
Personalize Your Experience
Log in or create an account for a personalized experience based on your selected interests.
Already have an account? Log In
Free standard shipping is valid on orders of $45 or more (after promotions and discounts are applied, regular shipping rates do not qualify as part of the $45 or more) shipped to US addresses only. Not valid on previous purchases or when combined with any other promotional offers.

Register for an enhanced, personalized experience.
Receive free access to exclusive content, a personalized homepage based on your interests, and a weekly newsletter with topics of your choice.
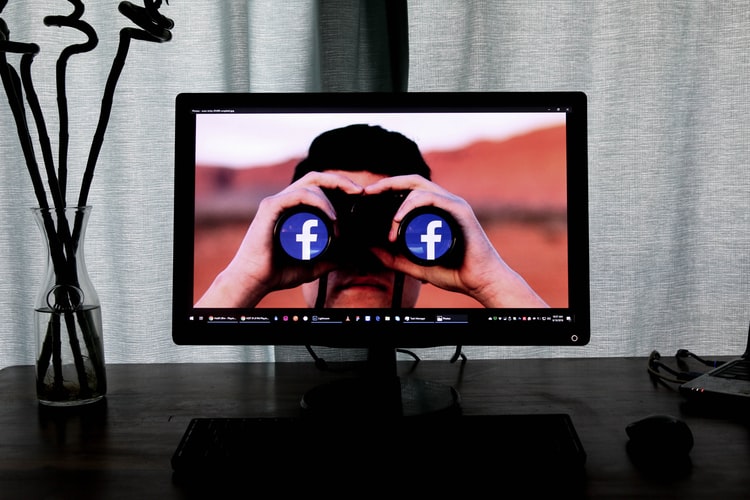
Home / Parenting, Kids & Teens / What is cyberbullying and how can it be prevented?
What is cyberbullying and how can it be prevented?
Please login to bookmark.
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Bullying has blighted childhood and growing up since time began. Bullying can include mean words, teasing, spiteful pranks, the spreading of false rumors, name-calling, the taking of personal items, exclusion from social groups and events, graffiti scrawled on a locker, pushing and shoving, harassment, threats, and in its worst form, physical violence. Bullying is repetitive, not just a single act of aggression.
Kids who are bullied often withdraw socially, begin to underperform academically, feel anxious, sleep badly, and may eventually become depressed and feel trapped if the bullying goes on long enough.
As seen in the media, extreme bullying scenarios have resulted in a tragic and growing list of young people who take their own lives, at least in part to escape persistent bullying.
Most forms of in-person bullying now also take place online, potentially doubling a child’s exposure to bullying. Online, screen-based or technology-based bullying, which can happen across any medium where social interaction takes place, is called cyberbullying.
What is cyberbullying?
Cyberbullying involves actions like:
- Sharing photos or videos of people without consent to embarrass them, make them feel bad about themselves, or enact revenge for a friendship or relationship that has broken down.
- Name-calling, teasing, belittling, mocking or social exclusion.
- Spreading false rumors.
- Creating fake social media accounts in an individual’s name and posting outrageous statements about a peer to isolate, degrade and prank both people.
- Circulating a person’s private messages sent in confidence to a group for amusement and the power of violating privacy.
- Sharing a person’s videos sent in confidence with a chat group or a class to cause embarrassment and ridicule.
- Sending anonymous critical, harassing or threatening messages to people to damage their self-esteem, make them doubt that their friendship group cares for them or instill a sense of not being safe.
- Texting or direct-messaging explicit, unsolicited images, real, altered or fake.
- Leaking an individual’s personal information such as home address or phone number to peer groups to invade privacy and encourage personal attacks.
- Unsolicited forwarding to an individual hurtful or hateful comments that were made by a social peer to undermine confidence and cause conflict within a social group.
- Posting mocking or spiteful comments on an individual’s social media accounts both to cause upset and to encourage other followers, usually from the same school, to join in, triggering group cyberbullying.
While cyberbullying seems at first glance different from in-person bullying, [WNJ1] experts see similarities.
“It’s the same sort of behavior,” says Bridget K. Biggs, Ph.D., L.P., a psychologist at Mayo Clinic. “Verbal aggression like name-calling, relational aggression like spreading rumors and trying to cut people out of relationships, and threatening or physical aggression — the effects are about the same, broadly speaking: lower mood, reduced self-esteem and anxiety, particularly social anxiety.”
Dr. Biggs underscores one key difference: unlike in-person bullying — unless it is caught on school security cameras — cyberbullying can be proved.
“Cyberbullying leaves a trail of indelible evidence, with the exception of disappearing message capabilities unless one can take a screenshot fast enough. But if a peer sends an unflattering or sexualized video or photo, that’s out in cyberspace forever. So there are positives and negatives to this permanence.”
What is the percentage of cyberbullying?
“The good news is that bullying overall, including cyberbullying, tends to decline after its prevalence peaks in mid-adolescence,” affirms Dr Biggs.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that cyberbullying is experienced by the highest percentage of kids in middle schools (33%) followed by high schools (30%) and primary schools (5%).
Among high school students in the U.S., 1 in 6 has been cyberbullied, compared with 1 in 5 who has been bullied in person. Furthermore, for children who identify as LGBTQ+, the Cyberbullying Research Center reports that 31% experience cyberbullying versus 21% of heterosexual students.
It’s no wonder that when Google surveyed U.S. teachers in 2019, bullying and cyberbullying headlined as their No. 1 concern.
What is the difference between cyberbullying and bullying?
Cyberbullying Facts: There are several ways that cyberbullying differs from in-person bullying:
What are the effects of cyberbullying?
If you were ever bullied at school, you’ll remember how quickly you felt shut out of life and how going into school each day was fraught with fear or a feeling of torture. Targets of cyberbullying are affected in much the same way as those bullied in person and can develop some or all of the following symptoms:
- Difficulties sleeping.
- Not wanting to go to school.
- Declining academic performance.
- Acting distracted at home.
- Reduced self-esteem.
- Feelings of not fitting in or belonging.
As the extent or longevity of bullying increase, it’s possible for more extreme reactions to occur, including:
- Self-harming behaviors such as cutting or burning.
- Depression.
- Thoughts of dropping out of school.
- Suicidal thoughts.
- Suicide attempts.
“With traditional face-to-face bullying,” says Dr. Biggs, “when you get home, you at least get a break from it. But if that social connection is also online, then you are still connected via cyberspace when you get home. Cyberspace therefore becomes just one more place to experience bullying.”
In a rare minority of cases, there have been tragic, high-profile stories of kids in the U.S. driven to suicide by cyberbullying. However, research on this subject by Pacer’s National Bullying Prevention Center is careful to underscore that suicide is always complex, with multifaceted drivers.
“There’s an increased risk for suicidality if a child is being bullied, yes,” Dr Biggs adds. “But note that of all the kids experiencing bullying, it’s a really small number who commit suicide. That’s important for parents to know.”
Why do people cyberbully?
As with in-person bullying, bullies court popularity and power and see bullying as a means to exert influence, control friendships, and dominate classrooms and playgrounds. In making others feel small, they feel bigger. There are often familial factors behind bullying and cyberbullying, and those can include witnessing verbal or physical aggression at home, which can lead to similar behavior socially or at school. With cyberbullying, if the bully has a high number of followers on social media, the validation of likes and shares for bullying behaviors can be intoxicating and signal a formula for popularity.
How to stop a child who is cyberbullying
- Explain what cyberbullying is, how it traumatizes others and its consequences.
- Set out what behaviors are unacceptable and explain that you will monitor behavior.
- Praise improved behaviors and set consequences, such as limiting gaming time, if your child cyberbullies again.
- Propose a meeting with administrators at your child’s school if behavior deteriorates.
Is cyberbullying illegal?
Strictly speaking, no. But if cyberbullying touches on laws around stalking, criminal online harassment or sexting that involves third-party possession or wider distribution of nude photos of minors, then authorities can be engaged. And if cyberbullying — as with in-person bullying — leads to a physical attack on the victim, then assault charges may become valid. Relative to state and federal law, schools can intervene when bullying of a student is taking place by another student or group of students, though according to Pew Research Center, only 34% of parents whose child is being cyberbullied report it to the child’s school.
How can parents prevent cyberbullying?
One can’t prevent cyberbullying. After all, it’s impossible to live screen-free in our world today. But Dr. Biggs does advocate parents helping their child divert focus toward building a healthy social circle.
“The effects of being bullied are mitigated when people have strong social support,” she explains. “Even one good-quality friendship can make a difference. If a child has this, then the child may feel able to say ‘That’s a chat group I don’t want to be part of.’ Parents can support their kids by encouraging the fostering of friendships and activities that are positive. You can even ask: ”Who do you want to surround yourself with?’ That’s a very positive coping strategy, surrounding yourself with good people.”
As well as encouraging positive friendships, parents can also help clarify context.
“With cyberbullying,” Dr Biggs says, “if children show you a message that upsets them, which the cyberbully is calling a joke, you might say something like, ‘Well I didn’t find that very funny — I suggest you shrug it off and don’t engage, because this person just wants to pull you in.’ “
Dr. Biggs, a mother of two herself, sees conversations about cyberbullying as just another part of teaching children about online safety.
“Start having conversations about safe behaviors online as soon as your kid begins using technology. That shouldn’t be one conversation; it should be ongoing. You need to talk about phishing, scamming, people who may say they’re somebody but they’re actually somebody else and what information is safe to provide. And you should warn that there are people who do mean things online who might also do mean things in person. If kids already have that awareness, then when it happens, they can think, ‘I remember, a safe adult told me about that and predicted that this is something that could happen.’ “
Overall, though, Dr Biggs advises a delicate balance of supervision and distance.
“Not helicopter parenting and not letting them fly the helicopter,” she says. “Kids are more likely to use the internet safely and positively when their parents pay attention to what they are doing, provide guidance and set limits around use — but also allow some choice, input and autonomous decision-making, all while keeping the lines of communication open between themselves and their kids. It seems that providing some education about the benefits and dangers of the internet — including the possibility of aggression occurring in digital platforms — is beneficial. As with other responsibilities, it makes sense to ease restrictions and allow greater autonomy and choice as kids get older and as they demonstrate their ability to use the resource responsibly.”
How kids can limit their exposure to cyberbullying
- Never respond unless a parent encourages you to assert a clear boundary and take a screenshot of your request — for example, “Please stop saying these things to me,” “I don’t want you to treat me this way” — so it can be used as evidence of online harassment, if needed.
- Take a screenshot of all hostilities to establish a record of evidence.
- Show a parent the messages or comments and talk it over.
- Block and report cyberbullies on social media if doing so won’t inflame an already difficult situation.
- If your parents agree, arrange a discrete meeting with a teacher.
- Use privacy settings to protect personal posts on social media from being accessed by strangers.
- Wait for at least 60 minutes before acting on an impulse to share sensitive photos, videos or information with a peer.
- Have designated digital-free time each day .
The future of cyberbullying
Because it is next to impossible to live in a device-free world while growing up nowadays, parents may fear that nothing can stop their child being cyberbullied. However, Dr. Biggs cites one effective peer-to-peer method that does work: upstanding.
“Upstanding is when witnesses speak up and communicate that aggression is not acceptable and that treating others with respect is socially desirable or ‘cool,’ ” Dr Biggs says. “That does reduce bullying.”
There are also small poignant ways parents can reduce bullying of any type though, as Dr Biggs concludes:
“I heard of a parent responding to news that her child had been bullying another child on the bus. She told her son that she had heard that bullying had been happening — without indicating that she knew who was doing it — and asked him to look out for the child, as she knew that child to be a kind and responsible person. The bullying stopped.”

Relevant reading
Human 2.0 celebrates groundbreaking achievements in medical engineering, offering a glimpse into the future of technology and biology. Advancements have transformed the lives of people with disabilities, enabling them to walk, hear, and create art. It showcases innovations like cochlear implants and pacemakers, along with the stories of pioneers in…

Discover more Parenting, Kids & Teens content from articles, podcasts, to videos.
Want more children’s health and parenting information? Sign up for free to our email list.
Children’s health information and parenting tips to your inbox.
Sign-up to get Mayo Clinic’s trusted health content sent to your email. Receive a bonus guide on ways to manage your child’s health just for subscribing.
You May Also Enjoy

by Pat McCaw, M.D.

Privacy Policy
We've made some updates to our Privacy Policy. Please take a moment to review.
Cyber Bullying Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on cyber bullying.
Cyber Bullying Essay: In today’s world which has been made smaller by technology, new age problems have been born. No doubt technology has a lot of benefits; however, it also comes with a negative side. It has given birth to cyberbullying. To put it simply, cyberbullying refers to the misuse of information technology with the intention to harass others.

Subsequently, cyberbullying comes in various forms. It doesn’t necessarily mean hacking someone’s profiles or posing to be someone else. It also includes posting negative comments about somebody or spreading rumors to defame someone. As everyone is caught up on the social network, it makes it very easy for anyone to misuse this access.
In other words, cyberbullying has become very common nowadays. It includes actions to manipulate, harass and defame any person. These hostile actions are seriously damaging and can affect anyone easily and gravely. They take place on social media, public forums, and other online information websites. A cyberbully is not necessarily a stranger; it may also be someone you know.
Cyber Bullying is Dangerous
Cyberbullying is a multi-faced issue. However, the intention of this activity is one and the same. To hurt people and bring them harm. Cyberbullying is not a light matter. It needs to be taken seriously as it does have a lot of dangerous effects on the victim.
Moreover, it disturbs the peace of mind of a person. Many people are known to experience depression after they are cyberbullied. In addition, they indulge in self-harm. All the derogatory comments made about them makes them feel inferior.
It also results in a lot of insecurities and complexes. The victim which suffers cyberbullying in the form of harassing starts having self-doubt. When someone points at your insecurities, they only tend to enhance. Similarly, the victims worry and lose their inner peace.
Other than that, cyberbullying also tarnishes the image of a person. It hampers their reputation with the false rumors spread about them. Everything on social media spreads like wildfire. Moreover, people often question the credibility. Thus, one false rumor destroys people’s lives.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
How to Prevent Cyber Bullying?
Cyberbullying prevention is the need of the hour. It needs to be monitored and put an end to. There are various ways to tackle cyberbullying. We can implement them at individual levels as well as authoritative levels.
Firstly, always teach your children to never share personal information online. For instance, if you list your home address or phone number there, it will make you a potential target of cyberbullying easily.

Secondly, avoid posting explicit photos of yourself online. Also, never discuss personal matters on social media. In other words, keep the information limited within your group of friends and family. Most importantly, never ever share your internet password and account details with anyone. Keep all this information to yourself alone. Be alert and do not click on mysterious links, they may be scams. In addition, teach your kids about cyberbullying and make them aware of what’s wrong and right.
In conclusion, awareness is the key to prevent online harassment. We should make the children aware from an early age so they are always cautious. Moreover, parents must monitor their children’s online activities and limit their usage. Most importantly, cyberbullying must be reported instantly without delay. This can prevent further incidents from taking place.
FAQs on Cyber Bullying
Q.1 Why is Cyberbullying dangerous?
A.1 Cyberbullying affects the mental peace of a person. It takes a toll on their mental health. Moreover, it tarnishes the reputation of an individual.
Q.2 How to prevent cyberbullying?
A.2 We may prevent cyberbullying by limiting the information we share online. In addition, we must make children aware of the forms of cyberbullying and its consequences.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Essay on Cyberbullying
Students are often asked to write an essay on Cyberbullying in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Cyberbullying
What is cyberbullying.
Cyberbullying is when someone uses the internet, cell phones, or other devices to send or post text or images intended to hurt or embarrass another person. It can happen through a message, email, or on social media sites.
Forms of Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying can take many forms. It can be public or private. Some examples are mean text messages, rumors sent by email or posted on social networking sites, and embarrassing pictures or videos.
Effects of Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying can make a person feel sad, lonely, or scared. They may want to avoid school or social events. In severe cases, it might lead to depression or even suicide.
Preventing Cyberbullying
To prevent cyberbullying, don’t share private information online, and think before you post. Always treat others with respect. If you’re a victim, don’t respond or retaliate. Instead, save the evidence and report it.
Role of Schools and Parents
Schools and parents play a crucial role in preventing cyberbullying. They should educate children about internet safety, monitor their online activities, and encourage them to speak up if they’re being bullied.
250 Words Essay on Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying is when someone uses the internet to hurt, embarrass, or scare another person. It can happen on social media, in online games, or in messages. The person doing the bullying might send mean messages, share personal information, or post embarrassing photos.
Cyberbullying can make a person feel sad, scared, or alone. They might not want to go to school or spend time with friends. It can also affect their grades and their health. Some people might even think about hurting themselves because of cyberbullying.
How to Deal with Cyberbullying
If you are being bullied online, tell a trusted adult. This could be a parent, teacher, or school counselor. You can also report the bullying to the website or app where it happened. Most websites and apps have rules against bullying and can take action.
To help stop cyberbullying, be kind online. Think before you post or send a message. Ask yourself, “Would I want someone to say this to me?” If the answer is no, don’t post it. Also, stand up for others. If you see someone being bullied online, report it.
Remember, everyone deserves to feel safe and respected, both in person and online. By understanding and taking action against cyberbullying, we can make the internet a better place for everyone.
500 Words Essay on Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying is when someone uses the internet, mobile phones, or other digital technologies to harm others. It is a type of bullying that happens online. Unlike regular bullying, cyberbullying can happen at any time and reach a person even when they are alone. It can include things like sending mean or threatening messages, spreading rumors, or posting embarrassing photos or videos.
How Cyberbullying Happens
Cyberbullying can happen in many ways. It can take place through social media sites, chat rooms, text messages, and emails. Sometimes, it can be public, like a mean comment on a social media post. Other times, it can be private, like a threatening text message. Cyberbullies can even create fake accounts to harass someone without revealing their identity.
Cyberbullying can hurt people deeply. It can make them feel scared, sad, or angry. It can also make them feel alone, like no one understands what they’re going through. Some people may even feel unsafe or worry about their reputation. In severe cases, cyberbullying can lead to mental health problems like depression and anxiety, or even self-harm.
There are many ways to prevent cyberbullying. One of the most important is to be kind and respectful online. Remember, the words you type can have a big impact on others. It’s also important to keep personal information private and to think before you post. If you wouldn’t say something in person, don’t say it online.
What to Do If You’re Cyberbullied
If you’re being cyberbullied, remember it’s not your fault. Don’t respond to the bully, as it could make things worse. Instead, save the evidence and report it. You can report it to the website or app where it happened, or to an adult you trust. If the bullying is threatening or severe, you may even need to report it to the police.
Cyberbullying is a serious problem that can hurt people both emotionally and mentally. But by being respectful online, protecting our personal information, and knowing how to respond if we’re bullied, we can help stop cyberbullying. Remember, everyone deserves to feel safe and respected, both in person and online.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Cybercrime Complaints In The Philippines
- Essay on Cyberbullying On Social Media
- Essay on Daily Routine Of A Student
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

Prevent Cyberbullying
Be Aware of What Your Kids are Doing Online
A child may be involved in cyberbullying in several ways. A child can be bullied, bully others, or witness bullying . Parents, teachers, and other adults may not be aware of all the digital media and apps that a child is using. The more digital platforms that a child uses, the more opportunities there are for being exposed to potential cyberbullying.
Warning Signs a Child is Being Cyberbullied or is Cyberbullying Others
Many of the warning signs that cyberbullying is occurring happen around a child’s use of their device. Some of the warning signs that a child may be involved in cyberbullying are:
- Noticeable increases or decreases in device use, including texting.
- A child exhibits emotional responses (laughter, anger, upset) to what is happening on their device.
- A child hides their screen or device when others are near, and avoids discussion about what they are doing on their device.
- Social media accounts are shut down or new ones appear.
- A child starts to avoid social situations, even those that were enjoyed in the past.
- A child becomes withdrawn or depressed, or loses interest in people and activities.
What to Do When Cyberbullying Happens
If you notice warning signs that a child may be involved in cyberbullying , take steps to investigate that child’s digital behavior. Cyberbullying is a form of bullying , and adults should take the same approach to address it: support the child being bullied, address the bullying behavior of a participant, and show children that cyberbullying is taken seriously. Because cyberbullying happens online, responding to it requires different approaches. If you think that a child is involved in cyberbullying, there are several things you can do:
- Notice – Recognize if there has been a change in mood or behavior and explore what the cause might be. Try to determine if these changes happen around a child’s use of their digital devices.
- Talk – Ask questions to learn what is happening, how it started, and who is involved.
- Document – Keep a record of what is happening and where. Take screenshots of harmful posts or content if possible. Most laws and policies note that bullying is a repeated behavior, so records help to document it.
- Report – Most social media platforms and schools have clear policies and reporting processes. If a classmate is cyberbullying, report it the school. You can also contact app or social media platforms to report offensive content and have it removed. If a child has received physical threats, or if a potential crime or illegal behavior is occurring, report it to the police.
- Support – Peers, mentors, and trusted adults can sometimes intervene publicly to positively influence a situation where negative or hurtful content posts about a child. Public Intervention can include posting positive comments about the person targeted with bullying to try to shift the conversation in a positive direction. It can also help to reach out to the child who is bullying and the target of the bullying to express your concern. If possible, try to determine if more professional support is needed for those involved, such as speaking with a guidance counselor or mental health professional.
How to Prevent Cyberbullying

This guide helps parents, caregivers, and youth learn ways to identify, prevent, and address cyberbullying.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Cyberbullying: Everything You Need to Know
- Cyberbullying
- How to Respond
Cyberbullying is the act of intentionally and consistently mistreating or harassing someone through the use of electronic devices or other forms of electronic communication (like social media platforms).
Because cyberbullying mainly affects children and adolescents, many brush it off as a part of growing up. However, cyberbullying can have dire mental and emotional consequences if left unaddressed.
This article discusses cyberbullying, its adverse effects, and what can be done about it.
FangXiaNuo / Getty Images
Cyberbullying Statistics and State Laws
The rise of digital communication methods has paved the way for a new type of bullying to form, one that takes place outside of the schoolyard. Cyberbullying follows kids home, making it much more difficult to ignore or cope.
Statistics
As many as 15% of young people between 12 and 18 have been cyberbullied at some point. However, over 25% of children between 13 and 15 were cyberbullied in one year alone.
About 6.2% of people admitted that they’ve engaged in cyberbullying at some point in the last year. The age at which a person is most likely to cyberbully one of their peers is 13.
Those subject to online bullying are twice as likely to self-harm or attempt suicide . The percentage is much higher in young people who identify as LGBTQ, at 56%.
Cyberbullying by Sex and Sexual Orientation
Cyberbullying statistics differ among various groups, including:
- Girls and boys reported similar numbers when asked if they have been cyberbullied, at 23.7% and 21.9%, respectively.
- LGBTQ adolescents report cyberbullying at higher rates, at 31.7%. Up to 56% of young people who identify as LGBTQ have experienced cyberbullying.
- Transgender teens were the most likely to be cyberbullied, at a significantly high rate of 35.4%.
State Laws
The laws surrounding cyberbullying vary from state to state. However, all 50 states have developed and implemented specific policies or laws to protect children from being cyberbullied in and out of the classroom.
The laws were put into place so that students who are being cyberbullied at school can have access to support systems, and those who are being cyberbullied at home have a way to report the incidents.
Legal policies or programs developed to help stop cyberbullying include:
- Bullying prevention programs
- Cyberbullying education courses for teachers
- Procedures designed to investigate instances of cyberbullying
- Support systems for children who have been subject to cyberbullying
Are There Federal Laws Against Cyberbullying?
There are no federal laws or policies that protect people from cyberbullying. However, federal involvement may occur if the bullying overlaps with harassment. Federal law will get involved if the bullying concerns a person’s race, ethnicity, national origin, sex, disability, or religion.
Examples of Cyberbullying
There are several types of bullying that can occur online, and they all look different.
Harassment can include comments, text messages, or threatening emails designed to make the cyberbullied person feel scared, embarrassed, or ashamed of themselves.
Other forms of harassment include:
- Using group chats as a way to gang up on one person
- Making derogatory comments about a person based on their race, gender, sexual orientation, economic status, or other characteristics
- Posting mean or untrue things on social media sites, such as Twitter, Facebook, or Instagram, as a way to publicly hurt the person experiencing the cyberbullying

Impersonation
A person may try to pretend to be the person they are cyberbullying to attempt to embarrass, shame, or hurt them publicly. Some examples of this include:
- Hacking into someone’s online profile and changing any part of it, whether it be a photo or their "About Me" portion, to something that is either harmful or inappropriate
- Catfishing, which is when a person creates a fake persona to trick someone into a relationship with them as a joke or for their own personal gain
- Making a fake profile using the screen name of their target to post inappropriate or rude remarks on other people’s pages
Other Examples
Not all forms of cyberbullying are the same, and cyberbullies use other tactics to ensure that their target feels as bad as possible. Some tactics include:
- Taking nude or otherwise degrading photos of a person without their consent
- Sharing or posting nude pictures with a wide audience to embarrass the person they are cyberbullying
- Sharing personal information about a person on a public website that could cause them to feel unsafe
- Physically bullying someone in school and getting someone else to record it so that it can be watched and passed around later
- Circulating rumors about a person
How to Know When a Joke Turns Into Cyberbullying
People may often try to downplay cyberbullying by saying it was just a joke. However, any incident that continues to make a person feel shame, hurt, or blatantly disrespected is not a joke and should be addressed. People who engage in cyberbullying tactics know that they’ve crossed these boundaries, from being playful to being harmful.
Effects and Consequences of Cyberbullying
Research shows many negative effects of cyberbullying, some of which can lead to severe mental health issues. Cyberbullied people are twice as likely to experience suicidal thoughts, actions, or behaviors and engage in self-harm as those who are not.
Other negative health consequences of cyberbullying are:
- Stomach pain and digestive issues
- Sleep disturbances
- Difficulties with academics
- Violent behaviors
- High levels of stress
- Inability to feel safe
- Feelings of loneliness and isolation
- Feelings of powerlessness and hopelessness
If You’ve Been Cyberbullied
Being on the receiving end of cyberbullying is hard to cope with. It can feel like you have nowhere to turn and no escape. However, some things can be done to help overcome cyberbullying experiences.
Advice for Preteens and Teenagers
The best thing you can do if you’re being cyberbullied is tell an adult you trust. It may be challenging to start the conversation because you may feel ashamed or embarrassed. However, if it is not addressed, it can get worse.
Other ways you can cope with cyberbullying include:
- Walk away : Walking away online involves ignoring the bullies, stepping back from your computer or phone, and finding something you enjoy doing to distract yourself from the bullying.
- Don’t retaliate : You may want to defend yourself at the time. But engaging with the bullies can make matters worse.
- Keep evidence : Save all copies of the cyberbullying, whether it be posts, texts, or emails, and keep them if the bullying escalates and you need to report them.
- Report : Social media sites take harassment seriously, and reporting them to site administrators may block the bully from using the site.
- Block : You can block your bully from contacting you on social media platforms and through text messages.
In some cases, therapy may be a good option to help cope with the aftermath of cyberbullying.
Advice for Parents
As a parent, watching your child experience cyberbullying can be difficult. To help in the right ways, you can:
- Offer support and comfort : Listening to your child explain what's happening can be helpful. If you've experienced bullying as a child, sharing that experience may provide some perspective on how it can be overcome and that the feelings don't last forever.
- Make sure they know they are not at fault : Whatever the bully uses to target your child can make them feel like something is wrong with them. Offer praise to your child for speaking up and reassure them that it's not their fault.
- Contact the school : Schools have policies to protect children from bullying, but to help, you have to inform school officials.
- Keep records : Ask your child for all the records of the bullying and keep a copy for yourself. This evidence will be helpful to have if the bullying escalates and further action needs to be taken.
- Try to get them help : In many cases, cyberbullying can lead to mental stress and sometimes mental health disorders. Getting your child a therapist gives them a safe place to work through their experience.
In the Workplace
Although cyberbullying more often affects children and adolescents, it can also happen to adults in the workplace. If you are dealing with cyberbullying at your workplace, you can:
- Let your bully know how what they said affected you and that you expect it to stop.
- Keep copies of any harassment that goes on in the workplace.
- Report your cyberbully to your human resources (HR) department.
- Report your cyberbully to law enforcement if you are being threatened.
- Close off all personal communication pathways with your cyberbully.
- Maintain a professional attitude at work regardless of what is being said or done.
- Seek out support through friends, family, or professional help.
Effective Action Against Cyberbullying
If cyberbullying continues, actions will have to be taken to get it to stop, such as:
- Talking to a school official : Talking to someone at school may be difficult, but once you do, you may be grateful that you have some support. Schools have policies to address cyberbullying.
- Confide in parents or trusted friends : Discuss your experience with your parents or others you trust. Having support on your side will make you feel less alone.
- Report it on social media : Social media sites have strict rules on the types of interactions and content sharing allowed. Report your aggressor to the site to get them banned and eliminate their ability to contact you.
- Block the bully : Phones, computers, and social media platforms contain options to block correspondence from others. Use these blocking tools to help free yourself from cyberbullying.
Help Is Available
If you or someone you know are having suicidal thoughts, dial 988 to contact the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline and connect with a trained counselor. To find mental health resources in your area, contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) National Helpline at 800-662-4357 for information.
Cyberbullying occurs over electronic communication methods like cell phones, computers, social media, and other online platforms. While anyone can be subject to cyberbullying, it is most likely to occur between the ages of 12 and 18.
Cyberbullying can be severe and lead to serious health issues, such as new or worsened mental health disorders, sleep issues, or thoughts of suicide or self-harm. There are laws to prevent cyberbullying, so it's essential to report it when it happens. Coping strategies include stepping away from electronics, blocking bullies, and getting.
Alhajji M, Bass S, Dai T. Cyberbullying, mental health, and violence in adolescents and associations with sex and race: data from the 2015 youth risk behavior survey . Glob Pediatr Health. 2019;6:2333794X19868887. doi:10.1177/2333794X19868887
Cyberbullying Research Center. Cyberbullying in 2021 by age, gender, sexual orientation, and race .
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: StopBullying.gov. Facts about bullying .
John A, Glendenning AC, Marchant A, et al. Self-harm, suicidal behaviours, and cyberbullying in children and young people: systematic review . J Med Internet Res . 2018;20(4):e129. doi:10.2196/jmir.9044
Cyberbullying Research Center. Bullying, cyberbullying, and LGBTQ students .
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: StopBullying.gov. Laws, policies, and regulations .
Wolke D, Lee K, Guy A. Cyberbullying: a storm in a teacup? . Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2017;26(8):899-908. doi:10.1007/s00787-017-0954-6
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: StopBullying.gov. Cyberbullying tactics .
Garett R, Lord LR, Young SD. Associations between social media and cyberbullying: a review of the literature . mHealth . 2016;2:46-46. doi:10.21037/mhealth.2016.12.01
Nemours Teens Health. Cyberbullying .
Nixon CL. Current perspectives: the impact of cyberbullying on adolescent health . Adolesc Health Med Ther. 2014;5:143-58. doi:10.2147/AHMT.S36456
Nemours Kids Health. Cyberbullying (for parents) .
By Angelica Bottaro Bottaro has a Bachelor of Science in Psychology and an Advanced Diploma in Journalism. She is based in Canada.
Cyber Bullying Essay Writing Guide — Means to Stop Cyberbullying
Did you know that one in three teenagers faces cyber threats on social networking sites? How about another interesting fact: many teens (more than 25%) have been bullied via their devices. Are these signs alarming? Should parents limit the children's access to mobile phones and computers or restrict their freedom for the sake of prevention from online attacks? Those are all great ideas for a cyber bullying essay. But what are the other features and requirements of this assignment? In our guide, we will go through the basics of a bullying essay and discuss different aspects of this matter. Also, you'll get some relevant tips that will be helpful if your homework is focused on cyberbullying issues.
If you cannot decide on the topic for your assignment or aren't confident about your writing skills — this article is for you.
What is a Cyberbullying Essay?
Without defining the purpose of an academic paper, it's hard to deal with it appropriately. An essay writing about cyberbullying aims to cover the issue of digital bullying by revealing different aspects of this subject and offering relevant examples. Here, you can define this phenomenon, express your attitude toward it, or propose effective solutions to prevent bullying in any manifestation. The main objective of your writing will always depend on the type of essay assigned:
- Descriptive
- Argumentative
- Cause-effect
- Compare-contrast
There is a whole range of factors that can influence your choice:
- The aspect of cyber bullying you want to study.
- A class for which you prepare an assignment.
- The main statement you want to challenge or prove, etc.
In the next section, we'll try to help you with this decision.
Which Genre to Pick for a Writing on Cyberbullying?
The type of essay you pick greatly changes the strategy of your writing. If you select a definition one, you have to identify/explain the term using both official sources, dictionaries, and your best guesses. Don't forget to support your interpretations with real-life examples and personal experience if you have something to say.
- In a descriptive paper, focus on the cyberbullying specifics or people who tend to become cyber bullies.
- In a reflective paper, express your own attitude toward the issue or analyze the consequences of bullying you or your friend have faced.
- In a narrative assignment, tell a story related to the problem. For example, you're an adult, and you want to save your child from the hooligan on the Internet.
- In argumentative writing, you can state that colleges and universities should strengthen campus security and protect students' personal information better. Then, you'll need to prove your idea is valid.
- If you work on the cause-and-effect cyber bullying essay paper, a good choice will be to focus on social media bullying and its influence on young people. So, hope you got the essence.
Also, to understand what to write about and how to meet the writing objectives, you may look for a sample essay on a topic similar to the one you picked. Or, if the cyberbullying is a too complicated subject matter for you, you can turn to our custom writing and editing services. If you need an expert to "do my homework for me," we will be glad to provide you with academic assistance anytime.
If you're going to write this essay yourself, the next aspect you have to consider is the structure.
Outline for a Cyberbullying Essay
The outline for your (for example) social media cyber bullying essay will be similar to the structure of any other writing assignment. You can either make it a 5-paragraph essay or add more sections depending on how many points you are going to discuss. For instance, a compare and contrast paper could be longer than a reflective assignment describing just one experience. Nevertheless, you cannot go wrong with a general essay outline:
- Title page (if needed).
- Introduction (hook sentence + topic presentation + thesis statement).
- Body section(3 or more paragraphs).
- Conclusion (paraphrased thesis + summary of the topic sentences + final statement).
- References/Works Cited (depends on the chosen format: MLA citation, APA citation, etc.).
Let's look at each section in detail.
Introduction to a Cyberbullying Essay
In a cyber bullying essay introduction, the primary goal is to capture the reader's attention from the first line. Thus, we recommend starting with something interesting. One of these hooks related to the topic of cyberbullying should work:
- Fact/Statistics
- Rhetorical question
Once you're done with the hook, explain why the question you plan to discuss is relevant today. End with the powerful thesis statement like: " Taking into account more than 50% of adolescents never tell their parents about being attacked by a cyber bully, schools and colleges should hire qualified experts with whom students will be ready to share intimate details of such situations. "
Body Paragraphs of a Cyberbullying Essay
Start the first body paragraph using a transition word to show its connection with the introduction. Transitions words are "first of all," "to begin with," "thus," "unlike," "in contrast," etc. They all have different purposes, so make sure to choose the best one from the corresponding category (addition, opposition, etc.)
Each body paragraph should start with a topic sentence expressing the major idea of that particular section. Do not forget to add in-text citations and examples to make the reader understand the topic in-depth. Reference the sources correctly on the last page, in your bibliography.
To back your ideas with reliable facts, you have to conduct thoughtful research. Where to look for info that can come in handy? Look thought bullying articles on the Internet, use data from cyber bullying infographic and statistics — even a blog entry with its comment section can turn out to be useful.
The Conclusion to a Cyberbullying Essay
A cyberbullying essay conclusion should persuade the audience about the importance of the issues related to cyberbullying. Or, you have to make the readers think of this matter and its consequences. You may stress why specific preventive measures should be taken, or conclude that restricting access to mobile devices will not resolve the problem. It's up to you and your research results. In the last part of your writing, we recommend including a hook like a rhetorical question to leave a long-lasting impression and keep the reader interested in the topic raised.
10 Thrilling Cyberbullying Essay Topics
The professor may not specify what exactly you should cover in your essay about cyberbullying. That's why we have a list of the best ideas for you:
- The ways mean messages can hurt.
- Reasons to be involved in cyberbullying.
- How a child can become a victim of cyberbullying.
- How to protect yourself from online threats.
- Preventive measures to avoid cyberbullying.
- Differences and similarities between traditional bullying and cyberbullying.
- A hidden name as a way to protect oneself from bullying on the Internet.
- Sexting and its impact on the mind of an average high school student.
- The role of cell phones in the problem of cyberbullying.
- Consequences of cyberbullying and actions to be taken.
There is nothing much to say about a title that you should formulate. If you need one, it has to be a shortened version of the full topic. For instance, is the topic refers to stalling someone's account information to break into their personal life and sending harmful messages, you can make it shorter by narrowing down to "Reasons to Steal One's Account." Make sure your title is no longer than 60-70 characters long, especially when submitting a paper online.
If you struggle to write a good cyberbullying paper but have no ideas on how to hit a good grade, try using our online writing services. We can provide you with an academic assignment 24/7!
- Our Services
- Book Review Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- Essay Editing Service
- Book Reports Online
- Assignment Writing Help
- Personal Statement Writing Service
- Custom Term Paper Writing
- Coursework Writing Service
- Case Study Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Services
- Thesis Writing Service
- Complete Coursework for Me
- Article Writing Service
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Research Proposal Writing Service
- Buy PowerPoint Presentation
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Group Project
- Find Waywriting.com Coupons at CouponChief.com
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Delivery Policy
- Cancellation Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Extras Terms
Don't waste your time Order now!
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Cyber Bullying
Essays on Cyber Bullying
Cyberbullying essay topics and outline examples, essay title 1: unmasking the digital threat: understanding cyberbullying, its impact, and prevention strategies.
Thesis Statement: This essay delves into the world of cyberbullying, examining its forms, the profound emotional and psychological impact on victims, and proactive strategies to prevent and combat this digital menace.
- Introduction
- Defining Cyberbullying: Online Harassment, Trolling, and Social Media Abuse
- Victims' Stories: The Emotional Toll of Cyberbullying
- Cyberbullying vs. Traditional Bullying: Key Differences and Similarities
- Online Platforms and Anonymity: Factors Facilitating Cyberbullying
- Mental Health Consequences: Depression, Anxiety, and Suicidal Ideation
- Prevention and Intervention: Educating Youth, Parental Guidance, and Legal Measures
- Conclusion: Creating Safer Digital Spaces for All
Essay Title 2: The Role of Social Media in Cyberbullying: Exploring Platforms, Trends, and Countermeasures
Thesis Statement: This essay investigates the prominent role of social media in cyberbullying, analyzes emerging trends, and discusses countermeasures employed by platforms and users to mitigate online harassment.
- Social Media and Cyberbullying: Platforms as Virtual Battlegrounds
- Cyberbullying Trends: Online Shaming, Doxxing, and Revenge Porn
- Platform Responsibility: Policies, Reporting Mechanisms, and Content Moderation
- User Empowerment: Digital Literacy, Privacy Settings, and Reporting Abuse
- Case Studies: High-Profile Cyberbullying Incidents and Their Impact
- Psychological Insights: Understanding the Mindset of Cyberbullies
- Conclusion: Navigating the Intersection of Social Media and Cyberbullying
Essay Title 3: Beyond the Screen: The Real-World Consequences of Cyberbullying and Advocating for Change
Thesis Statement: This essay sheds light on the real-world consequences of cyberbullying, including legal ramifications, societal attitudes, and the importance of advocacy in raising awareness and driving change.
- Legal Implications: Laws and Consequences for Cyberbullies
- Societal Attitudes: Victim Blaming, Empathy, and the Role of Media
- Advocacy and Support: Organizations and Movements Combatting Cyberbullying
- Personal Stories: Survivors and Activists Leading the Fight
- Educational Initiatives: Schools, Communities, and Digital Citizenship
- Building Empathy: Fostering Online Communities of Kindness and Respect
- Conclusion: A Call to Action - Eradicating Cyberbullying in the Digital Age
Cause and Effect of Cyber Bullying
Cyberbullying: problem and solution for children, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Cyberbullying: History and Causes, Negative Effects and Solutions
How cyberbullying can impact victims, cyberbullying in social media and the solutions to stop the act, the harm and effects of cyber bullying, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
The Problem of Cyberbullying Through The Form of Bodyshaming
The correlation between cyberbullying and parenting style, the gender differences in cyberbullying, impact of social media on teens: cyberbullying and social comparison, the impact of social media and the effects of cyberbullying, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Continuous Cycle of Cyber Bullying
Cyber bullying, its effects and ways to stop, what is cyberbullying, its bad effects and how to stop it, the social problem and consequences of cyberbullying, discussion on the issue of bullying and cyber bullying, the situation of bullying and cyberbullying in the world and its prevention, how does cyberbullying influence in children, cyber racism – the growth of right-wing extremists and hate speech, privacy and cyber harassment, a discussion on the effects of cyberbullying among the youth in namibia, analysis of the four types of cyber-stalking, a set of laws should be created to impede cyberbullying, cyber stalking: the effects of technology on our privacy, a very serious issue of cyberbullying in bangladesh, cyber stalking and its effect on people, cyber stalking as a form of cybercrime, bullying in the maldives: cyber and school bullying, teenage suicide epidemic and how we can prevent it, influence cyber and school bullying on the mental and physical health, short summary of cyber bullying.
Cyberbullying refers to the harmful and intentional use of digital technologies, such as social media platforms, online forums, or messaging apps, to harass, intimidate, or humiliate individuals. It involves the repeated and deliberate targeting of someone through electronic means, resulting in emotional, psychological, or even physical distress.
Cyberbullying remains a pressing issue in the United States today, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. With the widespread use of technology and social media platforms, instances of cyberbullying have increased, leaving a significant impact on the well-being of those involved. In the US, cyberbullying can take various forms, including sending hurtful messages, spreading rumors, sharing embarrassing photos or videos, or engaging in online harassment through social media platforms. The anonymity and ease of communication provided by digital platforms make it easier for perpetrators to target their victims without immediate consequences. Victims of cyberbullying often experience emotional distress, anxiety, depression, and even thoughts of self-harm. In some extreme cases, cyberbullying has tragically led to suicide. Educational institutions and organizations are increasingly implementing awareness campaigns and anti-cyberbullying policies to address this issue and provide support to victims. Legally, cyberbullying is a complex issue, as it often overlaps with freedom of speech concerns. While some states have enacted specific laws to combat cyberbullying, the legal framework is still evolving to keep pace with technological advancements.
While the term "cyberbullying" itself is relatively new, the underlying behavior has existed for as long as communication technologies have been accessible to individuals. The rise of the internet and social media platforms in the late 20th century provided new avenues for individuals to connect and communicate. However, it also created opportunities for malicious individuals to engage in online harassment, intimidation, and humiliation. The anonymity and perceived distance offered by online platforms have amplified the reach and severity of bullying behaviors. The historical context of cyberbullying also involves the increasing prevalence of smartphones, which have made access to the internet and social media more widespread. The ubiquity of digital devices has blurred the boundaries between online and offline worlds, making it challenging for individuals, particularly young people, to escape the negative effects of cyberbullying.
Harassment: This involves repeatedly sending offensive, threatening, or derogatory messages to an individual. It may include insults, slurs, or hate speech. Public Shaming: Cyberbullies may publicly humiliate or embarrass their victims by sharing personal information, sensitive photos or videos without consent, or spreading rumors online. Cyberstalking: In this form, individuals are repeatedly and obsessively followed or monitored online. Cyberstalkers may track their victims' online activities, gather personal information, or engage in intrusive behaviors. Exclusion and Social Manipulation: Cyberbullies may intentionally exclude or isolate individuals from online communities or social circles. They may spread rumors to damage their victim's reputation or manipulate social relationships. Impersonation: Cyberbullies may create fake profiles or accounts to impersonate their victims and engage in harmful behavior. This can lead to identity theft, reputation damage, and further harassment. Online Hate Groups: Certain online communities or forums may promote hate speech, discrimination, or harassment against specific individuals or groups. These groups may amplify the impact of cyberbullying through collective targeting.
1. Anonymity and Distance 2. Power Imbalance 3. Lack of Empathy 4. Reinforcement and Validation 5. Availability of Technology 6. Peer Influence
1. Emotional Distress 2. Academic Consequences 3. Social Isolation 4. Physical Health Issues 5. Risky Behaviors 6. Long-Term Psychological Effects
Films: Movies like "Cyberbully" (2011) and "Disconnect" (2012) explore the emotional turmoil and psychological effects of cyberbullying on individuals. They aim to convey the harsh realities and consequences of online harassment. Television Shows: TV series such as "13 Reasons Why" (2017-2020) and "Black Mirror" (2011-present) have episodes addressing cyberbullying and its implications. They portray the power dynamics, anonymity, and long-lasting effects of online harassment. Documentaries: Documentaries like "Bully" (2011) provide an in-depth examination of real-life cases, highlighting the experiences of both victims and perpetrators. They create a platform for open discussions and inspire action against cyberbullying.
1. According to a study by the National Center for Education Statistics, approximately 15% of students in the United States have reported being cyberbullied. 2. Cyberbullying often involves anonymous perpetrators who hide behind online identities, making it challenging to identify and hold them accountable for their actions. 3. Research shows that victims of cyberbullying are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. They may also be at a higher risk of suicidal ideation. 4. While cyberbullying is commonly associated with teenagers, it can occur among adults as well. Studies have shown that cyberbullying affects individuals of various age groups, including children, adolescents, and even professionals in the workplace. 5. Unlike traditional bullying, cyberbullying can have a prolonged impact on victims. Hurtful messages and images can be shared and distributed rapidly, leaving a lasting digital footprint that can haunt victims for years. 6. Many instances of cyberbullying involve bystanders who witness the harassment but choose not to intervene or report it. Bystanders can play a crucial role in preventing and stopping cyberbullying by speaking up and supporting the victim. 7. Research suggests that certain social media platforms, such as Instagram and Snapchat, are more commonly associated with cyberbullying incidents. The anonymity, accessibility, and wide reach of these platforms contribute to the prevalence of online harassment. 8. In many jurisdictions, cyberbullying is considered a criminal offense. Laws and regulations have been implemented to address cyberbullying, and perpetrators can face legal consequences, including fines and imprisonment.
The topic of cyberbullying is of utmost importance to write an essay about due to its significant impact on individuals, especially in the digital age we live in today. Cyberbullying has emerged as a pervasive form of harassment, affecting people across various age groups, from children to adults. Understanding and addressing this issue is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, cyberbullying can have severe emotional and psychological consequences on victims. It can lead to anxiety, depression, low self-esteem, and even suicidal ideation. By exploring the psychological effects, an essay can shed light on the urgency of providing support systems and intervention strategies for those affected. Secondly, the internet and social media platforms have become an integral part of our lives, making cyberbullying a widespread concern. Investigating the topic can provide insights into the dynamics of online interactions and help identify effective prevention and intervention measures. Lastly, cyberbullying raises important ethical and legal questions. Understanding the ethical implications of online behavior and the legal frameworks surrounding cyberbullying can contribute to the development of policies and regulations that protect individuals and promote responsible digital citizenship.
1. Campbell, M. A. (2005). Cyber bullying: An old problem in a new guise?. Journal of Psychologists and Counsellors in Schools, 15(1), 68-76. (https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-psychologists-and-counsellors-in-schools/article/abs/cyber-bullying-an-old-problem-in-a-new-guise/6BACCB0B9F027416CB527B72421C3EEC) 2. Fauman, M. A. (2008). Cyber bullying: Bullying in the digital age. American Journal of Psychiatry, 165(6), 780-781. (https://ajp.psychiatryonline.org/doi/full/10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.08020226) 3. Mishna, F., Saini, M., & Solomon, S. (2009). Ongoing and online: Children and youth's perceptions of cyber bullying. Children and Youth Services Review, 31(12), 1222-1228. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0190740909001200) 4. Slonje, R., & Smith, P. K. (2008). Cyberbullying: Another main type of bullying?. Scandinavian journal of psychology, 49(2), 147-154. (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1467-9450.2007.00611.x) 5. Smith, P. K., Del Barrio, C., & Tokunaga, R. S. (2012). Definitions of bullying and cyberbullying: How useful are the terms?. In Principles of cyberbullying research (pp. 26-40). Routledge. (https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780203084601-5/definitions-bullying-cyberbullying-peter-smith-cristina-del-barrio-robert-tokunaga) 6. Gardner, D., O’Driscoll, M., Cooper-Thomas, H. D., Roche, M., Bentley, T., Catley, B., ... & Trenberth, L. (2016). Predictors of workplace bullying and cyber-bullying in New Zealand. International journal of environmental research and public health, 13(5), 448. (https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/13/5/448) 7. Hamm, M. P., Newton, A. S., Chisholm, A., Shulhan, J., Milne, A., Sundar, P., ... & Hartling, L. (2015). Prevalence and effect of cyberbullying on children and young people: A scoping review of social media studies. JAMA pediatrics, 169(8), 770-777. (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/article-abstract/2337786) 8. Yao, M., Chelmis, C., & Zois, D. S. (2019, May). Cyberbullying ends here: Towards robust detection of cyberbullying in social media. In The World Wide Web Conference (pp. 3427-3433). (https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3308558.3313462) 9. Lowry, P. B., Zhang, J., Wang, C., & Siponen, M. (2016). Why do adults engage in cyberbullying on social media? An integration of online disinhibition and deindividuation effects with the social structure and social learning model. Information Systems Research, 27(4), 962-986. (https://pubsonline.informs.org/doi/abs/10.1287/isre.2016.0671) 10. Samghabadi, N. S., Monroy, A. P. L., & Solorio, T. (2020, May). Detecting early signs of cyberbullying in social media. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Trolling, Aggression and Cyberbullying (pp. 144-149). (https://aclanthology.org/2020.trac-1.23/)
Relevant topics
- Gun Violence
- Animal Testing
- Sexual Abuse
- Youth Violence
- Animal Rights
- Violence in Video Games
- Controversial Issue
- Homelessness
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Crime Cyber Bullying
The Solutions To Prevent And Avoid Cyberbullying
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Domestic Violence
- Drunk Driving
- School Shooting
- Sexual Harassment
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
150 Bullying Topics for Essays + Examples
Looking for an exciting research topic about bullying? This problem is very controversial, sensitive, and definitely worth studying
🔝 Top 10 Bullying Topics for Research Papers
📚 bullying subtopics, 🏆 best bullying topics to write about, 🧒 topics about bullying and child development, ⚡ most shocking bullying topics to write about, 🖊️ causes of bullying: title ideas, ✅ simple & easy shocking bullying essay titles, 🔎 effects of bullying: research questions, ✍️ bullying essay topics for college, 🏫 school bullying titles, ❓ research questions about bullying, 📱 topics on bullying on social media platforms, 📃 bullying essay: writing tips.
Examples of bullying can be found everywhere: in schools, workplaces, and even on the Internet (in the form of cyberbullying).
In this article, we’ve collected top bullying research paper topics and questions, as well as bullying essay samples and writing tips. Get inspired with us!
- The Problem of Bullying and Possible Solutions
- Character Traits of Bullying
- School Bullying and Moral Development
- The Effects of Cyber-Bullying and Cyber-Stalking on the Society
- Is Cyber Bullying Against Teenagers More Detrimental Than Face-To-Face Bullying?
- Cyber Bullying Issue
- Bullying and Its Effects in Society
- The Impact of Workplace Bullying
- Verbal Bullying at School: How It Should Be Stopped
- The ABC Model of Crisis: Bullying at School
Bullying means repeated aggressive behavior toward individuals. It comes in many forms, all of which hurt a victim’s physical and mental well-being. Read on to discover the most prevalent types of bullying.
Physical Bullying
Physical bullying is the most widespread type of bullying among teenagers. It involves using physical force or actions to scare or dominate someone and harm their body or belongings. Apart from the physical injuries sustained during the attacks, victims may develop many health issues, such as somatization.
Verbal Bullying
Verbal bullying is emotional abuse involving relentless insults, taunts, and name-calling to erode a person’s self-esteem over time. The victim can experience lasting damage, struggling with anxiety, depression, and social isolation. In severe cases, persistent negativity can even trigger thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
Social Bullying
Social bullying mainly relies on manipulation: spreading rumors, using humiliating nicknames, and poisoning someone’s online presence. The victim may not even realize they are being abused because the line between playful teasing and social bullying is often unclear. As a result, this can delay them from seeking help, potentially leading to severe consequences.
Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying is a form of aggression where modern technology is used to hurt others. Abusers spread offensive messages, tweets, posts, personal information, and other material to humiliate, frighten or upset their victim. Online bullying can be particularly damaging and frustrating as it is often anonymous or hard to trace.
- Bullying on Social Media Platforms It is consistent and repeating, taking advantage of the Internet’s anonymity with the main goal to anger, scare, or shame a victim.
- Moral Development and Bullying in Children The understanding of moral development following the theories of Kohlberg and Gilligan can provide useful solutions to eliminating bullying in American schools.
- Workplace Bullying and Its Impact on People and Society The paper follows a traditional structure with the introduction and body paragraphs that provide essential information devoted to the problem, and improve the understanding of the concept of bullying.
- Problem of Childhood Bullying in Modern Society To begin with, the family which is the basic and the most important unit in the society as well as the primary socializing agent plays a major role in shaping behavior of children include bullying.
- Social Influence on Bullying in Schools The theory helps us to understand why the stronger members of the school population are likely to “rule” over the weaker members of the school as described in the social hierarchy concept in the theory.
- Bullying and Cyberbullying in Modern Society Cyberbullying among adolescents and teenagers is defined as the purposeful and repetitive harm done by one or more peers in cyberspace as a result of using digital devices and social media platforms.
- Sexual Bullying in Schools and Its Influence The author states the difference in the mental and physical maturation of girls and boys as one of the core roots of the issue.
- Nature of Bullying In this paper, central focus is going to be on the nature of bullying of children in my hometown, Orlando Florida, how it can be solved, and most importantly; establishing the importance of having knowledge […]
- Bullying and Suicide Among Teenagers Specific objectives Analyze the causes of bullying among teenagers in the country Analyze the effects of bullying among victims, perpetrators and by-standers Analyze the relationship between bullying in school and suicide among teenagers in the […]
- Bullying: Violence in Children and Adolescents Bullying is one of the most common manifestations of peer violence in children and adolescents. Prevention of bullying, cyberbullying included, has to occur in accordance with the IBSE Standards of social and emotional learning.
- Bullying, Its Forms, and Counteractions In addition, it is necessary to support those at the center of this bullying, as this can protect them from harmful effects and consequences.
- Incivility, Violence, and Bullying in the Healthcare Workplace The following step is to gather the team and communicate the necessity of change, assigning some individuals for the positions related to the change, in other terms, a support team.
- Effective Ways to Deal With Bullying in US Schools Teachers should ensure the bully is aware of the improper behavior, why it is improper, and the repercussions of the behavior.
- Network Bullying: School Policy Framework The first step is to have a careful conversation with the student and an assessment by the school psychologist to ensure that there is a fright.
- How to Reduce Bullying in Senior Facilities One of the main reasons an individual may commit suicide due to bullying is because it may make an individual develop a negative self-image after the bullying incident. Some of the major bullying incidences that […]
- Active Shooter and Nursing Bullying Nurses should lock all doors and use tables and other objects to reinforce them to prevent any possibility of the active shooter getting to the patients’ room.
- Racist Bullying Among Black Students in US Universities This research focuses on the impact of bullying and racism among African American students in the country. What are the impacts of bullying and racism among Black students in U.S.universities?
- Bullying and Autism Spectrum Disorder In fact, bullying as a social phenomenon can be characterized as a social and interaction issue; therefore, it is possible to analyze the connection between autism and acts of bullying and inappropriate behavior.
- Eliminating the Problem of Online Bullying Eliminating the problem of online bullying is vital for improving the mental health of adolescents and young adults and allowing them to build their lives free of adverse external influences. It is possible to see […]
- Bullying and Harassment in the Healthcare Workplace This paper is written to explore the origins of discrimination and harassment in the healthcare workplace. Bullying begins early in medical college and residencies; it has been referred to as an element of the learning […]
- Queer (LGBT) Teenage Bullying at School The importance of this source to the research is associated with the significant role that youth organizations have to play towards minimizing bullying among LGBT students.
- Bullying of Children: Misconceptions and Preventive Measures As a result, the density of shows and articles devoted to bullying creates an illusion that this event appears more often than it does in reality.
- Bullying Behavior and Impact of Hegemonic Masculinity Rosen and Nofziger applied a quantitative research design to explore the relationships between students’ bullying experiences and race, age, and socioeconomic status and identify the frequency of bullying.
- Bullying and Incivility in Clinical Setting The problem of bullying and incivility in a clinical setting can negatively affect the quality of care provided, so it needs to be managed.
- Bullying and Its Influences on a Person It is common for victims of bullying to develop mental health issues, as they were placed in stressful situations and had a constant fear along with depression in some cases. Making friends is one of […]
- “Bullying in Schools”: The Aspects of Bullying In their article, Menesini and Salmivalli examine the current state of knowledge on the topic and thoroughly discuss all of the aspects of bullying.
- Analysis of Bullying and Parenting Style Since the given topic usually refers to children and adolescents, it is evident that their parents hold a portion of responsibility because the adults affect the growth and development of young individuals.
- Hate Crimes – Bullying More than two-thirds of children and adolescents experience bullying and more than one-fourth of them report extreme forms of coercion.
Bullying has been connected to many developmental issues in children. Increased risks of depression, anxiety, and social problems are just a few of them. Bullying may also lead to substance abuse, self-harm, and stunted academic and professional growth.
Here are some fresh topics about bullying and child development:
- The link between bullying and self-esteem in children.
- How does witnessing bullying affect young on-lookers?
- Poorer educational attainment as an outcome of school bullying.
- Bullying and its correlation with childhood depression and anxiety.
- Can bullying in elementary school jeopardize future opportunities for children?
- Bullying Management: Mass Awareness Program Bulletin.”Teachers, trained to help to rebuild trust, confidence, growth, and commitment through mass awareness to arrest bullying in high schools”. The proposed mass action program is meant to promote awareness on the need to stop […]
- An Anti-Bullying Program Integrated With PRAISE by Ackerman I chose to describe bullying because of the importance of the topic and due to my personal interest in it. Education will eliminate most of the reasons for bullying and provide students with the E […]
- Bullying Through Social Media: Methods An Informed Consent Document will be provided to participants prior to the research, explaining the purpose of the study and promising to protect their identity.
- Bullying Through Social Media: Research Proposal The hypothesis of the study is as follows: the role of adolescents in a cyberbullying situation is interconnected with their psychological characteristics.
- Bullying Through Social Media In particular, inequality in the position of the persecutor and the victim is evident – the aggressor can be anonymous, and there can be many of them.
- Bullying of Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic Then, the principles of adult learning will be used to develop and implement an information product to improve the nursing workforce’s bullying awareness and the knowledge of healthy conflict resolution in the workplace.
- Bullying in Healthcare Organizations: Impact on Nursing Practice Bullying in business entities is a common phenomenon, but the extent of its influence on the “production process” in healthcare and medicine institutions is only beginning to be recognized.
- Workplace Bullying Among Nurses in the Acute Setting Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the frequency of conflicts between nurses and their colleagues and managers has increased significantly in my workplace.
- Bullying Perpetration Among School-Aged Children Mucherah et al.examined how the school climate and teachers’ sanctions against bullying relate to the risk of becoming a victim or perpetrator of bullying.
- Programming for a Year 5 Class on Bullying As a result, in Lesson 6, they will offer their project addressing bullying behaviour and present it to their class, which is the main aim of the Unit Plan.
- Injury and Violence Prevention: – Bullying The aim of preventing injury and violence from bullying is to enable the student to have a healthy social and physical life that will enable them to perform well in their studies and live healthily.
- Cyber-Bullying vs. Traditional Bullying: Its Psychological Effects The researchers presented the recent statistics in order to illustrate the negative social and psychological effects of cyber-bullying in contrast to the traditional bullying in schools.
- Bullying in the Workplace Old Nurse to New Nurse This unvoiced scourge in nursing is characteristically encouraged by the need of bullies to have a total control of a person. Resignation of nurses due to bullying can lead to shortage of nurses in hospitals.
- Bullying and Peer Abuse Especially at work, targets fear coming to work and this will have an adverse result in the efficiency of the staff in the hospital.
- Bullying in the Nursing Workplace Bullying in the nursing workplace, in this case, causes the one bullied to have a feeling of defenselessness and takes away the nurses’ right to dignity at his or her workplace.
- Cyber Bullying and Positivist Theory of Crime Learning theory approaches to the explanation of criminal behavior have been associated with one of the major sociological theories of crime, the differential association theory.
- Cyberbullying and Bullying: Similarities While deciding on fitting and balanced sanctions, it is vital to reflect on the ways in which cyberbullying events differ in effect in comparison to other forms of bullying.
- Protection From Bullying: Methods That Work Because of this, it is vital that parents, teachers, and guardians educate themselves on the nature of bullying and work together to develop effective methods and strategies that would help to overcome the problem.
- Psychology: Social Media and Bullying The purpose of this paper is to discuss the issue of social media and bullying and express the author’s opinion on the matter.
- “Bullying Behavior Among Radiation Therapists” by Johnson and Trad The literature review encompassed a considerable number of sources pertinent to the study and recent enough to be relevant; all the publications were dated within the last fifteen years.
- Human Rights Issues in Australia: Bullying Among School-Going Age and Young People The focus of the topic of the day is on bullying. It is used to prevent or avoid the occurrence of a bullying experience.
- Bullying and Worker’s Harassment in Western Australia In most of the armed services in Australia, new recruits and women are commonly the victims of bullying and harassment despite the fact that it is unacceptable.
- Behaviour Management: Bullying The typical behaviors which I saw in the child who got bullied are: The victim of this bullying is physically weak and a soft-natured one.
- Cyber-Bullying Is a Crime: Discussion It is easy to see the effects of cyber-bullying but it is hard to find out who is the bully making it hard for authorities to pin the blame on the perpetrator of a crime […]
- Conflict Resolution Tactics and Bullying This study is interesting to the extent that it shows how the social environment impacts the development of a child and how it shapes his or her conflict resolution techniques.
- School Bullying: Case Analysis Even today there is no generally accepted definition of bullying but it is thought that when an individual is for a long period of time is exposed to repeat negative actions and behavior by one […]
- Bullying in the Workplace as a Psychological Harassment Another form of bullying in the workplace is physical assault in the sense that if the workers are not at ease with each other and when the rules and regulations are not at all observed, […]
Teenagers bully for various reasons, including a need for power or control, revenge, social status, etc. They may also bully to receive attention or seek validation or excitement by creating drama. Sometimes, bullying is a misguided attempt to fit in or avoid being bullied.
See some topics on causes of bullying:
- How does home life provoke bullying tendencies?
- Childhood trauma: a hidden factor in bullying behavior.
- Payback as one of the bullying causes.
- Analyzing bully development through the prism of peer pressure.
- Power, status, and pain: what drives teens to bully?
- “Adolescents’ Perception of Bullying” by Frisen et al. The second and the third aims of the study were “to describe how adolescents perceive bullies” and “to describe what adolescents believe to be important in order to stop bullying”, respectively.
- The Long Term Effects of Bullying in Elementary School Wolke and Lereya argue that the problem is that the majority of studies on bullying are cross-sectional and only use follow-ups after a short period of time.
- Workplace Bullying, Salivary Cortisol and Long-Term Sickness Absence The purpose of this cohort-based study was to investigate the extent to which cortisol levels were associated with sickness absence and the relationships between workplace bullying and sickness absence through the prism of cortisol use.
- Workplace Bullying in Australia It is possible to offer several recommendations that can reduce the risk of bullying in organisations. In this case, more attention should be paid to the absence of mechanisms that can protect the victims of […]
- Domestic Violence and Bullying in Schools It also states the major variables related to bullying in schools. They will confirm that social-economic status, gender, and race can contribute to bullying in schools.
- The “Bully-Free” Initiative: Bullying in Education The students need to have a clear idea that bullying goes against the rules of the school and which actions may be considered bullying.
- Gender and Bullying Issues in Nursing A lack of tolerance for workplace harassment and bullying is likely to lead to the deterioration of the situation and further misunderstanding and tension in an organization.
- Bullying and Cyberbullying Among Peers They are facing the dilemma of how to react, whether they have to fight a superior force of the enemy or to complain to teachers and parents, undermining their reputation.
- Bullying Prevention Programs Some teachers and professors claim that their students cannot show their potential in their hobbies due to the limitations they experience because of bullies around them. As it is mentioned above, educators do not control […]
- Bullying and Its Impact Thus, the current paper is dedicated to the issue of bullying and its effects as well as anti-bullying practices as related to peer victimization.
- Fights and Bullying Among Middle School Learners Alongside the positivist philosophy, the research adopted the survey strategy that involved the use of self-administered questionnaires to collect from the participants.
- Dealing With Workplace Bullying According to the report presented by the University of Louisville, workplace bullying is a repeated action of one employee or a group of employees towards another individual or group. Dealing with bullying in the workplace […]
- Amanda Todd’s Bullying and Suicide Story She was fifteen years old, and her story created a major uproar in the press, as it showed the true nature of bullying and the effects it has on the person.
- Bullying in America: Causes and Prevention That is why it is important to pay attention to the reasons why bullying occurs and ways in which it can be reduced.
- Bullying as Social and Criminal Deviance The most important step in the student’s guide to research that I would need to analyze bullying is defining the topic.
- Bullying and Legislation in Australian Workplace According to the authors of the article, workplace bullying can be characterized as internal violence. According to the authors of the article, bullying is a widespread phenomenon and is a common attribute of many organizations.
- Bullying at Australian School: Causes and Solution The technological breakthrough that was witnessed in the late 90s and the early 2000s also contributed to the development of the phenomenon, sparking the concepts such as cyberbullying and online bullying.
- Workplace Bullying in The Playground Never Ends The primary reason for becoming a bully is primarily seen in fear to lose authority or formal positions in an organization and have more institutional power than that of the targets.
- College Students: Suicide and Bullying-Methods The analysts used this tool to report the mood of the participants by posting quizzes, which the students answered while filling the questionnaire.
- Girl-To-Girl Bullying and Mean Stinks Program The positive results can be achieved by the implementation of the multiple educational programs, the increase in public awareness, and promotion of the values of the healthy relationships.”Mean Stinks” is exactly the program with the […]
- Association of Parenting Factors With Bullying The lack of the parental support is the main cause of students’ deviant behaviors at school, including the cases of bullying, and those parents who pay much attention to developing their career cannot provide the […]
- Workplace Bullying and Its Impact on Performance Workplace bullying refers to a deliberate, repeated, and continuous mistreatment of a worker or a group of workers by one or more colleagues in the workplace.
- The Problem of Workplace Bullying In particular, this paper will include the discussion of the research articles, reports and case studies that describe the causes of workplace bullying and the strategies used by companies in an effort to overcome it.
- College Students: Suicide and Bullying The misconception that bullying is a minor issue among college students has contributed to the high number of students who suffer because of bullying.
- Social Psychological Concepts of Bullying and Its Types Some of the factors that contribute to bullying include poor parenting, economic challenges, lack of mentorship, and jealousy among others. One of the main concepts used to explain bullying is that of parenting roles and […]
- Homosexual Students and Bullying Specifically, the section addresses the prevalence of bullying in schools and the level of bullying in bisexuals, gay males, and lesbians.
- Social Psychology of Violence and Bullying in Schools Bullying is a common phenomenon in schools and it is reported that it results in violence in learning institutions in the end.
- Bullying and Child Development Bullying is one of the common vices in schools that influences a lot of growth and development of children. Bullying also affects the ability of children to concentrate in school because they are always on […]
Bullying is a social virus that infects everyone around it. It leads to decreased self-esteem, escalated anxiety, and depression among victims. Additionally, witnesses of bullying often experience feelings of fear and helplessness, which can damage their mental health and social interactions.
Look at these research questions on bullying effects:
- Why do bullies and victims of bullying often turn to drugs or alcohol?
- How can hurtful words keep affecting someone’s mental health for years?
- How does bullying influence children’s physical health?
- How can the anonymity of online bullying contribute to anxiety development?
- Do bullying outcomes vary based on the victim’s age and gender?
- Bullying and Suicide: The Correlation Between Bullying and Suicide Nonetheless, the extensive research shows that the correlation exists and bullying is one of the risk factors for development of suicidal ideas in adolescents.
- Cyber Bullying Prevention in Learning Institutions: Systematic Approach To start with, the students are provided with ways of reporting their concern to the educational institution, and when the staff members of the institution receive the report, they evaluate the information together with the […]
- Discouraging and Eliminating Cyber Bullying Resources Role of the resource/input Statement forms To facilitate information transfer to the staff Counseling Personnel To arm students against the problem Bullying report system To create efficient internet enhance report system Regulation implementation documents […]
- School Bullying: Methods for Managing the Problem The investigation of relevant studies on the methods for stopping school bullying reveals that the most effective ways of eliminating this type of behavior include providing training for teachers, encouraging students to participate in the […]
- High School Bullying Effective Responses Emphasis will also be made on the kind of audience to read this article because the contents of this study need to be at par with other similar articles in the journal to be selected.
- Bullying as a Relational Aggression This resistance has been one of the obstacles to eliminating the cyber bullying in the schools. Schools and districts have been involved in the Challenge Day activities where children are advised on how to handle […]
- Bullying in the Workplace Organizational leaders have an ethical obligation to ensure that they deal with cases of bullying within the workplace in a professional manner that demonstrates equality, honesty, and high sensitivity to the needs of others.
- Social Bullying in Jeff Cohen’s “Monster Culture” It is clear that his part of character is mostly dominant in the childhood stages, as children are not able to develop a sense of morality and predict the consequences of their actions.
- Cyber Bullying and Its Forms The difference between the conventional way of bullying and cyber bullying is that in conventional bullying, there is contact between the bully and the victim.
- Problem of the Managing Bullying and Harassment in the Workplace Employees in an organization have a specific role that they are supposed to play and this means that there might be shortcomings which should not lead to bullying.
- School Bullying: Causes and Police Prevention It is for this reason that there has been need for the intervention of the community and the government to address the issue of bullying schools lest the school environment becomes the worst place to […]
- Cyber Bullying as a Virtual Menace The use of information and communication technologies to support a deliberate and most of the time repeated hostile behavior by an individual or groups of people with the sole intention of harming others, one is […]
- Ban High School Bullying A number of stakeholders contribute to the high prevalence of bullying in American schools. Schools that ignore bullying are a big part of the problem and they need to be held accountable.
- The Problem of Bullying While most states in the United States of America have laws to protect people from bullying, the federal government is yet to enact an anti-bullying law.
- Ethical Case: Facebook Gossip or Cyberbullying? The best option to Paige is to apologize publicly and withdraw her comments. The final stage is to act and reflect the outcome of the choice made.
- Bullying on the Rise: Should Federal Government Enact Federal-Bullying Laws? This paper will thus use both primary and secondary data to discuss the prevalence of bullying in schools and whether the federal govern should enact federal laws to curb the social vice at school.
- Bullying in School Face-to-face bullying is an interesting area of study because it clearly demonstrates bullying in school. Students consider bullying as a school culture even though it is contrary to the school rules and regulations of schools.
- Bullying in the Schools Furthermore, the law states that training should be done to the teachers as well as the other members of staff on how to deal with bullying and the law also needs the schools to report […]
- The Issue of Bullying in the Schools It gives me joy to know that the issue of bullying is now a pubic affair since bullying stories were unheard of when I was growing up.
- Troubled Adolescent due to Bullying His lowered self-esteem would make him to observe the common behaviours of the older boys quietly and accept the situation as a cultural practice.
According to statistics, around 19% of American middle and high school students reported being bullied in school in 2021-2022. School bullying involves ongoing physical, emotional, and verbal aggression, cyberbullying, sexual abuse, etc. The impact of these behaviors extends beyond immediate harm, damaging victims’ long-term mental health and academic progress.
Check out some school bullying titles:
- Exploring the prevalence of bullying among students with disabilities.
- The role of bystanders in school bullying.
- Warning signs of bullying in high school.
- The peculiarities of physical bullying in elementary students.
- The components of effective anti-bullying school policies.
- Workplace bullying: does it exist?
- What are the three key elements of bullying?
- How does bullying affect those who observe it?
- Direct and indirect bullying: what is the difference?
- What families do bullies typically come from?
- Aggressive children: what is their future?
- How to prevent bullying in schools?
- School bullying and domestic violence: is there a connection?
- Cyberbullying: how to prevent it?
- What can parents do to prevent their children from bullying?
The rise of technology has brought a dark side to social interaction: cyberbullying. Social media platforms, which were intended to connect people, have instead become breeding grounds for online harassment and targeting. Bullies take advantage of the perceived anonymity of these platforms to unleash cruelty. They often employ blackmailing, online stalking, grooming, and trolling.
We have prepared some topics on online bullying that can come in handy:
- The legal challenges of addressing cyberbullying on social media.
- Setting up a false profile as a form of cyberbullying.
- How can bullying on social media platforms be reported?
- The role of teachers and educators in addressing cyberbullying.
- How do memes and viral content contribute to bullying on Instagram?
A bullying essay is a popular assignment in various subjects, including psychology, sociology, and education. Writing an excellent paper on the matter requires more than just in-depth research and planning. Don’t worry; there are some tips that will make writing an essay on bullying much easier:
- Choose a topic that allows analyzing and interpreting the problem. Instead of merely describing what bullying is, try to dig deeper into its causes, consequences, and solutions. If your professor didn’t suggest any topics, you may research bullying essay topics online and select one that would be exciting for you to explore.
- Read sample articles and papers online to see how other students approached the subject. Notice the bits that work and don’t work, and write them out to make the process of creating your essay easier. If you’re struggling with finding enough examples online, you may want to expand your search to discrimination essay topics and materials.
- Research what scholars say about bullying. Articles in scholarly journals are an excellent source of information because they are usually trustworthy. If you’re still in school, your ability to navigate the library or online databases will also impress your tutor. As you start researching, you will find that there is a great variety of studies, and it’s challenging to find the relevant ones. Narrowing down your search would help you to do that. For instance, if you are writing a cyber bullying essay, try searching for social media bullying or online anti-bullying services.
- Include real-life experiences where relevant. Unfortunately, bullying is a common problem in many institutions, and if you haven’t experienced it, your friends or family members probably have. If your tutor allows personal input, explore real-life experiences with bullying. Note the effects, preventive measures that worked or didn’t work, and what a person used to cope with bullying. If personal input is not allowed, you could ask your friends or relatives for ideas and then find high-quality sources that discuss similar problems.
- If you can, be creative about it! A powerful bullying essay example draws from a variety of sources to present material in a creative way and engage readers. Hence, this might be an excellent opportunity for you to include images or graphs in your paper. For example, anti-bullying posters could complement the sections of your work that talks about solutions to the problem. Quotes about bullying coming from famous persons would also be influential, especially if you include them at the beginning of your piece. If you like drawing or painting, you could try to put some of your ideas in graphic form – this will definitely earn you some extra marks! Just make sure to check with your tutor to see whether or not creative input is allowed.
- Structure your paper well to avoid gaps or inconsistencies. It would be beneficial to create a detailed bullying essay outline before you start working. A typical essay should include an introduction, two to three main paragraphs, and a conclusion. The first paragraph of your work should consist of some background information, whereas the last one should restate the points and close up the paper. A good bullying essay introduction should also feature a thesis statement that shows what the piece is about.
These tips will help you to write top-notch essays on bullying, as well as on related subjects. Don’t forget to browse our blog some more to find other helpful materials, including essay titles!
- Children’s Rights Research Ideas
- Equality Topics
- Homophobia Topics
- School Violence Ideas
- Respect Essay Topics
- Social Inequality Paper Topics
- Suicide Topics
- Youth Violence Research Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, September 23). 150 Bullying Topics for Essays + Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/
"150 Bullying Topics for Essays + Examples." IvyPanda , 23 Sept. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '150 Bullying Topics for Essays + Examples'. 23 September.
IvyPanda . 2024. "150 Bullying Topics for Essays + Examples." September 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "150 Bullying Topics for Essays + Examples." September 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "150 Bullying Topics for Essays + Examples." September 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/bullying-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
Cyberbullying – how to Protect yourself
How it works
Cyber bullying is defined as misusing information to harass other people. Cyber bullying can come in many forms such as posting rude or negative words and rumors with the intent to publicly make fun of them in public. Cyber bullying is one of the main things that has become more frequent among teenagers, especially girls. Cyber bullying includes any kind of communications that want to do things such as control or manipulate any individual. A cyber bully’s actions are frequent, with the intention of ruining another person’s reputation.
Most cyber bullying is done on social media platforms such as Instagram, forum sites, or other information sites like Twitch or Discord. A cyber bully can be anyone. They can be some online stranger, or it can even be someone the victim knows. Statistics show that most cyber bullies are girls, while almost all victims of cyber bullying are girls. Nowadays, young people between the age of 12 to 18 spend most of their time on social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, etc. Sites like this pose many risks, which among them all, cyber bullying is the most common.
Cyber bullies post very offensive videos and pictures which can be from the past or present, misleading information or rumors, or expose fake secrets about the victim to ruin their reputation. Activities related to cyber bullying are so harmful that some victims may even consider the possibly of committing suicide. There have been a number of cases all over the world that involve teenagers who committed suicide because of humiliation or mistreatment on the internet such as Amanda Todd. Cyber bullying brought her to commit suicide because of a boy that sent a picture of her breasts to all her peers. She moved cities and schools but they continued to bully her through social media. There are may ways that any cyber bully that sends any kind of harassment, can be tracked by police with the help of the internet service providers and any necessary actions will be taken against the cyber bullies. All electronics messages carry information called ISPs that shows the path the message took to get to the victim’s computer or cellphone and those ISPs are used to track the cyber bully down. If someone becomes a cyber bully’s target, it’s important to not answer any posts or messages shared by him or her, regardless of it’s truthfulness or harmfulness.
Responses to such posts can only worsen the situation as cyber bullies mostly want any kind of reaction from their victim. Sending a message back will only provoke the cyber bully to continue their cyber assault and may make the situation spiral out of control. Over half of cyber bullying victims keep the bullying to themselves. Instead of replying to any messages, DMs, or emails; save it as evidence of the cyber bullying and then report the cyber bully to concerned individuals such as family members or school counselors and the police so that the cyber bully can get charged and prosecuted. Keeping the time, date, and messages from the cyber bully can also help determine how to confront the cyber bully. Parents or guardians should take these matters seriously and have the situation dealt with immediately. Cyber bully victims should be encouraged to inform someone if they receive any harassing messages or become a cyber bully target. Most cyber victims that are girls are targeted more often because most cyber bullying can come from a single selfie or Instagram story. The cyber bully can go onto their posts and comment things like ???That dress makes your look fat, ???Lose weight piggy, etc. This can really hurt a person as this is what they come to believe and think. It makes them unable to take certain compliments and praise from the people they know.
This can be prevented by putting your Instagram, Snapchat, Facebook, etc on private and only accepting family members and close friends. It can also be prevented by not having social media at all. I personally, do not use social media because of this reason. It’s much simpler to not use social media and get away from all of the unnecessary drama and rumors. There are other things that can be done to prevent cyber bullying like parental controls, but either putting your accounts on private or not using social media at all is the best way to keep yourself from becoming a cyber bullying victim altogether. Ultimately, cyberbullying is more serious that face to face bullying. Awareness is the main key to preventing online harassment. Children and teenagers alike must be made aware about the consequences of sharing personal pictures, videos, or information online with friends or strangers. At schools, campaigns should be conducted at all schools along with programs to teach all students about the consequences of cyber bullying and prevent them from doing it or becoming a victim to it. Cyber bullying cannot be kept in the dark any longer and it is the responsibility of everyone to report any kind of cyber bullying to the authorities immediately so that the bully can be prosecuted by the law.
Cite this page
Cyberbullying - How to Protect Yourself. (2019, Aug 04). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/cyberbullying-how-to-protect-yourself/
"Cyberbullying - How to Protect Yourself." PapersOwl.com , 4 Aug 2019, https://papersowl.com/examples/cyberbullying-how-to-protect-yourself/
PapersOwl.com. (2019). Cyberbullying - How to Protect Yourself . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/cyberbullying-how-to-protect-yourself/ [Accessed: 26 Oct. 2024]
"Cyberbullying - How to Protect Yourself." PapersOwl.com, Aug 04, 2019. Accessed October 26, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/cyberbullying-how-to-protect-yourself/
"Cyberbullying - How to Protect Yourself," PapersOwl.com , 04-Aug-2019. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/cyberbullying-how-to-protect-yourself/. [Accessed: 26-Oct-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2019). Cyberbullying - How to Protect Yourself . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/cyberbullying-how-to-protect-yourself/ [Accessed: 26-Oct-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
5 strategies on how to prevent cyberbullying
Cyberbullying , or online bullying, is bullying that’s done using technology. Cyberbullying examples include using the internet or a mobile phone to hurt, harass or embarrass someone. The consequences of cyberbullying can be serious and even life-threatening so it’s important to know how to recognise and deal with it effectively.
When you're experiencing cyberbullying, it can sometimes feel like no-one else understands, and like there’s nowhere to turn for help. But you're never alone in dealing with cyberbullying. Cyberbullying statistics from 2020 show that 44% of young people aged 12–17 had at least one negative online experience in a six month period.
If you're wondering how to deal with cyberbullying, then read on for our cyberbullying strategies.

Strategy 1: Don’t respond immediately to cyberbullying
The aim of a lot of cyberbullying is to annoy, upset or confuse the person who is being targeted, so that they react emotionally. If you’re being cyberbullied, keep in mind that the person who’s targeting you wants you to respond.
A good strategy for dealing with this is not to give them what they’re looking for. If someone says something to you online, tags you in a photo you don’t like, or just generally does something unkind, put down your phone for an hour or more. Take that time to give yourself some emotional distance, and think carefully before you respond.
Strategy 2: Follow up when you’re calmer
After an hour, you’ll hopefully feel a little calmer. Now you can go back online, if you feel up to it, maybe even with a friend or family member in the room with you. The idea at this stage is to get a proper feel for the situation before contacting the person who is cyberbullying you.
Using calm, neutral language, try to work out the situation with the person without letting them get to you. They might not even realise that you interpreted their actions as cyberbullying, so a calm conversation is a good place to start.
Strategy 3: Take screenshots
Screenshots are the best way for you to report an instance of cyberbullying. After all, the person who’s cyberbullying you may delete their comment or photo when they realise that it might get them in trouble. Screenshots will ensure you always have a copy of what was said. Note: if you take a screenshot on Snapchat, the other person will be notified that you did so.
Strategy 4: Try to stop frequently checking posts
When you’re in the thick of a cyberbullying attack, it can feel like the person who is cyberbullying you is literally in the room with you, shouting things in your ear and demanding your attention.
But it doesn’t have to be that way. You can always limit your social media time to a few hours a day, or whatever feels right for you. That way, the bullying doesn’t feel constant, and you can take a break from the online world to look after yourself.
My self-care at the time was to take a bit of a break from social networking … and to ensure that I spent a lot of quality time with family and friends.
Ashleigh, 23
Strategy 5: Report and block
Most social media sites want to help you feel safe online. They don’t want you to experience cyberbullying, either, so they have a lot of built-in tools to keep you safe.
If you’ve exhausted the reporting cyberbullying and blocking options within your social media platform and things are still really bad, you can make a report to The eSafety Commissioner by filling out this form . Before you make a complaint, you need to:
have copies of the cyberbullying material ready to upload (screenshots or photos)
report the material to the social media service (if possible) at least 48 hours before filling out the form
gather as much information as possible about where the material is located
allow 15-20 minutes to complete the form.
Learning how to avoid cyberbullying, and knowing how to respond when you experience cyberbullying can help you have a safer experience in online spaces. Knowing the signs can also help you keep others safe .
Remember that help for cyberbullying is available. You can talk with a mental health professional about your experience, share what’s going on with a trusted friend or adult, or use ReachOut’s Peer Chat to talk to an experienced peer worker.
What can I do now?
Hit up the eSafety Commissioner .
Talk to friends, family or your school counsellor about what’s been going on.
Find something else you can do for those times that you don’t want to be online.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Cyberbullying involves actions like: Sharing photos or videos of people without consent to embarrass them, make them feel bad about themselves, or enact revenge for a friendship or relationship that has broken down. Name-calling, teasing, belittling, mocking or social exclusion. Spreading false rumors.
A.1 Cyberbullying affects the mental peace of a person. It takes a toll on their mental health. Moreover, it tarnishes the reputation of an individual. Q.2 How to prevent cyberbullying? A.2 We may prevent cyberbullying by limiting the information we share online. In addition, we must make children aware of the forms of cyberbullying and its ...
Cyberbullying occurs when someone uses technology to demean, inflict harm, or cause pain to another person. It is "willful and repeated harm inflicted through the use of computers, cell phones, and other electronic devices.". Perpetrators bully victims in any online setting, including social media, video or computer games, discussion boards ...
Preventing Cyberbullying. There are many ways to prevent cyberbullying. One of the most important is to be kind and respectful online. Remember, the words you type can have a big impact on others. It's also important to keep personal information private and to think before you post. If you wouldn't say something in person, don't say it ...
Block the player who is bullying from the game and de-friend them on social media and in gaming communities. Report the player who is bullying to the game group, team, platform, community, or developers. Take a break from playing the game. Tell a parent or trusted adult and get some support.
Many of the warning signs that cyberbullying is occurring happen around a child's use of their device. Some of the warning signs that a child may be involved in cyberbullying are: Noticeable increases or decreases in device use, including texting. A child exhibits emotional responses (laughter, anger, upset) to what is happening on their device.
Research shows many negative effects of cyberbullying, some of which can lead to severe mental health issues. Cyberbullied people are twice as likely to experience suicidal thoughts, actions, or behaviors and engage in self-harm as those who are not. Other negative health consequences of cyberbullying are: Depression. Anxiety.
The effects of cyberbullying can be devastating for the victims, both emotionally and psychologically. Constant harassment and humiliation through online platforms can lead to a decline in self-esteem, increased anxiety, and depression. According to a study conducted by Kowalski et al. (2014), victims of cyberbullying experience higher levels ...
An essay writing about cyberbullying aims to cover the issue of digital bullying by revealing different aspects of this subject and offering relevant examples. Here, you can define this phenomenon, express your attitude toward it, or propose effective solutions to prevent bullying in any manifestation.
51 essay samples found. Cyber bullying is a modern form of bullying that occurs online or through digital devices, having a significant impact on the mental health of individuals, particularly adolescents. Essays on cyber bullying might discuss its various forms, the psychological and societal repercussions, and the measures taken by schools ...
Cyberbullying is the use of digital media (such as apps, text messages, and websites) to intimidate, upset, or harm someone. It includes repeatedly sending, posting, or sharing negative, harmful, or mean content about someone else on purpose. Usually, with cyberbullying, there are other people who see cyberbullying happen.
Essays on Cyber Bullying. Essay examples. Essay topics. General Overview. Essay Title 1: Unmasking the Digital Threat: Understanding Cyberbullying, Its Impact, and Prevention Strategies. Thesis Statement: This essay delves into the world of cyberbullying, examining its forms, the profound emotional and psychological impact on victims, and ...
The Solutions To Prevent And Avoid Cyberbullying. It is the 21st century and the world we are currently living in is full of technologies. In every aspect of our daily lives to our jobs, we mostly use technologies as a sort of support. We use technologies everytime and everyday such as our gadgets and laptops.
Bullying is one of the most common manifestations of peer violence in children and adolescents. Prevention of bullying, cyberbullying included, has to occur in accordance with the IBSE Standards of social and emotional learning. Bullying, Its Forms, and Counteractions.
Some sites, such as Instagram, allow messages to be left anonymously. Preventing and stopping bullying involves a commitment to creating a safe environment where children can thrive, socially and academically, without being afraid. APA recommends that teachers, parents, and students take the following actions to address bullying.
Cyber bullying is one of the main things that has become more frequent among teenagers, especially girls. Cyber bullying includes any kind of communications that want to do things such as control or manipulate any individual. A cyber bully's actions are frequent, with the intention of ruining another person's reputation.
Essay On How To Prevent Cyberbullying. 891 Words4 Pages. Recommended: Causes and effects of cyberbullying. My name is Joshua Westmoreland. I am a student of Nexus International School. I am writing to inform to you that there have been a case of suicide which are linked to cyberbullying in my university recently.
Strategy 2: Follow up when you're calmer. After an hour, you'll hopefully feel a little calmer. Now you can go back online, if you feel up to it, maybe even with a friend or family member in the room with you. The idea at this stage is to get a proper feel for the situation before contacting the person who is cyberbullying you.