
Essays About Literature: Top 6 Examples and 8 Prompts
Society and culture are formed around literature. If you are writing essays about literature, you can use the essay examples and prompts featured in our guide.
It has been said that language holds the key to all human activities, and literature is the expression of language. It teaches new words and phrases, allows us to better our communication skills, and helps us learn more about ourselves.
Whether you are reading poems or novels, we often see parts of ourselves in the characters and themes presented by the authors. Literature gives us ideas and helps us determine what to say, while language gives form and structure to our ideas, helping us convey them.
6 Helpful Essay Examples
1. importance of literature by william anderson, 2. philippine literature by jean hodges, 3. african literature by morris marshall.
- 4. Nine Questions From Children’s Literature That Every Person Should Answer by Shaunta Grimes
5. Exploring tyranny and power in Macbeth by Tom Davey
6. guide to the classics: homer’s odyssey by jo adetunji, 1. the importance of literature, 2. comparing and contrasting two works of literature , 3. the use of literary devices, 4. popular adaptations of literature, 5. gender roles in literature, 6. analysis of your chosen literary work, 7. fiction vs. non-fiction, 8. literature as an art form.
“Life before literature was practical and predictable, but in the present-day, literature has expanded into countless libraries and into the minds of many as the gateway for comprehension and curiosity of the human mind and the world around them. Literature is of great importance and is studied upon as it provides the ability to connect human relationships and define what is right and what is wrong.”
Anderson writes about why an understanding of literature is crucial. It allows us to see different perspectives of people from different periods, countries, and cultures: we are given the ability to see the world from an entirely new lens. As a result, we obtain a better judgment of situations. In a world where anything can happen, literature gives us the key to enacting change for ourselves and others. You might also be interested in these essays about Beowulf .
“So successful were the efforts of colonists to blot out the memory of the country’s largely oral past that present-day Filipino writers, artists and journalists are trying to correct this inequity by recognizing the country’s wealth of ethnic traditions and disseminating them in schools through mass media. The rise of nationalistic pride in the 1960s and 1970s also helped bring about this change of attitude among a new breed of Filipinos concerned about the “Filipino identity.””
In her essay, Hodges writes about the history of Philippine literature. Unfortunately, much of Philippine literary history has been obscured by Spanish colonization, as the written works of the Spanish largely replaced the oral tradition of the native Filipinos. A heightened sense of nationalism has recently led to a resurgence in Filipino tradition, including ancient Philippine literature.
“In fact, the common denominator of the cultures of the African continent is undoubtedly the oral tradition. Writing on black Africa started in the middle Ages with the introduction of the Arabic language and later, in the nineteenth century with introduction of the Latin alphabet. Since 1934, with the birth of the “Negritude.” African authors began to write in French or in English.”
Marshall explores the history of African literature, particularly the languages it was written over time. It was initially written in Arabic and native languages; however, with the “Negritude” movement, writers began composing their works in French or English. This movement allowed African writers to spread their work and gain notoriety. Marshall gives examples of African literature, shedding light on their lyrical content.
4. Nine Questions From Children’s Literature That Every Person Should Answer by Shaunta Grimes
“ They asked me questions — questions about who I am, what I value, and where I’m headed — and pushed me to think about the answers. At some point in our lives, we decide we know everything we need to know. We stop asking questions. To remember what’s important, it sometimes helps to return to that place of childlike curiosity and wonder.”
Grimes’ essay is a testament to how much we can learn from literature, even as simple as children’s stories. She explains how different works of children’s literature, such as Charlotte’s Web and Little Women, can inspire us, help us maximize our imagination, and remind us of the fleeting nature of life. Most importantly, however, they remind us that the future is uncertain, and maximizing it is up to us.
“This is a world where the moral bar has been lowered; a world which ‘sinks beneath the yoke’. In the Macbeths, we see just how terribly the human soul can be corrupted. However, this struggle is played out within other characters too. Perhaps we’re left wondering: in such a dog-eat-dog world, how would we fare?”
The corruption that power can lead to is genuine; Davey explains how this theme is present in Shakespeare’s Macbeth . Even after being honored, Macbeth still wishes to be king and commits heinous acts of violence to achieve his goals. Violence is prevalent throughout the play, but Macbeth and Lady Macbeth exemplify the vicious cycle of bloodshed through their ambition and power.
“Polyphemus is blinded but survives the attack and curses the voyage home of the Ithacans. All of Odysseus’s men are eventually killed, and he alone survives his return home, mostly because of his versatility and cleverness. There is a strong element of the trickster figure about Homer’s Odysseus.”
Adetunji also exposes a notable work of literature, in this case, Homer’s Odyssey . She goes over the epic poem and its historical context and discusses Odysseus’ most important traits: cleverness and courage. As the story progresses, he displays great courage and bravery in his exploits, using his cunning and wit to outsmart his foes. Finally, Adetunji references modern interpretations of the Odyssey in film, literature, and other media.
8 Prompts for Essays About Literature
In your essay, write about the importance of literature; explain why we need to study literature and how it can help us in the future. Then, give examples of literary works that teach important moral lessons as evidence.
For your essay, choose two works of literature with similar themes. Then, discuss their similarities and differences in plot, theme, and characters. For example, these themes could include death, grief, love and hate, or relationships. You can also discuss which of the two pieces of literature presents your chosen theme better.

Writers use literary devices to enhance their literary works and emphasize important points. Literary devices include personification, similes, metaphors, and more. You can write about the effectiveness of literary devices and the reasoning behind their usage. Research and give examples of instances where authors use literary devices effectively to enhance their message.
Literature has been adapted into cinema, television, and other media time and again, with series such as Lord of the Rings and Harry Potter turning into blockbuster franchises. Explore how these adaptations diverge from their source material yet retain the key themes the writer composed the work with in mind. If this seems confusing, research first and read some essay examples.
Literature reflects the ideas of the period it is from; for example, ancient Greek literature, such as Antigone, depicts the ideal woman as largely obedient and subservient, to an extent. For your essay, you can write about how gender roles have evolved in literature throughout the years, specifically about women. Be sure to give examples to support your points.
Choose a work of literature that interests you and analyze it in your essay. You can use your favorite novel, book, or screenplay, explain the key themes and characters and summarize the plot. Analyze the key messages in your chosen piece of literature, and discuss how the themes are enhanced through the author’s writing techniques.

Literature can be divided into two categories: fiction, from the writer’s imagination, and non-fiction, written about actual events. Explore their similarities and differences, and give your opinion on which is better. For a strong argument, provide ample supporting details and cite credible sources.
Literature is an art form that uses language, so do you believe it is more effective in conveying its message? Write about how literature compares to other art forms such as painting and sculpture; state your argument and defend it adequately.
Tip: If writing an essay sounds like a lot of work, simplify it. Write a simple 5 paragraph essay instead.
For help picking your next essay topic, check out the best essay topics about social media .

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
- Science & Math
- Sociology & Philosophy
- Law & Politics
- Importance of Literature: Essay
Literature is the foundation of life . It places an emphasis on many topics from human tragedies to tales of the ever-popular search for love. While it is physically written in words, these words come alive in the imagination of the mind, and its ability to comprehend the complexity or simplicity of the text.
Literature enables people to see through the lenses of others, and sometimes even inanimate objects; therefore, it becomes a looking glass into the world as others view it. It is a journey that is inscribed in pages and powered by the imagination of the reader.
Ultimately, literature has provided a gateway to teach the reader about life experiences from even the saddest stories to the most joyful ones that will touch their hearts.
From a very young age, many are exposed to literature in the most stripped-down form: picture books and simple texts that are mainly for the sole purpose of teaching the alphabet etc. Although these are not nearly as complex as an 800-page sci-fi novel, it is the first step that many take towards the literary world.
Progressively, as people grow older, they explore other genres of books, ones that propel them towards curiosity of the subject, and the overall book.
Reading and being given the keys to the literature world prepares individuals from an early age to discover the true importance of literature: being able to comprehend and understand situations from many perspectives.
Physically speaking, it is impossible to be someone else. It is impossible to switch bodies with another human being, and it is impossible to completely understand the complexity of their world. Literature, as an alternative, is the closest thing the world has to being able to understand another person whole-heartedly.
For stance, a novel about a treacherous war, written from the perspective of a soldier, allows the reader to envision their memories, their pain, and their emotions without actually being that person. Consequently, literature can act as a time machine, enabling individuals to go into a specific time period of the story, into the mind and soul of the protagonist.
With the ability to see the world with a pair of fresh eyes, it triggers the reader to reflect upon their own lives. Reading material that is relatable to the reader may teach them morals and encourage them to practice good judgment.
This can be proven through public school systems, where the books that are emphasized the most tend to have a moral-teaching purpose behind the story.
An example would be William Shakespeare’s stories, where each one is meant to be reflective of human nature – both the good and bad.
Consequently, this can promote better judgment of situations , so the reader does not find themselves in the same circumstances as perhaps those in the fiction world. Henceforth, literature is proven to not only be reflective of life, but it can also be used as a guide for the reader to follow and practice good judgment.
The world today is ever-changing. Never before has life been so chaotic and challenging for all. Life before literature was practical and predictable, but in the present-day, literature has expanded into countless libraries and into the minds of many as the gateway for comprehension and curiosity of the human mind and the world around them.
Literature is of great importance and is studied upon as it provides the ability to connect human relationships and define what is right and what is wrong. Therefore, words are alive more than ever before.
Related Posts
- What are Archetypes in Literature
- Literary Essay: Peer Editing Guidelines
- Tips for Essay Writing
- Dystopian Literature Essay: The Hunger Games
- Essay Analysis Structure
Author: William Anderson (Schoolworkhelper Editorial Team)
Tutor and Freelance Writer. Science Teacher and Lover of Essays. Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2024 | Creative Commons 4.0
17 Comments
Indeed literature is the foundation of life, people should know and appreciate these kind of things
its very useful info thanks
very helpful…..tnx
Hi, thanks!
First year student who wants to know about literature and how I can develop interest in reading novels.
Fantastic piece!
wonderful work
Literature is anything that is artistically presented through writtings or orally.
you may have tangible wealth untold, caskets of jewels and coffers of gold, richer than i you could never be, i know someone who told stories to me.
there’s a great saying that “the universe isn’t made up of at atoms, its made of stories” i hope none will argue this point, because this is the truest thing i have ever heard and its beautiful…….
I have learnt alot thanks to the topic literature.Literature is everything.It answers the questions why?,how? and what?.To me its my best and I will always treasure and embress literature to death.
I agree with the writer when says that Literature is the foundation of life. For me, reading is the most wonderful experience in life. It allows me to travel to other places and other times. I think that also has learnt me to emphathize with others, and see the world with other´s eyes and from their perspectives. I really like to read.
This is the first time i am presenting on a literature and i am surprised by the amount of people who are interested on the same subject. I regret my absence because i have missed much marvelous thing in that field.In fact literature is what is needed by the whole world,it brings the people of different culture together and by doing so it breaks the imposed barriers that divided people.My address now goes to the people of nowadays who prefer other source of entertainment like TV,i am not saying that TV is bad but reading is better of.COME BACK TO IT THEN.
literature is a mirror; a true reflection of our nature. it helps us see ourselves in a third persons point of view of first persons point of view. it instills virtues and condones vices. literature forms a great portion of fun and entertainment through plays, comedies and novels. it also educates individuals on life’s basic but delicate and sacred issues like love and death. it informs us of the many happenings and events that we would never have otherwise known about. literature also forms a source of livelihood to thousands of people, starting from writers,characters in plays, editors, printers,distributors and business people who deal with printed materials. literature is us and without it, we are void.
I believe that life without Literature would be unacceptable , with it i respect myself and loved human life . Next week i am going to make presentation about Literature, so i benefited from this essay.
Thanks a lot
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post comment

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.2: The Purpose of Literature
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 86405
What is literature for?
One of the primary goals of this course is to develop an understanding of the importance of literature as a vital source of cultural knowledge in everyday life. Literature is often viewed as a collection of made-up stories, designed to entertain us, to amuse us, or to simply provide us with an escape from the “real” world.
Although literature does serve these purposes, in this course, one of the ways that we will answer the question “What is literature for?” is by showing that literature can provide us with valuable insights about the world in which we live and about our relationships to one another, as well as to ourselves . In this sense, literature may be considered a vehicle for the exploration and discovery of our world and the culture in which we live. It allows us to explore alternative realities, to view things from the perspective of someone completely different to us, and to reflect upon our own intellectual and emotional responses to the complex challenges of everyday life.
By studying literature, it is possible to develop an in-depth understanding of the ways that we use language to make sense of the world. According to the literary scholars, Andrew Bennett and Nicholas Royle, “Stories are everywhere,” and therefore, “Not only do we tell stories, but stories tell us: if stories are everywhere, we are also in stories.” From the moment each one of us is born, we are surrounded by stories — oftentimes these stories are told to us by parents, family members, or our community. Some of these stories are ones that we read for ourselves, and still others are stories that we tell to ourselves about who we are, what we desire, what we fear, and what we value. Not all of these stories are typically considered “literary” ones, but in this course, we will develop a more detailed understanding of how studying literature can enrich our knowledge about ourselves and the world in which we live.
If literature helps us to make sense of, or better yet question, the world and our place in it, then how does it do this? It may seem strange to suggest that literature performs a certain kind of work. However, when we think of other subjects, such as math or science, it is generally understood that the skills obtained from mastering these subjects equips us to solve practical problems. Can the same be said of literature?
To understand the kind of work that literature can do, it is important to understand the kind of knowledge that it provides. This is a very complex and widely debated question among literary scholars. But one way of understanding the kind of knowledge that can be gained from literature is by thinking about how we use language to make sense of the world each day. (1)
What does literature do?
Every day we use metaphors to describe the world. What is a metaphor? According to A Dictionary of Literary Terms and Literary Theory , a metaphor is “a figure of speech in which one thing is described in terms of another.” You have probably heard the expressions, “Time is money” or “The administration is a train wreck.” These expressions are metaphors because they describe one less clearly defined idea, like time or the administration of an institution, in relation to a concept whose characteristics are easier to imagine.
A metaphor forms an implied comparison between two terms whereas a simile makes an explicit comparison between two terms using the words like or as — for example, in his poem, “A Red, Red Rose,” the Scottish poet Robert Burns famously announces, “O my Luve is like a red, red rose/That’s newly sprung in June.” The association of romantic love with red roses is so firmly established in our culture that one need only look at the imagery associated with Valentine’s Day to find evidence of its persistence. The knowledge we gain from literature can have a profound influence on our patterns of thought and behavior.
In their book Metaphors We Live By , George Lakoff and Mark Johnson outline a number of metaphors used so often in everyday conversation that we have forgotten that they are even metaphors, for example, the understanding that “Happy is up” or that “Sad is down.” Likewise, we might think “Darkness is death” or that “Life is light.” Here we can see that metaphors help us to recognize and make sense of a wide range of very complex ideas and even emotions. Metaphors are powerful, and as a result they can even be problematic.
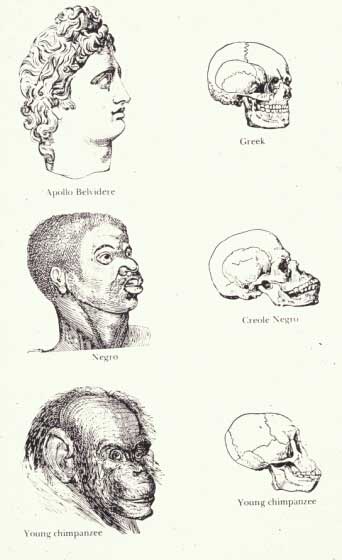
The author Toni Morrison has argued that throughout history the language used by many white authors to describe black characters often expresses ideas of fear or dread — the color black and black people themselves come to represent feelings of loathing, mystery, or dread. Likewise, James Baldwin has observed that whiteness is often presented as a metaphor for safety. (1)
Figure 1 is taken from a book published in 1857 entitled Indigenous Races of the Earth . It demonstrates how classical ideas of beauty and sophistication were associated with an idealized version of white European society whereas people of African descent were considered to be more closely related to apes. One of Morrison’s tasks as a writer is to rewrite the racist literary language that has been used to describe people of color and their lives.
By being able to identify and question the metaphors that we live by, it is possible to gain a better understanding of how we view our world, as well as our relationship to others and ourselves. It is important to critically examine these metaphors because they have very real consequences for our lives. (1)
- Authored by : Florida State College at Jacksonville. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Race and Skulls. Authored by : Nott, Josiah, and George R. Giddon. Provided by : Wikimedia Commons. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Races_and_skulls.png . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
beginner's guide to literary analysis
Understanding literature & how to write literary analysis.
Literary analysis is the foundation of every college and high school English class. Once you can comprehend written work and respond to it, the next step is to learn how to think critically and complexly about a work of literature in order to analyze its elements and establish ideas about its meaning.
If that sounds daunting, it shouldn’t. Literary analysis is really just a way of thinking creatively about what you read. The practice takes you beyond the storyline and into the motives behind it.
While an author might have had a specific intention when they wrote their book, there’s still no right or wrong way to analyze a literary text—just your way. You can use literary theories, which act as “lenses” through which you can view a text. Or you can use your own creativity and critical thinking to identify a literary device or pattern in a text and weave that insight into your own argument about the text’s underlying meaning.
Now, if that sounds fun, it should , because it is. Here, we’ll lay the groundwork for performing literary analysis, including when writing analytical essays, to help you read books like a critic.
What Is Literary Analysis?
As the name suggests, literary analysis is an analysis of a work, whether that’s a novel, play, short story, or poem. Any analysis requires breaking the content into its component parts and then examining how those parts operate independently and as a whole. In literary analysis, those parts can be different devices and elements—such as plot, setting, themes, symbols, etcetera—as well as elements of style, like point of view or tone.
When performing analysis, you consider some of these different elements of the text and then form an argument for why the author chose to use them. You can do so while reading and during class discussion, but it’s particularly important when writing essays.
Literary analysis is notably distinct from summary. When you write a summary , you efficiently describe the work’s main ideas or plot points in order to establish an overview of the work. While you might use elements of summary when writing analysis, you should do so minimally. You can reference a plot line to make a point, but it should be done so quickly so you can focus on why that plot line matters . In summary (see what we did there?), a summary focuses on the “ what ” of a text, while analysis turns attention to the “ how ” and “ why .”
While literary analysis can be broad, covering themes across an entire work, it can also be very specific, and sometimes the best analysis is just that. Literary critics have written thousands of words about the meaning of an author’s single word choice; while you might not want to be quite that particular, there’s a lot to be said for digging deep in literary analysis, rather than wide.
Although you’re forming your own argument about the work, it’s not your opinion . You should avoid passing judgment on the piece and instead objectively consider what the author intended, how they went about executing it, and whether or not they were successful in doing so. Literary criticism is similar to literary analysis, but it is different in that it does pass judgement on the work. Criticism can also consider literature more broadly, without focusing on a singular work.
Once you understand what constitutes (and doesn’t constitute) literary analysis, it’s easy to identify it. Here are some examples of literary analysis and its oft-confused counterparts:
Summary: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” the narrator visits his friend Roderick Usher and witnesses his sister escape a horrible fate.
Opinion: In “The Fall of the House of Usher,” Poe uses his great Gothic writing to establish a sense of spookiness that is enjoyable to read.
Literary Analysis: “Throughout ‘The Fall of the House of Usher,’ Poe foreshadows the fate of Madeline by creating a sense of claustrophobia for the reader through symbols, such as in the narrator’s inability to leave and the labyrinthine nature of the house.
In summary, literary analysis is:
- Breaking a work into its components
- Identifying what those components are and how they work in the text
- Developing an understanding of how they work together to achieve a goal
- Not an opinion, but subjective
- Not a summary, though summary can be used in passing
- Best when it deeply, rather than broadly, analyzes a literary element
Literary Analysis and Other Works
As discussed above, literary analysis is often performed upon a single work—but it doesn’t have to be. It can also be performed across works to consider the interplay of two or more texts. Regardless of whether or not the works were written about the same thing, or even within the same time period, they can have an influence on one another or a connection that’s worth exploring. And reading two or more texts side by side can help you to develop insights through comparison and contrast.
For example, Paradise Lost is an epic poem written in the 17th century, based largely on biblical narratives written some 700 years before and which later influenced 19th century poet John Keats. The interplay of works can be obvious, as here, or entirely the inspiration of the analyst. As an example of the latter, you could compare and contrast the writing styles of Ralph Waldo Emerson and Edgar Allan Poe who, while contemporaries in terms of time, were vastly different in their content.
Additionally, literary analysis can be performed between a work and its context. Authors are often speaking to the larger context of their times, be that social, political, religious, economic, or artistic. A valid and interesting form is to compare the author’s context to the work, which is done by identifying and analyzing elements that are used to make an argument about the writer’s time or experience.
For example, you could write an essay about how Hemingway’s struggles with mental health and paranoia influenced his later work, or how his involvement in the Spanish Civil War influenced his early work. One approach focuses more on his personal experience, while the other turns to the context of his times—both are valid.
Why Does Literary Analysis Matter?
Sometimes an author wrote a work of literature strictly for entertainment’s sake, but more often than not, they meant something more. Whether that was a missive on world peace, commentary about femininity, or an allusion to their experience as an only child, the author probably wrote their work for a reason, and understanding that reason—or the many reasons—can actually make reading a lot more meaningful.
Performing literary analysis as a form of study unquestionably makes you a better reader. It’s also likely that it will improve other skills, too, like critical thinking, creativity, debate, and reasoning.
At its grandest and most idealistic, literary analysis even has the ability to make the world a better place. By reading and analyzing works of literature, you are able to more fully comprehend the perspectives of others. Cumulatively, you’ll broaden your own perspectives and contribute more effectively to the things that matter to you.
Literary Terms to Know for Literary Analysis
There are hundreds of literary devices you could consider during your literary analysis, but there are some key tools most writers utilize to achieve their purpose—and therefore you need to know in order to understand that purpose. These common devices include:
- Characters: The people (or entities) who play roles in the work. The protagonist is the main character in the work.
- Conflict: The conflict is the driving force behind the plot, the event that causes action in the narrative, usually on the part of the protagonist
- Context : The broader circumstances surrounding the work political and social climate in which it was written or the experience of the author. It can also refer to internal context, and the details presented by the narrator
- Diction : The word choice used by the narrator or characters
- Genre: A category of literature characterized by agreed upon similarities in the works, such as subject matter and tone
- Imagery : The descriptive or figurative language used to paint a picture in the reader’s mind so they can picture the story’s plot, characters, and setting
- Metaphor: A figure of speech that uses comparison between two unlike objects for dramatic or poetic effect
- Narrator: The person who tells the story. Sometimes they are a character within the story, but sometimes they are omniscient and removed from the plot.
- Plot : The storyline of the work
- Point of view: The perspective taken by the narrator, which skews the perspective of the reader
- Setting : The time and place in which the story takes place. This can include elements like the time period, weather, time of year or day, and social or economic conditions
- Symbol : An object, person, or place that represents an abstract idea that is greater than its literal meaning
- Syntax : The structure of a sentence, either narration or dialogue, and the tone it implies
- Theme : A recurring subject or message within the work, often commentary on larger societal or cultural ideas
- Tone : The feeling, attitude, or mood the text presents
How to Perform Literary Analysis
Step 1: read the text thoroughly.
Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
It’s also important that you don’t skim or speed read. While those are helpful skills, they don’t apply to literary analysis—or at least not this stage.
Step 2: Take Notes as You Read
As you read the work, take notes about different literary elements and devices that stand out to you. Whether you highlight or underline in text, use sticky note tabs to mark pages and passages, or handwrite your thoughts in a notebook, you should capture your thoughts and the parts of the text to which they correspond. This—the act of noticing things about a literary work—is literary analysis.
Step 3: Notice Patterns
As you read the work, you’ll begin to notice patterns in the way the author deploys language, themes, and symbols to build their plot and characters. As you read and these patterns take shape, begin to consider what they could mean and how they might fit together.
As you identify these patterns, as well as other elements that catch your interest, be sure to record them in your notes or text. Some examples include:
- Circle or underline words or terms that you notice the author uses frequently, whether those are nouns (like “eyes” or “road”) or adjectives (like “yellow” or “lush”).
- Highlight phrases that give you the same kind of feeling. For example, if the narrator describes an “overcast sky,” a “dreary morning,” and a “dark, quiet room,” the words aren’t the same, but the feeling they impart and setting they develop are similar.
- Underline quotes or prose that define a character’s personality or their role in the text.
- Use sticky tabs to color code different elements of the text, such as specific settings or a shift in the point of view.
By noting these patterns, comprehensive symbols, metaphors, and ideas will begin to come into focus.
Step 4: Consider the Work as a Whole, and Ask Questions
This is a step that you can do either as you read, or after you finish the text. The point is to begin to identify the aspects of the work that most interest you, and you could therefore analyze in writing or discussion.
Questions you could ask yourself include:
- What aspects of the text do I not understand?
- What parts of the narrative or writing struck me most?
- What patterns did I notice?
- What did the author accomplish really well?
- What did I find lacking?
- Did I notice any contradictions or anything that felt out of place?
- What was the purpose of the minor characters?
- What tone did the author choose, and why?
The answers to these and more questions will lead you to your arguments about the text.
Step 5: Return to Your Notes and the Text for Evidence
As you identify the argument you want to make (especially if you’re preparing for an essay), return to your notes to see if you already have supporting evidence for your argument. That’s why it’s so important to take notes or mark passages as you read—you’ll thank yourself later!
If you’re preparing to write an essay, you’ll use these passages and ideas to bolster your argument—aka, your thesis. There will likely be multiple different passages you can use to strengthen multiple different aspects of your argument. Just be sure to cite the text correctly!
If you’re preparing for class, your notes will also be invaluable. When your teacher or professor leads the conversation in the direction of your ideas or arguments, you’ll be able to not only proffer that idea but back it up with textual evidence. That’s an A+ in class participation.
Step 6: Connect These Ideas Across the Narrative
Whether you’re in class or writing an essay, literary analysis isn’t complete until you’ve considered the way these ideas interact and contribute to the work as a whole. You can find and present evidence, but you still have to explain how those elements work together and make up your argument.
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay
When conducting literary analysis while reading a text or discussing it in class, you can pivot easily from one argument to another (or even switch sides if a classmate or teacher makes a compelling enough argument).
But when writing literary analysis, your objective is to propose a specific, arguable thesis and convincingly defend it. In order to do so, you need to fortify your argument with evidence from the text (and perhaps secondary sources) and an authoritative tone.
A successful literary analysis essay depends equally on a thoughtful thesis, supportive analysis, and presenting these elements masterfully. We’ll review how to accomplish these objectives below.
Step 1: Read the Text. Maybe Read It Again.
Constructing an astute analytical essay requires a thorough knowledge of the text. As you read, be sure to note any passages, quotes, or ideas that stand out. These could serve as the future foundation of your thesis statement. Noting these sections now will help you when you need to gather evidence.
The more familiar you become with the text, the better (and easier!) your essay will be. Familiarity with the text allows you to speak (or in this case, write) to it confidently. If you only skim the book, your lack of rich understanding will be evident in your essay. Alternatively, if you read the text closely—especially if you read it more than once, or at least carefully revisit important passages—your own writing will be filled with insight that goes beyond a basic understanding of the storyline.
Step 2: Brainstorm Potential Topics
Because you took detailed notes while reading the text, you should have a list of potential topics at the ready. Take time to review your notes, highlighting any ideas or questions you had that feel interesting. You should also return to the text and look for any passages that stand out to you.
When considering potential topics, you should prioritize ideas that you find interesting. It won’t only make the whole process of writing an essay more fun, your enthusiasm for the topic will probably improve the quality of your argument, and maybe even your writing. Just like it’s obvious when a topic interests you in a conversation, it’s obvious when a topic interests the writer of an essay (and even more obvious when it doesn’t).
Your topic ideas should also be specific, unique, and arguable. A good way to think of topics is that they’re the answer to fairly specific questions. As you begin to brainstorm, first think of questions you have about the text. Questions might focus on the plot, such as: Why did the author choose to deviate from the projected storyline? Or why did a character’s role in the narrative shift? Questions might also consider the use of a literary device, such as: Why does the narrator frequently repeat a phrase or comment on a symbol? Or why did the author choose to switch points of view each chapter?
Once you have a thesis question , you can begin brainstorming answers—aka, potential thesis statements . At this point, your answers can be fairly broad. Once you land on a question-statement combination that feels right, you’ll then look for evidence in the text that supports your answer (and helps you define and narrow your thesis statement).
For example, after reading “ The Fall of the House of Usher ,” you might be wondering, Why are Roderick and Madeline twins?, Or even: Why does their relationship feel so creepy?” Maybe you noticed (and noted) that the narrator was surprised to find out they were twins, or perhaps you found that the narrator’s tone tended to shift and become more anxious when discussing the interactions of the twins.
Once you come up with your thesis question, you can identify a broad answer, which will become the basis for your thesis statement. In response to the questions above, your answer might be, “Poe emphasizes the close relationship of Roderick and Madeline to foreshadow that their deaths will be close, too.”
Step 3: Gather Evidence
Once you have your topic (or you’ve narrowed it down to two or three), return to the text (yes, again) to see what evidence you can find to support it. If you’re thinking of writing about the relationship between Roderick and Madeline in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” look for instances where they engaged in the text.
This is when your knowledge of literary devices comes in clutch. Carefully study the language around each event in the text that might be relevant to your topic. How does Poe’s diction or syntax change during the interactions of the siblings? How does the setting reflect or contribute to their relationship? What imagery or symbols appear when Roderick and Madeline are together?
By finding and studying evidence within the text, you’ll strengthen your topic argument—or, just as valuably, discount the topics that aren’t strong enough for analysis.
Step 4: Consider Secondary Sources
In addition to returning to the literary work you’re studying for evidence, you can also consider secondary sources that reference or speak to the work. These can be articles from journals you find on JSTOR, books that consider the work or its context, or articles your teacher shared in class.
While you can use these secondary sources to further support your idea, you should not overuse them. Make sure your topic remains entirely differentiated from that presented in the source.
Step 5: Write a Working Thesis Statement
Once you’ve gathered evidence and narrowed down your topic, you’re ready to refine that topic into a thesis statement. As you continue to outline and write your paper, this thesis statement will likely change slightly, but this initial draft will serve as the foundation of your essay. It’s like your north star: Everything you write in your essay is leading you back to your thesis.
Writing a great thesis statement requires some real finesse. A successful thesis statement is:
- Debatable : You shouldn’t simply summarize or make an obvious statement about the work. Instead, your thesis statement should take a stand on an issue or make a claim that is open to argument. You’ll spend your essay debating—and proving—your argument.
- Demonstrable : You need to be able to prove, through evidence, that your thesis statement is true. That means you have to have passages from the text and correlative analysis ready to convince the reader that you’re right.
- Specific : In most cases, successfully addressing a theme that encompasses a work in its entirety would require a book-length essay. Instead, identify a thesis statement that addresses specific elements of the work, such as a relationship between characters, a repeating symbol, a key setting, or even something really specific like the speaking style of a character.
Example: By depicting the relationship between Roderick and Madeline to be stifling and almost otherworldly in its closeness, Poe foreshadows both Madeline’s fate and Roderick’s inability to choose a different fate for himself.
Step 6: Write an Outline
You have your thesis, you have your evidence—but how do you put them together? A great thesis statement (and therefore a great essay) will have multiple arguments supporting it, presenting different kinds of evidence that all contribute to the singular, main idea presented in your thesis.
Review your evidence and identify these different arguments, then organize the evidence into categories based on the argument they support. These ideas and evidence will become the body paragraphs of your essay.
For example, if you were writing about Roderick and Madeline as in the example above, you would pull evidence from the text, such as the narrator’s realization of their relationship as twins; examples where the narrator’s tone of voice shifts when discussing their relationship; imagery, like the sounds Roderick hears as Madeline tries to escape; and Poe’s tendency to use doubles and twins in his other writings to create the same spooky effect. All of these are separate strains of the same argument, and can be clearly organized into sections of an outline.
Step 7: Write Your Introduction
Your introduction serves a few very important purposes that essentially set the scene for the reader:
- Establish context. Sure, your reader has probably read the work. But you still want to remind them of the scene, characters, or elements you’ll be discussing.
- Present your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the backbone of your analytical paper. You need to present it clearly at the outset so that the reader understands what every argument you make is aimed at.
- Offer a mini-outline. While you don’t want to show all your cards just yet, you do want to preview some of the evidence you’ll be using to support your thesis so that the reader has a roadmap of where they’re going.
Step 8: Write Your Body Paragraphs
Thanks to steps one through seven, you’ve already set yourself up for success. You have clearly outlined arguments and evidence to support them. Now it’s time to translate those into authoritative and confident prose.
When presenting each idea, begin with a topic sentence that encapsulates the argument you’re about to make (sort of like a mini-thesis statement). Then present your evidence and explanations of that evidence that contribute to that argument. Present enough material to prove your point, but don’t feel like you necessarily have to point out every single instance in the text where this element takes place. For example, if you’re highlighting a symbol that repeats throughout the narrative, choose two or three passages where it is used most effectively, rather than trying to squeeze in all ten times it appears.
While you should have clearly defined arguments, the essay should still move logically and fluidly from one argument to the next. Try to avoid choppy paragraphs that feel disjointed; every idea and argument should feel connected to the last, and, as a group, connected to your thesis. A great way to connect the ideas from one paragraph to the next is with transition words and phrases, such as:
- Furthermore
- In addition
- On the other hand
- Conversely
Step 9: Write Your Conclusion
Your conclusion is more than a summary of your essay's parts, but it’s also not a place to present brand new ideas not already discussed in your essay. Instead, your conclusion should return to your thesis (without repeating it verbatim) and point to why this all matters. If writing about the siblings in “The Fall of the House of Usher,” for example, you could point out that the utilization of twins and doubles is a common literary element of Poe’s work that contributes to the definitive eeriness of Gothic literature.
While you might speak to larger ideas in your conclusion, be wary of getting too macro. Your conclusion should still be supported by all of the ideas that preceded it.
Step 10: Revise, Revise, Revise
Of course you should proofread your literary analysis essay before you turn it in. But you should also edit the content to make sure every piece of evidence and every explanation directly supports your thesis as effectively and efficiently as possible.
Sometimes, this might mean actually adapting your thesis a bit to the rest of your essay. At other times, it means removing redundant examples or paraphrasing quotations. Make sure every sentence is valuable, and remove those that aren’t.
Other Resources for Literary Analysis
With these skills and suggestions, you’re well on your way to practicing and writing literary analysis. But if you don’t have a firm grasp on the concepts discussed above—such as literary devices or even the content of the text you’re analyzing—it will still feel difficult to produce insightful analysis.
If you’d like to sharpen the tools in your literature toolbox, there are plenty of other resources to help you do so:
- Check out our expansive library of Literary Devices . These could provide you with a deeper understanding of the basic devices discussed above or introduce you to new concepts sure to impress your professors ( anagnorisis , anyone?).
- This Academic Citation Resource Guide ensures you properly cite any work you reference in your analytical essay.
- Our English Homework Help Guide will point you to dozens of resources that can help you perform analysis, from critical reading strategies to poetry helpers.
- This Grammar Education Resource Guide will direct you to plenty of resources to refine your grammar and writing (definitely important for getting an A+ on that paper).
Of course, you should know the text inside and out before you begin writing your analysis. In order to develop a true understanding of the work, read through its corresponding SuperSummary study guide . Doing so will help you truly comprehend the plot, as well as provide some inspirational ideas for your analysis.
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write an Essay
I. What is an Essay?
An essay is a form of writing in paragraph form that uses informal language, although it can be written formally. Essays may be written in first-person point of view (I, ours, mine), but third-person (people, he, she) is preferable in most academic essays. Essays do not require research as most academic reports and papers do; however, they should cite any literary works that are used within the paper.
When thinking of essays, we normally think of the five-paragraph essay: Paragraph 1 is the introduction, paragraphs 2-4 are the body covering three main ideas, and paragraph 5 is the conclusion. Sixth and seventh graders may start out with three paragraph essays in order to learn the concepts. However, essays may be longer than five paragraphs. Essays are easier and quicker to read than books, so are a preferred way to express ideas and concepts when bringing them to public attention.
II. Examples of Essays
Many of our most famous Americans have written essays. Benjamin Franklin, Thomas Paine, and Thomas Jefferson wrote essays about being good citizens and concepts to build the new United States. In the pre-Civil War days of the 1800s, people such as:
- Ralph Waldo Emerson (an author) wrote essays on self-improvement
- Susan B. Anthony wrote on women’s right to vote
- Frederick Douglass wrote on the issue of African Americans’ future in the U.S.
Through each era of American history, well-known figures in areas such as politics, literature, the arts, business, etc., voiced their opinions through short and long essays.
The ultimate persuasive essay that most students learn about and read in social studies is the “Declaration of Independence” by Thomas Jefferson in 1776. Other founding fathers edited and critiqued it, but he drafted the first version. He builds a strong argument by stating his premise (claim) then proceeds to give the evidence in a straightforward manner before coming to his logical conclusion.
III. Types of Essays
A. expository.
Essays written to explore and explain ideas are called expository essays (they expose truths). These will be more formal types of essays usually written in third person, to be more objective. There are many forms, each one having its own organizational pattern. Cause/Effect essays explain the reason (cause) for something that happens after (effect). Definition essays define an idea or concept. Compare/ Contrast essays will look at two items and show how they are similar (compare) and different (contrast).
b. Persuasive
An argumentative paper presents an idea or concept with the intention of attempting to change a reader’s mind or actions . These may be written in second person, using “you” in order to speak to the reader. This is called a persuasive essay. There will be a premise (claim) followed by evidence to show why you should believe the claim.
c. Narrative
Narrative means story, so narrative essays will illustrate and describe an event of some kind to tell a story. Most times, they will be written in first person. The writer will use descriptive terms, and may have paragraphs that tell a beginning, middle, and end in place of the five paragraphs with introduction, body, and conclusion. However, if there is a lesson to be learned, a five-paragraph may be used to ensure the lesson is shown.
d. Descriptive
The goal of a descriptive essay is to vividly describe an event, item, place, memory, etc. This essay may be written in any point of view, depending on what’s being described. There is a lot of freedom of language in descriptive essays, which can include figurative language, as well.
IV. The Importance of Essays
Essays are an important piece of literature that can be used in a variety of situations. They’re a flexible type of writing, which makes them useful in many settings . History can be traced and understood through essays from theorists, leaders, artists of various arts, and regular citizens of countries throughout the world and time. For students, learning to write essays is also important because as they leave school and enter college and/or the work force, it is vital for them to be able to express themselves well.
V. Examples of Essays in Literature
Sir Francis Bacon was a leading philosopher who influenced the colonies in the 1600s. Many of America’s founding fathers also favored his philosophies toward government. Bacon wrote an essay titled “Of Nobility” in 1601 , in which he defines the concept of nobility in relation to people and government. The following is the introduction of his definition essay. Note the use of “we” for his point of view, which includes his readers while still sounding rather formal.
“We will speak of nobility, first as a portion of an estate, then as a condition of particular persons. A monarchy, where there is no nobility at all, is ever a pure and absolute tyranny; as that of the Turks. For nobility attempers sovereignty, and draws the eyes of the people, somewhat aside from the line royal. But for democracies, they need it not; and they are commonly more quiet, and less subject to sedition, than where there are stirps of nobles. For men’s eyes are upon the business, and not upon the persons; or if upon the persons, it is for the business’ sake, as fittest, and not for flags and pedigree. We see the Switzers last well, notwithstanding their diversity of religion, and of cantons. For utility is their bond, and not respects. The united provinces of the Low Countries, in their government, excel; for where there is an equality, the consultations are more indifferent, and the payments and tributes, more cheerful. A great and potent nobility, addeth majesty to a monarch, but diminisheth power; and putteth life and spirit into the people, but presseth their fortune. It is well, when nobles are not too great for sovereignty nor for justice; and yet maintained in that height, as the insolency of inferiors may be broken upon them, before it come on too fast upon the majesty of kings. A numerous nobility causeth poverty, and inconvenience in a state; for it is a surcharge of expense; and besides, it being of necessity, that many of the nobility fall, in time, to be weak in fortune, it maketh a kind of disproportion, between honor and means.”
A popular modern day essayist is Barbara Kingsolver. Her book, “Small Wonders,” is full of essays describing her thoughts and experiences both at home and around the world. Her intention with her essays is to make her readers think about various social issues, mainly concerning the environment and how people treat each other. The link below is to an essay in which a child in an Iranian village she visited had disappeared. The boy was found three days later in a bear’s cave, alive and well, protected by a mother bear. She uses a narrative essay to tell her story.
VI. Examples of Essays in Pop Culture
Many rap songs are basically mini essays, expressing outrage and sorrow over social issues today, just as the 1960s had a lot of anti-war and peace songs that told stories and described social problems of that time. Any good song writer will pay attention to current events and express ideas in a creative way.
A well-known essay written in 1997 by Mary Schmich, a columnist with the Chicago Tribune, was made into a popular video on MTV by Baz Luhrmann. Schmich’s thesis is to wear sunscreen, but she adds strong advice with supporting details throughout the body of her essay, reverting to her thesis in the conclusion.

VII. Related Terms
Research paper.
Research papers follow the same basic format of an essay. They have an introductory paragraph, the body, and a conclusion. However, research papers have strict guidelines regarding a title page, header, sub-headers within the paper, citations throughout and in a bibliography page, the size and type of font, and margins. The purpose of a research paper is to explore an area by looking at previous research. Some research papers may include additional studies by the author, which would then be compared to previous research. The point of view is an objective third-person. No opinion is allowed. Any claims must be backed up with research.
VIII. Conclusion
Students dread hearing that they are going to write an essay, but essays are one of the easiest and most relaxed types of writing they will learn. Mastering the essay will make research papers much easier, since they have the same basic structure. Many historical events can be better understood through essays written by people involved in those times. The continuation of essays in today’s times will allow future historians to understand how our new world of technology and information impacted us.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
Importance of Literature in People Life Essay
Introduction.
Literature is still important, especially the radical one that tends to be challenging in many respects. It is good for people who have critical thinking and step out of the ideational comfort zone that conformity offers. Through such works as Don Quixote and Madame Bovary, one has the opportunity to live other lives through the novels’ characters. Literature can move beyond the confines of time and space. It helps reconcile, momentarily, with whatever unhappiness we have about our lives.
However, in the long run, the fantasy part of fiction paradoxically helps keep a reality check. If a novel helps us to travel momentarily outside our current times and beyond our geographic locations, in the long run, it makes us more aware of the limitations of our reality. Because some literature depicts a perfect world, after we read it we become aware of what is wrong in our reality and what should be changed for the better.
Regarding this power to incite challenging the status quo, some social institutions like the Government and the Church may be keen on censoring given works. However, it is difficult to say which work may create an upheaval because different people react differently. Moreover, the aesthetic of a book is not a criterion, as Uncle Tom’s cabin shows, for despite being aesthetically a flat novel, the significance of its theme –slavery- had influenced the then-American society.
In the end, challenging the status quo is what has made humanity progress. All the scientific and technological progress and the evolvement of such issues as human rights has been achieved because the status quo was being questioned. Therefore, the seditious quality of literature has a positive aspect to it.
Another important aspect of literature resides in language. The development of language goes on par with the development of communication within society. We have access to a wide range of words that help us express ourselves. Because society is made of individuals, many society members developing their language skills and by extension, their expressiveness will help develop communication in the society as a whole. As language develops through literature, the society to which it belongs becomes grows richer and people express themselves better.
Society becomes also richer from an ideational point of view. Indeed, thought develops and is expressed through language. Ideas without words are abstract concepts. Language is what gives them shape and makes them somehow more concrete. It is through words that we can formulate and grasp ideas. So the scope of influence of language is both verbal and intellectual.
Finally, it should be noted that media can never fill the shoes of literature. At the level of language, audiovisual media does not use language that measures up to literary language. Media language is prosaic and relegated to a secondary position. It seeks the minimum of oral expression. Therefore, the progress and continuity of language are linked to the continuity of literature. This primary role of the literature shows that the claim that books are obsolete is wrong.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 1). Importance of Literature in People Life. https://ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-literature-in-people-life/
"Importance of Literature in People Life." IvyPanda , 1 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-literature-in-people-life/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Importance of Literature in People Life'. 1 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Importance of Literature in People Life." November 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-literature-in-people-life/.
1. IvyPanda . "Importance of Literature in People Life." November 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-literature-in-people-life/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Importance of Literature in People Life." November 1, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/importance-of-literature-in-people-life/.
- Comparative Analysis of Texts in Ideational and Interpersonal Meanings
- Symbolism and Realism in Madame Bovary by Gustave Flaubert
- Realism of Wide Sargasso Sea and Madame Bovary
- Consumerism in "The Ladies’ Paradise" and "Madame Bovary"
- Don Quixote and Hamlet: Comparative Analysis
- Anna Karenina and Madame Bovary
- Don Quixote and Sancho Panza in Cervantes' Novel
- What Makes Don Quixote a Parody?
- Sanity vs. Madness (Don Quixote vs. Orgon)
- Analysis of Don Quixote’s Over-Romanticised Chivalric Acts and Beliefs
- “Memoirs of Geisha”: The Difference Between a Novel and a Movie
- Jonathan Kozol’s “Amazing Grace”
- Phrase “Women’s Movement” and Novel "The Awakening" by K. Chopin
- “The Road Not Taken” by Robert Frost: Advice for Life
- Gabriel Conroy’s Epiphany in “The Dead” by James Joyce

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction to Literature: What? Why? How?
When is the last time you read a book or a story simply because it interested you? If you were to classify that book, would you call it fiction or literature? This is an interesting separation, with many possible reasons for it. One is that “fiction” and “literature” are regarded as quite different things. “Fiction,” for example, is what people read for enjoyment. “Literature” is what they read for school. Or “fiction” is what living people write and is about the present. “Literature” was written by people (often white males) who have since died and is about times and places that have nothing to do with us. Or “fiction” offers everyday pleasures, but “literature” is to be honored and respected, even though it is boring. Of course, when we put anything on a pedestal, we remove it from everyday life, so the corollary is that literature is to be honored and respected, but it is not to be read, certainly not by any normal person with normal interests.
Sadly, it is the guardians of literature, that is, of the classics, who have done so much to take the life out of literature, to put it on a pedestal and thereby to make it an irrelevant aspect of American life. People study literature because they love literature. They certainly don’t do it for the money. But what happens too often, especially in colleges, is that teachers forget what it was that first interested them in the study of literature. They forget the joy that they first felt (and perhaps still feel) as they read a new novel or a poem or as they reread a work and saw something new in it. Instead, they erect formidable walls around these literary works, giving the impression that the only access to a work is through deep learning and years of study. Such study is clearly important for scholars, but this kind of scholarship is not the only way, or even necessarily the best way, for most people to approach literature. Instead it makes the literature seem inaccessible. It makes the literature seem like the province of scholars. “Oh, you have to be smart to read that,” as though Shakespeare or Dickens or Woolf wrote only for English teachers, not for general readers.
What is Literature?
In short, literature evokes imaginative worlds through the conscious arrangement of words that tell a story. These stories are told through different genres, or types of literature, like novels, short stories, poetry, drama, and the essay. Each genre is associated with certain conventions. In this course, we will study poetry, short fiction, and drama (in the form of movies).
Some Misconceptions about Literature
Of course, there are a number of misconceptions about literature that have to be gotten out of the way before anyone can enjoy it. One misconception is that literature is full of hidden meanings . There are certainly occasional works that contain hidden meanings. The biblical book of Revelation , for example, was written in a kind of code, using images that had specific meanings for its early audience but that we can only recover with a great deal of difficulty. Most literary works, however, are not at all like that. Perhaps an analogy will illustrate this point. When I take my car to my mechanic because something is not working properly, he opens the hood and we both stand there looking at the engine. But after we have looked for a few minutes, he is likely to have seen what the problem is, while I could look for hours and never see it. We are looking at the same thing. The problem is not hidden, nor is it in some secret code. It is right there in the open, accessible to anyone who knows how to “read” it, which my mechanic does and I do not. He has been taught how to “read” automobile engines and he has practiced “reading” them. He is a good “close reader,” which is why I continue to take my car to him.
The same thing is true for readers of literature. Generally authors want to communicate with their readers, so they are not likely to hide or disguise what they are saying, but reading literature also requires some training and some practice. Good writers use language very carefully, and readers must learn how to be sensitive to that language, just as the mechanic must learn to be sensitive to the appearances and sounds of the engine. Everything that the writer wants to say, and much that the writer may not be aware of, is there in the words. We simply have to learn how to read them.
Another popular misconception is that a literary work has a single “meaning” (and that only English teachers know how to find that meaning). There is an easy way to dispel this misconception. Just go to a college library and find the section that holds books on Shakespeare. Choose one play, Hamlet , for example, and see how many books there are about it, all by scholars who are educated, perceptive readers. Can it be the case that one of these books is correct and all the others are mistaken? And if the correct one has already been written, why would anyone need to write another book about the play? The answer is this:
Key Takeaways
There is no single correct way to read any piece of literature.
Again, let me use an analogy to illustrate this point. Suppose that everyone at a meeting were asked to describe a person who was standing in the middle of the room. Imagine how many different descriptions there would be, depending on where the viewer sat in relation to the person. For example, an optometrist in the crowd might focus on the person’s glasses; a hair stylist might focus on the person’s haircut; someone who sells clothing might focus on the style of dress; a podiatrist might focus on the person’s feet. Would any of these descriptions be incorrect? Not necessarily, but they would be determined by the viewers’ perspectives. They might also be determined by such factors as the viewers’ ages, genders, or ability to move around the person being viewed, or by their previous acquaintance with the subject. So whose descriptions would be correct? Conceivably all of them, and if we put all of these correct descriptions together, we would be closer to having a full description of the person.
This is most emphatically NOT to say, however, that all descriptions are correct simply because each person is entitled to his or her opinion
If the podiatrist is of the opinion that the person is five feet, nine inches tall, the podiatrist could be mistaken. And even if the podiatrist actually measures the person, the measurement could be mistaken. Everyone who describes this person, therefore, must offer not only an opinion but also a basis for that opinion. “My feeling is that this person is a teacher” is not enough. “My feeling is that this person is a teacher because the person’s clothing is covered with chalk dust and because the person is carrying a stack of papers that look like they need grading” is far better, though even that statement might be mistaken.
So it is with literature. As we read, as we try to understand and interpret, we must deal with the text that is in front of us ; but we must also recognize (1) that language is slippery and (2) that each of us individually deals with it from a different set of perspectives. Not all of these perspectives are necessarily legitimate, and it is always possible that we might misread or misinterpret what we see. Furthermore, it is possible that contradictory readings of a single work will both be legitimate, because literary works can be as complex and multi-faceted as human beings. It is vital, therefore, that in reading literature we abandon both the idea that any individual’s reading of a work is the “correct” one and the idea that there is one simple way to read any work. Our interpretations may, and probably should, change according to the way we approach the work. If we read The Chronicles of Narnia as teenagers, then in middle age, and then in old age, we might be said to have read three different books. Thus, multiple interpretations, even contradictory interpretations, can work together to give us a fuller and possibly more interesting understanding of a work.
Why Reading Literature is Important
Reading literature can teach us new ways to read, think, imagine, feel, and make sense of our own experiences. Literature forces readers to confront the complexities of the world, to confront what it means to be a human being in this difficult and uncertain world, to confront other people who may be unlike them, and ultimately to confront themselves.
The relationship between the reader and the world of a work of literature is complex and fascinating. Frequently when we read a work, we become so involved in it that we may feel that we have become part of it. “I was really into that movie,” we might say, and in one sense that statement can be accurate. But in another sense it is clearly inaccurate, for actually we do not enter the movie or the story as IT enters US; the words enter our eyes in the form of squiggles on a page which are transformed into words, sentences, paragraphs, and meaningful concepts in our brains, in our imaginations, where scenes and characters are given “a local habitation and a name.” Thus, when we “get into” a book, we are actually “getting into” our own mental conceptions that have been produced by the book, which, incidentally, explains why so often readers are dissatisfied with cinematic or television adaptations of literary works.
In fact, though it may seem a trite thing to say, writers are close observers of the world who are capable of communicating their visions, and the more perspectives we have to draw on, the better able we should be to make sense of our lives. In these terms, it makes no difference whether we are reading a Homeric epic poem like The Odysse y, a twelfth-century Japanese novel like The Tale of Genji , or a Victorian novel by Dickens, or even, in a sense, watching someone’s TikTok video (a video or movie is also a kind of text that can be “read” or analyzed for multiple meanings). The more different perspectives we get, the better. And it must be emphasized that we read such works not only to be well-rounded (whatever that means) or to be “educated” or for antiquarian interest. We read them because they have something to do with us, with our lives. Whatever culture produced them, whatever the gender or race or religion of their authors, they relate to us as human beings; and all of us can use as many insights into being human as we can get. Reading is itself a kind of experience, and while we may not have the time or the opportunity or or physical possibility to experience certain things in the world, we can experience them through reading. So literature allows us to broaden our experiences.
Reading also forces us to focus our thoughts. The world around us is so full of stimuli that we are easily distracted. Unless we are involved in a crisis that demands our full attention, we flit from subject to subject. But when we read a book, even a book that has a large number of characters and covers many years, the story and the writing help us to focus, to think about what they show us in a concentrated manner. When I hold a book, I often feel that I have in my hand another world that I can enter and that will help me to understand the everyday world that I inhabit.
Literature invites us to meet interesting characters and to visit interesting places, to use our imagination and to think about things that might otherwise escape our notice, to see the world from perspectives that we would otherwise not have.
Watch this video for a discussion of why reading fiction matters.
How to Read Literature: The Basics
- Read with a pen in hand! Yes, even if you’re reading an electronic text, in which case you may want to open a new document in which you can take notes. Jot down questions, highlight things you find significant, mark confusing passages, look up unfamiliar words/references, and record first impressions.
- Think critically to form a response. Here are some things to be aware of and look for in the story that may help you form an idea of meaning.
- Repetitions . You probably know from watching movies that if something is repeated, that means something. Stories are similar—if something occurs more than once, the story is calling attention to it, so notice it and consider why it is repeated. The repeated element can be a word or a phrase, an action, even a piece of clothing or gear.
- Not Quite Right : If something that happens that seems Not Quite Right to you, that may also have some particular meaning. So, for example, if a violent act is committed against someone who’s done nothing wrong, that is unusual, unexpected, that is, Not Quite Right. And therefore, that act means something.
- Address your own biases and compare your own experiences with those expressed in the piece.
- Test your positions and thoughts about the piece with what others think (we’ll do some of this in class discussions).
While you will have your own individual connection to a piece based on your life experiences, interpreting literature is not a willy-nilly process. Each piece of writing has purpose, usually more than one purpose–you, as the reader, are meant to uncover purpose in the text. As the speaker notes in the video you watched about how to read literature, you, as a reader, also have a role to play. Sometimes you may see something in the text that speaks to you; whether or not the author intended that piece to be there, it still matters to you.
For example, I’ve had a student who had life experiences that she was reminded of when reading “Chonguita, the Monkey Bride” and another student whose experience was mirrored in part of “The Frog King or Iron Heinrich.” I encourage you to honor these perceptions if they occur to you and possibly even to use them in your writing assignments. I can suggest ways to do this if you’re interested.
But remember that when we write about literature, our observations must also be supported by the text itself. Make sure you aren’t reading into the text something that isn’t there. Value the text for what is and appreciate the experience it provides, all while you attempt to create a connection with your experiences.
Attributions:
- Content written by Dr. Karen Palmer and licensed CC BY NC SA .
- Content adapted from Literature, the Humanities, and Humanity by Theodore L. Steinberg and licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The Worry Free Writer by Dr. Karen Palmer is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Introduction to Literature Copyright © by Judy Young is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Why Is Literature Important? (23 Reasons)
What’s the point of picking up a book when the world’s knowledge can be streamed directly into my ears or viewed on a screen, right?
But, stick with me for a moment.
With every turn of the page, literature challenges, comforts, and questions. It nurtures our capacity for empathy, enriches our language, and hones our critical thinking. It offers escape but also a confrontation with the truths of human existence—our joys, sorrows, ambitions, and fears.
Now, stick with me for a bit longer as we explore why literature is essential and how it has survived the test of time. Ready to turn the page? Let’s explore this together!
Table of Contents
Literature Fosters Empathy
Literature acts as a gateway into the lives, emotions, and experiences of others. By delving into a character’s journey, readers step out of their own lives and enter another’s world, broadening their emotional depth and fostering empathetic understanding.
- Connection to Others : Through narratives, we connect with characters who may be vastly different from ourselves, allowing us to appreciate their struggles, joys, and sorrows.
- Broadened Horizons : Exposure to diverse lifestyles and viewpoints broadens our worldview, aiding us in becoming more tolerant and appreciative of differences.
- Emotional Depth : A poignant scene or a touching dialogue engraves deeper emotional understanding within us, which we then carry into our real-life interactions.
An example of empathy in literature is found in Harper Lee’s classic, “To Kill a Mockingbird,” where readers learn to understand and feel compassion for characters who confront racial injustice.
This tale, among others, extends the boundaries of our compassion beyond our immediate life circle and has the potential to affect social change through this expanded empathy.
Literature Stimulates Emotional Intelligence and Growth
Emotional intelligence is the capacity to be aware of and manage one’s own emotions and to handle interpersonal relationships judiciously and empathetically. Literature educates the heart as much as the mind by illustrating the complexity of emotions.
- Self-awareness: Recognizing personal emotions and their effects.
- Self-regulation: Managing disruptive emotions and impulses.
- Motivation: Relating one’s emotions to personal goals and objectives.
- Empathy: Understanding the emotional makeup of others.
- Social skills: Building and managing relationships effectively.
Readers may find themselves growing alongside characters, experiencing a maturation that parallels the protagonists’ evolutions. By dealing with fictional situations and conflicts, individuals become better equipped to face their challenges, making literature a catalyst for personal growth and development.
Literature Trains the Mind in Critical Thinking and Analytical Skills
Critical thinking can be defined as the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment. It is a cornerstone of education and personal development.
In the context of literature, readers activate these skills by dissecting themes, symbols, and the motives of characters.
- Questioning the text: Readers must consider the reasons behind events and characters’ decisions.
- Analyzing structures: Understanding how stories are crafted, including plot, setting, and character development.
- Interpreting meaning: Delving into themes, symbols, and metaphors to grasp deeper significance.
This mental exercise enhances the ability to critique and argue points effectively, which is an essential skill in many professional environments.
Take, for example, Sherlock Holmes stories, which aren’t just about following the detective’s brilliant deductions. They invite readers to think alongside Holmes, practicing deductive reasoning by picking out important details and drawing conclusions from them.
Literature Encourages Lifelong Learning and Curiosity
The pursuit of knowledge and the joy of curiosity are deeply embedded in the human spirit. Each book, story, or poem offers a new opportunity to learn something unknown or to see the world from a different perspective.
- New topics and themes challenge readers to explore subjects they may never have considered.
- Exposure to different writing styles and genres can inspire further reading and investigation.
- Lifelong learning through literature contributes to personal fulfillment and professional success.
The diversity in learning styles and preferences illustrates how literature accommodates and nurtures an array of learning journeys, contributing to a well-rounded, informed individual.
Literature Enriches Language Skills and Vocabulary
Complex narratives challenge readers to understand context, double meanings, and sophisticated themes, expanding not only vocabulary but also cognitive abilities.
- Advanced Vocabulary: Reading exposes one to new words and ways of using them.
- Language Patterns: Various literary works employ distinct styles, enhancing one’s grasp of grammatical structures.
- Figurative Language: Metaphors, similes, and analogies in literature sharpen comprehension and usage of nuanced language.
Over time, frequent readers tend to articulate thoughts better, achieve higher academic performance, and become more effective communicators. Language mastery is foundational to success in many areas of life, and literature offers a rich, enjoyable path to achieving it.
Literature Enhances Communication and Writing Abilities
Literature offers readers a look into the art of conveying thoughts, emotions, and narratives effectively, laying the groundwork for strong speaking and writing abilities.
Enhancing Verbal Skills:
- Dialogue: Literature often includes examples of dialogue that reflect how people speak and interact, providing a model for effective verbal communication.
- Narrative Voice: The unique voices of characters or narrators teach us about tone and style, which can translate into better-spoken communication.
Writing, like communication, is refined through exposure to good literature. Analyzing an author’s crafting of sentences, or how they build tension and convey mood, can be immensely beneficial for one’s own writing.
Improving Written Expression:
- Style: Every author has a distinctive style—a personal fingerprint of word choice and syntax, which aspiring writers can learn from.
- Structure: The way a story is structured, from sentence length to paragraph layout, influences how readers perceive and understand content.
Literature Provides a Voice for Social and Political Discourse
Authors can influence public opinion and inspire change by presenting stories that highlight societal issues. Through the power of the written word, literature has the capacity to shine a light on injustice, question authority, and offer new perspectives.
- It stimulates discussions on social justice, equity, and human rights.
- Authors often use allegory and satire to comment on contemporary political climates.
- Literature can be a form of resistance and a catalyst for democratic change.
Reading literature that deals with complex social and political themes can be a transformative experience. It helps readers understand different viewpoints and teaches them about the struggles of others.
When Harriet Beecher Stowe wrote “Uncle Tom’s Cabin, ” it was said to have laid the groundwork for the American Civil War by bringing the reality of slavery to readers in a poignant and humanizing manner.
Literature Bridges Gaps Between Diverse Cultures and Societies
World literature introduces readers to ways of life and belief systems unlike their own, promoting cross-cultural sensitivity and global citizenship.
- Asian Literature: Explore Asian cultures through classic and contemporary works like “The Tale of Genji” and “The God of Small Things.”
- African Literature: Explore the vibrant traditions and contemporary challenges of African societies through authors like Chinua Achebe and Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie .
- Middle Eastern Literature: Discover tales from ancient Arabian nights or contemporary reflections in works by authors like Khaled Hosseini .
By walking in the shoes of characters from around the world, readers gain a deeper appreciation of our shared humanity and the diversity that colors it. Literature serves as a bridge, connecting the reader to the global community and fostering unity through understanding.
Literature Enhances Our Understanding of History
Literature is a witness to history, capturing the essence of historical moments and the intricacies of lives lived during different eras. As much as history books record facts, literature infuses those facts with emotion and human experience.
- Immersion into Periods: Whether through the accurate depictions of a period in historical fiction or symbolic representations in classics, literature offers an immersive view of the past.
- Insight into Mindsets: Reading works from or about a specific time period provides insight into the thoughts and values of people from that era.
- Comprehension of Events: Many authors incorporate significant historical events into their stories, allowing readers to understand the impact of these events on individuals and societies.
Books like “War and Peace” by Leo Tolstoy not only tell a tale but also bring the Napoleonic Wars to personal reality. They allow contemporary readers to feel the reverberations of the past in the comfort of the present.
Literature Develops Ethical Reasoning and Moral Understanding
Through stories, readers are exposed to complex scenarios where characters must make difficult choices. This exploration of right and wrong invites readers to contemplate moral complexities in a nuanced way.
- Presents moral dilemmas: Readers evaluate characters’ choices, considering their own values in the process.
- Reflects societal norms: Literature paints a picture of evolving ethical standards through various epochs and cultures.
- Encourages reflection on consequences: The outcomes of actions in literature serve as cautionary or exemplary tales.
Reading about scenarios that challenge characters ethically allows individuals to explore their moral compasses within a safe and contemplative space. This vicarious exploration can lead to more nuanced ethical reasoning in one’s own life.
Literature Serves as a Medium for Escape and Mental Relaxation
Literature provides a respite in a fast-paced, often stressful world—a door to other worlds where the mind can wander freely, unwind, and rejuvenate. The act of reading is in itself a form of mental reprieve, a break from the immediacy of one’s own life.
Furthermore, this form of escapism also contributes positively to mental health. Literature’s transportive nature allows individuals to disconnect, recharge, and often return to their lives with renewed energy and a fresh perspective.
Literature Preserves Cultural Heritage and Traditions
Literature is a primary vehicle for sustaining the traditions and legacies of cultures worldwide. Each story, poem, or novel is a time capsule, enveloping the mores, beliefs, and expressions of the period it represents.
- It captures and transmits oral and folk traditions.
- It encapsulates the historical context and the zeitgeist of eras past.
- It allows future generations to access and understand their cultural foundations and histories.
Epics like Homer’s “The Odyssey” faithfully conserve ancient Greece’s myths and social values, while classics like Chinua Achebe’s “Things Fall Apart” provide insight into pre-colonial life in Africa as well as the impact of colonialism on indigenous cultures.
Literature does not merely record cultural artifacts; it breathes life into them, ensuring their persistence through the ages and reinforcing a shared human heritage that transcends the written word.
Literature Encourages Imagination and Creativity
Losing oneself to a work of literature can ignite the spark of imagination and inspire creativity. Unlike the passive consumption of visual media, reading necessitates that we use our minds to visualize characters and worlds, thus exercising and expanding our creative muscles.
For both authors and readers, the creation and interpretation of stories serve as a means of personal expression and imaginative exploration.
Examples of this abound, one of which is C.S. Lewis’ s “Chronicles of Narnia” series, which has sparked not only the imagination of its readers but also numerous adaptations in film, theater, and music.
Literature Challenges Stereotypes
Often, stereotypes are simplified and widely held beliefs about a particular group of people or things that can be ingrained in society’s consciousness.
When we engage with literature, we encounter characters and cultures that are complex, nuanced, and diverse. Literature can make us question our preconceived notions about others by presenting us with a range of experiences and identities.
- Breaking down barriers: Stories can expose readers to different cultures, lifestyles, and belief systems, promoting empathy and understanding.
- A broader perspective: Through narratives that span various backgrounds, readers can question their own preconceived notions and potentially rethink their biases.
By offering an array of diverse perspectives within its pages, literature acts as a catalyst for broader thinking, urging us to consider viewpoints outside of our own experience.
Literature Can Help Us Develop Our Unique Voice
In the quest to find one’s voice—be it in writing, speaking, or through artistic expression—literature can be a guiding force. As we read, we unconsciously absorb these styles, which later influence the development of our own writing and speaking voices.
- Experimentation: Sampling different genres and authors provides a wealth of vocabulary and rhetorical techniques to draw from when crafting our language.
- Reflection: Analyzing authors’ choices in narrative and dialogue can lead to a more profound understanding of how we wish to present our ideas.
Whether inspired by the raw honesty of Maya Angelou or the piercing insight of George Orwell, as we read, we learn, and as we learn, we find new words for our feelings and thoughts, crafting a voice that’s truly our own.
Literature Encourages You to Learn Deeper
Engaging with literature often sparks a desire to dig deeper into a subject, whether motivated by a historical setting, a scientific concept, or a foreign culture described in a story. This pursuit of knowledge extends beyond the pages of the book into real-world understanding.
Readers not only gain insights from within the confines of the book’s universe but are also drawn to investigate and learn more about the real-world context. When a book like Dan Brown ‘s “The Da Vinci Code” entwines history with fiction, readers may find themselves delving into art history or religious studies.
Literature Can Inspire Us to Pursue Our Own Writing Dreams
For aspiring writers, the world of literature is not just an escape; it is a source of inspiration and a catalyst for one’s own creative endeavors. Each narrative is a nod to the potential writer within, suggesting, “You, too, have a story to tell.”
- A reader might start journaling after connecting with a character’s introspective diary.
- Another might draft a screenplay inspired by the vibrant imagery in a novel.
- Or perhaps a poem sparks a blog, a memoir, or even a new genre altogether.
Whether it is keeping a journal, starting a blog, or drafting a novel, the inspiration derived from literature is a powerful motivator in the pursuit of personal writing objectives.
Literature Reflects Human Experiences
The power of literature to mirror the full spectrum of human experiences is unparalleled. Through stories, one can find reflections of love, loss, triumph, and the mundanities of everyday life. Readers often see pieces of their reality within the pages, a testament to the universal nature of literary themes.
- Love and Relationships: From the romance of Elizabeth and Mr. Darcy in “Pride and Prejudice” to the tempestuous bond between Heathcliff and Catherine in “Wuthering Heights,” literature explores the complexities of relationships.
- Conflict and Resolution: The challenges faced by characters in narratives from “The Odyssey” to “The Lord of the Rings” reflect our own struggles and the pursuit of resolution.
Reading these stories validates our own experiences and emotions, giving us comfort and a sense of connection to others.
Literature Lets Us Time Travel
Imagine a machine that allows us to travel through time. Literature is that machine, not made of gears and levers but of words and ideas.
- Past: Journey to Victorian England with Charles Dickens or to Renaissance Italy with Dante Alighieri.
- Future: Explore dystopian societies through the lens of George Orwell or Aldous Huxley.
We travel back to learn or forward to dream, all within the span of pages. Unlike a history textbook’s linear recitation of facts, literature often weaves personal tales with the period’s cultural and social norms, giving a multidimensional view of the past or speculative futures.
Literature Lets Us Appreciate the Beauty of Words
The aesthetic pleasure derived from reading well-crafted sentences, the rhythm of poetry, and the eloquence of a compelling dialogue is one of literature’s greatest offerings. The beauty of words lies not just in their meaning but in their sound and structure, which can move and captivate readers.
Authors like Shakespeare and Jane Austen are celebrated for their eloquence and mastery of dialogue. The melodic potential of language comes to life in poetry, from the classics of Emily Dickinson to the contemporary works of Amanda Gorman.
Each passage, phrase, and word in literature holds the potential to inspire awe and admiration, reminding us of the evocative power of language.
Literature Gives You Something to Talk About With Others
Books are great conversation starters, providing endless topics for discussion. Whether it’s the latest bestseller or a timeless classic, literature opens the door for shared insights and lively debate.
- Book clubs gather to dissect the latest bestseller.
- Classroom debates over the themes of a classic novel.
- Friendships are formed through mutual appreciation of a beloved series.
Sharing thoughts about literature can lead to stronger social bonds and a better understanding of different viewpoints. Moreover, it’s an opportunity to learn from others’ interpretations and gain insights you might have missed.
Literature Can Take You on New Adventures Without Leaving Home
Adventures await within the pages of books, offering escapes into worlds unknown without ever having to step outside. Whether it’s fantasy, science fiction, or adventure novels, literature has the unique ability to transport readers to different realms of possibility and imagination.
- Explore New Worlds: Whether it’s through the magical wardrobe to Narnia in C.S. Lewis ‘s beloved series or the warring kingdoms in George R.R. Martin ‘s “Game of Thrones,” readers experience the thrill of exploration.
- Escape from Reality: During trying times or moments of ennui, literature offers a sanctuary, a place to escape and recharge emotionally and mentally.
A reader’s imagination is the only ticket needed for these boundless adventures, proving that one can travel the world without ever stepping foot outside.
Literature Can Make Children Smarter
Introducing children to literature is not just about storytelling; it’s an investment in their cognitive development. From enhanced vocabulary to improved memory and analytical skills, reading lays the foundation for a lifetime of learning.
- Cognitive Development: Stories stimulate young brains, fostering growth and connectivity.
- Academic Achievement: Reading proficiency is strongly linked to success in other academic areas.
- Imagination and Creativity: Literature opens doors to new worlds, encouraging innovative thinking.
Picture books, fairy tales, and young adult novels all contribute to the intellectual enrichment of children, showing that literature is not merely an amusement but a powerful educational tool.
Literature reminds us that despite our different paths, we all share experiences that stories capture so eloquently. Whether it’s a novel that keeps us company on a quiet evening or a poem that resonates with our deepest emotions, literature uniquely touches each of us on a personal level.
So next time you pick up a book, remember that you’re not just flipping through pages—you’re igniting a spark that can illuminate, transform, and heal. And it’s our collective responsibility to keep this flame alive, honoring the past and inspiring the future.
May the stories we read today light the way for the journeys of tomorrow!
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
As you found this post useful...
Share it on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Clariza Carizal
- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- Future Fables
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Just the Right Book
- Lit Century
- The Literary Life with Mitchell Kaplan
- New Books Network
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway

The 10 Best Essay Collections of the Decade
Ever tried. ever failed. no matter..
Friends, it’s true: the end of the decade approaches. It’s been a difficult, anxiety-provoking, morally compromised decade, but at least it’s been populated by some damn fine literature. We’ll take our silver linings where we can.
So, as is our hallowed duty as a literary and culture website—though with full awareness of the potentially fruitless and endlessly contestable nature of the task—in the coming weeks, we’ll be taking a look at the best and most important (these being not always the same) books of the decade that was. We will do this, of course, by means of a variety of lists. We began with the best debut novels , the best short story collections , the best poetry collections , and the best memoirs of the decade , and we have now reached the fifth list in our series: the best essay collections published in English between 2010 and 2019.
The following books were chosen after much debate (and several rounds of voting) by the Literary Hub staff. Tears were spilled, feelings were hurt, books were re-read. And as you’ll shortly see, we had a hard time choosing just ten—so we’ve also included a list of dissenting opinions, and an even longer list of also-rans. As ever, free to add any of your own favorites that we’ve missed in the comments below.
The Top Ten
Oliver sacks, the mind’s eye (2010).
Toward the end of his life, maybe suspecting or sensing that it was coming to a close, Dr. Oliver Sacks tended to focus his efforts on sweeping intellectual projects like On the Move (a memoir), The River of Consciousness (a hybrid intellectual history), and Hallucinations (a book-length meditation on, what else, hallucinations). But in 2010, he gave us one more classic in the style that first made him famous, a form he revolutionized and brought into the contemporary literary canon: the medical case study as essay. In The Mind’s Eye , Sacks focuses on vision, expanding the notion to embrace not only how we see the world, but also how we map that world onto our brains when our eyes are closed and we’re communing with the deeper recesses of consciousness. Relaying histories of patients and public figures, as well as his own history of ocular cancer (the condition that would eventually spread and contribute to his death), Sacks uses vision as a lens through which to see all of what makes us human, what binds us together, and what keeps us painfully apart. The essays that make up this collection are quintessential Sacks: sensitive, searching, with an expertise that conveys scientific information and experimentation in terms we can not only comprehend, but which also expand how we see life carrying on around us. The case studies of “Stereo Sue,” of the concert pianist Lillian Kalir, and of Howard, the mystery novelist who can no longer read, are highlights of the collection, but each essay is a kind of gem, mined and polished by one of the great storytellers of our era. –Dwyer Murphy, CrimeReads Managing Editor
John Jeremiah Sullivan, Pulphead (2011)
The American essay was having a moment at the beginning of the decade, and Pulphead was smack in the middle. Without any hard data, I can tell you that this collection of John Jeremiah Sullivan’s magazine features—published primarily in GQ , but also in The Paris Review , and Harper’s —was the only full book of essays most of my literary friends had read since Slouching Towards Bethlehem , and probably one of the only full books of essays they had even heard of.
Well, we all picked a good one. Every essay in Pulphead is brilliant and entertaining, and illuminates some small corner of the American experience—even if it’s just one house, with Sullivan and an aging writer inside (“Mr. Lytle” is in fact a standout in a collection with no filler; fittingly, it won a National Magazine Award and a Pushcart Prize). But what are they about? Oh, Axl Rose, Christian Rock festivals, living around the filming of One Tree Hill , the Tea Party movement, Michael Jackson, Bunny Wailer, the influence of animals, and by god, the Miz (of Real World/Road Rules Challenge fame).
But as Dan Kois has pointed out , what connects these essays, apart from their general tone and excellence, is “their author’s essential curiosity about the world, his eye for the perfect detail, and his great good humor in revealing both his subjects’ and his own foibles.” They are also extremely well written, drawing much from fictional techniques and sentence craft, their literary pleasures so acute and remarkable that James Wood began his review of the collection in The New Yorker with a quiz: “Are the following sentences the beginnings of essays or of short stories?” (It was not a hard quiz, considering the context.)
It’s hard not to feel, reading this collection, like someone reached into your brain, took out the half-baked stuff you talk about with your friends, researched it, lived it, and represented it to you smarter and better and more thoroughly than you ever could. So read it in awe if you must, but read it. –Emily Temple, Senior Editor
Aleksandar Hemon, The Book of My Lives (2013)
Such is the sentence-level virtuosity of Aleksandar Hemon—the Bosnian-American writer, essayist, and critic—that throughout his career he has frequently been compared to the granddaddy of borrowed language prose stylists: Vladimir Nabokov. While it is, of course, objectively remarkable that anyone could write so beautifully in a language they learned in their twenties, what I admire most about Hemon’s work is the way in which he infuses every essay and story and novel with both a deep humanity and a controlled (but never subdued) fury. He can also be damn funny. Hemon grew up in Sarajevo and left in 1992 to study in Chicago, where he almost immediately found himself stranded, forced to watch from afar as his beloved home city was subjected to a relentless four-year bombardment, the longest siege of a capital in the history of modern warfare. This extraordinary memoir-in-essays is many things: it’s a love letter to both the family that raised him and the family he built in exile; it’s a rich, joyous, and complex portrait of a place the 90s made synonymous with war and devastation; and it’s an elegy for the wrenching loss of precious things. There’s an essay about coming of age in Sarajevo and another about why he can’t bring himself to leave Chicago. There are stories about relationships forged and maintained on the soccer pitch or over the chessboard, and stories about neighbors and mentors turned monstrous by ethnic prejudice. As a chorus they sing with insight, wry humor, and unimaginable sorrow. I am not exaggerating when I say that the collection’s devastating final piece, “The Aquarium”—which details his infant daughter’s brain tumor and the agonizing months which led up to her death—remains the most painful essay I have ever read. –Dan Sheehan, Book Marks Editor
Robin Wall Kimmerer, Braiding Sweetgrass (2013)
Of every essay in my relentlessly earmarked copy of Braiding Sweetgrass , Dr. Robin Wall Kimmerer’s gorgeously rendered argument for why and how we should keep going, there’s one that especially hits home: her account of professor-turned-forester Franz Dolp. When Dolp, several decades ago, revisited the farm that he had once shared with his ex-wife, he found a scene of destruction: The farm’s new owners had razed the land where he had tried to build a life. “I sat among the stumps and the swirling red dust and I cried,” he wrote in his journal.
So many in my generation (and younger) feel this kind of helplessness–and considerable rage–at finding ourselves newly adult in a world where those in power seem determined to abandon or destroy everything that human bodies have always needed to survive: air, water, land. Asking any single book to speak to this helplessness feels unfair, somehow; yet, Braiding Sweetgrass does, by weaving descriptions of indigenous tradition with the environmental sciences in order to show what survival has looked like over the course of many millennia. Kimmerer’s essays describe her personal experience as a Potawotami woman, plant ecologist, and teacher alongside stories of the many ways that humans have lived in relationship to other species. Whether describing Dolp’s work–he left the stumps for a life of forest restoration on the Oregon coast–or the work of others in maple sugar harvesting, creating black ash baskets, or planting a Three Sisters garden of corn, beans, and squash, she brings hope. “In ripe ears and swelling fruit, they counsel us that all gifts are multiplied in relationship,” she writes of the Three Sisters, which all sustain one another as they grow. “This is how the world keeps going.” –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Hilton Als, White Girls (2013)
In a world where we are so often reduced to one essential self, Hilton Als’ breathtaking book of critical essays, White Girls , which meditates on the ways he and other subjects read, project and absorb parts of white femininity, is a radically liberating book. It’s one of the only works of critical thinking that doesn’t ask the reader, its author or anyone he writes about to stoop before the doorframe of complete legibility before entering. Something he also permitted the subjects and readers of his first book, the glorious book-length essay, The Women , a series of riffs and psychological portraits of Dorothy Dean, Owen Dodson, and the author’s own mother, among others. One of the shifts of that book, uncommon at the time, was how it acknowledges the way we inhabit bodies made up of variously gendered influences. To read White Girls now is to experience the utter freedom of this gift and to marvel at Als’ tremendous versatility and intelligence.
He is easily the most diversely talented American critic alive. He can write into genres like pop music and film where being part of an audience is a fantasy happening in the dark. He’s also wired enough to know how the art world builds reputations on the nod of rich white patrons, a significant collision in a time when Jean-Michel Basquiat is America’s most expensive modern artist. Als’ swerving and always moving grip on performance means he’s especially good on describing the effect of art which is volatile and unstable and built on the mingling of made-up concepts and the hard fact of their effect on behavior, such as race. Writing on Flannery O’Connor for instance he alone puts a finger on her “uneasy and unavoidable union between black and white, the sacred and the profane, the shit and the stars.” From Eminem to Richard Pryor, André Leon Talley to Michael Jackson, Als enters the life and work of numerous artists here who turn the fascinations of race and with whiteness into fury and song and describes the complexity of their beauty like his life depended upon it. There are also brief memoirs here that will stop your heart. This is an essential work to understanding American culture. –John Freeman, Executive Editor
Eula Biss, On Immunity (2014)
We move through the world as if we can protect ourselves from its myriad dangers, exercising what little agency we have in an effort to keep at bay those fears that gather at the edges of any given life: of loss, illness, disaster, death. It is these fears—amplified by the birth of her first child—that Eula Biss confronts in her essential 2014 essay collection, On Immunity . As any great essayist does, Biss moves outward in concentric circles from her own very private view of the world to reveal wider truths, discovering as she does a culture consumed by anxiety at the pervasive toxicity of contemporary life. As Biss interrogates this culture—of privilege, of whiteness—she interrogates herself, questioning the flimsy ways in which we arm ourselves with science or superstition against the impurities of daily existence.
Five years on from its publication, it is dismaying that On Immunity feels as urgent (and necessary) a defense of basic science as ever. Vaccination, we learn, is derived from vacca —for cow—after the 17th-century discovery that a small application of cowpox was often enough to inoculate against the scourge of smallpox, an etymological digression that belies modern conspiratorial fears of Big Pharma and its vaccination agenda. But Biss never scolds or belittles the fears of others, and in her generosity and openness pulls off a neat (and important) trick: insofar as we are of the very world we fear, she seems to be suggesting, we ourselves are impure, have always been so, permeable, vulnerable, yet so much stronger than we think. –Jonny Diamond, Editor-in-Chief
Rebecca Solnit, The Mother of All Questions (2016)
When Rebecca Solnit’s essay, “Men Explain Things to Me,” was published in 2008, it quickly became a cultural phenomenon unlike almost any other in recent memory, assigning language to a behavior that almost every woman has witnessed—mansplaining—and, in the course of identifying that behavior, spurring a movement, online and offline, to share the ways in which patriarchal arrogance has intersected all our lives. (It would also come to be the titular essay in her collection published in 2014.) The Mother of All Questions follows up on that work and takes it further in order to examine the nature of self-expression—who is afforded it and denied it, what institutions have been put in place to limit it, and what happens when it is employed by women. Solnit has a singular gift for describing and decoding the misogynistic dynamics that govern the world so universally that they can seem invisible and the gendered violence that is so common as to seem unremarkable; this naming is powerful, and it opens space for sharing the stories that shape our lives.
The Mother of All Questions, comprised of essays written between 2014 and 2016, in many ways armed us with some of the tools necessary to survive the gaslighting of the Trump years, in which many of us—and especially women—have continued to hear from those in power that the things we see and hear do not exist and never existed. Solnit also acknowledges that labels like “woman,” and other gendered labels, are identities that are fluid in reality; in reviewing the book for The New Yorker , Moira Donegan suggested that, “One useful working definition of a woman might be ‘someone who experiences misogyny.'” Whichever words we use, Solnit writes in the introduction to the book that “when words break through unspeakability, what was tolerated by a society sometimes becomes intolerable.” This storytelling work has always been vital; it continues to be vital, and in this book, it is brilliantly done. –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Valeria Luiselli, Tell Me How It Ends (2017)
The newly minted MacArthur fellow Valeria Luiselli’s four-part (but really six-part) essay Tell Me How It Ends: An Essay in Forty Questions was inspired by her time spent volunteering at the federal immigration court in New York City, working as an interpreter for undocumented, unaccompanied migrant children who crossed the U.S.-Mexico border. Written concurrently with her novel Lost Children Archive (a fictional exploration of the same topic), Luiselli’s essay offers a fascinating conceit, the fashioning of an argument from the questions on the government intake form given to these children to process their arrivals. (Aside from the fact that this essay is a heartbreaking masterpiece, this is such a good conceit—transforming a cold, reproducible administrative document into highly personal literature.) Luiselli interweaves a grounded discussion of the questionnaire with a narrative of the road trip Luiselli takes with her husband and family, across America, while they (both Mexican citizens) wait for their own Green Card applications to be processed. It is on this trip when Luiselli reflects on the thousands of migrant children mysteriously traveling across the border by themselves. But the real point of the essay is to actually delve into the real stories of some of these children, which are agonizing, as well as to gravely, clearly expose what literally happens, procedural, when they do arrive—from forms to courts, as they’re swallowed by a bureaucratic vortex. Amid all of this, Luiselli also takes on more, exploring the larger contextual relationship between the United States of America and Mexico (as well as other countries in Central America, more broadly) as it has evolved to our current, adverse moment. Tell Me How It Ends is so small, but it is so passionate and vigorous: it desperately accomplishes in its less-than-100-pages-of-prose what centuries and miles and endless records of federal bureaucracy have never been able, and have never cared, to do: reverse the dehumanization of Latin American immigrants that occurs once they set foot in this country. –Olivia Rutigliano, CrimeReads Editorial Fellow
Zadie Smith, Feel Free (2018)
In the essay “Meet Justin Bieber!” in Feel Free , Zadie Smith writes that her interest in Justin Bieber is not an interest in the interiority of the singer himself, but in “the idea of the love object”. This essay—in which Smith imagines a meeting between Bieber and the late philosopher Martin Buber (“Bieber and Buber are alternative spellings of the same German surname,” she explains in one of many winning footnotes. “Who am I to ignore these hints from the universe?”). Smith allows that this premise is a bit premise -y: “I know, I know.” Still, the resulting essay is a very funny, very smart, and un-tricky exploration of individuality and true “meeting,” with a dash of late capitalism thrown in for good measure. The melding of high and low culture is the bread and butter of pretty much every prestige publication on the internet these days (and certainly of the Twitter feeds of all “public intellectuals”), but the essays in Smith’s collection don’t feel familiar—perhaps because hers is, as we’ve long known, an uncommon skill. Though I believe Smith could probably write compellingly about anything, she chooses her subjects wisely. She writes with as much electricity about Brexit as the aforementioned Beliebers—and each essay is utterly engrossing. “She contains multitudes, but her point is we all do,” writes Hermione Hoby in her review of the collection in The New Republic . “At the same time, we are, in our endless difference, nobody but ourselves.” –Jessie Gaynor, Social Media Editor
Tressie McMillan Cottom, Thick: And Other Essays (2019)
Tressie McMillan Cottom is an academic who has transcended the ivory tower to become the sort of public intellectual who can easily appear on radio or television talk shows to discuss race, gender, and capitalism. Her collection of essays reflects this duality, blending scholarly work with memoir to create a collection on the black female experience in postmodern America that’s “intersectional analysis with a side of pop culture.” The essays range from an analysis of sexual violence, to populist politics, to social media, but in centering her own experiences throughout, the collection becomes something unlike other pieces of criticism of contemporary culture. In explaining the title, she reflects on what an editor had said about her work: “I was too readable to be academic, too deep to be popular, too country black to be literary, and too naïve to show the rigor of my thinking in the complexity of my prose. I had wanted to create something meaningful that sounded not only like me, but like all of me. It was too thick.” One of the most powerful essays in the book is “Dying to be Competent” which begins with her unpacking the idiocy of LinkedIn (and the myth of meritocracy) and ends with a description of her miscarriage, the mishandling of black woman’s pain, and a condemnation of healthcare bureaucracy. A finalist for the 2019 National Book Award for Nonfiction, Thick confirms McMillan Cottom as one of our most fearless public intellectuals and one of the most vital. –Emily Firetog, Deputy Editor
Dissenting Opinions
The following books were just barely nudged out of the top ten, but we (or at least one of us) couldn’t let them pass without comment.

Elif Batuman, The Possessed (2010)
In The Possessed Elif Batuman indulges her love of Russian literature and the result is hilarious and remarkable. Each essay of the collection chronicles some adventure or other that she had while in graduate school for Comparative Literature and each is more unpredictable than the next. There’s the time a “well-known 20th-centuryist” gave a graduate student the finger; and the time when Batuman ended up living in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, for a summer; and the time that she convinced herself Tolstoy was murdered and spent the length of the Tolstoy Conference in Yasnaya Polyana considering clues and motives. Rich in historic detail about Russian authors and literature and thoughtfully constructed, each essay is an amalgam of critical analysis, cultural criticism, and serious contemplation of big ideas like that of identity, intellectual legacy, and authorship. With wit and a serpentine-like shape to her narratives, Batuman adopts a form reminiscent of a Socratic discourse, setting up questions at the beginning of her essays and then following digressions that more or less entreat the reader to synthesize the answer for herself. The digressions are always amusing and arguably the backbone of the collection, relaying absurd anecdotes with foreign scholars or awkward, surreal encounters with Eastern European strangers. Central also to the collection are Batuman’s intellectual asides where she entertains a theory—like the “problem of the person”: the inability to ever wholly capture one’s character—that ultimately layer the book’s themes. “You are certainly my most entertaining student,” a professor said to Batuman. But she is also curious and enthusiastic and reflective and so knowledgeable that she might even convince you (she has me!) that you too love Russian literature as much as she does. –Eleni Theodoropoulos, Editorial Fellow
Roxane Gay, Bad Feminist (2014)
Roxane Gay’s now-classic essay collection is a book that will make you laugh, think, cry, and then wonder, how can cultural criticism be this fun? My favorite essays in the book include Gay’s musings on competitive Scrabble, her stranded-in-academia dispatches, and her joyous film and television criticism, but given the breadth of topics Roxane Gay can discuss in an entertaining manner, there’s something for everyone in this one. This book is accessible because feminism itself should be accessible – Roxane Gay is as likely to draw inspiration from YA novels, or middle-brow shows about friendship, as she is to introduce concepts from the academic world, and if there’s anyone I trust to bridge the gap between high culture, low culture, and pop culture, it’s the Goddess of Twitter. I used to host a book club dedicated to radical reads, and this was one of the first picks for the club; a week after the book club met, I spied a few of the attendees meeting in the café of the bookstore, and found out that they had bonded so much over discussing Bad Feminist that they couldn’t wait for the next meeting of the book club to keep discussing politics and intersectionality, and that, in a nutshell, is the power of Roxane. –Molly Odintz, CrimeReads Associate Editor
Rivka Galchen, Little Labors (2016)
Generally, I find stories about the trials and tribulations of child-having to be of limited appeal—useful, maybe, insofar as they offer validation that other people have also endured the bizarre realities of living with a tiny human, but otherwise liable to drift into the musings of parents thrilled at the simple fact of their own fecundity, as if they were the first ones to figure the process out (or not). But Little Labors is not simply an essay collection about motherhood, perhaps because Galchen initially “didn’t want to write about” her new baby—mostly, she writes, “because I had never been interested in babies, or mothers; in fact, those subjects had seemed perfectly not interesting to me.” Like many new mothers, though, Galchen soon discovered her baby—which she refers to sometimes as “the puma”—to be a preoccupying thought, demanding to be written about. Galchen’s interest isn’t just in her own progeny, but in babies in literature (“Literature has more dogs than babies, and also more abortions”), The Pillow Book , the eleventh-century collection of musings by Sei Shōnagon, and writers who are mothers. There are sections that made me laugh out loud, like when Galchen continually finds herself in an elevator with a neighbor who never fails to remark on the puma’s size. There are also deeper, darker musings, like the realization that the baby means “that it’s not permissible to die. There are days when this does not feel good.” It is a slim collection that I happened to read at the perfect time, and it remains one of my favorites of the decade. –Emily Firetog, Deputy Editor
Charlie Fox, This Young Monster (2017)
On social media as in his writing, British art critic Charlie Fox rejects lucidity for allusion and doesn’t quite answer the Twitter textbox’s persistent question: “What’s happening?” These days, it’s hard to tell. This Young Monster (2017), Fox’s first book,was published a few months after Donald Trump’s election, and at one point Fox takes a swipe at a man he judges “direct from a nightmare and just a repulsive fucking goon.” Fox doesn’t linger on politics, though, since most of the monsters he looks at “embody otherness and make it into art, ripping any conventional idea of beauty to shreds and replacing it with something weird and troubling of their own invention.”
If clichés are loathed because they conform to what philosopher Georges Bataille called “the common measure,” then monsters are rebellious non-sequiturs, comedic or horrific derailments from a classical ideal. Perverts in the most literal sense, monsters have gone astray from some “proper” course. The book’s nine chapters, which are about a specific monster or type of monster, are full of callbacks to familiar and lesser-known media. Fox cites visual art, film, songs, and books with the screwy buoyancy of a savant. Take one of his essays, “Spook House,” framed as a stage play with two principal characters, Klaus (“an intoxicated young skinhead vampire”) and Hermione (“a teen sorceress with green skin and jet-black hair” who looks more like The Wicked Witch than her namesake). The chorus is a troupe of trick-or-treaters. Using the filmmaker Cameron Jamie as a starting point, the rest is free association on gothic decadence and Detroit and L.A. as cities of the dead. All the while, Klaus quotes from Artforum , Dazed & Confused , and Time Out. It’s a technical feat that makes fictionalized dialogue a conveyor belt for cultural criticism.
In Fox’s imagination, David Bowie and the Hydra coexist alongside Peter Pan, Dennis Hopper, and the maenads. Fox’s book reaches for the monster’s mask, not really to peel it off but to feel and smell the rubber schnoz, to know how it’s made before making sure it’s still snugly set. With a stylistic blend of arthouse suavity and B-movie chic, This Young Monster considers how monsters in culture are made. Aren’t the scariest things made in post-production? Isn’t the creature just duplicity, like a looping choir or a dubbed scream? –Aaron Robertson, Assistant Editor
Elena Passarello, Animals Strike Curious Poses (2017)
Elena Passarello’s collection of essays Animals Strike Curious Poses picks out infamous animals and grants them the voice, narrative, and history they deserve. Not only is a collection like this relevant during the sixth extinction but it is an ambitious historical and anthropological undertaking, which Passarello has tackled with thorough research and a playful tone that rather than compromise her subject, complicates and humanizes it. Passarello’s intention is to investigate the role of animals across the span of human civilization and in doing so, to construct a timeline of humanity as told through people’s interactions with said animals. “Of all the images that make our world, animal images are particularly buried inside us,” Passarello writes in her first essay, to introduce us to the object of the book and also to the oldest of her chosen characters: Yuka, a 39,000-year-old mummified woolly mammoth discovered in the Siberian permafrost in 2010. It was an occasion so remarkable and so unfathomable given the span of human civilization that Passarello says of Yuka: “Since language is epically younger than both thought and experience, ‘woolly mammoth’ means, to a human brain, something more like time.” The essay ends with a character placing a hand on a cave drawing of a woolly mammoth, accompanied by a phrase which encapsulates the author’s vision for the book: “And he becomes the mammoth so he can envision the mammoth.” In Passarello’s hands the imagined boundaries between the animal, natural, and human world disintegrate and what emerges is a cohesive if baffling integrated history of life. With the accuracy and tenacity of a journalist and the spirit of a storyteller, Elena Passarello has assembled a modern bestiary worthy of contemplation and awe. –Eleni Theodoropoulos, Editorial Fellow
Esmé Weijun Wang, The Collected Schizophrenias (2019)
Esmé Weijun Wang’s collection of essays is a kaleidoscopic look at mental health and the lives affected by the schizophrenias. Each essay takes on a different aspect of the topic, but you’ll want to read them together for a holistic perspective. Esmé Weijun Wang generously begins The Collected Schizophrenias by acknowledging the stereotype, “Schizophrenia terrifies. It is the archetypal disorder of lunacy.” From there, she walks us through the technical language, breaks down the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual ( DSM-5 )’s clinical definition. And then she gets very personal, telling us about how she came to her own diagnosis and the way it’s touched her daily life (her relationships, her ideas about motherhood). Esmé Weijun Wang is uniquely situated to write about this topic. As a former lab researcher at Stanford, she turns a precise, analytical eye to her experience while simultaneously unfolding everything with great patience for her reader. Throughout, she brilliantly dissects the language around mental health. (On saying “a person living with bipolar disorder” instead of using “bipolar” as the sole subject: “…we are not our diseases. We are instead individuals with disorders and malfunctions. Our conditions lie over us like smallpox blankets; we are one thing and the illness is another.”) She pinpoints the ways she arms herself against anticipated reactions to the schizophrenias: high fashion, having attended an Ivy League institution. In a particularly piercing essay, she traces mental illness back through her family tree. She also places her story within more mainstream cultural contexts, calling on groundbreaking exposés about the dangerous of institutionalization and depictions of mental illness in television and film (like the infamous Slender Man case, in which two young girls stab their best friend because an invented Internet figure told them to). At once intimate and far-reaching, The Collected Schizophrenias is an informative and important (and let’s not forget artful) work. I’ve never read a collection quite so beautifully-written and laid-bare as this. –Katie Yee, Book Marks Assistant Editor
Ross Gay, The Book of Delights (2019)
When Ross Gay began writing what would become The Book of Delights, he envisioned it as a project of daily essays, each focused on a moment or point of delight in his day. This plan quickly disintegrated; on day four, he skipped his self-imposed assignment and decided to “in honor and love, delight in blowing it off.” (Clearly, “blowing it off” is a relative term here, as he still produced the book.) Ross Gay is a generous teacher of how to live, and this moment of reveling in self-compassion is one lesson among many in The Book of Delights , which wanders from moments of connection with strangers to a shade of “red I don’t think I actually have words for,” a text from a friend reading “I love you breadfruit,” and “the sun like a guiding hand on my back, saying everything is possible. Everything .”
Gay does not linger on any one subject for long, creating the sense that delight is a product not of extenuating circumstances, but of our attention; his attunement to the possibilities of a single day, and awareness of all the small moments that produce delight, are a model for life amid the warring factions of the attention economy. These small moments range from the physical–hugging a stranger, transplanting fig cuttings–to the spiritual and philosophical, giving the impression of sitting beside Gay in his garden as he thinks out loud in real time. It’s a privilege to listen. –Corinne Segal, Senior Editor
Honorable Mentions
A selection of other books that we seriously considered for both lists—just to be extra about it (and because decisions are hard).
Terry Castle, The Professor and Other Writings (2010) · Joyce Carol Oates, In Rough Country (2010) · Geoff Dyer, Otherwise Known as the Human Condition (2011) · Christopher Hitchens, Arguably (2011) · Roberto Bolaño, tr. Natasha Wimmer, Between Parentheses (2011) · Dubravka Ugresic, tr. David Williams, Karaoke Culture (2011) · Tom Bissell, Magic Hours (2012) · Kevin Young, The Grey Album (2012) · William H. Gass, Life Sentences: Literary Judgments and Accounts (2012) · Mary Ruefle, Madness, Rack, and Honey (2012) · Herta Müller, tr. Geoffrey Mulligan, Cristina and Her Double (2013) · Leslie Jamison, The Empathy Exams (2014) · Meghan Daum, The Unspeakable (2014) · Daphne Merkin, The Fame Lunches (2014) · Charles D’Ambrosio, Loitering (2015) · Wendy Walters, Multiply/Divide (2015) · Colm Tóibín, On Elizabeth Bishop (2015) · Renee Gladman, Calamities (2016) · Jesmyn Ward, ed. The Fire This Time (2016) · Lindy West, Shrill (2016) · Mary Oliver, Upstream (2016) · Emily Witt, Future Sex (2016) · Olivia Laing, The Lonely City (2016) · Mark Greif, Against Everything (2016) · Durga Chew-Bose, Too Much and Not the Mood (2017) · Sarah Gerard, Sunshine State (2017) · Jim Harrison, A Really Big Lunch (2017) · J.M. Coetzee, Late Essays: 2006-2017 (2017) · Melissa Febos, Abandon Me (2017) · Louise Glück, American Originality (2017) · Joan Didion, South and West (2017) · Tom McCarthy, Typewriters, Bombs, Jellyfish (2017) · Hanif Abdurraqib, They Can’t Kill Us Until they Kill Us (2017) · Ta-Nehisi Coates, We Were Eight Years in Power (2017) · Samantha Irby, We Are Never Meeting in Real Life (2017) · Alexander Chee, How to Write an Autobiographical Novel (2018) · Alice Bolin, Dead Girls (2018) · Marilynne Robinson, What Are We Doing Here? (2018) · Lorrie Moore, See What Can Be Done (2018) · Maggie O’Farrell, I Am I Am I Am (2018) · Ijeoma Oluo, So You Want to Talk About Race (2018) · Rachel Cusk, Coventry (2019) · Jia Tolentino, Trick Mirror (2019) · Emily Bernard, Black is the Body (2019) · Toni Morrison, The Source of Self-Regard (2019) · Margaret Renkl, Late Migrations (2019) · Rachel Munroe, Savage Appetites (2019) · Robert A. Caro, Working (2019) · Arundhati Roy, My Seditious Heart (2019).

Emily Temple
Previous article, next article.

- RSS - Posts
Literary Hub
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
If you could change one thing about college, what would it be?
Graduate faster
Better quality online classes
Flexible schedule
Access to top-rated instructors

College Success
Why Study Literature?
05.15.2023 • 5 min read
Learn about the value and benefits of studying literature: how it develops our skills as well as shapes our understanding of the society we live in.
What Is Literature?
The benefits of studying literature.
Literature & Outlier.org
Many libraries in the U.S. are under attack.
From small towns to big cities, it’s more common to see protests outside of libraries. Libraries are under the microscope and being scrutinized for what content they have on their shelves.
Some people see certain books as a threat to society. While others believe everyone has a right to access any information they wish. The fact is literature is so powerful some people see it as dangerous and want to choose what the public has a right to read.
This is not the first time in history that people have tried to censor literature for what it says. So what really is literature and why is it so powerful?
In this article, we’ll define literature, talk about the history of literature, and the benefits of studying literature in college.
Literature is an art form that uses language to create imaginative experiences. It includes poetry, drama, fiction, and nonfiction.
Literature communicates ideas and emotions.It entertains, educates, and inspires readers. Literature explores complex themes and is an important part of human culture.
From its original Latin derivative, "writing formed with letters," to its current definition, a "body of written works," our understanding of literature has evolved.
Literature explains society and culture. It both criticizes and affirms cultural values based on the writer’s perceptions. It expresses and explores the human condition. It looks back to the past and onward toward the future.
As literature represents the culture and history of a language or people, the study of literature has great value. To study literature means looking deeply into a large body of written work and examining it as an art form.
Of course, there are many different literary genres, or types of literature. At a liberal arts school , a literature program, a student would study these genres extensively and understand the historical and cultural context they represent.
Literary Fiction vs. Genre Fiction
Students in a college literature program examine many forms of literature, including:
Some definitions of literature separate fiction into 2 categories: literary fiction and genre fiction. Genre fiction consists of more popular literature read for entertainment. Some examples of genre fiction include crime, fantasy, and science fiction stories.
Literary fiction explores themes of the human condition. These stories cannot be further categorized and are read primarily for a philosophical search for the meaning of life. Examples of literary fiction include The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald and Beloved by Toni Morrison.
You can discover more distinctions by studying literature in depth.
1. Literature Develops Communication Skills
The foundation of literature is the English Language. By reading literature, you can improve your knowledge of language: vocabulary, grammar, sentence structure, content creation, and more. When you immerse yourself in William Shakespeare, Celeste Ng, or Chinua Achebe, you're absorbing new words, expressions, and ideas—without even realizing it.
You can use everything you learn to improve your own writing and communication skills . You will use these skills beyond high school and college. In our everyday lives, we navigate personal relationships, craft emails, present projects, collaborate with teammates, analyze data, and more.
Yuval Noah Harari has written much of his own literature on the history and success of the human race. In his book Sapiens, he emphasizes our ability to craft stories as one of our most valuable skills: " Fiction has enabled us not merely to imagine things, but to do so collectively.” Through these collective stories, we learn about the human experience, both in smaller interpersonal ways and on a larger, more global scale.
2. Literature Teaches Us About the Human Condition
Literature helps us reflect on the human experience, teaching us about who we are and the world we live in. It presents a range of emotions, from love to anger to grief to happiness. It gives us insight and context about societal norms and cultural traditions.
It explores our history and our present; it imagines our futures. It introduces us to new ways of thinking and living, compelling us to think critically and creatively about our own experiences.
Through literature, we see we're not alone in our thoughts and feelings. The characters we read about have already experienced similar difficulties and worked to solve or change them, giving us the blueprint to do the same.
Jane Austen's Pride and Prejudice goes beyond social commentary to explore the complexities of familial relationships, romantic relationships, and friendships. Mr. Darcy insults Elizabeth Bennet without meaning to, Elizabeth Bennet makes harsh judgments without knowing all the facts, and Mrs. Bennet worries about her daughter's future constantly. We can see ourselves in them.
3. Literature Teaches Us About Empathy
When we connect with literature's characters and narratives, we learn how to empathize with others. While we’re not physically experiencing the raging seas in Virginia Woolf's To the Lighthouse or the loss of a loved one in William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet, we are swept up in the story and the emotion. This helps us develop empathy and emotional intelligence.
In a 2006 study , professors at the University of Toronto concluded a lifetime exposure to literary fiction positively correlated with advanced social ability. In 2020, the Harvard Business Review encouraged business students to read literary works to enhance their abilities to keep an open mind, process information, and make effective decisions.
4. Literature Helps Us Explore New Ideas
With words, and not actions, authors create spaces where we can explore new ideas, new structures, new concepts, and new products. When the only limit is your imagination, anything is possible in creative writing.
We can dive into the past to understand British society at the turn of the 19th century in Austen's Pride and Prejudice or jump into potential futures through Harari's Homo Deus. We can consider alternative futures like that in George Orwell's 1984 or conduct experiments in Robert Louis Stevenson's The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde.
We don't encounter monsters or humanoid robots in our everyday lives (at least we hope not!). But when we explore them through literature, we’re equipped to consider, challenge, and analyze concepts we don't yet know or understand. This practice opens our minds and allows us to be more flexible when we face the new and unknown. These critical thinking skills enable us to process information easier.
5. Literature Changes the Way We Think
With everything we learn from literature and the skills it helps us develop, literature changes the way we think, work, and act.
When we can think more critically, we arrive at different conclusions. When we open our minds and empathize with others, we better accept and tolerate differences. When we can articulate and communicate effectively, we work better together to achieve and succeed.
Whether English literature or Russian literature or French literature, literature is the key to understanding ourselves and society.
Literature and Outlier.org
Looking to study literature and develop your own writing skills? Outlier.org’s cutting-edge College Writing course is a great place to start. Through interviews with celebrated writers and writing secrets from instructor John Kaag, you'll learn how to use words to express yourself and communicate more effectively.
The course explores:
How to level up your love letters
What writing and magic have in common
How to write better professional emails using The Princess Bride
How to get your writing published
How to create the perfect short sentence
Outlier courses are 100% online, so you can learn at your own pace from the comfort of your own home. At $149 per credit, you’ll save 50% compared to other college courses, all while earning transferable credits from the top-ranked University of Pittsburgh. If you decide to continue your education in literature, you can take the credit with you to the degree program of your choice.
It’s no doubt studying literature will give you a well-rounded education. It is through literature that societies have grown and developed—inspiring change throughout the world. Choosing to study literature will not only give you a glimpse into the past but help you articulate the present and inspire change in the future. By studying literature you will have the power to connect with others and truly touch their hearts and minds.
About the Author
Bob Patterson is a former Director of Admissions at Stanford University, UNC Chapel Hill, and UC Berkeley; Daisy Hill is the co-author of Uni in the USA…and beyond published by the Good Schools Guide 2019. Together, they have established MyGuidED, a new educational tool for students looking to apply to university (launching 2023).
Degrees+: Discover Online College Unlike Anything You’ve Experienced
Outlier (winner of TIME Best Inventions 2020) and Golden Gate University (#1 school for working professionals) have redesigned the experience of earning a college degree to minimize cost and maximize outcomes. Explore a revolutionary way to earn your college degree:
Related Articles

What Are the Liberal Arts in Education?
The article defines what liberal arts education is, explains the different degree fields, and lists possible professions you can do with the degree.
Jennifer Rivera
Subject Matter Expert

10 Amazing Jobs for Communication Majors [2023]
This article explains what a communications degree is and the benefits of studying it. It lists the skills a communication major has and the best-paid jobs, including the entry-level and average salaries.
Mia Frothingham

8 Reasons Why Having a College Degree Is Important
Learn more about why a college degree is important by understanding the benefits and value of having one.
Bob Patterson
Former Stanford Director of Admissions
Further Reading
Best 15 tips to make the most of college [2023], what are soft skills in college, thinking about going back to college in your 30s here’s everything you need to know, a complete guide on how to write a winning scholarship essay, 7 best self-paced online college programs [2023], what is community college.
Why Literature Is Important
By: Author Paul Jenkins
Posted on March 28, 2022
Categories Reading , Inspiration , Productivity , Self Improvement , Storytelling , Writing
The importance of literature is immense, what you learn will change your perception of the world and how you interact with people by using a wealth of literary devices such as tone, mood, and figurative language. You will be able to share your ideas and thoughts in better ways through writing that conveys meaning clearly to your reader. The best part is that you won’t even realize when you’ve started learning all these aspects. Reading literature will seep into your mind and work almost by osmosis!
What Do We Mean By Literature
Let’s define terms first: ‘literature’ means any collection of written work, but it tends to refer to writing produced with artistic intent: novels, plays, poems, and essays. In this way, literary work differs from – for example – journalism, business, or technical writing.
Literature is the art of discovering something extraordinary about ordinary people and saying with ordinary words something extraordinary. Boris Pasternak
Be a Better Communicator and Writer
The fact is that people who read a lot of literature are better 21st Century communicators. This might seem ironic, given the multitude of technology and media that surround us.
Reading gives you access to so many different points of view that you can understand different perspectives and make up your own thoughts and feelings about them.
People who get involved with literature – reading, writing, or both – have an advantage because they’re better at getting to the point or expressing themselves. If you’ve ever been in the situation of arguing a point or explaining something complex, all that practice will help you communicate.
Your communication will benefit both in terms of your written communications, and how effectively you can express your thoughts and feelings verbally.
Reading literature also helps you develop a sense of perspective about the way other people see the world, and helps you understand their point of view more clearly. All this will make you a better communicator, and it will make you a better writer, too.
Gain a Better Understanding of the World
Literature helps us understand others and the world around us. Works of literature are windows on other worlds, and windows on the worlds of others.
When we read books written by people from other backgrounds, we learn about and accept other cultures and ideas. We can learn about ways of doing things that are different from our own. This gives us a broader perspective and helps us think about things in a new way.
In my opinion, as we live in an increasingly globalized world, it is all the more important to retain sensitivity to its great diversity. Literature from other countries and cultures helps us do that.
By reading and discussing world literature, and investigating different literary genres, we gain an understanding not only of the authors’ ideas but also of the cultural and historical context in which the ideas originated.
It’s not only English literature or American literature that holds all the pearls, by the way. These days, you can find great translations of important literary works from:
- Chinese literature
- Latin American literature
- French literature
and many other literary traditions.
Get New Insights Into What Seemed Familiar
Conversely, it’s important to read books written by people who come from similar backgrounds to ours so they can give us perspectives we may not have considered before.
Related: Why Books Are Important .
Literature helps us understand and relate to others who’ve had experiences similar to our own, such as illness or family problems (just as reading about the loss of another person helped me process my own). It helps us to give our own real-life meaning.
When you read a work of literature, you can experience things that don’t happen in your life, and you can see yourself in different situations. You also learn about how people have dealt with problems throughout history, which can help you solve your own problems.
You’ll take a deep dive into human nature, and its many mysteries.
Language is an incredibly important part of the quest by humans for our identity. Therefore, as ‘linguistic beings’ literature is naturally a high expression of the human personality, every bit as much as painting or music.
Cultivate Empathy for Others
Literature enables us to develop empathy and understanding for others, which contributes to our social skills. It gives us a chance to imagine and live out in our minds social situations even though we may never experience them directly.
A famous academic study in 2013 (Kidd and Castano) found that literature increases empathetic skills more than nonfiction and popular fiction – perhaps because of the more complex character featured in literary works.
It is one of the important facets of literature that it explores the internal world of human life – the thoughts and feelings – of its characters in a way that visual and auditory media such as films and theater cannot. This is because character development in writing relies much more heavily on internal portrayal rather than external expression.
By connecting with the human experience of others, you enrich your own. Literature enables us to better understand what it is to be a human being.
Benefits of Literature in Education
It’s great to get kids excited about literature. Many children are social misfits and loners because they’ve difficulty forming bonds with others. When kids read about people who’re different from them, they begin to develop empathy and understanding for others. This can then be transferred to real life: children can better understand their classmates at school and make friends more easily.
Kids who read more children’s literature in high school show better social skills than children who don’t.
People who are in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) careers can also benefit greatly from literature. It’s noteworthy that many leading physicists, for example, are also avid readers of literature.
Literature adds to reality, it does not simply describe it. It enriches the necessary competencies that daily life requires and provides; and in this respect, it irrigates the deserts that our lives have already become. C. S. Lewis
Helps You Be More Creative
Literature can help you become more creative and improve “thinking outside the box.”
The most obvious reason for this is that literature by its very nature is an exercise in creativity, and relies on the imagination and curiosity of its readers to function. Ask any group of twenty readers of a piece of literature how they would describe the main character, and you’ll get twenty different responses! Readers enjoy thinking up their own scenarios (what the characters will do next) or plots (the way the story will be resolved, for example).
Literary fiction often leans heavily on the use of symbolism, allegory, and metaphor to project its power. All of which demands significant amounts of creativity on the part of the authors and their readership.
In this way, literature functions as an immediate and direct appeal and stimulus to our creativity.
No matter what your career goals are, creativity is a valuable skill. Most professions require you to think outside the box and find innovative solutions to problems; in fact, in some professions, such as art and design, it’s mandatory!
Reading classic literature has been shown to improve creative thinking and the ability to come up with new ideas. Even if you don’t immediately become an artist or designer by reading literature, it can help you become more creative and improve your lateral thinking.
It Helps Critical Thinking Also
Literature may also improve critical thinking skills. You have to spot the flaws in a story, analyze its plot, and figure out the motivations and meaning of the characters.
One important area where literature can help us reflect and find solutions is the area of human conflict.
A literary text is a playground to examine ideas and causality between them – why and how one thing follows another.
An Essential Part of Creative Writing Skill
If engaged in any kind of creative writing, then reading and studying literature to at least some degree is a must. You will learn a huge amount about character motivation, story structure, etc.
It’s well worth reading both classic literature and modern literature.
Develop a Better Memory
Reading can help you remember things better. When we read, our brains process the information we take in.
Literature, especially, with all its plot twists, flashbacks, foreshadowing, character arcs, and so on is like a playground for the mind and memory.
Poetry, with its rhythms and rhymes, can help your own associative mental processes. If using something like the Memory Palace technique, for example, then lines and ideas from poetry can be useful in the linking of objects in the rooms of your memory palace to something you wish to remember.
When people reading poetry have their brains scanned, the regions linked to memory and daydreaming are shown to increase activity.
Related: Memory Palaces
Improve Your Vocabulary
A wider vocabulary is beneficial for all aspects of your life, from school to work.
Reading literature increases your vocabulary and improves your understanding of language. The more you read, the better you can use words and choose the right ones for each situation.
The difficulty of literature is not to write, but to write what you mean; not to affect your reader, but to affect him precisely as you wish. Robert Louis Stevenson
A good practice is to use a dictionary and thesaurus when you study literature. Not only will this help your precise understanding of what the author wanted to say (especially with more high-flown works) but it will also serve you to improve your own vocabulary and language use.
This skill leads to better communication with others, as you can better explain yourself and help others understand new ideas.
A large vocabulary can also help you with your writing. If you know how words are used in different contexts, you’ll find it easier to use them in your own work. And if you’ve access to a wide range of words, you’ve many more options than if you were limited by a weak vocabulary.
Enhance Your Ability to Concentrate
There are so many distractions all around in everyday life. Not the least of which are the screens that surround us every minute of the day.
The great thing about settling in with a book is that, unlike a computer screen, a book has only one purpose – to take you somewhere. Once you have engaged with the words, it’s almost impossible to stop reading. Reading literature improves your concentration, so you’re less distracted by your surroundings and therefore more effective in your work.
Whenever you find yourself losing focus, why not try grabbing the latest book on your list. Personally, I use a Kindle to read – one of the things I love about it is the bookmark feature, meaning that a page I’m reading can be bookmarked for later. Sometimes, weeks or months later.
Or pick up a short story if pushed for time.
Alongside a detrimental effect on your work or learning, constant distractions increase your stress. And not in a healthy way. Therefore, reading literature not only helps you concentrate – it helps you relax at the same time!
An Opportunity to Interact With Family and Friends
Literature provides an opportunity to have a meaningful and deep conversation with family and friends.
Works of literature normally take on meaningful and important subjects. Consequently, your family and friends will be interested in what you have to say about the topic.
The topics can be as broad as religion, philosophy, politics, and so on, or as specific as Dickens’s David Copperfield or Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar.
This kind of interaction doesn’t only have to be in person, of course. Sites like Goodreads are great to shoot the breeze with fellow readers, and exchange not only reviews of stuff that you have read, but also get into a discussion about the themes and motivations of the books.
Or you can find a local book club on Meetup, for example.
Helps Your Profile and Career
Not all motivations for reading literature are altruistic!
Reading good literature makes you more cultured and enables you to exchange and project the ideas you’ll find within it at work, and on your social profiles. Whether you are a student, or already in the world of work.
In modern society, knowledge is power, and insight is even more powerful. Books contain information that takes years to acquire firsthand; they contain advice and wisdom from people who’ve been in a similar situation before; they also open up whole new worlds: in your imagination, in other works of fiction like stories and poems, or in nonfiction like biographies or travelogues of fictional novels.
You don’t need to be an English major to benefit!
Examples of Important Literature
- The Blue Sky by Galsan Tschinag
- Crime and Punishment by Feodor Dostoyevsky
- Teta by Barassa
- Heart of Darkness by Joseph Conrad
- Passage to India by E.M. Forster
- Master and Margarita by Mikhail Bulgakov
- The Prelude by William Wordsworth
- Jane Eyre by Charlotte Bronte
- A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens
- King Lear by William Shakespeare
World Literacy Foundation
Recommended

What Elie Wiesel Says About Humanity?

Something About Sam – ‘The Wolf and the Rain’
- Adventures of Huckleberry Finn
- African American Literature
- Angelou, Maya
- April Fool's Day
- Atwood, Margaret
- Austen, Jane
- Award Winners
- Banned Books
- Behn, Aphra
- Bestsellers
- Black History Month
- Book Adaptations
- Book Destination
- Book Publishing
- Book Reviews
- Books & Titles
- Bookshelves
- Children's Books
- Children’s Picture Book Day
- Christie, Agatha
- Controversy
- Don Quixote
- Entertainment
- Erdrich, Louise
- Evanovich, Janet
- Fitzgerald, F Scott
- Fitzgerald, Zelda
- Frank, Anne
- Harlem Renaissance
- Hemingway, Ernest
- Holidays and Events
- Holocaust Literature
- Homework Help
- Inspiration
- King Arthur
- King, Stephen
- Klein, Naomi
- Life Lessons
- Little Mermaid
- Lost Generation
- Momaday, N Scott
- Native American Literature
- Patterson, James
- Rowling, JK
- Science Fiction
- Sexual Assault Awareness Month
- Shakespeare, William
- Storytelling
- Top Authors
- Twain, Mark
- Uncategorized
- Wharton, Edith
- Wiesel, Elie
- Women's Literature
- Young Adult
Don't miss it

Unleash Your Inner Word Wizard: Scrabble’s Gen Z Makeover Takes Word Games to the Next Level!

The Enigmatic Eclipse: Ancient Mythological Stories that Illuminate the Skies

Unlocking Literary Freedom: Discover the Truth about Banned Books in Hong Kong

Shattering Silence: How Book Banning Hinders Progress in Sexual Assault Awareness Month

Join Reese Witherspoon’s Book Club and Dive Into a Captivating Multi-Generational Must-Read

Celebrate the Magic of Storytelling: Unveiling the Colorful Pages of Children’s Picture Book History
About a book geek.

We bring you the best news, reviews, and insights on everything related to books, literature, lifestyle, and beyond. Check back for more details.
What’s Happening?

The Role of Literature in Education: Why It Matters

Literature is more than just entertainment or a way to pass the time. It can shape our perspectives, challenge our beliefs, and inspire us to brood over the world. Literature is a valuable tool for developing critical thinking skills, empathy, and creativity in education. This post will explore why literature matters and how it can benefit students of all ages.
Literature Promotes Critical Thinking Skills
Reading literature requires active engagement and analysis, which helps develop critical thinking skills. When students read literature, they are forced to think deeply about the characters, themes, and messages presented in the text. They must analyze the author’s choices and consider how they contribute to the work’s overall meaning. Critical thinking is essential for success in many areas of life, including academics, careers, and personal relationships. Literature helps students become more thoughtful and independent thinkers by promoting critical thinking skills.
You might also like

How to Memorize Textbooks: Tips and Tricks for Success
Literature helps develop empathy and understanding.
Besides critical thinking skills, literature also helps students develop empathy and understanding. Through reading about characters from different backgrounds and experiences, students can gain a deeper understanding of the world around them. They can learn to see things from different perspectives and develop greater empathy for others. This is important in today’s diverse and interconnected world, where understanding and empathy are essential for building strong relationships and communities. By exposing students to a wide range of literature, educators can help foster a more compassionate and understanding society.
Literature Encourages Creativity and Imagination
Reading literature can spark creativity and imagination in students. By exposing them to different styles of writing, unique characters, and imaginative worlds, literature can inspire students to think outside the box and develop their creative ideas. This is important in a world where we value innovation and creativity. By encouraging students to read and engage with literature, educators can help foster a generation of creative thinkers and problem solvers.
Literature Provides a Window Into Different Cultures and Perspectives
One of the most critical roles of literature in education is its ability to provide a window into different cultures and perspectives. By reading literature from different parts of the world, students can better understand the experiences and perspectives of people from different backgrounds. This can help to promote empathy and understanding and can also help to break down stereotypes and prejudices. This is an essential skill for students to develop in a world that is becoming increasingly diverse.
Literature Can Inspire Personal Growth and Self-Reflection
Literature has the power to inspire personal growth and self-reflection in students. By reading about characters who face challenges and overcome them, students can learn valuable lessons about resilience, perseverance, and the importance of a positive attitude. Literature can help students reflect on their own experiences and emotions and provide a safe space to explore complex topics and feelings. This can be important for students who may not have access to other forms of emotional support or therapy.
Esther Lombardi
Esther A. Lombardi is a freelance writer and journalist with more than two decades of experience writing for an array of publications, online and offline. She also has a master's degree in English Literature with a background in Web Technology and Journalism.
Related Posts

Memorizing textbooks can be daunting, but it doesn't have to be. With the right techniques, you can make the process...
- 21.3k Followers

Introduction to Word Games and Their Popularity Word games have long been a beloved pastime for people of all ages....

Elie Wiesel’s ‘Night’ – Lines of Remembrance

Emily Dickinson: Examining the Influences and Impact of Her Revolutionary Poetry

Why Is ‘The Catcher In The Rye’ Important? 7 Ways

Practicing Gratitude Quotes

‘The Secret Garden’ of Writing

‘Little House’ – Writing the Story of Our Lives
© 2023 A Book Geek
Welcome Back!
Login to your account below
Remember Me
Retrieve your password
Please enter your username or email address to reset your password.
Add New Playlist
- Select Visibility - Public Private
You cannot copy content of this page
Discover more from A Book Geek
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
8 Prompts for Essays About Literature. 1. The Importance of Literature. In your essay, write about the importance of literature; explain why we need to study literature and how it can help us in the future. Then, give examples of literary works that teach important moral lessons as evidence. 2.
Literature is of great importance and is studied upon as it provides the ability to connect human relationships and define what is right and what is wrong. Therefore, words are alive more than ever before. Literature is the foundation of life. It places an emphasis on many topics from human tragedies to tales of the ever-popular search for love.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
The study of literature is important because it, at its most basic, improves reading skills. From this involved reading of quality literature a student then develops their writing skills, as the ...
We might even say that when it comes to knowing how to write a good English Literature essay, practising is more important than planning. 2. Make room for close analysis of the text, or texts. Whilst it's true that some first-class or A-grade essays will be impressive without containing any close reading as such, most of the highest-scoring ...
Literary analysis involves examining all the parts of a novel, play, short story, or poem—elements such as character, setting, tone, and imagery—and thinking about how the author uses those elements to create certain effects. A literary essay isn't a book review: you're not being asked whether or not you liked a book or whether you'd ...
Benefits of Literature. Studies show reading literature may help. promote empathy and social skills (Castano and Kidd) alleviate symptoms of depression (Billington et al.) business leaders succeed (Coleman) prevent dementia by stimulating the mind (Thorpe) These are just a few of the studied benefits of literature.
To understand the kind of work that literature can do, it is important to understand the kind of knowledge that it provides. This is a very complex and widely debated question among literary scholars. But one way of understanding the kind of knowledge that can be gained from literature is by thinking about how we use language to make sense of ...
Step 1: Read the Text Thoroughly. Literary analysis begins with the literature itself, which means performing a close reading of the text. As you read, you should focus on the work. That means putting away distractions (sorry, smartphone) and dedicating a period of time to the task at hand.
These 4 steps will help prepare you to write an in-depth literary analysis that offers new insight to both old and modern classics. 1. Read the text and identify literary devices. As you conduct your literary analysis, you should first read through the text, keeping an eye on key elements that could serve as clues to larger, underlying themes.
Essays are an important piece of literature that can be used in a variety of situations. They're a flexible type of writing, which makes them useful in many settings. History can be traced and understood through essays from theorists, leaders, artists of various arts, and regular citizens of countries throughout the world and time. For ...
How to write Essays, Dissertations and Theses in Literary Studies. Longman, 1993. INTRODUCTION While most of you have already had experience of essay writing, it is important to realise that essay writing at University level may be different from the practices you have so far encountered. This information outlines what is required of an English
Introduction. Literature is still important, especially the radical one that tends to be challenging in many respects. It is good for people who have critical thinking and step out of the ideational comfort zone that conformity offers. Through such works as Don Quixote and Madame Bovary, one has the opportunity to live other lives through the ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
One is that "fiction" and "literature" are regarded as quite different things. "Fiction," for example, is what people read for enjoyment. "Literature" is what they read for school. Or "fiction" is what living people write and is about the present. "Literature" was written by people (often white males) who have since died ...
Literature educates the heart as much as the mind by illustrating the complexity of emotions. Self-awareness: Recognizing personal emotions and their effects. Self-regulation: Managing disruptive emotions and impulses. Motivation: Relating one's emotions to personal goals and objectives.
Robin Wall Kimmerer, Braiding Sweetgrass (2013) Of every essay in my relentlessly earmarked copy of Braiding Sweetgrass, Dr. Robin Wall Kimmerer's gorgeously rendered argument for why and how we should keep going, there's one that especially hits home: her account of professor-turned-forester Franz Dolp.When Dolp, several decades ago, revisited the farm that he had once shared with his ex ...
Literature is an art form that uses language to create imaginative experiences. It includes poetry, drama, fiction, and nonfiction. Literature communicates ideas and emotions.It entertains, educates, and inspires readers. Literature explores complex themes and is an important part of human culture. From its original Latin derivative, "writing ...
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
The importance of literature is immense, ... poems, and essays. In this way, literary work differs from - for example - journalism, business, or technical writing. Literature is the art of discovering something extraordinary about ordinary people and saying with ordinary words something extraordinary. ...
"Writing" is usually understood as the expression of thought. This book redefines "writing" as the thought process itself. Writing is not what you do with thought. Writing is thinking. Better living through interpretation: that's the promise of academic writing, which is a foundational course in most schools because it's a
Literature has the power to inspire personal growth and self-reflection in students. By reading about characters who face challenges and overcome them, students can learn valuable lessons about resilience, perseverance, and the importance of a positive attitude. Literature can help students reflect on their own experiences and emotions and ...
For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts. In this context, you won't necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you're told otherwise.
This essay about Oscar Wilde's "The Importance of Being Earnest" offers fresh perspectives on its opening scene. It dissects the social commentary, explores themes of identity and masquerade, and appreciates Wilde's linguistic brilliance. Each analysis illuminates the play's satire and relevance, providing valuable insights into ...
Jack Helton Mr. Hendricks American Literature 11 April 2024 The Importance of Now Robert Frost's "Nothing Gold Can Stay"and T.S. Eliot's "The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock" concerns self identity through illuminating moments, the concepts of the passage of time and the importance of now.