

Complexity Navigation Test
Local & international standards.
JP has developed extensive experience in using the CNT in more than 180 organisations and across over 30 industries. We have worked across a broad geographical base applying CNT technologies within Africa, Australia, Europe, and the Middle East.
What We Offer

The Complexity Navigation Test (CNT)
The CNT is a proudly African psychology test that assesses a leader’s ability to manage complexity and ambiguity – a capability key to leading within an ever changing and complex world. It is based on both Stratified Systems Theory (SST) and complexity theory, and measures an individual’s current and potential ability to manage the demands of various levels and types of work problem-solving. Over the last 25 years the JP Team has built insight in the CNT, applying it across over 30 industries and 5 continents.

Our Experience With The CNT
We have been a Complexity Navigation Test (CNT) licensee, and the original CNT business partner since its inception in 2002. With this, comes deep insight and experience in applying the CNT to assist individuals and organisations understand and leverage the potential of their current and future leaders and leadership. Our passion for, and expertise in Africa and emerging markets, has led us to successfully utilise the CNT across a large number of African countries, including South Africa, Kenya, Nigeria, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Uganda, Zambia, Botswana, Tanzania, Mauritius, Namibia, and Ghana.
Online Testing Available
In 2012, JP and Complexity Metrics embarked on a joint venture and launched an interactive, online version of the CNT, aptly called the eCNT, enabling global accessibility and reach.

Measure Your Capabilities
Organisation and role appropriate business scenarios effectively establish here-and-now role fit and competence. They offer the opportunity to assess an individual ‘in action’; taking the individual out of their comfort zone to really gauge their ability to apply their knowledge in a manner which suits the organisational context and culture.
The assessment distinguishes people who can cope with the complexity of strategic problem-solving from those whose strengths lie in the area of operational work. Within these parameters, finer sub-distinctions relating to various types of operational and strategic problem-solving can be drawn, as well as the individual’s cognitive flexibility, mental efficiency, ability to manage ambiguity, work through ‘noise’, and integrate and apply learning.
The Assessment Process
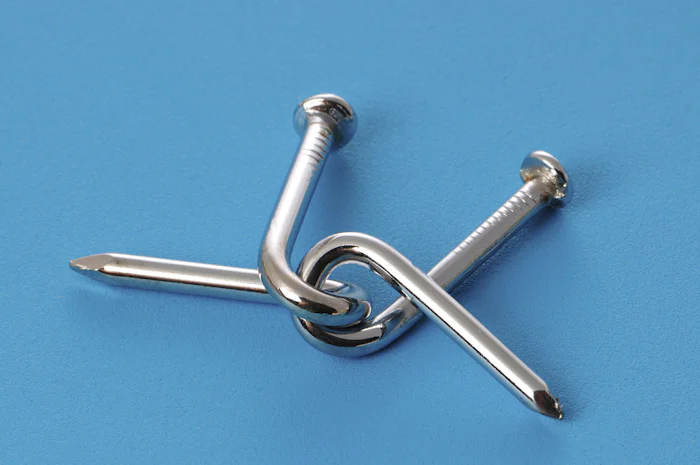
The CNT uses a set of universally recognisable symbols printed on playing cards. The assessor takes each candidate through several card games and the candidate is tasked with working out what rule or system governs that particular game. It relies on symbols and therefore does not discriminate on the basis of education, race, language, prior learning, culture, and is thus globally applicable.
The CNT extends and refines existing SST approaches significantly and is unique on two indices:
– It is the first ability assessment approach based in complexity theory. – A dynamic process assessment of how a person’s style of solving problems interacts with the ability to process different levels of complexity.
Connect with us
Johannesburg & cape town.
- +27 (0) 11 782 7007
- [email protected]
Stay Connected
Let's get started.
Get 25% off all test packages.
Get 25% off all test packages!
Click below to get 25% off all test packages.

Standard Bank Tests
- https://www.standardbank.com/sbg/careers
- Johannesburg, South Africa
- 141 questions
Standard Bank is a South African financial services group that has corporate headquarters in Johannesburg. Founded in 1862 as a subsidiary of a British overseas bank, Standard Bank now operates in 20 countries in Africa as well as elsewhere - they have locations in Brazil, the USA, England, Isle of Man, Jersey, China, and the UAE.
Careers at Standard Bank
The financial services on offer at Standard Bank include banking solutions for consumers, high net worth clients, corporate and investment services, and banking for business and commercial customers. Alongside these strands, there are several support departments that work across the global offices, including:
- Brand and Marketing
- Engineering
- Finance and Value Management
- Group Risk and Corporate Affairs
- Internal Audit
- People and Culture
Standard Bank offers roles for experienced professionals as well as a number of opportunities for early careers, including learnerships, internships and graduate schemes.
Working at Standard Bank comes with many benefits apart from a competitive salary, and there is great focus on personal and professional development in all roles thanks to a personalized and structured training and development plan that is put in place for all employees.
Other benefits (depending on location) include:
- Wellness programs
- Health insurance, life, personal accident and funeral cover
- Retirement funding
- Discounted banking products like loans and investments
- Multiple types of leave benefits, including paid holiday, parental, compassionate and sabbatical
Employees are offered a People Promise from Standard Bank when they get a job - a two-way commitment that encourages the best from staff while ensuring that a strong working culture is developed. This promise is structured around the following values:
- We are driven to win
- We are human at heart
- We are Africa to our core
The application process at Standard Bank is quite simple and straightforward, with different phases depending on the role you have applied for.
Standard Bank Application Process
Online application form, assessment center, final interview.
All roles at Standard Bank are advertised on the careers site , so this should be the first place you look before you apply.
In each job description, you will be given all the information you need about the role, what the daily activities are, what qualifications are required, and the skills that the recruiters are looking for.
When you click ‘apply now’, you will be invited to create an online SmartRecruiter profile, which will contain all of your contact details, an up-to-date CV, and any certifications that you might have from recognized professional bodies. Your SmartRecruiter profile is the hub of all your job-seeking activities, and where you can monitor the status of your application throughout the process.
Standard Bank Online Application Form
For each role, the prerequisites will differ - so you need to be aware of what the Talent Acquisition Team is looking for. When you fill out the application form, make sure that you are answering all the questions as fully as possible, and provide evidence where you can - such as any degrees or certificates, for example.
A cover letter is not mandatory for any of the roles that are available at Standard Bank, but the advice given is to provide one - especially if you are well-qualified or need some more space to demonstrate why you are the best candidate for the role.
The application form and the cover letter are likely to be the first time that the recruiters will have ‘met’ you, so make sure that you check your spelling and grammar before submitting to make the best impression.
Standard Bank Interview
The initial interview is a screening interview that usually takes place either by telephone or through a video chat. This is more about getting to know you and going through the information that you have provided in your SmartRecruiter profile than anything else, so you can expect some probing about what you have included in your application.
At this stage, clarification and a more in-depth discussion about your previous experience, your education, and what you are expecting from the position. Your interviewer is trying to get more information about you as a person to fill out what they can already see in your application details.
This is also an excellent chance for you to ask some questions about the role and about Standard Bank as a company, so be sure to have completed a good amount of research before the interview so you can ask some relevant questions.

The tests were well suited to the job that I’ve applied for. They are easy to do and loads of them.
Standard Bank Assessment Center
Assessment center days are often used during the application process for early careers, and candidates are expected to come to one of the main offices or another location to spend a day with the Talent Acquisition Team and other applicants for some in-depth pre-employment testing.
The assessment center is a chance for the recruiters to see how you act in the workplace and to assess your soft skills like leadership, communication, teamwork and negotiation. They want to see that you are able to put into practice the skills that you have mentioned in your application form and through the interview, and that you can cope well under pressure and in unfamiliar situations.
There are several types of tasks that you might take in an assessment center.
Standard Bank Aptitude Tests
Aptitude tests are used to check aptitude and skills. The content of these tests is not based on things that you will have learned in university or even through previous experience, but on the inherent skills and abilities you have. Some tests that you might take include:
- Numerical Reasoning - questions in the form of graphs and tables, with multiple choice answers that require you to read, understand and analyze numerical information and complete some basic calculations
Verbal reasoning tests
- Verbal Reasoning - candidates need to read, understand and analyze passages of text in order to be able to answer questions about the content.
Logical reasoning tests
Logical Reasoning are the most common type of assessment - the candidate is presented with a series of shapes or images that are in a sequence, with one item missing. They need to find the rule that governs the sequence and apply it to the multiple-choice options to find the right answer.
- Situational Strengths - this is an assessment of work behaviors and personality traits , with a series of sentences that describe different behaviors and traits. The candidate needs to decide how well each sentence describes them at work.
Case-study exercise
During a case study exercise, a group of candidates are given some information relating to a fictional customer, and need to work together to come up with a plan to solve the problem that the client has.
This is usually finished with a presentation to the recruitment team and the other groups, outlining the plan and the reasoning.
Sometimes, the case study might be an individual project, with the end product as a presentation or as a long-form written piece.
Standard Bank technical test
If you have applied for a role that needs a specific technical skill, such as programming or coding, you may be invited to complete a technical or skills test.
In this type of test, the Talent Acquisition Team is checking to be sure that you have the right level of skill to be successful in the role, and they do this using questions that are related to the type of tasks that you are likely to undertake - for example, if you are coding, you might be asked to debug a portion of code used in a banking app.
Standard Bank final Interview
The final interview is your chance to really shine - and show that you match not only the values of the business but also that you have all the skills and attributes that they are looking for specifically for the role.
The final interview might be a competency-based interview, where you will be invited to provide examples from your previous experience that demonstrate you have certain competencies. For instance, you might be asked to provide an example of where you have provided leadership for a project, and had to deal with things like competing deadlines and working with other people.
It is a good idea to prepare for this type of interview by looking at the specific attributes that the role requires, and think of some examples before you head into the interview so that you ensure you give all the information with no waffle.
Make sure that you know the role really well, including what is needed for successful applicants so that you are ready to show the panel you have what it takes. Be ready to demonstrate your commercial awareness - so stay up to date with financial news on a local and global scale, and find out all you can about the day-to-day business operations of Standard Bank. This will help you seem more knowledgeable and passionate, but it will also give you some ideas of what questions to ask at the end.
Practice Aptitude Tests is not associated with Standard Bank. We provide preparation services for Standard Bank psychometric tests. Our tests are not designed to be identical to any style, employer or industry. Visit https://www.standardbank.com/sbg/careers to find out more.
Sample Standard Bank Tests question Test your knowledge!
Considering the recent volatility in currency exchange rates, a financial analyst is preparing a report. Which of the following conclusions is valid based solely on this information?
- The report will likely highlight opportunities for currency trading.
- The analyst should focus exclusively on historical data to forecast future rates.
- Foreign exchange risks are heightened in volatile conditions, requiring more meticulous risk assessment.
- Recommend investing in currencies from stable economies only, regardless of potential returns.
All investment bankers must possess strong analytical skills. A subset of investment bankers who are strong in analytics also have expertise in international finance. Which of the following must be true?
- Some investment bankers with international finance skills might not be strong analytically.
- Every investment banker has expertise in international finance.
- Investment bankers with expertise in international finance always have strong analytical skills.
- All investment bankers with analytical skills also have international finance expertise.
- Strong analytical skills are not necessary for investment bankers.
A financial services company reported that its investment returns were up 15% in year one, 20% in year two, and declined by 10% in year three. If you invested $100 in year one, what would be the value of your investment at the end of year three?
In assessing the risk of personal loans, a bank manager noticed that default rates are higher when the loan amount exceeds three times the monthly income of the borrower. Which action aligns best with this finding?
- Increase interest rates on all personal loans
- Offer more loans that are above three times a borrower’s monthly income
- Limit loan amounts to not exceed three times the monthly income of the borrower
- Ignore the monthly income of the borrower when assessing loan risk
Following an announcement that interest rates might increase, a bank's fund manager has to decide which bonds to purchase. Which type of bond is generally considered the safest choice under these conditions?
- Long-term government bonds
- Short-term corporate bonds
- Long-term corporate bonds
- Short-term government bonds
Enjoy what you’ve read? Let others know!
- Share on whatsapp
- Share on linkedin
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
- Share via email
Try Standard Bank Tests for Free
Standard bank 01.
20 Questions | 20 Minutes
Standard Bank 02
Standard bank 03, improve your scores with our intelligent learning system.
Immediate access. Cancel anytime.
- 30 Numerical reasoning tests
- 30 Verbal reasoning tests
- 30 Diagrammatic reasoning tests
- 30 Situational judgement tests
- 34 Publisher packages e.g. Watson Glaser
- 252 Employer packages e.g. HSBC
- 29 Extra packages e.g Mechanical
- Dashboard performance tracking
- Full solutions and explanations
- Tips, tricks, guides and resources
- Access to free tests
- Basic performance tracking
- Solutions & explanations
- Tips and resources
Reviews of our Standard Bank tests
What our customers say about our Standard Bank tests
Manti Mafokwane
South Africa
July 19, 2023
Not much to complain about.There’s enough time to practice.It’s just that you can’t go back to re/do them again
January 27, 2023
It was hard
The test makes you have more concentration which is a good thing but is hard to think if you don't have enough time to write
Maditshego Seema
December 16, 2022
It’s nice practice
It’s a bit tricky cos one doesn’t know how to go with the sequence, whether from small to big or big to small
By using our website you agree with our Cookie Policy.
We have detected that your browser is not the correct version or that you do not have JavaScript enabled.. This site is best viewed in Firefox 3.5 or later, or Safari 4.0 or later. Internet Explorer 8 has limited support. Some functionality may not work correctly or at all.
- A Model for the National Assessment of Higher Order Thinking
- International Critical Thinking Essay Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Test
- Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Sample Test
Consequential Validity: Using Assessment to Drive Instruction
Translate this page from English...
*Machine translated pages not guaranteed for accuracy. Click Here for our professional translations.

Critical Thinking Testing and Assessment
The purpose of assessment in instruction is improvement. The purpose of assessing instruction for critical thinking is improving the teaching of discipline-based thinking (historical, biological, sociological, mathematical, etc.) It is to improve students’ abilities to think their way through content using disciplined skill in reasoning. The more particular we can be about what we want students to learn about critical thinking, the better we can devise instruction with that particular end in view.

The Foundation for Critical Thinking offers assessment instruments which share in the same general goal: to enable educators to gather evidence relevant to determining the extent to which instruction is teaching students to think critically (in the process of learning content). To this end, the Fellows of the Foundation recommend:
that academic institutions and units establish an oversight committee for critical thinking, and
that this oversight committee utilizes a combination of assessment instruments (the more the better) to generate incentives for faculty, by providing them with as much evidence as feasible of the actual state of instruction for critical thinking.
The following instruments are available to generate evidence relevant to critical thinking teaching and learning:
Course Evaluation Form : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students perceive faculty as fostering critical thinking in instruction (course by course). Machine-scoreable.
Online Critical Thinking Basic Concepts Test : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students understand the fundamental concepts embedded in critical thinking (and hence tests student readiness to think critically). Machine-scoreable.
Critical Thinking Reading and Writing Test : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students can read closely and write substantively (and hence tests students' abilities to read and write critically). Short-answer.
International Critical Thinking Essay Test : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students are able to analyze and assess excerpts from textbooks or professional writing. Short-answer.
Commission Study Protocol for Interviewing Faculty Regarding Critical Thinking : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, critical thinking is being taught at a college or university. Can be adapted for high school. Based on the California Commission Study . Short-answer.
Protocol for Interviewing Faculty Regarding Critical Thinking : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, critical thinking is being taught at a college or university. Can be adapted for high school. Short-answer.
Protocol for Interviewing Students Regarding Critical Thinking : Provides evidence of whether, and to what extent, students are learning to think critically at a college or university. Can be adapted for high school). Short-answer.
Criteria for Critical Thinking Assignments : Can be used by faculty in designing classroom assignments, or by administrators in assessing the extent to which faculty are fostering critical thinking.
Rubrics for Assessing Student Reasoning Abilities : A useful tool in assessing the extent to which students are reasoning well through course content.
All of the above assessment instruments can be used as part of pre- and post-assessment strategies to gauge development over various time periods.
Consequential Validity
All of the above assessment instruments, when used appropriately and graded accurately, should lead to a high degree of consequential validity. In other words, the use of the instruments should cause teachers to teach in such a way as to foster critical thinking in their various subjects. In this light, for students to perform well on the various instruments, teachers will need to design instruction so that students can perform well on them. Students cannot become skilled in critical thinking without learning (first) the concepts and principles that underlie critical thinking and (second) applying them in a variety of forms of thinking: historical thinking, sociological thinking, biological thinking, etc. Students cannot become skilled in analyzing and assessing reasoning without practicing it. However, when they have routine practice in paraphrasing, summarizing, analyzing, and assessing, they will develop skills of mind requisite to the art of thinking well within any subject or discipline, not to mention thinking well within the various domains of human life.
For full copies of this and many other critical thinking articles, books, videos, and more, join us at the Center for Critical Thinking Community Online - the world's leading online community dedicated to critical thinking! Also featuring interactive learning activities, study groups, and even a social media component, this learning platform will change your conception of intellectual development.
SIG Quantitative Evaluation – Full Guide and Practice [2024]
A quick yet challenging math test covering 4 main topics, used for screening sig candidates..
The SIG Quantitative Evaluation Assessment is a 20-minutes mathematical knowledge test used to screen candidates applying for quantitative trading position with SIG.
The following will provide you with exact details on the SIG test structure and content, including free practice and expert tips.
Basic Details
- Test Overview
- Test Invitation
Test Interface
Free practice.
Test geek and founder of Aptitude-Test-Prep.com
What Is the SIG Quantitative Evaluation?
The Susquehanna International Group (SIG) Quantitative Evaluation, is a brief test assessing your mathematical knowledge and problem-solving skills. It is one of the three major pre-employment assessments used by SIG, alongside the SIG Problem Solving Assessment and the SIG Capital Markets Assessment .
The Quantitative Evaluation test is provided by test proviuder Mettl and contains 16 questions . The overall time to complete the test is 20 minutes .
The evaluation covers 4 main topics. Further below we dive deeper into each of them, with sample questions included:
- Probability and Combinatorics
Let’s break down the various topics, with a sample questin of each.
Test Structure and Question Format
The 16 questions of the SIG Quantitative Evaluation can be divided into 4 categories, described below. The difficulty level of the questions varies during the test, and it constitutes of both simple and challenging questions.
Type #1 – Arithmetic
This type of question is usually the simplest in the assessment, and contains a basic mathematical drill that most experienced candidates can easily solve. The challenge here is that the questions are often intentionally tricky.
However, you are likely to come by at least one highly creative arithmetic question – see an example in the Free Practice section.
Sample Question
Alice and Bob played a number of card games. Each placed a $2 bet on each game. Bob won five games, but overall, lost $4. How many games did Alice and Bob play?
You may find the answer and explanation to this question, alongside additional sample questions from the SIG Quantitative Evaluation in the Free Practice section.
Type #2 – Probability and Combinatorics
This is the most common type of question in the assessment. These questions may be strictly about probability or combinatorics, but very often, they will combine the two. Throughout the assessment, these questions greatly vary in difficulty, from very easy to quite challenging.
You roll 4 dice. What is the probability that at least three dice show the same number?
It is extremely challenging to solve all 16 questions within the given time frame, and you shouldn’t try to. Focus on solving as many as you can, and if you spend too much time on a particular question, give your best answer and move on.
Type #3 – Geometry
This type of question is aimed less to assess your understanding of geometry, rather your ability to solve problems creatively.
What is the diameter (d) of the circle?
Type #4 – Logic
This type of question will normally appear only once or twice in the assessment. No mathematical knowledge is required to solve this type of question.
Five managers are seated around a round table.
- The CEO does not sit next to the CFO or the Head of Marketing.
- The CFO does not sit next to the HR Manager.
- The COO does not sit next to the Head of Marketing or the HR Manager.
- The COO is sitting to the left of the CFO.
Who is sitting to the left of the Head of Marketing?
Head over to the Free Practice section to try some questions for yourself.
The SIG Test Invitation
The test invitation is actually split into 2:
The SIG Invitation
- The Mettl (test provider) invitation.
Once you have passed the initial resume stage, you will get a test invitation from SIG, with some basic information about the test.
Here are the major things to consider:
- The assessment is held by a third-party testing company named Mettl .
- The invitation from SIG will not include a test link . That will be sent separately, directly from Mettl.
- You may use a pen, paper, and calculator , but no additional source.
- Do NOT try to cheat! If you navigate out of the testing window or open a new tab, your assessment will be instantly stopped.
- You have 7 days to complete the assessment.
The Mettl Invitation
The second email you will receive is from Mettl, the test provider. That is a very simple notification, containing a link to the test itself and a prerequisite system compatibility check.
Here is an illustration of how the SIG Quantitative Evaluation testing screen generally looks like:
Several things to note:
- The test instructions will state that the sections are “untimed”, but that only means that the time limit is for the overall test , and not for any particular section.
- Once you have started, you cannot pause the assessment in any way.
- Although “Next” and “Previous” arrows will appear on-screen, you CANNOT skip questions or move between them .
- Although a “Review for Later” button will appear on-screen, you CANNOT mark a question for later review .
This free practice contains 6 sample questions and answers , covering all question categories of the SIG Quantitative Evaluation.
These are intended to give you a feeling for the test’s world of content and level of difficulty. The recommended solving time is 7.5 minutes .
John is flipping a fair coin 5 times. What is the probability of getting the exact sequence Heads, Tails, Tails, Heads, Heads?
Answer and Explanation
The correct answer is 1/32 .
The chance of getting heads or tails is similar across all flips and equals 1/2.
Therefore, the probability of getting any specific sequence of 5 flips is (1/2) 5 = 1/32.
The correct answer is 12 .
This is a good example of a simple yet tricky question. Even experienced candidates are prone to solving such a question casually and carelessly.
- Games Bob won: 5 – earned $10
- Total sum earned by Bob: -$4
We’ll denote the number of games lost as L:
10 + L x (-2) = -4
This means that there were 7 games in which Bob lost, so overall, 5 + 7 = 12.
The correct answer is the CFO .
Since the table is round, we can start by placing anyone around it. Let’s start with the CFO and COO, as we have the most accurate information about them.
Neither the COO or CFO sits next to the HR Manager.
The COO does not sit next to the Head of Marketing.
The remaining seat belongs to the CEO, naturally.
The CFO is sitting left to the Head of Marketing.
The correct answer is 9.72% .
The total number of possible rolls in the dice is 6 4 = 1,296.
The number of options for three dice showing the same number is 6 x 5 x 4C3 = 120 [6 options for the number that appears three times, 5 options for the number that appears once, and 4C3 options for the three dice on which the two similar numbers will show].
The number of options for all four dice showing the same number is 6 x 4C4 = 6. This is quite intuitive.
Overall, the probability of at least three dice showing the same number is: (120 + 6) / 1,296 = 9.72%
The correct answer is R = 17 .
The main challenge here is to find the auxiliary line that would be most helpful to solve the question. In this case:
Now, it becomes as simple as using the Pythagorean theorem once:
(R – 9) 2 + (R – 2) 2 = R 2
This quadrartic equation has two solutions:
However, we can rule out R2 since R > 9. Therefore, R = 17 .
Given are 4 numbers – M, N, P, and Q (not necessarily integers). There are 6 possible ways to multiply the numbers: M·N, M·P, M·Q, N·P, N·Q, P·Q.
The results of these multiplications are (not respectively): 1, 5, 8, 30, 40, X.
The correct answer is 1.667
This is an example of a high-level question that requires a certain “spark” – you will find 2-3 such questions across the assessment.
We can see that every two pairs of the 6 that maintain the relationship:
(M·N)·(P·Q) = (N·Q)·(M·P) = (M·Q)·(N·P)
Of the 4 given multiplications, 1, 5, 8, and 40 maintain this relationship (1·40 = 5·8), but 30 does not.
Therefore, the remaining multiplication result X must also maintain:
30·X = 40. Therefore, X = 1.667

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Self-Assessment • 20 min read
How Good Is Your Problem Solving?
Use a systematic approach..
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Good problem solving skills are fundamentally important if you're going to be successful in your career.
But problems are something that we don't particularly like.
They're time-consuming.
They muscle their way into already packed schedules.
They force us to think about an uncertain future.
And they never seem to go away!
That's why, when faced with problems, most of us try to eliminate them as quickly as possible. But have you ever chosen the easiest or most obvious solution – and then realized that you have entirely missed a much better solution? Or have you found yourself fixing just the symptoms of a problem, only for the situation to get much worse?
To be an effective problem-solver, you need to be systematic and logical in your approach. This quiz helps you assess your current approach to problem solving. By improving this, you'll make better overall decisions. And as you increase your confidence with solving problems, you'll be less likely to rush to the first solution – which may not necessarily be the best one.
Once you've completed the quiz, we'll direct you to tools and resources that can help you make the most of your problem-solving skills.
How Good Are You at Solving Problems?
Instructions.
For each statement, click the button in the column that best describes you. Please answer questions as you actually are (rather than how you think you should be), and don't worry if some questions seem to score in the 'wrong direction'. When you are finished, please click the 'Calculate My Total' button at the bottom of the test.
Answering these questions should have helped you recognize the key steps associated with effective problem solving.
This quiz is based on Dr Min Basadur's Simplexity Thinking problem-solving model. This eight-step process follows the circular pattern shown below, within which current problems are solved and new problems are identified on an ongoing basis. This assessment has not been validated and is intended for illustrative purposes only.
Below, we outline the tools and strategies you can use for each stage of the problem-solving process. Enjoy exploring these stages!
Step 1: Find the Problem (Questions 7, 12)
Some problems are very obvious, however others are not so easily identified. As part of an effective problem-solving process, you need to look actively for problems – even when things seem to be running fine. Proactive problem solving helps you avoid emergencies and allows you to be calm and in control when issues arise.
These techniques can help you do this:
PEST Analysis helps you pick up changes to your environment that you should be paying attention to. Make sure too that you're watching changes in customer needs and market dynamics, and that you're monitoring trends that are relevant to your industry.
Risk Analysis helps you identify significant business risks.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis helps you identify possible points of failure in your business process, so that you can fix these before problems arise.
After Action Reviews help you scan recent performance to identify things that can be done better in the future.
Where you have several problems to solve, our articles on Prioritization and Pareto Analysis help you think about which ones you should focus on first.
Step 2: Find the Facts (Questions 10, 14)
After identifying a potential problem, you need information. What factors contribute to the problem? Who is involved with it? What solutions have been tried before? What do others think about the problem?
If you move forward to find a solution too quickly, you risk relying on imperfect information that's based on assumptions and limited perspectives, so make sure that you research the problem thoroughly.
Step 3: Define the Problem (Questions 3, 9)
Now that you understand the problem, define it clearly and completely. Writing a clear problem definition forces you to establish specific boundaries for the problem. This keeps the scope from growing too large, and it helps you stay focused on the main issues.
A great tool to use at this stage is CATWOE . With this process, you analyze potential problems by looking at them from six perspectives, those of its Customers; Actors (people within the organization); the Transformation, or business process; the World-view, or top-down view of what's going on; the Owner; and the wider organizational Environment. By looking at a situation from these perspectives, you can open your mind and come to a much sharper and more comprehensive definition of the problem.
Cause and Effect Analysis is another good tool to use here, as it helps you think about the many different factors that can contribute to a problem. This helps you separate the symptoms of a problem from its fundamental causes.
Step 4: Find Ideas (Questions 4, 13)
With a clear problem definition, start generating ideas for a solution. The key here is to be flexible in the way you approach a problem. You want to be able to see it from as many perspectives as possible. Looking for patterns or common elements in different parts of the problem can sometimes help. You can also use metaphors and analogies to help analyze the problem, discover similarities to other issues, and think of solutions based on those similarities.
Traditional brainstorming and reverse brainstorming are very useful here. By taking the time to generate a range of creative solutions to the problem, you'll significantly increase the likelihood that you'll find the best possible solution, not just a semi-adequate one. Where appropriate, involve people with different viewpoints to expand the volume of ideas generated.
Tip: Don't evaluate your ideas until step 5. If you do, this will limit your creativity at too early a stage.
Step 5: Select and Evaluate (Questions 6, 15)
After finding ideas, you'll have many options that must be evaluated. It's tempting at this stage to charge in and start discarding ideas immediately. However, if you do this without first determining the criteria for a good solution, you risk rejecting an alternative that has real potential.
Decide what elements are needed for a realistic and practical solution, and think about the criteria you'll use to choose between potential solutions.
Paired Comparison Analysis , Decision Matrix Analysis and Risk Analysis are useful techniques here, as are many of the specialist resources available within our Decision-Making section . Enjoy exploring these!
Step 6: Plan (Questions 1, 16)
You might think that choosing a solution is the end of a problem-solving process. In fact, it's simply the start of the next phase in problem solving: implementation. This involves lots of planning and preparation. If you haven't already developed a full Risk Analysis in the evaluation phase, do so now. It's important to know what to be prepared for as you begin to roll out your proposed solution.
The type of planning that you need to do depends on the size of the implementation project that you need to set up. For small projects, all you'll often need are Action Plans that outline who will do what, when, and how. Larger projects need more sophisticated approaches – you'll find out more about these in the article What is Project Management? And for projects that affect many other people, you'll need to think about Change Management as well.
Here, it can be useful to conduct an Impact Analysis to help you identify potential resistance as well as alert you to problems you may not have anticipated. Force Field Analysis will also help you uncover the various pressures for and against your proposed solution. Once you've done the detailed planning, it can also be useful at this stage to make a final Go/No-Go Decision , making sure that it's actually worth going ahead with the selected option.
Step 7: Sell the Idea (Questions 5, 8)
As part of the planning process, you must convince other stakeholders that your solution is the best one. You'll likely meet with resistance, so before you try to “sell” your idea, make sure you've considered all the consequences.
As you begin communicating your plan, listen to what people say, and make changes as necessary. The better the overall solution meets everyone's needs, the greater its positive impact will be! For more tips on selling your idea, read our article on Creating a Value Proposition and use our Sell Your Idea Skillbook.
Step 8: Act (Questions 2, 11)
Finally, once you've convinced your key stakeholders that your proposed solution is worth running with, you can move on to the implementation stage. This is the exciting and rewarding part of problem solving, which makes the whole process seem worthwhile.
This action stage is an end, but it's also a beginning: once you've completed your implementation, it's time to move into the next cycle of problem solving by returning to the scanning stage. By doing this, you'll continue improving your organization as you move into the future.
Problem solving is an exceptionally important workplace skill.
Being a competent and confident problem solver will create many opportunities for you. By using a well-developed model like Simplexity Thinking for solving problems, you can approach the process systematically, and be comfortable that the decisions you make are solid.
Given the unpredictable nature of problems, it's very reassuring to know that, by following a structured plan, you've done everything you can to resolve the problem to the best of your ability.
This assessment has not been validated and is intended for illustrative purposes only. It is just one of many Mind Tool quizzes that can help you to evaluate your abilities in a wide range of important career skills.
If you want to reproduce this quiz, you can purchase downloadable copies in our Store .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
4 logical fallacies.
Avoid Common Types of Faulty Reasoning
Problem Solving
Add comment
Comments (2)
Afkar Hashmi
😇 This tool is very useful for me.
over 1 year
Very impactful

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Tips for Creating an Inclusive Culture

NEW! Meaningful Conversations
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points - managing new hires.
Getting onboarding right
Managing the 4Ps of Delegates
Turning Passengers, Protesters and Prisoners into Participants
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Equipping your team to make decisions.
Empowering Your Team to Step Up
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Assessing Problem Solving
- First Online: 01 January 2013
Cite this chapter

- David H. Jonassen Ed.D. 5
30k Accesses
2 Citations
Methods for assessing problem-solving learning outcomes vary with the nature of the problem. For simpler well-structured problems, answer correctness and process may be used along with assessments of comprehension of problem schemas, including problem classification, text editing, and analogical comparisons. For more complex and ill-structured problems that have no convergent answers, solution criteria, or solution methods, problem solving may be assessed by constructing and applying solution rubrics to assess mental simulations (scenarios), arguments in support of solutions, and student-constructed problems. Problem solving processes are normally assessed by coding schemes. In addition to assessing problem solutions, assessments of critical cognitive skills, including causal reasoning and student models, may be used to infer problem-solving skills.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Allaire, J. C., & Marisiske, M. (1999). Everyday cognition: Age and intellectual ability correlates. Psychology and Aging, 14, 627–644.
Google Scholar
Arlin, P. K. (1989). Problem solving and problem finding in young artists and young scientists. In M. L. Commons, J. D. Sinnott, F. A. Richards, & C. Amon (Eds.), Adult development volume 1: comparisons and applications of developmental models (pp. 197–216). New York: Praeger.
Atman, C. J., & Turns, J. (2001). Studying engineering design learning: Four verbal protocol analysis studies. In C. Eastman, W. M. McCracken, & W. C. Newstetter (Eds.), Design knowing and learning: Cognition in design education (pp. 37–62). New York: Elsevier.
Barab, S. A., & Duffy, T. M. (2000). From practice fields to communities of practice. In D. H. Jonassen & S. M. Land (Eds.), Theoretical foundations of learning environments (pp. 25–55). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Barab, S. A., Squire, K. D., & Dueber, W. (2000). A co-evolutionary model for supporting the emergence of authenticity. Educational Technology Research and Development, 48 (2), 37–62.
Article Google Scholar
Brown, S. I., & Walter, M. I. (2005). The art of problem posing (3rd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Chapman, M., McBride, M. L. (1992). The education of reason: Cognitive conflict and its role inintellectyural development. In C. U. Shantz & WW. Hartup (Eds.), Conflict in child and adolescent development (pp. 36–89). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Chi, M. T. H., Feltovich, P. J., & Glaser, R. (1981). Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive Science, 5 , 121–152.
Cho, K. L., & Jonassen, D. H. (2002). The effects of argumentation scaffolds on argumentation and problem solving. Educational Technology Research and Development, 50 (3), 5–22.
Dufresne, R. J., Gerace, W. J., Hardiman, P. T., & Mestre, J. P. (1992). Constraining novices to perform expertlike problem analysis: Effects on schema acquisition. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 2 (3), 307–331.
Elliott, S. N. (1995). Creating Meaningful Performance Assessments. http://www.ed.gov/databases/ERIC_Digests/ed381985.html ; ERIC Digest E531; (ED381985).
Ericsson, K. A., & Simon, H. A. (1993) Protocol analysis: Verbal reports as data . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Greeno, J. G. (1980). Trends in the theory of knowledge for problem solving. In D. T. Turna & F. Reif (Eds.), Problem solving and education: Issues in teaching and research (pp. 9–25). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Halpern, D. F. (2003). Thought and knowledge: An introduction to critical thinking (4th ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Hong, N. S., Jonassen, D. H., & McGee, S. (2003). Predictors of well-structured and ill-structured problem solving in an astronomy simulation. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 40(1), 6–33.
Hardiman, P. T., Dufresne, R., & Mestre, J. P. (1989). The relationship between problem categorization and problem solving among experts and novices. Memory and Cognition, 17 (5), 627–638.
Jacobs, A. E. J. P., Dolmans, D. H. J. M., Wolfhagen, I. H. A. P., & Scherpbier, A. J. J. A. (2003). Validation of a short questionnaire to assess the degree of complexity and structuredness of PBL problems. Medical Education, 37 (11), 1001–1007.
Jacobson, M. J., & Archodidou, A. (2000). The design of hypermedia tools for learning: Fostering conceptual change and transfer of complex scientific knowledge. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 9 (2), 149–199.
Jonassen, D. H. (1997). Instructional design model for well-structured and ill-structured problem-solving learning outcomes. Educational Technology Research and Development, 45 (1), 65–95.
Jonassen, D. H. (2000). Toward a design theory of problem solving. Educational Technology Research and Development, 48 (4), 63–85.
*Jonassen, D. H. (2011). Learning to solve problems: A handbook for designing problem-solving learning environments. New York, NY: Routledge.
Jonassen, D. H., & Cho, Y. H. (2011). Fostering argumentation while solving engineering ethics problems. Journal of Engineering Education, 100 (4), 1–23.
Jonassen, D. H., & Grabowski, B. L. (1993). Handbook of individual differences, learning and instruction . Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Jonassen, D. H., & Hung, W. (2008). All problems are not equal: Implications for PBL. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 2(2), 6–28.
*Jonassen, D. H., & Kim, B. (2010). Arguing to learn and learning to argue: Design justifications and guidelines. Educational Technology: Research & Development , 58 (4), 439–457.
Jonassen, D. H., & Kwon, H. I. (2001). Communication patterns in computer-mediated vs. face-to-face group problem solving. Educational Technology Research & Development, 49(1), 35–52.
Jonassen, D. H., & Ionas, I. G. (2008). Designing effective supports for reasoning causally. Educational Technology Research & Development, 56 (3), 287–308.
Jonassen, D. H., Shen, D., Marra, R. M., Cho, Y. H., Lo, J. L., & Lohani, V. K. (2009). Engaging and supporting problem solving in engineering ethics. Journal of Engineering Education, 98 (3), 235–254.
Jonassen, D. H., Strobel, J., & Ionas, I. G. (2008). The evolution of a collaborative authoring system for non-linear hypertext: A design-based research study. Computers and Education, 51 , 67–85.
Jonassen, D. H., Strobel, J., & Lee, C. B. (2006). Everyday problem solving in engineering: Lessons for engineering educators. Journal of Engineering Education, 95(2), 1–14.
Kahn, H. (1965). On escalation: Metaphor and scenarios . New York, NY: Praeger.
Kitchner, K. S. (1983). Cognition, metacognition, and epistemistic cognition: A three-level model of cognitive processing. Human Development, 26, 222–232.
Littlefield, J., & Rieser, J. J. (1993). Semantic features of similarity and children’s strategies for identifying relevant information in mathematical story problems. Cognition and Instruction, 11 (2), 133–188.
Lave, J. (1988). Cognition in practice: Mind, mathematics and culture in everyday life. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
*Low, R., & Over, R. (1989) Detection of missing and irrelevant information within algebraic story problems. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 59 , 296–305.
Low, R., & Over, R. (1990). Text editing of algebraic word problems. Australian Journal of Psychology, 42 (1), 63–73.
Low, R., & Over, R. (1992). Hierarchical ordering of schematic knowledge relating to the area-of-rectangle problem. Journal of Educational Psychology, 84 , 62–69.
Low, R., Over, R., Doolan, L., & Michell, S. (1994). Solution of algebraic word problems following training in identifying necessary and sufficient information within problems. The American Journal of Psychology, 107 (3), 423–439.
Meacham, J. A., & Emont, N. M. (1989). The interpersonal basis of everyday problem solving. In J. D. Sinnnott (Ed.), Everyday problem solving: Theory and applications (pp. 7–23). New York: Praeger.
Mestre, J. (2002). Probing adults’ conceptual understanding and transfer of learning via problem posing. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 23 (1), 9–50.
Morrison, M., & Morgan, M. S. (1999). Models as mediating instruments. In M. S. Morgan & M. Morrison (Eds.), Models as mediators: Perspectives on natural and social science (pp. 10–37). Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Chapter Google Scholar
Newell, A., & Simon, H. A. (1972). Human problem solving. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Ngu, B. H., Lowe, R., & Sweller, J. (2002). Text editing in chemistry instruction. Instructional Science, 30 , 379–402.
Nicaise, M., Gibney, T., & Crane, M. (2000). Toward an understanding of authentic learning: Student perceptions of an authentic classroom. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 9 (1), 79–94.
Norris, S. P., & Ennis, R. H. (1989). Evaluating critical thinking . Pacific Grove, CA: Critical Thinking Press.
Nussbaum, E. M., & Kardash, C. M. (2005). The effects of goal instructions and text on the generation of counterarguments during writing. Journal of Educational Psychology, 97 (2), 157–169.
Radinsky, J., Buillion, L., Lento, E. M., & Gomez, L. (2001). Mutual partnership benefit: A curricular design for authenticity. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 33 (4), 405–430.
Rich, B. (1960). Schaum’s principles of and problems of elementary algebra . New York, NY: Schaum’s.
Rogoff, B., & Lave, J. (Eds.) (1984). Everyday cognition: Its development in social context. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Rumelhart, D. E., & Ortony, A. (1977). The representation of knowledge in memory. In R. C. Anderson, R. J. Spiro, & W. E. Montague (Eds.), Schooling and the acquisition of knowledge (pp. 99–135). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Savelsbergh, E. R., de Jong, T., & Ferguson-Hessler, M. G. M. (1998). Competence related differences in problem representations. In M. van Someren, P. Reimann, T. de Jong, & H. Boshuizen (Eds.), The role of multiple representations in learning and problem solving (pp. 263–282). Amsterdam: Elservier.
Silver, E. A., & Cai, J. (1996). An analysis of arithmetic problem posing by middle school students. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 27 (6), 521–539.
Simon, H. A. (1978). What the knower knows: Alternative strategies for problem-solving tasks. In F. Klix (Ed.), Human and artificial intelligence (pp. 89–100). Berlin: VEB Deutscher Verlag der Wissenschafter.
Smith, M. U. (Ed.) (1991). Toward a unified theory of problem solving: Views from the content domains . Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Toulmin, S. (1958). The uses of argument . Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
*Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1980). Causal schemas in judgments under uncertainty. In M. Fishbein (Ed.), Progress in social psychology (Vol. 1, pp. 49–72). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Van Heuvelen, A., & Maloney, D. P. (1999). Playing physics jeopardy. American Journal of Physics, 67 (3), 252–256.
Voss, J. F., & Post, T. A. (1988). On the solving of ill-structured problems. In M. T. H. Chi, Rl Glaser, & M. J. Farr (Eds.), The nature of expertise. NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Wood, P. K. (1983). Inquiring systems and problem structures: Implications for cognitive development. Human Development, 26, 249–265.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Educational Psychology and Learning Technologies, University of Missouri, 221C Townsend Hall, Columbia, MO, 65211, USA
David H. Jonassen Ed.D.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to David H. Jonassen Ed.D. .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
, Department of Learning Technologies, C, University of North Texas, North Elm 3940, Denton, 76207-7102, Texas, USA
J. Michael Spector
W. Sunset Blvd. 1812, St. George, 84770, Utah, USA
M. David Merrill
, Centr. Instructiepsychol.&-technologie, K.U. Leuven, Andreas Vesaliusstraat 2, Leuven, 3000, Belgium
Research Drive, Iacocca A109 111, Bethlehem, 18015, Pennsylvania, USA
M. J. Bishop
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Jonassen, D.H. (2014). Assessing Problem Solving. In: Spector, J., Merrill, M., Elen, J., Bishop, M. (eds) Handbook of Research on Educational Communications and Technology. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3185-5_22
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-3185-5_22
Published : 22 May 2013
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4614-3184-8
Online ISBN : 978-1-4614-3185-5
eBook Packages : Humanities, Social Sciences and Law Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 11 January 2023
The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving in promoting students’ critical thinking: A meta-analysis based on empirical literature
- Enwei Xu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6424-8169 1 ,
- Wei Wang 1 &
- Qingxia Wang 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 16 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
14k Accesses
13 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely embraced in the classroom instruction of critical thinking, which is regarded as the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field of education as well as a key competence for learners in the 21st century. However, the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking remains uncertain. This current research presents the major findings of a meta-analysis of 36 pieces of the literature revealed in worldwide educational periodicals during the 21st century to identify the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking and to determine, based on evidence, whether and to what extent collaborative problem solving can result in a rise or decrease in critical thinking. The findings show that (1) collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster students’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]); (2) in respect to the dimensions of critical thinking, collaborative problem solving can significantly and successfully enhance students’ attitudinal tendencies (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI[0.87, 1.47]); nevertheless, it falls short in terms of improving students’ cognitive skills, having only an upper-middle impact (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI[0.58, 0.82]); and (3) the teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), and learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01) all have an impact on critical thinking, and they can be viewed as important moderating factors that affect how critical thinking develops. On the basis of these results, recommendations are made for further study and instruction to better support students’ critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Similar content being viewed by others
Fostering twenty-first century skills among primary school students through math project-based learning
A meta-analysis to gauge the impact of pedagogies employed in mixed-ability high school biology classrooms

A guide to critical thinking: implications for dental education
Introduction.
Although critical thinking has a long history in research, the concept of critical thinking, which is regarded as an essential competence for learners in the 21st century, has recently attracted more attention from researchers and teaching practitioners (National Research Council, 2012 ). Critical thinking should be the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field of education (Peng and Deng, 2017 ) because students with critical thinking can not only understand the meaning of knowledge but also effectively solve practical problems in real life even after knowledge is forgotten (Kek and Huijser, 2011 ). The definition of critical thinking is not universal (Ennis, 1989 ; Castle, 2009 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). In general, the definition of critical thinking is a self-aware and self-regulated thought process (Facione, 1990 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). It refers to the cognitive skills needed to interpret, analyze, synthesize, reason, and evaluate information as well as the attitudinal tendency to apply these abilities (Halpern, 2001 ). The view that critical thinking can be taught and learned through curriculum teaching has been widely supported by many researchers (e.g., Kuncel, 2011 ; Leng and Lu, 2020 ), leading to educators’ efforts to foster it among students. In the field of teaching practice, there are three types of courses for teaching critical thinking (Ennis, 1989 ). The first is an independent curriculum in which critical thinking is taught and cultivated without involving the knowledge of specific disciplines; the second is an integrated curriculum in which critical thinking is integrated into the teaching of other disciplines as a clear teaching goal; and the third is a mixed curriculum in which critical thinking is taught in parallel to the teaching of other disciplines for mixed teaching training. Furthermore, numerous measuring tools have been developed by researchers and educators to measure critical thinking in the context of teaching practice. These include standardized measurement tools, such as WGCTA, CCTST, CCTT, and CCTDI, which have been verified by repeated experiments and are considered effective and reliable by international scholars (Facione and Facione, 1992 ). In short, descriptions of critical thinking, including its two dimensions of attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills, different types of teaching courses, and standardized measurement tools provide a complex normative framework for understanding, teaching, and evaluating critical thinking.
Cultivating critical thinking in curriculum teaching can start with a problem, and one of the most popular critical thinking instructional approaches is problem-based learning (Liu et al., 2020 ). Duch et al. ( 2001 ) noted that problem-based learning in group collaboration is progressive active learning, which can improve students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Collaborative problem-solving is the organic integration of collaborative learning and problem-based learning, which takes learners as the center of the learning process and uses problems with poor structure in real-world situations as the starting point for the learning process (Liang et al., 2017 ). Students learn the knowledge needed to solve problems in a collaborative group, reach a consensus on problems in the field, and form solutions through social cooperation methods, such as dialogue, interpretation, questioning, debate, negotiation, and reflection, thus promoting the development of learners’ domain knowledge and critical thinking (Cindy, 2004 ; Liang et al., 2017 ).
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely used in the teaching practice of critical thinking, and several studies have attempted to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of the empirical literature on critical thinking from various perspectives. However, little attention has been paid to the impact of collaborative problem-solving on critical thinking. Therefore, the best approach for developing and enhancing critical thinking throughout collaborative problem-solving is to examine how to implement critical thinking instruction; however, this issue is still unexplored, which means that many teachers are incapable of better instructing critical thinking (Leng and Lu, 2020 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). For example, Huber ( 2016 ) provided the meta-analysis findings of 71 publications on gaining critical thinking over various time frames in college with the aim of determining whether critical thinking was truly teachable. These authors found that learners significantly improve their critical thinking while in college and that critical thinking differs with factors such as teaching strategies, intervention duration, subject area, and teaching type. The usefulness of collaborative problem-solving in fostering students’ critical thinking, however, was not determined by this study, nor did it reveal whether there existed significant variations among the different elements. A meta-analysis of 31 pieces of educational literature was conducted by Liu et al. ( 2020 ) to assess the impact of problem-solving on college students’ critical thinking. These authors found that problem-solving could promote the development of critical thinking among college students and proposed establishing a reasonable group structure for problem-solving in a follow-up study to improve students’ critical thinking. Additionally, previous empirical studies have reached inconclusive and even contradictory conclusions about whether and to what extent collaborative problem-solving increases or decreases critical thinking levels. As an illustration, Yang et al. ( 2008 ) carried out an experiment on the integrated curriculum teaching of college students based on a web bulletin board with the goal of fostering participants’ critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving. These authors’ research revealed that through sharing, debating, examining, and reflecting on various experiences and ideas, collaborative problem-solving can considerably enhance students’ critical thinking in real-life problem situations. In contrast, collaborative problem-solving had a positive impact on learners’ interaction and could improve learning interest and motivation but could not significantly improve students’ critical thinking when compared to traditional classroom teaching, according to research by Naber and Wyatt ( 2014 ) and Sendag and Odabasi ( 2009 ) on undergraduate and high school students, respectively.
The above studies show that there is inconsistency regarding the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking. Therefore, it is essential to conduct a thorough and trustworthy review to detect and decide whether and to what degree collaborative problem-solving can result in a rise or decrease in critical thinking. Meta-analysis is a quantitative analysis approach that is utilized to examine quantitative data from various separate studies that are all focused on the same research topic. This approach characterizes the effectiveness of its impact by averaging the effect sizes of numerous qualitative studies in an effort to reduce the uncertainty brought on by independent research and produce more conclusive findings (Lipsey and Wilson, 2001 ).
This paper used a meta-analytic approach and carried out a meta-analysis to examine the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking in order to make a contribution to both research and practice. The following research questions were addressed by this meta-analysis:
What is the overall effect size of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking and its impact on the two dimensions of critical thinking (i.e., attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills)?
How are the disparities between the study conclusions impacted by various moderating variables if the impacts of various experimental designs in the included studies are heterogeneous?
This research followed the strict procedures (e.g., database searching, identification, screening, eligibility, merging, duplicate removal, and analysis of included studies) of Cooper’s ( 2010 ) proposed meta-analysis approach for examining quantitative data from various separate studies that are all focused on the same research topic. The relevant empirical research that appeared in worldwide educational periodicals within the 21st century was subjected to this meta-analysis using Rev-Man 5.4. The consistency of the data extracted separately by two researchers was tested using Cohen’s kappa coefficient, and a publication bias test and a heterogeneity test were run on the sample data to ascertain the quality of this meta-analysis.
Data sources and search strategies
There were three stages to the data collection process for this meta-analysis, as shown in Fig. 1 , which shows the number of articles included and eliminated during the selection process based on the statement and study eligibility criteria.
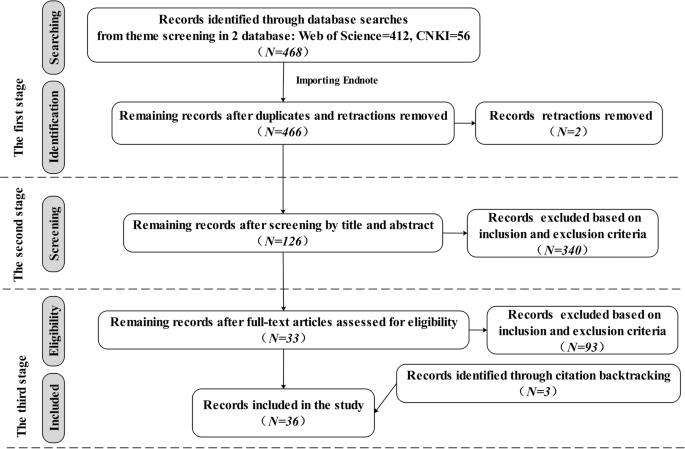
This flowchart shows the number of records identified, included and excluded in the article.
First, the databases used to systematically search for relevant articles were the journal papers of the Web of Science Core Collection and the Chinese Core source journal, as well as the Chinese Social Science Citation Index (CSSCI) source journal papers included in CNKI. These databases were selected because they are credible platforms that are sources of scholarly and peer-reviewed information with advanced search tools and contain literature relevant to the subject of our topic from reliable researchers and experts. The search string with the Boolean operator used in the Web of Science was “TS = (((“critical thinking” or “ct” and “pretest” or “posttest”) or (“critical thinking” or “ct” and “control group” or “quasi experiment” or “experiment”)) and (“collaboration” or “collaborative learning” or “CSCL”) and (“problem solving” or “problem-based learning” or “PBL”))”. The research area was “Education Educational Research”, and the search period was “January 1, 2000, to December 30, 2021”. A total of 412 papers were obtained. The search string with the Boolean operator used in the CNKI was “SU = (‘critical thinking’*‘collaboration’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘collaborative learning’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘CSCL’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem solving’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem-based learning’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘PBL’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem oriented’) AND FT = (‘experiment’ + ‘quasi experiment’ + ‘pretest’ + ‘posttest’ + ‘empirical study’)” (translated into Chinese when searching). A total of 56 studies were found throughout the search period of “January 2000 to December 2021”. From the databases, all duplicates and retractions were eliminated before exporting the references into Endnote, a program for managing bibliographic references. In all, 466 studies were found.
Second, the studies that matched the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the meta-analysis were chosen by two researchers after they had reviewed the abstracts and titles of the gathered articles, yielding a total of 126 studies.
Third, two researchers thoroughly reviewed each included article’s whole text in accordance with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Meanwhile, a snowball search was performed using the references and citations of the included articles to ensure complete coverage of the articles. Ultimately, 36 articles were kept.
Two researchers worked together to carry out this entire process, and a consensus rate of almost 94.7% was reached after discussion and negotiation to clarify any emerging differences.
Eligibility criteria
Since not all the retrieved studies matched the criteria for this meta-analysis, eligibility criteria for both inclusion and exclusion were developed as follows:
The publication language of the included studies was limited to English and Chinese, and the full text could be obtained. Articles that did not meet the publication language and articles not published between 2000 and 2021 were excluded.
The research design of the included studies must be empirical and quantitative studies that can assess the effect of collaborative problem-solving on the development of critical thinking. Articles that could not identify the causal mechanisms by which collaborative problem-solving affects critical thinking, such as review articles and theoretical articles, were excluded.
The research method of the included studies must feature a randomized control experiment or a quasi-experiment, or a natural experiment, which have a higher degree of internal validity with strong experimental designs and can all plausibly provide evidence that critical thinking and collaborative problem-solving are causally related. Articles with non-experimental research methods, such as purely correlational or observational studies, were excluded.
The participants of the included studies were only students in school, including K-12 students and college students. Articles in which the participants were non-school students, such as social workers or adult learners, were excluded.
The research results of the included studies must mention definite signs that may be utilized to gauge critical thinking’s impact (e.g., sample size, mean value, or standard deviation). Articles that lacked specific measurement indicators for critical thinking and could not calculate the effect size were excluded.
Data coding design
In order to perform a meta-analysis, it is necessary to collect the most important information from the articles, codify that information’s properties, and convert descriptive data into quantitative data. Therefore, this study designed a data coding template (see Table 1 ). Ultimately, 16 coding fields were retained.
The designed data-coding template consisted of three pieces of information. Basic information about the papers was included in the descriptive information: the publishing year, author, serial number, and title of the paper.
The variable information for the experimental design had three variables: the independent variable (instruction method), the dependent variable (critical thinking), and the moderating variable (learning stage, teaching type, intervention duration, learning scaffold, group size, measuring tool, and subject area). Depending on the topic of this study, the intervention strategy, as the independent variable, was coded into collaborative and non-collaborative problem-solving. The dependent variable, critical thinking, was coded as a cognitive skill and an attitudinal tendency. And seven moderating variables were created by grouping and combining the experimental design variables discovered within the 36 studies (see Table 1 ), where learning stages were encoded as higher education, high school, middle school, and primary school or lower; teaching types were encoded as mixed courses, integrated courses, and independent courses; intervention durations were encoded as 0–1 weeks, 1–4 weeks, 4–12 weeks, and more than 12 weeks; group sizes were encoded as 2–3 persons, 4–6 persons, 7–10 persons, and more than 10 persons; learning scaffolds were encoded as teacher-supported learning scaffold, technique-supported learning scaffold, and resource-supported learning scaffold; measuring tools were encoded as standardized measurement tools (e.g., WGCTA, CCTT, CCTST, and CCTDI) and self-adapting measurement tools (e.g., modified or made by researchers); and subject areas were encoded according to the specific subjects used in the 36 included studies.
The data information contained three metrics for measuring critical thinking: sample size, average value, and standard deviation. It is vital to remember that studies with various experimental designs frequently adopt various formulas to determine the effect size. And this paper used Morris’ proposed standardized mean difference (SMD) calculation formula ( 2008 , p. 369; see Supplementary Table S3 ).
Procedure for extracting and coding data
According to the data coding template (see Table 1 ), the 36 papers’ information was retrieved by two researchers, who then entered them into Excel (see Supplementary Table S1 ). The results of each study were extracted separately in the data extraction procedure if an article contained numerous studies on critical thinking, or if a study assessed different critical thinking dimensions. For instance, Tiwari et al. ( 2010 ) used four time points, which were viewed as numerous different studies, to examine the outcomes of critical thinking, and Chen ( 2013 ) included the two outcome variables of attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills, which were regarded as two studies. After discussion and negotiation during data extraction, the two researchers’ consistency test coefficients were roughly 93.27%. Supplementary Table S2 details the key characteristics of the 36 included articles with 79 effect quantities, including descriptive information (e.g., the publishing year, author, serial number, and title of the paper), variable information (e.g., independent variables, dependent variables, and moderating variables), and data information (e.g., mean values, standard deviations, and sample size). Following that, testing for publication bias and heterogeneity was done on the sample data using the Rev-Man 5.4 software, and then the test results were used to conduct a meta-analysis.
Publication bias test
When the sample of studies included in a meta-analysis does not accurately reflect the general status of research on the relevant subject, publication bias is said to be exhibited in this research. The reliability and accuracy of the meta-analysis may be impacted by publication bias. Due to this, the meta-analysis needs to check the sample data for publication bias (Stewart et al., 2006 ). A popular method to check for publication bias is the funnel plot; and it is unlikely that there will be publishing bias when the data are equally dispersed on either side of the average effect size and targeted within the higher region. The data are equally dispersed within the higher portion of the efficient zone, consistent with the funnel plot connected with this analysis (see Fig. 2 ), indicating that publication bias is unlikely in this situation.
This funnel plot shows the result of publication bias of 79 effect quantities across 36 studies.
Heterogeneity test
To select the appropriate effect models for the meta-analysis, one might use the results of a heterogeneity test on the data effect sizes. In a meta-analysis, it is common practice to gauge the degree of data heterogeneity using the I 2 value, and I 2 ≥ 50% is typically understood to denote medium-high heterogeneity, which calls for the adoption of a random effect model; if not, a fixed effect model ought to be applied (Lipsey and Wilson, 2001 ). The findings of the heterogeneity test in this paper (see Table 2 ) revealed that I 2 was 86% and displayed significant heterogeneity ( P < 0.01). To ensure accuracy and reliability, the overall effect size ought to be calculated utilizing the random effect model.
The analysis of the overall effect size
This meta-analysis utilized a random effect model to examine 79 effect quantities from 36 studies after eliminating heterogeneity. In accordance with Cohen’s criterion (Cohen, 1992 ), it is abundantly clear from the analysis results, which are shown in the forest plot of the overall effect (see Fig. 3 ), that the cumulative impact size of cooperative problem-solving is 0.82, which is statistically significant ( z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]), and can encourage learners to practice critical thinking.
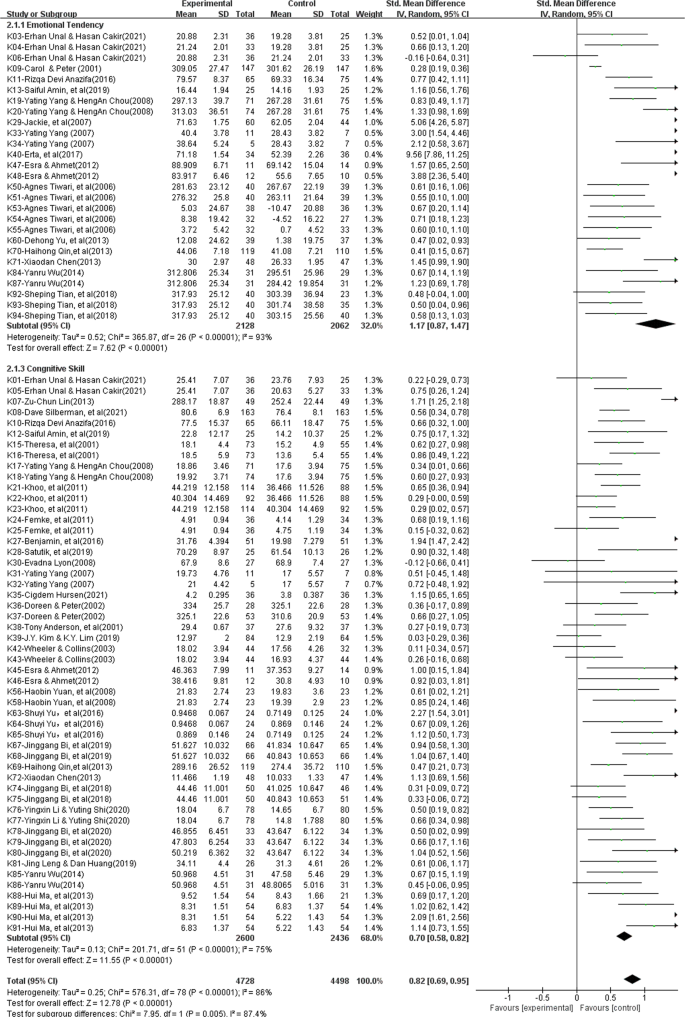
This forest plot shows the analysis result of the overall effect size across 36 studies.
In addition, this study examined two distinct dimensions of critical thinking to better understand the precise contributions that collaborative problem-solving makes to the growth of critical thinking. The findings (see Table 3 ) indicate that collaborative problem-solving improves cognitive skills (ES = 0.70) and attitudinal tendency (ES = 1.17), with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 7.95, P < 0.01). Although collaborative problem-solving improves both dimensions of critical thinking, it is essential to point out that the improvements in students’ attitudinal tendency are much more pronounced and have a significant comprehensive effect (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.87, 1.47]), whereas gains in learners’ cognitive skill are slightly improved and are just above average. (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.58, 0.82]).
The analysis of moderator effect size
The whole forest plot’s 79 effect quantities underwent a two-tailed test, which revealed significant heterogeneity ( I 2 = 86%, z = 12.78, P < 0.01), indicating differences between various effect sizes that may have been influenced by moderating factors other than sampling error. Therefore, exploring possible moderating factors that might produce considerable heterogeneity was done using subgroup analysis, such as the learning stage, learning scaffold, teaching type, group size, duration of the intervention, measuring tool, and the subject area included in the 36 experimental designs, in order to further explore the key factors that influence critical thinking. The findings (see Table 4 ) indicate that various moderating factors have advantageous effects on critical thinking. In this situation, the subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01), and teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05) are all significant moderators that can be applied to support the cultivation of critical thinking. However, since the learning stage and the measuring tools did not significantly differ among intergroup (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05, and chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05), we are unable to explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving. These are the precise outcomes, as follows:
Various learning stages influenced critical thinking positively, without significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05). High school was first on the list of effect sizes (ES = 1.36, P < 0.01), then higher education (ES = 0.78, P < 0.01), and middle school (ES = 0.73, P < 0.01). These results show that, despite the learning stage’s beneficial influence on cultivating learners’ critical thinking, we are unable to explain why it is essential for cultivating critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Different teaching types had varying degrees of positive impact on critical thinking, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05). The effect size was ranked as follows: mixed courses (ES = 1.34, P < 0.01), integrated courses (ES = 0.81, P < 0.01), and independent courses (ES = 0.27, P < 0.01). These results indicate that the most effective approach to cultivate critical thinking utilizing collaborative problem solving is through the teaching type of mixed courses.
Various intervention durations significantly improved critical thinking, and there were significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01). The effect sizes related to this variable showed a tendency to increase with longer intervention durations. The improvement in critical thinking reached a significant level (ES = 0.85, P < 0.01) after more than 12 weeks of training. These findings indicate that the intervention duration and critical thinking’s impact are positively correlated, with a longer intervention duration having a greater effect.
Different learning scaffolds influenced critical thinking positively, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01). The resource-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.69, P < 0.01) acquired a medium-to-higher level of impact, the technique-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.63, P < 0.01) also attained a medium-to-higher level of impact, and the teacher-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.92, P < 0.01) displayed a high level of significant impact. These results show that the learning scaffold with teacher support has the greatest impact on cultivating critical thinking.
Various group sizes influenced critical thinking positively, and the intergroup differences were statistically significant (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05). Critical thinking showed a general declining trend with increasing group size. The overall effect size of 2–3 people in this situation was the biggest (ES = 0.99, P < 0.01), and when the group size was greater than 7 people, the improvement in critical thinking was at the lower-middle level (ES < 0.5, P < 0.01). These results show that the impact on critical thinking is positively connected with group size, and as group size grows, so does the overall impact.
Various measuring tools influenced critical thinking positively, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05). In this situation, the self-adapting measurement tools obtained an upper-medium level of effect (ES = 0.78), whereas the complete effect size of the standardized measurement tools was the largest, achieving a significant level of effect (ES = 0.84, P < 0.01). These results show that, despite the beneficial influence of the measuring tool on cultivating critical thinking, we are unable to explain why it is crucial in fostering the growth of critical thinking by utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
Different subject areas had a greater impact on critical thinking, and the intergroup differences were statistically significant (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05). Mathematics had the greatest overall impact, achieving a significant level of effect (ES = 1.68, P < 0.01), followed by science (ES = 1.25, P < 0.01) and medical science (ES = 0.87, P < 0.01), both of which also achieved a significant level of effect. Programming technology was the least effective (ES = 0.39, P < 0.01), only having a medium-low degree of effect compared to education (ES = 0.72, P < 0.01) and other fields (such as language, art, and social sciences) (ES = 0.58, P < 0.01). These results suggest that scientific fields (e.g., mathematics, science) may be the most effective subject areas for cultivating critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving with regard to teaching critical thinking
According to this meta-analysis, using collaborative problem-solving as an intervention strategy in critical thinking teaching has a considerable amount of impact on cultivating learners’ critical thinking as a whole and has a favorable promotional effect on the two dimensions of critical thinking. According to certain studies, collaborative problem solving, the most frequently used critical thinking teaching strategy in curriculum instruction can considerably enhance students’ critical thinking (e.g., Liang et al., 2017 ; Liu et al., 2020 ; Cindy, 2004 ). This meta-analysis provides convergent data support for the above research views. Thus, the findings of this meta-analysis not only effectively address the first research query regarding the overall effect of cultivating critical thinking and its impact on the two dimensions of critical thinking (i.e., attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills) utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving, but also enhance our confidence in cultivating critical thinking by using collaborative problem-solving intervention approach in the context of classroom teaching.
Furthermore, the associated improvements in attitudinal tendency are much stronger, but the corresponding improvements in cognitive skill are only marginally better. According to certain studies, cognitive skill differs from the attitudinal tendency in classroom instruction; the cultivation and development of the former as a key ability is a process of gradual accumulation, while the latter as an attitude is affected by the context of the teaching situation (e.g., a novel and exciting teaching approach, challenging and rewarding tasks) (Halpern, 2001 ; Wei and Hong, 2022 ). Collaborative problem-solving as a teaching approach is exciting and interesting, as well as rewarding and challenging; because it takes the learners as the focus and examines problems with poor structure in real situations, and it can inspire students to fully realize their potential for problem-solving, which will significantly improve their attitudinal tendency toward solving problems (Liu et al., 2020 ). Similar to how collaborative problem-solving influences attitudinal tendency, attitudinal tendency impacts cognitive skill when attempting to solve a problem (Liu et al., 2020 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ), and stronger attitudinal tendencies are associated with improved learning achievement and cognitive ability in students (Sison, 2008 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ). It can be seen that the two specific dimensions of critical thinking as well as critical thinking as a whole are affected by collaborative problem-solving, and this study illuminates the nuanced links between cognitive skills and attitudinal tendencies with regard to these two dimensions of critical thinking. To fully develop students’ capacity for critical thinking, future empirical research should pay closer attention to cognitive skills.
The moderating effects of collaborative problem solving with regard to teaching critical thinking
In order to further explore the key factors that influence critical thinking, exploring possible moderating effects that might produce considerable heterogeneity was done using subgroup analysis. The findings show that the moderating factors, such as the teaching type, learning stage, group size, learning scaffold, duration of the intervention, measuring tool, and the subject area included in the 36 experimental designs, could all support the cultivation of collaborative problem-solving in critical thinking. Among them, the effect size differences between the learning stage and measuring tool are not significant, which does not explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
In terms of the learning stage, various learning stages influenced critical thinking positively without significant intergroup differences, indicating that we are unable to explain why it is crucial in fostering the growth of critical thinking.
Although high education accounts for 70.89% of all empirical studies performed by researchers, high school may be the appropriate learning stage to foster students’ critical thinking by utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving since it has the largest overall effect size. This phenomenon may be related to student’s cognitive development, which needs to be further studied in follow-up research.
With regard to teaching type, mixed course teaching may be the best teaching method to cultivate students’ critical thinking. Relevant studies have shown that in the actual teaching process if students are trained in thinking methods alone, the methods they learn are isolated and divorced from subject knowledge, which is not conducive to their transfer of thinking methods; therefore, if students’ thinking is trained only in subject teaching without systematic method training, it is challenging to apply to real-world circumstances (Ruggiero, 2012 ; Hu and Liu, 2015 ). Teaching critical thinking as mixed course teaching in parallel to other subject teachings can achieve the best effect on learners’ critical thinking, and explicit critical thinking instruction is more effective than less explicit critical thinking instruction (Bensley and Spero, 2014 ).
In terms of the intervention duration, with longer intervention times, the overall effect size shows an upward tendency. Thus, the intervention duration and critical thinking’s impact are positively correlated. Critical thinking, as a key competency for students in the 21st century, is difficult to get a meaningful improvement in a brief intervention duration. Instead, it could be developed over a lengthy period of time through consistent teaching and the progressive accumulation of knowledge (Halpern, 2001 ; Hu and Liu, 2015 ). Therefore, future empirical studies ought to take these restrictions into account throughout a longer period of critical thinking instruction.
With regard to group size, a group size of 2–3 persons has the highest effect size, and the comprehensive effect size decreases with increasing group size in general. This outcome is in line with some research findings; as an example, a group composed of two to four members is most appropriate for collaborative learning (Schellens and Valcke, 2006 ). However, the meta-analysis results also indicate that once the group size exceeds 7 people, small groups cannot produce better interaction and performance than large groups. This may be because the learning scaffolds of technique support, resource support, and teacher support improve the frequency and effectiveness of interaction among group members, and a collaborative group with more members may increase the diversity of views, which is helpful to cultivate critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
With regard to the learning scaffold, the three different kinds of learning scaffolds can all enhance critical thinking. Among them, the teacher-supported learning scaffold has the largest overall effect size, demonstrating the interdependence of effective learning scaffolds and collaborative problem-solving. This outcome is in line with some research findings; as an example, a successful strategy is to encourage learners to collaborate, come up with solutions, and develop critical thinking skills by using learning scaffolds (Reiser, 2004 ; Xu et al., 2022 ); learning scaffolds can lower task complexity and unpleasant feelings while also enticing students to engage in learning activities (Wood et al., 2006 ); learning scaffolds are designed to assist students in using learning approaches more successfully to adapt the collaborative problem-solving process, and the teacher-supported learning scaffolds have the greatest influence on critical thinking in this process because they are more targeted, informative, and timely (Xu et al., 2022 ).
With respect to the measuring tool, despite the fact that standardized measurement tools (such as the WGCTA, CCTT, and CCTST) have been acknowledged as trustworthy and effective by worldwide experts, only 54.43% of the research included in this meta-analysis adopted them for assessment, and the results indicated no intergroup differences. These results suggest that not all teaching circumstances are appropriate for measuring critical thinking using standardized measurement tools. “The measuring tools for measuring thinking ability have limits in assessing learners in educational situations and should be adapted appropriately to accurately assess the changes in learners’ critical thinking.”, according to Simpson and Courtney ( 2002 , p. 91). As a result, in order to more fully and precisely gauge how learners’ critical thinking has evolved, we must properly modify standardized measuring tools based on collaborative problem-solving learning contexts.
With regard to the subject area, the comprehensive effect size of science departments (e.g., mathematics, science, medical science) is larger than that of language arts and social sciences. Some recent international education reforms have noted that critical thinking is a basic part of scientific literacy. Students with scientific literacy can prove the rationality of their judgment according to accurate evidence and reasonable standards when they face challenges or poorly structured problems (Kyndt et al., 2013 ), which makes critical thinking crucial for developing scientific understanding and applying this understanding to practical problem solving for problems related to science, technology, and society (Yore et al., 2007 ).
Suggestions for critical thinking teaching
Other than those stated in the discussion above, the following suggestions are offered for critical thinking instruction utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
First, teachers should put a special emphasis on the two core elements, which are collaboration and problem-solving, to design real problems based on collaborative situations. This meta-analysis provides evidence to support the view that collaborative problem-solving has a strong synergistic effect on promoting students’ critical thinking. Asking questions about real situations and allowing learners to take part in critical discussions on real problems during class instruction are key ways to teach critical thinking rather than simply reading speculative articles without practice (Mulnix, 2012 ). Furthermore, the improvement of students’ critical thinking is realized through cognitive conflict with other learners in the problem situation (Yang et al., 2008 ). Consequently, it is essential for teachers to put a special emphasis on the two core elements, which are collaboration and problem-solving, and design real problems and encourage students to discuss, negotiate, and argue based on collaborative problem-solving situations.
Second, teachers should design and implement mixed courses to cultivate learners’ critical thinking, utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving. Critical thinking can be taught through curriculum instruction (Kuncel, 2011 ; Leng and Lu, 2020 ), with the goal of cultivating learners’ critical thinking for flexible transfer and application in real problem-solving situations. This meta-analysis shows that mixed course teaching has a highly substantial impact on the cultivation and promotion of learners’ critical thinking. Therefore, teachers should design and implement mixed course teaching with real collaborative problem-solving situations in combination with the knowledge content of specific disciplines in conventional teaching, teach methods and strategies of critical thinking based on poorly structured problems to help students master critical thinking, and provide practical activities in which students can interact with each other to develop knowledge construction and critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
Third, teachers should be more trained in critical thinking, particularly preservice teachers, and they also should be conscious of the ways in which teachers’ support for learning scaffolds can promote critical thinking. The learning scaffold supported by teachers had the greatest impact on learners’ critical thinking, in addition to being more directive, targeted, and timely (Wood et al., 2006 ). Critical thinking can only be effectively taught when teachers recognize the significance of critical thinking for students’ growth and use the proper approaches while designing instructional activities (Forawi, 2016 ). Therefore, with the intention of enabling teachers to create learning scaffolds to cultivate learners’ critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem solving, it is essential to concentrate on the teacher-supported learning scaffolds and enhance the instruction for teaching critical thinking to teachers, especially preservice teachers.
Implications and limitations
There are certain limitations in this meta-analysis, but future research can correct them. First, the search languages were restricted to English and Chinese, so it is possible that pertinent studies that were written in other languages were overlooked, resulting in an inadequate number of articles for review. Second, these data provided by the included studies are partially missing, such as whether teachers were trained in the theory and practice of critical thinking, the average age and gender of learners, and the differences in critical thinking among learners of various ages and genders. Third, as is typical for review articles, more studies were released while this meta-analysis was being done; therefore, it had a time limit. With the development of relevant research, future studies focusing on these issues are highly relevant and needed.
Conclusions
The subject of the magnitude of collaborative problem-solving’s impact on fostering students’ critical thinking, which received scant attention from other studies, was successfully addressed by this study. The question of the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking was addressed in this study, which addressed a topic that had gotten little attention in earlier research. The following conclusions can be made:
Regarding the results obtained, collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster learners’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]). With respect to the dimensions of critical thinking, collaborative problem-solving can significantly and effectively improve students’ attitudinal tendency, and the comprehensive effect is significant (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.87, 1.47]); nevertheless, it falls short in terms of improving students’ cognitive skills, having only an upper-middle impact (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.58, 0.82]).
As demonstrated by both the results and the discussion, there are varying degrees of beneficial effects on students’ critical thinking from all seven moderating factors, which were found across 36 studies. In this context, the teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), and learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01) all have a positive impact on critical thinking, and they can be viewed as important moderating factors that affect how critical thinking develops. Since the learning stage (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05) and measuring tools (chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05) did not demonstrate any significant intergroup differences, we are unable to explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included within the article and its supplementary information files, and the supplementary information files are available in the Dataverse repository: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/IPFJO6 .
Bensley DA, Spero RA (2014) Improving critical thinking skills and meta-cognitive monitoring through direct infusion. Think Skills Creat 12:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2014.02.001
Article Google Scholar
Castle A (2009) Defining and assessing critical thinking skills for student radiographers. Radiography 15(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radi.2007.10.007
Chen XD (2013) An empirical study on the influence of PBL teaching model on critical thinking ability of non-English majors. J PLA Foreign Lang College 36 (04):68–72
Google Scholar
Cohen A (1992) Antecedents of organizational commitment across occupational groups: a meta-analysis. J Organ Behav. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.4030130602
Cooper H (2010) Research synthesis and meta-analysis: a step-by-step approach, 4th edn. Sage, London, England
Cindy HS (2004) Problem-based learning: what and how do students learn? Educ Psychol Rev 51(1):31–39
Duch BJ, Gron SD, Allen DE (2001) The power of problem-based learning: a practical “how to” for teaching undergraduate courses in any discipline. Stylus Educ Sci 2:190–198
Ennis RH (1989) Critical thinking and subject specificity: clarification and needed research. Educ Res 18(3):4–10. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189x018003004
Facione PA (1990) Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research findings and recommendations. Eric document reproduction service. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ed315423
Facione PA, Facione NC (1992) The California Critical Thinking Dispositions Inventory (CCTDI) and the CCTDI test manual. California Academic Press, Millbrae, CA
Forawi SA (2016) Standard-based science education and critical thinking. Think Skills Creat 20:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2016.02.005
Halpern DF (2001) Assessing the effectiveness of critical thinking instruction. J Gen Educ 50(4):270–286. https://doi.org/10.2307/27797889
Hu WP, Liu J (2015) Cultivation of pupils’ thinking ability: a five-year follow-up study. Psychol Behav Res 13(05):648–654. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2015.05.010
Huber K (2016) Does college teach critical thinking? A meta-analysis. Rev Educ Res 86(2):431–468. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654315605917
Kek MYCA, Huijser H (2011) The power of problem-based learning in developing critical thinking skills: preparing students for tomorrow’s digital futures in today’s classrooms. High Educ Res Dev 30(3):329–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2010.501074
Kuncel NR (2011) Measurement and meaning of critical thinking (Research report for the NRC 21st Century Skills Workshop). National Research Council, Washington, DC
Kyndt E, Raes E, Lismont B, Timmers F, Cascallar E, Dochy F (2013) A meta-analysis of the effects of face-to-face cooperative learning. Do recent studies falsify or verify earlier findings? Educ Res Rev 10(2):133–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2013.02.002
Leng J, Lu XX (2020) Is critical thinking really teachable?—A meta-analysis based on 79 experimental or quasi experimental studies. Open Educ Res 26(06):110–118. https://doi.org/10.13966/j.cnki.kfjyyj.2020.06.011
Liang YZ, Zhu K, Zhao CL (2017) An empirical study on the depth of interaction promoted by collaborative problem solving learning activities. J E-educ Res 38(10):87–92. https://doi.org/10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2017.10.014
Lipsey M, Wilson D (2001) Practical meta-analysis. International Educational and Professional, London, pp. 92–160
Liu Z, Wu W, Jiang Q (2020) A study on the influence of problem based learning on college students’ critical thinking-based on a meta-analysis of 31 studies. Explor High Educ 03:43–49
Morris SB (2008) Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organ Res Methods 11(2):364–386. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428106291059
Article ADS Google Scholar
Mulnix JW (2012) Thinking critically about critical thinking. Educ Philos Theory 44(5):464–479. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-5812.2010.00673.x
Naber J, Wyatt TH (2014) The effect of reflective writing interventions on the critical thinking skills and dispositions of baccalaureate nursing students. Nurse Educ Today 34(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2013.04.002
National Research Council (2012) Education for life and work: developing transferable knowledge and skills in the 21st century. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Niu L, Behar HLS, Garvan CW (2013) Do instructional interventions influence college students’ critical thinking skills? A meta-analysis. Educ Res Rev 9(12):114–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2012.12.002
Peng ZM, Deng L (2017) Towards the core of education reform: cultivating critical thinking skills as the core of skills in the 21st century. Res Educ Dev 24:57–63. https://doi.org/10.14121/j.cnki.1008-3855.2017.24.011
Reiser BJ (2004) Scaffolding complex learning: the mechanisms of structuring and problematizing student work. J Learn Sci 13(3):273–304. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327809jls1303_2
Ruggiero VR (2012) The art of thinking: a guide to critical and creative thought, 4th edn. Harper Collins College Publishers, New York
Schellens T, Valcke M (2006) Fostering knowledge construction in university students through asynchronous discussion groups. Comput Educ 46(4):349–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2004.07.010
Sendag S, Odabasi HF (2009) Effects of an online problem based learning course on content knowledge acquisition and critical thinking skills. Comput Educ 53(1):132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.01.008
Sison R (2008) Investigating Pair Programming in a Software Engineering Course in an Asian Setting. 2008 15th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference, pp. 325–331. https://doi.org/10.1109/APSEC.2008.61
Simpson E, Courtney M (2002) Critical thinking in nursing education: literature review. Mary Courtney 8(2):89–98
Stewart L, Tierney J, Burdett S (2006) Do systematic reviews based on individual patient data offer a means of circumventing biases associated with trial publications? Publication bias in meta-analysis. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York, pp. 261–286
Tiwari A, Lai P, So M, Yuen K (2010) A comparison of the effects of problem-based learning and lecturing on the development of students’ critical thinking. Med Educ 40(6):547–554. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02481.x
Wood D, Bruner JS, Ross G (2006) The role of tutoring in problem solving. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 17(2):89–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.1976.tb00381.x
Wei T, Hong S (2022) The meaning and realization of teachable critical thinking. Educ Theory Practice 10:51–57
Xu EW, Wang W, Wang QX (2022) A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of programming teaching in promoting K-12 students’ computational thinking. Educ Inf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11445-2
Yang YC, Newby T, Bill R (2008) Facilitating interactions through structured web-based bulletin boards: a quasi-experimental study on promoting learners’ critical thinking skills. Comput Educ 50(4):1572–1585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2007.04.006
Yore LD, Pimm D, Tuan HL (2007) The literacy component of mathematical and scientific literacy. Int J Sci Math Educ 5(4):559–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-007-9089-4
Zhang T, Zhang S, Gao QQ, Wang JH (2022) Research on the development of learners’ critical thinking in online peer review. Audio Visual Educ Res 6:53–60. https://doi.org/10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2022.06.08
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the graduate scientific research and innovation project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region named “Research on in-depth learning of high school information technology courses for the cultivation of computing thinking” (No. XJ2022G190) and the independent innovation fund project for doctoral students of the College of Educational Science of Xinjiang Normal University named “Research on project-based teaching of high school information technology courses from the perspective of discipline core literacy” (No. XJNUJKYA2003).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Educational Science, Xinjiang Normal University, 830017, Urumqi, Xinjiang, China
Enwei Xu, Wei Wang & Qingxia Wang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Enwei Xu or Wei Wang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary tables, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Xu, E., Wang, W. & Wang, Q. The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving in promoting students’ critical thinking: A meta-analysis based on empirical literature. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01508-1
Download citation
Received : 07 August 2022
Accepted : 04 January 2023
Published : 11 January 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01508-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Impacts of online collaborative learning on students’ intercultural communication apprehension and intercultural communicative competence.
- Hoa Thi Hoang Chau
- Hung Phu Bui
- Quynh Thi Huong Dinh
Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Exploring the effects of digital technology on deep learning: a meta-analysis
Sustainable electricity generation and farm-grid utilization from photovoltaic aquaculture: a bibliometric analysis.
- A. A. Amusa
- M. Alhassan
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Find out how Siemens has benefited from our services
of the DAX 30 companies work with us
- Solutions Use cases Answer to your HR questions. smartData Market Intelligence Access to the world’s largest labor market database to tune your business and HR. smartPlan Future Workforce Planning Design your future workforce & uncover skills risks and gaps. smartPeople Skills Fulfillment Discover your internal skills and build a future-fit workforce.
- Podcasts & interviews
- ROI calculator
- HR Glossary
See why 100+ companies choose HRForecast.
- Book a demo
How to assess problem-solving skills

Human beings have been fascinated and motivated by problem-solving for as long as time. Let’s start with the classic ancient legend of Oedipus. The Sphinx aggressively addressed anyone who dared to enter Thebes by posing a riddle. If the traveler failed to answer the riddle correctly, the result was death. However, the Sphinx would be destroyed when the answer was finally correct.
Alas, along came Oedipus. He answered correctly. He unlocked this complex riddle and killed the Sphinx.
However, rationality was hardly defined at that time. Today, though, most people assume that it simply takes raw intelligence to be a great problem solver. However, it’s not the only crucial element.
Introduction to key problem-solving skills
You’ve surely noticed that many of the skills listed in the problem-solving process are repeated. This is because having these abilities and talents are so crucial to the entire course of getting a problem solved. Let’s look at some key problem-solving skills that are essential in the workplace.
Communication, listening, and customer service skills
In all the stages of problem-solving, you need to listen and engage to understand what the problem is and come to a conclusion as to what the solution may be. Another challenge is being able to communicate effectively so that people understand what you’re saying. It further rolls into interpersonal communication and customer service skills, which really are all about listening and responding appropriately.
Data analysis, research, and topic understanding skills
To produce the best solutions, employees must be able to understand the problem thoroughly. This is possible when the workforce studies the topic and the process correctly. In the workplace, this knowledge comes from years of relevant experience.
Dependability, believability, trustworthiness, and follow-through
To make change happen and take the following steps towards problem-solving, the qualities of dependability, trustworthiness, and diligence are a must. For example, if a person is known for not keeping their word, laziness, and committing blunders, that is not someone you’ll depend on when they provide you with a solution, will you?
Leadership, team-building, and decision-making
A true leader can learn and grow from the problems that arise in their jobs and utilize each challenge to hone their leadership skills. Problem-solving is an important skill for leaders who want to eliminate challenges that can otherwise hinder their people’s or their business’ growth. Let’s take a look at some statistics that prove just how important these skills are:
A Harvard Business Review study states that of all the skills that influence a leader’s success, problem-solving ranked third out of 16.
According to a survey by Goremotely.net, only 10% of CEOs are leaders who guide staff by example .
Another study at Havard Business Review found a direct link between teambuilding as a social activity and employee motivation.
Are you looking for a holistic way to develop leaders in your workplace?
Numerous skills and attributes define a successful one from a rookie when it comes to leaders. Our leadership development plan (with examples!) can help HR leaders identify potential leaders that are in sync with your company’s future goals.
Why is problem solving important in the workplace?
As a business leader, when too much of your time is spent managing escalations, the lack of problem-solving skills may hurt your business. While you may be hiring talented and capable employees and paying them well, it is only when you harness their full potential and translate that into business value that it is considered a successful hire.
The impact of continuing with poor problem-solving skills may show up in your organization as operational inefficiencies that may also manifest in product quality issues, defects, re-work and non-conformance to design specifications. When the product is defective, or the service is not up to the mark, it directly affects your customer’s experience and consequently reflects on the company’s profile.
At times, poor problem-solving skills could lead to missed market opportunities, slow time to market, customer dissatisfaction, regulatory compliance issues, and declining employee morale.
Problem-solving skills are important for individual business leaders as well. Suppose you’re busy responding to frequent incidents that have the same variables. In that case, this prevents you from focusing your time and effort on improving the future success of business outcomes.
Proven methods to assess and improve problem-solving skills
Pre-employment problem-solving skill assessment .
Recent research indicates that up to 85% of resumes contain misleading statements. Similarly, interviews are subjective and ultimately serve as poor predictors of job performance .
To provide a reliable and objective means of gathering job-related information on candidates, you must validate and develop pre-employment problem-solving assessments. You can further use the data from pre-employment tests to make informed and defensible hiring decisions.
Depending on the job profile, below are examples of pre-employment problem-solving assessment tests:
Personality tests: The rise of personality testing in the 20th century was an endeavor to maximize employee potential. Personality tests help to identify workplace patterns, relevant characteristics, and traits, and to assess how people may respond to different situations.
Examples of personality tests include the Big five personality traits test and Mercer | Mettl’s Dark Personality Inventory .
Cognitive ability test: A pre-employment aptitude test assesses individuals’ abilities such as critical thinking, verbal reasoning, numerical ability, problem-solving, decision-making, etc., which are indicators of a person’s intelligence quotient (IQ). The test results provide data about on-the-job performance. It also assesses current and potential employees for different job levels.
Criteria Cognitive Aptitude test , McQuaig Mental Agility Test , and Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory are commonly used cognitive ability assessment tests.
Convergent and divergent thinking methods
American psychologist JP Guilford coined the terms “convergent thinking” and “divergent thinking” in the 1950s.
Convergent thinking involves starting with pieces of information and then converging around a solution. An example would be determining the correct answer to a multiple-choice question.
The nature of the question does not demand creativity but rather inherently encourages a person to consider the veracity of each answer provided before selecting the single correct one.
Divergent thinking, on the other hand, starts with a prompt that encourages people to think critically, diverging towards distinct answers. An example of divergent thinking would be asking open-ended questions.
Here’s an example of what convergent thinking and a divergent problem-solving model would look like.
The 5 whys method , developed by Sakichi Toyoda, is part of the Toyota production system. In this method, when you come across a problem, you analyze the root cause by asking “Why?” five times. By recognizing the countermeasure, you can prevent the problem from recurring. Here’s an example of the 5 whys method.
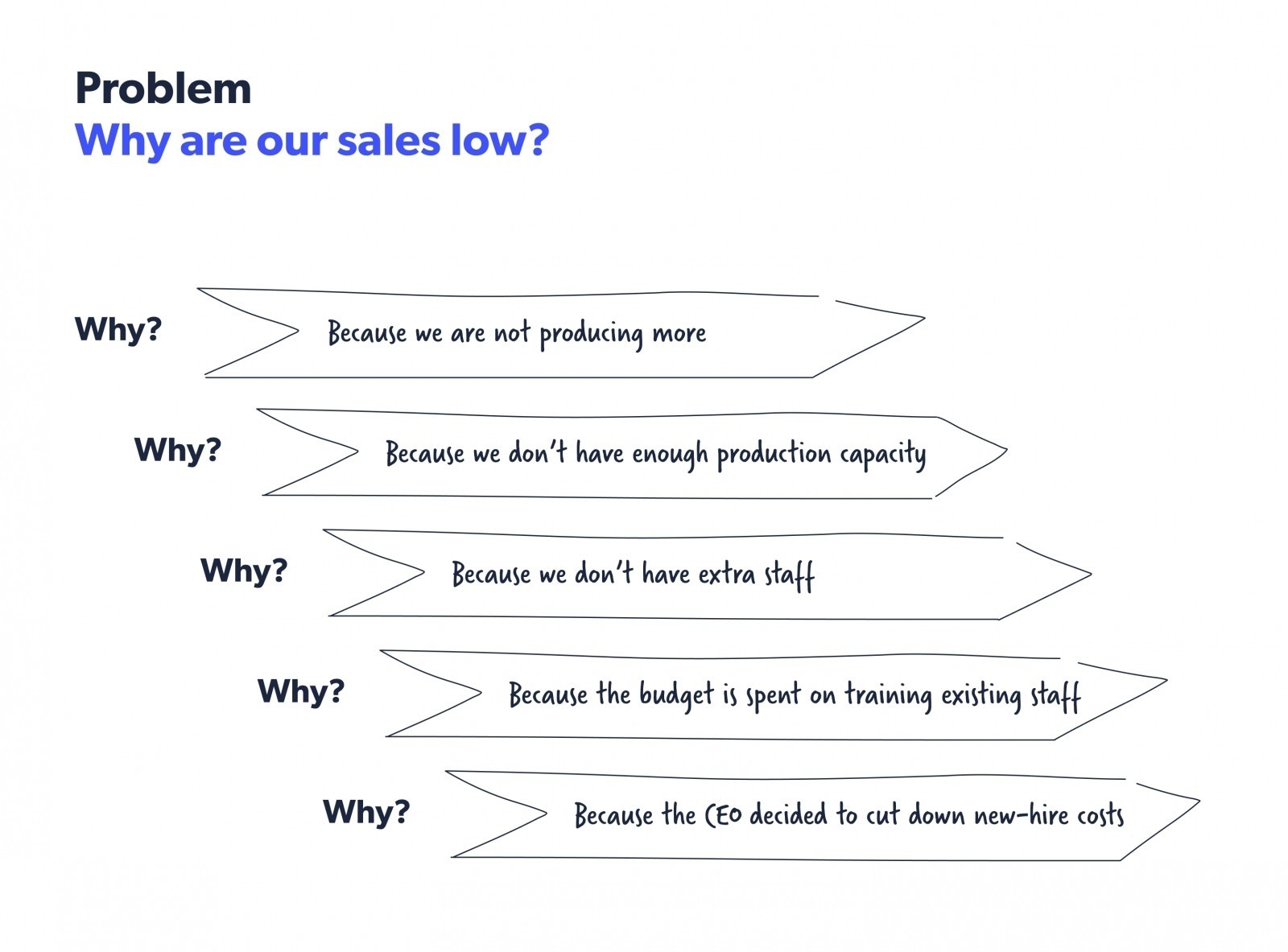
Source: Kanbanzie
This method is specifically useful when you have a recurring problem that reoccurs despite repeated actions to address it. It indicates that you are treating the symptoms of the problem and not the actual problem itself.
Starbursting
While brainstorming is about the team coming together to try to find answers, starbursting flips it over and asks everyone to think of questions instead. Here’s an example of the starbursting method.
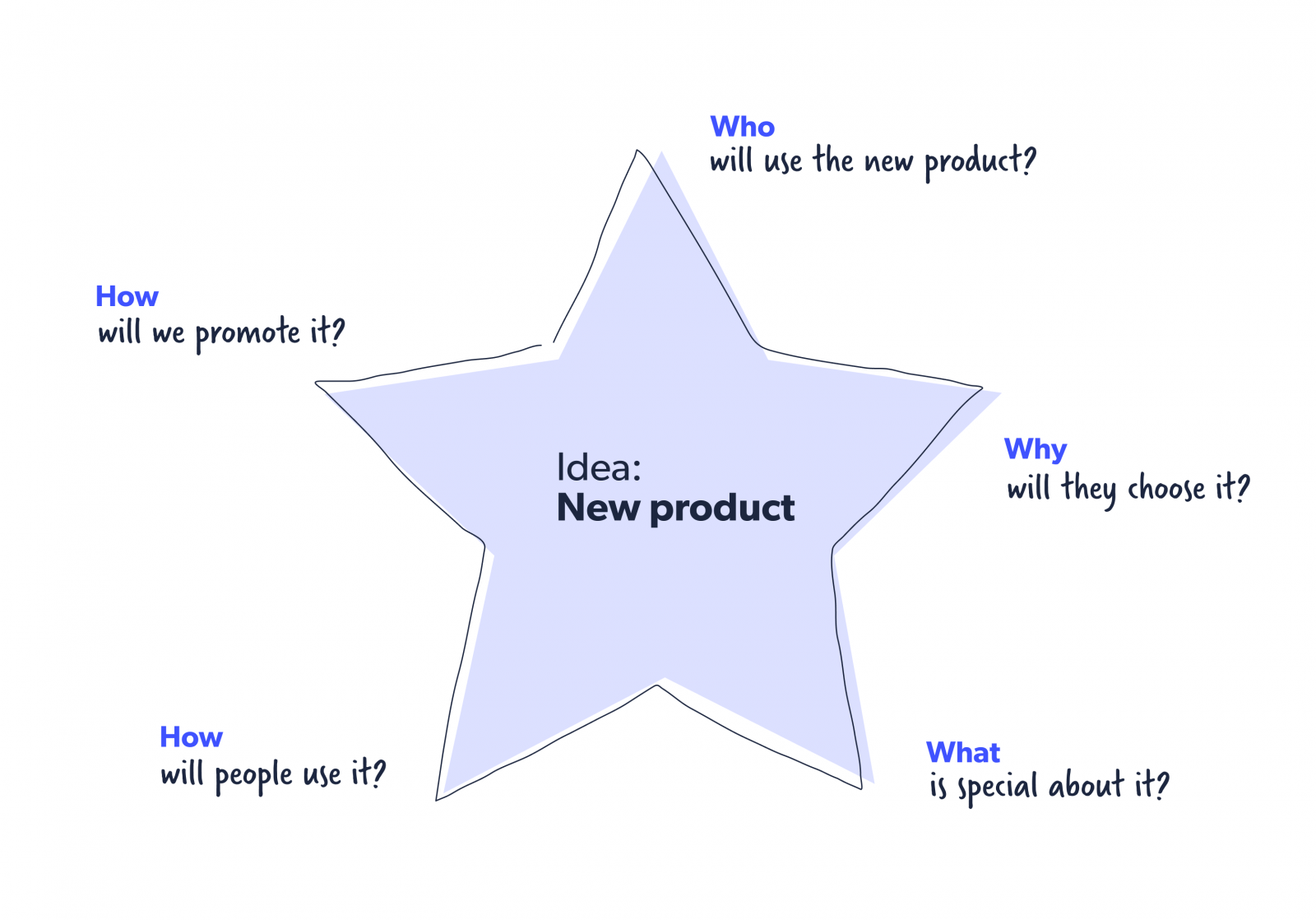
The idea of this method is to go and expand from here, layering more and more questions until you’ve covered every eventuality of the problem.
Use of data analysis to measure improvement in problem-solving skills for your organization
Problem-solving and data analytics are often used together. Supporting data is very handy whenever a particular problem occurs. By using data analytics, you can find the supporting data and analyze it to use for solving a specific problem.
However, we must emphasize that the data you’re using to solve the problem is accurate and complete. Otherwise, misleading data may take you off track of the problem at hand or even make it appear more complex than it is. Moreover, as you gain knowledge about the current problem, it further eases the way to solve it.
Let’s dig deeper into the top 3 reasons data analytics is important in problem-solving.
1. Uncover hidden details
Modern data analytics tools have numerous features that let you analyze the given data thoroughly and find hidden or repeating trends without needing any extra human effort. These automated tools are great at extracting the depths of data, going back way into the past.
2. Automated models
Automation is the future. Businesses don’t have enough time or the budget to encourage manual workforces to go through loads of data to solve business problems. Instead, the tools can collect, combine, clean, and transform the relevant data all by themselves and finally use it to predict the solutions.
3. Explore similar problems
When you use a data analytics approach to solve problems, you can collect all the data available and store it. It can assist you when you find yourself in similar problems, providing references for how such issues were tackled in the past.
If you’re looking for ways to help develop problem-solving skills in the workplace and want to build a team of employees who can solve their own problems, contact us to learn how we can help you achieve it.
Stay up to date with our newsletter
Every month, we’ll send you a curated newsletter with our updates and the latest industry news.
More stories we think you will like

Inclusive hiring practices and strategies for success

Business restructuring done right: what to consider

Gig economy examples and guides
HRForecast newsletter
Get only relevant and insightful letters from us every month

Not a customer yet? Contact us

Career at HRForecast
Why hrforecast.
- Customer Stories
- Trust and Security
- Data Analytics Approach
- IT Skills Analytics
- smartPeople

2023 © Copyright - HRForecast | Imprint | Privacy policy | Terms and conditions (MSA)


Stealth Agents
Hire Top 1% Virtual Assistant Talent
30 Problem-Solving Skill Assessment Questions
- May 1, 2024
In business, problem-solving is crucial. It’s the basis of innovation and strategic thinking. Whether you’re leading a team or running a startup, enhancing your problem-solving skills is essential.
It’s not just about having answers but asking the right questions to uncover complexities and create solutions. Developing this skill can make you a valuable asset to any company.
Unwrapping the Essence of Problem-Solving
Before we dive into the list of questions, let’s remind ourselves of the significance of this skill. Problem-solving involves defining a problem, evaluating alternatives, and finding a best-fit solution.
It helps organizations to untangle complexities, mature innovative ideas, and steer clear of potential hazards.
At its core, problem-solving is a problem of recognizing patterns, understanding complex systems, and finding effective paths to desired goals. It’s about being proactive rather than reactive—being the kind of individual who companies seek out when they want that issue solved yesterday.

The 30 Problem-Solving Skill Assessment Questions
Now that we’ve primed our mental engines, let’s unleash the challenge. Each question in this list stresses different aspects of problem-solving: critical thinking, lateral thinking, root cause analysis, and implementation strategies.
As you go through these questions, picture yourself in the role of a top-tier consultant, ready to tackle any puzzle that greets you.
1. What specific problem do you aim to solve? Describe it in detail.
2. what are the short and long-term consequences of not finding a solution, 3. how does solving this problem align with your organization’s strategic objectives, 4. what are the immediate obstacles you foresee in finding a solution, 5. who are the stakeholders affected by this problem and any potential solutions, 6. is this problem better suited to a data-driven approach, or an imaginative one, 7. have you encountered a similar problem in the past how was it resolved, and can that experience be applied in this context, 8. what are the unintended consequences of the most obvious solution you can think of, 9. how can you frame this problem to encourage the most creative thinking, 10. can you identify any sub-problems that need solving on the way to the big solution, 11. what are the ethical implications of the various solutions you’re considering, 12. does this problem require buy-in or action from other departments or teams, 13. are there industry standards or best practices that can guide your approach to this problem, 14. can you leverage technology to accelerate your problem-solving process, 15. if finances were unlimited, what solution would you implement why, 16. what assumptions have you made about this problem that could be challenged, 17. how does this problem present an opportunity for growth or innovation, 18. what’s the worst possible way to solve this problem what can you learn from that approach, 19. are there any trends or emerging market shifts that can influence this problem’s solution, 20. can you reframe the problem from a different perspective to unveil new solutions, 21. who outside your organization has faced similar challenges and how did they overcome them, 22. which steps can you take proactively to avoid this problem from occurring in the future, 23. what feedback mechanisms can you put in place to ensure the efficacy of the solution, 24. how can you make the solution most acceptable to everyone affected, 25. what metrics can you use to measure the success and roi of your solution, 26. can you break the solution-making process into smaller, more manageable parts, 27. can you visualize your solution from start to finish what does success look like, 28. what’s the simplest solution that could possibly work for this problem, 29. if you had a magic wand, how would you redesign the structure of your organization to prevent this kind of problem in future, 30. what would you advise your best friend to do if they were in your position, what is the problem-solving model of assessment.
The problem-solving model of assessment is versatile and effective. It involves identifying the problem, understanding its context, generating solutions, evaluating and selecting solutions, implementing the chosen solution, and reviewing and refining the outcome.
This structured approach makes problem-solving manageable, encourages innovative solutions, and promotes a culture of continuous improvement. It’s not just about solving the problem, but also learning from it.
In the marathon that is a business career, those with the swiftest, most innovative, and most pragmatic problem-solving feet often outrun the competition. These questions are milestones on your path to becoming a master problem-solver.
Remember, problem-solving is not about being infallible; it’s about being efficient, adaptive, and always ready to learn. So, take these 30 questions seriously, practice them often, and watch as the complex challenges of the business world turn into stepping stones on your journey to success.
Hire Top 1% Virtual Assistants
Let us handle your backend tasks using our top 1% virtual assistant professionals. Save up to 80% and produce more results for your company in the next 30 days!
45 Pre-Startup Venture Questions

40 Personalized Fashion Design Concepts

35 Niche Market Research Services
Virtual assistants for your business.
© 2024 All rights reserved
We create jobs to bless the lives of families
Reimagining Assessment Assessing the Transfer of Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills

Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him) Director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute in Washington, DC
Educators are rethinking the purposes, forms, and nature of assessment. Beyond testing mastery of traditional content knowledge—an essential task, but not nearly sufficient—educators are designing assessment for learning as an integral part of the learning process.
Two Rivers embarked on a multi-year project to define and assess critical thinking and problem solving in project-based learning expeditions.
Two Rivers Public Charter School in Washington, D.C., is a network of EL Education schools serving over 700 students in preschool through 8th grade. Throughout our twelve-year history, we have continued to champion the importance of embracing a broader definition of student success than what has been handed to us by state and national policy. While we believe that it is essential for all students to be proficient in math, literacy, and the sciences, we believe that that is not enough. Students also need a rich set of social and cognitive skills that span beyond any given discipline.
Furthermore, we believe that we can best teach students these skills through hands-on interdisciplinary project-based learning. As EL Education schools, our projects are defined as expeditions lasting 10 to 12 weeks in which students tackle messy, real world problems that don’t have easy paths to solutions nor do they have one clear right answer. Through intentional design of these projects, teachers address the core content and basic skills defined by literacy and content standards; the social skills of collaboration and communication; the intrapersonal skills defined by character; and the broadly applicable cognitive skills of critical thinking and problem solving.
In the life of our schools, we have seen the powerful way that our students through project-based learning have embraced deeper learning outcomes, and exhibited the habits of effective critical thinking, collaboration, and personal character. However, our evidence that this is working is only found in anecdotes and in the quality of student work. We have been unable to demonstrate neither the degree to which students are developing these skills within projects nor their ability to transfer the skills beyond the context of the current project.
Focusing just on the dimensions of critical thinking and problem solving, our teachers expressed frustration at not knowing in concrete terms what those cognitive skills looked like when students exhibited them. Building on our understanding of the essential role that assessment for learning plays in the learning process and the very practical consideration of how we help teachers and students define and work towards developing these skills, we have embarked on a multi-year project to define and assess critical thinking and problem solving.
Critical thinking and problem solving, as we define it, are the set of non-discipline specific cognitive skills people use to analyze vast amounts of information and creatively solve problems. We have broken those skills down into these five core components:
- Schema Development: The ability to learn vast amounts of information and organize it in ways that are useful for understanding
- Metacognition and Evaluation: The ability to think critically about what one is doing and evaluate many potential choices
- Effective Reasoning: The ability to create claims and support them with logical evidence
- Problem Solving: The ability to identify the key questions in a problem, develop possible paths to a solution, and follow through with a solution
- Creativity and Innovation: The ability to formulate new ideas that are useful within a particular context
Our project is working to create learning progressions in each of these core components with accompanying rubrics. The progressions of learning and rubrics will both help define for students and teachers the skills that all students should be developing as well as function as evaluative tools to provide a picture where each student sits in the development of these skills and what are the next steps for further learning.
However, we believe it is not enough for students to be able to develop these skills within the highly scaffolded context of our expeditions. If they have truly learned the skills, they should have the ability to transfer them. With this in mind, we are working to create short content-neutral performance tasks that will give teachers and students valuable information about each of the five core components listed above. Our hypothesis is that through having students tackle short novel tasks, we will be able to draw clear conclusions about their learning of critical thinking and problem solving skills.
Through the course of this work, we hope that our process will be useful to other educators interested in achieving deeper learning outcomes for their students. We realize that deeper learning will not become a reality in most schools until teachers and leaders have a clear vision for what it looks like on a day-to-day basis and how we can clearly demonstrate student growth in these essential skills. We hope that our work will help to inform how to make deeper learning a concrete reality. It is a work in progress, and we invite you to share your thoughts and follow our progress at our website https://learn.tworiverspcs.org .
Learn more about Two Rivers' Assessment for Learning Project on their grantee page .
Jeff Heyck-Williams (He, His, Him)
Director of the two rivers learning institute.
Jeff Heyck-Williams is the director of the Two Rivers Learning Institute and a founder of Two Rivers Public Charter School. He has led work around creating school-wide cultures of mathematics, developing assessments of critical thinking and problem-solving, and supporting project-based learning.
Read More About Reimagining Assessment

Three Ways Franklin Is Doing High School Differently
Carisa Corrow (she/hers)
November 13, 2023

Testing for Dummies: 5 Facts about Standardized Testing
John Tanner
August 31, 2023

Grades vs. Continuous Learning: Learners Are Entitled to the A
Catherine Thorn
August 24, 2023
- Precalculus
- Signup / Login

Free Lessons.
By math teachers, for math teachers..
Designed and tested with real students at East Kentwood High School, the most diverse public high school in Michigan.
Check out the NEW Math Medic Assessment Platform!
Our teaching philosophy, experience first, formalize later.
Every lesson begins with students working collaboratively in small groups through a sequence of carefully crafted questions that slowly build in complexity (Experience First). Following this activity, the teacher facilitates a discussion connecting students’ ideas with academic vocabulary and notation (Formalize Later). This approach encourages students to build strong math identities and take an active part in mathematical sense-making.
What We Offer

Lesson Plans
Free lesson plans and pacing guides for every high school math course, complete with teaching tips for every lesson.

Teacher Workshops
Online and in-person workshops supporting teachers to continually grow their teaching practice.

Get to Know Math Medic
Latest blog posts.

What Does It Mean to "Make Sense of Problems and Persevere in Solving Them?"

Unpacking Productive Struggle (Part 1)

What Does It Mean to "Construct Viable Arguments and Critique the Reasoning of Others"?
5 Myths About Math
Math medic help.
THE BEST TEST PRACTICE
Learn how to pass any reasoning test with my tips, training and free practice tests..

Recommended by:

Free Practice Aptitude Tests
Take 16 free practice aptitude tests . Each test comes with answers and fully explained solutions to each question.
What Is the Saville Wave Test?
The Saville Wave test is a personality questionnaire that comes in different versions to suit all sorts of job roles and levels of seniority.
Created by Saville Assessment, the Wave tests are designed to be the ‘best-in-class predictor of workplace performance and potential’.
They blend digital innovation and science to cover aspects of competency, potential, motivation, talent and preferred company culture in one short assessment.
The Wave tests are usually used in recruitment and selection, but they are also used for talent management and succession planning.
There are two main types of Wave tests used in recruitment:
- The Wave Focus Styles
- The Wave Professional Styles

It is becoming increasingly common for employers to ask potential new employees to complete a variety of assessments as part of their recruitment processes.
One example of this is the Thomas International PPA assessment , which is a personality test commonly used by employers who are looking for individuals with specific personality types or strengths in defined areas.
In this article, you’ll learn what the Thomas International PPA Test is, what you can expect if you are asked to take the assessment and how your test will be scored.
We have also included plenty of helpful tips and free Thomas International PPA sample test questions to help you prepare ahead of taking the Thomas PPA assessment.

The NWEA MAP Growth Test is used in thousands of schools across the US to assess children academically.
The test can be given three times in a school year and helps teachers to plan their lessons so that children can reach their potential and continue to grow throughout their time in education.
In this article, you will learn more about the different levels of the test and the way it is structured to suit different grades, what types of questions are on the tests and how best to prepare your child for success.

If your child is under the age of 12 and aims to get into a gifted school program, they will most likely be required to take the NNAT test to assess their skills.
If you know that your child is expected to take the exam, you can help them prepare for it by letting them know what to expect.
This article contains the most relevant information concerning the NNAT test, including its purpose, scoring system and levels.
You will also receive plenty of helpful tips on how to help your child prepare for the exam by completing a Naglieri Nonverbal Ability Test sample and working on their weaknesses in each question type.

The Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory (HBRI) is a scientifically-based aptitude test.
It is designed to assess cognitive ability and a candidate’s preferences for using qualitative and quantitative reasoning skills.
The HBRI is a popular tool for pre-employment screening, particularly in the management, sales and marketing sectors.
If you have been asked to take the HBRI, your test results will offer prospective employers insight into your decision-making skills, problem-solving abilities, approach to processing information and ability to learn from past experiences.
In this article, you can learn what to expect when taking the Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory HBRI test, see examples of the type of Hogan Business Reasoning Inventory questions you might be faced with and guidance on how to prepare for the assessment.

The MAP Kindergarten Test is a computer-adaptive test that measures your child’s progress throughout their academic career.
The grades K through 2 tests assess mathematics and reading abilities.
The results from these tests allow teachers to identify the gaps in your child’s knowledge and to better understand their ability to learn and retain information.
The MAP test is administered three times in the academic year to ensure your child’s progress is properly recorded.

The Ramsay Mechanical Aptitude Test is used as part of the pre-employment screening process for a number of roles in different industries.
It is an excellent indicator of how well you can learn on the job, as well as your ability to use basic physics principles and mechanical knowledge to solve problems.
In this article, you will learn more about which job roles require completion of the Ramsay MAT as part of the application process, and what different types of tests are available.
The format of the assessment, as well as the number of questions and the time limit, will also be discussed. You’ll also learn how the Ramsay MAT is scored and what happens next.
There will be example questions that are similar to those you are likely to find on the assessment, as well as some top tips for success.

The SHL OPQ32 test is the flagship personality test from SHL.
Used by major organizations all over the world, it is considered to be one of the best psychometric assessment tools currently available on the market.
It is a trait-based personality test that is designed to gauge a candidate’s personality attributes and behavioral preferences in the workplace.
A candidate’s test results are analyzed by recruiters, helping them to decide whether a candidate is a good match for the job role they have applied for.

OLSAT stands for Otis-Lennon School Ability Test.
Children take the test to help schools decide admissions into their gifted-and-talented programs.
Preparing your children for taking the OLSAT is a good idea as it could determine their eligibility and acceptance to extra academic programs that are offered by their schools.

If you are looking for a career working with the emergency services, then becoming a 911 call handler and dispatcher might be just the role for you.
If you can handle working under pressure, helping the public and are able to deal with difficult and uncomfortable situations with a calm head, then you might have what it takes to be the first port of call in an emergency.
Becoming a 911 call handler and dispatcher means you will need to have some very specific skills and abilities, and as part of the recruitment process, you will have the opportunity to demonstrate your suitability by taking the CritiCall 911 dispatch test .
Used throughout the US for recruiting people for 911 roles, the CritiCall test does not assess your previous experience or your knowledge of the role.
Instead, it is designed to assess candidates on the inherent aptitudes that are needed to be successful in the role.
This article will discuss what the CritiCall test is assessing, the types of questions that you are likely to face and what the recruiters will be looking for.
There will be some example questions, as well as details about what mark you will need to achieve to pass the test.
Finally, there are some CritiCall test prep tips to help you prepare for the assessment and what to think about on the day.

The McQuaig Word Survey is a type of personality assessment.
Survey responses are used to measure a candidate’s key personality traits and compare these with how they are currently behaving in the workplace.
The results from the survey indicate whether a candidate is behaving naturally in their current role, or whether they are making changes to their behaviour.
This article will help you pass the McQuaig Word Survey assessment test by giving you all the tools and practice questions you will need.

The Caliper test is an assessment used by employers to gain a better understanding of a candidate’s personality traits, cognitive abilities and motivations.
The Caliper test is used to help employers predict a candidate's suitability for a role.
In this article, we'll take a detailed look at what the Caliper test is and how it is scored.
We’ll also share some tips on how you can perform at your best when taking your Caliper assessment test.

More and more employers are choosing to use psychometric testing as a part of their recruitment processes as it helps to highlight those candidates who are most likely to be suited to the roles they are looking to fill.
Employers will often use this form of testing when recruiting for mid-to-high level managerial roles or positions that require a specific set of skills.
Using the results of assessments, recruiters and employers are able to see the strengths and skills of individuals as well as being able to predict future performance.
One of the most popular options for psychometric testing is the Criteria Cognitive Aptitude test – more commonly known as the CCAT.

The Bennett Mechanical Comprehension Test (BMCT) , also referred to as the Bennett Mechanical Aptitude Test, is considered the most popular mechanical aptitude test.
However, it is also believed to be the hardest one to pass.
The BMCT requires you to have a knowledge and understanding of physical principles and answer 55 questions about the application of these concepts within 25 minutes.
You typically need to score in the top 20% of candidates to progress to the next stage of recruitment.

If you have applied for a job, apprenticeship or college course in the UK or Australia, you may have been asked to complete a Basic and Key Skills Builder or BKSB assessment) .
The initial BKSB assessment determines suitable applicants for an apprenticeship or places a student in the correct class level on a college course. The assessment tests you on your maths and English skills to identify areas that need improvement.
This guide will explain the BKSB assessment in detail, provide example questions, and answer your queries about the test content and format.

There are a variety of tests and assessments that can be used by companies for candidates applying for jobs.
One of those is the Thomas GIA Test .
This article will define what the Thomas GIA Test is and who it is for, in addition to looking at what the test involves, how it is scored and tips for the next chance to pass the test.
You will also find Thomas GIA test examples and explanations for each answer.

The IE Global Admissions Test (ieGAT) is an entrance exam for the IE University (IEU) in Spain.
It covers numerical , logical and verbal reasoning .
Not every IE program requires an ieGAT score. However, as the programs that do are highly competitive, those who take the ieGAT Test must prepare themselves to achieve the best score possible.
This article will help you understand:
- What the ieGAT is
- The structure
- ieGAT scoring
- How to register for the ieGAT
- The best ways to prepare

More and more companies are introducing psychometric testing as a part of their recruitment processes.
This means that, if you are considering changing careers or applying for a new role within your existing industry, you may need to take an assessment.
One of the most popular tests for corporate employers is the test by Sova Assessment .

The United States Postal Service (USPS) provides extensive career opportunities and seemingly endless possibilities for professional development.
However, anyone looking to work at the USPS must pass a Virtual Entry Assessment designed to find suitable applicants for the role they are trying to fill.
This article covers the Postal Exam 474 , including its main parts, how to pass it and how to prepare for the Virtual Entry Assessment.
Let's start by looking at what exactly the 474 Virtual Entry Assessment is.

Developed by Drs Joyce and Robert Hogan in the 1980s, the Hogan assessment is a collection of tests designed to assess personality traits, leadership skills and cognitive abilities.
The Hogan assessment is generally used as a pre-employment test for management roles.
This article will guide you through the online Hogan tests , provide a range of sample questions, discuss how the Hogan Assessment results are calculated and recommend ways that you can prepare to take the Hogan assessment yourself.
If you’ve recently applied for a managerial or executive role, you may have been asked to take a Saville Analysis Aptitude Test , also known as the Swift Aptitude test.
The Swift Analysis Aptitude Test was created by Saville Assessment, which is a huge name in the test publishing market.

The CAT4 cognitive ability test is an examination designed to measure a student’s academic progress.
When the CAT4 test is scored, teachers and parents will be given a summary of the academic potential of the student.
Any student taking the test will be asked questions that will measure their non-verbal reasoning abilities, verbal reasoning skills, quantitative reasoning abilities and spatial awareness .
In this article, you’ll learn more about what types of questions are asked to examine these skills.

The Korn Ferry Leadership Potential Assessment (KFALP) is used to test candidates to see if they have the potential to become leaders and managers.
It uses seven different categories, known as Seven Signposts, to assess potential leaders:
- Learning Agility
- Leadership Traits
- Derailment Risks
This article will examine the theory behind the assessment, the different topics that are tested and how the assessment is scored.
There will also be example questions so that you know what to expect when you take the KFALP and some tips to help you score as highly as possible when you take the test.

Pymetrics tests identify specific behavioral characteristics and traits.
This article examines why pymetrics tests are used and what to expect in your assessment.
Tips are included to help you get the best results.

The McQuaig Mental Agility Test (MMAT) is a 15-minute timed test that is designed to assess your ability to think quickly.
In this short test, you will face questions that will allow you to demonstrate your speed of thought and general mental agility, which are useful aptitudes when it comes to many jobs in different industries.
In this article, find out more about the structure of the test, the different types of McQuaig Mental Agility test questions and what to expect on the day. You’ll also get some mental agility practice test questions and top tips to help you be successful in the MMAT.

The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is responsible for the enforcement of federal law and the protection of national security in the US.
Working for the FBI can be highly stressful. As a special agent for the FBI, the working week is likely to be 50 hours or more.
Special agents must be willing to be based anywhere in the world. They are expected to carry a firearm and work in potentially dangerous situations.
With this in mind, the FBI has a rigorous application and selection process for potential new recruits. It can take more than 20 months to complete the entire process and commence employment with the FBI.

This guide to the USPS postal exam 955 will take you through the different sections of the test, including example questions, provide tips on how you can prepare for the exam and answer several frequently asked questions.
The USPS postal exam 955 is used to screen applicants for mechanic and technician positions , such as electronic technicians or motor vehicle mechanics. It also sometimes referred to as the postal maintenance 955 exam, USPS maintenance mechanic 955 test or the 955 maintenance exam.
It tests applicants’ suitability by assessing personal characteristics, work experience, and electronic and technical knowledge and skills.
The USPS postal exam 955 replaced the previous 931, 932 and 933 exams .
The USPS postal exam 955 is free of charge , but you will need access to the internet and an email address.

If you are looking to work in the United States Postal Service, you will need to pass the USPS Postal Exam 476.
The USPS Postal Exam 476 is an online test that screens for the best candidates. The exam is used to find suitable candidates for a range of positions, including mail processing clerk, data conversion operator and clerk-related positions.
This article will outline what the USPS Postal Exam 476 includes, with particular attention to the separate sections of the examination.
In addition to this, how the exam is scored and how you can best prepare for it will be covered. There will also be a list of frequently asked questions for you to refer to if you have any doubts.

A List of Amazon Assessment Tests Available for Practice in 2024
- Amazon Work Simulation Assessment
- Amazon Maintenance Technician Test
- Amazon Coding Assessment
- Amazon Workstyle Assessment
- Amazon Area Manager Assessment
- Amazon Operations Manager Assessment
- Amazon Online MBA Assessment
- Amazon RME Apprenticeship Skills Battery Test
- Amazon Financial Analyst Assessment
- Amazon ATA Technical Assessment
- Amazon Control Systems Technician Test
- Amazon Warehouse Assessment Test
The Amazon assessment test is an essential way for the corporation to find the best-suited employees.
It is a series of challenges used to evaluate all its candidates during the recruitment process.
Amazon online assessments typically include both numerical and verbal reasoning tests.
These types of tests examine a potential candidate’s logical skills.
Candidates will also have to sit work-style assessments that simulate the working environment at Amazon.
Other Amazon exams include:
- The Amazon coding assessment (also known as the Amazon SDE online assessment)
- The work sample simulation
- An Amazon versant test
These last two, amongst others, will be discussed later in this article.
This Amazon reviewer job article will also discuss how to pass the Amazon assessment tests, some Amazon assessment answers you should know and what you need to do to best prepare yourself.
There is also a comprehensive list of frequently asked questions from those who are interested in taking these Amazon job tests to find employment with the company.

What Is the SHL Verbal Reasoning Test?
The SHL Verbal Reasoning Test is a graduate-level and above pre-employment aptitude test that is used in graduate and management recruitment for many roles across different industries.
The test is usually taken online, and it is designed to evaluate candidates on their ability to understand written information and make informed, reasoned and logical decisions based on that information.
SHL is a well-established test publisher, providing tests for more than 10,000 companies around the world. It offers a range of tests, including psychometric, behavioural and personality assessments that are based in occupational psychology and aptitude science.
The tests have specific aims – and recruitment teams use SHL tests like the Verbal Reasoning Test to filter through similarly qualified candidates to find the applicants who have what it takes to be successful in a graduate or management level role.
When taking a verbal reasoing test, bear in mind that you might also be asked to take numerical reasoning tests, logical reasoning tests or personality tests along side.

IQ stands for intelligence quotient and is usually thought to represent the reasoning skills of individuals.
The idea of intelligence relates to how quickly people can solve problems or puzzles, use logic to answer questions, or quickly recall information and facts they’ve heard.
The first type of IQ test was created by a French psychologist named Alfred Binet.
The assessment that he made is still used and is known as the Stanford-Binet intelligence test.

Considering cheating on your GMAT (Graduate Management Admission Test) Exam?
Want to know how to do it, if you should do it and what the consequences will be?
Well you came to the right place!
Read on to find out more about cheating on the GMAT exam, but be warned...
... it's certainly not something I advise!

Do you have an upcoming online aptitude test ?
Are you looking for the best aptitude test prep material to give you the very best chance of getting the highest possible grade?
If so, this article will help you.
Aptitude tests are a crucial part of your job search, and you usually only have one chance to showcase your skills.
Psychometric aptitude tests can measure many different aptitudes and skill sets, in many different formats:
- Numerical reasoning
- Verbal reasoning
- Diagrammatic or inductive reasoning
- Mechanical reasoning
- Personality types
- Situational judgement and work environment tests
- Work style tests
Aptitude tests can be challenging and it is important to be fully prepared before you attend your job interview or assessment centre.
Several free and paid aptitude test preparation websites offer preparation packs to help you score the best you can.

Those dreaming of working for the TSA will most likely need to take a challenging exam called the TSA CBT Test during the hiring process. Here we’ll look at exactly what it involves and how you can make sure you pass it. Read on to find out more.
If you plan to work as an inspector, manager, marshal or security officer in any agency governed by the Transportation Security Administration, you must pass the TSA CBT test as part of your application process.
Read on to learn more about this assessment, including its purpose, what types of questions it has, how challenging it is and how to prepare for it.
You'll also be provided with a few example questions to help you get an idea of what this test looks like.
Let’s get started.

Aptitude tests are administered to understand your inherent abilities to reason and respond to specific tasks.
They are widely used in various forms to screen candidates or evaluate existing employees for a future job role.
The most generic and widely used aptitude tests are curated to measure different facets of your abilities, mainly on the following areas:
- Abstract Reasoning
- Numerical Reasoning
- Logical Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- Attention to Detail
Apart from these base types, there are various other specialized aptitude tests which you may face in specific industries or based on your role in different career stages.
We have discussed each of the most common job related aptitude tests in detail.
Illustrative examples and helpful hints are provided throughout to aid your preparation.
Read on to find out more.

The Cognify test is a game-based cognitive assessment designed to measure an individual's cognitive aptitude to measure key job performance linked abilities and skills in a prospective candidate.
The Cognify test was once a product of Revelian, an Australian assessment company, but was later acquired by CriteriaCorp.
Moving away completely from the question-answer based template of traditional tests, Cognify uses an innovative approach where candidates don't face a series of questions on a screen.
Instead, the Cognify Assessment comprises 6-7 timed game-based mini-tests categorized into three cognitive abilities categories:
- Problem-Solving
- Verbal Knowledge
Well, before you start raising your eyebrows at the mention of ‘game-based’ and dismiss it as just another fad, pay attention!
Cognify assessment is credited as having brought a paradigm shift in the field of psychometric testing.
Many Tier-I graduate recruiters globally have started using this assessment in their candidate selection process.

The train driver test is used to establish whether a candidate is suitable for work as a train driver. This unique suite of tests includes psychometric assessment tools such as:
- The Group Bourdon Test (GBT)
- Test of Everyday Attention (TEA-OCC)
- Adaptive Tachistoscopic Traffic Perception Test (ATAVT)
- Situational judgement tests
- Vigilance tests
- Written communication tests
What Is the Train Driver Test?
In most countries, you will need to sit the train driver online test if you want to work as a train driver. If you have been asked to sit the assessments, there is no train driver psychometric test cost associated with the train driver exam.
Working as a train driver is a challenging and demanding role. As a train driver, you must be able to ensure the safety of passengers at all times.
The UK’s train driving tests are some of the most challenging. As well as testing aptitude for the job role, they are used to assess whether candidates have the mental abilities to cope with the stress and demands of the job role.
The train driver test is used to establish whether a candidate is suitable for work as a train driver. The train driver test is a unique group of psychometric tests for train drivers designed to assess the psychomotor and cognitive skills needed to work safely as a train driver.
![ecnt problem solving assessment Predictive Index Tests Fully Explained [With Example Questions + Answers]](https://www.datocms-assets.com/7756/1671731172-predictive-index-tests-none-x2.png?auto=%20compress%2C%20enhance%2Cformat&crop=focalpoint&fit=crop&fp-x=0.5&fp-y=0.5&h=300&w=300)
The Predictive Index (PI) test is a popular type of pre-employment testing used to accurately measure an individual’s cognitive ability and behavioral profile during the hiring process in a wide range of industries and organizations. They are most commonly used during the early stages of the recruitment process.
The PI cognitive test assesses verbal, numerical and analytical reasoning ability.
The PI behavioral test creates a behavioral persona that describes character traits and tendencies.

A mechanical aptitude reasoning test is an important way to assess your knowledge on mechanical topics for potential roles in the army, emergency services and many other professions. Here, you will get all the information you need on what a mechanical comprehension test is and how to pass it.
Those applying for jobs related to the army, the emergency services engineering service, and similar occupations that require mechanical aptitude, are likely to be asked to take a mechanical reasoning test as part of the recruitment process.
Mechanical aptitude tests assess knowledge in electricity, optics, pressure and other fields of mechanics related to a specific industry.
From this article, you'll learn what mechanical reasoning tests look like, when to take them, what to expect from these assessment types, and how to practise and prepare for them.
Let’s get started!

If you would like to take a free practice Cognitive Ability Test before reading this article, click here .
If you would like to purchase an online Cognitive Ability Test prep pack, visit our partner website JobTestPrep .
The following tests are common cognitive ability tests:
- Spatial Reasoning
- Mechanical Reasoning
- Logical Ability Tests
- Space Visualization
- Information Processing
- Visual Pursuit
- Manual Speed and Accuracy

Have you been asked to take a Deductive Reasoning test as part of an upcoming interview process?
Continue reading to find out more about this type of test, including:
- Why employers use Deductive Reasoning Tests.
- How you can improve your performance at Deductive Tests.
- What types of questions you will be asked during the Test.
What Is A Deductive Reasoning Test?
Logical thinking or deductive reasoning tests are used by employers to measure an applicant’s ability to make logical arguments and form sound conclusions.
During this type of test, you will be presented with a variety of scenarios, statements and arguments for which you will need to apply a given set of rules to determine the validity of the corresponding conclusion.

Spacial Reasoning Definition
A spatial awareness test is a type of assessment that tests your ability to think in three dimensions and use your imagination to see movement through space.
Someone with good spatial awareness will be able to see in their mind how different shapes interact and be able to manipulate them to make a reasoned and logical decision.
The test is based on pictures, diagrams and shapes. You will need to mentally manipulate the presented image by disassembling or reassembling, rotating, seeing it in a mirror image or from different angles, or otherwise visualizing it differently to find the right answer to the question from the multiple-choice options provided.
Spatial awareness is something that we use to a greater or lesser degree every day, from understanding our position relative to other things around us to imagining the route we will take to get from one place to another.
Spatial reasoning tests are distinct from other similar assessments such as diagrammatic reasoning tests and abstract reasoning tests. It is important to understand how they differ as they are often included in aptitude tests and cognitive assessments alongside spatial reasoning tests.

Psychometric tests are often used by organizations as part of the recruitment process. Different types of psychometric tests are designed to measure various aspects of cognitive ability, reasoning capabilities and personality traits. Potential employers use the results to assess a candidate’s suitability for a role. A psychometric test is generally administered online; this helps hiring managers filter applicants quickly and easily.

As Capp Assessment Tests become more common perhaps you have encountered one for the first time.
This can be a bit daunting and, since they look and feel a bit different to more traditional psychometric reasoning tests, it isn’t necessarily obvious what you need to do to be successful…
Don’t worry.
With the insight and tips we share with you below, you’ll be smashing your tests in no time.
FREE BONUS: Get free unlimited access to Capp test practice (for 30 minutes) on our partner website JobTestPrep.
What are Capp Assessment Tests?
Capp are a consultancy and psychometric test publisher who specialise in Strengths Based Assessments.
They also offer a number of different psychometric tests that are widely used many major organisations including Google, Atkins, Amazon and RBS.
Their Assessment Tests include critical reasoning, numerical reasoning, verbal reasoning .
Psychometric reasoning tests like these are very common.
This is because they are a cheap and efficient way for organisations to identify candidates who aren’t likely to be able to succeed in a particular job.
Because they are often used to filter candidates out of application processes, they are sometimes called screening tests or gateway tests.
Candidates like you have to achieve a particular level of performance in order to progress in the selection process.
With practice you can dramatically improve your performance. Practice is the best way to improve your test scores.
In the rest of this article we’ll show you how the tests work, suggest how you can prepare, and then direct you towards some practice tests so that when the big day comes you are ready.
Before you do anything else, take a look at the Capp website , where you can take free practice tests.
How do Psychometric Reasoning Tests Work?
In general, psychometric reasoning tests challenge users to answer a series of questions and compare their performance on a test with the average performance level of a reference or ‘norm’ group.
This is typically made up of individual with similar characteristics, such as education level, nationality or workplace seniority.
If you do better than most of the norm group you will receive a high score, whereas a low score suggests that your performance was weaker than most of the norm group.
Usually, a minimum standard of performance necessary for success in a role is identified at the start of an assessment process, and all candidates that don’t meet this level will be unable to progress through the process.
What makes Capp Assessment Tests Different?
Capp Assessments are ‘Next Generation’ psychometric aptitude tests ; this means they might look and feel a bit different to other psychometric tests you have completed in the past.
The main difference between the Capp tests and more traditional psychometric ability tests is that the Capp tests are responsive.
This means that the actual questions presented to a candidate will depend upon their performance on the previous questions.
Capp say that the responsiveness of their tests and the size of their question bank mean that the chances of two candidates taking exactly the same test is currently less than one in a billion .
In practice, this means that if you’ve been able to quickly and accurately solve the previous questions, you can expect to be presented with incrementally more challenging questions.
By contrast, if you have made a number of errors, the test will present questions at a lower level.
The aim of the tests is to work out what your maximum ability is. Or put another way, what the most challenging level you are capable of working at is.
Another thing that makes Capp Tests feel different is that they have no time limit (although the time you take to complete the test does effect the score so you still need to work as quickly as you can).
This takes a bit of the pressure off and can make taking these tests rather less stressful than others.
Finally, the variety of question types and the format of the questions in Capp Tests can be different to those used by more traditional test publishers.
Let’s take a closer look at this:
- Numerical Reasoning Tests
Traditionally numerical reasoning tests require candidates to select the correct answer from a number of potential options.
The Capp numerical reasoning test still does this, but it also requires candidates to rank potential answers or to type their answer into a free-text box.
This makes it harder to guess the correct answers.
- Verbal Reasoning Tests
Verbal reasoning tests typically give you a passage of text to read and then ask you whether a number of subsequent statements are true or false, based on the information contained in the passage.
This question type is included within the Capp Verbal Reasoning Test, but there are also a number of different question formats included.
This means that as well as testing verbal reasoning, the Capp test can also assess verbal dexterity, comprehension, interpretation, and adaptability.
As well as traditional multiple choice questions, the test also presents:
- Free text editing : This type of question requires you to type your answers directly into the question. You might be asked to correct spellings or grammar, or edit a passage of text.
- Bucket sort : You will be presented with two categories/styles of writing; your task is to place each item presented to the category/style of writing that it best fits.
- Drag and Drop : This type of question requires you to drag statements or words to the place that they best fit.
- Ranking : These questions can be quite subtle and require you to really understand the nuance of language and language use. You will be presented with a number of statements and asked to rank these based on some feature of the text, such as positivity.
- Selecting the most appropriate word to fill in the sentence : You will be presented with a passage of text with a number of blanks in it, for each blank space you must select the most appropriate word to fill the space from a drop down menu.
Critical Reasoning Tests
The Capp Critical Reasoning test evaluates your ability to think critically in a number of ways.
In each instance, a passage of information is presented followed by a series of statements, your task is to select the appropriate response from the drop down menu.
Questions focus around five areas:
- Inference: rating the probability of truth of inferences based on given information
- Recognition of assumptions: identifying unstated assumptions underlying given statements
- Deduction: determining whether conclusions follow logically from given information
- Interpretation: weighing evidence and deciding if generalisations or conclusions based on data are warranted
- Evaluation of arguments: evaluating the strength and relevance of arguments with respect to a particular question or issue.

Are you considering cheating on your upcoming SHL tests ?
In this full disclosure article, I’ll tell you why people cheat on tests, how people cheat, and whether or not it’s worth doing..
Don't cheat!
Practice... it's the only legitimate way to improve your scores, you'll sleep better at night and probably get better results in your tests too.
Still want to read about how to cheat on a test?

Numerical Reasoning Tests can be very tricky.
And when it comes to results, preparation and practice are key.
But that's easier said than done.
If you're researching this type of aptitude test for the first time or if you want to improve your numerical ability , perform better on tests and get more job offers this article will provide some practical strategies that you can use immediately .
For the best chance of success, read the article below slowly, work through the example questions , follow our tips and actionable advice and then start taking practice tests .
Ready to get started?
Let's go!...
Want to try a practice test before reading this article?
You can take our free numerical test right here:

Logical reasoning tests are a little different to your average psychometric test .
With this type of assessment, there are many different variations so it is sometimes difficult to determine which aspect of logical reasoning you will be assessed on.
With this guide, you’ll learn the difference between inductive and deductive reasoning tests , and some tips for maximising performance.
Designed to evaluate how you interpret patterns, shapes, numbers and other data to reach logical conclusions, the assessments are used across a number of different sectors at all levels of recruitment from entry right up to managerial positions.

The in tray exercise (also called an e-tray exercise ) is a popular assessment activity which employers use to evaluate the skills of applicants in a workplace situation.
If you have an In Tray exercise coming up as part of your interview process, this article will help you prepare.
Within these exercises, candidates will be presented with a given scenario, along with a set of tasks to complete which may include things like responding to email messages, reports or briefing documents.

Aptitude tests are short tests employers use to assess whether a candidate has the level of competency necessary for success in the role.
The tests are used to see if a candidate has the skills necessary to do the job.
Aptitude tests are standardized, for the most part, and the results of all the candidates are compared to each other to see which candidate may be the best for the job.
Aptitude tests provide employers with a quick way to assess a candidate’s ability to perform in high-pressure situations and think in critical ways as they would if they were on the job.

What Is a Situational Judgment Test?
A situational judgement test (SJT) is a psychometric test that is often used as part of the recruitment process for graduate and managerial positions as well as roles that are customer-facing in a wide range of industries.
The SJT is designed to assess how a candidate deals with work-related problems and situations, focusing on essential aptitudes , competencies and soft skills that are not always easy to evaluate in other ways.
Although SJTs are usually bespoke to the company (or in some cases, the specific role), they tend to follow the same basic structure.
Each question is formed by presenting a fictional yet realistic work-based scenario. This might be text-based, it may include some illustrations or it could be animated or acted out in a video.
Following the scenario, there will be several options that you can choose from, each giving a possible course of action to follow to solve the issue that is presented in the situation given.
The answer that you choose will be compared to the benchmark answers that the recruitment team is using – these represent the core competencies for the role, as well as alignment with company values.

SHL assessment tests are important steps in many job interviews and career advancement opportunities. Therefore, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of how the different types of SHL tests work and how you can prepare for them in order to get top scores.
In this article, we will provide an overview of how SHL assessments work, sample SHL test questions, tips on improving your test performance, and strategies for prepping and succeeding with any SHL test.
What Is an SHL Assessment Test?
SHL is a global assessment company that is well known and recognised as a leader in pre-employment psychometric tests; the tests that SHL publishes are used by 75% of the FTSE 100 and they are available in more than 40 languages.
So if you are applying for a new role (especially for a graduate position), you are likely to come across them in the recruitment process.
In addition, the company offers consultancy and management services via its TalentCentral platform.
The SHL assessment are a series of tests that can be delivered individually or in a battery, and some of them are bespoke to the company that is using them, making them an excellent way for the recruitment team to ensure that the applicants for a role have the basic competencies, personality traits, work behaviours and cognitive abilities to be successful.

Sind Sie auf der Suche nach kostenlosen psychometrischen Tests zur Übung?
Dann ist diese Seite genau das Richtige für Sie.
Was ist ein psychometrischer Test?
Psychometrische Tests (auch Eignungstests genannt) sind fester Bestandteil von Jobinterviews vieler Unternehmen auf der ganzen Welt.
Diese Tests bestehen normalerweise aus einer Reihe von zeitlich erfassten Fragen , die meist numerischen (mathematischen Fragen), verbalen (Fragen zum Leseverständnis) oder logischen (diagrammatischen Fragen) Ursprungs sind.

Testes psicométricos (também conhecidos como testes de aptidão) são uma parte comum do processo de entrevistas de emprego em muitas companhias no mundo todo.
Geralmente, esses testes consistem de uma série de questões com um certo tempo de resposta.
As questões costumam ser numéricas (questões matemáticas), verbais (compreensão textual) ou lógicas (questões de diagrama).

Testes SHL . Se você está lendo isso, há uma boa chance de você ter acabado de descobrir que fará um desses testes difíceis como parte de um processo de recrutamento em andamento.
Se você chegou tão longe e agora está se sentindo tenso para se sentar na frente de um ‘abstract quiz’, não se preocupe...
Nós cuidaremos de você.

El Razonamiento Inductivo está basado en patrones y es otra variante de las muchas pruebas psicométricas utilizadas por los empleadores como una forma de determinar la idoneidad de un candidato para sus roles.
En un nivel similar al del razonamiento esquemático , el razonamiento inductivo probará tu habilidad para aplicar la lógica y la razón para la resolución de problemas.
Cómo funcionan las pruebas inductivas
Dentro de la prueba se te presentará una serie de diagramas los cuales se vincularán mediante una regla subyacente.
Esta regla afectará el diseño del diagrama y tu tarea será identificar el patrón.
Bonificación: puedes obtener acceso ilimitado y gratuito a la práctica de prueba (durante 30 minutos) en nuestro sitio web asociado JobTestPrep: Clic aquí .
Por lo general, se espera que los candidatos seleccionen entre 4 y 6 posibles respuestas completas bajo condiciones de tiempo.
Las pruebas de razonamiento inductivo a menudo complementan otras pruebas como las de razonamiento verbal o numérico.
A veces las empresas requieren que complete una prueba de juicio situacional o un cuestionario de personalidad junto con la evaluación de razonamiento inductivo.
Los resultados de cada prueba se revisarán individualmente y luego colectivamente para determinar si tú serías una buena opción para la empresa.
¿Por qué los empleadores utilizan estas pruebas?
Algunas veces se las denomina prueba de razonamiento abstracto, las evaluaciones de razonamiento inductivo están diseñadas para evaluar tus habilidades en la resolución de problemas y el razonamiento lógico.
Cuando completes la prueba, los reclutadores buscarán tu capacidad para trabajar de manera efectiva con información desconocida para alcanzar una solución viable.
Las pruebas se utilizan a menudo para evaluar tu capacidad de pensar creativamente, aplicar habilidades analíticas y diseñar soluciones innovadoras, mientras que a menudo son un indicador de tu nivel general de inteligencia.
Como tal, es esencial que realices el trabajo preparatorio necesario antes de la prueba real para asegurarte de poder completarla exitosamente y crear una buena impresión.
La prueba de razonamiento inductivo es frecuentemente usada por empleadores corporativos; es común esperar que se complete al menos una prueba psicométrica como parte del proceso de reclutamiento.
Los empleadores utilizarán estas pruebas para ver la eficacia con la que trabajas bajo presión y tu enfoque de la evaluación.
Las pruebas de razonamiento inductivo son usadas predominantemente en los roles técnicos o aquellos que requieren una resolución frecuente de problemas y los empleadores las utilizan para evaluar cómo identificas patrones, con qué eficacia puedes identificar reglas y consistencias de datos y si puedes predecir la secuencia de objetos a medida que evolucionan.
En términos de evaluación psicométrica, el razonamiento inductivo, el razonamiento abstracto y el razonamiento esquemático son tres pruebas que a menudo se superponen con la evaluación. Los proveedores utilizan nombres diferentes para cada uno, lo que hace que las cosas sean un poco más confusas.
Estas pruebas ciertamente varían entre los empleadores y la etapa en el proceso de reclutamiento también será diferente.
Algunas empresas los utilizan como un ejercicio de selección previa a la entrevista para limitar un conjunto de candidatos, mientras que otras organizaciones pueden usarlos hacia el final del proceso de reclutamiento o como parte de los días de evaluación.
Contenido de la prueba de Razonamiento Inductivo
La mayoría de las pruebas de razonamiento inductivo presentan una serie de secuencia de palabras, ilustraciones o formas y te piden que decidas cuál es la siguiente.
Esto requiere prestar atención a los detalles, a la resolución de problemas y perseverancia para alcanzar la respuesta requerida, todo lo cual se evalúa en condiciones de tiempo, lo que agrega aún más presión.
La prueba en sí misma requerirá que compares varios elementos incluyendo colores y formas, o que los clasifiques basándote en cantidad o tamaño.
Como un ejemplo, se te proporcionará un juego de seis cuadros conteniendo una cantidad de formas y luego se te pedirá que elabores una secuencia lógica para cada cuadro.
Para obtener la respuesta correcta, deberías identificar un patrón tal como similitudes, diferencias o una combinación de ambos.
Estas tareas pueden parecer extremadamente complejas, por ello es importante realizar tantas prácticas de pruebas similares como sea posible antes de la prueba real y también tanta práctica como puedas antes de la entrevista o del día de evaluación.
Asegúrate de llegar a tiempo y haber dormido bien la noche anterior, de lo contrario, es posible que te falte la concentración y que parezca que no entiendes lo que te piden que hagas.
Una aproximación a las Pruebas de Razonamiento Inductivo
Cuando comienzas la prueba, lee la pregunta detenidamente y trata de observar solamente a un elemento de la forma a la vez.
Es muy fácil sentirse abrumado por el contenido de una evaluación de razonamiento inductivo, por lo que la mejor manera de abordarla es intentar y decidir el patrón, considerando específicamente el tamaño, la orientación y la ubicación de la forma interior.
Los patrones están diseñados para ser complicados en tomarte el tiempo y utilizar tu lógica para resolver el problema.
Si estás teniendo una particular dificultad en identificar un patrón, trata de observarlo desde el final en lugar del principio.
Esto puede resaltar de manera efectiva algo que quizás hayas omitido usando el método tradicional de revisar las formas.
Toma conciencia de la hora pero no mires el reloj, y no te asustes en la medida de lo posible; esto sólo hará las cosas más difíciles.
Las pruebas de razonamiento inductivo son creadas para ser completadas bajo presión, por lo que la práctica de completar las pruebas en condiciones de tiempo puede ayudar de manera significativa.
Practicar es una de las mejores maneras de prepararte mentalmente para cualquier prueba psicométrica y el razonamiento inductivo no es diferente a ello.
Nada te preparará mejor para la evaluación que realizar una cantidad de exámenes de práctica, muchos de las cuales puedes encontrar en línea gratuitamente.
Cuando te familiarizas con el formato de la prueba y te acostumbras a responder preguntas rápidamente y trabajar bajo presión, es mucho más probable que tengas éxito que si no realizas ningún trabajo de preparación o práctica anteriormente.

¿Qué son las pruebas psicométricas?
Las pruebas psicométricas (también conocidas como Pruebas de Aptitud ) son ahora una parte común de los procesos de selección y evanotluación, por lo tanto un requisito necesario para solicitar trabajo.
Si tú aún no has completado una, es muy probable que lo necesites en algún momento en el futuro. Con esto en mente, hemos preparado para ti la Guía actual para las pruebas psicométricas para explicar qué son, cómo se utilizan y cómo completarlas con éxito.
Antes de comenzar con el artículo a continuación, ten en cuenta que tenemos tres pruebas psicométricas de práctica disponibles para que las pruebes.

Las pruebas de razonamiento verbal están diseñadas para examinar tu nivel de comprensión del pasaje de un texto.
Estas pruebas son un ejemplo de una prueba de habilidad (a veces conocida como pruebas de aptitud) y son utilizadas por los empleadores en combinación con pruebas de razonamiento numérico y pruebas de razonamiento lógico .
Las pruebas de razonamiento verbal tienen como objetivo identificar tu capacidad máxima de comprensión, o en otras palabras, el párrafo de un texto más desafiante que tú podrás entender.

Numerische Tests können knifflig sein. Übung und die richtige Vorbereitung sind der Schlüssel zum Erfolg.
Aber das ist leichter gesagt als getan…
Wenn Du zum ersten Mal über diese Tests nachliest oder wenn Du nach Wegen suchst um deine Fähigkeiten zu verbessern, besser abzuschneiden und mehr Interviews und Jobangebote zu bekommen, ist dieser Artikel ideal für Dich.
Hier erfährst Du von Strategien die Du sofort praktisch einsetzen kannst.
Falls du einen Übungstest machen möchtest kannst du hier jederzeit einen der kostenlosen numerischen Tests ausprobieren. Dieser Test beinhaltet zehn Fragen (mit Antworten und ausführlichen Erklärungen).
Wie kann man sein Ergebnis so schnell und effektiv wie möglich verbessern , selbst bis in der 99% Bereich ?
Lies den Artikel am besten langsam durch, folge unseren Tipps und unseren Empfehlungen – so hast du die größten Erfolgschancen. Wenn du damit fertig bist kannst du einen unserer Übungstests kostenlos ausprobieren.
Bonus: Kostenloser uneingeschränkter Zugang zum Eignungs-Übungstest (für 30 Minuten) auf unserer Partner-Webseite JobTestPrep.

Microsoft is one of the world's most commonly used computer software.
If you're working in an office, you are almost certain to use applications such as Microsoft Word, Excel, Outlook or PowerPoint.
Therefore, it makes perfect sense that employers want to know that you are proficient in these applications as part of their hiring process.
If your job requires data analysis or compiling data streams, you will likely need to be adept at using Microsoft Excel.
In these circumstances, you may be asked to participate in an Excel assessment test so a hiring manager can confirm that you know how to make the most out of the program.
With this in mind, we will look at what you could expect from a Microsoft Excel test.
Then, we'll take you through a series of Microsoft Excel practice test questions, and we'll give you everything you need to know so you can prepare for the Excel assessment.

What Is a Cubiks Test?
The Cubiks tests were developed by the Cubiks assessment consultancy, which was founded in 2000.
In 2019, Cubiks was acquired by PSI Talent Management UK, an award-winning provider of psychometric assessments.
In 2022, PSI Services became Talogy.
Cubiks tests are available in more than 50 countries around the world. Many highly-regarded employers in the UK use Cubiks tests, including:
- The UK Civil Service
- National Audit Office
- National Health Service
Cubiks tests are designed to help employers and organisations with recruitment, employee development and talent management. They are well known for their intuitive interface and easy-to-interpret structure.
When applying for job roles, you may be asked to complete one or more types of Cubiks test as part of the screening and selection process.
If you are already working, your employer might ask you to sit a Cubiks test assessment as part of the career development programme or talent management process.
This article offers an overview of what to expect from the Cubiks test. It also includes some Cubiks online test example questions and tips on how to succeed when taking the Cubiks test.

The Korn Ferry assessment is a tool used in the recruiting process for leadership positions.
The tests assess candidates across a range of skills, including:
- Logic reasoning ability
- Numerical reasoning ability
- Verbal reasoning ability
- Personality traits
As a result, the Korn Ferry assessment allows businesses to secure the best talent and identify individuals to be promoted to management positions.
The Korn Ferry assessment is an evaluation tool used by companies across the globe to ensure they employ the best talent.
The assessment comprises a series of smaller tests focusing on:
- Reading comprehension
- Personality
- Leadership assessments
As well as a tool utilized during the interview process, the Korn Ferry assessments are often used when looking to promote team members into management positions.
This article will discuss the Korn Ferry assessment, explaining exactly what it involves and giving tips to enable the best chance of success.
If you are applying for an executive-level or management role, you might be expected to take an aptitude test as part of the recruitment process.
The Swift Executive Aptitude Test is a short assessment designed to measure specific aptitudes that are necessary for success in a leadership position.
In this article, you will discover more about the test, the structure of the assessment, and example questions.
You will also learn what you will need to bear in mind to be successful in the test, including tips about preparation and a breakdown of what to expect from the scoring.
This numerical reasoning practice test has 10 questions.
The test has a mixture of numerical questions that vary in difficulty.
Answers and full explanations are provided after you have completed a question. You should aim to complete the test within 10 minutes.
Make sure you read and fully understand each question before answering. Work quickly, but don't rush. You cannot afford to make mistakes on a real test.

What is a Verbal Reasoning Test?
A Verbal Reasoning Test is a type of cognitive assessment designed to evaluate an individual's ability to comprehend and analyze written information, make logical deductions and draw conclusions based on the presented text.
These tests are often used in various educational and employment settings to assess a person's verbal reasoning skills, which are essential for tasks that involve understanding and interpreting written or spoken language.

This inductive reasoning practice test has nine questions (and includes answers and full explanations).
This abstract reasoning practice test has 10 questions (and answers with full explanations).
For each question, choose which of the figures in the bottom line – A, B, C, D or E – completes the series in the top line.
The level of difficulty varies significantly, from easy to extremely hard. Items having the solution based on one rule are easy, while those with the solution based on four rules are extremely hard; the others are in between - medium and hard, respectively.
Your goal is to understand the logic of each question (the rules behind it). Do not despair if you can’t find the solution immediately, especially for the very hard questions!

What is a Cognitive Test?
A cognitive test is an assessment tool designed to measure an individual's cognitive abilities, which are the mental processes involved in acquiring, processing, storing and using information.
Cognitive assessments are used to evaluate various aspects of cognitive functioning, including memory, attention, problem-solving, reasoning, language comprehension, and more.
Cognitive function tests are commonly employed in several contexts, including education, clinical psychology, neuropsychology and employment assessment.
This cognitive ability practice test has been designed to help you prepare for the real thing.

What is a Deductive Reasoning Test?
A deductive reasoning test is a type of cognitive assessment that measures a person's ability to draw logical conclusions based on given information or premises.
Deductive reasoning is a form of logical thinking that involves moving from general statements or principles to specific conclusions. In other words, it is the process of applying a general rule or premise to a specific situation to determine a particular outcome.
In a deductive reasoning test, you are typically presented with a set of premises or statements that establish certain conditions or facts. You are then asked to use these premises to determine a valid conclusion.
The conclusions you reach must follow logically from the given premises, and the test assesses your ability to make accurate deductions based on the provided information.
Deductive reasoning tests are often used in educational settings, as part of standardized testing, and in various employment assessments.
They are designed to evaluate an individual's problem-solving skills, critical thinking ability, and their capacity to analyze information and reach logical conclusions.
These tests can take various formats, including multiple-choice questions, true or false questions or scenario-based questions where you need to determine the correct outcome based on the information provided.
Success in deductive reasoning tests often requires a strong understanding of logical principles and the ability to apply them effectively to specific situations.

What is Logical Reasoning?
Logical reasoning, often referred to as logical thinking or critical thinking, is a cognitive process that involves the ability to analyze information, identify patterns, make sound judgments and draw valid conclusions.
It is a fundamental skill that plays a crucial role in problem-solving, decision-making and rational thinking.
Logical reasoning involves breaking down complex information or situations into smaller, more manageable parts. It requires examining details and understanding the relationships between various elements.
What are the Types of Logical Reasoning Tests?
Logical reasoning tests come in various forms and are used by employers, educational institutions, and standardized testing organizations to assess an individual's ability to think critically and solve problems.
Here are some common types of logical reasoning tests:
Reading Comprehension: These tests assess your ability to understand and analyze written information, make inferences, and draw conclusions from passages of text.
Critical Thinking Tests: These tests evaluate your ability to analyze and evaluate arguments, identify assumptions, and assess the validity of statements or claims.
Analogical Reasoning Tests: Analogical reasoning involves recognizing relationships between words or concepts and applying these relationships to solve problems. For example, you might be asked to complete an analogy like "A is to B as C is to what?"
Numerical Computation: These tests assess your basic arithmetic skills, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Numerical Sequences: These tests require you to identify patterns and relationships within number sequences and use them to predict the next number.
Data Interpretation: In these tests, you are presented with data in the form of tables, graphs, or charts, and you must interpret the information to answer questions.
- Abstract Reasoning Tests
Non-Verbal Reasoning: Abstract reasoning tests evaluate your ability to recognize patterns, shapes, and relationships among visual elements. They often involve series of diagrams or figures, and you must identify the logical rules governing them.
Inductive Reasoning: Inductive reasoning tests present you with a series of visual or abstract patterns and require you to identify the underlying rules and predict the next pattern in the sequence.
- Spatial Reasoning Tests
Spatial Awareness: These tests measure your ability to visualize and manipulate objects in three-dimensional space. You may be asked to complete puzzles, identify rotated or mirrored images, or solve spatial problems. Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests:
Diagram Interpretation: Diagrammatic reasoning tests use diagrams or symbols to present problems. You must analyze the diagrams to draw conclusions or identify patterns.
Syllogism and Logic Tests
Syllogisms: Syllogism tests present logical statements and ask you to determine whether a conclusion is valid based on the given premises.
Symbolic Logic: These tests involve working with formal logic symbols to evaluate logical arguments.
Inference and Deduction Tests
Inference Tests: Inference tests assess your ability to make logical deductions and draw conclusions based on a set of statements or information.
Deductive Reasoning: Deductive reasoning tests require you to apply deductive logic principles to solve problems and make decisions.
- Mechanical Reasoning Tests
Mechanical Understanding: These tests evaluate your knowledge of mechanical and physical concepts, such as gears, pulleys, levers, and basic physics principles.
- Cognitive Ability Tests
Cognitive Ability Tests: These assessments often include a combination of various reasoning types and are designed to measure overall cognitive abilities.
What are the Common Logic Tests Employers Use?
Employers often use a variety of logic tests to assess the cognitive abilities and problem-solving skills of job applicants. The specific logic tests used can vary depending on the nature of the job and the industry.
Here are some common logic tests that employers may use during the hiring process:
- Logical Deduction and Syllogism Tests
- Data Interpretation Tests
- Diagrammatic Reasoning Tests
This is a 10 question practice logical reasoning test .
After you have given an answer to a question, the correct answer (and a full explanation of that answer) will be given.
What are the Topics Covered by a Logical Reasoning Test?
Syllogism, statements and assumptions, logical deduction, cause and effect, statements and conclusions, logical problems.

Set of 10 questions, along with correct answers and explanations for each.
Topics Covered:
General concepts, levers, springs, pulleys, area and volume, gears, inclined plane, basic electrical circuitry.
Difficulty Level:
Take a free practice mechanical reasoning test.

Situational awareness, evaluation of alternatives.
Take a Free Practice Situational Judgement Test

Block counting, 3D rotation, 2D rotation, reflection, broken shapes, transforming 2D to 3D, isometric view, difference in 2D versus 3D viewing.

What is the Watson Glaser Critical Thinking Test?
The Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Test, often referred to as the Watson-Glaser test, is a widely used assessment tool designed to evaluate an individual's critical thinking skills.
It is commonly administered as part of the hiring process for various professional and managerial positions, particularly in fields where critical thinking and problem-solving abilities are highly valued, such as law, finance and management.
This is a nine question diagrammatic reasoning practice test.
We recommend a time limit of nine minutes for this test.
After you have given your answer to a question, you will be shown the correct answer and given a full explanation.

What is the Critical Thinking Test?
The Critical Thinking Test is a comprehensive evaluation designed to assess individuals' cognitive capacities and analytical prowess.
This formal examination, often referred to as the critical thinking assessment, is a benchmark for those aiming to demonstrate their proficiency in discernment and problem-solving.
In addition, this evaluative tool meticulously gauges a range of skills, including logical reasoning, analytical thinking, and the ability to evaluate and synthesize information.
This article will embark on an exploration of the Critical Thinking Test, elucidating its intricacies and elucidating its paramount importance. We will dissect the essential skills it measures and clarify its significance in gauging one's intellectual aptitude.
We will examine examples of critical thinking questions, illuminating the challenging scenarios that candidates encounter prompting them to navigate the complexities of thought with finesse.
Critical Thinking Practice Test
Before going ahead to take the critical thinking test, let's delve into the realm of preparation. This segment serves as a crucible for honing the skills assessed in the actual examination, offering candidates a chance to refine their analytical blades before facing the real challenge. Here are some skills that will help you with the critical thinking assessment: Logical Reasoning: The practice test meticulously evaluates your ability to deduce conclusions from given information, assess the validity of arguments, and recognize patterns in logic. Analytical Thinking: Prepare to dissect complex scenarios, identify key components, and synthesize information to draw insightful conclusions—a fundamental aspect of the critical thinking assessment. Problem-Solving Proficiency: Navigate through intricate problems that mirror real-world challenges, honing your capacity to approach issues systematically and derive effective solutions. What to Expect: The Critical Thinking Practice Test is crafted to mirror the format and complexity of the actual examination. Expect a series of scenarios, each accompanied by a set of questions that demand thoughtful analysis and logical deduction. These scenarios span diverse fields, from business and science to everyday scenarios, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of your critical thinking skills. Examples of Critical Thinking Questions Scenario: In a business context, analyze the potential impacts of a proposed strategy on both short-term profitability and long-term sustainability. Question: What factors would you consider in determining the viability of the proposed strategy, and how might it affect the company's overall success? Scenario: Evaluate conflicting scientific studies on a pressing environmental issue.
Question: Identify the key methodologies and data points in each study. How would you reconcile the disparities to form an informed, unbiased conclusion?
Why Practice Matters
Engaging in the Critical Thinking Practice Test familiarizes you with the test format and cultivates a mindset geared towards agile and astute reasoning. This preparatory phase allows you to refine your cognitive toolkit, ensuring you approach the assessment with confidence and finesse.
We'll navigate through specific examples as we proceed, offering insights into effective strategies for tackling critical thinking questions. Prepare to embark on a journey of intellectual sharpening, where each practice question refines your analytical prowess for the challenges ahead.

This is a three question practice in-tray exercise.
If you get a question wrong, make sure you find out why and learn how to answer this type of question in the future.
Take a Free Practice In-Tray Exercise

What Is the PwC Assessment Test?
When you apply for a coveted role at PwC, you will be asked to undertake a PwC assessment test as part of the recruitment process.
The PwC test are used to evaluate candidates on measurable skills, abilities, aptitudes and personality traits that are needed for success in the type (and level) of the role that you have applied for.
PwC is one of the Big Four accounting firms globally, and from their headquarters in London, England, they have offices in 157 countries, a presence in 742 locations, and they currently employ nearly 300,000 staff.
With roles available in various departments, from consulting to legal, operations to audit, and tax to technology, competition for advertised jobs is fierce, and the PwC assessments are recognised as being particularly challenging to help narrow down the candidate pool to those applicants who really have what it takes to be successful.
In fact, less than 50% of candidates will advance past the screening tests as the benchmark for a passing mark is very high.

'AON assessments' are the new name for the cut-e tests, and they are often used as pre-employment evaluations for different skills, aptitudes, competencies and personality traits for various roles across different industries.
The AON assessments are characterized by being very short online assessment tests, and in many cases, candidates will be required to take more than one as part of a recruitment process.
With so much content to cover in all the different types of tests, it can be difficult to know what to expect from the AON assessments, which is where this guide will help.
Below you will learn more about why AON assessments are used and which companies use them as part of their hiring process.
We will discuss some of the features that the assessments have in common, as well as the most popular tests that are used by recruiters.
There will be some example questions with answers to get you familiar with the type of content you will be facing in certain tests and some helpful information regarding the way the AON assessments are scored and how you can give yourself the best chance to demonstrate that you have what it takes to be successful.
What Is the AON Assessment Test?
AON is well-known as a global financial services firm, and they acquired the cut-e testing battery so that they can provide top-of-the-range candidate evaluation and personnel development tools based on a scientific framework and testing methodology.

The CogAT Grade 4 test is used to understand a student’s thinking and reasoning abilities. It is not a test of learned knowledge; rather, it is a diagnosis of how they learn.
The 4th Grade CogAT test measures reasoning ability in three key areas: verbal, non-verbal and quantitative.
The assessment is often used to identify students for gifted and talented education programs.
If your child has been selected to sit the CogAT test in 4th grade, it can be confusing to know what to do to help.
This article will help you to answer these questions:
- What is the CogAT test ?
- What skills is the test assessing?
- What is the format of the test?
- How can I help my child prepare?
- What skills can we practice?
- What is the scoring system?

When applying for a job application, you may find that, along with providing your CV and attending an interview, you will be required to complete an IKM assessment .
This assessment will serve as a supplement to your overall application. So, you must understand what it entails and how it contributes to your application.
This article will explain the specifics of the IKM assessment, why it is important and how you can prepare for it.
What Is IKM?
The International Knowledge Measurement Service (IKM) offers organizations various assessments for employees and candidates among various career disciplines.
Among other things, this assessment ensures that employees hold the necessary requirements to go through the organization’s recruitment process.
Employee candidates will take the IKM assessment online remotely (self-supervised) or with client-side supervision from the organization.
The IKM assessment uses adaptive testing, meaning the difficulty of questions is dynamically selected based on the employee candidate’s previous answers .
This ensures that the assessment questions are neither too difficult nor too easy, greatly reducing the testing time.

The CAT4 Level D is a cognitive ability test used by a number of UK secondary schools. Typically taken by pupils in Year 7, the CAT4 Level D tests a child’s verbal, non-verbal, quantitative and spatial reasoning skills to give an accurate picture of their learning potential.

The Delta Assessment Test is a group of online tests that forms part of the Delta Airlines hiring process.
If you are applying for job roles with Delta, you may be asked to complete one or more of the Delta Assessment Tests.
Your test results will help the hiring manager to decide whether you are suitable for the job role you have applied for.
The tests you are asked to take will vary according to the job role.

The Deloitte immersive online assessment is a psychometric aptitude-style test. It is used to identify a candidate’s strengths and weaknesses.
Questions vary but are likely to include situational judgment style questions that link to the roles at Deloitte.
Candidates are also tested on their numerical reasoning and presented with personality questions.

Competition is tough for jobs on the Crossover recruitment platform.
There are thousands of applicants for each role, and only the top 1% are offered a contract .
After a successful initial application, the first step is taking the Crossover Cognitive Aptitude Test (CCAT).
To help you prepare, this article covers the following:
- How Crossover works
- The recruitment process
- What to expect in the CCAT
- The scoring system
- Tips to help you prepare

The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the USA.
The agency investigates serious offenses such as terrorism, public corruption, cyber-attacks, and violent and organized crime.
The FBI's mission is to protect the American people and uphold the American Constitution.
The FBI has over 37,000 employees across hundreds of locations in the US.
To work for the FBI, you must fulfill specific criteria which include:
- Be a US citizen
- Be able to obtain an FBI Top Secret clearance
- Pass the FBI polygraph examination
- Pass the FBI Phase 1 test
- Adhere to the FBI drug policy
Roles available at the FBI include computer scientists, nurses, engineers, technicians, contract specialists, and of course, police officers.
It is important to note that the recruitment process can take over one year, so you must be willing to wait several months for the chance of your dream role.
In this FBI Phase 1 test prep guide, we will delve into the role of FBI special agents – upholders of the law that seek out cybercrime and infiltrate organized attacks such as terrorism.
When applying to be a special agent, you are required to take the FBI Phase 1 test .
What Is the FBI Phase 1 Test?
The FBI Phase 1 test is an assessment that evaluates your personality and suitability for a role as a Special Agent at the FBI.
The test is conducted online and is split into five parts.
As the second stage of the process, the FBI Phase 1 test is done after the successful completion of a written application.
The test is designed to assess several skills and qualities that are required for a role as an FBI special agent.
These include critical thinking, logical reasoning and personality. The test will also assess your background experiences.
Your answers are then compared to the benchmark of what is suitable for an FBI agent.
The five sections of the FBI Phase 1 test are:
- Logical reasoning
- Figural reasoning
- Personality Test
- Preferences and interests
- Situational responses
The assessment takes three hours to complete.
When applying for roles at the FBI, long waiting times are typical. The full special agent recruitment process can take over 20 months to complete.
If this is your dream job, it is certainly worth the wait as it is one of the most attractive career paths within any government agency.
To reflect this, the recruitment process is challenging and designed to reduce the number of candidates who could move on to the next stage.
This ensures that only the very best move through the application phases. In fact, only 30% of candidates can pass the FBI Phase 1 test.
You may have taken a personality test before, but the FBI Phase 1 test questions are framed and marked in a different way to other assessments.
Therefore, you should ensure you use FBI Phase 1 test practice questions and prepare in advance of the test.
It can be hard to plan for, but this is essential to get into the top 30% of successful candidates.
If you pass the FBI Phase 1 test, you will undergo background checks and receive an invitation to a regional meet-and-greet interview.

The main purpose of the CogAT Test grade 3 is to find out if a third grader is showing signs of being very smart.
Most of the questions on the test are about verbal, numerical and non-verbal reasoning. It's meant to show how a child might compare to other kids his or her own age. The CogAT grade 3 test can also be used to make individualized learning plans for kids.
The CogAT (Cognitive Abilities Test) is a standardized test used to measure children's cognitive abilities in the 3rd grade – age 9.
This test assesses a range of cognitive abilities, including verbal, quantitative and nonverbal reasoning. The CogAT is often used to identify gifted children and help educators develop appropriate educational plans.
This article will give insights and tips into how your child could pass the CogAT Test for 3rd grade students.

The MAP Test 2nd grade is a computerized test taken by children in the 2nd grade. It is designed to evaluate what the children already know and what they are ready to learn.
The test includes three sections:
Schools may not administer all three sections and may instead focus on one or two sections to measure pupils’ progress in those subjects.

The NEO Personality Inventory is a psychometric tool used to evaluate personality traits.
It is acknowledged globally and is used by recruiters and employers before hiring and, more broadly, to evaluate career potential.
The NEO Personality Inventory test is heavily associated with the 'Five-Factor Model' (which you may also know as the 'Big Five Personality Test') to identify personality traits.
It is widely believed that each person's personality can be broken down into five main categories. The NEO PI personality test looks at each of these five categories separately to create an understanding of who you are.
In this article, we'll look at the NEO PI test, why employers use it, and what you could expect if invited to participate in a NEO Personality Inventory test.

The Air Traffic Controller (ATC) Test, also known as the Air Traffic Skills Assessment (ATSA) is an exam used as part of the air traffic controller hiring process. It is a challenging assessment consisting of seven subtests designed to evaluate an applicant's aptitude for the role.
Becoming an air traffic controller is a challenging and rewarding career that requires extensive training. The Air Traffic Controller Test (previously known as the Air Traffic Selection and Training (AT-SAT) exam) is an important part of the selection process.
The Air Traffic Skills Assessment (ATSA) measures a candidate's ability to handle the demands of the job.
In this article, you’ll find example questions, a guide and tips for preparing for the ATSA exam.
This article relates specifically to the ATC test used in the US. Candidates in other countries may be expected to take a different version of the test.

What is the CliftonStrengths test? This online assessment analyzes your personality and strengths for personal and professional development. You can purchase the basic test from Gallup for $19.99 and get a basic understanding of your top five personality themes. Or take the comprehensive version for $59.99 and receive a report that ranks all 34 themes and highlights your areas of excellence as well as your blind spots.
When applying for a job, you may find that the recruitment process consists of many different steps. There is the initial application form to start and usually an interview to finish. In the middle, there may be an assessment – an aptitude, intelligence or personality test.
The CliftonStrengths test is one assessment used by employers during the onboarding process. It was previously known as the CliftonStrengthsFinder.
In this guide, you will learn about the CliftonStrengths personality test and how it is used in recruitment.

The police psychological exam is a crucial part of the hiring process for law enforcement agencies. It is a personality test that confirms how suitable an applicant is for working in the police. The police psych test is used by most law enforcement agencies across the United States, although key details may differ from state to state.
What Is the Police Psychological Exam?
The police psychological exam is a series of tests and assessments administered to individuals who are seeking to become police officers.
The purpose of the exam is to evaluate a candidate's psychological fitness for the job and identify any potential psychological issues that may interfere with the candidate's ability to perform police work.

In this comprehensive guide , you’ll discover everything you need to know about the Capital One assessment and interview process.
These are designed to help the company select the best candidates for its team. To increase your chance of getting hired, it's important to be prepared.
Find out what to expect, how to prepare and the skills and qualities Capital One hiring managers are looking for in a candidate.
What Is the Capital One Assessment Test?
Capital One is an established financial services company with a focus on technology and innovation.
To become an employee, or ‘associate’, at Capital One you'll need to pass a series of online assessments and interviews .
The Capital One hiring process is as follows:

CogAT stands for Cognitive Abilities Test. These tests are normally administered by a classroom teacher or instructor, although some schools employ a specialist or test proctor to administer the test.
Many parents are interested in learning more about helping their children to succeed academically.
Achieving a high CogAT score could mean your child is eligible to join gifted or talented programs designed to enhance their development and learning.
In other schools, it is used as a tool to identify a pupil’s individual strengths or predict their future academic performance.
The CogAT test for 2nd grade is a cognitive ability test aimed at children around the age of eight years old.
It is often used as a pre-admission exam by gifted and talented schools and programs. It is designed to evaluate pupils’ cognitive abilities, including basic linguistic and math skills.
The test is made up of three sections or batteries:
- Non-verbal battery
- Verbal battery
- Quantitative battery
On the CogAT test 2nd grade, candidates are required to read the test questions instead of listening to the questions being read by the test proctor.
If you are looking for ideas on how to prepare your child for the CogAT test 2nd grade, read on to learn more.
What Is CogAT Test 2nd Grade?
The CogAT (Cognitive Abilities Test) was developed by Riverside Publishing, which is part of Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
It is designed to assess problem-solving and reasoning skills in the following areas:
- Quantitative
Research has shown that high levels of ability in these three areas is linked to academic success.
If your child is considered potentially talented or gifted, they may be asked to sit a CogAT as part of the program entrance process.
Different CogAT tests are available for different age groups, from Kindergarten (K) up to grade 12.
In this article, you can find more information on the CogAT test 2nd grade. The CogAT test is used by schools across the US to help them identify exceptionally gifted pupils.
Each of the test levels corresponds to the age of the pupil sitting the test. For example, if your child is in grade 6 (aged 12), they will be sitting the Level 12 version of the test. Occasionally, schools may choose to administer a higher level CogAT to talented or gifted pupils; however, this is unusual.
Second grade pupils being considered for gifted programs will usually sit the CogAT Level 8 test. This test is made up of 154 questions and takes 122 minutes to complete.

Many schools use the CogAT Test 6th Grade to assess the non-verbal, verbal and quantitative abilities of sixth-grade students.
The Level 12 CogAT test is a useful tool for checking a student’s individual academic strengths and weaknesses. It can also be used as a screening assessment for entry into the gifted and talented program.
What Is the CogAT Test 6th Grade?
'CogAT' is an acronym for Cognitive Aptitude Test .
CogAT tests are usually administered at school by a teacher or instructor, although some schools employ test proctors and specialists to administer the tests.
This guide is designed to support you and your child through the CogAT Test 6th Grade. You can use it to find out what to expect from the test and tips on how to prepare for it.
We have also included information on the purpose of the test and how to interpret your child’s results.

The Procter and Gamble Assessment Test describes a series of pre-employment screening tests used by Procter and Gamble (P&G).
If you have applied for a job at P&G, you will be expected to sit these tests as part of the hiring process.
Each of the different tests is designed to assess a specific aptitude that is required for a job role at P&G.
In this article, you can learn more about the different tests used by Procter and Gamble. We have also provided tips on how to prepare for the assessments.

This guide includes useful tips and Renaissance Star testing sample questions to help students prepare for the test and feel confident on test day.
You can find detailed information on interpreting and understanding your Renaissance Star Test scores in our dedicated article .

What Is the 6th Grade MAP Test?
The MAP Growth test system was created by educators from Oregon and Washington who established the Northwest Evaluation Association (NWEA) back in 1973.
Their goal was to create an assessment that could accurately measure and track academic progress in children to ensure they graduated high school with all the essential skills and knowledge they required.
In 2000, the first MAP Growth Test was published.
The test is administered in all grades and is based on a set of learning principles known as the Common Core Principles .

The CCAT test grade 3 is a standardized assessment administered to grade 3 students in Canada.
It measures verbal, quantitative and non-verbal reasoning skills and is used to identify a student's learning potential, typically for admission to gifted educational programs.
The CCAT test grade 3 is an assessment commonly used by schools in Canada.
If you’re the parent or guardian of a child preparing for the test, this CCAT grade 3 guide will tell you everything you need to know.
What Is the CCAT Test Grade 3?
The CCAT test (Canadian Cognitive Abilities Test) is a standardized assessment administered to students in grade levels K-12 in the Canadian educational system.
Rather than a measure of academic achievement, the test assesses a child's ability to learn, reason, and problem-solve.
The Independent School Entrance Examination (ISEE) test is used by many independent and magnet schools in the US and overseas as an admission test for children across the entire school age range, but more commonly from year five upwards.
It assesses a child’s academic levels of reasoning across math and literacy in comparison to children of the same age, the norm for that school grade and other applicants to the school.
Created and administered by the Educational Records Bureau (ERB), the ISEE test is available to be taken online or in a pen and paper format.
What Are the ISEE Levels?
There are four levels of the ISEE test.
- ISEE primary for entry into years two to four
- ISEE lower level for entry into years five to six
- ISEE middle level for entry into years seven to eight
- ISEE upper level for entry into years nine to 12
Each level of the ISEE test is created to be relevant to a specific school age group, increasing in complexity with each year and level.

An employer’s recruitment process can include a wide range of assessments and interviews for the candidate to take that indicate to the employer how an individual might fare in the job.
One common way to measure job performance though is by getting candidates to take the PI Cognitive Assessment, which measures mental ability and critical thinking skills.
This article will look in detail at the assessment, its format, who uses it, example questions and PI Cognitive Assessment tips on how to be successful when taking it.

The Raven’s Progressive Matrices is a test that is often used as part of the recruitment process for high-level management and analytical roles.
In this article, you will learn more about the test, its history and background, as well as the different types of tests that are available and what you can expect if you are going to be taking the test.
You will also find some example questions that you can expect to see in each type of test and get helpful pointers that you can use to prepare and do well in the assessment.

If you are applying for a role with the United States Postal Service (USPS) , you will usually be asked to complete at least one of four 477 Virtual Entry Assessments as part of the recruitment process.
These exams are used to evaluate various skills, aptitudes, personality traits and work preferences, which can show whether you have what it takes to be successful in the role in the future.
The USPS 477 Exam is sometimes referred to as the CS VEA, which relates to customer service.

An iReady level score of 3.00 or over means the student is working at or above the level required to meet the standard for their grade.
The level score is calculated in line with expectations when the test was administered, not in comparison to the expected score by the end of the school year.
What Are the iReady Diagnostic Scores?
The iReady diagnostic test is administered to US school children in grades K to eight.
The purpose of this school assessment test is to help parents and teachers check a student’s academic process at the beginning, middle and end of each school year.
It is a computer-adaptive test, which means the questions are adjusted to become more difficult if a series of correct answers is given.
As a result, the test is designed to challenge the skill level of the student sitting the test, as well as assess their strengths and opportunities for growth.
If a student answers a few questions in a row incorrectly, the questions that follow will be easier.
Many people find i-Ready Diagnostic scores difficult to interpret.
As a child progresses through each academic year and moves up the year groups, their expected score will change.
The average score increases year on year, too.
In this article, you can learn more about the different types of iReady diagnostic scores, how these scores are displayed, and how to interpret them to better understand a student’s iReady test performance.

There are two types of HESI Exam:
- The Admissions (A2) test
- The Exit exam
The minimum passing score for the Admissions test is usually between 75 and 80 for each section, although this varies between schools.
The composite score range for the Admissions (A2) test is 750 to 900, with 900 being the maximum possible score.
The HESI Exit Exam score ranges between 0 to 1,500. 850 is considered to be an acceptable score, although HESI recommends a minimum score of 900.
If you want to sit your NCLEX licensing exam, you will need to achieve a score of at least 850 on the HESI Exit Exam.
HESI is an acronym for Health Education Systems Incorporated .
As a company, HESI administers exams and provides study material to help prepare students for the NCLEX professional licensure exam.
If you want to work as a nurse in the US, many nursing and healthcare programs use HESI tests to screen prospective students and determine suitability and readiness for specific study routes.
In this article, you can learn more about the HESI score ranges and passing scores required for each of these tests and what impact your HESI results may have on acceptance into your preferred nursing program.

The CogAT Kindergarten Test is an assessment designed to measure a child's abilities in various cognitive areas.
It plays a critical role in identifying a child's strengths and weaknesses and determining their readiness for advanced academic programs.
In this comprehensive study guide for 2024, you will explore the purpose, format, and structure of the CogAT Kindergarten Test.
Additionally, you will get valuable insights on how to prepare your child for the test, sample questions to familiarize yourself with the test content, strategies for success and answers to frequently asked questions.
Understanding the CogAT Kindergarten Test: Purpose, Format, and Structure
The purpose of the CogAT Kindergarten Test is to assess a child's cognitive abilities in areas such as verbal, quantitative, and nonverbal reasoning.
By evaluating these different components, the test provides educators and parents with valuable information about a child's potential and can help guide educational decisions.

The ATI TEAS Test , also known as the Test of Essential Academic Skills, is an important exam for students looking to pursue a career in the healthcare field. The most recent version is the ATI TEAS 7.
This comprehensive exam assesses a student's knowledge in various areas, including reading, math, science and English language usage.
If you're planning to take the ATI TEAS Test in 2024, it's essential to understand what the exam entails and how to best prepare for it.
In this article, we'll cover everything you need to know about the 2024 ATI TEAS Test.

The ATI TEAS 7 Math Test is a crucial component of the ATI TEAS exam, which is widely used by nursing and allied health schools to assess prospective students' academic readiness for their programs.
In this comprehensive guide, you will delve into various aspects of the TEAS Maths 7 Test, including what it entails, when it is taken, ATI TEAS math practice test questions to help you prepare, and tips for success.
So, let's dive right in!

The 1st Grade CogAT test is an important assessment that measures a child's cognitive abilities. It is designed to identify a child's strengths and weaknesses in areas such as verbal, quantitative, and non-verbal reasoning.
This article will provide you with a comprehensive guide on understanding and preparing for the 1st Grade CogAT Test.

The CogAT (Cognitive Abilities Test) for Kindergarten is an assessment designed to evaluate the cognitive development and problem-solving abilities of young children.
Typically, this version of the test is tailored to children around five to six years old who are attending kindergarten.
The test is typically used for educational placement, identifying gifted and talented students, and understanding a child's cognitive strengths and weaknesses. It can be administered individually or in groups, and is often used by schools to tailor instruction to better meet the educational needs of their students.
Understanding the results of the CogAT can help educators and parents support the child's learning and development more effectively, by identifying areas where the child excels or may need additional focus.
In this article, you’ll find practice CoGAT Kindergarten practice test questions and tips to help your child prepare for the big day.

The Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT) 5th Grade Level is a crucial assessment tool for students between 10 and 11 years old.
Designed to measure verbal, nonverbal, and quantitative abilities, this standardized test plays a pivotal role in identifying students for gifted programs.
In this article, you’ll learn what the CogAT 5th grade test is, which subjects are tested, along with example questions and how best to prepare.

What Is the CogAT 5 Grade Test?
The Cognitive Abilities Test (CogAT) is a widely used standardized test designed to assess your child’s cognitive abilities in various areas.
The CogAT 5th Grade Level is specifically tailored for students in the 5th grade and measures their abilities in three main cognitive areas:
- Quantitative Reasoning
- Non-Verbal Reasoning

The MAP Test Grade 7 tests students’ proficiency in mathematics, reading and language usage.
Developed by the Northwest Evaluation Association (NWEA), it measures individual growth over time, adapting question difficulty based on responses.
This online test lasts around two to three hours, and the results are used to inform teaching or gauge students' ability levels.
Scoring is based on the RIT (Rasch Unit) scale, indicating a student's instructional level and growth potential in each subject area.
MAP Grade 7 Sample Question

The State of Texas Assessments of Academic Readiness (STAAR) test is a standardized assessment issued to public school students in Texas in grades 3 to 12.
Below you’ll find a range of STAAR test practice questions to help you prepare – whether you’re a parent coaching a child through their exam prep or a high school student revising for a test of your own.
For more info on the STAAR Test, read our dedicated article.

The STAR Early Literacy Test is an assessment tool used to measure children’s early literacy skills. It forms part of the wider Renaissance STAR (Standardized Test for the Assessment of Reading) assessment system by Renaissance Learning.
The STAR Early Literacy Assessment is mostly used to test students from pre-kindergarten to grade 3.
The test is designed to assess the following areas of early literacy:
- Phonemic awareness
- General vocabulary
- Comprehension
- Reading ability
- Early numeracy skills
STAR Early Literacy is a computer-adaptive test. This means that the difficulty of the questions adjusts according to a student’s responses.
The adaptive element of the test allows for more precise results and a better insight into a student’s overall literacy skills.
Word games are a great way to help your child prepare for the STAR Early Literacy Test.
You should also encourage your child to read daily.
You may wish to build this into their routine at certain times of the day. For example, reading before going to bed is often a good way to unwind.
If you are looking for other ways to help your child prepare, you can help them practice their time management skills, talk to them about maintaining a positive attitude towards the test and ensure they are getting sufficient rest.

The 7 best rated resume writing services:
- TopResume – Best for personalized expertise
- TopStack Resume – Best for navigating careers
- ResumeCompanion – Best for affordable excellence
- Resumeble – Best for ATS-optimized resumes
- ResumeSpice – Best for executive service
- Craft Resumes – Best for a quick turnaround
- Resume.com – Best for those on a budget

Administered at college and university level, the Accuplacer test is used by some educational institutions to determine how prepared a student is for the next steps in their academic career.
This guide looks specifically at Accuplacer test scores – how they are awarded and what they mean – so you can better understand how your Accuplacer score might impact your learning experience.
Accuplacer test scores are a set of metrics that evaluate a student's knowledge and skills in specific subject areas including reading, writing and math.

The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-V) is a commonly used assessment for judging a child's intelligence. More than that, it can help to understand their reasoning and thinking abilities to support their development.
Here’s everything you need to know about this test.
The Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children - Fifth Edition (WISC-V) is an individually administered and extensive evaluation tool used to assess children's reasoning and general thinking abilities.
It's typically given to children between ages 6 and 16.
After completing a test, children are awarded a Full-Scale Intelligence Quotient (IQ) score, along with age-based scores and rankings in several cognitive function fields.
Here we’ll provide an all-around study guide for parents whose children are required or scheduled to take the WISC-V test.
We’ll also include a comprehensive explanation of how it is constructed, its key features, tips for preparing, and a few example questions.
Let’s take a look!

The STAR assessments utilize a scoring system comprising scaled scores ranging from 0 to 1,400.
These scores reflect a student's proficiency level in subjects such as reading and math.
Benchmark categories provide descriptive labels for performance levels, while percentile rank compares a student's performance to a national reference group.
Additionally, grade equivalent scores and domain scores offer insights into grade-level equivalence and specific skill areas.
The STAR Assessment can play a crucial role in evaluating your child’s academic ability and guiding educational strategies.
Understanding its scoring system, test format and significance is important for parents and educators alike.
This article aims to provide comprehensive insights into the STAR Assessment, including its purpose, score interpretation and effective strategies to help children excel in these standardized tests.

The CogAT raw score represents how many questions were answered correctly on the CogAT test. This information is used to create the Universal Scale Score (between 100 and 150), which you will see on your child’s CogAT score report.
Here is an image of a typical score report:

With the MAP Growth Test used in many schools across the United States, MAP (Measures of Academic Progress) scores are an important part of your child’s life.
The MAP testing scores chart a student’s academic growth in a way that highlights areas of excellence and improvement.
It is essential that you understand how NWEA MAP scores are calculated so you can best support your child throughout their learning journey.
This guide will explain how to find and improve your child’s NWEA Map Scores.
The main three sections for the Upper and Middle level tests have a maximum score of 800. They have a total scaled score that ranges between 1,500 to 2,400.
Navigating the SSAT involves understanding its scoring system.
In this guide, you can explore the SSAT Score Chart and understand score ranges and percentile ranking and how they matter in private school admissions.
It's a comprehensive resource for decoding SSAT scores and making informed decisions about your child’s education.
What Is the SSAT Test?
The SSAT stands for the Secondary School Admission Test. The SSAT was first administered in 1957.
It is a standardized test designed for students seeking admission to private middle and high schools.
The primary purpose of the SSAT is to assess the skills and knowledge of students applying to independent or private schools.
It aims to provide an accurate measure of a student's academic abilities and readiness for a challenging curriculum.

As with other careers, joining the US military comes with its own set of recruitment processes, one of which is taking the ASVAB test .
If you’ve been looking to pursue a career in the US military, then it might be a test you’ve become familiar with or heard of before. It is an exam a recruiter will advise you to take prior to joining the armed forces.
The ASVAB , otherwise known as the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery , is a test the armed services use to determine which part of the US military you will be most suited to join.
Within this article we will discuss what your ASVAB score means and what score counts as a good ASVAB score .
Good ASVAB Score Defined
Whether you’re looking to join the Coast Guard, Army, Marine Corps or another sector within the US military, each branch will require its candidates to score a minimum amount to qualify for that specific area.
It is important to note that there is no single ASVAB score , and you will normally receive a variety of different scores on your final report.

The Microsoft Codility Test evaluates coding skills and algorithmic thinking.
Designed to streamline Microsoft’s recruitment process, the Microsoft Codility Test assesses candidates' ability to solve real-world problems efficiently.
Candidates can prepare using coding practice platforms and mastering programming languages. It's an integral tool in selecting skilled software engineers for Microsoft's diverse roles.

The Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium Test, known as the SBAC test, is a standardized assessment of English and math used by schools in participating states.
Administered to students in grades K to 12, it measures grade level proficiency and academic progress through computer-adaptive testing and performance tasks.
The Smarter Balanced Test is an educational tool developed and administered by the Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium (SBAC), hence the abbreviation SBAC test.
In this article we explore what the test involves, what the results mean and how to help a student prepare for their SBAC assessment.
What Is the SBAC Test?
The SBAC assessment is a set of standardized tests that evaluate how well students are performing in the subjects of English Language Arts (ELA) and mathematics.
These assessments are taken by students ranging from elementary school to high school in multiple states across the US.
The tests are developed and managed by the Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium (SBAC), a collaborative group of states working together.

FireTEAM Test Prep: Top Tips:
- Master time management
- Brush up on basic concepts
- Diversify your reading
- Play observational and memory games
- Assess your communication style
- Prioritize rest and sleep
If you're considering a career in firefighting, taking the FireTEAM test is a pivotal step that can open doors to various fire departments across the US.
This article covers everything you need to know to put in a strong performance, including an overview of its format, practice questions and FireTEAM test tips to help you create an effective study plan.
A career in the fire service is a challenging – but extremely rewarding – journey. Such an important, high-pressure job requires a high level of physical, mental and emotional skills.
As well as the necessary personality traits, you generally need a high school diploma or GED. If you have a college degree, you have a better chance of securing a role in the fire service.
You will also be required to take a series of assessments that evaluate your physical and mental strength. One of the assessments used by Californian fire departments is the FCTC Written Test. To become a firefighter in California, you must pass this entry-level test.
In this guide, we will explore what the FCTC Written Test includes and how you can prepare for success.

To successfully enlist in the US Marine Corps, certain standards must be met. Marines require both physical and mental strength as well as discipline, determination and the ability to overcome obstacles. This is sometimes referred to as the ‘Marine Mindset’.
One of the ways candidates who wish to enlist will be assessed is by taking a test known as the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB).
A good score on the test suggests that a candidate possesses the mental skillset to be successful in the military.
Marines need to be able to make quick, accurate decisions and adapt to and overcome threats and obstacles on the battlefield.

The PiCAT test is a commonly used assessment tool for those applying to military positions, such as those in the US Navy or the US Army.
This article explores the PiCAT test in more detail. We look at the test format to familiarize individuals with what the Navy PiCAT and Army PiCAT test covers.
Preparation is vital to performing to the best of your ability in the PiCAT test.
The article includes PiCAT practice test questions, answers to help you prepare, and tips to give you the best opportunity to approach the test positively.
The Mettl tests are developed by the world's largest assessment provider, Mercer Mettl.
The tests have been designed to analyze various competencies, including verbal, logical and numerical reasoning.
Alongside, the Mettl assessments evaluate candidates' personalities and working styles, establishing whether they are an accurate fit for the role and the broader company.
The Mettl tests are a comprehensive recruitment tool provided by Mercer Mettl – the world's largest assessment provider.
Moreover, the Mettl tests are designed to assess various skills, including numerical , verbal and abstract reasoning.
The assessments are also constructed to understand candidates' behaviors and personality types.
This guide explains everything you need to know about the Mettl test, including tips on how to pass the test in 2024.
What Is the Mettl Test?
As mentioned, the Mettl test is a comprehensive recruitment tool designed to test a range of skills.
It allows employers to ensure they recruit the most suitable candidates for the role.
Mastering the Pipefitter Test is crucial for those entering the field.
This guide provides valuable insights, a pipefitter sample test and strategies to conquer the examination.
Discover expert tips to excel in your pipefitting career by navigating the challenges of this important assessment.
What Is the Pipefitter Assessment Test?
The Pipefitter test is an important evaluation tool for individuals aspiring to secure roles as pipefitters in the construction and industrial sectors.
Qualifications and certifications necessary for such positions can vary by state. This makes the pipefitter assessment test a valuable method of demonstrating skills and knowledge.
The National Center for Construction Education and Research (NCCER) administers the most popular pipefitter assessment test, designed to assess the potential skills of candidates.
It covers the principles related to the installation and maintenance of both high and low-pressure pipe systems.
In addition, it focuses on how these are used across various sectors, including manufacturing, electricity generation and climate control systems in buildings.

The i-Ready Diagnostic Test is an internet-based adaptive diagnostic test linked to the i-Ready educational learning program.
Students from kindergarten to grade 12 take the test three times each year. The test is divided into two subtests:
i-Ready test results are used to help teaching staff create a personalized learning plan according to a student’s strengths and weaknesses.
What Is the i-Ready Diagnostic Test?
The i-Ready Diagnostic Test is a computer-adaptive, untimed assessment for students between grades K and 12.
Administered by Curriculum Associates , teachers can use it to monitor a student’s ability and progress throughout the school year.
In most cases, the i-Ready Diagnostic Test is administered three times each year. It is split into two subtests: math and reading.

The HSBC Online Immersive Assessment contains 38 questions over five subtests. The test includes a combination of behavioural questions and cognitive ability exercises.
It is an untimed assessment, but most candidates can answer all test questions within 50 minutes.
Some people find the test difficult, but adequate preparation will stand you in good stead to pass the assessment.
What Is the HSBC Hiring Process Like?
HSBC is a major global bank and financial institution. It offers services via three global businesses and serves millions of customers daily.
The hiring process at HSBC comprises four key stages:
- Initial Screening and Application
- HSBC Online Immersive Assessment
- Online Job Simulation Assessment
What Is the Electronic Data Processing Test?
The Electronic Data Processing Test (EDPT) is a pre-employment test taken by military candidates who want to transfer to IT or computer programming roles within the Marine Corps or Air Force.
The EDPT test is one of the most challenging pre-employment tests currently on the market with a pass rate of around 10%.
It is 90 minutes long and has 120 multiple-choice questions. This means you have around 45 seconds to answer each question.

While the minimum ASVAB score varies between military branches, the minimum acceptable score is 31.
However, as the majority of candidates score between 30 and 70, you want to aim for a percentile rank of at least 60.
The ASVAB Test Score Report is a valuable document that provides detailed information about your aptitudes, skills, and qualifications for military service.
It includes Career Exploration Scores to guide career choices, individual scores on ASVAB subtests to assess specific abilities and the critical AFQT score that determines your eligibility for enlistment.
Understanding the information presented in this report is essential for making informed decisions about your military career options.
What Is in the ASVAB Test Score Report?
The ASVAB (Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery) Test Score Report provides a comprehensive overview of your performance on the ASVAB test, which is a critical step in the military enlistment process.
The report helps you and military recruiters assess your aptitudes, skills, and potential for various military occupations.

What Is the MMPI Assessment?
The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) is one of the most widely used assessment tools used to help clinically diagnose mental health disorders.
Originally developed in the late 1930s, it is used by mental health professionals, lawyers and even in some cases by employers when they are hiring for positions that are considered to be high-risk, such as working in the police, in nuclear power plants or in air traffic control.
The MMPI is a self-reporting tool that is administered by professionals, and during the assessment, you will be asked to answer hundreds of true/false questions, which help paint a picture of your mental health and your personality traits.
As a diagnosis tool, the MMPI is considered to be clinically accurate. It has been updated multiple times over the years to make it more relevant, especially in terms of cultural sensitivity.
The MMPI offers results that show on a scale what symptoms a person has, and what mental health problems that could be indicative of.
In addition, the MMPI is usually used in tandem with other diagnosis tools to provide a clear picture of a person's mental health.
What Is the ACCUPLACER Reading Comprehension Test?
The Accuplacer Reading Comprehension test is part of a suite of assessments that are used to evaluate students prior to entry at college.
While the Accuplacer test battery is not used to determine whether a student will achieve a placement at college, the results are used to ensure that the student is studying at an appropriate level and is ready for education at this level.
Created by the College Board, which is a not-for-profit organization that is also responsible for creating assessments like the SATs, the Accuplacer tests are designed to offer better opportunities to students and make entry to top colleges accessible to all.

- Brain Development
- Childhood & Adolescence
- Diet & Lifestyle
- Emotions, Stress & Anxiety
- Learning & Memory
- Thinking & Awareness
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Childhood Disorders
- Immune System Disorders
- Mental Health
- Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Infectious Disease
- Neurological Disorders A-Z
- Body Systems
- Cells & Circuits
- Genes & Molecules
- The Arts & the Brain
- Law, Economics & Ethics
- Neuroscience in the News
- Supporting Research
- Tech & the Brain
- Animals in Research
- BRAIN Initiative
- Meet the Researcher
- Neuro-technologies
- Tools & Techniques
- Core Concepts
- For Educators
- Ask an Expert
- The Brain Facts Book

Test Your Problem-Solving Skills
Personalize your emails.
Personalize your monthly updates from BrainFacts.org by choosing the topics that you care about most!
Find a Neuroscientist
Engage local scientists to educate your community about the brain.
Image of the Week
Check out the Image of the Week Archive.

SUPPORTING PARTNERS
- Privacy Policy
- Accessibility Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Manage Cookies
Some pages on this website provide links that require Adobe Reader to view.

Assess your talent holistically
- Behavioral Tests
- Aptitude Tests
- Technical Tests
- Communication Skills Tests
Find the best coders efficiently
- Coding Skills Tests
- Advanced Coding Simulators
Assessments to hire the best talent
- Technical Hiring
- Sales Hiring
- Blue Collar Hiring
Hire right talent from right campus
- Campus Intelligence
- Student Engagement
- Screening Assessments
- Online Interviews
- Hire Only The Best Fit
Accelerate innovations
- For Corporates
- For Community
Find your most valuable employees
- High-Potential Identification
- Succession Planning
- Leadership Development
- Virtual ADC
Easy to use feedback tool
Build a future ready workforce
- Skills Gap Analysis
- Learning Agility & Proximity
- Training Effectiveness
Conduct scalable remote exams
- Examination Platform
- Entrance Exam
- Semester Exam
- Online Evaluation System
AI-based proctoring suite
- SecureProctor
- Mettl Secure Browser
Run online certification programs
- Take Your Exams Online
- Psychometric Tests
- Find The Right Talent
Explore And Address The Latest Advancements In Assessments, Online Exams, Hiring, And L&D
- Research & Reports
- Client Success Stories
- Webinar Recordings
Get the latest HR technology trends from the experts in talent assessment and management
Build Winning Teams with Competency Based Assessments
- Behavioral Competencies
- Cognitive Competencies
- Coding Competencies
- Domain Competencies
Your Guide To All Things Talent And Assessment
Our Customers in the Corporate Sector
Our Customers in the Education Sector
Problem-Solving Assessment for Finding and Hiring the Best Problem Solvers
A problem-solving test is an assessment to determine whether a candidate has problem-solving skills and whether they can contemplate positive and negative solutions to a problem. It measures the ability to use logic, creativity, and analytical skills to assess and respond to complex situations.
Ready to Use
30 Questions
problem-solving abilities of entry-level candidates and experienced professionals.
English Global, English UK, English India
About This Test
Skills & Subskills
Customize This Test
Assessment Features
Inside This Problem Solving Assessment
Problem-solving is an essential skill for individuals, teams and managers to progress toward achieving goals. It involves the ability to identify ways and means to solve various problems that come up as a challenge in any job/task. Problem-solving skills influence our career, whether we are solving a problem for a client or assisting those who are solving problems.
A problem-solving test evaluates the candidate's ability to outline a problem, deconstruct it, develop the most appropriate solution, and assess the effectiveness of the solution. It allows employers to find candidates who possess such abilities. The test assesses problem-solving ability through questions that evaluate someone's numerical knowledge, critical thinking, analytical ability and problem-solving skills.
The problem-solving assessment requires test-takers to respond correctly to the questions within the decided time. Qualified candidates can define the nature of a problem, are proactive in seeking the optimal solution for the problem, and consider all possible outcomes before settling on the best solution.
Employers can glean actionable insights from the problem-solving skills test to identify the best talent from a pool of resumes, which eventually translates to objective hiring decisions backed by data. In addition, since these tests are to be administered online, the administrative overhead of conducting too many interviews gets reduced, enabling the employers and recruiters to save more time and resources by screening out unqualified participants. This way, it becomes significantly easy to find the best candidates.
Why should you use this problem-solving ability test?
The problem-solving skills test is meticulously designed to successfully test a candidate's problem-solving skills that are essential for carrying out business and even maintaining interpersonal relationships. This test is planned and structured in such a way that it will effectively test a candidate’s ability to identify and address a problem. Moreover, it helps measure decision-making, reasoning, and numerical reasoning skills.
Sectional Details:
Test details:.
Use this problem-solving aptitude test for:
This test is suitable for all the profiles in the workplace. The test is planned and structured to assess problem-solving ability in fresher (for entry-level roles) and experienced candidates.
Key profiles the test is helpful for:
- All profiles in a workplace
Note: If required, we can also provide the problem-solving skills assessment in other languages. Please connect with us at [email protected] for any such requirements.
Problems never knock before entering our lives, be it professional or personal, and are not avoidable. An unexpected issue will likely surface, and we must have a plan to address it. The skill of solving problems is needed in all facets of life. People with problem-solving aptitude tend to forge challenges into lucrative opportunities. Employees with these highly coveted personality traits are indispensable for organizations. They understand that problems are there to help us grow and transform into a better person who undertakes every project with confidence and conviction.
Such people are favorably disposed toward handling unexpected/difficult situations calmly. This aptitude empowers them to use logic, creativity, and creative thinking to propose practical solutions to their problems. Undoubtedly, employers regard those people highly and want them placed in essential roles in the organization. That is where the part of the problem-solving test comes into play and helps employers to identify the right talent with the desired skills.
From an organizational viewpoint, problem-solving hinges on the employee's ability to devise processes that eliminate or circumvent obstacles that keep a company from accomplishing its goals. If not appropriately addressed, such blocks can create a divide between expected results and actual outcomes. Hence, problem-solving is a crucial skill in the workplace that dictates how any particular challenge can be undertaken and overcome. Roles such as project management, data analyst, programmers, customer service assistance, etc., entail working on strict deadlines and demanding tasks on a day-to-day basis. Hence, problem-solving skills become critical when finding talent for these roles in assessing job fit and matching the best person to the proper position.
The problem-solving skills assessment helps organizations gain insights into the problem-solving competencies of candidates. Even before the company interviews, evaluating applicants' skills can help recruiters understand their level of proficiency. This way, only those candidates with the skills most suited to the role will be shortlisted for the subsequent round of interviews.
Customize This Problem Solving Test
Flexible customization options to suit your needs
Choose easy, medium or hard questions from our skill libraries to assess candidates of different experience levels.
Add multiple skills in a single test to create an effective assessment. Assess multiple skills together.
Add, edit or bulk upload your own coding questions, MCQ, whiteboarding questions & more.
Get a tailored assessment created with the help of our subject matter experts to ensure effective screening.
The Mercer | Mettl Problem Solving Aptitude Test Advantage
Our robust platform empowers you to assess, interview, analyze test-takers.
- Cutting Edge proctoring capabilities
- Coding Simulators Designed By Developers
- 24 x 7 Support
- Robust Data security
- 20+ Languages in 80+ countries

- Industry Leading 24/7 Support
- State of the art examination platform
- Inbuilt Cutting Edge AI-Driven Proctoring
- Simulators designed by developers
- Tests Tailored to Your business needs
- Support for 20+ Languages in 80+ Countries Globally
Problem Solving Assessment Can Be Setup in 4 Steps
Add this test your tests
Share test link from your tests
Candidate take the test
You get their tests report
Assess & develop leadership competencies to future-proof your business
Measure the potential of your talent and make objective organizational decisions
Highly secure and seamless online examination platform
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. why do we use problem-solving tests.
Problem-solving tests help organizations identify appropriate skills in candidates that can assist in selecting individuals with required problem-solving abilities. These tests help determine a candidate's problem-solving skills, trainability, and learning agility.
2. How do you measure problem-solving skills?
The expertly formulated Problem-solving Assessment Test by Mercer | Mettl makes it easy for organizations to understand whether a candidate can analyze given information from different perspectives and use it to solve complex problems.
3. How do you practice problem-solving skills?
- Identify the nature of the issue.
- Research the intricacies and understand the nuances behind the problem.
- Visualize the situation to analyze data, break it into doable components, and arrive at a logical solution.
- Use active listening skills to include opinions and inputs from others.
- Identify the most viable solution and consider the potential risks involved.
4. How do you test problem-solving skills in an interview?
5. how can one refine their problem-solving skills, 6. how do you use problem-solving skills in the workplace.
Problem-solving tests help organizations identify appropriate skills in candidates that can assist in selecting individuals with required problem-solving abilities. These tests help determine a candidate's problem-solving skills, trainability, and learning agility.
Trusted by More Than 6000 Clients Worldwide
Sales Enq: +91-9555-11-4444
Test-Taker Support: +91-8047189190
INVITED FOR TEST?
2024 Mercer LLC, All Rights Reserved
Terms of Services
Privacy Notice
Sub-Processor

Self Evaluation Comments for Problem Solving (30 Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 19, 2023 — 9 minutes to read
Self-evaluation is an essential aspect of professional development. It helps you to identify areas of improvement and measure your progress towards achieving your goals. By evaluating your problem-solving skills, you can identify your strengths and weaknesses and take steps to improve your performance.
Problem Solving Self-Evaluation Comments Examples
- I was able to identify the root cause of the problem and develop a solution that addressed it effectively.
- I was able to think outside the box and come up with a creative solution to a complex problem.
- I was able to collaborate effectively with my team members to solve a challenging problem.
- I was able to prioritize tasks and allocate resources efficiently to solve a problem within a tight deadline.
- I was able to remain calm and composed under pressure while solving a critical problem.
- I was able to analyze data and information to identify patterns and trends that helped me solve a problem.
- I was able to communicate clearly and effectively with stakeholders to understand their needs and solve their problems.
- I was able to adapt to changing circumstances and adjust my problem-solving approach accordingly.
- I was able to learn from my mistakes and apply those lessons to future problem-solving situations.
- I was able to use critical thinking skills to evaluate multiple options and select the best solution to a problem.
- I was able to break down a complex problem into smaller, more manageable parts and solve each part individually.
- I was able to identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans to overcome them while solving a problem.
- I was able to leverage my technical expertise to solve a problem that required specialized knowledge.
- I was able to use my creativity and innovation to develop a unique solution to a problem.
- I was able to gather and analyze feedback from stakeholders to continuously improve my problem-solving approach.
- I was able to use my leadership skills to motivate and guide my team members towards a successful problem-solving outcome.
- I was able to effectively manage competing priorities and still solve a problem within the given timeline.
- I was able to use my communication skills to explain complex technical solutions to non-technical stakeholders.
- I was able to use my analytical skills to identify patterns and trends that helped me solve a problem more efficiently.
- I was able to use my problem-solving skills to identify opportunities for process improvements and implement them successfully.
- I was able to use my research skills to gather information that helped me solve a problem more effectively.
- I was able to use my project management skills to break down a large-scale problem into smaller, more manageable tasks.
- I was able to use my negotiation skills to reach a mutually beneficial solution to a problem.
- I was able to remain objective and unbiased while evaluating potential solutions to a problem.
- I was able to use my attention to detail to identify small but critical issues that were contributing to a larger problem.
- I was able to use my interpersonal skills to build strong relationships with stakeholders and work collaboratively towards a solution.
- I was able to use my problem-solving skills to find a solution that balanced the needs of multiple stakeholders.
- I was able to use my persistence and determination to keep working towards a solution even when faced with obstacles.
- I was able to use my time management skills to prioritize tasks and allocate my time efficiently while solving a problem.
- I was able to use my empathy and understanding of others’ perspectives to develop a solution that met everyone’s needs.
Improving Problem Solving Skills
To become a better problem solver, you need to develop critical thinking skills, effective communication skills, prioritize tasks, and use brainstorming techniques. Here are some tips to help you improve your problem-solving skills:
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze a situation, identify problems, and come up with creative solutions. To develop critical thinking skills, you need to:
- Ask questions: Don’t be afraid to ask questions to clarify the problem or gather more information.
- Challenge assumptions: Don’t accept things at face value. Question assumptions and look for evidence to support them.
- Evaluate evidence: Look for evidence that supports or contradicts your assumptions. Evaluate the quality and reliability of the evidence.
- Consider alternative perspectives: Try to see the problem from different angles and consider alternative solutions.
Effective Communication Skills
Effective communication is essential for problem-solving because it helps you:
- Understand the problem: Good communication skills help you clarify the problem and understand what is expected of you.
- Collaborate with others: Effective communication skills help you work with others to find solutions.
- Express your ideas clearly: Clear communication helps you convey your ideas and solutions to others.
To improve your communication skills, you need to:
- Listen actively: Listen to others and try to understand their perspective.
- Speak clearly: Speak clearly and concisely to avoid confusion.
- Use nonverbal cues: Pay attention to body language and other nonverbal cues to understand what others are saying.
Prioritizing Tasks
Prioritizing tasks is essential for effective problem-solving because it helps you:
- Focus on the most important tasks: Prioritizing helps you focus on the tasks that will have the most significant impact.
- Manage your time: Prioritizing helps you manage your time more effectively.
- Avoid procrastination: Prioritizing helps you avoid procrastination by breaking down large tasks into smaller, more manageable ones.
To prioritize tasks effectively, you need to:
- Identify the most important tasks: Identify the tasks that will have the most significant impact.
- Break down large tasks: Break large tasks into smaller, more manageable ones.
- Set deadlines: Set deadlines for each task to help you stay on track.
Brainstorming Techniques
Brainstorming is a technique used to generate creative ideas and solutions. To brainstorm effectively, you need to:
- Generate a lot of ideas: Don’t be afraid to come up with as many ideas as possible, even if they seem silly or unrealistic.
- Encourage creativity: Encourage creative thinking by allowing everyone to contribute ideas.
- Avoid criticism: Don’t criticize or judge ideas during the brainstorming process.
To brainstorm effectively, you can use techniques like mind mapping, free writing, or group brainstorming sessions.
Time Management and Productivity
Managing time effectively.
One of the biggest challenges when it comes to problem-solving is managing your time effectively. It’s easy to get bogged down in the details and lose track of the big picture. To avoid this, set specific goals and deadlines for yourself. Make a to-do list and prioritize your tasks based on their importance and urgency. Use a timer or a stopwatch to keep track of how much time you spend on each task, and try to minimize distractions as much as possible.
For example, if you’re working on a project that requires a lot of research, set a goal to finish the research phase by the end of the day. Break the research down into smaller tasks, such as reading a certain number of articles or books, and set deadlines for each task. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you’re making progress towards your goal.
Overcoming Overwhelm
Feeling overwhelmed is a common problem when it comes to problem-solving. When you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s easy to feel like you don’t know where to start. To overcome this, break the problem down into smaller, more manageable parts. Identify the key issues or questions that need to be addressed, and focus on one at a time.
For example, if you’re trying to solve a problem with a product or service, start by identifying the key issues that are causing the problem. Once you’ve identified these issues, break them down into smaller, more manageable parts. Focus on one issue at a time, and come up with a plan to address it. Once you’ve addressed all of the key issues, you’ll have a better understanding of the problem as a whole, and you’ll be better equipped to come up with a solution.
Being Proactive
Being proactive is an important part of problem-solving. Instead of waiting for problems to arise, take a proactive approach and try to anticipate potential problems before they occur. This will help you stay ahead of the curve and avoid potential roadblocks.
For example, if you’re working on a project with a tight deadline, don’t wait until the last minute to start working on it. Instead, start working on it as soon as possible, and set specific goals and deadlines for yourself. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you’re making progress towards your goal. Additionally, be proactive in identifying potential roadblocks or issues that could arise, and come up with a plan to address them before they become a problem.
Performance Review and Goal Setting
Setting objectives.
When preparing for a performance review, it’s important to set specific objectives that will guide the conversation. Start by reflecting on your current role and responsibilities, and consider areas where you could improve or grow. These objectives should be measurable and achievable, and should align with your personal and professional goals.
For example, one objective might be to improve your communication skills by attending a workshop or taking an online course. Another objective might be to take on more leadership responsibilities within your team or department.
Measuring Performance
During the performance review, your manager will likely evaluate your progress towards meeting your objectives. It’s important to come prepared with concrete examples of how you’ve worked towards your goals, as well as any challenges or obstacles you’ve faced.
For example, if your objective was to improve your project management skills, you might share how you’ve successfully led a project from start to finish, or how you’ve implemented new tools or processes to streamline your workflow. If you’ve faced challenges, be honest about what went wrong and what you learned from the experience.
Creating an Action Plan
After reviewing your performance, you and your manager should work together to create an action plan for the next review period. This plan should include specific goals and objectives, as well as a timeline for achieving them. It’s also important to identify any resources or support you may need to reach your goals.
For example, if your objective is to improve your technical skills, you might discuss opportunities for additional training or mentorship. If your goal is to take on more leadership responsibilities, you might discuss ways to gain experience through shadowing or cross-functional projects.
Overall, the performance review and goal setting process is an important opportunity to reflect on your progress and set a course for future growth and development. By setting specific, measurable objectives and working collaboratively with your manager, you can ensure that you’re on track to achieve your personal and professional goals.
When writing self-evaluation comments, it is important to be honest and objective. Avoid making exaggerated or false claims about your abilities or achievements. Instead, focus on specific examples that demonstrate your skills and accomplishments.
- Innovation and Creativity Self Evaluation Comments (30 Examples)
- Self Evaluation Sample Answers: Strengths and Weaknesses
- Authenticity: How to Be Your Authentic Self (Examples & Strategies)
- What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
- What is Self Compassion? (Exercises, Methods, Examples)
- How to Cultivate Self-Discipline: Essential Strategies
FREE Math Word Problem Assessments

Also included in

Description
The free Problem Solving Assessment Pack includes two tests, a pretest and a posttest, which were designed to help you assess your students' math problem-solving abilities. The pretest data will enable you to determine where to begin with your problem-solving instruction; the posttest data will help you track their progress later. A unique feature of this test is that it requires students to draw pictures to show how they are solving the problems. You'll be amazed at what you can learn from those pictures! Administering this test will also help you differentiate instruction after you analyze the results.
More Problem Solving Resources!
If you like this freebie, check out my Daily Math Puzzler books and Math Mindset Problem Solving resources. My Math Problem Solving Bundle includes all four levels of the Daily Math Puzzler books, the Math Problem Solving Mindsets Matter Webinar, and Math Mindset Challenges editable word problems pack.
Questions & Answers
Laura candler.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It is based on both Stratified Systems Theory (SST) and complexity theory, and measures an individual's current and potential ability to manage the demands of various levels and types of work problem-solving. Over the last 25 years the JP Team has built insight in the CNT, applying it across over 30 industries and 5 continents.
Standard Bank Assessment Center. Assessment center days are often used during the application process for early careers, and candidates are expected to come to one of the main offices or another location to spend a day with the Talent Acquisition Team and other applicants for some in-depth pre-employment testing.. The assessment center is a chance for the recruiters to see how you act in the ...
Welcome to the Joint Prosperity CNT assessment system. Candidate Login. Enter your token
The purpose of assessing instruction for critical thinking is improving the teaching of discipline-based thinking (historical, biological, sociological, mathematical, etc.) It is to improve students' abilities to think their way through content using disciplined skill in reasoning. The more particular we can be about what we want students to ...
It is one of the three major pre-employment assessments used by SIG, alongside the SIG Problem Solving Assessmentand the SIG Capital Markets Assessment. The Quantitative Evaluation test is provided by test proviuder Mettl and contains 16 questions. The overall time to complete the test is 20 minutes. The evaluation covers 4 main topics.
For problem solving assessments at lower levels, such as the PISA example, problems are less complex and require less extensive knowledge such that it is much easier to establish an "expert" decision. For most assessments, an instructor who is knowledgeable in the subject will produce an answer that is the same as someone very expert in the ...
This assessment has not been validated and is intended for illustrative purposes only. Below, we outline the tools and strategies you can use for each stage of the problem-solving process. Enjoy exploring these stages! Step 1: Find the Problem (Questions 7, 12) Some problems are very obvious, however others are not so easily identified.
Critical thinking is one of the most frequently discussed higher order skills, believed to play a central role in logical thinking, decision making, and problem solving (Butler, 2012; Halpern, 2003).It is also a highly contentious skill in that researchers debate about its definition; its amenability to assessment; its degree of generality or specificity; and the evidence of its practical ...
Abstract. Problem solving is the skill that coordinates all the cognitive, metacognitive and behavioral processes taking place when individuals encounter a previously unprecedented situation or ...
That is, all problems are alike and the normative processes used to solve all problems are similar. Based on that assumption, numerous models of problem solving have been suggested, most of which involve a sequence of steps, including: 1. Define the problem. 2. Analyze the problem (identify possible causes). 3.
n. In this module, we will be discussing assessing problem solving in terms of problem identification, identifying irrelevancies, describing multiple problem-solving strategies, modeling a problem, identifying obstacles, reasoning with data, using analogies, and solving problems backward. "Problem solving is cognitive processing directed at ...
Assessing patients, determining whether their conditions are stable or unstable, and defining care needs are important tasks for ECNs. 10 Failure to assess patients according to their individual care needs may lead to undesired consequences, such as incomplete nursing care and adverse health events. 13 In Sweden, patient assessment generally focuses on patients' physical and biomedical ...
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely embraced in the classroom instruction of critical thinking, which is regarded as the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field ...
Cognitive ability test: A pre-employment aptitude test assesses individuals' abilities such as critical thinking, verbal reasoning, numerical ability, problem-solving, decision-making, etc., which are indicators of a person's intelligence quotient (IQ). The test results provide data about on-the-job performance.
At its core, problem-solving is a problem of recognizing patterns, understanding complex systems, and finding effective paths to desired goals. It's about being proactive rather than reactive—being the kind of individual who companies seek out when they want that issue solved yesterday. The 30 Problem-Solving Skill Assessment Questions
Critical thinking and problem solving, as we define it, are the set of non-discipline specific cognitive skills people use to analyze vast amounts of information and creatively solve problems. We have broken those skills down into these five core components: Schema Development: The ability to learn vast amounts of information and organize it in ...
By Math Teachers, For Math Teachers. Designed and tested with real students at East Kentwood High School, the most diverse public high school in Michigan. Get Lesson Plans. Check out the NEW Math Medic Assessment Platform! More details. Our Teaching Philosophy. Experience First, Formalize Later. Every lesson begins with students working ...
Cognitive assessments are used to evaluate various aspects of cognitive functioning, including memory, attention, problem-solving, reasoning, language comprehension, and more. Cognitive function tests are commonly employed in several contexts, including education, clinical psychology, neuropsychology and employment assessment.
Test Your Problem-Solving Skills. Personalize Your Emails Personalize your monthly updates from BrainFacts.org by choosing the topics that you care about most! Sign Up Find a Neuroscientist Engage local scientists to educate your community about the brain. ...
Introduction. Since its inception, problem-based learning (PBL) has conquered the world (Donner and Bickley 1993).Its history is described in a number of publications (Schmidt 2012; Servant-Miklos 2019).What started in the mid-sixties at McMaster University as a radical break from lecture-based education (Barrows and Tamblyn 1980), turned out to be a successful didactic strategy which has ...
The problem-solving skills assessment helps organizations gain insights into the problem-solving competencies of candidates. Even before the company interviews, evaluating applicants' skills can help recruiters understand their level of proficiency. This way, only those candidates with the skills most suited to the role will be shortlisted for ...
Problem Solving Self-Evaluation Comments Examples. I was able to identify the root cause of the problem and develop a solution that addressed it effectively. I was able to think outside the box and come up with a creative solution to a complex problem. I was able to collaborate effectively with my team members to solve a challenging problem.
The Math Problem Solving Mega Bundle includes all 4 American versions of the Daily Math Puzzler books (A-D) and both of the International versions (A and B). Each Daily Math Puzzler product includes a folder of editable PowerPoint documents to create your own word problems and to customize your reco. 8. Products. $29.95 $49.70 Save $19.75.