Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples

Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples
Published on May 6, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on June 22, 2023.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test :
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): There’s no effect in the population .
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a or H 1 ) : There’s an effect in the population.
Table of contents
Answering your research question with hypotheses, what is a null hypothesis, what is an alternative hypothesis, similarities and differences between null and alternative hypotheses, how to write null and alternative hypotheses, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions.
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question . When the research question asks “Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?”:
- The null hypothesis ( H 0 ) answers “No, there’s no effect in the population.”
- The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) answers “Yes, there is an effect in the population.”
The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That’s because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample . Often, we infer whether there’s an effect in the population by looking at differences between groups or relationships between variables in the sample. It’s critical for your research to write strong hypotheses .
You can use a statistical test to decide whether the evidence favors the null or alternative hypothesis. Each type of statistical test comes with a specific way of phrasing the null and alternative hypothesis. However, the hypotheses can also be phrased in a general way that applies to any test.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The null hypothesis is the claim that there’s no effect in the population.
If the sample provides enough evidence against the claim that there’s no effect in the population ( p ≤ α), then we can reject the null hypothesis . Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Although “fail to reject” may sound awkward, it’s the only wording that statisticians accept . Be careful not to say you “prove” or “accept” the null hypothesis.
Null hypotheses often include phrases such as “no effect,” “no difference,” or “no relationship.” When written in mathematical terms, they always include an equality (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
You can never know with complete certainty whether there is an effect in the population. Some percentage of the time, your inference about the population will be incorrect. When you incorrectly reject the null hypothesis, it’s called a type I error . When you incorrectly fail to reject it, it’s a type II error.
Examples of null hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and null hypotheses. There’s always more than one way to answer a research question, but these null hypotheses can help you get started.
*Note that some researchers prefer to always write the null hypothesis in terms of “no effect” and “=”. It would be fine to say that daily meditation has no effect on the incidence of depression and p 1 = p 2 .
The alternative hypothesis ( H a ) is the other answer to your research question . It claims that there’s an effect in the population.
Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it’s the claim that you expect or hope will be true.
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. Null and alternative hypotheses are exhaustive, meaning that together they cover every possible outcome. They are also mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
Alternative hypotheses often include phrases such as “an effect,” “a difference,” or “a relationship.” When alternative hypotheses are written in mathematical terms, they always include an inequality (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >). As with null hypotheses, there are many acceptable ways to phrase an alternative hypothesis.
Examples of alternative hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and alternative hypotheses to help you get started with formulating your own.
Null and alternative hypotheses are similar in some ways:
- They’re both answers to the research question.
- They both make claims about the population.
- They’re both evaluated by statistical tests.
However, there are important differences between the two types of hypotheses, summarized in the following table.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To help you write your hypotheses, you can use the template sentences below. If you know which statistical test you’re going to use, you can use the test-specific template sentences. Otherwise, you can use the general template sentences.
General template sentences
The only thing you need to know to use these general template sentences are your dependent and independent variables. To write your research question, null hypothesis, and alternative hypothesis, fill in the following sentences with your variables:
Does independent variable affect dependent variable ?
- Null hypothesis ( H 0 ): Independent variable does not affect dependent variable.
- Alternative hypothesis ( H a ): Independent variable affects dependent variable.
Test-specific template sentences
Once you know the statistical test you’ll be using, you can write your hypotheses in a more precise and mathematical way specific to the test you chose. The table below provides template sentences for common statistical tests.
Note: The template sentences above assume that you’re performing one-tailed tests . One-tailed tests are appropriate for most studies.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, while the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
The null hypothesis is often abbreviated as H 0 . When the null hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an equality symbol (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
The alternative hypothesis is often abbreviated as H a or H 1 . When the alternative hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an inequality symbol (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (“ x affects y because …”).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses . In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Turney, S. (2023, June 22). Null & Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions, Templates & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 4, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/null-and-alternative-hypotheses/
Is this article helpful?

Shaun Turney
Other students also liked, inferential statistics | an easy introduction & examples, hypothesis testing | a step-by-step guide with easy examples, type i & type ii errors | differences, examples, visualizations, what is your plagiarism score.
9.1 Null and Alternative Hypotheses
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 , the — null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
H a —, the alternative hypothesis: a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are reject H 0 if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or do not reject H 0 or decline to reject H 0 if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example 9.1
H 0 : No more than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30 H a : More than 30 percent of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
Example 9.2
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ = 2.0 H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 66
- H a : μ __ 66
Example 9.3
We want to test if college students take fewer than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are the following: H 0 : μ ≥ 5 H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : μ __ 45
- H a : μ __ 45
Example 9.4
An article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third of the students pass. The same article stated that 6.6 percent of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4 percent pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6 percent. State the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p ≤ 0.066 H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40 percent pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40 percent pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- H 0 : p __ 0.40
- H a : p __ 0.40
Collaborative Exercise
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some internet articles. In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute Texas Education Agency (TEA). The original material is available at: https://www.texasgateway.org/book/tea-statistics . Changes were made to the original material, including updates to art, structure, and other content updates.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Statistics
- Publication date: Mar 27, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/statistics/pages/9-1-null-and-alternative-hypotheses
© Jan 23, 2024 Texas Education Agency (TEA). The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples
Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples
Published on 5 October 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on 6 December 2022.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test :
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): There’s no effect in the population .
- Alternative hypothesis (H A ): There’s an effect in the population.
The effect is usually the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable .
Table of contents
Answering your research question with hypotheses, what is a null hypothesis, what is an alternative hypothesis, differences between null and alternative hypotheses, how to write null and alternative hypotheses, frequently asked questions about null and alternative hypotheses.
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question . When the research question asks “Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?”, the null hypothesis (H 0 ) answers “No, there’s no effect in the population.” On the other hand, the alternative hypothesis (H A ) answers “Yes, there is an effect in the population.”
The null and alternative are always claims about the population. That’s because the goal of hypothesis testing is to make inferences about a population based on a sample . Often, we infer whether there’s an effect in the population by looking at differences between groups or relationships between variables in the sample.
You can use a statistical test to decide whether the evidence favors the null or alternative hypothesis. Each type of statistical test comes with a specific way of phrasing the null and alternative hypothesis. However, the hypotheses can also be phrased in a general way that applies to any test.
The null hypothesis is the claim that there’s no effect in the population.
If the sample provides enough evidence against the claim that there’s no effect in the population ( p ≤ α), then we can reject the null hypothesis . Otherwise, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Although “fail to reject” may sound awkward, it’s the only wording that statisticians accept. Be careful not to say you “prove” or “accept” the null hypothesis.
Null hypotheses often include phrases such as “no effect”, “no difference”, or “no relationship”. When written in mathematical terms, they always include an equality (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
Examples of null hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and null hypotheses. There’s always more than one way to answer a research question, but these null hypotheses can help you get started.
*Note that some researchers prefer to always write the null hypothesis in terms of “no effect” and “=”. It would be fine to say that daily meditation has no effect on the incidence of depression and p 1 = p 2 .
The alternative hypothesis (H A ) is the other answer to your research question . It claims that there’s an effect in the population.
Often, your alternative hypothesis is the same as your research hypothesis. In other words, it’s the claim that you expect or hope will be true.
The alternative hypothesis is the complement to the null hypothesis. Null and alternative hypotheses are exhaustive, meaning that together they cover every possible outcome. They are also mutually exclusive, meaning that only one can be true at a time.
Alternative hypotheses often include phrases such as “an effect”, “a difference”, or “a relationship”. When alternative hypotheses are written in mathematical terms, they always include an inequality (usually ≠, but sometimes > or <). As with null hypotheses, there are many acceptable ways to phrase an alternative hypothesis.
Examples of alternative hypotheses
The table below gives examples of research questions and alternative hypotheses to help you get started with formulating your own.
Null and alternative hypotheses are similar in some ways:
- They’re both answers to the research question
- They both make claims about the population
- They’re both evaluated by statistical tests.
However, there are important differences between the two types of hypotheses, summarized in the following table.
To help you write your hypotheses, you can use the template sentences below. If you know which statistical test you’re going to use, you can use the test-specific template sentences. Otherwise, you can use the general template sentences.
The only thing you need to know to use these general template sentences are your dependent and independent variables. To write your research question, null hypothesis, and alternative hypothesis, fill in the following sentences with your variables:
Does independent variable affect dependent variable ?
- Null hypothesis (H 0 ): Independent variable does not affect dependent variable .
- Alternative hypothesis (H A ): Independent variable affects dependent variable .
Test-specific
Once you know the statistical test you’ll be using, you can write your hypotheses in a more precise and mathematical way specific to the test you chose. The table below provides template sentences for common statistical tests.
Note: The template sentences above assume that you’re performing one-tailed tests . One-tailed tests are appropriate for most studies.
The null hypothesis is often abbreviated as H 0 . When the null hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an equality symbol (usually =, but sometimes ≥ or ≤).
The alternative hypothesis is often abbreviated as H a or H 1 . When the alternative hypothesis is written using mathematical symbols, it always includes an inequality symbol (usually ≠, but sometimes < or >).
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Turney, S. (2022, December 06). Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/stats/null-and-alternative-hypothesis/
Is this article helpful?

Shaun Turney
Other students also liked, levels of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio, the standard normal distribution | calculator, examples & uses, types of variables in research | definitions & examples.
Module 9: Hypothesis Testing With One Sample
Null and alternative hypotheses, learning outcomes.
- Describe hypothesis testing in general and in practice
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
H 0 : The null hypothesis: It is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt.
H a : The alternative hypothesis : It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to H 0 and what we conclude when we reject H 0 .
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make adecision. There are two options for a decision . They are “reject H 0 ” if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or “do not reject H 0 ” or “decline to reject H 0 ” if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
Mathematical Symbols Used in H 0 and H a :
H 0 always has a symbol with an equal in it. H a never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
H 0 : No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p ≤ 30
H a : More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. p > 30
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
H 0 : The drug reduces cholesterol by 25%. p = 0.25
H a : The drug does not reduce cholesterol by 25%. p ≠ 0.25
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
H 0 : μ = 2.0
H a : μ ≠ 2.0
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : μ __ 66 H a : μ __ 66
- H 0 : μ = 66
- H a : μ ≠ 66
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
H 0 : μ ≥ 5
H a : μ < 5
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : μ __ 45 H a : μ __ 45
- H 0 : μ ≥ 45
- H a : μ < 45
In an issue of U.S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
H 0 : p ≤ 0.066
H a : p > 0.066
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (=, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses. H 0 : p __ 0.40 H a : p __ 0.40
- H 0 : p = 0.40
- H a : p > 0.40
Concept Review
In a hypothesis test , sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis , typically denoted with H 0 . The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality (=, ≤ or ≥) Always write the alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with H a or H 1 , using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, i.e., (≠, >, or <). If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis. Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
Formula Review
H 0 and H a are contradictory.
- OpenStax, Statistics, Null and Alternative Hypotheses. Provided by : OpenStax. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:58/Introductory_Statistics . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Introductory Statistics . Authored by : Barbara Illowski, Susan Dean. Provided by : Open Stax. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]
- Simple hypothesis testing | Probability and Statistics | Khan Academy. Authored by : Khan Academy. Located at : https://youtu.be/5D1gV37bKXY . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Statistics
Course: ap®︎/college statistics > unit 10.
- Idea behind hypothesis testing
Examples of null and alternative hypotheses
- Writing null and alternative hypotheses
- P-values and significance tests
- Comparing P-values to different significance levels
- Estimating a P-value from a simulation
- Estimating P-values from simulations
- Using P-values to make conclusions
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Video transcript
Hypothesis Testing: Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
Join over 2 million students who advanced their careers with 365 Data Science. Learn from instructors who have worked at Meta, Spotify, Google, IKEA, Netflix, and Coca-Cola and master Python, SQL, Excel, machine learning, data analysis, AI fundamentals, and more.

Figuring out exactly what the null hypothesis and the alternative hypotheses are is not a walk in the park. Hypothesis testing is based on the knowledge that you can acquire by going over what we have previously covered about statistics in our blog.
So, if you don’t want to have a hard time keeping up, make sure you have read all the tutorials about confidence intervals , distributions , z-tables and t-tables .
We've also made a video on null hypothesis vs alternative hypothesis - you can watch it below or just scroll down if you prefer reading.

Confidence intervals provide us with an estimation of where the parameters are located. You can obtain them with our confidence interval calculator and learn more about them in the related article.
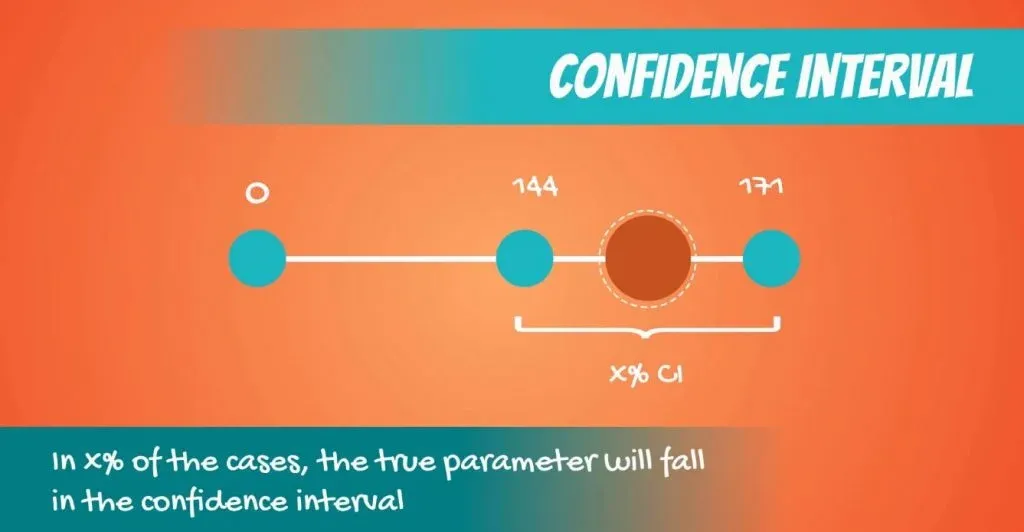
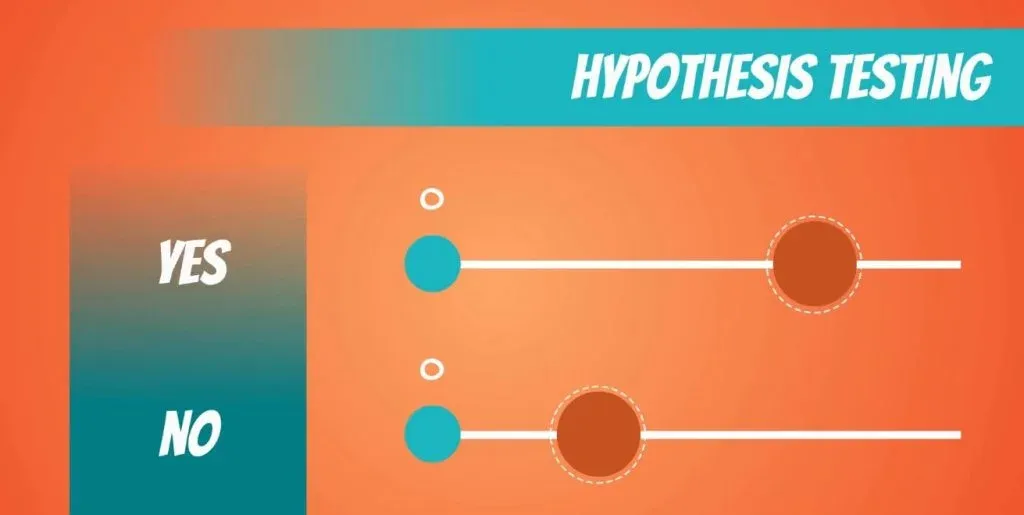
However, when we are making a decision, we need a yes or no answer. The correct approach, in this case, is to use a test .
Here we will start learning about one of the fundamental tasks in statistics - hypothesis testing !
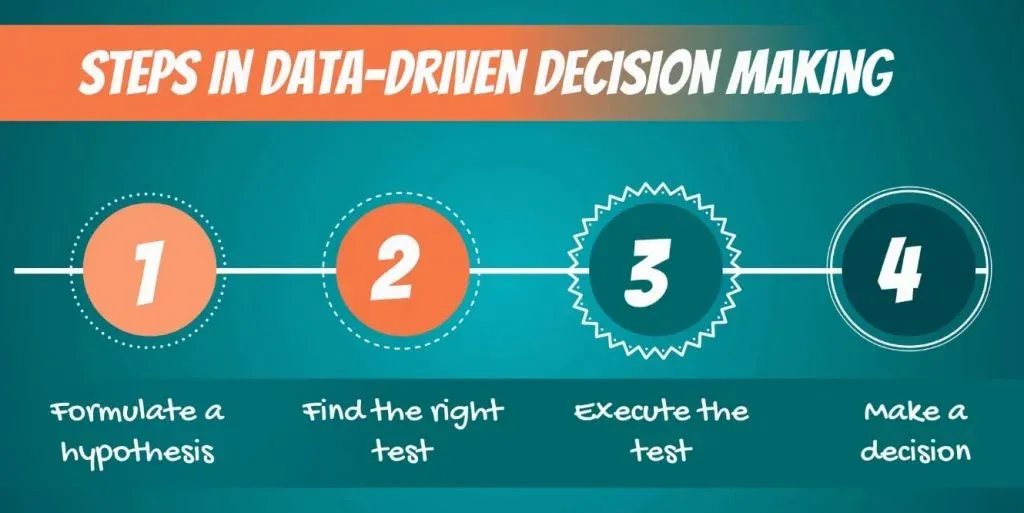
The Hypothesis Testing Process
First off, let’s talk about data-driven decision-making. It consists of the following steps:
- First, we must formulate a hypothesis .
- After doing that, we have to find the right test for our hypothesis .
- Then, we execute the test.
- Finally, we make a decision based on the result.
Let’s start from the beginning.
What is a Hypothesis?
Though there are many ways to define it, the most intuitive must be:
“A hypothesis is an idea that can be tested.”

This is not the formal definition, but it explains the point very well.
So, if we say that apples in New York are expensive, this is an idea or a statement. However, it is not testable, until we have something to compare it with.

For instance, if we define expensive as: any price higher than $1.75 dollars per pound, then it immediately becomes a hypothesis .

What Cannot Be a Hypothesis?
An example may be: would the USA do better or worse under a Clinton administration, compared to a Trump administration? Statistically speaking, this is an idea , but there is no data to test it. Therefore, it cannot be a hypothesis of a statistical test.
Actually, it is more likely to be a topic of another discipline.
Conversely, in statistics, we may compare different US presidencies that have already been completed. For example, the Obama administration and the Bush administration, as we have data on both.

A Two-Sided Test
Alright, let’s get out of politics and get into hypotheses . Here’s a simple topic that CAN be tested.
According to Glassdoor (the popular salary information website), the mean data scientist salary in the US is 113,000 dollars.
So, we want to test if their estimate is correct.
The Null and Alternative Hypotheses
There are two hypotheses that are made: the null hypothesis , denoted H 0 , and the alternative hypothesis , denoted H 1 or H A .

The null hypothesis is the one to be tested and the alternative is everything else. In our example:
The null hypothesis would be: The mean data scientist salary is 113,000 dollars.

While the alternative : The mean data scientist salary is not 113,000 dollars.

Author's note: If you're interested in a data scientist career, check out our articles Data Scientist Career Path , 5 Business Basics for Data Scientists , Data Science Interview Questions , and 15 Data Science Consulting Companies Hiring Now .
An Example of a One-Sided Test
You can also form one-sided or one-tailed tests.
Say your friend, Paul, told you that he thinks data scientists earn more than 125,000 dollars per year. You doubt him, so you design a test to see who’s right.

The null hypothesis of this test would be: The mean data scientist salary is more than 125,000 dollars.
The alternative will cover everything else, thus: The mean data scientist salary is less than or equal to 125,000 dollars.

Important: The outcomes of tests refer to the population parameter rather than the sample statistic! So, the result that we get is for the population.

Important: Another crucial consideration is that, generally, the researcher is trying to reject the null hypothesis . Think about the null hypothesis as the status quo and the alternative as the change or innovation that challenges that status quo. In our example, Paul was representing the status quo, which we were challenging.

Let’s go over it once more. In statistics, the null hypothesis is the statement we are trying to reject. Therefore, the null hypothesis is the present state of affairs, while the alternative is our personal opinion.

Why Hypothesis Testing Works
Right now, you may be feeling a little puzzled. This is normal because this whole concept is counter-intuitive at the beginning. However, there is an extremely easy way to continue your journey of exploring it. By diving into the linked tutorial, you will find out why hypothesis testing actually works.
Interested in learning more? You can take your skills from good to great with our statistics course!
Try statistics course for free
Next Tutorial: Hypothesis Testing: Significance Level and Rejection Region
World-Class
Data Science
Learn with instructors from:
Iliya Valchanov
Co-founder of 365 Data Science
Iliya is a finance graduate with a strong quantitative background who chose the exciting path of a startup entrepreneur. He demonstrated a formidable affinity for numbers during his childhood, winning more than 90 national and international awards and competitions through the years. Iliya started teaching at university, helping other students learn statistics and econometrics. Inspired by his first happy students, he co-founded 365 Data Science to continue spreading knowledge. He authored several of the program’s online courses in mathematics, statistics, machine learning, and deep learning.
We Think you'll also like

Statistics Tutorials
False Positive vs. False Negative: Type I and Type II Errors in Statistical Hypothesis Testing

Hypothesis Testing with Z-Test: Significance Level and Rejection Region
Calculating and Using Covariance and Linear Correlation Coefficient

Getting Familiar with the Central Limit Theorem and the Standard Error
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
10.1 - setting the hypotheses: examples.
A significance test examines whether the null hypothesis provides a plausible explanation of the data. The null hypothesis itself does not involve the data. It is a statement about a parameter (a numerical characteristic of the population). These population values might be proportions or means or differences between means or proportions or correlations or odds ratios or any other numerical summary of the population. The alternative hypothesis is typically the research hypothesis of interest. Here are some examples.
Example 10.2: Hypotheses with One Sample of One Categorical Variable Section
About 10% of the human population is left-handed. Suppose a researcher at Penn State speculates that students in the College of Arts and Architecture are more likely to be left-handed than people found in the general population. We only have one sample since we will be comparing a population proportion based on a sample value to a known population value.
- Research Question : Are artists more likely to be left-handed than people found in the general population?
- Response Variable : Classification of the student as either right-handed or left-handed
State Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Null Hypothesis : Students in the College of Arts and Architecture are no more likely to be left-handed than people in the general population (population percent of left-handed students in the College of Art and Architecture = 10% or p = .10).
- Alternative Hypothesis : Students in the College of Arts and Architecture are more likely to be left-handed than people in the general population (population percent of left-handed students in the College of Arts and Architecture > 10% or p > .10). This is a one-sided alternative hypothesis.
Example 10.3: Hypotheses with One Sample of One Measurement Variable Section

A generic brand of the anti-histamine Diphenhydramine markets a capsule with a 50 milligram dose. The manufacturer is worried that the machine that fills the capsules has come out of calibration and is no longer creating capsules with the appropriate dosage.
- Research Question : Does the data suggest that the population mean dosage of this brand is different than 50 mg?
- Response Variable : dosage of the active ingredient found by a chemical assay.
- Null Hypothesis : On the average, the dosage sold under this brand is 50 mg (population mean dosage = 50 mg).
- Alternative Hypothesis : On the average, the dosage sold under this brand is not 50 mg (population mean dosage ≠ 50 mg). This is a two-sided alternative hypothesis.
Example 10.4: Hypotheses with Two Samples of One Categorical Variable Section

Many people are starting to prefer vegetarian meals on a regular basis. Specifically, a researcher believes that females are more likely than males to eat vegetarian meals on a regular basis.
- Research Question : Does the data suggest that females are more likely than males to eat vegetarian meals on a regular basis?
- Response Variable : Classification of whether or not a person eats vegetarian meals on a regular basis
- Explanatory (Grouping) Variable: Sex
- Null Hypothesis : There is no sex effect regarding those who eat vegetarian meals on a regular basis (population percent of females who eat vegetarian meals on a regular basis = population percent of males who eat vegetarian meals on a regular basis or p females = p males ).
- Alternative Hypothesis : Females are more likely than males to eat vegetarian meals on a regular basis (population percent of females who eat vegetarian meals on a regular basis > population percent of males who eat vegetarian meals on a regular basis or p females > p males ). This is a one-sided alternative hypothesis.
Example 10.5: Hypotheses with Two Samples of One Measurement Variable Section

Obesity is a major health problem today. Research is starting to show that people may be able to lose more weight on a low carbohydrate diet than on a low fat diet.
- Research Question : Does the data suggest that, on the average, people are able to lose more weight on a low carbohydrate diet than on a low fat diet?
- Response Variable : Weight loss (pounds)
- Explanatory (Grouping) Variable : Type of diet
- Null Hypothesis : There is no difference in the mean amount of weight loss when comparing a low carbohydrate diet with a low fat diet (population mean weight loss on a low carbohydrate diet = population mean weight loss on a low fat diet).
- Alternative Hypothesis : The mean weight loss should be greater for those on a low carbohydrate diet when compared with those on a low fat diet (population mean weight loss on a low carbohydrate diet > population mean weight loss on a low fat diet). This is a one-sided alternative hypothesis.
Example 10.6: Hypotheses about the relationship between Two Categorical Variables Section
- Research Question : Do the odds of having a stroke increase if you inhale second hand smoke ? A case-control study of non-smoking stroke patients and controls of the same age and occupation are asked if someone in their household smokes.
- Variables : There are two different categorical variables (Stroke patient vs control and whether the subject lives in the same household as a smoker). Living with a smoker (or not) is the natural explanatory variable and having a stroke (or not) is the natural response variable in this situation.
- Null Hypothesis : There is no relationship between whether or not a person has a stroke and whether or not a person lives with a smoker (odds ratio between stroke and second-hand smoke situation is = 1).
- Alternative Hypothesis : There is a relationship between whether or not a person has a stroke and whether or not a person lives with a smoker (odds ratio between stroke and second-hand smoke situation is > 1). This is a one-tailed alternative.
This research question might also be addressed like example 11.4 by making the hypotheses about comparing the proportion of stroke patients that live with smokers to the proportion of controls that live with smokers.
Example 10.7: Hypotheses about the relationship between Two Measurement Variables Section
- Research Question : A financial analyst believes there might be a positive association between the change in a stock's price and the amount of the stock purchased by non-management employees the previous day (stock trading by management being under "insider-trading" regulatory restrictions).
- Variables : Daily price change information (the response variable) and previous day stock purchases by non-management employees (explanatory variable). These are two different measurement variables.
- Null Hypothesis : The correlation between the daily stock price change (\$) and the daily stock purchases by non-management employees (\$) = 0.
- Alternative Hypothesis : The correlation between the daily stock price change (\$) and the daily stock purchases by non-management employees (\$) > 0. This is a one-sided alternative hypothesis.
Example 10.8: Hypotheses about comparing the relationship between Two Measurement Variables in Two Samples Section
- Research Question : Is there a linear relationship between the amount of the bill (\$) at a restaurant and the tip (\$) that was left. Is the strength of this association different for family restaurants than for fine dining restaurants?
- Variables : There are two different measurement variables. The size of the tip would depend on the size of the bill so the amount of the bill would be the explanatory variable and the size of the tip would be the response variable.
- Null Hypothesis : The correlation between the amount of the bill (\$) at a restaurant and the tip (\$) that was left is the same at family restaurants as it is at fine dining restaurants.
- Alternative Hypothesis : The correlation between the amount of the bill (\$) at a restaurant and the tip (\$) that was left is the difference at family restaurants then it is at fine dining restaurants. This is a two-sided alternative hypothesis.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
A Beginner’s Guide to Hypothesis Testing in Business

- 30 Mar 2021
Becoming a more data-driven decision-maker can bring several benefits to your organization, enabling you to identify new opportunities to pursue and threats to abate. Rather than allowing subjective thinking to guide your business strategy, backing your decisions with data can empower your company to become more innovative and, ultimately, profitable.
If you’re new to data-driven decision-making, you might be wondering how data translates into business strategy. The answer lies in generating a hypothesis and verifying or rejecting it based on what various forms of data tell you.
Below is a look at hypothesis testing and the role it plays in helping businesses become more data-driven.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Hypothesis Testing?
To understand what hypothesis testing is, it’s important first to understand what a hypothesis is.
A hypothesis or hypothesis statement seeks to explain why something has happened, or what might happen, under certain conditions. It can also be used to understand how different variables relate to each other. Hypotheses are often written as if-then statements; for example, “If this happens, then this will happen.”
Hypothesis testing , then, is a statistical means of testing an assumption stated in a hypothesis. While the specific methodology leveraged depends on the nature of the hypothesis and data available, hypothesis testing typically uses sample data to extrapolate insights about a larger population.
Hypothesis Testing in Business
When it comes to data-driven decision-making, there’s a certain amount of risk that can mislead a professional. This could be due to flawed thinking or observations, incomplete or inaccurate data , or the presence of unknown variables. The danger in this is that, if major strategic decisions are made based on flawed insights, it can lead to wasted resources, missed opportunities, and catastrophic outcomes.
The real value of hypothesis testing in business is that it allows professionals to test their theories and assumptions before putting them into action. This essentially allows an organization to verify its analysis is correct before committing resources to implement a broader strategy.
As one example, consider a company that wishes to launch a new marketing campaign to revitalize sales during a slow period. Doing so could be an incredibly expensive endeavor, depending on the campaign’s size and complexity. The company, therefore, may wish to test the campaign on a smaller scale to understand how it will perform.
In this example, the hypothesis that’s being tested would fall along the lines of: “If the company launches a new marketing campaign, then it will translate into an increase in sales.” It may even be possible to quantify how much of a lift in sales the company expects to see from the effort. Pending the results of the pilot campaign, the business would then know whether it makes sense to roll it out more broadly.
Related: 9 Fundamental Data Science Skills for Business Professionals
Key Considerations for Hypothesis Testing
1. alternative hypothesis and null hypothesis.
In hypothesis testing, the hypothesis that’s being tested is known as the alternative hypothesis . Often, it’s expressed as a correlation or statistical relationship between variables. The null hypothesis , on the other hand, is a statement that’s meant to show there’s no statistical relationship between the variables being tested. It’s typically the exact opposite of whatever is stated in the alternative hypothesis.
For example, consider a company’s leadership team that historically and reliably sees $12 million in monthly revenue. They want to understand if reducing the price of their services will attract more customers and, in turn, increase revenue.
In this case, the alternative hypothesis may take the form of a statement such as: “If we reduce the price of our flagship service by five percent, then we’ll see an increase in sales and realize revenues greater than $12 million in the next month.”
The null hypothesis, on the other hand, would indicate that revenues wouldn’t increase from the base of $12 million, or might even decrease.
Check out the video below about the difference between an alternative and a null hypothesis, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content.
2. Significance Level and P-Value
Statistically speaking, if you were to run the same scenario 100 times, you’d likely receive somewhat different results each time. If you were to plot these results in a distribution plot, you’d see the most likely outcome is at the tallest point in the graph, with less likely outcomes falling to the right and left of that point.

With this in mind, imagine you’ve completed your hypothesis test and have your results, which indicate there may be a correlation between the variables you were testing. To understand your results' significance, you’ll need to identify a p-value for the test, which helps note how confident you are in the test results.
In statistics, the p-value depicts the probability that, assuming the null hypothesis is correct, you might still observe results that are at least as extreme as the results of your hypothesis test. The smaller the p-value, the more likely the alternative hypothesis is correct, and the greater the significance of your results.
3. One-Sided vs. Two-Sided Testing
When it’s time to test your hypothesis, it’s important to leverage the correct testing method. The two most common hypothesis testing methods are one-sided and two-sided tests , or one-tailed and two-tailed tests, respectively.
Typically, you’d leverage a one-sided test when you have a strong conviction about the direction of change you expect to see due to your hypothesis test. You’d leverage a two-sided test when you’re less confident in the direction of change.

4. Sampling
To perform hypothesis testing in the first place, you need to collect a sample of data to be analyzed. Depending on the question you’re seeking to answer or investigate, you might collect samples through surveys, observational studies, or experiments.
A survey involves asking a series of questions to a random population sample and recording self-reported responses.
Observational studies involve a researcher observing a sample population and collecting data as it occurs naturally, without intervention.
Finally, an experiment involves dividing a sample into multiple groups, one of which acts as the control group. For each non-control group, the variable being studied is manipulated to determine how the data collected differs from that of the control group.

Learn How to Perform Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a complex process involving different moving pieces that can allow an organization to effectively leverage its data and inform strategic decisions.
If you’re interested in better understanding hypothesis testing and the role it can play within your organization, one option is to complete a course that focuses on the process. Doing so can lay the statistical and analytical foundation you need to succeed.
Do you want to learn more about hypothesis testing? Explore Business Analytics —one of our online business essentials courses —and download our Beginner’s Guide to Data & Analytics .

About the Author

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Null Hypothesis Examples

The null hypothesis (H 0 ) is the hypothesis that states there is no statistical difference between two sample sets. In other words, it assumes the independent variable does not have an effect on the dependent variable in a scientific experiment .
The null hypothesis is the most powerful type of hypothesis in the scientific method because it’s the easiest one to test with a high confidence level using statistics. If the null hypothesis is accepted, then it’s evidence any observed differences between two experiment groups are due to random chance. If the null hypothesis is rejected, then it’s strong evidence there is a true difference between test sets or that the independent variable affects the dependent variable.
- The null hypothesis is a nullifiable hypothesis. A researcher seeks to reject it because this result strongly indicates observed differences are real and not just due to chance.
- The null hypothesis may be accepted or rejected, but not proven. There is always a level of confidence in the outcome.
What Is the Null Hypothesis?
The null hypothesis is written as H 0 , which is read as H-zero, H-nought, or H-null. It is associated with another hypothesis, called the alternate or alternative hypothesis H A or H 1 . When the null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis are written mathematically, they cover all possible outcomes of an experiment.
An experimenter tests the null hypothesis with a statistical analysis called a significance test. The significance test determines the likelihood that the results of the test are not due to chance. Usually, a researcher uses a confidence level of 95% or 99% (p-value of 0.05 or 0.01). But, even if the confidence in the test is high, there is always a small chance the outcome is incorrect. This means you can’t prove a null hypothesis. It’s also a good reason why it’s important to repeat experiments.
Exact and Inexact Null Hypothesis
The most common type of null hypothesis assumes no difference between two samples or groups or no measurable effect of a treatment. This is the exact hypothesis . If you’re asked to state a null hypothesis for a science class, this is the one to write. It is the easiest type of hypothesis to test and is the only one accepted for certain types of analysis. Examples include:
There is no difference between two groups H 0 : μ 1 = μ 2 (where H 0 = the null hypothesis, μ 1 = the mean of population 1, and μ 2 = the mean of population 2)
Both groups have value of 100 (or any number or quality) H 0 : μ = 100
However, sometimes a researcher may test an inexact hypothesis . This type of hypothesis specifies ranges or intervals. Examples include:
Recovery time from a treatment is the same or worse than a placebo: H 0 : μ ≥ placebo time
There is a 5% or less difference between two groups: H 0 : 95 ≤ μ ≤ 105
An inexact hypothesis offers “directionality” about a phenomenon. For example, an exact hypothesis can indicate whether or not a treatment has an effect, while an inexact hypothesis can tell whether an effect is positive of negative. However, an inexact hypothesis may be harder to test and some scientists and statisticians disagree about whether it’s a true null hypothesis .
How to State the Null Hypothesis
To state the null hypothesis, first state what you expect the experiment to show. Then, rephrase the statement in a form that assumes there is no relationship between the variables or that a treatment has no effect.
Example: A researcher tests whether a new drug speeds recovery time from a certain disease. The average recovery time without treatment is 3 weeks.
- State the goal of the experiment: “I hope the average recovery time with the new drug will be less than 3 weeks.”
- Rephrase the hypothesis to assume the treatment has no effect: “If the drug doesn’t shorten recovery time, then the average time will be 3 weeks or longer.” Mathematically: H 0 : μ ≥ 3
This null hypothesis (inexact hypothesis) covers both the scenario in which the drug has no effect and the one in which the drugs makes the recovery time longer. The alternate hypothesis is that average recovery time will be less than three weeks:
H A : μ < 3
Of course, the researcher could test the no-effect hypothesis (exact null hypothesis): H 0 : μ = 3
The danger of testing this hypothesis is that rejecting it only implies the drug affected recovery time (not whether it made it better or worse). This is because the alternate hypothesis is:
H A : μ ≠ 3 (which includes μ <3 and μ >3)
Even though the no-effect null hypothesis yields less information, it’s used because it’s easier to test using statistics. Basically, testing whether something is unchanged/changed is easier than trying to quantify the nature of the change.
Remember, a researcher hopes to reject the null hypothesis because this supports the alternate hypothesis. Also, be sure the null and alternate hypothesis cover all outcomes. Finally, remember a simple true/false, equal/unequal, yes/no exact hypothesis is easier to test than a more complex inexact hypothesis.
- Adèr, H. J.; Mellenbergh, G. J. & Hand, D. J. (2007). Advising on Research Methods: A Consultant’s Companion . Huizen, The Netherlands: Johannes van Kessel Publishing. ISBN 978-90-79418-01-5 .
- Cox, D. R. (2006). Principles of Statistical Inference . Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-68567-2 .
- Everitt, Brian (1998). The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics . Cambridge, UK New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0521593465.
- Weiss, Neil A. (1999). Introductory Statistics (5th ed.). ISBN 9780201598773.
Related Posts
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid.
A null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis are set up before performing the hypothesis testing. This helps to arrive at a conclusion regarding the sample obtained from the population. In this article, we will learn more about hypothesis testing, its types, steps to perform the testing, and associated examples.
What is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis testing uses sample data from the population to draw useful conclusions regarding the population probability distribution . It tests an assumption made about the data using different types of hypothesis testing methodologies. The hypothesis testing results in either rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Testing Definition
Hypothesis testing can be defined as a statistical tool that is used to identify if the results of an experiment are meaningful or not. It involves setting up a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis. These two hypotheses will always be mutually exclusive. This means that if the null hypothesis is true then the alternative hypothesis is false and vice versa. An example of hypothesis testing is setting up a test to check if a new medicine works on a disease in a more efficient manner.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a concise mathematical statement that is used to indicate that there is no difference between two possibilities. In other words, there is no difference between certain characteristics of data. This hypothesis assumes that the outcomes of an experiment are based on chance alone. It is denoted as \(H_{0}\). Hypothesis testing is used to conclude if the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. Suppose an experiment is conducted to check if girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5. The null hypothesis will say that they are the same height.
Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is an alternative to the null hypothesis. It is used to show that the observations of an experiment are due to some real effect. It indicates that there is a statistical significance between two possible outcomes and can be denoted as \(H_{1}\) or \(H_{a}\). For the above-mentioned example, the alternative hypothesis would be that girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5.
Hypothesis Testing P Value
In hypothesis testing, the p value is used to indicate whether the results obtained after conducting a test are statistically significant or not. It also indicates the probability of making an error in rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.This value is always a number between 0 and 1. The p value is compared to an alpha level, \(\alpha\) or significance level. The alpha level can be defined as the acceptable risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis. The alpha level is usually chosen between 1% to 5%.
Hypothesis Testing Critical region
All sets of values that lead to rejecting the null hypothesis lie in the critical region. Furthermore, the value that separates the critical region from the non-critical region is known as the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Formula
Depending upon the type of data available and the size, different types of hypothesis testing are used to determine whether the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. The hypothesis testing formula for some important test statistics are given below:
- z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\). \(\overline{x}\) is the sample mean, \(\mu\) is the population mean, \(\sigma\) is the population standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
- t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\). s is the sample standard deviation.
- \(\chi ^{2} = \sum \frac{(O_{i}-E_{i})^{2}}{E_{i}}\). \(O_{i}\) is the observed value and \(E_{i}\) is the expected value.
We will learn more about these test statistics in the upcoming section.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
Selecting the correct test for performing hypothesis testing can be confusing. These tests are used to determine a test statistic on the basis of which the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected. Some of the important tests used for hypothesis testing are given below.
Hypothesis Testing Z Test
A z test is a way of hypothesis testing that is used for a large sample size (n ≥ 30). It is used to determine whether there is a difference between the population mean and the sample mean when the population standard deviation is known. It can also be used to compare the mean of two samples. It is used to compute the z test statistic. The formulas are given as follows:
- One sample: z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing t Test
The t test is another method of hypothesis testing that is used for a small sample size (n < 30). It is also used to compare the sample mean and population mean. However, the population standard deviation is not known. Instead, the sample standard deviation is known. The mean of two samples can also be compared using the t test.
- One sample: t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: t = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{s_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{s_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing Chi Square
The Chi square test is a hypothesis testing method that is used to check whether the variables in a population are independent or not. It is used when the test statistic is chi-squared distributed.
One Tailed Hypothesis Testing
One tailed hypothesis testing is done when the rejection region is only in one direction. It can also be known as directional hypothesis testing because the effects can be tested in one direction only. This type of testing is further classified into the right tailed test and left tailed test.
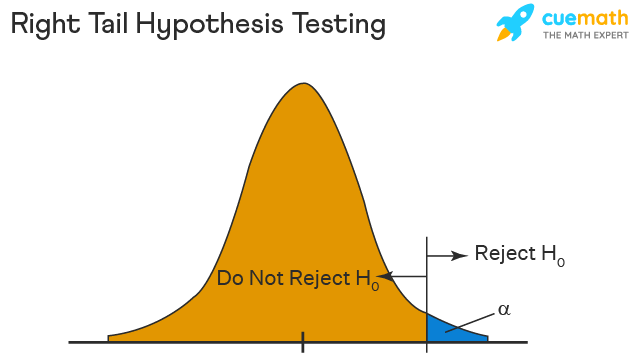
Right Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The right tail test is also known as the upper tail test. This test is used to check whether the population parameter is greater than some value. The null and alternative hypotheses for this test are given as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≤ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is > some value.
If the test statistic has a greater value than the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected
Left Tailed Hypothesis Testing
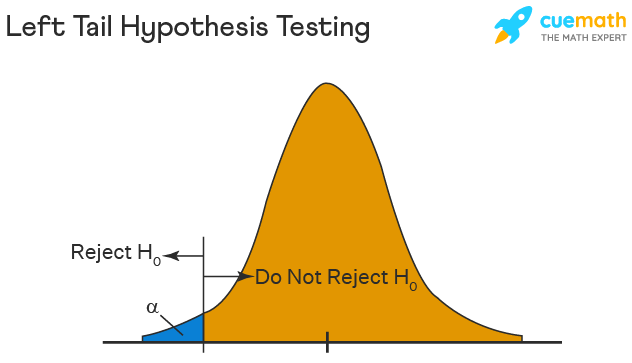
The left tail test is also known as the lower tail test. It is used to check whether the population parameter is less than some value. The hypotheses for this hypothesis testing can be written as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≥ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is < some value.
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value lesser than the critical value.
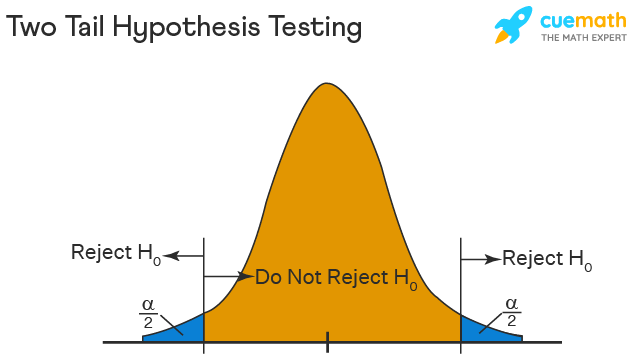
Two Tailed Hypothesis Testing
In this hypothesis testing method, the critical region lies on both sides of the sampling distribution. It is also known as a non - directional hypothesis testing method. The two-tailed test is used when it needs to be determined if the population parameter is assumed to be different than some value. The hypotheses can be set up as follows:
\(H_{0}\): the population parameter = some value
\(H_{1}\): the population parameter ≠ some value
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value that is not equal to the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Steps
Hypothesis testing can be easily performed in five simple steps. The most important step is to correctly set up the hypotheses and identify the right method for hypothesis testing. The basic steps to perform hypothesis testing are as follows:
- Step 1: Set up the null hypothesis by correctly identifying whether it is the left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed hypothesis testing.
- Step 2: Set up the alternative hypothesis.
- Step 3: Choose the correct significance level, \(\alpha\), and find the critical value.
- Step 4: Calculate the correct test statistic (z, t or \(\chi\)) and p-value.
- Step 5: Compare the test statistic with the critical value or compare the p-value with \(\alpha\) to arrive at a conclusion. In other words, decide if the null hypothesis is to be rejected or not.
Hypothesis Testing Example
The best way to solve a problem on hypothesis testing is by applying the 5 steps mentioned in the previous section. Suppose a researcher claims that the mean average weight of men is greater than 100kgs with a standard deviation of 15kgs. 30 men are chosen with an average weight of 112.5 Kgs. Using hypothesis testing, check if there is enough evidence to support the researcher's claim. The confidence interval is given as 95%.
Step 1: This is an example of a right-tailed test. Set up the null hypothesis as \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 100.
Step 2: The alternative hypothesis is given by \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 100.
Step 3: As this is a one-tailed test, \(\alpha\) = 100% - 95% = 5%. This can be used to determine the critical value.
1 - \(\alpha\) = 1 - 0.05 = 0.95
0.95 gives the required area under the curve. Now using a normal distribution table, the area 0.95 is at z = 1.645. A similar process can be followed for a t-test. The only additional requirement is to calculate the degrees of freedom given by n - 1.
Step 4: Calculate the z test statistic. This is because the sample size is 30. Furthermore, the sample and population means are known along with the standard deviation.
z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
\(\mu\) = 100, \(\overline{x}\) = 112.5, n = 30, \(\sigma\) = 15
z = \(\frac{112.5-100}{\frac{15}{\sqrt{30}}}\) = 4.56
Step 5: Conclusion. As 4.56 > 1.645 thus, the null hypothesis can be rejected.

Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals form an important part of hypothesis testing. This is because the alpha level can be determined from a given confidence interval. Suppose a confidence interval is given as 95%. Subtract the confidence interval from 100%. This gives 100 - 95 = 5% or 0.05. This is the alpha value of a one-tailed hypothesis testing. To obtain the alpha value for a two-tailed hypothesis testing, divide this value by 2. This gives 0.05 / 2 = 0.025.
Related Articles:
- Probability and Statistics
- Data Handling
Important Notes on Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis testing is a technique that is used to verify whether the results of an experiment are statistically significant.
- It involves the setting up of a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis.
- There are three types of tests that can be conducted under hypothesis testing - z test, t test, and chi square test.
- Hypothesis testing can be classified as right tail, left tail, and two tail tests.
Examples on Hypothesis Testing
- Example 1: The average weight of a dumbbell in a gym is 90lbs. However, a physical trainer believes that the average weight might be higher. A random sample of 5 dumbbells with an average weight of 110lbs and a standard deviation of 18lbs. Using hypothesis testing check if the physical trainer's claim can be supported for a 95% confidence level. Solution: As the sample size is lesser than 30, the t-test is used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 5, s = 18. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 Using the t-distribution table, the critical value is 2.132 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = 2.484 As 2.484 > 2.132, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: The average weight of the dumbbells may be greater than 90lbs
- Example 2: The average score on a test is 80 with a standard deviation of 10. With a new teaching curriculum introduced it is believed that this score will change. On random testing, the score of 38 students, the mean was found to be 88. With a 0.05 significance level, is there any evidence to support this claim? Solution: This is an example of two-tail hypothesis testing. The z test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 80, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) ≠ 80 \(\overline{x}\) = 88, \(\mu\) = 80, n = 36, \(\sigma\) = 10. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 / 2 = 0.025 The critical value using the normal distribution table is 1.96 z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) z = \(\frac{88-80}{\frac{10}{\sqrt{36}}}\) = 4.8 As 4.8 > 1.96, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: There is a difference in the scores after the new curriculum was introduced.
- Example 3: The average score of a class is 90. However, a teacher believes that the average score might be lower. The scores of 6 students were randomly measured. The mean was 82 with a standard deviation of 18. With a 0.05 significance level use hypothesis testing to check if this claim is true. Solution: The t test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) < 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 6, s = 18 The critical value from the t table is -2.015 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = \(\frac{82-90}{\frac{18}{\sqrt{6}}}\) t = -1.088 As -1.088 > -2.015, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Answer: There is not enough evidence to support the claim.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
FAQs on Hypothesis Testing
What is hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing in statistics is a tool that is used to make inferences about the population data. It is also used to check if the results of an experiment are valid.
What is the z Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The z test in hypothesis testing is used to find the z test statistic for normally distributed data . The z test is used when the standard deviation of the population is known and the sample size is greater than or equal to 30.
What is the t Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The t test in hypothesis testing is used when the data follows a student t distribution . It is used when the sample size is less than 30 and standard deviation of the population is not known.
What is the formula for z test in Hypothesis Testing?
The formula for a one sample z test in hypothesis testing is z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) and for two samples is z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
What is the p Value in Hypothesis Testing?
The p value helps to determine if the test results are statistically significant or not. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected based on the comparison between the p value and the alpha level.
What is One Tail Hypothesis Testing?
When the rejection region is only on one side of the distribution curve then it is known as one tail hypothesis testing. The right tail test and the left tail test are two types of directional hypothesis testing.
What is the Alpha Level in Two Tail Hypothesis Testing?
To get the alpha level in a two tail hypothesis testing divide \(\alpha\) by 2. This is done as there are two rejection regions in the curve.

Statistics Made Easy
4 Examples of Hypothesis Testing in Real Life
In statistics, hypothesis tests are used to test whether or not some hypothesis about a population parameter is true.
To perform a hypothesis test in the real world, researchers will obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data, using a null and alternative hypothesis:
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The sample data occurs purely from chance.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H A ): The sample data is influenced by some non-random cause.
If the p-value of the hypothesis test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then we can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that we have sufficient evidence to say that the alternative hypothesis is true.
The following examples provide several situations where hypothesis tests are used in the real world.
Example 1: Biology
Hypothesis tests are often used in biology to determine whether some new treatment, fertilizer, pesticide, chemical, etc. causes increased growth, stamina, immunity, etc. in plants or animals.
For example, suppose a biologist believes that a certain fertilizer will cause plants to grow more during a one-month period than they normally do, which is currently 20 inches. To test this, she applies the fertilizer to each of the plants in her laboratory for one month.
She then performs a hypothesis test using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ = 20 inches (the fertilizer will have no effect on the mean plant growth)
- H A : μ > 20 inches (the fertilizer will cause mean plant growth to increase)
If the p-value of the test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then she can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the fertilizer leads to increased plant growth.
Example 2: Clinical Trials
Hypothesis tests are often used in clinical trials to determine whether some new treatment, drug, procedure, etc. causes improved outcomes in patients.
For example, suppose a doctor believes that a new drug is able to reduce blood pressure in obese patients. To test this, he may measure the blood pressure of 40 patients before and after using the new drug for one month.
He then performs a hypothesis test using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ after = μ before (the mean blood pressure is the same before and after using the drug)
- H A : μ after < μ before (the mean blood pressure is less after using the drug)
If the p-value of the test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then he can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the new drug leads to reduced blood pressure.
Example 3: Advertising Spend
Hypothesis tests are often used in business to determine whether or not some new advertising campaign, marketing technique, etc. causes increased sales.
For example, suppose a company believes that spending more money on digital advertising leads to increased sales. To test this, the company may increase money spent on digital advertising during a two-month period and collect data to see if overall sales have increased.
They may perform a hypothesis test using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ after = μ before (the mean sales is the same before and after spending more on advertising)
- H A : μ after > μ before (the mean sales increased after spending more on advertising)
If the p-value of the test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then the company can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that increased digital advertising leads to increased sales.
Example 4: Manufacturing
Hypothesis tests are also used often in manufacturing plants to determine if some new process, technique, method, etc. causes a change in the number of defective products produced.
For example, suppose a certain manufacturing plant wants to test whether or not some new method changes the number of defective widgets produced per month, which is currently 250. To test this, they may measure the mean number of defective widgets produced before and after using the new method for one month.
They can then perform a hypothesis test using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ after = μ before (the mean number of defective widgets is the same before and after using the new method)
- H A : μ after ≠ μ before (the mean number of defective widgets produced is different before and after using the new method)
If the p-value of the test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then the plant can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the new method leads to a change in the number of defective widgets produced per month.
Additional Resources
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing Introduction to the One Sample t-test Introduction to the Two Sample t-test Introduction to the Paired Samples t-test
Published by Zach
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.2: Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 28124

The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
\(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
\(H_a\): The alternative hypothesis: It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to \(H_0\) and what we conclude when we reject \(H_0\). This is usually what the researcher is trying to prove.
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are "reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or "do not reject \(H_0\)" or "decline to reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
\(H_{0}\) always has a symbol with an equal in it. \(H_{a}\) never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
- \(H_{0}\): No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p \leq 30\)
- \(H_{a}\): More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p > 30\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}\): The drug reduces cholesterol by 25%. \(p = 0.25\)
- \(H_{a}\): The drug does not reduce cholesterol by 25%. \(p \neq 0.25\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 2.0\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 2.0\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol \((=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >)\) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 66\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 5\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 5\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 45\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
In an issue of U. S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \leq 0.066\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.066\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (\(=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >\)) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.40\)
COLLABORATIVE EXERCISE
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some Internet articles . In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
In a hypothesis test , sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we:
- Evaluate the null hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{0}\). The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality \((=, \leq \text{or} \geq)\)
- Always write the alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{a}\) or \(H_{1}\), using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, i.e., \((\neq, >, \text{or} <)\).
- If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
Formula Review
\(H_{0}\) and \(H_{a}\) are contradictory.
- If \(\alpha \leq p\)-value, then do not reject \(H_{0}\).
- If\(\alpha > p\)-value, then reject \(H_{0}\).
\(\alpha\) is preconceived. Its value is set before the hypothesis test starts. The \(p\)-value is calculated from the data.References
Data from the National Institute of Mental Health. Available online at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/publicat/depression.cfm .
- Machine Learning Tutorial
- Data Analysis Tutorial
- Python - Data visualization tutorial
- Machine Learning Projects
- Machine Learning Interview Questions
- Machine Learning Mathematics
- Deep Learning Tutorial
- Deep Learning Project
- Deep Learning Interview Questions
- Computer Vision Tutorial
- Computer Vision Projects
- NLP Project
- NLP Interview Questions
- Statistics with Python
- 100 Days of Machine Learning
- Data Analysis with Python
Introduction to Data Analysis
- What is Data Analysis?
- Data Analytics and its type
- How to Install Numpy on Windows?
- How to Install Pandas in Python?
- How to Install Matplotlib on python?
- How to Install Python Tensorflow in Windows?
Data Analysis Libraries
- Pandas Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial - Python Library
- Data Analysis with SciPy
- Introduction to TensorFlow
Data Visulization Libraries
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- Python Seaborn Tutorial
- Plotly tutorial
- Introduction to Bokeh in Python
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Univariate, Bivariate and Multivariate data and its analysis
- Measures of Central Tendency in Statistics
- Measures of spread - Range, Variance, and Standard Deviation
- Interquartile Range and Quartile Deviation using NumPy and SciPy
- Anova Formula
- Skewness of Statistical Data
- How to Calculate Skewness and Kurtosis in Python?
- Difference Between Skewness and Kurtosis
- Histogram | Meaning, Example, Types and Steps to Draw
- Interpretations of Histogram
- Quantile Quantile plots
- What is Univariate, Bivariate & Multivariate Analysis in Data Visualisation?
- Using pandas crosstab to create a bar plot
- Exploring Correlation in Python
- Mathematics | Covariance and Correlation
- Introduction to Factor Analysis
- Data Mining - Cluster Analysis
- MANOVA Test in R Programming
- Python - Central Limit Theorem
- Probability Distribution Function
- Probability Density Estimation & Maximum Likelihood Estimation
- Exponential Distribution in R Programming - dexp(), pexp(), qexp(), and rexp() Functions
- Mathematics | Probability Distributions Set 4 (Binomial Distribution)
- Poisson Distribution - Definition, Formula, Table and Examples
- P-Value: Comprehensive Guide to Understand, Apply, and Interpret
- Z-Score in Statistics
- How to Calculate Point Estimates in R?
- Confidence Interval
- Chi-square test in Machine Learning
Understanding Hypothesis Testing
Data preprocessing.
- ML | Data Preprocessing in Python
- ML | Overview of Data Cleaning
- ML | Handling Missing Values
- Detect and Remove the Outliers using Python
Data Transformation
- Data Normalization Machine Learning
- Sampling distribution Using Python
Time Series Data Analysis
- Data Mining - Time-Series, Symbolic and Biological Sequences Data
- Basic DateTime Operations in Python
- Time Series Analysis & Visualization in Python
- How to deal with missing values in a Timeseries in Python?
- How to calculate MOVING AVERAGE in a Pandas DataFrame?
- What is a trend in time series?
- How to Perform an Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test in R
- AutoCorrelation
Case Studies and Projects
- Top 8 Free Dataset Sources to Use for Data Science Projects
- Step by Step Predictive Analysis - Machine Learning
- 6 Tips for Creating Effective Data Visualizations
Hypothesis testing involves formulating assumptions about population parameters based on sample statistics and rigorously evaluating these assumptions against empirical evidence. This article sheds light on the significance of hypothesis testing and the critical steps involved in the process.
What is Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that is used to make a statistical decision using experimental data. Hypothesis testing is basically an assumption that we make about a population parameter. It evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement is best supported by the sample data.
Example: You say an average height in the class is 30 or a boy is taller than a girl. All of these is an assumption that we are assuming, and we need some statistical way to prove these. We need some mathematical conclusion whatever we are assuming is true.
Defining Hypotheses
Key Terms of Hypothesis Testing
- P-value: The P value , or calculated probability, is the probability of finding the observed/extreme results when the null hypothesis(H0) of a study-given problem is true. If your P-value is less than the chosen significance level then you reject the null hypothesis i.e. accept that your sample claims to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Test Statistic: The test statistic is a numerical value calculated from sample data during a hypothesis test, used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. It is compared to a critical value or p-value to make decisions about the statistical significance of the observed results.
- Critical value : The critical value in statistics is a threshold or cutoff point used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis in a hypothesis test.
- Degrees of freedom: Degrees of freedom are associated with the variability or freedom one has in estimating a parameter. The degrees of freedom are related to the sample size and determine the shape.
Why do we use Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is an important procedure in statistics. Hypothesis testing evaluates two mutually exclusive population statements to determine which statement is most supported by sample data. When we say that the findings are statistically significant, thanks to hypothesis testing.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Test
One tailed test focuses on one direction, either greater than or less than a specified value. We use a one-tailed test when there is a clear directional expectation based on prior knowledge or theory. The critical region is located on only one side of the distribution curve. If the sample falls into this critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
One-Tailed Test
There are two types of one-tailed test:
Two-Tailed Test
A two-tailed test considers both directions, greater than and less than a specified value.We use a two-tailed test when there is no specific directional expectation, and want to detect any significant difference.
What are Type 1 and Type 2 errors in Hypothesis Testing?
In hypothesis testing, Type I and Type II errors are two possible errors that researchers can make when drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data. These errors are associated with the decisions made regarding the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
How does Hypothesis Testing work?
Step 1: define null and alternative hypothesis.
We first identify the problem about which we want to make an assumption keeping in mind that our assumption should be contradictory to one another, assuming Normally distributed data.
Step 2 – Choose significance level
Step 3 – Collect and Analyze data.
Gather relevant data through observation or experimentation. Analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods to obtain a test statistic.
Step 4-Calculate Test Statistic
The data for the tests are evaluated in this step we look for various scores based on the characteristics of data. The choice of the test statistic depends on the type of hypothesis test being conducted.
There are various hypothesis tests, each appropriate for various goal to calculate our test. This could be a Z-test , Chi-square , T-test , and so on.
- Z-test : If population means and standard deviations are known. Z-statistic is commonly used.
- t-test : If population standard deviations are unknown. and sample size is small than t-test statistic is more appropriate.
- Chi-square test : Chi-square test is used for categorical data or for testing independence in contingency tables
- F-test : F-test is often used in analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare variances or test the equality of means across multiple groups.
We have a smaller dataset, So, T-test is more appropriate to test our hypothesis.
T-statistic is a measure of the difference between the means of two groups relative to the variability within each group. It is calculated as the difference between the sample means divided by the standard error of the difference. It is also known as the t-value or t-score.
Step 5 – Comparing Test Statistic:
In this stage, we decide where we should accept the null hypothesis or reject the null hypothesis. There are two ways to decide where we should accept or reject the null hypothesis.
Method A: Using Crtical values
Comparing the test statistic and tabulated critical value we have,
- If Test Statistic>Critical Value: Reject the null hypothesis.
- If Test Statistic≤Critical Value: Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Note: Critical values are predetermined threshold values that are used to make a decision in hypothesis testing. To determine critical values for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Method B: Using P-values
We can also come to an conclusion using the p-value,
Note : The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as, or more extreme than, the one observed in the sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true. To determine p-value for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Step 7- Interpret the Results
At last, we can conclude our experiment using method A or B.
Calculating test statistic
To validate our hypothesis about a population parameter we use statistical functions . We use the z-score, p-value, and level of significance(alpha) to make evidence for our hypothesis for normally distributed data .
1. Z-statistics:
When population means and standard deviations are known.
- μ represents the population mean,
- σ is the standard deviation
- and n is the size of the sample.
2. T-Statistics
T test is used when n<30,
t-statistic calculation is given by:
- t = t-score,
- x̄ = sample mean
- μ = population mean,
- s = standard deviation of the sample,
- n = sample size
3. Chi-Square Test
Chi-Square Test for Independence categorical Data (Non-normally distributed) using:
- i,j are the rows and columns index respectively.
Real life Hypothesis Testing example
Let’s examine hypothesis testing using two real life situations,
Case A: D oes a New Drug Affect Blood Pressure?
Imagine a pharmaceutical company has developed a new drug that they believe can effectively lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Before bringing the drug to market, they need to conduct a study to assess its impact on blood pressure.
- Before Treatment: 120, 122, 118, 130, 125, 128, 115, 121, 123, 119
- After Treatment: 115, 120, 112, 128, 122, 125, 110, 117, 119, 114
Step 1 : Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis : (H 0 )The new drug has no effect on blood pressure.
- Alternate Hypothesis : (H 1 )The new drug has an effect on blood pressure.
Step 2: Define the Significance level
Let’s consider the Significance level at 0.05, indicating rejection of the null hypothesis.
If the evidence suggests less than a 5% chance of observing the results due to random variation.
Step 3 : Compute the test statistic
Using paired T-test analyze the data to obtain a test statistic and a p-value.
The test statistic (e.g., T-statistic) is calculated based on the differences between blood pressure measurements before and after treatment.
t = m/(s/√n)
- m = mean of the difference i.e X after, X before
- s = standard deviation of the difference (d) i.e d i = X after, i − X before,
- n = sample size,
then, m= -3.9, s= 1.8 and n= 10
we, calculate the , T-statistic = -9 based on the formula for paired t test
Step 4: Find the p-value
The calculated t-statistic is -9 and degrees of freedom df = 9, you can find the p-value using statistical software or a t-distribution table.
thus, p-value = 8.538051223166285e-06
Step 5: Result
- If the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05, the researchers reject the null hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than 0.05, they fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion: Since the p-value (8.538051223166285e-06) is less than the significance level (0.05), the researchers reject the null hypothesis. There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different.
Python Implementation of Hypothesis Testing
Let’s create hypothesis testing with python, where we are testing whether a new drug affects blood pressure. For this example, we will use a paired T-test. We’ll use the scipy.stats library for the T-test.
Scipy is a mathematical library in Python that is mostly used for mathematical equations and computations.
We will implement our first real life problem via python,
In the above example, given the T-statistic of approximately -9 and an extremely small p-value, the results indicate a strong case to reject the null hypothesis at a significance level of 0.05.
- The results suggest that the new drug, treatment, or intervention has a significant effect on lowering blood pressure.
- The negative T-statistic indicates that the mean blood pressure after treatment is significantly lower than the assumed population mean before treatment.
Case B : Cholesterol level in a population
Data: A sample of 25 individuals is taken, and their cholesterol levels are measured.
Cholesterol Levels (mg/dL): 205, 198, 210, 190, 215, 205, 200, 192, 198, 205, 198, 202, 208, 200, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205.
Populations Mean = 200
Population Standard Deviation (σ): 5 mg/dL(given for this problem)
Step 1: Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is 200 mg/dL.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H 1 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is different from 200 mg/dL.
As the direction of deviation is not given , we assume a two-tailed test, and based on a normal distribution table, the critical values for a significance level of 0.05 (two-tailed) can be calculated through the z-table and are approximately -1.96 and 1.96.
Step 4: Result
Since the absolute value of the test statistic (2.04) is greater than the critical value (1.96), we reject the null hypothesis. And conclude that, there is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL
Limitations of Hypothesis Testing
- Although a useful technique, hypothesis testing does not offer a comprehensive grasp of the topic being studied. Without fully reflecting the intricacy or whole context of the phenomena, it concentrates on certain hypotheses and statistical significance.
- The accuracy of hypothesis testing results is contingent on the quality of available data and the appropriateness of statistical methods used. Inaccurate data or poorly formulated hypotheses can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Relying solely on hypothesis testing may cause analysts to overlook significant patterns or relationships in the data that are not captured by the specific hypotheses being tested. This limitation underscores the importance of complimenting hypothesis testing with other analytical approaches.
Hypothesis testing stands as a cornerstone in statistical analysis, enabling data scientists to navigate uncertainties and draw credible inferences from sample data. By systematically defining null and alternative hypotheses, choosing significance levels, and leveraging statistical tests, researchers can assess the validity of their assumptions. The article also elucidates the critical distinction between Type I and Type II errors, providing a comprehensive understanding of the nuanced decision-making process inherent in hypothesis testing. The real-life example of testing a new drug’s effect on blood pressure using a paired T-test showcases the practical application of these principles, underscoring the importance of statistical rigor in data-driven decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what are the 3 types of hypothesis test.
There are three types of hypothesis tests: right-tailed, left-tailed, and two-tailed. Right-tailed tests assess if a parameter is greater, left-tailed if lesser. Two-tailed tests check for non-directional differences, greater or lesser.
2.What are the 4 components of hypothesis testing?
Null Hypothesis ( ): No effect or difference exists. Alternative Hypothesis ( ): An effect or difference exists. Significance Level ( ): Risk of rejecting null hypothesis when it’s true (Type I error). Test Statistic: Numerical value representing observed evidence against null hypothesis.
3.What is hypothesis testing in ML?
Statistical method to evaluate the performance and validity of machine learning models. Tests specific hypotheses about model behavior, like whether features influence predictions or if a model generalizes well to unseen data.
4.What is the difference between Pytest and hypothesis in Python?
Pytest purposes general testing framework for Python code while Hypothesis is a Property-based testing framework for Python, focusing on generating test cases based on specified properties of the code.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- data-science
- Data Science
- Machine Learning
- 10 Best Todoist Alternatives in 2024 (Free)
- How to Get Spotify Premium Free Forever on iOS/Android
- Yahoo Acquires Instagram Co-Founders' AI News Platform Artifact
- OpenAI Introduces DALL-E Editor Interface
- Top 10 R Project Ideas for Beginners in 2024
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.2: Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 125722

The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses . They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis . These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints.
\(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
\(H_a\): The alternative hypothesis: It is a claim about the population that is contradictory to \(H_0\) and what we conclude when we reject \(H_0\). This is usually what the researcher is trying to prove.
Since the null and alternative hypotheses are contradictory, you must examine evidence to decide if you have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis or not. The evidence is in the form of sample data.
After you have determined which hypothesis the sample supports, you make a decision. There are two options for a decision. They are "reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information favors the alternative hypothesis or "do not reject \(H_0\)" or "decline to reject \(H_0\)" if the sample information is insufficient to reject the null hypothesis.
\(H_{0}\) always has a symbol with an equal in it. \(H_{a}\) never has a symbol with an equal in it. The choice of symbol depends on the wording of the hypothesis test. However, be aware that many researchers (including one of the co-authors in research work) use = in the null hypothesis, even with > or < as the symbol in the alternative hypothesis. This practice is acceptable because we only make the decision to reject or not reject the null hypothesis.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
- \(H_{0}\): No more than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p \leq 30\)
- \(H_{a}\): More than 30% of the registered voters in Santa Clara County voted in the primary election. \(p > 30\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A medical trial is conducted to test whether or not a new medicine reduces cholesterol by 25%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}\): The drug reduces cholesterol by 25%. \(p = 0.25\)
- \(H_{a}\): The drug does not reduce cholesterol by 25%. \(p \neq 0.25\)
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean GPA of students in American colleges is different from 2.0 (out of 4.0). The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 2.0\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 2.0\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We want to test whether the mean height of eighth graders is 66 inches. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol \((=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >)\) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 66\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 66\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 66\)
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if college students take less than five years to graduate from college, on the average. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 5\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 5\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
We want to test if it takes fewer than 45 minutes to teach a lesson plan. State the null and alternative hypotheses. Fill in the correct symbol ( =, ≠, ≥, <, ≤, >) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \_ 45\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 45\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 45\)
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
In an issue of U. S. News and World Report , an article on school standards stated that about half of all students in France, Germany, and Israel take advanced placement exams and a third pass. The same article stated that 6.6% of U.S. students take advanced placement exams and 4.4% pass. Test if the percentage of U.S. students who take advanced placement exams is more than 6.6%. State the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \leq 0.066\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.066\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
On a state driver’s test, about 40% pass the test on the first try. We want to test if more than 40% pass on the first try. Fill in the correct symbol (\(=, \neq, \geq, <, \leq, >\)) for the null and alternative hypotheses.
- \(H_{0}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p \_ 0.40\)
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.40\)
COLLABORATIVE EXERCISE
Bring to class a newspaper, some news magazines, and some Internet articles . In groups, find articles from which your group can write null and alternative hypotheses. Discuss your hypotheses with the rest of the class.
In a hypothesis test , sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we:
- Evaluate the null hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{0}\). The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise. The null statement must always contain some form of equality \((=, \leq \text{or} \geq)\)
- Always write the alternative hypothesis , typically denoted with \(H_{a}\) or \(H_{1}\), using less than, greater than, or not equals symbols, i.e., \((\neq, >, \text{or} <)\).
- If we reject the null hypothesis, then we can assume there is enough evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Never state that a claim is proven true or false. Keep in mind the underlying fact that hypothesis testing is based on probability laws; therefore, we can talk only in terms of non-absolute certainties.
Formula Review
\(H_{0}\) and \(H_{a}\) are contradictory.
- If \(\alpha \leq p\)-value, then do not reject \(H_{0}\).
- If\(\alpha > p\)-value, then reject \(H_{0}\).
\(\alpha\) is preconceived. Its value is set before the hypothesis test starts. The \(p\)-value is calculated from the data.References
Data from the National Institute of Mental Health. Available online at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/publicat/depression.cfm .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The null and alternative hypotheses offer competing answers to your research question. When the research question asks "Does the independent variable affect the dependent variable?": The null hypothesis ( H0) answers "No, there's no effect in the population.". The alternative hypothesis ( Ha) answers "Yes, there is an effect in the ...
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. \(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
Whenever we perform a hypothesis test, we always write a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, which take the following forms: H0 (Null Hypothesis): Population parameter =, ≤, ≥ some value. HA (Alternative Hypothesis): Population parameter <, >, ≠ some value. Note that the null hypothesis always contains the equal sign.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0, the —null hypothesis: a statement of no difference between sample means or proportions or no difference between a sample mean or proportion and a population mean or proportion. In other words, the difference equals 0.
The null and alternative hypotheses are two competing claims that researchers weigh evidence for and against using a statistical test: Null hypothesis (H0): There's no effect in the population. Alternative hypothesis (HA): There's an effect in the population. The effect is usually the effect of the independent variable on the dependent ...
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. H 0: The null hypothesis: It is a statement about the population that either is believed to be true or is used to put forth an argument unless it can be shown to be incorrect beyond a reasonable doubt.
It is the opposite of your research hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis--that is, the research hypothesis--is the idea, phenomenon, observation that you want to prove. If you suspect that girls take longer to get ready for school than boys, then: Alternative: girls time > boys time. Null: girls time <= boys time.
The Null and Alternative Hypotheses. There are two hypotheses that are made: the null hypothesis, denoted H 0, and the alternative hypothesis, denoted H 1 or H A. The null hypothesis is the one to be tested and the alternative is everything else. In our example: The null hypothesis would be: The mean data scientist salary is 113,000 dollars.
When your sample contains sufficient evidence, you can reject the null and conclude that the effect is statistically significant. Statisticians often denote the null hypothesis as H 0 or H A.. Null Hypothesis H 0: No effect exists in the population.; Alternative Hypothesis H A: The effect exists in the population.; In every study or experiment, researchers assess an effect or relationship.
10.1 - Setting the Hypotheses: Examples. A significance test examines whether the null hypothesis provides a plausible explanation of the data. The null hypothesis itself does not involve the data. It is a statement about a parameter (a numerical characteristic of the population). These population values might be proportions or means or ...
In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim. If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with \(H_{0}\). The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis ...
The organization thinks that, currently, the mean is higher. Fifteen randomly chosen teenagers were asked how many hours per week they spend on the phone. The sample mean was 4.75 hours with a sample standard deviation of 2.0. Conduct a hypothesis test. The null and alternative hypotheses are: \(H_{0}: \bar{x} = 4.5, H_{a}: \bar{x} > 4.5\)
1. Determine the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. 2. Collect and summarize the data into a test statistic. 3. Use the test statistic to determine the p-value. 4. The result is statistically significant if the p-value is less than or equal to the level of significance. Often media only presents results of step 4.
1. Alternative Hypothesis and Null Hypothesis. In hypothesis testing, the hypothesis that's being tested is known as the alternative hypothesis. Often, it's expressed as a correlation or statistical relationship between variables. The null hypothesis, on the other hand, is a statement that's meant to show there's no statistical ...
An example of the null hypothesis is that light color has no effect on plant growth. The null hypothesis (H 0) is the hypothesis that states there is no statistical difference between two sample sets. In other words, it assumes the independent variable does not have an effect on the dependent variable in a scientific experiment.
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid. A null hypothesis and an alternative ...
In statistics, hypothesis tests are used to test whether or not some hypothesis about a population parameter is true. To perform a hypothesis test in the real world, researchers will obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data, using a null and alternative hypothesis:. Null Hypothesis (H 0): The sample data occurs purely from chance.
The actual test begins by considering two hypotheses.They are called the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.These hypotheses contain opposing viewpoints. \(H_0\): The null hypothesis: It is a statement of no difference between the variables—they are not related. This can often be considered the status quo and as a result if you cannot accept the null it requires some action.
Review. In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim.If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with \(H_{0}\).The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise.
The null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis are always mathematically opposite. The possible outcomes of hypothesis testing: Reject the null hypothesis —a person is found guilty. ... One-sample t-test — compare the mean of one group against the specified mean generated from a population. For example, a manufacturer of mobile phones ...
If the sample falls into this critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis. One-Tailed Test. There are two types of one-tailed test: Left-Tailed (Left-Sided) Test: The alternative hypothesis asserts that the true parameter value is less than the null hypothesis. Example: H 0 : and H 1:
The mean length of time in jail from the survey was 3 years with a standard deviation of 1.8 years. Suppose that it is somehow known that the population standard deviation is 1.5. If you were conducting a hypothesis test to determine if the mean length of jail time has increased, what would the null and alternative hypotheses be?
Review. In a hypothesis test, sample data is evaluated in order to arrive at a decision about some type of claim.If certain conditions about the sample are satisfied, then the claim can be evaluated for a population. In a hypothesis test, we: Evaluate the null hypothesis, typically denoted with \(H_{0}\).The null is not rejected unless the hypothesis test shows otherwise.
Null hypothesis significance testing (NHST) has been under scrutiny for decades. The literature shows overwhelming evidence of a large range of problems affecting NHST. One of the proposed alternatives to NHST is using Bayes factors instead of p values. Here we denote the method of using Bayes factors to test point null models as "null hypothesis Bayesian testing" (NHBT).