

Essay and dissertation writing skills
Planning your essay
Writing your introduction
Structuring your essay
- Writing essays in science subjects
- Brief video guides to support essay planning and writing
- Writing extended essays and dissertations
- Planning your dissertation writing time
Structuring your dissertation
- Top tips for writing longer pieces of work
Advice on planning and writing essays and dissertations
University essays differ from school essays in that they are less concerned with what you know and more concerned with how you construct an argument to answer the question. This means that the starting point for writing a strong essay is to first unpick the question and to then use this to plan your essay before you start putting pen to paper (or finger to keyboard).
A really good starting point for you are these short, downloadable Tips for Successful Essay Writing and Answering the Question resources. Both resources will help you to plan your essay, as well as giving you guidance on how to distinguish between different sorts of essay questions.
You may find it helpful to watch this seven-minute video on six tips for essay writing which outlines how to interpret essay questions, as well as giving advice on planning and structuring your writing:
Different disciplines will have different expectations for essay structure and you should always refer to your Faculty or Department student handbook or course Canvas site for more specific guidance.
However, broadly speaking, all essays share the following features:
Essays need an introduction to establish and focus the parameters of the discussion that will follow. You may find it helpful to divide the introduction into areas to demonstrate your breadth and engagement with the essay question. You might define specific terms in the introduction to show your engagement with the essay question; for example, ‘This is a large topic which has been variously discussed by many scientists and commentators. The principle tension is between the views of X and Y who define the main issues as…’ Breadth might be demonstrated by showing the range of viewpoints from which the essay question could be considered; for example, ‘A variety of factors including economic, social and political, influence A and B. This essay will focus on the social and economic aspects, with particular emphasis on…..’
Watch this two-minute video to learn more about how to plan and structure an introduction:
The main body of the essay should elaborate on the issues raised in the introduction and develop an argument(s) that answers the question. It should consist of a number of self-contained paragraphs each of which makes a specific point and provides some form of evidence to support the argument being made. Remember that a clear argument requires that each paragraph explicitly relates back to the essay question or the developing argument.
- Conclusion: An essay should end with a conclusion that reiterates the argument in light of the evidence you have provided; you shouldn’t use the conclusion to introduce new information.
- References: You need to include references to the materials you’ve used to write your essay. These might be in the form of footnotes, in-text citations, or a bibliography at the end. Different systems exist for citing references and different disciplines will use various approaches to citation. Ask your tutor which method(s) you should be using for your essay and also consult your Department or Faculty webpages for specific guidance in your discipline.
Essay writing in science subjects
If you are writing an essay for a science subject you may need to consider additional areas, such as how to present data or diagrams. This five-minute video gives you some advice on how to approach your reading list, planning which information to include in your answer and how to write for your scientific audience – the video is available here:
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.
Short videos to support your essay writing skills
There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing, including:
- Approaching different types of essay questions
- Structuring your essay
- Writing an introduction
- Making use of evidence in your essay writing
- Writing your conclusion
Extended essays and dissertations
Longer pieces of writing like extended essays and dissertations may seem like quite a challenge from your regular essay writing. The important point is to start with a plan and to focus on what the question is asking. A PDF providing further guidance on planning Humanities and Social Science dissertations is available to download.
Planning your time effectively
Try not to leave the writing until close to your deadline, instead start as soon as you have some ideas to put down onto paper. Your early drafts may never end up in the final work, but the work of committing your ideas to paper helps to formulate not only your ideas, but the method of structuring your writing to read well and conclude firmly.
Although many students and tutors will say that the introduction is often written last, it is a good idea to begin to think about what will go into it early on. For example, the first draft of your introduction should set out your argument, the information you have, and your methods, and it should give a structure to the chapters and sections you will write. Your introduction will probably change as time goes on but it will stand as a guide to your entire extended essay or dissertation and it will help you to keep focused.
The structure of extended essays or dissertations will vary depending on the question and discipline, but may include some or all of the following:
- The background information to - and context for - your research. This often takes the form of a literature review.
- Explanation of the focus of your work.
- Explanation of the value of this work to scholarship on the topic.
- List of the aims and objectives of the work and also the issues which will not be covered because they are outside its scope.
The main body of your extended essay or dissertation will probably include your methodology, the results of research, and your argument(s) based on your findings.
The conclusion is to summarise the value your research has added to the topic, and any further lines of research you would undertake given more time or resources.
Tips on writing longer pieces of work
Approaching each chapter of a dissertation as a shorter essay can make the task of writing a dissertation seem less overwhelming. Each chapter will have an introduction, a main body where the argument is developed and substantiated with evidence, and a conclusion to tie things together. Unlike in a regular essay, chapter conclusions may also introduce the chapter that will follow, indicating how the chapters are connected to one another and how the argument will develop through your dissertation.
For further guidance, watch this two-minute video on writing longer pieces of work .
Systems & Services
Access Student Self Service
- Student Self Service
- Self Service guide
- Registration guide
- Libraries search
- OXCORT - see TMS
- GSS - see Student Self Service
- The Careers Service
- Oxford University Sport
- Online store
- Gardens, Libraries and Museums
- Researchers Skills Toolkit
- LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com)
- Access Guide
- Lecture Lists
- Exam Papers (OXAM)
- Oxford Talks
Latest student news
CAN'T FIND WHAT YOU'RE LOOKING FOR?
Try our extensive database of FAQs or submit your own question...
Ask a question
Writers' Center
Eastern Washington University
Reading and Study Strategies
- Annotating a Text
- Using a Dictionary
Timed Writing Strategies
Formulaic writing.
Preparing for a timed writing assignment or essay exam?
- Be Prepared . You will stay calm if you know you've studied the content well ahead of time. Try to anticipate exam questions.
- Read the questions slowly and with care . Pay attention to tricky vocabulary words. If your instructor allows it, use a paper dictionary to look up words you're unsure about.
- Watch the clock . Be aware of your available time.
- Think before you write . On a sheet of scratch paper, take the time during the exam to brainstorm and outline your responses before writing on the exam itself .
- State your thesis in the opening paragraph . More clarity is always better. Underline your main points.
- Keep to the point. If you're running out of time, skip wordy supporting examples.
- End well. Even if you aren't able to finish the supporting points you had planned, add a conclusion. Your reader may never know you weren't able to finish the body of the essay if your conclusion is strong.
Practice analyzing essay questions :
- Underline the topic words (what the question asks you to consider).
- Place the question word in red (what you’re asked to do).
- Highlight any restrictions or hints.
Compare and contrast the wet tropics and the wet-dry tropics . Give examples of each.
How did the Reformation affect the political structure of Western Europe ? Pay particular attention to the economic and educational results of the Reformation .
Analyze the causes of the American Civil War .
Christopher Lasch has criticized American society as a “culture of narcissism.” Explain what Lasch means by this term and write an essay in which you agree or disagree with this assessment.
What event in your life told you that you were no longer a child but an adult ? Discuss .
Academic writing is formulaic . This means you must organize and present information in a way that conforms to readers' expectations. Argumentative essays, personal narratives, research proposals, literary analyses, and lab reports all conform to specific conventions. Your job as a student is to learn the formula.
Read samples. Request samples from your instructor, ask a librarian to help you find published examples, search online for examples, or visit the Writers' Center and ask a Responder to point you toward resources.
Sketch outlines of these samples and use those outlines as rough blueprints for the structure of your paper. Studying another's work for guidance about organization and style is not plagiarism. The ideas are yours; the structure is borrowed. This is how you learn to talk the talk.
WARNING : Never copy the samples word for word.
Example formula for an argumentative paper:
- Introduction
- Body paragraph 1
- Body paragraph 2
- Body paragraph 3
- Concession/rebuttal
Example formula for a research project:
- Problem statement
- Historical view
- Literature review
- My findings
The bad news: If you have brilliant ideas, but do not conform to the academic formula, you will probably be unsuccessful.
The good news: Samples are everywhere. All writers can conform to academic expectations. Seek and ye shall find.
Good luck, scholars!
- << Previous: Using a Dictionary
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 2:50 PM
- URL: https://research.ewu.edu/writers_c_read_study_strategies
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- How to Do Research for an Excellent Essay: The Complete Guide

One of the biggest secrets to writing a good essay is the Boy Scouts’ motto: ‘be prepared’. Preparing for an essay – by conducting effective research – lays the foundations for a brilliant piece of writing, and it’s every bit as important as the actual writing part. Many students skimp on this crucial stage, or sit in the library not really sure where to start; and it shows in the quality of their essays. This just makes it easier for you to get ahead of your peers, and we’re going to show you how. In this article, we take you through what you need to do in order to conduct effective research and use your research time to best effect.
Allow enough time
First and foremost, it’s vital to allow enough time for your research. For this reason, don’t leave your essay until the last minute . If you start writing without having done adequate research, it will almost certainly show in your essay’s lack of quality. The amount of research time needed will vary according to whether you’re at Sixth Form or university, and according to how well you know the topic and what teaching you’ve had on it, but make sure you factor in more time than you think you’ll need. You may come across a concept that takes you longer to understand than you’d expected, so it’s better to allow too much time than too little.
Read the essay question and thoroughly understand it
If you don’t have a thorough understanding of what the essay question is asking you to do, you put yourself at risk of going in the wrong direction with your research. So take the question, read it several times and pull out the key things it’s asking you to do. The instructions in the question are likely to have some bearing on the nature of your research. If the question says “Compare”, for example, this will set you up for a particular kind of research, during which you’ll be looking specifically for points of comparison; if the question asks you to “Discuss”, your research focus may be more on finding different points of view and formulating your own.
Begin with a brainstorm
Start your research time by brainstorming what you already know. Doing this means that you can be clear about exactly what you’re already aware of, and you can identify the gaps in your knowledge so that you don’t end up wasting time by reading books that will tell you what you already know. This gives your research more of a direction and allows you to be more specific in your efforts to find out certain things. It’s also a gentle way of introducing yourself to the task and putting yourself in the right frame of mind for learning about the topic at hand.
Achieve a basic understanding before delving deeper
If the topic is new to you and your brainstorm has yielded few ideas, you’ll need to acquire a basic understanding of the topic before you begin delving deeper into your research. If you don’t, and you start by your research by jumping straight in at the deep end, as it were, you’ll struggle to grasp the topic. This also means that you may end up being too swayed by a certain source, as you haven’t the knowledge to question it properly. You need sufficient background knowledge to be able to take a critical approach to each of the sources you read. So, start from the very beginning. It’s ok to use Wikipedia or other online resources to give you an introduction to a topic, though bear in mind that these can’t be wholly relied upon. If you’ve covered the topic in class already, re-read the notes you made so that you can refresh your mind before you start further investigation.
Working through your reading list
If you’ve been given a reading list to work from, be organised in how you work through each of the items on it. Try to get hold of as many of the books on it as you can before you start, so that you have them all easily to hand, and can refer back to things you’ve read and compare them with other perspectives. Plan the order in which you’re going to work through them and try to allocate a specific amount of time to each of them; this ensures that you allow enough time to do each of them justice and that focus yourself on making the most of your time with each one. It’s a good idea to go for the more general resources before honing in on the finer points mentioned in more specialised literature. Think of an upside-down pyramid and how it starts off wide at the top and becomes gradually narrower; this is the sort of framework you should apply to your research.
Ask a librarian
Library computer databases can be confusing things, and can add an extra layer of stress and complexity to your research if you’re not used to using them. The librarian is there for a reason, so don’t be afraid to go and ask if you’re not sure where to find a particular book on your reading list. If you’re in need of somewhere to start, they should be able to point you in the direction of the relevant section of the library so that you can also browse for books that may yield useful information.
Use the index
If you haven’t been given specific pages to read in the books on your reading list, make use of the index (and/or table of contents) of each book to help you find relevant material. It sounds obvious, but some students don’t think to do this and battle their way through heaps of irrelevant chapters before finding something that will be useful for their essay.
Taking notes
As you work through your reading, take notes as you go along rather than hoping you’ll remember everything you’ve read. Don’t indiscriminately write down everything – only the bits that will be useful in answering the essay question you’ve been set. If you write down too much, you risk writing an essay that’s full of irrelevant material and getting lower grades as a result. Be concise, and summarise arguments in your own words when you make notes (this helps you learn it better, too, because you actually have to think about how best to summarise it). You may want to make use of small index cards to force you to be brief with what you write about each point or topic. We’ve covered effective note-taking extensively in another article, which you can read here . Note-taking is a major part of the research process, so don’t neglect it. Your notes don’t just come in useful in the short-term, for completing your essay, but they should also be helpful when it comes to revision time, so try to keep them organised.
Research every side of the argument
Never rely too heavily on one resource without referring to other possible opinions; it’s bad academic practice. You need to be able to give a balanced argument in an essay, and that means researching a range of perspectives on whatever problem you’re tackling. Keep a note of the different arguments, along with the evidence in support of or against each one, ready to be deployed into an essay structure that works logically through each one. If you see a scholar’s name cropping up again and again in what you read, it’s worth investigating more about them even if you haven’t specifically been told to do so. Context is vital in academia at any level, so influential figures are always worth knowing about.
Keep a dictionary by your side
You could completely misunderstand a point you read if you don’t know what one important word in the sentence means. For that reason, it’s a good idea to keep a dictionary by your side at all times as you conduct your research. Not only does this help you fully understand what you’re reading, but you also learn new words that you might be able to use in your forthcoming essay or a future one . Growing your vocabulary is never a waste of time!
Start formulating your own opinion
As you work through reading these different points of view, think carefully about what you’ve read and note your own response to different opinions. Get into the habit of questioning sources and make sure you’re not just repeating someone else’s opinion without challenging it. Does an opinion make sense? Does it have plenty of evidence to back it up? What are the counter-arguments, and on balance, which sways you more? Demonstrating your own intelligent thinking will set your essay apart from those of your peers, so think about these things as you conduct your research.
Be careful with web-based research
Although, as we’ve said already, it’s fine to use Wikipedia and other online resources to give you a bit of an introduction to a topic you haven’t covered before, be very careful when using the internet for researching an essay. Don’t take Wikipedia as gospel; don’t forget, anybody can edit it! We wouldn’t advise using the internet as the basis of your essay research – it’s simply not academically rigorous enough, and you don’t know how out of date a particular resource might be. Even if your Sixth Form teachers may not question where you picked up an idea you’ve discussed in your essays, it’s still not a good habit to get into and you’re unlikely to get away with it at a good university. That said, there are still reliable academic resources available via the internet; these can be found in dedicated sites that are essentially online libraries, such as JSTOR. These are likely to be a little too advanced if you’re still in Sixth Form, but you’ll almost certainly come across them once you get to university.
Look out for footnotes
In an academic publication, whether that’s a book or a journal article, footnotes are a great place to look for further ideas for publications that might yield useful information. Plenty can be hidden away in footnotes, and if a writer is disparaging or supporting the ideas of another academic, you could look up the text in question so that you can include their opinion too, and whether or not you agree with them, for extra brownie points.
Don’t save doing all your own references until last
If you’re still in Sixth Form, you might not yet be required to include academic references in your essays, but for the sake of a thorough guide to essay research that will be useful to you in the future, we’re going to include this point anyway (it will definitely come in useful when you get to university, so you may as well start thinking about it now!). As you read through various books and find points you think you’re going to want to make in your essays, make sure you note down where you found these points as you go along (author’s first and last name, the publication title, publisher, publication date and page number). When you get to university you will be expected to identify your sources very precisely, so it’s a good habit to get into. Unfortunately, many students forget to do this and then have a difficult time of going back through their essay adding footnotes and trying to remember where they found a particular point. You’ll save yourself a great deal of time and effort if you simply note down your academic references as you go along. If you are including footnotes, don’t forget to add each publication to a main bibliography, to be included at the end of your essay, at the same time.
Putting in the background work required to write a good essay can seem an arduous task at times, but it’s a fundamental step that can’t simply be skipped. The more effort you put in at this stage, the better your essay will be and the easier it will be to write. Use the tips in this article and you’ll be well on your way to an essay that impresses!
To get even more prepared for essay writing you might also want to consider attending an Oxford Summer School .
Image credits: banner
Research and study skills
Our research and study skills support programme provides learners with access to a range of activities and resources to excel in their research assignment and hone their study skills.
Extended project qualification
The extended project qualification (EPQ) is an independent research project undertaken by students in post-16 education. It’s a great way for students to develop their academic research skills, prepare for university study and can often make a difference to their application success.
A variety of online resources can also be accessed by students, in their own time, on our digital hub .
We offer a range of activities to support students, and teachers delivering the taught skills element of the EPQ. All our sessions are interactive, requiring an element of class participation – this can be facilitated by us in person, online, or as a bespoke on campus visit. Please note that delivery method is subject to availability.
The following workshops are listed in the order in which they can provide support to your students across their EPQ journey. If you would like to book an activity, please email the education outreach team at [email protected] .
Why do the EPQ
Duration: 60 minutes
This workshop introduces the EPQ, its benefits, challenges and the work involved to complete one. It helps students consider whether an EPQ is appropriate for them, and if it is, provides direction on what they might want to research. This workshop is most appropriate for the launch of the EPQ and for students who are considering undertaking it.
Production logs
This workshop breaks down the production log component of the EPQ. It helps students understand the value of the production log and how to effectively complete one as part of their EPQ journey. The workshop also explores each page of the log in detail, so students understand what they need to complete and when. It is most appropriate for those at the beginning of their EPQ.
Choosing a topic and writing a research question
This workshop focuses on selecting a topic for the EPQ and writing a research question. We help students identify their topic and plan their research around an appropriate EPQ question. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those at the beginning of their EPQ journey.
Time and project management
This workshop introduces students to the basic frameworks which support time and project management. Students will learn the skills needed to manage their time more effectively and productively, whilst developing an awareness of health, safety and risk management. Students will also explore the importance of communication skills to help them develop an understanding of using appropriate language and tone when working with others. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those at the beginning of their EPQ journey.
Starting to research
This session gives an overview of academic research and provides students with a basic framework to support them on their research project journey. Students will follow a case study and develop ideas around a topic to strengthen their understanding of research skills in relation to their own work. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those who have decided on the topic of their EPQ and are finalising their question.
Research ethics and methodologies
Duration: 60 minutes
This workshop introduces students to the principles of ethics and the research methods to inform their EPQ projects. Students will engage with different research methodologies – including those which are most common in university level study – and be guided through the ethical considerations when undertaking a research project. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those who have finalised their EPQ question.
Critical thinking
Duration: 60 minutes
This workshop introduces students to critical thinking and explores some of the skills students need to develop their critical thinking. Students will analyse a wide variety of sources and learn to think critically about the information presented to them. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those who are about to begin researching for their EPQ.
How to read an online journal
Duration: 60 minutes
This workshop helps students to start navigating the world of online journals. Students will explore what online journals are, why they are useful, the challenges they can create, and how to overcome these to successfully use them in their own EPQ. A fully interactive workshop with guided activities which will help students practice their newfound skills.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
This workshop focuses on the themes of artificial intelligence and academic integrity. It explores what artificial intelligence is, its uses and its pitfalls, and it defines academic integrity and why it is important for researchers. Through interactive elements, which can be incorporated into the student’s production log, the session develops students’ understanding of when AI can and cannot be used for their EPQ. This workshop is most appropriate for those in the research phase of their EPQ journey.
Note making
This workshop explores academic note making and the different techniques that can be used. Students will reflect on their note making abilities and develop their understanding of how to create meaningful notes. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those who are currently researching for their EPQ.
Referencing and plagiarism
This session explores referencing and the different styles students may encounter while researching their topic. Students will consider what it means to plagiarise the work of themselves – or others – and learn how to avoid doing so. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those who are currently researching for their EPQ.
Academic writing
Duration : 60 minutes
This workshop explores academic writing and the different writing stages involved when undertaking an independent research project. Students will reflect on their research question and develop their skills around understanding the key elements of composing an essay, including editing and proofreading. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those who are finishing their research phase and about to undertake writing their final report or extended essay.
Presentation skills
Duration: 60 minutes
This workshop introduces students to the different skills needed to deliver a strong presentation at the end of their research project. Students will reflect on their research and develop ideas for their presentation such as a PowerPoint or poster. This workshop is designed to build students’ confidence and prepare them for the final stage of their EPQ. This workshop uses interactive elements to incorporate into the student’s production log and is most appropriate for those who are preparing for the presentation element of the EPQ.
Study skills
Our range of interactive study skill workshops are designed to support the development of students’ study skills for exam success. Our programme provides tools and techniques for students to prepare for exams and supports the student journey from further education to university study. The following sessions are listed in order of how they can support the academic lifecycle from Year 11 onwards.
Subject to availability, our workshops can be delivered in person, online, or as a bespoke on campus visit for your students. If you would like more information, or to book an activity, please email the education outreach team at [email protected] .
Preparing and revising for exams: Note making
We explore the skills required to make good notes and the different techniques students can use when revising. Students will reflect on their note making abilities and develop their skills around understanding the importance of making effective notes for revision. This workshop uses interactive elements for students to discuss note making scenarios and reflect on their approaches.
Preparing and revising for exams: Managing your study time
This workshop explores the skills required to manage independent study time effectively. Students will learn how to effectively manage competing pressures and obstacles. This workshop also showcases different strategies that can be used to avoid and manage distractions. This workshop also uses interactive elements for students to discuss time management scenarios and reflect on their decision-making processes.
Managing exam anxiety
This session explores anxiety within the context of exams. It is designed to normalise exam nerves by helping students understand where their anxiety stems from and what they can do to help manage it. This workshop also considers student mental health/wellbeing and provides advice on where students can get support if they are struggling.
Understanding the question and writing an essay
This session is designed to support students in their understanding of a question and how to approach writing an essay. The skills covered in this workshop are applicable to both exam-based and coursework-based questions. Students will develop their skills around breaking down an essay question, understanding instructional verbs and writing within the parameters set in the question. The workshop guides students through a basic essay framework and provides tips on how to develop an academic writing structure, form a conclusion and incorporate evidence into an essay.
Online course: Skills to Succeed at University
This online course helps students transition to higher education smoothly. Designed to be flexible so students can learn at a time and pace that best suits them, the course covers essential academic skills such as essay writing and independent learning.
Current students who came to the University through different routes – after completing a BTEC, A-levels or as mature students – also provide first-hand advice on how to start and thrive at university.
Interested students can register on the skills to succeed at university course via the FutureLearn platform .
Related links
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
Academic and Writing Resources
- Effective Studying
How to Effectively Study
Research-supported techniques.
Outside of lecture, university students are commonly expected to master course content on their own. However, multiple research studies have found that many university students are commonly unaware of, and seldom use, effective learning techniques. 1,2 In the following section (and the linked pages below) we discuss important do’s and don’ts of successful learning, plus introduce several of the most promising and effective evidence-based learning methods . These are backed by a growing body of learning science research – a substantial portion of which has been conducted right here at UCSD and in this very department. By taking advantage of these methods, students can transform their learning activities to be more efficient (make better use of time) and more effective (resulting in learning that is more comprehensive and lasts longer).
What Students Need to Do to Succeed
Psychology courses, as well as those in many other departments and at other universities, revolve around high-stakes tests (for example, midterms, final exams). In fact, on average, 80% of the course grade in PSYC classes at UCSD is determined by exam performance. 3 In order to perform well on such exams, it is crucial for students to master a wide range of course content.
How can that objective be accomplished? Through the use of evidence-based learning methods. Note that these are not described as “study methods”. Although it is common to describe preparing for an exam as “studying”, which is why this page is titled as such, simply “studying” information multiple times (“restudying”, “rereading”, or “reviewing”) is by itself often not very effective. 4,5 Instead, as described below, other methods are far more powerful at improving the learning of course content.
The Most Effective Learning Techniques
If you have only limited time to read this page, at least check out the following two points. For further details, click on the links to learn more.
Based on decades of learning science research, the two most effective methods known to date are:
- Spaced practice / distributed practice – learning that occurs over multiple sessions at different points in time (for example, revisiting a textbook chapter once every three days). This technique refers to when you should be preparing for course exams (that is, multiple sessions spread out over several weeks).
► Further information: Spaced Practice
- Retrieval practice / practice testing – instead of simply restudying information, attempting to recall that information from memory (such as by taking a practice test). This technique refers to what you should be doing to prepare for course exams (that is, test yourself via practice tests or other recall-based techniques).
► Further information: Retrieval Practice
Spaced practice involves when you should “study” and retrieval practice involves how you should “study”. When you use both (for instance, you can prepare for your exams using a spaced practice schedule and then use retrieval practice during each session), they make a powerful combination.
Additionally, if you perform retrieval practice across multiple days – and, each time, practice recalling information until you attain 100% accuracy (a method called successive relearning ) – then recent research shows that your ability to retain that information over long periods of time is maximized. 6
Finally, besides spaced and retrieval practice, there are some additional learning techniques that you may wish to try. These included interleaved practice, self-explanation, and others.
► Further information: Other Learning Techniques
Workshops and Downloadable Resources
- For in-person discussion of these techniques, please consider attending this department’s “How to Study Less and Remember More” workshop (for dates and times, please check the undergraduate workshops calendar).
- How to Study Less and Remember More [ PDF ]
Further Resources
- UCSD Tutoring
- Scientific American article, “What Works, What Doesn’t" (2013)
- Make it Stick: The Science of Successful Learning (2014)
- Cornell University: How to Study Effectively (videos)
1 Kornell, N., & Bjork, R. A. (2007). The promise and perils of self-regulated study. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review , 14 (2), 219-224. 2 Karpicke, J. D., Butler, A. C., & Roediger III, H. L. (2009). Metacognitive strategies in student learning: do students practise retrieval when they study on their own? Memory , 17 (4), 471-479. 3 Based on analysis of PSYC 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 60, 101, 102, 103, 105, 106, 120, 144, 145, 154, 163, 164, 161, 171, 181, 182, 190, 191, and 193 courses at UCSD, taught between 2013-2017. 4 Pashler, H., Bain, P. M., Bottge, B. A., Graesser, A., Koedinger, K., McDaniel, M., & Metcalfe, J. (2007). Organizing Instruction and Study to Improve Student Learning. IES Practice Guide. NCER 2007-2004. National Center for Education Research . 5 Dunlosky, J., Rawson, K. A., Marsh, E. J., Nathan, M. J., & Willingham, D. T. (2013). Improving students’ learning with effective learning techniques: Promising directions from cognitive and educational psychology. Psychological Science in the Public Interest , 14 (1), 4-58. 6 Rawson, K. A., Dunlosky, J., & Sciartelli, S. M. (2013). The power of successive relearning: Improving performance on course exams and long-term retention. Educational Psychology Review , 25 (4), 523-548.
Prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology, graphic adapted with permission from ccnlab.net under creative commons attribution-share alike 4.0 international license..
Back to top
- Writing Research Papers
- Spaced Practice
- Retrieval Practice
- Self-Explanation, Interleaved Practice, and Other Learning Techniques
- Effective Study Techniques Videos

- LEARNING SKILLS
Study Skills
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
- Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Top Tips for Study
- Staying Motivated When Studying
- Student Budgeting and Economic Skills
- Getting Organised for Study
Finding Time to Study
- Sources of Information
- Assessing Internet Information
- Using Apps to Support Study
What is Theory?
Styles of Writing
Effective Reading
- Critical Reading
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
Planning an Essay
- How to Write an Essay
- The Do’s and Don’ts of Essay Writing
- How to Write a Report
Academic Referencing
Assignment Finishing Touches
- Reflecting on Marked Work
- 6 Skills You Learn in School That You Use in Real Life
- Top 10 Tips on How to Study While Working
- Exam Skills
Get the SkillsYouNeed Study Skills eBook

Part of the Skills You Need Guide for Students .
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
What are Study Skills?
Study skills are the skills you need to enable you to study and learn efficiently – they are an important set of transferable life skills.
Our pages provide generic study skills advice – appropriate to learners across all disciplines and in different life circumstances: full and part-time students, those returning to education later in life, those engaged in professional development and anybody who wants to learn how to learn effectively.
Key points about study skills:
You will develop your own personal approach to study and learning in a way that meets your own individual needs. As you develop your study skills you will discover what works for you, and what doesn’t.
Study skills are not subject specific - they are generic and can be used when studying any area. You will, of course, need to understand the concepts, theories and ideas surrounding your specific subject area. To get the most out of your studies, however, you’ll want to develop your study skills.
You need to practise and develop your study skills. This will increase your awareness of how you study and you’ll become more confident. Once mastered, study skills will be beneficial throughout your life.
Study skills are not just for students. Study skills are transferable - you will take them with you beyond your education into new contexts. For example, organisational skills, time management, prioritising, learning how to analyse, problem solving, and the self-discipline that is required to remain motivated. Study skills relate closely to the type of skills that employers look for. (See Transferable Skills and Employability Skills for more.)
At SkillsYouNeed we provide quality content on many life skills – and many of these are relevant to studying.
You’ll find two types of study skills pages – pages that directly relate to skills you need for study (such as How to Write an Essay ) and pages that are more general life skills but which are also important to studying (like Active Listening ).
Our Study Skills Pages Include:
Getting Organised to Study
Getting organised is an important first step to effective study. Our page covers the basic organisation skills you need to consider – fundamentals such as where and when to study and the importance of developing a network of contacts who can help you when you need it.
This page covers some of the basic principles of time management – with reference to study. If you manage your time badly then you will be less productive, which can lead to stress and anxiety. This page will help you by outlining the importance of a personal study timetable and how to set goals and prioritise your time.
Sources of Information for Study
Learn what is meant by, and the importance of, primary, secondary and tertiary documents and how you may source such information in a library or online.
By understanding different writing styles you can put what you read into perspective. This page covers the main writing styles that you are likely to come across, including academic, journal, and journalistic styles.
When studying, it is likely that you will need to read a lot of information – and you will wish to use this time effectively as possible by developing your reading skills. Discover ways that you can engage with your reading, form links, understand opinions and put ideas and research into perspective. In short, develop your reading skills.
Critical Reading and Reading Strategies
This page explains what is meant by critical reading and critical thinking – skills which are fundamental to true learning, personal development and advancement. The page also covers how to develop a personal reading strategy and use SQ3R to help you manage your reading.
Note-Taking
Learning to take notes effectively is not only important to study but also in many other situations, at work and in your personal life. Develop your note-taking skills with our pages: Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges and Note-Taking for Reading .
It pays to carefully think about and plan an essay or other piece of written work before you start writing. This page provides you with a framework for planning which will help ensure your work is relevant, well-constructed and produced efficiently.
Essay Writing
Learn about the processes involved in writing an essay, or other piece of assessed work. Avoid common mistakes and follow best practice to help ensure that the work you produce is of a high quality.
How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis
Working on a dissertation, thesis or other research project can be the most challenging part of study. Our guide offers practical advice and explains how to work on each part of a research document, including:
- How to Write a Research Proposal
- Ethical Issues in Research
- Researching and Writing a Literature Review
- Writing your Methodology
- Writing up your Results and Discussion
Learning how to reference correctly is vital if you are a student. This page not only covers why you should reference, and what may happen if you don’t, but also includes some detailed guidelines on how to reference different types of materials.
As a learner you will be required to engage with theory, but exactly what is a theory? A theory is an attempt to provide understanding - theories attempt to answer the question, 'why?' and therefore satisfy our curiosity. Learn more about theories and how they are usually developed.
Before you submit your assignment for school, university or work, run through a series of final checks. Avoid potentially embarrassing or costly mistakes and increase the credibility of your work.
Reflecting On Marked Work
This page, for students, encourages you to engage in the feedback you receive from a marker when your work is returned. Don’t just look at the bottom line, the mark, but understand the comments and feedback and learn from any mistakes.
Revision Skills
Revising for examinations can be a real challenge for many people. Learn and practice some key skills to make your revision time as productive and effective as possible, leaving you better prepared for exams and tests.
Further Reading from Skills You Need

The Skills You Need Guide for Students

Develop the skills you need to make the most of your time as a student.
Our eBooks are ideal for students at all stages of education, school, college and university. They are full of easy-to-follow practical information that will help you to learn more effectively and get better grades.
Other Areas Related to Study
Writing Skills
The writing skills section of SkillsYouNeed includes many other pages that we hope you’ll find useful.
Our pages: Spelling , Grammar and Punctuation for example can help with assignment writing. You may also find information on our pages: Gender Neutral Writing and Clichés to Avoid useful.
Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are the skills we use every day to interact with others and many are relevant to effective study.
For example see: Listening Skills , Problem Solving and Decision Making , Questioning and Types of Questions , Verbal Communication and Effective Speaking .
Personal Skills
Our Personal Skills section covers areas of personal development .
Useful pages for study include: Building Confidence and Self-Esteem , Tips for Dealing with Stress , Relaxation Techniques , and Self-Motivation .
Start with: Getting Organised to Study
See also: Employability Skills for Graduates How to Systemize Your Study Develop Your Online Learning Skills and Get More from Your Online Classes
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!

Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
This article is part of the research topic.
Building the Future of Education Together: Innovation, Complexity, Sustainability, Interdisciplinary Research and Open Science
Developing the Skills for Complex Thinking Research: A Case Study Using Social Robotics to Produce Scientific Papers Provisionally Accepted

- 1 Institute for the Future of Education, Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Education (ITESM), Mexico
- 2 University of Cienfuegos, Cuba
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
The development of university students' skills to successfully produce scientific documents has been a recurring topic of study in academia. This paper analyzes the implementation of a training experience using a digital environment mediated by video content materials starring humanoid robots. The research aimed to scale complex thinking and its subcompetencies as a hinge to strengthen basic academic research skills. Students from Colombia, Ecuador, and Mexico committed to preparing a scientific document as part of their professional training participated. A pretest to know their initial level of perception, a posttest to evaluate if there was a change, and a scientific document the students delivered at the end of the training experience comprised the methodology to demonstrate the improvement of their skills. The results indicated students' perceived improvement in the sub-competencies of systemic, creative, scientific, and innovative thinking; however, their perceptions did not align with that of the tutor who reviewed the delivered scientific product. The conclusion was that although the training experience helped strengthen the students' skills, variables that are determinants for a student to develop the knowledge necessary to prepare scientific documents and their derived products remain to be analyzed.
Keywords: higher education, research skills, Educational innovation, complex thinking, scientific thinking, Critical Thinking, Innovative thinking, social robotics
Received: 16 Oct 2023; Accepted: 17 May 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Lopez-Caudana, George-Reyes and Avello-Martínez. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Dr. Edgar O. Lopez-Caudana, Institute for the Future of Education, Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Education (ITESM), Monterrey, Mexico
People also looked at
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting
'I've learned from amazing professors who study the social impact of technology'
Tanvi Namjoshi: Computer Science
A&S Communications
Tanvi Namjoshi
Computer Science Basking Ridge, N.J.
Why did you choose Cornell?
I was drawn to Cornell and the College of Arts & Sciences because of the diversity of studies and the flexible path it offered. I came in as a computer science major, but I was also really passionate about policy and ethics, and at Cornell, these subjects weren’t taught as mutually exclusive but rather two sides of the same coin. As a scholar in the Milstein Program in Technology and Humanity, I saw Cornell’s investment in interdisciplinary studies and have had opportunities to learn from amazing professors who study the social impact of technology. I also believe that the diversity of Cornell’s academic programs draws in a student body that is unmatched – everyone has unique interests and backgrounds that they are invested in and that they are excited to share with you, either through events run by student organizations or simply over lunch.
What is your main extracurricular activity and why is it important to you?

My main extracurricular activity has been serving on the executive board for Women in Computing at Cornell (WICC) where we work to make the computer and information science departments more inclusive and accessible to women and other gender minorities. In WICC, I found a group of women who were excited to give advice about classes, jobs and navigating the college environment. This sense of community is extremely important for women, who are underrepresented in computer science. Through the years I’ve served various roles from faculty relations director, to social chair, to vice president. It has been extremely rewarding to run impactful events and to be a leader supporting other women as they make their visions for the CIS community come to life. My most cherished memory of WICC has been running a program called “Lunch Bunch.” Each week, a group of students has the opportunity to eat lunch with a rotating guest professor, reducing the divide between faculty and students. As a facilitator, I learned about many female professors’ paths to academia, research interests and motivations. Most importantly, hearing their stories, I realized that much about what they loved in computer science resonated with my own interests. This showed me that I would enjoy research – and it led me to start my research journey!
What Cornell memory do you treasure the most?
Taking the final bow at the first Nazaqat showcase during my junior year. It was the culmination of a year of hard work as both a dancer and a leader in the club. Seeing the support of the Cornell community, our alumni and our families made the hours of rehearsals and planning worth it. I have studied Kathak, the Indian classical dance form Nazaqat performs, for 12 years of my life – finding a club at Cornell where I could keep up with my dance practice truly changed my Cornell experience.

What are the most valuable skills you gained from your Arts & Sciences education?
The power to approach problems from different perspectives. As someone in a technical field, my instinct is to look for solutions in formulas and mathematical analysis. However, my humanities classes have taught me to step back and look at how social values and our laws may create or entrench these problems in society. My design thinking classes and independent studies have taught me how to interview those affected by the problem and look for solutions in their answers. And of course, if these techniques reveal that technology could be a part of the solution, my computer science classes have equipped me with the technical skills to innovate.
What have you accomplished as a Cornell student that you are most proud of?
I have participated in research at Cornell through three different departments: government, science and technology studies and computer science. I studied the behavior of candidates under different voting algorithms with Prof. Jon Kleinberg, worked with the Brooks School Tech Policy Institute and explored how generative AI affects art through interviews with local artists. Jumping into research is exciting, but also difficult coming from studying a subject only through coursework. My research journey has included many different fields and methodologies, but I am proud of my work in each project as it has all informed the work I want to do in graduate school.
Every year, our faculty nominate graduating Arts & Sciences students to be featured as part of our Extraordinary Journeys series. Read more about the Class of 202 4.
More News from A&S

American Sign Language has found a growing home on the Hill

Extraordinary Journeys: The Class of 2024

BTPI will research relationship between Bitcoin and financial freedom

Reynolds Foundation commits $1.25M to fund Brooks School initiatives

How To Stand Out In The Ivy League During Your Freshman Year
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Harvard College
This spring, many students felt the relief and exuberance that comes with an acceptance letter from one’s dream school. Many students attending Ivy League and other top universities are valedictorians and leaders in their high school communities; they excelled throughout their high school careers and graduated with the accolades to prove it. Yet, these students are often in for a rude awakening when they arrive on campus. Though they were exceptional at their high schools, they are a dime a dozen in the Ivy League. This realization can cause many students to feel imposter syndrome and wonder how they can stand out and make an impression on their professors and peers in such a competitive environment.
The more that students prepare themselves for this adjustment, the better. Standing out in college is a different endeavor than standing out in high school—it requires time, intentionality, and a willingness to be uncomfortable and challenge yourself. Most importantly, it takes practice, and if students seek to hone this skill from their first semester on campus, they will set themselves up for success for the next four years.
For students preparing for their first semester in college, here are five strategies to navigate the transition into the Ivy League with confidence, purpose, and distinction:
1. Make your voice heard in the classroom
At Ivy League and many other top schools, faculty-to-student ratios and class sizes tend to be small, allowing greater opportunity for you to establish yourself in the classroom and engage with your professors directly. Many students are weighed down by self-doubt and the desire to avoid making mistakes in their first semester, and as such, they are reluctant to raise their hands or offer their input. But one of the best ways to establish connections with professors is to use your voice in the classroom—college is about learning and growing, so don’t be afraid to get a question wrong or develop your ideas through conversation. Doing so will allow you to connect with others in class, build your intellectual skill set, and demonstrate your curiosity and earnest desire to learn.
2. Engage in activities outside of the classroom
Beyond academics, the Ivy League is known for vibrant opportunities to learn and connect with others outside of the classroom. Whether you're interested in student government, the performing arts, guest lectures, community service, or intramural athletics, there’s an opportunity to explore your passions. Join clubs and organizations that align with your interests and values, and consider taking on leadership roles to showcase your initiative and organizational skills. Engaging in extracurricular activities will not only enrich your college experience but also afford you the opportunity to get to know people outside of your major or residence hall.
Google Chrome Gets Third Emergency Update In A Week As Attacks Continue
Biden vs. trump 2024 election polls: biden losing support among key voting blocs, japanese fans are puzzled that yasuke is in assassin s creed shadows, 3. cultivate your network.
One of the most valuable assets you'll gain during your time in the Ivy League is your network of peers, professors, and mentors. Take the time to connect with your classmates and professors, attend faculty office hours, and engage in meaningful discussions. One of the best ways to build your network is to simply put yourself out there—a student’s college years are the prime opportunity to connect with even the most distinguished scholars in their field, as they not only likely have connections through their institution, but professors (even at other universities) are more likely to respond to students who reach out for their advice. If one knowledgeable person doesn’t respond or have the bandwidth to advise you on a particular project or query, move on to the next person on your list!
4. Pursue Research, Internship, and Study Abroad Opportunities
The Ivy League offers unparalleled access to research, internship, and study abroad opportunities that can complement your academic studies and expand your horizons. For instance, Harvard offers a multitude of distinguished research positions for undergraduates, ranging from thesis research to research assistantships. The University of Pennsylvania sent students to 48 countries through their study abroad offerings in the 2022-2023 academic year. Meanwhile, Princeton offers more than 400 programs in 140 countries through which students may study abroad. Whether conducting groundbreaking research in your field of study or gaining real-world experience through internships, the plethora of opportunities available to you at an Ivy League university will not only enhance your resume but also deepen your understanding of your chosen field and prepare you for future success.
5. Carve out your niche
Finally, just as high school is a time to hone your passions and demonstrate them in action in your community, college is a more rigorous opportunity to identify and make a name for yourself within a niche industry or discipline. The best way to begin doing so is to have conversations with professors, graduate students, and older students in your field. Ask them questions like: Where do you see the field expanding or moving in the next five years? What are the most significant recent developments in this profession/field? What subjects do you think have been largely unexplored? What advice would you give to emerging scholars in this discipline? While pursuing a subject of true interest to you is indeed important, it is also important to consider how you will contribute uniquely to your subject of interest, and thereby maximize your odds of success in the job market.
Finally, keep in mind that you can (and should) begin practicing these skills in high school. The more you engage in these activities, the more natural they will be when you are on campus at a top university.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 06 May 2024
APOE4 homozygozity represents a distinct genetic form of Alzheimer’s disease
- Juan Fortea ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1340-638X 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Jordi Pegueroles ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3554-2446 1 , 2 ,
- Daniel Alcolea ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3819-3245 1 , 2 ,
- Olivia Belbin ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6109-6371 1 , 2 ,
- Oriol Dols-Icardo ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2656-8748 1 , 2 ,
- Lídia Vaqué-Alcázar 1 , 4 ,
- Laura Videla ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9748-8465 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Juan Domingo Gispert 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ,
- Marc Suárez-Calvet ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2993-569X 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ,
- Sterling C. Johnson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8501-545X 10 ,
- Reisa Sperling ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1535-6133 11 ,
- Alexandre Bejanin ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9958-0951 1 , 2 ,
- Alberto Lleó ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2568-5478 1 , 2 &
- Víctor Montal ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5714-9282 1 , 2 , 12 na1
Nature Medicine ( 2024 ) Cite this article
15k Accesses
4488 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Alzheimer's disease
- Predictive markers
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of APOE4 homozygosity on Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by examining its clinical, pathological and biomarker changes to see whether APOE4 homozygotes constitute a distinct, genetically determined form of AD. Data from the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center and five large cohorts with AD biomarkers were analyzed. The analysis included 3,297 individuals for the pathological study and 10,039 for the clinical study. Findings revealed that almost all APOE4 homozygotes exhibited AD pathology and had significantly higher levels of AD biomarkers from age 55 compared to APOE3 homozygotes. By age 65, nearly all had abnormal amyloid levels in cerebrospinal fluid, and 75% had positive amyloid scans, with the prevalence of these markers increasing with age, indicating near-full penetrance of AD biology in APOE4 homozygotes. The age of symptom onset was earlier in APOE4 homozygotes at 65.1, with a narrower 95% prediction interval than APOE3 homozygotes. The predictability of symptom onset and the sequence of biomarker changes in APOE4 homozygotes mirrored those in autosomal dominant AD and Down syndrome. However, in the dementia stage, there were no differences in amyloid or tau positron emission tomography across haplotypes, despite earlier clinical and biomarker changes. The study concludes that APOE4 homozygotes represent a genetic form of AD, suggesting the need for individualized prevention strategies, clinical trials and treatments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
195,33 € per year
only 16,28 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
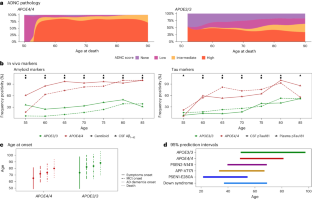
Similar content being viewed by others

APOE4/4 is linked to damaging lipid droplets in Alzheimer’s disease microglia
The Amyloid-β Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease
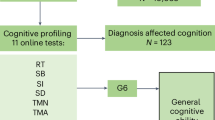
Dynamics of cognitive variability with age and its genetic underpinning in NIHR BioResource Genes and Cognition cohort participants
Data availability.
Access to tabular data from ADNI ( https://adni.loni.usc.edu/ ), OASIS ( https://oasis-brains.org/ ), A4 ( https://ida.loni.usc.edu/collaboration/access/appLicense.jsp ) and NACC ( https://naccdata.org/ ) can be requested online, as publicly available databases. All requests will be reviewed by each studyʼs scientific board. Concrete inquiries to access the WRAP ( https://wrap.wisc.edu/data-requests-2/ ) and ALFA + ( https://www.barcelonabeta.org/en/alfa-study/about-the-alfa-study ) cohort data can be directed to each study team for concept approval and feasibility consultation. Requests will be reviewed to verify whether the request is subject to any intellectual property.
Code availability
All statistical analyses and raw figures were generated using R (v.4.2.2). We used the open-sourced R packages of ggplot2 (v.3.4.3), dplyr (v.1.1.3), ggstream (v.0.1.0), ggpubr (v.0.6), ggstatsplot (v.0.12), Rmisc (v.1.5.1), survival (v.3.5), survminer (v.0.4.9), gtsummary (v.1.7), epitools (v.0.5) and statsExpression (v.1.5.1). Rscripts to replicate our findings can be found at https://gitlab.com/vmontalb/apoe4-asdad (ref. 32 ). For neuroimaging analyses, we used Free Surfer (v.6.0) and ANTs (v.2.4.0).
Bellenguez, C. et al. New insights into the genetic etiology of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Nat. Genet. 54 , 412–436 (2022).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Frisoni, G. B. et al. The probabilistic model of Alzheimer disease: the amyloid hypothesis revised. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 23 , 53–66 (2022).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bateman R. J. et al. Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 367 , 795–804 (2012).
Genin, E. et al. APOE and Alzheimer disease: a major gene with semidominant inheritance. Mol. Psychiatry 16 , 903–907 (2011).
Fortea, J. et al. Alzheimer’s disease associated with Down syndrome: a genetic form of dementia. Lancet Neurol. 20 , 930–942 (2021).
Fortea, J. et al. Clinical and biomarker changes of Alzheimer’s disease in adults with Down syndrome: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 395 , 1988–1997 (2020).
Jansen, W. J. et al. Prevalence of cerebral amyloid pathology in persons without dementia: a meta-analysis. JAMA 313 , 1924–1938 (2015).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Saddiki H. et al. Age and the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease: a cerebrospinal fluid biomarker-based case-control study. PLoS Med. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PMED.1003289 (2020).
Jack, C. R. et al. NIA‐AA Research Framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 14 , 535–562 (2018).
Article Google Scholar
Beekly, D. L. et al. The National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center (NACC) Database: an Alzheimer disease database. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 18 , 270–277 (2004).
PubMed Google Scholar
Montine, T. J. et al. National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease: a practical approach. Acta Neuropathol. 123 , 1–11 (2012).
Reiman, E. M. et al. Exceptionally low likelihood of Alzheimer’s dementia in APOE2 homozygotes from a 5,000-person neuropathological study. Nat. Commun. 11 , 1–11 (2020).
Iulita M. F. et al. Association of Alzheimer disease with life expectancy in people with Down syndrome. JAMA Netw. Open https://doi.org/10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2022.12910 (2022).
Corder, E. H. et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261 , 921–923 (1993).
Fortea, J., Quiroz, Y. T. & Ryan, N. S. Lessons from Down syndrome and autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 22 , 5–6 (2023).
Therriault, J. et al. Frequency of biologically defined Alzheimer’s disease in relation to age, sex, APOE ε4, and cognitive impairment. Neurology 96 , e975–e985 (2021).
Betthauser, T. J. et al. Multi-method investigation of factors influencing amyloid onset and impairment in three cohorts. Brain 145 , 4065–4079 (2022).
Snellman, A. et al. APOE ε4 gene dose effect on imaging and blood biomarkers of neuroinflammation and beta-amyloid in cognitively unimpaired elderly. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 15 , 71 (2023).
Ghisays, V. et al. Brain imaging measurements of fibrillar amyloid-β burden, paired helical filament tau burden, and atrophy in cognitively unimpaired persons with two, one, and no copies of the APOE ε4 allele. Alzheimers Dement. 16 , 598–609 (2020).
Mehta, R. I. & Schneider, J. A. What is ‘Alzheimer’s disease’? The neuropathological heterogeneity of clinically defined Alzheimer’s dementia. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 34 , 237–245 (2021).
van der Lee, S. J. et al. The effect of APOE and other common genetic variants on the onset of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia: a community-based cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 17 , 434–444 (2018).
Belloy, M. E., Napolioni, V. & Greicius, M. D. A quarter century of APOE and Alzheimera’s disease: progress to date and the path forward. Neuron 101 , 820–838 (2019).
Belloy, M. E. et al. APOE genotype and Alzheimer disease risk across age, sex, and population ancestry. JAMA Neurol. 80 , 1284–1294 (2023).
Jack, C. R. et al. Long-term associations between amyloid positron emission tomography, sex, apolipoprotein E and incident dementia and mortality among individuals without dementia: hazard ratios and absolute risk. Brain Commun. 4 , fcac017 (2022).
Morris, J. C. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology 43 , 2412–2414 (1993).
Weiner, M. W. et al. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 3: continued innovation for clinical trial improvement. Alzheimer’s Dement. 13 , 561–571 (2017).
Sperling R. A. et al. The A4 Study: stopping AD before symptoms begin? Sci. Transl. Med. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3007941 (2014).
Molinuevo, J. L. et al. The ALFA project: a research platform to identify early pathophysiological features of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement.: Transl. Res. Clin. Interventions 2 , 82–92 (2016).
Johnson, S. C. et al. The Wisconsin Registry for Alzheimer’s Prevention: a review of findings and current directions. Alzheimer’s Dement.: Diagnosis, Assess. Dis. Monit. 10 , 130–142 (2018).
Google Scholar
LaMontagne P. J. et al. OASIS-3: longitudinal neuroimaging, clinical and cognitive dataset for normal aging and Alzheimer disease. Preprint at MedRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2019.12.13.19014902 (2019).
La Joie, R. et al. Multisite study of the relationships between antemortem [ 11 C]PIB-PET Centiloid values and postmortem measures of Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology. Alzheimers Dement. 15 , 205–216 (2019).
Montal, V. APOE4-ASDAD. GitLab https://gitlab.com/vmontalb/apoe4-asdad (2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the contributions of several consortia that provided data for this study. We extend our appreciation to the NACC, the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, The A4 Study, the ALFA Study, the Wisconsin Register for Alzheimer’s Prevention and the OASIS3 Project. Without their dedication to advancing Alzheimer’s disease research and their commitment to data sharing, this study would not have been possible. We also thank all the participants and investigators involved in these consortia for their tireless efforts and invaluable contributions to the field. We also thank the institutions that funded this study, the Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitario, Carlos III Health Institute, the Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red sobre Enfermedades Neurodegenerativas and the Generalitat de Catalunya and La Caixa Foundation, as well as the NIH, Horizon 2020 and the Alzheimer’s Association, which was crucial for this research. Funding: National Institute on Aging. This study was supported by the Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitario, Carlos III Health Institute (INT21/00073, PI20/01473 and PI23/01786 to J.F., CP20/00038, PI22/00307 to A.B., PI22/00456 to M.S.-C., PI18/00435 to D.A., PI20/01330 to A.L.) and the Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red sobre Enfermedades Neurodegenerativas Program 1, partly jointly funded by Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional, Unión Europea, Una Manera de Hacer Europa. This work was also supported by the National Institutes of Health grants (R01 AG056850; R21 AG056974, R01 AG061566, R01 AG081394 and R61AG066543 to J.F., S10 OD025245, P30 AG062715, U54 HD090256, UL1 TR002373, P01 AG036694 and P50 AG005134 to R.S.; R01 AG027161, R01 AG021155, R01 AG037639, R01 AG054059; P50 AG033514 and P30 AG062715 to S.J.) and ADNI (U01 AG024904), the Department de Salut de la Generalitat de Catalunya, Pla Estratègic de Recerca I Innovació en Salut (SLT006/17/00119 to J.F.; SLT002/16/00408 to A.L.) and the A4 Study (R01 AG063689, U24 AG057437 to R.A.S). It was also supported by Fundación Tatiana Pérez de Guzmán el Bueno (IIBSP-DOW-2020-151 o J.F.) and Horizon 2020–Research and Innovation Framework Programme from the European Union (H2020-SC1-BHC-2018-2020 to J.F.; 948677 and 847648 to M.S.-C.). La Caixa Foundation (LCF/PR/GN17/50300004 to M.S.-C.) and EIT Digital (Grant 2021 to J.D.G.) also supported this work. The Alzheimer Association also participated in the funding of this work (AARG-22-923680 to A.B.) and A4/LEARN Study AA15-338729 to R.A.S.). O.D.-I. receives funding from the Alzheimer’s Association (AARF-22-924456) and the Jerome Lejeune Foundation postdoctoral fellowship.
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Juan Fortea, Víctor Montal.
Authors and Affiliations
Sant Pau Memory Unit, Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau - Biomedical Research Institute Sant Pau, Barcelona, Spain
Juan Fortea, Jordi Pegueroles, Daniel Alcolea, Olivia Belbin, Oriol Dols-Icardo, Lídia Vaqué-Alcázar, Laura Videla, Alexandre Bejanin, Alberto Lleó & Víctor Montal
Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Neurodegenerativas. CIBERNED, Barcelona, Spain
Juan Fortea, Jordi Pegueroles, Daniel Alcolea, Olivia Belbin, Oriol Dols-Icardo, Laura Videla, Alexandre Bejanin, Alberto Lleó & Víctor Montal
Barcelona Down Medical Center, Fundació Catalana Síndrome de Down, Barcelona, Spain
Juan Fortea & Laura Videla
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Institute of Neurosciences, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
Lídia Vaqué-Alcázar
Barcelonaβeta Brain Research Center (BBRC), Pasqual Maragall Foundation, Barcelona, Spain
Juan Domingo Gispert & Marc Suárez-Calvet
Neurosciences Programme, IMIM - Hospital del Mar Medical Research Institute, Barcelona, Spain
Department of Medicine and Life Sciences, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, Spain
Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red Bioingeniería, Biomateriales y Nanomedicina. Instituto de Salud carlos III, Madrid, Spain
Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), Madrid, Spain
Wisconsin Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI, USA
Sterling C. Johnson
Brigham and Women’s Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
Reisa Sperling
Barcelona Supercomputing Center, Barcelona, Spain
Víctor Montal
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
J.F. and V.M. conceptualized the research project and drafted the initial manuscript. V.M., J.P. and J.F. conducted data analysis, interpreted statistical findings and created visual representations of the data. O.B. and O.D.-I. provided valuable insights into the genetics of APOE. L.V., A.B. and L.V.-A. meticulously reviewed and edited the manuscript for clarity, accuracy and coherence. J.D.G., M.S.-C., S.J. and R.S. played pivotal roles in data acquisition and securing funding. A.L. and D.A. contributed to the study design, offering guidance and feedback on statistical analyses, and provided critical review of the paper. All authors carefully reviewed the manuscript, offering pertinent feedback that enhanced the study’s quality, and ultimately approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Juan Fortea or Víctor Montal .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
S.C.J. has served at scientific advisory boards for ALZPath, Enigma and Roche Diagnostics. M.S.-C. has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Almirall, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics and Roche Farma, received consultancy fees (paid to the institution) from Roche Diagnostics and served on advisory boards of Roche Diagnostics and Grifols. He was granted a project and is a site investigator of a clinical trial (funded to the institution) by Roche Diagnostics. In-kind support for research (to the institution) was received from ADx Neurosciences, Alamar Biosciences, Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Fujirebio, Janssen Research & Development and Roche Diagnostics. J.D.G. has served as consultant for Roche Diagnostics, receives research funding from Hoffmann–La Roche, Roche Diagnostics and GE Healthcare, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Biogen, Philips Nederlands, Esteve and Life Molecular Imaging and serves on an advisory board for Prothena Biosciences. R.S. has received personal consulting fees from Abbvie, AC Immune, Acumen, Alector, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Genentech, Ionis and Vaxxinity outside the submitted work. O.B. reported receiving personal fees from Adx NeuroSciences outside the submitted work. D.A. reported receiving personal fees for advisory board services and/or speaker honoraria from Fujirebio-Europe, Roche, Nutricia, Krka Farmacéutica and Esteve, outside the submitted work. A.L. has served as a consultant or on advisory boards for Almirall, Fujirebio-Europe, Grifols, Eisai, Lilly, Novartis, Roche, Biogen and Nutricia, outside the submitted work. J.F. reported receiving personal fees for service on the advisory boards, adjudication committees or speaker honoraria from AC Immune, Adamed, Alzheon, Biogen, Eisai, Esteve, Fujirebio, Ionis, Laboratorios Carnot, Life Molecular Imaging, Lilly, Lundbeck, Perha, Roche and outside the submitted work. O.B., D.A., A.L. and J.F. report holding a patent for markers of synaptopathy in neurodegenerative disease (licensed to Adx, EPI8382175.0). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Medicine thanks Naoyuki Sato, Yadong Huang and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editor: Jerome Staal, in collaboration with the Nature Medicine team.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
Supplementary Methods, Results, Bibliography, Figs. 1–7 and Tables 1–3.
Reporting Summary
Supplementary code.
This code is also available in the GitLab repository.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fortea, J., Pegueroles, J., Alcolea, D. et al. APOE4 homozygozity represents a distinct genetic form of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Med (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-02931-w
Download citation
Received : 03 November 2023
Accepted : 19 March 2024
Published : 06 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-02931-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This paper reports the results of a meta-analysis of 52 studies that investigated the relationship between a range of study strategies and outcomes measures.Low correlations were found between a range of different types of study skills and various outcome measures. Having many study skills (i.e. versatility), as assessed by total study skills scores, produced the largest correlations with both ...
study skills are grouped into four clusters: repetition-based skills, procedural study. skills, cognitive-based study skills, and metacognitive skills. Key elements of ef-. fective study-strategy ...
The researcher will use the unique combination of study skills and academic achievement of university students, and a questionnaire was developed as the instrument of the survey. The questionnaire ...
Many first-year college students are unprepared for the academic rigors of college, with as few as 27% of American high school students demonstrating proficiency in English, reading, mathematics, and science on the ACT college entrance exam ().College students may rely on study habits they have developed throughout their elementary and secondary education which served them sufficiently in the ...
As predicted, structural equation modeling (SEM) indicated that study self-efficacy mediated the study habits—procrastination relation. The mediation effects were medium to large. We conclude that training of, and advice on, study skills and habits should be accompanied by measures that build study self-efficacy.
4. Discussion Based on the research findings, it was observed that for all the study skills measured, students with a GPA of 15 and more scored significantly higher than students with a GPA of less than 15. This result is consistent with the findings of other researches in all of the 7 measured study skills.
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. Research papers are similar to academic essays , but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research.
The study aims to improve students' academic essay argumentation by cultivating higher-order thinking skills. The research is prompted by the identified knowledge gap in students' writing skills ...
Platform 1:1.7 Describe the principles of research and how research findings are . used to inform evidence-based practice. Platform 1:1.13 Demonstrate the numeracy, literacy, digital and technological skills . required to meet the needs of people in their care to ensure safe and effective practice.
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.. Short videos to support your essay writing skills. There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing ...
How to guides: Study skills. We've collated all our guidance on how to study. You can see what's here using the 'On this page' dropdown list, or find guidance for researchers, students, teachers or librarians under 'In this section'. See all 'how to' guides.
When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a source or collection of sources, you will have the chance to wrestle with some of the
Formulaic Writing. Academic writing is formulaic. This means you must organize and present information in a way that conforms to readers' expectations. Argumentative essays, personal narratives, research proposals, literary analyses, and lab reports all conform to specific conventions. Your job as a student is to learn the formula.
Allow enough time. First and foremost, it's vital to allow enough time for your research. For this reason, don't leave your essay until the last minute. If you start writing without having done adequate research, it will almost certainly show in your essay's lack of quality. The amount of research time needed will vary according to ...
Exercise 1. Now that you have learned some time-management basics, it is time to apply those skills. For this exercise, you will develop a weekly schedule and a semester calendar. Working with your class schedule, map out a week-long schedule of study time. Try to apply the "two- to three-hour" rule.
Many students are being left behind by an educational system that some people believe is in crisis. Improving educational outcomes will require efforts on many fronts, but a central premise of this monograph is that one part of a solution involves helping students to better regulate their learning through the use of effective learning techniques.
Study skills. Our range of interactive study skill workshops are designed to support the development of students' study skills for exam success. Our programme provides tools and techniques for students to prepare for exams and supports the student journey from further education to university study. The following sessions are listed in order ...
Based on decades of learning science research, the two most effective methods known to date are: Spaced practice / distributed practice - learning that occurs over multiple sessions at different points in time (for example, revisiting a textbook chapter once every three days). This technique refers to when you should be preparing for course ...
Study skills are transferable - you will take them with you beyond your education into new contexts. For example, organisational skills, time management, prioritising, learning how to analyse, problem solving, and the self-discipline that is required to remain motivated. Study skills relate closely to the type of skills that employers look for.
build ideas and write papers. - The Writing Process: These features show all the steps taken to write a paper, allowing you to follow it from initial idea to published article. - Into the Essay: Excerpts from actual papers show the ideas from the chapters in action because you learn to write best by getting
tion of research skills and which specific skills should be taught, practiced, and assessed at the undergraduate and master's levels in both thesis and non-thesis programs. In addition,
Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. ... To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author's research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect ...
The development of university students' skills to successfully produce scientific documents has been a recurring topic of study in academia. This paper analyzes the implementation of a training experience using a digital environment mediated by video content materials starring humanoid robots. The research aimed to scale complex thinking and its subcompetencies as a hinge to strengthen basic ...
A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing "sync up" with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at ...
As a scholar in the Milstein Program in Technology and Humanity, I saw Cornell's investment in interdisciplinary studies and have had opportunities to learn from amazing professors who study the social impact of technology. I also believe that the diversity of Cornell's academic programs draws in a student body that is unmatched ...
1. Make your voice heard in the classroom. At Ivy League and many other top schools, faculty-to-student ratios and class sizes tend to be small, allowing greater opportunity for you to establish ...
This paper first presents an organizing framework for the existing definitions, measurement instruments, and policy frameworks. It then delves into discussing two appropriate approaches for identifying green occupations to guide skills development policy: the task-content and the skills approaches.
Jessica Pappagianopoulos is studying Guild Chronicles, a role-playing game created by Andrew Harris. My (Boston) colleague Andrew Harris created the tabletop role-playing game Guild Chronicles, which is similar to Dungeons and Dragons, but is especially designed to target the development of social-emotional skills.He has continued to develop it over the years with input from autistic individuals.
The study on APOE4 homozygosity indicates a genetic variant of Alzheimer's disease with early symptom onset and distinct biomarker progression, highlighting the need for specialized treatment ...
Email: [email protected]. Abstract: The paper analyzes questionnaires administered to 135 English Language students in all four. years with an attempt to elaborate how developed the students ...