- Dictionaries home
- American English
- Collocations
- German-English
- Grammar home
- Practical English Usage
- Learn & Practise Grammar (Beta)
- Word Lists home
- My Word Lists
- Recent additions
- Resources home
- Text Checker
Definition of assignment noun from the Oxford Advanced American Dictionary
Take your English to the next level
The Oxford Learner’s Thesaurus explains the difference between groups of similar words. Try it for free as part of the Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary app


Nearby words
Should you give job applicants an assignment during the interview process? Be thoughtful about the ask

Hiring is a time-consuming and expensive endeavor. Companies need candidates who offer the right skills and experience for a given role, and who align with their organization’s vision and mission.
To find the best fit, many companies still lean on a strategy that continues to generate debate : the assignment. Some candidates believe their experience and interviews should give prospective employers enough information to determine whether they will fit the role. Employers have to ask themselves whether they are willing to turn off a strong candidate by asking them to do additional work.
Is the assignment valuable enough to the evaluation process that they cannot move someone forward without it? Sometimes it is—sometimes they help an employer decide between two strong candidates. And if they are necessary, how can employers make assignments fair and equitable for the candidate or candidates?
When done right, assignments help assess practical skills and problem-solving abilities, giving a clearer picture of a candidate beyond what their resume or interview reveals. But employers should be thoughtful about the ask. While it may make sense for roles that require specific technical expertise or creative thinking, it isn’t appropriate for all roles—so assignments should always be given with a clear reason for why they are needed.
Plus, they don’t just benefit the employer. For job seekers, an assignment during the interview process might also help them stand out from the competition. It can also offer a window into what their day-to-day in the new role might entail. Remember that the candidate should be interviewing the company, too. Having a test run of the work they’d be asked to do is a great way to see whether they believe the role is a fit.
However, there is a rift in how people perceive the assignment as part of the interview process. Workers today span many generations, each with unique values and expectations. Whereas older workers often prioritize stability and loyalty, younger millennials and Gen Zers are more focused on flexibility and work well-being, Indeed data shows .
This mindset impacts the amount of time and energy a candidate is willing to devote to each application. After multiple rounds of interviews and prep, taking on an in-depth assignment may feel like a bridge too far—especially if the expectations for the assignment are not clearly communicated ahead of time.
Some candidates are wary of providing free labor to a company that may use their work and not hire them. Hiring managers should be clear about how the work will be used. They may also consider offering compensation if the assignment requires more than a couple hours of someone’s time, or if they plan to use the work without hiring the candidate.
The key for early career candidates in particular is to ensure their time and efforts are respected. This is a win-win for employers: By providing clarity and transparency, they not only elicit the additional information they want from candidates, but they demonstrate that the organization is transparent and fair.
Equity is also imperative: Which candidates are being asked to complete assignments? Is the hiring team consistent in giving out assignments across ages, experience levels, and roles? There should always be a process and clear evaluation criteria in place to ensure fairness.
As we adapt to the rapidly evolving world of work, we must continue to think critically about each step in the hiring process. Candidate assignments can be a valuable tool, but only with appropriate respect for job seekers’ time and contributions.
With the right strategy, we can bridge the gap between generations in the workplace and build a hiring culture that values efficiency, talent, and integrity.
Eoin Driver is the global vice president of talent at Indeed.
More must-read commentary:
- Fannie Mae CEO: Beyoncé is right. Climate change has already hit the housing market—and homeowners aren’t prepared
Congress could soon spell the end of employment arbitration—but it’s not all good news for American workers
- Outdated laws prevent gig economy workers from getting benefits. This pilot program shows the path forward
- No, combustion engines won’t be supplanted by electric vehicles—and they’re critical for sustainable transport
The opinions expressed in Fortune.com commentary pieces are solely the views of their authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions and beliefs of Fortune .
Latest in Commentary

Apple says privacy is a ‘core value.’ Tim Cook shouldn’t compromise it to bridge the gap on AI

Employees have a once-in-a-generation chance to reimagine work—and they’re using it to demand an ‘emotional salary’

Birthing mothers’ near-death experience rates are 100 times higher than maternal mortality—and we don’t even know exactly why

Shark Tank entrepreneur: E-commerce giants are eating my sister’s lunch—and destroying the American Dream

Most Popular

Meet the boomers who’d rather spend $100k to renovate their homes than risk the frozen housing market: ‘It would be too hard to purchase anything else’

The collapsed Baltimore bridge will be demolished soon, and the crew of the ship that’s trapped underneath will be onboard when the explosives go off

The housing crisis in the U.S. is flipped upside down in Japan, where each home that’s occupied could be next to an empty one by 2033

Hedge fund billionaire Ken Griffin says college protests are the result of a ‘cultural revolution’ and Harvard should ’embrace our Western values’

Meet the 81-year-old CEO who built a $10.4 billion luxury cruise line tailored just for baby boomers: ‘They’re the richest group we have around’

Apple is finalizing a deal with OpenAI to put ChatGPT on the iPhone, while talks with Google to use Gemini are ongoing
Washington State Department of Enterprise Services (DES)
Capitol Campus
EAP | Capitol Campus
- Developmental Job Assignment
The state of Washington strives to attract, develop, and retain a talented and well-prepared workforce.
Providing employees opportunities to explore career interests through assignments that are uncommon in their daily work:
- Allow them to grow professionally.
- Allow the agency to pursue initiatives using resources that would not otherwise be available.
A developmental job assignment is a formal opportunity for an employee to develop professional knowledge, skills, and abilities that would not otherwise be available through their normal work activities.
Developmental job assignments should be primarily a product of the employee’s Performance and Development Plan (PDP). However, employees or the agency may pursue those assignments outside of this process.
Developmental job assignments are voluntary. Developmental job assignments will normally last no more than twelve months, and must have prior approval of the current Agency Head. Employees must have a six-month break between developmental job assignments. The time length and extensions of all assignments must include written justification.
Employees in developmental job assignments retain their own position number, draw their current salaries (including any scheduled periodic increments) and do not attain permanent status in any other classifications.
Funding is normally absorbed by the loaning (permanent) program unless prior arrangements are made to pay by the program with the developmental assignment. This includes travel and training. Developmental job assignments may be terminated by any of the parties with at least seven calendar days’ notice, unless a shorter notice period is mutually agreed upon.
Take Action
- The scope of the developmental job assignment should be clearly documented and approved by the supervising and hiring managers, the agency head and HR, before advertising the assignment.
- Learning goals should be established and documented before the employee begins the assignment.
- Developmental job assignments may be part-time or full-time.
- Employees are not expected to have all skills necessary to perform the tasks or project independently, but should have the aptitude, ability, and ambition to complete assignments with reasonable oversight.
- Since the primary purpose of a development job assignment is to support employee growth, assignments should be beyond current skill level. For example, a Fiscal Analysis with 10 years of experience in accounting would probably not be the best choice for a development assignment in entry level accounting. The assignment would not expand the employee’s skill set and would deprive a less experienced employee of the learning opportunity.
- The salary of an employee who accepts a developmental job assignment remains the same.
- There are no guarantees of future pay increase, promotion, or permanent job change.
- The developmental job assignment should not evolve into a permanent position without competitive recruitment.
- Employees are expected to go back to their previous position.
- Employees may not accept another developmental job assignment for at least six months after completing an assignment.
- At the end of the developmental job assignment, the supervisor and employee should complete a detailed evaluation of the learning experience, and place this documentation in the personnel file.
- Developmental job assignments are not transfers, and the employee is expected to return to their previous job. Therefore, the employee’s salary is typically paid by their home program. However, funding sources may be alternatively arranged through prior mutual agreement between programs.
- Developmental job assignments may be ended at any time by the employee or hiring manager (with approval by the appointing authority) with seven (7) days’ notice. Reasons to end a developmental job assignment early may include, but are not limited to: unexpected end of project; poor attendance or the unreliability of an employee; performance issues, etc.
Related Topics
- Developmental Job Assignment Agreement
- Access the Sole Source Contracts Database
- Buying Vehicles
- Contract Liaison Services
- Contract Usage Agreement for Public Benefit Nonprofits
- Current Commodity Pricing
- Customer Satisfaction
- Green Purchasing
- IT Professional Services Contracts
- Language Access Contracts
- Reporting Agency Contracts
- Reporting IT Contracts
- WEBS Enhancements for Supplier Diversity Policy
- Procurement Risk Assessment
- Technology Leasing
- Fleet Cards
- Amazon Business New Account Advanced Setup Guide
- Amazon Business New Account Simple Setup Guide
- Washington State Procurement Manual
- Register for Bid Opportunities
- State Contracts Assistance Network
- Tips for Small, Diverse and Veteran-Owned Businesses
- Bid Opportunities
- Bid in an Online Auction
- Surplus Digital Storefront
- Surplus Real Estate
- Federal Surplus
- Surplus for Eligible Organizations
- Register to use Surplus Property Disposal Request System
- What can my Organization Surplus?
- How to Surplus Items
- Transport & Storage
- Contact Surplus Operations
- Parents and Caregivers
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How do I become an EAP Network Provider?
- Information and Forms for Currently Contracted Providers
- Frequently Asked Questions for Providers
- Public Employers
- Brochures, Posters, and Guides
- Employee Newsletter
- Supervisor Newsletter
- Racism & Mental Health Resources
- Subscribe to Receive EAP News
- How EAP helps supervisors
- Incident Stress Management Tools
- Presentations
- Request an EAP organizational Consult
- Statewide Mediation Services
- Suicide Prevention and Intervention Resources
- Barrier Free Facilities
- Campus Color Initiative
- Capitol Campus Energy Meter Installation
- Capitol Childcare Center
- Distributed Antenna System
- East Plaza Water Infiltration Repair
- Irving R. Newhouse Building Replacement project
- Joel Pritchard Library project
- Legislative Modular Building
- LCM SEPA Checklist Supporting Documentation
- Old Capitol Flue Pipe and Fuel Storage Tank Replacement
- Plaza Garage Projects
- SEPA Environmental Review
- Sid Snyder Avenue Underground Utilities Project
- Sidewalk and ADA Access Improvements
- Photo Gallery
- Building Projects
- Childcare Options for State Employees
- Helen Sommers Building
- Accessibility Information for the Legislative (Capitol) Building
- Capitol Facts & History
- Visitor Accommodations
- Updating Emergency Notification Contact Method Settings - via the Everbridge App for Android
- Updating Emergency Notification Contact Method Settings - via the Everbridge portal
- Updating Your Emergency Notification Contact Method Settings - via the Everbridge App for iOS
- WA Agency Alerts Troubleshooting
- Capitol Campus Lost and Found
- Capitol Master Plan
- Featured Project Archive
- Getting to the Capitol
- Arc of Statehood
- Boiler Works
- Du Pen fountain
- George Bush monument
- Glass and Stone Mosaic Mural
- Helen Sommers Building Artwork
- Korean War memorial
- Law enforcement memorial
- Medal of Honor memorial
- Mysteries of Life
- POW-MIA memorial
- Senator Cal Anderson Memorial
- Territorial Sundial
- Tivoli fountain
- Untitled Stainless steel
- Vietnam Veterans memorial
- WW II Memorial Tile Search
- Water Garden
- Winged Victory monument
- Woman Dancing
- World War II memorial
- Open Carry of Weapons Prohibited in State Capitol Buildings and on West Campus Grounds
- Capitol Lake Trails
- Centennial Park
- Deschutes Parkway and Interpretive Center
- Heritage Park
- Marathon Park
- Pollinator Garden
- Sunken Garden
- Sylvester Park
- Campus Use Rates
- Schedule an Event
- Civic Education Tours
- Things to See on the Capitol Campus
- American White Elm
- Atlas Cedar
- Autumn Brilliance Amelanchier
- Big Leaf Maple
- Bush Butternut/White Walnut
- Centennial Challenge
- Cloud 9 Dogwood
- Crimson King Norway Maple
- Dawn Redwood
- Douglas Fir
- Eastern Flowering Dogwood
- English Oak
- Evergreen Magnolia/Southern Magnolia
- Giant Sequoia
- Japanese Cryptomeria
- Japanese Snowbell
- Kwanzan Flowering Cherry
- Northern Catalpa
- Norway Maple
- Purple-leaf European Beech
- Saucer Magnolia
- Serbian Spruce
- Sweetbay Magnolia
- Thornless Cockspur Hawthorn
- Tulip Tree/Yellow Poplar
- Washington Moon Trees
- Weeping Cutleaf Redleaf Japanese Maple Tree
- Western Hemlock
- Western Red Cedar
- Yoshino Flowering Cherry
- Young Weeping European White Birch Tree
- Visiting the Campus
- Volunteer as a State Capitol Tour Guide
- Changes to the Small Works Roster
- EDGE Program
- Forms/Reference Documents
- Public Works Bidding
- Become a Selection Panel Member
- Bid Information
- Current Projects Advertised for Consultant Selection
- Frequently Asked Questions about B2GNow & Diversity Compliance
- Join the Architect/Engineer Reference File for Public Agencies
- How Consultants Are Selected
- Join the Architect/Engineer Reference File
- Trade Categories & Specialties
- Glossary/Definitions
- Policies/Processes
- How to Bid on Public Works Projects
- Job Order Contracting
- Small Works Roster
- Reporting Apprentice Hours
- Guidelines for Design-Bid-Build
- GC/CM Project Selections
- About Green Building & LEED
- Building Commissioning
- ESPC Success Stories
- Energy Efficiency Resources
- Energy Life Cycle Cost Analysis
- Energy Program Contacts
- Energy Project Management Services
- Energy Savings Performance Contracting
- Energy Service Company Partners
- December 2016 Report
- December 2015 Report
- December 2014 Report
- December 2013 Report
- Green Building & LEED
- Reports and Case Studies
- Request Our Services
- Building Access
- Custodial Services
- General Information
- Maintenance & Operations/Building Automation
- Project management, alterations and additions
- How Real Estate Services can help
- Important Laws that Apply to State Facilities
- Leasing Property to the State
- Market Searches
- Properties For Sale
- Real Estate Services - Contact Information
- Requests for Information
- Service Fees
- Solicitations for Leased Space
- Client Workshops
- Contact My Project Manager
- Instructions for Public Agencies
- Project Delivery Systems
- Project Information & Reference for School Districts
- Accident Reporting
- 2022 Rate Adjustment FAQ
- Driving a State Fleet Vehicle: How-To Videos
- Electric Vehicles
- Fleet Management Best Practices
- Fleet Operations Mileage Reporting
- Fleet Operations Roadside Assistance
- Fleet Services and Repairs
- Fueling State Vehicles
- Register for Fleet Rentals
- Report Lost or Stolen Plates & Fuel Cards
- Services for Agency-Owned Vehicles
- Traffic Citations
- Vehicle Utilization
- Visitors and the General Public
- Windshield Repair or Replacement
- ADA Accessible Parking
- Agency Vehicle/Reserved Parking
- Benefits for Carpool/Rideshare Parkers
- Bicycle Registration & Agreement
- Capitol Campus Employee Parking Fees
- Capitol Campus Parking Fees
- Employee Capitol Campus Parking Frequently Asked Questions
- Employee Parking (for personal vehicles)
- General Public - Visitor Parking
- Parking Strategy Implementation Plan
- Policies & Other Requirements
- Visitor Parking on the Capitol Campus
- Where Do I Place My Parking Permit?
- Capitol Campus Daily Rental Fleet
- Contact Fleet Operations
- DOH Daily Rental Fleet
- Daily Rental Fleet Locations
- Enterprise Rent-A-Car
- Fleet Operations HQ Daily Rental
- Reservation Frequently Asked Questions
- State Vehicle Frequently Asked Questions
- Travel Calculator
- Tumwater Daily Rental Fleet (Vans)
- Air Travel FAQ
- Lodging FAQ
- Passenger Vehicle Purchase Request
- Per Diem Information
- Transit Buses
- Vehicle Purchasing Frequently Asked Questions
- Vehicle Purchasing
- Contact Your Customer Service Representative
- Customer Support
- Directions to the Printing Facility
- Forms and Templates
- How to complete the A21-A Printing Request Form?
- How to complete the A24-A Copy Center Request Form?
- About Mail Services
- Consolidated Mail Services Distribution Map
- Contact Mail Services
- Electronic Return Receipt
- Getting Started
- Inserting & Mailing Preparation Services
- How to use the Mailing Instruction Form or "Pink Slip"
- Mail guidelines
- Postal regulation regarding window envelopes
- Sending and receiving mail
- State Document and Mailing Standards
- Map and Directions to Consolidated Mail Services
- News and Updates
- Binding and Finishing
- Copy Center
- Fulfillment
- Large Volume and Specialized Printing
- Mailing and Shipping
- Merge/Purge
- Posters, Mounting, and Laminating
- Prepress Services
- Printing Services
- Printing and Imaging Inserting Services
- Specialty Printing
- Standard Folds
- Variable Printing
- Print Job Consultation Procedure
- Change brings challenges, encouragement and collaboration to Printing and Imaging
- Online Ordering
- Printing and Imaging program helps customers find the highest quality for the best value
- With a little coaching, Printing and Imaging employees are defining clear goals
- Production Services
- Request an Estimate
- How to Become a DES Printing and Imaging Customer
- How to Become a DES Printing and Imaging Vendor
- How to Check a Proof
- How to Create PDF Files
- How to Design Your Mail Piece
- How to Perform a Press Check
- How to Preflight Your Job File
- How to Prepare Your Address Files
- How to Prepare and Submit Files for Variable-Data Printing
- How to Send Us Your Electronic Mail Address Files
- How to Submit Word or Publisher Files
- Imagesetting Tips
- Money Saving Tips
- Printing Standards
- Proofreading Marks
- Sample A21-A Printing Request Form
- State Printing Services Bidding Process and the Use of WEBS
- Sustainable Printing
- Use of Printing and Imaging
- Trainings & Consultation
- Contracts and Procurement Support
- Agency Assignments
- Agency Required Policies - Quick Reference Guide
- Chart of Accounts
- Common Budget and Fiscal Terms
- Finance Toolkit
- Frequently Used Travel Websites
- Internal Control For Cash Receipts
- TEMS Access Request Form
- Travel Do's & Don'ts - Quick Reference Guide
- Travel Policies & Related Issues - Quick Reference Guide
- Travel and Expense Management System - TEMS
- Appointment Letter Templates
- Deferring Excess Vacation Leave
- Determine Insurance Eligibility
- Employee Information Changes
- Employee Performance Management
- Equal Pay and Opportunities Act Guidance
- Family Medical Leave Act
- Harassment, Discrimination, or Retaliation Complaint Process
- Leave & Holidays
- Leaving State Service
- Mobile Work
- New Hire Forms
- No-Call, No-Show Process
- Paid Family & Medical Leave
- Reasonable Accommodation - Employee
- Rehire Forms
- Shared Leave
- Transfer Employee Forms
- Voluntary Employees' Beneficiary Association - Medical Expense Plan
- 2018 Archive HR News
- 2019 Archive HR News
- 2020 Archive HR News
- Policy Information
- State Employee Services
- Small Agency HR
- Small Agency Meetings
- Exempt Management Service
- HR Liaison Resources
- Infants at Work
- Investigations
- Non-Traditional Workers
- Onboarding a New Employee
- Paid Family & Medical Leave - Employer
- Personnel/Payroll Data Sheet Guidance
- Policy Development
- Position Action Form Guidance
- Reasonable Accommodation
- Recognition
- FrequentlyAskedQuestions
- Job Seeker Support
- Diversity Recruitment Resources
- Veterans Outreach
- Getting Ready to Recruit
- Online Recruiting System
- Planning Your Recruitment
- Preparing for Your Recruitment-Checklist
- Recruiting a Diverse Candidate Pool
- Retaining Your Employees
- Tools & Resources
- Recruitment
- Required Workplace Posters
- Separating Employment - Disability Separation
- Separating Employment
- Shared Leave Pools
- Washington General Service
- Washington Management Service
- Small Agency Support - One Washington
- Workshop Materials
- Required and Recommended Training
- Training & Development Staff
- Training Manager Meeting
- Browse by Category
- Browse by Course
- Business Analysis Certificate
- Graphic Designer | Certificate
- Leadership Certificate
- Project Management Certificates Program
- Technical Solutions Delivery Certificate (Systems Analyst)
- Crucial Learning Toolkits and eLearnings
- Contract & Procurement Training Search
- DES Diversity, Equity and Inclusion Training
- Leading Organizations
- HR Leadership Resources
- Franklin Covey All Access Passes and eLearnings
- External User Training Request Registration Form
- LinkedIn Learning Administrators Toolkit
- Online Learning Resources for Workforce Development
- Attendance Policy
- Learner Expectations
- Training Locations and Maps
- Vendor Resources
- Training Professional Accessibility Resources
- Brand Style Guide
- User Guides & Resources
- WA State eLearning Classes
- Overnight and extended parking on Deschutes Parkway
- Pedestrian Bridge Banner Policy
- Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS)
- About Risk Management
- Commercial Insurance Claim Reporting Procedure
- Commercial Insurance Policies
- Enterprise Risk Management
- Health & Welfare Programs
- Insurance for State Agencies
- Joint Property & Liability Programs
- Local Government Self-Insurance Program Links
- Local Government Self-Insurance
- Loss Prevention Review Team Reports
- Loss Prevention Review Team
- Loss Prevention Services and Training
- Loss Prevention Requirements for Van Safety
- Notary Bonds
- File a Tort Claim
- Pool Reports
- Regulatory Action
- Related RCWs
- Reporting an Accident Involving a State Driver
- Risk Finance Program
- Risk Management Contacts
- State Agency Self-Insurance Liability Program
- State Vehicles and Drivers
- Vendor Debarment
- A to Z Index
- Jobs at DES
- Capitol Lake
- Public Works Business Diversity Program
- Cross-laminated timber pilot project
- Success Stories
- Business Diversity Advisory Group
- Capitol Campus Design Advisory Committee
- Background and Reference
- 2014 CPARB Meeting Archives
- 2015 CPARB Meeting Archives
- 2016 CPARB Meeting Archives
- 2017 CPARB Meeting Archives
- 2018 CPARB Meeting Archives
- 2019 CPARB Meeting Archives
- 2020 CPARB Meeting Archives
- Member Information and Bios
- Public Works Data Collection Effort
- Board Development Committee
- Business Equity/Diverse Business Inclusion Committee
- Education Connections Committee
- General Contractor/Construction Manager Committee
- JOC Evaluation Committee
- Legislation Writing\Drafting Committee
- Local Government Public Works Study Committee
- Project Feedback Process Workgroup
- SHB 1621 Review Committee
- Small Works Committee
- Task Force & Committee Archives
- WSDOT Project Delivery Method Review Task Force
- Procurement Customer Advisory Group
- Supplier Diversity Community of Practice
- 2014 PRC Meeting Archives
- 2015 PRC Meeting Archives
- 2016 PRC Meeting Archives
- 2017 PRC Meeting Archives
- 2018 PRC Meeting Archives
- 2019 PRC Meeting Archives
- 2020 PRC Meeting Archives
- State Building Code Council
- State Capitol Committee
- Training Advisory Group
- WACS - Archived Meetings
- Pro-Equity Anti-Racism at DES
- How To's
- LGBTQ+ Organizations
- Training & Education
- Publications & Reports
- Media Contacts
- Program Contacts
- Locations and Directions
- Capitol Campus Interactive Map
- Public Record Request
- Privacy Notice

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- English | en
- Spanish | ES
- French | FR
- German | DE
- Portuguese | PT
- Chinese | ZH
- Japanese | JA
5 Ways to Manage a Job Reassignment
Instead of laying people off, organizations are increasingly giving them new job assignments. How to manage what can be a jarring professional change.
For More Expert Insights

Associate Principal, Advisory

Senior Client Partner, North America

Career Coach, Korn Ferry Advance

Career & Leadership Coach, Senior Consultant

Career & Leadership Coach, Korn Ferry Advance
U.S. companies announced 42% fewer layoffs in July than in June, and 8% fewer cuts than in July of 2022. The underlying reason is unexpected, however: while companies are continuing to eliminate jobs, they’re often reassigning workers to new roles instead of laying them off. Experts believe this trend could continue.
“Chances are, these are the types of changes we can expect to see over time, whether it’s due to new technology, like AI, or economic trends,” says Korn Ferry Advance coach Frances Weir .
While it can be difficult for employees to suddenly step into a new role and work with a new manager and team, experts say reassignment can have an upside. It offers employees an opportunity to learn new skills and bolster their résumé. For instance, if you’re moved onto a team that is underresourced and needs help, there’s an opportunity for you to make notable contributions that could earn you recognition, says Mark Royal , a senior client partner for Korn Ferry Advisory.
Since a reassignment can potentially be advantageous, it’s worth considering what steps to take to help you adjust. Here are five ways to adapt to a job reassignment.
Manage your emotions.
Reassignments are often unexpected, so it’s important to take a step back from your emotions. It’s normal to feel surprise, anger, or a loss of control, Royal says. But making an immediate, emotional decision—like quitting immediately—could wind up being detrimental to your long-term career.
Be diplomatic with your manager and get ready for the new assignment. At the same time, do some self-reflection. “Understand why you feel this way, and know that if you choose to stay, it doesn’t have to be forever,” Weir says.
Treat it like a new job.
As with any new position, making a good impression during your first 90 days is important, says Alyson Federico, a career coach at Korn Ferry Advance. “No matter how familiar you already are with the team or your new manager, don’t make assumptions that you know what’s going on or what you’re supposed to do,” she says.
Remember that your relationship with these colleagues will evolve. Ask questions to understand expectations about deliverables and responsibilities, how the team communicates, and how you fit into the group, Federico says. Make sure you have a clear sense of how your new team defines success.
Determine the reassignment’s length.
“Is this an open-ended shift, or has it been presented as a short-term assignment with some expectation of other opportunities down the road?” Royal says.
Ask your manager whether there will be a probationary period. Determine how much grace you will get before you’re expected to be a full contributor. Ask if there’s an onboarding process to help you get up to speed.
Stay optimistic.
Your new role and new department might provide an opportunity to build additional skills for your résumé and provide future career options. “You might stumble into something you’re really good at that you were previously unaware of, or perhaps land on a team you really enjoy working with, or discover a new career interest,” says Tiffinee Swanson , a Korn Ferry Advance career coach.
Remind yourself that even though your old role was eliminated, your company decided to keep you. That is a strong signal that your organization values you and your work, Royal says.
Consider the role’s fit.
Even if the role seems to be a poor fit for your skills, you might consider staying if you can see a career path within the company where the fit might be better, Royal says.
Give it some time, experts say. However, if it continues to be a struggle, it’s OK to leave, especially if you have another job offer, you’re offered a severance package, or you’re burned out and don’t have energy to make a change to a reassigned role.
“The best insurance against job loss, or ending up in a position you don’t like, is consistent networking, keeping your résumé and LinkedIn profile up-to-date, and staying abreast of trends in your industry,” says Val Olson , a career coach at Korn Ferry Advance.
For more expert career advice, connect with a career coach at Korn Ferry Advance .
Read more This Week in Leadership articles
Related articles
Purpose and power, this week in leadership (may 6 - may 12), insights to your inbox.
Stay on top of the latest leadership news with This Week in Leadership—delivered weekly and straight into your inbox.
Recent articles

Best-selling author Dan Goleman shares what business leaders can learn from community organizers.

How to skillfully climb the corporate ladder. Plus, why baby boomers are giving Gen Zers the silent treatment at work (and vice versa).

The Silent Treatment—Between Gen Zers and Boomers
Forty percent of workers over 55 haven’t spoken to a Gen Zer at work in a year, and one in five Gen Z to someone over 50. Why corporate leaders should be worried.

Job Market: Still a Mess
Open roles have fallen an eye-popping 30% since peaking two years ago, but HR professionals still face massive workloads to find the right candidates.
- Capabilities
- Business Transformation
- Organization Strategy
- Total Rewards
- Assessment & Succession
- Talent Acquisition
- Leadership & Professional Development
- Intelligence Cloud
- Consumer Markets
- Financial Services
- Healthcare & Life Sciences
- Specialties
- Board & CEO Services
- Corporate Affairs
- Cybersecurity
- FInancial Services
- Human Resources
- Information Technology
- Risk Management
- Supply Chain
- Sustainability
- Partnerships
- Microsoft Alliance
- Duke University
- Cleveland Clinic
- Jobs with our clients
- Advance your career
- Join Korn Ferry
- Find a consultant
- Find an office
- Business impact
- Investor relations
- Press releases
© Korn Ferry. All rights reserved.
Terms of Use
Cookie Settings
Do Not Sell My Info
- Branch and Bound Tutorial
- Backtracking Vs Branch-N-Bound
- 0/1 Knapsack
- 8 Puzzle Problem
- Job Assignment Problem
- N-Queen Problem
- Travelling Salesman Problem
- Branch and Bound Algorithm
- Introduction to Branch and Bound - Data Structures and Algorithms Tutorial
- 0/1 Knapsack using Branch and Bound
- Implementation of 0/1 Knapsack using Branch and Bound
- 8 puzzle Problem using Branch And Bound
Job Assignment Problem using Branch And Bound
- N Queen Problem using Branch And Bound
- Traveling Salesman Problem using Branch And Bound
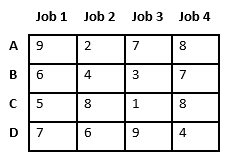
Let there be N workers and N jobs. Any worker can be assigned to perform any job, incurring some cost that may vary depending on the work-job assignment. It is required to perform all jobs by assigning exactly one worker to each job and exactly one job to each agent in such a way that the total cost of the assignment is minimized.
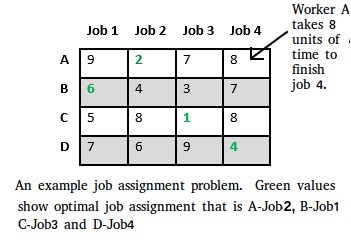
Let us explore all approaches for this problem.
Solution 1: Brute Force
We generate n! possible job assignments and for each such assignment, we compute its total cost and return the less expensive assignment. Since the solution is a permutation of the n jobs, its complexity is O(n!).
Solution 2: Hungarian Algorithm
The optimal assignment can be found using the Hungarian algorithm. The Hungarian algorithm has worst case run-time complexity of O(n^3).
Solution 3: DFS/BFS on state space tree
A state space tree is a N-ary tree with property that any path from root to leaf node holds one of many solutions to given problem. We can perform depth-first search on state space tree and but successive moves can take us away from the goal rather than bringing closer. The search of state space tree follows leftmost path from the root regardless of initial state. An answer node may never be found in this approach. We can also perform a Breadth-first search on state space tree. But no matter what the initial state is, the algorithm attempts the same sequence of moves like DFS.
Solution 4: Finding Optimal Solution using Branch and Bound
The selection rule for the next node in BFS and DFS is “blind”. i.e. the selection rule does not give any preference to a node that has a very good chance of getting the search to an answer node quickly. The search for an optimal solution can often be speeded by using an “intelligent” ranking function, also called an approximate cost function to avoid searching in sub-trees that do not contain an optimal solution. It is similar to BFS-like search but with one major optimization. Instead of following FIFO order, we choose a live node with least cost. We may not get optimal solution by following node with least promising cost, but it will provide very good chance of getting the search to an answer node quickly.
There are two approaches to calculate the cost function:
- For each worker, we choose job with minimum cost from list of unassigned jobs (take minimum entry from each row).
- For each job, we choose a worker with lowest cost for that job from list of unassigned workers (take minimum entry from each column).
In this article, the first approach is followed.
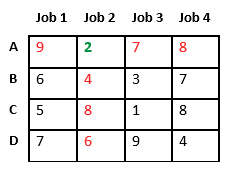
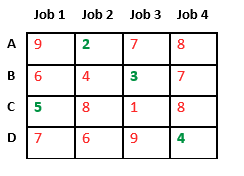
Let’s take below example and try to calculate promising cost when Job 2 is assigned to worker A.
Since Job 2 is assigned to worker A (marked in green), cost becomes 2 and Job 2 and worker A becomes unavailable (marked in red).
Now we assign job 3 to worker B as it has minimum cost from list of unassigned jobs. Cost becomes 2 + 3 = 5 and Job 3 and worker B also becomes unavailable.
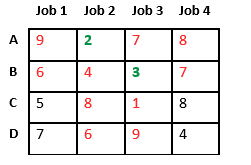
Finally, job 1 gets assigned to worker C as it has minimum cost among unassigned jobs and job 4 gets assigned to worker D as it is only Job left. Total cost becomes 2 + 3 + 5 + 4 = 14.
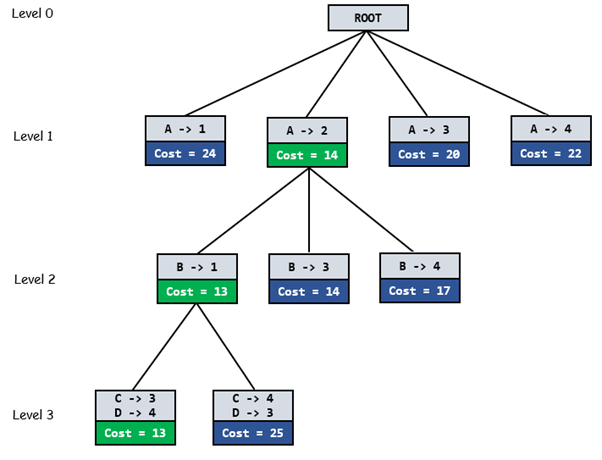
Below diagram shows complete search space diagram showing optimal solution path in green.
Complete Algorithm:
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
Time Complexity: O(M*N). This is because the algorithm uses a double for loop to iterate through the M x N matrix. Auxiliary Space: O(M+N). This is because it uses two arrays of size M and N to track the applicants and jobs.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Branch and Bound
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
What Does an Assignment Editor Do?
Learn About the Salary, Required Skills, & More
The Balance / Ellen Lindner
- Technology Careers
- Sports Careers
- Project Management
- Professional Writer
- Music Careers
- Legal Careers
- US Military Careers
- Government Careers
- Finance Careers
- Fiction Writing Careers
- Entertainment Careers
- Criminology Careers
- Book Publishing
- Animal Careers
- Advertising
- Assignment Editor Duties & Responsibilities

Assignment Editor Salary
- Education, Training, & Certification
- Assignment Editor Skills & Competencies
Job Outlook
Work environment, work schedule, comparing similar jobs.
- Mercer University
An assignment editor works at the assignment desk, which is the nerve center of any newsroom. This is where newsroom staff members monitor multiple sources for breaking news, including police and fire scanners. When possible news arises, the assignment editor works with reporters, photographers, producers, and other staff members to assign and develop story ideas.
Small companies sometimes have one assignment editor who is responsible for organizing the assignment desk to operate around the clock. In larger newsrooms, there may be a team of assignment editors that take turns staffing the desk.
Assignment Editor Duties & Responsibilities
The job generally requires the ability to perform the following duties:
- Monitor multiple sources for possible news stories
- Develop and propose a daily news coverage plan
- Lead newsroom staff meetings to review possible stories and assignments
- Help choose which journalists, photographers, and other staff members are assigned to cover stories
- Stay on top of all stories to ensure they're developing as planned and determine which ones are not coming together
- Be the main point of communication between reporters, production teams, and executive staff on developing stories
It's up to the assignment editor to assign people to investigate and report on news stories. The assignment editor's day is sometimes spent shifting people and equipment around so that as many stories get covered as possible, with an eye out on how to handle breaking news coverage at any moment.
When working in television, an assignment editor may also work with the tv producer to decide which crews will take live trucks or a helicopter to broadcast live during a newscast. Also, a TV news anchor who is reviewing scripts just before airtime will often turn to the assignment editor to confirm facts.
An assignment editor's salary can vary depending on location, experience, and employer. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics offers salary data for the broader editor category, but it doesn't offer separate data on the assignment editor subcategory:
- Median Annual Salary: $59,480
- Top 10% Annual Salary: $114,460
- Bottom 10% Annual Salary: $30,830
Education, Training, & Certification
Most assignment editors have the same types of degrees as other editors and journalists in a newsroom.
- Education: Most employers prefer candidates that have at least a bachelor’s degree in communications, journalism, or English.
- Experience: This is often key to getting this type of job, because experience is key to building a list of contacts and learning how to operate smoothly. Employers usually prefer candidates with a background in the type of media in which they specialize, whether it's television, digital, or print news.
- Training: Most training happens on the job. Aspiring assignment editors may want to find an internship position at a newsroom assignment desk.
Assignment Editor Skills & Competencies
To be successful in this role, you’ll generally need the following skills and qualities:
- Editorial judgment: Assignment editors need to be able to quickly decide whether a story is newsworthy. And although they aren't usually writing the stories themselves, they need to know all of the components of a good news story to guide reporters on coverage.
- Interpersonal skills: Successful assignment editors form relationships with many contacts that can help bring a story together. For example, someone in this role at a local TV news station may have all the county sheriffs' home telephone numbers on speed-dial and be on a first-name basis with the current and previous mayors.
- Organizational skills: An assignment editor must be able to organize the logistics and track the details of several stories at a time and keep everything on schedule.
- Communication skills: An assignment editor must skillfully communicate with all of the staff involved in making news stories come together, including reporters, photographers, production teams, and executive staff.
The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment in this field will grow 6 percent through 2026, which is slightly slower than the overall employment growth of 7 percent for all occupations in the country. The BLS it doesn't offer separate data on the assignment editor subcategory.
Most of this job is done in an office working under several tight deadlines at once. Those who thrive on pressure and get an adrenaline rush when something unexpected happens may be best suited for this occupation.
An assignment editor usually arrives in the newsroom earlier than the other managers to get a handle on what's happening that day to brief the newsroom. Most assignment editors work full time, and many work long hours, which include evenings and weekends.
People who are interested in becoming assignment editors may also consider other careers with these median salaries:
- Writers and authors: $61,820
- Reporters, correspondents, and broadcast news analysts: $40,910
- Desktop publishers: $42,350
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , 2017
How to Get the Job
Build a Contact List
Making a list of contacts is the best place to start for a budding assignment editor. That involves making personal connections with people so that you can turn to them when you need information.
Join a Professional Association
The American Media Institute offers a list of professional associations you can join. Which one you choose may depend on your specialty or medium (websites or television, for instance). This will help you build your contact list and stay up to date on the latest tools and techniques in the industry.
Search job sites that specialize in media careers, such as MediaBistro and iHire Broadcasting .
- What Does a TV Reporter Do?
- What Does a TV News Director Do?
- What Does a TV News Producer Do?
- What Does a Book Editor Do?
- What Does a TV News Anchor Do?
- What Does a Copy Editor Do?
- What Does a Zoologist Do?
- What Does a Sports Announcer Do?
- What Does an Advertising Media Director Do?
- What Does a Media Planner Do?
- What Does a Publicist Do?
- What Does a Producer Do?
- What Does a Screenwriter Do?
- What Does a Fact Checker Do?
- What Does a Copywriter Do?
- What Does a Home Typist Do?
Assignment Problem: Meaning, Methods and Variations | Operations Research
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations.
Meaning of Assignment Problem:
An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total cost or maximize total profit of allocation.
The problem of assignment arises because available resources such as men, machines etc. have varying degrees of efficiency for performing different activities, therefore, cost, profit or loss of performing the different activities is different.
Thus, the problem is “How should the assignments be made so as to optimize the given objective”. Some of the problem where the assignment technique may be useful are assignment of workers to machines, salesman to different sales areas.
Definition of Assignment Problem:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Suppose there are n jobs to be performed and n persons are available for doing these jobs. Assume that each person can do each job at a term, though with varying degree of efficiency, let c ij be the cost if the i-th person is assigned to the j-th job. The problem is to find an assignment (which job should be assigned to which person one on-one basis) So that the total cost of performing all jobs is minimum, problem of this kind are known as assignment problem.
The assignment problem can be stated in the form of n x n cost matrix C real members as given in the following table:
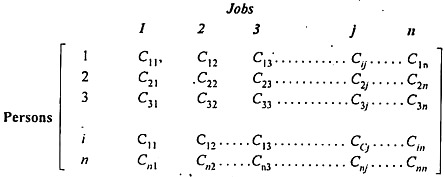
When is it sensible to use chore instead of assignment ?
While the synonyms chore and assignment are close in meaning, chore implies a minor routine activity necessary for maintaining a household or farm.
When is duty a more appropriate choice than assignment ?
Although the words duty and assignment have much in common, duty implies an obligation to perform or responsibility for performance.
When might job be a better fit than assignment ?
The synonyms job and assignment are sometimes interchangeable, but job applies to a piece of work voluntarily performed; it may sometimes suggest difficulty or importance.
When could stint be used to replace assignment ?
In some situations, the words stint and assignment are roughly equivalent. However, stint implies a carefully allotted or measured quantity of assigned work or service.
When can task be used instead of assignment ?
The meanings of task and assignment largely overlap; however, task implies work imposed by a person in authority or an employer or by circumstance.
Thesaurus Entries Near assignment
assignments
Cite this Entry
“Assignment.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/assignment. Accessed 13 May. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on assignment
Nglish: Translation of assignment for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of assignment for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 10, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.

Academic Assignment Writing Jobs Let Enjoy Freedom
Monetize your time and efforts
- WritingCreek is a freelance academic writing company which can offer you a trustworthy long-term cooperation.
- A simple application process, continuous career growth, a wide range of disciplines and subjects, are among the benefits of WritingCreek

Get decent freelance job
Simple application process.
Begin earning money in 3 days!

We believe you have all it takes
- Excellent communication skills
- Proficiency in the particular area of study
- Ability to conduct a research
- Original content writing
- Advanced level of English
Continuous career growth
Earn from $ 4 - 12 per page
- 1+ completed orders
- 5+ completed orders
- 80% + Success Rate
- 30+ completed orders
- 90% + Success Rate
- 50+ completed orders
- 95% + Success Rate
Reveal your skillset in academic writing
- Humanities 0 %
- Applied sciences 0 %
- Social sciences 0 %
- Formal sciences 0 %
- Natural sciences 0 %
- Other academic fields 0 %
Share of orders in the system for this branch of science

Some of the latest orders
Find the one that fits your expertise
You must have heard plenty of times about perks of specific jobs allowing to work without leaving your house on a permanent basis. They are true. Freelance occupation lets:
Determine your workload yourself. Due to this factor, you will not face the extreme fatigue when any amount of money for one more task doesn’t represent any interest because all you want to do is to fall asleep for a couple of days. With freelance writing jobs online, you are your own boss. You know how many regular duties you need to fulfill. You know how much time you need to devote to your significant other, your family, friends, hobby, sports, sleep, healthy lifestyle, etc. You are fully aware of how much time you need to spend on anything else but work to be happy. And only you can determine the golden middle!
Set the working hours. Striving to optimization of working process, you can set the hours when you feel like working most of all to focus on your tasks easier. When you have chosen one of the freelance writing jobs online , you are free to set the working hours. It is a very useful prerogative! You don’t have to ask if you can go home earlier today because you need to take your child from school or because you have a competition. You don’t need to provide explanations for being late for 15 minutes at the beginning of the day. You are the boss. Being one of the essay writers or those who accepted an offer of grant writing jobs, you become independent.
Choose tasks yourself. Having joined the team of freelance writers, you are given an opportunity to select your assignments: take the one you like and reject the one that seems not your cup of tea. You will no longer have to deal with a bundle of tasks you’d wish to burn. Freelance writing jobs give you a chance deal only with the tasks that are of interest to you. Thus, you will easily boost your knowledge and skills in professional sphere.
Such is a kind of position we gladly offer to experts in the wide variety of spheres:
- Human and social sciences. We invite for collaboration experts in Sociology, Psychology, Arts, Political science, Economics, Law, Management, Journalism, Pedagogics, Philosophy, Aesthetics, Linguistics, Law, and many other areas belonging to this group. On our website, you will find grant writing jobs to make use of your knowledge.
- Natural sciences. We are looking for freelance writers in Biology, Physics, Chemistry, Geology, Geography, Ecology, and Astronomy. If you have in-depth knowledge in Quantum or Cell biology, Space physics, or Nuclear chemistry (just as well as the rest of domains), and are looking for a position that gives you freedom in organizing your working hours – choose freelance writing jobs at biz.
- Technical studies. We are looking for specialists in Engineering, Informatics, Transport, Telecommunication, Architecture, Technology, Avionics, Food manufacturing industry, Computer science, Electronics, etc. We assume, we need writers specialized in any area of listed studies. Taking grant writing jobs at our website, you take your chance for independence. On our list, we include both the most common and the rarest spheres: from Radio electronics, Electrical engineering, and Modern architecture to Space syntax, Biological engineering, and Sumerian architecture.
- Exact studies. The connoisseurs of this group are always in high demand: due to the difficulties with assignments related to the subjects of this kind, every second student is looking for assistance with exact studies. Choose our freelance writing jobs! Make use of favorable terms of collaboration with a trustworthy website. Freelance experts in Algebra, Mathematical analysis, Geometry, Accounting, Trigonometry, Calculus, Discrete math, and Algorithms, welcome to biz.
Are you still hesitating? It’s high time to speed up your success with freelance writing.
You need to Log in or Sign up for a new account in order to create account
Please enter your email to proceed
By clicking "Continue", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We`ll occasionally send you promo and account related emails.
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- Premium News
- Biden Economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Personal Loans
- Student Loans
- Car Insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Should you give job applicants an assignment during the interview process be thoughtful about the ask.
Hiring is a time-consuming and expensive endeavor. Companies need candidates who offer the right skills and experience for a given role, and who align with their organization’s vision and mission.
To find the best fit, many companies still lean on a strategy that continues to generate debate : the assignment. Some candidates believe their experience and interviews should give prospective employers enough information to determine whether they will fit the role. Employers have to ask themselves whether they are willing to turn off a strong candidate by asking them to do additional work.
Is the assignment valuable enough to the evaluation process that they cannot move someone forward without it? Sometimes it is—sometimes they help an employer decide between two strong candidates. And if they are necessary, how can employers make assignments fair and equitable for the candidate or candidates?
When done right, assignments help assess practical skills and problem-solving abilities, giving a clearer picture of a candidate beyond what their resume or interview reveals. But employers should be thoughtful about the ask. While it may make sense for roles that require specific technical expertise or creative thinking, it isn’t appropriate for all roles—so assignments should always be given with a clear reason for why they are needed.
Plus, they don’t just benefit the employer. For job seekers, an assignment during the interview process might also help them stand out from the competition. It can also offer a window into what their day-to-day in the new role might entail. Remember that the candidate should be interviewing the company, too. Having a test run of the work they’d be asked to do is a great way to see whether they believe the role is a fit.
However, there is a rift in how people perceive the assignment as part of the interview process. Workers today span many generations, each with unique values and expectations. Whereas older workers often prioritize stability and loyalty, younger millennials and Gen Zers are more focused on flexibility and work well-being, Indeed data shows .
This mindset impacts the amount of time and energy a candidate is willing to devote to each application. After multiple rounds of interviews and prep, taking on an in-depth assignment may feel like a bridge too far—especially if the expectations for the assignment are not clearly communicated ahead of time.
Some candidates are wary of providing free labor to a company that may use their work and not hire them. Hiring managers should be clear about how the work will be used. They may also consider offering compensation if the assignment requires more than a couple hours of someone’s time, or if they plan to use the work without hiring the candidate.
The key for early career candidates in particular is to ensure their time and efforts are respected. This is a win-win for employers: By providing clarity and transparency, they not only elicit the additional information they want from candidates, but they demonstrate that the organization is transparent and fair.
Equity is also imperative: Which candidates are being asked to complete assignments? Is the hiring team consistent in giving out assignments across ages, experience levels, and roles? There should always be a process and clear evaluation criteria in place to ensure fairness.
As we adapt to the rapidly evolving world of work, we must continue to think critically about each step in the hiring process. Candidate assignments can be a valuable tool, but only with appropriate respect for job seekers’ time and contributions.
With the right strategy, we can bridge the gap between generations in the workplace and build a hiring culture that values efficiency, talent, and integrity.
Eoin Driver is the global vice president of talent at Indeed.
More must-read commentary:
Fannie Mae CEO: Beyoncé is right. Climate change has already hit the housing market—and homeowners aren’t prepared
Congress could soon spell the end of employment arbitration—but it’s not all good news for American workers
Outdated laws prevent gig economy workers from getting benefits. This pilot program shows the path forward
No, combustion engines won’t be supplanted by electric vehicles—and they’re critical for sustainable transport
The opinions expressed in Fortune.com commentary pieces are solely the views of their authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions and beliefs of Fortune .
This story was originally featured on Fortune.com
Search Jobs
What would you like to do?
- Administration
- Animation and Visual Effects
- Architecture and Design
- Asset Management
- Building, Construction and Facilities
- Business Strategy and Development
- Call Center
- Communications
- Data Science and Analytics
- Engineering
- Finance and Accounting
- Food and Beverage
- Governmental Affairs
- Graphic Design
- Health Services
- Horticulture and Landscaping
- Hotel and Resorts
- Human Resources
- Legal and Business Affairs
- Maritime and Cruise Operations
- Marketing and Digital Media
- Merchandising
- Project Management
- Quality Assurance
- Research and Development
- Retail Operations
- Sciences and Animal Programs
- Social Responsibility
- Sports and Recreation
- Stage Productions
- Supply Chain Management
- Theme Park Operations
Brand Select ABC News Aulani, A Disney Resort & Spa Consumer Products Games & Publishing Disney Advertising Disney Branded Television Disney Cruise Line Disney Direct to Consumer Disney Entertainment Disney Entertainment & ESPN Technology Disney Entertainment Television Disney Experiences Disney Music Group Disney Platform Distribution Disney Star Disney Store Disney Theatrical Group Disney Vacation Club Disney's Hilton Head Island Resort Disney+ Hotstar Disneyland Paris Disneyland Resort ESPN Hong Kong Disneyland Resort Industrial Light & Magic Lucasfilm Marvel Studios National Geographic Partners Federal Credit Union Pixar Animation Studios The Walt Disney Company (APAC) The Walt Disney Company (Corporate) The Walt Disney Company (EMEA) The Walt Disney Company (India) The Walt Disney Company (LATAM) The Walt Disney Studios Walt Disney Animation Studios Walt Disney Imagineering Walt Disney World Resort
Job Level Select Business Support / Administrative Executive Internships / Programs Management Operations / Production Professional
Where would you like to work?
Country/Region Select Argentina Australia Bahamas Brazil Bulgaria Canada Denmark Finland France Germany Hong Kong India Indonesia Italy Japan Mexico Netherlands Norway Philippines Poland Portugal Shipboard Singapore South Korea Sweden Switzerland Taiwan Thailand Turkey United Kingdom United States Vietnam
State/Province Select Arkansas Bangkok Bavaria British Columbia Buenos Aires F.D. California Canton of Zurich Capital Region Connecticut DC England Florida Haryana Hawaii Ho Chi Minh Île-de-France Region Illinois Islands District Istanbul Jakarta Special Capital Region Karnataka Lisbon District Lombardy Lower Saxony Maharashtra Massachusetts Mazovia Mecklenburg-Vorpommern Metro Manila Mexico City Missouri Nevada New Jersey New South Wales New York North Carolina North Holland Ohio Ontario Oregon Oslo County Pennsylvania São Paulo Seoul Sofia-grad South Carolina Stockholm County Taipei Taiwan Tamil Nadu Telangana Tennessee Texas Tokyo Uusimaa Victoria Washington West Bengal
City Select Amsterdam Anaheim Austin Bangkok Bay Lake Bengaluru Bentonville Branson Bristol Buenos Aires Burbank Celebration Charlotte Chennai Chessy Chicago Copenhagen Coral Gables Coupvray Destin Durham Elizabeth Emeryville Fresno Glendale Greater Manchester Gurgaon Helsinki Hilton Head Island Ho Chi Minh City Hyderabad Istanbul Iver Heath Jakarta Kapolei Kings Mountain Kissimmee Kolkata Lake Buena Vista Lancaster Lantau Island Las Vegas Lisbon Livermore London Los Angeles Makati City Manhattan Beach Marne-la-Vallée Mexico City Milan Minato-ku Monroe Montévrain Moore Park Morrisville Mumbai Munich Myrtle Beach New Taipei City New York Orlando Oslo Palm Desert Papenburg Paris Philadelphia Raleigh Rancho Mirage Richmond San Francisco Santa Monica São Paulo Seattle Seoul Serris Sevierville Singapore Sofia Stockholm Sydney Taipei Taipei City Tampa The Woodlands Tlalpan Toronto Tulalip Vancouver Warsaw Washington Wismar Woodburn Zurich

Be part of the story
Already applied?
Assignment Desk Editor I
Job summary:.
Hires camera crews, satellite trucks and studios, and arranges feeds and/or transfer of content. Strategizes and organizes movement of IP-based transmission devices for coverage. Coordinates the efforts of freelance and staff producers and associated production/technical personnel to provide video and audio sports/news material for ESPN platforms. Handles all ancillary crew needs, such as parking, credentials, Ethernet, phone lines, and permits. Understands basic rights and clearances issues. Participates in strategic editorial and logistical planning of coverage. Acts as the liaison between the Assignment Desk and Media Assets, Media Operations, and Transmission. Gathers and communicates content for use on ESPN platforms, working with ESPN staff and vendors, social media, affiliates and other networks. Shifts will include nights and weekends.
Responsibilities:
- Hires freelance ENG crews
- Possesses depth of knowledge in fiber, satellite, cellular, FTP, and viral newsgathering procedures
- Assigns and coordinates movement of IP-based transmission devices
- Clears social media content for ESPN platforms Reacts immediately to breaking news and requests; pursues story-related materials (sound and video) in a timely manner
- Collaborates with ABC NewsOne/ABC affiliates, as well as other networks, on breaking news stories, sharing of information, video and sound
- Gathers and enters transmission information (satellite, fiber, cable) for televised games
- Works well in a team setting, shows initiative and problem-solving skills; takes direction from assignment desk management, coordinating producers, news editors, producers and senior editors
- Stays informed and up-to-date on sporting events and has above-average sports knowledge
Basic Qualifications :
- Superior interpersonal and communication skills, with the capacity to handle high-volume email and phone traffic
- Demonstrated initiative and positive, solution-oriented outlook
- Advanced ability to organize and prioritize
- Commitment to accuracy and attention to detail
- Strong knowledge of sports
- Working knowledge of television production and electronic and social media newsgathering
- Working knowledge of Microsoft Office programs: Outlook, Excel, Word
Preferred Qualifications :
- Three-plus years’ experience in a television-related field
- Spanish speaker preferred.
Required Education :
- High School Degree or equivalent required
Preferred Education :
- Bachelor's Degree Preferred
About ESPN:
Working at ESPN is unlike anything else. That’s because we’re always finding new ways to interact with fans – however and wherever they connect with sports. Every day we’re doing things that no one has done, all in a dynamic culture where we defy odds and continuously outdo ourselves. When you have the latest technology, game-changing ideas and world-class talent on your team, every day is extraordinary.
About The Walt Disney Company:
The Walt Disney Company, together with its subsidiaries and affiliates, is a leading diversified international family entertainment and media enterprise that includes three core business segments: Disney Entertainment, ESPN, and Disney Experiences. From humble beginnings as a cartoon studio in the 1920s to its preeminent name in the entertainment industry today, Disney proudly continues its legacy of creating world-class stories and experiences for every member of the family. Disney’s stories, characters and experiences reach consumers and guests from every corner of the globe. With operations in more than 40 countries, our employees and cast members work together to create entertainment experiences that are both universally and locally cherished.
This position is with ESPN Productions, Inc , which is part of a business we call ESPN .
ESPN Productions, Inc is an equal opportunity employer. Applicants will receive consideration for employment without regard to race, color, religion, sex, age, national origin, sexual orientation, gender identity, disability, protected veteran status or any other basis prohibited by federal, state or local law. Disney fosters a business culture where ideas and decisions from all people help us grow, innovate, create the best stories and be relevant in a rapidly changing world.
Watch Our Jobs
Sign up to receive new job alerts and company information based on your preferences.
Job Category Select a Job Category Administration Animation and Visual Effects Architecture and Design Asset Management Banking Building, Construction and Facilities Business Strategy and Development Call Center Communications Creative Culinary Data Science and Analytics Engineering Finance and Accounting Food and Beverage Governmental Affairs Graphic Design Health Services Horticulture and Landscaping Hotel and Resorts Human Resources Legal and Business Affairs Maritime and Cruise Operations Marketing and Digital Media Merchandising Operations Production Project Management Publishing Quality Assurance Research and Development Retail Operations Sales Sciences and Animal Programs Security Social Responsibility Sports and Recreation Stage Productions Supply Chain Management Talent Technology Theme Park Operations
Location Select Location Amsterdam, Netherlands Anaheim, California, United States Austin, Texas, United States Bangkok, Thailand Bay Lake, Florida, United States Bengaluru, India Bentonville, Arkansas, United States Branson, Missouri, United States Bristol, Connecticut, United States Buenos Aires, Argentina Burbank, California, United States Celebration, Florida, United States Charlotte, North Carolina, United States Chennai, India Chessy, France Chicago, Illinois, United States Copenhagen, Denmark Coral Gables, Florida, United States Coupvray, France Destin, Florida, United States Durham, North Carolina, United States Elizabeth, New Jersey, United States Emeryville, California, United States Fresno, California, United States Glendale, California, United States Greater Manchester, United Kingdom Gurgaon, India Helsinki, Finland Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, United States Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam Hyderabad, India Istanbul, Turkey Iver Heath, United Kingdom Jakarta, Indonesia Kapolei, Hawaii, United States Kings Mountain, North Carolina, United States Kissimmee, Florida, United States Kolkata, India Lake Buena Vista, Florida, United States Lancaster, Pennsylvania, United States Lantau Island, Hong Kong Las Vegas, Nevada, United States Lisbon, Portugal Livermore, California, United States London, United Kingdom Los Angeles, California, United States Makati City, Philippines Manhattan Beach, California, United States Marne-la-Vallée, France Mexico City, Mexico Milan, Italy Minato-ku, Japan Monroe, Ohio, United States Montévrain, France Moore Park, Australia Morrisville, North Carolina, United States Mumbai, India Munich, Germany Myrtle Beach, South Carolina, United States New Taipei City, Taiwan New York, New York, United States Orlando, Florida, United States Oslo, Norway Palm Desert, California, United States Papenburg, Germany Paris, France Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States Raleigh, North Carolina, United States Rancho Mirage, California, United States Richmond, Australia San Francisco, California, United States Santa Monica, California, United States São Paulo, Brazil Seattle, Washington, United States Seoul, South Korea Serris, France Sevierville, Tennessee, United States Singapore, Singapore Sofia, Bulgaria Stockholm, Sweden Sydney, Australia Taipei, Taiwan Taipei City, Taiwan Tampa, Florida, United States The Woodlands, Texas, United States Tlalpan, Mexico Toronto, Canada Tulalip, Washington, United States Vancouver, Canada Warsaw, Poland Washington, DC, United States Wismar, Germany Woodburn, Oregon, United States Zurich, Switzerland
Job Level Select Professional Operations / Production Management Business Support / Administrative Internships / Programs Executive
Email Address
Country/Region of Residence Select Afghanistan Aland Islands Albania Algeria American Samoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bolivia, Plurinational State Of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Bouvet Island Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Brunei Darussalam Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia Comoros Congo Congo, the Democratic Republic of The Cook Islands Costa Rica Cote D'ivoire Croatia Cuba Curacao Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia French Southern Territories Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Great Britain Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guernsey Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands Holy See (Vatican City State) Honduras Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran, Islamic Republic Of Iraq Ireland Isle of Man Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea, Democratic People's Republic Of Korea, Republic Of Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Lao People's Democratic Republic Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macau Macedonia, the Former Yugoslav Republic Of Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Micronesia, Federated States Of Moldova, Republic Of Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Antilles Netherlands New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestinian Territory, Occupied Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Reunion Romania Russian Federation Rwanda Saint Barthelemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin (French Part) Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Sint Eustatius Sint Maarten (Dutch Part) Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syrian Arab Republic Tahiti Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania, United Republic Of Thailand Timor-leste Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States United States Minor Outlying Islands Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic Of Viet Nam Vietnam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S. Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
Confirm Email
- Book a Speaker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vivamus convallis sem tellus, vitae egestas felis vestibule ut.
Error message details.
Reuse Permissions
Request permission to republish or redistribute SHRM content and materials.
Job Rotation Policy
The purpose of [Company Name]'s job rotation policy is to enable staff members to develop knowledge, new skills and a broader understanding of our operations/programs and to utilize staff effectively.
Job rotation is the systematic movement of employees from one job to another within the organization to achieve various human resources objectives such as orienting new employees, training employees, enhancing career development, and preventing job boredom or burnout.
[Company Name] encourages staff to take the opportunity to develop their knowledge and skills using various learning opportunities, including job rotations and developmental assignments.
The job rotation program involves the temporary assignment of an employee in a position or department for a predetermined period to perform the specific duties of another position. This is normally a voluntary assignment where the employee treats the assigned duties as part of his or her regular responsibilities.
Any supervisor or employee may initiate a request for job rotation assignment after careful evaluation of other available workforce strategies. Job rotation may be inter-departmental, within a division of [Company Name], or in a cross-functional division.
All employees who have completed six months of regular (nontemporary) employment with [Company Name] are eligible to participate in job rotation.
An employee on job rotation assignment shall remain in the same position number and compensation classification and shall retain all rights, benefits and privileges of his or her regular position.
An employee on job rotation shall retain eligibility for promotional opportunities.
- A written request for job rotation must be submitted by the employee to his or her supervisor (the "sending supervisor"). The request should indicate the desired job, the location of the job, the duration of the assignment, and the expected outcome and benefit of the assignment. If a job rotation is suggested by a supervisor, the supervisor will assist the employee in completing the written request.
- The sending supervisor and employee should determine how the employee's current job duties will be performed before proceeding with a job rotation agreement.
- The employee, the sending supervisor and the receiving supervisor should meet to discuss the possibility of job rotation, the assigned duties, time frames, schedules, hours, etc., so that details can be negotiated and arranged. A job rotation request can be denied if it cannot be balanced with the needs of [Company Name].
- The sending supervisor, receiving supervisor and the employee shall collaborate to determine the duration of job rotation. Rotations may be full-time, half-time or one day a week. Rotations can also be based on an allocation of time where an employee works at his or her regular job for a portion of each workday and during the rest of the day rotates to another job.
- Both the sending and receiving supervisors should obtain approval for job rotation assignments through their appropriate chains of command.
- If the arrangement is acceptable by all parties, the receiving supervisor will complete the job rotation agreement and have it signed by the employee, the sending supervisor and appropriate directors. Copies of the signed agreement should be provided to all parties. The original, signed agreement should be forwarded to Human Resources where it will be recorded for workforce planning efforts and maintained in the employee's personnel file.
- An employee on job rotation shall receive a performance evaluation at the regular time. The sending and receiving supervisors shall collaborate as appropriate on the evaluation. The sending supervisor shall retain responsibility for timely completion of the evaluation.
- If travel expenses are involved in the job rotation assignment, the receiving area will be responsible for payment of travel expenses, unless other payment arrangements are made and agreed to by the parties involved.
- A job rotation assignment may be extended by mutual agreement of the parties. Management may terminate the assignment at any time. If the rotation assignment is extended or terminated, the extension or termination should be documented in writing, signed by all individuals on the original agreement and copied to all parties, including Human Resources.
- Questions or concerns regarding the job rotation assignment should be addressed with management and/or Human Resources.
Related Content

A 4-Day Workweek? AI-Fueled Efficiencies Could Make It Happen
The proliferation of artificial intelligence in the workplace, and the ensuing expected increase in productivity and efficiency, could help usher in the four-day workweek, some experts predict.

How One Company Uses Digital Tools to Boost Employee Well-Being
Learn how Marsh McLennan successfully boosts staff well-being with digital tools, improving productivity and work satisfaction for more than 20,000 employees.
Advertisement
Artificial Intelligence in the Workplace
An organization run by AI is not a futuristic concept. Such technology is already a part of many workplaces and will continue to shape the labor market and HR. Here's how employers and employees can successfully manage generative AI and other AI-powered systems.
HR Daily Newsletter
New, trends and analysis, as well as breaking news alerts, to help HR professionals do their jobs better each business day.
Success title
Success caption
- Subscribe Now (Opens in new window)
Your Marine Corps
- Air Force Times (Opens in new window)
- Army Times (Opens in new window)
- Navy Times (Opens in new window)
- Pentagon & Congress
- Defense News (Opens in new window)
- Flashpoints
- Benefits Guide (Opens in new window)
- Military Pay Center
- Military Retirement
- Military Benefits
- VA Loan Center (Opens in new window)
- Discount Depot
- Military Culture
- Military Fitness
- Military Movies & Video Games
- Military Sports
- Transition Guide (Opens in new window)
- Pay It Forward (Opens in new window)
- Black Military History (Opens in new window)
- Congressional Veterans Caucus (Opens in new window)
- Military Appreciation Month (Opens in new window)
- Vietnam Vets & Rolling Thunder (Opens in new window)
- Military History
- Honor the Fallen (Opens in new window)
- Hall of Valor (Opens in new window)
- Service Members of the Year (Opens in new window)
- Create an Obituary (Opens in new window)
- Medals & Misfires
- Installation Guide (Opens in new window)
- Battle Bracket
- CFC Givers Guide
- Task Force Violent
- Photo Galleries
- Newsletters (Opens in new window)
- Early Bird Brief
- Long-Term Care Partners
- Navy Federal
- Digital Edition (Opens in new window)
Marine combat instructors can avoid recruiting or drill instructor duty
The Marine Corps has made the combat instructor job a special duty assignment once more, effectively allowing those instructors to sidestep the sometimes-dreaded recruiter or drill instructor jobs .
Each year, a portion of Marine noncommissioned officers are given special duty assignments, which take them out of their regular jobs for a few years to perform other duties on behalf of the Corps. Now, the combat instructor job, which entails training Marines in combat skills, counts as a special duty assignment.
“It’s an extremely rewarding duty because you actually get to affect and to teach the warfighting skills that all Marines learn through the entry-level training pipeline, and it’s really critical for the operational readiness of the force,” Gunnery Sgt. Tyler Stokes , the enlisted assignments monitor for the combat instructor community, said in a video the Marine Corps recently posted to LinkedIn.
Marines get plucked from their regular jobs and placed into special duty assignments through the annual Headquarters Marine Corps Special Duty Assignment Screening Team screening process, often called HSST for short.
The Marine Corps itself said in an administrative message in 2023, “A successful SDA tour is a hallmark of a competitive Marine and makes him or her exceptionally qualified for promotion.”
The other special duty assignments are recruiter, drill instructor and Marine security guard detachment commander. Before a rule change that was announced in 2017, combat instructor and Marine security guard watchstander also counted as special duty assignments.
After that change, those two jobs became Type 1 screenable billets, a category that also includes Marine Corps security forces guards, staff noncommissioned officer academy faculty advisors and curriculum developers, and Marine special operators, among others, according to Marine spokeswoman Capt. Sarah Eason.
“Designation as a Special Duty Assignment increases the staffing priority of this duty, ensuring maximum fill of available billets,” Eason said of the recent redesignation of the combat instructor role via email May 3.
A 2019 analysis by the Marine Corps of the impact of special duty assignments — which at the time didn’t include combat instructor — on Marines’ lives found they were correlated with better promotion chances but also with higher rates of divorce, addiction and suicide attempts.
“Due to increased responsibilities and duties outside of one’s normal occupational field, SDA tours are often viewed as a Marine’s most stressful noncombat tour,” the analysis stated.
Now that being a combat instructor is a special duty assignment again, Marines who complete that role won’t end up on future HSST lists, according to Eason.
For the next special duty assignment season, fiscal year 2026, combat instructor may be an option for Marines who end up on the list “but will be subject to availability after the volunteer period,” Eason said.
“Unlike other SDAs, there are a limited number of Combat Instructor billets open to any primary military occupational specialty, and these routinely fill with volunteers,” the spokeswoman added. “The preponderance of Combat Instructor billets requires an infantry primary (military occupational specialty), so Marines in this field will likely be able to request Combat Instructor duty during the HSST.”
As a special duty assignment, the combat instructor role will come with incentives that include easier promotions and choice over a next duty station, according to Eason. Combat instructors will continue to receive special pay.
A plan to make the combat instructor job a special duty assignment again has been in the works since at least 2021, as the Corps planned to lengthen the infantry course from nine to 14 weeks, creating a demand for more instructors. Training Command did not respond by time of publication to a Marine Corps Times question about the current length of the course.
Irene Loewenson is a staff reporter for Marine Corps Times. She joined Military Times as an editorial fellow in August 2022. She is a graduate of Williams College, where she was the editor-in-chief of the student newspaper.
In Other News
House lawmakers cut back public hearings on annual defense bill
Defense and veterans hearings on capitol hill for the week of may 13, 2024..
A Marine combat instructor shielded his student from a grenade with his body — and survived
When then-sgt. brett meil saw a student inadvertently activate a grenade during infantry training, he covered him with his body and prepared to die..
VA to provide grants for veteran, spouse employment help
A new grant program will provide up to $500,000 to organizations helping veterans and spouses land post-military jobs..
Watchdog blasts VA for errors leading to $11M in improper bonuses
A watchdog report criticized va leaders for mistakes in handling $11 million in bonuses for senior department leaders..

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Work assignments are most common in creative and technical fields of work. For example, writers may need to complete a trial piece before being hired, and marketing professionals may have to create a campaign pitch and outline as part of their interview process. For more technical work, like information technology or computer science, the ...
ASSIGNMENT definition: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.
3. Outline Main Points, Only Tease the Details. More often than not, the primary reason companies dole out homework is to get a better sense of your thought process, as well as how you structure and convey your thoughts and ideas. There's not necessarily a "right" answer, nor is there a need to get way down in the weeds.
The meaning of ASSIGNMENT is the act of assigning something. How to use assignment in a sentence. Synonym Discussion of Assignment.
[countable] a task or piece of work that somebody is given to do, usually as part of their job or studies. Students are required to complete all homework assignments. You will need to complete three written assignments per semester. a business/special assignment ; I had set myself a tough assignment.
1. : a job or duty that is given to someone : a task someone is required to do. [count] My assignment was to clean the equipment. = They gave me the assignment of cleaning the equipment. The students were given a homework assignment. The reporter's assignment is to interview the candidate. The reporter is here on an assignment.
1 [countable, uncountable] a task or piece of work that someone is given to do, usually as part of their job or studies You will need to complete three written assignments per semester. She is in Greece on an assignment for one of the Sunday newspapers. one of our reporters on assignment in China I had given myself a tough assignment. a business/special assignment
For job seekers, an assignment during the interview process might also help them stand out from the competition. It can also offer a window into what their day-to-day in the new role might entail.
7 meanings: 1. something that has been assigned, such as a mission or task 2. a position or post to which a person is assigned.... Click for more definitions.
A developmental job assignment is a formal opportunity for an employee to develop professional knowledge, skills, and abilities that would not otherwise be available through their normal work activities. Developmental job assignments should be primarily a product of the employee's Performance and Development Plan (PDP).
The assignment's parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do. Interpreting the assignment. Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
The first answer is clearly correct. The job that Jonas is assigned to is the job of Receiver of Memory. The job of Receiver of Memory is unique in this community. It shows the essential weakness ...
Remember that your relationship with these colleagues will evolve. Ask questions to understand expectations about deliverables and responsibilities, how the team communicates, and how you fit into the group, Federico says. Make sure you have a clear sense of how your new team defines success. Determine the reassignment's length.
Solution 1: Brute Force. We generate n! possible job assignments and for each such assignment, we compute its total cost and return the less expensive assignment. Since the solution is a permutation of the n jobs, its complexity is O (n!). Solution 2: Hungarian Algorithm. The optimal assignment can be found using the Hungarian algorithm.
ASSIGNMENT meaning: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.
An assignment editor is the heartbeat of the newsroom. Here is a career profile and a job description. ... Training: Most training happens on the job. Aspiring assignment editors may want to find an internship position at a newsroom assignment desk. Assignment Editor Skills & Competencies .
1. Additionally, at school an assignment is a specific task for a student to do in class time or as homework, and the word also refers to the document which is produced during the assignment and handed in for correction. On the other hand a job is a task unrelated to the students studies, for example rubbish bin duty. - Peter.
Suppose there are n jobs to be performed and n persons are available for doing these jobs. Assume that each person can do each job at a term, though with varying degree of efficiency, let c ij be the cost if the i-th person is assigned to the j-th job. The problem is to find an assignment (which job should be assigned to which person one on-one basis) So that the total cost of performing all ...
Synonyms for ASSIGNMENT: task, job, duty, project, mission, chore, responsibility, function; Antonyms of ASSIGNMENT: dismissal, discharge, firing, expulsion ...
Literature Creative Writing "The Veldt" by Ray Bradbury Using the module literature on the 'division of labour', analyse and assess the relationship between the demise, or growth, of individual knowledge and the overall expansion of knowledge within society and its implication for social hierarchy. 4 Pages. $16-46 Rate.
For job seekers, an assignment during the interview process might also help them stand out from the competition. It can also offer a window into what their day-to-day in the new role might entail.
Jobs I got a job as 2A335 and just recently ForeverWingman updated their website to the different base locations. On those assignments it shows different levels, 3, 5, and 7.
Works well in a team setting, shows initiative and problem-solving skills; takes direction from assignment desk management, coordinating producers, news editors, producers and senior editors Stays informed and up-to-date on sporting events and has above-average sports knowledge
A job rotation assignment may be extended by mutual agreement of the parties. Management may terminate the assignment at any time. If the rotation assignment is extended or terminated, the ...
The English Learner Teacher on Special Assignment (TOSA) ensures that students, parents and staff are provided the support necessary to be successful. Serves as a resource to teachers (instructional practices), parents (information & communication), and students (English Language Acquisition skills, supervision, & activities) while assisting students/staff in attaining a meaningful, enriched ...
A plan to make the combat instructor job a special duty assignment again has been in the works since at least 2021, as the Corps planned to lengthen the infantry course from nine to 14 weeks ...