Problem Solving: 15 Examples for Setting Performance Goals
Problem Solving: Use these examples for setting employee performance goals. Help your employees master this skill with 5 fresh ideas that drive change.
Problem Solving is the skill of defining a problem to determine its cause, identify it, prioritize and select alternative solutions to implement in solving the problems and reviving relationships.

Problem Solving: Set Goals for your Employees. Here are some examples:
- To be accommodative of other people's ideas and views and to be willing to take them on board.
- Research well enough to gather factual information before setting out to solve a problem.
- Look at things in different perspectives and angles and to develop alternative options.
- Be willing enough to collaborate with other when it comes to problem-solving issues.
- Learn to articulate or communicate in a proper manner that can be well understood by people.
- Get first to understand what the problem really is before starting to solve it.
- Show great confidence and poise when making decisions and not afraid to make mistakes and learn from them.
- Keep a cool head when dealing with more pressing and exhausting issues.
- Try to ask the right questions that will act as a guide to coming up with proper solutions.
- Be more flexible to change and adapt to new tact and ways of finding new solutions.
Problem Solving: Improve and master this core skill with these ideas
- Identify the problem. determine the nature of the problem, break it down and come up with a useful set of actions to address the challenges that are related to it.
- Concentrate on the solution, not the problem. Looking for solutions will not happen if you focus on the problem all the time. Concentrating on finding the answer is a move that brings about new opportunities and ideas that can be lucrative.
- Write down as many solutions as possible. Listing down various solutions is important to help you keep an open mind and boost creative thinking that can trigger potential solutions. This list will also act as your reminder.
- Think laterally. Thinking laterally means changing the approach and looking at things differently as well as making different choices.
- Use positive language that creates possibilities. Using words that are active to speak to others, and yourself build a mind that thinks creatively encouraging new ideas and solutions to be set.
These articles may interest you
Recent articles.
- Skills needed to be a traffic engineer
- Skills needed to be a senior project estimator
- Outstanding Employee Performance Feedback: Inventory & Operations Auditor
- New Hire Offer Letter
- Presentation Skills: 15 Examples for Setting Performance Goals
- Poor Employee Performance Feedback: Comptroller/Controller
- 7 Steps For Developing A Performance Appraisal System
- Employee Performance Goals Sample: Chief Executive Officer
- Skills needed to be a benefits analyst
- Skills needed to be an it audit senior manager
- Employee Separation Definition, Formula And Examples
- Good Employee Performance Feedback: Invoice Control Clerk
- Good Employee Performance Feedback: Senior Cost Analyst
- Top 28 Employee Appreciation Day Activities
- Poor Employee Performance Feedback: Facilities Technician
12 SMART Goals Examples for Problem Solving
Everyone should aim to develop their problem-solving skills in life. It’s critical for career growth and personal development. That’s why establishing SMART goals is a valuable tool for achieving success and reaching desired outcomes.
This article will provide SMART goals examples for effective problem solving. Gaining inspiration to pursue these goals can help you become more organized and effective in problem-solving situations.
Table of Contents
What is a SMART Goal?
The SMART framework is an amazing way to establish practical goals . For those unaware, SMART stands for specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-based.
Still confused? SMART goals are:
- Specific: Accomplishing goals starts with defining them and how they will be achieved. The more detailed your goals for problem solving, the greater the likelihood you have of meeting them.
- Measurable: Having a quantifiable goal is a crucial SMART component. Tracking your progress makes modifying or adjusting the path forward easier if needed. You’ll also have a tangible way to determine whether or not your objectives have been met.
- Attainable: Try to decide on what is realistically possible before pursuing goals. If possible, break down your overarching goal into smaller objectives that fall within your current capabilities. Setting too high or unrealistic expectations cause you frustration and even giving up on your aspirations altogether.
- Relevant: You must align your actions with your core values . Hence, take some time to reflect on how you want your goals to reflect your interests and values.
- Time-based: Success doesn’t come without hard work and dedication, so you should have a specific timeline when working toward your dreams. You will stay organized and motivated throughout the journey when you set a deadline.
In today’s world, being able to identify and solve problems using analytical skills can’t be undervalued. Following the 5 SMART criteria above will allow you to achieve better results with fewer resources.
Here are 12 examples of SMART goals for better problem solving:
1. Define the Problem
“I’ll create a plan to define and describe the problem I’m trying to solve by the end of two weeks. This will allow me to identify the exact issue that needs to be addressed and develop an effective solution promptly.”
Specific: The goal outlines the task of defining and describing a problem.
Measurable: You can measure your progress by creating a plan after two weeks.
Attainable: The statement is within reach because it requires critical thinking and planning.
Relevant: Defining an issue is required for enhanced problem solving.
Time-based: There is a two-week timeline for accomplishing this goal.
2. Analyze Root Cause
“I will take the time to thoroughly analyze the root cause of a problem before I attempt to come up with a solution. Before jumping into a solution, I’ll consider the possible causes and try to figure out how they interact with each other.”
Specific: The SMART goal outlines what will be done to analyze the root cause of a problem.
Measurable: You could measure how often you take the time for analysis.
Attainable: This is realistic because taking the time to do a thorough analysis is possible.
Relevant: Gaining a better understanding of the root causes of a problem can lead to more effective solutions.
Time-based: You’ll follow this process every time you solve a problem, so this goal is ongoing.
3. Be Willing to Collaborate With Others
“For the duration of 10 months, my goal is to be willing to collaborate with others to find the best solution for any problem at hand. I want to be open to exchanging ideas and listening to the opinions of others so that we can solve our problems efficiently.”
Specific: The person must proactively strive to collaborate with others.
Measurable: You can keep track of how often you collaborate monthly.
Attainable: This is feasible because it requires only the willingness to collaborate and exchange ideas.
Relevant: Collaboration allows you to find better solutions and grow your network.
Time-based: You have 10 months to pursue this particular target.
4. Evaluate Alternatives
“I will review and evaluate at least three alternative solutions to the problem by the end of this month. I’ll evaluate the costs and benefits of each solution, prioritize them based on their potential effectiveness and make my recommendation.”
Specific: You will need to review and evaluate three alternative solutions.
Measurable: Count how many alternative solutions you listed.
Attainable: With enough time and effort, anybody can review and evaluate multiple solutions.
Relevant: This is related to problem solving, which can advance your professional career .
Time-based: You have one month for goal achievement.
5. Implement Action Plan
“To ensure that my action plans are implemented effectively, I will create a timeline with concrete steps and review it every two weeks for the 6 months ahead. I want all aspects of my plan to take place as scheduled and the process is running smoothly.”
Specific: The aim is to create a timeline and review it every two weeks for 6 months.
Measurable: The person can compare their timeline to the actual results and ensure that every aspect of the plan takes place as scheduled.
Attainable: This goal is achievable if the individual has the time, resources, and support.
Relevant: Realize that implementing an action plan applies to problem solving.
Time-based: Success will be reached after 6 whole months.
6. Ask the Right Questions
“I’ll learn to ask the right questions by reading two books on effective questioning strategies and attending a workshop on the same topic within the next quarter. This will allow me to get to the root of any problem more quickly.”
Specific: The goal states what to do (read two books and attend a workshop) to learn how to ask the right questions.
Measurable: You can check your progress by reading the books and attending the workshop.
Attainable: This is a reasonable goal and can be met within the given time frame.
Relevant: Asking the right questions is key to solving any problem quickly.
Time-based: Goal completion should be accomplished within a quarter.

7. Be More Flexible
“I will seek opportunities to be more flexible when problem solving for the following 8 months. This could include offering creative solutions to issues, brainstorming ideas with colleagues, and encouraging feedback from others.”
Specific: This SMART goal is explicit because the person wants to become more flexible when problem solving.
Measurable: Check how often and effectively you follow the three action items.
Attainable : This goal is achievable if you dedicate time to being more open-minded.
Relevant: Flexibility is integral to problem solving, so this goal is highly relevant.
Time-based: Eight months is the allotted time to reach the desired result.
8. Brainstorm Solutions
“I want to develop a list of 5 potential solutions by the end of this month for any problem that arises. I’ll brainstorm with my team and research to develop the options. We’ll use these options to evaluate the most feasible solution for a specific issue.”
Specific: You should come up with a list of 5 potential solutions with your team.
Measurable: Actively count how many potential solutions you come up with.
Attainable: This goal can be achieved with research and collaboration.
Relevant: Brainstorming solutions help you evaluate the best option for a certain issue.
Time-based: You should strive to meet this goal by the end of the month.
9. Keep a Cool Head
“When encountering a difficult problem, I will strive to remain calm and not rush into any decisions. For three months, I’ll take a few moments to pause, gather my thoughts and assess the situation with a clear head before taking action.”
Specific: The person identifies the goal of remaining calm when encountering complex problems.
Measurable: It is possible to measure success in terms of how long it takes to pause and assess the situation.
Attainable: Taking a few moments before taking action is realistic for most people.
Relevant: Keeping a cool head in difficult situations is beneficial for problem solving.
Time-based: This SMART statement has an end date of three months.
10. Don’t Make Rash Assumptions
“I will no longer make assumptions or jump to conclusions without gathering facts. I’ll strive to be more open-minded when finding solutions to problems and take the time to consider all perspectives before making a decision.”
Specific: The goal is explicit in that individuals aim to be open-minded.
Measurable: You can evaluate how often assumptions are made without gathering facts or considering all perspectives.
Attainable: Anyone can take the time to consider different perspectives before making a decision.
Relevant: This is suitable for those who want to be more mindful and make better decisions.
Time-based: Since the goal is ongoing, you will pursue it on a daily basis.
11. Take Responsibility
“I will take responsibility for all my mistakes and be open to constructive criticism to improve as a professional by the end of the next quarter. I’ll also learn from my mistakes and take steps to ensure they’re not repeated.”
Specific: The statement is evident in that you will take responsibility for all mistakes.
Measurable: Progress towards this goal can be measured by how well you respond to constructive criticism.
Attainable: This is possible since the person is willing to learn and improve with constructive criticism.
Relevant: Taking responsibility for your mistakes is an important skill, making this an appropriate goal.
Time-based: You have one quarter to complete the SMART goal.
12. Let Your Creativity Flow
“I want to explore the range of my creative problem-solving abilities and come up with solutions for difficult situations. To do this, I’ll take a course in creative problem solving and apply the principles I learn to practical scenarios within two months.”
Specific: You will take a course in creative problem solving and apply the principles learned to practical scenarios.
Measurable: By enrolling in the course, you can monitor your learning progress over time.
Attainable: The goal should be realistic concerning time and resources.
Relevant: Recognize that creativity is vital in many industries.
Time-based: You should ideally reach this goal after two months.
Final Thoughts
Setting SMART goals is a fantastic approach to solving any problem. They provide a clear structure for breaking down complex tasks into manageable chunks and encourage goal-oriented thinking.
While SMART goals may not work for every situation, they can offer a valuable framework for solving complex issues. Thus, it’s beneficial to experiment with this tool to develop problem-solving strategies tailored to individual needs.
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
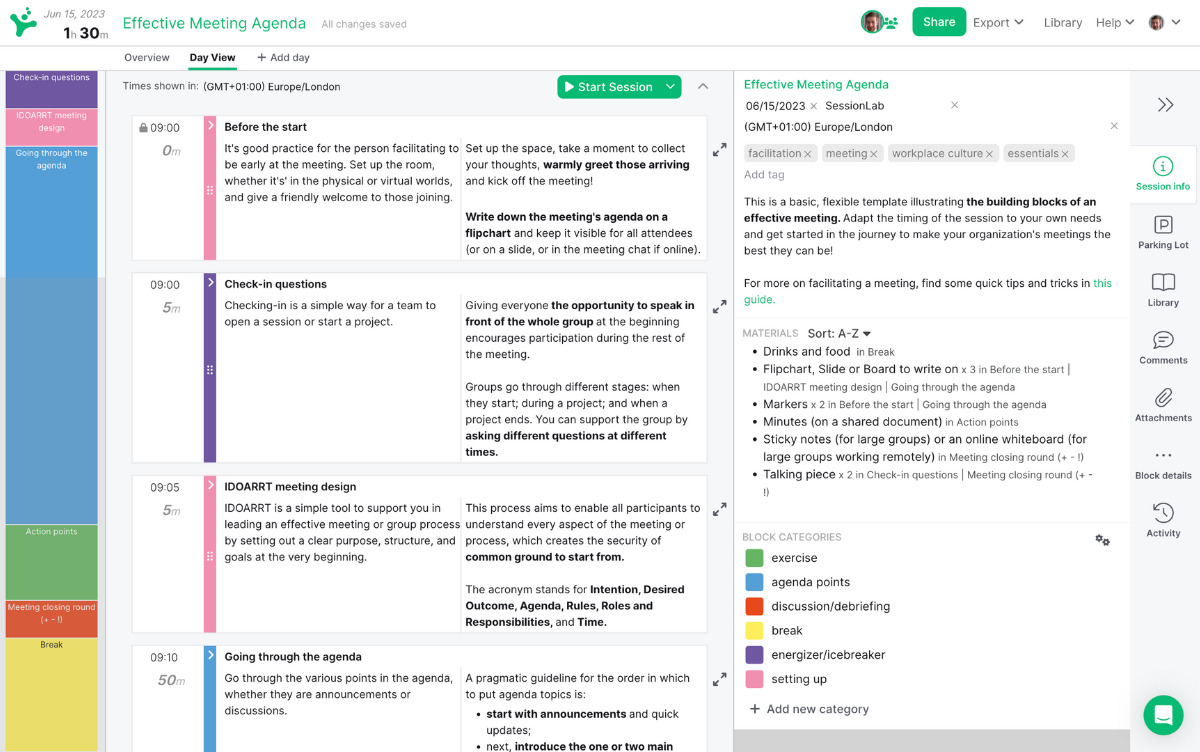
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix

21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
Join Pilot Waitlist

Home » Blog » General » Effective IEP Goals for Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills in Elementary Students

Effective IEP Goals for Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills in Elementary Students

Introduction: In special education, helping students develop essential skills is crucial for their success. One such skill is problem-solving, which plays a significant role in students’ learning, social interactions, and overall wellbeing.
Understanding Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills enable students to identify issues, analyze possible solutions, and make informed decisions. These skills impact students’ ability to navigate challenges in their learning, social interactions, and emotional wellbeing.
The Role of Specialists
Various specialists can support the development of problem-solving skills:
- Speech-Language Pathologists: Assist with communication strategies to express thoughts and ideas effectively.
- Social Workers: Provide guidance in navigating social situations and resolving interpersonal conflicts.
- Psychologists: Help students develop coping mechanisms and emotional regulation strategies for problem-solving.
- School Counselors: Offer support in setting achievable goals and creating action plans for addressing challenges.
IEP Goals for Problem-Solving Skills
Here are some specific SMART IEP goals to enhance problem-solving skills:
- Strategies/Activities: Role-playing, group discussions, and problem-solving worksheets.
- Strategies/Activities: Brainstorming sessions, using visual aids, and engaging in collaborative activities.
- Strategies/Activities: Pros and cons lists, guided reflection, and decision-making games.
Implementing and Measuring Progress
To implement these goals and measure progress:
- Collaborate with specialists to create a tailored plan.
- Monitor student performance through observation and assessment.
- Adjust strategies and goals as needed based on progress.
- Communicate with parents and other team members regularly.
Effective IEP goals for problem-solving skills can significantly impact a student’s success in learning and social interactions. Implement these goals and strategies to support your students’ growth. For more resources, explore Everyday Speech Sample Materials . We invite you to share your experiences and insights in the comments below.

Related Blog Posts:
Effective iep goals for improving students’ point of view skills.
Introduction In special education, it is essential to address various skills that contribute to the overall development of students. One such significant skill is understanding others' perspectives, which plays a crucial role in fostering healthy social interactions...
Effective IEP Goals for PreK Students: Developing the Target Skill
In special education, it is crucial to identify and address target skills that can significantly impact a student's learning, social interactions, and overall wellbeing. One such essential skill is controlling strong emotions, which enables students to make better...
Effective IEP Goals for Developing Problem-Solving Skills
Special education plays a crucial role in helping students develop essential life skills. One such skill is problem-solving, which has a significant impact on students' learning, social interactions, and overall wellbeing. In this blog post, we will explore...

FREE MATERIALS
Better doesn’t have to be harder, social skills lessons students actually enjoy.
Be the best educator you can be with no extra prep time needed. Sign up to get access to free samples from the best Social Skills and Social-Emotional educational platform.
Get Started Instantly for Free
Complete guided therapy.
The subscription associated with this email has been cancelled and is no longer active. To reactivate your subscription, please log in.
If you would like to make changes to your account, please log in using the button below and navigate to the settings page. If you’ve forgotten your password, you can reset it using the button below.
Unfortunately it looks like we’re not able to create your subscription at this time. Please contact support to have the issue resolved. We apologize for the inconvenience. Error: Web signup - customer email already exists
Welcome back! The subscription associated with this email was previously cancelled, but don’t fret! We make it easy to reactivate your subscription and pick up right where you left off. Note that subscription reactivations aren't eligible for free trials, but your purchase is protected by a 30 day money back guarantee. Let us know anytime within 30 days if you aren’t satisfied and we'll send you a full refund, no questions asked. Please press ‘Continue’ to enter your payment details and reactivate your subscription
Notice About Our SEL Curriculum
Our SEL Curriculum is currently in a soft product launch stage and is only available by Site License. A Site License is currently defined as a school-building minimum or a minimum cost of $3,000 for the first year of use. Individual SEL Curriculum licenses are not currently available based on the current version of this product.
By clicking continue below, you understand that access to our SEL curriculum is currently limited to the terms above.
Cognitive Remediation Therapy: 13 Exercises & Worksheets

This can result in concentration, organizational, and planning difficulties that impact their quality of life and independent living.
Cognitive Remediation Therapy (CRT) helps by increasing awareness of intellectual difficulties and improving thinking skills. While originally designed for people with thinking problems associated with schizophrenia, it has also proven successful for those with other diagnoses (Bristol Mental Health, n.d.).
CRT works by encouraging a range of exercises and activities that challenge memory, flexible thinking, planning, and concentration problems.
This article explores CRT and its potential to help clients and includes techniques, activities, and worksheets to build effective therapy sessions.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive CBT Exercises for free . These science-based exercises will provide you with detailed insight into Positive CBT and give you the tools to apply it in your therapy or coaching.
This Article Contains:
What is cognitive remediation therapy (crt), how does cognitive remediation work, 8 techniques for your sessions, 7 exercises, activities, & games, 6 helpful worksheets and manuals, implementing online crt programs, 3 best software programs for helping your clients, a take-home message.
“Cognitive remediation is a behavioral treatment for people who are experiencing cognitive impairments that interfere with daily functioning” (Medalia, Revheim, & Herlands, 2009, p. 1).
Successful cognitive functions, including memory, attention, visual-spatial analysis, and abstract reasoning, are vital for engaging with tasks, the environment, and healthy relationships.
CRT improves cognitive processing and psychosocial functioning through behavioral training and increasing individual confidence in people with mental health disorders (Corbo & Abreu, 2018). Training interventions focus on the skills and supports required to “improve the success and satisfaction people experience in their chosen living, learning, working, and social environments” (Medalia et al., 2009, p. 2).
Exercises typically focus on specific cognitive functions, where tasks are repeated (often on a computer) at increasing degrees of difficulty. For example:
- Paying attention
- Remembering
- Being organized
- Planning skills
- Problem-solving
- Processing information
Based on the principles of errorless learning and targeted reinforcement exercises , interventions involve memory, motor dexterity, and visual reading tasks. Along with improving confidence in personal abilities, repetition encourages thinking about solving tasks in multiple ways (Corbo & Abreu, 2018).
While initially targeted for patients with schizophrenia, CRT is an effective treatment for other mental health conditions , including mood and eating disorders (Corbo & Abreu, 2018).
CRT is particularly effective when the cognitive skills and support interventions reflect the individual’s self-selected rehabilitation goals. As a result, cognitive remediation relies on collaboration, assessing client needs, and identifying appropriate opportunities for intervention (Medalia et al., 2009).
Cognitive remediation vs cognitive rehabilitation
CRT is one of several skill-training psychiatric rehabilitation interventions. And yet, cognitive remediation is not the same as cognitive rehabilitation (Tchanturia, 2015).
Cognitive rehabilitation typically targets neurocognitive processes damaged because of injury or illness and involves a series of interventions designed to retrain previously learned cognitive skills along with compensatory strategies (Tsaousides & Gordon, 2009).

While initially done in person, they can subsequently be performed remotely as required (Corbo & Abreu, 2018; Bristol Mental Health, n.d.).
Well-thought-out educational software provides multisensory feedback and positive reinforcement while supporting success, choice, and control of the learning process. Its design can target either specific cognitive functions or non-specific learning skills and mechanisms (Medalia et al., 2009).
CRT successfully uses the brain’s neuroplasticity and is often more effective in younger age groups who haven’t experienced the effects of long-term psychosis. It works by increasing activation and connectivity patterns within and across several brain regions involved in working memory and high-order executive functioning (Corbo & Abreu, 2018).
The Neuropsychological Educational Approach to Cognitive Remediation (NEAR) is one of several approaches that provide highly individualized learning opportunities. It allows each client to proceed at their own pace on tasks selected and designed to engage them and address their cognitive needs (Medalia et al., 2009).
NEAR and other CRT techniques are influenced by learning theory and make use of the following (Medalia et al., 2009):
- Errorless learning Encouraging the client to learn progressively, creating a positive experience without relying on trial and error.
- Shaping and positive feedback Reinforcing behaviors that approximate target behaviors (such as good timekeeping) and offering rewards (for example, monthly certificates for attendance).
- Prompting Using open-ended questions that guide the client toward the correct response.
- Modeling Demonstrating how to solve a problem.
- Generalizing Learning how to generalize learned skills to other situations.
- Bridging Understanding how to apply skills learned inside a session outside in everyday life.
Encouraging intrinsic motivation (doing the tasks for the satisfaction of doing them rather than for external rewards) and task engagement are also essential aspects of successful CRT programs (Medalia et al., 2009).
Therapy is most effective when it successfully supports clients as they transfer learning skills into the real world.

Download 3 Free Positive CBT Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to find new pathways to reduce suffering and more effectively cope with life stressors.
Download 3 Free Positive CBT Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Cognitive remediation techniques must be selected according to the skills and needs of the client and typically fall into one of three major intervention categories (Medalia et al., 2009):
- Planning exercises, such as planning a trip to the beach to practice cognitive strategies
- Cueing and sequencing , such as adding signs or placing reminder notes at home to encourage completing everyday tasks (for example, brushing teeth)
Such techniques rely on several key principles, including “(1) teaching new, efficient, information processing strategies; (2) aiding the transfer of cognitive gains to the real world; and (3) modifying the local environment” (Medalia et al., 2009, p. 5).
- Restorative approaches Directly target cognitive deficits by repeating task practices and gradually increasing difficulty and complexity; along with regular feedback, they encourage accurate and high levels of performance.
Practice is often organized hierarchically, as follows:
- Elementary aspects of sensory processing (for example, improving auditory processing speed and accuracy)
- High-order memory and problem-solving skills (including executive functioning and verbal skills)
This technique assumes a degree of neuroplasticity that, with training, results in a greater degree of accuracy in sensory representations, improved cognitive strategies for grouping stimuli into more meaningful groups, and better recall.
- Repetition and reaching for increasing levels of task difficulty
- Modeling other people’s positive behavior
- Role-play to re-enact experienced or imagined behavior from different perspectives
- Corrective feedback to improve and correct unwanted or unhelpful behavior
Complex social cognitive processes are typically broken down into elemental skills for repetitive practice, role-play, and corrective feedback.
Professor Dame Til Wykes: cognitive remediation therapy
It is vital that activities within CRT are interesting and engaging for clients. They must foster the motivation required to persevere to the end of the task or game.
The following three games and puzzles are particularly valuable for children and adolescents (modified from Tchanturia, 2015):

SET is a widely available card game that practices matching based on color, shape, shading, etc.
Clients must shift their thinking to identify multiple ways of categorizing and grouping cards, then physically sort them based on their understanding.
It may be helpful to begin with a limited set of cards to reduce the likelihood of the clients becoming overwhelmed by the game or finding it less enjoyable.
2. Rush Hour

Rush Hour is another fun game that balances problem-solving skills with speed.
Puzzles start simple and increase in complexity, with additional elements involved. Skills developed include problem-solving and abstract thinking, and the game requires a degree of perseverance.

Other activities require no specialist equipment and yet can be highly engaging and support clients in learning transferable skills (modified from Tchanturia, 2015).
- Bigger picture thinking This involves the client picturing a shape in their minds or looking at one out of sight of the therapist. They then describe the shape (without naming it), while the therapist attempts to draw it according to the instructions. This practice is helpful with clients who get overwhelmed by detail and cannot see the bigger picture.
- Word searches Word searches encourage the client to focus on relevant information and ignore everything else – an essential factor in central coherence. Such puzzles also challenge memory, concentration, and attention.
- Last word response Last word response is a challenging verbal game promoting cognitive flexibility. The first player makes up and says a sentence out loud. Each subsequent player makes up a new sentence, starting with the last word of the previous player’s sentence. For example, ‘ I like cheese’ may be followed by the next player saying, ‘ Cheese is my favorite sandwich ingredient ,’ etc.
- Dexterity Using your non-dominant hand once a week (for example, combing your hair or brushing your teeth) stimulates different parts of your brain, creating alternative patterns of neuron firing and strengthening cognitive functions.
The following therapy worksheets help structure Cognitive Remediation Therapy sessions and ensure that the needs of clients are met using appropriately targeted CRT interventions (modified from Medalia et al., 2009; Medalia & Bowie, 2016):
Client referral to CRT
The Cognitive Remediation Therapy Referral Form captures valuable information when a client is referred from another agency or therapist so that the new therapist can identify and introduce the most appropriate CRT interventions. The form includes information such as:
Primary reasons
Secondary reasons
- Self-confidence
- Working with others
- Time management
- Goal-directed activities
Cognitive Appraisal for CRT
The Cognitive Appraisal for CRT form is helpful for identifying and recording areas of cognitive processing that cause difficulty for the client and require focus during Cognitive Remediation Therapy sessions.
Clients are scored on their degree of difficulty with the following:
- Paying attention during conversation
- Maintaining concentration in meetings
- Completing tasks once started
- Starting tasks
- Planning and organizing tasks and projects
- Reasoning and solving problems
Software Appraisal for CRT
The Software Appraisal for CRT form helps assess which software would be most helpful in a specific Cognitive Remediation Therapy session. It provides valuable input for tailoring treatment to the needs of the client.
For example:
- Level of reading ability required
- Cognitive deficits addressed by the software
- What is the multimedia experience like?
- How much input is required by the therapist?
Appraisal records become increasingly important as more software is acquired for clients with various cognitive deficits from multiple backgrounds.
Software Usage for CRT
The Software Usage for CRT form helps keep track of the software clients have tried and how effectively it supports them as they learn, develop, and overcome cognitive deficits.
The client considers the software they use and whether they practiced the following areas of cognition:
- Concentration
- Processing speed
- Multitasking
- Logic and reasoning
- Organization
- Fast responses
- Working memory
Thought Tracking During Cognitive Remediation Therapy
Thought Tracking During Cognitive Remediation Therapy is valuable for identifying and recording the client’s goals for that day’s Cognitive Remediation Therapy session and understanding how it relates to their overall treatment goals.
Planning to Meet Goals in CRT
The Planning to Meet Goals in CRT worksheet is for clients requiring support and practice in planning, goal-setting, and goal achievement.
Working with the client, answer the following prompts:
- What goal or project are you working toward?
- What date should it be completed by?
- Are there any obstacles to overcome to complete the goal?
- Are there any additional resources required?
- Then consider the steps needed to achieve the goal.
Other free resources
Happy Neuron provides several other free resources that are available for download .

Consider the five Cs when selecting online CRT programs (modified from Medalia et al., 2009):
- Cognitive – What target deficits are being addressed?
- Client – What interests and level of functioning does the client have?
- Computer – What computing requirements and compatibility factors need to be considered?
- Context – Does the software use real-world or fantasy activities and environments? Are they age and cognitive ability appropriate?
- Choice – Is the learner given choice and options to adapt the activity to their preferences?
Once you’ve ordered the software, give it a thorough review to understand when it is most appropriate to use and with whom.
For online CRT programs to be effective as teaching tools and activities, they should include the following features (modified from Medalia et al., 2009, p. 53):
- Intrinsically motivating
- Active use of information
- Multisensory strategies
- Frequent feedback
- Control over the learning process
- Positive reinforcement
- Application of newly acquired skills in appropriate contexts
- Errorless learning – challenging yet not frustrating
Therapists must become familiar with each program’s content and processes so that targeted deficits are fully understood and clients are engaged without confusion or risk of failure.

17 Science-Based Ways To Apply Positive CBT
These 17 Positive CBT & Cognitive Therapy Exercises [PDF] include our top-rated, ready-made templates for helping others develop more helpful thoughts and behaviors in response to challenges, while broadening the scope of traditional CBT.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
A great deal of software “targets different skills and offers a variety of opportunities for contextualization and personalization” (Medalia et al., 2009, p. 43).
We focus on three suppliers of extensive CRT software resources below (recommended by Medalia et al., 2009).
1. Happy Neuron

Happy Neuron provides a wide variety of online brain training exercises and activities to stimulate cognitive functioning in the following areas:
- Visual-spatial

When you’re performing well, the exercises become increasingly difficult.
The exercises are grouped into the following areas:
- Brain speed
- People skills
- Intelligence
3. Games for the Brain

Cognitive difficulties, such as challenges with paying attention, planning, remembering, and problem-solving, can further compound and exacerbate mental health issues
While initially created for schizophrenia, CRT is also valuable for other mental health problems, including eating and mood disorders. Treatments are effective in one-to-one and group sessions, and lessons can be transferred to the outside world, providing crucial gains for a client’s mental wellbeing and social interaction.
Through repeated and increasingly challenging skill-based interventions, CRT benefits cognitive functioning and provides confidence gains to its users. The treatment adheres to learning theory principles and targets specific brain processing areas such as motor dexterity, memory, and visual-spatial perception, along with higher-order functioning.
Involving clients in treatment choices increases the likelihood of ongoing perseverance, engagement, and motivation as activities repeat with increasing degrees of difficulty.
This article offers a valuable starting point for exploring CRT and its benefits, with several worksheets and forms to encourage effective treatment.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. For more information, don’t forget to download our three Positive CBT Exercises for free .
- Bristol Mental Health. (n.d.). Cognitive remediation therapy: Improving thinking skills . Retrieved December 15, 2021, from http://www.awp.nhs.uk/media/424704/cognitive-remediation-therapy-022019.pdf
- Corbo, M., & Abreu, T. (2018). Cognitive remediation therapy: EFPT psychotherapy guidebook . Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://epg.pubpub.org/pub/05-cognitive-remediation-therapy/release/3
- Medalia, A., & Bowie, C. R. (2016). Cognitive remediation to improve functional outcomes . Oxford University Press.
- Medalia, A., Revheim, N., & Herlands, T. (2009). Cognitive remediation for psychological disorders: Therapist guide . Oxford University Press.
- Tchanturia, K. (2015). Cognitive remediation therapy (CRT) for eating and weight disorders . Routledge.
- Tsaousides, T., & Gordon, W. A. (2009). Cognitive rehabilitation following traumatic brain injury: Assessment to treatment. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine: A Journal of Translational and Personalized Medicine , 76 (2), 173-181.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
To my surprise this is a treatment that has not been discussed in the area I live and work. I just stumbled upon this when I was researching cognitive impairments with schizophrenia. I currently work on a team with multiple mental health professionals that go out into the community, to work with people diagnosed with Schizophrenia. It seems like most of what we do is manage and monitor symptoms. Are you aware of anyone or any agency in Buffalo, NY that uses this method of treatment? I am trying to figure out how to get trained and use it in practice, if that is possible. Any help will be greatly appreciated.
This looks like the treatment my daughter needs. She has struggled for years with the cognitive problems associated with depression. How do we find a therapist near us who can use these techniques?
I’m sorry to read that your daughter is struggling. You can find a directory of licensed therapists here (and note that you can change the country setting in the top-right corner). You’ll also find that there are a range of filters to help you drill down to the type of support you need: https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/therapists
I hope you find the help you need.
– Nicole | Community Manager
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Holistic Therapy: Healing Mind, Body, and Spirit
The term “holistic” in health care can be dated back to Hippocrates over 2,500 years ago (Relman, 1979). Hippocrates highlighted the importance of viewing individuals [...]

Trauma-Informed Therapy Explained (& 9 Techniques)
Trauma varies significantly in its effect on individuals. While some people may quickly recover from an adverse event, others might find their coping abilities profoundly [...]

Recreational Therapy Explained: 6 Degrees & Programs
Let’s face it, on a scale of hot or not, attending therapy doesn’t make any client jump with excitement. But what if that can be [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (50)
- Coaching & Application (57)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (45)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (29)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (18)
- Positive Parenting (4)
- Positive Psychology (33)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (17)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

3 Positive CBT Exercises (PDF)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
14 Steps for Problem-Solving Therapy. Creators of PST D'Zurilla and Nezu suggest a 14-step approach to achieve the following problem-solving treatment goals (Dobson, 2011): Enhance positive problem orientation. Decrease negative orientation. Foster ability to apply rational problem-solving skills.
Solution-Focused Therapy is an approach that empowers clients to own their abilities in solving life's problems. Rather than traditional psychotherapy that focuses on how a problem was derived, SFT allows for a goal-oriented focus to problem-solving. This approach allows for future-oriented, rather than past-oriented discussions to move a ...
worksheet. Guide your clients and groups through the problem solving process with the help of the Problem Solving Packet. Each page covers one of five problem solving steps with a rationale, tips, and questions. The steps include defining the problem, generating solutions, choosing one solution, implementing the solution, and reviewing the ...
Outcome goal - I want to be the best at X in the world. Performance goal — I want to better at X. Process goal — I want to train or practice at doing X. Delivery-focused goal — I want to deliver a change, such as a business, technology, or construction project. The type of goal will influence your approach.
18 Problem-Solving Therapy PROBLEM-SOLVING WORKSHEET Briefl y describe the problem (Can it be changed?): State your problem-solving goal (BE REALISTIC): Describe the major obstacles to achieving your goal at this time: a. b. c. Think of alternative ways to achieve your goal. Be creative. List at least 3 solution ideas:
Be as clear and comprehensive as possible. If there are many parts to your problem, describe each of them. TIP: If you find it difficult to separate your emotions from the problem, try to complete this step from the perspective of an impartial friend. Develop Multiple Solutions. Write down at least three solutions to your problem.
the problem, defining your goals for therapy and identifying your values and strengths as a basis for ... worry with new problem-solving skills. To ... On the cost side of this balance sheet, Include the short-term difficulties, personal challenges and avoidance behaviours that you will be prepared to let go of or tolerate to achieve your goals
This easy-to-use template doubles as both a goal-setting tool and a problem-solving worksheet. Not only are you able to set SMART goals, but you also get a cheat sheet for solving even the most difficult problems. By using this template, you get to enjoy the best of both worlds. This template is completely customizable.
The underlying theories behind this worksheet include the principles of cognitive-behavioral theories and problem-solving theories. The relevant therapies may include: Cognitive behavioral therapy- is commonly used to address cognitive distortions and improve problem-solving abilities. Solution-focused brief therapy- focuses on the solutions ...
Part 2: Getting Started with CBT: Setting Goals. Before you can make changes and develop new habits and ways of thinking, it's important to understand exactly what you want to change and what differences you want to see. Once you have determined where you are now and where you would like to go, a beginning and an endpoint, you can use the ...
Problem Solving Worksheet. Step 1. Identify the Problem Break it down into smaller steps and decide what you need to action first. Step 2. Brainstorm and write down as many ideas as you can that might help solve the problem, no matter how silly they seem - don't dismiss any possible solutions. Step 3. Consider the pros and cons of each ...
Problem solving skills are essential for personal growth and success. By developing these skills, we become better equipped to navigate challenges, make informed decisions, and achieve our goals. Free problem solving worksheets offer practical tools that can enhance our problem-solving abilities and promote social emotional learning.
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Problem Solving: Set Goals for your Employees. Here are some examples: To be accommodative of other people's ideas and views and to be willing to take them on board. Research well enough to gather factual information before setting out to solve a problem. Look at things in different perspectives and angles and to develop alternative options.
Here are 12 examples of SMART goals for better problem solving: 1. Define the Problem. "I'll create a plan to define and describe the problem I'm trying to solve by the end of two weeks. This will allow me to identify the exact issue that needs to be addressed and develop an effective solution promptly.".
Avoidance and procrastination let a person avoid these uncomfortable emotions, at a cost. Using the Goal Breakdown worksheet, your clients will learn how to break their goals into smaller and more manageable tasks. The first page includes an example and tips for doing this effectively. The second page is a template for your clients to apply ...
Form Problem Solving Worksheet. The problem-solving skill helps you break down overwhelming sets of problems into more manageable chunks, prioritize which to work on first, and decide what action is best to take. 1.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session. Check-in/Check-out; Doodling Together; Show and Tell; Constellations; Draw a Tree; 28. Check-in ...
Goal Planning. worksheet. Having clear goals has been found to keep clients more engaged in therapy, and improve outcome measures at the end of treatment. Our Goal Planning worksheet is designed to help you accomplish this goal by providing a template for clients to generate short and long-term goals. This worksheet asks clients to come up with ...
Here are some specific SMART IEP goals to enhance problem-solving skills: Goal: The student will identify and define problems in 4 out of 5 situations. Strategies/Activities: Role-playing, group discussions, and problem-solving worksheets. Goal: The student will generate at least two possible solutions to a problem in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
The ADAPT model is a practical tool that can help clients focus on problem-solving. Why not try out the Resilient Problem-Solving Skills worksheet with your client as a way of exploring possible solutions to the problems they face? Ask the client to consider the following ADAPT prompts (modified from Neenan, 2018; Demiris et al., 2010):
Problem Solving Steps • The ProSolv problem solving framework is based on abundant research that supports systematically instructing a step-by-step approach to problem solving following brain injury. • We've chosen to emphasize the key categories and words Problem-
Q-bitz involves the completion of a puzzle made up of small wooden blocks that encourages manual dexterity and a variety of problem-solving approaches.. Other activities require no specialist equipment and yet can be highly engaging and support clients in learning transferable skills (modified from Tchanturia, 2015).