

About the Journal
Focus and scope.
Journal of Business Administration Research is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal specializing in business administration. The journal is aimed at providing innovative insights in the field of business administration.
The scope of the Journal of Business Administration Research includes:
- Production/operations management
- Global business
- Business processes
- Administration decisions
- Human resources management
- Supply chain management
- General/strategic management
- Organizational behavior
- Knowledge management
- Business finance and investment
Open Access Policy
This journal provides immediate Open Access to its content as it believes that making research freely available to the public which helps promoting the research results benefiting the scholarly community.
- Higher Visibility, Availability and Citations – free and unlimited accessibility of the publication over the internet without any restrictions increases citation of the article.
- Ease of search – publications are easily searchable in search engines and indexing databases.
- Rapid Publication – accepted papers are immediately published online.

Business Administration Research Guide: Top 25: Business Journals
- Top 25: Business Journals
- Books and eBooks
- Streaming Videos
- Research Help
Ask a Librarian
Chat with a Librarian
Lisle: (630) 829-6057 Mesa: (480) 878-7514 Toll Free: (877) 575-6050 Email: [email protected]
Book a Research Consultation Library Hours

Business & Leadership Journals
The following publications have been recognized as top leadership journals. Click on a title to search for articles within that journal. Impact Factors (IF) from recent years are listed when available.
- Academy of Management Journal -Full text available from 1985-present -IF(2009) 6.483
- Academy of Management Learning & Education Full text available from 2002-present
- Academy of Management Perspectives -Full text available from 2006-present -IF(2009) 0.594
- Academy of Management Review -Full text available from 1985-present more... less... The mission of the Academy of Management Review (AMR) is to publish new theoretical insights that advance our understanding of management and organizations.
- Administrative Science Quarterly -Full text available from 1985-present -IF(2010) 3.684
- Advancing Women in Leadership Journal 1997-2007. Link provides access to the current year. From current year page click on Archives tab to access previous years
- Business Ethics Quarterly -Full text available from 1991-present -IF(2010) 3.256
- Business Strategy & the Environment -Full text available from 1996-present
- California Management Review -Full text available from 1985-present -IF(2009) 1.983
- Greener Management International Full text available from 1996-2012
- Harvard business review -Full text available from 1985-present -IF(2009) 1.655
- International Journal of Servant-Leadership An annual publication that has published three online issues since 2010.
- Journal of Applied Behavioral Science -Full text available from 1965-present -IF(2010) 1.682
- Journal of Applied Psychology Full text available from 1965-present
- Journal of Business Ethics -Full text available from 1982-present -IF(2010) 1.125
- Journal of Change Management Full text 2001-2013
- Journal of Corporate Citizenship -Full text available from 2004-2014
- Journal of Industrial Ecology -Full text available from 1997-present
- Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies -Full text available from 1999-present
- Journal of Leadership Studies -Full text available from 2007-present
- Journal of Management Studies Full text available 1997-present
- Journal of Organizational Change Management -Full text available from 1988-present -IF(2009) 0.6
- Leadership Quarterly -Full text available from 1995-present -IF(2009) 2.202 more... less... This journal brings together a focus on leadership for scholars, consultants, practicing managers, executives and administrators, as well as those numerous university faculty members across the world who teach leadership as a college course. It provides timely publication of leadership research and applications and has a global reach. It also focuses on yearly reviews of a broad range of leadership topics on a rotating basis and emphasizes cutting edge areas through special issues.
- OD Practitioner -Full text available online from 2009-present
- Organization & Environment -Full text available from 1997-present
- Organization Development Journal -Full text available from 2004-2015
- Organizational Dynamics -Full text available from 1995-present
- Organization Science Full text available 1990-current
- Organization Studies Full text available 1999-current
- MIT Sloan Management Review A business journal that bridges the gap between management research and practice, evaluating and reporting on new research to help readers identify and understand significant trends in management. Full text from 1988-present.
- Strategic Management Journal -Full text available from 1996-present -IF(2009) 4.464
- Human Relations Full text available from June 1947 - October 2016
Other Leadership Journals
- Leadership & Organization Development Journal -Full text available online from 1980-present
- Organization Science -Full text online from 1990-present with a 48 month embargo
- Sustainability Accounting, Management and Policy Journal -Articles must be requested via interlibrary loan
- The Journal of Values-Based Leadership The Journal of Values-Based Leadership (JVBL) "promotes ethical and moral leadership and behavior by serving as a forum for ideas and the sharing of best practices." The JVBL is peer reviewed, open access and brought to you by ValpoScholar.
- Gender in Management: An International Journal "Gender in Management: An International Journal is committed to enabling the publication of high quality research, conceptual and thought pieces from both researchers and practitioners within the global gender in management field. GiM is the only journal which focuses on the subject of gender, grounded within management and leadership contexts."
Journals by Title
Go to Journals By Title Search and enter a journal title (e.g., Journal of Clinical Nursing ) in the search box to find out if we subscribe to it. When full text is available, notice the date range below each database. You'll find that some databases hold more volumes than others. Click the database with the date range most appropriate for your topic.
ILLiad Interlibrary Loan
Can't find the full text of an article you need in the BenU Library's databases? No problem! Request it through ILLiad at no cost to you and have it delivered electronically to your ILLiad account usually within 48-72 hours. Learn more on our Interlibrary Loan page.
- << Previous: Databases
- Next: Books and eBooks >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2023 10:39 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.ben.edu/business-administration
Kindlon Hall 5700 College Rd. Lisle, IL 60532 (630) 829-6050
Gillett Hall 225 E. Main St. Mesa, AZ 85201 (480) 878-7514
Business Administration
- Top Databases
- Top Journals
- Find Articles
- Find and Access Books
- Request Items not in Milner
Top Business Journals
- Academy of Management Review The mission of AMR is to publish theoretical insights that advance our understanding of management and organizations. To do this, researchers can develop new management and organization theory, significantly challenge or clarify existing theory, synthesize recent advances and ideas into fresh, if not entirely new theory, or initiate a search for new theory by identifying and delineating a novel theoretical problem.
- Academy of Management Journal The mission of AMJ is to publish empirical research that tests, extends, or builds management theory and contributes to management practice. All empirical methods including, but not limited to, qualitative, quantitative, field, laboratory, meta-analytic, and mixed methods are included.
- Journal of International Business Studies The journal publishes content from across the the six sub-domains of international business studies: (1) the activities, strategies, structures and decision-making processes of multinational enterprises; (2) interactions between multinational enterprises and other actors, organizations, institutions, and markets; (3) the cross-border activities of firms; (4) how the international environment affects the activities, strategies, structures and decision-making processes of firms; (5) the international dimensions of organizational forms and activities; and (6) cross-country comparative studies of businesses, business processes and organizational behavior in different countries and environments.
- Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science The Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science (JAMS) is devoted to the study and improvement of marketing and serves as a vital link between scholarly research and practice by publishing research-based articles in the substantive domain of marketing.
- Journal of Business Venturing The journal publishes entrepreneurship research from (1) the disciplines of economics, psychology, and sociology and welcomes research from other disciplines such as anthropology, geography, history, and so on, (2) the functions of finance/accounting, management, marketing, and strategy and welcomes research from other functions such as operations, information technology, public policy, medicine, law, music, and so on, and (3) the contexts of international and sustainability and welcomes research from other contexts such as high uncertainty, dynamism, time pressured, emotional, and so on.
- Journal of Consumer Research Empirical, theoretical, and methodological articles spanning fields such as psychology, marketing, sociology, economics, communications, and anthropology are featured in this interdisciplinary journal. The primary thrust of JCR is academic, rather than managerial, with topics ranging from micro-level processes (such as brand choice) to more macro-level issues (such as the development of materialistic values).
- Strategic Management Journal Strategic Management Journal publishes original refereed material concerned with all aspects of strategic management. It is devoted to the improvement and further development of the theory and practice of strategic management and it is designed to appeal to both practising managers and academics.
- Journal of Business Administration Research This is is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal specializing in business administration. The journal is aimed at providing innovative insights in the field of business administration. The scope of the Journal of Business Administration Research includes business operations, decision-making, management decisions, operations, administration decisions, general, strategic, international management, organizational behavior, marketing, accounting, and finance.
- American Journal of Economics and Business Administration The American Journal of Economics and Business Administration is a peer-reviewed journal that publishes original, innovative and novel work in various areas representing the intersection of economics as a scientific discipline and the professional practice of business management.
- Administrative Science Quarterly This journal is a peer-reviewed, interdisciplinary journal publishing theoretical and empirical work that advances the study of organizational behavior and theory. ASQ publishes articles that contribute to organization theory from a number of disciplines, including organizational behavior and theory, sociology, psychology and social psychology, strategic management, economics, public administration, and industrial relations.

- << Previous: Top Databases
- Next: Top Books >>
- Last Updated: Jun 2, 2023 11:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.illinoisstate.edu/businessadmin
Additional Links
- Directions and Parking
- Accessibility Services
- Library Spaces
- Staff Directory
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Journal of Business Administration Research, Sciedu Press
Journal of business administration research.
- Publisher Info
- Serial Info
Corrections
Contact information of journal of business administration research, sciedu press, serial information, impact factors.
- Simple ( last 10 years )
- Recursive ( 10 )
- Discounted ( 10 )
- Recursive discounted ( 10 )
- H-Index ( 10 )
- Euclid ( 10 )
- Aggregate ( 10 )
- By citations
- By downloads (last 12 months)
April 2023, Volume 12, Issue 1
October 2022, volume 11, issue 2, april 2022, volume 11, issue 1, october 2021, volume 10, issue 2, april 2021, volume 10, issue 1, october 2020, volume 9, issue 2, april 2020, volume 9, issue 1, october 2019, volume 8, issue 2, april 2019, volume 8, issue 1, october 2018, volume 7, issue 2, april 2018, volume 7, issue 1, october 2017, volume 6, issue 2, april 2017, volume 6, issue 1, october 2016, volume 5, issue 2, april 2016, volume 5, issue 1, october 2015, volume 4, issue 2, april 2015, volume 4, issue 1, october 2014, volume 3, issue 2, april 2014, volume 3, issue 1, october 2013, volume 2, issue 2, april 2013, volume 2, issue 1, october 2012, volume 1, issue 2, april 2012, volume 1, issue 1, more services and features.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
Advances in management research: a bibliometric overview of the Review of Managerial Science
- Original Paper
- Open access
- Published: 03 August 2020
- Volume 14 , pages 933–958, ( 2020 )

Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Alicia Mas-Tur 1 ,
- Sascha Kraus ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4886-7482 2 ,
- Mario Brandtner 3 ,
- Ralf Ewert 4 &
- Wolfgang Kürsten 3
8021 Accesses
79 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The Review of Managerial Science (RMS) is a leading international journal that publishes major advances related to business administration and management. The journal was launched in April 2007 and publishes eight issues per year (from 2021 onwards). The scope of RMS encompasses, but is not limited to, the functional areas of operations (such as production, operations management, and marketing), management (such as human resources management, strategic management, and organizational theory), information systems and their interrelations with capital markets (such as accounting, auditing, finance, and taxation), as well as questions of business strategy, entrepreneurship, innovation, and corporate governance. This study offers a bibliometric overview of the publication and citation structure of RMS from its inception in 2007 until 2020 in terms of topics, authors, institutions, and countries, thereby offering a comprehensive overview of the history of the journal so far. All the data for the study are from the Web of Science Core Collection database. To complement this analysis, VOSviewer software provides graphical analysis. The analysis is based on several bibliometric techniques such as co-citation analysis and bibliographic coupling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Digital transformation: a review, synthesis and opportunities for future research
Swen Nadkarni & Reinhard Prügl

Research Methodology: An Introduction

How to design bibliometric research: an overview and a framework proposal
Oğuzhan Öztürk, Rıdvan Kocaman & Dominik K. Kanbach
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The Review of Managerial Science (RMS) is an international journal that provides a forum for innovative research from all scientific areas of business administration and management. The scope of RMS encompasses, but is not limited to, the functional areas of operations (such as production, operations management, and marketing), management (such as human resources management, strategic management, and organizational theory), information systems and their interrelations with capital markets (such as accounting, auditing, finance, and taxation), as well as questions of business strategy, entrepreneurship, innovation, and corporate governance. RMS encourages the submission of papers combining ideas and/or approaches from different areas in an innovative way. The journal also welcomes review papers presenting the “state-of-the-art” of a research area and highlighting new directions for further research, a category that has been increasingly neglected in many other journals in recent years. The scientific standards of RMS are guaranteed by a rigorous (at least) double-blind peer review process with ad hoc referees and the journal’s international Editorial Board.
RMS first appeared in 2007, with the founding Co-Editors-in-Chief Ralf Ewert (University of Graz, Austria) and Wolfgang Kürsten (University of Jena, Germany), who still lead the journal. Since 2019, the two Editors-in-Chief are supported by a group of Associate Editors which has continuously been extended to accommodate the ongoing constant growth. From August 2020 onwards, this group consists of seven Associates: Ricarda B. Bouncken (University of Bayreuth, Germany; primary area: business strategy & innovation management), Laura Cabeza - García (University of Léon, Spain; primary area: corporate governance & corporate social responsibility), Reinhold Decker (Bielefeld University, Germany; primary area: marketing), Fabian Homberg (LUISS University, Rome, Italy; primary area: Human Resource Management), Sascha Kraus (Durham University, UK; primary area: entrepreneurship, SMEs, & family business), Marc - Steffen Rapp (University of Marburg, Germany; primary area: corporate governance, accounting, & finance), and Kirsten Thommes (University of Paderborn, Germany; primary area: Human Resource Management).
RMS started by publishing three issues per year and has increased this number over time to eight issues per year from 2021 onwards. The yearly page budget has correspondingly increased from approximately 250 pages in the founding years to around 1100 pages in recent years. The number of submissions strongly increased from approximately 40 during the founding years to more than 540 in 2019. At the same time, the acceptance rate decreased substantially to below 10% in 2018 and 2019 (see Table 1 ).
RMS is indexed and abstracted in major databases, including the Social Science Citation Index, Journal Citation Reports/Social Sciences Edition, SCOPUS, and EBSCO Discovery Service. In 2011, the journal’s first Journal Citation Reports (JCR) Impact Factor (IF) was announced. Since then, RMS has constantly increased its IF to its current IF of 3.00 in 2019. In Elsevier’s SCOPUS database, RMS is currently rated #25 out of 221 journals in the category “General Business, Management and Accounting” based on its 2019 CiteScore rank of 4.4. Additionally, RMS is rated “B” (on a scale from A to D) in the German VHB Jourqual (JQ3) journal ranking, and it has been listed in the British Academic Journal Guide (ABS) and the French CNRS ratings since their latest editions.
The purpose of this overview study is to examine the main factors that have influenced RMS so far, mainly focusing on the authors, institutions, and countries publishing in the journal, as well as the leading topics that have been published up to now. This in-depth analysis establishes a general overview of the journal’s publication structure.
In order to conduct this kind of analysis, several bibliometric techniques are applied. Bibliometrics is a library and information science research field where quantitative methods are used to study bibliographic material (Broadus 1987 ; Pritchard 1969 ). Using the Web of Science Core Collection (WoS CC) database, bibliometric analyses enable qualitative study of bibliographic material over the 13-year existence of the journal (2007–2019).
A bibliometric study of a journal is a popular approach for identifying the leading trends of a journal in terms of topics, highly cited papers, authors, institutions, and countries. Many journals have already published bibliometric analyses of their publication and citation structure, with notable examples including Accounting Review (Heck and Bremser 1986 ), Journal of Financial Economics (Schwert 1993 ), Technovation (García-Merino et al. 2006 ; Thongpapanl 2012 ), Journal of Business Research (Merigó et al. 2015 ), and Journal of Knowledge Management (Gaviria-Marín et al. 2018 ).
To thoroughly analyze bibliographic characteristics, mapping techniques are employed as well (Cobo et al. 2011 ; Small 1999 ). This article presents analysis of co-occurrences, co-citations, and bibliographic coupling based on the journal’s 10-year presence in the Web of Science (WoS) database. The results are visualized using VOSviewer software (Van Eck and Waltman 2010 ).
Bibliometrics can be defined as the research field in which the quantitative aspects of bibliographic material are studied (Broadus 1987 ). Bibliometrics was used as a key concept for the first time by Alan Pritchard in 1969 to replace the ambiguous concept of statistical bibliography (Pritchard 1969 ). Another term to refer to bibliometrics is scientometrics , which was coined by Nalimov and Mulchenko ( 1969 ) to define the study of all aspects of the literature of science and technology (Nalimov and Mulchenko 1969 ). Finally, Nacke ( 1979 ) proposed the term informetrics as a substitute for bibliometrics. Nowadays, bibliometrics, scientometrics, and informetrics are similar key concepts to define the discipline aimed at the quantitative study of bibliographic data (Sengupta 1992 ; Hood and Wilson 2001 ).
Bibliometrics is a library and information science research field where bibliographic material is studied using quantitative methods (Broadus 1987 ; Pritchard 1969 ). It is very useful for developing a comprehensive overview of the leading trends in a research field, journal, or country (Hood and Wilson 2001 ). It also enables identification of the most relevant authors on a given topic. A scientometric review provides a holistic approach because it involves a wide coverage of academic research (in this case, 285 publications) and provides objective analysis of a journal or a research field. This extensive review, which is based on a large number of published works, gives a more complete understanding of a journal or research field and can determine the qualitative and quantitative changes that occur. Likewise, it enables the creation of maps by generating groups of the main research topics. Essentially, scientometric maps give a holistic view of a particular domain and highlight trends and gaps in research (Suriñach Caralt et al. 2002 ).
Bibliometric studies are available in a wide range of fields including economics (Coupe 2003 ), management (Podsakoff et al. 2008 ), innovation (Fagerberg et al. 2012 ), entrepreneurship (Landström et al. 2012 ; Ferreira et al. 2019 ), family business (Xi et al. 2015 ), and operations research (Merigó and Yang 2017 ). In comparison with traditional literature reviews (e.g., Kraus et al. 2020 ), which are prone to subjective interpretation by researchers, scientometric reviews constitute a methodological innovation (Serrano Bedia et al. 2013 ). This innovation stems from their use of algorithms, data on production, dispersion, collaboration, and impact indexes (Moya and Prior 2008 ) to provide objectivity, consistency, and transparency (van Eck and Waltman 2014 ).
To perform a bibliometric analysis, it is important to define the bibliometric indicators that are used to analyze the data (Merigó et al. 2015 ). This study considers the number of publications and citations. The number of publications measures productivity, whereas the number of citations reflects popularity and influence. This study also considers the cites-per-paper ratio and the h-index (Hirsch 2005 ). The h-index indicates the maximum number ( h ) such that a given author (or journal) has published h papers that have each been cited at least h times. For the country analysis, the results are provided per million inhabitants in order to compare countries with different sizes (Table 7 ). For the university analysis, the general world ranking of the top universities with authors published in RMS is presented, according to the Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) and the Quacquarelli & Symonds (QS) University Ranking (Table 6 ).
The study offers further graphical analysis of the bibliographic data using VOSviewer software (Van Eck and Waltman 2010 , 2014 ). Using this software, two bibliometric techniques are presented: co-citation analysis (Small 1999 ) and bibliographic coupling (Kessler 1963 ). A co-citation occurs when two documents receive a citation from the same third document. Bibliographic coupling refers to situations where two studies cite the same third document. Co-citation analysis applies to authors, and bibliographic coupling applies to authors, institutions, and countries.
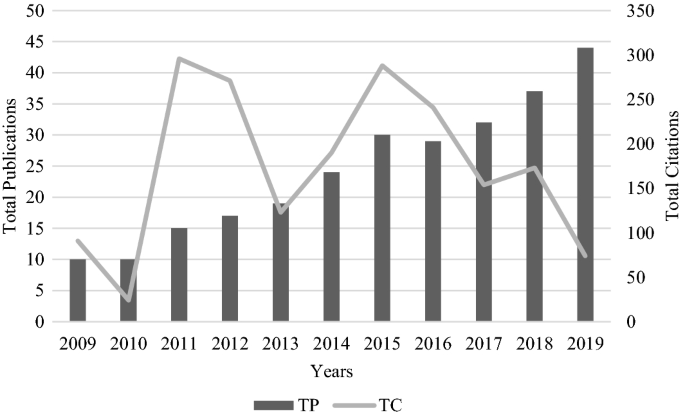
In the period 2009 to 2019, RMS published 285 documents indexed in WoS. These 285 documents encompass 248 original papers, 28 review papers, 7 editorials, and 2 other items such as proceedings or corrections. In this bibliometric analysis, 267 documents are considered. Notably, for 2019, 16 articles with early access are excluded. These articles were published online between October and November 2019, but had not been assigned to a regular issue at the time of the study.
Table 2 and Fig. 1 present the annual number of citations of RMS publications, as well as the number of publications reaching a certain citation threshold (more than 100 citations, more than 50 citations, etc.). The number of publications has increased over time. Simultaneously, there was a strong increase in the number of the citations from 2010 (24) to 2011 (296). The last few years show a decline in the number of citations. This decline can be regarded as normal and is due to the lag until articles which cite those papers have also undergone the necessary review process before acceptance or publication. Papers published in the years 2013 and 2014 seem to have attracted a smaller audience as well.
Annual citation structure of the journal
Figure 2 shows the evolution of the TOP 5 most cited papers. On an individual basis, three papers have received more than 100 citations: the 2011 paper by Gamerschlag et al. entitled “Determinants of voluntary CSR disclosure: empirical evidence from Germany”, the Kraus et al. 2012 paper by Kraus et al. entitled “Entrepreneurial orientation and the business performance of SMEs: a quantitative study from the Netherlands”, and the 2015 paper by Bouncken et al. entitled “Coopetition: a systematic review, synthesis, and future research directions”. These papers are from three separate subject areas: CSR, entrepreneurship, and strategy.
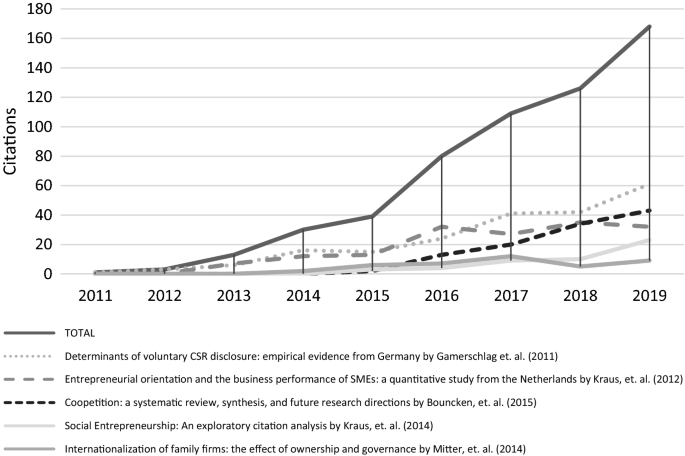
Evolution of the citations of the most cited RMS papers
Another relevant question is, Who cites RMS? The answer indicates the sources of RMS’s influence. During the years of 2009 to 2019, RMS received 1643 citations (February 2020). Table 3 presents the journals that have published more than 10 articles citing RMS.
As expected, RMS itself is the journal with the highest number of articles citing RMS publications because the research published in one journal tends to influence future research in the same journal, building an important foundation for the ongoing academic discourse on that topic. The journals Sustainability (90 documents), Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management (37 documents), Journal of Cleaner Production (32 documents), and Journal of Business Research (30 documents) also cite RMS frequently.
In the next step, the relationship between RMS and other journals is analyzed using a co-citation mapping of journals cited by RMS publications (Fig. 3 ). Co-citations can be defined as two documents that receive a citation from the same third document (Cancino et al. 2017 ). A co-citation mapping is valuable for understanding the clusters of journals that are most closely linked to RMS because they are cited by papers published in RMS.
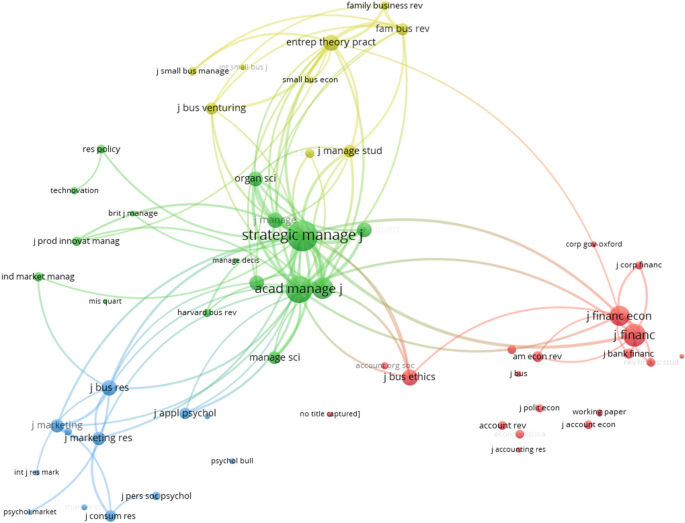
Co-citation of journals in RMS (minimum citation threshold of 10 and 100 lines)
There are four main clusters. The first one is led by Strategic Management Journal and Academy of Management Journal , the second is led by Journal of Finance and Journal of Financial Economics , the third is led by Journal of Business Research , and the fourth is led by Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice . The conclusion is that there are four main areas of research cited by the manuscripts published in RMS: management, finance, business, and entrepreneurship.
Table 4 presents a list of the 25 most cited studies published in RMS according to the results found in WoS. In 1927, the first article that used the citation count to evaluate the importance of scientific research was published (Gross and Gross 1927 ). In the article, the author argues that success breeds success and that a document with many citations is more likely to be cited again than a document with few citations. Similarly, an author with many articles is more likely than a less productive author to publish a new article, and it is more common to refer to a frequently consulted journal than a journal with a small readership (Price 1976 ). As Joseph ( 2003 ) reports, citations can be viewed as the “currency of modern science” (Marsh and Merton 1986 ; Garfield 1999 ), and the analysis of citations has become increasingly important to journal editors, authors, and readers (Merigó et al. 2015 ). The list of the 25 most cited papers reveals three main topics: corporate social responsibility (CSR), business sustainability, and entrepreneurship and management.
In the fields of CSR and business sustainability, the topics of social entrepreneurship and green innovation are receiving considerable attention due to the current concerns related to environmental destruction (Abdullah et al. 2016 ). The most cited papers in RMS dealing with CSR and business sustainability focus on: (1) voluntary CSR disclosure as a key issue for company visibility, shareholder structure, and the relationship with stakeholders (Gamerschlag et al. 2011 ); (2) the relationship between CSR disclosure and market valuations, especially in reference to firms operating in environmentally sensitive industries (Reverte 2016 ); (3) board independence as the main way to enhance the adoption of social activities (Fernández-Gago et al. 2016 ); and (4) the growth in CSR practices and its effect on managerial discretion (Ferrero et al. 2012 ). There are two main points that attract scholars’ attention in this field of research: CSR disclosure and managerial implications of social activities.
Regarding entrepreneurship and management, Bouncken is a leading author whose research in RMS is focused on different fields of entrepreneurship. (1) Entrepreneurial orientation: Bouncken et al. ( 2016 ) focus on entrepreneurial orientation in inter-organizational alliances. From the dynamic capabilities point of view, the authors conclude that the ability to absorb partners’ knowledge is a key point to improve joint product innovation; (2) entrepreneurial performance: Bouncken and Reuschl ( 2018 ) focus on entrepreneurial performance and opportunism. Opportunism is seen as knowledge leakage, which reduces organizational learning processes by decreasing trust and community building; (3) entrepreneurial coopetition: As previously outlined, Bouncken et al. ( 2015 ) focus on coopetition. This is a novel research field, and the authors highlight the importance of developing more theoretical and empirical approaches. They focus on the implications for innovation, taking into consideration the relationship between coopetition and knowledge flow.
In the field of entrepreneurship, some of the most cited papers in RMS deal with family business, focusing on the following topics: (1) internationalization in family firms (Mitter et al. 2014 ); (2) capital structure decisions of family firms (Ampenberger et al. 2013 ); and (3) corporate reputation and image (Sageder et al. 2018 ). In all cases, the studies focus on the influence of the family owners on the management of the company.
Table 5 lists the leading authors in terms of publications and impact. To be included in this list, the authors must have more than five citations and at least three publications. In academia, it has long been argued that more than one indicator must be evaluated to determine the overall contribution of an author or institution. Therefore, Table 5 provides different commonly used impact metrics: the total publications of the author, the h-index, the total number of citations, and, as a relative impact approach, the number of citations divided by the number of publications. The leading author in both number of publications and number of citations is Sascha Kraus, whose area of expertise is entrepreneurship, strategic management, and international management.
Finally, when analyzing the location of the authors’ affiliation, two main clusters can be found: one consists of authors from German institutions, and the other of authors from Austrian institutions.
Figure 4 a, b show the co-citations of authors in RMS. A co-citation (Small 1999 ; Marshakova-Shaikevich 2005 ) of authors occurs when the authors of two documents receive a citation from the same author in a third document. Thus, the co-citation establishes the number of documents in which they are cited together.
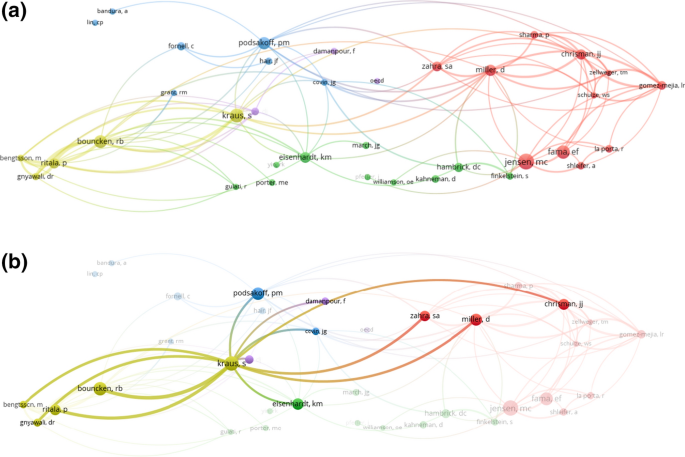
a Co-citation of authors in RMS (minimum citation threshold of 20 and 100 links). b Co-citation of authors in RMS: one special cluster (minimum citation threshold of 20 and 100 links)
Figure 4 a shows the relationship between authors in RMS, where four different clusters can be detected. This analysis shows that two of the most cited authors, Kraus and Bouncken, are especially related because of their common field of research: entrepreneurship and coopetition.
Figure 4 b shows that Kraus, the leading author publishing in RMS according to Table 5 , is the link between the clusters. As can be seen from Table 4 , Kraus investigates topics related to entrepreneurship, coopetition, and family firms, so it is unsurprising that he has relationships with different clusters.
Figure 5 shows the co-occurrence of author keywords in RMS. Keyword co-occurrence is also called co-word analysis. This analysis links the most used keywords in the published manuscripts to describe the conceptual framework of a research field—in this case, the research focus of RMS (Callon et al. 1983 ; Courtial 1994 ; Ding et al. 2001 ).
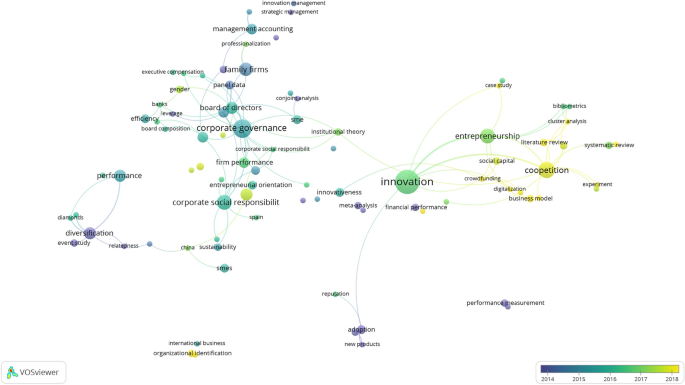
Co-occurrence of author keywords in RMS (minimum occurrence threshold of 2 and 100 links)
Figure 5 displays the evolution of topics in RMS. Table 4 shows that there are two predominant topics addressed in RMS: CSR and family business. This figure also shows the most novel keywords (RMS keywords from 2018 appear in yellow). In the last year, two new key topics appeared: innovation and coopetition.
Table 6 presents the 14 most productive and influential institutions with more than five publications in RMS, ranked by total number of publications. For the university analysis, this study presents the general world ranking of the top universities in RMS, according to the ARWU and the QS University Ranking (Table 6 ).
Table 6 shows that the University of Regensburg (Germany) tops the ranking. Two members of the RMS Editorial Board belong to this university. One of them, Roland Helm, is the third-ranked author in terms of number of publications. Second and third, with the same number of publications, are Johannes Kepler University of Linz (Austria) and the University of Liechtenstein.
Table 6 shows a strong European cluster. From the 14 universities included in the ranking, 12 are located in Europe. The two non-European institutions are the National Chiao Tung University in Taiwan and the University of Malaya in Malaysia.
Table 7 represents the annual evolution of contributions by countries. The dominant country in RMS with the most contributions is Germany (91), followed by Spain (33) and Austria (25). For the country analysis, the results are presented per million inhabitants in order to compare countries of different sizes (Table 7 ).
Figure 6 shows the bibliographic coupling of countries publishing in RMS with a minimum publication threshold of two documents and 50 links. According to Kessler ( 1963 ), bibliographic coupling can be defined as the number of shared references by citing documents (that is, two documents that cite the same third document).
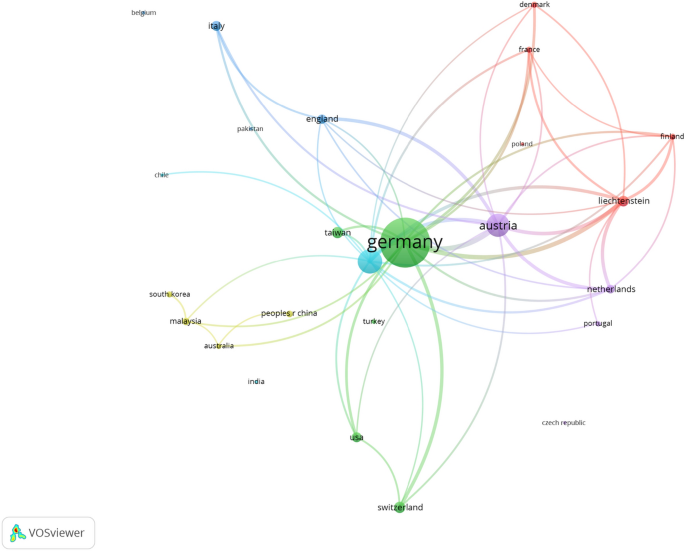
Bibliographic coupling of countries publishing in RMS (minimum publication threshold of 2 documents and 50 links)
As Fig. 6 shows, there are four country clusters. The first cluster contains Germany, Switzerland, Taiwan, and the United States. The second is composed of Spain, Chile, the United States, and Portugal. The third cluster comprises Austria, the Netherlands, Germany, and England. The fourth cluster is made up of Liechtenstein, Finland, Poland, and France. Additionally, there is a fifth cluster. Despite being small, this cluster should be mentioned because it contains countries such as China, South Korea, Malaysia, and Australia, all of which are Asia–Pacific countries that share research with each other.
Germany has by far the most bibliographic couplings and links with all other countries. This is unsurprising since Germany is the most productive and influential country publishing in RMS over time (Table 7 ). Moreover, Germany also has the most productive and influential institution, with the University of Regensburg (Table 6 ), and another six German universities appear in Table 6 among the most productive institutions. In addition, Fig. 5 shows other major clusters such as Austria, Taiwan, Liechtenstein, and England. Austria is also present in this research because it is the third country in Table 7 . Moreover, four Austrian institutions appear in Table 6 , where the most productive and influential institutions are shown, and six of the most influential authors belong to this country.
Furthermore, Spain (in blue) is closely related to Germany. Spain is also related to Chile, which is another Spanish-speaking country. As can be seen from Table 7 , Spain is the second most productive and influential country. Finally, Fig. 6 shows a close relationship between Germany, Austria, and Liechtenstein. This pattern is unsurprising because this paper has already shown that the authors and institutions from these countries–which all share the same language–are closely linked.
4 Conclusions
This study offers an overview of the structure of publications that have appeared in RMS from the journal’s launch in 2007 until the end of 2019. To carry out the study, bibliometric indicators from the WoS database are used. The analysis examines the number of citations of RMS by authors and other journals, as well as the most cited articles and the most productive and influential institutions and countries. In addition, the bibliometric study is complemented by VOSviewer analysis, which provides graphical analysis of the clusters of research topics, countries, and authors in the journal.
The results show a strong increase in publications and citations over time. It is worth highlighting the high impact of the articles published by the main authors, since they have managed to receive citations of all their articles published in RMS. The results also indicate that Germany is the leading country in the journal in terms of impact, followed by Spain, Austria, and Switzerland. In a similar vein, the most influential institution is the University of Regensburg in Germany, with a total of 15 publications, followed by other European universities. In addition, the VOSviewer analysis shows that Germany has the most bibliographic couplings and links with other countries.
Regarding the clusters obtained from the VOSviewer analysis of knowledge areas and topics, there are four main areas of research cited by the manuscripts published in RMS: management, finance, business, and entrepreneurship. Within these areas, there are two dominant topics in the journal’s publications throughout its history: CSR and family business. However, innovation and coopetition have recently become increasingly cited topics.
Although this study offers a comprehensive analysis of the main RMS publications, it of course has some limitations. The study of the journal’s publications refers to the period since the journal’s inception. Accordingly, the earliest published articles have normally received more citations than the most recent ones, even if the latter might be more influential; their long-term impact might not yet have been seen. Furthermore, by their very nature, the analyses are descriptive as well as backward-oriented. They can serve very well for presenting the past but can only give limited information about upcoming future trends in terms of the topics which will become influential. What can be concluded already, however, is that the journal is continuing to rise. As a result of the high quality of its publications, RMS has been indexed in the WoS since 2011, just four years after its launch. This achievement shows the high degree of interest of authors and readers in the topics of the journal, as well as its academic impact. Also the JCR Impact Factor is constantly increasing. RMS currently holds a JCR Impact Factor of 3.0 (as of 2019), and it is ranked in the second quartile of the “Management” category. RMS has gained international appeal and is continuing to actively shape academic discourse in several areas of management science.
All in all, RMS continues to welcome contributions from all areas within the wider business and management continuum that, regardless of the chosen method (quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods, experimental, conceptual, as well as review articles or meta-analyses, but usually excluding single case studies, student samples or samples from one single geographical area–such as cities or regions–with limited representativeness or generalizability), have the potential to set new foundations for a prominent future academic discourse within the journal and beyond.
Abdullah M, Zailani S, Iranmanesh M, Jayaraman K (2016) Barriers to green innovation initiatives among manufacturers: the Malaysian case. RMS 10(4):683–709
Google Scholar
Ampenberger M, Schmid T, Achleitner AK, Kaserer C (2013) Capital structure decisions in family firms: empirical evidence from a bank-based economy. RMS 7(3):247–275
Bouncken RB, Reuschl AJ (2018) Coworking-spaces: how a phenomenon of the sharing economy builds a novel trend for the workplace and for entrepreneurship. RMS 12(1):317–334
Bouncken RB, Gast J, Kraus S, Bogers M (2015) Coopetition: a systematic review, synthesis, and future research directions. RMS 9(3):577–601
Bouncken RB, Plüschke BD, Pesch R, Kraus S (2016) Entrepreneurial orientation in vertical alliances: joint product innovation and learning from allies. RMS 10(2):381–409
Broadus R (1987) Toward a definition of “bibliometrics”. Scientometrics 12(5–6):373–379
Callon M, Courtial JP, Turner WA, Bauin S (1983) From translations to problematic networks: an introduction to co-word analysis. Information (International Social Science Council) 22(2):191–235
Cancino CA, Merigó JM, Coronado FC (2017) A bibliometric analysis of leading universities in innovation research. J Innovations Knowl 2(3):106–124
Cobo MJ, López-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2011) Science mapping software tools: review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol 62(7):1382–1402
Coupe T (2003) Science is golden: academic R&D and university patents. J Technol Transf 28(1):31–46
Courtial J (1994) A coword analysis of scientometrics. Scientometrics 31(3):251–260
Ding Y, Chowdhury GG, Foo S (2001) Bibliometric cartography of information retrieval research by using co-word analysis. Inf Process Manag 37(6):817–842
Fagerberg J, Fosaas M, Sapprasert K (2012) Innovation: exploring the knowledge base. Res Policy 41(7):1132–1153
Ferrero-Ferrero I, Fernández-Izquierdo MÁ, Muñoz-Torres MJ (2012) The impact of the board of directors characteristics on corporateperformance and risk-taking before and during the global financial crisis. Rev Manag Sci 6(3):207–226
Fernández-Gago R, Cabeza-García L, Nieto M (2016) Corporate social responsibility, board of directors, and firm performance: an analysis of their relationships. RMS 10(1):85–104
Ferreira JJ, Fernandes CI, Kraus S (2019) Entrepreneurship research: mapping intellectual structures and research trends. RMS 13(1):181–205
Gamerschlag R, Möller K, Verbeeten F (2011) Determinants of voluntary CSR disclosure: empirical evidence from Germany. RMS 5(2–3):233–262
García-Merino MT, Pereira-do-Carmo ML, Santos-Álvarez MV (2006) 25 years of Technovation: characterisation and evolution of the journal. Technovation 26(12):1303–1316
Garfield E (1999) Journal impact factor: a brief review
Gaviria-Marín M, Merigó JM, Popa S (2018) Twenty years of the Journal of Knowledge Management: a bibliometric analysis. J Knowl Manag 22:1655–1687
Gross PL, Gross EM (1927) College libraries and chemical education. Science 66(1713):385–389
Heck JL, Bremser WG (1986) Six decades of the accounting review: a summary of author and institutional contributors. Account Rev 61(4):735–744
Hirsch JE (2005) An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(46):16569–16572
Hood W, Wilson C (2001) The literature of bibliometrics, scientometrics, and informetrics. Scientometrics 52(2):291–314
Joseph KS (2003) Quality of impact factors of general medical journals. BMJ 326(7383):283
Kessler MM (1963) Bibliographic coupling between scientific papers. Am Doc 14(1):10–25
Kraus S, Rigtering JC, Hughes M, Hosman V (2012) Entrepreneurial orientation and the business performance of SMEs: a quantitative study from the Netherlands. RMS 6(2):161–182
Kraus S, Breier M, Dasí-Rodríguez S (2020) The art of crafting a systematic literature review in entrepreneurship research. Int Entrep Manag J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-020-00635-4
Article Google Scholar
Landström H, Harirchi G, Åström F (2012) Entrepreneurship: Exploring the knowledge base. Res Policy 41(7):1154–1181
Marsh TA, Merton RC (1986) Dividend variability and variance bounds tests for the rationality of stock market prices. Am Econ Rev 76(3):483–498
Marshakova-Shaikevich I (2005) Bibliometric maps of field of science. Inf Process Manag 41(6):1534–1547
Merigó JM, Yang JB (2017) A bibliometric analysis of operations research and management science. Omega 73:37–48
Merigó JM, Mas-Tur A, Roig-Tierno N, Ribeiro-Soriano D (2015) A bibliometric overview of the Journal of Business Research between 1973 and 2014. J Bus Res 68(12):2645–2653
Mitter C, Duller C, Feldbauer-Durstmüller B, Kraus S (2014) Internationalization of family firms: the effect of ownership and governance. RMS 8(1):1–28
Moya S, Prior D (2008) ¿Quién publica en las revistas españolas de contabilidad? Análisis bibliométrico del periodo 1996–2005. Spanish J Finance Accounting/Revista Española de Financiación y Contabilidad 37(138):353–374
Nacke O (1979) Informetrics-definition, status of knowledge and development of principles. Nachrichten Fur Dokumentation 30(6):219–226
Nalimov VV, Mulchenko BM (1969) Scientometrics. Studies of science as a process of information. Science, Moscow
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Podsakoff NP, Bachrach DG (2008) Scholarly influence in the field of management: a bibliometric analysis of the determinants of university and author impact in the management literature in the past quarter century. J Manag 34(4):641–720
Price R (1976) The Guiana maroons: a historical and bibliographical introduction. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, p 12
Pritchard A (1969) Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics. J Doc 25(4):348–349
Reverte C (2016) Corporate social responsibility disclosure and market valuation: evidence from Spanish listed firms. RMS 10(2):411–435
Sageder M, Mitter C, Feldbauer-Durstmüller B (2018) Image and reputation of family firms: a systematic literature review of the state of research. RMS 12(1):335–377
Schwert GW (1993) The Journal of Financial Economics: a retrospective evaluation (1974–1991). J Financ Econ 33(3):369–424
Sengupta JK (1992) A fuzzy systems approach in data envelopment analysis. Comput Math Appl 24(8–9):259–266
Serrano Bedia AM, López Fernández MC, Pérez Pérez M (2013) Análisis de la relación entre flexibilidad en operaciones y performance empresarial mediante técnicas bibliométricas
Small H (1999) Visualizing science by citation mapping. J Am Soc Inf Sci 50(9):799–813
Suriñach Caralt J, Duque JC, Ramos Lobo R, Royuela Mora V (2002) La investigación regional en España: un análisis bibliométrico. Documents de treball (Facultat d’Economia i Empresa. Espai de Recerca en Economia), 2002, E02/89
Thongpapanl NT (2012) The changing landscape of technology and innovation management: an updated ranking of journals in the field. Technovation 32:257–271
Van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84(2):523–538
Van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2014) Visualizing bibliometric networks. In: Ding Y, Rousseu R, Wolfram D (eds) Measuring scholarly impact. Springer, Cham, pp 285–320
Xi JM, Kraus S, Filser M, Kellermanns FW (2015) Mapping the field of family business research: past trends and future directions. Int Entrep Manag J 11(1):113–132
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain
Alicia Mas-Tur
Durham University, Durham, UK
Sascha Kraus
Friedrich-Schiller-University of Jena, Jena, Germany
Mario Brandtner & Wolfgang Kürsten
Karl-Franzens-University Graz, Graz, Austria
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sascha Kraus .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Mas-Tur, A., Kraus, S., Brandtner, M. et al. Advances in management research: a bibliometric overview of the Review of Managerial Science. Rev Manag Sci 14 , 933–958 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-020-00406-z
Download citation
Received : 30 June 2020
Accepted : 01 July 2020
Published : 03 August 2020
Issue Date : October 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-020-00406-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometrics
- Co-citation
- Web of science
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Open Access
This is a Gold Open Access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. Users are allowed to read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of the articles, or use them for any other lawful purpose, without asking prior permission from the publisher or the author. This is in accordance with the Budapest Open Access Initiative (BOAI) definition of open access.
License & Copyright
The Journal of Comprehensive Business Administration Research applies the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license to published articles. Under this license, authors retain ownership of the copyright for their content, but they allow anyone to download, reuse, reprint, modify, distribute and/or copy the content as long as the original authors and source are cited. Appropriate attribution can be provided by simply citing the original article.
Article Processing Charge
All articles published in the Journal of Comprehensive Business Administration Research are published in Gold Open Access. In order to provide free access to readers, and to cover the costs of peer review, copyediting, typesetting, long-term archiving, and journal management, a one-time article processing charge (APC) of 800 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review.
Journal of Comprehensive Business Administration Research does not charge a submission fee which means there are no charges for rejected articles. The length of an article and figures or supplementary data are not subject to additional fees by the journal. Some items (Editorials, Corrections, Addendums, Retractions, Comments, etc.) are published free of charge.
The prices quoted do not include any value-added tax (VAT), goods and services tax (GST), or other sales taxes. Tax may be charged in addition to the price shown where required by law. The amount of tax charged will be calculated at the point of sale and identified separately. If you have a VAT, GST, or other sales tax identification number, you should provide this when requested.
The journal is currently free to the authors, and all Article Processing Charges (APCs) are waived until December 31st, 2024.
Waivers and Discounts List
To help support researchers who are unable to meet some or all of the costs associated with publishing open access, we operate a transparent waiver policy. Automatic 100% waiver for article processing charges on manuscripts where the corresponding author is based in any of the countries listed below.
journal information
Make a submission, announcements, stm membership announcement, bon view publishing formally joined open access scholarly publishing association(oaspa).
Bon View Publishing Pte. Ltd. has recently become a member of Open Access Scholarly Publishing Association(OASPA) . As the member of OASPA, Bon View Publishing is intrinsic to fulfilling the mission of encouraging and enabling open access as the predominant model of communication for scholarly outputs.
- Intelligent System of Estimation of Total Factor Productivity (TFP) and Investment Efficiency in the Economy with External Technology Gaps 253
- Evaluating Financial Support of Governmental Institutions and Private Banks to SMEs and Farmers: Case of Tokat City 154
- Probabilistic Interpretation of Entrepreneurial Opportunity Using the Many-Worlds Model 130
- Blockchain-Based NFT Warranty System: A Software Implementation 127
- Protection of Trademark Rights on E-commerce Platforms: An Updated Outlook 106

eISSN 3029-2697 | Published by Bon View Publishing Pte Ltd.
Member of

Jordan Journal of Business Administration
Subject Area and Category
- Business, Management and Accounting (miscellaneous)
- Management Information Systems
University of Jordan,Deanship of Scientific Research
Publication type
18158633, 23086149
Information
How to publish in this journal
The set of journals have been ranked according to their SJR and divided into four equal groups, four quartiles. Q1 (green) comprises the quarter of the journals with the highest values, Q2 (yellow) the second highest values, Q3 (orange) the third highest values and Q4 (red) the lowest values.
The SJR is a size-independent prestige indicator that ranks journals by their 'average prestige per article'. It is based on the idea that 'all citations are not created equal'. SJR is a measure of scientific influence of journals that accounts for both the number of citations received by a journal and the importance or prestige of the journals where such citations come from It measures the scientific influence of the average article in a journal, it expresses how central to the global scientific discussion an average article of the journal is.
Evolution of the number of published documents. All types of documents are considered, including citable and non citable documents.
This indicator counts the number of citations received by documents from a journal and divides them by the total number of documents published in that journal. The chart shows the evolution of the average number of times documents published in a journal in the past two, three and four years have been cited in the current year. The two years line is equivalent to journal impact factor ™ (Thomson Reuters) metric.
Evolution of the total number of citations and journal's self-citations received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. Journal Self-citation is defined as the number of citation from a journal citing article to articles published by the same journal.
Evolution of the number of total citation per document and external citation per document (i.e. journal self-citations removed) received by a journal's published documents during the three previous years. External citations are calculated by subtracting the number of self-citations from the total number of citations received by the journal’s documents.
International Collaboration accounts for the articles that have been produced by researchers from several countries. The chart shows the ratio of a journal's documents signed by researchers from more than one country; that is including more than one country address.
Not every article in a journal is considered primary research and therefore "citable", this chart shows the ratio of a journal's articles including substantial research (research articles, conference papers and reviews) in three year windows vs. those documents other than research articles, reviews and conference papers.
Ratio of a journal's items, grouped in three years windows, that have been cited at least once vs. those not cited during the following year.
Leave a comment
Name * Required
Email (will not be published) * Required
* Required Cancel
The users of Scimago Journal & Country Rank have the possibility to dialogue through comments linked to a specific journal. The purpose is to have a forum in which general doubts about the processes of publication in the journal, experiences and other issues derived from the publication of papers are resolved. For topics on particular articles, maintain the dialogue through the usual channels with your editor.

Follow us on @ScimagoJR Scimago Lab , Copyright 2007-2024. Data Source: Scopus®

Cookie settings
Cookie Policy
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy
International Journal of Business Administration
Journal Metrics
Google-based Impact Factor (2017): 1.22
h-index (2019): 37
i10-index (2019): 135
h5-index (2019): 16
h5-median (2019): 26
- Other Journals
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
Announcements
- Recruitment
- Editorial Board
- Ethical Guidelines
- Google Scholar Citations

International Journal of Business Administration is devoted to publishing research papers for academics and professors to share advances in business and management theory and practice. Issues that the journal covers include business administration, marketing, management, entrepreneurship, human resources, business innovation, organization theory, accounting, finance and other subjects related with business administration.
This journal is published quarterly ( March, June, September & December ) in both print and online versions. All publications are open access in full text and free to download.
Call for Papers - International Journal of Business Administration
We are calling for submission of papers for the forthcoming issue of Vol. 15, No. 2, June 2024 . The length of 3000-8000 words is preferred. All manuscripts should be prepared in MS-Word format, and submitted online .
If you are interested in submitting a paper to this journal, please refer to the Author Guidelines . For any question you have, please contact the editorial office via: [email protected]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2022: Articles Received: 102; Accepted: 63; Rejected: 46; Published: 36; Retracted: 0
2021: Articles Received: 113; Accepted: 58; Rejected: 39; Published: 46; Retracted: 0
2020: Articles Received: 131; Accepted: 69; Rejected: 51; Published: 43; Retracted: 0
2019: Articles Received: 117; Accepted: 70; Rejected: 32; Published: 45; Retracted: 0
- e-Version First TM (Vol. 15, No. 1, March, 2024)
- Current Issue (Vol. 14, No. 4, December, 2023)
e-Version First TM
e-Version First is a featured way of publishing articles in our journal. It allows PDF version of manuscripts that have been peer reviewed and accepted, to be hosted online prior to their inclusion in a final printed journal. Readers can freely access or cite the article.
Each paper published in International Journal of Business Administration is assigned with a DOI ® number , which appears beneath the author's affiliation in the published paper. Click HERE to know what is DOI (Digital Object Identifier). And click HERE to retrieve Digital Object Identifiers (DOIs) for journal articles, books, and chapters.
Paper Selection and Publication Process
a). Upon receipt of paper submission, the editorial assistant sends an E-mail of confirmation to the corresponding author within 1-3 working days. If you fail to receive this confirmation, your submission/e-mail may be missed. Please contact the editorial assistant in time for that.
b). Peer review. We use a double-blind system for peer review; both reviewers’ and authors’ identities remain anonymous. The paper will be peer-reviewed by three experts; one is an editorial staff and the other two are external reviewers. The review process may take four to ten weeks .
c). Notification of the result of review by E-mail.
d). If the submission is accepted, the authors revise paper and pay Article Processing Charge (300USD).
e). E-journal in PDF is available on the journal’s webpage, free of charge for download.
The publisher and journal have a policy of “Zero Tolerance on the Plagiarism”. We check the plagiarism issue with two methods: reviewer check and plagiarism prevention tool ( iThenticate ).
All submissions will be checked by iThenticate before being sent to reviewers.
Vol 15, No 1 (2024)
Table of contents.
International Journal of Business Administration ISSN 1923-4007(Print) ISSN 1923-4015(Online)
Copyright © Sciedu Press
To make sure that you can receive messages from us, please add the 'Sciedupress.com' domain to your e-mail 'safe list'. If you do not receive e-mail in your 'inbox', check your 'bulk mail' or 'junk mail' folders.
- 9986881177, 7204682715
- [email protected]
About IJBARR
International Journal of Business and Administration Research Review(IJBARR) , is a double blind peer reviewed Quarterly journal that publishes empirical, conceptual and review papers of exceptional quality that contribute to enrich business administration thinking .The objective of the Journal is to disseminate knowledge, which ensures good practice of professional management and its focal point is on research and reflections relevant to academicians and practicing managers/Administrators for sustainable business and social changes.
Scope & Area Coverage
IJBARR covers diverse areas of Management such as Marketing, International Business, Human Resource Management (HRM), Office Administration/Management, Operations Research, Operations Management, Organizational Behavior, and Theory, Banking & Finance, Marketing, Operation &SupplyChain Management, Management information system, Entrepreneurship, Strategic Management, Organizational Development, Production/Operations, Purchasing/Materials Management, Policy Making, Technology/Innovation, Tourism and Hospitality, Leisure, Transportation/Physical Distribution, Rural/Agricultural Management, Knowledge Management, Business Ethics, Corporate Governance, Corporate Social Responsibility. Anthropology, Sociology, Social Work, Social Welfare, Economics, Political Science, Psychology, Development Studies, Population Studies, Corporate Governance, Cross-Cultural Studies, Women Studies, Ethics, etc. Authors are invited to submit their research papers in the area of business/commerce and administration. The research paper will be published upon successful review and all issues of the journal are available for open online access.
- Editorial Board
- Archive Issues
- Copyright Form
- Publication Ethics
- Special Issue
- Track Print Copy

COMMENTS
Journal of Business Administration Research (JBAR) is a double-blind peer-reviewed journal which publishes scholarly work on business administration. It is published by Sciedu Press semiannually. The journal aims to encourage information exchange of relevant academic research. It covers a wide range of fields including accounting, finance ...
Journal name has been changed. 2021-11-18. Show all announcements ... ISSN: 2630-5194 (Online) Journal of Business Administration Research has been renamed Journal of Sustainable Business and Economics, from Volume 5 (2022).
Journal of Business Administration Research is an open-access, peer-reviewed journal specializing in business administration. The journal is aimed at providing innovative insights in the field of business administration. The scope of the Journal of Business Administration Research includes: Production/operations management; Global business
The Journal of Business Research aims to publish research that is rigorous, relevant, and potentially impactful. Recognizing the intricate relationships between the many areas of business activity, JBR examines a wide variety of business decision contexts, processes and activities, developing insights that are meaningful for theory, practice, and/or society at large.
The journal aims to foster debates and discussions on a wide array of topics and promote excellence in research by publishing high-quality, peer-reviewed, original research articles, case studies, and reviews that contribute to the advancement of knowledge in business administration. Research into innovative approaches and strategies within the ...
Journal of Business Administration Research. Reviewer Acknowledgements for Journal of Business Administration Research, Vol. 11, No. 2, 2022. [...] The COVID-19 pandemic has slowed down the ...
Journal of Business Administration Research. Published by Bilingual Publishing Group. Online ISSN: 2630-5194. Articles. Impacts of COVID-19 on Informal Workers and National Policies in China ...
A business journal that bridges the gap between management research and practice, evaluating and reporting on new research to help readers identify and understand significant trends in management. Full text from 1988-present.
The American Journal of Economics and Business Administration is a peer-reviewed journal that publishes original, innovative and novel work in various areas representing the intersection of economics as a scientific discipline and the professional practice of business management. This journal is a peer-reviewed, interdisciplinary journal ...
Journal of Business Administration Research; Previous studies on human resource management have emphasized the relationship between high performance work systems (HPWSs) and organizational performance in strategic human resource management. The extant literature on the intermediate linkage between HPWSs and performance has yield only limited ...
1-71 Reviewer Acknowledgements for Journal of Business Administration Research, Vol. 12, No. 1 by Grace Lee 25-38 The Relationship between Perceived Organizational Justice, Supervisor Support, and Turnover Intention by Abdallah M. Elamin & Ahmed Zain Elabdin Ahmed & Diaeldin Osman & Akash Dania
Business & Management. As an independent publisher, Sage Business & Management has been at the forefront of research and scholarship, marked by our influential journals, textbooks, and digital resources that unite theory and practice. We are committed to informing researchers and educating students to build a thriving global society and make a ...
The Review of Managerial Science (RMS) is a leading international journal that publishes major advances related to business administration and management. The journal was launched in April 2007 and publishes eight issues per year (from 2021 onwards). The scope of RMS encompasses, but is not limited to, the functional areas of operations (such as production, operations management, and marketing ...
Journal Metrics. Google Based Impact Factor: 0.8. h-index (January 2022): 21. i10-index (January 2022): 36. h5-index (January 2022): N/A. ... Journal of Business Administration Research (Submission E-mail: [email protected]) ISSN 1927-9507 (Print) ISSN 1927-9515 (Online) ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review ...
Journal of Business Administration and Management Sciences Research (JBAMSR- ISSN: 2315-8727) is an open access, peer reviewed journal that provides rapid monthly publication of articles in all fields of Business Administration and Management Sciences. The Journal welcomes the submission of manuscripts that meet the general criteria of impact and scientific excellence.
Outstanding Paper Entrepreneurial competencies and SMEs' growth: th... Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration (APJBA) is an essential forum for both established and early-career researchers in all aspects of management and business in the Asia-Pacific region. ISSN: 1757-4323. eISSN: 1757-4323.
The following article types are included in the Journal of Comprehensive Business Administration Research: Research Article: Report of original research findings and data. Review: Critically examines the body of research on a particular subject and gives insights/informed opinions on the direction and future of the research field.
Article Processing Charge. All articles published in the Journal of Comprehensive Business Administration Research are published in Gold Open Access. In order to provide free access to readers, and to cover the costs of peer review, copyediting, typesetting, long-term archiving, and journal management, a one-time article processing charge (APC ...
The Jordan Journal of Business Administration (JJBA) is an international, double-blind peer-reviewed academic journal. The JJBA publishes interdisciplinary research which informs a range of business-related fields. The JJBA comes as a result of collaborative efforts between the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Deanship of ...
International Journal of Business Administration is devoted to publishing research papers for academics and professors to share advances in business and management theory and practice. Issues that the journal covers include business administration, marketing, management, entrepreneurship, human resources, business innovation, organization theory, accounting, finance and other subjects related ...
International Journal of Business and Administration Research Review(IJBARR), is a double blind peer reviewed Quarterly journal that publishes empirical, conceptual and review papers of exceptional quality that contribute to enrich business administration thinking .The objective of the Journal is to disseminate knowledge, which ensures good practice of professional management and its focal ...