Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.

How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- Graduate School
Hardest Research Proposal Questions and Best Sample Answers
Featured Expert: Dr. Michela Insenga, PhD

Practicing with sample research proposal questions and answers can have great benefits for any major research project such as a dissertation or thesis. This is often the final step before you finally get your doctorate degree. However, before all of that, you must first craft a research proposal. This is a detailed outline that will transform into the thesis that you will eventually have to defend in front of a panel of distinguished academics. It is always important to be aware of what thesis defense questions you will be asked when it is all said and done, but you may have to start justifying your research a little earlier on with the completion of a research proposal.
In this article, we include sample questions and answers you could be faced with when submitting your research proposal, some tips for preparing your responses, as well as the benefits of seeking professional help from a grad school advisor .
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 13 min read
What to expect for your research proposal.
Early on in your PhD process, you may have to submit a research proposal that details the scope of your research and what you plan to for an eventual thesis or dissertation project. You have already learned how to find a PhD topic , so now it is time to put your passion for your field into practice and start to manifest the ideas swimming in your head.
This document should include the specific topic you would like to research, what angle you will be taking for your research, as well as your justification for choosing this subject. Regardless of whether or not your goals are the same as when you wrote your research interest statement sample , you must still provide an update about what your project is going to examine.
Should you go to grad school? Watch this video:
The purpose of the research proposal is to convince your supervisor that you are on the right direction. You are essentially providing a roadmap for your supervisor through your motives in undertaking this project and how you plan to complete it. Your supervisor will have to evaluate whether or not your project is relevant to the degree you are completing and manageable within the time constraints or other limitations you have.
As a result, you may have to undergo a research proposal defense or your supervisor will ask guiding questions about the state of your project. While this is still very early in the process, it is a great way for getting to know how to prepare for a thesis defense , as the questions you will be have a similar intent. Receiving guidance on your research before spending a lot of time on it can be more beneficial to you as you complete coursework or any other responsibilities as a graduate student. Questions from your supervisor can make your think critically about the end result of your result, and will hopefully lead to a better result.
Be Very Familiar With Your Proposal
This sounds like an obvious tip, but PhD research proposals can be 1500-2000 words long and can be a lot of information to remember at once. Once it is complete, try and have as great of a grasp of the material as you can. Before going into any meeting where you will discuss your work, make sure to become reacquainted with the information you have found and the goals you are hoping to achieve. Re-read your proposal several times to both proofread it for typos or other errors, but also to become comfortable with its contents. You want to make sure that your answers line up with the document you are officially submitting as your proposal.
Ask for Advice
If you are having trouble creating your proposal, you can always consult thesis writing services to help you plan out and put your thoughts into words. Professionals can also help with your speaking ability when responding and help you strategize so that you deliver efficient responses that sum up your research faithfully. Either together with an advisor or on your own, you can predict the obvious questions that are coming and prepare yourself to answer them. If your supervisor will be overseeing your proposal, try to anticipate what concerns they will have. Come up with a list of questions yourself, so you can workshop how you answer them.
Use Strategies to Answer Questions
Just like preparing for graduate school interview questions , you can develop strategies for how to answer questions about your research proposal. Keep your answers direct. You can also pose questions about areas you are unsure about. Do not be afraid to not have all the answers. At this point of your research, you are not expected to know everything point. The purpose of your proposal is to see where you are at right now and what you need to adjust on to make the best final product possible. Your supervisor or other academics that will pose questions about your proposal are not out to get you. They have years of experiences with similar projects, and are likely are qualified to give helpful feedback on your work in progress.
1. What is your research project about?
This answer should be a short summary about your research project. This question may seem like this simplest of them all, but you need to have a solid direction on where you want your thesis to go in order for it be effective. It does not need to be as complete as if you were to be summarizing your final product, since your project is still in its development stages. For instance, a sociological study regarding gendered tendencies towards deviant behaviors on the internet might be formatted in this manner:
For this research project, I plan to examine the rise of online deviant sociological behaviour on social media platforms during recent global shutdowns such as the COVID-19 pandemic and how gender identity and sexual orientation amplify these concerns. These acts of deviance can include instances of catfishing, deception, pornography, obscenity, cyber bullying, flaming, among others. I will also relate these findings to psychological impacts of both the perpetrators and victims or other relevant criminal behaviors that do not take place online, pointing out the differences between common trends for men vs. women in these altercations.
2. Why did you select this particular topic?
This question is meant to assess your motivation for choosing the subject of your research proposal. It is possible that you have previously touched on this kind of question during your graduate school interview when answering “Why do you want to do a PhD?” . This answer is one that could get a little more into your personal inclination towards the research you pursue. Focus on your particular interests and shape it to the goals of the project. For example, if you conducted a study called, “Forgotten Minds: Book History and Women’s Lost Contributions in 18th and 19th-century England” then you can frame your answer in this way:
As a scholar of the marriage industrial complex that permeated British society in past centuries, I am interested in the ways that a patriarchal structure can silence the marginalized voices of others, as matrimony often did for women. This is all the more evident in the interdisciplinary field of book history, where women’s contributions to the publishing were often ignored, erased, or overshadowed by their husbands. I wanted to indicate any trends that can be discovered by examining the roles of women in 18th and 19th-century printing houses and potentially unearth the forgotten stories of women who worked in these instances.
3. Does your project have a working title?
Titles are very important for academic articles or formal dissertation projects. If you have already learned how to publish as a graduate student , you will know that the title is how other academics or students will find your work when searching through journals and databases. You need to make sure your title is accurate to the research provided. At this point, your title will likely not be final, but it always important to be thinking about.
Sample Answer: My tentative title is “Take a Chill Pill: Natural and Traditional Methods for College Student Anxiety Levels”. I chose this title because it represents both the holistic self-care methods such as meditation and exercise as well as prescription medication. It also points out the focus group immediately, since the study will examine current college students between the ages of 18-24 and indicate any patterns for how they manage stress among unprecedented times.
4. What scope do you think your project will have?
Your proposal will likely touch on several points related to your topic, but it is not really plausible to have a project that considers every single aspect imaginable. You may need to narrow this down as you further develop your research. Start thinking of the boundaries you may have to set as you progress through your work.
Sample Answer: This study will examine consumption trends related to the snack food industry. To start with, I have chosen over 25 products from different companies will be able to be listed and reviewed in the final thesis submission.
5. What makes your project original?
Being a publishing academic is all about filling the gaps in scholarship. Make sure to point out what makes your project stand out from others in the field.
Sample Answer: The project focuses on how remote working and telemedicine shifts the delivery of family medicine procedures in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It does engage with similar studies on the topic of telemedicine, but will add a new perspective by discussing family doctors practicing in the greater Montreal area, specifically, which is a subset I have not yet found within existing scholarship.
6. How is your research in conversation with existing scholarship?
While your research must add something to the field, it also should be in a dialogue with other published works. Explain your process surrounding the other studies you have used to guide your own thesis.
Sample Answer: As my project is related to how autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis present themselves in young adults, I have included fundamental studies on the topic from Dr. Arthur Golden and Dr. Melina Rizzo, as well as other more current examples of scholarship. My study will utilize their concepts in relation to a focus group that is below the age of 30.
7. What kind of research methodology will you be using?
How you will be accessing this research is just as important as the research itself. Try to have a clear path about the measures you will take to complete your study.
Sample Answer: I aim to use detailed and meticulously written surveys about women’s birth experiences at hospitals or affiliated birthing centers. These results will act as the main foundation for my study on maternity health care and treatment.
8. Have you found there to be any interesting developments so far?
Was there any part of the part of the process that you did not expect? For this response, detail any new directions your research has taken as of writing your proposal.
Sample Answer: While looking for evidence that suggests that gender socialization of children affects their behaviour, I was surprised to find out that there is a discrepancy between the emotional responses in animated characters based on gender. Female or feminine-presenting characters are shown smiling on screen much more than their male counterparts, and the masculine-presenting characters were generally more likely to be shown as upset or even violent. That is a development in my research that I did not initially think of or foresee.
9. What do you think your biggest limitations for this research will be?
Look into the work you will have to do for your eventual full-length research project. What do you see being the most difficult part?
Sample Answer: I am looking into the nutritional benefits of drug store chewable gummy multivitamins. However, based on an individual’s prior health conditions or genetic makeup, the results may vary or be distorted. I am presuming that this will be a major limitation as I write my thesis.
10. What will be the dependent and independent variables of this project?
When researching, there are different variables that can potentially affect your results. An independent variable is not affected by other variables in your study, while dependent variables also change if other variables do.
Sample Answer: My study will investigate the impact of guidance counselling for junior and senior high school students. The independent variable is the type of help they require, such as college applications, social development skills, or academic performance. The dependent variable would be the actual outcomes of said counselling.
11. What is your provisional research timeline?
Even if it is not 100% stuck to, try to have a detailed timeline in mind about when research will be completed and how you will fulfill all of your obligations prior to the respective deadlines.
Sample Answer: The provisional research timeline for my proposal is designed to ensure systematic progress and timely completion of all research objectives. My timeline is divided into five phases:
Preparation Phase (4 weeks): In this initial stage, I will conduct a thorough literature review to familiarize myself with existing research and identify potential gaps. Simultaneously, I will finalize the research questions and establish the overall framework for my study.
Data Collection and Analysis (8 weeks): During this phase, I will gather primary data through surveys and interviews, ensuring data collection aligns with ethical guidelines. Once collected, I will proceed with data analysis, utilizing appropriate statistical methods to extract meaningful insights.
Literature Integration (4 weeks): Building upon the analyzed data, I will integrate my findings with existing literature to provide a comprehensive context for my research.
Drafting and Revision (6 weeks): I will dedicate this phase to writing the research proposal. The initial draft will be critically reviewed and refined through multiple iterations to enhance clarity and coherence.
Finalization and Submission (1 week): In the final phase, I will incorporate feedback from peers and advisors and polish the research paper to its final form. The completed research paper will be submitted by the designated deadline.
This provisional timeline, spanning 23 weeks, allows for flexibility and contingency plans to accommodate unforeseen challenges. Regular progress assessments and adjustments will be made to ensure timely completion and adherence to all obligations.
12. Who are the demographics who will be most interested in your research?
An important aspect of your research to think about will be who will be the most interested in reading it, as well as who it impacts the most.
Sample Answer: The demographics most interested in my research are likely to be professionals and policymakers within the healthcare industry. Given the focus of my research on implementing technology-driven solutions to enhance patient care and improve healthcare outcomes, healthcare practitioners, administrators, and researchers would find the findings particularly relevant.
Additionally, technology enthusiasts, innovators, and entrepreneurs interested in the intersection of healthcare and technology are also expected to show interest in the research. This group may be keen to explore potential commercial applications of the proposed solutions or seek opportunities for collaboration.
Moreover, the research would significantly impact patients and healthcare consumers. As technology increasingly plays a vital role in healthcare delivery, patients would be interested in understanding how these advancements can positively influence their healthcare experiences and overall well-being.
To ensure the research's reach and impact, I will disseminate the findings through academic publications, conferences, and workshops. Additionally, I will aim to engage with relevant professional organizations, healthcare institutions, and technology forums to stimulate interest and foster practical applications of the research outcomes.
By targeting these demographics, the research can make a meaningful contribution to the field of healthcare technology and help drive advancements that benefit both healthcare providers and patients alike.
13. What do you hope to be the significance of your research?
This is the “So what?” of your research. Will your research have lasting impacts? Evaluate which current issues your research could resolve.
Sample Answer:
The significance of my research lies in its potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery through technology-driven solutions. By addressing current issues such as inefficiencies in healthcare systems, lack of patient engagement, and suboptimal outcomes, my research aims to foster lasting impacts. Implementing technology to improve patient care, streamline processes, and enhance healthcare accessibility could lead to better health outcomes, reduced costs, and an overall improvement in the quality of healthcare services.
14. Are there any ethical issues or debates surrounding your research project?
Some projects are directly tied to ethics and moral issues that are currently being debated. It would be important to mention any ties to these issues and how your research is part of a larger conversation.
Sample Answer: While my research primarily focuses on technology-driven solutions to enhance healthcare, there are potential ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and security. As the research involves collecting and analyzing patient data, ensuring the confidentiality and informed consent of participants is paramount. Additionally, discussions about the responsible use of artificial intelligence in healthcare and potential biases in algorithms are relevant to the larger conversation on the ethical implications of technology in healthcare. Addressing these issues will be crucial to maintaining the integrity and societal benefit of the research.
15. Do you have any personal predictions for the outcome of your research?
If you haven’t yet conducted surveys or a thorough literature review, relay what you think will happen and any other concerns to your supervisor.
Sample Answer: As of now, without conducting surveys or an extensive literature review, I anticipate that the research will demonstrate the potential of technology in positively impacting healthcare outcomes and patient experiences. However, I am also aware that challenges related to data security, technology adoption, and ethical considerations may arise during the research. I will keep my supervisor informed about any unexpected findings and concerns throughout the study to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of the research outcomes.
Now that you have seen some sample answers, here are some additional questions you can take on:
- What sample groups are you using and why?
- What secondary sources do you plan to use?
- What do you believe is the strongest point in your research?
- Are there any biases that could exist in your research or your secondary sources?
- What are some ways your findings will be put into practice?
- What was the approach you took when starting your project?
- What phenomenon are you trying to understand with this research?
- How has your research project changed from when you started this degree?
- Do you see any foreseeable weaknesses or blind spots in your study?
- What measurement instrument did you use for this research?
- What theoretical framework is your research based on?
- Is the literature you chose up to date?
- What pertinent information have you found so far?
- Does your research have any use for policy makers?
- What do you plan to do with this research project once you have graduated?
When you are wondering, “should you pursue a master’s or a PhD?” , you truly need to consider the importance of research within the discipline you choose. Part of being an academic is the ability to contribute to the field and, by extension, society as a whole. The research proposal and the subsequent dissertation may be the last step to complete your degree, but it is also can be the first real step of your professional career.
Any meeting with your supervisor or instant where you have to defend your work is simply part of the process of being a working academic. This can have lasting implications for the future of your career, as knowing how to conduct and present research effectively is key to learning how to find a job in academia . That being said, the first step is putting yourself in the best position to succeed. Using PhD consultants can make all the difference for your project. If you are currently applying to graduate school, these trained experts can help you get into the school of your dreams or assist with finding programs that suit your skillset. They can also provide pointers on your research, as many of them have been in your shoes before.
A research proposal is a concise and structured document that outlines the key objectives, methodology, and significance of a proposed research project, aiming to convince others about the value and feasibility of the study.
A typical research proposal for a doctoral thesis is usually between 10 to 20 pages, depending on the specific requirements of the academic institution and the complexity of the research project.
To find the right research topic for a doctoral thesis, consider your interests, expertise, and the significance of the topic in your field. Engage with relevant literature, consult with advisors and experts, and identify gaps or unresolved issues to narrow down your focus.
Yes, you can and you should include your research on your grad school CV .
Most graduate programs will ask you to defend your research proposal. However, if it’s a smaller project, a review of the proposal may be sufficient.
To prepare for a research proposal or thesis defense, thoroughly review your research work, anticipate potential questions, and practice presenting your findings in a clear and concise manner to effectively communicate your research objectives, methodology, and results.
Some mistakes to avoid when writing a research proposal include: lack of clarity in research objectives, insufficient literature review, neglecting to address potential limitations, and failing to align the proposal with the funding agency's guidelines or the university's requirements.
Yes, you can always reach out to thesis writing services for some guidance.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Good Research Question (w/ Examples)
What is a Research Question?
A research question is the main question that your study sought or is seeking to answer. A clear research question guides your research paper or thesis and states exactly what you want to find out, giving your work a focus and objective. Learning how to write a hypothesis or research question is the start to composing any thesis, dissertation, or research paper. It is also one of the most important sections of a research proposal .
A good research question not only clarifies the writing in your study; it provides your readers with a clear focus and facilitates their understanding of your research topic, as well as outlining your study’s objectives. Before drafting the paper and receiving research paper editing (and usually before performing your study), you should write a concise statement of what this study intends to accomplish or reveal.
Research Question Writing Tips
Listed below are the important characteristics of a good research question:
A good research question should:
- Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose.
- Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper
- Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
- Be precise and complex enough that it does not simply answer a closed “yes or no” question, but requires an analysis of arguments and literature prior to its being considered acceptable.
- Be arguable or testable so that answers to the research question are open to scrutiny and specific questions and counterarguments.
Some of these characteristics might be difficult to understand in the form of a list. Let’s go into more detail about what a research question must do and look at some examples of research questions.
The research question should be specific and focused
Research questions that are too broad are not suitable to be addressed in a single study. One reason for this can be if there are many factors or variables to consider. In addition, a sample data set that is too large or an experimental timeline that is too long may suggest that the research question is not focused enough.
A specific research question means that the collective data and observations come together to either confirm or deny the chosen hypothesis in a clear manner. If a research question is too vague, then the data might end up creating an alternate research problem or hypothesis that you haven’t addressed in your Introduction section .
The research question should be based on the literature
An effective research question should be answerable and verifiable based on prior research because an effective scientific study must be placed in the context of a wider academic consensus. This means that conspiracy or fringe theories are not good research paper topics.
Instead, a good research question must extend, examine, and verify the context of your research field. It should fit naturally within the literature and be searchable by other research authors.
References to the literature can be in different citation styles and must be properly formatted according to the guidelines set forth by the publishing journal, university, or academic institution. This includes in-text citations as well as the Reference section .
The research question should be realistic in time, scope, and budget
There are two main constraints to the research process: timeframe and budget.
A proper research question will include study or experimental procedures that can be executed within a feasible time frame, typically by a graduate doctoral or master’s student or lab technician. Research that requires future technology, expensive resources, or follow-up procedures is problematic.
A researcher’s budget is also a major constraint to performing timely research. Research at many large universities or institutions is publicly funded and is thus accountable to funding restrictions.
The research question should be in-depth
Research papers, dissertations and theses , and academic journal articles are usually dozens if not hundreds of pages in length.
A good research question or thesis statement must be sufficiently complex to warrant such a length, as it must stand up to the scrutiny of peer review and be reproducible by other scientists and researchers.
Research Question Types
Qualitative and quantitative research are the two major types of research, and it is essential to develop research questions for each type of study.
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are specific. A typical research question involves the population to be studied, dependent and independent variables, and the research design.
In addition, quantitative research questions connect the research question and the research design. In addition, it is not possible to answer these questions definitively with a “yes” or “no” response. For example, scientific fields such as biology, physics, and chemistry often deal with “states,” in which different quantities, amounts, or velocities drastically alter the relevance of the research.
As a consequence, quantitative research questions do not contain qualitative, categorical, or ordinal qualifiers such as “is,” “are,” “does,” or “does not.”
Categories of quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions.
In quantitative research, research questions have the potential to relate to broad research areas as well as more specific areas of study. Qualitative research questions are less directional, more flexible, and adaptable compared with their quantitative counterparts. Thus, studies based on these questions tend to focus on “discovering,” “explaining,” “elucidating,” and “exploring.”
Categories of qualitative research questions
Quantitative and qualitative research question examples.

Good and Bad Research Question Examples
Below are some good (and not-so-good) examples of research questions that researchers can use to guide them in crafting their own research questions.
Research Question Example 1
The first research question is too vague in both its independent and dependent variables. There is no specific information on what “exposure” means. Does this refer to comments, likes, engagement, or just how much time is spent on the social media platform?
Second, there is no useful information on what exactly “affected” means. Does the subject’s behavior change in some measurable way? Or does this term refer to another factor such as the user’s emotions?
Research Question Example 2
In this research question, the first example is too simple and not sufficiently complex, making it difficult to assess whether the study answered the question. The author could really only answer this question with a simple “yes” or “no.” Further, the presence of data would not help answer this question more deeply, which is a sure sign of a poorly constructed research topic.
The second research question is specific, complex, and empirically verifiable. One can measure program effectiveness based on metrics such as attendance or grades. Further, “bullying” is made into an empirical, quantitative measurement in the form of recorded disciplinary actions.
Steps for Writing a Research Question
Good research questions are relevant, focused, and meaningful. It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier.
1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic
Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country’s culture or your university’s capabilities. Popular academic topics include healthcare and medical-related research. However, if you are attending an engineering school or humanities program, you should obviously choose a research question that pertains to your specific study and major.
Below is an embedded graph of the most popular research fields of study based on publication output according to region. As you can see, healthcare and the basic sciences receive the most funding and earn the highest number of publications.
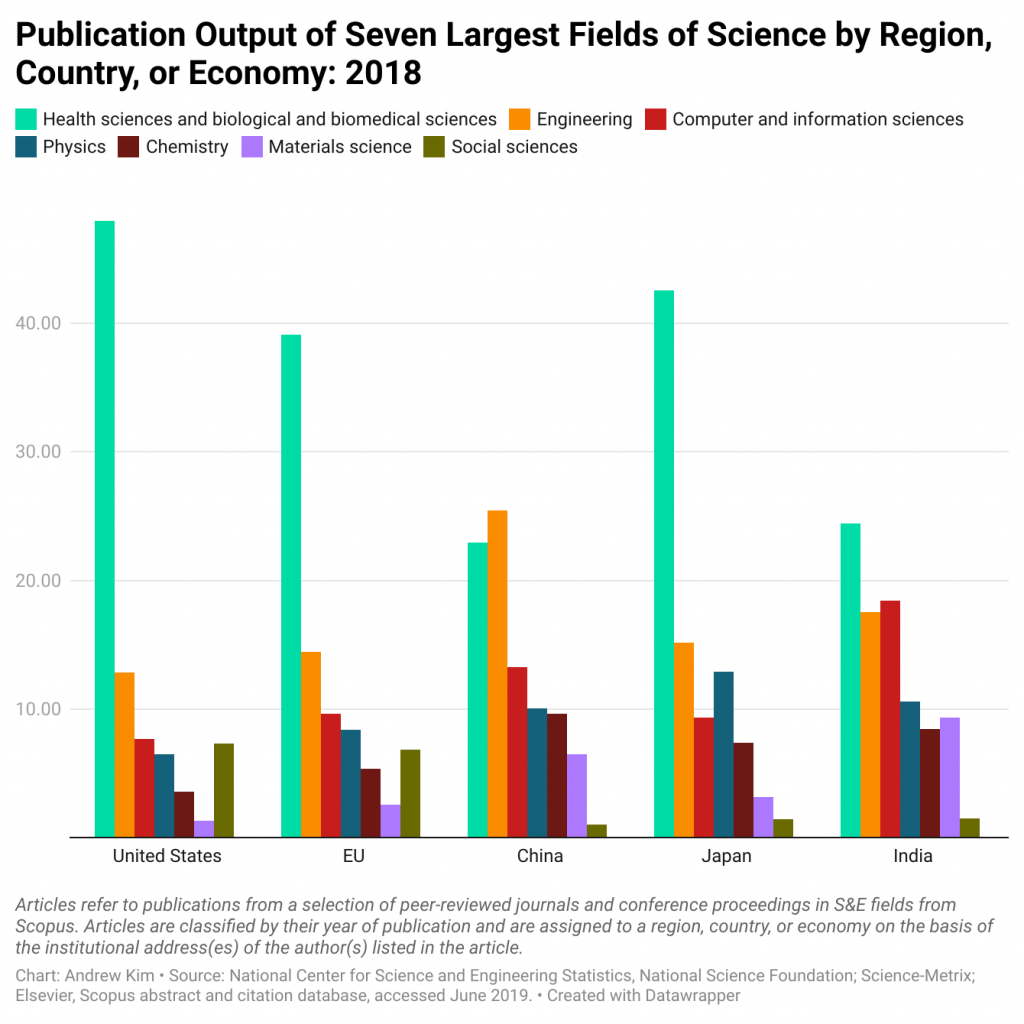
2. Do preliminary research
You can begin doing preliminary research once you have chosen a research topic. Two objectives should be accomplished during this first phase of research. First, you should undertake a preliminary review of related literature to discover issues that scholars and peers are currently discussing. With this method, you show that you are informed about the latest developments in the field.
Secondly, identify knowledge gaps or limitations in your topic by conducting a preliminary literature review . It is possible to later use these gaps to focus your research question after a certain amount of fine-tuning.
3. Narrow your research to determine specific research questions
You can focus on a more specific area of study once you have a good handle on the topic you want to explore. Focusing on recent literature or knowledge gaps is one good option.
By identifying study limitations in the literature and overlooked areas of study, an author can carve out a good research question. The same is true for choosing research questions that extend or complement existing literature.
4. Evaluate your research question
Make sure you evaluate the research question by asking the following questions:
Is my research question clear?
The resulting data and observations that your study produces should be clear. For quantitative studies, data must be empirical and measurable. For qualitative, the observations should be clearly delineable across categories.
Is my research question focused and specific?
A strong research question should be specific enough that your methodology or testing procedure produces an objective result, not one left to subjective interpretation. Open-ended research questions or those relating to general topics can create ambiguous connections between the results and the aims of the study.
Is my research question sufficiently complex?
The result of your research should be consequential and substantial (and fall sufficiently within the context of your field) to warrant an academic study. Simply reinforcing or supporting a scientific consensus is superfluous and will likely not be well received by most journal editors.

Editing Your Research Question
Your research question should be fully formulated well before you begin drafting your research paper. However, you can receive English paper editing and proofreading services at any point in the drafting process. Language editors with expertise in your academic field can assist you with the content and language in your Introduction section or other manuscript sections. And if you need further assistance or information regarding paper compositions, in the meantime, check out our academic resources , which provide dozens of articles and videos on a variety of academic writing and publication topics.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 December 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
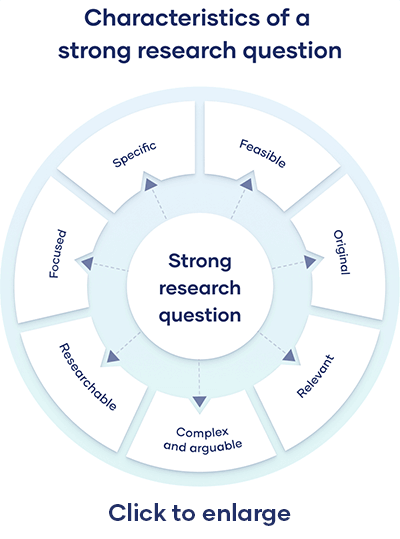
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, research questions quiz, frequently asked questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarised in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, December 12). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-question/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

11.2 Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in developing a research proposal.
- Choose a topic and formulate a research question and working thesis.
- Develop a research proposal.
Writing a good research paper takes time, thought, and effort. Although this assignment is challenging, it is manageable. Focusing on one step at a time will help you develop a thoughtful, informative, well-supported research paper.
Your first step is to choose a topic and then to develop research questions, a working thesis, and a written research proposal. Set aside adequate time for this part of the process. Fully exploring ideas will help you build a solid foundation for your paper.
Choosing a Topic
When you choose a topic for a research paper, you are making a major commitment. Your choice will help determine whether you enjoy the lengthy process of research and writing—and whether your final paper fulfills the assignment requirements. If you choose your topic hastily, you may later find it difficult to work with your topic. By taking your time and choosing carefully, you can ensure that this assignment is not only challenging but also rewarding.
Writers understand the importance of choosing a topic that fulfills the assignment requirements and fits the assignment’s purpose and audience. (For more information about purpose and audience, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” .) Choosing a topic that interests you is also crucial. You instructor may provide a list of suggested topics or ask that you develop a topic on your own. In either case, try to identify topics that genuinely interest you.
After identifying potential topic ideas, you will need to evaluate your ideas and choose one topic to pursue. Will you be able to find enough information about the topic? Can you develop a paper about this topic that presents and supports your original ideas? Is the topic too broad or too narrow for the scope of the assignment? If so, can you modify it so it is more manageable? You will ask these questions during this preliminary phase of the research process.
Identifying Potential Topics
Sometimes, your instructor may provide a list of suggested topics. If so, you may benefit from identifying several possibilities before committing to one idea. It is important to know how to narrow down your ideas into a concise, manageable thesis. You may also use the list as a starting point to help you identify additional, related topics. Discussing your ideas with your instructor will help ensure that you choose a manageable topic that fits the requirements of the assignment.
In this chapter, you will follow a writer named Jorge, who is studying health care administration, as he prepares a research paper. You will also plan, research, and draft your own research paper.
Jorge was assigned to write a research paper on health and the media for an introductory course in health care. Although a general topic was selected for the students, Jorge had to decide which specific issues interested him. He brainstormed a list of possibilities.
If you are writing a research paper for a specialized course, look back through your notes and course activities. Identify reading assignments and class discussions that especially engaged you. Doing so can help you identify topics to pursue.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) in the news
- Sexual education programs
- Hollywood and eating disorders
- Americans’ access to public health information
- Media portrayal of health care reform bill
- Depictions of drugs on television
- The effect of the Internet on mental health
- Popularized diets (such as low-carbohydrate diets)
- Fear of pandemics (bird flu, HINI, SARS)
- Electronic entertainment and obesity
- Advertisements for prescription drugs
- Public education and disease prevention
Set a timer for five minutes. Use brainstorming or idea mapping to create a list of topics you would be interested in researching for a paper about the influence of the Internet on social networking. Do you closely follow the media coverage of a particular website, such as Twitter? Would you like to learn more about a certain industry, such as online dating? Which social networking sites do you and your friends use? List as many ideas related to this topic as you can.
Narrowing Your Topic
Once you have a list of potential topics, you will need to choose one as the focus of your essay. You will also need to narrow your topic. Most writers find that the topics they listed during brainstorming or idea mapping are broad—too broad for the scope of the assignment. Working with an overly broad topic, such as sexual education programs or popularized diets, can be frustrating and overwhelming. Each topic has so many facets that it would be impossible to cover them all in a college research paper. However, more specific choices, such as the pros and cons of sexual education in kids’ television programs or the physical effects of the South Beach diet, are specific enough to write about without being too narrow to sustain an entire research paper.
A good research paper provides focused, in-depth information and analysis. If your topic is too broad, you will find it difficult to do more than skim the surface when you research it and write about it. Narrowing your focus is essential to making your topic manageable. To narrow your focus, explore your topic in writing, conduct preliminary research, and discuss both the topic and the research with others.
Exploring Your Topic in Writing
“How am I supposed to narrow my topic when I haven’t even begun researching yet?” In fact, you may already know more than you realize. Review your list and identify your top two or three topics. Set aside some time to explore each one through freewriting. (For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .) Simply taking the time to focus on your topic may yield fresh angles.
Jorge knew that he was especially interested in the topic of diet fads, but he also knew that it was much too broad for his assignment. He used freewriting to explore his thoughts so he could narrow his topic. Read Jorge’s ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Another way writers may focus a topic is to conduct preliminary research . Like freewriting, exploratory reading can help you identify interesting angles. Surfing the web and browsing through newspaper and magazine articles are good ways to start. Find out what people are saying about your topic on blogs and online discussion groups. Discussing your topic with others can also inspire you. Talk about your ideas with your classmates, your friends, or your instructor.
Jorge’s freewriting exercise helped him realize that the assigned topic of health and the media intersected with a few of his interests—diet, nutrition, and obesity. Preliminary online research and discussions with his classmates strengthened his impression that many people are confused or misled by media coverage of these subjects.
Jorge decided to focus his paper on a topic that had garnered a great deal of media attention—low-carbohydrate diets. He wanted to find out whether low-carbohydrate diets were as effective as their proponents claimed.
Writing at Work
At work, you may need to research a topic quickly to find general information. This information can be useful in understanding trends in a given industry or generating competition. For example, a company may research a competitor’s prices and use the information when pricing their own product. You may find it useful to skim a variety of reliable sources and take notes on your findings.
The reliability of online sources varies greatly. In this exploratory phase of your research, you do not need to evaluate sources as closely as you will later. However, use common sense as you refine your paper topic. If you read a fascinating blog comment that gives you a new idea for your paper, be sure to check out other, more reliable sources as well to make sure the idea is worth pursuing.
Review the list of topics you created in Note 11.18 “Exercise 1” and identify two or three topics you would like to explore further. For each of these topics, spend five to ten minutes writing about the topic without stopping. Then review your writing to identify possible areas of focus.
Set aside time to conduct preliminary research about your potential topics. Then choose a topic to pursue for your research paper.
Collaboration
Please share your topic list with a classmate. Select one or two topics on his or her list that you would like to learn more about and return it to him or her. Discuss why you found the topics interesting, and learn which of your topics your classmate selected and why.
A Plan for Research
Your freewriting and preliminary research have helped you choose a focused, manageable topic for your research paper. To work with your topic successfully, you will need to determine what exactly you want to learn about it—and later, what you want to say about it. Before you begin conducting in-depth research, you will further define your focus by developing a research question , a working thesis, and a research proposal.
Formulating a Research Question
In forming a research question, you are setting a goal for your research. Your main research question should be substantial enough to form the guiding principle of your paper—but focused enough to guide your research. A strong research question requires you not only to find information but also to put together different pieces of information, interpret and analyze them, and figure out what you think. As you consider potential research questions, ask yourself whether they would be too hard or too easy to answer.
To determine your research question, review the freewriting you completed earlier. Skim through books, articles, and websites and list the questions you have. (You may wish to use the 5WH strategy to help you formulate questions. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information about 5WH questions.) Include simple, factual questions and more complex questions that would require analysis and interpretation. Determine your main question—the primary focus of your paper—and several subquestions that you will need to research to answer your main question.
Here are the research questions Jorge will use to focus his research. Notice that his main research question has no obvious, straightforward answer. Jorge will need to research his subquestions, which address narrower topics, to answer his main question.
Using the topic you selected in Note 11.24 “Exercise 2” , write your main research question and at least four to five subquestions. Check that your main research question is appropriately complex for your assignment.
Constructing a Working ThesIs
A working thesis concisely states a writer’s initial answer to the main research question. It does not merely state a fact or present a subjective opinion. Instead, it expresses a debatable idea or claim that you hope to prove through additional research. Your working thesis is called a working thesis for a reason—it is subject to change. As you learn more about your topic, you may change your thinking in light of your research findings. Let your working thesis serve as a guide to your research, but do not be afraid to modify it based on what you learn.
Jorge began his research with a strong point of view based on his preliminary writing and research. Read his working thesis statement, which presents the point he will argue. Notice how it states Jorge’s tentative answer to his research question.
One way to determine your working thesis is to consider how you would complete sentences such as I believe or My opinion is . However, keep in mind that academic writing generally does not use first-person pronouns. These statements are useful starting points, but formal research papers use an objective voice.
Write a working thesis statement that presents your preliminary answer to the research question you wrote in Note 11.27 “Exercise 3” . Check that your working thesis statement presents an idea or claim that could be supported or refuted by evidence from research.
Creating a Research Proposal
A research proposal is a brief document—no more than one typed page—that summarizes the preliminary work you have completed. Your purpose in writing it is to formalize your plan for research and present it to your instructor for feedback. In your research proposal, you will present your main research question, related subquestions, and working thesis. You will also briefly discuss the value of researching this topic and indicate how you plan to gather information.
When Jorge began drafting his research proposal, he realized that he had already created most of the pieces he needed. However, he knew he also had to explain how his research would be relevant to other future health care professionals. In addition, he wanted to form a general plan for doing the research and identifying potentially useful sources. Read Jorge’s research proposal.

Before you begin a new project at work, you may have to develop a project summary document that states the purpose of the project, explains why it would be a wise use of company resources, and briefly outlines the steps involved in completing the project. This type of document is similar to a research proposal. Both documents define and limit a project, explain its value, discuss how to proceed, and identify what resources you will use.
Writing Your Own Research Proposal
Now you may write your own research proposal, if you have not done so already. Follow the guidelines provided in this lesson.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis.
- A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
- Defining and narrowing a topic helps writers conduct focused, in-depth research.
- Writers conduct preliminary research to identify possible topics and research questions and to develop a working thesis.
- A good research question interests readers, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has no obvious answer.
- A good working thesis expresses a debatable idea or claim that can be supported with evidence from research.
- Writers create a research proposal to present their topic, main research question, subquestions, and working thesis to an instructor for approval or feedback.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Student Grant Program Application Process
Student and faculty applicants must identify each other and develop a research proposal together before applying for a research award through Engineering Learning Initiatives.
Once faculty and student have agreed upon a proposal idea, each must separately complete and submit online applications.
You may preview application questions at these links.
Preview Faculty Application Questions
Preview Student Application Questions
Once faculty and student have agreed upon a proposal idea, and a plan for the research term, each must separately complete and submit online applications. The faculty application must be submitted first. The student will use the faculty application ID number to link their submissions. The ID number screen will appear a few seconds after the faculty mentor clicks "Submit" to submit the faculty application. Be sure to write this number down. The student will need it in order to submit the student application.
We recommend preparing your responses using a separate save-able document, and then pasting your responses into the application system once they are ready. Student applicants should be sure to ask their faculty mentors to review their drafted application responses prior to submitting. This will give you the opportunity to receive valuable feedback from your mentor, and to ensure that the mentor and student pieces are in full alignment.
Faculty Application
Student Application
To encourage high quality applications from students, we require all undergraduate applicants to obtain faculty approval for their proposals before submission. We ask that each faculty mentor review the student’s project proposal and personal statement. The faculty mentor should give his or her application ID number to the student, to enable submission of the student application, only after the mentor has reviewed and approved the student’s proposal and statement. Once approval has been secured, the student must then submit the online student application before the application deadline.
Please be aware that undergraduate research funds are available only for undergraduate students currently enrolled in the College of Engineering and Biological or Environmental Engineering (BEE) majors.
Important note: New word/character count maximums have been imposed on responses to each application question. Please use your word processing software to check the word/character counts on your responses before pasting them into the application response boxes. Responses that are too long will be truncated upon submission, such that any words beyond the limit will not appear for reviewers. Maximums are being enforced in order to keep review times reasonable. Please answer the questions with clear responses that are brief and to-the-point.
Projects Involving Multiple Students
Projects usually involve one student and one professor, although some projects may involve student teams.
Student Project Team proposals will not be considered for funding through the Engineering Learning Initiatives Student Undergraduate Research Grants Program. Teams of students working together with faculty mentors in faculty research programs may still apply as undergraduate research teams. However, Student Project Teams - largely student-run, competitive design teams - should not apply through this program. They will have the opportunity to be considered for College funding through a separate process.
If you are a faculty advisor who is considering applying for support for multiple students or your research team, please follow the bulleted guidelines below:
- If applying for team funding, the faculty advisor should submit one team application, listing the names of all student applicants on the team. Each team member must submit an individual application. The team application will be considered as a whole, and, if approved, awarded team funding. Individual team members will not be considered separately for individual funding.
- Please note: Team applications are discouraged during the summer term for cases in which full student wages are required for each team member. Due to the high costs of summer support, individual applications typically have a greater chance of success.
- If applying for individual funding for more than one student, please submit a separate application for each, with a unique project title, reflecting the specific research focus of each student. A maximum of 2 proposals per faculty member are allowable in any funding term.
- Selection Criteria
- Program Requirements
- Funding and Sources
Visit the Health Advisories website for the latest vaccination and mask information and to Report a Case.
Questions about FAFSA and CADAA?
Visit our Financial Aid and Scholarship Office for updated information, workshops and FAQs.
Research Foundation
April 2024 New Grants and Contracts
We are pleased to share the success of SJSU's principal investigators who were awarded grants and contracts during April 2024:
Monthly Awards at a Glance 15 Awards Received: Valued at $2,529,591.
Note: Some industry-sponsored awards are not listed due to their respective non-disclosure terms.
Lucas College and Graduate School of Business
Basu, Anuradha, School of Management Silicon Valley Center for Entrepreneurship - Encore Fellow Sponsor: The Fedcap Group – $25,000.
Division of Research & Innovation
Queale, Abby, Division of Research & Innovation The Spartan SBDC - Year 3 - Federal Sponsor: Humboldt State University – $200,000.
Connie L. Lurie College of Education
Love, Matthew, Special Education Data Adventures Sponsor: Santa Clara County Office of Education – $363,443.
Charles W. Davidson College of Engineering
Kumar, Anil R., Industrial & Systems Engineering Confidential Sponsor: Confidential – $41,351.
Mak, Ronald, Computer Engineering Confidential Sponsor: Confidential – $111,097.
Papadopoulos, Periklis / Chierichetti, Maria, Aerospace Engineering Axient Internship Program Sponsor: Axient LLC – $40,000.
College of Health and Human Sciences
Garcia, Moctezuma, Social Work Project COMPA (Comunidades Ofreciendo Más Prevenciones Agradables) Sponsor: Regents of The University of California – $336,999.
College of Science
Gardner, Luke, Moss Landing Marine Lab Western Regional Aquaculture Center-33rd Annual Work Plan FY 22 Sponsor: University of Washington – $78,838.
Harvey, James, Moss Landing Marine Lab Estuarine Wetland and Nearshore Ecology Studies along the Pacific Flyway Sponsor: U.S. Geological Survey – $24,000.
Van Wyngarden, Annalise L., Chemistry Nuclear Chemistry Summer School (NCSS) Sponsor: City University of New York – $256,577.
Wang, Ningkun, Chemistry Elucidating the Mechanism for Allosteric Regulation of SIRT1 through the N-Terminal Region 6 Sponsor: National Institutes of Health – $146,500.
Wilkin, Kate, Biological Sciences SJSU Prescribed Fire Monitoring and Research Program in the South Bay and Central Coast Sponsor: California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection | CAL FIRE – $80,000.
College of Social Sciences
Laraway, Sean P., Psychology Human Systems Integration: Collaborative Human Factors Research to Improve Safety, Efficiency, and Reliability of NASA's Aeronautics and Space Missions Phase 2 Sponsor: NASA – $710,033.
Snycerski, Susan M. / Padthe, Ashwani Dragonfly Collaboration Sponsor: The Johns Hopkins University– $28,753.
Snycerski, Susan M. Future Vertical Lift: Collaborative Research on Flight Control, Autonomous Rotorcraft, and Human-Systems Interface Design: Phase 2 Sponsor: NASA – $87,000.

What Are The Sections Of A Research Proposal?
L earning the structure of a research proposal can be helpful while writing one. Research proposal writing services often emphasize the importance of breaking down your proposal into clear sections to ensure clarity and coherence. Typically, a research proposal comprises several key components.
A research proposal is like a roadmap for a study, outlining its purpose, methods, and expected outcomes. Typically, it consists of several key sections. Firstly, there's the introduction, which introduces the research topic and explains its importance. Then comes the literature review, where existing research relevant to the study is discussed.
After that, the methodology section outlines how the research will be conducted, including the tools and techniques used. Next, the proposal includes a section on anticipated results and their significance. Lastly, there's often a section on the timeline and budget, detailing when and how resources will be allocated. This article will cover the sections of writing research proposal .
Main Features of a Research Proposal
To write research proposal, it's important to cover key elements. Look for the best research proposal writing services to ensure your proposal includes all vital aspects.
Introduction
Literature review, methodology.
Research Proposal title should be to the point but informative that clearly tell what the research is about. Avoid using too long titles and extra information in it. Choose the best title for your research proposal that is relevant to your project.
A good proposal title should contain the following
- Eye catching words to grab the attention of the reader
- Positive language toward the reader
Titles should be similar to your research questions or thesis statements.
The abstract is like a snapshot of your research proposal, or a brief summary giving a intro what your study is all about. It gives the basic fundamental about your topic so they can understand the importance of the proposal. It sums up the main points: the problem you're tackling, what you aim to achieve, how you plan to do it, and what you expect to find.
A strong abstract attracts the reader and grabs their interest in your proposal and its importance. This is the chance to make an excellent first impression and encourage readers to check out more of your research.
The introduction is the main point of the research proposal. It introduces the audience to the story by explaining the background and reasons behind your research. It highlights the main question or problem you're addressing and explains why it's important. By the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what you're studying, why it's significant, and what you hope to achieve. This section is crucial because it sets the stage for the rest of your proposal, helping the reader understand the context and purpose of your research.
The literature review acts as a map that shows the present state of information in your area of research. Here, you will be giving a summary and review of previous studies, concepts, and results related to the topic you chose. This makes it less difficult for you to see the larger context and figure out how your research fits in. In addition to underlining the importance of your work, an effective review of the literature highlights undiscovered areas and recommends places where future study may have an impact.
In the methodology section, you explain how you'll conduct your research. This includes describing the type of research you'll do, like whether it's qualitative or quantitative. You also talk about how you'll collect data, whether through surveys, interviews, or experiments.
It's important to explain your sampling strategy, which is how you'll select participants or data points. This ensures that your sample is representative of the population you're studying.
Additionally, you'll detail how you'll analyze the data once you've collected it. This could involve statistical tests, thematic analysis, or other methods depending on your research design.
Clarity and feasibility are key in this section. You want to make sure that your methods are clear and that you'll be able to actually carry them out. This helps ensure that your findings will be valid and reliable.
Your research proposal's schedule section acts as a sort of road map, detailing the actions you'll comply with to finish the project. It provides the timetable for gathering information, research, and distribution of findings. Having a clear period shows off your excellent ability to manage time but also gives people trust that your study will be finished on time. It improves the trust people have in your proposal. Having an extensive timetable helps you stay on target and complete your education in an appropriate length of time, much like when you create milestones for yourself. This part of your proposal is important because it displays that you have calculated the length of time of each study part, which will help you plan carefully and make sure you succeed in finishing your project on time.
In the budget section, you list all the money you'll need for your research. This covers things like buying equipment, getting materials, paying participants, and any staff you might need. By explaining why you need each expense, you show exactly how you plan to spend the money. This transparency helps funding agencies understand why your study is worth investing in, making it more likely they'll support your research.
You must list all of the sources that you included in your research proposal in the references section. This list follows to an APA or MLA format, which makes it easier for readers to find exactly which sources you used. To maintain the academic standard and show regard for the efforts of other researchers, it is important that you use references that are right and reliable. This section acknowledges the works of earlier researchers whose work you have found useful in your research.
A good research proposal has important sections that show why your study is important, how it can be done, and how reliable it is. Whether you need money or permission for your research, knowing these sections well is key to making a strong proposal. With help from trusted research proposal writing services in the UK , new researchers can get expert advice on writing proposals, making it easier for them to succeed.
Note: This article is for information purposes only and does not contain any recommendation.
This article may contain affiliate links that Microsoft and/or the publisher may receive a commission from if you buy a product or service through those links.
College of Education and Human Ecology

« All Events
CADRE Learning Series: Ethical Use of AI in STEM Education Research (Webinar)
May 15 @ 2:00 pm - 3:30 pm.
Rapid advances in artificial intelligence (AI) have changed the role of AI in education research. How do we navigate these changes ethically in our research and proposal writing? What questions should we be considering as education researchers? Join us on May 15 to hear from authors of an upcoming CADRE brief titled Towards Ethical and Just AI in Education Research to learn and discuss strategies to ethically navigating AI in education research.
Moderator: Ilana Horn, Vanderbilt University; Panelists: Tiffany Barnes, North Carolina State University, Joshua Danish, Indiana University, Samantha Finkelstein, Carnegie Mellon University, and Ole Molvig, Vanderbilt University
- Google Calendar
- Outlook 365
- Outlook Live
Office of Research, Innovation and Collaboration (ORIC) 153 Arps Hall 1945 N. High St. Columbus, OH 43210
Meet Our Staff
OFFICE HOURS
8 a.m. to 5 p.m. Monday–Friday
Phone: (614) 247-2412 Email: [email protected]

Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
10 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (collectively called the "golden thread") are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you're crafting a research proposal, dissertation or thesis.We receive questions almost every day about this "holy trinity" of research and there's certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we've crafted this post to help ...
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we'll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer. In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery. Without a clear target, you won't know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light ...
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions: ... Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they ...
There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research. There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection. The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Research questions should not be answerable with a simple "yes" or "no" or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with "How" or "Why.". Begin your research. After you've come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research ...
Practicing with sample research proposal questions and answers can have great benefits for any major research project such as a dissertation or thesis. This is often the final step before you finally get your doctorate degree. However, before all of that, you must first craft a research proposal. This is a detailed outline that will transform ...
A good research question should: Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose. Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper. Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
Aside from being interesting and novel, the research question should be relevant to the scientific community and people involved in your area of study. If possible, your research question should also be relevant to the public's interest. 5. Construct your research question properly.
Definition: Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
This is very important when the research problem is multifaceted or complex. State the rationale of your research proposal and explain, in an engaging way, why it is worthwhile to conduct. Present the core problems or issues that will be addressed. This can be made either in questions or statements.
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
What is a research proposal? Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it's worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).. The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that ...
Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis. A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer. [ 2] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
You may preview application questions at these links. Preview Faculty Application Questions. Preview Student Application Questions. Once faculty and student have agreed upon a proposal idea, and a plan for the research term, each must separately complete and submit online applications. The faculty application must be submitted first.
We are pleased to share the success of SJSU's principal investigators who were awarded grants and contracts during April 2024: Monthly Awards at a Glance. 15 Awards Received: Valued at $2,529,591. Note: Some industry-sponsored awards are not listed due to their respective non-disclosure terms.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
A research proposal is like a roadmap for a study, outlining its purpose, methods, and expected outcomes. Typically, it consists of several key sections.
How do we navigate these changes ethically in our research and proposal writing? What questions should we be considering as education researchers? Join us on May 15 to hear from authors of an upcoming CADRE brief titled Towards Ethical and Just AI in Education Research to learn and discuss strategies to ethically navigating AI in education ...
Research Proposal Example/Sample. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level ...