| Renewable energy has high upfront costs. | | Renewable energy has lower maintenance requirements. | Renewable energy is intermittent. |
| Renewables save money. | Renewables have limited storage capabilities. |
| Renewable energy has numerous environmental benefits. | Renewable energy sources have geographic limitations. |
| Renewables lower reliance on foreign energy sources. | Renewables aren’t always 100% carbon-free. |
| Renewable energy leads to cleaner water and air. | |
| Renewable energy creates jobs. | |
| Renewable energy can cut down on waste. | |
Advantages of renewable energy
Renewable energy has multiple advantages over fossil fuels. Here are some of the top benefits of using an alternative energy source:
Renewable energy won’t run out.
Renewable energy has lower maintenance requirements.
Renewables save money.
Renewable energy has numerous environmental benefits.
Renewables lower reliance on foreign energy sources.
Renewable energy leads to cleaner water and air.
Renewable energy creates jobs.
Renewable energy can cut down on waste.
1. Renewable energy won’t run out
Renewable energy technologies use resources straight from the environment to generate power. These energy sources include sunshine, wind, tides, and biomass. Renewable resources won’t run out, which cannot be said for many types of fossil fuels – as we use fossil fuel resources, they will be increasingly difficult to obtain, likely driving up both the cost and environmental impact of extraction.
2. Maintenance requirements are lower for renewable energy
Renewable energy systems usually require less overall maintenance than generators that use traditional fuel sources. This is because generating technology like solar panels and wind turbines either have few or no moving parts and don’t rely on flammable, combustible fuel sources to operate. Fewer maintenance requirements translate to more time and money saved.
3. Renewables save money
Using renewable energy can help you save money long term. Not only will you save on maintenance costs but also on operating costs. You don't have to pay to refuel when you’re using a technology that generates power from the sun, wind, steam, or natural processes. The amount of money you will save using renewable energy can vary depending on several factors, including the technology itself. In most cases, transitioning to renewable energy means anywhere from hundreds to thousands of dollars in savings—find out how much you can save by switching to solar energy .
4. Renewable energy has numerous environmental benefits
Renewable energy generation sources lead to lower greenhouse gas emissions than traditional fuel sources like natural gas. This means a smaller carbon footprint and an overall positive impact on the natural environment . During the combustion process, fossil fuels emit high amounts of greenhouse gases, which have been proven to exacerbate climate change, which in turn causes rising global temperatures and higher frequencies of extreme weather events.
The use of fossil fuels emits greenhouse gases and other harmful pollutants that lead to respiratory and cardiac health issues . With renewable energy, you’re helping decrease these pollutants' prevalence and contributing to a healthier atmosphere.
5. Renewables lower reliance on foreign energy sources
With renewable energy technologies, you can produce energy locally. The higher the amount of our energy use is renewable, the less we’ll rely on imported energy, and the more we’ll contribute to U.S. energy independence. Renewable energy sources can help us minimize the geo-political risks associated with fossil fuels, from trade disputes to political instability to pricing wars, which are often rooted in access to oil.
6. Renewable energy leads to cleaner water and air
When you burn fossil fuels to generate electricity, it contaminates the air and water we use. For example, coal power stations release high volumes of carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and harmful toxins like mercury, lead, and sulfur dioxide. Health problems from ingesting these elements can be dangerous and even fatal. Investing in renewable energy is a great way to work against these risks, as renewables have a far lower negative impact on our air and water.
The use of fossil fuels emits greenhouse gases and other harmful pollutants that lead to respiratory and cardiac health issues . With renewable energy, you’re helping decrease these pollutants' prevalence and contributing to a healthier environment.
7. Renewable energy creates new jobs
While the U.S. shifts its focus to combat global warming, we’re setting ambitious carbon-reduction goals that require labor to get the job done. Today, the renewable energy sector employs three times as many people as fossil fuels in the U.S. That number is expected to rise over the next few years—and as a plus, these jobs tend to pay above average wages, making it a desirable career option and an overall economic boom.
8. Renewable energy can help solve our waste problem
Specifically, biomass energy can offer a significant benefit in this way. Biomass generators consume used organic products like vegetable oil, corn and soybean byproducts, and even algae to generate energy. Because of this, using biomass as an energy source can reduce the amount of waste that goes into landfills, which helps cut down on carbon emissions and environmental contamination.
Disadvantages of renewable energy
Renewable energy has many benefits, but it’s not always sunny when it comes to renewable energy. Here are some cons of renewable energy when compared to traditional fuel sources:
Renewable energy has high upfront costs.
Renewable energy is intermittent.
Renewables have storage capabilities.
Renewable energy sources have geographic limitations.
Renewables aren’t always 100% carbon-free.
1. Higher upfront cost
While you can save money using renewable energy, the technologies are typically more expensive upfront than traditional energy generators. To combat this, financial incentives such as tax credits and rebates are available to help alleviate your initial costs of renewable technology.
2. Intermittency
Though renewable energy resources are available around the world, many of these resources aren’t available 24/7, year-round. Some days may be windier than others, the sun doesn’t shine at night, and droughts may occur for periods. Unpredictable weather events can disrupt these technologies, and the amount of energy we can get from renewable power sources can be inconsistent. Fossil fuels are not intermittent, and power plants can be turned on or off at any time to provide an energy supply. Wondering if you should make the switch to renewables? Find out if an energy source like solar power is a good fit for you .
3. Storage capabilities
Because of the intermittency of some renewable energy sources, there’s a high need for energy storage. Storage technologies are available but can be expensive, especially for large-scale renewable energy plants. It’s worth noting that energy storage capacity is growing as the technology progresses, and batteries are becoming more affordable as time passes.
4. Geographic limitations
The United States has a diverse geography with varying climates, topographies, vegetation, etc. This creates a beautiful melting pot of landscapes but also means that some geographies are more suitable for renewable technologies than others. For example, a large property in a rural area with open space may be an excellent place for a residential wind farm or a large-scale solar farm. At the same time, a townhome in a city covered in shade from taller buildings wouldn’t be able to reap the benefits of either technology. There are other options if your property isn’t suitable for a personal renewable energy technology. If you’re interested in solar but don’t have a sunny property, you can often still benefit from renewable energy by purchasing green power or enrolling in a community solar option .
5. Not 100% carbon-free
Although solar panels and other forms of renewable energy drastically reduce carbon emissions, these resources aren’t always completely clean. The manufacturing, transportation, and installation of renewable energy, like wind turbines, can create a carbon footprint since they’re usually produced in factories powered by fossil fuels —not to mention the diesel and gasoline needed to fuel the transport trucks. As the U.S. becomes more and more electrified – from solar panels on factories to electric transport trucks – carbon emissions associated with solar will continue to decrease.
6. Supply chain constraints
Renewables must have an effective distribution network created to transfer the energy where it’s needed on a large scale. These networks need non-renewable fuels to be generated, which offsets the benefits of renewable energy for a bit until it’s paid back. Additionally, politics can play a factor in installing renewable energy if it’s not a priority among local governments.
Types of renewable energy sources
There are a few types of renewable sources we can use for energy production:
Wind energy leverages the power of wind motion to generate electricity created by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface.
Solar power uses energy from the sun to generate electricity and heat.
Hydropower utilizes fast-moving water to spin turbines and generate electricity. This is also known as hydroelectric power or hydroelectricity.
Biomass generates electricity from organic plant matter.
Geothermal energy leverages heat from inside the earth to generate electricity.
Tidal produces electricity with special generators that leverage the surges of the ocean created during rising and falling tides. Hydrogen: utilized as fuel and electricity when separated from other elements like oxygen.
Nuclear energy , while not technically renewable, is often lumped in with the abovementioned sources. Nuclear power has the potential to provide electricity generation on a massive scale with zero emissions, making it an intriguing part of our energy future.
Renewable energy has more benefits than drawbacks
When it comes to renewable energy, the positives outweigh the negatives. Transitioning to renewables on a personal, corporate, or governmental level will help you save money and promote a cleaner, healthier environment for the future.
Installing solar panels is one of the easiest ways to go green. By signing up on the EnergySage Solar Marketplace , you can compare multiple quotes from local, pre-screened installers to see what solar costs and savings for your property. The quotes will also include estimates of the amount of carbon dioxide emissions you will offset over 20 years and what this equates to in both trees planted and gallons of gasoline burned.
Create your own clean energy with solar panels.
Enjoy the benefits of solar without rooftop panels.
Explore heat pumps, the latest in clean heating & cooling technology.
See solar prices near you.
Enter your zip code to find out what typical solar installations cost in your neighborhood.
- Our offerings
- Community solar
- Heating & cooling
- Backup power
- EV charging
- For your business
- Other energy options
- Solar calculator
- Solar rebates
- Home solar guide
- Market intel
- Refer a friend
- Mission & values
- How it works
- Editorial guidelines
- Work with us
- Solar & HVAC installers
- Corporate partnerships
- Community programs
- Utility programs
ENERGYSAGE is a registered trademark and the EnergySage logo is a trademark of EnergySage, Inc. Other trademarks are the property of either EnergySage, Inc. or our licensors and are used with permission.
© Copyright 2009-2024 EnergySage, Inc. All rights reserved.

Learn more about our success working with the U.S. Department of Energy.
Essay on Energy Resources in India
The below mentioned essay provides an anatomy of the Energy Resources of India. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Introduction to Energy Resources 2. Types of Energy Resource in India 3. The Energy Strategy 4. Energy Scenario.
Essay # Introduction to Energy Resources in India:
Energy resources are very much important in the context of economic development of the country. With the growing industrialisation, mechanisation of agriculture, and the development of transportation sector, the demand for energy resources is increasing day by day.
Thus a positive correlation exists between economic growth and demand for energy. Moreover, consumption of energy for domestic uses and public lighting has also been increasing.
In India between 1952-53 to 1987-88 the GDP had increased annually at the rate of 3.7 per cent while the energy consumption had increased at the rate of 6.2 per cent per annum. Inspite of this, the per capita consumption of energy in India is low in comparison to that of developed countries. In India, more than half of the population does not possess the capacity to purchase commercial energy.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Again out of the total energy consumed, about half of it is obtained from non-commercial energy. In India the noncommercial sources of energy, mostly used by rural poor, are obtained from firewood, dung cakes and agricultural waste. But the commercial energy is obtained from oil and natural gas, coal, hydro-electricity and a little volume of nuclear energy.
Essay # Types of Energy Resource in India:
Oil and coal :.
In India the consumption of commercial energy is too much dependent on oil and coal. About 47 per cent of the demand for commercial energy is met through petroleum oil. With the growing oil crisis, the importance of coal has also been realised in the country. Coal has an advantage over other fuels as it can be suitably converted into other types of energy like electricity, oil and gas.
In India, the coal is the principal source of electricity, at present with the significant development of thermal power projects based on coal. About 60 per cent of the total electricity generated in India is available from these coal based thermal power projects.
Power or electricity is considered as one of the major sources of commercial energy. Power contributed about 28.7 per cent of the total commercial energy consumption of the country in 1987-88. In India, the development of power is progressing at a considerable scale.
If we look at the installed capacity then the total installed generating capacity in India has increased from 2,300 M.W. in 1950 to 2,55,000 MW in 2015 (March).
Essay # The Energy Strategy in India:
Out of this total power generation in India about 60 per cent of it is generated through coal-based thermal power projects. The remaining 40 per cent of electricity is generated through hydro-electricity and atomic energy.
Considering the present power scenario of the country and the present energy crisis, proper steps should be taken for the proper utilisation of huge hydro-power potential of the country, which according to C.E.A. is equivalent to 75,400 M.W., along-with the development of non-conventional energy in the country.
The following elements are incorporated in the new energy strategy of the country:
(i) Accelerated exploitation of domestic conventional energy resources—oil, natural gas, coal, hydro, and nuclear power;
(ii) Proper management of oil demand;
(iii) Substitution of natural gas for oil products;
(iv) Conservation of energy;
(v) Exploitation of renewable sources of energy such as energy forestry and bio-gas, specially for meeting the energy requirements of the rural people; and
(vi) Intensify research and development on the emerging energy technologies.
In India, the shortage of energy is presently working as a major constraint of the industrial development. In view of the serious oil crisis faced at present due to soaring oil price, steps be taken for sustained increase in the production of coal.
Hydro-power potential should also be developed with a sense of urgency. Nuclear power, which is at present contributing a little more than 2 per cent of the total power generated, will have to be exploited with great vigour and urgency.
Moreover, in order to supplement the commercial energy produced in the country through the development of non-conventional energy, the Seventh Plan puts emphasis on “The development and accelerated utilisation of renewable energy sources wherever they are technically and economically viable, to improve the access to and availability of, renewable decentralised energy sources, particularly for the rural population and to reduce environment degradation resulting from deforestation.”
In order to realise these above mentioned objectives, the following efforts should be undertaken:
1. A large number of demonstration projects should be undertaken to popularise these new and renewable sources of non-conventional energy like wind, solar, bio-gas and bio-mass.
2. For developing indigenous technologies in this connection, the Government should support intensive R&D (Research and Development).
3. Attempts have to be made to create demand for this system through government intervention along with appropriate financial incentives as the initial cost of this system of renewable energy is very high.
4. An appropriate infrastructure for manufacturing, installation and servicing of this renewable energy system should be developed for its proper utilisation.
5. A large scale awareness programme should be undertaken to educate the people about the new technologies developed for the efficient utilisation of this system.
6. Lastly, substitution of non-commercial energy sources by commercial fuels should be discouraged and for that energy forestry should be developed.
Essay # Energy Scenario in India:
It is important to look at the present energy scenario of the country vis-a-vis other countries.
Latest finding from the Emerging Economy Report prepared by research and consultancy firm, Center for Knowledge Societies (CKS) shows that emerging economies could play pivotal roles in reducing the growing environmental anxieties worldwide. The report shows that most emerging economies remain for below the energy consumption as well as carbon emission levels of industrialised countries.
India’s per capita energy consumption of 12.6 million BTU and Indonesia’s (21.5) are almost negligible when compared to more economically developed nations like South Korea (170.2 m BTU per capita) and Taiwan (181.5 m BTU).
China’s carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) emission of 2.6 thousand metric tonnes per 1000 people is far below the 10.16 thousand metric tonnes per 1000 people in Germany.
The report has also identified several new energy paradigms that can fundamentally alter the ways in which end consumers access and use energy. Therefore, the new paradigm can dramatically change the adverse environmental effects of increased energy demand in the emerging economies.
The report highlighted that energy scarcity can lead to energy efficiency. To some extent the outstanding and latent demand for energy of most emerging economies, which is never met, can contribute to energy efficiency, at least in economic terms.
It is to the credit of India’s growth process that its energy intensity has fallen over time. In comparison to the rest of the world, particularly the emerging economies of Brazil and China, the use of energy per capita in India remained moderate and it increased at a slower pace.
Table 5.3 will clarify its position.
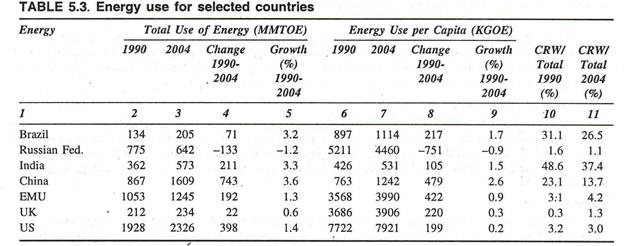
Table 5.3 reveals that total use of energy in India was 362 MMTOE in 1990 and then increased to 573 MMTOE in 2004 as compared to that of 1609 MMTOE for China, 205 MMTOE for Brazil, 1245 MMTOE for EMU and 2326 MMTOE for USA. The growth in the use of energy during the period 1990-2004 was 3.3 per cent in India as compared to that of 3.6 per cent in China, 3.2 per cent in Brazil and 1.4 per cent in USA.
However, the energy use per capita (KGOE) in India was 426 KGOE in 1990 increased to 531 KGOE in 2004 as compared to that of 1242 KGOE in China, 1114 KGOE for Brazil, 3906 KGOE for UK, 3990 for EMU and 7921 KGOE in the USA. Considering the huge size of population, the use of energy per capita in India is found to be moderate and its pace in also comparatively slower.
This could partly due to unsatisfied demand arising due to domestic capacity constraints. A large section of India’s population is still not in a position to buy and use any commercial sources of energy due to their poor economic capacity. Major portion of these energy resources are being used by a small section of rich and middle class people of the country.
Thus economic empowerment of this large section of poor people will lead to a huge demand for energy in near future leading to a serious energy crisis in our country. There is also enough evidence of wastage in use of scarce energy resources by the richer and middle class people of the country.
Sudden spurt in the use of private vehicles by these sections of population and the faulty vehicle policy pursued by the Government may lead to a serious energy crisis in near future in the context of shrinking national as well as global reserve of energy.
There is considerable room to improve energy efficiency, especially of motor vehicles and in the generation, transmission and end-use of electricity, commercially viable and economic attractive technology options in use in the developed world, should be considered and adopted.
Finally, wastage in the use of energy, especially in respect of petroleum and electricity needs to be immediately controlled both by pursuing the policy of imposition and awareness for attaining curtailment in consumption in the use of energy resources.
Thus under the present scenario of energy crisis, improving energy efficiency and demand side management measures like encouraging urban mass transport are quite important. Sustaining economic growth is critically dependant on significant supply augmentation and change in the composition of energy use.
Import dependence, for meeting the primary energy demand in the country, has been increasing over a long period since 1990-91 to 2006-07. In order to reduce incremental import dependence of country’s energy requirement in the medium term to long term entails a number of measures.
These include:
(a) Tapping India’s coal reserve with appropriate technology and reforms in the coal sector to increase competition
(b) Mitigating transportation constraints on availability of coal;
(c) Accelerating exploration of oil and gas within the country;
(d) Fully exploiting the nuclear and hydro-potential for power generation; and
(e) Expediting programmes for energy generation through renewable and non-conventional sources. Besides, a steps up of domestic production, the remaining deficit would have to be bridged by entering into strategic geo-political alliances to access the energy assets in the region. There is also a need for regulatory reform to implement open access in power sector to facilitate competition.
Finally, putting a curb on wasteful use of energy, especially in respect of petroleum and electricity is the urgent need of the hour. This needs to be attained by pursuing a rational policy of imposition and awareness for attaining the required curtailment in consumption in use of energy resources and also for pursuing a policy for conservation of energy in real and rational manner.
Related Articles:
- Conventional and Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
- 3 Main Sources of Electric Power
- Essay on Human Resources
- Solving Power Crisis in India
Benefits of Renewable Energy Use
Published Jul 14, 2008 Updated Dec 20, 2017
Wind turbines and solar panels are an increasingly common sight. But why? What are the benefits of renewable energies—and how do they improve our health, environment, and economy?
This page explores the many positive impacts of clean energy, including the benefits of wind , solar , geothermal , hydroelectric , and biomass . For more information on their negative impacts—including effective solutions to avoid, minimize, or mitigate—see our page on The Environmental Impacts of Renewable Energy Technologies .
Less global warming
Human activity is overloading our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and other global warming emissions . These gases act like a blanket, trapping heat. The result is a web of significant and harmful impacts , from stronger, more frequent storms, to drought, sea level rise, and extinction.
In the United States, about 29 percent of global warming emissions come from our electricity sector. Most of those emissions come from fossil fuels like coal and natural gas [ 1 , 2 ].
What is CO 2 e?
Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is the most prevalent greenhouse gas, but other air pollutants—such as methane—also cause global warming. Different energy sources produce different amounts of these pollutants. To make comparisons easier, we use a carbon dioxide equivalent , or CO2e—the amount of carbon dioxide required to produce an equivalent amount of warming.
In contrast, most renewable energy sources produce little to no global warming emissions. Even when including “life cycle” emissions of clean energy (ie, the emissions from each stage of a technology’s life—manufacturing, installation, operation, decommissioning), the global warming emissions associated with renewable energy are minimal [ 3 ].
The comparison becomes clear when you look at the numbers. Burning natural gas for electricity releases between 0.6 and 2 pounds of carbon dioxide equivalent per kilowatt-hour (CO2E/kWh); coal emits between 1.4 and 3.6 pounds of CO2E/kWh. Wind , on the other hand, is responsible for only 0.02 to 0.04 pounds of CO2E/kWh on a life-cycle basis; solar 0.07 to 0.2; geothermal 0.1 to 0.2; and hydroelectric between 0.1 and 0.5.
Renewable electricity generation from biomass can have a wide range of global warming emissions depending on the resource and whether or not it is sustainably sourced and harvested.
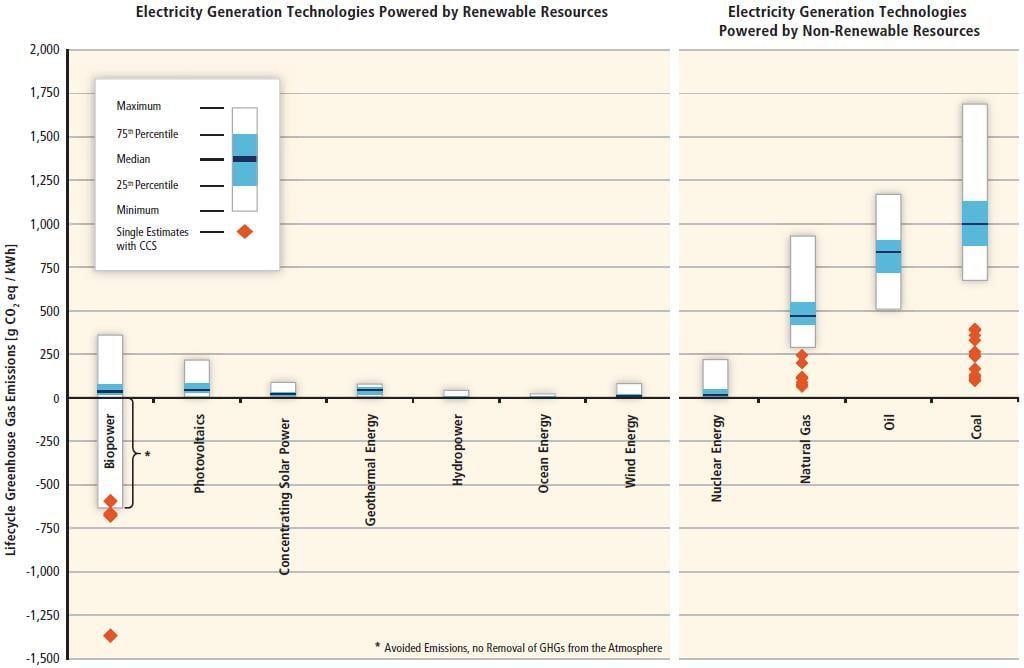
Increasing the supply of renewable energy would allow us to replace carbon-intensive energy sources and significantly reduce US global warming emissions.
For example, a 2009 UCS analysis found that a 25 percent by 2025 national renewable electricity standard would lower power plant CO2 emissions 277 million metric tons annually by 2025—the equivalent of the annual output from 70 typical (600 MW) new coal plants [ 4 ].
In addition, a ground-breaking study by the US Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) explored the feasibility of generating 80 percent of the country’s electricity from renewable sources by 2050. They found that renewable energy could help reduce the electricity sector’s emissions by approximately 81 percent [ 5 ].
Improved public health
The air and water pollution emitted by coal and natural gas plants is linked with breathing problems, neurological damage, heart attacks, cancer, premature death, and a host of other serious problems. The pollution affects everyone: one Harvard University study estimated the life cycle costs and public health effects of coal to be an estimated $74.6 billion every year . That’s equivalent to 4.36 cents per kilowatt-hour of electricity produced—about one-third of the average electricity rate for a typical US home [ 6 ].
Most of these negative health impacts come from air and water pollution that clean energy technologies simply don’t produce. Wind, solar, and hydroelectric systems generate electricity with no associated air pollution emissions. Geothermal and biomass systems emit some air pollutants, though total air emissions are generally much lower than those of coal- and natural gas-fired power plants.
In addition, wind and solar energy require essentially no water to operate and thus do not pollute water resources or strain supplies by competing with agriculture, drinking water, or other important water needs. In contrast, fossil fuels can have a significant impact on water resources : both coal mining and natural gas drilling can pollute sources of drinking water, and all thermal power plants, including those powered by coal, gas, and oil, withdraw and consume water for cooling.
Biomass and geothermal power plants, like coal- and natural gas-fired power plants, may require water for cooling. Hydroelectric power plants can disrupt river ecosystems both upstream and downstream from the dam. However, NREL's 80-percent-by-2050 renewable energy study, which included biomass and geothermal, found that total water consumption and withdrawal would decrease significantly in a future with high renewables [ 7 ].
Inexhaustible energy
Strong winds, sunny skies, abundant plant matter, heat from the earth, and fast-moving water can each provide a vast and constantly replenished supply of energy. A relatively small fraction of US electricity currently comes from these sources, but that could change: studies have repeatedly shown that renewable energy can provide a significant share of future electricity needs, even after accounting for potential constraints [ 9 ].
In fact, a major government-sponsored study found that clean energy could contribute somewhere between three and 80 times its 2013 levels, depending on assumptions [8]. And the previously mentioned NREL study found that renewable energy could comfortably provide up to 80 percent of US electricity by 2050.

Getting Excited About Energy: Expanding Renewables in the US
Jobs and other economic benefits.
Compared with fossil fuel technologies, which are typically mechanized and capital intensive, the renewable energy industry is more labor intensive. Solar panels need humans to install them; wind farms need technicians for maintenance.
This means that, on average, more jobs are created for each unit of electricity generated from renewable sources than from fossil fuels.
Renewable energy already supports thousands of jobs in the United States. In 2016, the wind energy industry directly employed over 100,000 full-time-equivalent employees in a variety of capacities, including manufacturing, project development, construction and turbine installation, operations and maintenance, transportation and logistics, and financial, legal, and consulting services [ 10 ]. More than 500 factories in the United States manufacture parts for wind turbines, and wind power project installations in 2016 alone represented $13.0 billion in investments [ 11 ].
Other renewable energy technologies employ even more workers. In 2016, the solar industry employed more than 260,000 people, including jobs in solar installation, manufacturing, and sales, a 25% increase over 2015 [ 12 ]. The hydroelectric power industry employed approximately 66,000 people in 2017 [ 13 ]; the geothermal industry employed 5,800 people [ 14] .
Increased support for renewable energy could create even more jobs. The 2009 Union of Concerned Scientists study of a 25-percent-by-2025 renewable energy standard found that such a policy would create more than three times as many jobs (more than 200,000) as producing an equivalent amount of electricity from fossil fuels [ 15 ].
In contrast, the entire coal industry employed 160,000 people in 2016 [ 26 ].
In addition to the jobs directly created in the renewable energy industry, growth in clean energy can create positive economic “ripple” effects. For example, industries in the renewable energy supply chain will benefit, and unrelated local businesses will benefit from increased household and business incomes [ 16 ].
Local governments also benefit from clean energy, most often in the form of property and income taxes and other payments from renewable energy project owners. Owners of the land on which wind projects are built often receive lease payments ranging from $3,000 to $6,000 per megawatt of installed capacity, as well as payments for power line easements and road rights-of-way. They may also earn royalties based on the project’s annual revenues. Farmers and rural landowners can generate new sources of supplemental income by producing feedstocks for biomass power facilities.
UCS analysis found that a 25-by-2025 national renewable electricity standard would stimulate $263.4 billion in new capital investment for renewable energy technologies, $13.5 billion in new landowner income from? biomass production and/or wind land lease payments, and $11.5 billion in new property tax revenue for local communities [ 17 ].
Stable energy prices
Renewable energy is providing affordable electricity across the country right now, and can help stabilize energy prices in the future.
Although renewable facilities require upfront investments to build, they can then operate at very low cost (for most clean energy technologies, the “fuel” is free). As a result, renewable energy prices can be very stable over time.
Moreover, the costs of renewable energy technologies have declined steadily, and are projected to drop even more. For example, the average price to install solar dropped more than 70 percent between 2010 and 2017 [ 20 ]. The cost of generating electricity from wind dropped 66 percent between 2009 and 2016 [ 21 ]. Costs will likely decline even further as markets mature and companies increasingly take advantage of economies of scale.
In contrast, fossil fuel prices can vary dramatically and are prone to substantial price swings. For example, there was a rapid increase in US coal prices due to rising global demand before 2008, then a rapid fall after 2008 when global demands declined [ 23 ]. Likewise, natural gas prices have fluctuated greatly since 2000 [ 25 ].
Using more renewable energy can lower the prices of and demand for natural gas and coal by increasing competition and diversifying our energy supplies. And an increased reliance on renewable energy can help protect consumers when fossil fuel prices spike.

Barriers to Renewable Energy Technologies
Reliability and resilience.
Wind and solar are less prone to large-scale failure because they are distributed and modular. Distributed systems are spread out over a large geographical area, so a severe weather event in one location will not cut off power to an entire region. Modular systems are composed of numerous individual wind turbines or solar arrays. Even if some of the equipment in the system is damaged, the rest can typically continue to operate.
For example, Hurricane Sandy damaged fossil fuel-dominated electric generation and distribution systems in New York and New Jersey and left millions of people without power. In contrast, renewable energy projects in the Northeast weathered Hurricane Sandy with minimal damage or disruption [ 25 ].
Water scarcity is another risk for non-renewable power plants. Coal, nuclear, and many natural gas plants depend on having sufficient water for cooling, which means that severe droughts and heat waves can put electricity generation at risk. Wind and solar photovoltaic systems do not require water to generate electricity and can operate reliably in conditions that may otherwise require closing a fossil fuel-powered plant. (For more information, see How it Works: Water for Electricity .)
The risk of disruptive events will also increase in the future as droughts, heat waves, more intense storms, and increasingly severe wildfires become more frequent due to global warming—increasing the need for resilient, clean technologies.
References:
[1] Environmental Protection Agency. 2017. Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks: 1990-2015.
[2] Energy Information Agency (EIA). 2017. How much of the U.S. carbon dioxide emissions are associated with electricity generation?
[3] Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 2011. IPCC Special Report on Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation . Prepared by Working Group III of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [O. Edenhofer, R. Pichs-Madruga, Y. Sokona, K. Seyboth, P. Matschoss, S. Kadner, T. Zwickel, P. Eickemeier, G. Hansen, S. Schlömer, C. von Stechow (eds)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1075 pp. (Chapter 9).
[4] Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS). 2009. Clean Power Green Jobs .
[5] National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). 2012. Renewable Electricity Futures Study . Volume 1, pg. 210.
[6] Epstein, P.R.,J. J. Buonocore, K. Eckerle, M. Hendryx, B. M. Stout III, R. Heinberg, R. W. Clapp, B. May, N. L. Reinhart, M. M. Ahern, S. K. Doshi, and L. Glustrom. 2011. Full cost accounting for the life cycle of coal in “Ecological Economics Reviews.” Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1219: 73–98.
[7] Renewable Electricity Futures Study . 2012.
[8] NREL. 2016. Estimating Renewable Energy Economic Potential in the United States: Methodology and Initial Results .
[9] Renewable Electricity Futures Study . 2012.
IPCC Special Report on Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation . Prepared by Working Group III of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 2011.
UCS. 2009. Climate 2030: A national blueprint for a clean energy economy .
[10] American Wind Energy Association (AWEA). 2017. AWEA U.S. Wind Industry Annual Market Report: Year Ending 2016. Washington, D.C.: American Wind Energy Association.
[11] Wiser, Ryan, and Mark Bolinger. 2017. 2016 Wind Technologies Market Report. U.S. Department of Energy.
[12] The Solar Foundation. 2017. National Solar Jobs Census 2016.
[13] Navigant Consulting. 2009. Job Creation Opportunities in Hydropower .
[14] Geothermal Energy Association. 2010. Green Jobs through Geothermal Energy .
[15] UCS. 2009. Clean Power Green Jobs .
[16] Environmental Protection Agency. 2010. Assessing the Multiple Benefits of Clean Energy: A Resource for States . Chapter 5.
[17] UCS. 2009. Clean Power Green Jobs .
[18] Deyette, J., and B. Freese. 2010. Burning coal, burning cash: Ranking the states that import the most coal . Cambridge, MA: Union of Concerned Scientists.
[20] SEIA. 2017. Solar Market Insight Report 2017 Q2.
[21] AWEA. 2017. AWEA U.S. Wind Industry Annual Market Report: Year Ending 2016. Washington, D.C.: American Wind Energy Association.
[22] UCS. 2009. Clean Power Green Jobs .
[23] UCS. 2011. A Risky Proposition: The financial hazards of new investments in coal plants .
[24] EIA. 2013. U.S. Natural Gas Wellhead Price .
[25] Unger, David J. 2012. Are renewables stormproof? Hurricane Sandy tests solar, wind . The Christian Science Monitor. November 19.
[26] Department of Energy. 2017 U.S. Energy and Employment Report

Related resources

The Electric Utility Toolkit
Siting for a Cleaner, More Equitable Grid in Massachusetts

Barriers and Solutions to Building Clean Energy in California

Accelerating Clean Energy Ambition
We use cookies to improve your experience. By continuing, you accept our use of cookies. Learn more .
Support our work
Other ways to give.
- Honor & memory
- Become a member
- Give monthly
- Make a planned gift
- Gift memberships
Your donation at work
Hydroelectric Power: Sustaining Our Energy Resources Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
The electricity sector has been damaging the environment for centuries, being the primary cause of carbon emissions. For example, when people rely on the combustion of fossil fuels, they increase greenhouse gases percentage contributing to global warming and climate change. Meanwhile, modern inventions such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power were invented to tackle this environmental concern and find another means to generate power without causing ozone depletion. Hydroelectric power, in turn, utilizes river flows as the only power source. It is more affordable and causes less harm as it establishes a tight connection with natural resources without exhausting them. Since utilizing hydropower requires building only a dam on the river, many nations can rely on this electricity source due to its simplistic architectural nature. This term is essential to know for people who want to live in a sustainable environment, supporting renewable energy sources. However, hydroelectric power is not as harmless as people might suspect since it includes anthropological intervention in natural processes. For example, it might disturb the river’s flow and affect aquatic organisms’ movements. Therefore, nations choosing hydroelectric power over fossil fuels should be mindful of its possible effects on aquatic life.
When discussing the effects of hydroelectric power on the physical world and human beings, it is essential to differentiate between positive and negative aspects. Primarily, it was invented to terminate carbon emissions from fossil fuels as a step towards a sustainable future with fewer environmental concerns. This fact hints at the idea that hydroelectric power benefits the atmosphere, being a more sustainable alternative for fossil fuel combustion in some regions. That is why it supplies Norway and Paraguay with electricity totally while meeting over 60% of Brazil’s demand (Benzel & Carbone, 2020). Considering that its contribution percentage to the global electricity demand rises annually, the current 16% sets more hopeful expectations. Since the global population is rising significantly, people cannot rely on outdated and harmful energy sources, finding hydropower as a renewable energy source with more advantageous outcomes due to reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels. Moreover, some nations receive a chance to reduce imports of fossil fuels, focusing on their natural assets. This decision, in turn, brings economic benefits as individuals pay for their domestic products instead of imported assets subjected to public fluctuations (Tkáč, 2018). For example, Ecuador’s reliance on fossil fuels hinders economic growth, so the country switched its focus to hydroelectric power, accounting for 4,409 GW of energy from the large hydroelectric power plants (Tkáč, 2018). Despite such positive associations with hydropower, building large constructions on water resources has more risks. They comprise a dam across a river and a reservoir storing the water behind it (Benzel & Carbone, 2020). Although it sounds harmless, as hydropower does not reduce the amount of water and ensures its constant flow, it still interferes with nature. Most importantly, building hydropower requires destroying the natural habitat of some species. Zeleňáková et al. (2018) environmental impact assessment of the small hydropower plant in Slovakia highlighted that construction machinery emits noise, methane, and dust, which is still dangerous for the planet. Additionally, these stressors result in changes in the migration of populations, negatively affecting aquatic organisms such as salmons as they alter their movement directions. Sometimes constructions even damage soil layers and surface water quality, causing lower oxygen levels which make water resources dangerous for the survival of some fish species. Therefore, hydroelectric power might be as damaging as effective, thus, forcing people to invent more sustainable ways to utilize them.
The first suggested action is to support organizations differentiating between more reliable hydroelectric power stations and those that could cause more harm. For example, the International Association of Hydropower and the World Commission on Dams establish the most comprehensive guidelines for dam construction for versatile and low-cost energy (Tkáč, 2018). Investing in these organizations helps to increase the number of hydropower plants, with the tunnels susceptible to fish and organisms’ migration. Moreover, World Commission on Dams recently invested in the students’ projects regarding the improvements of dams, meaning that they prioritize habitats’ safety over energy efficiency. Thus, this action would help to create transparency in the renewable energy section, enhance safer alternative constructions, and help international organizations to check all hydroelectric power plants for sustainability measures. Another action to eliminate the adverse effects of hydroelectric power in some regions is to collaborate with the research teams investigating this question. Most universities in the US are interested in creating fish-friendly turbines or dams that do not disturb the river’s flow, thus, giving students a chance to participate in their activities. The students can find a closer destination with the engaged research team and accessible technologies to evaluate the region’s water availability for the construction of dams. Sometimes active team members are sent to the areas with hydroelectric power to investigate the construction’s flaws and suggest new ideas to improve them. If the students gain more professional knowledge in the dams’ construction, their suggestions might bring positive outcomes for the environment. For example, Massachusetts Technical University students create the most fish-friendly turbines by proposing new shapes and parameters (Zeleňáková et al., 2018). Since there are some risks associated with this suggestion, as students might be unable to suggest an idea that might drive environmental changes, they can eliminate these risks by further spreading the knowledge. These agents with gained knowledge and research skills should provide lectures and presentations for their peers to ensure everyone avoids biases about the hydropower’s safety. Hence, every student can adopt these actions and potentially benefit the environment.
Bensel, T., & Carbone, I. (2020). Chapter 7: Sustaining our energy resources, Chapter 8: Sustaining our atmosphere and climate. In Sustaining our planet (pp. 1–88). Zovio.
Tkáč, Š. (2018). Hydro power plants, an overview of the current types and technology . Selected Scientific Papers-Journal of Civil Engineering, 13 (1), 115–126. Web.
Zeleňáková, M., Fijko, R., Diaconu, D. C., & Remeňáková, I. (2018). Environmental impact of small hydro power plant—a case study . Environments, 5 (1), 12–22. Web.
- Preserving Legacy and Managing Cultural Heritage Risks
- The Affect Weather Has on Human Life
- Alternative Sources of Energy: Solar, Wind, and Hydropower
- The Right Way to Identify and Assess Risks. Hydroelectric Development vs. Irrigation Scheme
- Rivers for Life
- Eco-Friendly Oil Sorbents for Oil Spill Cleanup
- The Responsibility of Businesses to Address Environmental Sustainability
- A Role of Human Beings in Protecting the Environment
- How to Make Planet Habitable for Future Generations
- The Green Victimology: Saving Non-Human Victims
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 23). Hydroelectric Power: Sustaining Our Energy Resources. https://ivypanda.com/essays/hydroelectric-power-sustaining-our-energy-resources/
"Hydroelectric Power: Sustaining Our Energy Resources." IvyPanda , 23 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/hydroelectric-power-sustaining-our-energy-resources/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Hydroelectric Power: Sustaining Our Energy Resources'. 23 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Hydroelectric Power: Sustaining Our Energy Resources." May 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/hydroelectric-power-sustaining-our-energy-resources/.
1. IvyPanda . "Hydroelectric Power: Sustaining Our Energy Resources." May 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/hydroelectric-power-sustaining-our-energy-resources/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Hydroelectric Power: Sustaining Our Energy Resources." May 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/hydroelectric-power-sustaining-our-energy-resources/.
- Natural Sources Of Energy
Sources of Energy
The sun is the main source of energy on Earth. Other energy sources include coal, geothermal energy, wind energy, biomass, petrol, nuclear energy, and many more. Energy is classified into various types based on sustainability as renewable sources of energy and non-renewable sources of energy.
What Is Energy?
The classical description of energy is the ability of a system to perform work, but as energy exists in so many forms, it is hard to find one comprehensive definition. It is the property of an object that can be transferred from one object to another or converted to different forms but cannot be created or destroyed. There are numerous sources of energy. In the next few sections, let us discuss the about different sources of energy in detail.
Sources Of Energy
Sources of energy can be classified into:
- Renewable Sources
- Non-renewable Sources
Renewable sources of energy are available plentiful in nature and are sustainable. These resources of energy can be naturally replenished and are safe for the environment.
Examples of renewable sources of energy are : Solar energy, geothermal energy, wind energy, biomass, hydropower and tidal energy.
A non-renewable resource is a natural resource that is found underneath the earth. These type of energy resources do not replenish at the same speed at which it is used. They take millions of years to replenish. The main examples of non-renewable resources are coal, oil and natural gas.
Examples of non-renewable sources of energy are: Natural gas, coal, petroleum, nuclear energy and hydrocarbon gas liquids.

Difference between Renewable and Non-renewable Sources of Energy
| | |
| The resources that can be renewed once they are consumed are called renewable sources of energy. | The resources that cannot be renewed once they are consumed are called non-renewable sources of energy. |
| These resources do not cause any environmental pollution. | These resources cause environmental pollution. |
| Renewable resources are inexhaustible. | Non- Renewable resources are exhaustible. |
| Renewable resources are not affected by human activities. | Non- Renewable resources are affected by human activities. |
| Examples of Renewable resources- Air, water and solar energy. | Examples of Non-renewable resources- natural gas, coal and nuclear energy. |
Natural Sources of Energy
During the stone age, it was wood. During the iron age, we had coal. In the modern age, we have fossil fuels like petroleum and natural gas. So how do we choose the source of energy?
Good sources of energy should have the following qualities:
- Optimum heat production per unit of volume/mass used
- Easy to transport
- Least Polluting
Types of Natural Sources of Energy
There are two types of natural sources of energy classified by their popularity and use,
- Conventional Sources of Energy
- Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
Difference between Conventional and Non-conventional Sources of Energy
| | |
| These resources are exhaustible. | These resources are inexhaustible. |
| These resources cause pollution as they emit smoke and ash. | These resources are usually pollution-free. |
| These resources are very expensive to be maintained, stored and transmitted. | These resources are less expensive for local use and can easily be maintained. |
| Examples- coal, natural gas, petroleum, and water power. | Examples- solar, biomass, wind, biogas, and tidal, geothermal. |
In this article, you learned about natural resources, energy sources, and what makes a good source of energy. Explore more such articles at BYJU’S, which provides detailed solutions to the questions of NCERT Book for the energy source so that one can compare their answers with the sample answers given for this chapter.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What sources of energy are renewable.
- Biomass energy
- Wind energy
- Tidal energy
- Hydro energy
What is the main source of energy in India?
What are the sources of energy in india.
Following are the sources of energy in India:
- Natural gas
- Thermal energy
- Mineral oil
Can any source of energy be pollution-free?
What are the advantages and disadvantages of wind power.
- There are no harmful gases released into the environment.
- It is a way for the generation of revenue in the local communities.
- It is one of the clean sources of energy.
Disadvantages:
- The storage of energy needs to be improved.
- The initial setup requires a lot of investment.
- Numerous lands will be used up.
List the examples of sources of energy
- Biofuel energy
- Geothermal energy
- Solar energy
- Nuclear energy
Watch the video and find out conservation measures we can take to save the natural resources depleting at an alarming rate.

Stay tuned with BYJU’S for more such interesting articles. Also, register to “BYJU’S – The Learning App” for loads of interactive, engaging Physics-related videos and unlimited academic assistance.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Physics related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment

Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Renewable resources.
Renewable resources are an energy source that cannot be depleted and are able to supply a continuous source of clean energy.
Geology, Earth Science, Engineering, Physics
Geothermal power is a form of renewable energy created by powering electrical generators with the heat of the earth and naturally occurring subterranean hot water reservoirs.
Photograph by stockphoto52

When it comes to energy resources, there is always the question of sustainability. It is important that resources provide enough energy to meet our needs—to heat our houses, power our cities, and run our cars. However, it is also important to consider how these resources can be used long term. Some resources will practically never run out. These are known as renewable resources . Renewable resources also produce clean energy , meaning less pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change.
The United States’ energy sources have evolved over time, from using wood prior to the 19th century to later adopting nonrenewable resources, such as fossil fuels, petroleum, and coal, which are still the dominant sources of energy today. But Earth has a limited supply of these resources. Recently, renewable resource use has begun to increase. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 11 percent of the nation's energy consumption came from renewable resources in 2017.
There are some challenges associated with using renewable resources . For instance, renewable energy can be less reliable than non renewable energy , with seasonal or even daily changes in the amount produced. However, scientists are continually addressing these challenges, working to improve feasibility and reliability of renewable resources .
Renewable resources include biomass energy (such as ethanol ), hydropower, geothermal power , wind energy , and solar energy .
Biomass refers to organic material from plants or animals. This includes wood, sewage, and ethanol (which comes from corn or other plants). Biomass can be used as a source of energy because this organic material has absorbed energy from the Sun. This energy is, in turn, released as heat energy when burned.
Hydropower is one of the oldest renewable resources and has been used for thousands of years. Today, every U.S. state uses some amount of hydroelectricity. With hydropower, the mechanical energy from flowing water is used to generate electricity. Hydroelectric power plants use the flow of rivers and streams to turn a turbine to power a generator, releasing electricity.
Geothermal energy comes from the heat generated deep within Earth’s core. Geothermal reservoirs can be found at tectonic plate boundaries near volcanic activity or deep underground. Geothermal energy can be harnessed by drilling wells to pump hot water or steam to a power plant . This energy is then used for heating and electricity.
Wind energy generates electricity by turning wind turbines . The wind pushes the turbine’s blades, and a generator converts this mechanical energy into electricity. This electricity can supply power to homes and other buildings, and it can even be stored in the power grid .
Radiation from the sun can be used as a power source as well. Photovoltaic cells can be used to convert this solar energy into electricity. Individually, these cells only generate enough energy to power a calculator, but when combined to create solar panels or even larger arrays, they provide much more electricity.
Searching for the right method of using renewable resources is a task that is growing ever more important as Earth’s supply of nonrenewable resources continues to dwindle. Converting to renewable energy will not only better sustain the world’s rapidly growing population, but it will also provide a cleaner, healthier environment for the generations to come.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
April 3, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Essay on Renewable Energy

Introduction to Renewable Energy
In the quest for a sustainable and environmentally conscious future, adopting renewable energy has emerged as a pivotal solution to mitigate the challenges posed by traditional fossil fuels. Take, for instance, the remarkable growth of solar power in countries like Germany, where the “Energiewende” policy has catapulted them to the forefront of green energy innovation. This transformative journey showcases the potential of harnessing solar energy as an alternative and a cornerstone for economic prosperity, reduced carbon emissions, and heightened energy security. As we delve into the world of renewable energy, it becomes evident that these innovations are key to shaping a cleaner, more resilient global energy landscape.

Importance of Transitioning to Renewable Sources
A sustainable future and resolving numerous global issues depend heavily on the switch to renewable energy sources. This shift is crucial for several reasons:
Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
- Environmental Preservation: Fossil fuel combustion contributes significantly to air and water pollution and climate change. Transitioning to renewables reduces greenhouse gas emissions, mitigates environmental degradation, and helps preserve ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Renewable energy is a key player in mitigating climate change . Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide, is crucial to prevent catastrophic outcomes such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
- Energy Security: Wind and solar power, as renewable energy sources, provide a diverse and decentralized energy supply. This reduces dependence on finite and geopolitically sensitive fossil fuel reserves, enhancing energy security and resilience.
- Economic Opportunities: The renewable energy sector fosters job creation and economic growth. Investments in clean energy technologies stimulate innovation, create employment opportunities, and contribute to developing a robust and sustainable economy.
- Public Health Improvement: Transitioning away from fossil fuels decreases the release of harmful pollutants, leading to improved air and water quality. This, in turn, positively impacts public health by reducing respiratory illnesses and other pollution-related diseases.
- Resource Conservation: Unlike finite fossil fuel reserves, renewable sources are inherently sustainable and inexhaustible. By harnessing the power of sunlight, wind, water, and geothermal heat, societies can meet their energy needs without depleting limited natural resources.
- Technological Advancements: The transition to renewables drives innovation and technological advancements. Research and development in clean energy technologies contribute to a cleaner environment and the advancement of scientific knowledge and industrial capabilities.
- Global Cooperation: The shift to renewable energy encourages international collaboration to address shared challenges. Collaborative efforts in research, development, and the adoption of clean energy technologies can foster diplomatic ties and strengthen global cooperation.
Types of Renewable Energy
Sources naturally replenished on a human timescale, making them sustainable and environmentally friendly, derive renewable energy. Listed below are the main types of renewable energy:
- Solar Power: While solar thermal systems use sunshine to heat a fluid that produces steam to power turbines, photovoltaic cells use sunlight to convert light into energy.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines are machines that use the wind’s kinetic energy to generate electricity through wind energy. When the wind rotates the turbine blades, a generator transforms that rotational energy into electrical energy. Onshore or offshore locations often host wind farms.
- Hydropower: Hydropower produces electricity by harnessing the energy of flowing water. Run-of-river systems divert a portion of a river’s flow, while dam-based hydropower involves the controlled release of stored water through turbines to generate power.
- Biomass Energy: Organic materials like wood, agricultural waste, and agricultural residues produce biomass energy. Biomass can produce heat, electricity, and biofuels through combustion or anaerobic digestion, offering a versatile energy source.
- Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy taps into the Earth’s internal heat by harnessing steam or hot water beneath the Earth’s surface. Geothermal power plants convert this thermal energy into electricity, providing a consistent and reliable power source.
- Tidal Energy: Tidal energy harnesses the moon’s and sun’s gravitational pull to create electricity as the tides rise and fall. Utilizing underwater turbines allows tidal stream devices to capture the energy of the water’s flow.
- Wave Energy: Wave energy captures the motion of ocean waves to generate electricity. Wave energy converters, including point absorbers and oscillating water columns, convert waves’ up and down motion into usable power.
- Hydrogen Energy: Hydrogen, often considered a carrier of energy, can be produced through electrolysis using renewable electricity. It is a clean fuel for various applications, including transportation and industrial processes, emitting only water vapor when used.
Technological advancements
Technological breakthroughs have shaped the modern world, revolutionizing industries and elevating people’s standard of living. Several key areas highlight the profound impact of technology on society:
- Information Technology (IT): The evolution of IT has transformed communication, information access, and business operations. The development of the Internet, cloud computing , and mobile technologies has facilitated instantaneous global communication, d ata storage , and access to vast amounts of information.
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning: AI and ML have ushered in a new era of automation and decision-making capabilities. From autonomous vehicles to predictive analytics in healthcare, these technologies continue to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and problem-solving across various industries.
- Biotechnology: Advances in biotechnology have revolutionized healthcare, agriculture, and environmental conservation. Gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 offer unprecedented possibilities in treating genetic disorders, while biotech applications in agriculture improve crop yield and resilience.
- Renewable Energy Technologies: Clean energy generation is now more economical and efficient thanks to renewable energy technology, including energy storage systems, wind turbines, and solar panels. These innovations are pivotal in addressing environmental challenges and promoting sustainable practices.
- Nanotechnology: Nanotechnology manipulates materials at the atomic or molecular level. Nanotechnology has transformed the fields of materials science, electronics, and medicine. As a result, scientists have created sophisticated materials with unique qualities, developed more compact and potent electrical devices, and improved medication delivery methods.
- 3D Printing: Layer-by-layer construction of three-dimensional items is possible with additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing. This technology utilizes diverse applications, from prototyping and manufacturing to healthcare, producing custom implants and prosthetics.
- Blockchain Technology: The decentralized and secure ledger technology known as blockchain powers cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin . Beyond finance, it finds applications in supply chain management , voting systems, and ensuring the integrity and transparency of various processes.
- Quantum Computing: Using the ideas of quantum mechanics, quantum computing can execute intricate calculations at a pace impossible for conventional computers. This can potentially revolutionize fields such as cryptography, optimization problems, and drug discovery.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The technology known as the Internet of Things (IoT) enables commonplace objects to be linked to the Internet and gather and share data. This interconnectedness enhances efficiency in smart homes, cities, and industries, optimizing resource utilization and overall productivity.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR): AR and VR technologies immerse users in virtual or augmented environments, transforming experiences in fields like gaming, education, healthcare, and training simulations.
Challenges and Solutions
Addressing the challenges posed by technological advancements, societal changes, and global issues requires proactive strategies and innovative solutions. Here are some main challenges and possible solutions:
- Cybersecurity Threats:
- Challenge: Due to the growing interconnectivity of systems and the dependence on digital technology, individuals and organizations are more vulnerable to cyber threats such as ransomware attacks and data breaches.
- Solution: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, regular updates, and user education can help mitigate cyber risks. Collaboration between governments, industries, and cybersecurity experts is crucial for developing effective strategies.
- Privacy Concerns:
- Challenge: The collection and utilization of personal data by companies and governments raise concerns about privacy infringement.
- Solution: Implemented to safeguard people’s privacy rights, GDPR (the General Data Protection Regulation) and other stricter laws and policies exist. Innovations like privacy-enhancing technologies and decentralized identity solutions offer alternative approaches.
- Job Displacement Due to Automation:
- Challenge: Automation and artificial intelligence technologies can lead to job displacement and economic inequality.
- Solution: Reskilling and upskilling programs and focusing on education in emerging fields can prepare the workforce for the changing job landscape. Social policies like universal basic income (UBI) may provide a safety net during transitions.
- Environmental Degradation:
- Challenge: Industrial activities and resource exploitation contribute to environmental degradation, climate change, and biodiversity loss.
- Solution: Sustainable practices, renewable energy adoption, and circular economy principles can mitigate environmental impact. International cooperation and stringent environmental regulations also play a crucial role.
- Ethical Concerns in AI:
- Challenge: Ethical issues surrounding artificial intelligence include biased algorithms, lack of transparency, and potential misuse.
- Solution: Implementing ethical guidelines and standards for AI development, promoting transparency in algorithms, and fostering interdisciplinary collaboration on AI ethics can help address these concerns.
- Healthcare Access Disparities:
- Challenge: Access to quality healthcare is unique globally, with disparities exacerbated by factors such as geography and socioeconomic status.
- Solution: Telemedicine, mobile health applications, and innovative healthcare delivery models can improve access. International collaborations and investment in healthcare infrastructure can reduce disparities.
- Digital Inequality:
- Challenge: Not everyone has equal access to digital technologies, leading to disparities in education, economic opportunities, and social inclusion.
- Solution: Initiatives focusing on digital literacy, affordable internet access, and technology inclusion programs can bridge the digital divide. Governments and organizations can also invest in infrastructure to expand connectivity.
- Global Public Health Crises:
- Challenge: Events like pandemics can strain healthcare systems, disrupt economies, and create social upheaval.
- Solution: Preparedness plans, early warning systems, and international cooperation in research and resource allocation are crucial. Advances in biotechnology and data analytics can aid in swift responses.
- Ethical Use of Biotechnology:
- Challenge: Biotechnological advancements like gene editing raise ethical concerns about human enhancement and unintended consequences.
- Solution: Robust ethical frameworks, public engagement, and interdisciplinary dialogues involving ethicists, scientists, and policymakers can guide responsible biotechnological development.
- Energy Transition Challenges:
- Challenge: Shifting from traditional to renewable energy sources faces infrastructure, economic viability, and societal acceptance challenges.
- Solution: Government incentives, public awareness campaigns, and investment in research and development can accelerate the transition. Community involvement and stakeholder engagement are critical for successful adoption.
Global Initiatives and Policies
Global initiatives and policies play a pivotal role in shaping the trajectory of technological, economic, and environmental progress. These initiatives often reflect the collective effort of nations to address shared challenges and promote cooperation in various domains. Here are some notable global initiatives and policies:
- Paris Agreement: Global leaders reached a global agreement to keep the rise in temperature to less than 2°C above pre-industrial levels. Nations aim to enhance climate resilience while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): The 17 goals address global issues, including poverty, inequality, and environmental sustainability. Goal 7 targets explicitly affordable and clean energy, promoting the transition to renewable sources.
- IRENA(International Renewable Energy Agency): An intergovernmental organization promoting the widespread use of renewable energy. IRENA facilitates cooperation among nations, provides policy advice, and supports capacity building for renewable energy projects.
- Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM): A forum bringing together energy ministers from various nations to promote clean energy policies, share best practices, and collaborate on initiatives to advance the global transition to low-carbon technologies.
- Mission Innovation: A global initiative involving 24 countries and the European Union, committed to doubling public investment in clean energy research and development over five years. It aims to accelerate innovation and make clean energy more affordable.
- European Green Deal: An ambitious EU policy framework aiming for climate neutrality by 2050. It describes plans to lower greenhouse gas emissions, support renewable energy, and completely revamp the European economy.
- Renewable Energy Policies at National Levels: Many countries have established specific policies and targets to promote renewable energy adoption. Examples include Germany’s Energiewende, India’s National Solar Mission, and China’s commitment to peak carbon emissions by 2030.
- Power Africa: An initiative by the U.S. government to increase access to electricity in sub-Saharan Africa. Its main objectives are to encourage investment in the region’s power sector and to facilitate the development of renewable energy projects.
- Global Geothermal Alliance: Launched at COP21, the alliance promotes geothermal energy deployment worldwide. It encourages collaboration between governments, development partners, and the private sector to harness the potential of geothermal resources.
- ESMAP (World Bank’s Energy Sector Management Assistance Program): ESMAP supports developing countries in building sustainable energy systems. It provides technical assistance, policy advice, and financial support for projects promoting renewable energy and energy efficiency.
Case Studies
- Germany’s Energiewende: Germany’s ambitious energy transition, known as Energiewende, aims to shift from conventional energy sources to renewable energy. The country has made significant investments in wind and solar energy, enacted energy-saving measures, and plans to phase out nuclear power. The Energiewende case study exemplifies the integration of renewables into the energy mix and the challenges of maintaining grid balance during this transition.
- China’s Renewable Energy Expansion: China has become a global leader in renewable energy deployment. The country has significantly invested in wind and solar energy projects, increasing capacity. The case study explores China’s policy incentives, market dynamics, and technological advancements that have facilitated its rapid expansion in the renewable energy sector.
- Denmark’s Wind Power Success: Denmark has been a pioneer in wind energy, with wind power contributing significantly to its electricity generation. The case study delves into Denmark’s wind energy policies, including favorable regulatory frameworks, community engagement, and advancements in wind turbine technology. It highlights the economic and environmental benefits of widespread wind power adoption.
- California’s Renewable Energy Leadership: In the US, California has used renewable energy. The state’s case study examines its aggressive renewable portfolio standards, innovative policies promoting solar power, and the role of technology companies in driving clean energy initiatives. California’s experience demonstrates the potential for subnational entities to lead in renewable energy transitions.
- Rural Electrification in India through Solar Power: India’s case study focuses on rural electrification efforts using solar power. Initiatives like the National Solar Mission and off-grid solar projects have brought electricity to remote areas, transforming lives and fostering economic development. The study explores the challenges faced and lessons learned in scaling up solar energy access in a diverse and populous country.
- Costa Rica’s Renewable Energy Achievement: Costa Rica stands out for achieving high levels of renewable energy generation, primarily from hydropower, wind, and geothermal sources. The case study examines the country’s commitment to environmental sustainability, policies promoting clean energy, and the role of hydropower in maintaining a reliable and renewable energy supply.
- South Australia’s Grid Transformation: South Australia’s case study illustrates its transition to a renewable energy-dominant grid. The state has faced challenges related to grid stability and intermittency but has also demonstrated successful integration of wind and solar power. The study delves into the policy measures, technological solutions, and lessons learned in South Australia’s journey toward a low-carbon energy system.
- Morocco’s Concentrated Solar Power Project: Morocco’s case study focuses on the Noor Ouarzazate Solar Complex, one of the world’s most significant concentrated solar power projects. The initiative aims to harness solar energy for electricity generation, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and contribute to national energy security. The study explores the project’s technological innovations, financing models, and the impact on Morocco’s energy landscape.
Future Prospects
The future of energy holds exciting possibilities as technological advancements and evolving societal priorities shape the landscape. Several key prospects are likely to influence the trajectory of the global energy sector:
- Emerging Technologies: Ongoing research and development in renewable energy technologies will likely yield breakthroughs in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and energy storage. Innovations such as advanced solar cells, next-generation wind turbines, and novel energy storage solutions will be crucial in shaping the future energy landscape.
- Tidal and Wave Energy: Tidal and wave energy, largely untapped at present, hold significant potential for sustainable power generation. As technologies mature, harnessing the kinetic energy of ocean tides and waves could contribute to a more diverse and reliable renewable energy mix.
- Advanced Solar Technologies: Continued advancements in solar technologies, including thin-film solar cells, tandem solar cells, and solar paint, are anticipated. These innovations aim to enhance the efficiency of solar energy capture and broaden its applications across various industries.
- Integration into Various Sectors: One of the most important aspects of the energy landscape of the future is integrating renewable energy into various sectors, including industrial processes and transportation. Electric vehicles, green hydrogen production, and sustainable manufacturing will likely gain prominence.
- Energy Transition in Developing Countries: A significant role in the global energy transition is expected to be played by developing countries. International collaborations, financial support, and technology transfer will empower these nations to leapfrog traditional fossil fuel-dependent phases of development and embrace cleaner energy solutions.
- Smart Grids and Energy Storage: Deploying smart power grids, in conjunction with advanced energy storage solutions, will simplify the integration of renewable energy resources in existing power systems. Battery technologies, grid-scale storage, and demand-response mechanisms will enhance grid reliability and flexibility.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: Decentralized energy systems, such as community microgrids and distributed energy resources, will likely become more prevalent. These systems empower communities to generate, store, and manage their energy locally, promoting resilience and energy independence.
- Circular Economy in Energy: The adoption of circular economy principles in the energy sector will gain traction, emphasizing resource efficiency, recycling, and waste reduction. This strategy seeks to mitigate the harmful consequences of energy production and consumption on nature.
- Policy and Regulatory Shifts: Governments worldwide are expected to implement more ambitious policies and regulations to accelerate the transition to renewable energy. Carbon pricing, renewable energy mandates, and incentives for sustainable practices will shape the regulatory environment.
- Global Collaboration: International cooperation and collaboration will be crucial for addressing global energy challenges. Shared research initiatives, technology transfer, and joint efforts to combat climate change will foster a collective approach to building a sustainable energy future.
The global shift towards renewable energy is pivotal in fostering a sustainable future. The imperative to mitigate climate change, ensure energy security, and promote economic prosperity underscores the significance of embracing clean technologies. The trajectory towards a low-carbon energy landscape becomes increasingly tangible as nations unite in initiatives like the Paris Agreement and implement robust policies. The successes of case studies from Germany to China demonstrate the feasibility and benefits of renewable energy adoption. By continuing to innovate, invest, and collaborate, humanity can unlock the full potential of renewable sources, ensuring a resilient and environmentally responsible energy paradigm for generations to come.

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW
Energy Conservation Essay for Students and Children
500 words energy conservation essay.
Energy conservation refers to the efforts made to reduce the consumption of energy. The energy on Earth is not in unlimited supply. Furthermore, energy can take plenty of time to regenerate. This certainly makes it essential to conserve energy. Most noteworthy, energy conservation is achievable either by using energy more efficiently or by reducing the amount of service usage.

Importance of Energy Conservation
First of all, energy conservation plays an important role in saving non-renewable energy resources. Furthermore, non-renewable energy sources take many centuries to regenerate. Moreover, humans consume energy at a faster rate than it can be produced. Therefore, energy conservation would lead to the preservation of these precious non-renewable sources of energy.
Energy conservation will reduce the expenses related to fossil fuels. Fossil fuels are very expensive to mine. Therefore, consumers are required to pay higher prices for goods and services. Energy conservation would certainly reduce the amount of fossil fuel being mined. This, in turn, would reduce the costs of consumers.
Consequently, energy conservation would strengthen the economy as consumers will have more disposable income to spend on goods and services.
Energy conservation is good for scientific research. This is because; energy conservation gives researchers plenty of time to conduct researches.
Therefore, these researchers will have more time to come up with various energy solutions and alternatives. Humans must ensure to have fossil fuels as long as possible. This would give me enough time to finding practical solutions.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Another important reason for energy conservation is environmental protection. This is because various energy sources are significantly harmful to the environment. Furthermore, the burning of fossil fuels considerably pollutes the atmosphere. Moreover, nuclear energy creates dangerous nuclear waste. Hence, energy conservation will lead to environmental protection.
Energy conservation would also result in the good health of humans. Furthermore, the pollution released due to energy sources is harmful to the human body. The air pollution due to fossil fuels can cause various respiratory problems. Energy sources can pollute water which could cause several harmful diseases in humans. Nuclear waste can cause cancer and other deadly problems in the human body.
Measures to Conserve Energy
Energy taxation is a good measure from the government to conserve energy. Furthermore, several countries apply energy or a carbon tax on energy users. This tax would certainly put pressure on energy users to reduce their energy consumption. Moreover, carbon tax forces energy users to shift to other energy sources that are less harmful.
Building design plays a big role in energy conservation. An excellent way to conserve energy is by performing an energy audit in buildings. Energy audit refers to inspection and analysis of energy use in a building. Most noteworthy, the aim of the energy audit is to appropriately reduce energy input.
Another important way of energy conservation is by using energy-efficient products. Energy-efficient products are those that use lesser energy than their normal counterparts. One prominent example can be using an energy-efficient bulb rather than an incandescent light bulb.
In conclusion, energy conservation must be among the utmost priorities of humanity. Mahatma Gandhi was absolutely right when he said, “the earth provides enough to satisfy every man’s needs but not every man’s greed”. This statement pretty much sums up the importance of energy conservation. Immediate implementation of energy conservation measures is certainly of paramount importance.
FAQs on Energy Conservation
Q1 state one way in which energy conservation is important.
A1 One way in which energy conservation is important is that it leads to the preservation of fossil fuels.
Q2 Why energy taxation is a good measure to conserve energy?
A2 Energy taxation is certainly a good measure to conserve energy. This is because energy taxation puts financial pressure on energy users to reduce their energy consumption.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Search the United Nations
- What Is Climate Change
- Myth Busters
- Renewable Energy
- Finance & Justice
- Initiatives
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Paris Agreement
- Climate Ambition Summit 2023
- Climate Conferences
- Press Material
- Communications Tips
What is renewable energy?
Renewable energy is energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed. Sunlight and wind, for example, are such sources that are constantly being replenished. Renewable energy sources are plentiful and all around us.
Fossil fuels - coal, oil and gas - on the other hand, are non-renewable resources that take hundreds of millions of years to form. Fossil fuels, when burned to produce energy, cause harmful greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon dioxide.
Generating renewable energy creates far lower emissions than burning fossil fuels. Transitioning from fossil fuels, which currently account for the lion’s share of emissions, to renewable energy is key to addressing the climate crisis.
Renewables are now cheaper in most countries, and generate three times more jobs than fossil fuels.
Here are a few common sources of renewable energy:

SOLAR ENERGY
Solar energy is the most abundant of all energy resources and can even be harnessed in cloudy weather. The rate at which solar energy is intercepted by the Earth is about 10,000 times greater than the rate at which humankind consumes energy.
Solar technologies can deliver heat, cooling, natural lighting, electricity, and fuels for a host of applications. Solar technologies convert sunlight into electrical energy either through photovoltaic panels or through mirrors that concentrate solar radiation.
Although not all countries are equally endowed with solar energy, a significant contribution to the energy mix from direct solar energy is possible for every country.
The cost of manufacturing solar panels has plummeted dramatically in the last decade, making them not only affordable but often the cheapest form of electricity. Solar panels have a lifespan of roughly 30 years , and come in variety of shades depending on the type of material used in manufacturing.

WIND ENERGY
Wind energy harnesses the kinetic energy of moving air by using large wind turbines located on land (onshore) or in sea- or freshwater (offshore). Wind energy has been used for millennia, but onshore and offshore wind energy technologies have evolved over the last few years to maximize the electricity produced - with taller turbines and larger rotor diameters.
Though average wind speeds vary considerably by location, the world’s technical potential for wind energy exceeds global electricity production, and ample potential exists in most regions of the world to enable significant wind energy deployment.
Many parts of the world have strong wind speeds, but the best locations for generating wind power are sometimes remote ones. Offshore wind power offers t remendous potential .
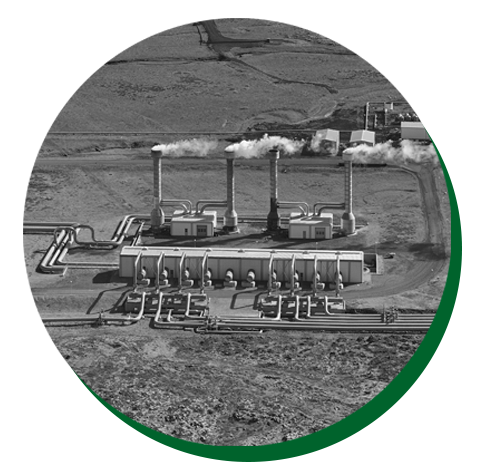

GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
Geothermal energy utilizes the accessible thermal energy from the Earth’s interior. Heat is extracted from geothermal reservoirs using wells or other means.
Reservoirs that are naturally sufficiently hot and permeable are called hydrothermal reservoirs, whereas reservoirs that are sufficiently hot but that are improved with hydraulic stimulation are called enhanced geothermal systems.
Once at the surface, fluids of various temperatures can be used to generate electricity. The technology for electricity generation from hydrothermal reservoirs is mature and reliable, and has been operating for more than 100 years .
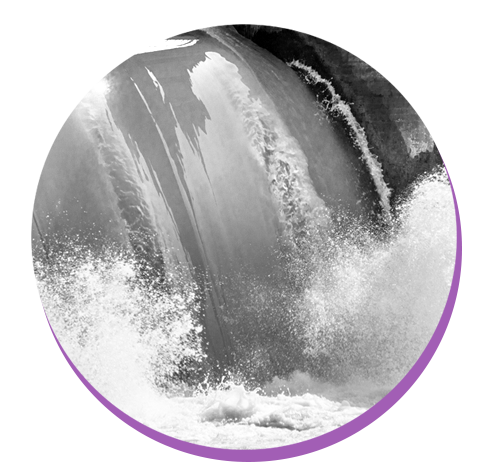

Hydropower harnesses the energy of water moving from higher to lower elevations. It can be generated from reservoirs and rivers. Reservoir hydropower plants rely on stored water in a reservoir, while run-of-river hydropower plants harness energy from the available flow of the river.
Hydropower reservoirs often have multiple uses - providing drinking water, water for irrigation, flood and drought control, navigation services, as well as energy supply.
Hydropower currently is the largest source of renewable energy in the electricity sector. It relies on generally stable rainfall patterns, and can be negatively impacted by climate-induced droughts or changes to ecosystems which impact rainfall patterns.
The infrastructure needed to create hydropower can also impact on ecosystems in adverse ways. For this reason, many consider small-scale hydro a more environmentally-friendly option , and especially suitable for communities in remote locations.

OCEAN ENERGY
Ocean energy derives from technologies that use the kinetic and thermal energy of seawater - waves or currents for instance - to produce electricity or heat.
Ocean energy systems are still at an early stage of development, with a number of prototype wave and tidal current devices being explored. The theoretical potential for ocean energy easily exceeds present human energy requirements.
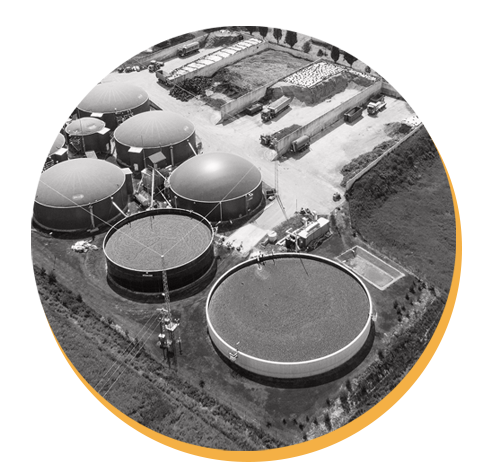

Bioenergy is produced from a variety of organic materials, called biomass, such as wood, charcoal, dung and other manures for heat and power production, and agricultural crops for liquid biofuels. Most biomass is used in rural areas for cooking, lighting and space heating, generally by poorer populations in developing countries.
Modern biomass systems include dedicated crops or trees, residues from agriculture and forestry, and various organic waste streams.
Energy created by burning biomass creates greenhouse gas emissions, but at lower levels than burning fossil fuels like coal, oil or gas. However, bioenergy should only be used in limited applications, given potential negative environmental impacts related to large-scale increases in forest and bioenergy plantations, and resulting deforestation and land-use change.
For more information on renewable sources of energy, please check out the following websites:
International Renewable Energy Agency | Renewables
International Energy Agency | Renewables
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change | Renewable Sources of Energy
UN Environment Programme | Roadmap to a Carbon-Free Future
Sustainable Energy for All | Renewable Energy

Renewable energy – powering a safer future
What is renewable energy and why does it matter? Learn more about why the shift to renewables is our only hope for a brighter and safer world.

Five ways to jump-start the renewable energy transition now
UN Secretary-General outlines five critical actions the world needs to prioritize now to speed up the global shift to renewable energy.

Climate issues
Learn more about how climate change impacts are felt across different sectors and ecosystems, and why we must nurture rather than exploit nature’s resources to advance climate action.
Facts and figures
- What is climate change?
- Causes and effects
- Myth busters
Cutting emissions
- Explaining net zero
- High-level expert group on net zero
- Checklists for credibility of net-zero pledges
- Greenwashing
- What you can do
Clean energy
- Renewable energy – key to a safer future
- What is renewable energy
- Five ways to speed up the energy transition
- Why invest in renewable energy
- Clean energy stories
- A just transition
Adapting to climate change
- Climate adaptation
- Early warnings for all
- Youth voices
Financing climate action
- Finance and justice
- Loss and damage
- $100 billion commitment
- Why finance climate action
- Biodiversity
- Human Security
International cooperation
- What are Nationally Determined Contributions
- Acceleration Agenda
- Climate Ambition Summit
- Climate conferences (COPs)
- Youth Advisory Group
- Action initiatives
- Secretary-General’s speeches
- Press material
- Fact sheets
- Communications tips










































IMAGES
COMMENTS
4 - 12. Coal, one of humankind's earliest fuel sources, is still used today to generate electricity. However, over time, there has been a shift in demand for cheaper and cleaner fuel options, such as the nonrenewable energy source of natural gas, and renewable options like solar power and wind energy. Each energy resource has its advantages ...
In contrast, renewable energy sources accounted for nearly 20 percent of global energy consumption at the beginning of the 21st century, largely from traditional uses of biomass such as wood for heating and cooking.By 2015 about 16 percent of the world's total electricity came from large hydroelectric power plants, whereas other types of renewable energy (such as solar, wind, and geothermal ...
A short essay on energy that discusses its importance, sources, problems and solutions. Learn about the fossil fuel crisis, the soft and hard paths of energy policy, and the concept of energy management and conservation.
Such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power. In this Alternative Sources of Energy essay, the author argues that the Sun and wind have the potential to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions. Read the paper to learn about the challenges, limitations, and benefits of implementing alternative energy sources.
10 Lines on Sources of Energy; 250 Words Essay on Sources of Energy Introduction. Energy is the driving force behind all natural and artificial phenomena. It is an indispensable resource in our daily lives, powering our homes, industries, and transportation. The sources of energy can be broadly classified into two categories: renewable and non ...
Energy is a fundamental requirement for modern civilization, and its generation comes from both renewable and nonrenewable resources. Examples of 10 Renewable Energy Sources. Solar Power: Energy from sunlight using solar panels. Wind Power: Energy from wind using turbines. Hydropower: Energy from the movement of water in rivers, dams, or tidal currents. ...
The wind, the sun, and Earth are sources of renewable energy . These energy sources naturally renew, or replenish themselves. Wind, sunlight, and the planet have energy that transforms in ways we can see and feel. We can see and feel evidence of the transfer of energy from the sun to Earth in the sunlight shining on the ground and the warmth we ...
Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass fuels. These energy sources are sustainable and generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels. Renewable and nonrenewable energy sources. Clockwise from top left: a solar power station, a wind farm, a hydroelectric power plant, and a coal-fired ...
Hydropower is the world's biggest source of renewable energy by far, with China, Brazil, Canada, the U.S., and Russia the leading hydropower producers. While hydropower is theoretically a clean ...
Background Info. Vocabulary. In any discussion about climate change, renewable energy usually tops the list of changes the world can implement to stave off the worst effects of rising temperatures. That's because renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, don't emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming.
Renewable energy has numerous environmental benefits. Renewables lower reliance on foreign energy sources. Renewable energy leads to cleaner water and air. Renewable energy creates jobs. Renewable energy can cut down on waste. 1. Renewable energy won't run out. Renewable energy technologies use resources straight from the environment to ...
The below mentioned essay provides an anatomy of the Energy Resources of India. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Introduction to Energy Resources 2. Types of Energy Resource in India 3. The Energy Strategy 4. Energy Scenario. Essay # Introduction to Energy Resources in India: Energy resources are very much important in the context of economic development of the country. With ...
A qualitative research was employed by reviewing papers in the scope of the study. Even though, the complete lifecycle of renewable energy sources have no net emissions which will help limit future global greenhouse gas emissions. ... If these suggestions are implemented, the sustainability of renewable energy resources would be addressed as ...
Increasing the supply of renewable energy would allow us to replace carbon-intensive energy sources and significantly reduce US global warming emissions. For example, a 2009 UCS analysis found that a 25 percent by 2025 national renewable electricity standard would lower power plant CO2 emissions 277 million metric tons annually by 2025—the ...
Hydroelectric Power: Sustaining Our Energy Resources Essay. ... Chapter 7: Sustaining our energy resources, Chapter 8: Sustaining our atmosphere and climate. In Sustaining our planet (pp. 1-88). Zovio. Tkáč, Š. (2018). Hydro power plants, an overview of the current types and technology.
These resources are very expensive to be maintained, stored and transmitted. These resources are less expensive for local use and can easily be maintained. Examples- coal, natural gas, petroleum, and water power. Examples- solar, biomass, wind, biogas, and tidal, geothermal. In this article, you learned about natural resources, energy sources ...
1. Introduction. Nowadays, more sustainable energy technologies are required to replace conventional electricity generation resources such as fossil fuel, due to the worldwide demands especially in developed and developing countries [1].Fossil fuel-based energy sources are causing detrimental environmental issues such as global warming and climate change [2].
Also, the energy sources that people use does have floss and can cause a negative impact on the environment, and humans. The most important goal is reducing the overall use of our energy sources. The main two kinds of energy used in my daily living are electricity, fossil fuel, which is a type of biomass. The main fuel people use is fossil fuels.
Renewable resources include biomass energy (such as ethanol ), hydropower, geothermal power, wind energy, and solar energy. Biomass refers to organic material from plants or animals. This includes wood, sewage, and ethanol (which comes from corn or other plants). Biomass can be used as a source of energy because this organic material has ...
Introduction to Renewable Energy. In the quest for a sustainable and environmentally conscious future, adopting renewable energy has emerged as a pivotal solution to mitigate the challenges posed by traditional fossil fuels. Take, for instance, the remarkable growth of solar power in countries like Germany, where the "Energiewende" policy ...
500 Words Energy Conservation Essay. Energy conservation refers to the efforts made to reduce the consumption of energy. The energy on Earth is not in unlimited supply. Furthermore, energy can take plenty of time to regenerate. This certainly makes it essential to conserve energy.
But investments in renewable energy will pay off. The reduction of pollution and climate impacts alone could save the world up to $4.2 trillion per year by 2030. Moreover, efficient, reliable ...
Solar energy is the most abundant of all energy resources and can even be harnessed in cloudy weather. The rate at which solar energy is intercepted by the Earth is about 10,000 times greater than ...