
Your way to the top of Grammar...

Indirect Speech: Formula and Rules
- July 3, 2021
We are talking about a very important and interesting topic. We are talking about direct and indirect speech in English and what is the correct formula of the usage.
Remember to read How to learn English with audiobooks for FREE
This topic can seem complicated at the beginning, but necessary to learn. Having this topic solved, you improve your English to a new level, so let’s start to deal with it.
What are Direct and Indirect speech?
In English, there are two ways how we can tell what another person said. Two ways you can say what someone else has said before.
- Direct Speech
- Indirect (Reported) Speech
Note : Indirect speech in different textbooks can be called differently: Indirect Speech or Reported Speech . But these two names mean the same.
Indirect Speech = Reported Speech

Direct speech in English is a type of speech when we retell someone’s speech as it was. We don’t change anything.
John says: I’m a good boy.
To tell what John said, we will say:
We say: John said, “I’m a good boy.”
Indirect speech differs from direct speech in that we DO NOT tell exactly what another person said. We are NOT repeating what someone else said. Indirect speech is when we tell the MEANING of what someone else said.
We say: John said he was a good boy.
Pay attention to what this sentence looks like. Earlier, when John said this, the sentence looked like this:
I am a good boy.
But after WE retell John’s words, in the indirect speech, this sentence looks like this:
John said he was a good boy.
The Quotes and the comma that stood after the name John, separating the speaker from his direct speech, disappeared from this sentence.
In indirect speech, we do not use the separating comma and quotation marks. Because now it is WE are retelling the meaning of what the other person (John) said.

In direct speech, the speaker most often speaks in the first person. That is, the speaker speaks from his person.
John will not talk about himself: John is a good boy . John will say it on his behalf: I am a good boy.
But when we retell the words of John (indirect speech), we cannot speak on his behalf. We cannot say “I am a good boy” because those are not our words. This is John a good boy.
Therefore, in indirect speech, we change “I” to the third person.
He says: I hate you but I need your help.
I retell: He said that he hated me but he needed my help.
To translate direct speech into indirect speech, we use certain rules that you should know.
Let’s take a look at these rules and formulas in order.
Quotation marks and comma
In direct speech, we use a comma to separate the speaker from what he is saying. Direct speech (what the speaker says) is in quotation marks.
When we translate direct speech into indirect speech, we remove quotes and commas.
Jessica says , “I’m from the future.”
We retell Jessica’s words: She said that she was from the future.
Personal and possessive pronouns
When translating direct speech into indirect speech, we change personal and possessive pronouns to third-person pronouns.
Direct Speech : He says, “ I couldn’t stay” Indirect Speech : He said that he couldn’t stay. Direct Speech : Tom says, “ I am deeply disturbed” Indirect Speech : Tom said that he was deeply disturbed.
Note: If in direct speech the speaker tells his own words, then we do not change personal and possessive pronouns.
Direct Speech: I said, “ I will do that” Indirect Speech: I said that I would do that.
Adverbs in direct speech
When we translate adverbs from direct speech to indirect, adverbs change their form.
You can see how adverbs look in direct speech and how adverbs look in indirect speech in this table:
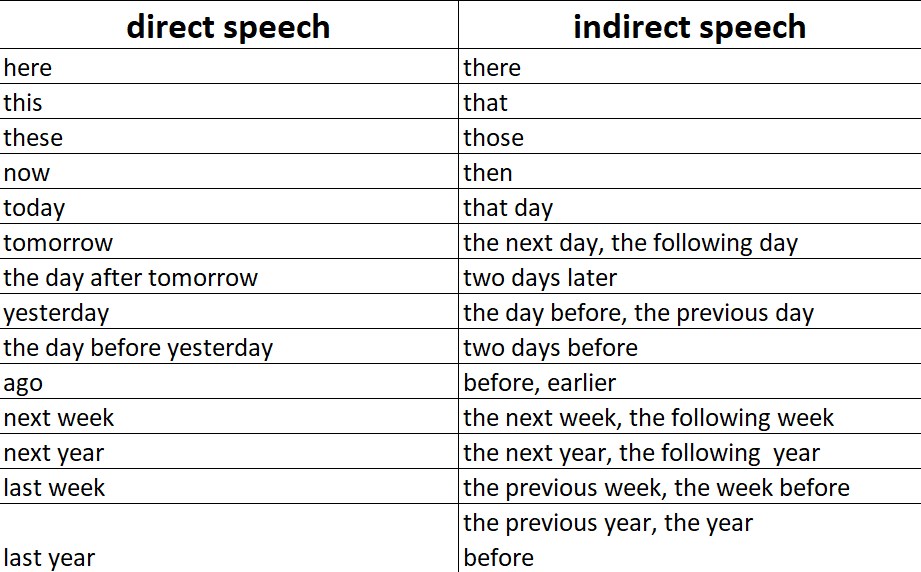
But we don’t always change adverbs this way. We change adverbs only if, when translating from direct speech into indirect speech adverbs cannot express the same meaning as in direct speech.
Take a look at an example:
Mom says, “ Tomorrow we will go to Uncle John’s.” Mom said that the next day we would go to Uncle John’s.
In these examples, we have replaced the adverb tomorrow with the next day . Because we retell Mom’s words on another day. We cannot say tomorrow anymore.
Now look at another example:
Mom says, “We went to visit Uncle John yesterday .”
Now imagine that we are retelling this the next day. We have to say:
Mom said that we went to visit Uncle John the day before yesterday .
If we said “ yesterday “, it would change the meaning of what we want to tell.
If in direct speech in the main sentence the predicate is in Past Simple, then in indirect speech we use the agreement rules.
We put the conjunction “ that ” in front of indirect speech.
Note: We may not use the conjunction that after verbs such as:
He said he found it on the island. He thought he was better than me. He knew he could call you anytime.

Prepositional object
If in direct speech after the verb to say there is a prepositional object, then in order to translate such a sentence into indirect speech, we change the verb to say to tell . In this case, tell is used without the preposition to .
Incorrect : to tell Correct : tell
This means:
She said to me … changes to She told me that …
Note : Remember that in this case we also change the adverbs of place and time and demonstrative pronouns, if they are in direct speech.
Modal verbs
For modals, we use several important rules.
We change modal verbs as well as main verbs when moving from direct to indirect speech.
But we do not change all modal verbs. We leave some verbs in their original form.
Let’s talk about modals in more detail.
Modal verb must
If in direct speech the verb must means an obligation or command, then in the subordinate clause in indirect speech must does NOT change and looks like must .
The teacher says, “You must behave well in class.” The teacher said that we must behave well in class.
If in direct speech the verb must expresses the need, then in the subordinate clause in indirect speech we change the verb must to had to .
Mom says, “You must visit the doctor.” Mom said that I had to visit the doctor.
The past form of Modal verbs in indirect speech
Can and could..
We change the modal verb can in direct speech to could in indirect speech. Could is the past form of the modal verb can .
She says, “I can swim.” She said that she could swim.
May and might.
We change the modal verb may in direct speech to might in indirect speech. Might is the past form of the modal verb may .
John says, “I may propose to Maria.” John said that he might propose to Maria.
Must and had to.
We change the modal verb must in direct speech to had to in indirect speech (if the verb must expresses the need). Had to is the past analog of the modal verb must .

Modal verbs that do not change in indirect speech
The following verbs move from direct to indirect speech in their original form. They don’t change in any way.
- must (if the verb must means an obligation or command)
He says, “I could do this.” He said he could do that.
Let’s take a closer look at these verbs:
The modal verb would in direct speech remains in the form would in indirect speech too.
Mom says, “I would bake a cake.” Mom said she would bake a cake.
If we use the modal verb could in direct speech, then we do not change this verb in any way in indirect speech. Because could is a past form already (It’s the past form of the modal verb can ).
John says, “I could learn to swim” John said he could learn to swim.
The modal verb might does not change its form when we translate this verb from direct to indirect speech. Because the modal might is the past form of the modal may .
He says, “I might ask the same question again”. He said that he might ask the same question again.
We do not change should when switching to indirect speech. Because should is considered the past form of the modal verb shall .
He says, “We should see Mr. Gannon” He said that we should see Mr. Gannon.
We do not change the modal verb OUGHT TO when translating this verb into indirect speech.
She says, “You ought to be angry with John” She said that I ought to be angry with John
Exceptions to the rules
Let’s talk about the important exceptions to the rules of this lesson.
- We can exclude the word that out of affirmative sentences in indirect speech. Because in indirect speech in affirmative sentences, the meaning of the sentence does not change, regardless of whether we use that or not.
He said ( that ) he thought you seemed depressed. He said ( that ) there was no need. He said ( that ) he had many friends.
- If in direct speech we are talking about a specific event that happened at exactly the specified time and did not happen anymore, then we translate the sentence into indirect speech without the agreement.
He says, “Gagarin went to space in 1961.” He said that Gagarin went to space in 1961.
The event that we are talking about in this example happened at exactly the specified time and did not happen anymore.

- If in direct speech we use verbs such as:
then when translating into indirect speech, we do not change the form of these verbs. These verbs remain in their form.
She says, “We might find some treasure” She said that we might find some treasure.
He says, “I should do it”. He said that he should do it.
- If indirect speech begins with the verb say or tell which is used in the form:
- Present Simple
- Present Perfect
- Future Simple
then we translate such a sentence into indirect speech without changing the tense to the past:
She says, “I cook deliciously.” She says that she cooks deliciously. He says, “I have a new smartphone.” He says that he has a new smartphone. She will say, “I didn’t know it.” He will say (that) he didn’t know it.
- If in direct speech we are talking about a well-known fact or law of nature, then we do not transfer to the past such a fact or the law of nature when translating from direct speech to indirect.
He says, “After winter comes spring.” He said that after winter comes spring. She says, “Lions don’t hunt camels.” She said that lions don’t hunt camels.
- If in direct speech we use tenses:
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
then when translating into indirect speech, we do not change the sentence, we do not translate the sentence into the past.
He says, “I had fixed my car.” He said he had fixed his car. He says, “I was skiing .” He said he was skiing . He says, “I had been all alone for a very long time”. He said that he had been all alone for a very long time.
Interrogative (question) sentences in indirect speech
Look at the following rules and nuances to know how to correctly translate interrogative (question) sentences from direct speech to indirect speech:
- When we translate a general question into indirect speech, we put one of the conjunctions between the main sentence and the question:
He asks, “Do you play dominoes?” He asked if I played dominoes. He asked whether I played dominoes.

- If we translate an interrogative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech, then we change the interrogative word order to direct word order.
We remove the auxiliary verb that was used in the interrogative sentence. We put the subject before the predicate as it should be for the direct word order.
He asks, “Where are you going?” He asked where I was going.
- If in an indirect sentence we ask a question using the verb say and if there is no indirect object in the main sentence, then we change the verb say to one of these words:
- want to know
She asks, “Where you are?” She wanted to know where you were.
- When translating an interrogative sentence from direct speech into indirect speech, we change all pronouns, verbs, adverbs of place, adverbs of time.
She asks, “What do these letters mean?” She asked what those letters mean.
Special questions in indirect speech
Special questions (or Wh-questions) are questions that begin with an additional, question word.
In indirect speech, such a question should also begin with a question word.
This question word also serves as conjunction. This word attaches the question part to the main sentence.
In the question part, we use direct word order.
At the same time, we comply with all the rules for the Sequence of tenses.
My dad asks, “What do you plan to do with yourself?” My dad asked what I planned to do with myself.

Imperative sentences in indirect speech
When translating imperative sentences from direct to indirect speech, we must take into account several nuances:
- Orders in indirect speech look like this:
He said, “ Go now!” He said to go then. She says, “ Carry my bag” She asked to carry her bag.
We use the verb to say when we translate an ordinary sentence into indirect speech. But in imperative sentences, we change the verb to say to a verb that expresses an order or request:
She says , “Carry my bag” She asked to carry her bag.

- In direct speech in the imperative mood, we often use:
let’s (let us)
let’s encourage the speaker and the person to do something together.
In indirect speech, we change let’s to to suggest . For example:
She says, “ let’s do that!” She suggested to do that.
- In indirect speech, we put a noun after the verb that expresses an order or request. The noun is the one to whom this request or order is addressed. Then we use the infinitive.
She says, “Replace him, John “ She asked John to replace him.
- We can strengthen the request or order in indirect speech if we add verbs such as:
- to recommend
- to urge etc.
She says , “Read this book” She ordered ( advised, recommend ) me to read that book.
- In order to make a negative imperative sentence in direct speech, we need:
not + infinitive
He says, “Don’t cry.” He said to me not to cry.
- In direct speech, we often do not name the person to whom the order or request is addressed. But when translating an imperative sentence from direct speech to indirect speech, we must indicate the one to whom the order or request is addressed.
For this, we use a noun or a pronoun.
She says, “Speak to him!” She asked me to speak to you.
Present and future tense in indirect speech
Most often, we translate the future and the present into the past.
He says, “I have two brothers” He says that he had two brothers She says, “I do this every time” She says that he did that every day. He says, “I write books” He says that he wrote books. She says, “I am reading” She said that she was reading. He says, “I can swim” He said that he could swim. He says, “I will help you” He said that he would help me.
Past tense in indirect speech
When we translate a sentence written in the past into indirect speech, we can leave it unchanged or we can change the past to the Past Perfect.
He says, “I saw this movie” He said that he saw that movie. He said that he had seen that movie.
What if in direct speech the main verb is already in Past Perfect?
In this case, the verb in Past Perfect remains unchanged. The verb in Past Perfect in direct speech remains in Past Perfect in indirect speech too.
He says, “I had bought I new house” He said that he had bought a new house.
I live in Ukraine. Now, this website is the only source of money I have. If you would like to thank me for the articles I wrote, you can click Buy me a coffee . Thank you! ❤❤❤
Recommended reading: Complex Sentence in English.
Related Posts

Prepositions of Place in English Grammar

Prepositions of Reason and Purpose

Direct Word Order in English Sentences

Word Order in Interrogative Sentence

Conditional Sentences Types in English

Apostrophe in English: All you need to know
Trending now.

- English Grammar
- Clause structure and verb patterns
Reported speech
Level: intermediate
Reporting and summarising
When we want to report what people say, we don't usually try to report their exact words. We usually give a summary , for example:
Direct speech (exact words) :
Mary : Oh dear. We've been walking for hours! I'm exhausted. I don't think I can go any further. I really need to stop for a rest. Peter : Don't worry. I'm not surprised you're tired. I'm tired too. I'll tell you what, let's see if we can find a place to sit down, and then we can stop and have our picnic.
Reported speech (summary) :
When Mary complained that she was tired out after walking so far, Peter said they could stop for a picnic.
Reporting verbs
When we want to report what people say, we use reporting verbs . Different reporting verbs have different patterns, for example:
Mary complained (that) she was tired . (verb + that clause) She asked if they could stop for a rest . (verb + if clause) Peter told her not to worry . (verb + to -infinitive) He suggested stopping and having a picnic . (verb + - ing form)
See reporting verbs with that , wh- and if clauses , verbs followed by the infinitive , verbs followed by the -ing form .
GapFillDragAndDrop_MTY1NTE=
GapFillTyping_MTY1NTI=
Tenses in reported speech
When reporting what people say or think in English, we need to remember that the rules for tense forms in reported speech are exactly the same as in the rest of the language.
This is a letter that Andrew wrote ten years ago:
If we wanted to report what Andrew said in his letter, we might say something like this:
Andrew said that when he was 22, he was an engineering student in his last month at university. He wanted to travel abroad after he had finished his course at the university, but he would need to earn some money while he was abroad so he wanted to learn to teach English as a foreign language. A friend had recommended a course but Andrew needed more information, so he wrote to the school and asked them when their courses started and how much they were . He also wanted to know if there was an examination at the end of the course.
We would naturally use past tense forms to talk about things which happened ten years ago. So, tenses in reports and summaries in English are the same as in the rest of the language.
Sometimes we can choose between a past tense form and a present tense form. If we're talking about the past but we mention something that's still true , we can use the present tense:
John said he'd stayed at the Shangri-la because it' s the best hotel in town. Mary said she enjoyed the film because Robert de Niro is her favourite actor. Helen said she loves visiting New York.
or the past tense:
John said he'd stayed at the Shangri-la because it was the best hotel in town. Mary said she enjoyed the film because Robert de Niro was her favourite actor. Helen said she loved visiting New York.
If we're talking about something that everybody knows is true , we normally use the present tense :
Michael said he'd always wanted to climb Everest because it' s the highest mountain in the world. Mary said she loved visiting New York because it' s such an exciting city.
Hi! I found the following paragraph from a grammar site while I was studying the reported speech. Can you help me? It says; --> We can use a perfect form with have + -ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past: He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’)
And my question is: How do we understand if it is a hypothetical event in the past or not? We normally don't change 'might' in reported speech. (e.g. ‘It might snow tonight,’ he warned. --> He warned that it might snow that night.) But why do we say 'He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters.' instead of 'He said that the noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ What's the difference between these two indirect reported speeches? Could you please explain the difference? And I also found this example which is about the same rule above: --> He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: a) ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or b) ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’) Can you also explain why we report this sentence like that. How can we both change a) and b) into the same indirect reported speech? Thank you very much!
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello Melis_06,
1. He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. 2. He said that the noise might be the postman delivering letters.
In sentence 1 it is clear that the noise has ended; it is a noise that 'he' could hear but it is not a noise that you can hear now. In sentence 2 the noise could have ended or it could be a noise that you can still hear now. For example, if the noise is one which is constant, such as a noise that comes from your car engine that you are still trying to identify, then you would use sentence 2. In other words, sentence 2 allows for a wider range of time possibilities - both past (ended) and present (still current).
Your second question is similar:
He said he would have helped us if we needed a volunteer - you no longer need a volunteer
He said he would help us if we needed a volunteer - this could still be relevant; you may still need a volunteer.
The LearnEnglish Team
Hello my friend : what are you doing now? me : I'm eating an apple now and My friend repeated his question now
my question
Can I repeat the sentence in the past ( I was eating an apple) and mean( I'm eating an apple now) ?
You can but it is unusual. If you say I was eating an apple (past continuous), it means that it was in the past. You already finished eating the apple and you are not eating it now. But if your friend asked you just a moment ago, I guess you are still eating the apple when she/he asks the second question, so I would say I'm eating an apple (because you are still doing it).
Alternatively, you can use a past tense reporting verb e.g. I said I was eating an apple (referring to the time of the first question), or I said I 'm eating an apple (to show that you are still eating it now, at the moment of speaking).
LearnEnglish team
Am I correct then? When someone wants us to repeat the sentence we have just said a moment ago we say 'I said I am doing...' if we are still doing that action. But if we are done with that action, then we say 'I said I was doing...' Did I get it right? Thanks!
Hello Meldo,
Yes, that's correct. Well done!
Hi. I wish to enquire if the verb tense used after a conjunction also changes in complex sentences as per tense transition rules, especially if it is already in simple past tense. In order to explain, could you please solve the following for me: 1. It has been quite a while since I last saw you. 2. Nevertheless, she has been quite desensitized to such perverse actions to the extent that it seldom ever seems obnoxious to her. 3. Let me keep this in my cupboard lest I misplace this. 4. I had arrived at the station before you even left your house. 5. I met my grandfather before he died.
Hi Aamna bluemoon,
The verb may or may not be backshifted, depending on whether the original speaker's point of view and the reporter's point of view are the same or not. For example:
- She said it had been quite a while since she last saw me . (it seems relatively recent, for both the original speaker and the reporter)
- She said it had been quite a while since she had last seen us . (a lot of time has passed between speaking and reporting this, or the situation has changed a lot since then e.g. they have met frequently since then)
- She said she had met her grandfather before he died . (seems quite recent)
- She said she had met her grandfather before he'd died . (a lot of time has passed between speaking and reporting this)
I hope that helps.
Hi, can you help me, please? How could I report this famous quotation: 'There's no such things as good news in America'.
Hi bri.q630,
First of all, the sentence is not grammatically correct. The phrase is 'no such thing' (singular), not 'things'.
How you report it depends. Using 'said' as the reporting verb we have two possibilities:
1. They said (that) there's no such thing as good news in America. 2. They said (that) there was no such thing as good news in America.
Sentence 2 tells that only about the time when 'they' said it. It does not tell us if it is still true or not.
Sentence 1 tells us that what 'they' said is still relevant today. In other words there was no good news (in their opinion) when they spoke, and there is still no good news now.
Thank you Peter,
All things are getting clear to me.
So, you mean, I can use both sentences depending on what I want to indicate, can't I?
then the possible indications are bellow, are those correct?
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.)
1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945. (This would be indicated I might missunderstand.)
2-a I felt time is money. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.)
2-b I felf time was money. (This would be indicated I might not feel any more.)
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. (This would be indicated the statement is still true.)
3-b I knew the sun rase in the east. (This would be indicated I might misunderstand or forget.)
4-a I guessed* that Darth Vader is Luke's father. (This would be indicated I still believe he is.*sorry for the typo)
4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father. (This would be indicated I might know he is not.)
Thank you in advance.
Hello again Nobori,
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.) 1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945. (This would be indicated I might missunderstand.)
Both forms are possible here. The 'ending' is a moment in the past; after this there is no war. By the way, we treat 'World War 2' as a name so there is no article before it.
2-a I felt time is money. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.) 2-b I felf time was money. (This would be indicated I might not feel any more.)
That's correct. Remember that backshifting the verb does not mean something is no longer true; it simply does not tell us anything about the present. Here, it tells the reader how you felt at a given moment in time; you may
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. (This would be indicated the statement is still true.) 3-b I knew the sun rase in the east. (This would be indicated I might misunderstand or forget.)
That's also correct. Again, remember that backshifting the verb does not mean something is no longer true; it simply does not tell us anything about the present.
4-a I guessed* that Darth Vader is Luke's father. (This would be indicated I still believe he is.*sorry for the typo) 4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father. (This would be indicated I might know he is not.)
Again, correct. In the second example it might still be true that he is Luke's father, or it might have turned out to be not true. The sentence does not tell us.
Hi Peter, Thank you for your thoughtful answer. Allthing is now very clear to me. Best
Hi, I am translating a fiction novel into English and need your help regarding the reporting speech as for few things I am not getting any clear understanding over the internet. As you know in fiction, we need to write in non-ordinary way to create unique impressions of the word and academic writing is different than speaking. Will be grateful if you could give your insight below, especially considering in the context of fiction/academic writing.
1) Let’s say If someone is giving a speech or presentation, I want to mix their speech, indirect-direct and past tense- present tense. Below are three examples:
-He said, their company makes excellent profit every year OR their company made excellent profit every year ( can both be correct? As the sentence)
- Roger had given his speech yesterday. He said, their company makes excellent profit every year and your company will sustain for next hundred years.(Can YOUR be used in the sentence)
- Roger said people wants to feel important OR Roger said people wanted to feel important (which will be correct as this is a trait which is true in past and present)
2) He thought why he is talking to her OR He thought why he was talking to her (are both write? As usually I see in novels the second example with WAS)
3) Gia was sitting with Jake and she told him she had met with her last year. Her mother had taken her to the dinner. Her mother had told her about her future plans. Her mother also had paid the bill for the dinner. (Do I need to use every time past perfect in this example though it doesn’t feel natural? As a rule of thumb I think past perfect needs to be used when we talk about another past event in the past )
Hello Alamgir3,
We're happy to help with a few specific grammar questions, but I'm afraid we can't help you with your translation -- I'd suggest you find an editor for that.
1) In the second clause, you can use present or past. We often use the present when it's still true now, but the past is not wrong. FYI we don't normally use a comma after 'said' in reported speech.
2) 'Why was he talking to her?' he thought.
3) This is really more of a question of style than grammar. Here I would suggest doing something like combining the four sentences into two and then leaving out 'had' in the second verb in each sentence. Even if it isn't written, it's understood to be past perfect.
All the best, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hello teachers, I'm sorry, I could not find where to new post. Could you tell me about the back-sifting of thoughts bellow? Which forms are correct?
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. 1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945.
2-a I felt time is money. 2-b I felf time was money.
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. 3-b I knew the sun rase in the east.
4-a I guess that Darth Vader is Luke's father. 4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father.
Do those questions have the same conclusion as indirect speech, such as say and tell?
Hello Nobori,
The verb form remains the same when we want to make it clear that the situation described by the verb is still true, and this works in the same way as indirect speech. For example:
She said she loves me. [she loved me then and she loves me still] She said she loved me. [she loved me then; no information on how she feels now]
Other than this rule, the choice is really contextual and stylistic (up to the speaker). Sometimes a choice implies something. For example, the saying 'time is money' is a general statement, so if you choose to backshift here the listener will know it is an intentional choice and suspect that something has changed (you no longer believe it).
Hi teachers, I've read almost the section of comments below and my summarize is the present tense only can be used if the statement is still true now and past simple only tells the statement was true in the past and doesn't tell the statement is true or not now. Just to make sure, I wanna ask, If I'm not sure whether the statement is still true or not now, can I choose backshift instead (this is still apply to past tense become past perfect)? Thank you
Hello rahmanagustiansyah,
It sounds to me as if you've got the right general idea. Could you please give a couple of example sentences that illustrate your question?
Thanks in advance, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
For example, Steve said "Anna hates you." Then I wanna tell about that to my friend, but I'm not sure whether Anna still hates me or not now. What should I choose between these two options. Answer 1:Steve said Anna hates me or Answer 2 : Steve said Anna hated me. Thank you
Hi rahmanagustiansyah,
In that case, I would choose answer 2. I might even add "... but I don't know if she still does" to the sentence to clarify, if that is the key point you want to communicate.
Jonathan The LearnEnglish Team
Hello Natasa Tanasa,
Both sentences are grammatically possible.
The first sentence is only possible if when the person asks the original question the woman is no longer there (she has already gone). The second sentence can be used in this situation too, or in a situation in which the woman was still there when the original question was asked. As the past tense is used in the original question ( Who was... ), both sentences are possible.
Hello Ahmed Imam,
When the situation is still true at the time of reporting, we can leave the verb form unchanged. For example:
1. She told me she loved me.
2. She told me she loves me.
In sentence 1 we know she loved me when she told me but we don't know whether or not she loves me now. In sentence 2, we know she loved me when she told me and we know that she loves me now.
In your example, if the supermarket is still in the same place then we can use either form. If the supermarket has been closed down or moved to another location then we need to use was .
As for which is 'safer', you'll need to make your own mind up! Keeping the verb in the same form carries more specific information and that may be appropriate or even important.
Hello eugelatina87,
I'll give you a hint: a verb is missing from the question.
Does that help you complete it?
All the best,
The first two sentences are possible and they can both mean that he is still Mary's boyfriend now. The first one makes this more clear, but the second one doesn't only refer to the past.
Hello magnuslin
Regarding your first question, the most common way of saying it is the second one. In some very specific situation, perhaps the first option would be possible.
This also answers your second question. It is not necessary to always backshift using the tenses you mention.
As for your third question, no, it is not necessary. In fact, it is probably more common to use the past simple in the reported speech as well.
All the best
Hello manu,
Both forms are possible. If you use had been then we understand that he was there earlier but not when he said it - in other words, when he said it he had already left. If you use was then he may have left at the time of speaking, or he may have still been there.
Hello _princess_
I would recommend using answer a) because this is the general pattern used in reported speech. Sometimes the verb in the reported clause can be in the present tense when we are speaking about a situation that is still true, but the reported verb in the past tense can also have the same meaning. Since here the time referred to could be either past or present, I'd recommend using the past form.
Hello mwright,
This is an example of an indirect question. An indirect question reports a question, but is not a question itself, which is why we do not use a question mark at the end. Since it is not a question, we use the normal word order without inversion or auxiliary verbs. For example:
Indicative: He lives in Rome. Interrogative: Does he live in Rome? (Where does he live?) Reported: She asked if he lives in Rome. (She asked where he lives.)
Hello ahlinthit
There are different styles of punctuating direct speech -- in other words, you might find other sources that will disagree with me -- but what I would use here is something different: "The boss is dead!" said the doctor.
Hope this helps.
Best wishes
Hello Timmosky,
The form that comes after the auxiliary verb 'do' (or 'does' or 'did') is not the plural present simple verb, but rather the bare infinitive (also known as 'base form' or 'first form') of the verb. Does that make sense?
All the best, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
Hello sky-high,
This is very formal language. The phrase 'to the effect that' means 'with the meaning that'. In this context it can be understood to mean 'with the result that'.
Best wishes,
The difference is quite logical. If we use 'said' then we are talking about a claim by Peter in the past which he may or may not still maintain. If we use 'says' then we are talking about an opinion expressed by Peter which he still holds.
The reported information (whether or not Rooney is in good shape) can refer to only the past or to the present as well and the statement (what Peter thinks) can separately refer to only the past or the present as well. Of course, all of this is from the point of view of the person reporting Peter's opinion, and whether or not they think that Peter still thinks now what he thought then.
Both are possible. If you use the present tense then it is clear that the statement is still true (i.e. the business was not growing when Mary spoke and is still not growing now). If you use the past tense then no information is given regarding the present (i.e. the business was growing when Mary spoke and may or may not be growing now).
Hello aseel aftab,
It should be 'if they had'. This is not from this page, is it? I don't see it anywhere here, but if I've missed it please let me know.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In direct speech, the speaker most often speaks in the first person. That is, the speaker speaks from his person. John will not talk about himself: John is a good boy. John will say it on his behalf: I am a good boy. But when we retell the words of John (indirect speech), we cannot speak on his behalf.
Converting Direct to Indirect Speech. 1. Eliminate the quotation marks that enclose the relayed text. 2. Retain the tense of the reporting verb and add the word “that” after it. 3. Change the tense of the verb in the reported speech, if needed. 4. Change the pronouns accordingly.
Tenses in reported speech. When reporting what people say or think in English, we need to remember that the rules for tense forms in reported speech are exactly the same as in the rest of the language. This is a letter that Andrew wrote ten years ago: