
Home » English Grammar in Hindi » Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi (Narration) Rules, Examples, Exercises

Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi (Narration) Rules, Examples, Exercises
Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi (Narration) Rules, Examples and Exercises. Learn Direct and Indirect Narration in Hindi. प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन हिंदी में सीखिए। Rules of Indirect Speech in Hindi and English with examples. Direct and Indirect Speech को Hindi में प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन कहते हैं। जब आप किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही गई बात को दो तरह से कहा जाता है; Direct और Indirect के नीचे दिए गए उदाहरणों को देखें:
Direct: He said to me, “I am a rich man.” प्रत्यक्ष: उसने मुझसे कहा, “मैं एक अमीर आदमी हूं।”
Indirect : He told me that he was a rich man. अप्रत्यक्ष: उसने मुझे बताया कि वह एक अमीर आदमी है।
Note: ऊपर भी गए वाक्यों में Direct Speech के वाक्य में किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही ही बात को ज्यों का त्यों inverted commas में quote कर लिखा गया है जबकि Indirect Speech के वाक्य को ज्यों का त्यों न लिखकर वक्ता (speaker) द्वारा अपने शब्दों में लिखा गया है।
इस पोस्ट के माध्यम से आप Direct and Indirect Speech के Rules, Examples Hindi में पढ़ेंगे। सभी नियम विस्तार से समझाए गए।

Page Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi (Narration)
Direct का प्रत्यक्ष अर्थात सीधा तथा Indirect का अर्थ अप्रत्यक्ष होता है। Speech या Narration का अर्थ ‘वर्णन’ होता है। इस तरह से किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही हुई बात को दो प्रकार से व्यक्त किया जा सकता है।
Direct Speech in Hindi
किसी वक्ता के शब्दों को ज्यों का त्यों बिना किसी प्रकार का परिवर्तन किये कहा जाता है, उसे Direct Speech या Direct Narration कहते हैं। Direct Speech के शब्दों को inverted commas (“………”) के अंदर लिखते हैं।
जैसे –
- Dileep said, ” I can speak English fluently.” दिलीप ने कहा, ” मैं धाराप्रवाह अंग्रेजी बोल सकता हूं।”
Note : इस वाक्य में Dileep वक्ता (speaker) है। उसके द्वारा कहा जा रहा है कि वह धाराप्रवाह अंग्रेजी बोल सकता है।
Parts of Direct Speech or Narration
Direct Speech के दो भाग होते हैं; Reporting Speech तथा Reported Speech
Reporting Speech: Commas से बाहर वाले वाक्य को Reporting Speech कहते हैं। नीचे दिए गए वाक्य में ‘He said to me’ Reporting Speech है।
- जैसे – He said to me, “I am fine.”
Reporting Speech के Part
ऊपर दिए गए वाक्य के part नीचे दिए गए हैं;
Reported Speech: Commas के अंदर आए हुए वाक्य को Reported Speech कहते हैं। नीचे दिए गए वाक्य “I was busy yesterday.” Reported Speech है। यह वह हिस्सा होता है जिसे ज्यों का त्यों लिखते हैं।
जैसे – I said, “I was busy yesterday.”
Indirect Speech in Hindi
जब वक्ता द्वारा कही हुई बात को ज्यों का त्यों न लिखकर अपने शब्दों में उसका भावार्थ लिखते या बोलते हैं, उसे Indirect Speech या Indirect Narration कहते हैं।
Dileep said that he could speak English fluently. दिलीप ने कहा कि वह धाराप्रवाह अंग्रेजी बोल सकता है।
Note : इस वाक्य में inverted commas का प्रयोग नहीं हुआ है। Speaker (वक्ता) की कही बात को अपने शब्दों में लिखा गया है।
Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
Assertive Sentences को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम के अनुसार सबसे पहले commas बाहर परिवर्तन करते हैं। उसके बाद commas के अंदर परिवर्तन किया जाता है। इन सभी परिवर्तनों को कैसे और कब करना है, यह सभी नियम नीचे दिए गए हैं।
Reporting Speech में Change
वाक्य के बाहर का part (Commas के बाहर) Reporting Speech कहलाता है। Commas के बाहर परिवर्तन करने के rules निम्नलिखित हैं।
Commas के बाहर Changes
यदि Reporting Verb में said to आये तो उसे told, says to को tells में, say to को tell में बदलते हैं। यदि वाक्य में said, says, तथा say के बाद to न आया हो तो इन्हें indirect speech में ज्यों का त्यों लिखते हैं।
Commas में Change
Assertive Sentence को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलते समय commas को हटाकर that लिखते हैं।
- He said , “ I am not sure.” He said that he was not sure.
Change of Pronouns (सर्वनाम के परिवर्तन)
Direct से Indirect Speech में बनाते समय Pronoun के परिवर्तन में निम्नलिखित नियमों का पालन किया जाता है।
Rule – 1 यदि Reporting Speech में I Person के Pronoun आता है तो Reporting Speech के Subject के Person के अनुसार बदला जाता है।
- She said, ”I am writing a letter.” She said that she was writing a letter.
- Teena says to me, ”You can invite me.” Teena tells me that I could invite her.
Rule – 2 यदि Reported Speech के वाक्य में कोई Second Person Pronoun आया है तो Reporting Speech के Object (कर्म) के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
- He said to me, “You do it well.” He told me that I did it well.
Rule – 3 Reported Speech में आये सभी Third Person Pronoun को बदला नहीं जाता है।
- My friend said, “He is a good postman.” My friend said that he was a good postman.
Rule – 4 यदि Reporting Speech का object न दिया हो तथा Reported Speech का Subject II Person हो और Reporting Verb का Subject Second First Person का हो तो Reported Speech के second person को Indirect Speech में III person के Subject में बदल देते हैं।
- I said, “You have a nice dress.” I told him that he had a nice dress. I told her that she had a nice dress.
- Noun in Hindi
- Adjective in Hindi
- Verb in Hindi
Change of Tense
Rule – 1 यदि Reporting Speech के verb का Tense ‘Present या Future Tense’ में है तो Reported Speech के Verb का Tense नहीं बदला जाता है।
1. He says, “I am doing it now.” He says that he is doing it then.
2. Seeta says, ‘I sang a song.” Seeta says that she sang a song.
3. The man will say to me, ”I cannot find my purse.” The man will tell me that he could not find his purse.
4. Ram says to Rohan, “I am ready.” Ram tells Rohan that he is ready.
5. He has said, “The girl was poor” He has said that the girl was poor.
Rule – 3 यदि Reporting Speech के Verb का Tense ‘Past Tense’ है तो Reported Speech का Tense नीचे दी गई टेबल के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
Direct Speech या Narration का Tense
Rule – 4 यदि Reporting Speech Past Tense में तथा Reported Speech Future Tense में है तो नीचे दिए table के अनुसार चेंज करते हैं।
1. Raj said to me, ” I shall play with you.” Raj told me that he would play with me.
2. Kamal said to Vimal, “You will be driving your car.” Kamal told Vimal that he would be driving his car.
3. They said to him, ‘You will have completed your registration.” They told him that he would have completed his registration.”
4. I said to you, “I shall have been buying milk for five days.” I told you that I should have been buying milk for five days.”
- Future Indefinite Tense in Hindi
- Future Continuous Tense in Hindi
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Other Verb changes
Rule – 1 यदि Reporting Speech Past Tense में है तथा Reported Speech में नीचे दी गई Auxiliary Verbs का प्रयोग हो तो नीचे दी गई सूची के अनुसार Indirect Speech में बदलते हैं।
1. He said to me, ”I can solve this problem.” He told that he could solve that problem.
2. Sita said to her friend, ”You may sleep here.” Sita told her friend that she might sleep there.
3. Mohandas said to her sister, ”She is better than you.” Mohandas told her sister that she was better than her.
4. The teacher said to us, “I am your new teacher of English.” The teacher told us that he was their new teacher.
5. They said to me, “We are playing cricket here.” They told me that they were playing cricket cricket.
6. Gagan said to her sister, “I do my work on time.” Gagan told her sister that he did her work on time.
7. She said, ”I have a nice dress.” She said that she had a nice dress.
8. Teena said to her friend, “I have to carry the lunch box with me.” Teena told her friend that he had to carry the lunch box with her.
Rule – 2 यदि Reporting Verb Past Tense में है तथा Reported Speech में Subject + Could/Should/Would/Might + Verb I का प्रयोग हो तो could, should, would, might को बिना बदले ज्यों का त्यों लिखते हैं।
1. Father said, ”I could buy 5 kg mangoes.” Father said that he could buy 5 kg mangoes.
2. He said to him, “He should do it honestly.” He told him that he should do it honestly.
Important Rules for changing the tense
Rule – 1 यदि Reported Speech में कोई सदा सच रहने वाली बात (Universal Truth), आदत (Habit), ऐतिहासिक तथ्य या घटना (Historical Truth or Event), कहावत (Proverb) आदि दी हो तो Indirect Speech में बनाते समय Reported Speech के टेंस में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं करते हैं।
Universal Truth
- The grandfather said, ” The earth moves round the sun.” The grandfather said that the earth moves round the sun.
- He said, ”I go to school everyday.” He said that He goes to school everyday.
Historical Truth
- Rajesh said, “India got freedom in 1947.” Rajesh said that India got freedom in 1947.”
- My said to me, ” Honesty is the best policy.” My told me that honesty is the best policy.
Rule – 2 यदि Reported Speech का Simple Past Tense में एक साथ दो कार्यों का होने का बोध हो तथा time clause का प्रयोग हो रहा हो तब Indirect बनाते समय Simple Past Tense तथा Past Continuous Tense मैं परिवर्तन नहीं करते हैं।
1. He said, “When I came to your house, you were teaching your child.” He said that when he came to his house, I was teaching my child.
2. She said, ‘When the movie started, current went.” She said that when the movie started the current went.
Change in words showing nearness
Examples of Assertive Sentences of Indirect Speech
Assertive Sentences को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम ऊपर बताये जा चुके हैं। यहां उनके Examples दिए जा रहे हैं। Assertive Sentences के अंतर्गत affirmative sentences तथा negative sentences आते हैं।
1. He says to me, ”I am ill.” He tells me that he is ill.
2. I say to you, ”The man is out. I tell you that the man is out.
3. Shyam said to me, ”I am you best friend.” Shyam told me that he was my best friend.
4. You said to me, ”He plays cricket with friends.” You told me that he played cricket with friends.
5. Gagan said to me, ”I am waiting for you.” Gagan told me that he was waiting for you.
Interrogative Sentences
Direct Speech के Interrogative Sentences को Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम नीचे दिए गए हैं।
Yes-No Type Questions को direct speech से Indirect speech में बदलना
यदि Reported Speech में Interrogative Sentences Helping Verb से शुरू है तो वाक्य को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए नीचे दिए गए rules को फॉलो करते हैं।
Rule – 1
(1) Commas के बाहर Reporting Verb में आये भाव के अनुसार
- say या say to को ask/demand/enquire/want to know में बदलते हैं।
- says या says to को asks/demands/enquires/wants to know में बदलते हैं।
- said या said to asked/demanded/enquired/wanted to know में बदलते हैं।
(2) Inverted commas को हटाकर if या whether करते हैं। (3) इसके बाद interrogative sentence को affirmative में बदलकर लिखते हैं। (4) अंत में full stop लगाते हैं। (5) अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्यों की तरह होते हैैं।
1. She said to her mother, ”Are you ill?” She asked her if she was ill.
2. He said to me, ”Is your brother here?” He asked me if my brother was ill.
3. Seeta said, ”Am I Right?” Seeta asked if she was right.
4. We said to him, “Are you sleeping now” We asked him if he was sleeping then.
5. You said, “Do you know your rights?” You asked him/her if he/she knew her/his rights.
6. The man said to me, “Have you taken your medicine?” The man asked me if I had taken my medicine.
7. Golu said to his brother, ”Have you been playing here for two hours? Golu asked his brother if he had been playing there for two hours.
8. Ravi said to me, ”Did you write a letter to your client? Ravi asked me if I had written a letter to my client.
9. Alok asked, ”Were you beating your child yesterday? Alok asked me/him if I/he had been beating my/his child the previous day.
10. Roshani said to him, “Is New Delhi is the capital of India?” Roshani asked him if New Delhi is the Capital of India.
Wh-word Questions को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech (Narration) में बदलना
Wh-word Questions को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech/Narration से बदलने के नियम नीचे दिए गए हैं।
Rule – 1 यदि रिपोर्टेड स्पीच का Interrogative Sentence Wh-words से शुरू है तो Sentence को indirect speech बदलने के लिए नीचे दिए गए हो स्टेप्स को फॉलो करते हैं।
1. सबसे पहले Reporting Verb को अर्थ के अनुसार ask/asks/asked, demands/demands/demanded, enquire/enquires/enquired मैं बदलते हैं।
2. उसके बाद Inverted commas को हटाकर if/whether/that आदि का प्रयोग नहीं करते हैं। इसकी जगह उसी प्रश्नवाचक शब्द (interrogative word) का प्रयोग करते हैं जो सेंटेंस में आता है।
3. Direct Speech में हुए वाक्य (Wh-word + helping verb + sub + verb + object + other +?) को Indirect Speech में Assertive Sentence (question word + subject + verb + object के आधार पर) में बदल कर लिखते हैं।
4. Pronouns तथा Tense में change सिंपल सेंटेंसेस की तरह होते हैं।
5. अंत में full stop (.) रखते हैं।
1. The policeman said to the thief, “Why have you stolen this ring?” The policeman asked the thief why he had stolen that ring.
2. Roshni said to Rani, “Why did you not come yesterday? Roshni asked Rani why she had not come the previous day.
3. The patient said, “Where is the doctor?” The patient wanted to know where the doctor was.
4. My friend said to me, “Where do you live?” My friend asked me where I lived.
5. He said, “When does the milk man come yesterday?” He asked when the milk man had come the previous day.
6. Father asked me, “What do you want?” Father asked me what I wanted.
7. The magician said to the boy, “What did you see in the box?” The magician asked the boy what he had seen in the box.
8. I said to the students, “How can you solve this question?” I asked the students how you could solve that question.
9. The captain said to the players,” Why did you come late?” The caption asked the players why they had come late.
10. Mother said to her daughter, “Which movie did you see last night?” Mother asked her daughter which film she had watched the previous night.
Imperative Sentences
Verb I, Do not, Never Always Please Kindly शुरू होने वाले वाक्य आज्ञासूचक (imperative) होते हैं। इनसे आज्ञा, आदेश, इच्छा, मना करना, निर्देश आदि का भाव प्रकट होता है।
1. Open the box now. 2. Clean the house. 3. Do not hesitate to call me. 4. Please refresh the page. 5. Kindly send me your address. 6. Always Remember this thing.
Imperative Sentences को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना
Imperative Sentences को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
यदि Direct Speech में कोई Imperative Sentence आता है तो नीचे दिए rules के अनुसार Indirect Speech में उसे बदला जाता है।
Rule – 1 यदि Indirect Speech में आया हुआ Imperative Sentence ‘Verb I’ से शुरु है तो नीचे दिए rules को फॉलो करते हैं;
(1) यदि Reporting Speech में say, said, says या say to, said to, says to आयें तो नीचे दी गई टेबल के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
Note : ऊपर दी गई टेबल के अनुसार Reporting verb मैं परिवर्तन करते हैं तथा इसके अलावा नीचे दिए गए शब्दों को भी reporting verb के स्थान पर प्रयोग किया जाता है।
Words : warn, implore, threaten, persuaded, entreat, urge, beg
(2) Commas को हटा देते हैं तथा उनके स्थान पर to का प्रयोग करते हैं।
(3) यदि वाक्य में sir, madam, please, kindly आया है तो उन्हें हटा दिए जाता है। ऐसे Sentences में Reporting Verb को request, requests या requested में बदलते हैं।
(4) अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्यों की तरह किये जाते हैं।
1. Ram said to Shyam, “Have a seat.” Ram told/requested Shyam to have a seat.
2. Father said to me, “Get out of my room.” Father ordered me to get out of his room.
3. The teacher says, “Open your books.” The teacher orders to open the books.
4. Shyam said to me, “Please help me.” Shyam requested me to help him.
5. The doctor said, ”Sleep for seven hours.” The doctor advised me to sleep for seven hours.
1. यदि Direct Speech के Reported Speech में Sir या Madam आता है तो उनको हटाकर उनके स्थान पर respectfully का प्रयोग करते हैं।
2. यदि Reporting Verb के बाद कोई object नहीं आया है तो sir/madam के स्थान पर respectfully का प्रयोग object के बाद करते हैं।
1. She said to the shopkeeper, “Sir, please help me.” She requested the shopkeeper respectfully to help her.
2. The student said to the teacher, “Sir, grant me leave for two days” The the student requested the teacher respectfully to grant him leave for two days.
3. The driver said, “Madam, please close the door.” The driver requested respectfully to close the door.
4. He said to the policeman, “Sir please catch the thief.” He requested the policeman respectfully to catch the thief.
Negative Imperative Sentences को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलना
जो वाक्य सामान्य Do not/Don’t से शुरू होते हैं वे Negative Imperative Sentences कहलाते हैं।
1. Don’t worry. (चिंता मत करो।) 2. Don’t forget it. (इसे मत भूलना।) 3. Do not hesitate. (मत हिचकिचाओ।) 4. Please do not go. ( कृपया मत जाइए।) 5. Kindly don’t talk here. (कृपया यहां बातें मत करो)
Rule – 1 Reporting Verb – say, says, said को अर्थ के अनुसार ask, asks, asked/tell, tells, told/order, orders, oerderd में बदलते हैं।
Rule – 2 Commas को हटाकर Do not के स्थान पर not to लगाते हैं।
Rule – 3 बचा हुआ वाक्य not to के बाद जोड़ देते हैं।
Rule – 4 अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्यों की तरह होते हैं।
1. He said to me, “Don’t complain.” He asked/told me not to complain.
2. My friend said to me, “Do not open the window.” My friend asked/told me not to open the window.
3. The teacher says, ”Don’t read it.” The teacher told me not to read it.
4. I said to her, “Don’t walk there.” I asked/told her not to walk there.
Forbid/Forbids/Forbade का प्रयोग
Do not वाले नकारात्मक आज्ञा सूचक वाक्यों को forbade का प्रयोग करके भी indirect speech मैं बदलते हैं।
Rule – 1 say/says/said को forbid/forbids/forbade में बदलते हैं।
Rule – 2 Do not को हटा देते हैं तथा उसके स्थान पर to का प्रयोग करते हैं।
Rule – 3 अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्यों की तरह होते हैं।
1. Father said to me, “Don’t eat this mango.” Father forbade me to eat that mango.
2. She said to me, “Do not play in the sun.” She forbade me to play in the sun.
3. I said to my son, “Don’t run on the road.” I forbade my son to run on the road.
निषेध सूचक वाक्य
यदि Direct Speech में कोई निषेध सूचक वाक्य आया है तो उसे निम्न प्रकार से बदलते हैं।
1. She said to him, “Stop writing.” She prevented/prohibited him from writing.
2. Gagan said to us, “Don’t play with strangers.” Gagan prohibited us from playing with strangers. Gagan forbade us to play with strangers.
3. My teacher said to me, “Never abuse anyone.” My teacher prevented/prohibited me from abusing anyone.
Do + Verb I + Object + Other Words पर आधारित वाक्य
यदि कोई आगे सूचक वाक्य do से शुरू है तो उसको इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में बदलते समय नीचे दिए गए स्टेप्स को फॉलो करते हैं;
1. said या said to अर्थ के अनुसार requested/ordered में बदलते हैं। 2. Inverted Commas को हटा देते हैं और to लगाते हैं। 3. बचे हुए अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्य करते हैं।
1. He said to me, “Do learn your lesson.” He asked me to learn my lesson.
2. Gagan said to her, “Do open the letter.” Gagan asked her to open the letter.
Let से शुरू होने वाले वाक्य को indirect speech change करना
Imperative Sentences जो let से शुरू होते हैं, यदि उनसे प्रस्ताव या सुझाव का बोध हो तो इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में बदलने के नियम निम्नलिखित हैं।
Rules –
1. Reporting Verb को proposed या suggested में बदलते हैं; यदि suggest या propose की बात कोई ऑब्जेक्ट आया है तो उससे पहले to का प्रयोग अवश्य करते हैं।
2. Inverted commas को हटाकर that लिख देते हैं। 3. लेट को हटा देते हैं। 4. यदि सेंटेंस में objective case के प्रोनाउंस us का प्रयोग हुआ है तो अर्थ के अनुसार nominative case के प्रोनाउन भी we या they में बदलते हैं। 5. इसके बाद should तथा मुख्य क्रिया की First Form का प्रयोग करते हैं। 6. अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्य की तरह करते हैं।
1. He said to his father, ” Let us go to park.” He suggested/proposed to his father that we/they should go to park.
2. He said, “Let us help the poor.” He suggested that they should help the poor.
3. I said to him, “Let us go to market.” I suggested/proposed to him that they/we should go to market.
4. Grandfather said to his grandson, “Let us go a for a walk.” Grandfather suggested to his grandson that they should go for a walk.
5. Sohan said to her, “Let us go out.” Sohan proposed her that we/they should go out.
Let से Wish या Desire का बोध होने वाले वाक्यों को indirect speech में बदलना
यदि let से शुरू होने वाले direct speech वाक्यों से किसी इच्छा का भाव प्रकट हो तो उसे इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में निम्न प्रकार से बदलते हैं;
1. Reporting Verb say/says/said को wish/wishes/wished में भाव के अनुसार बदलते हैं। 2. Inverted Commas को हटाकर that में बदलते हैं। 3. Let को हटा देते हैं। 4. Let के बाद आए हुए ऑब्जेक्टिव केस के प्रोनाउंस को नॉमिनेटिव केस के pronouns में बदलते हैं। ये बदलाव persons को बदलने के नियम के अनुसार होता है। 5. Nominative case के pronouns तथा मुख्य क्रिया की First Form का प्रयोग करते हैं। 6. अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्य की तरह होते हैं।
1. He said, “Let me know this matter.” He wished that he should know that matter.
2. Gagan said, “Let him take a rest.” Gagan wished that he should take a rest.
3. She said, Let me help the needy.” She wished that she should help the needy.
4. You said, “Let me watch this movie.” You wished that you should watch that movie.
Note : यदि लेट से शुरू होने वाले वाक्य में अनुमति का बोध हो तो Reporting Verb को ordered/requested में बदलकर लिखते हैं। Commas तथा let को हटा देते हैं। उसके to allow बाद लिखते हैं। आप to allow के स्थान पर to let का प्रयोग कर सकते हैं।
1. The master said to his servant, “Let him go home.” The master ordered his servant to allow him to go home. The master ordered his servant to let him go home.
2. The son said to father, “Let me sleep now. The son requested father to let him sleep.
Optative Sentences को Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
Optative Sentences (इच्छा सूचक वाक्य) वे वाक्य होते हैं जिनसे प्रार्थना, इच्छा, अभिशाप तथा आशीर्वाद का बोध होता है। ऐसे वाक्यों को डायरेक्ट स्पीच से इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में बदलने के नियम निम्नलिखित हैं;
1. Reporting Verb को भाव तथा tense के अनुसार wish/wishes/wished, pray/prays/prayed, curse/curses/cursed, bless/blesses/blessed में बदलते हैं।
2. Inverted Commas को हटाकर that लिखते हैं।
3. Direct Speech में आए हुए optative sentence को assertive sentence (Subject + might + verb I + object + other words) में बदलकर लिखते हैं।
4. अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्य की तरह होते हैं।
1. She said to me, “May you live long!” She blessed me that I might live long.
2. They said, “May God bless you!” They prayed that God might bless him.
3. Mohan said to me, “May you succeed in your life!” Mohan wished me that I might succeed in my life.
4. Father said to his son, “May you pass in the examination!” Father wished his son that he might pass in the examination.
5. People said, “Long live our prime minister!” People prayed that their prime minister might live long.
6. My mother said to me, “You be happy!” My mother wished me that I might be happy.
Note : यदि यदि डायरेक्ट स्पीच के optative sentence में may ना आया हो तो वहां may अपने आप ही मान लेते हैं।
Exclamatory Sentences को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना
Exclamatory Sentences से joy sorrow surprise, anger, contempt, applause, regret, happiness आदि का बोध होता है। यह वाक्य अक्सर hello!, Alas!, Hurrah!, Ah!, Oh!, Well done!, Bravo! Ha! Ha!, Oh dear! आदि से प्रारंभ होते हैं।
Exclamatory Sentences डायरेक्ट स्पीच इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में बदलने के नियम निम्नलिखित हैं;
1. Reporting Verb को नीचे दी गई टेबल के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
2. Inverted Commas को को हटा देते हैं तथा उनके स्थान पर that लिख देते हैं।
3. उसके बाद वाक्य में आए हुए सभी interjection (विस्मय सूचक शब्दों) को हटा देते हैं।
4. इसके बाद Exclamatory Sentence को Assertive Sentences में बदलकर लिखते हैं।
5. अंत में exclamation mark को हटाकर full stop लगाते हैं।
1. The boy said, ”Alas! I am ruined.” The boy exclaimed with sorrow that he was ruined.
2. He said, “How beautiful the rainbow is!” He exclaimed with joy that the rainbow was very beautiful. He exclaimed that the rainbow was very beautiful.
3. Father said, “Alas! My daughter hasn’t come.” Father exclaimed with sorrow that his daughter hadn’t come.
4. The foreigner said, “What a place it is!” The foreigner exclaimed with joy/surprise that it was a very beautiful place.
5. The students said to the teacher, “Happy Diwali, sir!” The students wished the teacher respectfully a happy Diwali.
6. The captain said, “Ah! we have lost the game.” The captain exclaimed with sorrow that they had lost the game.
7. The boy said to the girl, “How beautiful you are!”
The boy exclaimed with joy/surprise that she was very beautiful.
8. The sports teacher said, “Bravo! you have done well!” The sports teacher exclaimed with joy that he had done well.
9. He said, “Nice!” He gave an exclamation of pleasure.
10. He said, “Good bye!” He bade me good bye.
11. She said to her friends, “Good Night!” She bade her friends good night.
12. Raju said, “How happy I am!” Raju exclaimed with joy that he was very happy.
13. Father said, “Well done! You have done well!” Father exclaimed with praise that I had done well.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
Here are some Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for practice. Solve them and match your answer below. These exercises are very helpful for the students. After learning the above rules of Indirect Speech.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise – 1 – Assertive Sentences
- He says, “I am very happy today.”
- The girls say, “We are free.”
- Father said, “I am not able to run.”
- I said to my client. “You have not told me anything.
- The teacher said to the students, “There are twelve months in a year.”
- The judge said to the criminal, “You can’t speak loudly here.”
- I said, “I will pay my bill.”
- The teacher said to the student, “you never come late.”
- He said, “I am doing my work.”
- My mother said, “Honesty is the best policy.”
- He said the earth pulls everything towards it.”
- Sham set to me, “I will attend the class tomorrow.”
- The principal said to the students, ”The school will be closed tomorrow.”
- The old woman says, “I have become very old.”
- The teacher says to me, “You have written the essay correctly.”
- The man said, “My does not eat anything.”
- The student said to the teacher, “I didn’t understand the last example.”
- Raju said to Rohan, “I don’t know the name of the minister of education.”
- Sita said to her father, “I haven’t read the chapter two of this book.”
- Grandfather said, “You can jump.”
Interrogative Sentences – Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise – 2
Exercise – 2
- She said to me, “Are you fine?”
- Pawan said to her, “Do you know me?”
- Rahul sad to his mother, ” Have you cooked something to eat?”
- The girl says to the man, “Did you see my brother yesterday?”
- The patient said, “Where is the doctor?”
- The teacher said to the student Have you done your homework?”
- The police man said to the thief, “Who stole the money?”
- Father said to mother, “Where is Sohan going?”
- She said, “When does your washerman come everyday?”
- “Who has broken this chair?” said grandfather.
- He said to me, “Will you open the door?”
- The customer say to the shopkeeper, “Do you sale this a special kind of coffee?”
- The doctor said to the patient, “When should I take this medicine?”
- They said to the passenger, “Where did you come from?”
- Vinod said to Aruna do you know Rakhi’s address?
- Mr Sharma asked Mr Verma, “Where have you been playing since morning?”
Watch the Direct and Indirect Speech Video in Hindi for better understanding.
- Recent Posts
- Easy Hindi to English Translation - March 20, 2024
- Present Tense in Hindi – परिभाषा, प्रकार तथा उदाहरण - March 17, 2024
- Personal Pronoun in Hindi – Definition, Examples and Rules - March 8, 2024
Related Posts
Sentence in hindi – types/kinds of sentences in hindi, interrogative sentences in hindi – definition, rules and examples, use of about to in hindi – rules, examples and exercises, use of these and those in hindi – meaning, rules and examples, use of this and that in hindi – meaning, rules and examples, 10 thoughts on “direct and indirect speech in hindi (narration) rules, examples, exercises”.
Thank you so much sir ❤❤
Thanks for correction to Kunal Kumar from Bihar
Thi is best for everyone
Hi sir I want to read narration
Very useful for me Thanks ❤️❣️
Thank you for your feedback!
Leave a comment…sir thank you so much . this is a very useful topic
Thank you so much sir or ma’am
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
ExamTricksAdda
Direct से Indirect बनाने के लिए महत्त्वपूर्ण नियम & PDF

1. Reporting Verb & Reported Speech
2. change of pronouns, 3. change of tense, 4. change of modals /helping verbs, 5. change in time : , 6. universal truth or a habitual fact ( सार्वभौमिक सत्य / तथ्य अथवा आदत ), ... please share this..., related links -, पढ़ें: टॉपर्स नोट्स / स्टडी मटेरियल-, 6 comments:.

टेन्स
स्टडी मटेरियल
- पढ़ें और सीखें: अंग्रेजी English [All Topics/ Notes] Translations / Grammar in Hindi
- प्रतियोगी गणित [सभी अध्याय] - All Mathematics Topics & Tricks in Hindi (फार्मूला/ शार्टकट्स/ उदाहरण)
- सामान्य ज्ञान के सभी टॉपिक्स | Govt. Exams General Knowledge Notes | Complete GK Topics in Hindi
- रीजनिंग [सभी अध्याय] - All Reasoning Tricks in Hindi
- हिंदी साहित्य: पढ़ें- सम्पूर्ण नोट्स सरल भाषा में | Hindi Sahitya - All Topics
- हिंदी व्याकरण / Complete Hindi Vyakaran Notes / Guide in Hindi
- तैयारी हेतु - DOWNLOAD 100% Free BOOK / PDF Notes | Study Material for Sarkari, Govt. Job & Board Exams
Narration in Hindi – Rules, Examples, Definition, Meaning
अंग्रेजी बोलने के लिए ग्रामर के बेसिक रूल्स और स्पोकन को समझना आवश्यक होता है. लेकिन ग्रामर के अनुसार इंग्लिश बोलने या एग्जाम में इंग्लिश क्वेश्चन को हल करने के लिए इंग्लिश ग्रामर का अध्ययन बारीकी से करना महत्वपूर्ण होता है. यहाँ ग्रामर के सबसे कठिन टॉपिक Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi के बारे में अध्ययन करेंगे.
प्रत्यक्ष कथन और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन उतना कठिन नही है जितना आप समझते है. Narration के कुछ बेसिक रूल्स है जिसका अध्ययन कर इसे सरल बनाया जा सकता है. यहाँ Direct Indirect Narrations के सभी आवश्यक रूल्स, examples, Tense के अनुसार वाक्य बदलने आदि के नियम का अध्ययन करेंगे जो Narration in Hindi को सरलता से समझने में मदद करेगा.
इंग्लिश ग्रामर में Narration का अध्ययन Direct Speech और Indirect Speech के रूप में किया जाता है. क्योंकि, ये किसी वक्ता के कथन को अपने शब्दों में Arrange करने का हुनर सिखाता है. अर्थात, किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही गई बातों को Direct और Indirect Speech में व्यक्त किया जाता है. जैसे;
Direct Speech: उसने लड़के से कहा, ” तुम बच्चे हो.” He said to the boy, ” You are child.”
Indirect Speech: उसने लड़के से बताया कि वह एक बच्चा था. He said to the boy that he was a child.
Table of Contents
Narration किसे कहते है? Narration Grammar in Hindi
किसी की कही गई बात को दुसरें को बताना ही Narration कहलाता है.
Narration का इंग्लिश में परिभाषा: Reporting the words of a speaker to another is called Narration.
दुसरे शब्दों में,
Narration शब्द का शाब्दिक अर्थ “कथन” होता है. इस शब्द का निर्माण Narrate शब्द से हुआ है. Narrate शब्द का शाब्दिक अर्थ to say / to state अर्थात कहना होता है. Narration का समानार्थक शब्द Assertion / Statement / Declaration इत्यादि होता है.
किसी के द्वारा कही बातों को व्यक्त करने के लिए इस (“….”) Punctuation marks का प्रयोग किया जाता है.
Types of Narration in Hindi
ग्रामर में Narration के दो प्रकार होता है, जिसके अंतर्गत सभी रूल्स, स्पेशल नियम, change of tense रूल्स आदि का अध्ययन किया जाता है. इसे सामान्यतः Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi से संबोधित किया जाता है.
- Direct Speech /Direct Narration (प्रत्यक्ष कथन)
- Indirect Speech / Indirect Narration (अप्रत्यक्ष कथन)
1. Direct Speech किसे कहते है
प्रत्यक्ष कथन यानि Direct Speech: जब कोई श्रोता/व्यक्ति किसी वक्ता (Speaker) के कथन (Statement) को वक्ता के शब्दों में या भाषा में अभिव्यक्त करता है, उसे Direct Speech कहते है.
दुसरें शब्दों में,
जब कोई व्यक्ति वक्ता द्वारा कही गयी बातों को ज्यों का त्यों यानि हू -ब-हू किसी किसी व्यक्ति को व्यक्त करता हैं, तो उसे Direct Narration/ Speech कहा जाता है.
Note: Direct Speech के शब्दों यानि Statement को Inverted Comma (“….”) के बिच रखा जाता है.
Direct Speech के प्रकार:
Narration में डायरेक्ट स्पीच के दो भाग होते है जिसके अनुसार कथन को हु-ब-हु या बदलकर व्यक्त किया जाता है.
- Reporting Speech
- Reported Speech
इन दो भागो का अध्ययन यहाँ विस्तार से करेंगे ताकि narration को सरलता से समझ सके.
Reporting Speech क्या है?
Direct Speech का वह भाग जो Inverted Comma (“….”) के बहार रहता है, Reporting Speech कहलाता है.
- The teacher says, “The girl was lazy.”
- Ram said, “Sita has done her work.”
- Mohan said, ” I am busy.”
- She said, “he loves me a lot.”
दिए गए नरेशन यानि Narration उदाहरण में The teacher says, Ram said, Mohan said, or She said Reporting Speech है.
Reporting Speech के प्रकार
Narration को समझने के लिए Reporting Speech मुख्यतः तीन भागो में विभाजित किया गया है. जो इस प्रकार है:
Reporter : वक्ता अर्थात कथन या कोई बात कहने वाले को Reporter कहा जाता है. जैसे;
- She said to me, ” I had no time for you.”
- They said to us, ” We are giving a nice present.”
इस उदाहरण में she और they Reporter है.
Note: Reporter को दुसरें शब्दों में The subject of Reporting Verb भी कहा जाता है.
Reporting Verb : किसी वक्ता द्वारा जिस Verb का प्रयोग किसी कथन को करने के लिए किया जाता है, उसे Reporting Verb कहते हैं. जैसे;
- Meera said to Munni, ” you are a good girl.”
- I said to her, ” I love you so much.”
उपरोक्त उदाहरण में said Reporting Verb है.
Reporting Object :- वक्ता किसी कथन को जिससे कहता है , उस object को Reporting Object कहते हैं. जैसे;
- They said to the boys, ” you sang well.”
- He said to me, ” I can defeat you.”
उपरोक्त उदाहरण में the boys और me Reporting Object है.
Reported Speech क्या होता है?
Direct Speech का वह भाग जो Inverted Comma (“….”) के भीतर रहता है, उसे Reported Speech करते है. जैसे;
- She says to them, ” This is mine and that is yours.”
- The girl said to her mother, ” I shall obey you.”
- They said, ” We can not escape death.”
- My father said, ” Labour never goes in vain
उपरोक्त उदाहरण में Inverted Comma के अन्दर वाले वाक्य जैसे This is mine and that is yours आदि Reported Speech है.
Verb of Reported Speech : Reported Speech के verb को Verb of Reported Speech कहा जाता है. जैसे;
- She said, ” I have seen this boy before.”
- He said, ” I shall do my best.”
उपरोक्त वाक्यों में Have और Shall Verb of Reported Speech है.
Note: Direct Speech के सभी भागों को एक उदाहरण के अनुसार निम्न प्रकार समझे:
उदाहरण: The teacher said to me, ” you have done well in the examination.”
2. Indirect Speech किसे कहते है?
जब कोई ऑडियंस यानि वक्ता किसी Speaker के कथन को अपने शब्दों या भाषा में व्यक्त या अभिव्यक्त करता है, तो उसे Indirect Speech कहते है.
जब किसी वक्ता के मूल कथन में हम कुछ हेर-फेर कर उसके आशय या सारांश को अपने शब्दों में व्यक्त करते है, तो उस कथन को Indirect Speech कहते है.
Note: Indirect Speech को Inverted Comma के अंदर नही रखा जाता है. जैसे;
- You said that she had written a letter.
- They said that we are social animals.
- Mukesh told her that he had been teaching her lover for years.
- He said that I had been absent in the class.
उपरोक्त उदाहरण में sentences को inverted comma से बहार रखा गया है. इसलिए, ये सभी Indirect Speech है.
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules in Hindi
इंग्लिश ग्रामर में Narration के वाक्यों को Direct Speech से Indirect में बदलने के लिए विभिन्न प्रकार के नियम को फॉलो करना पड़ता है. Narration के सभी रूल्स वाक्य के बनावट , Tense और Person के अनुसार अलग-अलग होते है. Narration के वाक्यों को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के दो नियम होते है:
- General Rules (सामान्य नियम )
- Special Rules (विशेष नियम )
Direct Speech को Indirect Speech में change करने के लिए कुछ General Rules और कुछ Special Rules को फॉलो किया जाता है.
General Rules वैसे Rules को कहते है, जो हर प्रकार के Sentences के साथ लागु किए जाते है, जबकि Special Rules विभिन्न प्रकार के वाक्यों के लिए अलग-अलग होता है. यहाँ General और Special Rules का अध्ययन भिन्न-भिन्न रूप में करेंगे.
1. Narration Rules in Hindi
ऐसा नियम जो सभी तरह के वाक्यों में लागू होता है उसे General Rules कहते है.
जनरल रूल्स के अंतर्गत Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के निम्न नियम होते है:
1. Change of Persons
2. Change of Tenses
3. Change of Other Parts of Speech
Narration Rules in Hindi के माध्यम से Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के सभी नियम का अध्ययन निचे विस्तार से करेंगे.
Important Note:
- यदि Reporting Verb के बाद कोई Object न हो, तो Reporting Verb को नही बदला जाता है.
- लेकिन यदि Reporting Verb के बाद कोई Object हो, तो say to को tell में, says to को tells में, और said to को told में बदल दिया जाता है.
- Indirect Speech में Assertive Sentence / Affirmative Sentece को “That” से जोड़ा जाता है.
इसे भी पढ़े, Active and Passive Voice in Hindi
1. Change of Persons ( सर्वनाम का परिवर्तन )
Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलते समय Inverted Commas (“….”) के अंतर जितने भी Persons जैसे First, Second और Third Person रहते है, वे सभी SON फार्मूला के क्रमानुसार बदल जाते है.

Note: SON Formula का अर्थ
Change of Persons के मुख्य नियम:
Rule: 1. यदि Reported Speech का Subject First Person ( I, We) का हो, तो वह Reporting Verb के Subject के Number, Person तथा Case के मुताबिक बदल जाता है. जैसे;
- Direct: he said to me, ” I am ready.”
- Indirect: He told me that he was ready.
Rule: 2. यदि Reported Speech का Subject Second Person (You) का हो, तो वह Reporting Verb के Object के Number Person तथा Case के मुताबिक change होगा. जैसे;
- Direct: he said to me, “you are late.”
- Indirect: he told me that I was late.
Rule: 3. यदि Reported Speech का Subject Third Person का हो, तो Indirect Speech में इनमे कोई परिवर्तन नही होता है. जैसे;
- Direct: You said, “She wrote a letter.”
- Indirect: You said that she had written a letter.
Rule: 4. Persons में परिवर्तन करते समय Number तथा Case में परिवर्तन नही होता है.

Note: ऊपर दिए गए टेबल के अनुसार ही Persons में बदलाव करे: जैसे;
- Direct : Binay says to me, “I am your friend.”
- Indirect: Binay tells me that he is my friend.
- He said to me, “I help you.” Direct
- Indirect: He told me that he helped me.
2. Narration: Change of Tenses (टेंस का परिवर्तन)
Rule: 1. यदि Reporting Verb Present या Future Tense में हो, तो Indirect Speech में Reported Speech के Tense में कोई परिवर्तन नही होता है. अर्थान, जिस Tense में Reported Speech रहता है, उसी Tense का प्रयोग ज्यों का त्यों Indirect Speech में होता है. जैसे;
Rule: 2. यदि Reporting Verb Past Tense में तथा Reported Speech Present और Past Tense में हो, तो Indirect Speech में Reported Speech का Tense निम्न प्रकार बदला जाता है.
Note: Tense में परिवर्तन का ट्रिक: “Present का जिसमे, Past का उसमे”
लेकिन यदि Reporting Verb Past Tense में हो तथा Reported Speech Future में हो, तो Indirect Speech में वाक्य इस प्रकार बदलता है:
इसे भी पढ़े,
For Examples:
- Direct: He said to me, “I shall write a letter.”
- Indirect: He told me that he should write a letter.
- He said to me, “I shall be writing a letter.”
- Indirect: He told me that he should be writing a letter.
Narration: Verb में Changes
इसे भी पढ़े,
यदि Reported Verb Past Tense में हो, तो Reported Speech में प्रयुक्त निकटता के अर्थ सूचक शब्दों को दुरी के अर्थ सूचक शब्दों में Indirect Speech में बदल दिया जाता है. जैसे;
Note: Reported Speech में प्रयुक्त निकटता सूचक शब्दों से यह ज्ञात हो कि प्रयुक्त वस्तु/जगह/समय/परिस्थिति/वक्ता के साथ Present Tense में मौजूद है. ऐसी स्थिति में निकटता सूचक शब्दों को दुरी सूचक शब्दों में नही बदलता जाता है. जैसे;
1. Mohan said, “This is my book.” Moahn said that this was his book.
2. This morning she said, “I will go out today.” This morning she said that she would go out today.
उदाहरण में निकटम सूचक शब्द है, लेकिन वाक्य Present Tense में है. इसलिए, This और Today को दुरी सूचक शब्दों में नही बदला गया है.
Tense Narration Rules in Hindi
Rule: यदि Reporting Speech, Past Tense में हो और Reported Speech सार्वभौमिक तथ्य (Universal Truth), आदतन सत्य (Habitual Facts), ऐतिहासिक सत्य (Historical Facts), या कहावत से सम्बंधित हो, तो Indirect Speech में उनके Tense या Verb Form को नही बदला जाता है. जैसे;
Universal Truth:
- The teacher said, “The sun rises in the East.”
- The teacher said that the sun rises in the East.
Habitual Facts:
- He said, ” I walk in the morning.”
- He said that he walks in the morning.
Historical Facts:
- The Prime Minister said, ” Indian got freedom in 1947.”
- The Prime Minister said that India got freedom in 1947.
- Mukesh said to me, ” Honesty is the best policy.”
- Mukesh told me that honesty is the best policy.
2. Special Rules in Narration
वे रूल्स जो भिन्न-भिन्न प्रकार के Sentences यानि वाक्यों के लिए भिन्न-भिन्न होते है. उसे Narration में Special Rules कहते है.
Reported Speech में अर्थात Inverted Commas के भीतर Assertive Sentence, Imperative Sentence, Interrogative Sentence , Optative Sentence, Exclamatory Sentence का प्रयोग होने पर Special Rules को फॉलो किया जता है.
ऐसे वाक्यों में एक ही प्रकार के नियमों का पालन करने से Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने पर गलती होने की संभावना अधिक होती है. इसलिए, ऐसे वाक्यों का Narration, स्पेशल रूल्स से किया जाता है.
Special Rules के प्रकार :
Narration में Special Rules का प्रयोग 5 प्रकार के वाक्यों को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए किया जाता है.
- Assertive Sentence
- Imperative Sentence
- Interrogative Sentence
- Optative Sentence
- Exclamatory Sentence
इन सभी टॉपिक का अध्ययन नियम के अनुसार निचे करेंगे.
1. Assertive Sentence: Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना
यदि Reported Speech में अर्थात, Inverted Commas के अन्दर Assertive Sentence का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में निचे दिए गए नियम के अनुसार बदला जाएगा.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verbs – say to, says to, said to को क्रमशः tell, tells, told में बदल दिया जाता है. लेकिन say , says, said यानि बिना “to” वाले वर्ब को tell, tells, told में नही बदला जाता है.
Note: tell, tells, told, Transitive Verbs है, इसलिए, इनके बाद Object का प्रयोग आवश्यक किया जता है. To का प्रयोग tell, tells, told के बाद नही होता है. जैसे;
- Direct: She says to her husband, “You must come come back home in time.”
- Indirect: She tells her husband that he has to come back home in time.
Rule: 2. Inverted Commas को हटाकर, इसके बदले That का प्रयोग किया जाता है.
Rule: 3. Assertive Sentence में General Rules को फॉलो किया जाता है. जैसे;
Rule: 4. यदि Reported Speech में must का प्रयोग हो तथा must से नैतिक कर्तव्य/जिम्मदारी/नियम/सिद्धांत आदि का बोध हो, तो Indirect Speech में must का प्रयोग ज्यों का त्यों होता है. अर्थात, ऐसे वाक्यों में कोई परिवर्तन नही होता है. जैसे;
- Direct: He said, “One must do one’s duty.”
- Indirect: He said that one must do one’s duty.
Rule: 5. यदि Reported speech में स्वागत या विदाई सूचक शब्दों जैसे Good Morning, Good Evening, Good night आदि का प्रयोग हो, तो इसे Indirect में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
- Direct: My classmate said to me, “Good morning, You have finished your home work.
- Indirect: My classmate wished me good morning and said that I had finished my home work.
2. Interrogative Sentence: Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना
यदि Reported Speech में अर्थात, Inverted Commas के अन्दर Yes-No Questions या WH-Questions का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस नियम के अनुसार बदला जाता है.
दरअसल, Interrogative Sentences दो प्रकार से बनाया जाता है. जैसे ऊपर दर्शाया गया है. ऐसे वाक्यों का अनुवाद Indirect Speech में करने के लिए अलग-अलग नियम को फॉलो किया जाता है.
Yes-No Questions: Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलना
यदि Reported Speech में वाक्य Helping Verb or Auxiliary Verb से शुरू हो, तो उसे Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए निम्न नियम को फॉलो किया जाता है.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verb – say/says to, says / says to, said / said to, को Sentence के अर्थ के अनुसार ask / demand / enqure / want to know, asks / demands / enquires / wants to know, asked / demanded / enquired / wanted to know में बदल दें.
- Inverted Commas के बदले if या Whether का प्रयोग करे
- Interrogative Sentence को Assertive Sentence में change करे.
- Persons को change करने के लिए General Rules को फॉलो करे.
Interrogative to Assertive Rules:
- demand / want to know के बाद Object के पहले of preposition का प्रयोग होता है.
- Whether का प्रयोग एग्जाम में ज्यादातर होता है. इसलिए, If के बदले Whether का प्रयोग करे.
- Question marks के बदले Full Stop का प्रयोग करे.
WH-Questions: Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलना
यदि Reporting Speech में अर्थात Inverted Commas (“….”) के भीतर Wh-Questions का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verbs को sentence के अर्थ तथा Tenses के मुताबिक ask / asks / asked, enquire / enquires / enquired, demand / demands / demanded, want to know आदि में बदले.
- Inverted Commas को हटा कर if / whether आदि का प्रयोग न करे. जिस Interrogative Words / Interrogative Pronouns का प्रयोग हो, उसे ज्यों का त्यों प्रयोग करे.
- अंत में Full Stop का प्रयोग करे.
Note: asked के बाद प्रयुक्त Object के पहले of का प्रयोग नही होता है.
3. Imperative Sentences: Narration
सामान्य रूप से Imperative Sentences से order, command, request, pray, suggest आदि का बोध होता है. जैसे; Bring a glass of water. आदि.
यदि Reported Speech में Imperative sentence का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verbs- Say, Says, Said के बदले निचे दिए गए words को अर्थ के अनुसार बदले:
Imperative Verb का Hindi Meaning
- Inverted Commas को हटाकर “to” का प्रयोग करे.
- Inverted Commas के अन्दर संबोधन के रूप में किसी Noun का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Reporting Verb का Object बना दें.
- Reporting Verb के बाद Object का प्रयोग रहे या ना रहे Indirect Speech में Reporting Verb के बाद Object का प्रयोग अवश्य करे.
- Please, Kindly, Sir, Madam को हटा दें.
- Sir, Madam के स्थान पर Respectfully का प्रयोग करे.
- Reporting Verb के बाद object का प्रयोग हो, तो Sir, madam के स्थान पर Respectfully का प्रयोग object के बाद किया जाता है.
- persons को बदलने के लिए जरूरत के मुताबिक General Rules का प्रयोग करे.
Negative Imperative Sentence
सामान्तः Negative Imperative Sentence “Don’t से शुरू होता है.
Reported Speech में Negative Imperative Sentence का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस प्रकार बदले:
- Reporting Verb-say, says, said को अर्थ के अनुसार ask/asks/asked, tell, tells, told आदि में बदलें
- Inverted Commas को हटा कर not to का प्रयोग करे.
- जरुरत के मुताबिक General Rules का प्रयोग करे.
1. He said to me, “Don’t open the door.” He asked me not to open the door.
2. He said to me, “Don’t disturb me.” He asked me not to disturb him.
Imperative Sentence Forbid का प्रयोग
Reporting Verb को Forbid/forbids/forbade में अर्थनुसार बदल कर और Inverted Commas के बदले to का प्रयोग करे. जैसे;
- Direct: The teacher said to the student, “Don’t make a noise in the class.”
- Indirect: The teacher forbade the student to make a noise in the class.
Let से शुरू होने वाले वाक्य का Indirect Speech
यदि Let से शुरू होने वाले Imperative Sentence से प्रस्ताव या सुझाव का बोध हो, तो उसे Indirect Speech में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
- Propose या suggest के बाद Object का प्रयोग करना हो, तो propose या suggest के बाद तथा object के पहले “to” preposition का प्रयोग निश्चित रूप से होता है.
- we का प्रयोग उस समय करना चाहिए जब Reported स्वयं प्रस्तावित कार्य में शामिल हो.
Let + Wish or Desire वाले वाक्यों का Indirect Speech
यदि Let से शुरू होने वाले Imperative Sentence से wish / desire का बोध हो, तो उसे Indirect speech में इस प्रकार बदला जाता है.
- Reporting Verb को wish / wishes / wished में change करे.
- Inverted Commas के बदले that का प्रयोग करे.
- Let को वाक्य से हटा दें.
- Let के बाद प्रयुक्त Objective Case के Pronouns को Nominative Case में change करे.
- Nominative Case के Pronouns – I, she, he आदि के बाद should +V1 का प्रयोग करे. जैसे
4. Optative Sentence का Indirect Speech
सामान्यतः Optative sentence के वाक्यों से इच्छा, अभिशाप, आशीर्वाद आदि जैसे भावों का बोध होता है.
यदि Reported Speech में Optative sentence का प्रयोग हो, तो उसका Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi निम्न प्रकार बनाया जाता है.
- say, says, said को sentence के अर्थ के अनुसार wish/wished/pray/curse आदि में change करे.
- may को might में change करे.
- Exclamation mark (!) के बदले Full Stop का प्रयोग करे.
- Persons को change करने के लिए General Rules को फॉलो करे. जैसे;
यदि Optative sentence “May” से शुरू न हो, तो “may” को understood करके Indirect speech में बदलना चाहिए. अर्थात, वाक्य में might का प्रयोग करना चाहिए.
5. Exclamatory Sentence: Narration
सामान्यतः exclamatory sentence से हर्ष, घृणा, आश्चर्य, प्रसंशा, संदेह, क्रोध, तिरस्कार, पश्चाताप, आदि जैसे मानसिक भावनाओं का बोध होता है. इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में Oh !, Ah !, Alas !, Hurrah !, Bravo !, Well done!, आदि का प्रयोग भी होता है.
Note: ऐसे वाक्यों में What और How का भी प्रयोग होता है.
Exclamatory Sentence का Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए निम्न प्रक्रिया को फॉलो किया जाता है.
Rule: 1. Reporting Verb – say/says/ said को sentence के अर्थ के अनुसार exclaimed with joy / exclaimed with sorrow आदि में change करे.
Also Read, Parts of Speech in Hindi
Note: Exclamatory Sentence में प्रयुक्त exclamatory words:
- Inverted Commas को हटाकर that का प्रयोग करे
- Interjectional Words – oh, ah, alas जैसे words को हटा दें.
- Exclamation marks को हटाकर full stop का प्रयोग करे.
Note: Exclamatory Sentence को Assertive sentence में change इस प्रकार करे.
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
Direct and indirect speech in hindi exercise.
- Mohan said, “I am very busy now.”
- I said to you, “Did you buy a watch?”
- He said, “The horse has been fed.”
- She said to him, “Can you do this work?”
- “I know her name and address,” said John.
- They said to the boy, ” you sang well.”
- “English is easy to learn,” she said.
- You said, ” Girl is here.”
- He said, “I am writing letters.”
- Pooja said, “Today is fine day.”
- “It is too late to go out,” Alice said.
- She said, “How are you?”
- He said to me, “I don’t believe you.”
- She said, “What are you?”
- He says, “I am glad to be here this evening.”
- I asked her, “Which class do you read in?”
- He said to me, “What are you doing?”
- I said to old man, “Do you like this book?”
- “Where is the post office?” asked the stranger.
- She said, ” I was present.”
- He said, “Will you listen to me?”
- She said to me, “Do you love a lot?”
- Mukesh said to Pooja, “Go away.”
- He said, “I love you”
- She said to me, “Please wait here till I return.”
- She says to them, “This is mine and that is yours.”
- “Call the witness,” said the judge.
- She said to me, “Can you speak English?”
- The speaker said, “Be quiet and listen to my words.”
Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi से सम्बंधित सभी आवश्यक रूल्स, तथ्य एवं परिभाषा यहाँ उपलब्ध किया गया है जो Narration in Hindi को समझने एवं बनाने में मदद करता है. यदि Narration रूल्स से समबन्धित कोई समस्या अभी भी हो, तो कृपया हमें कमेंट अवश्य करे.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Indian Constitution
- Full Form in Hindi
- Hindi Essay
- Synonyms Hindi
- Rules and Other

Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi
इस Lesson में हम आज बहुत ही महत्वपूर्ण Topic को पढ़ेंगे जिसका नाम है Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi अप्रत्यक्ष कथन Indirect Speech यह कुछ छात्रों को बहुत कठिन Lesson लगता है जिसे हम आज अच्छे से बहुत सारे उदहारण के साथ सभी नियमों के साथ समझेंगे जिसके बाद आपको कभी Indirect Speech के Lesson में कोई परेशानी नहीं होगा।
Friends… आप हमारे Telegram Channel से अवश्य जुड़ें यहाँ हर रोज नये English Grammar के Lesson से जुड़े प्रश्न और उत्तर और Images या PDF Version में सभी महत्वपूर्ण SSC, IPS, IAS, Bank परीक्षा में पूछे जाने वाले महत्वपूर्ण Study Content और साथ में GK Questions के बहुत सारे जानकारी उपलब्ध कराई जाती है और साथ में प्रेरणादायक अनमोल वचन, Motivational Videos भी उपलब्ध कराई जाती है।
यहाँ Click करें → Telegram Channel

Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi “किसी की कही गई शब्दों या बात को हम दूसरे व्यक्ति को दो तरीकों से बता सकते हैं। पहला तरीका ये है कि, हम कहने वाले शब्दों या बात को दूसरे व्यक्ति को जैसे के तैसे ही बता सकते हैं; और दूसरा तरीका ये है कि कहने वाले शब्दों को हम दूसरे व्यक्ति को अपने शब्दों में उसके कहे गये अर्थ को बता दें कहें।”
अर्थात “दूसरे शब्दों में कहे गये शब्दों को अपने शब्दों में कहें परन्तु शब्दों का अर्थ बिलकुल बदलना नहीं चाहिए, यही शब्द या वाक्य को ही अप्रत्यक्ष कथन Indirect Speech कहते हैं।”
जब हम प्रत्यक्ष कथन Direct Speech को अप्रत्यक्ष कथन Indirect Speech में परिवर्तन करते हैं तो हमें कुछ नियमों का पालन करना आवश्यक होता है जिससे अप्रत्यक्ष कथन Indirect Speech बनाना आसान हो जाता है। आइये इस नियम को अच्छे से उदाहरण के साथ समझें…
He said , “I am going to cinema now.”
यह Direct Speech का वाक्य है, अब हम इसका Indirect Speech बनाते हैं जिसे आप देखिये;
He said that he was going to cinema.
ऊपर दिए गए उदाहरण से हम कुछ नियमों को समझने की कोशिश करते हैं कि कैसे Direct Speech को हम Indirect Speech में बदल सकते हैं।
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules in Hindi
1. Direct Speech के दो भागों को आपस में जोड़ने के लिए किसी शब्द का प्रयोग पड़ सकता है। जैसे कि ( उदा. में देखिये that का प्रयोग किया गया है। )
2. Indirect Speech के शब्द बनाते समय सर्वनाम Pronoun बदलना पड़ सकता है। जैसे कि ( उदा. में देखिये I को he में बदला गया है। )
3. Indirect Speech के शब्दों बनाते समय कुछ समय काल Tense को भी बदलना पड़ सकता है। जैसे कि ( उदा. में देखिये अपूर्ण वर्तमानकाल Present Continuous Tense को अपूर्ण भूतकाल Past Continuous Tense में बदला गया है। )
इसे अवश्य पढ़ें → Blockchain क्या है
इसे अवश्य पढ़ें → Cryptocurrency Kya Hai क्या है
इसे अवश्य पढ़ें → बिटकॉइन कैसे खरीदें
4. कुछ समय वाक्यों में आवश्यकतानुसार काल Tense को दर्शाने वाले शब्द को और सहायक क्रियाओं Helping Verbs को बदलना पड़ सकता है। जैसे कि ( उदा. में देखिये कि now को then में बदला गया है। )
Indirect Speech बनाते समय कुछ Terms का Use किया जाता है जिसे हमें समझना आवश्यक है, आइये इसे समझें
1. Reporting Verb
Inverted commas के बाहर जो Sentence होता है, उसके क्रिया Verb को Reporting verb कहते हैं । जैसे
He said, “I am going to cinema now.”
इस उदाहरण के वाक्य में said Reporting verb है।
2. Reporting Speech
Inverted commas के अंदर जो Sentence रहता है, उसे Reported Speech कहा जाता है। जैसे
इसे भी पढ़ें → Tense in Hindi
इस उदाहरण के वाक्य में “I am going to cinema now.” Reporting Speech है।
3. Verb of the Reported Speech
Reported speech में उपयोग होने वाला Verb को ही Verb of the Reported Speech कहते हैं । जैसे
इस उदाहरण के वाक्य में going verb of the reported Speech है।
जब हम Direct Speech को Indirect Speech में Change करते हैं तो इसके लिए कुछ General Rules और कुछ Special Rules बनाये गये हैं, General Rules के उन नियमों को हर प्रकार के Sentence के साथ बनाया जाता है, परन्तु Special Rules के विभिन्न प्रकार के Sentence जैसे Assertive, Interrogative, Imperative, Optative, Exclamatory. के लिए अलग अलग Rules होते हैं।
NOTE : सबसे पहले General Rules को समझने के लिए 3 प्रकार में बाँटा गया है जो कि निम्नलिखित है;
1. Change of Person
Direct speech को Indirect speech में बदलने के लिए Reported speech में उपयोग किये गये सर्वनाम Pronouns को निम्नलिखित प्रकार से बदलते हैं;
1. First Person को Reporting Verb के Subject के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
2. Second Person को Reporting Verb के Object के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
3. Third Person को Reporting Verb में कोई भी बदलाव नहीं किय जाता है।
2. Change the Tense
यदि Direct speech को Indirect speech में बदलते समय Reporting verb में Present tense या Future tense हो तो Reported speech के Tense में कोई भी बदलाव नहीं होता है, केवल जरुरत के हिसाब से Pronoun को Change किया जाता है। लेकिन यदि Reporting verb, Past tense में हो तो Reported speech के Tense को निम्नलिखित प्रकार से Change किया जाता है;
और यदि Reporting verb, Past tense में हो तो Reported speech में उपयोग होने वाला Modals और Helping Verbs को निम्नलिखित प्रकार से Change किया जाता है।
3. Change of Other Parts of Speech
Direct speech को Indirect speech में बदलते समय Reporting verb यदि Past tense में हो तो Reported speech में उपयोग होने वाला निकटता सूचक शब्द और दूरी सूचक शब्द और समय को दर्शाने वाले शब्द निम्नलिखित प्रकार से Change किया जाता है।
Narration Rules in Hindi
1. assertive sentences कथनवाचक वाक्य ( rules ), [ a ] reporting verb in present tense and future tense.
1. यदि Reporting Verb, Present Tense में या Future Tense हो, तब Repotred speech के Tense में कोई भी बदलाव नहीं होता है।
2. जब Inverted Commas ( ” …. “ ) के अंदर Assertive Sentence रहता है, तब Indirect Speech में Inverted Commas के बजाय That का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
3. जब Reporting Verb, say / says / said रहे और इसके बाद Object रहता है तो Indirect Speech में इस बदलते समय tell / tells / told में Change किया जाता है। और अगर Object न रहे तो उसे जैसे के तैसे ही रखा जाता है अर्थात कोई बदलाव नहीं होता है।
Modals in Hindi
4. यदि Reported Speech में कोई वाक्य Universal Truth, General Truth, Natural Law प्राकृतिक नियम वाले वाक्यों से सम्बन्ध हो तो Tense में कोई भी बदलाव नहीं होता है।
आइये कुछ उदाहरण से समझते हैं
1. शिवम कहता है कि मैं बहुत खुश हूँ।
1. Shivam says, ” I am very happy.” (Direct)
1. Shivam says that he is very happy. (Indirect)
2. वे लोग कहेंगे कि मैं अच्छा लड़का हूँ।
2. They will say, ” I am a good boy.” (Direct)
2. They will say that he is a good boy. (Indirect)
[ B ] Reporting Verb in Past Tense
1. सोनम ने कहा कि मै दुखी हूँ।
1. Sonam said, ” I am sad.” (Direct)
1. Sonam said that she was sad. (Indirect)
2. शुभम ने मुझसे कहा कि, ” मैं आज स्कूल जा रहा था।”
2. Shubham said to me, ” I was going to school today.” (Direct)
2. Shubham told me that he had been going to school that day. (Indirect)
3. सुनिधि ने रचना से कहा मैं अगले सप्ताह मुंबई जाउंगी।
3. Sunidhi said to Rachna, ” I shall go to Mumbai next week.” (Direct)
3. Sunidhi told Rachna that she would go to Mumbai the following week. (Indirect)
2. Interrogative Sentences प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य ( Rules )
Interrogative Sentences का प्रयोग मुख्यतः वाक्य में प्रश्न पूछने के लिए किया जाता है। General Rules के अनुसार से Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में Change करते समय निम्नलिखित Rules को Follow करते हैं;
1. Reporting Verb में say के स्थान में ask, enquire, want to know या wonder में परवर्तित किया जाता है, लेकिन अगर say to का परिवर्तन सिर्फ ask में किया जाता है और said का परिवर्तन asked में किया जाता है।
2. Inverted commas ( “…” ) को हटा दिया जाता है और Reported speech के पहले if या whether वाक्य का प्रयोग करते हैं, परन्तु if या whether का प्रयोग तभी होगा जब Interrogative Sentence किसी Verb से शुरू होता है।
3. Indirect speech में Tense और Pronoun आदि का परिवर्तन Assertive Sentence की तरह ही किया जाता है।
4. सबसे महत्वपूर्ण बात ये कि वाक्य के अंत में Interrogative Sign ( ? ) के स्थान पर Full Stop ( . ) का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
5. Inverted commas ( “…” ) के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता है, लेकिन अगर Sentences की शुरुआत Question word ( what / when / how / where / who … etc ) से हो तो that के स्थान पर उस जगह में प्रयुक्त Question word का ही प्रयोग होता है।
1. उसने मुझसे कहा कि क्या तुम गुस्सा हो ?
1. He said to me, ” Are you angry ?” (Direct)
1. He asked me if / whether I was angry. (Indirect)
2. मैंने सुनिधि से कहा कि तुम क्या चाहती हो ?
2. I said to Sunidhi, ” What do you want ?” (Direct)
2. I asked Sunidhi what she wanted. (Indirect)
इसे भी पढ़ें → Preposition in Hindi
3. राम ने मुझसे कहा कि तुम्हारा क्या नाम है ?
3. Ram said to me, ” What is your name ?” (Direct)
3. Ram asked me what my name was. (Indirect)
3. Imperative Sentences आज्ञावाचक वाक्य ( Rules )
Imperative Sentences का प्रयोग मुख्यतः Order ( आदेश ), Advice ( सलाह ) Request ( अनुरोध ) Prohibition ( निषेध ) के अर्थ की भावना को व्यक्त करने के लिए Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में Change करते समय निम्नलिखित Rules को Follow करते हैं –
1. Reporting Verb को Sense के अनुसार से order, command, tell, ask, forbid, request, implore, beg, entreat, advise, remind, warn, encourage शब्दों को Indirect speech में Change किया जाता है।
2. इन क्रियाओं के साथ Object साथ में होना चाहिए। जैसे कि He ordered to go. लेकिन ये सही नहीं होगा, बल्कि इसे हमें कहना होगा He ordered me to go. इसलिए अगर Direct speech के वाक्य में आज्ञा किसे दिया गया है इसका उल्लेख नहीं भी होता है तब भी हमें दिए गये वाक्य में Verb के अनुसार से Object लिखना होता है।
3. Direct speech में Reporting Verb के बाद Object रहे या ना रहे Indirect speech में Reporting Verb के बाद Object हमेशा दिया जाता है।
4. Inverted commas ( “…” ) को हटा कर उसके स्थान पर to या not to कर दिया जाता है।
1. शिक्षक ने छात्र से कहा कि एक पेन लाओ।
1. The teacher said to the student, ” Bring a pen.” (Direct)
1. The teacher ordered the student to bring a pen. (Indirect)
2. मेरे पिताजी ने शुभांगी से कहा कि चुप रहो।
2. My father said to Shubhangi, ” Keep quiet.” (Direct)
इसे भी पढ़ें → Simple Present Tense in Hindi
2. My father ordered Shubhangi to keep quiet. (Indirect)
3. पिताजी ने अपने बेटे से कहा कि शराब का सेवन मत करो।
3. The father said to his son, ” Don’t drink wine.” (Direct)
3. The father prohibited his son from drink wine. (Indirect)
4. Optative Sentences प्रार्थना वाचक वाक्य ( Rules )
Optative Sentence का प्रयोग Prayer ( प्रार्थना ), Wish ( इच्छा ), Blessing ( आशीर्वाद ), या Curse ( अभिशाप ) आदि के भावना को व्यक्त करते समय Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में Change करते समय निम्नलिखित Rules को Follow करते हैं
1. Reporting Verb में say / said को Sentence के Sense के अनुसार pray / prayed / wish / wished / bless / blessed / curse / cursed में Change किया जाता है।
2. Inverted Commas को हटा कर that का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
3. Optative Sentence को Assertive Sentence में Change कर दिया जाता है, मतलब Subject के बाद Verb का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
4. वाक्य के अंत में Exclamation Sign ( ! ) को हटा कर Full Stop ( . ) का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
1. माँ ने मुझसे से कहा कि तुम दीर्घायु रहो !
1. The mother said to me, ” May you live long.”
1. The mother blessed me that i might live long.
2. पिताजी ने मुझसे से कहा कि भगवान तुम्हारा भला करे !
2. The father said to me, ” May God bless you.”
2. The father wished taht God might bless me.
इसे भी पढ़ें → Solar System in Hindi
5. Exclamatory Sentences विस्मयादिबोधक वाक्य ( Rules )
Exclamatory Sentence का प्रयोग joy ( ख़ुशी ), sorrow ( दुःख ), Surprise ( आश्चर्य ), Anger ( गुस्सा ), contempt ( घृणा ), Applause ( प्रशंसा ), Regret ( अफ़सोस ) आदि के भावना को व्यक्त करते समय Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में Change करते समय निम्नलिखित Rules को Follow करते हैं;
1. Reporting Verb में say / says / said को Sentence के Sense के अनुसार से हमें वाक्य में आवश्यकतानुसार exclaimed with joy, exclaimed with sorrow, exclaimed with surprise, exclaimed with anger, exclaimed with contempt, exclaimed with applause, exclaimed with regret आदि शब्दों में परिवर्तित किया जाता है।
2. Inverted Commas को हटा कर उसके स्थान पर that का Use किया जाता है।
3. Ah! Oh! Alas! Bravo! Hurrah! आदि शब्दों को दिए गये Sentence से हटा दिया जाता है।
4. Sentence के अंत में Exclamation sign ( ! ) को हटा कर Full Stop ( . ) का Sign का Use करते हैं।
5. कभी कभी किसी वाक्य में Inverted Commas के अंदर में अधूरे या छोटे वाक्य होते हैं, तब उस स्थिति में आवश्यकतानुसार हमें कोई उचित Verb / Adjective / Adverb / Pronoun का प्रयोग करना पड़ सकता है जिससे कि वाक्य में अर्थ पूरी तरह बना रहे।
आइये कुछ उदाहरण से समझते हैं;
1. सूर्या ने कहा कितना सुन्दर पेन है ये !
1. Surya said, ” How beautiful this pen is !” (Direct)
1. Surya exclaimed with joy that that was a very beautiful pen. (Indirect)
2. सुहाना ने कहा कितना अजीब लड़का है वह !
2. Suhana said , ” What a peculiar boy he is !” (Direct)
2. Suhana exclaimed with surprise that he was a very peculiar boy. (Indirect)
इसे भी पढ़ें → Adverb in Hindi
3. Nonsense ! (Direct)
3. It is nonsense. (Indirect)
4. Enough ! (Direct)
4. It is enough. (Indirect)
5. What a fall ! (Direct)
5. It is a big fall. (Indirect)
Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi & Narration Rules in Hindi
के इस Lesson में अगर आपको कोई समस्या है तो आप हमें Comment Box में पूछ सकते हैं और ये Lesson आपको पसंद आया तो इसे आप अपने दोस्तों के साथ Share कर सकते हैं जिससे आपके दोस्त को भी ये Lesson समझने में मदद मिले।
Thank You … Friends
Table of Contents
Similar Articles
Present continuous tense sentences in hindi, active and passive voice in hindi.
Direct and indirect speech very nice ???? solution thanks
Thank You ! Reshma ji
Thank u sir ji .. bahut achhe se aapne karwaya hai
Wahhh ! Ye To Acchi Baat Hai. Ki Aapko Concept Samajh me AAA Gaya. Hume Khushi Ki Aapki Help Ho Payi.
KYA MATLAB ?
Samajh thoda sa aaya
Ok… Good
Sir apne chote word me sb kuch smja diya TX sir
OK Good… anu
So helpful ????Thnqqq????
Hame Bahut Khushi Hai Aapki Help Karke …
Thank you so much mam esse hamara bahut help hua saare concept samjh aa gaye????????
Aapka Swagat Hai … Megha Sister … Hame Khushi Hai Ki Aapki Hamne Help Ki …
Kya concept likhe ho yrrr maja aa gaya Thanks ???? shuhana
Thank You ! Dear Kunal … Hame Bahut Khushi Hai Aapki Help Karke.
Very nice ???? I am also an English teacher
Thank You! Sir
Thanks❤????????
Welcome Meena ji
Thank you ???????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????? ???????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????? ????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????♥️♥️♥️
सच बता रहा हूं कसम से पहले मैंने जितना पढ़ा था समझ में नही आता था पर जब मैंने इसको पढ़ा तो एकदम अच्छे से समझ आ गया पूरा डाउट क्लियर हो गया थैंक्स मैम
It’s very good ????????
Thankyou so much sir ji ????????????????
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Popular Articles
पार्वती का पर्यायवाची शब्द, प्रभु का पर्यायवाची शब्द, antariksh ka paryayvachi shabd.
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © HindiToEnglish

Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi- Meaning, Example & Rules
हम यहाँ Hindi To English Grammar के इस चपेटर में English के Sentences अर्थात Direct Indirect को Indirect Speech में बदलना / परिवर्तित करना उदाहरण के साथ में सीखेंगें | Direct and Indirect speech In Hindi
Direct or Indirect Speech
Direct और indirect speech से तात्पर्य यह होता है कि जब कोई कथन वक्ता द्वारा श्रोता से प्रत्यक्ष रूप से कह दिया जाता है या उस बात को श्रोता तक वक्ता के कहेनुसार ही पहुंचा दिया जाता है। तब उसे Direct speech कहते हैं। जबकि वक्ता द्वारा कही गई कोई बात श्रोता तक दूसरे व्यक्ति के शब्दों के माध्यम से पहुंचाई जाए। तब उसे indirect speech कहते हैं। सरल शब्दों में, जब कोई बात वक्ता द्वारा सामने वाले व्यक्ति से प्रत्यक्ष ही कह दी जाती है। तब उसे Direct speech कहते हैं। जबकि एक तरीका यह भी होता है कि हम सामने वाले की बात को अपने शब्दों के माध्यम से दूसरे तक पहुंचाते हैं, तब उसे indirect speech कहते हैं।
Example –
- Direct speech – Ram said, ”I am going to school”. (राम ने कहा, मैं स्कूल जा रहा हूं।)
- Indirect speech – Ram said that He was going to school. (राम ने कहा कि वह स्कूल जा रहा था।)
उपरोक्त पहले उदाहरण में, वाक्य के दो भाग हैं। जिन्हें inverted commas (” “) के भीतर रखा गया है। यहां Ram said को reporting speech कहते हैं। जबकि I am going to school, reported speech कहलाएगा।
Reporting speech के तीन भाग होते हैं।
- Reporter – उपरोक्त उदाहरण में Ram एक reporter है। जिसके द्वारा बात कही गई है।
- Reporting verb – जिस काल या क्रिया के माध्यम से reporter द्वारा बात कही जाती है, उसे reporting verb कहा जाता है। जैसे – said या say.
- Reporting object – उपरोक्त उदाहरण में ram said के बाद यदि किसी व्यक्ति का name या pronoun लगा होता है, जिससे वक्ता द्वारा कोई बात कहीं जाती है। तो उसे reporting object कहते हैं।
Rules of Direct or Indirect Speech
Direct से indirect बनाते समय कुछ नियमों को ध्यान में रखना आवश्यक है।
- Direct से किसी वाक्य को indirect speech में बदलते समय inverted commas हटा दिए जाते हैं।
- साथ ही Direct से indirect में बदलते समय reporting speech और reported speech को that लगाकर जोड़ा जाता है।
- Direct से indirect बदलते समय जब reporting speech में verb present और future में होती है, तब आगे reported speech का verb नहीं बदलता है। He says, “I am poor”. – He says that he is poor. अगर say/says के साथ आगे object लगा हो तब इसे tell/tells में बदल देते हैं। जबकि past में said/ said to को told में बदलते हैं।
- Reported speech में यदि subject Third person हो तब उसे indirect में बनाते समय कोई बदलाव नहीं किया जाता है। जबकि first person को reporting speech के subject और second person को object के अनुसार बदलते हैं। Pooja said to me, ” I am going to Mumbai”. – Pooja told me that she was going to Mumbai. यहां Reported speech के subject में प्रयुक्त I (First person) को reporting speech के subject (pooja) के object से परिवर्तित किया गया है।
- Direct से indirect बनाते समय सार्वभौमिक सत्य (universal truth), आदतें (habits), कहावतें (proverb) इत्यादि नहीं बदलते हैं।
- Present indefinite Tense को past indefinite Tense में बदला जाता है।
- Present continuous Tense को past continuous Tense में बदला जाता है।
- Present perfect Tense को past perfect Tense में बदला जाता है।
- Present perfect continuous Tense को past perfect continuous Tense में बदला जाता है।
- Past indefinite Tense को past perfect Tense में बदला जाता है। जबकि past continuous Tense को past perfect continuous Tense में बदलते हैं।
इसके अलावा, past perfect और past perfect continuous Tense में कोई बदलाव नहीं किया जाता है। साथ ही future के भी किसी प्रकार को नहीं बदला जाता है।
Direct से indirect बनाते समय जब reported speech में Future प्रदर्शित करने वाले शब्द आएं। तब उन्हें निम्न प्रकार से बदला जाता है।
- Will – would
- Shall – should
- Can – could
- May – might
इसके अलावा अन्य शब्दों को भी बदला जाता है।
- This – That
- Now – Then
- Hence – Thence
- These – Those
- Here – There
- Thus – So
- Today – That day
- Tomorrow – The next day
- Tonight – That night
- Yesterday – The day before
- A year ago – A year before
- Next day – The following day
Examples of Tenses
Present Indefinite Tense/ Past Indefinite Tense You said to me, “I do not love to read”. You told me that you did not love to read.
Present continuous tense/ past continuous tense Geeta said to me, “I am reading newspaper”. Geeta told me that she was reading newspaper.
Present perfect tense/ past perfect tense Ram said, “I have already paid him”. Ram said that He had already paid him.
Present perfect continuous Tense/ past perfect continuous Tense Reena said to me, “I have been sleeping for 2 hours”. Reena told me that she had been sleeping for 2 hours.
Past indefinite Tense/ past perfect Tense He said to me, “I went there yesterday”. He told me that he had gone there the previous day.
Past continuous Tense/ past perfect continuous Tense He said to me, “I was thinking about you”. He told me that he had been thinking about me.
इसके साथ ही Interrogative sentence के साथ reporting speech में said की जगह asked का प्रयोग होता है। साथ ही question words को reporting speech और reported speech को जोड़ने के तौर पर प्रयोग में लाया जाता है और वाक्य को साधारण बना दिया जाता है।
I said to him, “what are you doing?” I asked him what he was doing.
जबकि imperative Sentence में reporting speech और reported speech को to लगाकर जोड़ा जाता हैं। साथ ही said to को वाक्य के भाव के अनुरूप बदला जाता है।
Father said to me, “Give me your pen”. Father ordered me to give him my pen.
Optative Sentence में भी reporting speech और reported speech को that लगाकर जोड़ा जाता है। साथ ही वाक्य को साधारण वाक्य में बदला जाता है। और said के स्थान पर wished/blessed का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
The sadhu said to me, “may god bless u!” The sadhu wished me that God might bless me.
Exclamatory Sentence में भी reporting speech और reported speech को that लगाकर जोड़ा जाता है और वाक्य को साधारण बनाया जाता है। साथ ही said/ said to के स्थान पर exclaimed लगाते हैं।
He said, “what a pleasant surprise it is!” He exclaimed with surprise that it was a pleasant.
आशा करते हैं कि आपको हमारे द्वारा दी गई उपरोक्त जानकारी अवश्य पसंद आई होगी। ऐसे ही अन्य ज्ञानवर्धक लेख पढ़ने के लिए हमें फॉलो करना ना भूलें।

अंशिका जौहरी
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
most recent

जीवन के अनमोल वचन | Life Anmol Vachan

How to become rich? अमीर बनना चाहते हैं, तो अपनाएं ये 5 आदतें


Facts , Motivational
Self discipline बढ़ाने के 10 तरीके.

महाभारत युद्ध के समय भगवान श्रीकृष्ण प्रतिदिन मूंगफली क्यों खाते थे?

भगवान श्री राम को 14 वर्षों का ही वनवास क्यों मिला?

Religious , Mahabharat
जानिए महाभारत के उन 12 योद्धाओं के बारे में, जो युद्ध के बाद जीवित बचे थे.
Dharm | Mahabharat | Motivational | Quotes | Jivani | Hindi Grammar | Nibandh | English Grammar
Trending Articles
Free SEO Course in Hindi | Free Blogging Course in Hindi | Education Quotes in Hindi | जीवन के अनमोल वचन | Mahabharat Quotes in Hindi | Mahabharat Story in Hindi | Ganesh Quotes | Jivani kya hai | Motivational Poems in Hindi | Krishna Quotes in Hindi
About Us | Contact Us | Disclaimer | Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy | Affiliate Disclosure © 2024 Gurukul99
[ Narration ] Direct and Indirect Speech Rules, Example in Hindi
तो दोस्तों आज हम एक ऐसे विषय पर चर्चा करेंगे जो कुछ छात्रों को थोडा कठिन लगता है जो है Reported Speech (Direct-Indirect Narrations) in Hindi . हम आपको Narration with Rules and Examples के साथ बताएँगे। जिससे आपको Narration in Hindi आसानी से समझ आ सके।

Table of Contents
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules, Example in Hindi
तो सबसे पहले जानते है Narration Meaning in Hindi -Narration का शाब्दिक अर्थ होता है -‘ कथन ‘। Narration शब्द की उत्पत्ति अंग्रेजी भाषा के शब्द Narrate से हुई है ,जिसका शाब्दिक अर्थ होता है -कहना (to say / to state )।
हम किसी के द्वारा कही गयी बातों को किसी से दो तरह से बता सकते हैं- एक को Direct Speech(प्रत्यक्ष कथन ) कहते हैं तथा दूसरे को Indirect Speech (अप्रत्यक्ष कथन ) । आइये अब जानते हैं कि Direct and Indirect Speech (प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन ) क्या होता है ।
- Direct Speech /Direct Narration (प्रत्यक्ष कथन) :- जब वक्ता द्वारा कही गयी बात को ज्यों का त्यों (हू -ब-हू) किसी को व्यक्त करते हैं ,तो उसे Direct Narration कहा जाता है। Direct Narration को Inverted Commas में बंद किया जाता है। जैसे-She said to me,”I am going to Jaipur”. Sachin said to Lavi,”I shall go to college tomorrow”.
- Indirect Speech / Indirect Narration(अप्रत्यक्ष कथन) :- जब हम वक्ता द्वारा कहे गये कथन को अपने शब्दों में व्यक्त करते हैं तो उसे Indirect Narration कहते हैं। जैसे -He said that he was going to college.ध्यान रखें -Indirect Narration में वक्ता के कथन का अर्थ नही बदलता है केवल कथन का तरीका बदल जाता है
Parts of Narration in Hindi with Examples-
Narration में Direct Speech के दो भाग होते हैं- 1.Reporting Speech 2.Reported Speech .
Reporting Speech क्या है ?
Direct Speech का वह भाग जो Inverted Commas(“….”) के बाहर होता है उसे Reporting Speech कहते हैं। जैसे – Ragini said to me ,”I am going to Jaipur”. इस वाक्य में ‘ She said to me ‘ Reporting Speech है।
Reporting Speech के भाग | Parts of Reporting Speech
Reporter :- वक्ता अर्थात कथन कहने वाले को Reporter कहा जाता है ,उपरोक्त वाक्य में Ragini को Reporter कहा जाएगा। Reporting Verb :- वक्ता द्वारा जिस Verb का प्रयोग किया जाता है उसे Reporting Verb कहते हैं। उपरोक्त वाक्य में Reporting Verb ‘said’ है। Reporting Object :- वक्ता कथन जिससे कह रहा है ,उस object को Reporting Object कहते हैं, उपरोक्त वाक्य में Reporting Object ‘me’ है।
Reported Speech क्या है ?
Direct Speech का वह भाग जो Inverted Commas(”….’) के अन्दर होता है , उसे Reported Speech कहा जाता है।
जैसे – Sachin said to Lavi ,” I shall go to college tomorrow “. इस वाक्य में inverted commas(“…”) के अन्दर के वाक्य “ I shall go to college ” Reported Speech है।
Reported Speech के भाग | Parts of Reported Speech
Verb of Reported Speech :- Reporting Speech (Inverted commas के अन्दर के वाक्य ) की verb को Verb of Reported Speech कहा जाता है ,उपरोक्त वाक्य में ‘ shall go ‘ Reported Speech की Verb है।
Rules of Changing Direct Speech into Indirect Speech in Hindi-
आइये अब जानते हैं की DIrect Narration को Indirect Narration में बदलने के नियम । Direct Speech को Indirect Speech में परिवर्तन के नियमों को दो भागों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है –
- General Rules(सामान्य नियम ) :- वो नियम जो सभी प्रकार के वाक्यों पर साधारणतया लागू होते हैं।
- Specific Rules(विशेष नियम ) :- वो नियम जो अलग अलग प्रकार के वाक्यों के लिए अलग -अलग हैं।
DIrect Speech को Indirect में बदलने के General Rules-
Rule-1 Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में परिवर्तन होने पर Inverted Commas हटा दिए जाते हैं।
Rule-2 उसके बाद Reporting Verb का Tense देखें –
यदि Direct Narration में Reporting Verb, Present या Future tense में है तो Indirect में परिवर्तन करते समय Reported Speech के tense में कोई परिवर्तन नही किया जाता है।
Reporting Verb के Past, में होने की स्थिति में निम्नलिखित प्रकार से Tense में परिवर्तन किया जाता है –
Rules for Change in Future Sentences (Reported Speech)
Rule-3 . Indirect Speech में परिवर्तन होने पर Reported Speech के Persons का परिवर्तन निम्न प्रकार से होता है –
First Person :- Reporting verb के subject के अनुसार बदलता है।
Second Person :- Reporting verb के object के अनुसार बदलता है।
Third Person :- इसमें कोई परिवर्तन नही होता है।
Person :-का परिवर्तन करते समय यह ध्यान रखें की यदि person बहुवचन है तो परिवर्तन बहुवचन के अनुसार होगा। यदि Person ,Possessive case में है तो परिवर्तन उसी के अनुसार होगा। Person का परिवर्तन Direct से Indirect में परिवर्तन का एक महत्वपूर्ण भाग है ,ध्यान रखें कि Person का number एवं case नही बदला जाता है। Pronouns का परिवर्तन निम्न table के अनुसार होता है। Forms of Personal Pronouns:-
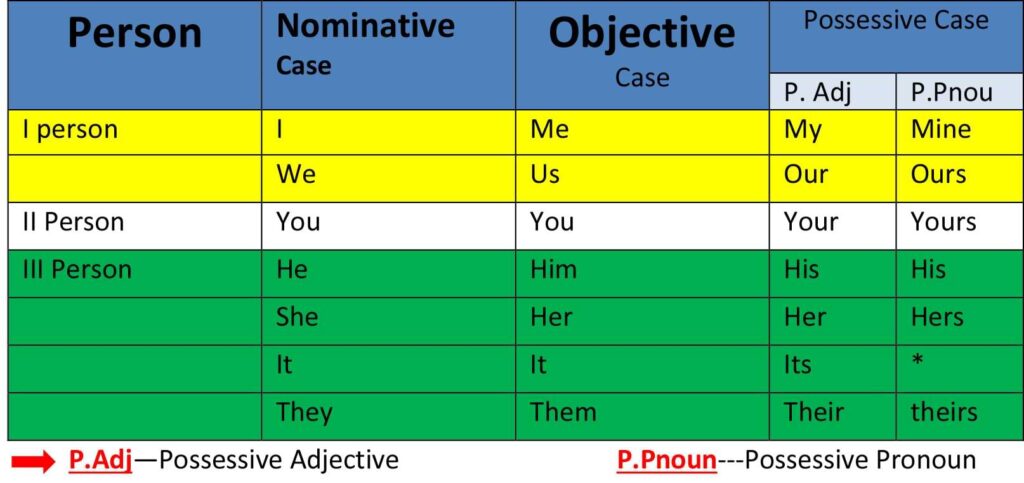
Rule-4 .यदि Reporting Verb say,says,will say या said रहे तो Indirect Speech में भी say,says,will say या said ही रहेगी ,लेकिन यदि Reporting verb के साथ ‘to’ लगा हो तो परिवर्तन निम्न प्रकार से होता है – say to—-tell says to—tells said to—told
Rule-5 Indirect Speech में बदलने पर पर Reporting Verb के बाद सामान्य वाक्यों में that का प्रयोग किया जाता है। उक्त नियमों को ध्यान में रखते हुए निम्न वाक्यों का Direct से Indirect में परिवर्तन पर ध्यान दें – Direct :-He says,”I am going to Jaipur.” Indirect :-He says that he is going to Jaipur.
- Direct से Indirect बनाते समय सबसे पहले देखें की Reporting verb का Tense क्या है। यह Present tense है। अतः Reporting Speech के tense में कोई परिवर्तन नही होगा।
- Reporting verb ,says है। अतः Indirect में भी says ही रहेगी।
- Reported Speech में ,I First Person pronoun है जो की Subject(he) के अनुसार बदलकर I का He हो जाएगा और am,verb बदलकर is हो जायेगी।
Direct :- She says to me,”You are writing a letter to him.” Indirect :-She tells me that I am writing a letter to him.
- उपरोक्त वाक्य में Reporting Verb ,says to बदलकर tells हो जायेगी।
- Reported Speech में you एवं him ,II एवं III person pronouns हैं। II person pronoun(you)-object के अनुसार बदलता है। अतः object’me ‘ के अनुसार I हो जाएगा ,III person pronoun–him में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होगा।
Rule-7 जब Reporting Verb,Past Tense में हैं तो Reported Speech में आये कुछ शब्दों में परिवर्तन होता है ,जैसे –
Tensewise Solved Examples of Direct-Indirect Narration
Present Indifinite:-
Direct -He said to me,”I never eat sweets.” Indirect -He told me that he never ate sweets. Present Continuous:-
Direct -Ram said to Shyam,”I am watching T.V.” Indirect-R am told Shyam that he was watching T.V.
Present Perfect:-
Direct -Sita said,”I have already cooked.” Indirect -Sita said that she had already cooked.
Present Perfect Continuous:-
Direct – Sonu said to me,”I have been reading for an hour” Indirect- Sonu told me that he had been reading for an hour.
Past Indefinite;-
Direct -She said to Ram,”I went to Jaipur last week.” Indirect- She told Ram that she had gone to Jaipur the previous week
Past Continuous:-
Direct -She said to me,”I was waiting for you.” Indirect -She told me that she had been waiting for me.
Past Perfect:-
Direct -He said to me,”I had completed my project.” Indirect- He told me that he had completed his project .
Past Perfect Continuous:-
Direct -He said,”I had been playing chess for two hours” Indirect -He said that he had been playing chess for two hours.
Future Indefinite:-
Direct -Ram said to Meena,”I shall write a letter.” Indirect- Ram told Meena that he would write a letter.
Future Continuous:-
Direct -Rahim said to Ram,”Sita will be waiting for you.” Indirect- Rahim told Ram that Sita would be waiting for him.
Future Perfect:-
Direct -Sita said to Ram,”I will have completed my work.” Indirect- Sita told Ram that she would have completed her work.
Future Perfect Continuous:-
Direct -Nisha said to me,”I shall have been reading the book.” Indirect -Nisha told me that she wold have been reading the book.
नियमानुसार यदि Reporting verb,Past Tense में हैं तो Reported speech वाक्य का Tense, नियमानुसार परिवर्तित किया जाता है। लेकिन इस नियम के कुछ अपवाद हैं, यदि Reported Speech में कोई –
- Universal Truth(सर्वकालिक सत्य)
- Proverb(कहावत )
- Mathematical fact(गणितीय तथ्य)
- Historical fact(ऐतिहासिक तथ्य)
- Habitual Act(आदतन क्रिया )
- Morality(नैतिकता )
का सन्दर्भ हो तो ऐसे वाक्यों का Reporting Verb .Past tense में होते हुए भी इनका Tense नही बदलता है। Examples:
Direct -He said,”The sun sets in the west.” Indirect -He said that the sun sets in the west.
Direct -The teacher said,”India became Republic on 26th January 1950″ Indirect -The teacher said that India became Republic on 26th January,1950. Direct -She said ,”Two and two is four” Indirect -She said that two and two is four.
Direct -He said,”London is the capital of U.K.” Indirect -He said that London is the capital of U.K. Direct -He said,”Mr Narendra Modi is the P.M. of India” Indirect -He said that Mr.Narendra Modi is the P.M of India.
Direct -He said to me,”I go for a walk daily.” Indirect -He told me that he goes for a walk daily.
Direct -The teacher said,”Something is better than nothing.” Indirect -The teacher said that something is better than nothing.
वाक्य नं.4 और 5 में यदि कोई परिवर्तन नही हुआ है तो(अर्थात U.K की राजधानी और भारत के प्रधानमंत्री नही बदले हैं तो Reported Speech के Tense में कोई परिवर्तन नही होता है यदि परिवर्तन हो गया हो तो Tense नियमानुसार बदल देते है .
Interrogative Sentences को Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
Optative Sentences को Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
Imperative Sentences को Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
16 thoughts on “[ Narration ] Direct and Indirect Speech Rules, Example in Hindi”
Ek number padaya maja aagya
Thanku so much kl mera exam hai or aapne meri bhut help ki
Oho! Kis class mai hai aap
Fablous knowledge
Thanku aajtak smjh nhi aaya..aapne acha smjhaya thanku sir 🙏🙏
Genral english puri pdf dal do sir/madem
Absolutely right this rule 💫💫💫😍
Very nice 🇮🇳🇮🇳🇮🇳🇮🇳🇮🇳🇮🇳
Thank you sir
Thanks sir, tomorrow is my exam this helps me
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Ads Blocker Detected!!!
We have detected that you are using extensions to block ads. Please support us by disabling these ads blocker.
Angreji Masterji
Become Your Own Boss
Direct And Indirect Narration In Hindi
आज आप इस पोस्ट के माध्यम से सीखने जा रहे हैं Direct and indirect narration in Hindi ; यदि आप इस पोस्ट को मन लगाकर पूरा पढ़ते हैं और इसमें दिए गए सभी Rules और examples को ध्यान से समझते हैं; तो आपके लिए किसी भी Tense के वाक्य को Direct से indirect में बदलना आसान नहीं बहुत आसान हो जाएगा.
आगे बढ़ने से पहले हम यह जान लेते हैं कि Direct and indirect narration in Hindi में क्या कहते हैं – Direct narration को हिन्दी में ‘प्रत्यक्ष कथन’ और Indirect narration को ‘अप्रत्यक्ष कथन’ कहते हैं;

मतलब वक्ता के शब्दों को व्यक्त करने की कला को अंग्रेजी में ‘Narration’ कहते हैं; चलिए अब हम इनके बारे में एक-एक कर विस्तार से जानेंगे और Direct speech से Indirect speech बनाना सीखेंगे.
Learn Direct And Indirect Narration In Hindi With Rules And Examples
चलिए Direct and indirect narration in Hindi में सबसे पहले हम जानते हैं कि Direct speech क्या होता है – जब वक्ता की बात को ठीक उसी के शब्दों में प्रकट कर दिया जाता है तो उस कथन (Narration) को अंग्रेजी में Direct speech कहते हैं;
जैसे – My father said, “I watch the movie” ध्यान दीजिए इस वाक्य में – पिता जी कहते हैं कि “मैं मूवी देखता हूँ.” जब हम इसी वाक्य को Indirect speech में बोलेंगे तो इस प्रकार बोलेंगे – Father said that he watched the movie – पिता जी ने कहा कि वे मूवी देखते थे.
इस बात पर ध्यान दीजिए – Direct speech के दो भाग होते हैं पहला Reporting part और दूसरा Reported speech ; चलिए अब इनके बारे में अच्छे से पढ़ते और समझते हैं.
- Reporting Part – वक्ता की बात को जिस Subject, Verb और object से शुरू करते हैं; उसे Reporting parts कहते हैं और इस Part को Inverted Commas ( “……. ”) के बाहर रखते हैं; जैसे – He said to me, “I am going to market.” – इस वाक्य में (He said to me) Reporting parts है.
- Reported Speech – जो कुछ वक्ता के द्वारा कहा जाता है उसे Reported speech कहते हैं. इसको Inverted Commas (“….”) के अन्दर लिखा जाता है; जैसे – He said to me, “I am going to market.” – इस वाक्य में ( “I am going to market.” ) Reported speech है.
Direct speech के कुछ महत्वपूर्ण नियम हैं जिन्हें आपको याद रखना चाहिए –
- वक्ता की कही हुई बात को Inverted Commas के अंदर लिखा जाता है; जैसा कि ऊपर हमने आपको बताया है.
- जो शब्द Inverted Commas में बंद होते हैं उन्हें Reported speech कहा जाता है; इसका पहला शब्द Capital Letter (बड़े अक्षर) से शुरू होता है.
- जो Verb (क्रिया) Inverted Commas के बाहर होता है वह Reporting verb कहलाता है; यह क्रिया Reported speech के बारे में बताती है.
- Reporting Verb का Tense कभी नहीं बदलता है.

चलिए अब हम Direct and indirect narration in Hindi पोस्ट में सीखते हैं कि Indirect speech क्या होता है; और इसका प्रयोग कैसे किया जाता है; तो चलिए बिना देर किए हम आगे बढ़ते हैं और सीखना शुरू करते हैं.
Indirect Speech – जब हम वक्ता की कही हुई बात को अपने शब्दों में कहते हैं मतलब वक्ता की बात को बदलकर अपने शब्दों में प्रकट करते हैं तो इसे Indirect Speech कहते हैं; जैसे – He told me that he was going to market.
Indirect Speech के इन नियमों को ध्यान से सीखें ताकि आप Direct speech को Indirect speech में बदल सकें –
- इसमें कोई Inverted Commas नहीं होते और वक्ता के कथन को बदलकर लिखा जाता है.
- Reported speech का पहला अक्षर Capital नहीं होता.
- Reporting part के बाद कोई Commas नहीं लगाया जाता.
- Reported speech के पहले नियमानुसार Conjunction ‘that, if, to’ का प्रयोग किया जाता है.
- पुरुषवाचक सर्वनाम (Personal Pronouns) और Reported speech की क्रिया में नियमानुसार कुछ परिवर्तन होता है.
Rules For Changing Direct Speech Into Indirect Speech – Direct forms को Indirect में बदलने के लिए जो नियम हैं नीचे दिए जा रहे; जिन्हें आप ध्यान से समझें ताकि आपको Direct से Indirect बनाते समय कोई गलती ना करें.
(1) Change In Pronouns (सर्वनामों में परिवर्तन) – Reported speech के First person pronoun (प्रथम पुरुष सर्वनाम) I, We, My, Mine, Us, Our, Ours को Reporting verb के Subject (कर्ता) के अनुसार बदला जाता है; नीचे कुछ उदाहरण दिए जा रहे हैं जिन्हें ध्यान से समझेें.

- Direct : He said, “I am a good boy.” Indirect : He said that he was a good boy.
- Direct : My mother said, “I am going to market.” Indirect : My mother said that she was going to market.
- Direct : They said, “We have watched this movie.” Indirect : They said that they had watched that movie.
- Direct : Gita said, “This is my home.” Indirect : Gita said that that was her home.
- Direct : She said, “I am an English teacher.” Indirect : She said that she was an English teacher.
- Direct : My father said, “I am not going to college.” Indirect : My father said that he was not going to college.
चलिए अब हम और आगे बढ़ते हैं और Direct and indirect narration in Hindi पोस्ट में दिए गए सभी नियमों को अच्छे से पढ़ते हैं और Direct से Indirect speech बनाना सीखते हैं.
Reported Speech के Second Person Pronoun (मध्यम पुरुष सर्वनाम) You को Reporting verb के object या उसके बाद आए हुए Noun या Pronoun के अनुसार बदल देते हैं; जैसे नीचे कुछ उदाहरण दिए गए हैं.
- Direct : He said to me, “You are a good student.” Indirect : He told me that I was a good student.
- Direct : She said to her father, “You will go to the office.” Indirect : She told her father that he would go to the office.
- Direct : Neha said to me, “I study at home daily.” Indirect : Neha told me that she studied at home everyday.
- Direct : My mother said to me, “You will not do a job in this company. Indirect : My mother told me that I would not do a job in that company.
Reported Speech में आए हुए Third person pronoun (अन्य पुरुष सर्वनाम) He, She, It, They, Them, आदि में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता है, जैसे –
- Direct : Sohan said, “He is a good teacher.“ Indirect : Sohan said that he was a good teacher.
- Direct : All teachers said to us, “They will not go to college.” Indirect : All teachers told us that they would not go to college.
मुझे उम्मीद है कि आपको Direct से Indirect बनाते समय Pronouns में किस तरह से परिर्वतन करते हैं समझ में आ गया होगा; यदि हाँ तो चलिए अब हम आगे बढ़ते हैं और Direct and indirect narration in Hindi पोस्ट में दिए गए बाकी नियमों को अच्छे से सीखते हैं.
(2) Change In Tenses And Assertive Sentences (काल एवं साधारण वाक्यों में परिवर्तन) – Reporting verb यदि Present, Present perfect या Future Tense में हो तो Reported speech का Tense नहीं बदलता है;
मतलब Inverted Commas के अंदर वाली क्रिया वैसे ही रहती है; केवल ‘Person’ में नियमानुसार परिवर्तन होता है और ‘That’ लग जाता है; नीचे दिए गए सभी examples को ध्यान से पढ़ें और समझें.
- Direct : He says, “I was studying at home.” Indirect : He says that he was studying at home.
- Direct : He has said to me, “I am very sad.” Indirect : He has told me that he is very sad.
- Direct : Radha will say, “She stole her pen. Indirect : Radha will say that she stole her pen.
Direct and indirect narration in Hindi पोस्ट में दिए गए सभी नियम को ध्यान से पढ़ें और समझें क्योंकि बिना नियम के आप कभी भी Direct speech को Indirect में नहीं बदल सकते हैं; चलिए नीचे दिए जा रहे बाकी नियम को भी पढ़ लेते हैं.
जब Reporting verb भूत काल (Past tense) में हो और Reported speech का Verb (क्रिया) वर्तमान काल (Present Tense) में हो तो वह भी Past Tense में बदल दिया जाता है; इसके नियम कुछ इस कुछ इस प्रकार हैं.
- Present Indefinite Tense को Past Indefinite में बदलते हैं; जैसे – Direct : Rakesh said, “I want a book.” Indirect : Rakesh said that he wanted a book.
- Present Continuous Tense को Past Continuous में बदलते हैं; जैसे – Direct : He said, “I am going to college with my friends. Indirect : He said that he was going to college with his friends.
- Present Perfect को Past Perfect में बदला जाता है; जैसे – Direct : She said, “I have watched this movie.” Indirect : She said that she had watched that movie.
- Present Perfect Continuous को Past Perfect Continuous में बदला जाता है; जैसे – Direct : Mohan said, “They have been studying in this college since 2005.” Indirect : Mahan said that they had been studying in that college since 2005.
चलिए Direct and indirect narration in Hindi पोस्ट में अगला नियम सीखना शुरू करते हैं; मैं आपको इस बात का भरोसा दिलाता हूँ कि यदि आप सभी नियम को मन लगाकर पढ़ और समझ लेते हैं तो आप बहुत ही आसानी से Direct speech को Indirect speech में बदल सकते हैं.
यदि Reporting verb भूतकाल (Past tense) में हो और Reported speech का verb भी Past tense में हो तो वह इस प्रकार बदल जाता है.
- Past Indefinite को Past perfect में बदला जाता है; जैसे – Direct : She said, “I went to Delhi.” Indirect : She said that she had gone to Delhi.
- ध्यान दीजिए Past Continuous Tense को Past Perfect Continuous में बदला जाता है; जैसे – Direct : She said, “All were doing a job.” Indirect : She said that all had been doing a job.
आप Direct and indirect narration in Hindi पोस्ट को पढ़कर इस बात को हमेशा याद रखिएगा जब भी Reported speech का verb Past Perfect Tense और Past Perfect Continuous Tense कभी नहीं बदलता है.
कभी-कभी Past Indefinite Tense और Past Continuous Tense भी नहीं बदलते हैं; जैसे – Direct : He said, “His friend lived in Varanasi for five years.” Indirect : He said that his friend lived in Varanasi for ten years. / Direct : He said, “I was dancing while he was working.” Indirect : He said that he was dancing while he was working.
Direct and indirect narration in Hindi पोस्ट में कुछ और महत्वपूर्ण नियम दिए जा रहे हैं जिन्हें आप अच्छे से तैयार करें.
- यदि Direct speech में Shall, will, can, may हो तो Indirect speech में बदलते समय Should, would, could, might हो जाएगा.
- सभी निकटता बताने वाले शब्दों को आमतौर से दूरी बताने वाले शब्दों में बदल देते हैं; जैसे – Now का Then, This का That, These का Those, Here का There, Yesterday का The previous day or the day before, Hither का Thither, Hence का Thence, Come का Go, Thus का So or in that way,
- Last night का The previous night or the night before, Yet का Till then, Last week or month का The previous week or month, Tonight का That night, Today का That day, Tomorrow का The next day, Ago का Before, Next week का The following week, Just का Then हो जाता है.
- Here, This, Now आदि का There, that, then आदि में परिवर्तन नहीं होता है यदि वे ऐसी चीज़ को बतायें, जो Report करते समय मौजूद हो; यदि मौजूद नहीं है तो बदल जाएगा.
मैं आशा करता हूँ कि आपको Direct and indirect narration in Hindi , अच्छे से समझ में आ गया होगा; और अब आप Direct से Indirect speech में बदल सकते हैं.
2 thoughts on “Direct And Indirect Narration In Hindi”
I found your blog is very informative, for competitive exam preparation
11th, 12th Supplementary Original Question Papers
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
NARRATION-Direct and Indirect Speech Rules in hindi.
NARRATION is derived from the word narrate which means to tell someone .
The art of reporting the speech from a speaker's point of view is called narration.
TYPES OF NARRATION .
1. Direct speech or narration.
When we say from a person's point of view without making any changes as he/ she was saying.
(ज़ब हम किसी व्यक्ति की बात को बिना किसी बदलाव किए जैसा उसने कहाँ था वैसे ही कहते हैँ,)
पहचान : इस तरह के कथन को Inverted commas (") मे रखा जाता हैँ
She said to me " I shall play now "
उसने मुझसे कहा "मैं अब खेलूंगी"
2. Indirect speech or narration.
When we change someone's point of view and tell that thing to someone else.
(ज़ब हम किसी व्यक्ति की बात मे बदलाव करके किसी अन्य को वह बात बताते है,)
पहचान : इस तरह के कथन मे Inverted commas (") को हटाकर reporting verb और reporting speech के बीच that लगाया जाता हैँ
- She told me that she would play then.
उसने मुझसे कहा कि वह तब खेलेगी
Points to remember.
1. who is reporter what are the reporting verbs and reporting speech .
- Reporter : a person who makes statements, as she .
- Reporting verb : That verbs conveying the action of speaking, as said to me.
- Reporting speech : In narration usually used to talk about the past, "I shall play now" .

2. Changing Pronouns of reported speech.
3. changes in tense while making indirect speech from direct., 5. changes with modals., 6. exceptional rules..
- He said "priya lived here".
- He said that priya had lived here.
- The stranger said "here I slept for five hours".
- The stranger said that here he had slept for five hours.
- She said to me "this is her pursue".
- She told me that this was her purse.
- Our teacher said "we all live on the earth".
- Our teacher said that we all live on the earth.
- Ashok said to me "I write with my left hand".
- Ashok told me that he writes with his left hand.
- He said "If i were rich, I would help her".
- He said that If he was rich, he would help her.
- He said "Mr. Gandhi started the quit India movement".
- He said that Mr. Gandhi started the quit India movement.
- She said "My mother was cooking while I was playing".
- She said that her mother was cooking while she was playing.
- She said to me " I had met him before the party. ".
- She told me that She had met him before the party.
- The hindu says " we are trying our best to keep you well informed".
- The hindu says " It is trying it's best to keep us well informed".
- She said "you are guilty".
- She said that he was guilty.
- She said that I was guilty.
- She said "you are all guilty"
- She said that we were all guilty.
7. Assertive sentence.
- She says " I am in 10th class".
- She says that she is in 10the class".
- Say - Tell
- Says - Tells
- Said - Told
- He says to her " you have done your homework".
- He Tells her that she had done her homework.
- Rama said to her mother " I am having a headache"
- Rama told her mother that he was having a headache.
- Ritu says to me "laughing is a good exercise".
- Ritu tells me that laughing is a good exercise".
- She said to me "I shall play now".
- He said to her " The water boils at 100° Celsius".
- He told her that the water boils at 100° Celsius.
8. Interrogative sentence
- They said to her " Are we wasting your time? "
- They asked her if they were wasting her time.
- He said to me "Do I sing a song now?"
- He asked me if he sang a song then.
- She said to me "Do I not accept your proposal".
- She asked me if she did not accept my proposal.
- He said to them "Does she not serve her mother in law".
- He asked them if she did not serve mother in law.
- The student asked the teacher " May I come in sir ? "
- The student asked the teacher respectfully if he might come in.
- Aman said to his brother "My dear, Did I not tell you a story?"
- Aman enquired to his brother affectionately if he had not told him a story".
9. Imperative sentence
- Said to - Begged (क्षमा के लिए)
- Said to - Ordered / command (आदेश के लिए)
- Said to - Advised/ suggested (सलाह के लिए)
- Said to - Requested (प्रार्थना के लिए)
- Said to - Warned (चेतावनी के लिए)
- Said to - Forbade (मना करने के लिए)
- I said to him "Go there".
- I ordered him to go there.
- The teacher said to boys "Don't make a noise".
- The teacher command the boys not to make a noise.
- I said to her "kindly give me a lift".
- I requested her to give me a lift.
- Father said to me "avoid bad company".
- Father suggested me to avoid bad company.
- I said to my son "Don't pluck flowers".
- I forbade my son to pluck flowers.
- The convict said to the judge "please pardon me"
- The convict begged pardon to the judge.
- The general said to the soldiers "March forward and attack the foe".
- The general commanded the soldiers to March forward and attack the foe.
- She said to me "Do not go ffurther".
- She warned me not to go for further.
- "Sit down boys" said the teacher.
- The teacher ordered the boys to sit down.
- She said to me "let us go to see a movie"
- She proposed me that we should go to see a movie.
- She proposed to me to go to see a movie .
- He said to them "let us do our work sincerely".
- He suggested them that they should do their work sincerely.
- He proposed to them to do their work sincerely.
10. Exclamatory sentence.
- The team said "Hurrah! We have won".
- The team exclaimed with joy that they had won.
- Vinod said to me "What! Nice shirt it is".
- Vinod explained with surprise that what a nice shirt it was.
- She said to me "Oh! My mother is seriously ill".
- She exclaimed with Sorrow that her mother was seriously ill.
- The chief said to soldiers, Bravo! You fought bravely".
- The chief applauded soldiers that they fought bravely.

3 comments:

Please Make sure to comment and share the post to your friends.

Thank you! We are gald you liked this post. Please share with your friends to learn together.🙂
Thank you! Your comment will prove very useful for us because we shall get to know what you have learned and what you want to learn?
- सामान्य हिंदी व्याकरण
- अग्रिम हिंदी व्याकरण
- BASIC GRAMMAR
- ADVANCE GRAMMAR
Advertisement

Popular Posts
भाषा और उसके प्रकार, महत्त्व और विशेषताएं, हिंदी व अन्य भाषाओ का विकास और लिपि क्या होती है?

Change The Gender In English Grammar.

Change The Number In English Grammar

परिश्रम ही सफलता की कुंजी है

व्याकरण क्या है? व्याकरण के अंग, परिभाषा और महत्व

विद्यालय छोड़ने का प्रमाण पत्र प्राप्त करने के लिए प्राचार्या को प्रार्थना पत्र
- Change The Gender In English Grammar. A category of noun as either masculine (पुल्लिंग), feminine (स्त्रीलिंग) or Neuter (नपुंसकलिंग) MASCULINE :- Masculine nouns are words for...
- Change The Number In English Grammar In grammar, the number refers to the count of a noun or pronoun. Example: Boy-Boys, Wife-Wives, My-Our, Ox-Oxen, etc. Types of Number: 1.S...
- परिश्रम ही सफलता की कुंजी है संस्कृत में कहा गया है-' उद्यमेन हि सिद्धन्ति कार्याणि न मनोरथैः ।' अर्थात् परिश्रम से ही सारे कार्य सफल होते हैं, केवल मन में इच्छा...
Contact Form
Copyright (c) 2020-2023 MY GRAMMAR GURUJI All Right Reseved
404 Not found
404 Not found

Narration Rules in Hindi

Learn about the rules of direct and indirect speech in Hindi with examples.
Narration, जिसे direct and indirect speech, के रूप में भी जाना जाता है, communication और storytelling कहने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है। यह English Grammar में पिछली घटनाओं, वार्तालापों और narratives को व्यक्त करने के लिए उपयोग किया जाने वाला एक शक्तिशाली उपकरण है। वर्णन का कुशल उपयोग लिखित और बोली जाने वाली अंग्रेजी दोनों में गहराई, संदर्भ और जीवंतता जोड़ता है। इस लेख में, हम अंग्रेजी व्याकरण के इस पहलू में महारत हासिल करने के लिए narration के मूल सिद्धांतों, इसके नियमों और विभिन्न तकनीकों का पता लगाएंगे।
Direct Speech को समझना: Direct Speech किसी के द्वारा बोले गए सटीक शब्दों को संदर्भित करता है और उद्धरण चिह्नों के भीतर प्रस्तुत किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए: He said, "I am going to the store." Direct speech में, tense, pronouns, और adverbs अपरिवर्तित रहते हैं। हालाँकि, वाक्य का Subject बदलने पर pronouns और adverbs में परिवर्तन होता है। Indirect Speech को समझना: दूसरी ओर, Indirect Speech, किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा अपने सटीक शब्दों का उपयोग किए बिना क्या कहा गया है, इसकी रिपोर्ट करने का एक तरीका है। इसका उपयोग अक्सर किसी के speech को संक्षेप में प्रस्तुत करने या व्याख्या करने के लिए किया जाता है। उदाहरण के लिए: He said that he was going to the store. Indirect speech में, verb tense, pronouns और adverbs को रिपोर्ट किए गए भाषण के नियमों के अनुसार समायोजित किया जाता है। Indirect speech में “said," "told," या “asked" जैसी रिपोर्टिंग verbs का उपयोग भी आम है।
Rules of Narration:
Direct speech को indirect speech में बदलने के लिए दो तरह के rules होते हे जिनको हम General Rules और Special Rules बोलते है। General rules उन्हें कहते है जो सभी sentences के साथ लागु होते है। और special rules अला senteces के साथ अलग होते है।
General rules
- Change of persons.
- Change of Tense.
- Change of other Parts of Speech.
1. Change of Person
Direct speech से जब हम indirect speech में बदलने पर inverted commas के भीतर जीतनेय भी person (first, second, third) रहते है। वे इस नियम के अनुशार बदल जाते है।
1. First Person Reporting Verb ke subject ke anushar. 2. Second person reporting verb ke object ke anushar. 3. Third person – No Change. हम इस को इस rules से भी समझ सकते है। 1 2 3 S o N
1 ka matlab he first person 2 ka matla he second person 3 ka matla he third person S ka matlab he Subject O ka matlab he Object N ka matlab he Ni change
इसका मतलब ये हुआ की First person Subject ke sath change hoga. Second person Object ke sath change hoga. Thrid person no change hoga.
कुछ विशेष points को धियान में रखना बहुत जरुई है।
- जब Reporting verbs present या future में रहता है , तब indirect speech में कही भी tense में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता है।
- जब inverted comms के भीतर assertive sentences रहता है , तब indirect speech में inverted commas के बदले that का use होता है ।
- जब reporting verb say/says/said रहे और उसकी बाद object रहे , तो आप यहाँ इसे indirect speech में tell/tells/told में बदल दे। अगर object न रहे , तो reporting verb me परिवर्तन नहीं करे।
- Person बदलते समाये number or case पर विशेष धियान दे , क्योकि ये नहीं बदलते। आपकी सुविधा के लिए सभी personal pronoun के सभी forms को आगे table में दिया जा रहा है जिस हमेश धियान में रखे।
जब direct and indirect speech के नियमों की बात आती है, तो "Change of Person" किसी अन्य के शब्दों की रिपोर्ट करते समय pronouns और verb forms में बदलाव को संदर्भित करता है। याद रखें, "Change of Person" के ये नियम pronouns और verb forms दोनों रूपों पर लागू होते हैं। tense परिवर्तन पर भी ध्यान दें, जैसे present tense से past tense में बदलाव।
Solved Examples
1. Change of Person: First Person to Third Person
- Direct speech: She says to me, “I am his sister.” - वह मुझसे कहती है, "मैं उसकी बहन हूं।"
- Indirect speech: She tells me that she is his sister. - वह मुझसे कहती है कि वह उसकी बहन है।
2. Change of Person: First Person to Third Person
- Direct speech: Rahul says to me, “I am your friend.” - राहुल मुझसे कहते हैं, "मैं आपका दोस्त हूं।"
- Indirect speech: Rahul tells me that he is my friend. - राहुल मुझसे कहते हैं कि वह मेरे दोस्त हैं.
3. Change of Person: First Person to Third Person
- Direct speech: They say to me, “We help you.” - वे मुझसे कहते हैं, "हम आपकी मदद करते हैं।"
- Indirect speech: They tell me that they help me. - वे मुझसे कहते हैं कि वे मेरी मदद करते हैं।
4. Change of Person: First Person to Third Person
- Direct speech: Sarah said, "I am going to the store." - सारा ने कहा, "मैं स्टोर जा रही हूं।"
- Indirect speech: Sarah said that she was going to the store. - सारा ने कहा कि वह स्टोर जा रही थी।
5. Change of Person: Second Person to Third Person
- Direct speech: John said, "You should study harder." - जॉन ने कहा, "तुम्हें और अधिक मेहनत करनी चाहिए।"
- Indirect speech: John said that he should study harder. - जॉन ने कहा कि उसे और अधिक अध्ययन करना चाहिए।
6. Change of Person: Third Person to First Person
- Direct speech: The teacher said, "They need to submit their assignments." - शिक्षक ने कहा, "उन्हें अपना असाइनमेंट जमा करना होगा।"
- Indirect speech: The teacher said that we need to submit our assignments. - शिक्षक ने कहा कि हमें अपना असाइनमेंट जमा करना होगा।
7. Change of Person: First Person Plural to Third Person
- Direct speech: We said, "We are going to the park." - हमने कहा, "हम पार्क जा रहे हैं।"
- Indirect speech: We said that they were going to the park. - हमने कहा कि वे पार्क में जा रहे थे।
8. Change of Person: Third Person to Second Person
- Direct speech: The doctor said, "She should take the medication." - डॉक्टर ने कहा, "उसे दवा लेनी चाहिए।"
- Indirect speech: The doctor said that you should take the medication. - डॉक्टर ने कहा कि आपको दवा लेनी चाहिए।
9. Change of Person: Second Person to First Person
- Direct speech: The officer said, "You must show your ID." - अधिकारी ने कहा, "आपको अपनी आईडी दिखानी होगी।"
- Indirect speech: The officer said that we must show our ID. - अधिकारी ने कहा कि हमें अपनी आईडी दिखानी होगी.
10. Change of Person: First Person to Second Person
- Direct speech: Mary said, "I will help you." - मैरी ने कहा, "मैं आपकी मदद करूंगी।"
- Indirect speech: Mary said that she would help me. - मैरी ने कहा कि वह मेरी मदद करेगी।
11. Change of Person: Third Person Plural to First Person
- Direct speech: They said, "They have completed the project." - उन्होंने कहा, "उन्होंने परियोजना पूरी कर ली है।"
- Indirect speech: They said that we have completed the project. - उन्होंने कहा कि हमने प्रोजेक्ट पूरा कर लिया है.
12. Change of Person: Second Person to Third Person Plural
- Direct speech: The coach said, "You should practice more." - कोच ने कहा, "आपको और अधिक अभ्यास करना चाहिए।"
- Indirect speech: The coach said that they should practice more. - कोच ने कहा कि उन्हें और अधिक अभ्यास करना चाहिए।
2. Change of Tense
- जब reporting verb present/future tense में रहता है , तब indirect speech में कभी भी tense में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता है। अभी तक दिए गए उदाहरण से यहाँ पूर्णतः स्पष्ट है।
- जब reporting verb past tense में रहता है , तब inverted commas के भीतर परुक्त tense में परिवर्तन होता है। यहाँ परिवर्तन इस प्रकार होता है।
Direct -> indirect Present Simple -> Past Simple Present Continuous -> Past Continuous Present Perfect-> Past Perfect Present Perfect Continuous-> Past Perfect Continuous Past Simple -> past Perfect Past continuous -> Past perfect Continuous Past Perfect -> no change of tense Past perfect Continuous -> no change of tense Shall/Will -> Should/ Would Can -> Could May -> might Am/is/are -> was/were Have/has -> had Had to + Verb first form -> had had to + verb first form Could/should/would/might -> generally does not change
Example: Change of Tense
1. Present Simple changes to Past Simple:
- Direct speech: Rakesh told to her. “I like you.” - राकेश ने उससे कहा। "मुझे आप पसंद हो।"
- Indirect speech: Rakes told to her that he liked her. - रेक्स ने उससे कहा कि वह उसे पसंद करता है।
2. Present Simple changes to Past Simple:
- Direct speech: She said to me, “I wan to give you my book.” - उसने मुझसे कहा, "मैं तुम्हें अपनी किताब देना चाहती हूँ।"
- Indirect speech: She told to me that she wanted to give me her book. - उसने मुझसे कहा कि वह मुझे अपनी किताब देना चाहती है।
3. Present Simple changes to Past Simple:
- Direct speech: "I like ice cream." - "मुझे आइसक्रीम पसंद है।"
- Indirect speech: She said that she liked ice cream. - उसने कहा कि उसे आइसक्रीम पसंद है।
4. Present Continuous changes to Past Continuous:
- Direct speech: "I am watching a movie." - "मैं एक फिल्म देख रहा हूं।"
- Indirect speech: He said that he was watching a movie. - उन्होंने कहा कि वह एक फिल्म देख रहे थे।
5. Present Perfect changes to Past Perfect:
- Direct speech: "I have seen that movie." - "मैंने वह फिल्म देखी है।"
- Indirect speech: They said that they had seen that movie. - उन्होंने कहा कि उन्होंने वह फिल्म देखी है।
6. Present Perfect Continuous changes to Past Perfect Continuous:
- Direct speech: "I have been studying all day." - "मैं पूरे दिन पढ़ रहा हूं।"
- Indirect speech: She said that she had been studying all day. - उसने कहा कि वह पूरे दिन पढ़ती रही।
7. Past Simple remains Past Simple:
- Direct speech: "I went to the park." - "मैं पार्क गया था।"
- Indirect speech: He said that he went to the park. - उन्होंने कहा कि वह पार्क में गए थे।
8. Past Continuous remains Past Continuous:
- Direct speech: "I was cooking dinner." - "मैं रात का खाना बना रहा था।"
- Indirect speech: She said that she was cooking dinner. - उसने कहा कि वह रात का खाना बना रही थी।
9. Past Perfect remains Past Perfect:
- Direct speech: "I had already finished." - "मैं पहले ही समाप्त कर चुका था।"
- Indirect speech: They said that they had already finished. - उन्होंने कहा कि वे पहले ही समाप्त कर चुके हैं।
10. Past Perfect Continuous remains Past Perfect Continuous:
- Direct speech: "I had been waiting for hours." - "मैं घंटों से इंतज़ार कर रहा था।"
- Indirect speech: He said that he had been waiting for hours. - उन्होंने कहा कि वह घंटों से इंतजार कर रहे थे.
11. Future tenses change as follows:
1. Future Simple changes to Conditional:
- Direct speech: "I will help you." - "मैं आपकी मदद करूंगा।"
- Indirect speech: She said that she would help me. - उसने कहा कि वह मेरी मदद करेगी।
2. Future Continuous changes to Conditional Continuous:
- Direct speech: "I will be waiting for you." - "मैं आपका इंतजार करूंगा।"
- Indirect speech: He said that he would be waiting for me. - उन्होंने कहा कि वह मेरा इंतजार कर रहे होंगे.
3. Future Perfect changes to Conditional Perfect:
- Direct speech: "I will have finished by then." - "मैं तब तक समाप्त कर चुका होऊंगा।"
- Indirect speech: They said that they would have finished by then. - उन्होंने कहा कि वे तब तक समाप्त कर चुके होंगे।
12. Modals change as follows:
1. Can changes to Could:
- Direct speech: "I can swim." - सीधा भाषण: "मैं तैर सकता हूँ।"
- Indirect speech: She said that she could swim. - अप्रत्यक्ष भाषण: उसने कहा कि वह तैर सकती है।
2. May changes to Might:
- Direct speech: "I may go to the party." - "मैं पार्टी में जा सकता हूं।"
- Indirect speech: He said that he might go to the party. - उन्होंने कहा कि वह पार्टी में जा सकते हैं.
3. Must changes to Had to:
- Direct speech: "I must finish this." - "मुझे इसे ख़त्म करना ही होगा।"
- Indirect speech: They said that they had to finish that. - उन्होंने कहा कि उन्हें इसे खत्म करना होगा।
4. Change of other Parts of Speech
जब reporting speech tense में रहता है , तब reporting speech me जीतने भी निकट सूचक शब्द रहते है , वे सब के सब indirect speech में दुरी सूचक सब्दो में बदल जाते है जैसे
Direct -> Indirect
- This -> that
- These -> those
- Here -> there
- Hence -> thence
- Now -> then
- Today - >that day
- Yesterday -> the day before / the previous day
- The day before yesterday -> two days before.
- Tomorrow - > the next day/ the following day
- The day after tomorrow -> in two day’s time
- Next week/year etc -> year, etc
- A year ago -> the previous year.
Sloved Example
Direct speech: He said, “I will do it tomorrow.” - उन्होंने कहा, "मैं इसे कल करूंगा।" Indirect speech: He said that he would do it the next day. - उन्होंने कहा कि वह इसे अगले दिन करेंगे.
Direct speech: She said, “I am starting the day after tomorrow.” - उसने कहा, "मैं परसों से शुरू कर रही हूं।" Indirect speech: She said that she was staring in two days time. - उसने कहा कि वह दो दिनों के समय में घूर रही थी।
Direct speech: She said, "I have just finished my homework." - उसने कहा, "मैंने अभी-अभी अपना होमवर्क पूरा किया है।" Indirect speech: She said that she had just finished her homework. - उसने कहा कि उसने अभी-अभी अपना होमवर्क पूरा किया है।
Direct speech: He said, "I bought a new car last week." - उन्होंने कहा, "हम पूरे दिन इस परियोजना पर काम कर रहे हैं।" Indirect speech: He said that he had bought a new car the previous week. - उन्होंने कहा कि वे पूरे दिन उस परियोजना पर काम कर रहे थे।
Direct speech: They said, "We have been working on this project all day." - उसने कहा, "मैं सप्ताहांत में अपने दादा-दादी से मिलने गई।" Indirect speech: They said that they had been working on that project all day. - उसने कहा कि वह सप्ताहांत में अपने दादा-दादी से मिलने गई थी।
Direct speech: She said, "I visited my grandparents over the weekend." - उसने कहा, "मैं सप्ताहांत में अपने दादा-दादी से मिलने गई।" Indirect speech: She said that she had visited her grandparents over the weekend. - उसने कहा कि वह सप्ताहांत में अपने दादा-दादी से मिलने गई थी।
Direct speech: He said, "I have known her for years." - उन्होंने कहा, "मैं उन्हें वर्षों से जानता हूं।" Indirect speech: He said that he had known her for years. - उन्होंने कहा कि वह उन्हें वर्षों से जानते हैं।
Direct speech: They said, "We have just moved to a new house." - उन्होंने कहा, "हम अभी नए घर में आए हैं।" Indirect speech: They said that they had just moved to a new house. - उन्होंने कहा कि वे अभी नए घर में आये हैं।
Direct speech: She said, "I have finished reading the book." - उसने कहा, "मैंने किताब पढ़ ली है।" Indirect speech: She said that she had finished reading the book. - उसने कहा कि उसने किताब पढ़ ली है।
Direct speech: He said, "I have been studying Spanish for six months." - उन्होंने कहा, "मैं छह महीने से स्पेनिश सीख रहा हूं।" Indirect speech: He said that he had been studying Spanish for six months. - उन्होंने कहा कि वह छह महीने से स्पेनिश सीख रहे थे।
Direct speech: They said, "We have traveled to many countries." - उन्होंने कहा, ''हमने कई देशों की यात्रा की है." Indirect speech: They said that they had traveled to many countries. - उन्होंने कहा कि वे कई देशों की यात्रा कर चुके हैं.
Direct speech: She said, "I have recently started a new job." - उन्होंने कहा, ''मैंने हाल ही में एक नई नौकरी शुरू की है.'' Indirect speech: She said that she had recently started a new job. - उसने कहा कि उसने हाल ही में एक नई नौकरी शुरू की है।
Special Case: Interrogative Sentence:
Direct Speech: एक interrogative sentence एक प्रश्न पूछता है और एक question mark के साथ समाप्त होता है। जब हम किसी interrogative sentence की रिपोर्ट करते हैं या उसे indirect speech में परिवर्तित करते हैं, तो हमें कुछ नियमों का पालन करने की आवश्यकता होती है:
1. Question form को statement form. में बदलें। 2. Question mark हटाएँ. 3. उपयुक्त reporting verb (such as ask, inquire, wonder) का प्रयोग करें और उसके बाद If या whether शब्द का प्रयोग करें। 4. यदि reported किए गए speech में where, when, why, how आदि शब्द हैं, तो उन्हें भी तदनुसार बदल दिया जाना चाहिए।
Interrogative sentences के लिए direct और indirect speech के 10 examples यहां दिए गए हैं:
Direct: She asked, "Will you attend the party?". - उसने पूछा, "क्या आप पार्टी में शामिल होंगे?" Indirect: She asked if I would attend the party. - उसने पूछा कि क्या मैं पार्टी में शामिल होऊंगा।
Direct: The teacher asked the students, "Did you finish your homework?". - शिक्षक ने छात्रों से पूछा, "क्या आपने अपना होमवर्क पूरा कर लिया?" Indirect: The teacher asked the students if they had finished their homework. - शिक्षक ने छात्रों से पूछा कि क्या उन्होंने अपना होमवर्क पूरा कर लिया है।
Direct: "Can I borrow your pen?" he asked his friend. - "क्या मैं आपकी कलम उधार ले सकता हूँ?" उसने अपने दोस्त से पूछा. Indirect: He asked his friend if he could borrow his pen. - उसने अपने मित्र से पूछा कि क्या वह उसकी कलम उधार ले सकता है।
Direct: "Have you seen my keys?" she asked her sister. - "क्या तुमने मेरी चाबियाँ देखी हैं?" उसने अपनी बहन से पूछा. Indirect: She asked her sister if she had seen her keys. - उसने अपनी बहन से पूछा कि क्या उसने उसकी चाबियाँ देखी हैं।
Direct: "Are you coming with us?" they asked their neighbor. - "क्या आप हमारे साथ आ रहे हैं?" उन्होंने अपने पड़ोसी से पूछा। Indirect: They asked their neighbor if he/she was coming with them. - उन्होंने अपने पड़ोसी से पूछा कि क्या वह उनके साथ आ रहा है।
Direct: "Did you enjoy the movie?" he asked his girlfriend. - "क्या आपने फिल्म का आनंद लिया?" उसने अपनी प्रेमिका से पूछा। Indirect: He asked his girlfriend if she had enjoyed the movie. - उसने अपनी प्रेमिका से पूछा कि क्या उसने फिल्म का आनंद लिया है।
Direct: "Will you help me with my project?" she asked her brother. - "क्या आप मेरे प्रोजेक्ट में मेरी मदद करेंगे?" उसने अपने भाई से पूछा. Indirect: She asked her brother if he would help her with her project. - उसने अपने भाई से पूछा कि क्या वह उसके प्रोजेक्ट में उसकी मदद करेगा।
Direct: "Has she arrived yet?" he asked his colleague. - "क्या वह अभी तक आई है?" उसने अपने सहकर्मी से पूछा। Indirect: He asked his colleague if she had arrived yet. - उसने अपने सहकर्मी से पूछा कि क्या वह अभी तक आई है।
Direct: "Do you want some coffee?" the waiter asked the customer. - "क्या आप कुछ कॉफ़ी चाहेंगे?" वेटर ने ग्राहक से पूछा। Indirect: The waiter asked the customer if he/she wanted some coffee. - वेटर ने ग्राहक से पूछा कि क्या उसे कुछ कॉफ़ी चाहिए।
Direct: "Can you swim?" the coach asked the student. - "क्या आप तैर सकते हैं?" कोच ने छात्र से पूछा। Indirect: The coach asked the student if he/she could swim. - कोच ने छात्र से पूछा कि क्या वह तैर सकता है।

What is Shoonya Meditation?
When we do Meditation then we experience many things Shoonya is one of them. Shoonya is a very deep....

How to do Morning Meditation?
Doing Meditation in morning add more value to whole day and if we do continue practice then we can also see its positive effects in our life....

How to do Evening Meditation?
Evening Meditation is a wonderful thing to finish your day in a piece. As you have noticed that, whatever thoughts are in your....
- Privacy Policy

- Hindi to English Translation
- Verb Forms v1,v2,v3,v4,v5
- Daily Use English Words
- Daily Use English Sentences
Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi Rules Examples Exercises etc
Direct & indirect speech narration in hindi with all rules examples exercises etc..

Direct & Indirect Speech में Persons को कैसे Change किया जाता है ?
Direct & indirect speech examples in hindi., direct & indirect speech examples in english., you may like these posts, post a comment.

Kya aap ke Chanel par dobara se Oxford ka solutions aayenge kya ??
हम कोशिश कर रहे हैं । और फिलहाल आप हमारे Social media Sites पर जाकर प्रश्न पूछ सकते हैं । वहाँ आपको Answer बता दिया जाएगा ।
Ek telegram group bhi bana dijiye Comfortable hoga sab ke liye

Ok, I will try. Thanks for your opinion
Direct ko indirect karte time coma inverted coma ki jageh par to Kab aata h
सभी Rules को इस पोस्ट मे बताया गया है । आप ध्यान से Rules को पढिये । Inverted comma के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग किया जाता है ।
Sir modal auxiliary verb ka post kab ayega
Modal auxiliary verb के 5 पोस्ट अपलोड किया हुआ है । आप Hindi to English all translation link list page मे चेक कीजिए । और कल से परसो तक एक और पोस्ट अपलोड कर दिया जाएगा ।
आपलोगों से अनुरोध है कि कमेंट में किसी भी प्रकार के लिंक को Enter ना करें, और यदि आप ऐसा करते हैं तो फिर आपके कमेंट को Approve नहीं किया जाएगा और ना ही आपको कोई Reply दिया जाएगा ।
Some Provide Categories List 🔗Ⓜ️
- Active And Passive Voice 8
- Articles A An and The 1
- Direct & Indirect Speech 7
- Modal Auxiliary Verbs 7
- Parts of Speech 8
- Simple Sentences 12
- Time & Tense 13
Social Media पर हमें Follow करें ↓🔗Ⓜ️
Note : सभी स्टूडेंट्स जरा यहाँ ध्यान दें 🔗Ⓜ️, translation सीखें 🔗Ⓜ️.
- Time And Tense सीखें ♻️
- Simple Sentence सीखें 🌿
- Active & Passive Voice सीखें : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : 🔰
- Direct & Indirect Speech सीखें : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :- 🔰
Spoken English सीखें 🔗Ⓜ️
- Daily Use English Words link List Page : : : : : : : ♻️
- Daily Use Sentences link list Page : : : : : : : : : : : 🌿
- Verb form v1,v2,v3,v4,v5 link List Page : : : : : : : 🔰
- Hindi to English Translat ion link list Page : : : : 🔰
Menu Footer Widget
- Privacy policy
- Terms And Conditions
- Our Other Website : Online Hindi Me Help
Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi (Narration) Rules, Examples, Exercises
Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi (Narration) Rules, Examples and Exercises. Learn Direct and Indirect Narration in Hindi. प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन हिंदी में सीखिए। Rules of Indirect Speech in Hindi and English with examples. Direct and Indirect Speech को Hindi में प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन कहते हैं। जब आप किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही गई बात को दो तरह से कहा जाता है; Direct और Indirect के नीचे दिए गए उदाहरणों को देखें:
Note:– ऊपर भी गए वाक्यों में Direct Speech के वाक्य में किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही ही बात को ज्यों का त्यों inverted commas में quote कर लिखा गया है जबकि Indirect Speech के वाक्य को ज्यों का त्यों न लिखकर वक्ता (speaker) द्वारा अपने शब्दों में लिखा गया है।
इस पोस्ट के माध्यम से आप Direct and Indirect Speech के Rules, Examples Hindi में पढ़ेंगे। सभी नियम विस्तार से समझाए गए।

Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi (Narration)
Direct का प्रत्यक्ष अर्थात सीधा तथा Indirect का अर्थ अप्रत्यक्ष होता है। Speech या Narration का अर्थ ‘वर्णन’ होता है। इस तरह से किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही हुई बात को दो प्रकार से व्यक्त किया जा सकता है।
Direct Speech in Hindi
किसी वक्ता के शब्दों को ज्यों का त्यों बिना किसी प्रकार का परिवर्तन किये कहा जाता है, उसे Direct Speech या Direct Narration कहते हैं। Direct Speech के शब्दों को inverted commas (“………”) के अंदर लिखते हैं।
जैसे की:–
Note:– इस वाक्य में Dileep वक्ता (speaker) है। उसके द्वारा कहा जा रहा है कि वह धाराप्रवाह अंग्रेजी बोल सकता है।
Parts of Direct Speech or Narration
Direct Speech के दो भाग होते हैं; Reporting Speech तथा Reported Speech
Reporting Speech: Commas से बाहर वाले वाक्य को Reporting Speech कहते हैं। नीचे दिए गए वाक्य में ‘He said to me’ Reporting Speech है।
Reporting Speech के Part s
ऊपर दिए गए वाक्य के part नीचे दिए गए हैं;
Reported Speech: Commas के अंदर आए हुए वाक्य को Reported Speech कहते हैं। नीचे दिए गए वाक्य “I was busy yesterday.” Reported Speech है। यह वह हिस्सा होता है जिसे ज्यों का त्यों लिखते हैं।
Indirect Speech in Hindi
जब वक्ता द्वारा कही हुई बात को ज्यों का त्यों न लिखकर अपने शब्दों में उसका भावार्थ लिखते या बोलते हैं, उसे Indirect Speech या Indirect Narration कहते हैं।
Note:– इस वाक्य में inverted commas का प्रयोग नहीं हुआ है। Speaker (वक्ता) की कही बात को अपने शब्दों में लिखा गया है।
Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
Assertive Sentences को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम के अनुसार सबसे पहले commas बाहर परिवर्तन करते हैं। उसके बाद commas के अंदर परिवर्तन किया जाता है। इन सभी परिवर्तनों को कैसे और कब करना है, यह सभी नियम नीचे दिए गए हैं।
Reporting Speech में Change
वाक्य के बाहर का part (Commas के बाहर) Reporting Speech कहलाता है। Commas के बाहर परिवर्तन करने के rules निम्नलिखित हैं।
Commas के बाहर Changes
यदि Reporting Verb में said to आये तो उसे told, says to को tells में, say to को tell में बदलते हैं। यदि वाक्य में said, says, तथा say के बाद to न आया हो तो इन्हें indirect speech में ज्यों का त्यों लिखते हैं।
Commas में Change
Assertive Sentence को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलते समय commas को हटाकर that लिखते हैं।
Change of Pronouns (सर्वनाम के परिवर्तन)
Direct से Indirect Speech में बनाते समय Pronoun के परिवर्तन में निम्नलिखित नियमों का पालन किया जाता है।
Rule – 1 यदि Reporting Speech में I Person के Pronoun आता है तो Reporting Speech के Subject के Person के अनुसार बदला जाता है।
Rule – 2 यदि Reported Speech के वाक्य में कोई Second Person Pronoun आया है तो Reporting Speech के Object (कर्म) के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
Rule – 3 Reported Speech में आये सभी Third Person Pronoun को बदला नहीं जाता है।
Rule – 4 यदि Reporting Speech का object न दिया हो तथा Reported Speech का Subject II Person हो और Reporting Verb का Subject Second First Person का हो तो Reported Speech के second person को Indirect Speech में III person के Subject में बदल देते हैं।
Change of Tense
Rule – 1 यदि Reporting Speech के verb का Tense ‘Present या Future Tense’ में है तो Reported Speech के Verb का Tense नहीं बदला जाता है।
1. Seeta says, ‘I sang a song.” Seeta says that she sang a song.
2. He says, “I am doing it now.” He says that he is doing it then.
3. He has said, “The girl was poor” He has said that the girl was poor.
4. Ram says to Rohan, “I am ready.” Ram tells Rohan that he is ready.
5. The man will say to me, ”I cannot find my purse.” The man will tell me that he could not find his purse.
Rule – 3 यदि Reporting Speech के Verb का Tense ‘Past Tense’ है तो Reported Speech का Tense नीचे दी गई टेबल के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
Direct Speech या Narration का Tense
Rule – 4 यदि Reporting Speech Past Tense में तथा Reported Speech Future Tense में है तो नीचे दिए table के अनुसार चेंज करते हैं।
1. Raj said to me, ” I shall play with you.” Raj told me that he would play with me.
2. Kamal said to Vimal, “You will be driving your car.” Kamal told Vimal that he would be driving his car.
3. I said to you, “I shall have been buying milk for five days.” I told you that I should have been buying milk for five days.”
4. They said to him, ‘You will have completed your registration.” They told him that he would have completed his registration.”
Other Verb changes
Rule – 1 यदि Reporting Speech Past Tense में है तथा Reported Speech में नीचे दी गई Auxiliary Verbs का प्रयोग हो तो नीचे दी गई सूची के अनुसार Indirect Speech में बदलते हैं।
1. She said, ”I have a nice dress.” She said that she had a nice dress.
2. He said to me, ”I can solve this problem.”He told that he could solve that problem.
3. Sita said to her friend, ”You may sleep here.” Sita told her friend that she might sleep there.
4. They said to me, “We are playing cricket here.” They told me that they were playing cricket.
5. The teacher said to us, “I am your new teacher of English.” The teacher told us that he was their new teacher.
6. Gagan said to her sister, “I do my work on time.” Gagan told her sister that he did her work on time.
7. Mohandas said to her sister, ”She is better than you.” Mohandas told her sister that she was better than her.
8. Teena said to her friend, “I have to carry the lunch box with me.” Teena told her friend that he had to carry the lunch box with her.
Rule – 2 यदि Reporting Verb Past Tense में है तथा Reported Speech में Subject + Could/Should/Would/Might + Verb I का प्रयोग हो तो could, should, would, might को बिना बदले ज्यों का त्यों लिखते हैं।
1. He said to him, “He should do it honestly.” He told him that he should do it honestly.
2. Father said, ”I could buy 5 kg mangoes.” Father said that he could buy 5 kg mangoes.
Important Rules for changing the tense
Rule – 1 यदि Reported Speech में कोई सदा सच रहने वाली बात (Universal Truth), आदत (Habit), ऐतिहासिक तथ्य या घटना (Historical Truth or Event), कहावत (Proverb) आदि दी हो तो Indirect Speech में बनाते समय Reported Speech के टेंस में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं करते हैं।
Universal Truth
Historical Truth
Rule – 2 यदि Reported Speech का Simple Past Tense में एक साथ दो कार्यों का होने का बोध हो तथा time clause का प्रयोग हो रहा हो तब Indirect बनाते समय Simple Past Tense तथा Past Continuous Tense मैं परिवर्तन नहीं करते हैं।
Change in words showing nearness
Examples of Assertive Sentences of Indirect Speech
Assertive Sentences को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम ऊपर बताये जा चुके हैं। यहां उनके Examples दिए जा रहे हैं। Assertive Sentences के अंतर्गत affirmative sentences तथा negative sentences आते हैं।
1. He says to me, ”I am ill.” He tells me that he is ill.
2. I say to you, ”The man is out. I tell you that the man was out.
3. Shyam said to me, ”I am you best friend.” Shyam told me that he was my best friend.
4. Gagan said to me, ”I am waiting for you.” Gagan told me that he is waiting for you.
5. You said to me, ”He plays cricket with friends.” You told me that he played cricket with friends.
Interrogative Sentences
Direct Speech के Interrogative Sentences को Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम नीचे दिए गए हैं।
Yes-No Type Questions को direct speech से Indirect speech में बदलना
यदि Reported Speech में Interrogative Sentences Helping Verb से शुरू है तो वाक्य को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए नीचे दिए गए rules को फॉलो करते हैं।
{1} Commas के बाहर Reporting Verb में आये भाव के अनुसार
{2} Inverted commas को हटाकर if या whether करते हैं। {3} इसके बाद interrogative sentence को affirmative में बदलकर लिखते हैं। {4} अंत में full stop लगाते हैं। {5} अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्यों की तरह होते हैैं।
1. She said to her mother, ”Are you ill?” She asked her if she was ill.
2. He said to me, ”Is your brother here?” He asked me if my brother was ill.
3. Geeta said, ”Am I Right?” Geeta asked if she was right.
4. We said to him, “Are you sleeping now” We asked him if he was sleeping then.
5. You said, “Do you know your rights?” You asked him/her if he/she knew her/his rights.
6. The man said to me, “Have you taken your med The man asked me if I had taken my medicine.
7. Molu said to his brother, ”Have you been playing here for two hours? Molu asked his brother if he had been playing there for two hours.
8. Savi said to me, ”Did you write a letter to your client? Savi asked me if I had written a letter to my client.
9. Ashok asked, ”Were you beating your child yesterday? Ashok asked me/him if I/he had been beating my/his child the previous day.
10. Neha said to him, “Is New Delhi is the capital of India?” Neha asked him if New Delhi is the Capital of India.
Wh-word Questions को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech (Narration) में बदलना
Wh-word Questions को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech/Narration से बदलने के नियम नीचे दिए गए हैं।
Rule – 1 यदि रिपोर्टेड स्पीच का Interrogative Sentence Wh-words से शुरू है तो Sentence को indirect speech बदलने के लिए नीचे दिए गए हो स्टेप्स को फॉलो करते हैं।
1. Father asked me, “What do you want?” Father asked me what I wanted.
2. My friend said to me, “Where do you live?” My friend asked me where I lived.
3. The patient said, “Where is the Doctor?” The patient wanted to know where the Doctor was.
4. Neha said to Soni, “Why did you not come yesterday? Neha asked Soni why she had not come the previous day.
5. He said, “When does the milkman come yesterday?” He asked when the milkman had come the previous day.
6. The captain said to the players,” Why did you come late?” The caption asked the players why they had come late.
7. The magician said to the boy, “What did you see in the box?” The magician asked the boy what he had seen in the box.
8. I said to the students, “How can you solve this question?” I asked the students how you could solve that question.
9. The policeman said to the thief, “Why have you stolen this ring?” The policeman asked the thief why he had stolen that ring.
10. Mother said to her daughter, “Which movie did you see last night?” Mother asked her daughter which film she had watched the previous night.
Imperative Sentences
Verb I, Do not, Never Always Please Kindly शुरू होने वाले वाक्य आगे सूचक होते हैं। इनसे आज्ञा, आदेश, इच्छा, मना करना, निर्देश आदि का भाव प्रकट होता है।
Imperative Sentences को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना
Imperative Sentences को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
यदि Direct Speech में कोई Imperative Sentence आता है तो नीचे दिए rules के अनुसार Indirect Speech में उसे बदला जाता है।
Rule – 1 यदि Indirect Speech में आया हुआ Imperative Sentence ‘Verb I’ से शुरु है तो नीचे दिए rules को फॉलो करते हैं;
(1) यदि Reporting Speech में say, said, says या say to, said to, says to आयें तो नीचे दी गई टेबल के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
Note:– ऊपर दी गई टेबल के अनुसार Reporting verb मैं परिवर्तन करते हैं तथा इसके अलावा नीचे दिए गए शब्दों को भी reporting verb के स्थान पर प्रयोग किया जाता है।
Words : warn, implore, threaten, persuaded, entreat, urge, beg
(2) Commas को हटा देते हैं तथा उनके स्थान पर to का प्रयोग करते हैं।
(3) यदि वाक्य में sir, madam, please, kindly आया है तो उन्हें हटा दिए जाता है। ऐसे Sentences में Reporting Verb को request, requests या requested में बदलते हैं।
(4) अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्यों की तरह किये जाते हैं।
1. Shyam said to me, “Please help me.” Shyam requested me to help him.
2. The teacher says, “Open your books.” The teacher orders to open the books.
3. Ram said to Shyam, “Have a seat.” Ram told/requested Shyam to have a seat.
4. Father said to me, “Get out of my room.” Father ordered me to get out of his room.
5. The doctor said, ”Sleep for seven hours.” The doctor advised me to sleep for seven hours.
Note:–
1. यदि Direct Speech के Reported Speech में Sir या Madam आता है तो उनको हटाकर उनके स्थान पर respectfully का प्रयोग करते हैं।
2. यदि Reporting Verb के बाद कोई object नहीं आया है तो sir/madam के स्थान पर respectfully का प्रयोग object के बाद करते हैं।
1. The driver said, “Madam, please close the door.” The driver requested respectfully to close the door.
2. She said to the shopkeeper, “Sir, please help me.” She requested the shopkeeper respectfully to help her.
3. He said to the policeman, “Sir please catch the thief.” He requested the policeman respectfully to catch the thief.
4. The student said to the teacher, “Sir, grant me leave for two days” The the student requested the teacher respectfully to grant him leave for two days.
Negative Imperative Sentences को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलना
जो वाक्य सामान्य Do not/Don’t से शुरू होते हैं वे Negative Imperative Sentences कहलाते हैं।
Rule – 1 Reporting Verb – say, says, said को अर्थ के अनुसार ask, asks, asked/tell, tells, told/order, orders, oerderd में बदलते हैं।
Rule – 2 Commas को हटाकर Do not के स्थान पर not to लगाते हैं।
Rule – 3 बचा हुआ वाक्य not to के बाद जोड़ देते हैं।
Rule – 4 अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्यों की तरह होते हैं।
1. I said to her, “Don’t walk there.” I asked/told her not to walk there.
2. The teacher says, ”Don’t read it.” The teacher told me not to read it.
3. He said to me, “Don’t complain.” He asked/told me not to complain.
4. My friend said to me, “Do not open the window.” My friend asked/told me not to open the window.
Forbid/Forbids/Forbade का प्रयोग
Do not वाले नकारात्मक आज्ञा सूचक वाक्यों को forbade का प्रयोग करके भी indirect speech मैं बदलते हैं।
Rule – 1 say/says/said को forbid/forbids/forbade में बदलते हैं।
Rule – 2 Do not को हटा देते हैं तथा उसके स्थान पर to का प्रयोग करते हैं।
Rule – 3 अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्यों की तरह होते हैं।
1. She said to me, “Do not play in the sun.” She forbade me to play in the sun.
2. I said to my son, “Don’t run on the road.” I forbade my son to run on the road.
3. Father said to me, “Don’t eat this mango.” Father forbade me to eat that mango.
निषेध सूचक वाक्य
यदि Direct Speech में कोई निषेध सूचक वाक्य आया है तो उसे निम्न प्रकार से बदलते हैं।
Do + Verb I + Object + Other Words पर आधारित वाक्य
यदि कोई आगे सूचक वाक्य do से शुरू है तो उसको इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में बदलते समय नीचे दिए गए स्टेप्स को फॉलो करते हैं;
1. He said to me, “Do learn your lesson.” He asked me to learn my lesson.
2. Mahesh said to her, “Do open the letter.” Mahesh asked her to open the letter.
Let से शुरू होने वाले वाक्य को indirect speech change करना
Imperative Sentences जो let से शुरू होते हैं, यदि उनसे प्रस्ताव या सुझाव का बोध हो तो इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में बदलने के नियम निम्नलिखित हैं।
Rules –
1. He said, “Let us help the poor.” He suggested that they should help the poor.
2. Sohan said to her, “Let us go out.” Sohan proposed her that we/they should go out.
3. He said to his father, ” Let us go to park.” He suggested/proposed to his father that we/they should go to park.
4. Grandfather said to his grandson, “Let us go a for a walk.” Grandfather suggested to his grandson that they should go for a walk.
5. I said to him, “Let us go to market.” I suggested/proposed to him that they/we should go to market.
Let से Wish या Desire का बोध होने वाले वाक्यों को indirect speech में बदलना
यदि let से शुरू होने वाले direct speech वाक्यों से किसी इच्छा का भाव प्रकट हो तो उसे इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में निम्न प्रकार से बदलते हैं;
1. Mohan said, “Let him take a rest.” Mohan wished that he should take a rest.
2. She said, Let me help the needy.” She wished that she should help the needy.
3. He said, “Let me know this matter.” He wished that he should know that matter.
4. You said, “Let me watch this movie.” You wished that you should watch that movie.
Note:– यदि लेट से शुरू होने वाले वाक्य में अनुमति का बोध हो तो Reporting Verb को ordered/requested में बदलकर लिखते हैं। Commas तथा let को हटा देते हैं। उसके to allow बाद लिखते हैं। आप to allow के स्थान पर to let का प्रयोग कर सकते हैं।
Optative Sentences को Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियम
Optative Sentences (इच्छा सूचक वाक्य) वे वाक्य होते हैं जिनसे प्रार्थना, इच्छा, अभिशाप तथा आशीर्वाद का बोध होता है। ऐसे वाक्यों को डायरेक्ट स्पीच से इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में बदलने के नियम निम्नलिखित हैं;
1. अन्य परिवर्तन साधारण वाक्य की तरह होते हैं।
2. Inverted Commas को हटाकर that लिखते हैं।
3. Direct Speech में आए हुए optative sentence को assertive sentence (Subject + might + verb I + object + other words) में बदलकर लिखते हैं।
4. Reporting Verb को भाव तथा tense के अनुसार wish/wishes/wished, pray/prays/prayed, cruse/curses/cursed, bless/blesses/blessed में बदलते हैं।
1. They said, “May God bless you!” They prayed that God might bless him.
2. She said to me, “May may you live long!” She blessed me that I might live long.
3. My mother said to me, “You be happy! My mother wished me that I might be happy.
4. Mohan said to me, “May you succeed in your l Mohan wished me that I might succeed in my life.
5. People said, “Long live our prime minister!” People prayed that their prime minister might live long.
6. Father said to his son, “May you pass in the examination!” Father wished his son that he might pass in the examination.
Note:– यदि यदि डायरेक्ट स्पीच के optative sentence में may ना आया हो तो वहां may अपने आप ही मान लेते हैं।
Exclamatory Sentences को Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना
Exclamatory Sentences से joy sorrow surprise, anger, contempt, applause, regret, happiness आदि का बोध होता है। यह वाक्य अक्सर hello!, Alas!, Hurrah!, Ah!, Oh!, Well done!, Bravo! Ha! Ha!, Oh dear! आदि से प्रारंभ होते हैं।
Exclamatory Sentences डायरेक्ट स्पीच इनडायरेक्ट स्पीच में बदलने के नियम निम्नलिखित हैं;
1. Reporting Verb को नीचे दी गई टेबल के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
2. Inverted Commas को को हटा देते हैं तथा उनके स्थान पर that लिख देते हैं।
3. उसके बाद वाक्य में आए हुए सभी interjection (विस्मयसूचक शब्दों) को हटा देते हैं।
4. इसके बाद Exclamatory Sentence को Assertive Sentences में बदलकर लिखते हैं।
5. अंत में exclamation mark को हटाकर full stop लगाते हैं।
1. The boy said, ”Alas! I am ruined.” The boy exclaimed with sorrow that he was ruined.
2. He said, “How beautiful the rainbow is!” He exclaimed with joy that the rainbow was very beautiful. He exclaimed that the rainbow was very beautiful.
3. Father said, “Alas! My daughter hasn’t come.” Father exclaimed with sorrow that his daughter hadn’t come.
4. The foreigner said, “What a place it is!” The foreigner exclaimed with joy/surprise that it was a very beautiful place.
5. The students said to the teacher, “Happy Diwali, sir!” The students wished the teacher respectfully a happy Diwali.
6. The captain said, “Ah! we have lost the game.” The captain exclaimed with sorrow that they had lost the game.
7. The boy said to the girl, “How beautiful you are!”
The boy exclaimed with joy/surprise that she was very beautiful.
8. The sports teacher said, “Bravo! you have done well!” The sports teacher exclaimed with joy that he had done well.
9. He said, “Nice!” He gave an exclamation of pleasure.
10. He said, “Goodbye!” He bade me goodbye.
11. She said to her friends, “Good Night!” She bade her friends good night.
12. Raju said, “How happy I am!” Raju exclaimed with joy that he was very happy.
13. Father said, “Well done! You have done well!” Father exclaimed with praise that I had done well.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
Here are some Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for practice. Solve them and match your answer below. These exercises are very helpful for the students. After learning the above rules of Indirect Speech.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise – 1 – Assertive Sentences
- I said, “I will pay my bill.”
- The girls say, “We are free.”
- He said, “I am doing my work.”
- Father said, “I am not able to run.”
- Grandfather said, “You can jump.”
- He says, “I am very happy today.”
- The man said, “My does not eat anything.”
- My mother said, “Honesty is the best policy.”
- He said the earth pulls everything towards it.”
- The old woman says, “I have become very old.”
- Sham set to me, “I will attend the class tomorrow.”
- I said to my client. “You have not told me anything.
- The teacher said to the student, “you never come late.”
- The judge said to the criminal, “You can’t speak loudly here.”
- The teacher says to me, “You have written the essay correctly.”
- Sita said to her father, “I haven’t read the chapter two of this book.”
- The teacher said to the students, “There are twelve months in a year.”
- The student said to the teacher, “I didn’t understand the last example.”
- The principal said to the students, ”The school will be closed tomorrow.”
- Raju said to Rohan, “I don’t know the name of the minister of education.”
Interrogative Sentences – Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise – 2
Exercise – 2
- She said to me, “Are you fine?”
- The patient said, “Where is the doctor?”
- Pawan said to her, “Do you know me?”
- He said to me, “Will you open the door?”
- Father said to mother, “Where is Sohan going?”
- “Who has broken this chair?” said grandfather.
- Vinod said to Aruna do you know Rakhi’s address?
- She said, “When does your washerman come everyday?”
- They said to the passenger, “Where did you come from?”
- The police man said to the thief, “Who stole the money?”
- The girl says to the man, “Did you see my brother yesterday?”
- Rahul sad to his mother, ” Have you cooked something to eat?”
- The teacher said to the student Have you done your homework?”
- The doctor said to the patient, “When should I take this medicine?”
- Mr Sharma asked Mr Verma, “Where have you been playing since morning?”
- The customer say to the shopkeeper, “Do you sale this a special kind of coffee?”
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are some Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for practice. Solve them and match your answer below. These exercises are very helpful for the students. After learning the above rules of Indirect Speech. Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise - 1 - Assertive Sentences. He says, "I am very happy today." The girls say, "We are free."
Direct And Indirect Speech Rules in Hindi & Download PDF Direct à He said , "I am going to America now." Indirect à He said that he was going to America then. 1. Direct Speech के दो भाग होते है - Reporting Verb तथा Reported Speech (i) Reporting Verb Inverted commas के बाहर जो वाक्य होता है, उसकी Verb Reporting verb ...
Narration: Change of Tenses (टेंस का परिवर्तन) 3. Change of Other Parts of Speech. 2. Special Rules in Narration. 1. Assertive Sentence: Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना. 2. Interrogative Sentence: Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलना.
Direct and Indirect Speech Rules in Hindi. 1. Direct Speech के दो भागों को आपस में जोड़ने के लिए किसी शब्द का प्रयोग पड़ सकता है। जैसे कि ( उदा. में देखिये that का प्रयोग किया ...
If you get confused about Direct Indirect Speech or Narration in English grammar, watch this simple and easy lesson to learn direct indirect speech in Hindi ...
Direct speech - Ram said, "I am going to school". (राम ने कहा, मैं स्कूल जा रहा हूं।) Indirect speech - Ram said that He was going to school. (राम ने कहा कि वह स्कूल जा रहा था।) उपरोक्त पहले उदाहरण ...
Indirect -The teacher said that India became Republic on 26th January,1950. Direct -She said ,"Two and two is four". Indirect -She said that two and two is four. Direct -He said,"London is the capital of U.K.". Indirect -He said that London is the capital of U.K. Direct -He said,"Mr Narendra Modi is the P.M. of India".
Hey!Be ready to learn Narration in Hindi like you never did. In this video we are going to learn Narration Rules and Narration Change. We will learn "What is...
Direct : She said to her father, "You will go to the office.". Indirect : She told her father that he would go to the office. Direct : Neha said to me, "I study at home daily.". Indirect : Neha told me that she studied at home everyday. Direct : My mother said to me, "You will not do a job in this company.
If First Person (I, We) - according to the SUBJECT of the Reporting Speech. If Second Person (You) - according to the OBJECT of the Reporting Speech. If Third Person (He, She, They, Any name) - NO CHANGE. Pronuns. 3. Changes in Tense while making indirect speech from direct. Please! Tap to view clear. 4.
Direct Press Indirect Address Rules in Hindi & Download PDFDirect à He babbled , "I am moving to Us now." Indirect à I said that he was going to America then. 1. Direct Language के दो भाग होते है - Reported Verb तथा Reported Speech (i) Reporting Verb Inverted decimal के बाहर जो वाक्य होता है, उसकी Participle Media ...
Direct Indirect Speech | Narration In Hindi | Reported Speech Rules | English Grammar in Hindi with Michelle #ireportedspeech #directindirectspeech #english...
जैसे - I said, "I was busy yesterday.". Indirect Speech in Hindi. जब वक्ता द्वारा कही हुई बात को ज्यों का त्यों न लिखकर अपने शब्दों में उसका भावार्थ लिखते या बोलते हैं, उसे Indirect Speech या Indirect Narration ...
Get Started. Learn about the rules of direct and indirect speech in Hindi with examples. Understand the changes in tense and pronouns when converting from direct to indirect speech. Improve your language skills with these English grammar concepts.
संक्षिप्त विवरण : इस पोस्ट में Direct & Indirect Speech की पूरी जानकारी दी गई है इसके हर एक छोटे से छोटे Points को इस पोस्ट में विस्तार से बताया गया है । और साथ ही साथ ढेर सारे ...
Direct and Indirect | Reported Speech | Narration in Hindi | English GrammarDownload the App Now 🔥Link-https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.gya...
English Grammar | Narration In Hindi | Direct And Indirect Speech | Rules + Examples | Fab English🔔 Subscribe Our YouTube Channel - Fab English:https://www....
Direct and Indirect Speech in Indian (Narration) Rules, Examples and Workout. Get Direct and Indirect Narration in Hindi. प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन हिंदी में सीखिए। Rules of Indirect Speech in Hindi and English with examples.
Ab aap Direct and Indirect speech / Narration rules me maharath hasil karke sare exams ko chutkiyon me clear kar lenge. Narration in Hindi to English, Narrat...
Direct and Indirect Speech को Hindi में प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन कहते हैं। जब आप किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कही गई बात को दो तरह से कहा जाता है; Direct और Indirect के ...
direct and indirect speechdirect and indirect speech for class 10direct and indirect speech rulesdirect and indirect speech exercisesdirect and indirect spee...
Narration in Hindi | Direct and Indirect Speech in English | Narration Change/Rules for SSC CGLYour Quarries :-narration in hindidirect and indirect speech i...
Direct & Indirect | Reported Speech | Reporting Verb | Narration in Hindi || English Grammar #grammer #narration #direcspeech #indirectspeech #reportedspeech...