APA Citation Style
Citation examples.
- Paper Format
- Style and Grammar Guidelines
- Citation Management Tools
- What's New in the 7th Edition?
- APA Style References Guidelines from the American Psychological Association
- APA Style (OWL - Online Writing Lab, Purdue University)
- Common Reference Examples Handout
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Edited Book Chapter
- Dictionary Entry
- Government Report
- YouTube Video
- Facebook Post
- Webpage on a Website
- Supplemental Reference Examples
- Archival Documents and Collections
| Grady, J. S., Her, M., Moreno, G., Perez, C., & Yelinek, J. (2019). Emotions in storybooks: A comparison of storybooks that represent ethnic and racial groups in the United States. , (3), 207–217. Jerrentrup, A., Mueller, T., Glowalla, U., Herder, M., Henrichs, N., Neubauer, A., & Schaefer, J. R. (2018). Teaching medicine with the help of “Dr. House”. , (3), Article e0193972. |
Parenthetical citations: (Grady et al., 2019; Jerrentrup et al., 2018)
Narrative citations: Grady et al. (2019) and Jerrentrup et al. (2018)
- If a journal article has a DOI, include the DOI in the reference.
- If the journal article does not have a DOI and is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range (for an explanation of why, see the database information page). The reference in this case is the same as for a print journal article.
- Do not include database information in the reference unless the journal article comes from a database that publishes original, proprietary content, such as UpToDate (see an example on the database information page).
- If the journal article does not have a DOI but does have a URL that will resolve for readers (e.g., it is from an online journal that is not part of a database), include the URL of the article at the end of the reference.
- If the journal article has an article number instead of a page range, include the article number instead of the page range (as shown in the Jerrentrup et al. example).
| Rabinowitz, F. E. (2019). . American Psychological Association. Sapolsky, R. M. (2017). . Penguin Books. |
Parenthetical citations: (Rabinowitz, 2019; Sapolsky, 2017)
Narrative citations: Rabinowitz (2019) and Sapolsky (2017)
- If the book includes a DOI, include the DOI in the reference after the publisher name.
- Do not include the publisher location.
- If the book does not have a DOI and comes from an academic research database, end the book reference after the publisher name. Do not include database information in the reference. The reference in this case is the same as for a print book.
| Schaefer, N. K., & Shapiro, B. (2019, September 6). New middle chapter in the story of human evolution. , (6457), 981–982. Schulman, M. (2019, September 9). Superfans: A love story. . |
Parenthetical citations: (Schaefer & Shapiro, 2019; Schulman, 2019)
Narrative citations: Schaefer and Shapiro (2019) and Schulman (2019)
- If a magazine article has a DOI, include the DOI in the reference.
- If the magazine article does not have a DOI and is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range. Do not include database information in the reference. The reference in this case is the same as for a print magazine article.
- If the magazine article does not have a DOI but does have a URL that will resolve for readers (e.g., it is from an online magazine that is not part of a database), include the URL of the article at the end of the reference.
- If the magazine article does not have volume, issue, and/or page numbers (e.g., because it is from an online magazine), omit the missing elements from the reference (as in the Schulman example).
| Carey, B. (2019, March 22). Can we get better at forgetting? |
Parenthetical citation: (Carey, 2019)
Narrative citation: Carey (2019)
- If the newspaper article is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range. Do not include database information in the reference. The reference in this case is the same as for a print newspaper article.
- If the newspaper article has a URL that will resolve for readers (e.g., it is from an online newspaper), include the URL of the article at the end of the reference.
- If the newspaper article does not have volume, issue, and/or page numbers (e.g., because it is from an online newspaper), omit the missing elements from the reference, as shown in the example.
- If the article is from a news website (e.g., CNN, HuffPost)—one that does not have an associated daily or weekly newspaper—use the format for a webpage on a website instead.
| Aron, L., Botella, M., & Lubart, T. (2019). Culinary arts: Talent and their development. In R. F. Subotnik, P. Olszewski-Kubilius, & F. |
Parenthetical citation: (Aron et al., 2019)
Narrative citation: Aron et al. (2019)
- If the edited book chapter includes a DOI, include the chapter DOI in the reference after the publisher name.
- If the edited book chapter does not have a DOI and comes from an academic research database, end the edited book chapter reference after the publisher name. Do not include database information in the reference. The reference in this case is the same as for a print edited book chapter.
- Do not create references for chapters of authored books. Instead, write a reference for the whole book and cite the chapter in the text if desired (e.g., Kumar, 2017, Chapter 2).
| Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Culture. In . Retrieved September 9, 2019, from |
Parenthetical citation: (Merriam-Webster, n.d.)
Narrative citation: Merriam-Webster (n.d.)
- Because entries in Merriam-Webster’s Dictionary are updated over time and are not archived, include a retrieval date in the reference.
- Merriam-Webster is both the author and the publisher, so the name appears in the author element only to avoid repetition.
- To quote a dictionary definition, view the pages on quotations and how to quote works without page numbers for guidance. Additionally, here is an example: Culture refers to the “customary beliefs, social forms, and material traits of a racial, religious, or social group” (Merriam-Webster, n.d., Definition 1a).
| National Cancer Institute. (2019). (NIH Publication No. 18-2059). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. |
Parenthetical citation: (National Cancer Institute, 2019)
Narrative citation: National Cancer Institute (2019)
The specific agency responsible for the report appears as the author. The names of parent agencies not present in the group author name appear in the source element as the publisher. This creates concise in-text citations and complete reference list entries.
| Harvard University. (2019, August 28). [Video]. YouTube. |
Parenthetical citation: (Harvard University, 2019)
Narrative citation: Harvard University (2019)
- Use the name of the account that uploaded the video as the author.
- If the account did not actually create the work, explain this in the text if it is important for readers to know. However, if that would mean citing a source that appears unauthoritative, you might also look for the author’s YouTube channel, official website, or other social media to see whether the same video is available elsewhere.
| APA Databases [@APA_Databases]. (2019, September 5). [Tweet]. Twitter. Gates, B. [@BillGates]. (2019, September 7). [Thumbnail with link attached] [Tweet]. Twitter. |
Parenthetical citations: (APA Databases, 2019; Gates, 2019)
Narrative citations: APA Databases (2019) and Gates (2019)
- Present the name of the individual or group author the same as you would for any other reference. Then provide the Twitter handle (beginning with the @ sign) in square brackets, followed by a period.
- Provide the first 20 words of the tweet as the title. Count a URL, a hashtag, or an emoji as one word each, and include them in the reference if they fall within the first 20 words.
- If the tweet includes an image, a video, a poll, or a thumbnail image with a link, indicate that in brackets after the title: [Image attached], [Video attached], [Thumbnail with link attached].
- The same format used for Twitter is also used for Instagram.
| News From Science. (2019, June 21). [Image attached] [Status update]. Facebook. |
Parenthetical citation: (News From Science, 2019)
Narrative citation: News From Science (2019)
- Provide the first 20 words of the Facebook post as the title. Count a URL or other link, a hashtag, or an emoji as one word each, and include them in the reference if they fall within the first 20 words.
- If a status update includes images, videos, thumbnail links to outside sources, or content from another Facebook post (such as when sharing a link), indicate that in square brackets.
| Fagan, J. (2019, March 25). . OER Commons. Retrieved September 17, 2019, from National Institute of Mental Health. (2018, July). . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health. Woodyatt, A. (2019, September 10). . CNN. World Health Organization. (2018, May 24). . |
Parenthetical citations: (Fagan, 2019; National Institute of Mental Health, 2018; Woodyatt, 2019; World Health Organization, 2018)
Narrative citations: Fagan (2019), National Institute of Mental Health (2018), Woodyatt (2019), and World Health Organization (2018)
- Provide as specific a date as is available on the webpage. This might be a year only; a year and month; or a year, month, and day.
- Italicize the title of a webpage.
- When the author of the webpage and the publisher of the website are the same, omit the publisher name to avoid repetition (as in the World Health Organization example).
- When contents of a page are meant to be updated over time but are not archived, include a retrieval date in the reference (as in the Fagan example).
- Use the webpage on a website format for articles from news websites such as CNN and HuffPost (these sites do not have associated daily or weekly newspapers). Use the newspaper article category for articles from newspaper websites such as The New York Times or The Washington Post .
- Create a reference to an open educational resources (OER) page only when the materials are available for download directly (i.e., the materials are on the page and/or can be downloaded as PDFs or other files). If you are directed to another website, create a reference to the specific webpage on that website where the materials can be retrieved. Use this format for material in any OER repository, such as OER Commons, OASIS, or MERLOT.
- Do not create a reference or in-text citation for a whole website. To mention a website in general, and not any particular information on that site, provide the name of the website in the text and include the URL in parentheses. For example, you might mention that you used a website to create a survey.
The following supplemental example references are mention in the Publication Manual:
- retracted journal or magazine article
- edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)
- edition of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD)
- religious work
- annotated religious work
Archival document and collections are not presented in the APA Publication Manual, Seventh Edition . This content is available only on the APA Style website . This guidance has been expanded from the 6th edition.
Archival sources include letters, unpublished manuscripts, limited-circulation brochures and pamphlets, in-house institutional and corporate documents, clippings, and other documents, as well as such nontextual materials as photographs and apparatus, that are in the personal possession of an author, form part of an institutional collection, or are stored in an archive such as the Archives of the History of American Psychology at the University of Akron or the APA Archives. For any documents like these that are available on the open web or via a database (subscription or nonsubscription), follow the reference templates shown in Chapter 10 of the Publication Manual.
The general format for the reference for an archival work includes the author, date, title, and source. The reference examples shown on this page may be modified for collections requiring more or less specific information to locate materials, for different types of collections, or for additional descriptive information (e.g., a translation of a letter). Authors may choose to list correspondence from their own personal collections, but correspondence from other private collections should be listed only with the permission of the collector.
Keep in mind the following principles when creating references to archival documents and collections:
- As with any reference, the purpose is to direct readers to the source, despite the fact that only a single copy of the document may be available and readers may have some difficulty actually seeing a copy.
- Include as much information as is needed to help locate the item with reasonable ease within the repository. For items from collections with detailed finding aids, the name of the collection may be sufficient; for items from collections without finding aids, more information (e.g., call number, box number, file name or number) may be necessary to help locate the item.
- If several letters are cited from the same collection, list the collection as a reference and provide specific identifying information (author, recipient, and date) for each letter in the in-text citations (see Example 3).
- Use square brackets to indicate information that does not appear on the document.
- Use “ca.” (circa) to indicate an estimated date (see Example 5).
- Use italics for titles of archival documents and collections; if the work does not have a title, provide a description in square brackets without italics.
- Separate elements of the source (e.g., the name of a repository, library, university or archive, and the location of the university or archive) with commas. End the source with a period.
- If a publication of limited circulation is available in libraries, the reference may be formatted as usual for published material, without the archival source.
- Note that private letters (vs. those in an archive or repository) are considered personal communications and cited in the text only.

1. Letter from a repository
Frank, L. K. (1935, February 4). [Letter to Robert M. Ogden]. Rockefeller Archive Center (GEB Series 1.3, Box 371, Folder 3877), Tarrytown, NY, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Frank, 1935)
- Narrative citation: Frank (1935)
- Because the letter does not have a title, provide a description in square brackets.
2. Letter from a private collection
Zacharius, G. P. (1953, August 15). [Letter to William Rickel (W. Rickel, Trans.)]. Copy in possession of Hendrika Vande Kemp.
- Parenthetical citation: (Zacharius, 1953)
- Narrative citation: Zacharius (1953)
- In this example, Hendrika Vande Kemp is either the author of the paper or the author of the paper has received permission from Hendrika Vande Kemp to cite a letter in Vande Kemp’s private collection in this way. Otherwise, cite a private letter as a personal communication .
3. Collection of letters from an archive
Allport, G. W. (1930–1967). Correspondence. Gordon W. Allport Papers (HUG 4118.10), Harvard University Archives, Cambridge, MA, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Allport, 1930–1967)
- Narrative citation: Allport (1930–1967)
To cite specific letters in the text, provide the author and range of years as shown in the reference list entry, plus details about who wrote the specific letter to whom and when the specific letter was written.
- Parenthetical citation: (Allport, 1930–1967, G. Boring to Allport, December 26, 1937)
- Narrative citation: Allport (1930–1967, Allport to G. Boring, March 1, 1939)
- Use the parenthetical citation format to cite a letter that E. G. Boring wrote to Allport because Allport is the author in the reference. Use either the parenthetical or narrative citation format to cite letters that Allport wrote.
4. Unpublished papers, lectures from an archive or personal collection
Berliner, A. (1959). Notes for a lecture on reminiscences of Wundt and Leipzig. Anna Berliner Memoirs (Box M50), Archives of the History of American Psychology, University of Akron, Akron, OH, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Berliner, 1959)
- Narrative citation: Berliner (1959)
5. Archival/historical source for which the author and/or date is known or is reasonably certain but not stated on the document
Allport, A. (presumed). (ca. 1937). Marion Taylor today—by the biographer [Unpublished manuscript]. Marion Taylor Papers, Schlesinger Library, Radcliffe College, Cambridge, MA, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Allport, ca. 1937)
- Narrative citation: Allport (ca. 1937)
- Because the author is reasonably certain but not stated on the document, place the word “presumed” in parentheses after the name, followed by a period.
- Because the date is reasonably certain but not stated on the document, the abbreviation “ca.” (which stands for “circa”) appears before the year in parentheses.
6. Archival source with group author
Subcommittee on Mental Hygiene Personnel in School Programs. (1949, November 5–6). Meeting of Subcommittee on Mental Hygiene Personnel in School Programs. David Shakow Papers (M1360), Archives of the History of American Psychology, University of Akron, Akron, OH, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Subcommittee on Mental Hygiene Personnel in School Programs, 1949)
- Narrative citation: Subcommittee on Mental Hygiene Personnel in School Programs (1949)
7. Interview recorded and available in an archive
Smith, M. B. (1989, August 12). Interview by C. A. Kiesler [Tape recording]. President’s Oral History Project, American Psychological Association, APA Archives, Washington, DC, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Smith, 1989)
- Narrative citation: Smith (1989)
- For interviews and oral histories recorded in an archive, list the interviewee as the author. Include the interviewer’s name in the description.
8. Transcription of a recorded interview, no recording available
Sparkman, C. F. (1973). An oral history with Dr. Colley F. Sparkman/Interviewer: Orley B. Caudill. Mississippi Oral History Program (Vol. 289), University of Southern Mississippi, Hattiesburg, MS, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Sparkman, 1973)
- Narrative citation: Sparkman (1973)
9. Newspaper article clipping, historical, in personal collection
Psychoanalysis institute to open. (1948, September 18). [Clipping from an unidentified Dayton, OH, United States, newspaper]. Copy in possession of author.
- Parenthetical citation: (“Psychoanalysis Institute to Open,” 1948)
- Narrative citation: “Psychoanalysis Institute to Open” (1948)
- Use this format only if you are the person who is in possession of the newspaper clipping.
10. Historical publication of limited circulation
Sci-Art Publishers. (1935). Sci-Art publications [Brochure]. Roback Papers (HUGFP 104.50, Box 2, Folder “Miscellaneous Psychological Materials”), Harvard University Archives, Cambridge, MA, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (Sci-Art Publishers, 1935)
- Narrative citation: Sci-Art Publishers (1935)
11. Archived photographs, no author and no title
[Photographs of Robert M. Yerkes]. (ca. 1917–1954). Robert Mearns Yerkes Papers (Box 137, Folder 2292), Manuscripts and Archives, Yale University Library, New Haven, CT, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: ([Photographs of Robert M. Yerkes], ca. 1917–1954)
- Narrative citation: [Photographs of Robert M. Yerkes] (ca. 1917–1954)
- Because the archived photographs do not have a title, provide a bracketed description instead.
- Because the archived photographs do not have an author, move the bracketed description to the author position of the reference.
12. Microfilm
U.S. Census Bureau. (1880). 1880 U.S. census: Defective, dependent, and delinquent classes schedule: Virginia [Microfilm]. NARA Microfilm Publication T1132 (Rolls 33–34), National Archives and Records Administration, Washington, DC, United States.
- Parenthetical citation: (U.S. Census Bureau, 1880)
- Narrative citation: U.S. Census Bureau (1880)
Read the full APA guidelines on citing ChatGPT
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
- Parenthetical citation: (OpenAI, 2023)
- Narrative citation: OpenAI (2023)
Author: The author of the model is OpenAI.
Date: The date is the year of the version you used. Following the template in Section 10.10, you need to include only the year, not the exact date. The version number provides the specific date information a reader might need.
Title: The name of the model is “ChatGPT,” so that serves as the title and is italicized in your reference, as shown in the template. Although OpenAI labels unique iterations (i.e., ChatGPT-3, ChatGPT-4), they are using “ChatGPT” as the general name of the model, with updates identified with version numbers.
The version number is included after the title in parentheses. The format for the version number in ChatGPT references includes the date because that is how OpenAI is labeling the versions. Different large language models or software might use different version numbering; use the version number in the format the author or publisher provides, which may be a numbering system (e.g., Version 2.0) or other methods.
Bracketed text is used in references for additional descriptions when they are needed to help a reader understand what’s being cited. References for a number of common sources, such as journal articles and books, do not include bracketed descriptions, but things outside of the typical peer-reviewed system often do. In the case of a reference for ChatGPT, provide the descriptor “Large language model” in square brackets. OpenAI describes ChatGPT-4 as a “large multimodal model,” so that description may be provided instead if you are using ChatGPT-4. Later versions and software or models from other companies may need different descriptions, based on how the publishers describe the model. The goal of the bracketed text is to briefly describe the kind of model to your reader.
Source: When the publisher name and the author name are the same, do not repeat the publisher name in the source element of the reference, and move directly to the URL. This is the case for ChatGPT. The URL for ChatGPT is https://chat.openai.com/chat . For other models or products for which you may create a reference, use the URL that links as directly as possible to the source (i.e., the page where you can access the model, not the publisher’s homepage).
What to include and what to exclude
Works included in a reference list.
The reference list provides a reliable way for readers to identify and locate the works cited in a paper. APA Style papers generally include reference lists, not bibliographies.
In general, each work cited in the text must appear in the reference list, and each work in the reference list must be cited in the text. Check your work carefully before submitting your manuscript or course assignment to ensure no works cited in the text are missing from the reference list and vice versa, with only the following exceptions.
Works Excluded From a Reference List
There are a few kinds of works that are not included in a reference list. Usually a work is not included because readers cannot recover it or because the mention is so broad that readers do not need a reference list entry to understand the use.
Information on works included in a reference list is covered in Sections 2.12 and 8.4 of the APA Publication Manual, Seventh Edition
*This guidance has been expanded from the 6th edition.*
- Personal communications such as emails, phone calls, or text messages are cited in the text only, not in the reference list, because readers cannot retrieve personal communications.
- General mentions of whole websites, whole periodicals, and common software and apps in the text do not require in-text citations or reference list entries because the use is broad and the source is familiar.
- The source of an epigraph does not usually appear in the reference list unless the work is a scholarly book or journal. For example, if you open the paper with an inspirational quotation by a famous person, the source of the quotation does not appear in the reference list because the quotation is meant to set the stage for the work, not substantiate a key point.
- Quotations from research participants in a study you conducted can be presented and discussed in the text but do not need citations or reference list entries. Citations and reference list entries are not necessary because the quotations are part of your original research. They could also compromise participants’ confidentiality, which is an ethical violation.
- References included in a meta-analysis, which are marked with an asterisk in the reference list, may be cited in the text (or not) at the author’s discretion. This exception is relevant only to authors who are conducting a meta-analysis.
DOIs and URLs
The DOI or URL is the final component of a reference list entry. Because so much scholarship is available and/or retrieved online, most reference list entries end with either a DOI or a URL.
- A DOI is a unique alphanumeric string that identifies content and provides a persistent link to its location on the internet. DOIs can be found in database records and the reference lists of published works.
- A URL specifies the location of digital information on the internet and can be found in the address bar of your internet browser. URLs in references should link directly to the cited work when possible.
Follow these guidelines for including DOIs and URLs in references:
- Include a DOI for all works that have a DOI, regardless of whether you used the online version or the print version.
- If a print work does not have a DOI, do not include any DOI or URL in the reference.
- If an online work has both a DOI and a URL, include only the DOI.
- For works without DOIs from websites (not including academic research databases), provide a URL in the reference (as long as the URL will work for readers).
- For works without DOIs from most academic research databases , do not include a URL or database information in the reference because these works are widely available. The reference should be the same as the reference for a print version of the work.
- For works from databases that publish original, proprietary material available only in that database (such as the UpToDate database) or for works of limited circulation in databases (such as monographs in the ERIC database), include the name of the database or archive and the URL of the work. If the URL requires a login or is session-specific (meaning it will not resolve for readers), provide the URL of the database or archive home page or login page instead of the URL for the work. See the page on including database information in references for more information.
- If the URL is no longer working or no longer provides readers access to the content you intend to cite, follow the guidance for works with no source .
- Other alphanumeric identifiers such as the International Standard Book Number (ISBN) and the International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) are not included in APA Style references.
Follow these guidelines to format DOIs and URLs:
- Present both DOIs and URLs as hyperlinks (i.e., beginning with “http:” or “https:”).
- Because a hyperlink leads readers directly to the content, it is not necessary to include the words “Retrieved from” or “Accessed from” before a DOI or URL.
- It is acceptable to use either the default display settings for hyperlinks in your word-processing program (e.g., usually blue font, underlined) or plain text that is not underlined.
- Leave links live if the work is to be published or read online.
- Follow the current recommendations of the International DOI Foundation to format DOIs in the reference list, which as of this publication is as follows:
https://doi.org/ xxxxx
- The string “https://doi.org/” is a way of presenting a DOI as a link, and “xxxxx” refers to the DOI number.
- The preferred format of the DOI has changed over time. Although older works use previous formats (e.g., “http:/dx.doi.org/” or “doi:” or “DOI:” before the DOI number), in your reference list, standardize DOIs into the current preferred format for all entries. For example, use https://doi.org/10.1037/a0040251 in your reference even though that article, published in 2016, presented the number in an older format.
- Copy and paste the DOI or URL from your web browser directly into your reference list to avoid transcription errors. Do not change the capitalization or punctuation of the DOI or URL. Do not add line breaks manually to the hyperlink; it is acceptable if your word-processing program automatically adds a break or moves the hyperlink to its own line.
- Do not add a period after the DOI or URL because this may interfere with link functionality.
When a DOI or URL is long or complex, you may use shortDOIs or shortened URLs if desired.
- Use the shortDOI service provided by the International DOI Foundation to create shortDOIs. A work can have only one DOI and only one shortDOI; the shortDOI service will either produce a new shortDOI for a work that has never had one or retrieve an existing shortDOI.
- Some websites provide their own branded shortened URLs, and independent URL shortening services are available as well. Any shortened URL is acceptable in a reference as long as you check the link to ensure that it takes you to the correct location.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Paper Format >>
- Last Updated: Jul 15, 2024 10:05 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/apa
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / APA Citation Examples
APA Citation Examples
This guide will show you how to structure APA citations according to the Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th edition) and will show you example citations for different source types. For information on other APA topics—such as formatting your paper, creating a title page, etc.—check out the EasyBib APA format guide. It even has an example paper.
Table of Contents
- The Basics of APA Citations
- References vs. Citations
Formatting Author Information
- Formatting Titles and Dates
Citation Examples
- Citing Books
- Citing Journals and Articles
- Citing Various Digital Sources
- Citing Various Media Sources
- Citing Additional Sources
- APA Citation Template
Troubleshooting
The basics of apa.
We’re going to start from the beginning for all of you newbies out there, or for those of you looking for a refresher.
APA is an abbreviation which stands for American Psychological Association. This is a massive organization, responsible for creating and sharing psychology-related publications, research, and databases.
Basically, they keep psychologists and other similar roles in the loop with what’s happening in the world of psychology. With close to 120,000 members, this is THE leading world organization related to psychology.They are not officially associated with this guide, but the information here talks about their citing format and rules in depth.
Why were APA citations created and why did my teacher ask me to use this style?
Are you scratching your head, wondering what is APA style is and how this all relates to your research project? To make a long story short, the American Psychological Association did something really cool. Back in 1952, they created a way for ALL psychology researchers to structure their citations. This standard method did three things:
- Psychology researchers were all able to display the sources they used in a systematic way.
- Readers were able to easily understand the information shown in citations.
- There was enough information displayed in the citations for readers to go out and find the exact sources on their own.
APA citations were such a hit, they were so good, that other science disciplines soon adopted the citation format as well. In fact, other disciplines outside of the science world use APA style today, too. So, whether you’re creating a psychology-related research project or not, there’s a good chance you were asked to create your citations in APA style.
Currently in its 7th edition, the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is one of the most frequently used style guides for academic writing today!
With the 7th edition just coming onto the scene in 2020, the American Psychological Association does not expect to see widespread usage of the 7th edition until later in 2020. This is why you should always double-check with your teacher on whether they want you to use the 6th edition or the 7th edition for your projects.
Click here for more basics on this style.
Another widely used style is MLA format . Believe it or not, there are thousands of other styles, so perhaps your teacher or professor requested a completely different one. If you’re in that boat, head to EasyBib.com to check out more styles . While you’re at it, poke around and check out our APA reference generator. It may be just what you’re looking for.
References vs. Citations – What’s the difference?
References and citations are two terms that are thrown around a lot and quite often mean the same thing. A reference, or citation, shows the reader that a piece of information originated elsewhere. But, along came APA and decided to throw a curveball at us. In APA, the two terms have two different meanings.
A citation is found in the actual writing of an APA research paper.
In-text citation example:
“Lecture-rooms are numerous and large, but the number of young people who genuinely thirst after truth and justice is small” (Einstein, 2007, p. 5).
A reference is found on the reference page, which is the last page of a research paper.
Reference Page Example:
Einstein, A. (2007). The world as I see it. Google Books. https://books.google.com/books?id=aNKOo94tO6cC&source=gbs_navlinks_s (Original work published 1934)
The information included in an APA citation is just a snapshot of the information found in the full reference. For more information on when it’s appropriate to include a citation in your paper, head to section 8.1-8.10 of the Publication manual.
Now, what makes things even trickier is that most teachers and professors use the term “APA citations” when they’re actually talking about the full references. How many times have you heard your teacher say, “Make sure you have your citations on the last page!”
Eek! So, to stay on the same page as your teacher, this guide shows you how to make references for an APA reference page, but we’re calling the page “APA Citations.” Someone’s gotta give in, right? Looks like it’s us.
If you’re looking for a quick read on the citations found in the body of the paper, check out our APA Parenthetical Citation page. It’s just one of the many free APA citation guides available on EasyBib.com. Need an APA citation generator? You can find one at EasyBib.com as well!
If you’re looking for help with the writing or grammar in your paper, check out our research , pronoun , and determiner pages. We have tons of other free grammar pages too!
A rundown on references
Before we get into the nitty-gritty details on how to structure references for your APA paper, let’s get one more quick piece of information off the table.
References are added to research papers and projects only when a source is included in the writing itself.
We don’t add references to a reference page if we want to simply suggest other, similar titles. No! We create references when an actual piece of information from another source is added into the project.
Does your paper include a piece of data from a report? Great! You copied a line of text from a case study and put it in your project (with quotation marks around it)? Perfect! You included a bar graph you found in a brochure? Fantastic! Make sure you create an APA citation in the text of your paper and include the reference on the final page.
The only exception to the above rule is if you’re creating an “annotated bibliography.” For more on that, check out our APA annotated bibliography page.
In case you were wondering, the same goes for MLA in-text & parenthetical citations on the MLA works cited page.
Ready to get started? The next section of the guide is going to explain, step-by-step, how to structure every nook and cranny of your references.
But, if you’re dreaming of an APA citation maker to help make the pain go away from building your references from scratch, you’re in luck. EasyBib.com has an APA citation maker! In just a few clicks, our technology structures and styles each and every APA citation for you. If you don’t know much about it, head to the EasyBib homepage to learn more.
While you’re at it, try out our APA cover page maker, found on the main page as well!
Fundamentals of an APA citation
This entire section goes into detail on each component of a reference. If you’re looking to learn how to style the names of the authors, the title, publishing information, and other aspects related to the reference, this section is for you!
If you want to skip the small talk and see an APA style paper example, go to the “Citation Resources” menu on this page and select “APA Format Guide.” It includes a title page example, an APA paper example, and an APA reference page example.It’s all there for you and the best part about it is it’s free! Do yourself a favor and take a peek at it now!
Author information
The very first piece of information in most references is the author’s name(s). We say “most,” because some sources may not have an author (such as websites, the Bible…). If your source doesn’t have an author, do not include any information about an author in your reference.
Citing a Source with 1 Author
Apa structure:.
Last name of the Author, First initial. Middle initial.
APA Example:
To see some examples, scroll down to the bottom half of this page.
Citing a Source with 2 Authors
Does your source have two authors? Do not put the names in alphabetical order. They should be written in the order they’re displayed on the source.
Last name of the 1st listed Author, First Initial. Middle Initial., & Last name of the 2nd listed Author, First initial. Middle initial.
Doe, J. B. & Chen, W. I.
For an example of a reference with two authors according to the 7th edition of the Publication manual , scroll down to the “Journal Articles found in Print” section, or check out section 9.7-9.12 in the Publication manual.
Citing a Source with 3 to 20 Authors
Does your source have three to twenty authors? The American Psychological Association has made some updates on how to list multiple authors in your citations. If you have between three to twenty authors, list all the authors names (Last Name, Initials). Put them in the same order they’re listed in the source. Commas separate names, and put an ampersand right before the last name.
Bos, G., Hajek, S., Kogman-Appel, K., & Mensching, G. (2019). A Glossary of Latin and Italo-Romance Medico-Botanical Terms in Hebrew Characters on an Illustrated Manuscript Page (Ms. Oxford, Bodleian Opp. 688, fol. 177b). Aleph: Historical Studies in Science and Judaism 19 (2), 169-199. https://www.muse.jhu.edu/article/747571
Citing a Source with 21+ Authors
If your source has over twenty authors, list the last name and initials of the first 19 authors, placing a comma between each name. After the name of the 19th author, use an ellipsis in place of the remaining authors’ names. Then, list the final author’s name in front of it.
Here’s a formatting example for 21+ names using the U.S. presidents (this is NOT a reference example):
Washington, G., Adams, J., Jefferson, T., Madison, J., Monroe, J., Adams, J. Q., Jackson, A., Van Buren, M., Harrison, W. H., Tyler, J., Polk, J., Taylor, Z., Fillmore, M., Pierce, F., Buchanan, J., Lincoln, A., Johnson, A., Grant, U. S., Hayes, R. B., … Trump, D. J.
Citing an Author that is an organization or company
If your source is written by an organization or company:
Some sources are written and released by companies, not necessarily individual people. For example, most brochures at museums only display the institution’s name. Advertisements also only show the company’s name. If the source you’re attempting to cite only shows a group or organization’s name, place it in the reference in the place you’d normally include an individual person’s name.
Write out the name of the group in full; do not use abbreviations. For example, it may seem okay to use USDA, but APA writing style prefers you write out United States Department of Agriculture.
If you’re looking for information on how to style your own name in APA headings, find the example paper on EasyBib.com.
Formatting Titles & Dates
Formatting the date of publication.
The date the source was published is the next item shown in a reference. It’s directly after the author’s name.
For the majority of sources, include only the year in parentheses.
If you’re citing an article in a magazine, include the year and the month.
Peterzell, J. (1990, April). Better late than never. Time, 135 (17), 20–21.
Check out the examples towards the bottom of the page, or head to sections 9.13-9.17 of the Publication manual to see how dates are displayed.
Title rules and capitalization
Titles are the next piece of information shown in a reference. Titles are often tricky for people to style. Students often wonder, “Should I type out the title as it’s shown on the source?” “Should the title be written in italics or underlined?” Here are the answers to (hopefully) all of your title-related questions:
Which letters are capitalized?
Most titles are written with a capital letter in these places:
- At the beginning of the title
- At the beginning of a proper noun
- At the beginning of the subtitle
It may be tempting to write the title as you see it shown on the source, or with capital letters at the beginning of every important word, but that’s not how APA referencing does it.
Here are a few examples of proper lettering:
- A star is born
- Spider-Man: Into the spiderverse
- Harry Potter and the deathly hallows
The only source types that are written with a capital letter at the beginning of every important word are periodicals. Some examples include the titles of newspapers, journals, and magazines.
- The New York Times
- School Library Journal,
How should I style the title?
- Anything that stands alone is written in italics. When we say “stands alone,” we mean it isn’t part of a larger collection. Most books are a single source, so they’re written in italics. Other examples include movies, brochures, dissertations, and music albums.
- Sources that are part of a collection are written without italics. Website pages, journal articles, chapters in books, and individual songs (from an album) are written without italics.
- Remember, the styling information above is for the APA reference page only! Citations in the text of the paper are styled differently. If you need to see a full APA sample paper, check out the other resources on EasyBib.com!
Check out some of the examples below to see how the titles are typed out and styled. You can also head to section 9.18-9.22 of the Publication Manual for more details
If it’s not the actual title, but an APA title page for your paper that you need help with, check out the Title Page APA creator on the homepage of EasyBib.com! Or, check out the main guide for this style, which includes an APA cover page template.
Additional information about a source
It can be difficult to understand a source type just by looking at an APA style citation. Sometimes it isn’t clear if you’re looking at a citation for a presentation, a blog post, lecture notes, or a completely different source type.
To clear up any confusion for your reader, you can include additional information directly after the title. This additional information about the source type is written in brackets with the first word having a capital letter.
Wilson, T. V. & Frey, H. (2019, May 13). Godzilla: The start of his story [Audio podcast]. iHeart Radio. https://www.missedinhistory.com/podcasts/godzilla-the-start-of-his-story.htm
Thanks to the information in the brackets, the reader can easily see that the source is an audio podcast.
Check out the various examples towards the bottom of this page.
Publication information
Publication information includes the name of the publisher. In most cases, the publication information is only included for print sources. Check out the book reference below to see the publication information in action.
Citing Books in APA
You’ll find plenty of source types below. If you don’t see what you’re looking for, try out our APA reference generator on EasyBib.com! Or, here’s a great informative site we like. If you’d like to see a full APA sample paper, take a glance at the main citation guide for this style on EasyBib.com.
Citing books in print in APA
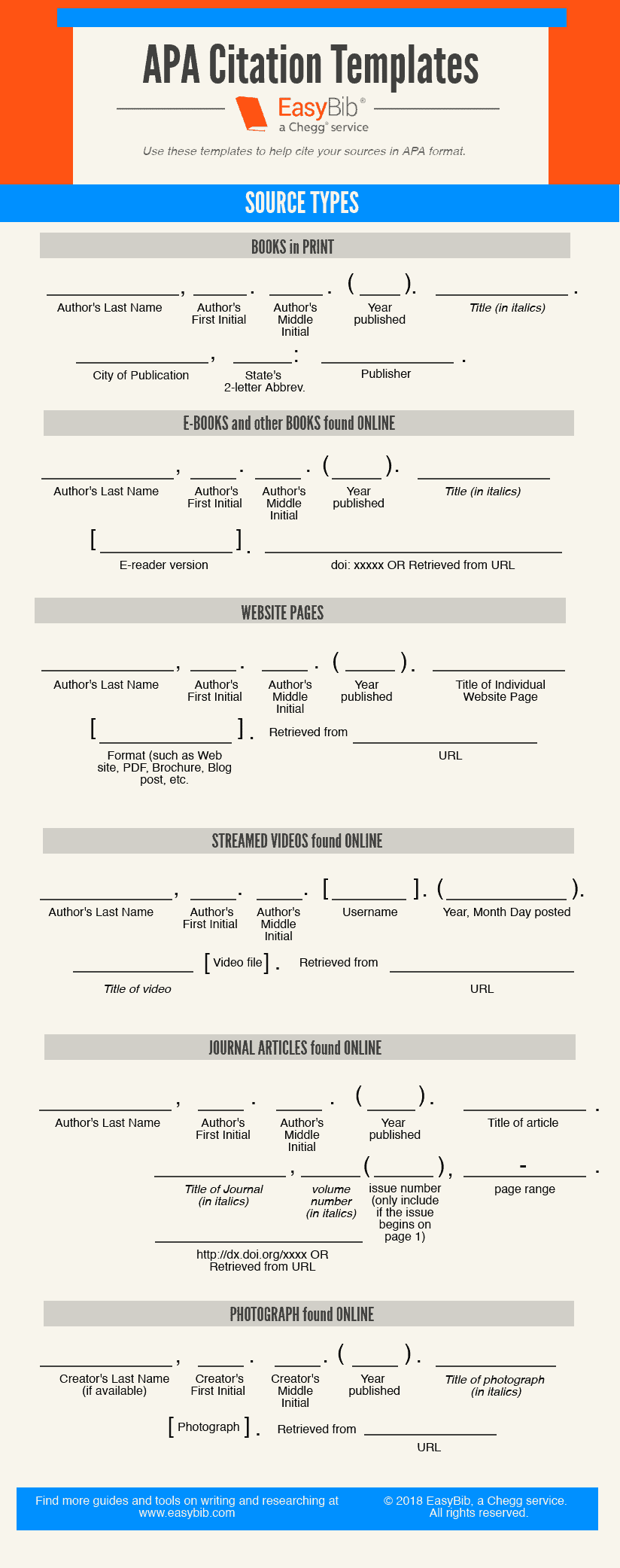
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of the book . Publisher.
Gaiman, N. (1996). Neverwhere . HarperCollins.
Looking for more examples? Check out our APA book citation page.
Citing a chapter in a print book in APA
A reference page APA citation for a chapter in a print book is styled the same way as the entire book. It is not necessary to showcase or display the individual chapter. However, in the text of the paper, the chapter is shown like this: (Author’s Last name, Year, Chapter #).
Citing a chapter in an edited book in print in APA
An edited book is one that was compiled by an author. Each individual chapter, or section, is written by someone else. Since you’re probably citing the specific chapter, rather than the whole entire book, place the name of the chapter’s author in the first position.
Chapter Author’s Last Name, F. M. (Year published). Chapter title. In F. M. Editor’s Last Name (Ed.), Title of book (Xrd ed., pp. x-x). Publisher.
Alexander, G. R. (2015). Multicultural education in nursing. In D. M. Billings, & J. A. Halstead (Eds.), Teaching in nursing: A guide for faculty (5th ed., pp. 263-281). Google Books. https://books.google.com/books?id=YxzmCgAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=edited+book&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwja47-0kL_iAhUV7XMBHXzQBxAQ6AEIODAD#v=onepage&q&f=false
Citing an e-book in APA
To cite an eBook, cite it the same way as you would a print book.
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of book . Publisher. URL
Alcott, L. M. (1905). Under the lilacs. Little, Brown, and Company. https://archive.org/stream/underlilacs00alco2?ref=ol#page/n9/mode/2up
If you’re using the EasyBib APA citation generator to cite your e-books, click on the “book” source type.
Gaiman, N. (2009). Coraline . HarperCollins. https://amzn.to/3cQqXAL
If you’re using EasyBib.com’s APA citation generator to cite your e-books, click on the “book” source type.
Wondering what to do if you’re using a book that was reprinted? Check out the example of Einstein’s book, found towards the top of this guide.
Citing The Bible in APA
Since the bible is considered a “classical work,” and widely known, it is not necessary to create a full reference. Only include a citation in the text of the paper.
Two items need to be included:
- The title and version of the source, such as the New Living Bible
- The names, verses, chapters, or any numbers associated with the section you’re referring to.
“Then the king asked her, “What do you want, Esther? What is your request? I will give it to you, even if it’s half the kingdom” (Esther 5:5 New Living Translation).
Citing Journals and Articles in APA
Citing journal articles found in print in apa.
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of journal article. Title of Journal, Volume (Issue), page range.
Reeve, A. H., Fjeldsa, J., & Borregaard, M. K. (2018). Ecologically flexible endemics dominate Indo-Pacific bird communities. Journal of Biogeography, 45 (8), 1980-1982.
Your APA style paper is easy to piece together with the tools and services on EasyBib.com. Try out our APA citation machine, which structures your references in just a few clicks. If you’re looking for the perfect APA cover page, give our APA title page maker a whirl.
Citing journal articles found online in APA
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year published). Title of journal article. Title of Journal, Volume (Issue), page range. //dx.doi.org/10xxxxxxx
Reeve, A. H., Fjeldsa, J., & Borregaard, M. K. (2018). Ecologically flexible endemics dominate Indo-Pacific bird communities. Journal of Biogeography, 45 (8), 1980-1982. //dx.doi.org/10.1111/jbi.13384
For more on journals, take a peek at our APA journal page. Or, make your citations in just a few clicks with our APA citation generator.
Citing newspaper articles in print in APA
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day of Publication). Article’s title. Title of Newspaper, pp. xx-xx.
Boutilier, A. (2019, May 29). Facebook won’t pull fake content for election: Official says it’s not company’s role to draw line as MPs blast Zuckerberg for not testifying. Toronto Star, p. 1.
Citing newspaper articles found on the Internet in APA
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day of Publication). Article’s title. Title of Newspaper . URL
Boutilier, A. (2019, May 28). Facebook refuses to remove false content during Canadian election. The Star . https://www.thestar.com/news/canada/2019/05/28/facebook-wont-remove-doctored-content-during-canadian-election.html
Kale, S. (2020, March 9). How to keep your hands clean – without getting dry skin. The Guardian . https://www.theguardian.com/society/shortcuts/2020/mar/09/how-to-keep-your- hands-clean-without-getting-dry-skin
Citing magazines read in print in APA
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year, Month or Season). Title of article. Title of Magazine, Volume (Issue), page range.
Freedman, A. (2019, June). How to choose a gaming laptop: You can play your game and take it with you. TechLife Australia, 90, 78-81.
Citing magazine articles read over the internet in APA
Author’s Last Name, F. M. (Year, Month). Title of magazine article. Title of Magazine, Volume (Issue), page range. URL
Savage, P. (2019, May). Double dragon: Yakuza Kiwami 2 is a return to form for the singular crime series. PC Gamer , 319, 80. https://www-pressreader-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/usa/pc-gamer-us/20190521
Citing a Source on the Internet in APA
Citing digital sources in this style is much easier than other styles. If you’re wondering why, it’s because a lot of information isn’t included in the reference.
For most digital sources, only five items are usually needed:
- The name of the author
- The date the source was published
- The title of the source
- The medium (blog post, audio file, pdf, etc.)
- The website address
Here’s some more information related to web content:
- Only include the medium if it’s unique or if it will help the reader understand the source type.
- Include the website address at the end of the citation.
- Do not place a period at the end of the website address.
Have a digital source? Need to cite APA? Check out some of the examples below.
Citing a blog in APA
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Day of posting). Title of post. Blog or Website name. URL
Chockrek, E. (2019, May 29). 7 summer activities that help boost your college applications. EasyBib. https://www.easybib.com/guides/7-summer-activities-that-help-boost-your-college-applications/
See another example on our APA citation website page.
Citing social media in APA
Here’s the APA template for most social media platforms:
Last name, F. M. [Username]. (Year, Month Day of posting). Content of the post up to the first 20 words [Describe any attachment] [Tweet OR Facebook page OR Instagram photo OR Instagram post] . Site Name. URL
Lem, E. [@lemesther]. (2019, October 2). Spotted @Chegg promo celebration. Ladies who…”leopard.” Cheers to all the upcoming promos. #marketing #UEx. [Image attached [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/lemesther/status/1179549293289627650
If the name of the individual is unknown or unlisted on the profile (such as Lady Gaga), place the username first, without brackets
Ladygaga. (2019, May 20). I’m so proud of @momgerm for being asked to serve as Goodwill Ambassador for @WHO. The goal of @btwfoundation is [Image attached] [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/ladygaga/status/1130578727539052544
If there are emojis, try to recreate them or describe them in brackets.
Hawaii Volcanoes NPS [@Volcanoes_NPS]. (2020, February 26). Half the park is after dark! [flashlight emoji] In addition to dark night skies, evening in the park provides a great chance. [Image attached] [Tweet]. Twitter. https://twitter.com/Volcanoes_NPS/status/1232776372801589248
For more about citing social media, head to section 10.15 of the Publication manual.
Citing online encyclopedias & dictionaries – Group author
If you conducted or watched a personal interview and the transcript or audio is not available for the reader, then there really isn’t any point to create a full reference. These types of sources are not recoverable and the reader would be unable to find the interview on their own. Instead, only create a citation in the text of the paper. Use the first initial, middle initial, and last name of the person being interviewed, along with “personal communication,” and the date of the interview.
Institution or organization name. (n.d.). Entry title. In Title of Website or reference . Retrieved Month Day, Year, from URL
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Doleful. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary. Retrieved March 1, 2020, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/doleful
Citing online encyclopedias & dictionaries – Known author
If there is a known author, cite the source this way:
Last name, F. M. (Date published). Entry title. In F. M. Last name (ed.), In Title of Website or reference . Retrieved Month Day, Year, from URL
Mann, M. E. & Selin, H. (n.d.). Global warming. In Encyclopaedia Britannica . Retrieved March 1, 2020, from https://www.britannica.com/science/global-warming
Citing Wikipedia
Cite a Wikipedia page just like a normal webpage, but use an archived version. Go to the “View history” tab at the top of a Wikipedia page to find these archived versions, their publishing date, and their URL.
Article title. (Year, Month Day). In Wikipedia . URL
Kinetic energy (2019, December 27). In Wikipedia . https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Kinetic_energy&oldid=932724138
If you want to learn how to cite websites in MLA , click on the link.
An APA generator is available to you on EasyBib.com Take the stress out of building the references for your APA style paper and try it out!
While you’re at it, it may be helpful to take a glance at our APA paper template. It can be found on the EasyBib Writing Center page. You can use the APA paper example to help structure your own APA title page and paper.
Citing Media Sources in APA
Citing a song or music listened to online in apa.
Modern songs (e.g., that song you heard on the radio this morning) should list the name of the recording artist’s name. Classical music lists the song’s composer (e.g., think Mozart, Beethoven, etc.).
Note: include a URL in the reference if that location is the only means of retrieval (like if they only post their music to SoundCloud or on their own specific website). If the song is available across multiple platforms, no URL is needed.
APA Structure for a modern song:
Artist’s Last Name, F. M. (Year published). Song’s title [Song]. On Title of album . Publisher(s).
Grande, A. (2019). 7 rings [Song]. On thank u, next . Republic Records.
APA Structure for a classical song:
Artist’s Last Name, F. M. (Year published). Song’s title [Song recorded by Artist’s Name]. On Title of album . Publisher.
Bach, J. S. (1997). Toccata and Fugue in D minor [Song recorded by William McVicker]. On Great organ classics. Sony Music Entertainment UK Limited.
Sheet music in APA
To cite APA sheet music, cite it exactly the same as a book. If it’s found online, cite it as a website.
Citing streamed videos in APA
Use this format if you’re citing a video found online (such as an APA citation for a YouTube video ).
Person who posted the video’s Last Name, F. M. [Username]. (Year, Month Day of posting or publishing). Video’s title [Video]. URL
Vliegenthart, S. [booksandquills]. (2018, December 3). Books from uni we didn’t hate [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9G52GCgpEZg
If the name of the individual isn’t available, start with the username, and remove the brackets.
APA Examples:
Chegg. (2018, November 15). One common grammar error to avoid [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5Bfx50f853g
Maroon 5. (2018, May 30). Girls like you ft. Cardi B [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/aJOTlE1K90k
If you’re in need of an APA citation machine to do the work for you, check out the homepage on EasyBib.com! We even have a free Title Page APA creator on the main page as well!
Citing a film or movie in APA
Director’s Last Name. F. M. (Director). (Year published). Film’s title [Film]. Publisher(s) or URL
Gerwig, G. (Director). (2017). Lady bird [Video]. IAC Films; Scott Rudin Productions.
Citing Additional Sources in APA
Citing a published thesis or dissertation from a database in apa.
Author’s Last Name, F. M. (Year created). Thesis or Dissertation’s title [Master’s thesis OR Doctoral dissertation, Name of Institution]. Name of database or archive.
Schluckebier, M. E. (2013). Dreams worth pursuing: How college students develop and articulate their purpose in life [Doctoral dissertation, University of Iowa]. ERIC.
If you’re looking for an APA citation builder to do the work for you, check out EasyBib.com’s APA generator!
Citing a conference paper in APA
Author’s Last name, F. M. (Year, Month Days of Conference). Title of conference paper [Type of presentation]. Conference Name, Location. URL or DOI.
Fowle, M. (2018, September). The entrepreneurial dream: Happiness, depression, and freedom [Conference presentation]. European Conference on Innovation and Entrepreunership, Aviero, Portugal.
Citing an interview in APA
W. I. Ikemoto (personal communication, June 2, 2019)
If the interview is recoverable, include the full reference on the final page of the project. If the interview was found in a magazine, use the magazine structure. If the interview was read on a blog, use the blog structure. Look for the APA headings above that match your specific source type.
Don’t forget, our APA citation machine structures pretty much everything for you. Find it on EasyBib.com’s homepage and give our APA citation generator a try.
Didn’t find what you needed? Still a bit confused? Learn more here . You can also take the guesswork out of making your references with our handy APA citation generator, found at the top of this page.
Putting it All Together
You’ve structured your sources correctly, right? You have the periods, italics, and commas where they belong? Capital letters where they’re supposed to be? Great! You’re almost through! The last step is organizing your citations properly on the page. For easy to follow, in-depth instructions on structuring the last page in your project, check out our APA reference page . If you’d like to see a sample APA paper, check out the main guide for this style on EasyBib.com!
Before you hit submit, make sure you run your paper through our plagiarism checker . It checks for instances of accidental plagiarism and scans for spelling and grammatical errors. Even if you think you have every verb , adverb , or interjection where it belongs, you may be surprised with what our innovative technology suggests.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
Solution #1: How to cite a photo with no creator, date, or title in APA
- Describe the photo and place brackets around it.
- Add “n.d” with parentheses around it.
- List where the reference was found without italics.
- Follow with the URL information of where you found the photo if it was found online.
Example of a photo citation with no creator, date, or title
[Photograph of two hens in a barn]. (n.d). Theoretical Prints. http://Theoretical_Prints.org/two-hypothetical-hens/
Solution #2: How to cite a dictionary entry in APA
Dictionary entry in print
- List the organization or the author’s name in last name, first name initial, and middle name initial (if there is one) with a period following.
- Use n.d if the date is not listed.
- List the name of the dictionary term. Capitalize the first letter and use a period after.
- Write “In” followed by the name of the dictionary used. The dictionary name should be italicized.
- In parentheses, write the volume abbreviated as “Vol.” followed by the volume number and page number. Add a period after it.
Examples for a printed dictionary entry citation
Hypothetical Association of Learning. (2014). Cake. In The Hypothetical Learner’s Dictionary (Vol. 2, p. 3).
Johnson, C. K. (2014). Cake. In The Hypothetical Learner’s Dictionary (Vol. 2, p. 3).
Dictionary entry from an online source
- Use “n.d” if the date is not listed.
- Write the name of the dictionary in italics and follow it with a period.
- Write “Retrieved” then the date you accessed the entry online in this format: Month Day, Year. End it with a comma.
- Write “from” and add the page URL.
Examples for an online dictionary entry citation
Hypothetical Association of Learning. (2014). Cake. In The Hypothetical Learner’s Dictionary. Retrieved November 7, 2021, from https;//dictionary.hypothetical.org/dictionary/English/cake
Johnson, C. K. (2014). Cake. In The Hypothetical Learner’s Dictionary. Retrieved November 7, 2021, from https;//dictionary.hypothetical.org/dictionary/English/cake
Solution #3: How to ensure that an auto-generated citation in APA style is correct
- Ensure that the correct number of people are accredited by counting the names in the source and the website citation.
- Ensure that all names are spelled correctly.
- If 2-20 authors are used, ensure that an ampersand is used before the last name.
- If more than twenty authors are used, ensure that an ellipsis is used before the final author.
- Check to make sure that the date is correct and that the month or year do not need to be adjusted.
- Generally, works cited as a whole, such as books, are written in italics, while shorter works that are part of a bigger work, such as a chapter in a book or articles from a periodical (e.g., journal, magazine, newspaper, etc.), are usually in regular font.
- The title of webpages are italicized, while the title of the site they are on is in regular font.
- Social media post citations use the written post content (up to 20 words) as the title. This “title” should be italicized.
- If using a chapter, make sure that the editor is accredited.
- If using an article, make sure that the journal number is italicized and that the volume number is in parentheses.
- Make sure that your links are active and that they bring you to the correct location. You may need to rewrite the link.
Published August 2, 2019. Updated March 10, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau . Michele Kirschenbaum is a dedicated school library media specialist and one of the in-house EasyBib librarians. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Go to www.easybib.com and follow the directions to create a citation. After you create a citation or citation list, you can choose APA as your citation style (default is MLA). APA is a premium style, so you will need a subscription or trial to EasyBib Plus in order to create citations in APA. Upgrade your account at https://www.easybib.com/upgrade .
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

APA Style (7th ed.)
- Cite: Why? When?
- Book, eBook, Dissertation
- Article or Report
- Business Sources
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- In-Text Citation
- Format Your Paper
American Psychological Association (APA) Style is used by writers in the social sciences:
Business, Communications, Education, Geography, Political Science, Psychology, Sociology & Anthropology, and Women's & Gender Studies
Editable Template Documents for Student Papers
- APA 7th ed. Template Document This is an APA format template document in Google Docs. Click on the link -- it will ask for you to make a new copy of the document, which you can save in your own Google Drive with your preferred privacy settings.
- APA 7th ed. Template Document A Microsoft Word document formatted correctly according to APA 7th edition.
- APA 7th ed. Annotated Bibliography template A Microsoft Word document formatted correctly for an annotated bibliography.
Example Student Paper
- APA Example Paper An annotated sample student paper from APA.
Printable Handouts & Tutorial
- Citing References: APA Style [PDF]
Get the Book
- << Previous: Cite: Why? When?
- Next: Book, eBook, Dissertation >>
- Last Updated: Aug 15, 2024 5:13 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uww.edu/apa
We apologize for any inconvenience as we update our site to a new look.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Reference List: Common Reference List Examples
Article (with doi).
Alvarez, E., & Tippins, S. (2019). Socialization agents that Puerto Rican college students use to make financial decisions. Journal of Social Change , 11 (1), 75–85. https://doi.org/10.5590/JOSC.2019.11.1.07
Laplante, J. P., & Nolin, C. (2014). Consultas and socially responsible investing in Guatemala: A case study examining Maya perspectives on the Indigenous right to free, prior, and informed consent. Society & Natural Resources , 27 , 231–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941920.2013.861554
Use the DOI number for the source whenever one is available. DOI stands for "digital object identifier," a number specific to the article that can help others locate the source. In APA 7, format the DOI as a web address. Active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list. Also see our Quick Answer FAQ, "Can I use the DOI format provided by library databases?"
Jerrentrup, A., Mueller, T., Glowalla, U., Herder, M., Henrichs, N., Neubauer, A., & Schaefer, J. R. (2018). Teaching medicine with the help of “Dr. House.” PLoS ONE , 13 (3), Article e0193972. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193972
For journal articles that are assigned article numbers rather than page ranges, include the article number in place of the page range.
For more on citing electronic resources, see Electronic Sources References .
Article (Without DOI)
Found in a common academic research database or in print.
Casler , T. (2020). Improving the graduate nursing experience through support on a social media platform. MEDSURG Nursing , 29 (2), 83–87.
If an article does not have a DOI and you retrieved it from a common academic research database through the university library, there is no need to include any additional electronic retrieval information. The reference list entry looks like the entry for a print copy of the article. (This format differs from APA 6 guidelines that recommended including the URL of a journal's homepage when the DOI was not available.) Note that APA 7 has additional guidance on reference list entries for articles found only in specific databases or archives such as Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, UpToDate, ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global, and university archives. See APA 7, Section 9.30 for more information.

Found on an Open Access Website
Eaton, T. V., & Akers, M. D. (2007). Whistleblowing and good governance. CPA Journal , 77 (6), 66–71. http://archives.cpajournal.com/2007/607/essentials/p58.htm
Provide the direct web address/URL to a journal article found on the open web, often on an open access journal's website. In APA 7, active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list.
Weinstein, J. A. (2010). Social change (3rd ed.). Rowman & Littlefield.
If the book has an edition number, include it in parentheses after the title of the book. If the book does not list any edition information, do not include an edition number. The edition number is not italicized.
American Nurses Association. (2015). Nursing: Scope and standards of practice (3rd ed.).
If the author and publisher are the same, only include the author in its regular place and omit the publisher.
Lencioni, P. (2012). The advantage: Why organizational health trumps everything else in business . Jossey-Bass. https://amzn.to/343XPSJ
As a change from APA 6 to APA 7, it is no longer necessary to include the ebook format in the title. However, if you listened to an audiobook and the content differs from the text version (e.g., abridged content) or your discussion highlights elements of the audiobook (e.g., narrator's performance), then note that it is an audiobook in the title element in brackets. For ebooks and online audiobooks, also include the DOI number (if available) or nondatabase URL but leave out the electronic retrieval element if the ebook was found in a common academic research database, as with journal articles. APA 7 allows for the shortening of long DOIs and URLs, as shown in this example. See APA 7, Section 9.36 for more information.
Chapter in an Edited Book
Poe, M. (2017). Reframing race in teaching writing across the curriculum. In F. Condon & V. A. Young (Eds.), Performing antiracist pedagogy in rhetoric, writing, and communication (pp. 87–105). University Press of Colorado.
Include the page numbers of the chapter in parentheses after the book title.
Christensen, L. (2001). For my people: Celebrating community through poetry. In B. Bigelow, B. Harvey, S. Karp, & L. Miller (Eds.), Rethinking our classrooms: Teaching for equity and justice (Vol. 2, pp. 16–17). Rethinking Schools.
Also include the volume number or edition number in the parenthetical information after the book title when relevant.
Freud, S. (1961). The ego and the id. In J. Strachey (Ed.), The standard edition of the complete psychological works of Sigmund Freud (Vol. 19, pp. 3-66). Hogarth Press. (Original work published 1923)
When a text has been republished as part of an anthology collection, after the author’s name include the date of the version that was read. At the end of the entry, place the date of the original publication inside parenthesis along with the note “original work published.” For in-text citations of republished work, use both dates in the parenthetical citation, original date first with a slash separating the years, as in this example: Freud (1923/1961). For more information on reprinted or republished works, see APA 7, Sections 9.40-9.41.
Classroom Resources
Citing classroom resources.
If you need to cite content found in your online classroom, use the author (if there is one listed), the year of publication (if available), the title of the document, and the main URL of Walden classrooms. For example, you are citing study notes titled "Health Effects of Exposure to Forest Fires," but you do not know the author's name, your reference entry will look like this:
Health effects of exposure to forest fires [Lecture notes]. (2005). Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
If you do know the author of the document, your reference will look like this:
Smith, A. (2005). Health effects of exposure to forest fires [PowerPoint slides]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
A few notes on citing course materials:
- [Lecture notes]
- [Course handout]
- [Study notes]
- It can be difficult to determine authorship of classroom documents. If an author is listed on the document, use that. If the resource is clearly a product of Walden (such as the course-based videos), use Walden University as the author. If you are unsure or if no author is indicated, place the title in the author spot, as above.
- If you cannot determine a date of publication, you can use n.d. (for "no date") in place of the year.
Note: The web location for Walden course materials is not directly retrievable without a password, and therefore, following APA guidelines, use the main URL for the class sites: https://class.waldenu.edu.
Citing Tempo Classroom Resources
Clear author:
Smith, A. (2005). Health effects of exposure to forest fires [PowerPoint slides]. Walden University Brightspace. https://mytempo.waldenu.edu
Unclear author:
Health effects of exposure to forest fires [Lecture notes]. (2005). Walden University Brightspace. https://mytempo.waldenu.edu
Conference Sessions and Presentations
Feinman, Y. (2018, July 27). Alternative to proctoring in introductory statistics community college courses [Poster presentation]. Walden University Research Symposium, Minneapolis, MN, United States. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/symposium2018/23/
Torgerson, K., Parrill, J., & Haas, A. (2019, April 5-9). Tutoring strategies for online students [Conference session]. The Higher Learning Commission Annual Conference, Chicago, IL, United States. http://onlinewritingcenters.org/scholarship/torgerson-parrill-haas-2019/
Dictionary Entry
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Leadership. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary . Retrieved May 28, 2020, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/leadership
When constructing a reference for an entry in a dictionary or other reference work that has no byline (i.e., no named individual authors), use the name of the group—the institution, company, or organization—as author (e.g., Merriam Webster, American Psychological Association, etc.). The name of the entry goes in the title position, followed by "In" and the italicized name of the reference work (e.g., Merriam-Webster.com dictionary , APA dictionary of psychology ). In this instance, APA 7 recommends including a retrieval date as well for this online source since the contents of the page change over time. End the reference entry with the specific URL for the defined word.
Discussion Board Post
Osborne, C. S. (2010, June 29). Re: Environmental responsibility [Discussion post]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
Dissertations or Theses
Retrieved From a Database
Nalumango, K. (2019). Perceptions about the asylum-seeking process in the United States after 9/11 (Publication No. 13879844) [Doctoral dissertation, Walden University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
Retrieved From an Institutional or Personal Website
Evener. J. (2018). Organizational learning in libraries at for-profit colleges and universities [Doctoral dissertation, Walden University]. ScholarWorks. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=6606&context=dissertations
Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis
Kirwan, J. G. (2005). An experimental study of the effects of small-group, face-to-face facilitated dialogues on the development of self-actualization levels: A movement towards fully functional persons [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Saybrook Graduate School and Research Center.
For further examples and information, see APA 7, Section 10.6.
Legal Material
For legal references, APA follows the recommendations of The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation , so if you have any questions beyond the examples provided in APA, seek out that resource as well.
Court Decisions
Reference format:
Name v. Name, Volume Reporter Page (Court Date). URL
Sample reference entry:
Brown v. Board of Education, 347 U.S. 483 (1954). https://www.oyez.org/cases/1940-1955/347us483
Sample citation:
In Brown v. Board of Education (1954), the Supreme Court ruled racial segregation in schools unconstitutional.
Note: Italicize the case name when it appears in the text of your paper.
Name of Act, Title Source § Section Number (Year). URL
Sample reference entry for a federal statute:
Individuals With Disabilities Education Act, 20 U.S.C. § 1400 et seq. (2004). https://www.congress.gov/108/plaws/publ446/PLAW-108publ446.pdf
Sample reference entry for a state statute:
Minnesota Nurse Practice Act, Minn. Stat. §§ 148.171 et seq. (2019). https://www.revisor.mn.gov/statutes/cite/148.171
Sample citation: Minnesota nurses must maintain current registration in order to practice (Minnesota Nurse Practice Act, 2010).
Note: The § symbol stands for "section." Use §§ for sections (plural). To find this symbol in Microsoft Word, go to "Insert" and click on Symbol." Look in the Latin 1-Supplement subset. Note: U.S.C. stands for "United States Code." Note: The Latin abbreviation " et seq. " means "and what follows" and is used when the act includes the cited section and ones that follow. Note: List the chapter first followed by the section or range of sections.
Unenacted Bills and Resolutions
(Those that did not pass and become law)
Title [if there is one], bill or resolution number, xxx Cong. (year). URL
Sample reference entry for Senate bill:
Anti-Phishing Act, S. 472, 109th Cong. (2005). https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/senate-bill/472
Sample reference entry for House of Representatives resolution:
Anti-Phishing Act, H.R. 1099, 109th Cong. (2005). https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/1099
The Anti-Phishing Act (2005) proposed up to 5 years prison time for people running Internet scams.
These are the three legal areas you may be most apt to cite in your scholarly work. For more examples and explanation, see APA 7, Chapter 11.
Magazine Article
Clay, R. (2008, June). Science vs. ideology: Psychologists fight back about the misuse of research. Monitor on Psychology , 39 (6). https://www.apa.org/monitor/2008/06/ideology
Note that for citations, include only the year: Clay (2008). For magazine articles retrieved from a common academic research database, leave out the URL. For magazine articles from an online news website that is not an online version of a print magazine, follow the format for a webpage reference list entry.
Newspaper Article (Retrieved Online)
Baker, A. (2014, May 7). Connecticut students show gains in national tests. New York Times . http://www.nytimes.com/2014/05/08/nyregion/national-assessment-of-educational-progress-results-in-Connecticut-and-New-Jersey.html
Include the full date in the format Year, Month Day. Do not include a retrieval date for periodical sources found on websites. Note that for citations, include only the year: Baker (2014). For newspaper articles retrieved from a common academic research database, leave out the URL. For newspaper articles from an online news website that is not an online version of a print newspaper, follow the format for a webpage reference list entry.
OASIS Resources
Oasis webpage.
OASIS. (n.d.). Common reference list examples . Walden University. https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/apa/references/examples
For all OASIS content, list OASIS as the author. Because OASIS webpages do not include publication dates, use “n.d.” for the year.
Interactive Guide
OASIS. (n.d.). Embrace iterative research and writing [Interactive guide]. Walden University. https://academics.waldenu.edu/oasis/iterative-research-writing-web
For OASIS multimedia resources, such as interactive guides, include a description of the resource in brackets after the title.
Online Video/Webcast
Walden University. (2013). An overview of learning [Video]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
Use this format for online videos such as Walden videos in classrooms. Most of our classroom videos are produced by Walden University, which will be listed as the author in your reference and citation. Note: Some examples of audiovisual materials in the APA manual show the word “Producer” in parentheses after the producer/author area. In consultation with the editors of the APA manual, we have determined that parenthetical is not necessary for the videos in our courses. The manual itself is unclear on the matter, however, so either approach should be accepted. Note that the speaker in the video does not appear in the reference list entry, but you may want to mention that person in your text. For instance, if you are viewing a video where Tobias Ball is the speaker, you might write the following: Tobias Ball stated that APA guidelines ensure a consistent presentation of information in student papers (Walden University, 2013). For more information on citing the speaker in a video, see our page on Common Citation Errors .
Taylor, R. [taylorphd07]. (2014, February 27). Scales of measurement [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PDsMUlexaMY
OASIS. (2020, April 15). One-way ANCOVA: Introduction [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/_XnNDQ5CNW8
For videos from streaming sites, use the person or organization who uploaded the video in the author space to ensure retrievability, whether or not that person is the speaker in the video. A username can be provided in square brackets. As a change from APA 6 to APA 7, include the publisher after the title, and do not use "Retrieved from" before the URL. See APA 7, Section 10.12 for more information and examples.
See also reference list entry formats for TED Talks .
Technical and Research Reports
Edwards, C. (2015). Lighting levels for isolated intersections: Leading to safety improvements (Report No. MnDOT 2015-05). Center for Transportation Studies. http://www.cts.umn.edu/Publications/ResearchReports/reportdetail.html?id=2402
Technical and research reports by governmental agencies and other research institutions usually follow a different publication process than scholarly, peer-reviewed journals. However, they present original research and are often useful for research papers. Sometimes, researchers refer to these types of reports as gray literature , and white papers are a type of this literature. See APA 7, Section 10.4 for more information.
Reference list entires for TED Talks follow the usual guidelines for multimedia content found online. There are two common places to find TED talks online, with slightly different reference list entry formats for each.
TED Talk on the TED website
If you find the TED Talk on the TED website, follow the format for an online video on an organizational website:
Owusu-Kesse, K. (2020, June). 5 needs that any COVID-19 response should meet [Video]. TED Conferences. https://www.ted.com/talks/kwame_owusu_kesse_5_needs_that_any_covid_19_response_should_meet
The speaker is the author in the reference list entry if the video is posted on the TED website. For citations, use the speaker's surname.
TED Talk on YouTube
If you find the TED Talk on YouTube or another streaming video website, follow the usual format for streaming video sites:
TED. (2021, February 5). The shadow pandemic of domestic violence during COVID-19 | Kemi DaSilvalbru [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PGdID_ICFII
TED is the author in the reference list entry if the video is posted on YouTube since it is the channel on which the video is posted. For citations, use TED as the author.
Walden University Course Catalog
To include the Walden course catalog in your reference list, use this format:
Walden University. (2020). 2019-2020 Walden University catalog . https://catalog.waldenu.edu/index.php
If you cite from a specific portion of the catalog in your paper, indicate the appropriate section and paragraph number in your text:
...which reflects the commitment to social change expressed in Walden University's mission statement (Walden University, 2020, Vision, Mission, and Goals section, para. 2).
And in the reference list:
Walden University. (2020). Vision, mission, and goals. In 2019-2020 Walden University catalog. https://catalog.waldenu.edu/content.php?catoid=172&navoid=59420&hl=vision&returnto=search
Vartan, S. (2018, January 30). Why vacations matter for your health . CNN. https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/why-vacations-matter/index.html
For webpages on the open web, include the author, date, webpage title, organization/site name, and URL. (There is a slight variation for online versions of print newspapers or magazines. For those sources, follow the models in the previous sections of this page.)
American Federation of Teachers. (n.d.). Community schools . http://www.aft.org/issues/schoolreform/commschools/index.cfm
If there is no specified author, then use the organization’s name as the author. In such a case, there is no need to repeat the organization's name after the title.
In APA 7, active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list.
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Common Reference List Examples
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Reference List: Overview
- Next Page: Common Military Reference List Examples
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Social Work: Research Overview
- School of Social Work
- Literature Reviews
- Scoping Vs Systematic Reviews
- Search Strategies
- APA Tutorials and Software
- Paper Formatting Basics
- Citation Tips
- Qualitative Vs Quantitative
- Primary Vs Secondary Resources
- Data Management
- Research Help UTA
- Research Mavs
Sample APA Papers

Sample Student Paper
In this webinar, the style experts demonstrate how to set up student papers (font, line spacing, margins, page numbers, etc.), with an emphasis on how default word-processing software settings align with seventh edition style and make papers easier to format. The experts then address needs for formatting in the sections often included in student papers: title page, text, tables and figures, and reference list. The session concludes with steps for organizing papers and improving their quality.
The annotated diagrams from the webinar are available in this handout (PDF, 3.4MB) .
- Student Paper Example This is a student paper example from the 7th Edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association.
Sample Student Paper with Annotations

- << Previous: APA Tutorials and Software
- Next: Citation Tips >>
- Last Updated: Aug 15, 2024 1:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/c.php?g=1388834
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Generative ai and information literacy.
- What is Generative AI?
- AI and Information Literacy
- AI, Bias, and DEIA
- Other Ethical Challenges with AI
Academic Integrity
Citing generative ai, citation styles and examples, additional resources.
- More Resources
As a student, am I allowed to use a Gen-AI tool like ZotGPT in my coursework?
The UCI Policy on Academic Integrity for students states:
“All students are expected to complete a course in compliance with the Instructor's standards. No student shall engage in any activity involving any Academic Integrity Policy Violations. No student shall engage in any activity that involves attempting to receive a grade by means other than honest effort, and shall not aid another student who is attempting to do so.”
Before you use any AI tool, ask yourself:
- Is using this tool in compliance with the course instructor’s standards?
- Does using this tool undermine your “honest effort” in this course to receive a grade?
If you have any doubts, it is best to ask your instructor, and keep in mind that each course may have different standards of what might be acceptable.
If you are permitted to use an AI tool in your work and you have made the decision to use one, it may be a good idea to acknowledge your use as follows:
- Which tool(s) did you use?
- How did you use the tool (for what purpose, in what sections, etc.)?
- How did you prompt the tool?
- When did you use the tool?
At this time, citing Generative AI is an evolving conversation, and some style guides have released official guidance on how to cite AI-generated text or images, while others have not. In addition, style guides have differing guidelines of whether tools (or companies) are “authors.”
Here are some examples of differences of how Gen-AI information might be cited in different style guides:
No official guidelines have been released, but the following blog post offers suggestions : “If you’ve used ChatGPT or other AI tools in your research, describe how you used the tool in your Method section or in a comparable section of your paper. For literature reviews or other types of essays or response or reaction papers, you might describe how you used the tool in your introduction. In your text, provide the prompt you used and then any portion of the relevant text that was generated in response.”
For example:
When prompted with “Is the left brain right brain divide real or a metaphor?” the ChatGPT-generated text indicated that although the two brain hemispheres are somewhat specialized, “the notation that people can be characterized as ‘left-brained’ or ‘right-brained’ is considered to be an oversimplification and a popular myth” (OpenAI, 2023).
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
The Chicago Style FAQ suggests that “conversations” with Gen-AI chatbots can be treated in a similar fashion to private emails or phone conversations that couldn’t be accessed by others. It recommends including information about how the AI tool was prompted, and suggests “you must credit ChatGPT when you reproduce its words within your own work, but unless you include a publicly available URL, that information should be put in the text or in a note–not in a bibliography or reference list.”
For example, if a prompt was not given in-text:
1. ChatGPT, response to “Explain how to make pizza dough from common household ingredients,” OpenAI, March 7, 2023.
The IEEE Editorial Style Manual for Authors (2023) does not offer any official guidance on citing AI-generated content. Some suggest treating AI-generated text similarly to private communication.
The MLA style guide uses a template of core citation elements that are flexible enough to accommodate citing AI-generated text or images. While MLA recommends that you do not treat an AI tool as an author, it suggests you should:
- cite a generative AI tool whenever you paraphrase, quote, or incorporate into your own work any content (whether text, image, data, or other) that was created by it
- acknowledge all functional uses of the tool (like editing your prose or translating words) in a note, your text, or another suitable location
- take care to vet the secondary sources it cites
An example of a works cited entry for a paraphrase of text output by ChatGPT might look like this:
“Describe the symbolism of the green light in the book The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald” prompt. ChatGPT, 13 Feb. version, OpenAI, 8 Mar. 2023, chat.openai.com/chat.
- Citing ChatGPT in STEM fields (UCSB guide)
- Generative AI citation (UCI Digital Learning Lab)
- UCI Academic Integrity Information for Faculty/Staff
- UCI Academic Integrity Information for Students
- << Previous: Other Ethical Challenges with AI
- Next: More Resources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 13, 2024 10:45 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/gen-ai
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.

How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
Free Al Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
- Articles of Word
How to Write an Argumentative Essay- Steps with Examples
Being a student and writing essays is not something everybody enjoys, but in my personal opinion as a writer, anyone can find contentment and pleasure in writing, especially when it comes to argumentative essays. While they may seem tricky to navigate, they offer this unique opportunity to express your opinions and make your voice heard. Consider this a growing process—once you overcome the challenges of writing argumentative essays, you will learn the art of agreeing or disagreeing with popular opinions and defending your stance. As far as the essay is concerned, I will show you how to master this process on how to write an argumentative essay.
When is an Argumentative Essay Written?
You will likely be required to write argumentative essays throughout your academic life, from high school to university. These assignments will present opportunities to develop and showcase your critical thinking and persuasive writing skills. Here are some scenarios where you might encounter the need to write argumentative essays:
Academic Assignments
Often assigned in school or college courses to help students develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills. These assignments encourage students to research thoroughly, form coherent arguments, and present their viewpoints convincingly.
Debates and Discussions
Serve as the basis for presenting and defending viewpoints in academic or competitive settings. Argumentative essays provide a structured way to organize thoughts and evidence, helping participants articulate their arguments effectively during debates.
Opinion Pieces
Commonly used in newspapers, magazines, and online publications to influence public opinion on current issues. These essays allow writers to present their stance on controversial topics, backed by evidence and reasoning, to sway readers' views.
Policy Proposals
Utilized in government and policy-related fields to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems. Argumentative essays in this context present well-researched arguments to persuade policymakers and stakeholders of the necessity and viability of the proposed changes.
Persuasive Speeches
Prepared as a foundation for delivering persuasive speeches. Writing an argumentative essay helps speakers organize their thoughts and evidence logically, providing a solid framework for their oral presentations.
What is the Structure of an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay uses factual evidence and logical support to convince the reader of a particular point of view. Here's a breakdown of the structure and what goes into each part of an argumentative essay:
Basic Argumentative Essay Structure
1.Introduction
Purpose: Introduce the topic, present the thesis, and set up the argument.
Hook: A sentence to grab the reader’s attention.
Background Information: Brief context about the topic.
Thesis Statement: The main argument or claim.
2.Body Paragraphs
Purpose: Present arguments and evidence to support the thesis and refute opposing arguments.
Topic Sentence: Introduces the main idea of the paragraph.
Evidence and Analysis: Present facts, statistics, quotes, or examples to support the argument.
Counterarguments and Rebuttals: Address opposing views and explain why they are invalid or less significant.
3.Conclusion
Purpose: Summarize the arguments, restate the thesis in light of the evidence presented, and offer final thoughts.
Restate Thesis: Reiterate the main argument.
Summarize Key Points: Highlight the main points made in the body paragraphs.
Final Thought: A closing statement that underscores the importance of the topic
How to Write an Argumentative Essay [4 Steps with Examples]
As an experienced writer, I've come to understand the structure of argumentative essays quite well. But what I found truly challenging when I first started was nailing the right approach. Many beginners, myself included at one point, fall into traps like letting personal biases creep in or thinking that being argumentative means being aggressive. Trust me, that's not the case at all!
In this section, I'm going to lay out an effective approach on how to write an argumentative essay step by step for beginners. I'll break it down in a way that I wish someone had done for me when I was starting out. Plus, I'll share some insider tips on tools like WPS Office that I've come to rely on to streamline my writing process. So let's learn how to write an argumentative essay with a few examples.
1.Brainstorming
When I sit down to craft an argumentative essay, my first step is to engage in a comprehensive brainstorming session. This is your opportunity to let your creativity run wild and explore every angle of your topic. Write down every idea that comes to you, whether it supports or opposes your topic. Remember, at this stage, there are no bad ideas.
Now, while there's nothing wrong with the classic pen and paper approach, I've found that using WPS Office takes my brainstorming to a whole new level. It's not just about having a digital notepad; the AI features often toss out ideas that I might never have thought of on my own. It's like having a creative partner who never gets tired! Let me show you how I use it:
Let's say our topic is "Are Electric Cars Better for the Environment?"
Step 1: Open WPS Office and type "@AI" on a blank document to activate WPS AI.
Step 2: Click on the "Brainstorm" option and enter your prompt. Make sure it's detailed and clearly explains what you want. Here's an example of an effective prompt:
"Generate a list of arguments both for and against the idea that electric cars are better for the environment. Consider factors like emissions, manufacturing processes, battery disposal, and energy sources"
Step 3: WPS AI will generate several arguments on both sides. If you want more, simply click "Rewrite”.
Jot down any valuable arguments before hitting "Rewrite", as you might not see the same ones again.
With these arguments in hand, you'll likely find yourself leaning towards one side of the debate. Armed with a variety of points and counterpoints, you'll be well-equipped to write an effective argumentative essay. Remember, a strong argumentative essay is built on a foundation of thorough preparation and diverse ideas.
2.Preparing
Now that we've generated our initial arguments and counterarguments, it's time to dive deeper into research to strengthen our position. Let's continue with our example topic: "Are Electric Cars Better for the Environment?"
Let's continue with our example topic: "Are Electric Cars Better for the Environment?" Our next step is to select the most impactful supporting arguments and conduct in-depth research to substantiate them with solid evidence. Simultaneously, we'll identify the strongest counterarguments and explore ways to address or neutralize them through our research.
All of this might seem a little overwhelming, but with the help of WPS AI, the research phase becomes significantly more manageable. As we gather research papers, we can upload them to WPS Office and quickly gain insights using the AI features.
Here's how to leverage WPS AI for efficient research:
Step 1: Open your research paper PDFs in WPS Office, then click on the WPS AI widget in the top right corner.
Step 2: In the WPS AI panel that appears on the right side of your screen, click "Upload" to add your PDF.
Step 3: Once processed, WPS AI will provide you with key insights from the PDF at a glance.
Step 4: For more specific information, click on the "Inquiry" tab and use the WPS AI chatbot to ask further questions about the PDF contents.
As you conduct your research, begin organizing your findings into an outline. Remember to structure your outline according to the elements we discussed in previous sections. This will ensure your outline contains all the necessary components for an effective argumentative essay.
3.First Drafting
Now that we have our research and outline ready, it's time to start writing our first draft. This is where your essay really starts to take shape. Don't worry about perfection at this stage—the goal is to get your ideas down coherently.
Using the outline we prepared during our research, you'll find it easier to organize your thoughts for your essay. To make things simpler, use WPS Office editing tools. When I write my essay, I always ensure it is properly formatted, giving it a cleaner look and helping me focus better.
Now, simply start your draft on WPS Office with an introduction, followed by a body paragraph, and conclude with a strong summary that reviews your main points and leaves the reader with something to think about.
Once you have your draft ready, make use of WPS Office's AI features, which can help you improve writing, shorten or elongate your paragraphs, and much more. Let's say you've written your first body paragraph, and it's a bit too long. So, let's shorten it with WPS AI:
Step 1: Select the paragraph you want to shorten, then click on the WPS AI icon in the hover menu.
Step 2: From the list of options, simply click on "Make shorter" to shorten your paragraph.
Step 3: WPS AI will display the shorter version on a small screen. Click on "Replace" to replace the original text with the shorter version.
4.Revising & Proofreading
Congratulations on completing your first draft! However, there is one crucial step remaining: revising and proofreading. Revising and proofreading are where good essays become great essays.
A method I find most effective for revising my essay is reading it aloud. This technique helps in identifying awkward phrasing and run-on sentences that may go unnoticed when reading silently. As you read, ask yourself:
Does my introduction effectively grab the reader's attention and clearly state my thesis?
Do my body paragraphs each focus on a single main idea that supports my thesis?
Have I provided enough evidence to support each of my arguments?
Have I addressed potential counterarguments?
Does my conclusion effectively summarize my main points and leave a lasting impression?
You might find that you need to make some structural changes. For instance, you might realize that your second body paragraph would be more effective if it came first. Don't be afraid to move things around!
Once you have made the necessary changes to your essay, the next step is to ensure it does not have any grammatical errors. For this, I use WPS AI's spell check feature. With just a single click, WPS AI spell check ensures that my essay is complete and ready to be submitted!
Bonus Tips: How to Polish your argumentative Essay with WPS AI
WPS Office is already a premium choice among students, offering all the features needed to write a perfect essay. With WPS Office, students can write better without payment issues, annoying ads, or difficulty navigating the tools. It's a free tool with advanced features, including WPS AI, which supports the entire writing process.
1.Check for Grammar and Spelling:
WPS AI carefully scans your essay for grammatical errors and spelling mistakes, ensuring that your writing is polished and professional. This feature not only helps you avoid common errors but also enhances the readability and credibility of your work.
2.Seek Style and Tone Adjustments:
WPS AI offers suggestions to improve the style and tone of your writing, making it more engaging and suitable for your target audience. Whether your essay requires a formal academic tone or a more conversational approach, WPS AI tailors its recommendations to fit your needs, ensuring your writing is coherent and compelling.
Here's an example of WPS AI's 'Improve Writing' feature in action, enhancing the formality and persuasiveness of my body paragraph for the reader.
3.Writing Assistance:
From the initial brainstorming phase to the final touches, WPS AI provides comprehensive writing assistance. It helps you structure your arguments logically, develop clear and concise thesis statements, and refine your conclusions. WPS AI also offers suggestions for enhancing clarity and coherence, making the writing process smoother and more efficient.
With the assistance of WPS AI's 'Continue Writing' feature, we can extend our essays by seamlessly incorporating additional sections that complement the existing content's flow and tone.
FAQs about Writing an Argumentative Essay
1. what’s the difference between an expository essay and an argumentative essay.
An argumentative essay is typically more extensive and requires independent research to establish a unique claim regarding a specific topic. It includes a thesis statement that presents a debatable assertion, which must be supported by objective evidence. In contrast, an expository essay strives for objectivity but does not propose an original argument. Instead, it aims to clarify and explain a topic straightforwardly, such as a process or concept. Generally, expository essays are shorter and do not rely as heavily on research.
2. When do I need to cite sources?
In a college environment, accurately citing sources is vital for essays, research papers, and other academic assignments, but this requirement does not extend to exams or in-class tasks. Proper citations are needed for direct quotes, paraphrased material, and summaries, and it is necessary to provide complete source information in a bibliography or reference list. Following the specified citation style, such as APA or MLA, is essential for maintaining academic integrity. Whenever you utilize information or ideas from another work in college-level writing, proper citation is required to acknowledge the original source.
3. What is an Argumentative essay?
An argumentative essay is a type of writing that asserts a specific stance on a debatable issue, backing it up with reasoning and evidence. The main objective is to convince the reader to accept or seriously consider the author's viewpoint. This essay usually contains a clear thesis statement and develops arguments while addressing opposing views to reinforce its position. Ultimately, it seeks to encourage critical engagement with the topic at hand.
Excel the Art of Persuasion With WPS Office
Argumentative essays are possibly the most thought-provoking when it comes to writing, presenting a higher difficulty level. Despite the challenge on how to write an argumentative essay, they are also the most fun to write, as they allow you to express your opinions in a highly opinionated form. WPS Office strives to enhance your writing experience, and as a writer, I can vouch for this. WPS Office not only offers advanced tools like WPS AI to help refine and improve your writing skills but also provides options to make your work as presentable as you want it to be. Download WPS Office today to experience the difference.
- 1. How to write an essay report like a Pro
- 2. Amazing AI Essay Generator - Make Your Essay Writing Easier
- 3. How to Write a Proposal [ Steps & Examples]
- 4. How to Start An Essay- Steps with Examples
- 5. How to Write a New Year Resolution Essay - A Comprehensive Guide
- 6. How to Craft the Perfect Academic Essay Steps & Examples

15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.

Sample Papers
This page contains sample papers formatted in seventh edition APA Style. The sample papers show the format that authors should use to submit a manuscript for publication in a professional journal and that students should use to submit a paper to an instructor for a course assignment. You can download the Word files to use as templates and edit them as needed for the purposes of your own papers.
Most guidelines in the Publication Manual apply to both professional manuscripts and student papers. However, there are specific guidelines for professional papers versus student papers, including professional and student title page formats. All authors should check with the person or entity to whom they are submitting their paper (e.g., publisher or instructor) for guidelines that are different from or in addition to those specified by APA Style.
Sample papers from the Publication Manual
The following two sample papers were published in annotated form in the Publication Manual and are reproduced here as PDFs for your ease of use. The annotations draw attention to content and formatting and provide the relevant sections of the Publication Manual (7th ed.) to consult for more information.
- Student sample paper with annotations (PDF, 5MB)
- Professional sample paper with annotations (PDF, 2.7MB)
We also offer these sample papers in Microsoft Word (.docx) format with the annotations as comments to the text.
- Student sample paper with annotations as comments (DOCX, 42KB)
- Professional sample paper with annotations as comments (DOCX, 103KB)
Finally, we offer these sample papers in Microsoft Word (.docx) format without the annotations.
- Student sample paper without annotations (DOCX, 36KB)
- Professional sample paper without annotations (DOCX, 96KB)
Sample professional paper templates by paper type
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different professional paper types. Professional papers can contain many different elements depending on the nature of the work. Authors seeking publication should refer to the journal’s instructions for authors or manuscript submission guidelines for specific requirements and/or sections to include.
- Literature review professional paper template (DOCX, 47KB)
- Mixed methods professional paper template (DOCX, 68KB)
- Qualitative professional paper template (DOCX, 72KB)
- Quantitative professional paper template (DOCX, 77KB)
- Review professional paper template (DOCX, 112KB)
Sample papers are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 2 and the Concise Guide Chapter 1
Related handouts
- Heading Levels Template: Student Paper (PDF, 257KB)
- Heading Levels Template: Professional Paper (PDF, 213KB)
Other instructional aids
- Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS)
- APA Style Tutorials and Webinars
- Handouts and Guides
- Paper Format
View all instructional aids
Sample student paper templates by paper type
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
APA does not set formal requirements for the nature or contents of an APA Style student paper. Students should follow the guidelines and requirements of their instructor, department, and/or institution when writing papers. For instance, an abstract and keywords are not required for APA Style student papers, although an instructor may request them in student papers that are longer or more complex. Specific questions about a paper being written for a course assignment should be directed to the instructor or institution assigning the paper.
- Discussion post student paper template (DOCX, 31KB)
- Literature review student paper template (DOCX, 37KB)
- Quantitative study student paper template (DOCX, 53KB)
Sample papers in real life
Although published articles differ in format from manuscripts submitted for publication or student papers (e.g., different line spacing, font, margins, and column format), articles published in APA journals provide excellent demonstrations of APA Style in action.
APA journals began publishing papers in seventh edition APA Style in 2020. Professional authors should check the author submission guidelines for the journal to which they want to submit their paper for any journal-specific style requirements.
Credits for sample professional paper templates
Quantitative professional paper template: Adapted from “Fake News, Fast and Slow: Deliberation Reduces Belief in False (but Not True) News Headlines,” by B. Bago, D. G. Rand, and G. Pennycook, 2020, Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 149 (8), pp. 1608–1613 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000729 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Qualitative professional paper template: Adapted from “‘My Smartphone Is an Extension of Myself’: A Holistic Qualitative Exploration of the Impact of Using a Smartphone,” by L. J. Harkin and D. Kuss, 2020, Psychology of Popular Media , 10 (1), pp. 28–38 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000278 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Mixed methods professional paper template: Adapted from “‘I Am a Change Agent’: A Mixed Methods Analysis of Students’ Social Justice Value Orientation in an Undergraduate Community Psychology Course,” by D. X. Henderson, A. T. Majors, and M. Wright, 2019, Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology , 7 (1), 68–80. ( https://doi.org/10.1037/stl0000171 ). Copyright 2019 by the American Psychological Association.
Literature review professional paper template: Adapted from “Rethinking Emotions in the Context of Infants’ Prosocial Behavior: The Role of Interest and Positive Emotions,” by S. I. Hammond and J. K. Drummond, 2019, Developmental Psychology , 55 (9), pp. 1882–1888 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000685 ). Copyright 2019 by the American Psychological Association.
Review professional paper template: Adapted from “Joining the Conversation: Teaching Students to Think and Communicate Like Scholars,” by E. L. Parks, 2022, Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology , 8 (1), pp. 70–78 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/stl0000193 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Credits for sample student paper templates
These papers came from real students who gave their permission to have them edited and posted by APA.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
- The Basics of In-Text Citation | APA & MLA Examples
The Basics of In-Text Citation | APA & MLA Examples
Published on March 14, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on February 28, 2024.
An in-text citation is a short acknowledgement you include whenever you quote or take information from a source in academic writing. It points the reader to the source so they can see where you got your information.
In-text citations most commonly take the form of short parenthetical statements indicating the author and publication year of the source, as well as the page number if relevant.
We also offer a free citation generator and in-depth guides to the main citation styles.
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What are in-text citations for, when do you need an in-text citation, types of in-text citation, frequently asked questions about in-text citations.
The point of an in-text citation is to show your reader where your information comes from. Including citations:
- Avoids plagiarism by acknowledging the original author’s contribution
- Allows readers to verify your claims and do follow-up research
- Shows you are engaging with the literature of your field
Academic writing is seen as an ongoing conversation among scholars, both within and between fields of study. Showing exactly how your own research draws on and interacts with existing sources is essential to keeping this conversation going.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An in-text citation should be included whenever you quote or paraphrase a source in your text.
Quoting means including the original author’s words directly in your text, usually introduced by a signal phrase . Quotes should always be cited (and indicated with quotation marks), and you should include a page number indicating where in the source the quote can be found.
Paraphrasing means putting information from a source into your own words. In-text citations are just as important here as with quotes, to avoid the impression you’re taking credit for someone else’s ideas. Include page numbers where possible, to show where the information can be found.
However, to avoid over-citation, bear in mind that some information is considered common knowledge and doesn’t need to be cited. For example, you don’t need a citation to prove that Paris is the capital city of France, and including one would be distracting.
Different types of in-text citation are used in different citation styles . They always direct the reader to a reference list giving more complete information on each source.
Author-date citations (used in APA , Harvard , and Chicago author-date ) include the author’s last name, the year of publication, and a page number when available. Author-page citations (used in MLA ) are the same except that the year is not included.
Both types are divided into parenthetical and narrative citations. In a parenthetical citation , the author’s name appears in parentheses along with the rest of the information. In a narrative citation , the author’s name appears as part of your sentence, not in parentheses.
| Parenthetical citation | Narrative citation | |
|---|---|---|
| Author-date (APA) | The treatment proved highly effective (Smith, 2018, p. 11). | Smith states that the treatment was highly effective (2018, p. 11). |
| Author-page (MLA) | The treatment proved highly effective (Smith 11). | Smith states that the treatment was highly effective (11). |
Note: Footnote citations like those used in Chicago notes and bibliography are sometimes also referred to as in-text citations, but the citation itself appears in a note separate from the text.
An in-text citation is an acknowledgement you include in your text whenever you quote or paraphrase a source. It usually gives the author’s last name, the year of publication, and the page number of the relevant text. In-text citations allow the reader to look up the full source information in your reference list and see your sources for themselves.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, February 28). The Basics of In-Text Citation | APA & MLA Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/in-text-citation-styles/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to quote | citing quotes in apa, mla & chicago, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, what is your plagiarism score.
Grab your spot at the free arXiv Accessibility Forum
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Artificial Intelligence
Title: the ai scientist: towards fully automated open-ended scientific discovery.
Abstract: One of the grand challenges of artificial general intelligence is developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. While frontier models have already been used as aides to human scientists, e.g. for brainstorming ideas, writing code, or prediction tasks, they still conduct only a small part of the scientific process. This paper presents the first comprehensive framework for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling frontier large language models to perform research independently and communicate their findings. We introduce The AI Scientist, which generates novel research ideas, writes code, executes experiments, visualizes results, describes its findings by writing a full scientific paper, and then runs a simulated review process for evaluation. In principle, this process can be repeated to iteratively develop ideas in an open-ended fashion, acting like the human scientific community. We demonstrate its versatility by applying it to three distinct subfields of machine learning: diffusion modeling, transformer-based language modeling, and learning dynamics. Each idea is implemented and developed into a full paper at a cost of less than $15 per paper. To evaluate the generated papers, we design and validate an automated reviewer, which we show achieves near-human performance in evaluating paper scores. The AI Scientist can produce papers that exceed the acceptance threshold at a top machine learning conference as judged by our automated reviewer. This approach signifies the beginning of a new era in scientific discovery in machine learning: bringing the transformative benefits of AI agents to the entire research process of AI itself, and taking us closer to a world where endless affordable creativity and innovation can be unleashed on the world's most challenging problems. Our code is open-sourced at this https URL
| Subjects: | Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG) |
| Cite as: | [cs.AI] |
| (or [cs.AI] for this version) | |
| Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite |
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Citation Examples | Books, Articles, Websites & More. Published on April 9, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 17, 2024. The most common citation styles are APA and MLA. To cite a source in these styles, you need a brief in-text citation and a full reference. Use the interactive tool to understand how a citation is structured and see ...
Works Included in a Reference List. The reference list provides a reliable way for readers to identify and locate the works cited in a paper. APA Style papers generally include reference lists, not bibliographies. In general, each work cited in the text must appear in the reference list, and each work in the reference list must be cited in the ...
The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation is the main style guide for legal citations in the US. It's widely used in law, and also when legal materials need to be cited in other disciplines. Bluebook footnote citation. 1 David E. Pozen, Freedom of Information Beyond the Freedom of Information Act, 165, U. P🇦 . L.
Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper. However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style. Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples.
APA in-text citations The basics. In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else's ideas or words to avoid plagiarism.. An APA in-text citation consists of the author's last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system).
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual.Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual.. To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of ...
This guide contains examples of common types of APA Style references. Section numbers indicate where to find the examples in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). More information on references and reference examples are in Chapters 9 and 10 of the Publication Manual as well as the Concise Guide to APA ...
Another example is "Nordic Pulp and Paper Research," a style used by an international scientific magazine covering science and technology for the areas of wood or bio-mass constituents. 4. More citations were created on EasyBib.com in the first quarter of 2018 than there are people in California.
A citation is found in the actual writing of an APA research paper. In-text citation example: "Lecture-rooms are numerous and large, but the number of young people who genuinely thirst after truth and justice is small" (Einstein, 2007, p. 5). A reference is found on the reference page, which is the last page of a research paper.
Research, Citation, & Class Guides; APA Style (7th ed.) Reference Examples ... paper types as well as guidelines on citing course materials Dedicated chapter for new users of APA Style covering paper elements and format, including sample papers for both professional authors and student writers New chapter on journal article reporting standards ...
Basic Principles of Citation. APA Style uses the author-date citation system, in which a brief in-text citation directs readers to a full reference list entry. The in-text citation appears within the body of the paper (or in a table, figure, footnote, or appendix) and briefly identifies the cited work by its author and date of publication.
Sample citation: The Anti-Phishing Act (2005) proposed up to 5 years prison time for people running Internet scams. ... However, they present original research and are often useful for research papers. Sometimes, researchers refer to these types of reports as gray literature, and white papers are a type of this literature. See APA 7, Section 10 ...
APA Citation Basics. When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
All titles used in the reference section of a Chicago-style paper use title case. Here are the general guidelines of Chicago style citations: Book: First Name Last Name, Title of Book. State of Publication, Publisher, Year of Publication. Example: Simon Thompson, The Year of the Wolf. Texas, Preston and Buchanan, 1982.
This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use. This resource contains a sample MLA paper that adheres to the 2016 updates. To download the MLA sample paper, click this link.
Example: Note citation (Chicago) ... At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays, research papers, and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises). Add a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or ...
For three or more authors, provide the first author's name surname first then followed by "et al." Books with three or more authors : Joseph, Gary, et al. Changing shirts. Generic Publishing House, 2011. When you want to cite a chapter or an essay in a book, follow this basic format.
Narrative citation: Grady et al. (2019) If a journal article has a DOI, include the DOI in the reference. Always include the issue number for a journal article. If the journal article does not have a DOI and is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range (for an explanation of why, see the database information ...
Before we dive into examples, let's review the key formatting requirements: APA Formatting Requirements: Title the page "References" centered at the top. Double-space all entries. Use a hanging indent for each entry (first line flush left, subsequent lines indented 0.5 inches). ... and especially involved extensive digging into research papers ...
The experts then address needs for formatting in the sections often included in student papers: title page, text, tables and figures, and reference list. The session concludes with steps for organizing papers and improving their quality. The annotated diagrams from the webinar are available in this handout (PDF, 3.4MB).
In this sample paper, we've put four blank lines above the title. Commented [AF3]: Authors' names are written below the title, with one double-spaced blank line between them. Names should be written as follows: First name, middle initial(s), last name. Commented [AF4]: Authors' affiliations follow immediately after their names.
Citation Styles and Examples. APA; Chicago; IEEE; MLA; No official guidelines have been released, but the following blog post offers suggestions: "If you've used ChatGPT or other AI tools in your research, describe how you used the tool in your Method section or in a comparable section of your paper. For literature reviews or other types of ...
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines: Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides. Double-space all text, including headings. Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches. Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
8. Citations Always ensure to cite all sources referred to while writing the proposal. Any citation method could be used as long as it is consistent and adheres to a specific format. Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing.
The length of a research paper depends on its topic and specific requirements. Generally, research papers vary between 4,000 to 6,000 words, with shorter papers around 2,000 words and longer ones exceeding 10,000 words. Adhering to the length requirements provided for academic assignments is essential.
In contrast, an expository essay strives for objectivity but does not propose an original argument. Instead, it aims to clarify and explain a topic straightforwardly, such as a process or concept. Generally, expository essays are shorter and do not rely as heavily on research. 2. When do I need to cite sources?
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
Recent years have seen substantial advances in our understanding of high-dimensional ridge regression, but existing theories assume that training examples are independent. By leveraging recent techniques from random matrix theory and free probability, we provide sharp asymptotics for the in- and out-of-sample risks of ridge regression when the data points have arbitrary correlations. We ...
In-text citations most commonly take the form of short parenthetical statements indicating the author and publication year of the source, as well as the page number if relevant. Example: APA Style in-text citation (Jackson, 2005, p. 16) We also offer a free citation generator and in-depth guides to the main citation styles.
One of the grand challenges of artificial general intelligence is developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. While frontier models have already been used as aids to human scientists, e.g. for brainstorming ideas, writing code, or prediction tasks, they still conduct only a small part of the scientific process. This paper presents the first ...