who held this role before me do that was appreciated but not required based on the job description?" I suggest this one because I want my audience to put themselves in the role already. It's an assumptive selling tactic. I always say go into the interview and sell yourself.
I asked that question one time — "What are you going to miss most about this person?" — and the interviewer said, "Oh, they got Starbucks all the time." And I was like, "Great, I guess we'll be getting Starbucks for the office all the time."
What do my colleagues require?
The third question was, "How can I best suit the needs of my direct counterparts?" That came from wanting to understand — in the most professional way — the team you're walking into. It helps me understand and identify how I would fit into the team.
I've seen teams before where they just don't get along. But you don't know that until you sit down on the first day. And at that point, it's already too late. You're either leaving, or you've got to deal with this until you can figure out another job.
How successful is the team?
No. 4 is what the current state of the department is in reference to the bottom line. That has to do with asking about sales, of course, but I'm also asking: "Am I walking into a failing department? Are you expecting me to turn things around? Are you expecting me to just take the blame for something that's already failing? Or are you guys seeing numbers you've never seen before and need more people?" And, if so, "What did you do to see those numbers?"
What does the company's future look like?
My fifth question is my favorite. It's, "What's the company's three-year, five-year, and 10-year plan?" I love this one because I've never walked into a job and thought, "I'm only going to be here for one year," or "I'm only doing this to collect a paycheck." I always say, "Think like the CEO." I never want to go into a job and strive to just be an associate. That's just where you start.
All you really need — or maybe have time for — is one of these questions. So many people on my TikTok said, "That is too many questions. You're so high maintenance." I was like, "Just use one of them, and they'll be blown away." Because you're starting a whole other conversation that doesn't have to do with their questions for you. These are just concepts that I hope people can take with them as they go — little nuggets — to nail these interviews.
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- This Mother and Daughter Were 'Kind of Fringe Weirdos' When They Started an Uncommon Business in Their Garage. Now They're in Major Retailers — and Victoria Beckham Is a Fan.
- Lock A Leadership Shortage Is Coming. Here's What Needs to Happen to Prevent It.
- Lock The Author of 'Million Dollar Weekend' Says This Is the Only Difference Between You and the Many 'Very, Very Dumb People' Making a Lot of Money
- What the NLRB Appeal of the Expanded Joint Employer Rule Judgment Means for Your Business
- Lock 12 Books That Self-Made Millionaires Swear By
- The Sweet Side Hustle She Started in an Old CVS Made $800,000 in One Year. Now She's Repeating the Success With Her Daughter — and They've Already Exceeded 8 Figures.
Most Popular Red Arrow
Get microsoft office plus windows 11 pro for $70 this week only.
Use Microsoft Office to streamline productivity and Windows 11 Pro for security, collaboration, and more.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
Save 20% and Stay Loose with This Massager
Tension can be a distraction, which is bad for business.
How Small Businesses Can Master a Complex Labor Market
Navigating today's labor market is a high-stakes game for small businesses as they compete to attract top talent. Here are a few strategies for small businesses to consider as they build and strengthen their teams.
Drive Safe on Business Trips with This Car Display, Discounted to $90
Compatible with Apple CarPlay and Android Auto, this touchscreen display makes safer navigation easier.
My Startup Couldn't Raise VC Funding, So We Became Profitable. Here's How We Did It — And How You Can Too.
Four months ago, my startup reached profitability for the first time. It came after more than a year of active work and planning, and here's what it took.
Successfully copied link
I've been offered every job I've interviewed for. Here are 5 questions I ask interviewers.
- Kendal Lindstrom started a career-change consultancy after struggling to change jobs.
- She shared her strategy for acing job interviews , which includes having five key questions ready.
- They focus on areas such as company culture, team dynamics, and the employer's long-term plans.

This as-told-to essay is based on a conversation with Kendal Lindstrom, 25, who lives in Scottsdale, Arizona. She runs a career-change consulting firm named Doux and works in tech. She recently posted a TikTok about five questions she has ready for a job interview. Lindstrom says she believes asking at least some of these questions is why she's always landed a role she interviewed for. The following has been edited for brevity and clarity.
I started Doux because I never liked to be put in a box in terms of my career. Coming out of college, I thought, "I just want to be known as the girl in fashion." I was so wrong. But I didn't know how to pivot into a new industry . It took me two years of connecting, trying, and failing. I found the framework of what Doux is now by failing.
After working in fashion, I got myself into medical sales. I then switched to tech because that's where my passions lie. It took me two years to go from fashion to medical sales. But from the day I decided I wanted to be a tech consultant, it only took me three weeks to get my offer letter.
The difference was I knew how to write my résumé. I knew how to become the candidate that they needed.
My formula is to map your résumé to the career you're going to, not the career you've been in. To get to my current job, I created a résumé that was unstoppable.
Usually, I tell my clients to reach out to the hiring manager. In this case, the hiring manager got to me within minutes of me submitting my résumé. The interview process was extensive, but, like I always tell my clients, it's about follow-ups.
I followed up three times because they had great candidates. But I needed to stay in front, and I needed to be the person they chose.
I had the drive
It's funny when I look back and talk to the executives who hired me. They're like: "You had no business being in tech. You had nothing on your résumé that told us that you would do a good job in this. But the way you presented yourself, it was a no-brainer to hire you because we knew you would get it." So, it's often more how you're presenting yourself in a professional realm rather than what you're saying to answer the questions.
I had drive, and that's what they were looking for. They were looking for someone young to grow with the company. If they wanted someone young, they weren't going to get all the experience in the software that they needed. But I was eager to learn, and however many hours outside work that took, I was willing to do it. I really drove home that it doesn't stop at 5 p.m. My job stops when my job is done.
Each day after work, I spent 30 minutes reading a training book my company had given me. Then, I tried to apply the knowledge for 30 minutes. The next day, I would get time on my boss's calendar and say: "This is what I learned yesterday. Tell me how you have seen this applied in scenarios with a client."
It took me about a year to really digest everything. It was tough, but it came down to whether I was willing to ask questions when I needed help rather than having too much pride and not asking anyone.
Related stories
I've done a lot of interviews for my age because I kept my options open no matter where I was in my career. I've never wanted to be stagnant. So I have done upwards of 10 or 11 interviews, and I've never been told no because my goal was to make an employer feel like I had their best interests at heart and I wanted to be part of their company, which meant I needed to sell myself as a solution. And it's more about the questions you ask than the answers you get.
I have pretty thick skin
When I worked in medical sales — or even with some of the comments on my TikTok — so much was about my image. I was like, "What does my blonde hair have to do with the knowledge that I have?" Not that it ever hurt my feelings because I have pretty thick skin. In any industry, there will be people who would want to discredit someone's abilities because of how they look. But at the end of the day, I can use my brain to where people are like, "We need to listen to you."
@kendallindstrom it’s more about the questions you ask than the answers you get. people want to talk about themselves. #interviewquestions #jobinterview #resume #careerchange #womeninbusines ♬ original sound - DOUX | CAREER CHANGE MGMT
Some of the comments on my TikTok have been so far off the mark. At the time of my interviews for my current job, I didn't have a website, and my social media wasn't publicly available. So, I got the job because of the things I said and the questions I asked, and not because of my appearance.
These are my five key questions:
What's the company culture like?
The first thing I tell people to ask is about company culture. That's a big one. It's such a make-it-or-break-it for enjoying your job. I wanted my audience to know that asking about it is so important because if you're miserable in your job, you're only setting yourself up to fail.
What's the lowdown on my predecessor?
The second one is, "What did the person who held this role before me do that was appreciated but not required based on the job description?" I suggest this one because I want my audience to put themselves in the role already. It's an assumptive selling tactic. I always say go into the interview and sell yourself.
I asked that question one time — "What are you going to miss most about this person?" — and the interviewer said, "Oh, they got Starbucks all the time." And I was like, "Great, I guess we'll be getting Starbucks for the office all the time."
What do my colleagues require?
The third question was, "How can I best suit the needs of my direct counterparts?" That came from wanting to understand — in the most professional way — the team you're walking into. It helps me understand and identify how I would fit into the team.
I've seen teams before where they just don't get along. But you don't know that until you sit down on the first day. And at that point, it's already too late. You're either leaving, or you've got to deal with this until you can figure out another job.
How successful is the team?
No. 4 is what the current state of the department is in reference to the bottom line. That has to do with asking about sales, of course, but I'm also asking: "Am I walking into a failing department? Are you expecting me to turn things around? Are you expecting me to just take the blame for something that's already failing? Or are you guys seeing numbers you've never seen before and need more people?" And, if so, "What did you do to see those numbers?"
What does the company's future look like?
My fifth question is my favorite. It's, "What's the company's three-year, five-year, and 10-year plan?" I love this one because I've never walked into a job and thought, "I'm only going to be here for one year," or "I'm only doing this to collect a paycheck." I always say, "Think like the CEO." I never want to go into a job and strive to just be an associate. That's just where you start.
All you really need — or maybe have time for — is one of these questions. So many people on my TikTok said, "That is too many questions. You're so high maintenance." I was like, "Just use one of them, and they'll be blown away." Because you're starting a whole other conversation that doesn't have to do with their questions for you. These are just concepts that I hope people can take with them as they go — little nuggets — to nail these interviews.
Watch: Marketing leaders from Amazon, LinkedIn, Lego Group and more tell Insider what pandemic-fueled business changes are likely to stick around
- Main content
- Video Idea Generator
- Video Script Generator
- Video Hook Generator
- YouTube Title
- YouTube Description
- YouTube Tags Generator
- YouTube Video SEO Generator
- Video Promotion Generator
- Facebook Caption
- Instagram Caption
- Twitter Caption
- Pinterest Description
- LinkedIn Caption
- TikTok Caption
- eBook Idea Generator
- eBook Title Generator
- eBook Outline Generator
- eBook Chapter Generator
- eBook Promotion Generator
- Blog Outline
- Google Ad Headline
- Google Ad Description
- Facebook Ad Copy
- LinkedIn Ad Copy
- Social Media Ideas
- Podcast ideas
- Email Subject Line
- Email Copy Generator
- Paraphrase Generator
- Text Extender
- AI Tone Changer
- Survey Questions
- Campaign Builder
- Start for free
AI Survey Questions Generator – Questionnaire Maker [Start For Free]
Come up with meaningful questions in seconds.
What Is StoryLab.ai’s Survey Questions Generator – Questionnaire Maker
StoryLab.ai is an online AI Tool that helps you improve your marketing.
One of our AI-Powered Tools is a Suvey Question Generator. Some call it a Questionnaire Maker, Survey Maker or Random Question Generator. The tool helps you brainstorm questions to create meaningful surveys and get the data you need to improve your marketing campaigns, product, onboarding, you name it.
Simply describe the topic of your Survey and get ideas in seconds.
Don’t simply copy/paste the questions in your survey and send it out. You know your audience best. AI is here to help you broaden your creativity. By running the AI Questionnaire maker a couple of times, we’re sure you’ll be inspired to set up meaningful questions for your Survey.
Get started for free with the AI Survey Questions Generator.
StoryLab.ai – More than just an AI Survey Questions Generator
StoryLab.ai is an AI-Powered Content Creation Platform and the AI Questionnaire Maker is just one of our tools. Check out the video to see our Platform in action.
How the AI Survey Question Maker Works
It can be difficult to come up with the right questions for your Survey and you basically have one shot to get your audience to answer your questions and get the data you need to improve your marketing, product, onboarding, you name it.
Make sure the questions you’re asking are on point.
Spar with AI to come up with a long list of potential questions before selecting the best ones.
For this example, we wanted to come up with Survey Questions to learn more about how much our customers love our product.
Our input was: ‘How do you like our product’
Here’s what the AI came up with on our first run:
Outputs we’ve received from the AI Questionnaire maker on the first run:
1. On a scale of 1-10, how would you rate your overall satisfaction with our product?
2. Can you briefly describe your initial impression when you first started using our product?
3. What features of our product do you find the most useful, and why?
4. Have you encountered any difficulties while using our product? If yes, please provide details.
5. Compared to similar products in the market, how would you rate the quality of our product?
6. How well do you think our product meets your needs or solves your problems?
7. If you could change one thing about our product, what would it be and why?
8. Would you recommend our product to a colleague or friend? Why or why not?
9. How would you describe your customer service experience related to our product?
10. Are there any additional features or improvements you would like to see in future versions of our product? Please provide as much detail as you can.
As mentioned earlier. We don’t want to settle for the first couple of questions AI or we came up with. Here are the questions we got on the second run.
1. On a scale of 1 to 10, how satisfied are you with the overall performance of our product?
2. Which features of our product do you find the most useful, and why?
3. Can you identify any aspects of our product that could be improved? If yes, please elaborate.
4. How often do you use our product, and in what contexts?
5. Have you encountered any challenges or difficulties while using our product? If so, could you please describe them?
6. Compared to similar products on the market, how would you rate our product and why?
7. How well does our product meet your needs or solve the problems you face?
8. Have you utilized our customer support services? If yes, how would you rate your experience and what improvements, if any, would you suggest?
9. Would you recommend our product to others? Please explain your reasons.
10. How can we enhance our product or services to better meet your needs and expectations in the future?
We got 20 inspirational pieces for our Survey in just a couple of seconds. We can now fine-tune our inputs or take these and brainstorm further with the team to really nail our Survey.
Create Great Survey Questions in half the time
Make sure the questions you’re asking in your Survey are meaningful. Here are the top benefits of using an AI Survey Question Maker at a glance.
Top benefits of the AI Survey Question Maker
Best practices for writing great survey questions.

Writing effective survey questions is essential for gathering accurate and meaningful data. Here are some best practices to consider:
Start with Clear Objectives:
Understand the purpose of your survey. What information do you want to gather? Having clear objectives will guide your question-writing process.
Keep it Simple:
Use simple and concise language. Avoid jargon, technical terms, or complex sentence structures that might confuse respondents.
Avoid Leading Questions:
Frame questions neutrally to avoid influencing respondents’ answers. For example, instead of asking “Don’t you agree that…”, ask “What is your opinion on…”.
Use Specific Language:
Be specific in your questions to ensure accurate responses. Avoid vague terms like “often” or “sometimes,” and use quantifiable terms like “weekly” or “monthly.”
One Question at a Time:
Each question should focus on a single topic. Avoid combining multiple questions into one, as it can lead to confusion.
Use Closed and Open-Ended Questions:
Closed-ended questions (multiple choice, yes/no) are easy to analyze, while open-ended questions provide valuable insights. Use a mix of both for a comprehensive view.
Provide Balanced Response Options:
In multiple-choice questions, offer a balanced range of response options that cover the spectrum of possible answers.
Include a “Prefer Not to Answer” Option:
Some respondents might prefer not to answer certain questions. Including this option respects their privacy and maintains data accuracy.
Consider Response Order:
Responses to the first few options in a list can be favored. Randomize the order of response options to avoid bias.
Avoid Double Negatives:
Refrain from using double negatives, as they can confuse respondents. Keep questions positively framed.
Avoid Assumptions:
Don’t assume respondents have knowledge they might not possess. If you need to ask about a complex topic, provide context or definitions.
Use Likert Scale Wisely:
If using a Likert scale (e.g., strongly agree to strongly disagree), keep the scale consistent across questions and avoid using too many scale points.
Pilot Test:
Before sending out the survey, test it with a small group to identify any issues with wording, question flow, or response options.
Avoid Sensitive or Personal Questions:
If possible, avoid asking respondents to divulge sensitive or personal information that they might be uncomfortable sharing.
Limit the Number of Questions:
Long surveys can lead to respondent fatigue and lower completion rates. Keep the survey concise and relevant.
Use Skip Logic:
If certain questions are only relevant to specific respondents, use skip logic to show or hide questions accordingly.
Prioritize Important Questions:
Place crucial questions at the beginning or middle of the survey to capture responses from more engaged participants.
Provide Clear Instructions:
If a question requires a specific format (like dates), provide clear instructions on how to answer.
Test for Clarity:
Ask colleagues or friends to review your survey for clarity and potential issues.
Thank and Provide Context:
Start with a thank-you message and a brief context for the survey. This can increase respondent engagement.
Remember that crafting effective survey questions requires a combination of writing skills and an understanding of your target audience. Following these best practices will help you create a survey that generates valuable insights.
AI Questionnaire Generator Pricing
Our pricing is set up as followed:
- Free – get 3 runs a month to try our tools out for free;
- Pro – $15 a month – 100 runs a month;
- Unlimited – $19 a month – unlimited runs a month;
You can also opt-in for the yearly membership and receive a 20% price reduction.
You can check out our full pricing here .
What is an AI Survey Questions Generator? It’s a tool that uses artificial intelligence to create relevant and effective survey questions based on the desired topics, audience, and objectives of the survey.
How does an AI Survey Questions Generator work? The generator uses natural language processing and machine learning to understand the survey’s context and goals, then generates questions that are tailored to gather the needed information.
What are the benefits of using an AI Survey Questions Generator? Benefits include time-saving in question creation, ensuring question relevance and clarity, and potentially improving response rates and data quality due to well-crafted questions.
Can AI Survey Questions Generators customize questions for different industries? Yes, it can be tailored to generate questions specific to various industries by analyzing industry-related data and using relevant language and terminology.
How accurate are AI Survey Questions Generators? The accuracy can be high but you should still review to ensure the questions fully meet the survey’s objectives.
Are AI-generated survey questions biased? While AI strives to be unbiased, the quality and diversity of the data it was trained on can affect this. Human oversight is recommended to check for and correct any potential biases.
Can AI Survey Questions Generators handle open-ended questions? Yes, these generators are capable of creating open-ended questions, though the complexity and depth of such questions can vary based on the AI’s programming and training.
How do AI Survey Questions Generators improve survey engagement? By creating relevant, clear, and engaging questions, these generators can enhance respondent engagement, leading to more thoughtful responses and higher completion rates.
What should be considered when using an AI Survey Questions Generator? It’s important to consider the target audience, survey objectives, and the need for potential customization or human editing to ensure the questions fully align with the survey goals.
Can AI Survey Questions Generators create multilingual questions? Yes. Simply enter your inputs in the preferred language and you´ll get outputs in the same language.
How do AI Survey Questions Generators ensure question clarity? These generators use natural language processing techniques to create questions that are clear, concise, and free of ambiguity, enhancing the reliability of survey responses.
What types of surveys can benefit from AI Survey Questions Generators? They can be used for a wide range of surveys, including market research, customer satisfaction, employee feedback, and academic research.
Can these generators suggest question formats (e.g., multiple choice, rating scale)? Yes, The AI generator can suggest appropriate question formats based on the survey’s objectives and the type of data needed.
Are AI-generated questions customizable by the user? Yes. We always advise you to check the outputs before using the questions in your survey.
Can AI Survey Questions Generators adapt to different target audiences? Yes, these generators can adapt the style and complexity of questions to suit different target audiences, based on input parameters and training data.
How cost-effective are AI Survey Questions Generators for businesses? You can start for free and get 3 runs and upgrade if you need more. Check out our pricing to learn more.
What future advancements can be expected in AI Survey Questions Generators? Future advancements may include more nuanced understanding of complex topics, better integration with survey platforms, and enhanced customization options to cater to specific research needs.
Jump back to a section
- O que é StoryLab.aiGerador de perguntas de pesquisa - Criador de questionários
- Como funciona o criador de perguntas de pesquisa de IA
- Crie ótimas perguntas de pesquisa na metade do tempo
- Melhores práticas para escrever ótimas perguntas de pesquisa
- Preço do Gerador de Questionário de IA
- Perguntas frequentes
YouTube Video Title Generator
Create catchy titles for your next videos.
YouTube Description Generator
Write great descriptions in half the time.
AI eBook Generator
Create full eBooks
Social Media Caption Generator
Get the most out of your Social Marketing.
Instagram Caption Generator
Stand out on Insta with great captions.
LinkedIn Caption Generator
Awesome captions in half the time
YouTube Video Idea Generator
Effective Video ideas
YouTube Video Script Generator
Engaging Videos
AI Video Hook Generator
Create Engaging Videos
All Marketing Copy Generator
See all our AI Geenrators

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
9. Describe a time when you had to present your research findings in a clear and concise manner. Researchers often have to communicate their findings to colleagues, stakeholders, and the public. The ability to communicate complex research findings in an understandable way is a key skill for someone in this role.
There are several types of interviews, often differentiated by their level of structure. Structured interviews have predetermined questions asked in a predetermined order. Unstructured interviews are more free-flowing. Semi-structured interviews fall in between. Interviews are commonly used in market research, social science, and ethnographic ...
The Qualitative Report 2020 Volume 25, Number 9, How To Article 1, 3185-3203. Qualitative Interview Questions: Guidance for Novice Researchers. Rosanne E. Roberts. Capella University, Minneapolis ...
In your answer, describe the extent of involvement for each individual. Example: "The participant is the individual who is involved in the research from the initial investigative stages to the findings and conclusions. Collaborators are the individuals who contribute to the final report writing and finalization of the research.
The first task is to figure out who to interview. Usually the research question specifies the participants. For example, a research question on the doctors' perception of their working conditions naturally suggests that doctors will make up the participant group. Following this example, doctors are the "population" this study is based on.
Vancouver, Canada. Abstract. Interviews are one of the most promising ways of collecting qualitative data throug h establishment of a. communication between r esearcher and the interviewee. Re ...
3. People's espoused theories differ from their theories-in-practice. Get them to tell a story. Ask "how" questions not "do". Use "tell me about" and "tell me more about that". Use open-ended questions. Approach your topic sideways. Don't take the first answer as a final answer. Ask for elaboration.
If you need 10 interviews, it is a good idea to plan for 15. Likely, a few will cancel, delay, or not produce useful data. 5. Not keeping your golden thread front of mind. We touched on this a little earlier, but it is a key point that should be central to your entire research process.
Do not expect interviewees to be able to directly address your research question. Instead, interviews should be structured around several focal questions designed to cover the main aspects of the research question o Questions should be designed to elicit an individual's experiences and understanding.
Related: 100 Common Job Interview Questions Interview questions about experience and background To impress the employer, consider elaborating on the credentials you listed in your resume. Your employment history and skill set can illustrate that you can be a competent research analyst. Example questions include:
Indeed Editorial Team. Updated August 11, 2022. A research interview is useful for researchers to gather information on a certain topic. You may interview a group of people, and you'll have a range of choices to ask specific questions. Research interviews allow an interviewee to elaborate on their responses to render a clear context to you.
A qualitative research interview is a one-to-one data collection session between a researcher and a participant. Interviews may be carried out face-to-face, over the phone or via video call using a service like Skype or Zoom. There are three main types of qualitative research interview - structured, unstructured or semi-structured.
A Successful Interviewer is: 1. Knowledgeable: is thoroughly familiar with the focus of the interview; pilot interviews of the kind used in survey interviewing can be useful here. 2. Structuring: gives purpose for interview; rounds it off; asks whether interviewee has questions. 3. Clear: asks simple, easy, short questions; no jargon. 4. Gentle: lets people finish; gives them time to think ...
Develop an interview guide. Introduce yourself and explain the aim of the interview. Devise your questions so interviewees can help answer your research question. Have a sequence to your questions / topics by grouping them in themes. Make sure you can easily move back and forth between questions / topics. Make sure your questions are clear and ...
Researchers aim to look into the individual's life journey. As a result, this type of interview allows participants to construct and share their own narratives, providing rich qualitative data. Qualitative research, oral history, or studies focusing on individual experiences and identities uses narrative interviews. 6.
Research scientists usually work in laboratories or other research environments where they help design and implement trials and experiments and analyse the results. To secure a research scientist role, employers typically expect candidates to attend an interview and answer a range of questions that assess their skills and competencies.
Example: "There are many important skills for a researcher, but some of the most important include: -The ability to ask clear and concise research questions. -The ability to design effective research studies. -The ability to collect high-quality data. -The ability to analyze data effectively.
It is a good idea to prepare and even rehearse your answers. If you are confident in answering all of these you will be well-prepared. About your research. General research questions. About you and your capabilities. About your ability to gain funding. About your proposed research. About your role as supervisor/teacher.
Related: A guide to interview methods in research (With examples) 4. Please describe in your own words what coding means in qualitative research. This question looks to explore your fundamental understanding of an important aspect of qualitative research. It relates to qualitative data analysis.
The majority of questions and sample answers covered in this free guide were obtained directly from WSO's very own Hedge Fund Interview Course, which features: 814 questions across 165 hedge funds. 10+ exclusive case videos with detailed pitches. Long, short, equity, credit, event-driven, macro+ questions.
1 Stay Calm. When faced with questions about your research methodologies during an interview, the first step is to stay calm. Take a deep breath and remember that such inquiries are not personal ...
The STAR method stands for Situation, Task, Action, Result. It's a formula worth memorizing because it can help you structure your responses to behavioral interview questions. Situation: Start by establishing the situation and sharing any important details. Task: Recount your specific task or responsibility.
Before an interview, take a moment to write down some questions—around five is a good start, but some people feel more comfortable preparing closer to 10 questions. This way, if any of your questions come up during the interview, you can ask them mid-conversation and still have more on hand to ask at the end of the interview.
The first thing I tell people to ask is about company culture. That's a big one. It's such a make-it-or-break-it for enjoying your job. I wanted my audience to know that asking about it is so ...
The first thing I tell people to ask is about company culture. That's a big one. It's such a make-it-or-break-it for enjoying your job. I wanted my audience to know that asking about it is so ...
Here's what you can do before, on and after the day of your interview to set yourself up for success. 1. Research the company you're applying to. No two companies are exactly alike, so it helps to learn more about the company where you're applying. Reviewing the job description and the company's online presence allows you to emphasize ...
One of our AI-Powered Tools is a Suvey Question Generator. Some call it a Questionnaire Maker, Survey Maker or Random Question Generator. The tool helps you brainstorm questions to create meaningful surveys and get the data you need to improve your marketing campaigns, product, onboarding, you name it. Simply describe the topic of your Survey ...