

Past Continuous Tense: Capturing the Dynamic Past in English Grammar
In the intricate landscape of English grammar, tenses stand as pillars, each supporting a unique dimension of expression. Among these, the past continuous tense emerges as a dynamic and intriguing facet, capturing the ongoing essence of actions in the past. Like a snapshot of a moving scene, the past continuous tense portrays actions that were in progress at specific moments in the bygone days, painting a vivid canvas of time.
This essay embarks on a journey through the realm of the past continuous tense, unraveling its structure, exploring its various applications, and illuminating its significance in both language and communication. As we delve into its intricacies, we uncover a past continuous tense that breathes life into narratives, adds depth to descriptions, and enriches our ability to convey the fluidity of the past.
1. Definition of past continuous tense
The past continuous tense, also known as the past progressive tense, is a grammatical form used to describe ongoing actions or events that were happening at a specific moment in the past. It emphasizes the duration, progress, or interruption of an action in the past, providing a sense of continuity to the narrative. This tense is formed using the past tense of the verb “to be” (was/were) and the base form of the main verb with the -ing suffix (e.g., was/were + verb + -ing). The past continuous tense helps convey a dynamic view of the past, allowing for a more vivid and detailed description of past actions or events in a given context.
2. Past continuous tense structure
The structure of the past continuous tense in English is formed using the past tense of the verb “to be” (either “was” or “were”) and the base form of the main verb with the -ing suffix. Here’s the breakdown of the structure:
2.1. Affirmative Form
Subject + was/were + Verb (base form + -ing)
I was reading a book.
They were playing football.
2.2. Negative Form
Subject + was not (wasn’t)/were not (weren’t) + Verb (base form + -ing)
I was not (wasn’t) reading a book.
They were not (weren’t) playing football.
2.3. Interrogative Form
Was/were + Subject + Verb (base form + -ing)?
Was I reading a book?
Were they playing football?
These structures help in constructing sentences in the past continuous tense, which is typically used to describe actions or events that were ongoing at a specific time in the past or actions that were happening around a particular moment in the past.
>> Suggested article: past simple tense

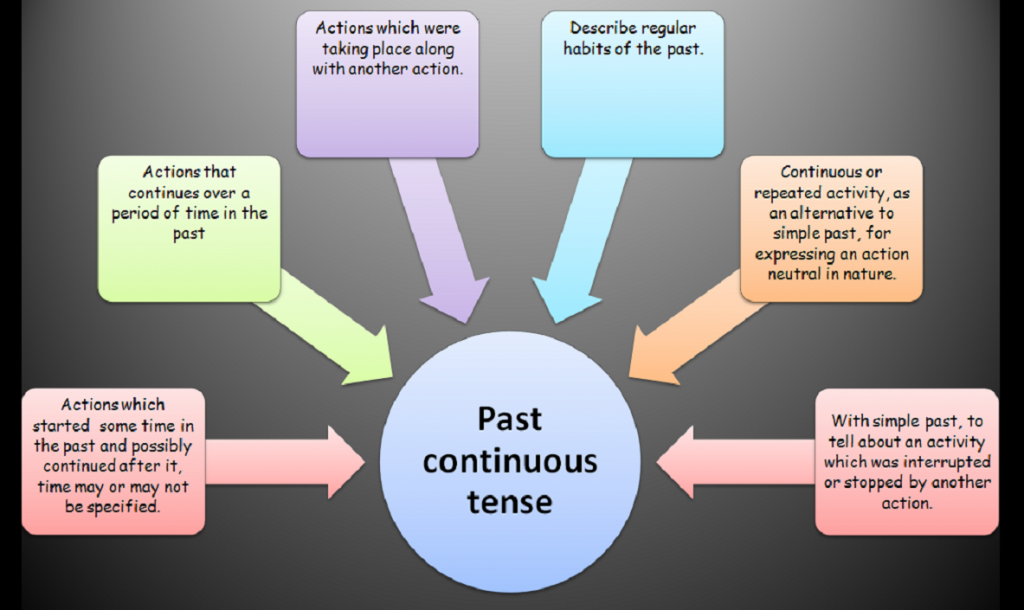
3. Usage of past continuous tense
The past continuous tense, also known as the past progressive tense, is used in English for several specific purposes:
3.1. Describing Ongoing Actions in the Past
The primary use of the past continuous tense is to describe actions, events, or situations that were in progress at a specific moment in the past. It emphasizes the duration and continuity of the action.
For example: “I was studying when the phone rang.” (The action of studying was in progress when the phone rang.)
3.2. Setting the Scene in Narratives
In storytelling or narrative writing, the past continuous tense is used to set the scene or describe background actions, creating a vivid and immersive atmosphere.
For instance: “It was raining heavily, and thunder was rumbling in the distance as she was walking home.”
3.3. Expressing Parallel Actions
It is used to describe two or more actions that were happening simultaneously in the past. This helps convey the idea that multiple events were occurring at the same time.
For example: “While he was cooking dinner, she was watching TV.”
3.4. Indicating Actions in Progress at a Specific Time
The past continuous tense can be used to specify an action that was happening at a particular time in the past. It often includes time expressions such as “at 3 o’clock,” “at that moment,” or “while.”
For example: “At 8 PM last night, I was having dinner.”
3.5. Politeness or Softening Statements
In more formal or polite communication, the past continuous tense can be used to soften statements, make requests, or express courtesy.
For instance: “I was wondering if you could help me with this.”
3.6. Expressing Irritation or Annoyance
In some cases, the past continuous tense can be used to express irritation or annoyance about an ongoing situation in the past.
For example: “He was constantly talking during the movie, which was really annoying.”
It’s important to note that the past continuous tense is often used in conjunction with the past simple tense to provide context and clarify the sequence of events in narratives or descriptions of the past. This combination of tenses allows for a more comprehensive portrayal of past actions and events.
3.4. Past continuous tense’s role in the IELTS test
The past continuous tense holds a notable role in the grammar for IELTS (International English Language Testing System), which evaluates a candidate’s proficiency in using the English language. Here’s how the past continuous tense is relevant in different sections of the IELTS test:
Speaking Section
In the IELTS Speaking test , candidates may use the past continuous tense to narrate past events, describe activities or experiences from a particular time in the past, or set the scene for a story. It allows them to showcase their ability to use varied tenses, including continuous tenses, to describe past actions in a fluent and accurate manner.
Writing Section
In the IELTS Writing test , specifically in Task 1 (Academic module), candidates might describe trends or changes that were happening at a particular time in the past using the past continuous tense. This could involve interpreting and describing data in a graph or chart that represents a historical or past scenario.
Additionally, in Task 2 of both the Academic and General Training modules, candidates might use the past continuous tense when providing examples or anecdotes to support their opinions or arguments.
Listening Section
The past continuous tense is encountered in the Listening section of the IELTS test in audio materials, including conversations, interviews, or lectures. Candidates need to understand this tense to comprehend and interpret events or activities described in the past, as well as to answer related questions accurately.
Reading Section
The Reading section of the IELTS test may present passages or texts that use the past continuous tense. Candidates must be able to recognize and understand this tense to grasp the timeline of events and actions, aiding comprehension and accurate answering of questions.

5. Past continuous tense exercise
Ex1: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate form of the verb in the past continuous tense:
While they __________ (cook) dinner, the guests arrived.
I __________ (read) a book when the power went out.
They __________ (play) football while it was raining.
He __________ (watch) TV while she was working on her assignment.
The kids __________ (swim) in the pool at this time yesterday.
While they were cooking dinner, the guests arrived.
I was reading a book when the power went out.
They were playing football while it was raining.
He was watching TV while she was working on her assignment.
The kids were swimming in the pool at this time yesterday.
Ex2: Fill in the blanks with the appropriate form of the verb in the past continuous tense:
She __________ (sing) a song while he __________ (play) the guitar.
The students __________ (work) on their projects during the class.
We __________ (wait) for the bus when it __________ (start) raining.
While they __________ (have) dinner, the phone __________ (ring).
I __________ (walk) in the park when I __________ (see) the beautiful sunset.
She was singing a song while he was playing the guitar.
The students were working on their projects during the class.
We were waiting for the bus when it started raining.
While they were having dinner, the phone was ringing.
I was walking in the park when I saw the beautiful sunset.
She reads a book.
They eat breakfast in the morning.
He writes a letter to his friend.
I listen to music on my way to work.
The dog barks loudly at strangers.
She was reading a book.
They were eating breakfast in the morning.
He was writing a letter to his friend.
I was listening to music on my way to work.
The dog was barking loudly at strangers.
The essay thoroughly explores the past continuous tense, shedding light on its grammatical structure and multifaceted usage. It begins by defining the past continuous tense, showcasing its fundamental role in conveying ongoing actions or events in the past. The structure of the tense is elucidated, emphasizing the use of “was/were” and the base form of verbs with the “-ing” suffix.
The essay delves into the nuanced ways in which the past continuous tense is utilized, including its primary purpose of describing ongoing actions at specific moments in the past. It underlines its relevance in setting the scene in narratives, expressing parallel actions, pinpointing actions at a given time, conveying politeness, and highlighting annoyance or irritation.
Furthermore, the essay explores the crucial role of the past continuous tense in the IELTS test across its speaking, writing, listening, and reading sections. Proficiency in using this tense is essential to effectively communicate past experiences and comprehend auditory or written material in the test.
Overall, the essay underscores the significance of the past continuous tense as a vital linguistic tool that enriches communication, allowing for precise and vivid expression of events that were unfolding at distinct points in the past. Let’s take some IELTS practice test now!
- Student Login:

#263: The Past Continuous Tense: How and When to Use It (With 6 Examples)
Jan 18, 2023 | Grammar , Verb Tenses

If you avoid some grammar tenses because you’re not sure how to use them correctly, it can lead to unnecessary grammar mistakes .
It can also make it more difficult to express exactly what you want in English conversation.
In today’s Confident English lesson, we’ll explore the past continuous tense in English . Also known as the past progressive .
That means a review of the past continuous structures so you can use them accurately. And, more importantly, you’ll learn 6 real-life examples of when to use the past continuous.
By the end, you’ll be able to use the past continuous form to confidently answer 3 questions I have for you.
The Past Continuous Tense: How and When to Use It | 6 Examples
Before we look at 6 specific examples of how and when to use the past continuous, let’s review the structure so you use the tense accurately.
The structures for the past progressive tense are as follows:
Positive : Subject + [was/were] + verb[ing]
- I was planning to call you but lost track of time.
Negative : Subject + [was/were] + not verb[ing]
- She wasn’t sleeping when you called. She was working with her phone on silent mode.
Also, be careful with your verb choice.
Stative verbs are not used in the past continuous form. These verbs, which describe a state of mind, opinion, need, or awareness, never use the past progressive.
Stative verbs include verbs such as believe , dislike , hate , like , love , need , prefer , realize , seem , understand , want , etc.
For example, we would not say, “I was preferring the winter weather before it got too cold.” Instead, we use the simple past to say, “I preferred the winter weather before it got too cold.” Stative verbs imply a continuous or ongoing action, so the use of the past progressive is not necessary.
Use 1: Provide Context/Background for Telling Stories
When you tell a story, you reference the past. You’re describing something that already happened or something you experienced.
To help make the story interesting, you provide context. The background. This helps to set the tone or mood. You’re providing a mental picture for your listener.
And that’s where you want to use the past continuous tense.
Scenario 1: Imagine your telling someone about a recent vacation. To highlight how relaxing it was on your day, you might provide some background details such as:
“When I woke up, the waves were rolling on shore, the sun was inching up over the mountains, warming the sand, and the palm leaves were rustling in the breeze. It was the perfect start to the vacation.”
Scenario 2: Think about an important historical event you’ve experienced. Imagine someone asking you, “What were you doing when…”
For example, “What were you doing when you heard the election results?
In describing the context, you might say, “I was at an election party. A group of us were chatting and the music was blaring when they announced the results. There was so much noise that we didn’t hear them right away.”
And that leads me to Use 2.
Use 2: Highlight Overlapping Events and Interruptions
Overlapping events .
The second scenario in Use 1 also describes overlapping events. In other words, two events happening at the same time.
To show that two events are overlapping – and to show which one started first – you’ll use the past continuous.
There are 2 structures we use to do this:
- When + Past Simple
- I was chatting with friends when they announced the results.
- When they announced the results, I was chatting with friends.
In both cases, I was chatting with friends first. Then the other action happened.
- At midnight, At 7:00 PM, In September, By the age of 12
These specific indications of time show that an event was ongoing before and after.
For example:
- By the age of 12 , I was playing concerts in major cities across the country. (This was true before and after the age of 12.)
- By the time I was in my mid-30s , I was putting a significant part of my paychecks toward my retirement fund.”
- In September , I was preparing for our next major project.
- I was cooking dinner at 7 PM last night.
Interruptions
The past continuous also shows what was happening when an interruption occurred.
Scenario 3: Imagine you missed a call from a loved one and they ask you what was going on.
You might say, “I was cooking in the kitchen and the kids were watching TV with the volume on high when you called the first time. I didn’t hear the phone.”
Scenario 4: Say you’ve had a chaotic morning and you’re retelling the events to a coworker.
You might share, “The kids were sleeping deeply when the alarm rang and jolted them awake.”
Notice in those examples we’re using the same when + past simple structure.
Use 3: Emphasize Length of Time (All Day, All Morning, etc.)
Why might this be useful?
Scenario 5: Imagine you’ve accomplished a major milestone at work. You and your team recently finished an all-consuming project. And you want to emphasize how much time you’ve spent on this project.
The past continuous combined with phrases that explain the length of time help you do this.
Example phrases include:
- All day/month/year
- All morning/afternoon/evening
- All day/night
- For hours/days/weeks/months/years
In describing the effort to others, you might say:
“We were working on this – non-stop – all year . It’s hard to believe we’re finally finished.”
Here’s another example.
Scenario 6: Say you’re a new parent and you’re telling your friend how difficult last night was with your infant.
During that conversation, you might express, “It was a terrible night. She was crying all night and we hardly slept.”
Use 4: Discuss Past Habits (Always, Constantly, Usually)
Usually, when we talk about habits, we use the present simple. For example, “I always read at night before bed.”
But what if the habit is no longer true? You might have broken a bad habit. Or your younger brother grew out of a childhood habit.
This is where the past continuous is helpful. It tells us that habits from the past are no longer true.
To do this, we combine the past continuous with adverbs and adverb phrases to describe the frequency, including:
- All the time
- The entire time
Scenario 7: Imagine you’re reminiscing about your first few years at a company. In doing so, you might say, “During my first year, I was constantly making mistakes. There was so much to learn.”
Scenario 8: You can use the tense to describe where you used to live and your neighbor’s (annoying) habits. “ The entire time we lived there, our neighbors were partying and yelling every other day. In the end, we decided to sell the house and move to a more peaceful neighborhood.”
Use 5: Make a Polite Request (I was wondering if…)
You’ll notice when English speakers make polite requests, they use the past continuous.
There is a simple sentence structure we use for this: I was wondering if…
- Asking your friend for a favor: “I was wondering if we could borrow your truck for our move?”
- Inviting a coworker to your house for the first time: “I was wondering if you’d like to come to our house this weekend? We’re having some friends over for a backyard BBQ.”
Sidenote: You can use this same structure – without ‘if’ – to ask indirect questions.
This might be useful if you’re not sure it’s appropriate to ask a question.
- What are you doing this weekend? (Direct)
- When will you have a decision? (Direct)
Be careful not to overuse this. The ‘I was wondering (if)…” structure is vague language. It can make the meaning less clear.
Use 6: Indicate a Change of Mind
Have you ever made a plan and then changed your mind at the last minute?
Of course, you have. We all have.
The past continuous helps us show what our original plan was and then we decided to do in the end.
Scenario 9: Imagine made plans to move to another city at some point in the past. You started making plans for 1 location but then changed your mind. You could say: “I was thinking about moving to Washington DC, but decided to move to New York instead.”
Scenario 10: Let’s say you talking about your plans for a vacation. In the process, the cost of airline tickets and airport delays changed your plans. You might tell a friend, “We were planning to go back to Europe. We haven’t visited in years. But the flight costs and the long delays made us change our minds. We’re going to travel somewhere closer to home instead.”
Now I have 3 questions for you to help you practice.
Using what you learned in this lesson, how would you answer these questions?
- Think of your most recent vacation. What was the first day like? Describe it or provide the context.
- What is a past habit you broke or grew out of? Use “When I was a kid, I always/never/constantly…”
- Tell me about a time when you changed your mind. What were you originally thinking? And what did you decide in the end?
You can share your answers — as well as your questions — with me in the comments below.
~ Annemarie

Get the Confidence to Say What You Want in English
Follow my 3-step solution to speak English with clarity, fluency, and freedom so you can say what you want with confidence.
You'll also get my Confident English lessons delivered by email every Wednesday and occasional information about available courses. You can unsubscribe any time.
More Like This

5 Smart Questions to Ask in an English Job Interview
It’s the last question in your job interview in English and you hear: Do you have any questions for me? What should you say? Is it okay to ask a question in a job interview? Find out exactly what you should do plus 5 smart questions to ask.

How to Disagree in English Politely
Want to say “I disagree” without creating tension in the conversation? Master the art of disagreement in this lesson on, “How to Disagree in English Politely.”

#310: The Right Grammar for English Introductions
Get your English introductions just right with this step-by-step video on Grammar for English Introductions when you’re meeting someone new.

#309: How to Go Off Topic in English | English Conversation Skills
Learn how to gracefully go off topic in English without losing your audience. Whether you’re in a meeting or chatting with friends, in this lesson we dive deep into the art of smoothly navigating tangents while enhancing your English conversation skills.
![past continuous essay #308: How to Use ‘Though’ in English [+ FREE Worksheet]](https://www.speakconfidentenglish.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/How-to-Use-Though-in-English-400x250.png)
#308: How to Use ‘Though’ in English [+ FREE Worksheet]
Learn and practice how to correctly use though, although, even though, and as thought in your English conversations.

#307: How to Use English Abbreviations in Emails, Texts, and Conversations
Follow this comprehensive guide to learn how to use English abbreviations for emails, texts, and conversations.
© Copyright 2014-2024 Speak Confident English | Privacy Policy | Terms & Disclaimer | Online Class Policies
Thanks once again for your exhaustive explanations, Anne-Marie! Having read the material, two questions have come to my mind:
1) as for the Use 4, is Past Continuous applicable in case of bad habits only? 2) can we use Past Perfect Continuous in the examples under the Use 6?
It would be great if you help us sort this out.
Thanks, Liana
Hi Liana, thanks for the comment and questions. For your first question, I want to make sure I understand correctly. Are you asking if this is the only way to highlight bad habits? If so, the answer is there are multiple ways we can discuss bad habits – this is just one possible option. As for use case 6, yes, we could also use past perfect continuous. By using the past continuous, we are setting the scene. You can think of it as providing background information. With the past perfect continuous, we would indicate that one past action had stopped … Read more »
Additional resource for honing English grammar skills – typeng.com. This cost-free web-based simulator offers the chance to enhance your grasp of English verb tenses. You need to peruse the inquiry and respond using the keyboard, utilizing solely the words provided beneath. Completely free of charge, and no need for registration.
When I was a kid I always preferred extra salted food but now I could never eat anything that is so salty.
I was planning to work at a call center after graduation but after hearing about my friends’ experiences I decided to work somewhere else where I can gain new skills.
The very first morning after arriving at Alex. I woke up to a wonderful view where I saw different shades of blue waves from the balcony.
Finally, here l finish the task.
l was the founder of a Club where kids were attending sessions to read books for pleasure that ‘s mean they were not forced to read a specific book. They were free to chose the author and the story. This activity took place for many years in my agenda and I was planning to continue the activity until l got retired, but the COVID made a mess in all my programmes.
*that means*
Here l answer the second question
When l was young , l ‘ve never got the opportunity to go to the movie theatre with my school mate. I always should be with my brothers.
Hello Anne Marie, Thank You for every thing. It’s extremely interesting.
When I was young my favorit destination to spend vacations was grandparents’ place. They were living in a Small farm. There were many animals,as ducks hens pigeons and cats. There was a pond where around fifty coloured fishes were swimming. I remember, l woke up early to join grandpa in the field . there were many fruits ‘ trees.we picked up some figues for breakfast …. I liked those days, since we spent weeks in the nature , breathing frech air and eating good food .
Sorry Anne Marie i couldn’t control my fingers because of the parkinson
Pin It on Pinterest

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6 Simple Past and Past Continuous
Simple Past and Past Continuous
Annapurna Madhuri
Introduction
The past continuous or the past progressive tense is used to tell about some action happening at some time in the past. The time of happening of the action/event may or may not be specified.
Any temporary action, and/or an incomplete action happening in the past is expressed in the past continuous tense.
The verb in the past continuous tense is made of two parts:
- The past tense form of verb ‘to be’ – was/were
- ‘ing’ form of the base verb.
Sentences in the past continuous form have a specified structure:
The affirmative sentence structure.
subject + past tense form of verb ‘to be’ + base verb+ing
Example: She (subject)+ was (past tense form of ‘to be’)+ sing (base-verb)+ing ==> She was singing.
Negative sentence structure:.
subject+ past tense form of verb ‘to be’ + not + base verb + ‘ing’
Example: She was not singing
Interrogative structure:.
Past tense form of verb ‘to be’ + subject + base verb + ing + Question tag
Example: Was she singing?
Previous Knowledge
Recap of simple past tense:
Knowledge of past continuous tense:
Learning Objectives
At the end of this chapter, all learners will be able to
- Use past continuous tense form of the verb to show actions happening in the past
- Know the sentence structures in each of the sentence forms.
- Construct sentences in past continuous tense in affirmative, interrogative and negative forms.
Given below is an account of a day in some time in the past. Read carefully and note the usage of verbs in the paragraph.
The last few months were so hectic. I was doing so many things all at the same time. I was planning to go to the mall with my friend Sadhana. We were always looking forward for the opportunity to go out together. As we were going to the mall, my car broke down. We were standing by the side of the road. We were waiting for the mechanic. When we were returning home from the garage, it started raining. We reached home completely drenched. It was raining for the rest of the day. Since, we could not go out, Sadhana and I were playing cards at home. We were feeling tired of being at home. So, we planned to cook our favourite food. We were cooking food, when the phone rang. Sadhana’s mother was calling. She was coming to pick up Sadhana from my home. She was bringing some ice-cream for us to eat. It was still raining outside, while we were enjoying our ice-cream at home. After a while, the rain stopped and Sadhana went home with her mother. We were having a great time together.
In the above paragraph, we see usage of past continuous tense in various situations. Let us now discuss.
The situations in which past continuous tense is used:
- Example : I was planning to go to the mall with my friend Sadhana. (time unspecified) It was raining for the rest of the day. (time specified)
- Example: We were waiting for the mechanic.
- Example : It was still raining outside, while we were enjoying our ice-cream at home.
- Example: We were always looking forward to the opportunity to go out together.
- Example: We were feeling tired of being at home. /We felt tired of being at home.
- Example: We were cooking food, when the phone rang.
- As we were going to the mall, my car broke down.
Please note : Words such as as, when, while are used to link two actions taking place in a given situation.
Exercise: Choose the correct form of the verb and complete the sentences:
Summing up
Signal words: while, when, as
Exercise: Read each sentence carefully and use the correct form of verb as per the signal words, to complete the sentences.
Interrogative sentences:
Negative sentences:
Self Check Exercises for additional practice
Choose the correct form of verb, to fill in the blanks with suitable forms of verbs given in the bracket:
Make sentences from the jumbled words
Simple Past and Past Continuous Copyright © 2019 by Annapurna Madhuri is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Digital Object Identifier (DOI)
https://doi.org/Effective English for Teachers
Share This Book
Improve your writing in one of the largest and most successful writing groups online
Join our writing group!
What You Need to Know as a Writer About Narrative Tenses

by Holly Riddle
Narrative tenses are one of those things that you likely take for granted as a reader, but that are all too important for writers. While schools usually teach narrative tenses in English classes, these verb tenses are often forgotten once they’re no longer needed, leaving you without really any thorough knowledge of how each tense works and when it should be used.
What are narrative tenses?
Narrative tenses are verb tenses that are used to talk about things that happened in the past. Different tenses can communicate different things about how and when these actions were taken. There are four narrative tenses: past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous.
Using the right verb tense as you describe events in your book or build any sort of narrative is crucial to creating immersive stories. The wrong verbs and related words can make a sentence clunky and distracting, pulling your reader out of your story.
Here’s what you need to know about narrative tenses as a writer.
The four narrative tenses
There are four primary narrative tenses: past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous.
What about future and present tense?
You probably learned about other verb tenses in school, like future or present, but narrative tenses aren’t just any old verb tenses. The term “narrative tenses” is specifically used to tell stories that happened in the past. While many modern authors play with future and present tenses in their novels or short stories (especially present tense in the young adult story space), “narrative tenses” technically only refers to past tenses.
Past simple tense
This is the simplest narrative tense there is. These verbs are used to talk about and describe past events that were fully completed at some point in the past. That’s it.
You’ll find this tense used broadly in most fiction and spoken accounts. A story that’s set in past tense overall will use past simple tense to describe most actions within the plot.
Past simple examples
Here’s an example of how past simple tense looks in fiction, with the past simple verbs highlighted. These sentences are from The Wonderful Wizard of Oz by L. Frank Baum.
Toto jumped out of Dorothy’s arms and hid under the bed, and the girl started to get him. Aunt Em, badly frightened, threw open the trap door in the floor and climbed down the ladder into the small, dark hole. Dorothy caught Toto at last and started to follow her aunt. When she was halfway across the room there came a great shriek from the wind, and the house shook so hard that she lost her footing and sat down suddenly upon the floor.

Past perfect tense
Past perfect tense is a little more complex than past simple tense. One easy way to recognize past perfect tense, though? Look for the word “had.” Generally, past perfect tense is used to talk about past events or an action that occurred even before the main event of the plot.
Past perfect examples
Here’s another snapshot for context, also from The Wonderful Wizard of Oz , with the past perfect verb phrases highlighted.
Not a tree nor a house broke the broad sweep of flat country that reached to the edge of the sky in all directions. The sun had baked the plowed land into a gray mass, with little cracks running through it. Even the grass was not green, for the sun had burned the tops of the long blades until they were the same gray color to be seen everywhere. Once the house had been painted , but the sun blistered the paint and the rains washed it away, and now the house was as dull and gray as everything else.

As you can see when you read this passage, the sun had baked and burned the land, and the house had been painted, at some point in time before the sun blistered the paint and before the rains washed it away.
This tense comes in handy when you’re telling a story, but, in order for the story to make sense in the correct order, you need to provide background information and refer to something that occurred before the main events of the story you’re telling.
Past continuous tense
Past continuous tense refers to something that is occurring at the same time as your story. You can recognize past continuous tense by looking out for the “-ing” suffix.
Past continuous examples
Here, the past continuous verbs in this passage from The Wonderful Wizard of Oz are again bolded.
There were lovely patches of greensward all about, with stately trees bearing rich and luscious fruits. Banks of gorgeous flowers were on every hand, and birds with rare and brilliant plumage sang and fluttered in the trees and bushes. A little way off was a small brook, rushing and sparkling along between green banks, and murmuring in a voice very grateful to a little girl who had lived so long on the dry, gray prairies.

Here you can see how these actions—bearing, sparkling, rushing, murmuring—are continuously occurring right when the story is happening. They’re not occurring in the distant past. They’re not one-off actions that are completed and done. They continue on.
Past perfect continuous tense
Lastly, we have past perfect continuous tense, which is a combination of both past perfect tense and past continuous tense. These verbs reference an action that occurred in the distant past, but that was continuously occurring for a certain, defined amount of time.
These verbs can usually be identified by both the presence of “had been” and that “-ing” suffix. They also usually include a few words telling you how long the action continued before it ended.
Past perfect continuous examples
Here’s our last excerpt:
They had hardly been walking an hour when they saw before them a great ditch that crossed the road and divided the forest as far as they could see on either side.

In this sentence, the subjects had been walking continuously, and did so until something else in the story happened and stopped this continuous action. The text provides more background information related to the story’s main event.
Choose the right narrative tense for your short story or novel
If you’re writing in the past tense, you’ll very likely use all of these narrative tenses at some point. The key is to know when to use them correctly to describe your characters’ actions in your stories or your own actions, if you’re writing a memoir or personal essay. Once you get the hang of them, you’ll find that using the right narrative tense comes easily and without a second thought.
Get feedback on your writing today!
Scribophile is a community of hundreds of thousands of writers from all over the world. Meet beta readers, get feedback on your writing, and become a better writer!
Join now for free

Related articles

Freytag’s Pyramid: Definitions and Examples of Dramatic Structure

Active vs. Passive Voice: What’s the Difference?

Cliché vs. Trope in Writing: How They Differ, with Examples

What is an Oxymoron? Easy Definition, With Examples from Literature

Writing the Hero’s Journey: Steps, Examples & Archetypes

Story Archetypes: 50+ Plot Archetypes to Craft Your Narrative
Apart vs A part
Billow vs bellow vs below | definitions, uses and examples.
- All 8 PARTS OF SPEECH
Lay vs Lie – Definitions, uses and examples
XSTREAMENGLISH
PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE

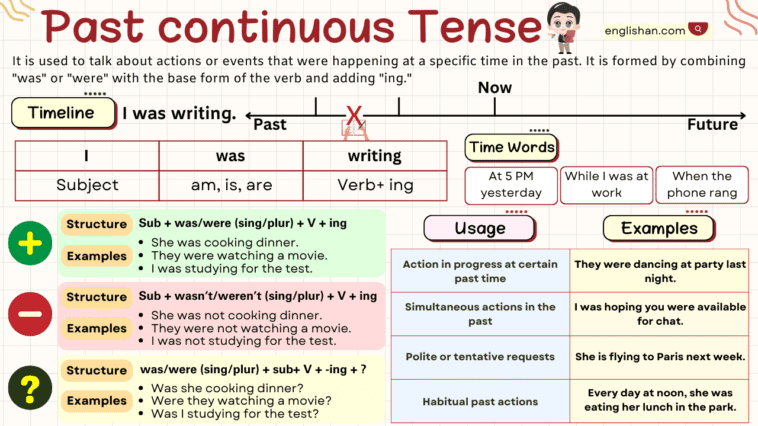
The Past Continuous Tense( also known as the past continuous tense) is used to express a continued or ongoing action which occurred in past and was completed at some point in past. It expresses an ongoing nature of an action in past.
The form of past continuous tense is To be(was/were) + Verb- ing[present participle]
Examples of past continuous tense
- Rohit was writing a letter.
- She was sleeping.
- We were going to market.
- Tim was studying.
- They were playing football.
- He was going to the office.
- He was singing a song.
- It was snowing .
- I was playing.
- You were washing clothes.
Structure of the Past Continuous Tense


Examples Of Past Continuous Tense
Affirmative sentences.
- The students were working hard.
- She was cooking food.
- The birds were flying in the sky.
- The boys were writing an essay.
- I was listening to the news.
- He was reading a book.
- Rina was singing a song.
- She was cleaning the home.
- They were watching a movie.
- She was swimming in the river.
Negative Sentences
- The students were not working hard.
- She was not cooking food.
- The birds were not flying in the sky.
- The boys were not writing an essay.
- I was not listening to the news.
- He was not reading a book.
- Rina was not singing a song.
- She was not cleaning the home.
- They were not watching a movie.
- She was not swimming in the river.
Interrogative Sentences
- Were the students working hard?
- Was she cooking food?
- Were the birds flying in the sky?
- Were the students writing an essay?
- Was I listening to the news?
- Was he reading a book?
- Was Rina singing a song?
- Was she cleaning the home?
- Were they watching a movie?
- Was she swimming in the river?
Interrogative Negative Sentences
- Were the students not working hard?
- Was she not cooking food?
- Were the birds not flying in the sky?
- Were the students not writing an essay?
- Was I not listening to the news?
- Was he not reading a book?
- Was Rina not singing a song?
- Was she not cleaning the home?
- Were they not watching a movie?
- Was she not swimming in the river?
USES OF PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE
A. Actions that were going on continuously in the past.
- He was playing football.
- They were watching TV.
- Chris was doing his homework.
- David was swimming in the pool.
B. For such work which the person had been doing habitually and frequently in the past. In such sentences adverbs like always, continually, constantly etc are used.
- He was constantly crying those days.
- She was always grumbling.
- They were continually threatening us.
- He was always abusing others.
C. Past continuous is also used in such a situation when some other event has happened, and any other work is also going on.
- The sun just setting as they reached the hill.
- The boy was knocked down by a car when he was crossing the road.
- When he arrived his wife was sleeping.
D. Past continuous is also used when two tasks were happening simultaneously
- While she was cooking, I was washing the clothes.
- While he was reading, I was playing.
- While I was singing, Tim was dancing.
How to Form the Passive Voice of Past Continuous Tense
The Passive voice creates a sentence in which the subject receives the action expressed by the verb .
Active Voice : Subject +was/were + V1+ing + Object.
Passive Voice: Subject( Objective Case) +was/ were +being+ V3 + by + Object ( Subjective case).
- Active Voice : She was reading “The Hard Times”.
- Passive Voice : “The hard times” was being read by her.
- Active Voice: The people were staring at the lady.
- Passive Voice: The lady was being stared at by the people.
- Active Voice: Tina was singing a song.
- Passive Voice: A song was being sung by Tina.
- Active Voice: I was writing a letter.
- Passive Voice: A letter was being written by me.
Test Your Understanding of Past Continuous Tense
Fill in the blanks with the right form of the verb given in the brackets in the following sentences:
- At 8:00 am today I ________(to drive) to work.
- The children ________ (to play) when their mother came home.
- What were you _______(to do) yesterday evening?
- Sam ________(to do) his homework when Susie rang and asked him out.
- My brother and sister__________(to play) tennis at 9 am yesterday.
- I ______(to live) in Japan when we met.
- Jacob_________(to drive) a car when I saw him yesterday.
- While Rohit _______ (to sleep) last night, someone ________(to stole) his motorbike.
- While we were having the picnic, it ______(start) to rain.
- I ________(to read) a ghost story when I heard a noise.
- At 8:00 am today I was driving to work.
- The children were playing when their mother came home.
- what were you doing yesterday evening?
- Sam was doing his homework when Susie rang and asked him out.
- My brother and sister were playing tennis at 9 am yesterday.
- I was living in Japan when we met.
- Jacob was driving a car when I saw him yesterday.
- While Rohit was sleeping last night, someone stole his motorbike.
- While we were having the picnic, it started to rain.
- I was reading a ghost story when I heard a noise.
Frequently Asked Questions On Past Continuous Tense
What is past continuous tense.
The Past Continuous Tense( also known as the past continuous tense) is used to express a continued or ongoing action which occurred in past and was completed at some point in past. It expresses the ongoing nature of an action in past.
What are the examples of Past Continuous Tense?
1. It was raining throughout the night. 2. I was reading a story for a long time yesterday. 3. He was watching TV when I called. 4. What was he doing when the rain started? 5. I was reading when he came in.
What are the uses of Past Continuous Tense?
A. Actions that were going on continuously in the past. B. For such work which the person had been doing habitually and frequently in the past. In such sentences adverbs like always, continually, constantly etc are used C. Past continuous is also used in such a situation, when some other event has happened, and any other work is also going on. D. Past continuous is also used when two tasks were happening simultaneously
What is the structure of Past Continuous Tense?
The structure of the past indefinite tense is as follows: Subject +was/were + V1+ing + Object.
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts
Understanding the Difference and Usage of This vs That with Examples
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Common Issues with Tenses

4-minute read
- 6th June 2022
Using verbs correctly is one of the trickiest parts of writing . Anyone can make mistakes with verb tenses, but it’s especially easy for those who aren’t native English speakers. In this post, we’ll explain the nine main tenses and highlight the most common mistakes writers make when using them. So, read on if you want to make verb tense mistakes a thing of the past!
What Are the Main Tenses in English?
Every action happens in the past, present, or future. Each of these time frames is further divided into the simple , continuous, or perfect form. Here’s an example of each:
● Simple past – things that happened before now:
I wrote an essay last week.
● Past continuous – an ongoing action in the past:
He was writing a poem yesterday morning.
● Past perfect – an action that ended before a point in the past:
By lunchtime, he had written six lines.
● Simple present – a habitual action:
She writes at her desk by the window.
The simple present is also used to describe actions happening at this moment:
I want a desk like that.
● Present continuous – an ongoing action happening right now:
I am writing a future bestseller!
● Present perfect – an action that began in the past and is still happening now, or one that happened at an unspecified time:
He has written stories since he was a child.
I have written 1000 birthday cards.
● Simple future – things that’ll happen and then stop happening:
I will read the first chapter of the book tomorrow.
● Future continuous – things that’ll begin in the future and continue for some time:
I will be writing a book report.
● Future perfect – an action that’ll end at some point in the future:
I will have written it by the end of the week.
With so many tenses to choose from, it’s no wonder people make mistakes. Don’t worry, though, because for most academic writing, you don’t need to use all of them. Essays and assignments are nearly always written in the simple present tense, and if you’re describing your own research methodology (e.g., an experiment or survey), you would use the simple past tense.
What Are the Most Common Verb Tense Errors?
Mistakes with verb tenses usually fall into one of three categories:
- Changing from one tense to another.
- Overusing continuous tenses.
- Confusion with irregular verbs.
Use tenses consistently
Your readers will get confused if you switch tenses unexpectedly:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
The car drove into the tunnel, and it comes out the other end. ✘
The car drove into the tunnel, and it came out the other end. ✔
The car drives into the tunnel, and it comes out the other end. ✔
This doesn’t mean changing tense mid-sentence is always wrong. But make sure you’re saying what you intend to say!
I practiced using different tenses, and now I understand them better. ✔
Limit your use of continuous tenses
Your writing can easily become quite clunky if you use a lot of continuous verb forms:
It was pouring rain while we were camping, and the children were complaining because their blankets were getting wet.
It poured rain while we were camping, and the children complained because their blankets got wet.
The first sentence contains four present participles (i.e., verb forms that end in ing ), which makes it quite a chore to read and rather repetitive. In the second version, we’ve replaced three of them with the simple past tense. This makes the writing more concise and easier to read.
Watch out for irregular verbs
We form the simple past tense and the past participle of most verbs by simply adding ed to the base verb (e.g., walk – walked; open – opened ). However, there are many verbs that don’t obey such rules, and we call these irregular verbs . Unfortunately, there’s no easy way to learn how to conjugate irregular verbs because they don’t follow an obvious pattern, as these examples show:
I buyed bought a gigantic jar of honey.
It costed cost $10.
I hided hid it in the back of the cupboard.
I soon forgetted forgot all about it.
As you read English texts and listen to people speaking in conversation, you’ll recognize more irregular verbs and become familiar with how they work.
Proofreading for Perfect Grammar
We hope you now feel confident about using different tenses in your writing. If you’d like an expert to check your work for incorrect verbs and any other mistakes in grammar, spelling, or punctuation, our proofreaders are here to help. Send us a free trial document to find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Past Continuous Tense With Examples, Rules, Usage
The Past Continuous Tense talks about things that were happening in the past. It uses words like “was” or “were” plus the action word with “-ing” at the end.
- I was eating.
- They were playing.
- She wasn’t studying when I called her.
- They weren’t watching TV at 9 p.m. last night.
- Were you sleeping when the phone rang?
- Was he working late yesterday evening?
Table of Contents
Usages of the Simple Past Tense
Continuous Actions in the Past
Describes actions or events that were in progress at a specific point in the past.
- She was reading a book when the doorbell rang.
- The children were playing in the garden all afternoon.
- While I was cooking, my friend was singing in the living room.
- At 10 AM yesterday, he was jogging in the park.
- She wasn’t watching TV when I called her.
- The dog wasn’t barking when we arrived home.
- While they were at the party, they weren’t dancing .
- Was she sleeping when the phone rang?
- Were they laughing during the movie?
- What were you doing at this time yesterday?
Interrupted Actions
Indicates an action that was happening when another action occurred.
- She was cooking dinner when the phone rang .
- The kids were playing outside when it started raining .
- I was reading . My friend came over to visit.
- Was she sleeping when the fire alarm went off ?
- Were they laughing when the teacher entered the room?
Parallel Actions
Describes two or more actions happening simultaneously in the past.
- While he was reading , she was watching TV.
- While I was cooking , my friend was singing in the living room.
- The team was practicing for the big game, and the coach was giving them feedback.
- She wasn’t watching TV; she was reading a book.
- He wasn’t working on the puzzle; he was playing with his toys.
- Will you be studying while she is cooking dinner?
- Will they be playing outside while we are watching a movie?
- Will he be reading a book while they are playing video games?
Past Continuous Tense Chart
Duration and Emphasis on Continuity
- Refers to how long an action lasted in the past. It emphasizes the length of time the action was ongoing.
Emphasis on Continuity
- Highlights that the action was ongoing without significant interruptions or breaks. It underscores the uninterrupted nature of the action or event.
- They were playing football for two hours.
- We were playing in the park for hours.
- She was reading a novel all afternoon.
- They weren’t watching TV for long; they preferred reading.
- While the party was going on, she wasn’t dancing , she was talking with friends.
- The cat wasn’t sleeping all day; it was exploring the house.
- Were they chatting for a long time at the cafe?
- What were you doing during the long train journey?
- Were they practicing the play all day for the school event?
Time Expressions
- Words or phrases often used with the Past Continuous Tense include:
While, when, as, at this time yesterday, at 7 o’clock last night, all day, all night, During, Throughout, etc.
- He was reading while she was cooking.
- When I called, she was watching.
- As the sun set, they played.
- At 7 p.m. last night , they were having dinner.
- They studied all afternoon. .
- They weren’t watching TV when the show was on.
- I wasn’t playing outside while it was raining.
- The cat wasn’t sleeping during the noisy party.
- Were they laughing when the clown came out?
- What were you doing while your mom was cooking?
- Were they singing when the music stopped?
Stative Verbs and Non-Continuous Verbs
Stative verbs.
- Stative Verbs describe states or conditions and don’t involve ongoing actions. They express things like feelings, thoughts, ownership, or senses. Examples: love, hate, believe, own, and understand.
Non-Continuous Verbs
- Non-continuous verbs include stative verbs and other verbs that don’t typically work with continuous (ongoing) tenses. They describe states or conditions rather than ongoing actions. Examples: like, belong, need, and cost.
- Some verbs (like believe, like, love, hate, etc.) are not typically used in the continuous form because they represent a state rather than an action.
Here are some common examples of stative verbs:
- She loves chocolate.
- He hates spiders.
- I believe in honesty.
- They own a beautiful house.
- She understands the concept.
- She doesn’t believe in ghosts.
- He doesn’t like spicy food.
- They don’t own a car.
- Do you understand the instructions?
- Does she believe in aliens?
- Did he like the movie?
Here are some common examples of non-continuous verbs:
- She likes ice cream.
- The book belongs to him.
- They need help.
- The car costs a lot of money.
- She doesn’t need any more help.
- They don’t belong to this club.
- It doesn’t cost much.
- Do you own a pet?
- Does he need assistance?
- Did they belong to the same team?
Forming the Past Continuous Tense
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences in the past continuous tense describe ongoing actions in the past.
Here’s the basic structure for affirmative sentences in the past continuous tense:
Subject + was/were + verb (1st form) ing + object.
- She was cooking dinner at 6 PM yesterday.
- They were playing football in the park.
- I was reading a novel last night.
- The baby was sleeping peacefully.
- While it was raining, they were watching movies.
- The students were studying for their exams all day.
- He was fixing his bike in the garage.
- The birds were chirping outside my window.
- We were having a picnic at the beach.
- While I was cleaning the house, my friend was listening to music.
- She was knitting a sweater for her grandmother.
- They were laughing at a funny movie.
- He was jogging in the park at sunrise.
- The cat was chasing a butterfly in the garden.
- While the storm was raging, we were sitting by the fireplace.
- I was teaching English at the language school.
- They were building a sandcastle on the beach.
- She was practicing the piano for hours.
- The workers were renovating the old house.
- While I was shopping, my sister was trying on dresses.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences in the past continuous tense deny that an action was happening at a specific time in the past. They use “wasn’t” (for singular subjects) or “weren’t” (for plural subjects), followed by the base form of the main verb with “-ing”.
Here’s the basic structure for forming negative sentences in the past continuous tense:
Subject + was/were + not + verb(1st form) ing + object.
- They weren’t playing outside in the rain.
- I wasn’t listening to music during the thunderstorm.
- The cat wasn’t sleeping when the dog barked.
- While it was snowing, they weren’t skiing.
- The children weren’t swimming in the pool.
- He wasn’t working on his computer.
- The birds weren’t singing in the evening.
- We weren’t hiking in the mountains.
- While I was at the store, my friend wasn’t shopping.
- She wasn’t baking cookies in the kitchen.
- They weren’t studying for the test.
- He wasn’t playing his guitar at the party.
- The dog wasn’t chasing its tail.
- While the concert was going on, some people weren’t listening.
- I wasn’t painting a picture.
- They weren’t chatting at the coffee shop.
- She wasn’t reading a book in the garden.
- The workers weren’t fixing the road.
- While I was at the gym, my brother wasn’t exercising.
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences in the past continuous tense ask about ongoing actions in the past. They start with “Was” (for singular subjects) or “Were” (for plural subjects), followed by the subject, and then the base form of the main verb with “-ing”.
Here’s the basic structure for forming interrogative sentences in the past continuous tense:
Was/were + subject + verb(1st form) ing + object?
- Was she watching TV when you called her?
- Were they playing outside in the rain?
- Was I listening to music during the thunderstorm?
- Was the cat sleeping when the dog barked?
- Were they skiing while it was snowing?
- Were the children swimming in the pool?
- Was he working on his computer?
- Were the birds singing in the evening?
- Were we hiking in the mountains?
- Was your friend shopping while you were at the store?
- Was she baking cookies in the kitchen?
- Were they studying for the test?
- Was he playing his guitar at the party?
- Was the dog chasing its tail?
- Were people listening during the concert?
- Was I painting a picture?
- Were they chatting at the coffee shop?
- Was she reading a book in the garden?
- Were the workers fixing the road?
- Was your brother exercising while you were at the gym?
Past Continuous Tense Example Sentences
- The fountains were playing.
- Lions were roaring in the forest.
- The boys were playing.
- She was smiling.
- You were performing ablutions.
- The teacher was calling the roll.
- Baji Zeb was winding her watch.
- The farmers were sowing the wheat.
- The peacock was dancing in the zoo.
- A cool breeze was blowing.
- The chef was preparing a delicious meal for the guests.
- The children were playing hide and seek in the backyard.
- He was painting a beautiful landscape.
- The orchestra was rehearsing for the concert.
- She was riding her bike in the park.
- They were talking about their upcoming vacation.
- I was baking cookies for the party.
- The neighbors were planting flowers in their garden.
- While the kids were at school, their parents were working.
- The dog was chasing its tail in circles.
- The bell was not ringing.
- We were not joking.
- He was not spitting on the floor.
- They were not eating apples.
- It was not raining heavily.
- You were not writing a good hand.
- The patient was not taking medicine.
- The maid servant was not cleaning the house.
- She wasn’t watching TV when you called her.
- The dog wasn’t chasing its tail in circles.
- She wasn’t singing along with the radio.
- While the party was going on, he wasn’t dancing.
- The cat wasn’t interested in the new toy.
- They weren’t playing with the video game console.
- While the movie was playing, he wasn’t paying attention.
- She wasn’t wearing a hat in the hot sun.
- They weren’t swimming in the cold water.
- While the concert was happening, he wasn’t listening.
- She wasn’t reading a book in the noisy cafe.
- Was it hailing?
- Was she combing her hair?
- Was Sana cooking food?
- Who was running after the thief?
- Why were you teasing him?
- Was the doctor Feeling the pulse of the patient?
- Were you dancing at the party?
- Was the baby crying all night?
- Were they talking on the phone?
- Was he playing soccer in the rain?
- Were you singing along with the radio?
- Were they laughing at the comedy show?
- Was the cat interested in the new toy?
- Were you running in the park?
- Were they discussing the project?
- Was she writing a letter in the library?
- Were the kids playing video games?
- Were you enjoying the concert?
1. She ___________ (read) a book when the phone rang.
a) was reading b) is reading c) read
2. While they ___________ (play) outside, it started raining.
a) were playing b) play c) played
3. What ___________ you ___________ (do) when the power went out?
a) were, doing b) did, do c) was, doing
4. He ___________ (watch) a movie at 8 PM last night.
a) watched b) was watching c) watches
5. They ___________ (cook) dinner while I ___________ (study).
a) were cooking, studied b) cooked, was studying c) cooks, am studying
6. When I called, she ___________ (read) a magazine.
7. We ___________ (have) a picnic in the park all day yesterday.
a) had b) have c) were having
8. The cat ___________ (sleep) when the dog barked.
a) sleeps b) was sleeping c) slept
9. While it ___________ (rain), they ___________ (watch) movies.
a) was raining, watched b) rains, are watching c) is raining, were watching
10. She ___________ (knit) a scarf for her friend.
a) knitted b) was knitting c) knits
11. The workers ___________ (renovate) the old building last month.
a) renovated b) were renovating c) renovate
12. They ___________ (laugh) at a funny joke.
a) are laughing b) were laughing c) laughed
13. He ___________ (jog) in the park every morning.
a) jogged b) was jogging c) jogs
14. The birds ___________ (sing) in the trees.
a) sing b) were singing c) sung
15. While the storm ___________ (rage), we ___________ (sit) inside by the fireplace.
a) raged, sat b) is raging, are sitting c) was raging, were sitting
16. I ___________ (teach) English at the language school last year.
a) teach b) taught c) was teaching
17. They ___________ (build) a sandcastle on the beach.
a) build b) were building c) built
18. She ___________ (practice) the piano for hours every day.
a) practices b) practiced c) was practicing
- a) was reading
- a) were playing
- a) were, doing
- b) was watching
- a) were cooking, studied
- c) were having
- b) was sleeping
- a) was raining, watched
- b) was knitting
- b) were renovating
- b) were laughing
- b) was jogging
- b) were singing
- c) was raging, were sitting
- c) was teaching
- b) were building
- c) was practicing
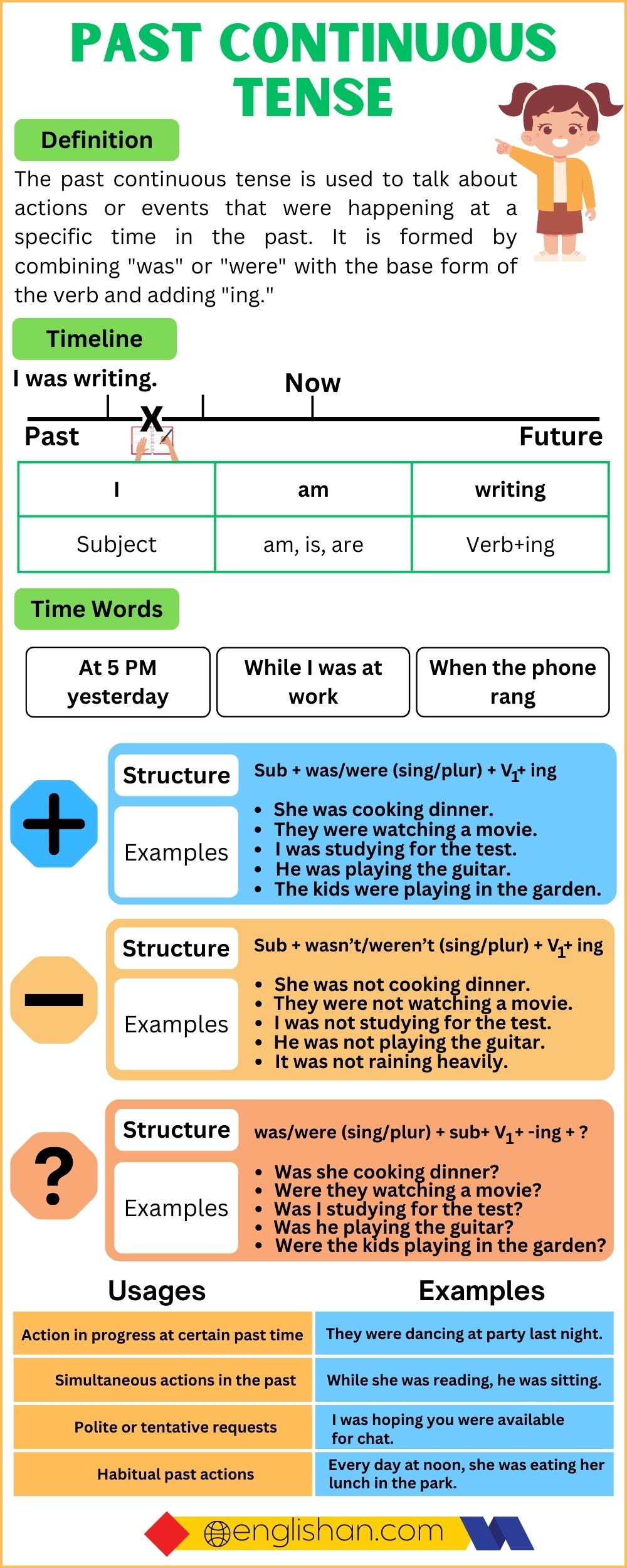
- The past continuous tense is formed using the past tense of the auxiliary verb “to be” (was/were) and the base form of the main verb with “-ing” (e.g., was/were + verb + ing).
- We use the past continuous tense to describe actions or events that were in progress at a specific time in the past or to emphasize the duration of an action.
- Common time expressions include “while,” “when,” “at this time yesterday,” “at 6 PM last night,” and others that specify a particular time in the past.
- Yes, the past continuous tense can be used to describe actions that were in progress when they were interrupted by another event in the past.
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
- Worksheet Tenses
- English Worksheets
- Action Verbs Worksheets
- Past Continuous Tense Worksheets
You May Also Like
- Was Were Worksheets in English
- Simple Present Tense
- Simple Past Tense
- Simple Future Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
Past Continuous Past Continuous Tense Past Continuous Tense Definition Past Continuous Tense Example Sentences Past Continuous Tense Exercise Past Continuous Tense Formula Past Continuous Tense In English Past Continuous Tense In Grammar Past Continuous Tense Rules Past Continuous Tense Structure
Present Continuous Tense With Examples, Rules, Usage
Past Perfect Continuous Tense Worksheets and Exercises
Copyright © 2024 by englishan
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Forgot password?
Enter your account data and we will send you a link to reset your password.
Your password reset link appears to be invalid or expired.
Privacy policy.
To use social login you have to agree with the storage and handling of your data by this website. %privacy_policy%
Add to Collection
Public collection title
Private collection title
No Collections
Here you'll find all collections you've created before.
Past Continuous Tense Examples
Past continuous tense is one of the four types of past tense. This article will give you a list of past continuous tense examples to help you out. Let’s have a look at them.

Table of Contents
What is past continuous tense, examples of past continuous tense, how can past continuous tense be formed.
- FAQs on Past Continuous Tense Examples
Past continuous tense refers to/denotes those actions/events that were happening for a particular time in the past. For example, “Sam was writing a letter to his friend.” Here, ‘was writing’ refers to an action that Sam was doing in the past.
The following examples will help students understand better all about past continuous tense.
List of Past Continuous Tense Examples
- It was snowing yesterday.
- They were eating at the restaurant.
- You were working yesterday.
- I was studying last night.
- I was waiting for the cab when I met Raj.
- The children were shouting when the teacher came in.
- It was midnight when it was raining .
- Everyone was clapping .
- Raj was practising the guitar after classes.
- The baby was laughing when I came into the room.
- The children were playing in the garden.
- The girls were dancing as the music played.
- The child was eating an apple.
- Trina was going to the library.
- The dog was barking at night.
- The students were not studying for the test.
- They were going to play football.
- My mother was baking a cake for me.
- The birds were chirping in the sky.
- The kite was flying in the sky.
Knowing how a particular tense is formed will help you learn and identify tenses easily, so take a look at the structure of a sentence in the past continuous tense.
Subject + Be form (was/were) + ‘ing’ form of verb + object/adjunct
For example, “My brother was cooking dinner yesterday.” Here, the subject is ‘my brother’, which is used with the ‘be’ form, i.e. ‘was’, and with the ‘ing’ form of the verb, i.e. cooking.
Frequently Asked Questions on Past Continuous Tense Examples
What is past continuous tense.
Past continuous tense refers to those actions/events that were happening for a particular time in the past.
Example of past continuous tense.
“Sheldon was going on a college trip.” This sentence is an example of past continuous tense.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Past Continuous Quiz
You can do this grammar quiz online or print it on paper. It tests what you learned on the Past Continuous page.
1. My brother and sister _____ playing tennis at 11am yesterday.
2. _____ you still working at 7pm last night?
3. At 8.30am today I _____ driving to work.
4. We _____ sleeping when the police came.
5. Why _____ he having lunch at 4pm?
6. Was he not _____ his homework?
7. Snow _____ lightly. Suddenly a reindeer appeared.
8. Somebody threw a shoe at him _____ he was speaking.
9. They ________ TV when I arrived.
10. I was reading a detective story _____ I heard a noise.
Your score is:
Correct answers:

25 past continuous conversation questions
Past continuous conversation questions.
Here is a worksheet of easy past continuous conversation questions to practice using this grammatical structure. Answers to these questions should contain either was or were, depending on the subject. The rules are – ( I, he, she, it + was ), and – ( We, you, they +were ).
At the top of the worksheet, there are three pictures to describe using the present continuous. Here are some examples of possible sentences –
Jane was walking her dog yesterday morning.
Tom was shopping in a supermarket at 1 pm in the afternoon.
Mary was at home reading a book on her sofa last night.
To expand the discussion questions, think about adding some appropriate follow-up questions using who, what when why and how. This will allow for more speaking practice. Just remember to make sure the questions and their responses continue to use the past continuous.
The past continuous conversation questions are –
What were you doing before you came to this class?
What were you eating at lunchtime yesterday?
What kind of music were you listening to 5 years ago?
What were you doing at 9 pm last night?
Who were you talking to the last time you spoke English?
Where were you going the last time you were on a bus?
How were you feeling the last time you saw a doctor?
What were you doing last Sunday afternoon?
Who were you with the last time that you laughed?
What were your parents doing for work 10 years ago?
What exercise were you doing to stay healthy last month?
Where were you the last time that it started raining?
What were you buying the last time you went shopping ?
What was your best friend doing on their birthday last year?
What were you dreaming of becoming when you were a child?
What sports were you playing 5 years ago?
Where were you living 2 years ago?
Was it raining last Tuesday at 3 pm?
What were you reading about last week?
What kind of clothing were you wearing 3 years ago?
What were you doing the last time that your telephone rang?
What were you cooking the last time you made a meal?
Who were you with the last time you got angry?
Where were you going the last time you saw a rainbow?
What were you doing to stay warm last winter?
You might also like these

25 construction and building conversation questions

25 extreme sports conversation questions

25 beauty conversation questions
Free ESL and English teaching resources, no sign up required. Just find what you like, download it and head to class!
Privacy Policy
Share ESL Vault with your friends!
- Writing Worksheets
- Vocabulary Worksheets
- Pronunciation
- Kids worksheets
- Idioms and Expressions
- ESL Puzzles
- ESL Pair Work Activities
- ESL Conversation Questions
- Coloring Pages
- Articles, Lists and Ideas
- Art and Craft Activities
- Past Continuous — Mixed — Exercise 3
- 1. Chloe an English essay at this time yesterday. (write) was writing
- 2. My little brother at 8 pm yesterday. (not / sleep) wasn't sleeping
- 3. they the dishes when their mother came? (wash) Were washing
- 4. What Michael when you saw him? (eat) was eating
- 5. We chess the whole evening. (not / play) weren't playing
- 6. Why you when I met you? (laugh) were laughing
- 7. When I came into the kitchen, the cat milk from its bowl. (drink) was drinking
- 8. Emily and John the whole evening. (rest) were resting
- 9. I at Andrew. (not / look) wasn't looking
- 10. While they TV, they fell asleep. (watch) were watching
- 11. the students at their desks when the teacher opened the door? (sit) Were sitting
- 12. Who Lilly dinner with at 6 pm yesterday? (have) was having
- 13. Sue with her husband when somebody knocked at the door. (argue) was arguing
- 14. David the whole evening. (not / call) wasn't calling
- 15. What you about? (dream) were dreaming
- Past Continuous — Mixed
- Past Continuous — Mixed — Exercise 2
- Past Continuous — Positive
- Past Continuous — Negative
- Past Continuous — Negative — Short forms

COMMENTS
Revised on October 23, 2023. The past progressive tense is a verb form used to refer to an action that was ongoing at a time in the past. The past progressive is formed using the past tense of the auxiliary verb "be" (i.e., "was/were") along with the present participle ("ing" form) of a main verb (e.g., "I was thinking").
The different tenses are identified by their associated verb forms. There are three main verb tenses: past , present , and future. In English, each of these tenses can take four main aspects: simple , perfect , continuous (also known as progressive ), and perfect continuous. The perfect aspect is formed using the verb to have, while the ...
The essay thoroughly explores the past continuous tense, shedding light on its grammatical structure and multifaceted usage. It begins by defining the past continuous tense, showcasing its fundamental role in conveying ongoing actions or events in the past. The structure of the tense is elucidated, emphasizing the use of "was/were" and the ...
Create Atmosphere with the Past Progressive. If your students need a refresher with this not-so-common verb tense, remind them how the past progressive ( was/were + -ing verb) is used in English (see Simple Past Vs. Past Progressive for teaching tips). Then tell your students they can do one or more of the following to begin their stories: 1.
This helps to set the tone or mood. You're providing a mental picture for your listener. And that's where you want to use the past continuous tense. Scenario 1: Imagine your telling someone about a recent vacation. To highlight how relaxing it was on your day, you might provide some background details such as:
The Past Continuous Tense is a grammatical structure that describes actions or events that were ongoing or in progress at a specific point in the past. It is formed by combining the past tense of the verb "to be" (was/were) with the present participle (the -ing form) of the main verb. For example, in the sentence "She was reading a book ...
The past continuous, or past progressive, tense describes an action or situation that began in the past and is still going on in the present time. The past continuous is easily formed by pairing up the verb to be' with a verb ending in -ed' instead of -ing' (e.g. was talking). The second section below has some great examples of how to use ...
To describe regular habits of the past. Example: We were always looking forward to the opportunity to go out together. Continuous or repeated activity, as an alternative to simple past, for expressing an action neutral in nature. Example: We were feeling tired of being at home. /We felt tired of being at home.
The past continuous tense (also called the past progressive) is a verb form used to refer to an action that was ongoing at a time in the past (e.g., " I was walking when I fell"). The past continuous is formed using the past tense of the auxiliary verb "be" (i.e., "was/were") along with the present participle ("ing" form) of a ...
There are four narrative tenses: past simple, past continuous, past perfect, and past perfect continuous. Using the right verb tense as you describe events in your book or build any sort of narrative is crucial to creating immersive stories. The wrong verbs and related words can make a sentence clunky and distracting, pulling your reader out of ...
Formula and Structure of the Past Continuous Tense. Conjugating a verb in the past continuous tense can be made easier if you know and understand its formula and structure. Here is the formula with which you can structure a sentence in the past continuous tense. Subject + was/were + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence.
The Past Continuous Tense( also known as the past continuous tense) is used to express a continued or ongoing action which occurred in past and was completed at some point in past.It expresses an ongoing nature of an action in past. The form of past continuous tense is To be(was/were) + Verb- ing[present participle]. Examples of past continuous tense ...
Every action happens in the past, present, or future. Each of these time frames is further divided into the simple, continuous, or perfect form. Here's an example of each: Simple past - things that happened before now: I wrote an essay last week. Past continuous - an ongoing action in the past: He was writing a poem yesterday morning.
The Past Continuous Tense talks about things that were happening in the past. It uses words like "was" or "were" plus the action word with "-ing" at the end. Examples: I was eating. They were playing. She wasn't studying when I called her. They weren't watching TV at 9 p.m. last night.
List of Past Continuous Tense Examples. It was snowing yesterday. They were eating at the restaurant. You were working yesterday. I was studying last night. I was waiting for the cab when I met Raj. The children were shouting when the teacher came in. It was midnight when it was raining. Everyone was clapping.
Past continuous. The past continuous is used to write about longer events or actions that were in progress at the moment when something happened. In the middle of the night, I was woken up by a noise. Someone was creeping around in my room! Would. You can use would to talk about the future when writing a story in the past. For example, in this ...
Past Continuous Quiz. You can do this grammar quiz online or print it on paper. It tests what you learned on the Past Continuous page. 1. My brother and sister _____ playing tennis at 11am yesterday. are was were a) are b) was c) were. 2. _____ you still working at 7pm last night? Were Are
Here is a worksheet of easy past continuous conversation questions to practice using this grammatical structure. Answers to these questions should contain either was or were, depending on the subject. The rules are - ( I, he, she, it + was ), and - ( We, you, they +were ). At the top of the worksheet, there are three pictures to describe ...
Here you have the second part of the set about inspector clueless and paws in another investigation. Now students write a story using the prompt given and the ch... 128 uses. A selection of English ESL past simple vs continuous tense printables with creative writing prompt, writing practice.
Make the Past Continuous (this exercise includes positive, negative, Yes/No and Wh-question form). Show example. 1. Chloe an English essay at this time yesterday. (write) was writing. 2. My little brother at 8 pm yesterday. (not / sleep) wasn't sleeping. 3.