- Insights & Analysis
- Nonprofit Jobs

Business Planning for Nonprofits
Business planning is a way of systematically answering questions such as, “What problem(s) are we trying to solve?” or “What are we trying to achieve?” and also, “Who will get us there, by when, and how much money and other resources will it take?”
The business planning process takes into account the nonprofit’s mission and vision, the role of the board, and external environmental factors, such as the climate for fundraising.
Ideally, the business planning process also critically examines basic assumptions about the nonprofit’s operating environment. What if the sources of income that exist today change in the future? Is the nonprofit too reliant on one foundation for revenue? What happens if there’s an economic downturn?
A business plan can help the nonprofit and its board be prepared for future risks. What is the likelihood that the planned activities will continue as usual, and that revenue will continue at current levels – and what is Plan B if they don't?
Narrative of a business plan
You can think of a business plan as a narrative or story explaining how the nonprofit will operate given its activities, its sources of revenue, its expenses, and the inevitable changes in its internal and external environments over time. Ideally, your plan will tell the story in a way that will make sense to someone not intimately familiar with the nonprofit’s operations.
According to Propel Nonprofits , business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure.
A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine running – how much will be earned, how much from government grants or contracts, how much will be contributed? Within each of those broad categories, how much diversification exists, and should they be further diversified? Are there certain factors that need to be in place in order for today’s income streams to continue flowing?
The plan should address the everyday costs needed to operate the organization, as well as costs of specific programs and activities.
The plan may include details about the need for the organization's services (a needs assessment), the likelihood that certain funding will be available (a feasibility study), or changes to the organization's technology or staffing that will be needed in the future.
Another aspect of a business plan could be a "competitive analysis" describing what other entities may be providing similar services in the nonprofit's service and mission areas. What are their sources of revenue and staffing structures? How do their services and capacities differ from those of your nonprofit?
Finally, the business plan should name important assumptions, such as the organization's reserve policies. Do your nonprofit’s policies require it to have at least six months of operating cash on hand? Do you have different types of cash reserves that require different levels of board approval to release?
The idea is to identify the known, and take into consideration the unknown, realities of the nonprofit's operations, and propose how the nonprofit will continue to be financially healthy. If the underlying assumptions or current conditions change, then having a plan can be useful to help identify adjustments that must be made to respond to changes in the nonprofit's operating environment.
Basic format of a business plan
The format may vary depending on the audience. A business plan prepared for a bank to support a loan application may be different than a business plan that board members use as the basis for budgeting. Here is a typical outline of the format for a business plan:
- Table of contents
- Executive summary - Name the problem the nonprofit is trying to solve: its mission, and how it accomplishes its mission.
- People: overview of the nonprofit’s board, staffing, and volunteer structure and who makes what happen
- Market opportunities/competitive analysis
- Programs and services: overview of implementation
- Contingencies: what could change?
- Financial health: what is the current status, and what are the sources of revenue to operate programs and advance the mission over time?
- Assumptions and proposed changes: What needs to be in place for this nonprofit to continue on sound financial footing?
More About Business Planning
Budgeting for Nonprofits
Strategic Planning
Contact your state association of nonprofits for support and resources related to business planning, strategic planning, and other fundamentals of nonprofit leadership.
Additional Resources
- Components of transforming nonprofit business models (Propel Nonprofits)
- The matrix map: a powerful tool for nonprofit sustainability (Nonprofit Quarterly)
- The Nonprofit Business Plan: A Leader's Guide to Creating a Successful Business Model (David La Piana, Heather Gowdy, Lester Olmstead-Rose, and Brent Copen, Turner Publishing)
- Nonprofit Earned Income: Critical Business Model Considerations for Nonprofits (Nonprofit Financial Commons)
- Nonprofit Sustainability: Making Strategic Decisions for Financial Viability (Jan Masaoka, Steve Zimmerman, and Jeanne Bell)
Disclaimer: Information on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is neither intended to be nor should be construed as legal, accounting, tax, investment, or financial advice. Please consult a professional (attorney, accountant, tax advisor) for the latest and most accurate information. The National Council of Nonprofits makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy or timeliness of the information contained herein.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated April 17, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

4 Min. Read
How to Develop a Positioning Statement for Your Business
6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

9 Min. Read
Free Etsy Business Plan Template [2024 PDF + Sample Plan]

8 Min. Read
How to Plan Your Exit Strategy
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to write a nonprofit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan ensures your organization’s fundraising and activities align with your core mission.

Every nonprofit needs a mission statement that demonstrates how the organization will support a social cause and provide a public benefit. A nonprofit business plan fleshes out this mission statement in greater detail. These plans include many of the same elements as a for-profit business plan, with a focus on fundraising, creating a board of directors, raising awareness, and staying compliant with IRS regulations. A nonprofit business plan can be instrumental in getting your organization off the ground successfully.
Start with your mission statement
The mission statement is foundational for your nonprofit organization. The IRS will review your mission statement in determining whether to grant you tax-exempt status. This statement also helps you recruit volunteers and staff, fundraise, and plan activities for the year.
[Read more: Writing a Mission Statement: A Step-by-Step Guide ]
Therefore, you should start your business plan with a clear mission statement in the executive summary. The executive summary can also cover, at a high level, the goals, vision, and unique strengths of your nonprofit organization. Keep this section brief, since you will be going into greater detail in later sections.
Identify a board of directors
Many business plans include a section identifying the people behind the operation: your key leaders, volunteers, and full-time employees. For nonprofits, it’s also important to identify your board of directors. The board of directors is ultimately responsible for hiring and managing the CEO of your nonprofit.
“Board members are the fiduciaries who steer the organization towards a sustainable future by adopting sound, ethical, and legal governance and financial management policies, as well as by making sure the nonprofit has adequate resources to advance its mission,” wrote the Council of Nonprofits.
As such, identify members of your board in your business plan to give potential donors confidence in the management of your nonprofit.
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain.
Describe your organization’s activities
In this section, provide more information about what your nonprofit does on a day-to-day basis. What products, training, education, or other services do you provide? What does your organization do to benefit the constituents identified in your mission statement? Here’s an example from the American Red Cross, courtesy of DonorBox :
“The American Red Cross carries out their mission to prevent and relieve suffering with five key services: disaster relief, supporting America’s military families, lifesaving blood, health and safety services, and international service.”
This section should be detailed and get into the operational weeds of how your business delivers on its mission statement. Explain the strategies your team will take to service clients, including outreach and marketing, inventory and equipment needs, a hiring plan, and other key elements.
Write a fundraising plan
This part is the most important element of your business plan. In addition to providing required financial statements (e.g., the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement), identify potential sources of funding for your nonprofit. These may include individual donors, corporate donors, grants, or in-kind support. If you are planning to host a fundraising event, put together a budget for that event and demonstrate the anticipated impact that event will have on your budget.
Create an impact plan
An impact plan ties everything together. It demonstrates how your fundraising and day-to-day activities will further your mission. For potential donors, it can make a very convincing case for why they should invest in your nonprofit.
“This section turns your purpose and motivation into concrete accomplishments your nonprofit wants to make and sets specific goals and objectives,” wrote DonorBox . “These define the real bottom line of your nonprofit, so they’re the key to unlocking support. Funders want to know for whom, in what way, and exactly how you’ll measure your impact.”
Be as realistic as possible about the impact you can make with the funding you hope to gain. Revisit your business plan as your organization grows to make sure the goals you’ve set both align with your mission and continue to be within reach.
[Read more: 8 Signs It's Time to Update Your Business Plan ]
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Join us for our Small Business Day event!
Join us at our next event on Wednesday, May 1, at 12:00 p.m., where we’ll be kicking off Small Business Month alongside business experts and entrepreneurs. Register to attend in person at our Washington, D.C., headquarters, or join us virtually!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
How startups contribute to innovation in emerging industries, how entrepreneurs can find a business mentor, 5 business metrics you should analyze every year.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.

How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan in 12 Steps (+ Free Template!)
The first step in starting a nonprofit is figuring out how to bring your vision into reality. If there’s any tool that can really help you hit the ground running, it’s a nonprofit business plan!
With a plan in place, you not only have a clear direction for growth, but you can also access valuable funding opportunities.
Here, we’ll explore:
- Why a business plan is so important
- The components of a business plan
- How to write a business plan for a nonprofit specifically
We also have a few great examples, as well as a free nonprofit business plan template.
Let’s get planning!
What Is a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan is the roadmap to your organization’s future. It lays out where your nonprofit currently stands in terms of organizational structure, finances and programs. Most importantly, it highlights your goals and how you aim to achieve them!
These goals should be reachable within the next 3-5 years—and flexible! Your nonprofit business plan is a living document, and should be regularly updated as priorities shift. The point of your plan is to remind you and your supporters what your organization is all about.
This document can be as short as one page if you’re just starting out, or much longer as your organization grows. As long as you have all the core elements of a business plan (which we’ll get into below!), you’re golden.
Why Your Nonprofit Needs a Business Plan
While some people might argue that a nonprofit business plan isn’t strictly necessary, it’s well worth your time to make!
Here are 5 benefits of writing a business plan:
Secure funding and grants
Did you know that businesses with a plan are far more likely to get funding than those that don’t have a plan? It’s true!
When donors, investors, foundations, granting bodies and volunteers see you have a clear plan, they’re more likely to trust you with their time and money. Plus, as you achieve the goals laid out in your plan, that trust will only grow.
Solidify your mission
In order to sell your mission, you have to know what it is. That might sound simple, but when you have big dreams and ideas, it’s easy to get lost in all of the possibilities!
Writing your business plan pushes you to express your mission in the most straightforward way possible. As the years go on and new opportunities and ideas arise, your business plan will guide you back to your original mission.
From there, you can figure out if you’ve lost the plot—or if it’s time to change the mission itself!
Set goals and milestones
The first step in achieving your goals is knowing exactly what they are. By highlighting your goals for the next 3-5 years—and naming their key milestones!—you can consistently check if you’re on track.
Nonprofit work is tough, and there will be points along the way where you wonder if you’re actually making a difference. With a nonprofit business plan in place, you can actually see how much you’ve achieved over the years.
Attract a board and volunteers
Getting volunteers and filling nonprofit board positions is essential to building out your organization’s team. Like we said before, a business plan builds trust and shows that your organization is legitimate. In fact, some boards of directors actually require a business plan in order for an organization to run!
An unfortunate truth is that many volunteers get taken advantage of . With a business plan in place, you can show that you’re coming from a place of professionalism.
Research and find opportunities
Writing a business plan requires some research!
Along the way, you’ll likely dig into information like:
- Who your ideal donor might be
- Where to find potential partners
- What your competitors are up to
- Which mentorships or grants are available for your organization
- What is the best business model for a nonprofit like yours
With this information in place, not only will you have a better nonprofit business model created—you’ll also have a more stable organization!
Free Nonprofit Business Plan Template
If you’re feeling uncertain about building a business plan from scratch, we’ve got you covered!
Here is a quick and simple free nonprofit business plan template.
Basic Format and Parts of a Business Plan
Now that you know what a business plan can do for your organization, let’s talk about what it actually contains!
Here are some key elements of a business plan:
First of all, you want to make sure your business plan follows best practices for formatting. After all, it’ll be available to your team, donors, board of directors, funding bodies and more!
Your nonprofit business plan should:
- Be consistent formatted
- Have standard margins
- Use a good sized font
- Keep the document to-the-point
- Include a page break after each section
- Be proofread
Curious about what each section of the document should look like?
Here are the essential parts of a business plan:
- Executive Summary: This is your nonprofit’s story—it’ll include your goals, as well as your mission, vision and values.
- Products, programs and services: This is where you show exactly what it is you’re doing. Highlight the programs and services you offer, and how they will benefit your community.
- Operations: This section describes your team, partnerships and all activities and requirements your day-to-day operations will include.
- Marketing : Your marketing plan will cover your market, market analyses and specific plans for how you will carry out your business plan with the public.
- Finances: This section covers an overview of your financial operations. It will include documents like your financial projections, fundraising plan , grants and more
- Appendix: Any additional useful information will be attached here.
We’ll get into these sections in more detail below!
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan in 12 Steps
Feeling ready to put your plan into action? Here’s how to write a business plan for a nonprofit in 12 simple steps!
1. Research the market
Take a look at what’s going on in your corner of the nonprofit sector. After all, you’re not the first organization to write a business plan!
- How your competitors’ business plans are structured
- What your beneficiaries are asking for
- Potential partners you’d like to reach
- Your target donors
- What information granting bodies and loan providers require
All of this information will show you what parts of your business plan should be given extra care. Sending out donor surveys, contacting financial institutions and connecting with your beneficiaries are a few tips to get your research going.
If you’re just getting started out, this can help guide you in naming your nonprofit something relevant, eye-catching and unique!
2. Write to your audience
Your business plan will be available for a whole bunch of people, including:
- Granting bodies
- Loan providers
- Prospective and current board members
Each of these audiences will be coming from different backgrounds, and looking at your business plan for different reasons. If you keep your nonprofit business plan accessible (minimal acronyms and industry jargon), you’ll be more likely to reach everyone.
If you’d like, it’s always possible to create a one page business plan AND a more detailed one. Then, you can provide the one that feels most useful to each audience!
3. Write your mission statement
Your mission statement defines how your organization aims to make a difference in the world. In one sentence, lay out why your nonprofit exists.
Here are a few examples of nonprofit mission statements:
- Watts of Love is a global solar lighting nonprofit bringing people the power to raise themselves out of the darkness of poverty.
- CoachArt creates a transformative arts and athletics community for families impacted by childhood chronic illness.
- The Trevor Project fights to end suicide among lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, and questioning young people.
In a single sentence, each of these nonprofits defines exactly what it is their organization is doing, and who their work reaches. Offering this information at a glance is how you immediately hook your readers!
4. Describe your nonprofit
Now that your mission is laid out, show a little bit more about who you are and how you aim to carry out your mission. Expanding your mission statement to include your vision and values is a great way to kick this off!
Use this section to highlight:
- Your ideal vision for your community
- The guiding philosophy and values of your organization
- The purpose you were established to achieve
Don’t worry too much about the specifics here—we’ll get into those below! This description is simply meant to demonstrate the heart of your organization.
5. Outline management and organization
When you put together your business plan, you’ll want to describe the structure of your organization in the Operations section.
This will include information like:
- Team members (staff, board of directors , etc.)
- The specific type of nonprofit you’re running
If you’re already established, make a section for how you got started! This includes your origin story, your growth and the impressive nonprofit talent you’ve brought on over the years.
6. Describe programs, products and services
This information will have its own section in your nonprofit business plan—and for good reason!
It gives readers vital information about how you operate, including:
- The specifics of the work you do
- How that work helps your beneficiaries
- The resources that support the work (partnerships, facilities, volunteers, etc!)
- If you have a membership base or a subscription business model
Above all, highlight what needs your nonprofit meets and how it plans to continue meeting those needs. Really get into the details here! Emphasize the work of each and every program, and if you’re already established, note the real impact you’ve made.
Try including pictures and graphic design elements so people can feel your impact even if they’re simply skimming.
7. Create an Executive Summary
Your Executive Summary will sit right at the top of your business plan—in many ways, it’s the shining star of the document! This section serves as a concise and compelling telling of your nonprofit’s story. If it can capture your readers’ attention, they’re more likely to read through the rest of the plan.
Your Executive Summary should include:
- Your mission, vision and values
- Your goals (and their timelines!)
- Your organization’s history
- Your primary programs, products and services
- Your financing plan
- How you intend on using your funding
This section will summarize the basics of everything else in your plan. While it comes first part of your plan, we suggest writing it last! That way, you’ll already have the information on hand.
You can also edit your Executive Summary depending on your audience. For example, if you’re sending your nonprofit business plan to a loan provider, you can really focus on where the money will be going. If you’re trying to recruit a new board member, you might want to highlight goals and impact, instead.
8. Write a marketing plan
Having a nonprofit marketing plan is essential to making sure your mission reaches people—and that’s especially true for your business plan.
If your nonprofit is already up and running, detail the work you’re currently doing, as well as the specific results you’ve seen so far. If you’re new, you’ll mostly be working with projections—so make sure your data is sound!
No matter what, your Marketing Plan section should market research such as:
- Beneficiary information
- Information on your target audience/donor base
- Information on your competitors
- Names of potential partners
Data is your friend here! Make note of market analyses and tests you’ve run. Be sure to also document any outreach and campaigns you’ve previously done, as well as your outcomes.
Finally, be sure to list all past and future marketing strategies you’re planning for. This can include promotion, advertising, online marketing plans and more.
9. Create a logistics and operations plan
The Operations section of your business plan will take the organizational information you’ve gathered so far and expand the details! Highlight what the day-to-day will look like for your nonprofit, and how your funds and resources will make it possible.
Be sure to make note of:
- The titles and responsibilities of your core team
- The partners and suppliers you work with
- Insurance you will need
- Necessary licenses or certifications you’ll maintain
- The cost of services and programs
This is the what and how of your business plan. Lean into those details, and show exactly how you’ll accomplish those goals you’ve been talking about!
10. Write an Impact Plan
Your Impact Plan is a deep dive into your organization’s goals. It grounds your dreams in reality, which brings both idealists and more practically-minded folks into your corner!
Where your Executive Summary lays out your ambitions on a broader level, this plan:
- Clarifies your goals in detail
- Highlights specific objectives and their timelines
- Breaks down how you will achieve them
- Shows how you will measure your success
Your Impact Plan will have quite a few goals in it, so be sure to emphasize which ones are the most impactful on your cause. After all, social impact is just as important as financial impact!
Speaking of…
11. Outline the Financial Plan
One of the main reasons people want to know how to write a nonprofit business plan is because of how essential it is to receiving funding. Loan providers, donors and granting bodies will want to see your numbers—and that’s where your Financial Plan comes in.
This plan should clearly lay out where your money is coming from and where it will go. If you’re just getting started, check out what similar nonprofits are doing in order to get realistic numbers. Even if you’re starting a nonprofit on a tight budget , every bit of financial information counts!
First, map out your projected (or actual) nonprofit revenue streams , such as:
- Expected membership contributions
- Significant donations
- In-kind support
- Fundraising plan
Then, do the same with your expenses:
- Startup costs
- Typical bills
- Web hosting
- Membership management software
- Subscription
- Costs of programs
If your nonprofit is already up and running, include your past accounting information. Otherwise, keep working with those grounded projections!
To make sure you have all of your information set, include documents like:
- Income statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
This information comes together to show that your nonprofit can stay above water financially. Highlighting that you can comfortably cover your operational costs is essential. Plus, building this plan might help your team find funding gaps or opportunities!
12. Include an Appendix
Your appendix is for any extra pieces of useful information for your readers.
This could be documents such as:
- Academic papers about your beneficiaries
- Publications on your nonprofit’s previous success
- Board member bios
- Organizational flow chart
- Your IRS status letter
Make sure your additions contribute to your nonprofit’s story!
Examples of Business Plans for Nonprofits
Here are two great examples of nonprofit business plans. Notice how they’re different depending on the size of the organization!
Nonprofit Recording Co-op Business Plan
This sample nonprofit business plan shows what a basic plan could look like for a hobbyists’ co-op. If your nonprofit is on the smaller, more local side, this is a great reference!
What we like:
- Details on running a basic membership model
- Emphasis on what it means to specifically be a sustainable cooperative
- A list of early milestones, such as hitting their 100th member
- Clarification that all recordings will be legal
Nonprofit Youth Services Business Plan
This sample nonprofit business plan is for a much larger organization. Instead of focusing on the details of a membership model, it gets deeper into programs and services provided.
What we like
- The mission is broken down by values
- A detailed look at what each program provides
- A thorough sales plan
- Key assumptions are included for the financial plan
How to Create a Nonprofit Business Plan With Confidence
We hope this sheds some light on how creating a nonprofit business plan can help your organization moving forward! Remember: you know what you want for your organization. A business plan is simply a tool for making those dreams a reality.
Is a membership program part of your business plan? Check out WildApricot ’s award-winning membership management software!
With our 60-day free trial , you’ll have all the time you need to fall in love with what we have to offer.
Related Organizational Management Articles

30 Free Nonprofit Webinars for April 2024
Managing Human Resources for Nonprofits

Engaging Association Members in Advocacy Initiatives: 3 Tips
The Membership Growth Report:
Benchmarks & insights for growing revenue and constituents.
Raise More & Grow Your Nonprofit.
The complete guide to writing a nonprofit business plan.
August 14, 2019
Leadership & Management
July 7, 2022
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Statistics from the National Center for Charitable Statistics (NCCS) show that there are over 1.5 million nonprofit organizations currently operating in the U.S. alone. Many of these organizations are hard at work helping people in need and addressing the great issues of our time. However, doing good work doesn’t necessarily translate into long-term success and financial stability. Other information has shown that around 12% of non-profits don’t make it past the 5-year mark, and this number expands to 17% at the 10-year mark.
12% of non-profits don’t make it past the 5-year mark and 17% at the 10-year mark
There are a variety of challenges behind these sobering statistics. In many cases, a nonprofit can be sunk before it starts due to a lack of a strong nonprofit business plan. Below is a complete guide to understanding why a nonprofit needs a business plan in place, and how to construct one, piece by piece.
The purpose of a nonprofit business plan
A business plan for a nonprofit is similar to that of a for-profit business plan, in that you want it to serve as a clear, complete roadmap for your organization. When your plan is complete, questions such as "what goals are we trying to accomplish?" or "what is the true purpose of our organization?" should be clear and simple to answer.

Your nonprofit business plan should provide answers to the following questions:
1. What activities do you plan to pursue in order to meet the organization’s high level goals?
2. What's your plan on getting revenue to fund these activities?
3. What are your operating costs and specifically how do these break down?
Note that there’s a difference between a business plan and a strategic plan, though there may be some overlap. A strategic plan is more conceptual, with different ideas you have in place to try and meet the organization’s greater vision (such as fighting homelessness or raising climate change awareness). A business plan serves as an action plan because it provides, in as much detail as possible, the specifics on how you’re going to execute your strategy.
More Reading
- What is the Difference Between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan?
- Business Planning for Nonprofits
Creating a nonprofit business plan
With this in mind, it’s important to discuss the individual sections of a nonprofit business plan. Having a proper plan in a recognizable format is essential for a variety of reasons. On your business’s end, it makes sure that as many issues or questions you may encounter are addressed up front. For outside entities, such as potential volunteers or donors, it shows that their time and energy will be managed well and put to good use. So, how do you go from conceptual to concrete?
Step 1: Write a mission statement
Having a mission statement is essential for any company, but even more so for nonprofits. Your markers of success are not just how the organization performs financially, but the impact it makes for your cause.
One of the easiest ways to do this is by creating a mission statement. A strong mission statement clarifies why your organization exists and determines the direction of activities.

At the head of their ethics page , NPR has a mission statement that clearly and concisely explains why they exist. From this you learn:
- The key point of their mission: creating a more informed public that understands new ideas and cultures
- Their mechanism of executing that vision: providing and reporting news/info that meets top journalistic standards
- Other essential details: their partnership with their membership statement
You should aim for the same level of clarity and brevity in your own mission statement.
The goal of a mission statement isn’t just about being able to showcase things externally, but also giving your internal team something to realign them if they get off track.
For example, if you're considering a new program or services, you can always check the idea against the mission statement. Does it align with your higher level goal and what your organization is ultimately trying to achieve? A mission statement is a compass to guide your team and keep the organization aligned and focused.
Step 2: Collect the data
You can’t prepare for the future without some data from the past and present. This can range from financial data if you’re already in operation to secured funding if you’re getting ready to start.
Data related to operations and finances (such as revenue, expenses, taxes, etc.) is crucial for budgeting and organizational decisions.
You'll also want to collect data about your target donor. Who are they in terms of their income, demographics, location, etc. and what is the best way to reach them? Every business needs to market, and answering these demographic questions are crucial to targeting the right audience in a marketing campaign. You'll also need data about marketing costs collected from your fundraising, marketing, and CRM software and tools. This data can be extremely important for demonstrating the effectiveness of a given fundraising campaign or the organization as a whole.
Then there is data that nonprofits collect from third-party sources as to how to effectively address their cause, such as shared data from other nonprofits and data from governments.
By properly collecting and interpreting the above data, you can build your nonprofit to not only make an impact, but also ensure the organization is financially sustainable.
Step 3: Create an outline
Before you begin writing your plan, it’s important to have an outline of the sections of your plan. Just like an academic essay, it’s easier to make sure all the points are addressed by taking inventory of high level topics first. If you create an outline and find you don’t have all the materials you need to fill it, you may need to go back to the data collection stage.
Writing an outline gives you something simple to read that can easily be circulated to your team for input. Maybe some of your partners will want to emphasize an area that you missed or an area that needs more substance.
Having an outline makes it easier for you to create an organized, well-flowing piece. Each section needs to be clear on its own, but you also don’t want to be overly repetitive.
As a side-note, one area where a lot of business novices stall in terms of getting their plans off the ground is not knowing what format to choose or start with. The good news is there are a lot of resources available online for you to draw templates for from your plan, or just inspire one of your own.
Using a business plan template
You may want to use a template as a starting point for your business plan. The major benefit here is that a lot of the outlining work that we mentioned is already done for you. However, you may not want to follow the template word for word. A nonprofit business plan may require additional sections or parts that aren’t included in a conventional business plan template.
The best way to go about this is to try and focus less on copying the template, and more about copying the spirit of the template. For example, if you see a template that you like, you can keep the outline, but you may want to change the color scheme and font to better reflect your brand. And of course, all your text should be unique.
When it comes to adding a new section to a business plan template, for the most part, you can use your judgment. We will get into specific sections in a bit, but generally, you just want to pair your new section with the existing section that makes the most sense. For example, if your non-profit has retail sales as a part of a financial plan, you can include that along with the products, services and programs section.
- Free Nonprofit Sample Business Plans - Bplans
- Non-Profit Business Plan Template - Growthink
- Sample Nonprofit Business Plans - Bridgespan
- Nonprofit Business Plan Template - Slidebean
- 23+ Non Profit Business Plan Templates - Template.net
Nonprofit business plan sections
The exact content is going to vary based on the size, purpose, and nature of your nonprofit. However, there are certain sections that every business plan will need to have for investors, donors, and lenders to take you seriously. Generally, your outline will be built around the following main sections:
1. Executive summary
Many people write this last, even though it comes first in a business plan. This is because the executive summary is designed to be a general summary of the business plan as a whole. Naturally, it may be easier to write this after the rest of the business plan has been completed.
After reading your executive summary a person should ideally have a general idea of what the entire plan covers. Sometimes, a person may be interested in learning about your non-profit, but doesn’t have time to read a 20+ page document. In this case, the executive summary could be the difference between whether or not you land a major donor.
As a start, you want to cover the basic need your nonprofit services, why that need exists, and the way you plan to address that need. The goal here is to tell the story as clearly and and concisely as possible. If the person is sold and wants more details, they can read through the rest of your business plan.
2. Products/Services/Programs
This is the space where you can clarify exactly what your non-profit does. Think of it as explaining the way your nonprofit addresses that base need you laid out earlier. This can vary a lot based on what type of non-profit you’re running.

This page gives us some insight into the mechanisms Bucks County Historical Society uses to further their mission, which is “to educate and engage its many audiences in appreciating the past and to help people find stories and meanings relevant to their lives—both today and in the future.”
They accomplish this goal through putting together both permanent exhibits as well as regular events at their primary museum. However, in a non-profit business plan, you need to go further.
It’s important here not only to clearly explain who benefits from your services, but also the specific details how those services are provided. For example, saying you “help inner-city school children” isn’t specific enough. Are you providing education or material support? Your non-profit business plan readers need as much detail as possible using simple and clear language.
3. Marketing
For a non-profit to succeed, it needs to have a steady stream of both donors and volunteers. Marketing plays a key role here as it does in a conventional business. This section should outline who your target audience is, and what you’ve already done/plan on doing to reach this audience. How you explain this is going to vary based on what stage your non-profit is in. We’ll split this section to make it more clear.
Nonprofits not in operation
Obviously, it’s difficult to market an idea effectively if you’re not in operation, but you still need to have a marketing plan in place. People who want to support your non-profit need to understand your marketing plan to attract donors. You need to profile all the data you have about your target market and outline how you plan to reach this audience.
Nonprofits already in operation
Marketing plans differ greatly for nonprofits already in operation. If your nonprofit is off the ground, you want to include data about your target market as well, along with other key details. Describe all your current marketing efforts, from events to general outreach, to conventional types of marketing like advertisements and email plans. Specific details are important. By the end of this, the reader should know:
- What type of marketing methods your organization prefers
- Why you’ve chosen these methods
- The track record of success using these methods
- What the costs and ROI of a marketing campaign
4. Operations
This is designed to serve as the “how” of your Products/Services/Programs section.
For example, if your goal is to provide school supplies for inner-city schoolchildren, you’ll need to explain how you will procure the supplies and distribute them to kids in need. Again, detail is essential. A reader should be able to understand not only how your non-profit operates on a daily basis, but also how it executes any task in the rest of the plan.
If your marketing plan says that you hold community events monthly to drum up interest. Who is in charge of the event? How are they run? How much do they cost? What personnel or volunteers are needed for each event? Where are the venues?
This is also a good place to cover additional certifications or insurance that your non-profit needs in order to execute these operations, and your current progress towards obtaining them.
Your operations section should also have a space dedicated to your team. The reason for this is, just like any other business plan, is that the strength of an organization lies in the people running it.

For example, let’s look at this profile from The Nature Conservancy . The main points of the biography are to showcase Chief Development Officer Jim Asp’s work history as it is relevant to his job. You’ll want to do something similar in your business plan’s team section.
Equally important is making sure that you cover any staff changes that you plan to implement in the near future in your business plan. The reason for this is that investors/partners may not want to sign on assuming that one leadership team is in place, only for it to change when the business reaches a certain stage.
The sections we’ve been talking about would also be in a traditional for profit business plan. We start to deviate a bit at this point. The impact section is designed to outline the social change you plan to make with your organization, and how your choices factor into those goals.
Remember the thoughts that go into that mission statement we mentioned before? This is your chance to show how you plan to address that mission with your actions, and how you plan to track your progress.
Let’s revisit the idea of helping inner-city school children by providing school supplies. What exactly is the metric you’re going to use to determine your success? For-profit businesses can have their finances as their primary KPI, but it’s not that easy for non-profits. Let’s say that your mission is to provide 1,000 schoolchildren in an underserved school district supplies for their classes. Your impact plan could cover two metrics:
- How many supplies are distributed
- Secondary impact (improved grades, classwork completed, etc).
The primary goal of this section is to transform that vision into concrete, measurable goals and objectives. A great acronym to help you create these are S.M.A.R.T. goals which stands for: specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely.

Vitamin Angels does a good job of showing how their action supports the mission. Their goal of providing vitamins to mothers and children in developing countries has a concrete impact when we look at the numbers of how many children they service as well as how many countries they deliver to. As a non-profit business plan, it’s a good idea to include statistics like these to show exactly how close you are to your planned goals.
6. Finances
Every non-profit needs funding to operate, and this all-important section details exactly how you plan to cover these financial needs. Your business plan can be strong in every other section, but if your financial planning is flimsy, it’s going to prove difficult to gather believers to your cause.
It's important to paint a complete, positive picture of your fundraising plans and ambitions. Generally, this entails the following parts:
- Current financial status, such as current assets, cash on hand, liabilities
- Projections based off of your existing financial data and forms
- Key financial documents, such as a balance sheet, income statements, and cash flow sheet
- Any grants or major contributions received
- Your plan for fundraising (this may overlap with your marketing section which is okay)
- Potential issues and hurdles to your funding plan
- Your plans to address those issues
- How you'll utilize surplus donations
- Startup costs (if your non-profit is not established yet)
In general, if you see something else that isn’t accounted for here, it’s better to be safe than sorry, and put the relevant information in. It’s better to have too much information than too little when it comes to finances, especially since there is usually a clear preference for transparent business culture.
- How to Make a Five-Year Budget Plan for a Nonprofit
- Financial Transparency - National Council of Nonprofits
7. Appendix
Generally, this serves as a space to attach additional documents and elements that you may find useful for your business plan. This can include things like supplementary charts or a list of your board of directors.
This is also a good place to put text or technical information that you think may be relevant to your business plan, but might be long-winded or difficult to read. A lot of the flow and structure concerns you have for a plan don’t really apply with an appendix.
In summary, while a non-profit may have very different goals than your average business, the ways that they reach those goals do have a lot of similarities with for-profit businesses. The best way to ensure your success is to have a clear, concrete vision and path to different milestones along the way. A solid, in-depth business plan also gives you something to refer back to when you are struggling and not sure where to turn.
Alongside your business plan, you also want to use tools and resources that promote efficiency at all levels. For example, every non-profit needs a consistent stream of donations to survive, so consider using a program like GiveForms that creates simple, accessible forms for your donors to easily make donations. Accounting and budgeting for these in your plans can pay dividends later on.
Share this Article
Related articles, start fundraising today.

How to Write a Business Plan For a Nonprofit Organization + Template

Creating a business plan is essential for any business, but it can be especially helpful for nonprofits. A nonprofit business plan allows you to set goals and track progress over time. It can also help you secure funding from investors or grant-making organizations.
A well-crafted business plan not only outlines your vision for the organization but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it. In order to create an effective business plan, you must first understand the components that are essential to its success.
This article will provide an overview of the key elements that every nonprofit founder should include in their business plan.
Download the Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template
What is a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan is a formal written document that describes your organization’s purpose, structure, and operations. It is used to communicate your vision to potential investors or donors and convince them to support your cause.
The business plan should include information about your target market, financial projections, and marketing strategy. It should also outline the organization’s mission statement and goals.
Why Write a Nonprofit Business Plan?
A nonprofit business plan is required if you want to secure funding from grant-making organizations or investors.
A well-crafted business plan will help you:
- Define your organization’s purpose and goals
- Articulate your vision for the future
- Develop a step-by-step plan to achieve your goals
- Secure funding from investors or donors
- Convince potential supporters to invest in your cause
Entrepreneurs can also use this as a roadmap when starting your new nonprofit organization, especially if you are inexperienced in starting a nonprofit.
Writing an Effective Nonprofit Business Plan
The key is to tailor your business plan to the specific needs of your nonprofit. Here’s a quick overview of what to include:
Executive Summary
Organization overview, products, programs, and services, industry analysis, customer analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, management team.
- Financial Plan
The executive summary of a nonprofit business plan is a one-to-two page overview of your entire business plan. It should summarize the main points, which will be presented in full in the rest of your business plan.
- Start with a one-line description of your nonprofit organization
- Provide a short summary of the key points of each section of your business plan.
- Organize your thoughts in a logical sequence that is easy for the reader to follow.
- Include information about your organization’s management team, industry analysis, competitive analysis, and financial forecast.
This section should include a brief history of your nonprofit organization. Include a short description of how and why you started it and provide a timeline of milestones the organization has achieved.
If you are just starting your nonprofit, you may not have a long history. Instead, you can include information about your professional experience in the industry and how and why you conceived your new nonprofit idea. If you have worked for a similar organization before or have been involved in a nonprofit before starting your own, mention this.
You will also include information about your chosen n onprofit business model and how it is different from other nonprofits in your target market.
This section is all about what your nonprofit organization offers. Include information about your programs, services, and any products you may sell.
Describe the products or services you offer and how they benefit your target market. Examples might include:
- A food bank that provides healthy meals to low-income families
- A job training program that helps unemployed adults find jobs
- An after-school program that helps kids stay out of gangs
- An adult literacy program that helps adults learn to read and write
Include information about your pricing strategy and any discounts or promotions you offer. Examples might include membership benefits, free shipping, or volume discounts.
If you offer more than one product or service, describe each one in detail. Include information about who uses each product or service and how it helps them achieve their goals.
If you offer any programs, describe them in detail. Include information about how often they are offered and the eligibility requirements for participants. For example, if you offer a job training program, you might include information about how often the program is offered, how long it lasts, and what kinds of jobs participants can expect to find after completing the program.
The industry or market analysis is an important component of a nonprofit business plan. Conduct thorough market research to determine industry trends, identify your potential customers, and the potential size of this market.
Questions to answer include:
- What part of the nonprofit industry are you targeting?
- Who are your competitors?
- How big is the market?
- What trends are happening in the industry right now?
You should also include information about your research methodology and sources of information, including company reports and expert opinions.
As an example, if you are starting a food bank, your industry analysis might include information about the number of people in your community who are considered “food insecure” (they don’t have regular access to enough nutritious food). You would also include information about other food banks in your area, how they are funded, and the services they offer.
For each of your competitors, you should include a brief description of their organization, their target market, and their competitive advantage. To do this, you should complete a SWOT analysis.
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis is a helpful tool to assess your nonprofit’s current position and identify areas where you can improve.
Some questions to consider when conducting a SWOT analysis include:
- Strengths : What does your nonprofit do well?
- Weaknesses : What areas could your nonprofit improve?
- Opportunities : What trends or changes in the industry could you take advantage of?
- Threats : What trends or changes in the industry could hurt your nonprofit’s chances of success?
After you have identified your nonprofit’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, you can develop strategies to improve your organization.
For example, if you are starting a food bank, your SWOT analysis might reveal that there is a need for more food banks in your community. You could use this information to develop a marketing strategy to reach potential donors who might be interested in supporting your organization.
If you are starting a job training program, your SWOT analysis might reveal that there is a need for more programs like yours in the community. You could use this information to develop a business plan and marketing strategy to reach potential participants who might be interested in enrolling in your program.
This section should include a list of your target audience(s) with demographic and psychographic profiles (e.g., age, gender, income level, profession, job titles, interests). You will need to provide a profile of each customer segment separately, including their needs and wants.
For example, if you are starting a job training program for unemployed adults, your target audience might be low-income adults between the ages of 18 and 35. Your customer analysis would include information about their needs (e.g., transportation, childcare, job readiness skills) and wants (e.g., good pay, flexible hours, benefits).
If you have more than one target audience, you will need to provide a separate customer analysis for each one.
You can include information about how your customers make the decision to buy your product or use your service. For example, if you are starting an after-school program, you might include information about how parents research and compare programs before making a decision.
You should also include information about your marketing strategy and how you plan to reach your target market. For example, if you are starting a food bank, you might include information about how you will promote the food bank to the community and how you will get the word out about your services.
Develop a strategy for targeting those customers who are most likely to use your program, as well as those that might be influenced to buy your products or nonprofit services with the right marketing.
This part of the business plan is where you determine how you are going to reach your target market. This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about your marketing goals, strategies, and tactics.
- What are your marketing goals? Include information about what you hope to achieve with your marketing efforts, as well as when and how you will achieve it.
- What marketing strategies will you use? Include information about public relations, advertising, social media, and other marketing tactics you will use to reach your target market.
- What tactics will you use? Include information about specific actions you will take to execute your marketing strategy. For example, if you are using social media to reach your target market, include information about which platforms you will use and how often you will post.
Your marketing strategy should be clearly laid out, including the following 4 Ps.
- Product/Service : Make sure your product, service, and/or program offering is clearly defined and differentiated from your competitors, including the benefits of using your service.
- Price : How do you determine the price for your product, services, and/or programs? You should also include a pricing strategy that takes into account what your target market will be willing to pay and how much the competition within your market charges.
- Place : Where will your target market find you? What channels of distribution will you use to reach them?
- Promotion : How will you reach your target market? You can use social media or write a blog, create an email marketing campaign, post flyers, pay for advertising, launch a direct mail campaign, etc.
For example, if you are starting a job training program for unemployed adults, your marketing strategy might include partnering with local job centers and adult education programs to reach potential participants. You might also promote the program through local media outlets and community organizations.
Your marketing plan should also include a sales strategy, which includes information about how you will generate leads and convert them into customers.
You should also include information about your paid advertising budget, including an estimate of expenses and sales projections.
This part of your nonprofit business plan should include the following information:
- How will you deliver your products, services and/or programs to your target market? For example, if you are starting a food bank, you will need to develop a system for collecting and storing food donations, as well as distributing them to the community.
- How will your nonprofit be structured? For example, will you have paid staff or volunteers? How many employees will you need? What skills and experience will they need to have?
- What kind of facilities and equipment will you need to operate your nonprofit? For example, if you are starting a job training program, you will need space to hold classes, as well as computers and other office equipment.
- What are the day-to-day operations of your nonprofit? For example, if you are starting a food bank, you will need to develop a system for accepting and sorting food donations, as well as distributing them to the community.
- Who will be responsible for each task? For example, if you are starting a job training program, you will need to identify who will be responsible for recruiting participants, teaching classes, and placing graduates in jobs.
- What are your policies and procedures? You will want to establish policies related to everything from employee conduct to how you will handle donations.
- What infrastructure, equipment, and resources are needed to operate successfully? How can you meet those requirements within budget constraints?
The operations plan is the section of the business plan where you elaborate on the day-to-day execution of your nonprofit. This is where you really get into the nitty-gritty of how your organization will function on a day-to-day basis.
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about the individuals who will be running your organization.
- Who is on your team? Include biographies of your executive director, board of directors, and key staff members.
- What are their qualifications? Include information about their education, work experience, and skills.
- What are their roles and responsibilities? Include information about what each team member will be responsible for, as well as their decision-making authority.
- What is their experience in the nonprofit sector? Include information about their work with other nonprofits, as well as their volunteer experiences.
This section of your plan is important because it shows that you have a team of qualified individuals who are committed to the success of your nonprofit.
Nonprofit Financial Plan
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include the following information:
- Your budget. Include information about your income and expenses, as well as your fundraising goals.
- Your sources of funding. Include information about your grants, donations, and other sources of income.
- Use of funds. Include information about how you will use your income to support your programs and operations.
This section of your business plan is important because it shows that you have a clear understanding of your organization’s finances. It also shows that you have a plan for raising and managing your funds.
Now, include a complete and detailed financial plan. This is where you will need to break down your expenses and revenue projections for the first 5 years of operation. This includes the following financial statements:
Income Statement
Your income statement should include:
- Revenue : how will you generate revenue?
- Cost of Goods Sold : These are your direct costs associated with generating revenue. This includes labor costs, as well as the cost of any equipment and supplies used to deliver the product/service offering.
- Net Income (or loss) : Once expenses and revenue are totaled and deducted from each other, what is the net income or loss?
Sample Income Statement for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
Balance sheet.
Include a balance sheet that shows what you have in terms of assets, liabilities, and equity. Your balance sheet should include:
- Assets : All of the things you own (including cash).
- Liabilities : This is what you owe against your company’s assets, such as accounts payable or loans.
- Equity : The worth of your business after all liabilities and assets are totaled and deducted from each other.
Sample Balance Sheet for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
Cash flow statement.
Include a cash flow statement showing how much cash comes in, how much cash goes out and a net cash flow for each year. The cash flow statement should include:
- Income : All of the revenue coming in from clients.
- Expenses : All of your monthly bills and expenses. Include operating, marketing and capital expenditures.
- Net Cash Flow : The difference between income and expenses for each month after they are totaled and deducted from each other. This number is the net cash flow for each month.
Using your total income and expenses, you can project an annual cash flow statement. Below is a sample of a projected cash flow statement for a startup nonprofit.
Sample Cash Flow Statement for a Startup Nonprofit Organization
Fundraising plan.
This section of your nonprofit business plan should include information about your fundraising goals, strategies, and tactics.
- What are your fundraising goals? Include information about how much money you hope to raise, as well as when and how you will raise it.
- What fundraising strategies will you use? Include information about special events, direct mail campaigns, online giving, and grant writing.
- What fundraising tactics will you use? Include information about volunteer recruitment, donor cultivation, and stewardship.
Now include specific fundraising goals, strategies, and tactics. These could be annual or multi-year goals. Below are some examples:
Goal : To raise $50,000 in the next 12 months.
Strategy : Direct mail campaign
- Create a mailing list of potential donors
- Develop a direct mail piece
- Mail the direct mail piece to potential donors
Goal : To raise $100,000 in the next 24 months.
Strategy : Special event
- Identify potential special event sponsors
- Recruit volunteers to help with the event
- Plan and execute the special event
Goal : To raise $250,000 in the next 36 months.
Strategy : Grant writing
- Research potential grant opportunities
- Write and submit grant proposals
- Follow up on submitted grants
This section of your business plan is important because it shows that you have a clear understanding of your fundraising goals and how you will achieve them.
You will also want to include an appendix section which may include:
- Your complete financial projections
- A complete list of your nonprofit’s policies and procedures related to the rest of the business plan (marketing, operations, etc.)
- A list of your hard assets and equipment with purchase dates, prices paid and any other relevant information
- A list of your soft assets with purchase dates, prices paid and any other relevant information
- Biographies and/or resumes of the key members of your organization
- Your nonprofit’s bylaws
- Your nonprofit’s articles of incorporation
- Your nonprofit’s most recent IRS Form 990
- Any other relevant information that may be helpful in understanding your organization
Writing a good business plan gives you the advantage of being fully prepared to launch and grow your nonprofit organization. It not only outlines your vision but also provides a step-by-step process of how you are going to accomplish it. Sometimes it may be difficult to get started, but once you get the hang of it, writing a business plan becomes easier and will give you a sense of direction and clarity about your nonprofit organization.
Finish Your Nonprofit Business Plan in 1 Day!
Other helpful articles.
How to Write a Grant Proposal for Your Nonprofit Organization + Template & Examples
How To Create the Articles of Incorporation for Your Nonprofit Organization + Template
How to Develop a Nonprofit Communications Plan + Template
How to Write a Stand-Out Purpose Statement + Examples
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Strategic planning |
Nonprofit business plan template
Success doesn’t just happen—it’s planned. Stay focused on the work that supports your nonprofit’s mission with a business plan template.
Sign up to use this template.
- A library of 70+ templates
- Hundreds of app integrations
- AI features to get more done—faster
Like any business, nonprofits rely on business plans to get funding and stay on mission. But even though they often operate like a traditional for-profit organization, nonprofits need their business plans to highlight slightly different aspects of their organization. Showing cash spend becomes very important when you’re a nonprofit, so donors, board members, and government agencies recognize that you’re putting your money where your mission is. Here, we’ll show you what to include in your own custom nonprofit template, and how to use it to move your mission forward.
![profit business plan [Product ui] Nonprofit business plan project in Asana, spreadsheet-style project view (List)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/dd266e4d-783e-49a4-a61e-12485a66dc0e/TG23-web-hero-027-non-profit-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
What is a nonprofit business plan template
A nonprofit business plan template provides a strategic overview of your nonprofit. It’s a breakdown of all higher-level information about your organization, such as the board of directors and your core mission. Use your nonprofit business plan template to give your staff, the board, potential donors, and government funding agencies an overview of your mission and strategies.
Nonprofit business plan vs. strategic plan template
Both business and strategic plan templates share certain sections, such as your core mission. However, your nonprofit business plan template should also include relevant action plans , such as your fundraising plan and marketing strategy. Normally, you share your business plan with internal and partner stakeholders as opposed to the general public. Think of your nonprofit business plan as a roadmap or higher-level operational plan—it tells you what you’re currently doing to pursue your mission, and the steps you’re taking to go even further.
Why nonprofit business plan templates are important
Nonprofits know how to do more with less—a nonprofit business plan template will outline how. There are many benefits to creating your own, including:
Transparency. Visibility is a crucial piece of engaging with donors and board members. Nonprofit business plans showcase the work you’re doing and why others should care.
Reduce work about work . Nonprofits don’t always have the same resources as for-profit companies. As a result, freeing up time for your employees to work on their highest-impact tasks is critical—not just for your bottom line, but for your overall mission.
One source of truth. As a nonprofit, you’re constantly fielding requests for information about your finances, mission, and structure. When compiled with project management software , you can create and share your nonprofit business plan template with anyone who asks, without any additional work on your end.
Save 50% on Asana
Partner with Asana to put more resources toward your mission. The Asana for Nonprofits program helps nonprofits do more mission-critical work. Qualified organizations can save 50% on a one-year subscription, plus get numerous free Asana resources.
How to create your non-profit business plan template
Your nonprofit business plan template should include all relevant information about how your organization operates. If you’re using a digital tool, such as project management software , be sure to attach relevant documents and projects. Your template is essentially your nonprofit business plan outline that you’ll fill in during your planning process.
As you’re going through your nonprofit business plan template, make sure to include the following sections so you can get the most from your template.
Non-profit description
Describe the basics of your organizational structure. Include:
Executive summary
Mission and vision statement
Community benefit
Staff and management team
Board of directors
Partnerships
List any items related to what you do as an organization, including reports that demonstrate results. For example, you can include:
Core problem we solve
Demographics we reach
Past results
Business model
Marketing plan
This is a space for your marketing strategy (the methods you'll use to reach your target audience) and the analyses you used to build that strategy. Here, you can attach:
Target market research
Target audience and social media messaging
Market analysis (including a competitive analysis)
Your positioning (on hot button issues related to your mission)
Outreach plan
Financial plan
Nonprofits need to be very clear with how they spend money. Being transparent with your financial statements restores confidence for potential donors, so you can hit your fundraising goals and boost financial projections. Here’s what to include in this section:
Income statements
Cash flow statements
Grant management plan
Fundraising plan and projections
Integrated features
List View . List View is a grid-style view that makes it easy to see all of your project’s information at a glance. Like a to-do list or a spreadsheet, List View displays all of your tasks at once so you can not only see task titles and due dates, but also view any relevant custom fields like Priority, Status, or more. Unlock effortless collaboration by giving your entire team visibility into who’s doing what by when.
Goals . Goals in Asana directly connect to the work you’re doing to hit them, making it easy for team members to see what they’re working towards. More often than not, our goals live separate from the work that goes into achieving them. By connecting your team and company goals to the work that supports them, team members have real-time insight and clarity into how their work directly contributes to your team—and company—success. As a result, team members can make better decisions. If necessary, they can identify the projects that support the company’s strategy and prioritize work that delivers measurable results.
Milestones . Milestones represent important project checkpoints. By setting milestones throughout your project, you can let your team members and project stakeholders know how you’re pacing towards your goal. Use milestones as a chance to celebrate the little wins on the path towards the big project goal.
Custom fields . Custom fields are the best way to tag, sort, and filter work. Create unique custom fields for any information you need to track—from priority and status to email or phone number. Use custom fields to sort and schedule your to-dos so you know what to work on first. Plus, share custom fields across tasks and projects to ensure consistency across your organization.
Recommended apps
Google Workplace . Attach files directly to tasks in Asana with the Google Workplace file chooser, which is built into the Asana task pane. Easily attach any My Drive file with just a few clicks.
OneDrive . Attach files directly to tasks in Asana with the Microsoft OneDrive file chooser, which is built into the Asana task pane. Easily attach files from Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and more.
Dropbox . Attach files directly to tasks in Asana with the Dropbox file chooser, which is built into the Asana task pane.
Slack . Turn ideas, work requests, and action items from Slack into trackable tasks and comments in Asana. Go from quick questions and action items to tasks with assignees and due dates. Easily capture work so requests and to-dos don’t get lost in Slack.
How do you write a nonprofit business plan template? .css-i4fobf{-webkit-transition:-webkit-transform 200ms ease-in-out;transition:transform 200ms ease-in-out;-webkit-transform:rotateZ(0);-moz-transform:rotateZ(0);-ms-transform:rotateZ(0);transform:rotateZ(0);}
First, create your template including sections for your executive summary, mission statement and purpose, marketing plans, and finances. Then when you’re ready to write your nonprofit business plan, fill in the blanks and customize it to fit your organization.
Do nonprofits have business plans?
Yes, nonprofits often have business plans. Nonprofit business plans provide a structured overview of your nonprofit strategies, and can be used to share your accomplishments and goals with stakeholders . You only have to create your nonprofit business plan template once—then you can reuse it every time you need to create a new nonprofit business plan.
How do nonprofit business plans help corporations get involved in nonprofit organizations?
Nonprofit business plans show corporations your organization’s impact, including how you’re spending any potential money they donate to you. Often, corporations want to see the numbers before they decide to invest in a nonprofit, and a nonprofit business plan can help you share that information.
What should be in a nonprofit business plan template?
Include all higher-level summaries of your nonprofit, plus actionable plans like your executive summary, mission and purpose, marketing strategy, and financial plans.
Related templates
Action plan template
Taking action has never been easier. Learn how to create a reusable action plan template in Asana to take the guesswork out of strategic planning.

Marketing strategy
A marketing strategy template is a useful tool that helps your marketing team achieve their goals. Learn how to create your marketing strategy with Asana.

PEST analysis
A PEST analysis template helps compile info on the external environment affecting your business. Learn how to prevent risk with a PEST analysis template.
Objectives and key results (OKR) template
Learn how to create an OKR template in Asana so you can standardize the goal-setting process for everyone.
Cost benefit analysis template
Digital cost benefit analysis templates are a useful framework to see if a new project or idea is viable. Learn how to create your own in a few simple steps, with Asana.
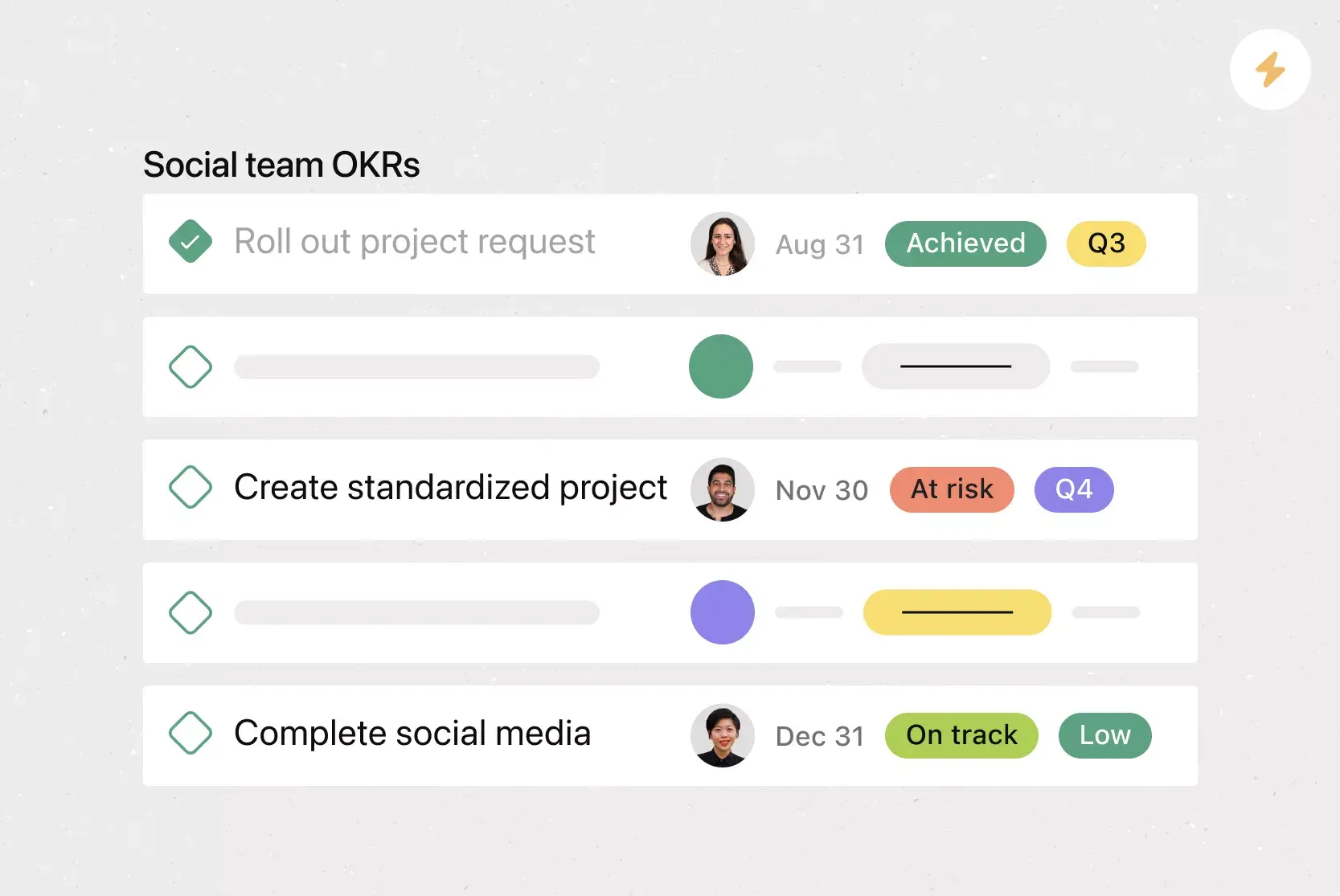
Contingency plan
Using a contingency plan template will help you create well-developed strategies to help you protect your business from potential risk. Learn how Asana can help.

Requirements traceability matrix
A requirements traceability matrix template is a tool to help organize project requirements in a concise manner. Learn how to create one for your team.
Creating a digital punch list template can help streamline the final bits of a project for your team. Here’s how to create one.
Go-to-market strategy template
Simplify your GTM strategy with a go-to-market strategy template that aligns teams and keeps work on track. Learn how in Asana.
Project closure template
Endings are important. Create a project closure template to help your team tie up loose ends and finish their projects with confidence.
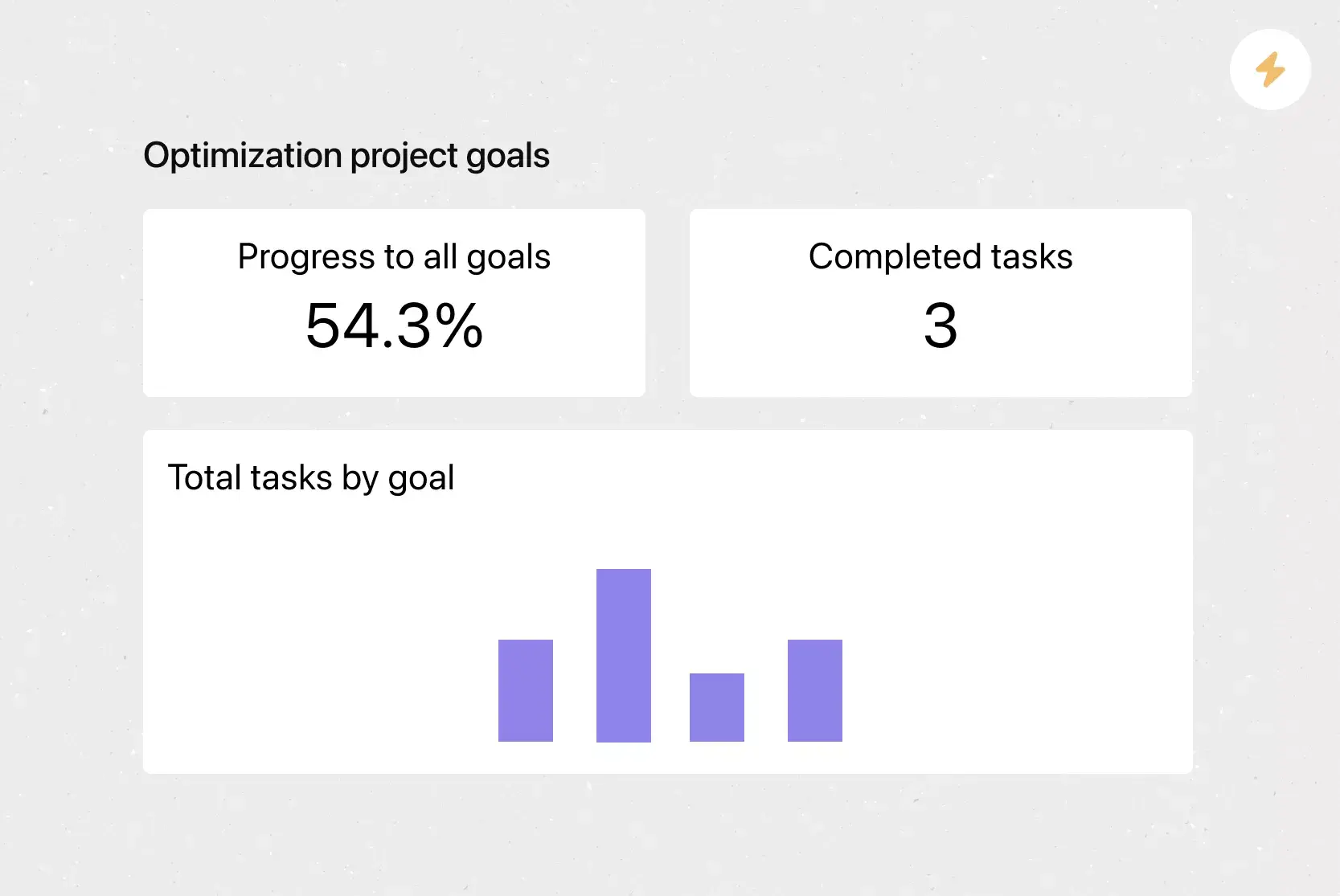
Project reporting
Stay on top of your project’s performance. Keep everyone on the same page about what’s been completed and where your project is headed.
![profit business plan [Templates] Product Roadmap (Card image)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/2728edf4-eb35-4dd5-8d03-25ba8cbe5864/TG23-web-thumbnail-028-scrumban-feature-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Product roadmap
What if you could create, share, and update your product roadmap in one place? Everyone could see you’re tackling the right priorities. Start planning your product roadmap with this template.

Program roadmap
Create a program roadmap template and know the exact structure of each program, how they operate, and their future plans—company-wide.

Operational plan template
Learn how Asana’s operations team uses standardized processes to streamline strategic planning—no matter how many stakeholders are involved.
Strategic planning template
When you’re launching a new product, team, or even a new business, strategic planning templates keep you laser-focused and on task.

Annual planning template
Set clear goals and streamline your planning process—so every level of your company is aligned on what’s important.
Competitive analysis template
The more you know about your competitors, the better your strategy will be. Competitive analysis templates use a data-driven approach to see exactly how your business, products, and features compare to your competition.


Crisis management plan
Does your team know what to do during a crisis? Using a crisis management plan template can help keep all your employees on the same page.
Business plan
A business plan is the first step to start your business and secure financing. Use our business plan template so you don’t have to start from scratch.
SIPOC template
Use your SIPOC template to ensure that the processes outlined in your SIPOC diagrams are consistent and up to your standards.
Create templates with Asana
Learn how to create a customizable template in Asana. Get started today.
Experience Convene Learn how Convene can give your boards a superior meeting experience. Enquire for a free demo with no cost or obligation.
Nonprofit Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
- by Jess Convocar on February 21, 2024
- last update on February 22, 2024
- Reading Time: 7 minutes

Like any other business, nonprofit organizations need careful, structured planning to ensure sustainable growth. This is possible by creating a business plan that not only serves as a roadmap but also helps in attracting donors and volunteers needed to bring the organization’s vision to fruition.
Crafting the perfect business plan involves many things, but the most important part is understanding what it should look like and how it can help the organization forward its mission. This guide simplifies the process, breaks down its unique components, and provides step-by-step instructions on how to write a nonprofit business plan.
What is a business plan for nonprofits?
A business plan for nonprofits is a strategic document that outlines a nonprofit organization’s goals and operational approach. While similar to for-profit business plans, the focus here is on achieving social impact rather than financial profit.
Projects implemented by nonprofit organizations typically revolve around fostering social welfare, advocacy, education, or humanitarian aid. For instance, a nonprofit working to address homelessness might outline projects such as providing shelter and meals, offering job training programs, and collaborating with local agencies to advocate for affordable housing policies.
A typical business plan for nonprofits includes:
- The nonprofit’s mission, which sets the foundation for the entire plan;
- Specific objectives,
- Fundraising strategies,
- Resource allocation,
- And how it plans to measure success in terms of societal or community benefit.
But one thing to note is that there is no one-size-fits-all plan. Every little detail incorporated into the plan must be tailored to the organization’s needs, where it currently stands, and how it can contribute to its primary purpose – guiding the nonprofit to success.
Why Your Nonprofit Needs a Business Plan
A good plan does not only help attract external support but also benefits the organization internally. Listed below are the key reasons why your nonprofit needs a business plan:
Clarity of Mission, Vision, and Strategic Direction
Running a nonprofit organization isn’t the easiest task, and there may be times when you question whether you’re truly making an impact. Having a business plan gives you a perspective of the progress you’ve made and provides a distinct path moving forward.
This clear-cut framework ensures that the mission, vision, and strategic direction remain focused, helping the nonprofit make informed decisions and navigate challenges with purpose.
Proper Resource Planning and Financial Management
Poor financial management can lead to many problems, especially in nonprofits. With a business plan, this can easily be taken care of.
Since nonprofit organizations rely on various external funds, there should be an emphasis on resource planning and management. This involves forecasting the organization’s needs, such as financial, human, and technological resources, and strategically allocating them to support the mission and vision. Doing so also demonstrates fiscal responsibility to donors and stakeholders.
Strategic Fundraising and Sustainability
One of the most common and effective ways nonprofits gain support is through fundraising activities. A business plan helps you develop a targeted fundraising strategy that aligns with the organization’s goals. Clearly outlining the fundraising objectives, target audiences, and specific tactics provides a roadmap for effective resource mobilization.
Additionally, a structured plan attracts and retains donors by instilling confidence in them about the tangible impact their contributions can make.
Risk Management
A business plan is vital for developing strategies to handle risks and potential challenges. This proactive approach helps minimize the impact of unforeseen events, like economic recessions or natural disasters, on the nonprofit’s operations.
A robust risk management strategy not only saves time and money but also improves decision-making , avoids surprises, and, most importantly, prevents harm to the people your nonprofit serves.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Because the business plan already lays out how the organization works, it’s easier to understand and adhere to nonprofit laws like tax exemption and revenue regulations.
Dealing with these things from the start helps prevent potential problems, maintains transparency, and builds trust with stakeholders. This allows you to focus on carrying out the mission without legal conflicts.
How to Create a Business Plan Strategy
When gearing up to create a business plan for your nonprofit organization, it’s important to begin by thoroughly understanding the unique aspects of your mission. This solid foundation will guide you through the next steps of crafting a well-thought-out plan, which includes:
1. Create a strategy
Before anything else, you must identify your why .
Ask yourself what you want to happen. What does the organization stand for? Who does it serve? What do you hope for it to become?
If your long-term goal is to create a lasting impact and expand the community you serve, establish a strategy that mirrors your mission. Begin by assessing your organization’s current position, strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. Based on your assessment, leverage the strengths and address weaknesses that may hinder progress.
Next, clearly define who your target audience is. Understand their specific needs and preferences to tailor your approach effectively.
Once the key factors have been determined and written down, it will serve as the starting point for the strategy.
2. Plan programs
The planning step is where you delve into the how. What are your plans to sustain and amplify the impact you aim to create?
Since you are not selling products or providing services to generate revenue, you’ll need to rely on fundraising events to support your cause. To do this effectively, create detailed program plans covering goals, activities, timelines, and expected outcomes. As always, ensure these plans align with your organization’s mission.
After establishing the programs, set up a monitoring system that tracks their effectiveness and evaluates them regularly. This helps you make informed changes as the nonprofit or the community’s needs evolve.
3. Ensure financial sustainability
Nonprofits receive financial support from various channels, such as individual donations, grants, sponsorships, and fundraising events. To ensure economic sustainability, building relationships with potential donors, individuals, institutions, and various funding sources is important to avoid relying too much on a single avenue.
In this sense, a well-thought-out budget is crucial for financial stability. Make sure to allocate resources carefully, considering program costs, administration expenses, and other needs. A clear and transparent budget not only aids in financial planning but also boosts trust with supporters.
4. Prioritize legal considerations
Even though dealing with changing rules might seem to lead to more paperwork than focusing on your mission, remember that compliance is as important as pursuing your organization’s goals. Some vital legal considerations include:
- Legal structure and registration
- Tax exemption (if applicable)
- Fundraising compliance
- Financial accountability
- Intellectual property (such as logos, trademarks, and copyrights)
- Data protection and privacy
Maintaining a good standing is crucial for obtaining licenses, securing grants and funding, protecting your organization’s reputation, and keeping the right to solicit support.
If you don’t have an in-house legal counsel, it’s a good idea to seek advice from experts who know nonprofit laws in your area when planning your business.
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

Now that you’ve covered all the essential details, the next step is to create the business plan outline. There’s no strict format to follow, as it all depends on your organization’s specifics. However, make sure not to exclude these essential components when creating a nonprofit business plan:
1. Executive Summary
This part is a quick overview of the whole document. Since it’s the first thing people see in the business plan, it’s crucial to make it clear and interesting enough to grab their attention and encourage them to read the entire plan. Include the organization’s fundamentals – its history, objectives, and financing plans.
2. Organizational Overview
Provide a gist of who you are and who you serve. Here, express the organization’s mission, vision, and specific short-term and long-term goals.
3. Products, Programs, or Services Rendered
In this section, you must provide a detailed description of all the products and services mentioned in the executive summary. Highlight any unique aspects, such as innovative features and distinct advantages, that set you apart. State how instrumental these are to the success of your initiatives and how each one addresses the industry need.
4. Operational Plan
This is where you detail how your nonprofit will function on a day-to-day basis. Outline each team member’s daily, weekly, and monthly tasks, specifying responsibilities, timelines, and collaboration points to ensure a cohesive and efficient operation.
Additionally, spotlight any key processes, workflows, or systems necessary to achieve your mission.
5. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan should reflect the mission of the organization. Under this section, outline the strategies and channels to get your nonprofit out there. Include details about your target audience, methods for reaching them, and any promotional activities. This section may also cover partnerships, collaborations, and outreach efforts.
6. Financial Plan
The financial plan provides a comprehensive overview of your nonprofit’s financial health and projections. Include a budget, funding sources, and a breakdown of how funds will be allocated to support your operations and programs. This part is vital for demonstrating sustainability and helping make better-informed decisions.
7. Appendix
In the appendix, incorporate all the additional documents and information supporting the business plan’s main body. This may include resumes of key personnel, detailed financial statements, legal documents, or any other relevant materials.
Here’s a quick step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan:
- Start by outlining the executive summary providing a concise overview of the plan.
- Develop the organizational overview, which includes the mission and vision of the nonprofit.
- Conduct a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) analysis to identify and address internal and external factors.
- Clearly articulate short-term and long-term goals and objectives.
- Describe the programs and activities that will help achieve these goals.
- Develop a marketing and outreach strategy to engage the community and attract support.
- Create a detailed financial plan, including budgets, revenue streams, and financial projections.
- Outline the governance and management structure, including roles and responsibilities.
- Detail monitoring and evaluation processes to assess program effectiveness.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Once you have a clear grasp of your organizational goals and strategies, here’s a sample nonprofit business plan template to get you started:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Nonprofit Business Plan
Q: how often should a non-profit business plan be updated.
Although nonprofit plans usually set up a roadmap for at least three to five years, they should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure they remain relevant and aligned with the organization’s purpose and changing external factors. For younger companies, an annual update with six monthly reviews may be sufficient, while more established nonprofits might opt for an annual review with quarterly check-ins.
Q: What role does evaluation play in a non-profit business plan?
Smaller nonprofits often conduct formal evaluations because their funders require it, but the benefits extend in both directions. Internally, evaluations help the organization assess its performance, impact, and effectiveness. In doing so, the nonprofit meets funder expectations and gains valuable insights for improvement, ensuring transparency and better alignment with its mission.
Q: How can a non-profit maintain adaptability in its strategies?
To stay adaptable, a nonprofit can follow three basic practices. First, keep the business plan up-to-date to align with the changing goals and environment. Second, stay on top of current industry trends to anticipate shifts in the landscape and prepare ahead of time. Lastly, revamp tools and approaches to ensure strategies remain innovative and effective.
Plan for Nonprofit Success with Convene

A well-crafted nonprofit business plan is crucial for success. To achieve this, cooperation is necessary within the internal teams and partners. However, communication can be a common roadblock, especially in a remote workplace.
This is where Convene comes into play.
Convene is a reliable board portal for nonprofits that facilitates effective planning through its interactive and secure features. Easily collaborate with everyone in the organization by leveraging Convene’s live meeting capabilities, such as annotations and digital sign-offs. Also, keep track of the updates and reports with its secure document management features.
Check out this page to learn more about Convene and how it can benefit your nonprofit organizations.
Related Articles

Board Portals for Nonprofits: A New Necessity?

A Definitive Guide to Effective Board Governance

Embracing Virtual Meetings for Nonprofits and Religious Institutions
Take your organization’s meetings to the next level.
Learn how Convene can give your boards a superior meeting experience. Enquire for a free demo with no cost or obligation.
Free Nonprofit Business Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | September 18, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up the most useful list of nonprofit business plan templates, all free to download in Word, PDF, and Excel formats.
Included on this page, you’ll find a one-page nonprofit business plan template , a fill-in-the-blank nonprofit business plan template , a startup nonprofit business planning timeline template , and more. Plus, we provide helpful tips for creating your nonprofit business plan .
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Use this customizable nonprofit business plan template to organize your nonprofit organization’s mission and goals and convey them to stakeholders. This template includes space for information about your nonprofit’s background, objectives, management team, program offerings, market analysis, promotional activities, funding sources, fundraising methods, and much more.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template
One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Template
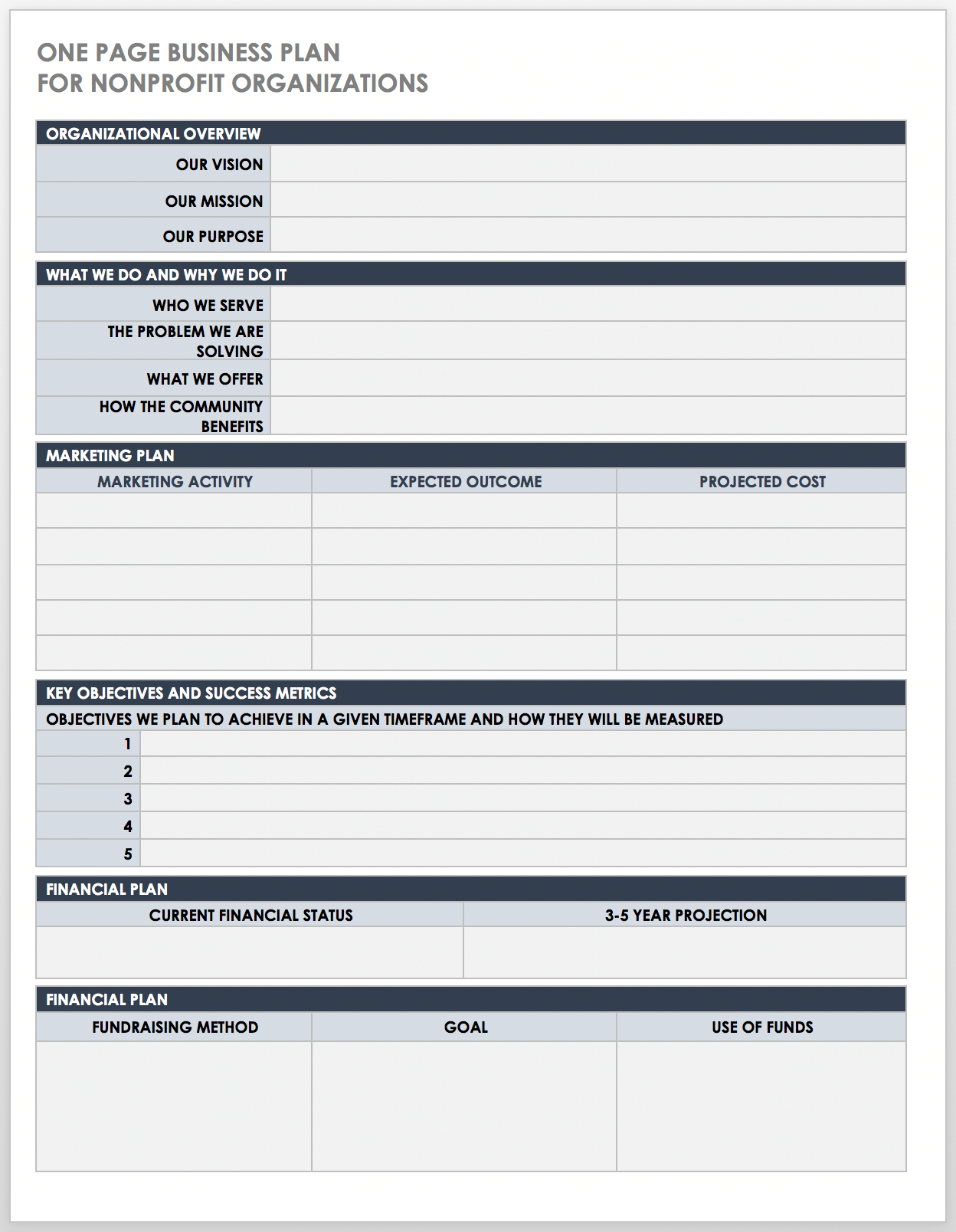
This one-page nonprofit business plan template has a simple and scannable design to outline the key details of your organization’s strategy. This template includes space to detail your mission, vision, and purpose statements, as well as the problems you aim to solve in your community, the people who benefit from your program offerings, your key marketing activities, your financial goals, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Template
Excel | Word | PDF
For additional resources, including an example of a one-page business plan , visit “ One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide .”
Fill-In-the-Blank Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Use this fill-in-the-blank template as the basis for building a thorough business plan for a nonprofit organization. This template includes space to describe your organization’s background, purpose, and main objectives, as well as key personnel, program and service offerings, market analysis, promotional activities, fundraising methods, and more.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Nonprofit Business Plan Template
For additional resources that cater to a wide variety of organizations, visit “ Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates .”
Startup Nonprofit Business Planning Template with Timeline
Use this business planning template to organize and schedule key activities for your business. Fill in the cells according to the due dates, and color-code the cells by phase, owner, or category to provide a visual timeline of progress.
Download Startup Nonprofit Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program
Use this template as a foundation for building a powerful and attractive nonprofit business plan for youth programs and services. This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization’s background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program
Word | PDF | Google Doc
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan Outline Template
You can customize this sample nonprofit business plan outline to fit the specific needs of your organization. To ensure that you don’t miss any essential details, use this outline to help you prepare and organize the elements of your plan before filling in each section.
Download Sample Nonprofit Business Plan Outline Template
Nonprofit Startup Business Planning Checklist Template
Use this customizable business planning checklist as the basis for outlining the necessary steps to get your nonprofit organization up and running. You can customize this checklist to fit your individual needs. It includes essential steps, such as conducting a SWOT analysis , fulfilling the research requirements specific to your state, conducting a risk assessment , defining roles and responsibilities, creating a portal for board members, and other tasks to keep your plan on track.
Download Nonprofit Startup Business Planning Checklist Template
Tips to Create Your Nonprofit Business Plan
Your nonprofit business plan should provide your donors, volunteers, and other key stakeholders with a clear picture of your overarching mission and objectives. Below, we share our top tips for ensuring that your plan is attractive and thorough.
- Develop a Strategy First: You must aim before you fire if you want to be effective. In other words, develop a strategic plan for your nonprofit in order to provide your team with direction and a roadmap before you build your business plan.
- Save Time with a Template: No need to start from scratch when you can use a customizable nonprofit business plan template to get started. (Download one of the options above.)
- Start with What You Have: With the exception of completing the executive summary, which you must do last, you aren’t obligated to fill in each section of the plan in order. Use the information you have on hand to begin filling in the various parts of your business plan, then conduct additional research to fill in the gaps.
- Ensure Your Information Is Credible: Back up all the details in your plan with reputable sources that stakeholders can easily reference.
- Be Realistic: Use realistic assumptions and numbers in your financial statements and forecasts. Avoid the use of overly lofty or low-lying projections, so stakeholders feel more confident about your plan.
- Strive for Scannability: Keep each section clear and concise. Use bullet points where appropriate, and avoid large walls of text.
- Use Visuals: Add tables, charts, and other graphics to draw the eye and support key points in the plan.
- Be Consistent: Keep the voice and formatting (e.g., font style and size) consistent throughout the plan to maintain a sense of continuity.
- Stay True to Your Brand: Make sure that the tone, colors, and overall style of the business plan are a true reflection of your organization’s brand.
- Proofread Before Distribution: Prior to distributing the plan to stakeholders, have a colleague proofread the rough version to check for errors and ensure that the plan is polished.
- Don’t Set It and Forget It: You should treat your nonprofit business plan as a living document that you need to review and update on a regular basis — as objectives change and your organization grows.
- Use an Effective Collaboration Tool: Use an online tool to accomplish the following: collaborate with key personnel on all components of the business plan; enable version control for all documents; and keep resources in one accessible place.
Improve Your Nonprofit Business Planning Efforts with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Business Plan Outline
- Nonprofit Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
You’ve come to the right place to write a nonprofit business plan.
We have helped over 10,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create nonprofit business plans and many have used them to start or grow their nonprofit organizations.
Below are links to the essential sections of our sample nonprofit business plan template to help you with the business planning process for your organization:
- Executive Summary – The Executive Summary of your nonprofit business plan explains your overall strategic plan to achieve success as a nonprofit. It will include your organization’s mission statement, goals, and objectives. This section will also include information on your target market, competition, and marketing strategy.
- Company Overview – Also called the Organization Overview, you will include the mission statement and history of your nonprofit including any significant milestones achieved to date.
- Industry Analysis – Sometimes referred to as the Market Analysis, this section will provide an overview of the nonprofit industry, trends, and the competitive landscape.
- Customer Analysis – The Customer Analysis section details the demographics and psychographics of your target audience and how you plan to reach them.
- Competitive Analysis – In your Competitive Analysis, you will identify and describe the competition, both direct and indirect, including other nonprofits with the same mission. You will also include your strategic plan for competing in the market.
- Marketing Plan – This section of your nonprofit business plan will detail your products, programs and services, your overall marketing strategies and tactics, and how you will measure success. It should include information on your target market, positioning, branding, communications, and lead generation.
- Operations Plan – In the Operations Plan, you will outline your day-to-day operations as well as your long-term business goals and how you will measure success.
- Management Team – In the Management Team section of your business plan, you should include the organizational structure of your nonprofit business as well as bios of your executive team and board members.
- Financial Plan – The Financial Plan is one of the most important sections of your nonprofit business plan. You will establish your financial goals and include financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statement to show how your nonprofit will be sustainable.
Next Section: Executive Summary >
Nonprofit Business Plan FAQs
What is a non profit business plan.
A nonprofit business plan is a road map to start and/or grow your nonprofit organization. Among other things, it outlines your charitable concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections. Your non profit business plan should be a living document that is updated frequently as your nonprofit grows.
You can easily complete your nonprofit business plan using our Nonprofit Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Nonprofit Organizations?
There are many types of nonprofits, but each has a charitable mission to help an underserved segment of society. For example, there are nonprofits that serve the underserved youth, abused or abandoned animals, homeless, veterans and impoverished. There are also many nonprofits that support social awareness and global issues such as the environment, education and equality.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenue and Expenses for a Nonprofit Business?
The primary source of revenue for nonprofit organizations are monetary donations from sponsors, government grants and funding, and tax incentives through 501c3 designations.
The key expenses for a nonprofit business are staffing, supplies, rent, utilities, program costs and working capital to ensure the sustainability of the non profit. Proper strategic planning will help your nonprofit thrive financially.
This differs from a for profit business plan because you do not have to show profitability. Nonprofits focus away from profit and instead center on accountability.
How Do You Secure Funding For Your Nonprofit Organization?
Most nonprofit organizations are likely to receive funding from banks, grants, and donors. As the majority of the funding will come from government grants and funds, grant proposals will need to be compiled and proposed to the necessary funding organization.
A solid business plan is key to showing investors you are well-prepared to start your own business. A nonprofit business plan template is key to proper business planning and getting started quickly.
Where can I download a Nonprofit Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free nonprofit business plan template PDF here . This is a sample nonprofit business plan outline that you can use in PDF format.
How to Build a Profit Plan for Your Business
By Eric Dickmann
February 6, 2023
In order to achieve business goals, a profit plan is crucial. It serves as a financial roadmap for the company. However, with competing demands, it can be challenging to begin. Market demand and competitive factors, along with seasonal cash-flow changes, can be unpredictable.
To build a profit plan, start by understanding your business goals. Get all key stakeholders involved to align the plan with those goals. Decide on key metrics to track and what tools to use for tracking. Ensure you're relying on relevant and legitimate data sources. Everyone should agree on the validity of the numbers. Analytical tools can help track and measure progress against goals.
What is a Profit Plan?
A profit plan is a detailed financial plan that outlines a company's strategies and goals for generating revenue and managing expenses in order to achieve a specific level of profitability. The profit plan typically includes a detailed budget that outlines projected revenues and expenses, as well as a forecast of the company's cash flow, balance sheet, and income statement. The profit plan is an essential tool for any business, as it helps managers make informed decisions about how to allocate resources, invest in growth opportunities, and manage risk. It also serves as a roadmap for the company's financial future, providing a framework for monitoring performance and making adjustments as necessary. A typical profit plan will include the following components:
- Revenue Projections: This includes estimates of sales, pricing, and volume for the coming year.
- Cost Projections: This includes estimates of all direct and indirect costs associated with producing and delivering goods and services, such as labor, materials, overhead, and marketing expenses.
- Cash Flow Analysis: This includes projections of cash inflows and outflows, as well as a plan for managing cash reserves.
- Balance Sheet Projections: This includes estimates of the company's assets, liabilities, and equity over the coming year.
- Income Statement Projections: This includes estimates of the company's revenue, expenses, and net income for the coming year.
By creating a comprehensive profit plan, a business can set realistic goals and targets, monitor progress toward those goals, and make informed decisions about how to allocate resources and manage risk. It can also help to identify potential areas for improvement and optimization, which can ultimately help the business to achieve greater profitability and success over time.
Benefits of a Profit Plan
A formal profit plan prepares a company for possible challenges and ensures maximum profit. CPAsNet noted that profit plans are beneficial to:
- Help owners achieve their financial goals
- Improve and measure performance
- Establish a framework for making decisions
- Educate and motivate key employees
Building a Profit Plan for Your Business
It is important to consider profit when making plans for your business because profit is the ultimate goal of any business. Without profit, a business cannot sustain itself, pay its employees, or invest in growth and development. Profit is also a key indicator of a business's success and can attract investors and potential partners. By considering profit in their plans, business owners can make informed decisions about pricing, marketing, and investment strategies that will help them maximize their revenue and achieve their goals. Ultimately, profit is the lifeblood of any business, and considering it in every decision is crucial for long-term success.
Profit doesn’t happen by itself. Look over your processes and envision how you want it all to unfold. Here are some suggested steps to consider when making your plan:
- Set a Profit Goal- Set clear targets and make a plan for how you should get there. A target profit gives your business a set of goals to work throughout the year. Consider the number of units sold with its fixed and variable cost. When it comes to expected profit, slightly underestimate rather than overestimate.
- Create a Budget- Make a detailed budget plan. Have a look at financing options for your business. Set a potential plan B in case “things” happen. Estimate just how much you perceive your business is going to spend in a certain amount of time.
- List Expenses- Be sure to write down every single expense the business makes during its operations. It lets you know where you are spending too much. Use costing sheets to track all cost associated with each product. In this way, you can calculate the gross profit.
- Calculate the Profit Margin- A margin is what keeps you in business. It is equal to the gross profit divided by the revenue and multiplied by 100. It will vary per industry, but according to The Corporate Finance Institute , a 10% net profit margin is considered average.
- Keep the Costs Down- Entrepreneurs don’t need to spend a lot of money. Find smart ways to start with less money. Set a margin that covers your costs including overhead. Make a realistic budget to help you achieve your goals.
The best way to start profit planning is to understand your business goals. Then make a detailed budget plan based on those goals. List down the income and expenses and keep your costs down as much as possible. The higher the profit margin, the more it can sustain your business and put you on the road to success.
It's time to grow your company!
Learn how a fractional CMO can help your business grow!
Contact us today to learn more about our Virtual CMO advisory service.
Eric Dickmann
About the author
Eric Dickmann is the Founder / CMO of The Five Echelon Group, host of the weekly podcast "The Virtual CMO" and YouTube series "Work-Life" and a fractional CMO for a variety of small and midsize companies. An executive leader with over 30 years of experience in marketing, product development, and digital transformation, he has worked with large, global companies and small startups to develop and execute marketing strategies to bring innovative products to the market.
You might also like
Is Your Business Struggling to Make a Profit?
What is profit planning, ways to increase profit for your business.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.

3 Sample Nonprofit Business Plans For Inspiration
Download our Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template here
Below are sample plans to help guide you in writing a nonprofit business plan.
- Example #1 – Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) – a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL
- Example #2 – Church of the Sacred Heart – a Nonprofit Church based in St. Louis, MO
- Example #3 – Finally Home – a Nonprofit Homeless Shelter in Los Angeles, CA
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan #1 – Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) – a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL
Executive summary.
Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) is a 501(c)3 nonprofit youth organization that seeks to provide opportunities for students who might otherwise not have access to the arts and humanities. We believe all students should have the opportunity to discover and develop their interests and talents, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location. We offer completely free after-school programming in music production, digital photography, creative writing, and leadership development to 12-18-year-olds at risk of dropping out of high school.
Our organization has been active for over five years and has run highly successful programs at two schools in the city of Chicago. We have been awarded an active grant from a local foundation for this coming year, but we will need to cover all costs on our own after that point. Nonprofit administrators have seen a lot of turnovers, leaving the organization without a sustainable plan for reaching its goals.
Organization Overview
The Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) is a 501(c)3 nonprofit youth organization with a mission to provide opportunities for development and self-expression to students who might otherwise not have access. Audiences include at-risk, low-income students from elementary through high school in the Chicago area.
Our programs are built around creative learning with two goals: firstly, creating a space for learning and growth; secondly, encouraging students to share their work with the world.
KAOFP runs three different programs in partnership with closely related nonprofit organizations, providing after-school programming for elementary, middle, and high school-aged children. Programs take place twice a week at different schools around Chicago. While each program is unique in its goals and activities, all programs focus on creative development in the arts and humanities.
Products, Programs, and Services
The three programs offered by KAOFP are Leadership Development (LD), Creative Writing (CW), and Music Production (MP). Students learn in small groups led by skilled instructors. All activities are designed to encourage student engagement, creativity, expression, and community building. Instructors encourage students to share their work with the world through presentations on- and off-site.
Leadership Development (LD)
The Leadership Development program is designed to provide leadership opportunities for high school students who might not otherwise have access to these experiences. Students learn about facilitation, collaboration, communication, and organizational skills as they plan and run projects of their own design. The program’s goal is to provide a structured environment that encourages students to become more confident and comfortable being leaders in their schools, communities, and future careers.
Creative Writing (CW)
Students learn how to use writing creatively as a tool for expression, discovery, and communication. In small groups led by skilled instructors, students write poetry, short stories, and essays of their own design. They also learn about the publishing industry, read each others’ work, and share their writing with the community.
Music Production (MP)
Students learn how to use digital media as a tool for expression, discovery, and communication. In weekly sessions led by skilled instructors, students explore music production through computer software and recording equipment. Students produce their own music and write about their experiences in weekly journals. Industry professionals in the community often volunteer to lead special workshops and seminars.
Industry Analysis
The youth arts and humanities field is extremely competitive. There are many different types of nonprofit organizations doing similar work, but few credible providers with long-term commitments to their communities. KAOFP’s greatest strengths and competitive advantages are our stable and qualified staff, a strong foundation of funding and community support, and a diverse set of programs.
Our biggest competitors include national non-profits with large budgets for advertising and marketing as well as commercial programs that offer music lessons and creative writing courses which may be more cost-effective than our programs. We feel that by focusing on specific areas of creative expression, KAOFP can better serve its communities and differentiate itself from other nonprofit organizations effectively.
Customer Analysis
KAOFP serves elementary, middle, and high school-aged students with programs that include both after-school and summer programming.
Our focus is on low-income neighborhoods with a high population of at-risk youth. In these areas, KAOFP fills a void in the education system by providing opportunities for creative expression and leadership development to students who would not otherwise have access to these resources.
The demographics of our current students are as follows:
- 91% African-American/Black
- 6% Hispanic/Latino
- 5% Multiracial
- 3.9% Low Income
- 4.9% Not Identified
Our main target is low-income African American and Latino youth in Chicago Public Schools. We would like to expand our outreach to include other communities in need of creative enrichment opportunities.
Marketing Plan
KAOFP’s marketing program is designed to support student, parent, and staff recruitment by promoting the organization’s goals and programs. Our main target audience consists of parents seeking after-school enrichment opportunities for their children that emphasize creativity and the arts.
To reach this audience, we advertise in public schools as well as on social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter. We intend to begin marketing online through a company-sponsored blog, which will feature regular updates about KAOFP events and activities. We also intend to use word of mouth as a form of marketing.
Strategic partnerships with local schools and community centers will provide us with additional exposure as well as additional resources to secure funding.
Operations Plan
KAOFP’s day-to-day operation is structured around its programs on Tuesdays from 4 pm to 8 pm.
Administrative offices are located in the same space as each program, allowing instructors to closely monitor their students and provide support as needed. The administrative offices serve the essential function of fundraising, communications, record-keeping, and volunteer coordination. KAOFP’s Board of Directors meets bi-monthly to provide further leadership, guidance, and oversight to our board members and volunteers.
Customer service is conducted by phone and email during our regular business hours of Monday – Friday 9 am to 12 pm. We are not open on weekends or holidays.
Management Team
KAOFP’s organizational structure includes a Board of Directors, an Executive Director, and Program Directors. The Board of Directors provides guidance and oversight to the organization, while the Executive Director manages day-to-day operations. The Program Directors oversee each of KAOFP’s programs.
KAOFP has a small but dedicated staff that is committed to our students and our mission. Our team has a wide range of experience in the arts, education, and nonprofit sector.
Executive Director
The Executive Director is responsible for the overall management of KAOFP. This includes supervising staff, developing and implementing programs, overseeing finances, and representing the organization to the public.
Our Executive Director, Susie Brown, has been with KAOFP since its inception in 2010. She has a B.A. in Fine Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and an M.F.A. in Creative Writing from Columbia College Chicago. Susie is responsible for the overall management of KAOFP, including supervising staff, developing and implementing programs, overseeing finances, and representing the organization to the public.
Program Directors
Each of KAOFP’s programs is overseen by a Program Director. The Program Directors are responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Art Program Director
The Art Program Director, Rachel Smith, has a B.A. in Fine Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. She is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Music Program Director
The Music Program Director, John Jones, has a B.A. in Music Education from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Theatre Program Director
The Theatre Program Director, Jane Doe, has a B.A. in Theatre Arts from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. She is responsible for developing and implementing the program curricula, recruiting and training program instructors, and evaluating student progress.
Board of Directors
KAOFP’s Board of Directors provides guidance and oversight to the organization. The Board consists of community leaders, educators, artists, and parents. Board members serve three-year terms and can be renewed for one additional term.
Financial Plan
KAOFP’s annual operating budget is approximately $60,000 per year, with an additional one-time cost of about $10,000 for the purchase of equipment and materials. The agency makes very efficient use of its resources by maintaining low overhead costs. Our biggest expense is instructor salaries, which are approximately 75% of total expenses.
Pro Forma Income Statement
Pro forma balance sheet, pro forma cash flow statement, nonprofit business plan example #2 – church of the sacred heart – a nonprofit church based in st. louis, mo.
The Church of Sacred Heart is a nonprofit organization located in St. Louis, Missouri that provides educational opportunities for low-income families. We provide the best quality of education for young children with tuition rates significantly lower than public schools. It has been voted Best Catholic Elementary School by the St Louis Post Dispatch for four years running, and it has maintained consistently high ratings of 4.5 out of 5 stars on Google Reviews since its opening in 1914.
The Church of Sacred Heart strives to build strong relationships with our community by making an impact locally but not forgetting that we operate on global principles. As such, our school commits 10% of its profits to charitable organizations throughout the world every year, while also conducting fundraisers throughout the year to keep tuition rates affordable.
We are currently transitioning from a safe, high-quality learning environment to an even more attractive facility with state-of-the-art technology and modern materials that will appeal to young students and their families. New facilities, such as additional classrooms and teachers’ lounges would allow us not only to accommodate new students but also attract current families by having more places within the school where they can spend time between classes.
By taking full advantage of available opportunities to invest in our teachers, students, and facilities, we will be able to achieve steady revenue growth at 4% per year until 20XX.
The Church of Sacred Heart provides a safe learning environment with an emphasis on strong academics and a nurturing environment that meets the needs of its young students and their families. Investing in new facilities will allow us to provide even better care for our children as we continue to grow as a school.
Mission Statement: “We will strive diligently to create a safe, respectful environment where students are encouraged and inspired to learn through faith.”
Vision Statement: “Sacred Heart believes education gives every child the opportunity to achieve their full potential.”
The Church of the Sacred Heart was built in 1914 and is located in the Old North St. Louis neighborhood, an area with a high concentration of poverty, crime, unemployment, and abandoned buildings.
The church houses the only Catholic school for low-income families in the north city; together they formed Sacred Heart’s educational center (SCE). SCE has strived to provide academic excellence to children from low-income families by providing a small, nurturing environment as well as high academic standards.
The facility is in need of renovations and new equipment to continue its mission.
The Church of the Sacred Heart is a small nonprofit organization that provides a variety of educational and community services.
The services provided by Sacred Heart represent a $5 billion industry, with nonprofit organizations accounting for $258.8 billion of that total.
The health care and social assistance sector is the largest among nonprofits, representing 32 percent of revenues, followed by educational services (18 percent), and human and other social service providers (16 percent).
The key customers for the Church of the Sacred Heart are families in need of affordable education. The number of students in the school has increased from 500 when it opened in 1914 to 1,100 at its peak during 20XX-20XX but has since declined due to various reasons.
The children at Sacred Heart are from low-income families and 91 percent qualify for free or reduced lunches. Most parents work or have a family member who works full-time, while others don’t work due to child care restraints. The number of children enrolled in Sacred Heart is stable at 1,075 students because there is a lack of affordable alternatives to Catholic education in the area.
SCE offers K-5th grade students a unique learning experience in small groups with individualized instruction.
Sacred Heart has an established brand and is well known for its high standards of academic excellence, which include a 100 percent graduation rate.
Sacred Heart attracts prospective students through promotional materials such as weekly bulletins, mailers to homes that are located in the area served, and local churches.
Parents and guardians of children enrolled in Sacred Heart are mainly referrals from current families, word-of-mouth, and parishioners who learn about the school by attending Mass at Sacred Heart.
The Church of Sacred Heart does not currently advertise; however, it is one of the few Catholic schools that serve low-income families in St. Louis, MO, and therefore uses word of mouth to attract new students to its school.
The Church of Sacred Heart has an established brand awareness within the target audience despite not having direct marketing plans or materials.
The operations section for the Church of the Sacred Heart consists of expanding its after-school program as well as revamping its facility to meet the growing demand for affordable educational services.
Sacred Heart is located in an area where more than one-third of children live below the poverty line, which helps Sacred Heart stand out among other schools that are more upscale. Expansion into after-school programs will allow it to capture a larger market share by providing additional services to its target audience.
In order to expand, Sacred Heart will have to hire additional personnel as well as invest in new equipment and supplies for both the school and the after-school program.
The Church of Sacred Heart’s financial plan includes a fundraising plan that would help renovate the building as well as acquire new equipment and supplies for the school.
According to the National Center for Education Statistics, Catholic elementary schools across all grade levels spend an average of $6,910 per pupil on operating expenses. A fundraising initiative would help Sacred Heart acquire additional revenue while expanding its services to low-income families in St Louis, MO.
Financial Overview
The Church of the Sacred Heart expects to generate revenues of about $1.2 million in fiscal year 20XX, representing a growth rate of 2 percent from its 20XX revenue level. For 20XX, the church expects revenues to decrease by 4 percent due to a decline in enrollment and the lack of new students. The Church of Sacred Heart has experienced steady revenue growth since its opening in 1914.
- Revenue stream 1: Tuition – 22%
- Revenue stream 2: Investment income – 1%
Despite being located in a poverty-stricken area, the Church of Sacred Heart has a stable revenue growth at 4 percent per year. Therefore, Sacred Heart should be able to attain its 20XX revenue goal of $1.2 million by investing in new facilities and increasing tuition fees for students enrolled in its after-school program.
Income Statement f or the fiscal year ending December 31, 20XX
Revenue: $1.2 million
Total Expenses: $910,000
Net Income Before Taxes: $302,000
Statement of Financial Position as of December 31, 20XX
Cash and Cash Equivalents: $25,000
Receivables: $335,000
Property and Equipment: $1.2 million
Intangible Assets: $0
Total Assets: $1.5 million
Balance Statement
The board of directors has approved the 20XX fiscal year budget for Sacred Heart Catholic Church, which is estimated at $1.3 million in revenues and $920,000 in expenditures.
Cash Flow Statement f or the Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 20XX
Operating Activities: Income Before Taxes -$302,000
Investing Activities: New equipment and supplies -$100,000
Financing Activities: Fundraising campaign $200,000
Net Change in Cash: $25,000
According to the 20XX fiscal year financial statements for Sacred Heart Catholic Church, it expects its investments to decrease by 4 percent and expects to generate $1.3 million in revenues. Its total assets are valued at $1.5 million, which consists of equipment and property worth approximately 1.2 million dollars.
The Church of Sacred Heart’s financial statements demonstrate its long-term potential for strong revenue growth due to its steady market share held with low-income families in St. Louis, MO.
Nonprofit Business Plan Example #3 – Finally Home – a Nonprofit Homeless Shelter in Los Angeles, CA
Finally Home is a nonprofit organization that aims to provide low-income single-parent families with affordable housing. The management team has a strong background in the social service industry and deep ties in the communities they plan to serve. In addition, Finally Home’s CEO has a background in real estate development, which will help the organization as they begin developing its operations.
Finally Home’s mission is to reinvent affordable housing for low-income single-parent families and make it more sustainable and accessible. They will accomplish this by buying homes from families and renting them out at an affordable price. Finally Home expects its model of affordable housing to become more sustainable and accessible than any other model currently available on the market today. Finally Home’s competitive advantage over similar organizations is that it will purchase land and buildings from which to build affordable housing. This gives them a greater amount of ownership over their communities and the properties in which the homes are located, as well as freedom when financing these projects.
Finally Home plans on accomplishing this by buying real estate in areas with high concentrations of low-income families who are ready to become homeowners. These homes will be used as affordable housing units until they are purchased by Finally Home’s target demographic, at which point the organizations will begin renting them out at a base rate of 30% of the family’s monthly household income.
Finally Home plans on financing its operations through both private donations and contributions from foundations, corporations, and government organizations.
Finally Home’s management team has strong backgrounds in the social service industry, with deep ties to families that will be prepared to take advantage of Finally Home’s affordable housing opportunities. The CEO of Finally Home also brings extensive real estate development experience to the organization, an asset that will be especially helpful as Finally Home begins its operations.
Finally Home is a nonprofit organization, incorporated in the State of California, whose mission is to help homeless families by providing them with housing and support services. The centerpiece of our program, which will be replicated nationwide if successful, is an apartment complex that offers supportive living for single parents and their children.
The apartments are fully furnished, and all utilities are paid.
All the single parents have jobs, but they don’t earn enough to pay market-rate rent while still paying for other necessities such as food and transportation.
The organization was founded in 20XX by Henry Cisneros, a former U.S. Secretary of Housing and Urban Development who served under President Bill Clinton. Cisneros is the chairman of Finally Home’s board of directors, which includes leaders with experience in banking, nonprofit management, and housing professions.
The core values are family unity, compassion for the poor, and respect for our clients. They are the values that guide our employees and volunteers at Finally Home from start to finish.
According to the United States Conference of Mayors’ Task Force on Hunger and Homelessness 20XX Report, “Hunger & Homelessness Survey: A Status Report on Hunger & Homelessness in America’s Cities,” almost half (48%) of all homeless people are members of families with children. Of this number, over one quarter (26%) are under the age of 18.
In 20XX, there were 9.5 million poor adults living in poverty in a family with children and no spouse present. The majority of these families (63%) have only one earner, while 44% have zero earners because the person is not old enough or does not work for other reasons.
The total number of people in poverty in 20XX was 46.5 million, the largest number since Census began publishing these statistics 52 years ago.
Finally Home’s goal is to help single parents escape this cycle of poverty through providing affordable housing and case management services to support them long term.
Unique Market Position
Finally Home creates unique value for its potential customers by creating housing where it does not yet exist.
By helping single parents escape poverty and become self-sufficient, Finally Home will drive demand among low-income families nationwide who are experiencing homelessness. The high level of need among this demographic is significant nationwide. However, there are no other organizations with the same market position as Finally Home.
Finally Home’s target customers are low-income families who are experiencing homelessness in the Los Angeles area. The organization will actively seek out these families through national networks of other social service providers to whom they refer their clients regularly.
Finally Home expects to have a waiting list of families that are interested in the program before they even open their doors.
This customer analysis is based on the assumption that these particular demographic groups are already active users of other social service programs, so referrals will be natural and easy for Finally Home.
Industry Capacity
This information is based on the assumption that these particular demographic groups are already active users of other social service programs, so referrals will be natural and easy for Finally Home.
There is a growing demand for low-income single-parent housing nationwide, yet there is no one organization currently providing these services on a national level like Finally Home.
Thus, Finally Home has a competitive advantage and market niche here because it will be the only nonprofit organization of its kind in the country.
Finally Home’s marketing strategies will focus on attracting potential customers through national networks of other social service providers. They will advertise to their referral sources using materials developed by the organization. Finally Home will also advertise its services online, targeting low-income families using Google AdWords.
Finally Home will be reinventing affordable housing to make it more accessible and sustainable for low-income single parents. In this new model, Finally Home will own the land and buildings on which its housing units are built, as well as the properties in which they are located.
When a family is ready to move into an affordable housing unit, Finally Home will buy the home they currently live in. This way, families can take advantage of homeownership services like property tax assistance and financial literacy courses that help them manage their newfound wealth.
Finally Home has already partnered with local real estate agents to identify properties for purchase. The organization expects this to result in homes that are at least 30% cheaper than market value.
Finally Home will finance its operational plan through the use of private contributions and donations from public and private foundations, as well as corporate sponsorships.
Finally Home’s management team consists of:
- Veronica Jones, CEO, and Founder
- Mark MacDonald, COO
- Scott Bader, CFO
Management Summary
The management team has a strong history of social service advocacy and deep ties in the communities they plan to serve. In addition, the organization’s CEO has a background in real estate development that will be helpful as Finally Home begins operations.
- Year 1: Operation startup costs to launch first five houses ($621,865)
- Year 2: Deliver on market offer and complete first capital raise ($4,753,000)
- Year 3: Deliver on market offer and complete $5 million capital raise ($7,950,000)
- Year 4+: Continue to grow market share with a national network of social services providers ($15,350,000).
This nonprofit business plan will serve as an effective road map for Finally Home in its efforts to create a new model for affordable housing.
Nonprofit Business Plan Example PDF
Download our non-profit business plan pdf here. This is a free nonprofit business plan example to help you get started on your own nonprofit plan.
How to Finish Your Nonprofit Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your nonprofit business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Nonprofit Business Planning Articles
- Non-Profit Business Plan
- How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan
- 10 Tips to Make Your Nonprofit’s Business Plan Stand Out
- How to Write a Mission Statement for Your Nonprofit Organization
- Strategic Planning for a Nonprofit Organization
- How to Write a Marketing Plan for Your Nonprofit Business
- 4 Top Funding Sources for a Nonprofit Organization
- What is a Nonprofit Organization?
- 20 Nonprofit Organization Ideas For Your Community


- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056

11 Best Non Profit Business Plan Examples + Template (2024)

What Is Non Profit Organization?
The non-profit sector, also known as the nonprofit business sector or the third sector, consists of organizations that operate for purposes other than making a profit. These organizations focus on serving the public or specific communities by addressing social, cultural, educational, environmental, or humanitarian needs.
Non-profit organizations rely on donations, grants, fundraising, and government support to finance their operations and fulfill their mission. They encompass a wide range of entities, including charities, foundations, religious organizations, educational institutions, social service agencies, healthcare providers, environmental organizations, and arts and cultural organizations. Non-profit organizations play a vital role in advocating for social change, providing essential services, and improving the well-being of society.
In the United States, non-profit organizations often seek tax-exempt status under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code . This designation allows them to receive tax-deductible donations and grants. Non-profit organizations are governed by a board of directors or trustees, ensuring adherence to legal and ethical standards. They are subject to specific regulations and reporting requirements to maintain transparency and accountability. Through the dedication of volunteers, support from donors and funders, and the commitment of staff members, the non-profit sector makes a significant impact by addressing societal issues and fostering positive change in communities.
Things to Consider When Starting a Non-Profit Business
- Clearly define your non-profit’s mission and vision for guidance.
- Research the non-profit sector to understand opportunities and challenges.
- Identify your target audience to tailor programs and services.
- Develop a strategic plan with clear goals and objectives.
- Choose a suitable legal structure for your non-profit organization.
- Establish a dedicated board of directors for guidance and governance.
- Create a strong fundraising strategy to secure funds.
- Build partnerships for collaboration and extra support.
- Implement effective marketing and outreach plans to raise awareness.
- Manage finances wisely for transparency and sustainability.
- Recruit passionate individuals who share your mission.
- Track and evaluate impact using measurable indicators.
- Stay informed about legal and regulatory changes affecting non-profits.
- Continuously learn and improve to meet evolving needs.
- Nurture relationships with stakeholders for engagement and support.
Need a comprehensive guide on developing a non-profit business plan, check out our sample non-profit business plans .
Here are 11 best non profit business plan examples for your inspiration.
When it comes to creating a business plan for a non-profit organization, following a traditional business plan format can provide a solid framework. Here are 11 examples of non-profit business plans that adhere to the traditional structure:
Executive Summary
For instance, a non-profit focused on providing education to underprivileged children may have an executive summary that highlights the organization’s mission, the target population, and the key strategies for achieving educational goals.
Executive Summary: Samaritan’s Purse is a non-profit organization dedicated to helping communities worldwide that are affected by natural disasters and humanitarian crises. Our mission is to show God’s love in action by providing physical aid, spiritual support, and hope to those in need. We work quickly to respond to emergencies and provide immediate help like food, shelter, and medical assistance. Our caring team, made up of professionals and volunteers, is committed to helping communities recover and rebuild after a disaster. We believe in working together with local partners and using efficient strategies to make a lasting difference in the lives of those affected. Through our core values of compassion, integrity, and faith, Samaritan’s Purse strives to be a source of hope and support during difficult times.
Organizational Description
An example of an organizational description could be a non-profit that supports environmental conservation, providing details about its establishment, the board of directors, and the legal status as a registered non-profit organization.
Organizational Description: Samaritan’s Purse, established in 1970 by Franklin Graham, has evolved into a worldwide organization, supported by a dedicated team of staff and volunteers. As a registered non-profit, we prioritize transparency, accountability, and meaningful outcomes in everything we do. Our reach extends across the globe, enabling us to respond swiftly to emergencies and provide assistance to communities in need. With a strong commitment to making a positive impact, we uphold the highest standards of integrity and efficiency in our operations. By leveraging the combined efforts of our compassionate workforce and the support of our generous donors, we are able to deliver essential aid and long-term solutions to those affected by natural disasters and humanitarian crises. At Samaritan’s Purse, we remain resolute in our mission to provide practical support and spiritual comfort to individuals and communities facing hardship, fostering hope and promoting resilience in the face of adversity.
Mission Statement
A non-profit dedicated to empowering women in entrepreneurship may have a mission statement that states, “Our mission is to provide resources, training, and support to women entrepreneurs, enabling them to thrive and succeed in their business ventures.
Ready to get started on your custom business plan? Take just two easy steps to receive personalized pricing tailored to your specific needs. Click here to begin your journey toward a professionally crafted business plan that sets you up for success!
Mission Statement: Samaritan’s Purse is driven by a mission to extend spiritual and physical aid to individuals facing adversity worldwide. We diligently offer solace and care, imparting the Good News of Jesus Christ to bring hope during times of crisis. With a profound commitment to serving the hurting, we strive to alleviate suffering, restore dignity, and foster transformation. Our dedicated team passionately delivers practical support, comforting the afflicted, and embodying God’s love in action. Through compassionate engagement, we aim to be a beacon of hope, touching lives and communities with lasting impact. By combining spiritual nourishment with tangible assistance, Samaritan’s Purse seeks to inspire faith, uplift hearts, and empower individuals to embrace a brighter future. Together, we are united in our mission to demonstrate unwavering compassion, as we extend a helping hand and share the message of hope to those in need across the globe.
Looking for a company that writes business plans ?
Vision statement.
For instance, a non-profit focused on reducing homelessness might have a vision statement that envisions a future where every individual has access to safe and affordable housing, free from homelessness and its associated challenges.
Vision Statement: At Samaritan’s Purse, we have a profound vision of a world that undergoes a remarkable transformation, where suffering is alleviated, hearts discover profound healing, and lives experience enduring change. We envision this transformation being brought about through the unwavering power of God’s love, which we demonstrate through our dedicated actions. In this transformed world, we envisage pain and anguish being replaced by comfort and relief, broken hearts finding solace and restoration, and individuals experiencing profound personal growth and empowerment. Through our commitment to service and compassion, we aspire to be agents of positive change, bringing hope, love, and light to even the darkest corners of the world. We believe that God’s love knows no bounds and can permeate every aspect of society, ultimately leading to a world where justice, equality, and compassion prevail. With unwavering determination, we work towards this vision, striving to make a lasting impact on the lives of those we serve.
Market Analysis
An example of market analysis could involve a non-profit conducting research on the local community’s needs, analyzing existing social service organizations, and identifying gaps in services that they can fill.
Market Analysis: Samaritan’s Purse diligently conducts comprehensive research to assess the specific needs of communities that have been affected by disasters. We recognize the importance of collaborating closely with local partners and government agencies to gain a deep understanding of the challenges and vulnerabilities faced by these communities. Through this collaborative approach, we identify areas where our assistance can make the greatest impact, both in the immediate aftermath of the disaster and in the long term. By carefully analyzing the data and insights gathered, we ensure that our resources and interventions are tailored to address the specific needs and priorities of each community. This approach allows us to deliver effective and targeted assistance, maximizing the positive outcomes and sustainable impact of our programs. Through ongoing research and analysis, we remain adaptive and responsive to the ever-evolving needs of disaster-affected communities, continually refining our strategies to best serve those we seek to assist.
Programs and Services
A non-profit dedicated to animal welfare may outline programs and services such as animal adoption, spay/neuter initiatives, veterinary care, and community education on responsible pet ownership.
Programs and Services: Samaritan’s Purse is dedicated to providing a comprehensive range of programs and services to meet the diverse needs of communities. We understand that each community has unique challenges and requirements, and we strive to address them effectively. Our offerings include emergency medical care to provide immediate relief and save lives. We also focus on providing clean water and sanitation facilities, recognizing their vital role in promoting health and preventing the spread of diseases. Shelter and housing assistance are crucial components of our response, ensuring that individuals and families have a safe and secure place to rebuild their lives. We also provide livelihood support to help communities recover economically, offering training and resources for income-generating activities. Education and vocational training programs empower individuals to acquire valuable skills and knowledge for sustainable futures. Lastly, we provide spiritual counseling and discipleship, recognizing the significance of emotional and spiritual well-being in times of crisis. Through these varied programs and services, we aim to holistically address the needs of communities and contribute to their long-term recovery and development.
Marketing and Outreach Strategy
Marketing and Outreach Strategy: Samaritan’s Purse implements a comprehensive marketing and outreach strategy to raise awareness and foster engagement among supporters. We utilize various digital platforms, including websites, social media channels, and online campaigns, to effectively communicate our mission and share impactful stories of those we serve. Direct mail appeals are also employed to reach individuals who may prefer traditional forms of communication. Strategic partnerships with churches, organizations, and influential stakeholders help amplify our message and extend our reach to diverse audiences. Additionally, we leverage high-profile events to create opportunities for increased visibility and networking, enabling us to connect with potential supporters and collaborators. By employing a multi-faceted approach, we strive to maximize our impact, ensuring that our mission resonates with a broad audience and mobilizing the necessary resources to support our vital work. Through these marketing and outreach efforts, we seek to inspire compassion, build lasting relationships, and garner the support needed to bring hope and aid to those in need.
Operational Plan
A non-profit operating a community food bank may include details about the facility, the staff responsible for daily operations, and the systems in place to receive, store, and distribute food to those in need.
Operational Plan: Samaritan’s Purse operates through a well-established network of regional offices and field teams strategically positioned across the globe. Our dedicated staff members play a vital role in ensuring the efficient coordination of resources, logistics, and partnerships. By strategically locating our offices and teams, we can respond swiftly and effectively to crises and emergencies, reaching those in need promptly. Our operational plan focuses on streamlining processes and optimizing the use of resources, enabling us to deliver aid and support in a timely manner. We prioritize effective communication and collaboration among our teams, fostering a cohesive and coordinated approach to our operations. Through strong partnerships with local organizations, governments, and communities, we maximize our impact and ensure the delivery of aid reaches the most vulnerable populations. With a well-structured operational plan in place, we are able to navigate complex logistical challenges and deliver our services promptly, efficiently, and effectively.
Financial Plan
An example of a financial plan could involve a non-profit outlining its projected revenue sources, such as grants, donations, and fundraising events, as well as the anticipated expenses for program implementation, staffing, and administrative costs.
53 Best Non-Profit Business Ideas
Financial Plan: The financial plan of Samaritan’s Purse focuses on ensuring the efficient and effective allocation of resources to support our mission of providing aid and assistance to those in need. Here are some key aspects of our financial plan:
Diverse Funding Sources: We rely on a range of funding sources to sustain our operations. In the previous fiscal year, our total funding amounted to $10 million. This included $6 million in individual and corporate donations, $2 million in grants from foundations and government agencies, $1 million from partnerships with organizations, and $1 million from fundraising events.
Strong Financial Stewardship: We prioritize responsible financial management and transparency. Our dedicated team ensures that funds are allocated effectively and transparently to maximize the impact of our programs. In the past year, 85% of our total expenses went directly towards program activities, with only 10% allocated to administrative costs and 5% to fundraising expenses.
Budgeting and Financial Planning: We develop comprehensive budgets and financial plans to guide our activities. For the upcoming year, we have projected a budget of $12 million, allowing us to expand our reach and enhance the impact of our programs. This includes allocating $8 million toward direct program expenses, $2 million for administrative costs, and $2 million for fundraising efforts.
Monitoring and Reporting: We implement robust monitoring and reporting systems to track the financial performance of our programs and projects. Monthly financial statements and quarterly reports are prepared, reviewed, and shared with our board, stakeholders, and donors to ensure accountability and transparency. We also conduct annual audits by independent auditing firms to maintain financial integrity.
Compliance and Legal Requirements: We comply with all applicable laws and regulations related to financial management, taxation, and reporting. We work closely with legal and financial professionals to stay up-to-date with the latest requirements and maintain compliance. This includes filing annual tax returns as a registered non-profit organization.
Risk Management: We identify potential financial risks and develop risk management strategies to mitigate them. This includes ensuring appropriate insurance coverage, maintaining strong internal controls, and conducting regular risk assessments. We allocate a contingency fund of 5% of our total budget to address unforeseen circumstances or emergencies.
Donor Stewardship: We prioritize building and maintaining strong relationships with our donors. We provide regular updates on our programs and their impact, express gratitude for their support, and ensure donor funds are used in accordance with their intentions. Last year, we achieved a donor retention rate of 85%, reflecting the trust and satisfaction of our supporters.
Here are some more business plan examples you can use as a starting point to plan your new business.
Evaluation and Measurement
A non-profit focused on youth development may establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of their programs, such as tracking the percentage of participants who graduate high school and pursue higher education.
Evaluation and Measurement:
Evaluation and measurement are crucial components of Samaritan’s Purse’s approach to ensuring the effectiveness and impact of our programs. We are committed to continuously assessing our work and making data-informed decisions. Here’s an overview of our evaluation and measurement practices:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): We establish specific KPIs for each program to track progress and measure outcomes. For example, in our clean water and sanitation program, our KPIs include providing access to clean water for 10,000 people and constructing 500 latrines in underserved communities.
Monitoring Systems: We implement rigorous monitoring systems to collect data throughout the duration of our programs. For instance, in our health program, we conduct monthly health screenings and track the number of patients treated for various illnesses. Last year, we conducted 500 health screenings and provided medical treatment to over 2,000 individuals.
Post-Project Assessments: Once a program is completed, we conduct comprehensive post-project assessments to evaluate its overall impact and sustainability. In our education program, we conducted a post-project assessment that showed a 30% increase in literacy rates among children who participated in our literacy classes.
Learning and Adaptation: Insights and lessons learned from our evaluations inform the design and implementation of future programs. For example, based on feedback from beneficiaries and partners, we adapted our livelihood support program by introducing vocational training in high-demand sectors. As a result, we saw a 50% increase in income generation for program participants.
Beneficiary Feedback: We actively seek feedback from the communities we serve. In our recent survey, 90% of respondents reported improved access to basic healthcare services as a result of our medical outreach program.
Collaboration and Research: We collaborate with research institutions to conduct studies that contribute to the knowledge and understanding of effective humanitarian practices. In partnership with a local university, we conducted a study on the long-term impact of our housing assistance program, which showed a 40% decrease in homelessness among program participants after one year.
Transparency and Reporting: We regularly communicate our evaluation findings, outcomes, and impact to our donors, supporters, and stakeholders. Last year, our annual report highlighted that 95% of funds were allocated directly to program activities, demonstrating our commitment to financial stewardship.
Risk Management
An example of risk management could involve a non-profit identifying potential risks, such as changes in government regulations or funding cuts, and developing contingency plans to mitigate those risks, ensuring the organization’s sustainability.
Want to prepare a business plan?
Hire our professional business plan preparers now!
Risk Management: Risk management involves careful analysis and preparation to mitigate potential risks. While it primarily focuses on qualitative assessments, there are instances where quantitative calculations are relevant. Here are some examples:
Risk Probability Assessment: We assign probabilities to various risks based on historical data or expert opinions. For instance, if we determine there is a 30% chance of a security threat in a specific region, we factor that into our risk assessment.
Risk Impact Evaluation: We quantify the potential impact of identified risks. For example, if we assess that a regulatory change may lead to a 20% reduction in funding for a particular program, we can calculate the financial implications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: In evaluating risk mitigation measures, we conduct cost-benefit analyses. This involves comparing the expected costs of implementing preventive measures against the potential losses from the identified risks. By quantifying these factors, we make informed decisions about risk mitigation strategies.
Insurance Coverage: We calculate the insurance coverage required for different types of risks. For example, we determine the value of property and assets at risk in a specific location and secure insurance coverage accordingly.
Financial Reserves: We allocate financial reserves to mitigate potential risks. By estimating the potential financial impact of various risks, we calculate the appropriate level of reserves needed to address unforeseen events.
Non Profit Business Plan Faq's
A non-profit organization, also known as a nonprofit or not-for-profit organization, is an entity that operates for a specific purpose or mission other than making a profit. Its primary goal is to serve the public or a particular cause.
The main difference is the purpose and distribution of funds. Non-profits reinvest their surplus back into the organization to further their mission, while for-profit organizations distribute profits to their owners or shareholders.
The purpose of a non-profit organization is to address a specific societal or community need. It can be focused on various areas such as education, healthcare, environment, social services, or arts and culture.
Non-profits rely on various sources of funding, including donations from individuals, grants from foundations or government agencies, corporate sponsorships, fundraising events, and revenue from services or programs they provide.
In many countries, donations to registered non-profit organizations are tax-deductible for the donors. However, tax laws may vary, so it’s important to consult local regulations or seek professional advice.
Non-profit organizations are typically governed by a board of directors or trustees. The board provides oversight, sets strategic direction, and ensures the organization’s compliance with legal and ethical standards.
Starting a non-profit involves several steps, including defining your mission, drafting bylaws, incorporating the organization, applying for tax-exempt status, and establishing governance and financial management structures. Consulting with legal and accounting professionals is recommended.
Board members of non-profit organizations have various responsibilities, including strategic planning, financial oversight, fundraising, hiring and evaluating the executive director, ensuring legal compliance, and representing the organization in the community.
Non-profit organizations use various metrics and evaluation methods to measure their impact. This can include tracking the number of beneficiaries served, outcomes achieved, changes in the community, and feedback from stakeholders. Evaluations help assess the effectiveness and adjust strategies as needed.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

Meta earnings results: shares tumble 17% after hours despite beating estimates; stock down on weak revenue guidance
- Meta reported first-quarter earnings on Wednesday.
- Mark Zuckerberg talked about Meta's plans to invest more in AI.
- Shares tumbled 17% in after-hours trading.

Meta reported first-quarter earnings on Wednesday after the closing bell.
The company reported revenue and earnings-per-share that beat consensus analyst estimates. But shares slid after Meta gave a range for second-quarter sales that was on the light side of forecasts and said it's going to spend more than it expected this year.
The report is Meta's first without monthly- and daily-average-user numbers specifically broken out for Facebook. The company instead reported overall "Family of Apps" results that also included Instagram and WhatsApp . The combined group saw $36 billion of revenue, beating the consensus estimate of $35.5 billion.
Meta's stock fell as much as 17% in after-hours trading, having slipped 0.5% on Wednesday. It had previously gained a robust 39% in 2024.
CEO Mark Zuckerberg's main focus on the investor call was Meta's plans to invest more significantly in AI. He also hyped up the company's recent partnership with Ray-Ban.
Meta's stock shows no sign of recovery as the Q&A ends.
Shares remain down nearly 17% in after-hours trading as the call draws to a close.
Meta CFO Susan Li is pretty tight-lipped about TikTok
Li says Meta has been following the potential for a TikTok ban closely, but it's too soon to comment on how it could impact Meta's business — for example, Instagram Reels.
The call moves on to the Q&A portion
Time for investors and analysts to (try to) get more details.
Zuckerberg appears to take a dig at Apple's Vision Pro
Zuckerberg hypes up Meta's Ray-Ban AI glasses. The company introduced new styles and features on Tuesday.
"You know, I used to think that AR glasses wouldn't really be a mainstream product until we had full holographic displays. And I still think that that's gonna be awesome and is the long-term mature state for the product. But now, it seems pretty clear that there's also a meaningful market for fashionable AI glasses without a display," he says.
It could be seen as a dig at Apple's Vision Pro headset, which has been accused of being clunky and uncomfortable. Or it could just be another step forward in Zuck's recent fashion journey .
Zuckerberg starts the call by getting straight into Meta's AI plans and spending
He says the company plans to invest "significantly more" in AI, but warns it will take "several years" to build "the leading AI."
"Realistically, even with shifting many of our existing resources to focus on AI, we will still grow our investment envelope meaningfully before we make much revenue from some of these new products," he says.
The CEO says Meta has a "strong track record of monetizing" its work, especially after spending time building up its products over time. But that doesn't seem to reassure investors right now, with shares slumping even further in postmarket trading.
The call kicks off.
Mark Zuckerberg and CFO Susan Li are here to discuss the results.
Meta's AI plans are going to cost them more than they expected.
Heading into the call, investors were looking for news about Meta's future AI plans, but — whatever they are — they're going to cost way more than the company predicted just a few months ago.
"Our full-year 2024 capital expenditures will be in the range of $35-40 billion, increased from our prior range of $30-37 billion as we continue to accelerate our infrastructure investments to support our artificial intelligence (AI) roadmap," the report says, noting Meta plans to "invest aggressively to support our ambitious AI research and product development efforts."
Total expenses will be in the range of $96-99 billion, up from a prior $94-99 billion forecast due to higher infrastructure and legal costs.
Still, Max Willens, senior analyst at market research firm Emarketer, a sister company to Business Insider, says it's not surprising Meta changed its guidance.
"Companies investing in this space, especially at the scope Meta is investing in it, may struggle with costs in the near term," Willens says.
Meta stock falls 10% in after-hours training after light 2nd-quarter revenue forecast.
Meta beats 1st-quarter sales and EPS estimates, but issues weaker-than-expected 2nd-quarter guidance.
1st quarter
Revenue: $36.46 billion, +27% y/y, estimate $36.12 billion
Advertising revenue: $35.64 billion, +27% y/y, estimate $35.57 billion
Family of Apps revenue: $36.02 billion, +27% y/y, estimate $35.53 billion
Reality Labs revenue: $440 million, +30% y/y, estimate $494.1 million
Other revenue: $380 million, +85% y/y, estimate $300.1 million
Family of Apps operating income: $17.66 billion, +57% y/y, estimate $17.76 billion
Reality Labs operating loss: $3.85 billion, -3.7% y/y, estimate loss $4.51 billion
Operating margin: 38% vs. 25% y/y, estimate 37.2%
EPS: $4.71 vs. $2.20 y/y, estimate $4.30
Average Family service users per day: 3.24 billion, +7.3% y/y, estimate 3.16 billion
2nd quarter
Revenue: $36.5 billion to $39 billion, estimate $38.24 billion
Goldman Sachs says Meta's platforms offer 'sizable opportunity' ahead.
Meta looks geared for strength as it's a key beneficiary of a robust advertising environment, Goldman Sachs said.
The bank expects continued investment in digital channels, advertiser verticals to recover, and digital products to expand, such as short-form video monetization.
Meta's Instagram Reels is a prime example of this, with the platform reaching revenue neutrality
"We still see a sizable opportunity for Reels to remain a key revenue growth tailwind for META in the coming years as the CPM gap closes further and as Reels continues to increase as a % of total ad impressions," analysts led by Eric Sheridan said.
Goldman Sachs rates Meta at "Buy" and holds a 12-month price target of $555.
JPMorgan sees Meta as 'built for the long term.'
JPMorgan considers Meta one of its top picks among internet stocks for its scale, growth, and profitability.
"We believe Meta's virtual ownership of the social graph, strong competitive moat, and focus on the user experience position it to become an enduring blue-chip company built for the long term," analysts led by Doug Anmuth wrote last week.
The bank expects Meta advertising to continue outperforming, bolstered by AI investments and Instagram Reels revenue expansions. Cost discipline will continue on through 2024, even if investments start rising.
Still, the bank did note some room for concern after this quarter's earnings, as Meta may need to find new catalysts for further expansion.
"META remains well-owned, but there is growing caution into earnings on almost-certain growth deceleration beyond 1Q due to tough comps & perception of lack of new drivers vs. '23. We believe slower growth is well-anticipated, & likely taken into account in META's undemanding multiple," the bank wrote.
JPMorgan rates Meta at "Overweight" with a $535 price target.
Wells Fargo says AI upside is accelerating Meta's growth.
Meta is an accelerating growth story led by emerging AI upside, uplifting everything from the firm's ad tools to consumer messaging products, Wells Fargo said.
The bank projects above-consensus revenue growth, with Meta boosted higher by a healthy e-commerce environment.
"Combined with a newfound appetite for efficiency, we believe META should be a steady earnings compounder at a reasonable multiple," analysts led by Ken Gawrelski said.
However, revenue could moderate into the second-quarter, and Meta will have to demonstrate another product-cycle catalyst to keep momentum rolling, the bank wrote.
"We view WhatsApp as an under-appreciated asset w/ sizable potential, should Meta invoke more direct monetization beyond Click-to-Message ads," Gawrelski wrote.
Wells Fargo rates Meta at "Overweight" with a $600 price target.
RBC Capital spotlights Meta's growing lead in the ad business.
The Canadian bank touted a significant ramp up in ad volumes across Meta services, with Instagram Reels advertising taking center stage.
In fact, ad loads on Reels jumped 22% from January's 16.4%, outpacing declining volumes among competitors such as TikTok.
"While slower growth out of Facebook is to be expected going forward, we believe few others in the space can come close to matching META's scale for incremental spend, and we therefore expect META to at least maintain share going forward," analysts led by Brad Erickson wrote last Thursday.
The bank also considers Meta to be trading at a discount to the broader internet segment, a gap that will persist or narrow based on whether the firm can demonstrate stability in the ad business.
However, some pullback could occur in the first half of the year given China's economic slowdown, which could impact ad spending. Still, the firm offers other positives, analysts said.
RBC rates Meta at "Outperform" with a $600 price target.
Bank of America sees Meta's AI assets as under-appreciated.
Bank of America expects to see upside in Meta's first-quarter report, citing higher ad spending that was boosted by seasonal events, such as Easter.
Meanwhile, Meta's AI assets remain under-appreciated, and the firm will benefit by highlight its growing capabilities in the space, the bank said in a note last week.
"We remain positive on Meta and reiterate our thesis that Reels, Messaging, and AI driven ad improvements are still early, and could lead to positive product surprises & revenue momentum in 2024," analysts Justin Post and Nitin Bansal said.
Meta also looks to be the biggest winner amid a possible TikTok ban , which has now made its way through the Senate.
Bank of America rates Meta at "Buy" with a $550 price target.
Meta's consensus first-quarter revenue estimate is $36.12 billion.
Revenue estimate: $36.12 billion
Advertising rev. estimate: $35.57 billion
Family of Apps revenue estimate: $35.52 billion
Reality Labs revenue estimate: $494.1 million
Other revenue estimate: $286.4 million
Adjusted operating income estimate: $13.45 billion
Family of Apps operating income estimate: $17.76 billion
Reality Labs operating loss estimate: $4.52 billion
Operating margin estimate: 37.2%
EPS estimate: $4.30
Facebook daily active users estimate: 2.11 billion
Facebook monthly active users estimate: 3.08 billion
Ad impressions estimate: +17.1%
Average price per ad estimate: +5.85%
Average Family service users per day estimate: 3.16 billion
Average Family service users per month estimate: 3.97 billion
Revenue estimate: $38.24 billion
Full-year 2024
Total expenses estimate: $96.87 billion
Capital expenditure estimate: $34.5 billion
- Main content
Tesla 1Q profit falls 55%, but stock jumps as company moves to speed production of cheaper vehicles
Tesla’s first-quarter net income plummeted 55%, but its stock price surged in after-hours trading Tuesday as the company said it would accelerate production of new, more affordable vehicles.
The Austin, Texas, company said it made $1.13 billion from January through March compared with $2.51 billion in the same period a year ago.
Investors and analysts were looking for some sign that Tesla will take steps to stem its stock’s slide this year and grow sales. The company did that in a letter to investors Tuesday, saying that production of smaller, more affordable models will start ahead of previous guidance.
The smaller models, which apparently include the Model 2 small car that is expected to cost around $25,000, will use new generation vehicle underpinnings and some features of current models. The company said it would be built on the same manufacturing lines as its current products.
On a conference call with analysts, CEO Elon Musk said he expects production to start in the second half of next year “if not late this year.”
New factories or massive new production lines won’t be needed for the new vehicles, Musk said.
“This update may result in achieving less cost reduction than previously expected but enables us to prudently grow our vehicle volumes in a more capex efficient manner during uncertain times,” the investor letter said.
But Musk gave few specifics on just what the new vehicles will be and whether they would be variants of current models. “I think we’ve said all we will on that front,” he told an analyst.
He did say that he expects Tesla to sell more vehicles this year than last year’s 1.8 million.
The company also appears to be counting on a vehicle built to be a fully autonomous robotaxi as the catalyst for future earnings growth. Musk has said the robotaxi will be unveiled on Aug. 8.
Shares of Tesla rose 11% in trading after Tuesday’s closing bell, but they are down more than 40% this year. The S&P 500 index is up about 5% for the year.
Morningstar analyst Seth Goldstein said the company gave guidance about its future that was clearer than in the past, allaying investor concerns about production of the Model 2 and future growth. “I think for now we’re likely to see the stock stabilize,” he said. “I think Tesla provided an outlook today that can make investors feel more assured that management is righting the ship.”
But if sales fall again in the second quarter, the guidance will go out the window and concerns will return, he said.
Tesla reported that first-quarter revenue was $21.3 billion, down 9% from last year as worldwide sales dropped nearly 9% due to increased competition and slowing demand for electric vehicles.
Excluding one-time items such as stock-based compensation, Tesla made 45 cents per share, falling short of analyst estimates of 49 cents, according to FactSet.
The company’s gross profit margin, the percentage of revenue it gets to keep after expenses, fell once again to 17.4%. A year ago it was 19.3%, and it peaked at 29.1% in the first quarter of 2022.
Over the weekend, Tesla lopped $2,000 off the price of the Models Y, S and X in the U.S. and reportedly made cuts in other countries including China as global electric vehicle sales growth slowed. It also slashed the cost of “Full Self Driving” by one third to $8,000 .
Tesla also announced last week that it would cut 10% of its 140,000 employees , and Chief Financial Officer Vaibhav Taneja said Tuesday the cuts will be across the board. Growth companies build up duplication that needs to be pruned like a tree to continue growing, he said.
Musk has been touting the robotaxi as a growth catalyst for Tesla since the hardware for it went on sale late in 2015.
In 2019, Musk promised a fleet of autonomous robotaxis by 2020 that would bring income to Tesla owners and make their car values appreciate. Instead, they’ve declined with price cuts, as the autonomous robotaxis have been delayed year after year while being tested by owners as the company gathers road data for its computers.
Neither Musk nor other Tesla executives on Tuesday’s call would specify when they expect Tesla vehicles to drive themselves as well as humans do. Instead, Musk touted the latest version of Tesla’s autonomous driving software — which the company misleadingly brands as “Full Self Driving” despite the fact that it still requires human supervision — and said that “it’s only a matter of time before we exceed the reliability of humans, and not much time at that.”
It didn’t take the Tesla CEO long to begin expounding on the possibility of turning on self-driving capabilities for millions of Tesla vehicles at once, although again without estimating when that might actually occur. He went on to insist that “if somebody doesn’t believe that Tesla is going to solve autonomy, I think they should not be an investor in the company.”
Early last year the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration made Tesla recall its “Full Self-Driving” system because it can misbehave around intersections and doesn’t always follow speed limits. Tesla’s less-sophisticated Autopilot system also was recalled to bolster its driver monitoring system.
Some experts don’t think any system that relies solely on cameras like Tesla’s can ever reach full autonomy.
Hamilton contributed to this report from San Francisco.

We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Tesla 1Q profit falls 55%, but stock jumps as company moves to speed production of cheaper vehicles
FILE - The logo for the Tesla Supercharger station is seen in Buford, Ga, April 22, 2021. Faced with falling global sales and a tumbling stock price, Tesla has slashed prices again on some of its electric vehicles and its “Full Self Driving” system. Tesla releases first-quarter earnings Tuesday, April 23, 2024. (AP Photo/Chris Carlson, File)
- Copy Link copied
Tesla’s first-quarter net income plummeted 55%, but its stock price surged in after-hours trading Tuesday as the company said it would accelerate production of new, more affordable vehicles.
The Austin, Texas, company said it made $1.13 billion from January through March compared with $2.51 billion in the same period a year ago.
Investors and analysts were looking for some sign that Tesla will take steps to stem its stock’s slide this year and grow sales. The company did that in a letter to investors Tuesday, saying that production of smaller, more affordable models will start ahead of previous guidance.
The smaller models, which apparently include the Model 2 small car that is expected to cost around $25,000, will use new generation vehicle underpinnings and some features of current models. The company said it would be built on the same manufacturing lines as its current products.
On a conference call with analysts, CEO Elon Musk said he expects production to start in the second half of next year “if not late this year.”
New factories or massive new production lines won’t be needed for the new vehicles, Musk said.
“This update may result in achieving less cost reduction than previously expected but enables us to prudently grow our vehicle volumes in a more capex efficient manner during uncertain times,” the investor letter said.
But Musk gave few specifics on just what the new vehicles will be and whether they would be variants of current models. “I think we’ve said all we will on that front,” he told an analyst.
He did say that he expects Tesla to sell more vehicles this year than last year’s 1.8 million.
The company also appears to be counting on a vehicle built to be a fully autonomous robotaxi as the catalyst for future earnings growth. Musk has said the robotaxi will be unveiled on Aug. 8.
Shares of Tesla rose 11% in trading after Tuesday’s closing bell, but they are down more than 40% this year. The S&P 500 index is up about 5% for the year.
Morningstar analyst Seth Goldstein said the company gave guidance about its future that was clearer than in the past, allaying investor concerns about production of the Model 2 and future growth. “I think for now we’re likely to see the stock stabilize,” he said. “I think Tesla provided an outlook today that can make investors feel more assured that management is righting the ship.”
But if sales fall again in the second quarter, the guidance will go out the window and concerns will return, he said.
Tesla reported that first-quarter revenue was $21.3 billion, down 9% from last year as worldwide sales dropped nearly 9% due to increased competition and slowing demand for electric vehicles.
Excluding one-time items such as stock-based compensation, Tesla made 45 cents per share, falling short of analyst estimates of 49 cents, according to FactSet.
The company’s gross profit margin, the percentage of revenue it gets to keep after expenses, fell once again to 17.4%. A year ago it was 19.3%, and it peaked at 29.1% in the first quarter of 2022.
Over the weekend, Tesla lopped $2,000 off the price of the Models Y, S and X in the U.S. and reportedly made cuts in other countries including China as global electric vehicle sales growth slowed. It also slashed the cost of “Full Self Driving” by one third to $8,000 .
Tesla also announced last week that it would cut 10% of its 140,000 employees , and Chief Financial Officer Vaibhav Taneja said Tuesday the cuts will be across the board. Growth companies build up duplication that needs to be pruned like a tree to continue growing, he said.
Musk has been touting the robotaxi as a growth catalyst for Tesla since the hardware for it went on sale late in 2015.
In 2019, Musk promised a fleet of autonomous robotaxis by 2020 that would bring income to Tesla owners and make their car values appreciate. Instead, they’ve declined with price cuts, as the autonomous robotaxis have been delayed year after year while being tested by owners as the company gathers road data for its computers.
Neither Musk nor other Tesla executives on Tuesday’s call would specify when they expect Tesla vehicles to drive themselves as well as humans do. Instead, Musk touted the latest version of Tesla’s autonomous driving software — which the company misleadingly brands as “Full Self Driving” despite the fact that it still requires human supervision — and said that “it’s only a matter of time before we exceed the reliability of humans, and not much time at that.”
It didn’t take the Tesla CEO long to begin expounding on the possibility of turning on self-driving capabilities for millions of Tesla vehicles at once, although again without estimating when that might actually occur. He went on to insist that “if somebody doesn’t believe that Tesla is going to solve autonomy, I think they should not be an investor in the company.”
Early last year the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration made Tesla recall its “Full Self-Driving” system because it can misbehave around intersections and doesn’t always follow speed limits. Tesla’s less-sophisticated Autopilot system also was recalled to bolster its driver monitoring system.
Some experts don’t think any system that relies solely on cameras like Tesla’s can ever reach full autonomy.
Hamilton contributed to this report from San Francisco.
Verizon posts fewer quarterly subscriber losses on flexible plan demand
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Harshita Mary Varghese; Editing by Pooja Desai
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

BHP planning potential buyout offer for Anglo American, says source
Global mining giant BHP Group has approached British multinational mining company Anglo American about a potential acquisition, according to a person with knowledge of the matter.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
According to Propel Nonprofits, business plans usually should have four components that identify revenue sources/mix; operations costs; program costs; and capital structure. A business plan outlines the expected income sources to support the charitable nonprofit's activities. What types of revenue will the nonprofit rely on to keep its engine ...
10-Step Guide on Writing a Business Plan for Nonprofits. Note: Steps 1, 2, and 3 are in preparation for writing your nonprofit business plan. Step 1: Data Collection. Before even getting started with the writing, collect financial, operating, and other relevant data. If your nonprofit is already in operation, this should at the very least ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Avoid using jargon, acronyms, or any unfamiliar terms. Write for a general audience, and you'll be more likely to keep the reader engaged. 2. Outline your plan. Make a nonprofit business plan outline. Once you know what information will be put into the plan, you'll understand what data you need to source to write it.
A nonprofit business plan fleshes out this mission statement in greater detail. These plans include many of the same elements as a for-profit business plan, with a focus on fundraising, creating a board of directors, raising awareness, and staying compliant with IRS regulations. A nonprofit business plan can be instrumental in getting your ...
11. Outline the Financial Plan. One of the main reasons people want to know how to write a nonprofit business plan is because of how essential it is to receiving funding. Loan providers, donors and granting bodies will want to see your numbers—and that's where your Financial Plan comes in.
Step 6: Fill in Your Nonprofit Business Plan Outline. Finally, you've made it to the last step in putting together your nonprofit business plan. By this point, you've answered just about every detail that goes into your plan—we just did it in a not-so-boring, roundabout way. Let's fill in the details.
Sample Nonprofit Business Plans - Bridgespan; Nonprofit Business Plan Template - Slidebean; 23+ Non Profit Business Plan Templates - Template.net; Nonprofit business plan sections. The exact content is going to vary based on the size, purpose, and nature of your nonprofit. However, there are certain sections that every business plan will need ...
A nonprofit business plan is required if you want to secure funding from grant-making organizations or investors. A well-crafted business plan will help you: Define your organization's purpose and goals. Articulate your vision for the future. Develop a step-by-step plan to achieve your goals. Secure funding from investors or donors.
A nonprofit business plan template provides a strategic overview of your nonprofit. It's a breakdown of all higher-level information about your organization, such as the board of directors and your core mission. Use your nonprofit business plan template to give your staff, the board, potential donors, and government funding agencies an ...
Analyzing your time and how it's spent helps bring far more awareness of how your time is helping — or hurting — your profits. And if it's the latter, you can adjust your plan to ...
A business plan for nonprofits is a strategic document that outlines a nonprofit organization's goals and operational approach. While similar to for-profit business plans, the focus here is on achieving social impact rather than financial profit. Projects implemented by nonprofit organizations typically revolve around fostering social welfare ...
That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks: Product goals and deadlines for each month. Monthly financials for the first two years. Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years. Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years.
This template has all the core components of a nonprofit business plan. It includes room to detail the organization's background, management team key personnel, current and future youth program offerings, promotional activities, operations plan, financial statements, and much more. Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template for Youth Program.
Marketing Plan - This section of your nonprofit business plan will detail your products, programs and services, your overall marketing strategies and tactics, and how you will measure success. It should include information on your target market, positioning, branding, communications, and lead generation. Operations Plan - In the Operations ...
Profit planning refers to setting up a profitability goal for a particular budgeting period and the steps undertaken by a business to achieve it. It is an essential process of running a company, as businesses are all about profits, and firms follow many measures to attain desired profitability levels.
The profit plan is an essential tool for any business, as it helps managers make informed decisions about how to allocate resources, invest in growth opportunities, and manage risk. It also serves as a roadmap for the company's financial future, providing a framework for monitoring performance and making adjustments as necessary.
The plan may vary depending on the specific organization, however, there are a couple of things that should be included in every non-profit business plan. 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary is a brief breakdown of the contents outlined in the business plan. The trick here is to provide an interesting summary that will keep the reader ...
Download our Ultimate Nonprofit Business Plan Template here. Below are sample plans to help guide you in writing a nonprofit business plan. Example #1 - Kids Are Our First Priority (KAOFP) - a Nonprofit Youth Organization based in Chicago, IL. Example #2 - Church of the Sacred Heart - a Nonprofit Church based in St. Louis, MO.
This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization your startup will take, roles and ...
Develop a strategic plan with clear goals and objectives. Choose a suitable legal structure for your non-profit organization. Establish a dedicated board of directors for guidance and governance. Create a strong fundraising strategy to secure funds. Build partnerships for collaboration and extra support.
By Matt Hooke - Reporter, Baltimore Business Journal. Apr 24, 2024. The University of Maryland Medical School is creating a for-profit entity to add a new revenue stream and establish a network ...
Advertising rev. estimate: $35.57 billion. Family of Apps revenue estimate: $35.52 billion. Reality Labs revenue estimate: $494.1 million. Other revenue estimate: $286.4 million. Adjusted ...
The company's gross profit margin, the percentage of revenue it gets to keep after expenses, fell once again to 17.4%. A year ago it was 19.3%, and it peaked at 29.1% in the first quarter of 2022.
The company said in its earnings presentation that its current installed capacity is more than 2.35 million. Tesla will continue work on a new module-based "unboxed" manufacturing process for ...
The company's gross profit margin, the percentage of revenue it gets to keep after expenses, fell once again to 17.4%. A year ago it was 19.3%, and it peaked at 29.1% in the first quarter of 2022. Over the weekend, Tesla lopped $2,000 off the price of the Models Y, S and X in the U.S. and reportedly made cuts in other countries including ...
Verizon's consumer business also saw its best first-quarter performance since 2018, with 158,000 wireless retail postpaid phone net losses, compared with 263,000 losses a year ago.