
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Indian Independence and Partition
Published by Madison Gilbert Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Indian Independence and Partition"— Presentation transcript:

What is now India Pakistan Bangladesh Sri Lanka.

Chapter 9: South Asia in Transition Section 1: Freedom and Partition.
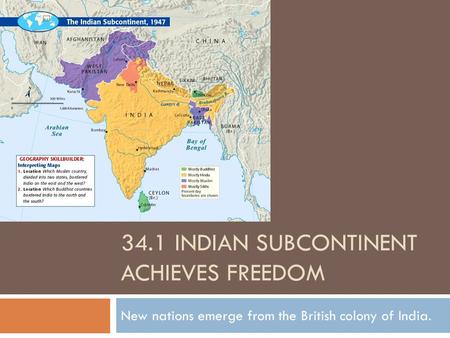
34.1 Indian Subcontinent Achieves Freedom

Objectives Explain what motivated the Indian independence movement after World War I. Analyze how Mohandas Gandhi influenced the independence movement.

The Indian Subcontinent Achieves Freedom

Nationalism post WWI TurkeyIndiaKenya. Turkey Mustafa Kemal Mustafa Kemal changed name to Kemal Ataturk (father of Turks) Fought against an invasion by.

HWH UNIT 13 CHAPTER Review British East India Company Sepy Rebellion The “Jewel in the Crown” The Indian National Congress (Congress Party)

Objectives Understand why independence brought partition to South Asia. Describe how Indian leaders built a new nation. Summarize how Pakistan and Bangladesh.

After WWI, increasing nationalism in India led to harsher laws that limited rights General Reginald Dyer banned all public gatherings after five British.

Mohandas K. GANDHI Mohandas K. GANDHI and Indian Independence.

The Indian Nationalist Movement and Gandhi

The Road to Independence

Indian Independence. Amritsar Massacre ► Indian nationalist increase their demands for freedom. ► Britain began limiting freedoms (press, speech)
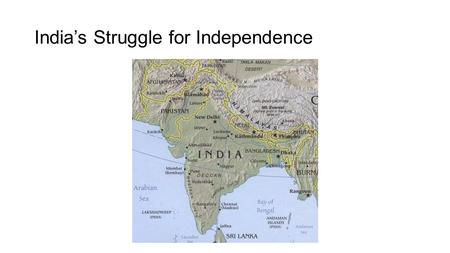
India’s Struggle for Independence. Early independence movements A. Indian National Congress founded 1885 B. Muslim League formed 1907 C. During W.W.I.

INDIA’S INDEPENDENCE MOVEMENT. INDIA AS A COLONY OF GREAT BRITAIN For most of the Nineteenth Century, India was ruled by the British. India was considered.

Indian Nationalism & Nation-building

Indian Independence Growing Unrest In 1919, new laws from Britain Limited freedom of the press and other rights Protested by nationalists Five.

The Indian Subcontinent Gains Independence

FREEDOM AND PARTITION.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

- Modern History
Indian Independence and the Partition explained

On August 15th, 1947, India finally gained its independence from British rule after decades of struggle.
This event is one of the most important in Indian history, and it had a huge impact on the region as a whole. However, it was not a smooth transition.
On August 14th, just one day before India's independence, the Muslim state of Pakistan also gained its independence from British rule.
This was in comparison to India, which was predominantly Hindu.
This was accomplished through the partition of India into two separate countries. The consequences of this partition were devastating.
Over the course of just a few months, millions of people were killed and displaced in what is considered to be one of the worst humanitarian disasters in history.
The background of Indian independence and partition dates back to the 18th century when the British first began to colonise India.
For centuries, India had been ruled by a number of different dynasties and empires.
The British East India Company was established in 1600 and slowly began to take control of more and more territory.
The East India Company eventually dominated regions of the Indian subcontinent beginning in 1757, when it began ruling Bengal, a time period known as Company Rule or Company Raj.
In 1858, after the Sepoy Rebellion , the British Crown took over direct rule of India from the East India Company.
From that point on, India was effectively a colony of Britain.
Rise of Sectarianism
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, there was a growing movement for Indian independence from British rule.
This was led by figures such as Mahatma Gandhi who believed in nonviolent resistance. However, not all Indians wanted independence.
There were also those who wanted to maintain the British Raj because they believed it was a stabilising force in the region.
In the late 19th century, there was also a growing movement among Indian Muslims for a separate Muslim state.
This was in response to fears that Hindus would dominate an independent India.
In 1885, the Hindu-dominated Indian National Congress was founded to fight for Indian independence from British rule.
At first, the Muslim minority in India was not supportive of the Congress's goals. However, this changed when Muhammad Ali Jinnah, a lawyer and politician, joined the Congress in 1906.
The British divided electoral districts among different religious groups in 1909, which resulted in sectarianism hardening of boundaries.
The colonial regime emphasised these distinctions by, for example, having separate toilet and water facilities for Muslims and Hindus at railway terminals.
Jinnah advocated for Hindu-Muslim unity and helped to found the All-India Muslim League in 1912.
The Muslim League's goal was to protect the rights of Muslims within India.
The World Wars
During World War I, India was formally a part of the British Empire. This meant that Indian soldiers were fighting for Britain in Europe and the Middle East.
At the same time, Muslims in India felt a sense of loyalty to the Ottoman Empire which was also fighting against Britain.
This led to tensions between Hindus and Muslims in India.
In exchange for the service of over a million Indian soldiers in the British Army during WWI, Indians expected political concessions as far as, and including, independence.
However, after the conflict, Britain made no such offers.
At the time, Mahatma Gandhi was referred to as "The Father of the Nation," and he became the most prominent figure in Congress.
Although he pushed for a unified Hindu and Muslim India with equal rights for all people, other members of Congress were less eager to cooperate with Muslims against the British.
As a result, the Muslim League began formulating separatist plans.
During World War II, India once more contributed to the conflict as part of the British Empire.
However, this time there was much greater support for independence among Indians.
In response to this, Britain promised independence to India after the war, if they fought on their side.
At the end of the Second World War, the Labour Party was voted into office in Britain, and they pushed for Indian independence.
Labour sought almost immediate independence for India, as well as a slower schedule for decolonisation of other British imperial possessions.
Separate Muslim State
With Indian independence finally a possibility, Muhammed Ali Jinnah, the leader of the Muslim League, began a public battle in support of a separate Muslim state as well, while Jawaharlal Nehru of the Congress suggested a unified India.
The country was on the verge of a sectarian civil war as independence approached. Despite Gandhi's calls for Indians to come together in peaceful resistance to British rule, the Muslim League scheduled "Direct Action Day" for August 16, 1946.
This was meant to be a day of peaceful protest, calling for a separate Muslim state.
However, the day saw violence from Muslim crowds against Hindus. By the end of the day, approximately 3,500 Hindus and Sikhs had been killed in Calcutta.
The next day, there were reports of Hindu reprisal attacks, with some 400 Muslims killed.
The Indian Independence Act of 1947 was an act passed by the British Parliament that granted independence to India.
The act came into effect on August 15th, 1947, making August 15th the official date of Indian independence.
The Radcliffe Line
The Radcliffe Line was the boundary line between India and Pakistan that was drawn up by British lawyer Cyril Radcliffe.
The line was intended to be a fair and impartial division of the country, but it ended up being highly controversial.
The Award was a report published by the British government in August 1947 that proposed the partition of India into two separate states: India and Pakistan.
The Award was highly controversial as millions of Hindus and Muslims were forced to leave their homes and cross the border into either India or Pakistan.
The problem was severe in the fertile and prosperous Punjab, where Hindus and Muslims lived nearly side by side.
Both sides refused to give up this valuable real estate, and religious animosity was strong.
The Partition of India
The partition of India was the division of the country into two separate states: India and Pakistan.
The partition took place on August 14th, 1947 and led to mass violence and displacement as millions of Hindus and Muslims were forced to leave their homes and cross the border into either India or Pakistan.
Around 10 million people escaped north or south, depending on their religion. An estimated 500,000 people were killed in fighting.
The partition also led to the division of families, with some members going to India while others went to Pakistan.
The partition was a difficult and traumatic experience for many people.
On January 30, 1948, Mohandas Gandhi was murdered by a Hindu extremist opposed to his goal of building a secular state.
The assassin, Nathuram Godse, was motivated by his belief that Gandhi was appeasing Muslims at the expense of Hindus.
Burma and Ceylon gained independence from Britain in 1948, and Bangladesh separated from Pakistan in 1971.
Since August 1947, India and Pakistan have been engaged in three major conflicts and one minor conflict regarding border issues.
Also, the demarcation of the borders in Jammu and Kashmir remains a major issue.
Today, the partition is still a highly sensitive issue. The events of 1947 continue to have a profound impact on the lives of people in India and Pakistan.
What do you need help with?
Download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

teacher appreciation
11 templates

memorial day
12 templates

9 templates

rain forest
23 templates

55 templates
Indian Independence Day
Indian independence day presentation, free google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
The Indian Independence Day is celebrated every year on the 15th of August and it commemorates the nation’s independence from the United Kingdom. On this day, Indians honor of those who fought for their liberty, so it’s a very special day in their culture. If you want to make a presentation about this event, use this template from Slidesgo. The slides have a colorful design with different patterns that remind Indian aesthetics and they’re full of different resources that can make it easier to give historical details about this important day: maps, graphs, infographics… the only thing you need to do is download the template and start editing it!
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 35 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?

Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


Indian Independence and Partition
Aug 16, 2014
570 likes | 1.62k Views
Indian Independence and Partition. India: Indian National Congress. Goals: Democracy, Local Self-Rule (BCW), Prevent mass peasant uprising (like China) by keeping power centered on middle class leaders. India: The Muslim League Forms. Goals:
Share Presentation
- religious conflict
- middle class leaders
- congress government
- middle class
- muslim league forms

Presentation Transcript
India: Indian National Congress Goals: Democracy, Local Self-Rule (BCW), Prevent mass peasant uprising (like China) by keeping power centered on middle class leaders.
India: The Muslim League Forms Goals: Protect the interests, liberties and rights of Muslims Promote an understanding between the Muslim community and other Indians - discourage violence. Educating the Muslim and Indian community at large on the actions of the government
WWI: 1914-1919 Britain promises India self-rule if they help fight in the war Gandhi supports war effort in hopes of achieving self-rule for India When war ends, Britain made a few reforms and refused to grant India self-government Major Events
The Amritsar Massacre of 1919 Major Events How did the Amritsar massacre change the attitude and goal of the Indian National Congress and Muslim League? General Dyer
Gandhi said, “Cooperation in any shape or form with this satanic government is sinful.”
Civil Disobedience is the refusing to obey unjust laws and purposely breaking them Passive resistance is non-violent protests using two major aspects: Satyagraha Ahimsa Mohandas K. Gandhi, The “Mahatma” or Great Soul “Satyagraha is a weapon of the strong; it admits of no violence under any circumstance whatsoever; and it ever insists upon truth.”
According to Gandhi, what are his three goals to win independence from Great Britain? Message to the Masses 1. Hindu-Muslim Unity 2. Must end “untouchability” 3. Must defy the British – Not through violence
Boycotts British goods Goes on Hunger strikes in prison and to stop violent protests. Gandhi Leads Non-Violent Protests
The Salt March • British law claimed that the British had sole right to produce and sell salt in India • Gandhi wrote to Viceroy stating his intent to break the law • With 78 followers he marched 240 miles to the sea. By the time he reached the sea, thousands of people had joined the march
The Salt March 4. Gandhi and others harvested salt from the sea and were arrested 5. Reporters around the world reported the incident. The event embarrassed the British government who prided themselves on their democratic traditions. March 12, 1930, Gandhi and 78 male satyagrahis started their 23-day-long journey
Muhammad Ali Jinnah A. Middle Class lawyer educated in Britain B. First supported Hindu-Muslim Unity – called “Ambassador of Hindu-Muslim Unity” C. Proposed Lucknow Pact
Muhammad Ali Jinnah D. Disagreement with Gandhi led to Muslim- Congress split E. Jinnah began to fear Hindu domination of Congress – A “Hindu Raj” F. Began to support the idea for an independent Muslim homeland, Pakistan or “land of the pure”.
India Independence and Partition Grants full Independence to India in 1947 Partitions India by creating East and West Pakistan to avoid religious conflict – Gandhi not pleased Jinnah planned to say a joke when he met Lady Mountbatten when he said, “A rose between two thorns.” However, he thought she would be in the middle. Jinnah was able to get equal say at negotiations and refused to accept living under “Hindu Rule.”
Indian Independence and Partition India was, therefore, partitioned into two nations: Indiain the center and Pakistan to the west and east. Burma (Myanmar) and Ceylon (Sri Lanka) became independent the following year.
India Independence and Partition Why was Pakistan created with such odd borders? Muslims Hindus Hindus What do you think will happen with the Muslims in India and the Hindus in Pakistan? Muslims
Golden Temple of the Sikhs
Indian Independence and Partition Due to this Hindu-Muslim split, a Great Migration occurred where Hindus in Pakistan and Muslims in India left their homes in an attempt to go where they felt accepted. Unfortunately, this led to horrendous violence that killed millions of people.
Indian Independence and Partition Nehru led the developing nations in practicing Non-alignment with the Superpowers and thus, received enormous aid from both the U.S. and the U.S.S.R.
Indian Independence and Partition Religious and political conflict remained a problem. In the 1980s, Sikhs demanded an independent state of Punjab and assassinated Prime Minister, Indira Gandhi (Nehru’s Daughter) in 1984.
Indian Independence and Partition Other Developments in the region: After fierce fighting, Bangladesh (East Pakistan) split from West Pakistan in 1971. In 1983, an endless war erupted in Sri Lanka with Hindu Tamils, the minority who wanted their own independent nation, fighting against the majority BuddhistSinhalese. In the first of these clashes, India sent troops to restore order. As a result, the Terrorist group known as the Tamil Tigers assassinated Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi(Indira Gandhi’s son) in 1991. Terrorism continues there today.
Indian Independence and Partition Relations between Pakistan and India remain unstable. Both nations want to control the Jammu and Kasmir regions near the Pakistan-India border. Tensions based on religious and ethnic claims continued to increase after both India and Pakistan tested nuclear weapons in 1998.
Indian Independence and Partition In 1992, Hindu fundamentalists supported by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) stormed the Babri Masjid mosque and razed it because it was said to be built on the site of a former Hindu temple. The incident sparked violent clashes that claimed dozens of Hindu and Muslim lives. The Congress government, which had ruled India almost uninterrupted for four decades, began to face increasing voter resentment for policies that failed. In 1998, the BJP has dominated the coalition government in New Delhi and has challenged Pakistan to a fourth and final war.
- More by User

GANDHI and Indian Independence
GANDHI and Indian Independence . “ Satyagraha” _________. Convert the _____________? The MAHATMA: Gandhi’s goals: 1. Equality w/t British Later became Independence from the British 2. Hindu-Muslim unity, thus NO division o/t country into India for Hindus and Pakistan for Muslims
188 views • 15 slides

Indian Independence
506 views • 28 slides

Indian Independence. Mahatma Gandhi spinning yarn, in the late 1920s Gandhi and Nehru in 1942. Create a Venn diagram for India and South Africa’s struggle to independence. Compare and contrast independence movements in India and South Africa. Use notes and pages 696 - 704. Directions: .
568 views • 17 slides

Indian Independence. Mohandas Gandhi. Indian Civil Rights leader B. “Great Soul” – Mahatma “Father of India” C. Civil Disobedience - Not following unjust laws, but doing so non violently. Civil Disobedience . British tax on salt. Civil Disobedience . British taking Indian raw cotton
349 views • 17 slides

Imperialism, Independence and Partition
Imperialism, Independence and Partition. From Bad to Worse?. India 1857. The British Players. Prime Minister Atlee. Lord Mountbatten.
501 views • 20 slides

Indian Independence . Geography of India. Indian Sub-Continent of Asia British India . Evolution of the Indian Independence Movement. British rule of India Indian National Congress Leadership of Mohandas Gandhi Role of Civil disobedience and passive resistance. Colonial India.
621 views • 14 slides

Indian Independence and the
Indian Independence and the . By : Bryan Ramirez. Bus Boycott. Bus Boycott.
201 views • 11 slides

Indian Independence. India became independent in 1947 Indians had been fighting steadily for independence since the 19 th century The most important leader of the resistance movement was Mohandas Gandhi Advocated nonviolence
236 views • 3 slides

Indian Subcontinent get Independence
1. Final exam essay – Thursday, Jan 5– see website for final exam essay questions on the top of the important course documents page. Please Complete Graphic organizer for each of the three essays. You may use this completed g.o . on the day of the final. Complete Asia map – packet page 1
773 views • 8 slides

The U.N. Partition Plan and The War of Independence
The U.N. Partition Plan and The War of Independence. By Zoe and Gavi. The United Nations. The UN stands for the United Nations. The United Nations is an organization in New York. It has representatives from each country that vote on problems that effect the whole world.
197 views • 7 slides

Development of Indian Nationalism and Independence
Development of Indian Nationalism and Independence. Focus on Role of Gandhi. Defining Nationalism and Causes of Nationalism in India. Nationalism – the loyalty to a group with whom one shares a common history, culture, and/or religion. Nationalism is……………….
2.42k views • 181 slides

Indian Independence. Nationalism. Being loyal to those with whom you share a common history, pride for one’s country. India as a colony. Colony of Great Britain Treated unfairly- best jobs and schools for British
258 views • 11 slides

India Lesson 3. Indian Independence. Explain the origin & impact of British rule in India. Describe the path to independence. Objectives. Warm Up. What role does reincarnation play in the Hindu religion and Indian way of life?.
288 views • 11 slides

Indian Independence Movement
Indian Independence Movement. Mohandas Gandhi. Background information: Member of merchant class, lawyer First experienced discrimination in Africa 1906 - started his first non-violent campaign
278 views • 6 slides

Indian Independence and Gandhi
Indian Independence and Gandhi. DESIRE FOR INDEPENDENCE. INDIAN NATIONAL CONGRESS: Organized by nationalists in 1885 to gain greater rights for Indians WORLD WAR I: Indians were forced to fight for Britain. DELHI GATE. Dedicated to the 70,000 Indian troops who died during WWI.
616 views • 33 slides

Indian Independence Movement. What methods did Gandhi use and were his methods successful?. Rise of Indian Nationalism. Despite helping Britain in WWI, Indians were once again treated as 2 nd class citizens after the war
404 views • 3 slides

Indian Independence. The Crusade of Mahatma Gandhi. Introduction.
513 views • 26 slides

Indian Politics Beyond Independence
Indian Politics Beyond Independence. An Introduction. India: A Social Profile. Population in India today stands at 1,027,015,247. Though India occupies nearly 2% of the earth’s surface it harbors nearly 15% of world’s population.
179 views • 5 slides

Development of Indian Nationalism and Independence. With Detailed Focus on Role of Gandhi. Timeline Overview. Summary Slides. INDIA. Nationalist Challenge to the British Raj India colonized long before Africa, Asia Was first to establish independence movements
1.99k views • 197 slides

1.37k views • 135 slides

Indian Independence. The Amritsar Massacre. In 1919 India was a major part of the British Empire. But many Indians wanted to be free from British rule and so the formed a party which wanted Indian Independence.
213 views • 14 slides

COMMENTS
63 likes • 50,964 views. Suhas Mandlik. ICSE Grade X History Chapter- Indian Independence and Partition of India. Education. Indian Independence and Partition of India. Independence and Partition. Causes that. Introduction World War. Events that led.
What is the Partition of India? The partition of India is the separation of India on Aug. 14, 1947 and Aug. 15, 1947 into the states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India, respectively. India was separated on the day of gaining independence from British, due to tensions between the Hindus and the Muslims living in the country.
Indian Independence and Partition PPT.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. The partition of British India in 1947 along religious lines led to sectarian violence that killed over a million people and displaced millions more. India and Pakistan gained independence but remained divided over the disputed ...
16 India Independence and Partition Grants full Independence to India in 1947 Partitions India by creating East and West Pakistan to avoid religious conflict - Gandhi not pleased Jinnah planned to say a joke when he met Lady Mountbatten when he said, "A rose between two thorns." However, he thought she would be in the middle.
India's Independence and Partition - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Helpful ppt for studying about India's independence.
Partition. •The partition of India is the separation of India on Aug. 14, 1947 and Aug. 15, 1947 into the states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India, respectively. •India was separated on the day of gaining independence from British, due to tensions between the Hindus and the Muslims living in the country.
Presentation Transcript. Indian Independence and Partition. Sepoy Rebellion 1857-1859 • A mutiny arose by Indian troops stationed in Delhi. • Results • 1.) British and Indian attitudes changed towards British rule of India • 2.) Year long insurrection • 3.) Dissolution of the British East India Company • 4.)
Indian Independence and Partition PPT - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.
The background of Indian independence and partition dates back to the 18th century when the British first began to colonise India. For centuries, India had been ruled by a number of different dynasties and empires. The British East India Company was established in 1600 and slowly began to take control of more and more territory.
Pakistan. partition of India, division of British India into the independent countries of India and Pakistan according to the Indian Independence Act passed by the British Parliament on July 18, 1947. Set to take effect on August 15, the rapid partition led to a population transfer of unprecedented magnitude, accompanied by devastating communal ...
Indian Independence and Partition PPT (1) - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. ppt based on indian independecne
The Indian Independence Day is celebrated every year on the 15th of August and it commemorates the nation's independence from the United Kingdom. On this day, Indians honor of those who fought for their liberty, so it's a very special day in their culture. If you want to make a presentation about this event, use this template from Slidesgo.
it is an example of power point presentation on the topic - INDIA'S INDEPENDENCE AND PARTITION.#POWER POINT#PPT#INDIA #INDEPENDENCE #PARTITION#power point r...
India's Independence Movement PowerPoint is a summary of important series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending the British rule in India. The movement spanned from 1857 to 1947. During the lesson, the children will have a better understanding of the origins of the Indian Independence movement as well as key freedom fighters and revolutionaries prominent in the movement. This ...
Indian Independence and Partition PPT - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. history icse project. add name slide.
Indian Independence and Partition In 1992, Hindu fundamentalists supported by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) stormed the Babri Masjid mosque and razed it because it was said to be built on the site of a former Hindu temple. The incident sparked violent clashes that claimed dozens of Hindu and Muslim lives.
Indian Independence and Partition PPT - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. jk
Indian Independence and Partition PPT - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.