Patterns of news dissemination through online news media: A case study in China
- Published: 06 July 2012
- Volume 16 , pages 557–570, ( 2014 )

Cite this article

- Youzhong Wang 1 ,
- Daniel Zeng 1 , 2 ,
- Bin Zhu 3 ,
- Xiaolong Zheng 1 &
- Feiyue Wang 1
1453 Accesses
10 Citations
Explore all metrics
Along with the rapid development of online news production and consumption, information spreads rapidly among news portals through reprinting and re-posting. Understanding the dissemination process of online news has important implications for policy making, crisis management, and brand imaging. As the frequency of news reprinting between two news portals expresses the social relationship between them, the topological properties of complex networks of news portals indicate the dynamic patterns of online news dissemination. This research is the first study that examines patterns and organizational structure of online news networks based on historical data collected from more than one thousand Chinese news portals. Main findings reveal that information can spread widely and rapidly through online news portals. Specifically, some major news portals exchange information with each other frequently and they exchange information with small news portals directly, implying that hot-spot events, even they are first reported by a small news portal, can be re-posted by many major news portals in a short time and then spread over the Internet quickly. The dense connections between many major news portals ensure that the spread will not be influenced greatly by the refusal to report typical events of a small part of major news portals.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

An Alternative Media Experience: LiveLeak

The future of social media in marketing
Social media marketing strategy: definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and future agenda
Albert, R., & Barabási, A.-L. (2002). Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Reviews of Modern Physics, 74 (1), 47–97.
Article Google Scholar
Barabasi, A., & Albert, R. (1999). Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science, 286 (5439), 509.
Barrat, A., Barthelemy, M., Pastor-Satorras, R., & Vespignani, A. (2004). The architecture of complex weighted networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 101 (11), 3747–3752.
Barrat, A., Barthlemy, M., & Vespignani, A. (2008). Dynamical processes on complex networks . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Barthélemy, M., Barrat, A., Pastor-Satorras, R., & Vespignani, A. (2005). Dynamical patterns of epidemic outbreaks in complex heterogeneous networks. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 235 (2), 275–288.
Boczkowski, P. J. (2002). The development and use of online newspapers: What research tells us and what we might want to know. In L. Lievrouw and S. Livingstone (Eds.), The handbook of new media (pp. 270–286). London: Sage.
Borgatti, S. P., & Everett, M. G. (2000). Models of core/periphery structures. Social Networks, 21 (4), 375–395.
Bustamante, E. (2004). Cultural industries in the digital age: some provisional conclusions. Media, Culture & Society, 26 (6), 803.
Chyi, H., & Sylvie, G. (1998). Competing with whom? Where? And how? A structural analysis of the electronic newspaper market. Journal of Media Economics, 11 (2), 1–18.
CNNIC. (2012). the 29th China Internet Development Status Survey Report. http://www.cnnic.cn/research/bgxz/tjbg/201201/P020120116330880247967.pdf . Accessed 1.18 2012.
Cohen, R., & Havlin, S. (2003). Scale-free networks are ultrasmall. Physical Review Letters, 90 (5), 58701.
Crucitti, P., Latora, V., Marchiori, M., & Rapisarda, A. (2003). Efficiency of scale-free networks: error and attack tolerance. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 320 , 622–642. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4371(02)01545-5 .
Dasgupta, N., Mandl, K. D., & Brownstein, J. S. (2009). Breaking the news or fueling the epidemic? Temporal association between news media report volume and opioid-related mortality. PLoS ONE, 4 (11), e7758. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007758 .
Deuze, M. (2003). The web and its journalisms: considering the consequences of different types of newsmedia online. New Media & Society, 5 (2), 203.
Dorogovtsev, S. N., Goltsev, A. V., & Mendes, J. F. F. (2006). k-core organization of complex networks. Physical Review Letters, 96 (4), 040601.
Fan, W., & Yeung, K. H. (2011). Online social networks—Paradise of computer viruses. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 390 , 189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2010.09.034 .
Flaounas, I., Turchi, M., Ali, O., Fyson, N., De Bie, T., Mosdell, N., et al. (2010). The structure of the EU mediasphere. PLoS One, 5 (12), e14243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014243 .
Gonçalves, B., Perra, N., & Vespignani, A. (2011). Modeling users’ activity on twitter networks: validation of Dunbar’s number. PLoS One, 6 (8), e22656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022656 .
Harwit, E., & Clark, D. (2001). Shaping the internet in China: evolution of political control over network infrastructure and content. Asian Survey, 41 (3), 377–408.
Herbert, J., & Thurman, N. (2007). Paid content strategies for news websites. Journalism Practice, 1 (2), 208–226.
Hindman, M. (2007). A mile wide and an inch deep: measuring media diversity online and offline. Media diversity and localism: Meaning and metrics, 40 (2), 327–348.
Hindman, M. (2009). The myth of digital democracy . Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
Hoffman, L. (2006). Is Internet content different after all? A content analysis of mobilizing information in online and print newspapers. Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly, 83 (1), 58.
Holme, P. (2005). Core-periphery organization of complex networks. Physical Review E, 72 , 046111.
Journalism.org (2010). The state of the news media 2010: Online: Audience behavior. http://www.stateofthemedia.org/2010/online_audience.php . Accessed 2010.06.10.
Kaye, B. K., & Johnson, T. J. (2003). From here to obscurity?: media substitution theory and traditional media in an on-line world. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 54 (3), 260–273. doi: 10.1002/Asi.10212 .
Kohut, A., Doherty, D., & Dimock, M. (2008). Key news audiences now blend online and traditional sources . Washington, D.C.: The Pew Research Center for the People and the Press.
Google Scholar
Latora, V., & Marchiori, M. (2001). Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Physical Review Letters, 87 (19), 198701.
Lee, A., & Carpini, M. (2010). News consumption revisited: Examining the power of habits in the 21st century.
Leskovec, J., Krause, A., Guestrin, C., Faloutsos, C., VanBriesen, J., & Glance, N. (2007). Cost-effective outbreak detection in networks. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 13th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, San Jose, California, USA.
Moore, C., & Newman, M. E. J. (2000). Epidemics and percolation in small-world networks. Physical Review E, 61 (5), 5678.
Newman, M. E. (2001). The structure of scientific collaboration networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98 (2), 404–409.
Newman, M. E. J. (2003). The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Review, 45 (2). doi: 10.1137/s003614450342480 .
Newman, M. E. J., Forrest, S., & Balthrop, J. (2002). Email networks and the spread of computer viruses. Physical Review E, 66 (3), 035101.
Ni, S., Weng, W., & Zhang, H. (2011). Modeling the effects of social impact on epidemic spreading in complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 390 (23–24), 4528–4534. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2011.07.042 .
Panzarasa, P., Opsahl, T., & Carley, K. (2009). Patterns and dynamics of users’ behavior and interaction: network analysis of an online community. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 60 (5), 911–932.
Paulussen, S. (2006). Online news production in Flanders: how Flemish online journalists perceive and explore the internet’s potential. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 9 (4).
Peng, F., Tham, N., & Xiaoming, H. (1999). Trends in online newspapers: a look at the US web. Newspaper Research Journal, 20 (2).
Quandt, T. (2008). (NO) News on the world wide web? Journalism Studies, 9 (5), 717–738.
Scott, J. (2007). Social network analysis: A handbook . London, UK: Sage.
Singer, J. (2003). Who are these guys?: the online challenge to the notion of journalistic professionalism. Journalism, 4 (2), 139.
Thelwall, M. (2004). Link analysis: An information science approach . Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Pub Ltd.
Varian, H. R., Farrell, J., & Shapiro, C. (2004). The economics of information technology . Boston: Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Wan, X., & Yang, J. (2007). Learning information diffusion process on the web. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 16th international conference on World Wide Web, Banff, Alberta, Canada.
Wang, Y., Zeng, D., Zheng, X., & Wang, F. (2009a). Internet news media analysis based on complex network theory. Complex Systems and Complexity Science, 6 (3), 11–21.
Wang, Y., Zeng, D., Zheng, X., & Wang, F. (2009b). Propagation of online news: dynamic patterns. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE international conference on Intelligence and security informatics, Richardson, Texas, USA.
Watts, D. J., & Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature, 393 (6684), 440–442.
Weber, M., & Monge, P. (2011). The flow of digital news in a network of sources, authorities, and hubs. Journal of Communication, 61 (6), 1062–1081.
Weldon, M. (2008). Everyman news: The changing American front page . Columbia, MO: University of Missouri Press.
Zhang, X. (2007). Breaking news, media coverage and ‘citizen’s right to know’in China. Journal of Contemporary China, 16 (53), 535–545.
Zhang, J., Cao, X.-B., Du, W.-B., & Cai, K.-Q. (2010). Evolution of Chinese airport network. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 389 (18), 3922–3931. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2010.05.042 .
Zheng, X., Zeng, D., Li, H., & Wang, F. (2008). Analyzing open-source software systems as complex networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 387 (24), 6190–6200. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2008.06.050 .
Download references
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge research support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 71103180, 71025001, 91124001, 91024030, 90924302, and 70890084.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
State Key Laboratory of Management and Control for Complex Systems, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190, China
Youzhong Wang, Daniel Zeng, Xiaolong Zheng & Feiyue Wang
Department of Management Information Systems, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA
Daniel Zeng
College of Business, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Daniel Zeng .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wang, Y., Zeng, D., Zhu, B. et al. Patterns of news dissemination through online news media: A case study in China. Inf Syst Front 16 , 557–570 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-012-9358-9
Download citation
Published : 06 July 2012
Issue Date : September 2014
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-012-9358-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online news
- Information diffusion
- Social network analysis
- Dynamic pattern
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Online News Portals in Nepal: An Overview

2010, Bodhi: An Interdisciplinary Journal
Related Papers
Abdul Kabil Khan, PhD
The Internet has opened borderless opportunities in the field of journalism and mass communication, especially significant on how journalistic stories will be created and distributed across the multiple platforms. Since 2006 Bangladeshi mainstream news organizations have been transforming and reshaping their strategy towards being a digital-only news outlet. News organizations are now using different features of mobile devices and social media to tell stories and engage with their target audiences. We consider digital-only platforms as a new media, social media and convergence media platforms. Almost each traditional media outlet observed has the analogue or another version on the web. Social media platforms, like Facebook, Twitter, weblogs, Tik Tok have provided the opportunity for the traditional journalists to share news quickly, get feedback from the audience and have two-way communication with the reader. Over the years they have created thousands of new jobs for aspiring journ...
EUREKA: Social and Humanities
This article refers to the brief history of the development of online media in Bangladesh starting from the beginnings of the Internet to the contemporary stage. Since 2006 Bangladeshi news organizations have been reshaping their strategy towards being a digital-only news outlet. News organizations are now using different features of mobile devices and social media to tell stories and engage with their target audiences. Today both the digital-only news outlets and mainstream media use QR codes, messengers, social media platforms, which enable them to reach a wider area of audiences. By using yet inexpensive digital tools journalists can easily create and distribute content for digital-only platforms. We consider digital-only platforms as new media, social media, and convergence media platforms. Social media platforms have provided the opportunity for traditional journalists to share news quickly, get feedback from the audience, and have two-way communication with the reader. Previou...
In Ritta Brusila and Hannu Vanhanen (eds.), Integrated Media in Change. Rovaniemi: Lapland University Press.
Fahmidul Haq
The steady growth of online community has offered the journalism practices going online. The quick shift of journalism from print to digital has brought online journalism into a close scrutiny by the media owners, journalists as well as the academics. In the Western and developed countries, many print newspapers have closed down, but journalism is continuing on the cyberspace. At least, newspapers are strengthening their online versions, if the print version is not completely shut down. Moreover, fresh online news media are appearing without having any print version. Other than these two types of news media, there are also instances of either independent or alternative news media in the cyberspace. Independent news media do not have corporate investment but practice conventional journalism. But alternative news media practice radical and left leaning journalism. These examples of online journalism are also seen in developing countries which could be slightly different from Western experiences. In the third world and developing countries, the Internet penetration is quite lower than Western countries; hence the online journalism is slowly developing there. In many countries, print media is still expanding. In Bangladesh, all print, broadcast and online journalism industries are expanding. Interestingly, even after a recent boom in the broadcast media, the print media is continuing to expand. In every year, one or more newspaper is beginning their operations. Because of the low Internet penetration in the country, the online news media is not flourished yet. Even though, there might be found four categories of online news practices: online version of the mainstream print media, conventional news media with corporate investment, independent and small scale news media and citizen journalism in the blog sites and social media. This article portrays the picture of online journalism in a developing country like Bangladesh – the trends, challenges and opportunities will be the focal point while studying this new kind of journalism practices.
The Journalist (ISSN 2231-2943)
Sudarsan Sahoo
Hypertexts, interactivity and multimedia are the features of the Web. Features like blog, podcast, flash, RSS, hyperlinks and instant messaging has made the designing and delivering news online very innovative. Web features are designed to allow greater user participation, user-generated content, and user-friendly online environments. In short, Web features can engage and empower Web users. However, online journalism in Odisha is still undermined and underestimated. Most of the main stream Odia newspapers use their websites only 'shovelling' news from their print versions, though some of them provide some special features. This research is an attempt to make a comparative feature analysis of five online leading Odia newspapers. The features are listed out in tables and then discussed from different perspectives.
Najma Akhther
STUDIA I ANALIZY NAUK O POLITYCE
Prof. Dr. and Dr. Honoris Causa Sabahudin Hadžialić
According to statistics from the Ministry of Information and Communications, as of December 2022, the whole country has 127 news agencies; 670 journal agencies (there are 327 journals of political theory and science, 72 journals of literature and art); 72 radio and television agencies. Personnel operating in the field of journalism are about 41,000 people, of which the radio and television sector is approximately 16,500 people. Compared with 2021, personnel is relatively stable and the number of personnel granted journalist cards increases significantly. There have been 19,356 cases of being granted journalist cards. It is easy for the public to check the names of long-term online newspapers and major readers such as "VnExpress," "Dan Tri," "Vietnamplus," "VietNamNet," etc. The emergence of multimedia journalism is an important step towards shaping the new type of digital storytelling and the future of journalism. In the process of renovation, the Vietnamese press is also gradually transforming and approaching new media products (Long-form/E-Magazine/ * This study was supported by a fellowship grant from the Thai Nguyen University of Science, Vietnam. We want to express sincere appreciation to the Faculty of Journalism Communication (FJC), TNU-University of Science, for their academic and financial. These acknowledgements are not complete without thanking online offices for their useful advice and moral support toward the success of this study.
Amar Baduwal
Jurnal Komunikasi Massa Vol
mahfud anshori
Jurnal Visi Komunikasi
Daniel Handoko
News aggregator is as a process of taking news from published sources, then reshaping the news, and republishing it in a shorter form in one presentation. LINE today as news aggregator appeared on the third stage of the time line of online journalism in Indonesia. This paper attempts to highlight previous studies findings about LINE Today as news aggregator. News aggregator faces domino effect in which audiences think that news aggregator is not credible as a result of data mining gibing repetitive information. On the other hand, it is urgent that there should be encouragement of digital journalist competence to be familiar with aggregation. Later, this leads to the idea of slow technology as an antithesis of interactive technology (news aggregator) that is based on human-centered activity.
RELATED PAPERS
Singularity Theory - Dedicated to Jean-Paul Brasselet on His 60th Birthday - Proceedings of the 2005 Marseille Singularity School and Conference
Walter Neumann
Yung-Jong Shiah
The Journal of Urology
Fiona Burkhard
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy
Mathias Vrolix
Jean M Létang
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
Marjorie Zettler
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Law, Social Sciences, and Education, ICLSSE 2021, 09 September 2021, Singaraja, Bali, Indonesia
Made Sarmita
Moses Rodriguez
Dario Bullitta
Lecture Notes in Computer Science
Md.Moshiur Rahman
Anne Shepler
Zaheer Ahmed
Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences
daniel mendez
Journal of Human Ecology
American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
Samuel Forjuoh
FEBS Letters
essegbemon akpo
Lidia Fransiska
lidia fransiska
IOP conference series
Ronnie Susman Natawidjaja
Journal of Family Violence
Raghda Alnabilsy
IJSES Editor
Jitender Jakhar
Materia socio-medica
erika Zelko
masitoh siregar
Israel Studies Review
Ian S. Lustick
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
The Rise of Digital Journalism: Past, Present, and Future
March 15, 2021

Tables of Contents
The Evolution of Modern Journalism in America
What is journalism in the digital age, the state of modern journalism in america, how different types of journalism adjusted to the digital age, digital journalism skills, the future of digital journalism.

Advanced communication is one of the things that set humans apart from the rest of the animal kingdom. No other species communicates with the depth and complexity we do. We’ve developed more and more intricate ways to express ourselves, from cave paintings to the written word and illuminated manuscripts to Twitter, the telephone, and FaceTime.
The 20th and 21st centuries have revolutionized how humans communicate, accelerating a process hundreds of thousands of years in the making and launching it forward with astonishing speed. Just a few centuries after books became widespread, people are now walking around with devices capable of connecting them with anybody around the world in a matter of seconds.
Communication advancements have revolutionized the field of journalism, as journalists and reporters around the world operate in ways almost unrecognizable from the profession of a century ago. As the 21st century marches on, different types of journalists and media outlets will continue to evolve in response to digital journalism trends.
Though the spirit of journalism was alive before and during the American Revolution — Benjamin Franklin was a famous early newspaper printer — independent newspapers with full-time reporters didn’t emerge until the 19th century. The concept of popular media developed during the 1900s, starting with radio and newspapers in the first half of the century, before television’s domination in the 1950s. The ability for average citizens to bring the world into their living room became an irresistible and integral part of American culture and home life, with families gathering around the tube to watch everything from the moon landing to MTV.
The turn of the 21st century saw the rise of a new journalism medium for a new millennium: the internet. Another major development was the proliferation of different media and distinct voices. The omniscient, “objective” news bureaus of the three major networks dominated American television news, but that quickly fractured into a range of cable channels, internet sites, and social media feeds.
Revolutionizing global commerce and communication seemingly overnight, the internet has also fundamentally changed how journalists and media outlets operate. Old-school journalism outlets have found it difficult to adjust, but newer types of journalism have flourished in a media landscape that’s almost unrecognizable from a few decades ago.
Journalism has changed rapidly in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. The traditional ideal of journalism was for reporters to serve as independent sources, attempting to deliver the news in a fact-based, objective manner. While this tradition remains intact in some news avenues, increased access to technologies has led to the proliferation of citizen and activist journalists who openly have a bias or point of view, but still attempt to promote that perspective through a lens that includes fair framing, editing, and reporting.
Some also take advantage of these technologies to advance propaganda under the guise of news. In addition, the internet has allowed for all of us to become authors: Anyone can create a blog and put an opinion out into the world, where it can go viral without any fact-checking or editing.
Journalists in the digital age must operate in a world where the news cycle moves faster. As a result, striking a balance between timely and in-depth reporting is often more difficult.

Modern journalists need a few indispensable tools to get the job done. Computers: Computers with internet access allow journalists to write and file stories and run professional audio, video, and text editing software from global locations. Videoconferencing software: Journalists need to connect with far-flung subjects, sources, and editorial teams. Smartphones: Smartphones allow for enhanced audio, video, and data transmission capabilities. They also make it easier for citizens to get involved in the reporting process. Social media data tracking: In-depth visualizations of clicks, shares, and interactions tell journalists what stories are trending and where research is needed.
Back To Top
To facilitate speedy, accurate reporting, modern journalists use various recent inventions and innovations:
- Internet: Before the digital age, reporters had to either call in their stories or drive to the newsroom to type it out, and then submit it to their editors; after that, the story would have to find its way to the printing press. Now, the internet means journalists can file stories on location from a phone or laptop, allowing organizations to get breaking news on their websites within minutes of it happening.
- Specialty software : Modern programs and apps allow journalists to do everything from video editing to graphics work, research, and transcription from the comfort of their living rooms.
- Videoconferencing software: Applications like Zoom and Google Meet allow journalists to conduct interviews and staff meetings remotely.
- Smartphones: Arguably the most important tool in modern journalism is the smartphone, most commonly iPhones and Android devices. Capable of shooting images and video, recording audio, accessing the internet, and more, journalists can produce professional work using nothing other than their smartphones .
- Social media: Journalists use social media networks, such as Twitter, Instagram, and Facebook, to promote their work, stay on top of breaking news, seek sources, and interact with the public.
- Digital recorders and transcription services: In the early days of modern journalism, reporters had to rely on shorthand to accurately quote a subject, not an easy task when listening to a politician’s speech or a star player’s postgame interview. Now, recorders that cost less than $100 can easily record, store, sort, and play back dozens of hours of audio on a single charge, and advanced voice-recognition software can generate transcripts from audio files with increasing accuracy.
- Digital cameras (dual purpose): When cameras were film-based only, journalistic photography was an expensive, time-consuming practice reserved almost solely for professionals. Now, with the proliferation of digital and smartphone cameras, almost everybody has a dual-purpose device that can take both high-definition photographs and video. Most professionals still rely on more advanced digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) cameras and newer mirrorless digital cameras, which come with interchangeable lens systems that allow the cameras to shoot everything from close-ups to a football field far away.
Even in a country such as the U.S. that legally protects freedom of the press, journalism jobs around the country have drastically declined. Pew Research reports that American newspapers lost half their newsroom employees between 2008 and 2019, with journalism as a whole losing 23% of newsroom jobs. The jobs that remain are typically low-paying, with half of all journalists making less than $40,000 a year , despite often putting in more than the typical 40-hour workweek.
One of the largest contributing factors to newsroom decline in the U.S. was a bad gamble on the newspaper industry’s part. When newspapers first started putting their content online, they did so for free, assuming that online advertising revenue would make up for the loss of subscribers and in-person newspaper sales. However, that revenue was nowhere near as lucrative as expected, and when outlets pivoted to paywalls, their readers balked, now used to getting the product for free and therefore unwilling to pay for it.
As a result, there has been increased industry consolidation as large conglomerate companies, such as Sinclair Media and Alden Global Capital, purchase smaller news outlets struggling to make a profit. In some cases, these conglomerates have used their vast networks to push their own viewpoints via content that can border on propaganda. Many of these conglomerates have a reputation for cutting jobs to turn a profit .
More recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has hurt many industries, including journalism. Many smaller news outlets have closed during the pandemic, and even larger news providers have had to scale back due to revenue loss and a decline in news events to cover (such as sports and live entertainment events). With so many people stuck at home, however, broadcast and online outlets have thrived, as have social media news reporters, who have been best positioned to pivot and respond to the new reality.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that there were 52,000 reporters, correspondents, and broadcast news analysts in 2019. There were also 118,700 editors , 35% of whom worked for newspaper and other print media publishers. However, the field of journalism comprises numerous different subspecialties, all of which require different skill sets, tools, and approaches.
No matter the role, the digital journalism era has brought wholesale changes to the industry. Here’s how the digital age has affected different types of journalism roles and how they’ve adjusted.
Traditional Journalism
In what’s known as traditional journalism, newspaper reporters and editors work for a local paper of record, the primary paper in a town or an area. In the nation’s capital, it’s The Washington Post ; in the City of Angels, it’s the Los Angeles Times . Regardless of location, the newspapers have an established history of professional news reporting, a neutral political stance, and thorough coverage of their regions.
Most traditional journalism outlets were too slow to respond to the digital age, and have suffered for it. The BLS expects both reporting and editorial jobs in newspapers to decline by 40% over the next 10 years, and small papers across the U.S. are shutting down or reducing operations seemingly every day. Declining advertising revenue, the loss of the classifieds section to the internet, and increased costs have forced many news outlets to slash their staff or sell outright to conglomerates such as Gannett or Advance Publications, which often downscale the publications anyway .
Broadcast and Cable Journalism
Since radio’s invention in the early 20th century, American families have welcomed broadcasters into their homes. From Edward R. Murrow and Walter Cronkite to Rachel Maddow and Anderson Cooper, top broadcast journalists command audiences of millions who tune in for their knowledge and authoritative voices on the nation’s news and current affairs. According to the BLS, about 17,000 journalists worked in broadcast as of 2019, making up 32% of the jobs within the reporters and correspondent categories.
Broadcast and cable are still relevant, with leading anchors drawing millions of viewers, whether for afternoon political shows or programs such as 60 Minutes . That doesn’t mean that the digital transition hasn’t affected broadcast journalism. Television news has embraced infotainment as it competes for viewers, showcasing stories that engage emotion and outrage over drier, policy-driven ones with far greater real-world impact.
At the same time, comedians such as Stephen Colbert and Samantha Bee further obscure the old lines with current events comedy shows that some feel follow journalistic standards of research and fact-checking more rigorously than news channels such as Fox News and MSNBC.
The rise of independent broadcast outlets has also challenged broadcast journalism. Streaming apps such as Facebook Live and Twitch allow citizen journalists and entrepreneurial journalists to spread compelling, high-definition video and attract big audiences in the span of a few minutes. National protests such as the George Floyd marches in 2020 and the U.S. Capitol riot in January 2021 were both extensively covered by citizen journalists, who captured never-before-seen angles of social unrest and social commentary from the center of the action.
Investigative Journalism
The 2015 Academy Award winner for best picture, “Spotlight,” told the true story of the Boston Globe ’s investigative team as it investigated the Catholic Church abuse scandal that rocked the city at the turn of the 21st century. It was a compelling portrayal of how the team went to great lengths to convince dozens of abuse victims to come forward with their stories, and how the team spent hours digging through volumes of physical directories and microfiche records from the print and electronic ages.
Investigative journalism in the digital age has come to lean on new tools . A major development has been the rise of big data. The ability to comb through years of financial data, browsing history, cellphone logs, and all sorts of other data sets gives investigative journalists endless amounts of information to analyze to put together their stories.
Sports Journalism
Americans love sports. Whether it’s a professional league such as the NFL or WNBA or a beloved local high school team, people love following their favorite teams and players. Sportswriters from Grantland Rice to Michael Lewis have left their mark on American culture through their writing, and the best writers at many local papers are in the sports section, shining a light on local athletes.
ESPN was the first major disruptor in sports journalism. In the late 20th century, the Connecticut-based company quickly became the dominant force in American sports coverage. ESPN’s networks, although still the biggest names in sports, have seen their online presence hurt by the arrival of new players, such as the subscription sports site The Athletic, which has quickly become the go-to digital news media site for sportswriters. With athletes now also reaching customers directly through sites such as The Players’ Tribune and social media accounts, sports journalists have branched out into analytics and long-form journalism to stay relevant.
Outside of newspapers, journalists work in magazines, tabloids, and other print publications. The publications are often among the hardest hit in the industry, with high printing costs for color pages and full-bleed photos, along with high costs for quality writers who often produce long features that take weeks or months to complete.
Long-form journalism of the type that traditionally appeared in magazines has moved onto sites such as The Athletic or Medium. Former powerhouse magazines, from Newsweek and Time to GQ to Sports Illustrated, have all had to cut back on staff and the size of their product and increasingly pivot to an online format to try and stay afloat, leading some to wonder how much longer magazines will be around.
Social Media News
Social media journalists have only existed since the rise of digital journalism. The first social media journalists started appearing on sites such as Facebook and Twitter, but now work on photo sites such as Instagram and specialty platforms such as Signal and VSCO as well.
Social media journalists are learning to grow with the times: As new platforms emerge and attract users, social media journalists evaluate whether it benefits their personal brand to build a following there. They’ve also found ways to monetize their work through advertisements, sponsored posts, or paywalls that reserve content for subscribers through services such as Patreon.
Resources: Defining Journalism Jobs
- The Balance Careers, “What Does a TV Reporter Do?” — A brief rundown of broadcast journalism
- The Balance Small Business, “Understanding the Role of a Social Media Reporter” — A discussion of the profession and its key skills, including how they differ from traditional journalism
- Konrad Adenauer Stiftung, “Investigative Journalism Manual” — An in-depth examination of what it takes to become an investigative journalist, from identifying a story and developing research to interviewing subjects and writing a piece
- Houston Chronicle , “How to Become a Sports Reporter” — The path to becoming a sports reporter and the skills required to land the job
- Houston Chronicle , “Job Requirements to Be a Print Journalist” — The education, experience, and skills it takes to make it in the world of print
- KRTV, “A Day in the Life of a Reporter” — An inside look at a TV reporter’s daily routine

The following skills were mentioned in a high percentage of journalism job postings in the U.S. in 2019: writing, 86%; multimedia, 80%; marketing, 45%; reporting, 45%; interviewing, 28%; professional ethics, 25%; subject knowledge, 15%; multilingual proficiency, 10%.
Having a smartphone and the right editing software is a good way to start off in the field of modern journalism. However, tools without the ability and know-how to use them won’t matter much in an ultracompetitive field. Some skills that can help lead to a career as a journalist in the digital age are:
- Investigation: At its core, journalism is a storytelling profession, and the best stories aren’t always obvious. They often require hours of interviews, chasing down sources and leads, going down dead ends, and trying new paths. Whether working for a major news organization or paving their own route, the ability to hit on a story and track it to its conclusion is the hallmark of good journalists.
- Research: Research and investigation, although cut from the same cloth, are different skills. While investigators track down leads and work sources for new information, research involves studying books, old newspapers, and other media as background for stories. Like investigations, research stages can take weeks or months to discover a story’s full background, or to gain a proper appreciation of the bigger picture.
- Written communication: You can be a great interviewer or video editor, but without the ability to write a compelling script or story, technical abilities won’t matter. Writing will always remain a central tenet of journalism, and the best journalists all have the ability to file a strong story on deadline, even if their focus is in a different area.
- Basic web design: Using programs such as Adobe Photoshop, Adobe InDesign, and Adobe Illustrator, journalists can create graphics, video backgrounds, illustrations, and data visualizations to supplement their work. Although blogging platforms make it easy for independent journalists to establish their own sites cheaply, the ability to personalize a site and make it stand out makes a great first impression and can help hold readers’ attention.
- Self-motivation: Newsrooms are shrinking, and more journalists are working remotely or for their own publications. For self-publishing or entrepreneurial journalists, it can take several years of working around the clock to build up enough of a following or subscriber base to make a living, much less to grow their operation.
- A/V editing : Digital journalists need to know how to compile video, audio, images, and graphics into informative, captivating, compact multimedia stories — called “packages” in newspeak — for broadcast or the web. Understanding camera basics and proper framing and lighting doesn’t cost journalists any extra but will make their product look professional; the ability to use the right postproduction programs to add graphics and enhance video and sound is also becoming commonplace.
Resources: Skills for Digital Journalists
- Pew Research Center, “Most Important Skills for Online Journalists” — The results of a survey of 239 members of online journalism organizations
- Poynter, “Want to Get a Journalism Job? Here Are the Skills You Need ” — What newsrooms are looking for according to a survey of 39 leaders at 31 news companies
- European Journalism Observatory, “New Skills for the Next Generation of Journalists” — An analysis of journalism education in several European countries that reveals certain trends
- Poynter, “Audience Work Is More Important to Journalism Than Ever” — Some debunked myths regarding journalism work for new college graduates
What will journalism look like in the next century? While change is inevitable, it’s clear that the internet and digital age are here to stay, and humanity will continue to find new ways to connect and interact as the 21st century goes on.
The recent decline of journalism jobs and attacks on the “fake news” media have some outlets wondering whether journalism has any future at all . That’s likely an overreaction; Americans are guaranteed the right to a free press by the First Amendment, and enough people want to hold those in power accountable as journalists do to keep the profession alive. Eventually, journalism could become a certified profession similar to an attorney, therapist, or any other licensed professional who requires approval from a governing board to operate.
Regardless of whether that happens, journalists in the digital age are going to have to continue to adapt. New technologies, platforms, and tools are sure to pop up over the years, and the best journalists will find ways to work them into their repertoire or explore new niches in the field. According to the Poynter Institute , journalists in the next 10 to 20 years will need the same curiosity, writing skill, and ability to discern the facts as today’s journalists, though they’ll need to increasingly lean on digital film, photo, and editing skills, as well as their own ability to “build their brand.” While the top names in the field may be able to stick to one specialty, other journalists should look to explore new areas and take on new challenges.
Journalism in the Digital Age: A Constant Evolution
The field of journalism has evolved from its pre-industrial revolution beginnings to its current iteration of citizen journalism and media conglomerates. Journalists and journalism students of the 21st century need to be ready to adapt to new platforms and technologies and stay in tune with the public consciousness to perform their jobs effectively.
While journalists may face an uncertain future, avenues for entrepreneurial people with an understanding of technology and humanity to tell compelling stories will always exist. No matter what they call themselves, that’s certainly the definition of journalism.
Infographic Sources
Journalism Practice, “(Re)defining Journalistic Expertise in the Digital Transformation: A Content Analysis of Job Announcements”
Journalist’s Resource, “Journalism job ads show demand for marketing expertise, certain personality traits”
Poynter, “Here Are All the Tools and Technology Journalists Are Using to Tell the Coronavirus Story”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
Readers and Online News Websites Research Paper
This paper will be a case study of News.com.au. The objective will be to use this site to explore some of the factors mentioned above. It will show that the success of online broadcasts relies on more than just the readers. The paper will also take into account the thoughts of the readers on their role in that success, and members of the site’s staff on the news and the new developments they wish to adopt.
This will be done through a questionnaire. The paper will also explore the organization and structure of News.com.au website, and how this helps it sell itself to the readers.
Introduction
With the prevalence of online media today, more and more media houses are going online. Not only are new media houses adopting online broadcasting, but the ones that are already online are increasing their online portals. These media houses hope to retain their customers.
Their adoption of online media is an attempt to chase after their customers who are already on line, as well as winning new online users. The participation of readers is pivotal for the success of the sites (Cushion 2001; Cameron 2000).
Based on their perceptions on the sites, the readers could inform other people; their friends, families, workmates, et cetera. Although getting more people coming in is a good thing, the real question is not whether a person logs in, but whether he/she keeps returning to the portal. Retaining old customers makes it possible to identify the new readers, and to evaluate whether the portal is popular amongst readers (Emmerichs et al 2004).
News.com is an organization of editors based in Sydney. It has a large number of online editors who manage its work in many cities and mast-head sections all over the world (Burden 2008; Chappel 2000, p. 12). It has reporters and newspapers that contribute greatly in many states including territories all over Australia and goes further to include correspondents from different parts of the world (Chaston 1999, p. 34).
In Asia, it has correspondents from various cities that include Beijing in China, Bangkok in Thailand, Tokyo in Japan and Jakarta in Indonesia. In Europe, London takes the lion share and takes the representation of United Kingdom and the larger European continent. In the United States, the cities of Washington, Wellington, New York and Los Angeles have been inhabited by the correspondents of this organization (Chaston 1999, p. 30).
It has in the last decade drawn its global power of incorporating news and the act of gathering parallel news from News Limited. This is the largest new gathering network in Australia (De Botton 2002; Denu 2011).
Within its rank, is an out-and-about team of online reporters who work hard to contribute their daily reports to the millions of the Australian population (Little 2007, p. 41; Alysen 2002, p. 35).It presents the content it gathers from the vast network of the News Limited network which has in its ranks news on a range issues such as business, weather, entertainment, and sports.
The portal makes almost minute to minute update of its news. For example, it can be noticed that the Breaking News column in the News.com.au bears headlines only minutes apart (Young 2007).
It has a wide range of contributing factors in its daily to daily news that range from newspapers which include the daily telegraph, the advertiser, the Australian, the herald sun, the Sunday times, the courier mail and the mercury. The posting of the newspapers is done every night at around 2am.
The reporting teams give an update on the events that happen each and every-day, and get its daily update from its efficiently developed network of printing activities and the other resources of the associated press of Australia and other press resources like the Agence France-Presse and the associated press (Erdelez 1995).
Literature review
Print media thrive on readership. As has been briefly mentioned above, media houses count on readers to keep their sites running. Variety and the consequent competitiveness helped by the internet makes it necessary for these media houses to adopt suitable ways to attract and retain more readers.
For this reason, various media houses have adopted a number of audience-based tactics. Since the primary objective is to win and retain these customers, the news content, which is the primary product that these media houses are selling, becomes only a small part of the overall methods used to win readers (Valentine 2011, p. 65).
For instance, Bowman and Willis (2003, p. 7) pointed out how MSNBC.com, CNN, Washington Post and The Wall Street Journal offered their readers certain degrees of personalization on their sites’ front pages. Personalization means that readers can customize the portals to satisfy some of their tastes.
Also another phenomenon of online activity is what Erdelez (1995, p. 20) referred to as information encountering. This is the ability of the internet to get readers to news without them really intending to. This thrives upon the opportunistic reading habits and emotional response of the readers.
Tewksbury et al. (2001, p. 34) argued that due to the prevalence of news online, many people come by news items without necessarily setting out to find the news. In the same line, Nguyen (2008) agrees that the structure of online media has facilitated unintended encounter of news and its reading.
What these examples reveal is that it is not only the place of readers to keep the get to the site. While the end target is humans, there are other elements of the internet that helps keep the sites running. The irony here is that people may not really go to the site for the purpose of reading the news, but maybe to reach a gateway to other portals.
But the fact still remains that they have gotten the readers to their site. Another Irony is that the very nature of internet structure that leads readers to these sites may be the same thing that directs them away. Nonetheless, the case of New.com.au shows clearly just how important readers are to keeping news website running.
News.com.au has also adopted a readers-centered tactic of retaining its readers. This has involved different forms of reader-participation. For instance, readers participate in the site by posting their comments on various issues on the company site.
These posts include the reader’s reaction(s) to various issues, including the news or certain new adoptions in the site-structure and organization, amongst others. This paper will show that this reader-centered tactic is having a positive effect on winning readers to their online portal.
As it were, this tactic has been a direct way to hear what the readers want from their own lips. The company has an online portal dedicated to collecting the readers’ views fro critical assessment and evaluation. It has constantly used the information from the readers to know what they perceive as negative and make necessary adjustments.
In other words, the company realizes and acknowledges the role of the readers in keeping their site running. Their primary goal then becomes satisfying the readers (Goggin 2001, p. 44).
It is as if the company has explicitly set out to answer a question it has set itself: How do we expect to have the most captivating news when the readers do not have the right platforms to express themselves and air their satisfactions or dissatisfactions?
A good media house cannot emerge without the resurgent action of its readers, so the readers ought to be given the chance to help the media houses online make the right decisions and changes (Heracleous, Wirtz & Pangarkar 2006; Berridge 2007).
Research Questions
The research seeks to answer the question like; how has the general setting of the online portal of the News.com.au helped it win and keep readers? And what other new tactics should the company adopt to ensure that it retains a close relation with its readers?
Methodology
The research made use of multiple methods of data collection, including where experimentation, surveys, questionnaires and observation of the site to enhance the accuracy and reproducibility of the results, and to increase the likeliness of getting more results from other sources relating to online media organization, especially News.com.au (Karol & Nelson 2007).
Experimentation: the research emphasized on studying the trend of relations between the readers and the organization.
For instance, the number of readers who have visited their websites of the organization, what kinds of comments the readers have made: positive or negative, and how these comments have influenced certain changes in the site, and the company’s general operations. The decisions of the managers and the readers’ involvement in online media were used for the experimentation (Gillespie, Jeannette & Hennessey 2010).
Some of the data was obtained from the company’s history from the company website sites. Other data that was gotten from the company website including the recent activities of the company and what the managers have done to deal with the pressure of the increasing online readership and how they have reacted to the different comments.
The correspondence between the company and the readers on the company website was equally witnessed. Moreover, more data was gotten from the company’s history, its position on online reading and the effects it has had on the general online media broadcasts from other secondary results like journals and magazines (Atwood 2007; Cohen 2011).
Questionnaires were used to interview specific groups of people over the internet. The different questions that were required for the research were composed and sent to the News Limited office in Australia via email. In this case, the researcher identified the target group from the players within this organization.
Since these persons were located in various places around Australia, the internet was the only effective means of communicating with them. Questionnaires were developed on word format and sent to the identified study group, which included the managers and the executive chairman of the organization who had been consulted before the study. As already stated, the questionnaires were sent over through email.
The results were received back from these persons by the same means. This study identified 40 potential interviewees who signed consent forms, received the questionnaire over the net, but only 35 of them returned the questionnaires. Out of the 35 returned questionnaires, 2 were found ineligible for the study. In the end, only 33 of the of the study sample were eligible for the study (MacGinley 2004; Erdley & Kesterson 2002).
The annual reports released by News.com Australian media for the last five years shows their performances regarding the number of online readers who visited its online portal. I obtained permission to study the data from the organization which had been identified as the study center and place.
The researcher sought for permission from the managers and the various stakeholders of the organization. The executive chairman was the main person contacted with a request to allow an explicit study on his organization on their activities and everything revolving around their reader-data collection methods. The permission was granted.
These study populations formed the first study section, where the causes of the divergent opinions and comments in the online Medias were determined. These study populations were considered for the qualitative research, given that the study was both quantitative and qualitative. For the quantitative research, the researcher sent questionnaires to the main organization offices in Australia.
Because all the study populations identified in this research understood and used English, the questionnaires were in English language. The researcher obtained important financial aid from the professionals working at the News.com.au branch in the region.
The study targeted the organization, which, it felt, was the best in Australia- being the major media house in Australia (Kenyon 2008; Austin 2010). The data was not tampered with in for one month that data collection was carried out.
The qualitative data was cumulated in individual’s interviews and then documented. For the Quantitative data, the questionnaires were gathered by the researcher and distributed through email to the staff of News.com.au. Responses were collected via the email (Bunzel 2000; Karol & Nelson 2007).
Data analysis
Statistical data analysis tools and procedures were used to derive information from the data obtained in the questionnaires. Specifically, the Statistical Packages software as well as the Microsoft access and database tools was used for the study. The data analysis procedure was done within a period of one week which was well within the stipulated time (Donald & Keane 2002; Bowman & Willis 2003).
The questionnaires were responded to according to the instructions given. On analyzing the questionnaires, it was revealed that there were several positive questions for the researched organization. The organization conveyed that there was an average of more than 5% difference between the comments and the opinions which the online readers gave out in 2009.
The difference rose by 6 percent in 2010.
The organization further reported that they had a negative difference when handling readers from other countries who had read and sampled its news portal, mainly because it was not so enriched in terms of experience compared to other well established media sites in Australia like the News Limited which has acted as an all-time leading online portal in the past decade (Newton & Morrison 2007, p. 45).
Most readers preferred other up to date and the emerging news precisely the political news.
Study results
The research found out that the organization had taken into key consideration the increased feedbacks and the opinions that it received from its daily readers through their portal. As the managers explained in their questionnaires, this had impacted greatly on the company positively since they were able to receive prompt feedbacks when an error occurred in their site.
For instance, whenever their broadcast is not streaming properly, they have learnt it from the readers and used the information to avert and counter the problem promptly. And by observing the website and witnessing the correspondence between the readers and the site staff, it was noticed that the handlers of the portal responded promptly to the readers’ questions and comments (Berridge 2007; Bretford 2010).
After the end of research on the organization and the readers’ participation on online media, it can be concluded that each and every media that feeds news to the people through an online platform should instill efficient platforms where readers’ can air and interact directly with the organization, for example, the help-platform in the organization’s website.
The use of online feeds will give the readers a one-on-one platform to air their opinions: satisfactions and dissatisfactions, and their views on various pieces of information.
For an efficient growth of the online Media, the readers should be allowed to be involved in the day to day running of the organization. The research also found out that news.com had involved their online readers a lot and this had been a major help to their immense growth in the past decade (Young 2007).
Alysen, B 2002, Broadcast Journalism in Australia , McGraw Hill, New York.
Atwood, C G 2007, Australian studies in journalism , Society for Training and Development, Massachusetts.
Austin, J 2010, Online journalism , Cengage Learning, Mason.
Berridge, G 2007, Understanding online media, Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford.
Bowman, S & Willis, C 2003, We Media, The Media Centre at The American Press Institute, Virginia.
Bretford, A 2010, A methodology approach to journalism , Gower Publishing, Ltd, Hampshire.
Bunzel, D 2000, Australian media organizations, University of Western Sydney, Sydney.
Burden, D, Joyce, P and Mustard, J 2008, Adoption of the World Wide Web by Traditional Australian Media Organizations. Web.
Cameron, D 2000, Media and the web , Sage Publications Ltd, London.
Chappel, S 2000, News limited in perspective , University of South Australia, Melbourne.
Chaston, I 1999, New-Media Strategies: Evolving Flexible Processes to Fit Information Seeking , Syracuse University, Syracuse.
Cohen, R 2011, An analysis on Australian online Media? Springer, New York.
Cushion, S 2001, The rise of 24-hour news television: Global perspectives , UMI Research Press, New York.
De Botton, A 2002, The art of media , Hamish Hamilton, New Delhi.
Denu, B 2011, Institutions and media houses: Europe and Australia , LIT, Munich.
Donald, S H & Keane, M 2002, “Responses to crisis: convergence, content industries, and media governance”, Media in China: Consumption, Content and Crisis , pp. 200-211.
Emmerichs, R M, Marcum, C Y & Robbert, A A 2004, An operational process for workforce planning, RAND, California.
Erdelez, S 1995, Information Encountering: An Exploration Beyond Market Circumstance , SAGE, New York.
Erdley, M & Kesterson, T 2002, American and Australian media houses , IBM Future Series, New York.
Gillespie, K, Jeannet, J P & Hennessey, H D 2010, Global Marketing , Cengage Learning, Masson.
Goggin, G 2001, Virtual Nation: The Internet in Australia , McGraw-Hill Professional, New York.
Heracleous, L T, Wirtz, J & Pangarkar, N 2006, Information technology and innovation in language education , McGraw Hill, New York.
Karol, R & Nelson, B 2007, National library for Australian news , For Dummies, New Jersey.
Kenyon, A 2008, TV futures: digital television policy in Australia , OECD publishing, Paris.
Little, J 2007, “Perspectives on Assessment Practices in Australian Journalism Education”, Australian Studies in Journalism , pp. 90-103.
MacGinley, R 2004, The Golding Centre for online portals, Australian Catholic University, Melbourne.
Newton, M & Morrison, J 2007, World’s Journalism , Emerald Group Publishing, Bingley.
Nguyen, A 2008, The Contribution of Online News Attributes To It Diffusion . Web.
Tewksbury, D, Hals, M & Bibart, A 2008, “The Efficacy of News Browsing: The American Press Institute, Virginia” Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly , 85 (2), pp. 257-272.
Valentine, F 2011, Readers and Journalism , LIT Verlag, Munich.
Young, S A 2007, Government communication in Australia , Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, July 11). Readers and Online News Websites. https://ivypanda.com/essays/readers-and-online-news-websites/
"Readers and Online News Websites." IvyPanda , 11 July 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/readers-and-online-news-websites/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Readers and Online News Websites'. 11 July.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Readers and Online News Websites." July 11, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/readers-and-online-news-websites/.
1. IvyPanda . "Readers and Online News Websites." July 11, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/readers-and-online-news-websites/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Readers and Online News Websites." July 11, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/readers-and-online-news-websites/.
- Google Inc. in the Internet Portal Services Industry
- The Rick Racer Amusements Web Portal's Requirements
- E-Business Strategies: Corporate Portal Implementation
- Newspaper Article Analysis
- Newspapers Are Under Attack From The Net. What Strategies Might Be Followed To Survive?
- The History of Print Media and Its Competition With the Internet
- How the range and value of news have been influenced by technological advances in news production
- Content Analysis: Why Is It That Many Us Citizens Are Not Well Informed About International Events
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Americans’ Changing Relationship With Local News
As news consumption habits become more digital, U.S. adults continue to see value in local outlets
Table of contents.
- 1. Attention to local news
- 2. Local news topics
- Americans’ changing local news providers
- How people feel about their local news media’s performance
- Most Americans think local journalists are in touch with their communities
- Interactions with local journalists
- 5. Americans’ views on the financial health of local news
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology

The Pew-Knight Initiative supports new research on how Americans absorb civic information, form beliefs and identities, and engage in their communities.
Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. Knight Foundation is a social investor committed to supporting informed and engaged communities. Learn more >
Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand the local news habits and attitudes of U.S. adults. It is a follow-up to a similar study conducted in 2018 .
The survey of 5,146 U.S. adults was conducted from Jan. 22 to 28, 2024. Everyone who completed the survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Refer to the topline for the questions used for this survey , along with responses, and to the methodology for more details.
This is a Pew Research Center report from the Pew-Knight Initiative, a research program funded jointly by The Pew Charitable Trusts and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Find related reports online at https://www.pewresearch.org/pew-knight/ .
The local news landscape in America is going through profound changes as both news consumers and producers continue to adapt to a more digital news environment. We recently asked U.S. adults about the ways they access local news, as well as their attitudes toward local journalism, finding that:
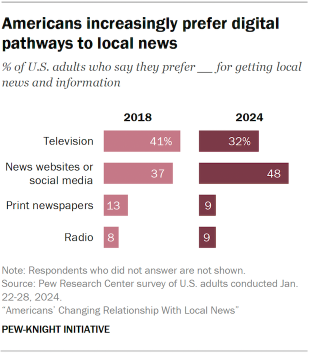
- A growing share of Americans prefer to get local news online, while fewer are getting news on TV or in print. And newspapers are no longer primarily consumed as a print product – the majority of readers of local daily newspapers now access them digitally.
- The share of U.S. adults who say they are paying close attention to local news has dropped since our last major survey of attitudes toward local news in 2018, mirroring declining attention to national news.
- Americans still see value in local news and local journalists. A large majority say local news outlets are at least somewhat important to the well-being of their local community. Most people also say local journalists are in touch with their communities and that their local news media perform well at several aspects of their jobs, such as reporting the news accurately.
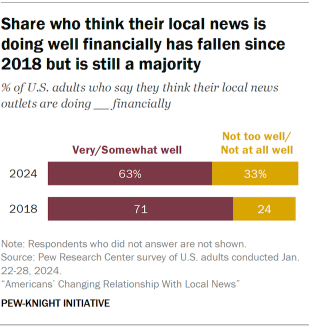
- At the same time, a relatively small share of Americans (15%) say they have paid for local news in the last year. And many seem unaware of the major financial challenges facing local news: A 63% majority (albeit a smaller majority than in 2018) say they think their local news outlets are doing very or somewhat well financially.
- Majorities of both major parties say local media in their area are doing their jobs well. While Republicans and GOP-leaning independents are slightly less positive than Democrats and Democratic leaners in their opinions of local media, views of local news don’t have the same stark political divides that exist within Americans’ opinions about national media .
- Most Americans say local journalists should remain neutral on issues in their community, but a substantial minority say local journalists should take a more active role. About three-in-ten say local journalists should advocate for change in their communities, a view that’s especially common among Democrats and younger adults.
These are some of the key findings from a new Pew Research Center survey of about 5,000 U.S. adults conducted in January 2024. This is the first in a series of Pew Research Center reports on local news from the Pew-Knight Initiative, a research program funded jointly by The Pew Charitable Trusts and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation.
Americans largely hold positive views of local news organizations
At a time when many local news outlets are struggling and Americans’ trust in the news media has waned, the vast majority of U.S. adults (85%) say local news outlets are at least somewhat important to the well-being of their local community. This includes 44% who say local journalism is extremely or very important to their community
About seven-in-ten U.S. adults (69%) say that local journalists in their area are mostly in touch with their community, up from 63% who said this in 2018. And most Americans also say their local news organizations are doing well at four key roles:
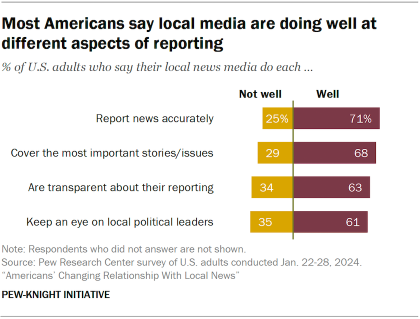
- Reporting news accurately (71%)
- Covering the most important stories (68%)
- Being transparent (63%)
- Keeping an eye on local political leaders (61%).
These are relatively positive views compared with how Americans see news organizations more broadly. For instance, a 2022 Pew Research Center survey found that fewer than half of U.S. adults say that news organizations in general do a very or somewhat good job of covering the most important stories, reporting the news accurately and serving as a watchdog over elected leaders.
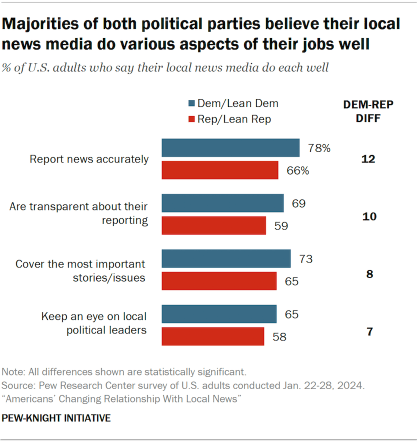
What’s more, views toward local news are not as politically polarized as Americans’ opinions about the news media overall. While Republicans and GOP-leaning independents are not quite as positive as Democrats and Democratic leaners in some of their assessments of local journalists, most Republicans still say the local media in their area are doing their jobs well.
For example, roughly three-quarters of Democrats (78%) say their local media do well at reporting news accurately, compared with about two-thirds of Republicans (66%).
By comparison, the 2022 survey found that 51% of Democrats and just 17% of Republicans say that news organizations in general do a very or somewhat good job of reporting the news accurately.
Jump to more information on views toward local news organizations.
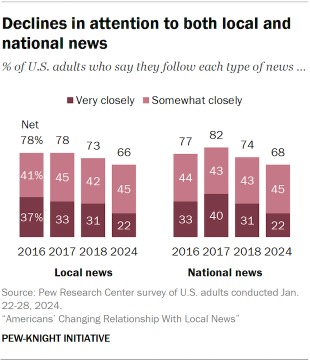
Fewer Americans are closely following local news – and other types of news
Despite these positive views toward local news organizations, there are signs that Americans are engaging less with local journalism than they used to.
The share of Americans who say they follow local news very closely has fallen by 15 percentage points since 2016 (from 37% to 22%). Most U.S. adults still say they follow local news at least somewhat closely (66%), but this figure also has dropped in recent years.
This trend is not unique to local news – Americans’ attention to national and international news also has declined.
The local news landscape is becoming more digital
The ways in which Americans access local news are changing, reflecting an increasingly digital landscape – and matching patterns in overall news consumption habits .
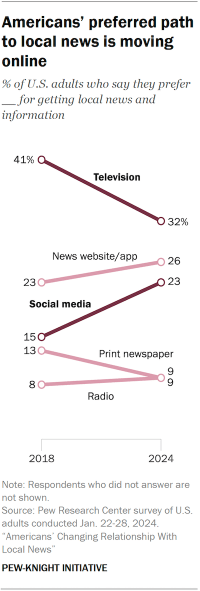
Preferred pathways to local news
- Fewer people now say they prefer to get local news through a television set (32%, down from 41% who said the same in 2018).
- Americans are now more likely to say they prefer to get local news online, either through news websites (26%) or social media (23%). Both of these numbers have increased in recent years.
- Smaller shares prefer getting their local news from a print newspaper or on the radio (9% each).
Specific sources for local news
The types of sources (e.g., outlets or organizations) Americans are turning to are changing as well:
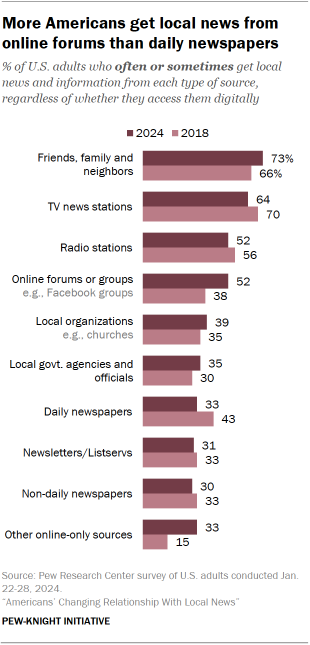
- While local television stations are still the most common source of local news beyond friends, family and neighbors, the share who often or sometimes get news there has declined from 70% to 64% in recent years.
- Online forums, such as Facebook groups or the Nextdoor app, have become a more common destination for local news: 52% of U.S. adults say they at least sometimes get local news from these types of forums, up 14 percentage points from 2018. This is on par with the percentage who get local news at least sometimes from local radio stations.
- Meanwhile, a third of Americans say they at least sometimes get local news from a daily newspaper, regardless of whether it is accessed via print, online or through a social media website – down 10 points from 2018. The share of Americans who get local news from newspapers is now roughly on par with the share who get local news from local government agencies (35%) or local newsletters or Listservs (31%).
Not only are fewer Americans getting local news from newspapers, but local daily newspapers are now more likely to be accessed online than in print.
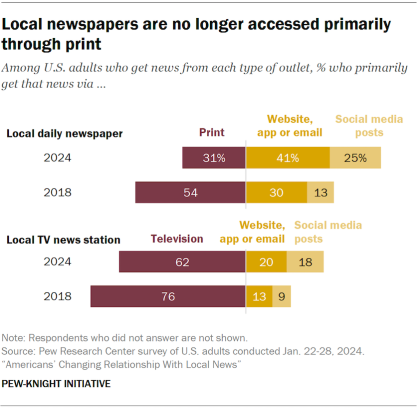
- 31% of those who get news from daily newspapers do so via print, while far more (66%) do so digitally, whether through websites, apps, emails or social media posts that include content from the paper.
- In 2018, just over half of those who got news from local daily newspapers (54%) did so from print, and 43% did so via a website, app, email or social media site.
There is a similar move toward digital access for local TV stations, though local TV news is still mostly consumed through a TV set.
- In 2024, 62% of those getting news from local TV stations do so through a television, compared with 37% who do so through one of the digital pathways.
- An even bigger majority of local TV news consumers (76%) got that news through a TV set in 2018.
Jump to more information on how people access local news.
The financial state of local news
The turmoil for the local news industry in recent years has come with major financial challenges. Circulation and advertising revenue for newspapers have seen sharp declines in the last decade, according to our analysis of industry data , and other researchers have documented that thousands of newspapers have stopped publishing in the last two decades. There also is evidence of audience decline for local TV news stations, although advertising revenue on local TV has been more stable.
When asked about the financial state of the news outlets in their community, a majority of Americans (63%) say they think their local news outlets are doing very or somewhat well, with a third saying that they’re not doing too well or not doing well at all. This is a slightly more pessimistic view than in 2018, when 71% said their local outlets were doing well, though it is still a relatively positive assessment of the financial state of the industry.
Just 15% of Americans say they have paid or given money to any local news source in the past year – a number that has not changed much since 2018. The survey also asked Americans who did not pay for news in the past year the main reason why not. The most common explanation is that people don’t pay because they can find plenty of free local news, although young adults are more inclined to say they just aren’t interested enough in local news to pay for it.
Jump to more information on how people view the financial state of local news.
Other key findings in this report
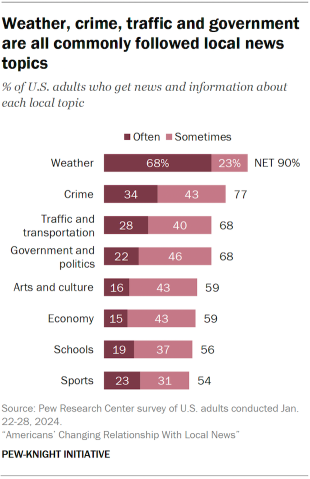
Americans get local news about a wide variety of topics. Two-thirds or more of U.S. adults at least sometimes get news about local weather, crime, government and politics, and traffic and transportation, while smaller shares (but still at least half) say they get local news about arts and culture, the economy, schools, and sports.
Relatively few Americans are highly satisfied with the coverage they see of many topics. The survey also asked respondents who at least sometimes get each type of local news how satisfied they are with the news they get. With the exception of weather, fewer than half say they are extremely or very satisfied with the quality of the news they get about each topic. For example, about a quarter of those who consume news about their local economy (26%) say they are extremely or very satisfied with this news. Read more about different local news topics in Chapter 2.
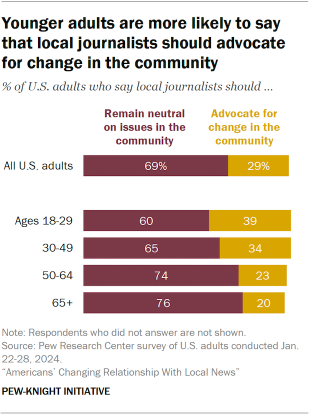
When asked whether local journalists should remain neutral on community issues or advocate for change in the community, a majority of Americans (69%) say journalists should remain neutral, reflecting more traditional journalistic norms. However, 29% say that local journalists should be advocating for change in their communities. Younger adults are the most likely to favor advocacy by journalists: 39% of those ages 18 to 29 say that local journalists should push for change, as do 34% of those 30 to 49. Read more about Americans’ views of the role of local journalists in Chapter 4.
Americans who feel a strong sense of connection to their community are more likely to engage with local news, say that local news outlets are important to the community, and rate local media more highly overall. For example, 66% of those who say they are very attached to their community say local news outlets are extremely or very important to the well-being of their local community, compared with 46% of those who are somewhat attached and 31% of those who are not very or not at all attached to their community.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Digital News Landscape
- Journalists
- Trust in Media
Introducing the Pew-Knight Initiative
8 facts about black americans and the news, audiences are declining for traditional news media in the u.s. – with some exceptions, how black americans engage with local news, local tv news fact sheet, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Top Science News
Latest top headlines.
- Language Acquisition
- Bird Flu Research
- Pregnancy and Childbirth
- K-12 Education
- Public Health Education
- Artificial Intelligence
- Diseases and Conditions
- Energy and the Environment
- Renewable Energy
- Thermodynamics
- Extrasolar Planets
- Virtual Reality
- Virtual Environment
- Video Games
- Evolutionary Biology
- New Species
- Biotechnology
- Biotechnology and Bioengineering
- Dolphins and Whales
- Marine Biology
- No Inner Voice Linked to Poorer Verbal Memory
- Bird Flu A(H5N1) Transmitted from Cow to Human
- Polygenic Embryo Screening for IVF: Opinions
- What Makes a Memory? Did Your Brain Work Hard?
Top Physical/Tech
- Robots' Sense of Touch as Fast as Humans?
- Reaching 1,000 Degrees C With Solar Power
- Giant ' Cotton Candy' Planet
- VR With Cinematoghraphics More Engaging
Top Environment
- Avian Flu Detected in NYC Wild Birds
- Iconic Baobab Tree's Origin Story
- Nature's 3D Printer: Bristle Worms
- A Young Whale's Journey
Health News
Latest health headlines.
- Diet and Weight Loss
- Breastfeeding
- Nature of Water
- Drought Research
- Sleep Disorder Research
- Sleep Disorders
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Alzheimer's
- Alzheimer's Research
- Healthy Aging
- Racial Issues
- Racial Disparity
- Relationships
- Brain Tumor
- Nervous System
- Brain-Computer Interfaces
- Distributed Computing
- Computer Science
- Personalized Medicine
- Microbes and More
- Robotics Research
- Public Health
- Social Psychology
- STEM Education
- Travel and Recreation

Health & Medicine
- Lactate as Beneficial 'Fuel' After a Big Meal
- Petroleum, Chlorine in Water: Harmful Byproducts
- Sleep Apnea Severity and Verbal Memory
- Alzheimer's: Epigenetics and Environment
Mind & Brain
- Don't Matter If You're This or That
- Some Brain Cells Age Faster in Alzheimer's
- Tiny Brains in a Petri Dish
- Placebo Effect and AI
Living Well
- When Good Bacteria Go Bad: Probiotics
- Would You Trust a Robot Care for Your Cat?
- Infectious Language Epidemic
- AI Systems Are Skilled at Manipulating Humans
Physical/Tech News
Latest physical/tech headlines.
- Medical Technology
- Photography
- Materials Science
- 3-D Printing
- Engineering and Construction
- Solar Energy
- Geomagnetic Storms
- Energy Issues
- Solar System
- Asteroids, Comets and Meteors
- Astrophysics
- Kuiper Belt
- Animal Learning and Intelligence
- Computer Modeling
- Telecommunications
- Information Technology
- Heart Disease
- Stroke Prevention
Matter & Energy
- Boosting Image Quality of Metalens Camera
- Recyclable Future for 3D Printing
- Promising Solar Cell Technology
- The Case for Sharing Carbon Storage Risk
Space & Time
- Ozone's Influence On Exoplanetary Climate
- ONe Nova to Rule Them All
- Planet Glows With Molten Lava
- Hunting the First Stars
Computers & Math
- Diffusion in Multicomponent Alloys
- AI for Computing Plasma Physics in Fusion
- Efficient and Secure Communications
- AI Tool to Improve Heart Failure Care
Environment News
Latest environment headlines.
- Coral Reefs
- Environmental Awareness
- Food and Agriculture
- Agriculture and Food
- Global Warming
- Energy and Resources
- Early Climate
- Natural Disasters
- Earth Science
- Earthquakes
Plants & Animals
- Key to Fighting Crown-Of-Thorns Starfish
- New Insect Killing Utah's Fir Trees
- Water-Efficient Chickens
- Benefits of Mosaic Grassland Landscapes
Earth & Climate
- Measuring Ice Loss in Greenland
- Affordable Sensor for Lead Contamination
- Converting CO2 Into Valuable Chemicals
- How Wildfires Change Soil Chemistry
Fossils & Ruins
- Fastest Rate of CO2 Rise Over Last 50,000 Years
- Improving Volcanic Eruption Forecasts
- Micro-Earthquakes at Carbon Sequestration Site
- Interpreting Oceans' Past
Society/Education News
Latest society/education headlines.
- Environmental Policies
- Energy Policy
- Environmental Policy
- Alternative Fuels
- Engineering
- Mathematical Modeling
- Neuroscience
- Educational Psychology
- Education and Employment
- Computer Programming
- Sustainability
- Educational Policy
- Educational Technology
- Mathematics
- Land Management
Science & Society
- 90% of Floridians Believe Climate Is Changing
- The Price Tag of Phasing-Out Coal
- Limited Climate Ambition On 'Residual' Emissions
- Carbon-Neutral Hydrogen Economy
Education & Learning
- AI Knowledge Gets Your Foot in the Door
- New Tool for Predicting Neurotransmitters
- Cybersecurity Education Varies Widely in US
- Self-Critical Perfectionism Gnaws On Students
Business & Industry
- Pulling Power of Renewables
- Can AI Simulate Multidisciplinary Workshops?
- New Sensing Checks Overhaul Manufacturing
- Sustainability in Agricultural Trade
- Earth-Sized Planet Orbiting Ultra-Cool Dwarf
- Metro-Area Quantum Computer Network Demo
- 'Warm-Blooded' Dinos: 180 Million Years Ago
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat, about this site.
ScienceDaily features breaking news about the latest discoveries in science, health, the environment, technology, and more -- from leading universities, scientific journals, and research organizations.
Visitors can browse more than 500 individual topics, grouped into 12 main sections (listed under the top navigational menu), covering: the medical sciences and health; physical sciences and technology; biological sciences and the environment; and social sciences, business and education. Headlines and summaries of relevant news stories are provided on each topic page.
Stories are posted daily, selected from press materials provided by hundreds of sources from around the world. Links to sources and relevant journal citations (where available) are included at the end of each post.
For more information about ScienceDaily, please consult the links listed at the bottom of each page.
Feature Extraction based Online Job Portal
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
May 6, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Online patient portal usage increasing, study shows
by UT Southwestern Medical Center
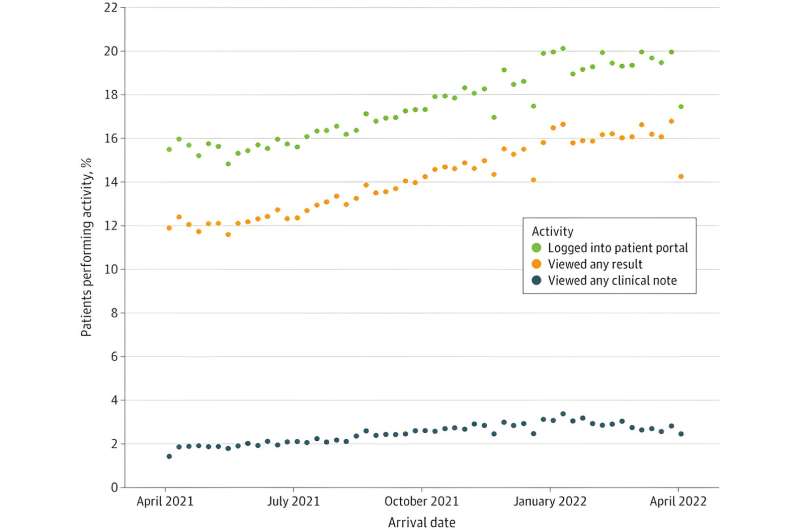
More people are using online patient portals to view their information while in the emergency room, but access is challenging for members of medically underserved communities and the elderly, UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers and national colleagues found in a new study.
"Patient portals such as Epic's MyChart have grown in popularity in recent years, but they are still often seen as a tool for ambulatory chronic disease management," said Robert Turer, M.D., Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine at UT Southwestern and the study's corresponding author.
"Our research suggests portals can be an asset in emergency medicine too, both to help patients with exacerbations of chronic conditions and to support those experiencing acute illness during and after the emergency department (ED) visit."
The research, published in JAMA Network Open , studied patient data from 36 teaching and community EDs affiliated with eight academic medical centers in seven states over the year ending in April 2022. Researchers found that 17.4% of the 1,280,924 adults who visited participating EDs logged into their patient portals to view test results or read clinical notes while at the hospital, and participation increased as the study progressed.
The research also found that most portal users were white, insured, and English-speaking and had portal accounts before arriving at the emergency room. Patients who were male or Black or had no insurance logged in at lower rates, as did older patients.
"Emergency departments often serve as a safety net for patients without an ongoing relationship with a health care provider , so they have no patient portal account," Dr. Turer said. "Or, in many cases, there is a lack of familiarity with technology—which is especially true with older patients . There is a tremendous opportunity for EDs to help bridge this gap by supporting and aiding enrollment and educating patients on the portal's key functions, using patient navigators or registration staff."
The study—the largest and most representative evaluation of real-time portal use among ED patients in the U.S.—builds on earlier single-site research at UT Southwestern that had similar results.
"Our findings in both studies support the need for further research to help us better understand portal features that are most useful within the ED," Dr. Turer said. "For example, status updates, point-of-care education, and coordination of follow-up appointments are potential solutions to explore."
Explore further
Feedback to editors
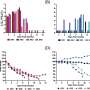
Study finds H5N1 virus from 2022 mink outbreak capable of inefficient airborne transmission
17 minutes ago

Researchers find microplastics in canine and human testicular tissue
27 minutes ago

Two decades of studies suggest health benefits associated with plant-based diets, but caution urged
49 minutes ago
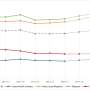
Racial disparities in childhood obesity on the rise in study of NYC public schools

Scientists want to know how the smells of nature benefit our health
Bluetooth tracking devices provide new view into care home quality

Wearing face masks did not reduce risk of COVID infection after first omicron wave, research suggests
Scientists unravel genetic basis for neurodegenerative disorders that affect vision
AI may improve doctor–patient interactions for older adults with cancer
Day-long workshop in cognitive behavioral therapy found to effectively reduce depression in 16- to 18-year-olds
Related stories.

Do you use a patient portal? Study finds differences between portal users versus nonusers
Jun 9, 2023

Higher use of health care portal seen during COVID-19 pandemic
Mar 6, 2024

Patient portal use explored for older adults with dementia diagnosis
Jul 7, 2023

Medicare pays for message-based e-visits. Are older adults using them?
Apr 8, 2024

Electronic portals may help patients with multiple complex conditions
Jun 19, 2019

Logging on for health: More older adults use patient portals, but access and attitudes vary widely
May 24, 2023
Recommended for you

New tool can help surgeons quickly search videos and create interactive feedback
10 hours ago

Machine learning sheds light on gene transcription
May 14, 2024

Artificial intelligence tool detects sex-related differences in brain structure

Study shows ChatGPT can accurately analyze medical charts for clinical research, other applications
May 13, 2024

Team studies factors related to a sense of economic insecurity in older adults
Let us know if there is a problem with our content.
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Gatekeepers in an Online News Environment. The Internet has brought various changes to the way people consume news, as it (1) allows people to have increased control over the news they select; (2) provides a wide variety of sources to keep informed about public issues; and, (3) changes the gatekeeping process so that it is less controlled by traditional media (see Majó-Vázquez, Cardenal, and ...
The aim of this study is to structure and analyzed the literature related to data veracity research that can be used to the profile of digital news portal. The method that has been used in this paper is to classify and define data veracity; a systematic literature review is a conduct. It includes journal and conference proceedings.
structure and analyzed the literature related to data veracity research that can be used to the profile of digital news. portal. The method that has been used in this paper is to classify and ...
This paper studies the patterns of online news reprinting between Chinese online news portals. The Chinese online news portals have been developing rapidly as more and more people have gained access to the Internet in China. As of the end of June 2011, the scale of China's Internet users reached 513 million people (CNNIC 2012).
Journal of Advances in Humanities and Social Sciences JAHSS 2018, 4(2): 70-83 PRIMARY RESEARCH A critical discourse analysis of headlines in online news portals Glorilyn M. Montejo1*, Teresita Q. Adriano 2 1, 2 Department of Education, University of Immaculate Conception, Davao City, Philippines Keywords Abstract Applied linguistics Headlines ...
It is argued that analysing online news using content analysis requires a different procedure especially in terms of capturing the ever changing content of the news portal. Content analysis is a well-established research technique that has been used to examine myriad type of texts including political messages. In the field of media research, it is a popular method to examine media contents ...
Abstract. This study observes the significant roles and responsibilities of online news portals during this Covid-19 outbreakin Bangladesh. The findings and result analysis of this study ...
Around the world, legacy news publishers are suffering from the deep decline of revenues and face the challenge of survival. As the situation continues, conflicts between online portal and news producers are also intensifying. Under these circumstances, Naver, the biggest internet portal in Korea, and several Korean news publishers have begun to seek a new breakthrough—media joint ventures.
of users of an online news portal to provide insights for bet-ter design of news recommendation systems. As headlines may directly impact reading habits, we hope our study adds a complementary perspective to the above studies. News Coverage and Popularity. A few studies have used a large scale dataset of online news to understand how
reported in a news portal; Malaysiakini. We argued that analysing online news using content analysis requires a different procedure especially in terms of capturing the ever changing content of the news portal. The paper also highlighted issues and challenges of adopting established content analysis technique on online news.
The vast majority of adults in the United States get at least some news from digital devices, and the online space has become a host for the digital homes of both legacy news outlets and new, "born on the web" news outlets.Digital advertising revenue across all digital entities (beyond just news) continues to grow, with technology companies playing a large role in the flow of both news and ...
This has opened avenues for the development of online news portals. If legal status and recognition by the professional bodies and professionals to online news portals is given, it can develop as one of the vibrant mass medium. References Acharya, B. (2007). Online news portals in Nepal: An exploratory study (Unpublished M.A. Thesis).
Among the top 25 sites, power users visiting at least 10 times make up an average of just 7% of total users, but that number ranged markedly, from as high as 18% (at CNN.com) to as low as 1% (at BingNews.com). Even among the top nationally recognized news site brands, Google remains the primary entry point.
The Jagran.com news portal has a capacity for interactivity features that allows users to participate in a survey, voting, winning prizes and watching videos. This research paper used descriptive analysis of Dainik Jagran news portals discusses the use of interactive features available on it.
The electronic news system is an information platform developed with the help of Internet technology based on the online information release needs of news propaganda organizations. Through the electronic news system, people can not only see the same information as regular paper newspapers, but also help realize the standardized management of news information, and bring convenience for readers ...
Even in a country such as the U.S. that legally protects freedom of the press, journalism jobs around the country have drastically declined. Pew Research reports that American newspapers lost half their newsroom employees between 2008 and 2019, with journalism as a whole losing 23% of newsroom jobs. The jobs that remain are typically low-paying, with half of all journalists making less than ...
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Download This Paper. Open PDF in Browser. Add Paper to My Library. ... Using these links will ensure access to this page indefinitely. Copy URL. Copy DOI. News Portal. 5 Pages Posted: 19 May 2021. See all articles by Phani Vikas Telu Durga Phani Vikas Telu Durga. jain university ... Research Paper Series; Conference Papers; Partners in ...
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
This paper will be a case study of News.com.au. The objective will be to use this site to explore some of the factors mentioned above. It will show that the success of online broadcasts relies on more than just the readers. The paper will also take into account the thoughts of the readers on their role in that success, and members of the site ...
Preferred pathways to local news. Fewer people now say they prefer to get local news through a television set (32%, down from 41% who said the same in 2018). Americans are now more likely to say they prefer to get local news online, either through news websites (26%) or social media (23%). Both of these numbers have increased in recent years.
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
Breaking science news and articles on global warming, extrasolar planets, stem cells, bird flu, autism, nanotechnology, dinosaurs, evolution -- the latest discoveries ...
Job search portals and proper portal log-ins are the main goals of this research project. Placements are becoming increasingly important, and many people's lives are dependent on them. Both job seekers and recruiters can use a job portal to find the ideal company for their needs. In the event of activity seekers, their educational qualifications and their preferences are taken into ...
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Temporal Trends of Real-Time Emergency Department Patient Portal Use. Credit: JAMA Network Open (2024). DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.9831