thesis statements about love
Before you write a love essay, read this to get examples.
The day will come when you can’t escape the fate of all students: You will have to write a what is love essay.
No worries:
Here you’ll find tons of love essay topics and examples. No time to read everything? Scroll down to get a free PDF with original samples.

Definition: Essay on Love
First, let’s define what is love essay?
The most common topics are:
- Definition of love
- What is love?
- Meaning of love
Why limit yourself to these hackneyed, general themes? Below, I’ll show how to make your paper on love original yet relevant to the prompt you get from teachers.
Love Essay Topics: 20 Ideas to Choose for Your Paper
Your essay on love and relationship doesn’t have to be super official and unemotional. It’s ok to share reflections and personal opinions when writing about romance.
Often, students get a general task to write an essay on love. It means they can choose a theme and a title for their paper. If that’s your case, feel free to try any of these love essay topics:
- Exploring the impact of love on individuals and relationships.
- Love in the digital age: Navigating romance in a tech world.
- Is there any essence and significance in unconditional love?
- Love as a universal language: Connecting hearts across cultures.
- Biochemistry of love: Exploring the process.
- Love vs. passion vs. obsession.
- How love helps cope with heartbreak and grief.
- The art of loving. How we breed intimacy and trust.
- The science behind attraction and attachment.
- How love and relationships shape our identity and help with self-discovery.
- Love and vulnerability: How to embrace emotional openness.
- Romance is more complex than most think: Passion, intimacy, and commitment explained.
- Love as empathy: Building sympathetic connections in a cruel world.
- Evolution of love. How people described it throughout history.
- The role of love in mental and emotional well-being.
- Love as a tool to look and find purpose in life.
- Welcoming diversity in relations through love and acceptance.
- Love vs. friendship: The intersection of platonic and romantic bonds.
- The choices we make and challenges we overcome for those we love.
- Love and forgiveness: How its power heals wounds and strengthens bonds.
Love Essay Examples: Choose Your Sample for Inspiration
Essays about love are usually standard, 5-paragraph papers students write in college:
- One paragraph is for an introduction, with a hook and a thesis statement
- Three are for a body, with arguments or descriptions
- One last passage is for a conclusion, with a thesis restatement and final thoughts
Below are the ready-made samples to consider. They’ll help you see what an essay about love with an introduction, body, and conclusion looks like.
What is love essay: 250 words
Lao Tzu once said, “Being deeply loved by someone gives you strength while loving someone deeply gives you courage.” Indeed, love can transform individuals, relationships, and our world.
A word of immense depth and countless interpretations, love has always fascinated philosophers, poets, and ordinary individuals. This emotion breaks boundaries and has a super power to change lives. But what is love, actually?
It’s a force we feel in countless ways. It is the warm embrace of a parent, filled with care and unwavering support. It is the gentle touch of a lover, sparking a flame that ignites passion and desire. Love is the kind words of a friend, offering solace and understanding in times of need. It is the selfless acts of compassion and empathy that bind humanity together.
Love is not confined to romantic relationships alone. It is found in the family bonds, the connections we forge with friends, and even the compassion we extend to strangers. Love is a thread that weaves through the fabric of our lives, enriching and nourishing our souls.
However, love is not without its complexities. It can be both euphoric and agonizing, uplifting and devastating. Love requires vulnerability, trust, and the willingness to embrace joy and pain. It is a delicate balance between passion and compassion, independence and interdependence.
Finally, the essence of love may be elusive to define with mere words. It is an experience that surpasses language and logic, encompassing a spectrum of emotions and actions. Love is a profound connection that unites us all, reminding us of our shared humanity and the capacity for boundless compassion.
What is love essay: 500 words

A 500-word essay on why I love you
Trying to encapsulate why I love you in a mere 500 words is impossible. My love for you goes beyond the confines of language, transcending words and dwelling in the realm of emotions, connections, and shared experiences. Nevertheless, I shall endeavor to express the depth and breadth of my affection for you.
First and foremost, I love you for who you are. You possess a unique blend of qualities and characteristics that captivate my heart and mind. Your kindness and compassion touch the lives of those around you, and I am grateful to be the recipient of your unwavering care and understanding. Your intelligence and wit constantly challenge me to grow and learn, stimulating my mind and enriching our conversations. You have a beautiful spirit that radiates warmth and joy, and I am drawn to your vibrant energy.
I love the way you make me feel. When I am with you, I feel a sense of comfort and security that allows me to be my true self. Your presence envelops me in a cocoon of love and acceptance, where I can express my thoughts, fears, and dreams without fear of judgment. Your support and encouragement inspire me to pursue my passions and overcome obstacles. With you by my side, I feel empowered to face the world, knowing I have a partner who believes in me.
I love the memories we have created together. From the laughter-filled moments of shared adventures to the quiet and intimate conversations, every memory is etched in my heart. Whether exploring new places, indulging in our favorite activities, or simply enjoying each other’s company in comfortable silence, each experience reinforces our bond. Our shared memories serve as a foundation for our relationship, a testament to the depth of our connection and the love that binds us.
I love your quirks and imperfections. Your true essence shines through these unique aspects! Your little traits make me smile and remind me of the beautiful individual you are. I love how you wrinkle your nose when you laugh, become lost in thought when reading a book, and even sing off-key in the shower. These imperfections make you human, relatable, and utterly lovable.
I love the future we envision together. We support each other’s goals, cheering one another on as we navigate the path toward our dreams. The thought of building a life together, creating a home filled with love and shared experiences, fills my heart with anticipation and excitement. The future we imagine is one that I am eager to explore with you by my side.
In conclusion, the reasons why I love you are as vast and varied as the universe itself. It is a love that defies logic and surpasses the limitations of language. From the depths of my being, I love you for the person you are, the way you make me feel, the memories we cherish, your quirks and imperfections, and the future we envision together. My love for you is boundless, unconditional, and everlasting.
A 5-paragraph essay about love

I’ve gathered all the samples (and a few bonus ones) in one PDF. It’s free to download. So, you can keep it at hand when the time comes to write a love essay.

Ready to Write Your Essay About Love?
Now that you know the definition of a love essay and have many topic ideas, it’s time to write your A-worthy paper! Here go the steps:
- Check all the examples of what is love essay from this post.
- Choose the topic and angle that fits your prompt best.
- Write your original and inspiring story.
Any questions left? Our writers are all ears. Please don’t hesitate to ask!
- Essay samples
- Essay writing
- Writing tips
Recent Posts
- Writing the “Why Should Abortion Be Made Legal” Essay: Sample and Tips
- 3 Examples of Enduring Issue Essays to Write Yours Like a Pro
- Writing Essay on Friendship: 3 Samples to Get Inspired
- How to Structure a Leadership Essay (Samples to Consider)
- What Is Nursing Essay, and How to Write It Like a Pro

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Thesis Statement About Love
Love thesis statement: perfection always betrays our prudence and even our interest.
Mutual love is the most beautiful that can be felt, when there is a bond so formed, so beautiful, so complicit. That you feel that nothing in the world can corrupt that affective bond. Everything works well; it goes on track in your own way, in your way of seeing life. When you’re in love everything seems nicer, you’re happy, nothing bothers you, and you do not even care about the problems, sometimes in a different way “with love”. Everyday life seems more wonderful in fact everything goes spectacular. “Love is long-suffering, it is benign; love has no envy, love is not boastful, it is not puffed up; He does not do anything wrong, he does not seek his own, he does not get irritated, he does not hold a grudge.
Infamous! How can you believe that this way of thinking is correct? Humans are not machines, not plastic, they have feelings, love, hate, sadness and they are governed day by day with them. Why would you ever believe in the man who was unfaithful? Loss of self-esteem: your woman’s ego is trampled, you feel ugly, nothing fits you, you fight with everyone for stupidity, this guy mentally and emotionally ruined you, you start to see problems in you … when it’s not like that.
Page Contents
Thesis statement about love: Love and property
If indeed love is experienced outside of property then people are imprisoned for love.
The improper of the experience of love is its public and community condition; that is, a particular form of intervention on the community violated in the materiality of its territory.
People are guilty of this, above all.
And for such a crime, there is no jurisprudence or law; only a reaffirmation of the universal rights: property as a foundation and property as a social relation. As long as this is assumed as a given thing, every loving expression will be condemned and materially punished.
People stressed the very fabric of the political apparatus of Jujuy to publicly re-establish the ethics of the inappropriate. It gave rise to scenes of public embraces between injured parties and festive experiences outside the private sphere.
Loving is outside of property.
Thesis about love: Love and iconoclasm
If indeed love produces iconoclasm then people are prey for love.
Iconoclasm is presented as a type of register that produces imbalances on the recount of the sensitive. People inscribed the images of the violated of the province on the terrain of the prohibited, on the prohibition of its condition.
The public irruption of this love experience in Jujuy could only occur at the cost of producing intolerable gestures as a way of undoing the sediment images of neatness. To demolish that and to summon the communitarian manifestation of expressions of divertimento and affection between the displaced ones, turned out to be an impossible postcard in the eyes of the ruling businessmen.
People have recovered a portrait of celebration that was historically confined to the back of the neat room. The drive to enroll in the terrain of mountainous civility has been a flagrant crime and a form of plebeian violence: the cursed gesture of insinuating celebratory equity.
Thematic statement examples for love: Love and the archive
If it could not be erased it is because its instructive character is deeper than its grace. Its walls and images today become historical documents, in the registration of signings and nomenclatures, in marks of truth.
A file that, even destroyed, shows a scene acquired rights – exceptionally exceptional – detached from the welfare and donative practice. It illuminates a movement within the limits of what is possible, in its frames of social intelligibility. It illuminates the modes of an affective expression and the daily forms of attachment in precariousness.
A damaged landscape can become an official file especially when you never had one before. Granting that entity is a political gesture that allows us to assume that traditionally relegated expressions of the public scene can effectively be institutionalized.
Theme statements about love: Love and hermeneutics
Love is declared, it is public. And it is also ambivalent since its expression never appears alone but through the emergence of a superposition of affections: shame, pain, pleasure.
To declare is to take the floor and introduce it in an interpretation register. An affective hermeneutics. From there, another story can then be written whose parameters are not fully governed by the criteria of neatness.
The Alto Feeder and the pools, the schools, the recreation and meeting spaces are inscribed as a record of the history of the violated subjects in Jujuy. They give an account of an interpretation of the materiality of the present and construct a prism through which to look at the political, social and cultural processes of the past.
It is an experiential hermeneutics that transcends mere community. That’s why it becomes dangerous: because it pretends to become official and to dispute other ways of interpreting things.
Love and democracy – love thesis statement
Love has no sovereign power.
It does not offer guarantees.
It is not a state.
Maybe because of this, it can be a democratic gesture: a gesture that incorporates, with all its lability, the possibility of a dignified and genuine existence in public life.
Perhaps for this reason, it is also an act of responsibility of and against the violated: a way of responding to the interpellations of power and a community “taking charge” of those actions.
People thus understood love and democracy; moving away from naive and fallible views and, above all, motivated by the commitment to institutionalize – symbolically and materially – an experience of extending rights. He understood that this passage, from a love ethic to a genuinely democratic gesture, is the testimony of a praxis that effectively touched deep-rooted interests in the economic, political and cultural frameworks of a province historically unpunished.
25 Thesis Statement Examples
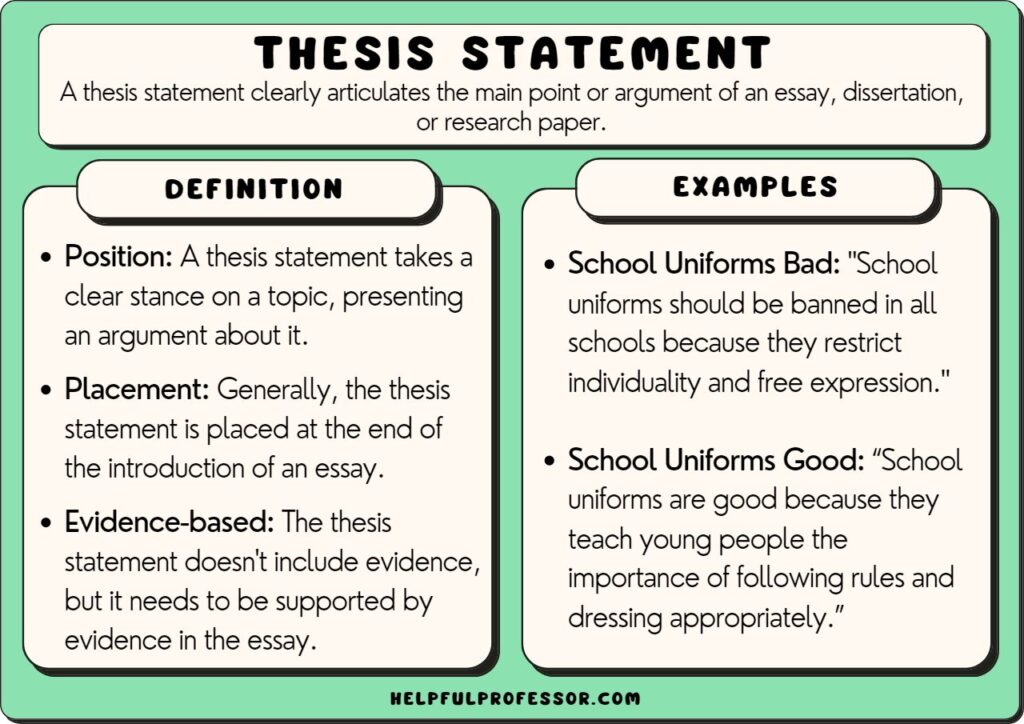
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
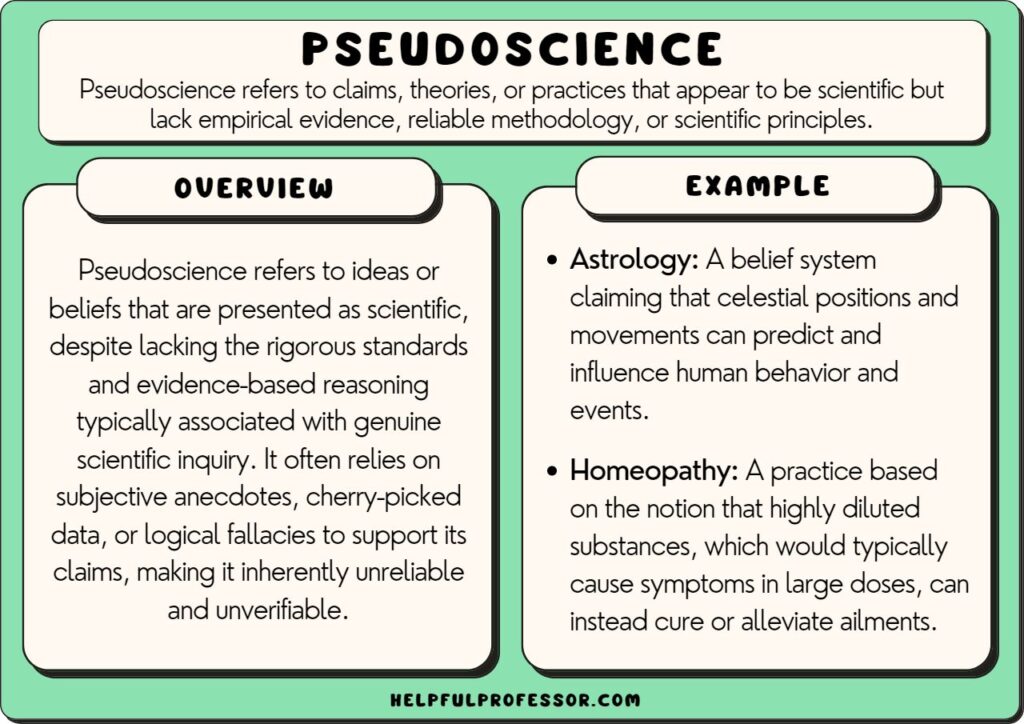
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
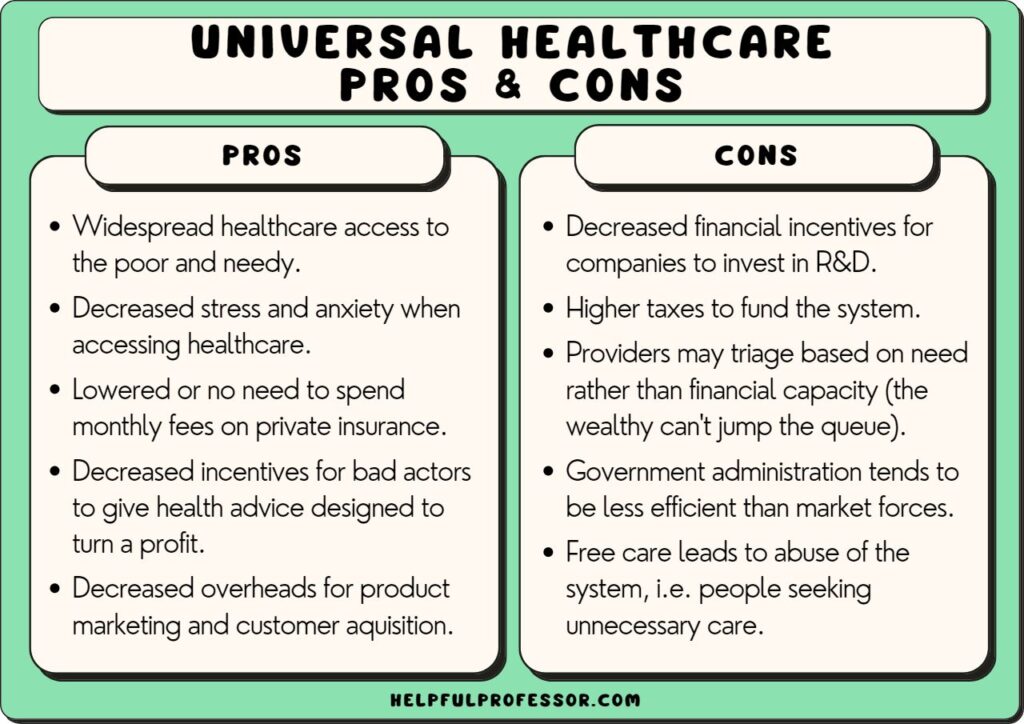
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Benefits to Participating Communities
- Participating School Districts
- Evaluations and Results
- Recognition Accorded
- National Advisory Committee
- Establishing New Institutes
- Topical Index of Curriculum Units
- View Topical Index of Curriculum Units
- Search Curricular Resources
- View Volumes of Curriculum Units from National Seminars
- Find Curriculum Units Written in Seminars Led by Yale Faculty
- Find Curriculum Units Written by Teachers in National Seminars
- Browse Curriculum Units Developed in Teachers Institutes
- On Common Ground
- Reports and Evaluations
- Articles and Essays
- Documentation
- Video Programs
Have a suggestion to improve this page?
To leave a general comment about our Web site, please click here
Share this page with your network.
Examining Poems about Love and Loss
Leonardo da Vinci, the master of art and science, is said to have been asked the great secret of his creativity and brilliance. His answer? "Saper Vedere," or to know how to see. 1 By studying poetry, with a focus on sonnets, elegies, and ecphrasis, my hope is to arm my students with the tools they will need to know how to "see" literature, poetry and art in a deeper and more meaningful way.
Unlike da Vinci, my AP English Literature students often struggle when they attempt to examine, no to mention articulate, what they see. As Deborah Samuel notes, students "resist understanding why they respond in the way that they do." 2 This is particularly troubling for me because, despite the emphasis that is placed on metacognition (awareness of one's own strategies for learning or thinking) at my school, my students want to resist being metacognitive. Furthermore, when faced with the daunting task of studying poetry, many students are stopped in their tracks. "I hate poetry" is a phrase I hear often. Perhaps some students feel, as Richard Andrews (as quoted by Benton) says, that poetry is "an enclosed, self–referential world to which only an elite gain access" 3 . Or, some students may resist poetry due to "its associations with the feminine for 'macho' boys, many of whom [resist] reading of any sort and [reserve] a special contempt for poetry". 4 Whatever the case may be, it seems to me that when studying poetry, my students are likely to be apathetic, if not downright resistant.
Thus, I will work to counteract these feelings about poetry in my unit, "Examining Poems about Love and Loss", which will take place in my Advanced Placement English Literature course. This class is comprised of thirty–two 11 th graders. For many of these students, this will be their first high school course dedicated solely to literature, since we teach a Humanities–based curriculum in the 9 th and 10 th grade, focused more on history and literature about history than dedicated to the study of literature. This unit, devoted to sonnets, elegies, and ecphrasis, will take approximately four weeks, during which time I will meet with my students for two or three blocks a week (blocks are 100 minute class periods).
As an AP English Literature teacher, one of my responsibilities is to foster an understanding of poetic form and its connection to meaning. Until I began teaching this course, I shied away from teaching poetry at all. Part of this was due to student resistance, as I indicated previously, but much of my hesitation was due to my own aversion to poetry. I had never studied it formally, and found it obscure and enigmatic. However, once I began to read essays on poetry, and discovered Mary Oliver's A Poetry Handbook , I was converted.
Oliver's book expatiates on the value of teaching poetic writing, emphasizing the need to study poetry in order to write it. She states that "poetry is a river; many voices travel in it; poem after poem moves along in the exciting crests and falls of the river waves". 5 For me, Oliver's words confirmed the importance of teaching poetry to my students. The poem itself is a conversation between the poet and the reader. If I could help my students learn the vocabulary to be a part of this conversation, then they would gain educational capital that could enhance their learning experience and potential for success on the AP exam.
Poetry also allows me to instill "saper vedere" in my students. According to Dinah Livingstone, poets were once thought to be "seers" and "the germ of a poem is a moment of intense seeing (which includes feeling), an insight , becoming a 'seeing how to say it', which both clarifies the seeing for the seer…and [helps] others see with you". 6 I want to provide an entry point for my students to become part of this conversation regarding "seeing".
How do I open my students' eyes to truly see poetry? Initially, I will do this through a study of poetic forms. Generally, the form of a poem refers to its architectural makeup. For instance, does it fit into a commonly used structure, such as a fourteen–line sonnet, or even more specifically, three quatrains and a couplet? Or might it fit into the category of free verse, which, despite its description as "free", challenges poets to compensate for the lack of conventional form? These distinctions are crucial for my students, so that their opinions can become infused with the nomenclature surrounding poetry. Also, I want them to recognize aspects of meaning that are shaped by these forms. As Frances Mayes indicates, "The form of a good poem occurs simultaneously with the meaning, not as a separate phenomenon." 7 The interplay between the form and the meaning will help my students know how to see.
In an ongoing effort to cull from the multitude of available materials, I wanted to narrow my unit to a theme that can be found both in poetry and in my students' lives. I looked no further than the themes dealing with love and loss. For my students, who are 16 or 17, love is omnipresent, whether they are in the throes of adolescent crushes and relationships themselves, or live vicariously through the portrayal of love in the media. All such relationships shape and impact teenagers' identity. And with love comes its crushing counterpart, loss. Students experience loss in a variety of ways, from the loss of innocence to the breakup of the traditional family unit or even the loss of a family member or loved one. In exploring poems that center on these two themes, my students will have a built–in frame of reference: their own lives.
Finally, I have needed to narrow down the poetic forms we will address in this unit. Naturally, sonnets and elegies lend themselves well to themes of love and loss. Sonnets, in their brevity and strict form, are likely to emphasize one central idea, and build on that idea as the poem continues. It forces the poet to focus on this one central idea, and thus will allow my students to grapple with that idea undistractedly. Elegies, though not as strict in form, are "most often a poem of meditation, usually on love or death", 8 and are thus a natural complement to my unit. Finally, ecphrasis will enhance our study of sonnets and elegies by providing visual images to accompany the poems and reveal the dialogue that exists not only between artists and viewers, but also between artists and writers. In some cases, these ecphrastics may pair with art that embodies love or loss. The layering of art and poetry will provide new entry points for my students, particularly those who are visual or spatial learners—versus my verbal or linguistic learners.
Discussion Goals
One of my primary goals as a teacher is to help my students find, and then use, their voices in academic settings and beyond. In order to achieve that goal, I first need to lessen my students' affective filters. "Affective filter" is a term coined by Steven Krashen, based on his research in second language acquisition, and it is "a screen of emotion that can block language acquisition or learning if it [makes] the users…too self–conscious or too embarrassed to take risks during communicative exchanges". 9 My AP students enter my classroom lacking the requisite vocabulary to speak about poetry. As we uncover basic terms and strategies for studying poetry, I believe that my students' affective filters will be reduced. My hope is that this will diminish the stress that students tend to feel when studying poetry, and will open their eyes to the underlying beauty and complexity of poetry. Also, since the language and structure of the poems may be foreign or challenging to my students, the subjects of love and loss provide entry points through which students can discuss the less verbally current poems in the unit. Once my students recognize that they can conquer the daunting task of analyzing poetry, they can apply this confidence to other areas of their lives in which they have felt silenced or subdued.
Writing Goals
By the end of this unit, I want my students to have gained momentum regarding academic writing. First of all, I want them to learn the language of analyzing poetry, such terms of vocabulary as stanza, couplet, and volta, as well as rhetorical devices like personification or metonymy. Once they gain more facility with this language, I would like my students to be able to develop written assertions about a particular poem in the form of a thesis, and be able to prove the validity of this thesis through the use of well–chosen evidence in an effectively written essay. I would also like my students to be able to draw comparisons between poems, as well as between a poem and a work of art.
Finally, my other objectives are all grounded in the California state standards and in the goals in the College Board's AP English Literature Course Descriptions. The standards being met by this unit can be found in Appendix 1. They focus on reading and writing skills.
Poetic Forms
Sonnets were originally created in Sicily in the thirteenth century, and were named after the Italian word for "little song": sonneto . Sonnets, even in this earliest period, contained fourteen lines. The sonnet form made its way to Italy later in the century, and the most famous Italian writers of sonnets were Dante Alighieri and Francesco Petrarca (also known as Petrarch). According to Burt and Mikics, "Petrarch is the most influential sonnet writer in history." 1 0 The Sicilian form was popularized by Petrarch and is now commonly referred to as the Petrarchan sonnet. This form contains an octave (an eight line section) and a sestet (a six line section). The rhyme scheme in a Petrarchan poem follows this pattern: abbaabba cdecde (or, in the sestet, it may be cdcdcd ). Often, the octave "offers an admirably unified pattern and leads to the volta or "turn" of thought in the more varied sestet…the sestet, on the other hand, with its element of unpredictability…implies an acceleration of thought and feeling." 1 1
Petrarch and Dante both wrote extensively about love. Petrarch's poems often center on Laura, his beloved, who may or may not have existed. He wrote over three hundred poems (including many sonnets) about this unrequited love, typically discussing everything from her lovely features to metaphors comparing her beauty to precious objects and nature.
In the late 1500s, Sir Thomas Wyatt and Henry Howard brought sonnets to England after their travels in Italy. William Shakespeare is perhaps the best known of the British sonnet writers in the early 1600s, having written 154 sonnets that were published in 1609. It was through Shakespeare's work that a new form of sonnet was popularized, and was thus known as the Shakespearean sonnet. This sonnet is marked by three quatrains (four line stanzas), ending with a couplet. The typical rhyme scheme for a Shakespearean sonnet is abab cdcd efef gg .
Shakespeare's sonnets, as with many poets who succeeded him, focused on secular love. The sonnet sequence was, in a sense, a journal for these poets to express their feelings, frustrations, and judgments about love. During the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, poets such as Samuel Coleridge and William Wordsworth took up the sonnet, extending it to be a form "into which poets could pour almost anything." 1 2 Elizabeth Barrett Browning, for instance, subsequently used sonnets to document her courtship with her eventual husband, Robert Browning, while Christina Rossetti used the form to expound on everything from erotic love to political issues. The twentieth century, in its embrace of modernism, was when some poets looked to sonnets to reclaim a poetic history of sorts. Edna St. Vincent Millay, for instance, rejected modernism in favor of the sonnet, as did Harlem Renaissance poets like Claude McKay. As poets continue to play with (and break) the form of the sonnet, this form provides an opportunity for poets to "remind us that the present is surprisingly like the past…that we do not differ so much from the people who love and fear and grieve in poems by Sidney and Shakespeare." 1 3
One sonnet that I plan to use in my unit is "A Superscription" by Italian–British poet Dante Gabriel Rossetti, who wrote it in 1869, seven years after his wife committed suicide. It contains overtones of both love and loss. The poem reads:
After my students participate in small group work to analyze the poem, we will reconvene to unpack this work together. What do my students see? What poetic devices are being used? What are we learning about the complicated nature of love and loss?
The title gestures towards the possibility that this may, in fact, be an ecphrastic poem (which is explained in more detail below). A superscription is something written or engraved on the surface of, outside, or above something else. In this case, perhaps Rossetti is referring to the writing of an artist at the bottom of a finished canvas. Hence, Rossetti is beckoning us to imagine that the poem is a painting, with an allegorical figure (the "I" narrator) at its center. According to Burt and Mikics, this "I" is the poet's muse, "which also encompass(es) the poet in (her) relentless grip." 1 4 She is described as "Might–have–been", "No–more", "Too–late" and "Farewell", as if to say that this figure is a lost love, or a grim reminder of what the reader could have had. With my students, I would look for evidence of who this speaker is. Is it Rossetti's wife, who slipped into alcoholism and killed herself after having a stillborn baby? This might be the case, since she is a "shaken shadow." Or is it one of his alleged mistresses, such as Jane Burden, the wife of his business partner? After all, he does describe her as "Might–have–been", which could be a clue that he wishes he had married Jane Burden before his partner had the chance. Next, we would examine the structure. How does the poem build momentum from the octave to the sestet? Does it change tone dramatically? I would push my students in the direction of the sestet, and particularly the last line, as it is the culmination of the sleepless terror of the sestet. Why did Rossetti use the term "sleepless"? It could be a description of the lack of emotion in the muse's eyes, but more likely, it is a reflection of the poet's own agony over these lost loves. The eyes are described as "commemorative', which is a meditation on this lost love. Further still, the "co– (meaning 'with') implies the lasting bondage of the poet to his muse, who ambushes his heart." 1 5 This exploration of diction in the poem would enhance my students' ability to closely examine every turn of phrase in poetry. As Paul Fry suggests, these turns of phrase are the "tricks that only poetry can play."
One other area that I would encourage my students to examine is the use of symbolism in the poem. Rossetti mentions glass (to describe the muse's eyes) and a shell that she holds up to her ear (another ecphrastic reference to a Renaissance iconography of shells). It is crucial to remember that a shell creates echoes when placed next to one's ear, and "the sounds it makes are dead, a mere trace of the past, as is the vision in the glass in the second quatrain." 1 6 Thus, these inanimate objects could speak to the belief that love is frail and fleeting, like a shell or glass, condemned to reflect the deathly echoes of a lost love.
The term elegy derives from the Greek word, elegos, or mournful song. 1 7 The form of an elegy is not standard; in other words, some poets wrote elegies in iambic couplets, but throughout the centuries, poets have experimented with many forms found under the umbrella of elegy. More commonly, the elegy is marked by a commonality in theme, rather than form. Elegies are meant to "lament, praise and console. All are responses to the experience of loss." 1 8 The term elegy has been used to describe poetry and songs as far back as 7 th century BC. Most commonly, these poems were set to music and commemorated a particular event, such as the death of a loved one. These poems eventually became commemorations of the passing of a famous or influential person (also known as a funeral elegy).
By the twelfth and thirteenth century, elegies began to deal not just with death, but other topics as well. They could include political commentaries or allegories, for instance. These commentaries and allegories were still frequently related to death and grieving, but poets found it easier to shroud grief in these other topics. In the sixteenth century in England, the "connection between death and elegies may have been strengthened by Donne…[and] Milton, [who], in his pastoral Lycidas establish(ed) definitely the elegy as a separate genre in English, the concerns of which are lamenting for the dead and searching for consolation." 1 9 Often, poets used a three quatrain progression to elucidate the stages of coping with death—the first stage being the occasion of grief, then the expression of that grief, and finally the acceptance or transcendence of that grief. 2 0
In the last one hundred years, elegies have become an important reminder of the power of mourning. According to Jahan Ramazani, mourning rites have been stripped of their power due to industrialization—with the upsurge of hospitals, hospices, and funeral homes, death has increasingly been relegated to these spaces or perceived as a "taboo" subject. 2 1 In contrast to the elegies of earlier periods, which provided a sense of consolation to those who mourn, Ramazani suggests that many modern elegies express a lack of resolution, often marked by a resistance to consolation or an outright anger at the dead, or at God, or even at elegies themselves. Modern elegies of this type that I will study with my students may include Elizabeth Bishop's "One Art", William Carlos Williams' "Death", and Anne Sexton's "A Curse Against Elegies."
Another poem I intend to use is "Bells for John Whiteside's Daughter" by John Crowe Ransom, which deals with the precarious nature of human life. The poem is about the death of a young, graceful girl. This poem will meet my need to look at how form influences the meaning of an elegy, because the poem is written in four quatrains, each rich with imagery ("noon apple dreams and scuttle goose–fashion"), hyperbole ("such speed in her little body"), symbolism (the geese, the bells), juxtaposition (her vivacity juxtaposed with her death) and paradox (life–death). This poem is also an ideal vehicle for teaching my students how to "see". Ransom never says that word "death" in the poem. Rather, he indicates her death through the euphemistic description of "her brown study", a repetition of his description of her in the beginning of the poem, when she was alive. This movement of thought is in fact reminiscent of the initial shock at a death, when mourners are awakened to their memories of the deceased being alive, and may feel an inability to articulate, much less accept, that their loved one is gone. Finally, this poem can serve as a meditation on death in general. No matter how much "lightness" one has, life will eventually be "stopped" by death.
Ecphrasis (ekphrasis) is the poetic description of a man–made object. The word is derived from the Greek, with the roots ek and phrasis , or 'out' and 'speak'. Ecphrastic poems, according to John Hollander, may be described as "those which involve descriptions or other sorts of verbal representation of works of art." 2 2 The first type is known as notional ecphrasis, or the description of purely fictional art. Early examples include Homer's description of the shield of Achilles in The Iliad , or Dante's description of the white marble bank full of carvings in Purgatory. On the other hand, actual ecphrasis is a poem that deals with a physical object that actually exists or has existed, such as Emma Lazarus describing the Statue of Liberty in her poem "The New Colossus". Finally, unassessable actual ecphrastics are poems that discuss an actual piece of art that is no longer in existence or unavailable to be seen, such as the clock in Gjertrud Schnackenberg's "Nightfishing."
Ecphrastic poetry deals with the interaction between the poet and the painter, or the poem and painting. At times, this relationship is tense. Poets may express their own beliefs in the poem, and imbue meaning in or make sense of what they are writing. The painter, though, may be free to luxuriate in the silence of art—the painting can simply "be" (or so the poet thinks). Additionally, poets may, at times, impose their own gaze on the painting, as in the very male point of view in XJ Kennedy's "Nude Descending a Staircase", written in response to Duchamp's painting of the same name.
In other poems about art, though, there is a reverence attached to the art's silence, conveyed by the poet's use of hushed language, with words like "stillness" or "silence." Poetry is, by nature, a conversation, and poets may admire painting for its ability to be still. However, another way of approaching ecphrasis is that it encourages an equal exchange and interdependency between the two forms of art. The process of writing about art allows both media to build on and supplement one another.
Teaching Philosophy
Before diving into the strategies of this specific unit, I feel I must say a few words about my pedagogical approach. Essentially, my belief is that the optimal situation in which learning occurs is one where students are actively engaged. Paulo Freire, best known for his book, Pedagogy of the Oppressed , supports this belief. Among his many ideas, Freire places great emphasis on the use of dialogue in an educational setting. As M. K. Smith states:
Paulo Freire's…insistence [was] that dialogue involves respect. It should not involve one person acting on another, but rather people working with each other. Too much education, Paulo Freire argues, involves "banking" – the educator making "deposits" in the educatee. 2 3
Thus, in my classroom, I encourage peer–to–peer dialogue, as well as small group discussion and whole class discussion, facilitated (but not led) by me. Rather than taking center stage, I encourage my students to make meaning together and become more autonomous in their thinking, rather than relying on me for the "right" answer. This, according to Freire, leads to a sense of community and social awareness. Freire also postulates that those who have been forced into voicelesness, in other words the oppressed, are thus given a voice in this mode of education. 2 4 Since many students feel voiceless—owing to being raised to defer to adults' voices, or because of second language barriers, or general shyness—helping them find a voice in my classroom is a central goal. If they achieve this goal, my students may find a voice not only in class, but also in their communities and beyond.
Building on the Freirian model, I look towards the constructivist theory to guide my pedagogy. Jacqueline Grennon Brooks writes that "constructing knowledge talks about how we as the learners are reformulating, refiltering, relooking at…the way that we see our world, that the teacher can't give away explanations, the teacher can't give away knowledge, the student can't receive it passively from the teacher." 2 5 In my classroom, this constructivist approach leads to a spiral of learning, where we often return to and deepen our knowledge of concepts, such as symbolism or imagery, rather than declare "we've learned that" and move on. Consequently, my unit will build on the notion that we are all learners in my classroom, and need to be constantly revisiting and re–envisioning our ideas in order to gain a deep and authentic understanding of what we study.
In this poetry unit, I plan to use a series of sonnets and elegies, some of which are ecphrastic, to build poetic vocabulary and writing skills in my AP English Literature class. This unit will take place over a four–week period. My school has a rotating block schedule, so I see my students every other day, either Monday–Wednesday–Friday or Tuesday–Thursday, depending on the week. Thus, in those four weeks, I will have ten class sessions to complete this unit.
In the first week, we will begin with introductory activities. I usually start with Seamus Heaney's "Sonnet #5" and show my students how to annotate it—noting the meaning of the poem by looking at its structure, speaker, tone, poetic devices, and deeper truths. We will then read an article about how to analyze poetry, and this session will end with a homework assignment in which students will be given an article on how to read Shakespeare's poems, as well as an illustrated version of Shakespeare's "Sonnet 18." In the second session, I will conduct a mini–lesson on the history of the sonnet. Then, we will discuss our ideas about "Sonnet 18," which will segue into studying Shakespeare's "Sonnet 138" ("When my love swears that she is made of truth") as a classic example of a Shakespearean sonnet. Students will be given a homework assignment to read, annotate, and develop a thesis for "Shakespeare's "Sonnet 130" ("My mistress' eyes are nothing like the sun"). To end the first week, I will work with my students on how to build a strong compare/contrast essay, and will have them read "Sonnet 43" ("How Do I Love Thee") by Elizabeth Barrett Browning. Their homework will be to read "Paradise Saved (Another Version of the Fall)" by A.D. Hope and complete a writing exercise in which they contrast the poem with the Bible version of the Adam and Eve story. Throughout these lessons, I will point my students towards new vocabulary, such as the terminology of the sonnet form and any new literary devices that appear in the poems. They will have a master list of literary vocabulary to reference as well.
The second week of class will begin with a fishbowl discussion based on the students' homework from the previous weekend. This fishbowl will conclude with a timed write in which I ask students to compare/contrast the poem to the Bible story. Following that session, I will introduce ecphrasis, and end this portion of the unit by giving a lesson on "Not My Best Side" by UA Fanthorpe, which is not only an ecphrastic poem but one that also provides a feminist perspective on classic notions of Arthurian romance.
In the third week, we will transition into elegies. To begin, we will read "Bells for John Whiteside's Daughter" by John Crowe Ransom, followed by activities regarding Elizabeth Bishop's "One Art", William Carlos Williams' "Death", and Anne Sexton's "A Curse Against Elegies." Throughout these lessons, students will be learning how to see, through pair work, small group work, and fishbowl discussions, as well as in–class timed writes. We will close out the section on elegies by doing a case study of Gjertrud Schnackenberg, in which we carefully read her ecphrastic poems "Nightfishing" and "Self Portrait of Ivan Generalic."
Finally, we will go to the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art. After a docent–led tour, I will ask my students to choose a piece of art in the museum that inspires feelings of love or loss for them. They will spend time in silent reflection with their chosen piece of art, and will begin to construct an ecphrastic poem, which they will revise and complete as their final project of the unit.
Throughout the unit, we will keep a class list of themes regarding love and loss, which we learn through the study of each of the poems. Additionally, students will write at least three in–class timed writes and one or two practice multiple choice tests, modeled after the multiple choice portions of the AP English Literature exam.
Discussion Strategies
In keeping with my constructivist approach, I place great emphasis on discussion in my classroom. This takes on different forms, depending on the day and the poem we will be discussing. Generally, though, I use four discussion strategies: small group work, write–pair–share, jigsaws, and fishbowl discussions.
Small Group Work
When the unit begins, I split my class into eight poetry groups, with four students in each group. Whenever possible, I try to group students heterogeneously by skill level, gender, and, to some extent, personality and general speaking skills. These groups will meet three to four times during the course of the unit, within which time they will be given four copies of a poem that I have chosen, and will use the SOAPSTone strategy, discussed below. My expectation, repeated often to the students, is that they will actively participate and take notes. Students will come to expect that I will call on them at random when we reconvene as a whole class, so they use their small group work notes to contribute to class discussions on the poem they have worked through in their small group. I have found that shy students gain confidence when they can look to their notes, which allows richer conversations overall.
Write–Pair–Share
Write–Pair–Share is a discussion strategy that was originally developed by Frank Lyman, and its goal is to foster discussion where many students feel empowered to participate. First, the teacher poses a question, or problem, or quotation. Students then silently write their responses. I typically give two to five minutes, depending on the complexity of my question. Next, students pair up (or I choose pairs for them) and they discuss their responses out loud. Finally, the class reconvenes as a whole, and I call on a number of students to share out what they discussed with their partner. At times, students may be asked to share their own ideas, but in other instances, students may be asked to share their partner's ideas.
I like this strategy for several reasons. It allows my students to gather their thoughts, particularly when I ask them an open–ended or provocative question. Additionally, it allows space for students to then "test" their answers out on one another. They may find, in the Pair portion of the activity, that they could rephrase their idea for clarity's sake. Or, they may find their partner's idea compelling, complementary, or contradictory to their own, which may force them to re–think or deepen their own response. Once the students have processed their own ideas, tested them out with a partner, and gained clarity on their ideas, they may have more confidence to speak during the whole class discussion.
Throughout the year, I use the fishbowl technique in my AP Lit class. Since I have thirty–two students in my class, whole–class discussions tend to be dominated by eight to ten students. In order to quell these powerful voices, I provide space for my quieter students to take the stage.
The fishbowl strategy has three parts: preparation, discussion, and debrief. In the first part, students prepare for the fishbowl discussion in their aforementioned poetry groups. I provide students with a poem to study and a handout, such as the SOAPSTone handout described below, for them to structure their conversation. Then, after a predetermined amount of time (usually about 40 minutes), we reorganize the room into two concentric circles. The "inside" circle (or fishbowl) is populated by one third of my students, or roughly 11 students, whom I have chosen. The "outside" circle consists of the rest of the class. We complete this activity three times during the unit, so that each student participates in one fishbowl.
For the next 30 to 45 minutes, the fishbowl group participates in a discussion that is observed by the outside circle and by me. My general rule of thumb is that I say nothing during these discussions, but I do allow for an empty desk, which can be used by students from the outside circle who have something compelling and brief to contribute. Otherwise, the outside circle is taking notes. Once the discussion is over, the class reviews how the fishbowl went. I ask first for "warm" feedback (what went well) from the outside circle, then the inside circle. I then ask for "cool" feedback (what could have gone better) from the outside, then inside, circles. Finally, I give warm and cool feedback and explain what I would like to see in the next fishbowl, and afterwards, I grade the students on a fishbowl rubric (see Appendix 2).
The Jigsaw strategy is a prime example of cooperative learning, or students actively learning from and engaging with one another. Simply put, jigsaw is a classroom–based team sport. No student can be successful unless all students work together as a team, or cooperate, and equally value all voices.
The basic structure of a Jigsaw is twofold. First, students shift into small groups, typically of four students (in my class, this would be their poetry group). These groups are given a task that is different from those of the rest of the groups in the class. In this unit, I would use a jigsaw if I wanted to address several poems in one class period, and would give a different poem to each group and ask them to do SOAPSTone with their poem. I would then give them an allotted amount of time to work together with their group to complete their task, making sure that every member of their group has written proof of the work they've done. When the allotted time is over, they shift into new groups, based on numbers I have handed out during their poetry group work time. Once they are in their new groups, I give them a new task (which usually involves sharing out what they did in their first group) to complete. Thus, each student becomes an expert on the work they did in their poetry group, and shares their knowledge with a new group of students.
Analysis and Writing Strategies
When students get into their poetry groups, the most common exercise that I ask them to complete is SOAPSTone. In brief, here are the guidelines for SOAPSTONE, which I either project on an overhead projector or distribute in handout form:
- Subjec t––elevator pitch. Describe what the poem is about in no more than 3–4 sentences.
- Occasion ––did something happen to make the speaker want to express something?
- Audience ––To whom is the speaker speaking? Why?
- Purpose ––What will the speaker gain from this poem? What might the poet gain?
- Speaker(s) ––Who is the speaker? Why did the poet choose this narrative style?
- Tone —what adjectives would you use to describe this poem? Why?
Each group is then expected to interact with the poem to figure out the answers to each element of SOAPSTone. They make annotations on the poems by underlining words that stand out to them, circling literary devices, and writing in the margins. They also take notes on their discoveries and support their ideas with quotes (words or phrases) from the poem. An additional question that I always include with SOAPSTone is: What literary devices are used in the poem, and how do they add to the meaning of the overall poem? Students may use the literary devices they find to support their ideas on tone, speaker, or any other part of SOAPSTone. Finally, I ask students to discuss what they think the message of the poem is. I request that they steer clear of clichs and instead focus on the "truth" of the poem. When they are finished examining the poem in small groups, we share out ideas in a larger group discussion.
Thesis Drills
This strategy typically follows some of the previous strategies, but always occurs after students have been exposed to a poem and have arrived, as a class, at an understanding of the form and meaning of the poem.
In a thesis drill, I give my students an essay prompt, modeled after (or taken directly from) an AP English Literature essay question from a previous AP exam. Typically, the students then go home and write a thesis in response to the essay question, as their homework assignment. Their thesis should show their ability to exhibit clarity and sophistication in their writing. Below their thesis idea, I ask them to brainstorm evidence from the poem that they could use to support their thesis. Most students complete this task by creating a bullet point list, each bullet being one piece of evidence followed by brief ideas about how to use the evidence. When the class meets again, we begin the day by sharing out thesis ideas. I may ask a student to write their thesis on the board and then ask the others to assess it and brainstorm ideas about how to develop the thesis into an essay, or might do a Pair–Share activity to have students compare their thesis statements. At times, these thesis statements may be used in a timed write (a fifty minute in–class essay) that day, but often, the thesis drill is the culminating exercise of a lesson.
Timed Writes
On the AP English Literature exam, students are expected to write three essays in 120 minutes, which means that they should be able to write an effective and sophisticated essay in approximately forty minutes. In order to prepare my students to write under time constraints, I give them two or three in–class timed writes in each unit we complete. In the fall, I allow students up to sixty minutes to complete their timed writes, which usually take place in the second half of the class, after a discussion of thesis statements or immediately following a fishbowl discussion. I do this so that my students have had the chance to formulate their ideas in conversation with others. As the year progresses, I take off the training wheels, as it were, and ask students to write under pressure with less and less discussion and support. By the end of the year, they are given a poem or excerpt from a novel and asked to write on command for forty minutes, with no discussion.
Classroom Activities
Lesson 1: introducing the poetry unit.
On the first day of this poetry unit, I plan to start by projecting Seamus Heaney's "Sonnet 5", from Clearances , on the board. This poem, a variation on a sonnet, centers on two people in the act of folding laundry from an outdoor laundry line. After reading the poem aloud, I will ask for two students to get up and silently act out what has taken place in the poem. The class will analyze how well they performed the actions of the poem. This will be followed by a discussion of how we, as readers, can take a poem and act it out. What clues are we given? Some discussion questions might include:
- What words resonate with you or seem rich with meaning?
- Do you recognize any literary devices? How do they add to the meaning of the poem? (students will likely mention onomatopoeia and perhaps syntax, imagery, and diction)
- Who is speaking in the poem? Is there anyone else in the poem?
- What is Heaney trying to say?
After this brief discussion, we will discuss the idea that reading poetry is like solving a puzzle. You need to look for many types of clues to fully understand it. For instance, the clues we just uncovered in "Sonnet 5" dealt with form, literary devices, speaker and theme. In other instances, we might look to rhyme, meter, historical context, or even other poems by the same author, to develop assertions about the poem. In order to keep track of these clues, we must annotate the poem. This would be the next step in this lesson.
Throughout the unit, I will expect my students to annotate any poem they receive from me, so this introductory exercise is crucial. I will pass out a handout with instructions and an example for how to annotate (See Appendix 3). We will then follow the instructions on the handout to begin to annotate "Sonnet 5." After we have completed a line or two together as a class, I will ask students to pair up and finish their annotations, and then we will share out the clues that students discovered through the annotation exercise.
I will finish the day by providing three handouts: a copy of Shakespeare's "Sonnet 18", along with an article on how to read Shakespeare's writing, and a copy of a cartoon version of the same poem, taken from Poetry Comics by David Morice. Their assignment will be to read the article on understanding Shakespeare, then read and annotate the sonnet, and finally read the comic version of the poem. My hope is that they will not only begin to understand Shakespeare's language and themes, but will see that poetry can be playful as well.
Lesson 2: Ecphrastic Poetry
Once we have spent approximately one week studying love sonnets, my goal is to complicate my students' understanding of love. Traditional love, according to many of my students, could be defined by the Cinderella story—a man comes in and whisks a woman out of a difficult situation, and they live happily ever after. However, this is not reality. Thus, I want to read "Not My Best Side" by UA Fanthorpe, in order to discriminate reality from "Disney" romance.
The day will begin with a write–pair–share activity. On the board, I will write the following questions: What lessons do Disney movies typically teach us about love? According to these movies, what is the role of women in courtship, love and marriage? What about men? Finally, pick a Disney movie and discuss it—what lessons are being taught about love? After students have had roughly five to ten minutes to write, they will pair up with someone sitting near them and converse about their thoughts on these questions. We will then have a class conversation about these ideas.
We will transition from this discussion into "Not My Best Side." Fanthorpe's poem is structured in three parts. The first is from the point of view of a dragon, the second from a typically fairy tale princess, and the third from the knight in shining armor. I will split my students into three groups, and give each group one section of the poem. It will be their task to read their section, and then discuss who the speaker is and what the main concerns of this speaker are. I will ask each group to have a recorder, who takes notes on their discussion, and a reporter, who will share out their findings. After a brief discussion, we will reconvene as a whole class. I will ask one member of each group to read their section to the whole class, and discuss who their speaker is. As a class, we will establish who the three voices are in the poem, and how their priorities differ. I will then ask for a volunteer to sketch the poem on the board in the form of a cartoon. What might a visual image of this poem look like? Other students may chime in with ideas for the artist. Once the visual has been completed, I will display Paolo Uccello's painting, "St. George and the Dragon" on my whiteboard.
We will review the term ecphrasis , having discussed it earlier in the unit, and I will ask my students to discuss Uccello's painting in comparison to Fanthorpe's poem. How are they similar? What are their differences, specifically regarding theme?
Subsequently, I will move students into their poetry groups, and ask them to complete two exercises. First, they will do SOAPSTone on this poem, annotating the poem on a handout that I will provide. Second, in framing the theme of the poem, I want them to discuss the following quote, from Hilary Crew in her article "Spinning New Tales from Traditional Texts": Feminists…have written of the importance of issues of giving voice, agency, and subjectivity to those who have been previously silenced and objectified." My hope is that students will dig beneath the surface humor of the poem to see the underlying feminist message.
The final piece of this lesson will be homework that the students will be expected to complete. I will give them a slip of paper with the following two essay prompts:
- Read carefully the poem by U.A. Fanthorpe. Then write an essay analyzing how Fanthorpe employs dramatic voice to add meaning to the poem.
- Write a well–organized essay in which you analyze the techniques the poet uses to convey her attitude towards traditional notions of love in fairy tales.
Their job will be to pick one of the prompts, write a thesis statement and brainstorm ways that they would develop that thesis statement. We will discuss their ideas when we meet in the next session.
Lesson 3: Analyzing Elegies
This final lesson will take place during the elegy portion of my unit. Prior to entering class for this lesson, students will have read "Death" by William Carlos Williams and "A Curse Against Elegies" by Anne Sexton, both of which are ruminations on death and rail against death, and even against elegies in general. For homework, they will annotate these poems, specifically looking for thematic clues regarding death.
To start the day, I will review the terms euphony and cacophony with my students. When words sound harmonious and create a soothing effect, it's known as euphony. Alternately, when words sound harsh or discordant, they are thought to be cacophonous. I will ask my students to identify which letters/sounds seem euphonic to them, and which sound cacophonic. Since "Death" and "A Curse Against Elegies" both have many cacophonous sounds, I wanted to raise their awareness of these terms so they can use them in their discussions.
For the next twenty minutes, I will ask my students to get into their poetry groups. In their groups, they will go over one of the poems they were given for homework (I will determine which groups will discuss which poems). During their discussion, their primary goal is to complete SOAPSTone, as well as identify literary devices found within their poem. When the twenty minutes are up, we will rearrange the room to get into the fishbowl configuration. The students who analyzed "A Curse Against Elegies" will join the middle circle. For the next twenty–five minutes, it will be their job to discuss the deeper truths of the poem. On the board, I would put these guiding questions:
- What aspects of SOAPSTone stand out, and how do those aspects help you understand the deeper meaning of the poem?
- How does the form (elegy, use of stanzas, etc) impact the meaning of the poem?
- What is the overall theme of the poem, and how does it reflect the themes we've discussed regarding grief?
- How do the literary devices help to further develop this theme?
These are the questions that will guide the fishbowl discussion. When twenty–five minutes have passed, the groups will switch, and the second set of students will use the same guiding questions to discuss "Death."
To conclude this lesson, I will ask my students to complete an exit ticket, in which they write a thesis statement based on this essay prompt: Choose one of the poems we just discussed. Write an essay in which you describe the speaker's attitude toward death. Using specific references to the text, show how the use of language reveals the speaker's attitude.
Annotated Bibliography
Burt, Stephen, and David Mikics. The Art of the Sonnet . Cambridge: Belknap Press Of Harvard University Press, 2010. Excellent resource regarding the history of the sonnet, with many examples included.
Freire, Paulo. Pedagogy of the Oppressed . New York: Continuum International Publishing Group, 2000. This is a groundbreaking book, based on Freire's experiences with helping adult Brazilians achieve literacy. The book is a wonderful introduction to anti–oppressionist education, with an emphasis on dialogue and mutual respect.
Hollander, John. The Gazer's Spirit: Poems Speaking to Silent Works of Art. 1 ed. Chicago: University Of Chicago Press, 1995. Hollander's book offers an expanded look at ecphrastic poetry.
Kennedy, David. ELEGY (The New Critical Idiom) . 1 ed. New York: Routledge, 2007. Part of the New Critical Idiom series, this book speaks of the origins of elegies, and also provides close reading and analysis of elegies.
Livingstone, Dinah. Poetry Handbook : For Readers and Writers. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company, 1993. This is a good resource for teaching meter, rhythm, and poetic form.
Morice, Dave. Poetry Comics . T&W Books, 2002. I will use this book to show my students a comic version of "Sonnet 18". It also features comic versions of "The Raven", "Some Trees" and many more.
Oliver, Mary. A Poetry Handbook . 1 ed. New York: Harvest Books, 1994. This slim volume extols the value of studying poetry as a means towards writing poetry.
The New Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics . 3 ed. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1993. This encyclopedia offers rich explanations of poetic terms, genres, and movements.
California English Language Arts Standards met by this unit
- Analyze the way in which clarity of meaning is affected by the patterns of organization, hierarchical structures, repetition of the main ideas, syntax, and word choice in the text.
- Analyze characteristics of subgenres (e.g., satire, parody, allegory, pastoral) that are used in poetry, prose, plays, novels, short stories, essays, and other basic genres.
- Analyze the way in which the theme or meaning of a selection represents a view or comment on life, using textual evidence to support the claim.
- Analyze the ways in which irony, tone, mood, the author's style, and the "sound" of language achieve specific rhetorical or aesthetic purposes or both.
- Analyze ways in which poets use imagery, personification, figures of speech, and sounds to evoke readers' emotions.
- Analyze recognized works of world literature from a variety of authors.
- Structure ideas and arguments in a sustained, persuasive, and sophisticated way and support them with precise and relevant examples.
- Enhance meaning by employing rhetorical devices, including the extended use of parallelism, repetition, and analogy;
- Use language in natural, fresh, and vivid ways to establish a specific tone.
College Board Course Description for AP English Literature
Writing: Writing instruction includes attention to developing and organizing ideas in clear, coherent and persuasive language. It includes study of the elements of style. And it attends to matters of precision and correctness as necessary.
Throughout the course, emphasis is placed on helping students develop stylistic maturity, which, for AP English, is characterized by the following:
- a wide–ranging vocabulary used with denotative accuracy and connotative resourcefulness;
- a variety of sentence structures, including appropriate use of subordinate and coordinate constructions;
- a logical organization, enhanced by specific techniques of coherence such as repetition, transitions and emphasis.
Fishbowl Rubric
Scoring is somewhat dependent on the quality of comments, but as a general practice, I score on the following scale:
Comments more than 10 times, including several references to text, as well as analytical comments: A–A+
Comments more than 10 times, but lacks analysis or textual references: B+
Comments 7–10 times: B–/B
Comments 4–6 times: C/C+
Comments fewer than 4 times: C– or lower, depending on quality of comments
Annotating a Poem
Annotation means to mark critically. When reading poetry, it is crucial to mark the poem, noting all kinds of details that will help you understand the poem better. In other words, it is using the method of close reading to further your understanding of poetry. Annotation can provide you with wonderful ideas to offer in small groups and whole class discussions.
What to annotate:
- Literary devices—note them and then try to figure out why they are used
- Form—look carefully at rhyme and meter. This may help you uncover the mood or tone, or establish that this is a particular type of poem, such as a sonnet. You can number the lines or mark the rhyme scheme using alphabetical notations.
- Binaries—these are ideas that are in opposition to each other, such as light/dark. Think about why the poet might create these binaries in the poem.
- Speaker—look for clues about who is speaking. What point of view is the poem written in? What do you learn about the speaker? Remember—the speaker is not the poet, in most cases!
- Word choice—do you notice use of dialect? Jargon? Big vocabulary words? Mark these words if they stand out to you.
How to annotate:
Use your instincts. You can circle or star words that stand out, or underline key phrases. Be sure to make lots of comments in the margins. Please use our annotation of "Sonnet 5" by Seamus Heaney as an example as you go forward in this unit.
Resources for Teachers
Modern American Poetry http://www.english.illinois.edu/maps/
This online journal and online companion to the Anthology of Modern American Poetry is valuable to teachers and students alike. The site offers analysis and commentary on a wide range of poems, mostly from the 20 th and 21 st centuries.
Poetry Foundation http://www.poetryfoundation.org
This website is another wonderful location for finding and understanding poetry. I particularly like their "Poetry Tool", where you can search for poems by title, author, occasion, glossary term, or most popular. Also, the "Learning Lab" offers annotations and analysis of many poems.
Poets.org http://www.poets.org
Created and maintained by the Academy of American Poets, this website is my first stop when looking for online versions of poems dating back to Shakespeare. The Academy also offers poetry writing contests for high school students.
Read Write Think http://www.readwritethink.org
Maintained by the National Council of Teachers of English (NCTE), this website has a wealth of lesson plans on many subjects, including poetry.
Sonnet Central http://www.sonnets.org/
This website is also very helpful to all teachers and students studying the sonnet. Almost all of the sonnets referred to in this curriculum unit can be found at this website.
Resources for Students
Poetry reading list.
"Sonnet 18" Shakespeare
"Sonnet 130" Shakespeare
"Sonnet 138" Shakespeare
"How do I Love Thee" by Elizabeth Barrett Browning
"A Superscription" by Dante Gabriel Rossetti*
"Paradise Saved (Another Version of the Fall)" by AD Hope*
"One Art" by Elizabeth Bishop
"Sonnet 5" by Seamus Heaney
"Not My Best Side" UA Fanthorpe*
"Bells for John Whiteside's Daughter" by John Crowe Ransom
"Death" by William Carlos Williams
"A Curse Against Elegies" by Anne Sexton
"Nightfishing" by Gjertrud Schnackenberg*
"Ivan Generalic" by Gjertrud Schnackenberg*
(Ecphrastic poems are noted with an asterisk. Most images that pair with these poems can be found online using a simple Google search)
- Rutledge, John . "Saper Vedere." Rutledge Capital . 25 Mar. 2008. rutledgecapital.com/2008/03/25/saper–vedere/ >. (accessed 5 June 2010).
- Samuel, Deborah. "Detecting Shakespeare's Sonnets." Yale National Initiative . teachers.yale.edu/curriculum/search/viewer.php?skin=h&id=initiative_08.01.10_u >. (accessed 5 July 2010).
- Benton, Peter. "Unweaving the Rainbow: Poetry Teaching in the Secondary School ." Oxford Review of Education 25 .4 (1999): 521–531.
- Oliver, Mary. A Poetry Handbook . Harcourt Brace and Company: San Diego 1994.
- Livingstone, 68.
- Mayes, Frances. The Discovery of Poetry: A Field Guide to Reading and Writing Poems. New York: Harvest Books, 2001. 302.
- The New Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics , 322.
- "Language Acquisition." Earth Renewal. 8 July 2010. earthrenewal.org/secondlang.htm>.
- Burt and Mikics. 8
- The New Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics , 1168.
- Burt and Mikics, 18.
- Burt and Mikics 199
- Burt and Mikics 201
- Burt and Mikics, 200
- Kennedy, 11.
- The New Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics , 324.
- "On "Bells for John Whiteside's Daughter"." Modern American Poetry . University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. www.english.illinois.edu/maps/poets/m_r/ransom/bells.htm >. (accessed 10 July 2010).
- Ramazani, Jahan. Poetry of Mourning: The Modern Elegy from Hardy to Heaney . 1 ed. Chicago: University Of Chicago Press, 1994. 1.
- Hollander, 4.
- Smith, M.K.. "Paulo Freire and informal education." Informal Education . 4 Nov. 2009. Web. http://www.infed.org/thinkers/et–freir.htm>. (accessed 7 July 2010).
- "Constructivism as a Paradigm for Teaching and Learning." THIRTEEN . http://www.thirteen.org/edonline/concept2class/constructivism/index_sub3.html>. (accessed 10 July 2010).
Comments (0)
Be the first person to comment

Thesis Statements for a Literature Assignment
A thesis prepares the reader for what you are about to say. As such, your paper needs to be interesting in order for your thesis to be interesting. Your thesis needs to be interesting because it needs to capture a reader's attention. If a reader looks at your thesis and says "so what?", your thesis has failed to do its job, and chances are your paper has as well. Thus, make your thesis provocative and open to reasonable disagreement, but then write persuasively enough to sway those who might be disagree.
Keep in mind the following when formulating a thesis:
- A Thesis Should Not State the Obvious
- Use Literary Terms in Thesis With Care
- A Thesis Should be Balanced
- A Thesis Can be a Blueprint
Avoid the Obvious
Bland: Dorothy Parker's "Résumé" uses images of suicide to make her point about living.
This is bland because it's obvious and incontestable. A reader looks at it and says, "so what?"
However, consider this alternative:
Dorothy Parker's "Résumé" doesn't celebrate life, but rather scorns those who would fake or attempt suicide just to get attention.
The first thesis merely describes something about the poem; the second tells the reader what the writer thinks the poem is about--it offers a reading or interpretation. The paper would need to support that reading and would very likely examine the way Parker uses images of suicide to make the point the writer claims.
Use Literary Terms in Thesis Only to Make Larger Points
Poems and novels generally use rhyme, meter, imagery, simile, metaphor, stanzas, characters, themes, settings and so on. While these terms are important for you to use in your analysis and your arguments, that they exist in the work you are writing about should not be the main point of your thesis. Unless the poet or novelist uses these elements in some unexpected way to shape the work's meaning, it's generally a good idea not to draw attention to the use of literary devices in thesis statements because an intelligent reader expects a poem or novel to use literary of these elements. Therefore, a thesis that only says a work uses literary devices isn't a good thesis because all it is doing is stating the obvious, leading the reader to say, "so what?"
However, you can use literary terms in a thesis if the purpose is to explain how the terms contribute to the work's meaning or understanding. Here's an example of thesis statement that does call attention to literary devices because they are central to the paper's argument. Literary terms are placed in italics.
Don Marquis introduced Archy and Mehitabel in his Sun Dial column by combining the conventions of free verse poetry with newspaper prose so intimately that in "the coming of Archy," the entire column represents a complete poem and not a free verse poem preceded by a prose introduction .
Note the difference between this thesis and the first bland thesis on the Parker poem. This thesis does more than say certain literary devices exist in the poem; it argues that they exist in a specific relationship to one another and makes a fairly startling claim, one that many would disagree with and one that the writer will need to persuade her readers on.
Keep Your Thesis Balanced
Keep the thesis balanced. If it's too general, it becomes vague; if it's too specific, it cannot be developed. If it's merely descriptive (like the bland example above), it gives the reader no compelling reason to go on. The thesis should be dramatic, have some tension in it, and should need to be proved (another reason for avoiding the obvious).
Too general: Edna St. Vincent Millay wrote many poems with love as the theme. Too specific: Edna St. Vincent Millay wrote "Love is not all: it is not meat nor drink" in <insert date> after <insert event from her life>. Too descriptive: Edna St. Vincent Millay's "Love is not all: it is not meat nor drink" is a sonnet with two parts; the first six lines propose a view of love and the next eight complicate that view. With tension and which will need proving: Despite her avowal on the importance of love, and despite her belief that she would not sell her love, the speaker in Edna St. Vincent Millay's "Love is not all: it is not meat nor drink" remains unconvinced and bitter, as if she is trying to trick herself into believing that love really does matter for more than the one night she is in some lover's arms.
Your Thesis Can Be A Blueprint
A thesis can be used as roadmap or blueprint for your paper:
In "Résumé," Dorothy Parker subverts the idea of what a résumé is--accomplishments and experiences--with an ironic tone, silly images of suicide, and witty rhymes to point out the banality of life for those who remain too disengaged from it.
Note that while this thesis refers to particular poetic devices, it does so in a way that gets beyond merely saying there are poetic devices in the poem and then merely describing them. It makes a claim as to how and why the poet uses tone, imagery and rhyme.
Readers would expect you to argue that Parker subverts the idea of the résumé to critique bored (and boring) people; they would expect your argument to do so by analyzing her use of tone, imagery and rhyme in that order.
Carbone, Nick. (1997). Thesis Statements for a Literature Assignment. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=51
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .

Themes of Marriage & Love in Literature: Examples & Quotes
Have you ever loved? Even if you haven’t, you’ve seen it in countless movies, heard about it in songs, and read about it in some of the greatest books in world literature.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!

If you want to find out more about love as a literary theme, you came to the right place. In this article by Custom-Writing.org , we will examine love’s different manifestations. We’ll also look into the concept of marriage, closely connected with the theme of love.
- 💕 Love in Literature: Definition & History
- 💑 Types of Love Themes
- 💎 Marriage in Literature
- Pride and Prejudice
- Wuthering Heights
- The Great Gatsby
🔍 References
💕 theme of love in literature: definition & history.
Love as a literary theme deals with relationships between people based on affection or desire. It’s a fundamental component of many literary works and one of the most prominent themes in art.
It’s not surprising that people find it universally relatable and infinitely compelling. We come across the theme of love in many genres, but it is mainly associated with medieval and classic romance literature.
Medieval Romance Literature Characteristics
Medieval romance literature, as we understand it, dates back to 12th-century France. Chivalry was the centerpiece of most romances, and it was, of course, accompanied by love.
Courtly Love Definition
Courtly love is the central concept of medieval romance. Why was it so important? Well, the essence of chivalry did not boil down to being brave and masterful in battle. More critical was the knight’s dedication and reverence to his lady, as well as unswerving allegiance to his friends and the king. This devotion of a knight to a lady is called courtly love.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Interestingly, it didn’t matter whether the parties were married or not. According to Medieval Life and Times, one of the rules of courtly love stated that “ Marriage is no real excuse for not loving .”
Tragedy was also present in chivalric romances. A great example is Thomas Malory’s Le Morte d’Arthur . Lancelot and Queen Guinevere’s doomed affair couldn’t end in any other way but grievous.
Classic Romance Novels
As you may have guessed, romance novels focus on romantic relationships. For centuries, people have been finding escape in the fictional world of love with its hardships, obstacles, and high emotional stakes, usually resulting in weddings.
There are a few subgenres of a classic romance novel. The most prominent ones are the following:
💑 Types of Love Themes in Literature
Have you ever wondered why there’s no one concise explanation of what love is? One of the main reasons is that there certainly isn’t just one type of love. Instead, there are many, and in some languages, there are even separate words for them .
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
What exactly are these types? Well, examples may include romantic, platonic, unrequited, forbidden, and familial love. Since there are so many variations, there must be just as many corresponding plots, each with distinctive features. Let’s talk about them.

Definition of Romantic Love in Literature
Romantic love in literature is a feeling of intense affection and desire of one character for another. It usually implies intimate relationships between those involved and is distinguished by intensity, idealization, and passion.
Romantic love has a ubiquitous presence across all arts and not just literature. It has been pivotal in shaping our culture and understanding interpersonal relationships. Since it’s been around for so long, it’s hard to tell whether it evolved naturally and found its way into art or was born as a literary construct that found its way into our lives.
Platonic Love vs. Romantic Love Themes
Platonic love is synonymous with friendship and is never physically intimate. In contrast, romantic love involves friendship as well as intimacy, usually culminating in sexual contact. Both types play an important role in people’s lives and can be great literary material.
Unrequited Love Stories
Unrequited love is the romantic feeling that is not reciprocated. The dreaded state of not being loved back has been the source of inspiration for numerous literary works.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
There is no unanimous consensus on whether unrequited love is good or bad for a person. Compare these two instances:
- If we look back at the chivalric romance novels, we will see that unrequited love was the source of motivation and a call to action. It required a knight to perform all kinds of heroic deeds to prove his love to a lady. In this, they found the meaning of life.
- In contrast, works such as Goethe’s The Sorrows of Young Werther depict a situation far removed from the 12th century’s image of knightly devotion. Young Werther’s unrequited love is the epitome of sorrow, leading to his untimely end.
Love Triangle Stories
In love triangle stories, there are at least three main characters—a hero and two suitors. The hero has to choose between the two lovers, resulting in either one or three broken hearts. Whatever the outcome is, it’s never a win-win situation.
Famous Love Triangles in Literature
- Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen . Written in 1813, it tells about the slowly developing affair between Elizabeth Bennet and Mr.Darcy, with Wickham serving as the third party in the triangle.
- Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë . Heavily influenced by Gothic fiction, this sad, cheerless book talks about a troubled relationship between Heathcliff, Catherine, and her husband Edgar, which is bound to end in disaster.
- The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald . This one is the story of a man who refuses to give up on the desire to reconnect with the married woman he once called his own.
Forbidden Love Stories
Forbidden love in literature is characterized by an almost immediate attraction between characters. But, like in Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet , the idyllic picture is blurred by an obligatory obstacle on the way to perfect love, such as:
Familial Love in Literature
A familial kind of love is cultivated within a family unit. It is rooted in trust, commitment, affection, and loyalty, regardless whether you are connected to your family members by blood or not. This kind of love is distinctively different from others. It doesn’t include the same level of intimacy as in romance, but it doesn’t take away from the deep connection, friendship, and trust.
Familial love is fertile soil for writers. The 19th-century heart-warming classic Little Women by Louisa May Alcott may be one of the most splendid examples of family love portrayal in literature. Another example is the 21st-century post-apocalyptic novel The Road by Cormac McCarthy .
💎 Stories of Marriage in Literature
Much like in real life, marriage in literature has many faces. Some stories portray happily married people exuding joy, while others are depictions of deep sorrow. Marriage can be a source of bliss, but at times it gets corrupted by oppression and patriarchy. As Leo Tolstoy told us in Anna Karenina , “All happy families are alike; each unhappy family is unhappy in its own way.”

- A happy story will most likely end in an equally happy marriage. The main characters will inevitably possess key features that make them perfect for each other.
- Tragic stories usually look at experienced couples battling marital problems. It’s often connected with the issue of appearance vs. reality. We all have an idea of a happy family, and people try to stick to it no matter what. However, only they can see what goes on behind closed doors. It may be an issue of jealousy, untrusting or untrustworthy spouses, disrespectful attitudes, and downright boredom.
Happy Marriage Stories
So, what are those key factors of a happy marriage that we have mentioned? There are a few popular ones that you are likely to encounter in literature, as well as in reality:
- Mutual respect. By default, love should come with mutual appreciation. Otherwise, it is no love at all.
- Support. A loving husband or wife will stand behind their spouse’s decision. It’s a logical outcome of respect.
- Partnership. Decisions are made together, and responsibility is divided between the two.
- Room to evolve. Nothing holds you back from becoming the best version of yourself.
Loveless Marriage Stories
Loveless marriage stories are abundant in world literature. Some can be a result of people misinterpreting their feelings for one another. Others come as an tragic result of an arrangement. Since arranged marriages are made with money and status in mind rather than love and respect, it is no wonder they fall apart.
Married but in Love with Someone Else
One of the types of an unhappy marriage is when the protagonist is married and in love. But—plot twist—they have feelings for someone other than their spouse. It is closely connected with the love triangle theme and often results in adultery and a tragic ending, like in Anna Karenina or Gustave Flaubert’s Madame Bovary . This type of story can also tell about two characters in love with one another but married to someone else.
📚 Marriage and Love Themes in Literature: Examples & Quotes
Seeing that love and marriage are so prevalent in fiction, there is no shortage of examples and quotes we can share with you.
Love in Pride and Prejudice
No conversation about love is complete without mentioning Pride and Prejudice by the English novelist Jane Austen. Love comes in many forms in this masterpiece. Let’s have a look at a few of them:
Theme of Marriage in Pride and Prejudice
Much like the theme of love, the marriage theme is equally nonuniform in Pride and Prejudice . We see both positive and negative examples of relationships built on very different things:
- Lydia and Wickham. “ A disaster waiting to happen” would be a good description of Lydia’s elopement with Wickham. He doesn’t love her, and she is not sure of her feelings but hopes for marriage. While Darcy and Elizabeth eventually develop a true love for each other, the relationships between Lydia and Wickham are built on the prospects of Wickham getting away from debt.
- The Gardiner family . A great contrast to Mr. and Mrs. Bennet, the Gardiners are well-intended, intelligent, and reasonable people who play a key role in Elizabeth and Darcy’s blooming relationship. Mr. Gardiner, being Mrs. Bennet’s brother, is portrayed as someone drastically different from his sister. The relationships between the Gardiners are also more mature and respectful than those of the Bennet couple.
Eager to learn more about the novel and its themes? Check out our analysis of Pride and Prejudice .
Pride and Prejudice: Love Quotes
No one is better at portraying the relationships in a novel than its author. Here are a few most famous quotes about love, which show the true feelings of the well-known characters, from Jane Austen herself:
She began now to comprehend that he was exactly the man who, in disposition and talents, would most suit her. His understanding and temper, though unlike her own, would have answered all her wishes. It was a union that must have been to the advantage of both: by her ease and liveliness, his mind might have been softened, his manners improved; and from his judgement, information, and knowledge of the world, she must have received benefit of greater importance. Pride and Prejudice, Chapter 50
In vain, have I struggled. It will not do. My feelings will not be repressed. You must allow me to tell you how ardently I admire and love you. Pride and Prejudice, Chapter 34
Oh, Lizzy! do anything rather than marry without affection. Pride and Prejudice, Chapter 59
Love in Wuthering Heights
This timeless classic by Emily Bronte is also not on the list of novels with a happy ending. Nevertheless, it’s a gift that keeps on giving: love is abundant here, but it’s also very different. Let’s have a look at the shapes it takes in Wuthering Heights :
- The love between Catherine and Heathcliff — the two main characters—is not the typical romantic attachment we’re used to seeing in films and novels. It is passionate but obsessive , destructive , and filled to the brim with jealousy . There is no happy ending when two people can neither be together nor apart. The situation is further convoluted by the societal prejudice of the time, Heathcliff’s troublesome and vengeful nature, and Catherine’s desire to rise through the ranks of society.
- There’s also love between Catherine and Edgar —the man she eventually marries and has a daughter with. Edgar, being very different from Heathcliff, treats Catherine with affection and tenderness . He is not tormented by social class inequality and lack of money. While he’s weaker and softer in personality than Heathcliff, he can give Catherine the status that she desires. Unfortunately, none of this can bring Catherine true love.
Theme of Marriage in Wuthering Heights
Catherine’s love triangle between hetself, Heathcliff, and Edgar makes her face a painful choice: to surrender to her love for forever agonizing Heathcliff, a man of lowly background, or to marry an affectionate man of much higher class.
At one point, Catherine declares: “I am Heathcliff!” meaning that their identities are so alike that they’re essentially one person; they share a soul. But in the same conversation, she admits that marrying Heathcliff would “degrade” her.
On the contrary, marrying Edgar Linton can lift her up. She hopes that his money will help not only her but also her soulmate, Heathcliff. In her eagerness to preserve both relationships and get the best of both worlds, Catherine chooses to marry Edgar. This selfish act drives Heathcliff away and later proves to be a tragic mistake.
Feel free to read our Wuthering Heights summary to learn more about the novel’s plot.
Wuthering Heights: Love Quotes
To better understand the tragic torment of the main characters in this outstanding gothic novel, let’s take a look at a few quotes:
He shall never know I love him: and that, not because he’s handsome, but because he’s more myself than I am. Whatever our souls are made out of, his and mine are the same. Wuthering Heights , Chapter 9
Catherine Earnshaw, may you not rest as long as I am living. You said I killed you–haunt me then. The murdered do haunt their murderers. I believe–I know that ghosts have wandered the earth. Be with me always–take any form–drive me mad. Only do not leave me in this abyss, where I cannot find you! Oh, God! It is unutterable! I cannot live without my life! I cannot live without my soul! Wuthering Heights , Chapter 16
If he loved with all the powers of his puny being, he couldn’t love as much in eighty years as I could in a day. Wuthering Heights , Chapter 14
Theme of Love in The Great Gatsby
The Great Gatsby is a story of pain, longing, and obsession . The love triangle here is somewhat reminiscent of the one in Wuthering Heights . Jay Gatsby and Daisy are in love, Jay goes to war, and Daisy marries Tom Buchanan, breaking Gatsby’s heart upon his return five years later.
What might appear as a choice between two lovers really is a choice between love and prestige:
- Jay Gatsby , being the nouveau riche, can only offer Daisy his imperfect version of love.
- Tom Buchanan can offer safety, status, and endless money for her wishes.
Daisy shows her true colors when she chooses Tom and, by association, wealth and security.
Unfortunately, Gatsby cannot give up on the idea of having Daisy all to himself. He finds it difficult to accept that the last piece of the perfect puzzle that constitutes his dream is missing. This unreadiness to come to terms with defeat is what ultimately destroys the Great Gatsby.
Marriage in The Great Gatsby
As we’ve already mentioned, Daisy marries Tom not because she’s in love with him. Their marriage is loveless. Her glittering persona hides superficiality, and she doesn’t suffer much when making her choice. Let’s see why.
The main issue here is that of old vs. new money . Jay represents new money obtained through shady ways. Tom is old money , which is undeniably more powerful, alluring, and prestigious. And that’s the main reason why Daisy chooses in Tom’s favor.
You will find even more info in our article on The Great Gatsby characters . Check it out!
The Great Gatsby: Love Quotes
Here’s how F.S. Fitzgerald conveyed the theme of love and obsession in The Great Gatsby :
He hadn’t once ceased looking at Daisy, and I think he revalued everything in his house according to the measure of response it drew from her well-loved eyes. Sometimes, too, he stared around at his possessions in a dazed way, as though in her actual and astounding presence none of it was any longer real. Once he nearly toppled down a flight of stairs. The Great Gatsby , Chapter 5
He wanted nothing less of Daisy than that she should go to Tom and say: ‘I never loved you.’ After she had obliterated four years with that sentence they could decide upon the more practical measures to be taken. One of them was that, after she was free, they were to go back to Louisville and be married from her house – just as if it were five years ago. The Great Gatsby , Chapter 6
His heart beat faster and faster as Daisy’s white face came up to his own. He knew that when he kissed this girl, and forever wed his unutterable visions to her perishable breath, his mind would never romp again like the mind of God. So he waited, listening for a moment longer to the tuning-fork that had been struck upon a star. Then he kissed her. At his lips’ touch she blossomed for him like a flower and the incarnation was complete. The Great Gatsby , Chapter 6
As you can see, much has been written about love—both happy and tragic. We hope that our article inspired your interest in further exploration of the topic. Tell us about your favorite literary work about love in the comment section below!
❓ Theme of Love and Marriage FAQs
Courtly love literature speaks extensively about the cult of chivalry and knighthood. A truly chivalrous knight is kind yet brave and steadfast in battle, loyal to his king and brothers in arms, and faithful to his lady.
Catherine’s one true love is Heathcliff. She believes they are alike and considers him her only true friend. She says “yes” to Edgar’s proposal to secure her position in society and help Heathcliff but realizes she’s made a mistake when it’s too late.
Gatsby thought that he loved Daisy, but he only loved what she represented to him—a perfect life, the American dream, and wealth. He once said: “Her voice is full of money,” which clearly indicates his true feelings.
Romance in medieval literature is associated with chivalry as a set of characteristics and actions of a knight. One of the most notable examples of chivalry is found in Sir Thomas Malory’s The Death of Arthur , which is about the Knights of the Round Table.
Wuthering Heights has a lot in common with a love story, but it is also more than that. The theme of love is inseparable from that of destruction and revenge. Heathcliff seeks vengeance for his broken heart, and his disturbing love eventually becomes a dark obsession.
- The Abject Lover of the Courtly Love Era: Research Gate
- Romance: Literature and Performance: Britannica
- Love and Chivalry in the Middle Ages: British Library
- Writing 101: What Is a Romance Novel?: Masterclass
- Romantic Love: A Literary Universal?: Project MUSE
- Love in Literature: The Guardian
- Reading Remedy: Books to Help You Deal with Unrequited Love
- Family Love: What It Is, What It Looks Like, And How To Make It Happen: Better Help
- Why Family Is The One Thing Authors Will Always Write About: Huffpost
- Why the Marriage Plot Need Never Get Old: The New Yorker
- 10 Novels That Teach You Something About Marriage: Barnes and Noble
- 11 of the Worst Marriages in Literature: Electric Literature
- Lost Loves in Wuthering Heights: Georgetown University
- Daisy Buchanan: Love, Folly and Money in The Great Gatsby: The Artifice
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Humans are social creatures. Most of us enjoy communication and try to build relationships with others. It’s no wonder that the inability to be a part of society often leads to emotional turmoil. World literature has numerous examples of characters who are disconnected from their loved ones or don’t fit...

Death is undoubtedly one of the most mysterious events in life. Literature is among the mediums that allow people to explore and gain knowledge of death—a topic that in everyday life is often seen as taboo. This article by Custom-Writing.org will: introduce the topic of death in literature and explain...

Wouldn’t it be great if people of all genders could enjoy equal rights? When reading stories from the past, we can realize how far we’ve made since the dawn of feminism. Books that deal with the theme of gender inspire us to keep fighting for equality. In this article, ourcustom-writing...

What makes a society see some categories of people as less than human? Throughout history, we can see how people divided themselves into groups and used violence to discriminate against each other. When groups of individuals are perceived as monstrous or demonic, it leads to dehumanization. Numerous literary masterpieces explore the meaning of monstrosity and show the dire consequences of dehumanization. This article by Custom-Writing.org will: explore...
Revenge provides relief. Characters in many literary stories believe in this idea. Convinced that they were wronged, they are in the constant pursuit of revenge. But is it really the only way for them to find peace? This article by Custom-Writing.org is going to answer this and other questions related...

Is money really the root of all evil? Many writers and poets have tried to answer this question. Unsurprisingly, the theme of money is very prevalent in literature. It’s also connected to other concepts, such as greed, power, love, and corruption. In this article, our custom writing team will: explore...

Have you ever asked yourself why some books are so compelling that you keep thinking about them even after you have finished reading? Well, of course, it can be because of a unique plotline or complex characters. However, most of the time, it is the theme that compels you. A...
The American Dream theme encompasses crucial values, such as freedom, democracy, equal rights, and personal happiness. The concept’s definition varies from person to person. Yet, books by American authors can help us grasp it better. Many agree that American literature is so distinct from English literature because the concept of...
Imagine that things you have always enjoyed no longer brighten your existence. You feel alien among your friends and relatives, and nobody seems to understand you. Your mental state is getting worse every day, and you no longer find the reason to live. This is what happened to Esther, the...

The Bell Jar was banned for many reasons, including its blasphemous words and discourse on the topics of suicide and sexual life. But the most critical reason for such rejection was that the book undermined the traditional ideals of a woman’s role as a mother and wife. More Information Sylvia...

The novel by Sylvia Plath cannot be limited to only one central theme. Feminism, social pressure, gender inequality, sanity and mental diseases, mother-and-daughter relationships, body vs. mind, and personal ambitions are some of the controversial issues raised in the book. Still, the themes of gender inequality, depression, and body vs....

A bell jar is a metaphor for loneliness in a mental illness. The protagonist lives in a vicious circle of her thoughts and anxieties. To achieve improvement, she needs to lift the bell jar. However, Esther needs medical help to do that. At the end of the book, the bell...
Essay Writing Guide
Thesis Statement Examples
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?

People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
20+ Hook Examples to Grab Reader’s Attention
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
Are you finding it tough to come up with a strong thesis statement? Well, you're not alone!
Creating a short and clear thesis statement might seem tricky, but it's a really important part of your essays and research papers. It's like the main message of your whole paper in just one sentence.
But don't worry, we're here to help. In this blog, we've gathered over 20 examples of different kinds of essays. These examples will show you exactly how to do it.
So, let's dive in and read on to learn more.
- 1. Thesis Statement Examples for Different Essay Types
- 2. Thesis Statement Examples for Research Paper
- 3. Elements of a Good Thesis Statement
Thesis Statement Examples for Different Essay Types
A thesis statement is like the central message of your essay. It states the main claim along with the reason or rationale that supports the claim. It's a single sentence that sums up what your essay is all about.
When someone reads your essay, they should know from the thesis statement what your essay is trying to prove or explain.
Now, in some cases, like more complex essays or research papers, you might use a three-point thesis statement. This means your thesis statement has not just one, but three main ideas or arguments that your essay will explore.
Here are some good thesis statement examples for the common types of essays:
Argumentative Thesis Statement Examples
An argumentative essay persuades by presenting evidence on a debatable topic. Here is what a thesis statement looks like for an argumentative essay:
Claim + Reasons/Evidence
Here are argumentative essay thesis statement examples:
- "Social media negatively impacts mental health by fostering excessive comparison and cyberbullying, leading to increased stress and anxiety among users."
- "Stricter gun control laws are necessary to reduce firearm-related violence in our society, as evidenced by lower rates of gun violence in countries with stringent gun control measures and the potential to prevent potentially dangerous individuals from acquiring firearms."
Informative Thesis Statement Examples
An informative essay educates by presenting facts and details on a specific topic. The thesis statement typically takes this form:
Topic + Main Points
Here are informative essay thesis statement examples:
- "The history, symptoms, and available treatments for diabetes provide essential knowledge for individuals managing this chronic condition."
- "Exploring the causes, effects, and preventive measures of climate change sheds light on the urgent need for global environmental action."
Literary Analysis Thesis Statement Examples
In a literary analysis essay , the writer examines a specific element of a literary work. The thesis statement for literary analysis generally follows this structure:
Analysis of Element in Literary Work + Significance
Here are literary analysis thesis statement examples:
- "The symbolism of the 'green light' in 'The Great Gatsby' represents Gatsby's unattainable American Dream and the disillusionment of the Jazz Age."
- "Examining the character of Macbeth's descent into madness in 'Macbeth' reveals the tragic consequences of unchecked ambition in Shakespearean tragedy."
Analytical Thesis Statement Examples
An analytical essay delves into a topic by evaluating and presenting multiple perspectives. The thesis statement in an analytical essay often appears as:
Topic + Analysis/Examination
Here are analytical essay thesis statement examples:
- "Analyzing the economic impact of globalization on developing countries reveals both opportunities for growth and potential challenges."
- "An examination of societal norms in 'The Catcher in the Rye' underscores the alienation experienced by the protagonist, Holden Caulfield."
Expository Thesis Statement Examples
Expository essays aim to explain or inform by providing details and facts on a subject. The typical expository thesis statement format is:
Subject + Key Aspects
Here are expository essay thesis statement examples:
- "The exploration of the solar system, including the sun, planets, and asteroids, showcases the vastness and complexity of our cosmic neighborhood."
- "Understanding the process of photosynthesis, its significance in plant growth, and its role in producing oxygen is vital for comprehending Earth's ecosystems."
Cause And Effect Thesis Statement Examples
Cause and effect essays investigate the relationships between events or phenomena. The thesis statement structure in a cause and effect essay is:
Cause + Effect
Here are cause and effect essay thesis statement examples:
- "The increase in technology usage has led to a decline in face-to-face social interactions among young adults, contributing to feelings of isolation."
- "The depletion of the ozone layer results in harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation reaching the Earth's surface, leading to various environmental and health consequences."
Narrative Thesis Statement Examples
Narrative essays recount personal experiences or stories. The thesis statement in a narrative essay is often shaped as:
Personal Experience/Story + Significance
Here are narrative essay thesis statement examples:
- "My backpacking adventure through the Appalachian Trail taught me resilience, self-reliance, and a deep appreciation for the beauty of nature."
- "The story of my grandmother's immigration journey reflects the strength, determination, and sacrifices made by countless immigrants seeking a better life."
Thesis Statement Examples For Opinion Essays
Opinion essays express the author's viewpoint on a particular subject. You can follow this structure to write a thesis statement in an opinion essay:
Topic + Opinion/Position
Here are thesis statement examples for opinion essays:
- "Universal healthcare is a fundamental right that should be accessible to all citizens, ensuring equitable access to medical services."
- "The widespread use of technology in education enhances learning opportunities, preparing students for a tech-driven world."
Thesis Statement Examples for Problem Solution Essay
In a problem-solution essay, the writer identifies a specific problem and proposes a viable solution or solutions to address it. The thesis statement in a problem-solution essay typically follows this structure:
Problem + Solution
Here are thesis statement examples for problem solution essays:
- "The rising prevalence of food insecurity can be mitigated through community-based programs that promote urban farming and food distribution initiatives."
- "To combat the issue of plastic pollution in oceans, a comprehensive approach involving strict regulations, public awareness campaigns, and sustainable alternatives is necessary."
Thesis Statement Examples for English Essays
English essays encompass a wide range of topics, from literary analysis to language studies. The thesis statement for English essays can take various forms depending on the specific focus of the essay.
Here are thesis statement examples for different types of English essays:
- For a Literary Analysis Essay: "The use of symbolism in Nathaniel Hawthorne's 'The Scarlet Letter' underscores the theme of societal hypocrisy and the journey of self-redemption."
- For a Language and Linguistics Essay: "Exploring the evolution of the English language through historical context reveals the influences and transformations that have shaped it into its current form."
- For a Comparative Literature Essay: "Comparing the themes of love and tragedy in Shakespeare's 'Romeo and Juliet' and Jane Austen's 'Pride and Prejudice' highlights the universal aspects of human emotions."
Thesis Statement Examples for Research Paper
A research paper often critically analyzes a specific topic or issue, conducting in-depth exploration and analysis.
While all academic papers require a thesis statement to convey the central message, they differ in scope and depth.
Research paper thesis statements are broad and involve in-depth research, often including empirical research, while essay thesis statements are shorter and focus on a specific argument.
Here are some examples of research papers of different natures:
- For an Analytical Research Paper: "An analysis of historical voting patterns reveals shifts in political ideologies over the past century, shedding light on changing voter demographics and their impact on contemporary elections."
- For an Experimental Research Paper: "Through controlled experiments and statistical analysis, this research examines the effects of a new drug on patients with a specific medical condition, offering insights into its potential for widespread therapeutic use."
- For a Comparative Research Paper: "This research paper compares and contrasts the educational systems of two countries, Japan and Finland, exploring the factors contributing to their respective success in student performance and learning outcomes."
- For a Case Study Research Paper: "Through an in-depth case study of a successful tech startup, this research paper analyzes the key factors behind its rapid growth and profitability, offering valuable insights for aspiring entrepreneurs."
These examples illustrate the diversity of research paper thesis statements, each tailored to the specific focus and methodology of the research.
Elements of a Good Thesis Statement
A strong and clear thesis statement exhibits several crucial elements:
- Specific Topic: It addresses a well-defined subject or issue.
- Debatable Stance: The thesis takes a position that can be debated or questioned.
- Narrow Focus: It doesn't encompass too broad a scope but rather hones in on a specific aspect.
- Single Central Idea: It conveys a solitary, precise main point.
- Supportable: It answers the question with evidence, facts, or reasons in the essay.
- Clear Position: It presents a distinct viewpoint on the topic.

Example of a Good Thesis Statement
"Increasing access to quality education in underserved communities is essential for addressing socio-economic disparities, and this can be achieved through improved school funding, qualified educators, and community involvement."
Here is an analysis of the elements of the above thesis statement example:
This thesis statement exemplifies these elements well. It explicitly addresses the topic of "increasing access to quality education in underserved communities."
It takes a debatable stance as the strategies for achieving this goal can vary. It narrows the focus by discussing specific solutions: "improved school funding, qualified educators, and community involvement."
The central idea is that these actions are necessary to address socio-economic disparities through education. While the evidence isn't in the thesis itself, it's implied that the essay will support these claims . The position is clear: these actions are essential.
Here’s an example of a good thesis statement versus a bad one:

You now have a wide range of thesis statement examples to learn from.
But if you're running low on time or confidence, our reliable essay writing service is here to assist you. Our skilled writers can create clear and strong thesis statements in top-notch essays.
With their experience and expertise, you can be sure you’ll receive original, unique, and quality essays every time.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
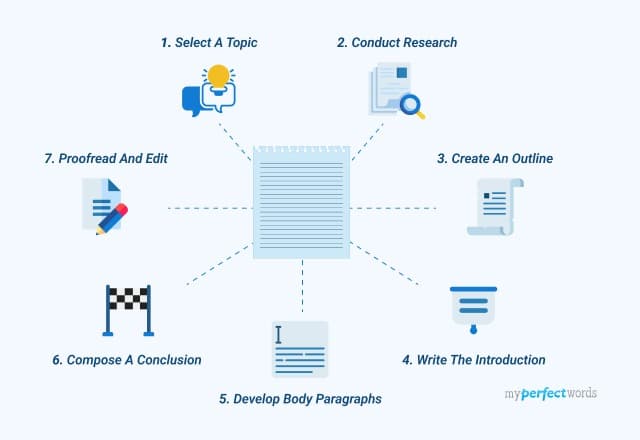
The Merchant of Venice
William shakespeare, everything you need for every book you read..
In connection with mercy and generosity, The Merchant of Venice also explores love and friendship between its characters. The central romantic relationship of the play is that between Bassanio and Portia . Their marriage is paralleled by several others: the elopement of Shylock's daughter, Jessica , with the Christian, Lorenzo ; and the marriage of Portia's servant, Nerissa , to Bassanio's companion, Gratiano . In addition, numerous critics have suggested that the strongest friendship in the play—between Antonio and Bassanio—also approaches romantic love. In addition, the play shows how strong the amicable ties are that connect all the various Venetian characters.
Given the generosity that they motivate between characters, love and friendship might seem to offer alternatives to the ugly emotions of prejudice, greed, and revenge on display in The Merchant of Venice . However, beginning with Bassanio's borrowing money from his friend Antonio in order to woo Portia, the play also demonstrates that the apparent purity of love and friendship can be tainted by selfish economic concerns. In addition, love and friendship are also at the mercy of the law, as seen in Portia's being subject to the terms of her father's riddle of the caskets .
Love and Friendship ThemeTracker

Love and Friendship Quotes in The Merchant of Venice
The word love has a number of different meanings. It can mean liking, affection, desire, friendship, kindness and more. But it is obvious that the interpersonal relationships are based on love irrespective of the type of love. Love is the theme of a vast majority of literary and art works. Love is a deeply discussed topic in Philosophy and the ...
Love and forgiveness: How its power heals wounds and strengthens bonds. Love Essay Examples: Choose Your Sample for Inspiration. Essays about love are usually standard, 5-paragraph papers students write in college: One paragraph is for an introduction, with a hook and a thesis statement; Three are for a body, with arguments or descriptions
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement About Love. Conduct the first research; You can write a thesis statement about love from different angles: this could be romantic, platonic, love between family, love as a sacrifice, etc. Whichever angle you choose to write from, make sure to read previously written works on the subject first. ...
In essence it is a self-sacrificing act wherein a person puts another person's happiness and well-being above their own. For example in the poem "To my Dear and Loving Husband" by Anne Bradstreet she compares her love for her spouse as "more than whole mines of gold or all the riches that the East doth hold" (Bradstreet, 1).
In love essays, the thesis statement often explores the definition of love, how it affects individuals and society, and its role in fulfilling human needs for connection and vulnerability. In order to support your thesis statement, it is crucial to do thorough research on the topic. You can choose to include scientific studies, cultural ...
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Here are some essay topics and thesis ideas about the romantic movement from a retired British Literature teacher. With these tips and ideas, your essay will come together in no time! ... Sir Walter Scott, and Thomas Love Peacock. Romantic novels you might be familiar with are Frankenstein (Mary Shelley), Ivanhoe (Sir Walter Scott), ...
Here are some sample thesis statements you could try. Thesis idea 1: Love has been defined very differently in different times and cultures, so that what we think of as love now is not at all how it was considered 500 years ago. Thesis idea 2: Falling in love at first sight is the subject of many songs, poems, and romance novels, but it is also ...
Cognisant being must be involved in all aspects and movements involving love. (Vacek, 1996) Thesis Statement. This paper is a critical analysis over the characteristics associate with the definition of love. It firmly takes the notion, "Falling in love entails spiritually nurturing personal and populace growth". Relation of love and stress
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
romantic love is the valuing of the qualities had by our partners as well as the appreciation of a. relationship from the perspective of the participants in that relationship, and the valuing of one's. beloved. Later in we worked to get clearer on the ideal of stability. Stability is the ideal that we.
For more information, please contact [email protected] . Running head: LOVE. Love: A biological, psychological and philosophical study. Heather Chapman. University of Rhode Island Dedication. This paper is dedicated to the love of my life. Jason Matthew Nye. October 4,1973 - January 26, 2011 Abstract.
Love and democracy - love thesis statement. Love has no sovereign power. It does not offer guarantees. It is not a state. Maybe because of this, it can be a democratic gesture: a gesture that incorporates, with all its lability, the possibility of a dignified and genuine existence in public life. Perhaps for this reason, it is also an act of ...
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
At times, these thesis statements may be used in a timed write (a fifty minute in-class essay) that day, but often, the thesis drill is the culminating exercise of a lesson. Timed Writes On the AP English Literature exam, students are expected to write three essays in 120 minutes, which means that they should be able to write an effective and ...
The thesis should be dramatic, have some tension in it, and should need to be proved (another reason for avoiding the obvious). Too general: Edna St. Vincent Millay wrote many poems with love as the theme. Too specific: Edna St. Vincent Millay wrote "Love is not all: it is not meat nor drink" in <insert date> after <insert event from her life>.
A thesis statement is a statement that makes an argument that you will attempt to prove through the body of the paper. What has been provided is the initial statement. Romeo and Juliet do not love ...
It is a brief statement of your paper's main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the ...
Romantic love in literature is a feeling of intense affection and desire of one character for another. It usually implies intimate relationships between those involved and is distinguished by intensity, idealization, and passion. Romantic love has a ubiquitous presence across all arts and not just literature.
Here are expository essay thesis statement examples: "The exploration of the solar system, including the sun, planets, and asteroids, showcases the vastness and complexity of our cosmic neighborhood." "Understanding the process of photosynthesis, its significance in plant growth, and its role in producing oxygen is vital for comprehending Earth ...
Share Cite. Some possible thesis statements below: 1. Although Jay Gatsby lived his life loving Daisy, she did not even attend his funeral. 2. Although the night life was all glitter and glamor at ...
In connection with mercy and generosity, The Merchant of Venice also explores love and friendship between its characters. The central romantic relationship of the play is that between Bassanio and Portia.Their marriage is paralleled by several others: the elopement of Shylock's daughter, Jessica, with the Christian, Lorenzo; and the marriage of Portia's servant, Nerissa, to Bassanio's ...
This thesis will explore the love of God in biblical and Reformed theology. Chapters 1 and 2 will look at the love of God in the Old and New Testaments, focusing on key Hebrew and Greek words, and there will be exegesis of key New Testament texts in chapter 3 to
- dissertation tips
- phd analysis
- phd writing
- thesis format
- thesis template

thematicstatement.com
writing a thematic statement has never been so easy
Thesis Statement About Love Tips + Example
How do you write a thesis statement about love? In this article, you will be getting tips for writing about thematic statement love so keep reading.
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement About Love
- Conduct the first research
You can write a thesis statement about love from different angles: this could be romantic, platonic, love between family, love as a sacrifice, etc. Whichever angle you choose to write from, make sure to read previously written works on the subject first.
- Write a proposal
The information you get from your first research will help you to draft a proposal for your thesis statement. When you write a proposal, the dominant tense to use is the present future tense. This is because a proposal tells the reader what you intend to do rather than what you have done.
- Conduct a second research
After your proposal has been approved, the next thing to do is conduct another research. This second research will be more in-depth than the first because you will need to show the results of your work. However, you can still use the information you have in your proposal to write your thesis.
- Structure your work
To make your thesis come together, it will need a structure. This structure comprises chapters such as the introduction, the literature review, the methodology, the results and discussion, and the conclusion.
How to Write a Thematic Statement About Love
- Understand the literature
If you do not understand the literature first, there is no way you will be able to write a good thematic statement about it. So, make sure you focus on core things like the story’s plot, the characters, the writing style, among others.
- Be original
When writing a thematic statement love, try to use your own words as much as possible. Now, using your own words does not mean you should try to distort the message of the literary work for which you are writing your thematic statement. Try to use your words but make sure you maintain the message that the author was trying to pass across.
- Avoid cliches
When writing a thematic statement, do not write like this:
“The theme of this novel is pride and prejudice.”
Rather, write:
“Pride and prejudice play a crucial role in the human response to certain situations in this novel.”
After writing your thematic statement, make sure you edit for any mistakes. Rephrase any confusing words and also check for spelling errors.
Examples of Good and Bad Thematic Statement About Love
Theme: Love and other emotions
Bad Thematic Statement: Love is the predominant theme in this novel.
Good Thematic Statement: Love is stronger than anger, hate, and other painful emotions.
Theme: Family Love
Bad Thematic Statement: Love is strong in the family.
Good Thematic Statement: Love is what keeps the family together even after many fights and arguments.
With these tips, you do not have to worry about writing a thematic statement about love. Just put these tips to work and you will be able to write a successful thematic statement.

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
What Love Is and Why It Matters Research Paper
Thesis statement, relation of love and stress, personal perspective of love, validation of love in relation to perk, works cited.
Lack of love during the early childhood life causes poor emotional development during adult life. (Hurlock, 47)The way people respond to stress is not present at birth but is natured as people develop especially during the first few years when the brain is still fresh and young and thus the emotional development is crucial. High activity in the brain is an association to fear, irritability and a reaction of withdrawal from other people.
What is a legacy plan? It is associated with love because it is an arrangement of what one wishes to have but it should include the gift of good record, direction, family and personality. The plan stands to benefit the family, children, and grandchildren beside the personal gains.
It calls for one to keep in touch with the wonderful personality, which existed back when things give the impression of extreme credibility. It is more fun and meaningful to plan for, and wish others well more than it is to have a working financial plan. The family love is a priceless offer. Unlike Oedipus, love is not blind, tragic or compulsive. The true meaning of life is to create love in the human consciousness. Cognisant being must be involved in all aspects and movements involving love. (Vacek, 1996)
This paper is a critical analysis over the characteristics associate with the definition of love. It firmly takes the notion, “ Falling in love entails spiritually nurturing personal and populace growth ”.
What is stress? Probably it is equitable to physical, mental, emotional or spiritual strain. The most common theory behind measures of controlling stress revolves around love, regular rest and exercise. (Lazarus, 254) Arguably, money cannot buy these quantifiers.
The love for something influences one to fight and attain it. As Peck would put it, our love to achieve anything forces us to willingly focus and change the attitude through pain. Everything that happens to human beings is designed so to conceal what one loves, thus the need to overcome the obstacle.
There is significance in giving a legacy plan to people with a close relation to their obsessions, beside the personal treats. If capturing and delivering love is not possible, as it ought to be, then it looses it eminent value. In line with Lazarus, (254) Lack of internal expression and thought over someone or something causes an under-attraction thus leading to forgetfulness.
Naturally, People forget something as a soon as they stop thinking about it. When one loves something /someone, all the love virtues are intrinsically achievable after one goes through some enduring amount of constructive suffering.
The secret to happiness would probably be falling in love especially with oneself. Love creates the feeling of having enough energy thus the probably that it is an inborn feature that does not require nurturing but has a feeling that lives within as long as a person keeps taking care of it.
People luck the love because of spending too much time looking for it elsewhere while it is close to them. The external world is made of parents, friends or even strangers and their failure to express love disappoints and causes devastation to someone. The opinion of others especially when negative or against one’s anticipation shatters the personal sense of self-esteem and love.
Everyone wants to feel loved and affectionate. This is almost certainly the true meaning of the peace in the mind. It affects the inner fear and doubts and thus people are able to communicate freely concerning any subject matter. Bestowing wisdom requires an open and free dialogue and that is the reason why children are encouraged to create good rapport with others. Lack of practice over the issue of love early in a person’s life causes an awkward and clumsy feeling thus affecting how one handles some of these affectionate sentiments.
The child’s development with respect to personality and character revolves about love shown or given by the parents. Those children lacking the feel of love experiences negligence and fall short of proper foundation to build character. They undergo deficient in strength for a progressive growth. This is the explanation to existence of enough scientific evidence or correlation regarding the fact that lack of love for the baby diminishes its chances for survival. (Lerner and Damon, 2)
Peck went into deeper details over the definition of love by arguing whether falling in love translates to “romantic love, dependency, self-sacrifice, or even a feeling.” According to him, it probably has something to do with “nurturing one’s own or another’s spiritual growth”. (81) “Love is the will to extend one’s self for the purpose of nurturing one’s own or another’s spiritual growth… Love is as love does.
Love is an act of will namely, both an intention and an action”. Personal motivation also entails ones option, meaning that it is not necessary for people to love but they choose to love.
It is impossible for a person to be a friend to others unless they are a friend to themselves. Originally, this concept applies for the analysis of love as well. The secrecy of attracting admiration depends on ability to attract and respect the personal attributes. Loving in a legitimate manner may be equitable to a desire as opposed to emotional.
The personal decision to love enables one to decide on venturing into a commitment to love regardless of the present feeling in the inner self at that particular period. Conversely, the possibility for a person to shun the personal acts catalyzed by the inner feelings of love is eminent.
One should love others than desire for the same offer of love from them. This calls for the ability to give love to others before they can reciprocate the same aspect. In line with Carter, (10) Loving others first requires one to stretch out of their personal limits, to do what they never longed to. When one stretches to do what they initially thought they would never be able to achieve, they feel victorious over great weakness that existed at the status quo.
Opening ones heart to embrace anyone who comes by or the situation that arises is the best life transformation experience. It is also one of the most important and courageous measure one would take since it entails personal will. When one is expressing love to strangers, then they are taking motivation to be acquainted with a new territory.
According to McGraw, (107) the development of the wisdom and love from the heart is therefore courage, which makes a person bold to taking the right, necessary and honourable action even when it is temporary and uncomfortable. In line with Perk, (80) “We must be willing to fail and to appreciate the truth that often “Life is not a problem to be solved, but a mystery to be lived.””
In his writing of, “The road less travelled”, Perk portrays love as the willingness to extend offer of self-service to others with the aim of nurturing personal and spiritual growth.
According to Perk (81), “A genuine loving individual will often take love as a constructive action towards a person he or she consciously dislikes or lacks actual feeling of love towards. One may perhaps even find the person repugnant in some way.” If a person stops, extending their will to give because of a feeling of poor encouragement, then the loving stops.
This is because love shows that people share their similarities while celebrating their differences. When such kind of relationship fails to exist, then the love is non-existantent.
People grow financially, socially, mentally and spiritually when they stretch their limits to help others. It is quite often to face challenges or coincidental situations when still attending other’s chores. The obvious test for love comes when one is tired. When it is the last thing one would wish to do, that is when someone emerges with dreadful need for assistance. The person then is arm-twisted to make a choice on what to undertake next among the possibilities in existence.
Helping others at their most eminent time of need calls, for one to emerge from the comfort zone past the point of pain, but the consents come in handy thereafter. (McGraw, 107) When working under this strain or stress, the ability to persevere to a point of agility is evident and thus the next time one faces similar situations, then the undertaking becomes easier. This is a good indication that loves for performance depends on the ability to undertake a task in a smooth manner.
It is human nature for one to become accustomed to a challenge if they faced similar position earlier and conquered. This causes the feeling for a need to face a more advanced or different challenge. The wish for growth depends on the ability to tackle the challenges involved. By allowing a move beyond the arbitrary accepted limitations, the capacity for love extends. (Perk, 82)
Relationships are the anxious and notorious opportunities to stretch the limits to a next level. This is because the soul is always ready to receive or exceed the limits whenever an opportunity arises.
Consistent with Fisher’s writing, (128) the initiation of love for a stranger or new task involves some deep soul concentration concerning the unrealistic expectations. This attention in most cases calls for some malleability to accommodate the involved persons. Most experienced people will definitely indicate that love would rarely cause them to remain at one point.
It provides a different chance, way of life or routine. The philosophy of love indicates that one should not seek love or affectionate from very far. In most cases, there is someone right behind the door waiting to help. The actions associated with the heart or those concerning love are very strong practically regardless of whether the language is poetic or not
In his writing (230), Perk considers love as a natural driving force that exists behind spiritual augmentation. The writer consideration over the existence of romantic love probably provides a view indicating some misconceptions in today’s or future understanding. He considers the issue of romantic love as mythical.
On the current understandings, love blossoms as a very tender, beautiful touch, a concern regarding care and provides the only moment one can stand out beyond personal feelings to embrace others and feel part of the whole. Most of the time people feel the need to compel their needs as opposed to revealing them. Exposure of personal wounds and weaknesses enable one to be accommodative of others needs too.
The most important feature is the love that arises through this kind of sharing. According to Pecks, (230) analysis, natural love is concern with dependency whereby the truth of love does not entail falling in love but the act of expanding boundaries of one’s ego to accommodate others. True love does not put up with the issue of “falling in love” but the spiritual nurturing of others’ feelings therefore that kind of love requires an effort.
In his perspective of love, Perk, (85) writing of “The Road Less Travelled” show that Love is not a feeling but an investment or probably an important activity. In line with his definition of love, “it is the will to extend one’s self for the purpose of nurturing one’s own or another’s spiritual growth” (85). It is a prime action of nurturing them than just the spiritual growth.
In the writing of “The road less travelled,” Perk, (231) also seeks to address the issue of Cathexis (explanation behind attraction of the opposite sex and love). The attraction is not love but an instinct controlling one to behave in a caring manner such as, cuddling something that they like for instance their pets or kids.
The issue of true love does not survive in isolation. Attraction has to exist in a sufficient and close manner for a consideration of straightforwardness. Love begins after one completes the attraction phase. Therefore it is an action proceeded by another.
It consists of what one does to another. As Perk (231) indicates in “The Road Less Travelled” writing, “Love is as love does”. It is an offer to others of what they need for growth. One must truly know and understand what the other person needs, to be in a position to provide. This indicates the need for initializing at ‘cathexis’ phase.
The issue of loving especially true loving might appear complicated from these perspective. When someone designates their love, then it is not from their want or because they cannot be in a position to own what they claim to love. The issue has nothing to do with the person. People love others from what they do and how they try to undertake tasks. This occurs through the analysis of personality, character, motivation, ability or strength.
Doubtlessly, one need to have sighted the best and the worst of the person they admire. What they see also need to be well and clearly understood. Through openness, people are in a position to express who they are. Living an open-ended lifestyle provides chance for others to consider their offers and it does not require one to dedicate the whole truth. This exercised courage assists one to step out and fight fear.
From a personal point of view, love is certainly a mystery that forms its basis from nature. It is probably comparable to gravitational pull, an unstoppable force or a vast, invisible anxiety that connects things that are alike. People always long for love and wish to love events without any strong basis for their actions. When they find the love, then they awaken to it because it presents care and well wishes without an expectation or demand for any kind of remuneration.
This is a good indication that the well-being of the loved person is not different from the person who expresses that love. True love calls for one to be trustworthy and therefore the love expressed to others is an indication that there exists trust. This is also an indication that the person expressing it is confident and despite the type of outcome, the aspect of love can still exist.
The importance of love for the community is to unite lives, expand people’s thoughts especially about others, connect different people regardless of their origin, race or ethnical group, enhance their personal views and dignify them by nurturing the inner feelings.
Love is a universal feeling experienced by everyone or every living being on the earth. The living being in this case is an indication that conceivably, love is not an attribute that is limited to human beings. It is a strange but unique emotional feeling that most likely has no certain definition one could use to describe it.
The characteristic of love revolves about an attached feeling whereby someone feels affectionate towards another or something else. The feeling is very strong and most certainly the reason why it forms a basis for discussion. The reason why people consider love is for the reason that it is a very important aspect in human life that satisfies human emotional needs.
Humans have the innate responsibility to offer and feel loved. The biological structure indicates that the feeling of love is responsible for the formation and maintenance of the societal development especially morally and socially. The birth of a child causes the parents to forget their urgent needs and divert all their attention to the newborn due to the strong feeling of love.
Love is therefore a great thriller or catalyst that enables people to achieve exigent tasks, which probably would remain unaccomplished if love never existed. “Love is an enigmatic emotion that exceeds all the boundaries to change people’s lives”. (Wallerstein, Judith and Sandra, 19)
The magnificence experience of love allows humans to express each other’s feelings with kindness and concern such that love can take a number of emotions. It is an ambiguous ubiquitous relation binding people together in different formats.
Love can be expressed in various ways including the “a passionate lover’s kiss, a tender mother’s touch, a fatherly concern or a brotherly, sisterly affection”. (Wallerstein, Judith and Sandra, 19) The sages have found out that everything and everyone has the ability to expresses love if they nurture their feelings.
Carter, Kasey. M. “ Loving Others: Faithful Crushers ”, Juvenile fiction journal Tate Publishing, 2009, Vol 1, p 10, pp24
Fisher, Helen .E. “Why we love: the nature and chemistry of romantic love” H. Holt Publishers, 2004
Hurlock, Elizabeth. B. “ Developmental psychology: a life-span approach” Tata McGraw-Hill, 2001
Lazarus, Richard. S. “ Stress and Emotion: A New Synthesis ”. New York, Springer. 1999, pp.254
Lerner, Richard. M. and Damon, William. “ Handbook of Child Psychology: Social, Emotional, and personality development: Volume 3 of Handbook of Child Psychology”, John Wiley and Sons publishers, 2006, pp 2
McGraw, Patricia Romano. “Seeking the Wisdom of the Heart: Reflection on the Seven Stages of Spiritual Development”. Baha’i Publishing Trust, 2007
Perk, Scott. M. “The Road Less Travelled: A New Psychology of Love, Traditional Values and Spiritual Growth” . New York, NY: Simon and Schuster, Touchstone, 1978, pp.81, 116-117
Vacek, Edward Collins. “Love, Human and Divine: The Heart of Christian Ethics Moral Traditions and Moral Arguments Series ” Georgetown University Press, 1996, pp 248
Wallerstein, Judith and Sandra, Blakeslee (1995), “ The good marriage: How and Why love lasts”. Boston: Houghton Mifflin publishers
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, October 18). What Love Is and Why It Matters. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-love-is-and-why-it-matters/
"What Love Is and Why It Matters." IvyPanda , 18 Oct. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/what-love-is-and-why-it-matters/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'What Love Is and Why It Matters'. 18 October.
IvyPanda . 2019. "What Love Is and Why It Matters." October 18, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-love-is-and-why-it-matters/.
1. IvyPanda . "What Love Is and Why It Matters." October 18, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-love-is-and-why-it-matters/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "What Love Is and Why It Matters." October 18, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-love-is-and-why-it-matters/.
- Racial Bias in "How I Met Your Mother" and "Friends" Shows
- Human Resource Policies and Practices: A Case Study of Patagonia
- David Is a Man by God’s Heart: Life and Humility
- Communication: Improving Listening Skills
- Community-Based Organizations and Healthcare Sectors Partnership
- Lead Generation and Nurturing in Marketing
- Nurturing Successful Team Communication
- Mutual Responsibility for Child Care and Nurturing
- Parenting and Discipline: Nurturing Values and Behavior
- Nurturing Opportunities for Educational Leadership
- College Technology Application
- Are Women Better Parents Than Men? Essay
- Are Parents Responsible for Their Children's Behavior?
- How Does Society View Single Parents?
- Single Life vs. Married Life Essay

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
This essay focuses on personal love, or the love of particular persons as such. Part of the philosophical task in understanding personal love is to distinguish the various kinds of personal love. For example, the way in which I love my wife is seemingly very different from the way I love my mother, my child, and my friend. This task has typically proceeded hand-in-hand with philosophical analyses of these kinds of personal love, analyses that in part respond to various puzzles about love. Can love be justified? If so, how? What is the value of personal love? What impact does love have on the autonomy of both the lover and the beloved?
1. Preliminary Distinctions
2. love as union, 3. love as robust concern, 4.1 love as appraisal of value, 4.2 love as bestowal of value, 4.3 an intermediate position, 5.1 love as emotion proper, 5.2 love as emotion complex, 6. the value and justification of love, other internet resources, related entries.
In ordinary conversations, we often say things like the following:
- I love chocolate (or skiing).
- I love doing philosophy (or being a father).
- I love my dog (or cat).
- I love my wife (or mother or child or friend).
However, what is meant by ‘love’ differs from case to case. (1) may be understood as meaning merely that I like this thing or activity very much. In (2) the implication is typically that I find engaging in a certain activity or being a certain kind of person to be a part of my identity and so what makes my life worth living; I might just as well say that I value these. By contrast, (3) and (4) seem to indicate a mode of concern that cannot be neatly assimilated to anything else. Thus, we might understand the sort of love at issue in (4) to be, roughly, a matter of caring about another person as the person she is, for her own sake. (Accordingly, (3) may be understood as a kind of deficient mode of the sort of love we typically reserve for persons.) Philosophical accounts of love have focused primarily on the sort of personal love at issue in (4); such personal love will be the focus here (though see Frankfurt (1999) and Jaworska & Wonderly (2017) for attempts to provide a more general account that applies to non-persons as well).
Even within personal love, philosophers from the ancient Greeks on have traditionally distinguished three notions that can properly be called “love”: eros , agape , and philia . It will be useful to distinguish these three and say something about how contemporary discussions typically blur these distinctions (sometimes intentionally so) or use them for other purposes.
‘ Eros ’ originally meant love in the sense of a kind of passionate desire for an object, typically sexual passion (Liddell et al., 1940). Nygren (1953a,b) describes eros as the “‘love of desire,’ or acquisitive love” and therefore as egocentric (1953b, p. 89). Soble (1989b, 1990) similarly describes eros as “selfish” and as a response to the merits of the beloved—especially the beloved’s goodness or beauty. What is evident in Soble’s description of eros is a shift away from the sexual: to love something in the “erosic” sense (to use the term Soble coins) is to love it in a way that, by being responsive to its merits, is dependent on reasons. Such an understanding of eros is encouraged by Plato’s discussion in the Symposium , in which Socrates understands sexual desire to be a deficient response to physical beauty in particular, a response which ought to be developed into a response to the beauty of a person’s soul and, ultimately, into a response to the form, Beauty.
Soble’s intent in understanding eros to be a reason-dependent sort of love is to articulate a sharp contrast with agape , a sort of love that does not respond to the value of its object. ‘ Agape ’ has come, primarily through the Christian tradition, to mean the sort of love God has for us persons, as well as our love for God and, by extension, of our love for each other—a kind of brotherly love. In the paradigm case of God’s love for us, agape is “spontaneous and unmotivated,” revealing not that we merit that love but that God’s nature is love (Nygren 1953b, p. 85). Rather than responding to antecedent value in its object, agape instead is supposed to create value in its object and therefore to initiate our fellowship with God (pp. 87–88). Consequently, Badhwar (2003, p. 58) characterizes agape as “independent of the loved individual’s fundamental characteristics as the particular person she is”; and Soble (1990, p. 5) infers that agape , in contrast to eros , is therefore not reason dependent but is rationally “incomprehensible,” admitting at best of causal or historical explanations. [ 1 ]
Finally, ‘ philia ’ originally meant a kind of affectionate regard or friendly feeling towards not just one’s friends but also possibly towards family members, business partners, and one’s country at large (Liddell et al., 1940; Cooper, 1977). Like eros , philia is generally (but not universally) understood to be responsive to (good) qualities in one’s beloved. This similarity between eros and philia has led Thomas (1987) to wonder whether the only difference between romantic love and friendship is the sexual involvement of the former—and whether that is adequate to account for the real differences we experience. The distinction between eros and philia becomes harder to draw with Soble’s attempt to diminish the importance of the sexual in eros (1990).
Maintaining the distinctions among eros , agape , and philia becomes even more difficult when faced with contemporary theories of love (including romantic love) and friendship. For, as discussed below, some theories of romantic love understand it along the lines of the agape tradition as creating value in the beloved (cf. Section 4.2 ), and other accounts of romantic love treat sexual activity as merely the expression of what otherwise looks very much like friendship.
Given the focus here on personal love, Christian conceptions of God’s love for persons (and vice versa ) will be omitted, and the distinction between eros and philia will be blurred—as it typically is in contemporary accounts. Instead, the focus here will be on these contemporary understandings of love, including romantic love, understood as an attitude we take towards other persons. [ 2 ]
In providing an account of love, philosophical analyses must be careful to distinguish love from other positive attitudes we take towards persons, such as liking. Intuitively, love differs from such attitudes as liking in terms of its “depth,” and the problem is to elucidate the kind of “depth” we intuitively find love to have. Some analyses do this in part by providing thin conceptions of what liking amounts to. Thus, Singer (1991) and Brown (1987) understand liking to be a matter of desiring, an attitude that at best involves its object having only instrumental (and not intrinsic) value. Yet this seems inadequate: surely there are attitudes towards persons intermediate between having a desire with a person as its object and loving the person. I can care about a person for her own sake and not merely instrumentally, and yet such caring does not on its own amount to (non-deficiently) loving her, for it seems I can care about my dog in exactly the same way, a kind of caring which is insufficiently personal for love.
It is more common to distinguish loving from liking via the intuition that the “depth” of love is to be explained in terms of a notion of identification: to love someone is somehow to identify yourself with him, whereas no such notion of identification is involved in liking. As Nussbaum puts it, “The choice between one potential love and another can feel, and be, like a choice of a way of life, a decision to dedicate oneself to these values rather than these” (1990, p. 328); liking clearly does not have this sort of “depth” (see also Helm 2010; Bagley 2015). Whether love involves some kind of identification, and if so exactly how to understand such identification, is a central bone of contention among the various analyses of love. In particular, Whiting (2013) argues that the appeal to a notion of identification distorts our understanding of the sort of motivation love can provide, for taken literally it implies that love motivates through self -interest rather than through the beloved’s interests. Thus, Whiting argues, central to love is the possibility that love takes the lover “outside herself”, potentially forgetting herself in being moved directly by the interests of the beloved. (Of course, we need not take the notion of identification literally in this way: in identifying with one’s beloved, one might have a concern for one’s beloved that is analogous to one’s concern for oneself; see Helm 2010.)
Another common way to distinguish love from other personal attitudes is in terms of a distinctive kind of evaluation, which itself can account for love’s “depth.” Again, whether love essentially involves a distinctive kind of evaluation, and if so how to make sense of that evaluation, is hotly disputed. Closely related to questions of evaluation are questions of justification: can we justify loving or continuing to love a particular person, and if so, how? For those who think the justification of love is possible, it is common to understand such justification in terms of evaluation, and the answers here affect various accounts’ attempts to make sense of the kind of constancy or commitment love seems to involve, as well as the sense in which love is directed at particular individuals.
In what follows, theories of love are tentatively and hesitantly classified into four types: love as union, love as robust concern, love as valuing, and love as an emotion. It should be clear, however, that particular theories classified under one type sometimes also include, without contradiction, ideas central to other types. The types identified here overlap to some extent, and in some cases classifying particular theories may involve excessive pigeonholing. (Such cases are noted below.) Part of the classificatory problem is that many accounts of love are quasi-reductionistic, understanding love in terms of notions like affection, evaluation, attachment, etc., which themselves never get analyzed. Even when these accounts eschew explicitly reductionistic language, very often little attempt is made to show how one such “aspect” of love is conceptually connected to others. As a result, there is no clear and obvious way to classify particular theories, let alone identify what the relevant classes should be.
The union view claims that love consists in the formation of (or the desire to form) some significant kind of union, a “we.” A central task for union theorists, therefore, is to spell out just what such a “we” comes to—whether it is literally a new entity in the world somehow composed of the lover and the beloved, or whether it is merely metaphorical. Variants of this view perhaps go back to Aristotle (cf. Sherman 1993) and can also be found in Montaigne ([E]) and Hegel (1997); contemporary proponents include Solomon (1981, 1988), Scruton (1986), Nozick (1989), Fisher (1990), and Delaney (1996).
Scruton, writing in particular about romantic love, claims that love exists “just so soon as reciprocity becomes community: that is, just so soon as all distinction between my interests and your interests is overcome” (1986, p. 230). The idea is that the union is a union of concern, so that when I act out of that concern it is not for my sake alone or for your sake alone but for our sake. Fisher (1990) holds a similar, but somewhat more moderate view, claiming that love is a partial fusion of the lovers’ cares, concerns, emotional responses, and actions. What is striking about both Scruton and Fisher is the claim that love requires the actual union of the lovers’ concerns, for it thus becomes clear that they conceive of love not so much as an attitude we take towards another but as a relationship: the distinction between your interests and mine genuinely disappears only when we together come to have shared cares, concerns, etc., and my merely having a certain attitude towards you is not enough for love. This provides content to the notion of a “we” as the (metaphorical?) subject of these shared cares and concerns, and as that for whose sake we act.
Solomon (1988) offers a union view as well, though one that tries “to make new sense out of ‘love’ through a literal rather than metaphoric sense of the ‘fusion’ of two souls” (p. 24, cf. Solomon 1981; however, it is unclear exactly what he means by a “soul” here and so how love can be a “literal” fusion of two souls). What Solomon has in mind is the way in which, through love, the lovers redefine their identities as persons in terms of the relationship: “Love is the concentration and the intensive focus of mutual definition on a single individual, subjecting virtually every personal aspect of one’s self to this process” (1988, p. 197). The result is that lovers come to share the interests, roles, virtues, and so on that constitute what formerly was two individual identities but now has become a shared identity, and they do so in part by each allowing the other to play an important role in defining his own identity.
Nozick (1989) offers a union view that differs from those of Scruton, Fisher, and Solomon in that Nozick thinks that what is necessary for love is merely the desire to form a “we,” together with the desire that your beloved reciprocates. Nonetheless, he claims that this “we” is “a new entity in the world…created by a new web of relationships between [the lovers] which makes them no longer separate” (p. 70). In spelling out this web of relationships, Nozick appeals to the lovers “pooling” not only their well-beings, in the sense that the well-being of each is tied up with that of the other, but also their autonomy, in that “each transfers some previous rights to make certain decisions unilaterally into a joint pool” (p. 71). In addition, Nozick claims, the lovers each acquire a new identity as a part of the “we,” a new identity constituted by their (a) wanting to be perceived publicly as a couple, (b) their attending to their pooled well-being, and (c) their accepting a “certain kind of division of labor” (p. 72):
A person in a we might find himself coming across something interesting to read yet leaving it for the other person, not because he himself would not be interested in it but because the other would be more interested, and one of them reading it is sufficient for it to be registered by the wider identity now shared, the we . [ 3 ]
Opponents of the union view have seized on claims like this as excessive: union theorists, they claim, take too literally the ontological commitments of this notion of a “we.” This leads to two specific criticisms of the union view. The first is that union views do away with individual autonomy. Autonomy, it seems, involves a kind of independence on the part of the autonomous agent, such that she is in control over not only what she does but also who she is, as this is constituted by her interests, values, concerns, etc. However, union views, by doing away with a clear distinction between your interests and mine, thereby undermine this sort of independence and so undermine the autonomy of the lovers. If autonomy is a part of the individual’s good, then, on the union view, love is to this extent bad; so much the worse for the union view (Singer 1994; Soble 1997). Moreover, Singer (1994) argues that a necessary part of having your beloved be the object of your love is respect for your beloved as the particular person she is, and this requires respecting her autonomy.
Union theorists have responded to this objection in several ways. Nozick (1989) seems to think of a loss of autonomy in love as a desirable feature of the sort of union lovers can achieve. Fisher (1990), somewhat more reluctantly, claims that the loss of autonomy in love is an acceptable consequence of love. Yet without further argument these claims seem like mere bullet biting. Solomon (1988, pp. 64ff) describes this “tension” between union and autonomy as “the paradox of love.” However, this a view that Soble (1997) derides: merely to call it a paradox, as Solomon does, is not to face up to the problem.
The second criticism involves a substantive view concerning love. Part of what it is to love someone, these opponents say, is to have concern for him for his sake. However, union views make such concern unintelligible and eliminate the possibility of both selfishness and self-sacrifice, for by doing away with the distinction between my interests and your interests they have in effect turned your interests into mine and vice versa (Soble 1997; see also Blum 1980, 1993). Some advocates of union views see this as a point in their favor: we need to explain how it is I can have concern for people other than myself, and the union view apparently does this by understanding your interests to be part of my own. And Delaney, responding to an apparent tension between our desire to be loved unselfishly (for fear of otherwise being exploited) and our desire to be loved for reasons (which presumably are attractive to our lover and hence have a kind of selfish basis), says (1996, p. 346):
Given my view that the romantic ideal is primarily characterized by a desire to achieve a profound consolidation of needs and interests through the formation of a we , I do not think a little selfishness of the sort described should pose a worry to either party.
The objection, however, lies precisely in this attempt to explain my concern for my beloved egoistically. As Whiting (1991, p. 10) puts it, such an attempt “strikes me as unnecessary and potentially objectionable colonization”: in love, I ought to be concerned with my beloved for her sake, and not because I somehow get something out of it. (This can be true whether my concern with my beloved is merely instrumental to my good or whether it is partly constitutive of my good.)
Although Whiting’s and Soble’s criticisms here succeed against the more radical advocates of the union view, they in part fail to acknowledge the kernel of truth to be gleaned from the idea of union. Whiting’s way of formulating the second objection in terms of an unnecessary egoism in part points to a way out: we persons are in part social creatures, and love is one profound mode of that sociality. Indeed, part of the point of union accounts is to make sense of this social dimension: to make sense of a way in which we can sometimes identify ourselves with others not merely in becoming interdependent with them (as Singer 1994, p. 165, suggests, understanding ‘interdependence’ to be a kind of reciprocal benevolence and respect) but rather in making who we are as persons be constituted in part by those we love (cf., e.g., Rorty 1986/1993; Nussbaum 1990).
Along these lines, Friedman (1998), taking her inspiration in part from Delaney (1996), argues that we should understand the sort of union at issue in love to be a kind of federation of selves:
On the federation model, a third unified entity is constituted by the interaction of the lovers, one which involves the lovers acting in concert across a range of conditions and for a range of purposes. This concerted action, however, does not erase the existence of the two lovers as separable and separate agents with continuing possibilities for the exercise of their own respective agencies. [p. 165]
Given that on this view the lovers do not give up their individual identities, there is no principled reason why the union view cannot make sense of the lover’s concern for her beloved for his sake. [ 4 ] Moreover, Friedman argues, once we construe union as federation, we can see that autonomy is not a zero-sum game; rather, love can both directly enhance the autonomy of each and promote the growth of various skills, like realistic and critical self-evaluation, that foster autonomy.
Nonetheless, this federation model is not without its problems—problems that affect other versions of the union view as well. For if the federation (or the “we”, as on Nozick’s view) is understood as a third entity, we need a clearer account than has been given of its ontological status and how it comes to be. Relevant here is the literature on shared intention and plural subjects. Gilbert (1989, 1996, 2000) has argued that we should take quite seriously the existence of a plural subject as an entity over and above its constituent members. Others, such as Tuomela (1984, 1995), Searle (1990), and Bratman (1999) are more cautious, treating such talk of “us” having an intention as metaphorical.
As this criticism of the union view indicates, many find caring about your beloved for her sake to be a part of what it is to love her. The robust concern view of love takes this to be the central and defining feature of love (cf. Taylor 1976; Newton-Smith 1989; Soble 1990, 1997; LaFollette 1996; Frankfurt 1999; White 2001). As Taylor puts it:
To summarize: if x loves y then x wants to benefit and be with y etc., and he has these wants (or at least some of them) because he believes y has some determinate characteristics ψ in virtue of which he thinks it worth while to benefit and be with y . He regards satisfaction of these wants as an end and not as a means towards some other end. [p. 157]
In conceiving of my love for you as constituted by my concern for you for your sake, the robust concern view rejects the idea, central to the union view, that love is to be understood in terms of the (literal or metaphorical) creation of a “we”: I am the one who has this concern for you, though it is nonetheless disinterested and so not egoistic insofar as it is for your sake rather than for my own. [ 5 ]
At the heart of the robust concern view is the idea that love “is neither affective nor cognitive. It is volitional” (Frankfurt 1999, p. 129; see also Martin 2015). Frankfurt continues:
That a person cares about or that he loves something has less to do with how things make him feel, or with his opinions about them, than with the more or less stable motivational structures that shape his preferences and that guide and limit his conduct.
This account analyzes caring about someone for her sake as a matter of being motivated in certain ways, in part as a response to what happens to one’s beloved. Of course, to understand love in terms of desires is not to leave other emotional responses out in the cold, for these emotions should be understood as consequences of desires. Thus, just as I can be emotionally crushed when one of my strong desires is disappointed, so too I can be emotionally crushed when things similarly go badly for my beloved. In this way Frankfurt (1999) tacitly, and White (2001) more explicitly, acknowledge the way in which my caring for my beloved for her sake results in my identity being transformed through her influence insofar as I become vulnerable to things that happen to her.
Not all robust concern theorists seem to accept this line, however; in particular, Taylor (1976) and Soble (1990) seem to have a strongly individualistic conception of persons that prevents my identity being bound up with my beloved in this sort of way, a kind of view that may seem to undermine the intuitive “depth” that love seems to have. (For more on this point, see Rorty 1986/1993.) In the middle is Stump (2006), who follows Aquinas in understanding love to involve not only the desire for your beloved’s well-being but also a desire for a certain kind of relationship with your beloved—as a parent or spouse or sibling or priest or friend, for example—a relationship within which you share yourself with and connect yourself to your beloved. [ 6 ]
One source of worry about the robust concern view is that it involves too passive an understanding of one’s beloved (Ebels-Duggan 2008). The thought is that on the robust concern view the lover merely tries to discover what the beloved’s well-being consists in and then acts to promote that, potentially by thwarting the beloved’s own efforts when the lover thinks those efforts would harm her well-being. This, however, would be disrespectful and demeaning, not the sort of attitude that love is. What robust concern views seem to miss, Ebels-Duggan suggests, is the way love involves interacting agents, each with a capacity for autonomy the recognition and engagement with which is an essential part of love. In response, advocates of the robust concern view might point out that promoting someone’s well-being normally requires promoting her autonomy (though they may maintain that this need not always be true: that paternalism towards a beloved can sometimes be justified and appropriate as an expression of one’s love). Moreover, we might plausibly think, it is only through the exercise of one’s autonomy that one can define one’s own well-being as a person, so that a lover’s failure to respect the beloved’s autonomy would be a failure to promote her well-being and therefore not an expression of love, contrary to what Ebels-Duggan suggests. Consequently, it might seem, robust concern views can counter this objection by offering an enriched conception of what it is to be a person and so of the well-being of persons.
Another source of worry is that the robust concern view offers too thin a conception of love. By emphasizing robust concern, this view understands other features we think characteristic of love, such as one’s emotional responsiveness to one’s beloved, to be the effects of that concern rather than constituents of it. Thus Velleman (1999) argues that robust concern views, by understanding love merely as a matter of aiming at a particular end (viz., the welfare of one’s beloved), understand love to be merely conative. However, he claims, love can have nothing to do with desires, offering as a counterexample the possibility of loving a troublemaking relation whom you do not want to be with, whose well being you do not want to promote, etc. Similarly, Badhwar (2003) argues that such a “teleological” view of love makes it mysterious how “we can continue to love someone long after death has taken him beyond harm or benefit” (p. 46). Moreover Badhwar argues, if love is essentially a desire, then it implies that we lack something; yet love does not imply this and, indeed, can be felt most strongly at times when we feel our lives most complete and lacking in nothing. Consequently, Velleman and Badhwar conclude, love need not involve any desire or concern for the well-being of one’s beloved.
This conclusion, however, seems too hasty, for such examples can be accommodated within the robust concern view. Thus, the concern for your relative in Velleman’s example can be understood to be present but swamped by other, more powerful desires to avoid him. Indeed, keeping the idea that you want to some degree to benefit him, an idea Velleman rejects, seems to be essential to understanding the conceptual tension between loving someone and not wanting to help him, a tension Velleman does not fully acknowledge. Similarly, continued love for someone who has died can be understood on the robust concern view as parasitic on the former love you had for him when he was still alive: your desires to benefit him get transformed, through your subsequent understanding of the impossibility of doing so, into wishes. [ 7 ] Finally, the idea of concern for your beloved’s well-being need not imply the idea that you lack something, for such concern can be understood in terms of the disposition to be vigilant for occasions when you can come to his aid and consequently to have the relevant occurrent desires. All of this seems fully compatible with the robust concern view.
One might also question whether Velleman and Badhwar make proper use of their examples of loving your meddlesome relation or someone who has died. For although we can understand these as genuine cases of love, they are nonetheless deficient cases and ought therefore be understood as parasitic on the standard cases. Readily to accommodate such deficient cases of love into a philosophical analysis as being on a par with paradigm cases, and to do so without some special justification, is dubious.
Nonetheless, the robust concern view as it stands does not seem properly able to account for the intuitive “depth” of love and so does not seem properly to distinguish loving from liking. Although, as noted above, the robust concern view can begin to make some sense of the way in which the lover’s identity is altered by the beloved, it understands this only an effect of love, and not as a central part of what love consists in.
This vague thought is nicely developed by Wonderly (2017), who emphasizes that in addition to the sort of disinterested concern for another that is central to robust-concern accounts of love, an essential part of at least romantic love is the idea that in loving someone I must find them to be not merely important for their own sake but also important to me . Wonderly (2017) fleshes out what this “importance to me” involves in terms of the idea of attachment (developed in Wonderly 2016) that she argues can make sense of the intimacy and depth of love from within what remains fundamentally a robust-concern account. [ 8 ]
4. Love as Valuing
A third kind of view of love understands love to be a distinctive mode of valuing a person. As the distinction between eros and agape in Section 1 indicates, there are at least two ways to construe this in terms of whether the lover values the beloved because she is valuable, or whether the beloved comes to be valuable to the lover as a result of her loving him. The former view, which understands the lover as appraising the value of the beloved in loving him, is the topic of Section 4.1 , whereas the latter view, which understands her as bestowing value on him, will be discussed in Section 4.2 .
Velleman (1999, 2008) offers an appraisal view of love, understanding love to be fundamentally a matter of acknowledging and responding in a distinctive way to the value of the beloved. (For a very different appraisal view of love, see Kolodny 2003.) Understanding this more fully requires understanding both the kind of value of the beloved to which one responds and the distinctive kind of response to such value that love is. Nonetheless, it should be clear that what makes an account be an appraisal view of love is not the mere fact that love is understood to involve appraisal; many other accounts do so, and it is typical of robust concern accounts, for example (cf. the quote from Taylor above , Section 3 ). Rather, appraisal views are distinctive in understanding love to consist in that appraisal.
In articulating the kind of value love involves, Velleman, following Kant, distinguishes dignity from price. To have a price , as the economic metaphor suggests, is to have a value that can be compared to the value of other things with prices, such that it is intelligible to exchange without loss items of the same value. By contrast, to have dignity is to have a value such that comparisons of relative value become meaningless. Material goods are normally understood to have prices, but we persons have dignity: no substitution of one person for another can preserve exactly the same value, for something of incomparable worth would be lost (and gained) in such a substitution.
On this Kantian view, our dignity as persons consists in our rational nature: our capacity both to be actuated by reasons that we autonomously provide ourselves in setting our own ends and to respond appropriately to the intrinsic values we discover in the world. Consequently, one important way in which we exercise our rational natures is to respond with respect to the dignity of other persons (a dignity that consists in part in their capacity for respect): respect just is the required minimal response to the dignity of persons. What makes a response to a person be that of respect, Velleman claims, still following Kant, is that it “arrests our self-love” and thereby prevents us from treating him as a means to our ends (p. 360).
Given this, Velleman claims that love is similarly a response to the dignity of persons, and as such it is the dignity of the object of our love that justifies that love. However, love and respect are different kinds of responses to the same value. For love arrests not our self-love but rather
our tendencies toward emotional self-protection from another person, tendencies to draw ourselves in and close ourselves off from being affected by him. Love disarms our emotional defenses; it makes us vulnerable to the other. [1999, p. 361]
This means that the concern, attraction, sympathy, etc. that we normally associate with love are not constituents of love but are rather its normal effects, and love can remain without them (as in the case of the love for a meddlesome relative one cannot stand being around). Moreover, this provides Velleman with a clear account of the intuitive “depth” of love: it is essentially a response to persons as such, and to say that you love your dog is therefore to be confused.
Of course, we do not respond with love to the dignity of every person we meet, nor are we somehow required to: love, as the disarming of our emotional defenses in a way that makes us especially vulnerable to another, is the optional maximal response to others’ dignity. What, then, explains the selectivity of love—why I love some people and not others? The answer lies in the contingent fit between the way some people behaviorally express their dignity as persons and the way I happen to respond to those expressions by becoming emotionally vulnerable to them. The right sort of fit makes someone “lovable” by me (1999, p. 372), and my responding with love in these cases is a matter of my “really seeing” this person in a way that I fail to do with others who do not fit with me in this way. By ‘lovable’ here Velleman seems to mean able to be loved, not worthy of being loved, for nothing Velleman says here speaks to a question about the justification of my loving this person rather than that. Rather, what he offers is an explanation of the selectivity of my love, an explanation that as a matter of fact makes my response be that of love rather than mere respect.
This understanding of the selectivity of love as something that can be explained but not justified is potentially troubling. For we ordinarily think we can justify not only my loving you rather than someone else but also and more importantly the constancy of my love: my continuing to love you even as you change in certain fundamental ways (but not others). As Delaney (1996, p. 347) puts the worry about constancy:
while you seem to want it to be true that, were you to become a schmuck, your lover would continue to love you,…you also want it to be the case that your lover would never love a schmuck.
The issue here is not merely that we can offer explanations of the selectivity of my love, of why I do not love schmucks; rather, at issue is the discernment of love, of loving and continuing to love for good reasons as well as of ceasing to love for good reasons. To have these good reasons seems to involve attributing different values to you now rather than formerly or rather than to someone else, yet this is precisely what Velleman denies is the case in making the distinction between love and respect the way he does.
It is also questionable whether Velleman can even explain the selectivity of love in terms of the “fit” between your expressions and my sensitivities. For the relevant sensitivities on my part are emotional sensitivities: the lowering of my emotional defenses and so becoming emotionally vulnerable to you. Thus, I become vulnerable to the harms (or goods) that befall you and so sympathetically feel your pain (or joy). Such emotions are themselves assessable for warrant, and now we can ask why my disappointment that you lost the race is warranted, but my being disappointed that a mere stranger lost would not be warranted. The intuitive answer is that I love you but not him. However, this answer is unavailable to Velleman, because he thinks that what makes my response to your dignity that of love rather than respect is precisely that I feel such emotions, and to appeal to my love in explaining the emotions therefore seems viciously circular.
Although these problems are specific to Velleman’s account, the difficulty can be generalized to any appraisal account of love (such as that offered in Kolodny 2003). For if love is an appraisal, it needs to be distinguished from other forms of appraisal, including our evaluative judgments. On the one hand, to try to distinguish love as an appraisal from other appraisals in terms of love’s having certain effects on our emotional and motivational life (as on Velleman’s account) is unsatisfying because it ignores part of what needs to be explained: why the appraisal of love has these effects and yet judgments with the same evaluative content do not. Indeed, this question is crucial if we are to understand the intuitive “depth” of love, for without an answer to this question we do not understand why love should have the kind of centrality in our lives it manifestly does. [ 9 ] On the other hand, to bundle this emotional component into the appraisal itself would be to turn the view into either the robust concern view ( Section 3 ) or a variant of the emotion view ( Section 5.1 ).
In contrast to Velleman, Singer (1991, 1994, 2009) understands love to be fundamentally a matter of bestowing value on the beloved. To bestow value on another is to project a kind of intrinsic value onto him. Indeed, this fact about love is supposed to distinguish love from liking: “Love is an attitude with no clear objective,” whereas liking is inherently teleological (1991, p. 272). As such, there are no standards of correctness for bestowing such value, and this is how love differs from other personal attitudes like gratitude, generosity, and condescension: “love…confers importance no matter what the object is worth” (p. 273). Consequently, Singer thinks, love is not an attitude that can be justified in any way.
What is it, exactly, to bestow this kind of value on someone? It is, Singer says, a kind of attachment and commitment to the beloved, in which one comes to treat him as an end in himself and so to respond to his ends, interests, concerns, etc. as having value for their own sake. This means in part that the bestowal of value reveals itself “by caring about the needs and interests of the beloved, by wishing to benefit or protect her, by delighting in her achievements,” etc. (p. 270). This sounds very much like the robust concern view, yet the bestowal view differs in understanding such robust concern to be the effect of the bestowal of value that is love rather than itself what constitutes love: in bestowing value on my beloved, I make him be valuable in such a way that I ought to respond with robust concern.
For it to be intelligible that I have bestowed value on someone, I must therefore respond appropriately to him as valuable, and this requires having some sense of what his well-being is and of what affects that well-being positively or negatively. Yet having this sense requires in turn knowing what his strengths and deficiencies are, and this is a matter of appraising him in various ways. Bestowal thus presupposes a kind of appraisal, as a way of “really seeing” the beloved and attending to him. Nonetheless, Singer claims, it is the bestowal that is primary for understanding what love consists in: the appraisal is required only so that the commitment to one’s beloved and his value as thus bestowed has practical import and is not “a blind submission to some unknown being” (1991, p. 272; see also Singer 1994, pp. 139ff).
Singer is walking a tightrope in trying to make room for appraisal in his account of love. Insofar as the account is fundamentally a bestowal account, Singer claims that love cannot be justified, that we bestow the relevant kind of value “gratuitously.” This suggests that love is blind, that it does not matter what our beloved is like, which seems patently false. Singer tries to avoid this conclusion by appealing to the role of appraisal: it is only because we appraise another as having certain virtues and vices that we come to bestow value on him. Yet the “because” here, since it cannot justify the bestowal, is at best a kind of contingent causal explanation. [ 10 ] In this respect, Singer’s account of the selectivity of love is much the same as Velleman’s, and it is liable to the same criticism: it makes unintelligible the way in which our love can be discerning for better or worse reasons. Indeed, this failure to make sense of the idea that love can be justified is a problem for any bestowal view. For either (a) a bestowal itself cannot be justified (as on Singer’s account), in which case the justification of love is impossible, or (b) a bestowal can be justified, in which case it is hard to make sense of value as being bestowed rather than there antecedently in the object as the grounds of that “bestowal.”
More generally, a proponent of the bestowal view needs to be much clearer than Singer is in articulating precisely what a bestowal is. What is the value that I create in a bestowal, and how can my bestowal create it? On a crude Humean view, the answer might be that the value is something projected onto the world through my pro-attitudes, like desire. Yet such a view would be inadequate, since the projected value, being relative to a particular individual, would do no theoretical work, and the account would essentially be a variant of the robust concern view. Moreover, in providing a bestowal account of love, care is needed to distinguish love from other personal attitudes such as admiration and respect: do these other attitudes involve bestowal? If so, how does the bestowal in these cases differ from the bestowal of love? If not, why not, and what is so special about love that requires a fundamentally different evaluative attitude than admiration and respect?
Nonetheless, there is a kernel of truth in the bestowal view: there is surely something right about the idea that love is creative and not merely a response to antecedent value, and accounts of love that understand the kind of evaluation implicit in love merely in terms of appraisal seem to be missing something. Precisely what may be missed will be discussed below in Section 6 .
Perhaps there is room for an understanding of love and its relation to value that is intermediate between appraisal and bestowal accounts. After all, if we think of appraisal as something like perception, a matter of responding to what is out there in the world, and of bestowal as something like action, a matter of doing something and creating something, we should recognize that the responsiveness central to appraisal may itself depend on our active, creative choices. Thus, just as we must recognize that ordinary perception depends on our actively directing our attention and deploying concepts, interpretations, and even arguments in order to perceive things accurately, so too we might think our vision of our beloved’s valuable properties that is love also depends on our actively attending to and interpreting him. Something like this is Jollimore’s view (2011). According to Jollimore, in loving someone we actively attend to his valuable properties in a way that we take to provide us with reasons to treat him preferentially. Although we may acknowledge that others might have such properties even to a greater degree than our beloved does, we do not attend to and appreciate such properties in others in the same way we do those in our beloveds; indeed, we find our appreciation of our beloved’s valuable properties to “silence” our similar appreciation of those in others. (In this way, Jollimore thinks, we can solve the problem of fungibility, discussed below in Section 6 .) Likewise, in perceiving our beloved’s actions and character, we do so through the lens of such an appreciation, which will tend as to “silence” interpretations inconsistent with that appreciation. In this way, love involves finding one’s beloved to be valuable in a way that involves elements of both appraisal (insofar as one must thereby be responsive to valuable properties one’s beloved really has) and bestowal (insofar as through one’s attention and committed appreciation of these properties they come to have special significance for one).
One might object that this conception of love as silencing the special value of others or to negative interpretations of our beloveds is irrational in a way that love is not. For, it might seem, such “silencing” is merely a matter of our blinding ourselves to how things really are. Yet Jollimore claims that this sense in which love is blind is not objectionable, for (a) we can still intellectually recognize the things that love’s vision silences, and (b) there really is no impartial perspective we can take on the values things have, and love is one appropriate sort of partial perspective from which the value of persons can be manifest. Nonetheless, one might wonder about whether that perspective of love itself can be distorted and what the norms are in terms of which such distortions are intelligible. Furthermore, it may seem that Jollimore’s attempt to reconcile appraisal and bestowal fails to appreciate the underlying metaphysical difficulty: appraisal is a response to value that is antecedently there, whereas bestowal is the creation of value that was not antecedently there. Consequently, it might seem, appraisal and bestowal are mutually exclusive and cannot be reconciled in the way Jollimore hopes.
Whereas Jollimore tries to combine separate elements of appraisal and of bestowal in a single account, Helm (2010) and Bagley (2015) offer accounts that reject the metaphysical presupposition that values must be either prior to love (as with appraisal) or posterior to love (as with bestowal), instead understanding the love and the values to emerge simultaneously. Thus, Helm presents a detailed account of valuing in terms of the emotions, arguing that while we can understand individual emotions as appraisals , responding to values already their in their objects, these values are bestowed on those objects via broad, holistic patterns of emotions. How this amounts to an account of love will be discussed in Section 5.2 , below. Bagley (2015) instead appeals to a metaphor of improvisation, arguing that just as jazz musicians jointly make determinate the content of their musical ideas through on-going processes of their expression, so too lovers jointly engage in “deep improvisation”, thereby working out of their values and identities through the on-going process of living their lives together. These values are thus something the lovers jointly construct through the process of recognizing and responding to those very values. To love someone is thus to engage with them as partners in such “deep improvisation”. (This account is similar to Helm (2008, 2010)’s account of plural agency, which he uses to provide an account of friendship and other loving relationships; see the discussion of shared activity in the entry on friendship .)
5. Emotion Views
Given these problems with the accounts of love as valuing, perhaps we should turn to the emotions. For emotions just are responses to objects that combine evaluation, motivation, and a kind of phenomenology, all central features of the attitude of love.
Many accounts of love claim that it is an emotion; these include: Wollheim 1984, Rorty 1986/1993, Brown 1987, Hamlyn 1989, Baier 1991, and Badhwar 2003. [ 11 ] Thus, Hamlyn (1989, p. 219) says:
It would not be a plausible move to defend any theory of the emotions to which love and hate seemed exceptions by saying that love and hate are after all not emotions. I have heard this said, but it does seem to me a desperate move to make. If love and hate are not emotions what is?
The difficulty with this claim, as Rorty (1980) argues, is that the word, ‘emotion,’ does not seem to pick out a homogeneous collection of mental states, and so various theories claiming that love is an emotion mean very different things. Consequently, what are here labeled “emotion views” are divided into those that understand love to be a particular kind of evaluative-cum-motivational response to an object, whether that response is merely occurrent or dispositional (‘emotions proper,’ see Section 5.1 , below), and those that understand love to involve a collection of related and interconnected emotions proper (‘emotion complexes,’ see Section 5.2 , below).
An emotion proper is a kind of “evaluative-cum-motivational response to an object”; what does this mean? Emotions are generally understood to have several objects. The target of an emotion is that at which the emotion is directed: if I am afraid or angry at you, then you are the target. In responding to you with fear or anger, I am implicitly evaluating you in a particular way, and this evaluation—called the formal object —is the kind of evaluation of the target that is distinctive of a particular emotion type. Thus, in fearing you, I implicitly evaluate you as somehow dangerous, whereas in being angry at you I implicitly evaluate you as somehow offensive. Yet emotions are not merely evaluations of their targets; they in part motivate us to behave in certain ways, both rationally (by motivating action to avoid the danger) and arationally (via certain characteristic expressions, such as slamming a door out of anger). Moreover, emotions are generally understood to involve a phenomenological component, though just how to understand the characteristic “feel” of an emotion and its relation to the evaluation and motivation is hotly disputed. Finally, emotions are typically understood to be passions: responses that we feel imposed on us as if from the outside, rather than anything we actively do. (For more on the philosophy of emotions, see entry on emotion .)
What then are we saying when we say that love is an emotion proper? According to Brown (1987, p. 14), emotions as occurrent mental states are “abnormal bodily changes caused by the agent’s evaluation or appraisal of some object or situation that the agent believes to be of concern to him or her.” He spells this out by saying that in love, we “cherish” the person for having “a particular complex of instantiated qualities” that is “open-ended” so that we can continue to love the person even as she changes over time (pp. 106–7). These qualities, which include historical and relational qualities, are evaluated in love as worthwhile. [ 12 ] All of this seems aimed at spelling out what love’s formal object is, a task that is fundamental to understanding love as an emotion proper. Thus, Brown seems to say that love’s formal object is just being worthwhile (or, given his examples, perhaps: worthwhile as a person), and he resists being any more specific than this in order to preserve the open-endedness of love. Hamlyn (1989) offers a similar account, saying (p. 228):
With love the difficulty is to find anything of this kind [i.e., a formal object] which is uniquely appropriate to love. My thesis is that there is nothing of this kind that must be so, and that this differentiates it and hate from the other emotions.
Hamlyn goes on to suggest that love and hate might be primordial emotions, a kind of positive or negative “feeling towards,” presupposed by all other emotions. [ 13 ]
The trouble with these accounts of love as an emotion proper is that they provide too thin a conception of love. In Hamlyn’s case, love is conceived as a fairly generic pro-attitude, rather than as the specific kind of distinctively personal attitude discussed here. In Brown’s case, spelling out the formal object of love as simply being worthwhile (as a person) fails to distinguish love from other evaluative responses like admiration and respect. Part of the problem seems to be the rather simple account of what an emotion is that Brown and Hamlyn use as their starting point: if love is an emotion, then the understanding of what an emotion is must be enriched considerably to accommodate love. Yet it is not at all clear whether the idea of an “emotion proper” can be adequately enriched so as to do so. As Pismenny & Prinz (2017) point out, love seems to be too varied both in its ground and in the sort of experience it involves to be capturable by a single emotion.
The emotion complex view, which understands love to be a complex emotional attitude towards another person, may initially seem to hold out great promise to overcome the problems of alternative types of views. By articulating the emotional interconnections between persons, it could offer a satisfying account of the “depth” of love without the excesses of the union view and without the overly narrow teleological focus of the robust concern view; and because these emotional interconnections are themselves evaluations, it could offer an understanding of love as simultaneously evaluative, without needing to specify a single formal object of love. However, the devil is in the details.
Rorty (1986/1993) does not try to present a complete account of love; rather, she focuses on the idea that “relational psychological attitudes” which, like love, essentially involve emotional and desiderative responses, exhibit historicity : “they arise from, and are shaped by, dynamic interactions between a subject and an object” (p. 73). In part this means that what makes an attitude be one of love is not the presence of a state that we can point to at a particular time within the lover; rather, love is to be “identified by a characteristic narrative history” (p. 75). Moreover, Rorty argues, the historicity of love involves the lover’s being permanently transformed by loving who he does.
Baier (1991), seeming to pick up on this understanding of love as exhibiting historicity, says (p. 444):
Love is not just an emotion people feel toward other people, but also a complex tying together of the emotions that two or a few more people have; it is a special form of emotional interdependence.
To a certain extent, such emotional interdependence involves feeling sympathetic emotions, so that, for example, I feel disappointed and frustrated on behalf of my beloved when she fails, and joyful when she succeeds. However, Baier insists, love is “more than just the duplication of the emotion of each in a sympathetic echo in the other” (p. 442); the emotional interdependence of the lovers involves also appropriate follow-up responses to the emotional predicaments of your beloved. Two examples Baier gives (pp. 443–44) are a feeling of “mischievous delight” at your beloved’s temporary bafflement, and amusement at her embarrassment. The idea is that in a loving relationship your beloved gives you permission to feel such emotions when no one else is permitted to do so, and a condition of her granting you that permission is that you feel these emotions “tenderly.” Moreover, you ought to respond emotionally to your beloved’s emotional responses to you: by feeling hurt when she is indifferent to you, for example. All of these foster the sort of emotional interdependence Baier is after—a kind of intimacy you have with your beloved.
Badhwar (2003, p. 46) similarly understands love to be a matter of “one’s overall emotional orientation towards a person—the complex of perceptions, thoughts, and feelings”; as such, love is a matter of having a certain “character structure.” Central to this complex emotional orientation, Badhwar thinks, is what she calls the “look of love”: “an ongoing [emotional] affirmation of the loved object as worthy of existence…for her own sake” (p. 44), an affirmation that involves taking pleasure in your beloved’s well-being. Moreover, Badhwar claims, the look of love also provides to the beloved reliable testimony concerning the quality of the beloved’s character and actions (p. 57).
There is surely something very right about the idea that love, as an attitude central to deeply personal relationships, should not be understood as a state that can simply come and go. Rather, as the emotion complex view insists, the complexity of love is to be found in the historical patterns of one’s emotional responsiveness to one’s beloved—a pattern that also projects into the future. Indeed, as suggested above, the kind of emotional interdependence that results from this complex pattern can seem to account for the intuitive “depth” of love as fully interwoven into one’s emotional sense of oneself. And it seems to make some headway in understanding the complex phenomenology of love: love can at times be a matter of intense pleasure in the presence of one’s beloved, yet it can at other times involve frustration, exasperation, anger, and hurt as a manifestation of the complexities and depth of the relationships it fosters.
This understanding of love as constituted by a history of emotional interdependence enables emotion complex views to say something interesting about the impact love has on the lover’s identity. This is partly Rorty’s point (1986/1993) in her discussion of the historicity of love ( above ). Thus, she argues, one important feature of such historicity is that love is “ dynamically permeable ” in that the lover is continually “changed by loving” such that these changes “tend to ramify through a person’s character” (p. 77). Through such dynamic permeability, love transforms the identity of the lover in a way that can sometimes foster the continuity of the love, as each lover continually changes in response to the changes in the other. [ 14 ] Indeed, Rorty concludes, love should be understood in terms of “a characteristic narrative history” (p. 75) that results from such dynamic permeability. It should be clear, however, that the mere fact of dynamic permeability need not result in the love’s continuing: nothing about the dynamics of a relationship requires that the characteristic narrative history project into the future, and such permeability can therefore lead to the dissolution of the love. Love is therefore risky—indeed, all the more risky because of the way the identity of the lover is defined in part through the love. The loss of a love can therefore make one feel no longer oneself in ways poignantly described by Nussbaum (1990).
By focusing on such emotionally complex histories, emotion complex views differ from most alternative accounts of love. For alternative accounts tend to view love as a kind of attitude we take toward our beloveds, something we can analyze simply in terms of our mental state at the moment. [ 15 ] By ignoring this historical dimension of love in providing an account of what love is, alternative accounts have a hard time providing either satisfying accounts of the sense in which our identities as person are at stake in loving another or satisfactory solutions to problems concerning how love is to be justified (cf. Section 6 , especially the discussion of fungibility ).
Nonetheless, some questions remain. If love is to be understood as an emotion complex, we need a much more explicit account of the pattern at issue here: what ties all of these emotional responses together into a single thing, namely love? Baier and Badhwar seem content to provide interesting and insightful examples of this pattern, but that does not seem to be enough. For example, what connects my amusement at my beloved’s embarrassment to other emotions like my joy on his behalf when he succeeds? Why shouldn’t my amusement at his embarrassment be understood instead as a somewhat cruel case of schadenfreude and so as antithetical to, and disconnected from, love? Moreover, as Naar (2013) notes, we need a principled account of when such historical patterns are disrupted in such a way as to end the love and when they are not. Do I stop loving when, in the midst of clinical depression, I lose my normal pattern of emotional concern?
Presumably the answer requires returning to the historicity of love: it all depends on the historical details of the relationship my beloved and I have forged. Some loves develop so that the intimacy within the relationship is such as to allow for tender, teasing responses to each other, whereas other loves may not. The historical details, together with the lovers’ understanding of their relationship, presumably determine which emotional responses belong to the pattern constitutive of love and which do not. However, this answer so far is inadequate: not just any historical relationship involving emotional interdependence is a loving relationship, and we need a principled way of distinguishing loving relationships from other relational evaluative attitudes: precisely what is the characteristic narrative history that is characteristic of love?
Helm (2009, 2010) tries to answer some of these questions in presenting an account of love as intimate identification. To love another, Helm claims, is to care about him as the particular person he is and so, other things being equal, to value the things he values. Insofar as a person’s (structured) set of values—his sense of the kind of life worth his living—constitutes his identity as a person, such sharing of values amounts to sharing his identity, which sounds very much like union accounts of love. However, Helm is careful to understand such sharing of values as for the sake of the beloved (as robust concern accounts insist), and he spells this all out in terms of patterns of emotions. Thus, Helm claims, all emotions have not only a target and a formal object (as indicated above), but also a focus : a background object the subject cares about in terms of which the implicit evaluation of the target is made intelligible. (For example, if I am afraid of the approaching hailstorm, I thereby evaluate it as dangerous, and what explains this evaluation is the way that hailstorm bears on my vegetable garden, which I care about; my garden, therefore, is the focus of my fear.) Moreover, emotions normally come in patterns with a common focus: fearing the hailstorm is normally connected to other emotions as being relieved when it passes by harmlessly (or disappointed or sad when it does not), being angry at the rabbits for killing the spinach, delighted at the productivity of the tomato plants, etc. Helm argues that a projectible pattern of such emotions with a common focus constitute caring about that focus. Consequently, we might say along the lines of Section 4.3 , while particular emotions appraise events in the world as having certain evaluative properties, their having these properties is partly bestowed on them by the overall patterns of emotions.
Helm identifies some emotions as person-focused emotions : emotions like pride and shame that essentially take persons as their focuses, for these emotions implicitly evaluate in terms of the target’s bearing on the quality of life of the person that is their focus. To exhibit a pattern of such emotions focused on oneself and subfocused on being a mother, for example, is to care about the place being a mother has in the kind of life you find worth living—in your identity as a person; to care in this way is to value being a mother as a part of your concern for your own identity. Likewise, to exhibit a projectible pattern of such emotions focused on someone else and subfocused on his being a father is to value this as a part of your concern for his identity—to value it for his sake. Such sharing of another’s values for his sake, which, Helm argues, essentially involves trust, respect, and affection, amounts to intimate identification with him, and such intimate identification just is love. Thus, Helm tries to provide an account of love that is grounded in an explicit account of caring (and caring about something for the sake of someone else) that makes room for the intuitive “depth” of love through intimate identification.
Jaworska & Wonderly (2017) argue that Helm’s construal of intimacy as intimate identification is too demanding. Rather, they argue, the sort of intimacy that distinguishes love from mere caring is one that involves a kind of emotional vulnerability in which things going well or poorly for one’s beloved are directly connected not merely to one’s well-being, but to one’s ability to flourish. This connection, they argue, runs through the lover’s self-understanding and the place the beloved has in the lover’s sense of a meaningful life.
Why do we love? It has been suggested above that any account of love needs to be able to answer some such justificatory question. Although the issue of the justification of love is important on its own, it is also important for the implications it has for understanding more clearly the precise object of love: how can we make sense of the intuitions not only that we love the individuals themselves rather than their properties, but also that my beloved is not fungible—that no one could simply take her place without loss. Different theories approach these questions in different ways, but, as will become clear below, the question of justification is primary.
One way to understand the question of why we love is as asking for what the value of love is: what do we get out of it? One kind of answer, which has its roots in Aristotle, is that having loving relationships promotes self-knowledge insofar as your beloved acts as a kind of mirror, reflecting your character back to you (Badhwar, 2003, p. 58). Of course, this answer presupposes that we cannot accurately know ourselves in other ways: that left alone, our sense of ourselves will be too imperfect, too biased, to help us grow and mature as persons. The metaphor of a mirror also suggests that our beloveds will be in the relevant respects similar to us, so that merely by observing them, we can come to know ourselves better in a way that is, if not free from bias, at least more objective than otherwise.
Brink (1999, pp. 264–65) argues that there are serious limits to the value of such mirroring of one’s self in a beloved. For if the aim is not just to know yourself better but to improve yourself, you ought also to interact with others who are not just like yourself: interacting with such diverse others can help you recognize alternative possibilities for how to live and so better assess the relative merits of these possibilities. Whiting (2013) also emphasizes the importance of our beloveds’ having an independent voice capable of reflecting not who one now is but an ideal for who one is to be. Nonetheless, we need not take the metaphor of the mirror quite so literally; rather, our beloveds can reflect our selves not through their inherent similarity to us but rather through the interpretations they offer of us, both explicitly and implicitly in their responses to us. This is what Badhwar calls the “epistemic significance” of love. [ 16 ]
In addition to this epistemic significance of love, LaFollette (1996, Chapter 5) offers several other reasons why it is good to love, reasons derived in part from the psychological literature on love: love increases our sense of well-being, it elevates our sense of self-worth, and it serves to develop our character. It also, we might add, tends to lower stress and blood pressure and to increase health and longevity. Friedman (1993) argues that the kind of partiality towards our beloveds that love involves is itself morally valuable because it supports relationships—loving relationships—that contribute “to human well-being, integrity, and fulfillment in life” (p. 61). And Solomon (1988, p. 155) claims:
Ultimately, there is only one reason for love. That one grand reason…is “because we bring out the best in each other.” What counts as “the best,” of course, is subject to much individual variation.
This is because, Solomon suggests, in loving someone, I want myself to be better so as to be worthy of his love for me.
Each of these answers to the question of why we love understands it to be asking about love quite generally, abstracted away from details of particular relationships. It is also possible to understand the question as asking about particular loves. Here, there are several questions that are relevant:
- What, if anything, justifies my loving rather than not loving this particular person?
- What, if anything, justifies my coming to love this particular person rather than someone else?
- What, if anything, justifies my continuing to love this particular person given the changes—both in him and me and in the overall circumstances—that have occurred since I began loving him?
These are importantly different questions. Velleman (1999), for example, thinks we can answer (1) by appealing to the fact that my beloved is a person and so has a rational nature, yet he thinks (2) and (3) have no answers: the best we can do is offer causal explanations for our loving particular people, a position echoed by Han (2021). Setiya (2014) similarly thinks (1) has an answer, but points not to the rational nature of persons but rather to the other’s humanity , where such humanity differs from personhood in that not all humans need have the requisite rational nature for personhood, and not all persons need be humans. And, as will become clear below , the distinction between (2) and (3) will become important in resolving puzzles concerning whether our beloveds are fungible, though it should be clear that (3) potentially raises questions concerning personal identity (which will not be addressed here).
It is important not to misconstrue these justificatory questions. Thomas (1991) , for example, rejects the idea that love can be justified: “there are no rational considerations whereby anyone can lay claim to another’s love or insist that an individual’s love for another is irrational” (p. 474). This is because, Thomas claims (p. 471):
no matter how wonderful and lovely an individual might be, on any and all accounts, it is simply false that a romantically unencumbered person must love that individual on pain of being irrational. Or, there is no irrationality involved in ceasing to love a person whom one once loved immensely, although the person has not changed.
However, as LaFollette (1996, p. 63) correctly points out,
reason is not some external power which dictates how we should behave, but an internal power, integral to who we are.… Reason does not command that we love anyone. Nonetheless, reason is vital in determining whom we love and why we love them.
That is, reasons for love are pro tanto : they are a part of the overall reasons we have for acting, and it is up to us in exercising our capacity for agency to decide what on balance we have reason to do or even whether we shall act contrary to our reasons. To construe the notion of a reason for love as compelling us to love, as Thomas does, is to misconstrue the place such reasons have within our agency. [ 17 ]
Most philosophical discussions of the justification of love focus on question (1) , thinking that answering this question will also, to the extent that we can, answer question (2) , which is typically not distinguished from (3) . The answers given to these questions vary in a way that turns on how the kind of evaluation implicit in love is construed. On the one hand, those who understand the evaluation implicit in love to be a matter of the bestowal of value (such as Telfer 1970–71; Friedman 1993; Singer 1994) typically claim that no justification can be given (cf. Section 4.2 ). As indicated above, this seems problematic, especially given the importance love can have both in our lives and, especially, in shaping our identities as persons. To reject the idea that we can love for reasons may reduce the impact our agency can have in defining who we are.
On the other hand, those who understand the evaluation implicit in love to be a matter of appraisal tend to answer the justificatory question by appeal to these valuable properties of the beloved. This acceptance of the idea that love can be justified leads to two further, related worries about the object of love.
The first worry is raised by Vlastos (1981) in a discussion Plato’s and Aristotle’s accounts of love. Vlastos notes that these accounts focus on the properties of our beloveds: we are to love people, they say, only because and insofar as they are objectifications of the excellences. Consequently, he argues, in doing so they fail to distinguish “ disinterested affection for the person we love” from “ appreciation of the excellences instantiated by that person ” (p. 33). That is, Vlastos thinks that Plato and Aristotle provide an account of love that is really a love of properties rather than a love of persons—love of a type of person, rather than love of a particular person—thereby losing what is distinctive about love as an essentially personal attitude. This worry about Plato and Aristotle might seem to apply just as well to other accounts that justify love in terms of the properties of the person: insofar as we love the person for the sake of her properties, it might seem that what we love is those properties and not the person. Here it is surely insufficient to say, as Solomon (1988, p. 154) does, “if love has its reasons, then it is not the whole person that one loves but certain aspects of that person—though the rest of the person comes along too, of course”: that final tagline fails to address the central difficulty about what the object of love is and so about love as a distinctly personal attitude. (Clausen 2019 might seem to address this worry by arguing that we love people not as having certain properties but rather as having “ organic unities ”: a holistic set of properties the value of each of which must be understood in essential part in terms of its place within that whole. Nonetheless, while this is an interesting and plausible way to think about the value of the properties of persons, that organic unity itself will be a (holistic) property held by the person, and it seems that the fundamental problem reemerges at the level of this holistic property: do we love the holistic unity rather than the person?)
The second worry concerns the fungibility of the object of love. To be fungible is to be replaceable by another relevantly similar object without any loss of value. Thus, money is fungible: I can give you two $5 bills in exchange for a $10 bill, and neither of us has lost anything. Is the object of love fungible? That is, can I simply switch from loving one person to loving another relevantly similar person without any loss? The worry about fungibility is commonly put this way: if we accept that love can be justified by appealing to properties of the beloved, then it may seem that in loving someone for certain reasons, I love him not simply as the individual he is, but as instantiating those properties. And this may imply that any other person instantiating those same properties would do just as well: my beloved would be fungible. Indeed, it may be that another person exhibits the properties that ground my love to a greater degree than my current beloved does, and so it may seem that in such a case I have reason to “trade up”—to switch my love to the new, better person. However, it seems clear that the objects of our loves are not fungible: love seems to involve a deeply personal commitment to a particular person, a commitment that is antithetical to the idea that our beloveds are fungible or to the idea that we ought to be willing to trade up when possible. [ 18 ]
In responding to these worries, Nozick (1989) appeals to the union view of love he endorses (see the section on Love as Union ):
The intention in love is to form a we and to identify with it as an extended self, to identify one’s fortunes in large part with its fortunes. A willingness to trade up, to destroy the very we you largely identify with, would then be a willingness to destroy your self in the form of your own extended self. [p. 78]
So it is because love involves forming a “we” that we must understand other persons and not properties to be the objects of love, and it is because my very identity as a person depends essentially on that “we” that it is not possible to substitute without loss one object of my love for another. However, Badhwar (2003) criticizes Nozick, saying that his response implies that once I love someone, I cannot abandon that love no matter who that person becomes; this, she says, “cannot be understood as love at all rather than addiction” (p. 61). [ 19 ]
Instead, Badhwar (1987) turns to her robust-concern account of love as a concern for the beloved for his sake rather than one’s own. Insofar as my love is disinterested — not a means to antecedent ends of my own—it would be senseless to think that my beloved could be replaced by someone who is able to satisfy my ends equally well or better. Consequently, my beloved is in this way irreplaceable. However, this is only a partial response to the worry about fungibility, as Badhwar herself seems to acknowledge. For the concern over fungibility arises not merely for those cases in which we think of love as justified instrumentally, but also for those cases in which the love is justified by the intrinsic value of the properties of my beloved. Confronted with cases like this, Badhwar (2003) concludes that the object of love is fungible after all (though she insists that it is very unlikely in practice). (Soble (1990, Chapter 13) draws similar conclusions.)
Nonetheless, Badhwar thinks that the object of love is “phenomenologically non-fungible” (2003, p. 63; see also 1987, p. 14). By this she means that we experience our beloveds to be irreplaceable: “loving and delighting in [one person] are not completely commensurate with loving and delighting in another” (1987, p. 14). Love can be such that we sometimes desire to be with this particular person whom we love, not another whom we also love, for our loves are qualitatively different. But why is this? It seems as though the typical reason I now want to spend time with Amy rather than Bob is, for example, that Amy is funny but Bob is not. I love Amy in part for her humor, and I love Bob for other reasons, and these qualitative differences between them is what makes them not fungible. However, this reply does not address the worry about the possibility of trading up: if Bob were to be at least as funny (charming, kind, etc.) as Amy, why shouldn’t I dump her and spend all my time with him?
A somewhat different approach is taken by Whiting (1991). In response to the first worry concerning the object of love, Whiting argues that Vlastos offers a false dichotomy: having affection for someone that is disinterested —for her sake rather than my own—essentially involves an appreciation of her excellences as such. Indeed, Whiting says, my appreciation of these as excellences, and so the underlying commitment I have to their value, just is a disinterested commitment to her because these excellences constitute her identity as the person she is. The person, therefore, really is the object of love. Delaney (1996) takes the complementary tack of distinguishing between the object of one’s love, which of course is the person, and the grounds of the love, which are her properties: to say, as Solomon does, that we love someone for reasons is not at all to say that we only love certain aspects of the person. In these terms, we might say that Whiting’s rejection of Vlastos’ dichotomy can be read as saying that what makes my attitude be one of disinterested affection—one of love—for the person is precisely that I am thereby responding to her excellences as the reasons for that affection. [ 20 ]
Of course, more needs to be said about what it is that makes a particular person be the object of love. Implicit in Whiting’s account is an understanding of the way in which the object of my love is determined in part by the history of interactions I have with her: it is she, and not merely her properties (which might be instantiated in many different people), that I want to be with; it is she, and not merely her properties, on whose behalf I am concerned when she suffers and whom I seek to comfort; etc. This addresses the first worry, but not the second worry about fungibility, for the question still remains whether she is the object of my love only as instantiating certain properties, and so whether or not I have reason to “trade up.”
To respond to the fungibility worry, Whiting and Delaney appeal explicitly to the historical relationship. [ 21 ] Thus, Whiting claims, although there may be a relatively large pool of people who have the kind of excellences of character that would justify my loving them, and so although there can be no answer to question (2) about why I come to love this rather than that person within this pool, once I have come to love this person and so have developed a historical relation with her, this history of concern justifies my continuing to love this person rather than someone else (1991, p. 7). Similarly, Delaney claims that love is grounded in “historical-relational properties” (1996, p. 346), so that I have reasons for continuing to love this person rather than switching allegiances and loving someone else. In each case, the appeal to both such historical relations and the excellences of character of my beloved is intended to provide an answer to question (3) , and this explains why the objects of love are not fungible.
There seems to be something very much right with this response. Relationships grounded in love are essentially personal, and it would be odd to think of what justifies that love to be merely non-relational properties of the beloved. Nonetheless, it is still unclear how the historical-relational propreties can provide any additional justification for subsequent concern beyond that which is already provided (as an answer to question (1) ) by appeal to the excellences of the beloved’s character (cf. Brink 1999). The mere fact that I have loved someone in the past does not seem to justify my continuing to love him in the future. When we imagine that he is going through a rough time and begins to lose the virtues justifying my initial love for him, why shouldn’t I dump him and instead come to love someone new having all of those virtues more fully? Intuitively (unless the change she undergoes makes her in some important sense no longer the same person he was), we think I should not dump him, but the appeal to the mere fact that I loved him in the past is surely not enough. Yet what historical-relational properties could do the trick? (For an interesting attempt at an answer, see Kolodny 2003 and also Howard 2019.)
If we think that love can be justified, then it may seem that the appeal to particular historical facts about a loving relationship to justify that love is inadequate, for such idiosyncratic and subjective properties might explain but cannot justify love. Rather, it may seem, justification in general requires appealing to universal, objective properties. But such properties are ones that others might share, which leads to the problem of fungibility. Consequently it may seem that love cannot be justified. In the face of this predicament, accounts of love that understand love to be an attitude towards value that is intermediate between appraisal and bestowal, between recognizing already existing value and creating that value (see Section 4.3 ) might seem to offer a way out. For once we reject the thought that the value of our beloveds must be either the precondition or the consequence of our love, we have room to acknowledge that the deeply personal, historically grounded, creative nature of love (central to bestowal accounts) and the understanding of love as responsive to valuable properties of the beloved that can justify that love (central to appraisal accounts) are not mutually exclusive (Helm 2010; Bagley 2015).
- Annas, J., 1977, “Plato and Aristotle on Friendship and Altruism”, Mind , 86: 532–54.
- Badhwar, N. K., 1987, “Friends as Ends in Themselves”, Philosophy & Phenomenological Research , 48: 1–23.
- –––, 2003, “Love”, in H. LaFollette (ed.), Practical Ethics , Oxford: Oxford University Press, 42–69.
- Badhwar, N. K. (ed.), 1993, Friendship: A Philosophical Reader , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- Bagley, B., 2015, “Loving Someone in Particular”, Ethics , 125: 477–507.
- –––, 2018. “(The Varieties of) Love in Contemporary Anglophone Philosophy”, in Adrienne M. Martin (ed.), The Routledge Handbook of Love in Philosophy , New York, NY: Routledge, 453–64.
- Baier, A. C., 1991, “Unsafe Loves”, in Solomon & Higgins (1991), 433–50.
- Blum, L. A., 1980, Friendship, Altruism, and Morality , London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- –––, 1993, “Friendship as a Moral Phenomenon”, in Badhwar (1993), 192–210.
- Bransen, J., 2006, “Selfless Self-Love”, Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 9: 3–25.
- Bratman, M. E., 1999, “Shared Intention”, in Faces of Intention: Selected Essays on Intention and Agency , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 109–29.
- Brentlinger, J., 1970/1989, “The Nature of Love”, in Soble (1989a), 136–48.
- Brink, D. O., 1999, “Eudaimonism, Love and Friendship, and Political Community”, Social Philosophy & Policy , 16: 252–289.
- Brown, R., 1987, Analyzing Love , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Clausen, G., 2019, “Love of Whole Persons”, The Journal of Ethics , 23 (4): 347–67.
- Cocking, D. & Kennett, J., 1998, “Friendship and the Self”, Ethics , 108: 502–27.
- Cooper, J. M., 1977, “Aristotle on the Forms of Friendship”, Review of Metaphysics , 30: 619–48.
- Delaney, N., 1996, “Romantic Love and Loving Commitment: Articulating a Modern Ideal”, American Philosophical Quarterly , 33: 375–405.
- Ebels-Duggan, K., 2008, “Against Beneficence: A Normative Account of Love”, Ethics , 119: 142–70.
- Fisher, M., 1990, Personal Love , London: Duckworth.
- Frankfurt, H., 1999, “Autonomy, Necessity, and Love”, in Necessity, Volition, and Love , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 129–41.
- Friedman, M. A., 1993, What Are Friends For? Feminist Perspectives on Personal Relationships and Moral Theory , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press.
- –––, 1998, “Romantic Love and Personal Autonomy”, Midwest Studies in Philosophy , 22: 162–81.
- Gilbert, M., 1989, On Social Facts , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- –––, 1996, Living Together: Rationality, Sociality, and Obligation , Rowman & Littlefield.
- –––, 2000, Sociality and Responsibility: New Essays in Plural Subject Theory , Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
- Grau, C. & Smuts, A., 2017, Oxford Handbook of the Philosophy of Love , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Hamlyn, D. W., 1989, “The Phenomena of Love and Hate”, in Soble (1989a), 218–234.
- Han, Y., 2021, “Do We Love for Reasons?”, Philosophy & Phenomenological Research , 102: 106–126.
- Hegel, G. W. F., 1997, “A Fragment on Love”, in Solomon & Higgins (1991), 117–20.
- Helm, B. W., 2008, “Plural Agents”, Noûs , 42: 17–49.
- –––, 2009, “Love, Identification, and the Emotions”, American Philosophical Quarterly , 46: 39–59.
- –––, 2010, Love, Friendship, and the Self: Intimacy, Identification, and the Social Nature of Persons , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Howard, C., 2019, “Fitting Love and Reasons for Loving” in M. Timmons (ed.), Oxford Studies in Normative Ethics (Volume 9). doi:10.1093/oso/9780198846253.001.0001
- Jaworska, A. & Wonderly, M., 2017, “Love and Caring”, in C. Grau & A. Smuts (2020). doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199395729.013.15
- Jollimore, T, 2011, Love’s Vision , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Kolodny, N., 2003, “Love as Valuing a Relationship”, The Philosophical Review , 112: 135–89.
- Kraut, Robert, 1986 “Love De Re ”, Midwest Studies in Philosophy , 10: 413–30.
- LaFollette, H., 1996, Personal Relationships: Love, Identity, and Morality , Cambridge, MA: Blackwell Press.
- Lamb, R. E., (ed.), 1997, Love Analyzed , Westview Press.
- Liddell, H. G., Scott, R., Jones, H. S., & McKenzie, R., 1940, A Greek-English Lexicon , Oxford: Clarendon Press, 9th edition.
- Martin, A., 2015, “Love, Incorporated”, Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 18: 691–702.
- Montaigne, M., [E], Essays , in The Complete Essays of Montaigne , Donald Frame (trans.), Stanford: Stanford University Press, 1958.
- Naar, H., 2013, “A Dispositional Theory of Love”, Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 94(3): 342–357.
- Newton-Smith, W., 1989, “A Conceptual Investigation of Love”, in Soble (1989a), 199–217.
- Nozick, R., 1989, “Love’s Bond”, in The Examined Life: Philosophical Meditations , New York: Simon & Schuster, 68–86.
- Nussbaum, M., 1990, “Love and the Individual: Romantic Rightness and Platonic Aspiration”, in Love’s Knowledge: Essays on Philosophy and Literature , Oxford: Oxford University Press, 314–34.
- Nygren, A., 1953a, Agape and Eros , Philadelphia, PA: Westminster Press.
- –––, 1953b, “ Agape and Eros ”, in Soble (1989a), 85–95.
- Ortiz-Millán, G., 2007, “Love and Rationality: On Some Possible Rational Effects of Love”, Kriterion , 48: 127–44.
- Pismenny, A. & Prinz, J., 2017, “Is Love an Emotion?”, in C. Grau & A. Smuts (2017). doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199395729.013.10
- Price, A. W., 1989, Love and Friendship in Plato and Arisotle , New York: Clarendon Press.
- Rorty, A. O., 1980, “Introduction”, in A. O. Rorty (ed.), Explaining Emotions , Berkeley: University of California Press, 1–8.
- –––, 1986/1993, “The Historicity of Psychological Attitudes: Love is Not Love Which Alters Not When It Alteration Finds”, in Badhwar (1993), 73–88.
- Scruton, R., 1986, Sexual Desire: A Moral Philosophy of the Erotic , New York: Free Press.
- Searle, J. R., 1990, “Collective Intentions and Actions”, in P. R. Cohen, M. E. Pollack, & J. L. Morgan (eds.), Intentions in Communication , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 401–15.
- Setiya, K., 2014, “Love and the Value of a Life”, Philosophical Review , 123: 251–80.
- Sherman, N., 1993, “Aristotle on the Shared Life”, in Badhwar (1993), 91–107.
- Singer, I., 1984a, The Nature of Love, Volume 1: Plato to Luther , Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2nd edition.
- –––, 1984b, The Nature of Love, Volume 2: Courtly and Romantic , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- –––, 1989, The Nature of Love, Volume 3: The Modern World , Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2nd edn.
- –––, 1991, “From The Nature of Love ”, in Solomon & Higgins (1991), 259–78.
- –––, 1994, The Pursuit of Love , Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press.
- –––, 2009, Philosophy of Love: A Partial Summing-up , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Soble, A. (ed.), 1989a, Eros, Agape, and Philia: Readings in the Philosophy of Love , New York, NY: Paragon House.
- –––, 1989b, “An Introduction to the Philosophy of Love”, in Soble (1989a), xi-xxv.
- –––, 1990, The Structure of Love , New Haven: Yale University Press.
- –––, 1997, “Union, Autonomy, and Concern”, in Lamb (1997), 65–92.
- Solomon, R. C., 1976, The Passions , New York: Anchor Press.
- –––, 1981, Love: Emotion, Myth, and Metaphor , New York: Anchor Press.
- –––, 1988, About Love: Reinventing Romance for Our Times , New York: Simon & Schuster.
- Solomon, R. C. & Higgins, K. M. (eds.), 1991, The Philosophy of (Erotic) Love , Lawrence: Kansas University Press.
- Stump, E., 2006, “Love by All Accounts”, Presidential Address to the Central APA, Proceedings and Addresses of the American Philosophical Association , 80: 25–43.
- Taylor, G., 1976, “Love”, Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , 76: 147–64.
- Telfer, E., 1970–71, “Friendship”, Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , 71: 223–41.
- Thomas, L., 1987, “Friendship”, Synthese , 72: 217–36.
- –––, 1989, “Friends and Lovers”, in G. Graham & H. La Follette (eds.), Person to Person , Philadelphia, PA: Temple University Press, 182–98.
- –––, 1991, “Reasons for Loving”, in Solomon & Higgins (1991), 467–476.
- –––, 1993, “Friendship and Other Loves”, in Badhwar (1993), 48–64.
- Tuomela, R., 1984, A Theory of Social Action , Dordrecht: Reidel.
- –––, 1995, The Importance of Us: A Philosophical Study of Basic Social Notions , Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Velleman, J. D., 1999, “Love as a Moral Emotion”, Ethics , 109: 338–74.
- –––, 2008, “Beyond Price”, Ethics , 118: 191–212.
- Vlastos, G., 1981, “The Individual as Object of Love in Plato”, in Platonic Studies , 2nd edition, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 3–42.
- White, R. J., 2001, Love’s Philosophy , Rowman & Littlefield.
- Whiting, J. E., 1991, “Impersonal Friends”, Monist , 74: 3–29.
- –––, 2013, “Love: Self-Propagation, Self-Preservation, or Ekstasis?”, Canadian Journal of Philosophy , 43: 403–29.
- Willigenburg, T. Van, 2005, “Reason and Love: A Non-Reductive Analysis of the Normativity of Agent-Relative Reasons”, Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 8: 45–62.
- Wollheim, R., 1984, The Thread of Life , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Wonderly, M., 2016, “On Being Attached”, Philosophical Studies , 173: 223–42.
- –––, 2017, “Love and Attachment”, American Philosophical Quarterly , 54: 235–50.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- Aristotle , Nicomachean Ethics , translated by W.D. Ross.
- Moseley, A., “ Philosophy of Love ,” in J. Fieser (ed.), Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy
character, moral | emotion | friendship | impartiality | obligations: special | personal identity | Plato: ethics | Plato: rhetoric and poetry | respect | value: intrinsic vs. extrinsic
Copyright © 2021 by Bennett Helm < bennett . helm @ fandm . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2024 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

The Oxford Handbook of the Philosophy of Love
Christopher Grau is Associate Professor Emeritus of Philosophy at Clemson University. He specializes in ethics, topics in metaphysics, and philosophical work on film. He has published articles in a variety of journals including the Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , the Journal of Moral Philosophy , Midwest Studies in Philosophy , Philosophical Topics , The Review of Philosophy and Psychology , and The Southern Journal of Philosophy . He is also the editor of three books. The most recent, Understanding Love: Philosophy, Film, and Fiction , is co-edited with Susan Wolf and published by Oxford University Press.
Aaron Smuts was an Associate Professor of Philosophy at Rhode Island College. His interests ranged across a wide variety of topics in theoretical ethics. Aaron published over three dozen articles in a variety of books and academic journals, including: American Philosophical Quarterly , the Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , Midwest Studies in Philosophy, Pacific Philosophic Quarterly, Philosophical Studies , and the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy . His book Welfare, Meaning, and Worth (Routledge) was published in 2020.
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Love offers a wide array of original essays on the nature and value of love. The editors, Christopher Grau and Aaron Smuts, have assembled an esteemed group of thinkers, including both established scholars and younger voices. The volume contains thirty-three essays addressing both issues about love as well as key philosophers who have contributed to the philosophy of love, such as Plato, Kierkegaard, Schopenhauer, and Murdoch. The topics range from central issues about the nature and variety of love, the possibility of its rational justification, and whether it is an emotion, to the significance of love for law, economics, morality, and free will. The volume also contains an introduction to the subject as well as essays on love's relation to jealousy, religion, knowledge, biotechnology, and several other topics. This wide-ranging handbook will be a key resource for specialists working on the philosophy of love, and a helpful guide for those looking to learn more about the area.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

New Philosophical Essays on Love and Loving
- © 2021
- Simon Cushing 0
University of Michigan–Flint, Flint, USA
You can also search for this editor in PubMed Google Scholar
New philosophical essays on love by a diverse group of international scholars
Includes contributions to the ongoing debate on whether love is arational or if there are reasons for love
Also whether love can explain the difference between nationalism and patriotism
5351 Accesses
3 Citations
1 Altmetric
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (14 chapters)
Front matter, introduction.
Simon Cushing
Making Room for Love in Kantian Ethics
- Ernesto V. Garcia
Iris Murdoch and the Epistemic Significance of Love
- Cathy Mason
‘Love’ as a Practice: Looking at Real People
- Lotte Spreeuwenberg
Love, Choice, and Taking Responsibility
- Christopher Cowley
Not All’s Fair in Love and War: Toward Just Love Theory
- Andrew Sneddon
Doubting Love
- Larry A. Herzberg
Love and Free Agency
- Ishtiyaque Haji
Sentimental Reasons
- Edgar Phillips
Wouldn’t It Be Nice: Enticing Reasons for Love
- N. L. Engel-Hawbecker
Love, Motivation, and Reasons: The Case of the Drowning Wife
- Monica Roland
Can Our Beloved Pets Love Us Back?
- Ryan Stringer
Romantic Love Between Humans and AIs: A Feminist Ethical Critique
- Andrea Klonschinski, Michael Kühler
Patriotism and Nationalism as Two Distinct Ways of Loving One’s Country
- Maria Ioannou, Martijn Boot, Ryan Wittingslow, Adriana Mattos
Back Matter
- Rationality
- Artificial Intelligence
- Iris Murdoch
- Non-Human Animals
About this book
Editors and affiliations, about the editor, bibliographic information.
Book Title : New Philosophical Essays on Love and Loving
Editors : Simon Cushing
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72324-8
Publisher : Palgrave Macmillan Cham
eBook Packages : Religion and Philosophy , Philosophy and Religion (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021
Hardcover ISBN : 978-3-030-72323-1 Published: 21 September 2021
Softcover ISBN : 978-3-030-72326-2 Published: 22 September 2022
eBook ISBN : 978-3-030-72324-8 Published: 20 September 2021
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XII, 322
Topics : Philosophy of Mind , Ethics , Social Philosophy , Emotion
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Essays About Love and Relationships: Top 5 Examples
Love, romance, and relationships are just as complicated and messy as they are fascinating. Read our guide on essays about love and relationships.
We, as humans, are social beings. Humanity is inclined towards living with others of our kind and forming relationships with them. Love, whether in a romantic context or otherwise, is essential to a strong relationship with someone. It can be used to describe familial, friendly, or romantic relationships; however, it most commonly refers to romantic partners.
Love and relationships are difficult to understand, but with effort, devotion, and good intentions, they can blossom into something beautiful that will stay with you for life. This is why it is important to be able to discern wisely when choosing a potential partner.
5 Essay Examples
1. love and marriage by kannamma shanmugasundaram, 2. what my short-term relationships taught me about love and life by aaron zhu, 3. true love waits by christine barrett, 4. choosing the right relationship by robert solley, 5. masters of love by emily esfahani smith, 1. what is a healthy romantic relationship, 2. a favorite love story, 3. relationship experiences, 4. lessons relationships can teach you, 5. love and relationships in the 21st century, 6. is marriage necessary for true love.
“In successful love marriages, couples have to learn to look past these imperfections and remember the reasons why they married each other in the first place. They must be able to accept the fact that neither one of them is perfect. Successful love marriages need to set aside these superior, seemingly impossible expectations and be willing to compromise, settling for some good and some bad.”
Shanmugasundaram’s essay looks at marriage in Eastern Cultures, such as her Indian traditions, in which women have less freedom and are often forced into arranged marriages. Shanmugasundaram discusses her differing views with her parents over marriage; they prefer to stick to tradition while she, influenced by Western values, wants to choose for herself. Ultimately, she has compromised with her parents: they will have a say in who she marries, but it will be up to her to make the final decision. She will only marry who she loves.
“There is no forever, I’ve been promised forever by so many exes that it’s as meaningless to me as a homeless person promising me a pot of gold. From here on out, I’m no longer looking for promises of forever, what I want is the promise that you’ll try your best and you’ll be worth it. Don’t promise me forever, promise me that there will be no regrets.”
In Zhu’s essay, he reflects on his lessons regarding love and relationships. His experiences with past partners have taught him many things, including self-worth and the inability to change others. Most interestingly, however, he believes that “forever” does not exist and that going into a relationship, they should commit to as long as possible, not “forever.” Furthermore, they should commit to making the relationship worthwhile without regret.
“For life is a constant change, love is the greatest surprise, friendship is your best defense, maturity comes with responsibility and death is just around the corner, so, expect little, assume nothing, learn from your mistakes, never fail to have faith that true love waits, take care of your friends, treasure your family, moderate your pride and throw up all hatred for God opens millions of flowers without forcing the buds, reminding us not to force our way but to wait for true love to happen perfectly in His time.”
Barrett writes about how teenagers often feel the need to be in a relationship or feel “love” as soon as possible. But unfortunately, our brains are not fully matured in our teenage years, so we are more likely to make mistakes. Barrett discourages teenagers from dating so early; she believes that they should let life take its course and enjoy life at the moment. Her message is that they shouldn’t be in a rush to grow up, for true love will come to those who are patient. You might also be interested in these essays about commitment and essays about girlfriends .
“A paucity of common interests gets blamed when relationships go south, but they are rarely the central problem. Nonetheless, it is good to have some — mostly in terms of having enough in common that there are things that you enjoy spending time doing together. The more important domains to consider are personality and values, and when it comes to personality, the key question is how does your potential partner handle stress.”
Solley, from a more psychological perspective, gives tips on how one can choose the ideal person to be in a relationship with. Love is a lifetime commitment, so much thought should be put into it. One should look at culture, values regarding spending money, and common interests. Solley believes that you should not always look for someone with the same interests, for what makes a relationship interesting is the partners’ differences and how they look past them.
“There are two ways to think about kindness. You can think about it as a fixed trait: Either you have it or you don’t. Or you could think of kindness as a muscle. In some people, that muscle is naturally stronger than in others, but it can grow stronger in everyone with exercise. Masters tend to think about kindness as a muscle. They know that they have to exercise it to keep it in shape. They know, in other words, that a good relationship requires sustained hard work.”
Smith discusses research conducted over many years that explains the different aspects of a relationship, including intimacy, emotional strength, and kindness. She discusses kindness in-depth, saying that a relationship can test your kindness, but you must be willing to work to be kind if you love your partner. You might also be interested in these essays about divorce .
6 Writing Prompts On Essays About Love and Relationships

Everyone has a different idea of what makes a great relationship. For example, some prioritize assertiveness in their partner, while others prefer a calmer demeanor. You can write about different qualities and habits that a healthy, respectful relationship needs, such as quality time and patience. If you have personal experience, reflect on this as well; however, if you don’t, write about what you would hope from your future partner.
Love and relationships have been an essential element in almost every literary work, movie, and television show; an example of each would be Romeo and Juliet , The Fault in Our Stars , and Grey’s Anatomy . Even seemingly unrelated movies, such as the Star Wars and Lord of the Rings franchises, have a romantic component. Describe a love story of your choice; explain its plot, characters, and, most importantly, how the theme of love and relationships is present.
If you have been in a romantic relationship before, or if you are in one currently, reflect on your experience. Why did you pursue this relationship? Explore your relationship’s positive and negative sides and, if applicable, how it ended. If not, write about how you will try and prevent the relationship from ending.
All our experiences in life form us, relationships included. In your essay, reflect on ways romantic relationships can teach you new things and make you better; consider values such as self-worth, patience, and positivity. Then, as with the other prompts, use your personal experiences for a more interesting essay. Hou might find our guide on how to write a vow helpful.
How love, romance, and relationships are perceived has changed dramatically in recent years; from the nuclear family, we have seen greater acceptance of same-sex relationships, blended families, and relationships with more than two partners—research on how the notion of romantic relationships has changed and discuss this in your essay.

More and more people in relationships are deciding not to get married. For a strong argumentative essay, discuss whether you agree with the idea that true love does not require marriage, so it is fine not to get married in the first place. Research the arguments of both sides, then make your claim.
Check out our guide packed full of transition words for essays . If you’re still stuck, check out our general resource of essay writing topics .

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
Before You Write a Love Essay, Read This to Get Examples
The day will come when you can’t escape the fate of all students: You will have to write a what is love essay.
No worries:
Here you’ll find tons of love essay topics and examples. No time to read everything? Scroll down to get a free PDF with original samples.
Definition: Essay on Love
First, let’s define what is love essay?
The most common topics are:
- Definition of love
- What is love?
- Meaning of love
Why limit yourself to these hackneyed, general themes? Below, I’ll show how to make your paper on love original yet relevant to the prompt you get from teachers.
Love Essay Topics: 20 Ideas to Choose for Your Paper
Your essay on love and relationship doesn’t have to be super official and unemotional. It’s ok to share reflections and personal opinions when writing about romance.
Often, students get a general task to write an essay on love. It means they can choose a theme and a title for their paper. If that’s your case, feel free to try any of these love essay topics:
- Exploring the impact of love on individuals and relationships.
- Love in the digital age: Navigating romance in a tech world.
- Is there any essence and significance in unconditional love?
- Love as a universal language: Connecting hearts across cultures.
- Biochemistry of love: Exploring the process.
- Love vs. passion vs. obsession.
- How love helps cope with heartbreak and grief.
- The art of loving. How we breed intimacy and trust.
- The science behind attraction and attachment.
- How love and relationships shape our identity and help with self-discovery.
- Love and vulnerability: How to embrace emotional openness.
- Romance is more complex than most think: Passion, intimacy, and commitment explained.
- Love as empathy: Building sympathetic connections in a cruel world.
- Evolution of love. How people described it throughout history.
- The role of love in mental and emotional well-being.
- Love as a tool to look and find purpose in life.
- Welcoming diversity in relations through love and acceptance.
- Love vs. friendship: The intersection of platonic and romantic bonds.
- The choices we make and challenges we overcome for those we love.
- Love and forgiveness: How its power heals wounds and strengthens bonds.
Love Essay Examples: Choose Your Sample for Inspiration
Essays about love are usually standard, 5-paragraph papers students write in college:
- One paragraph is for an introduction, with a hook and a thesis statement
- Three are for a body, with arguments or descriptions
- One last passage is for a conclusion, with a thesis restatement and final thoughts
Below are the ready-made samples to consider. They’ll help you see what an essay about love with an introduction, body, and conclusion looks like.
What is love essay: 250 words
Lao Tzu once said, “Being deeply loved by someone gives you strength while loving someone deeply gives you courage.” Indeed, love can transform individuals, relationships, and our world.
A word of immense depth and countless interpretations, love has always fascinated philosophers, poets, and ordinary individuals. This emotion breaks boundaries and has a super power to change lives. But what is love, actually?
It’s a force we feel in countless ways. It is the warm embrace of a parent, filled with care and unwavering support. It is the gentle touch of a lover, sparking a flame that ignites passion and desire. Love is the kind words of a friend, offering solace and understanding in times of need. It is the selfless acts of compassion and empathy that bind humanity together.
Love is not confined to romantic relationships alone. It is found in the family bonds, the connections we forge with friends, and even the compassion we extend to strangers. Love is a thread that weaves through the fabric of our lives, enriching and nourishing our souls.
However, love is not without its complexities. It can be both euphoric and agonizing, uplifting and devastating. Love requires vulnerability, trust, and the willingness to embrace joy and pain. It is a delicate balance between passion and compassion, independence and interdependence.
Finally, the essence of love may be elusive to define with mere words. It is an experience that surpasses language and logic, encompassing a spectrum of emotions and actions. Love is a profound connection that unites us all, reminding us of our shared humanity and the capacity for boundless compassion.
What is love essay: 500 words

A 500-word essay on why I love you
Trying to encapsulate why I love you in a mere 500 words is impossible. My love for you goes beyond the confines of language, transcending words and dwelling in the realm of emotions, connections, and shared experiences. Nevertheless, I shall endeavor to express the depth and breadth of my affection for you.
First and foremost, I love you for who you are. You possess a unique blend of qualities and characteristics that captivate my heart and mind. Your kindness and compassion touch the lives of those around you, and I am grateful to be the recipient of your unwavering care and understanding. Your intelligence and wit constantly challenge me to grow and learn, stimulating my mind and enriching our conversations. You have a beautiful spirit that radiates warmth and joy, and I am drawn to your vibrant energy.
I love the way you make me feel. When I am with you, I feel a sense of comfort and security that allows me to be my true self. Your presence envelops me in a cocoon of love and acceptance, where I can express my thoughts, fears, and dreams without fear of judgment. Your support and encouragement inspire me to pursue my passions and overcome obstacles. With you by my side, I feel empowered to face the world, knowing I have a partner who believes in me.
I love the memories we have created together. From the laughter-filled moments of shared adventures to the quiet and intimate conversations, every memory is etched in my heart. Whether exploring new places, indulging in our favorite activities, or simply enjoying each other’s company in comfortable silence, each experience reinforces our bond. Our shared memories serve as a foundation for our relationship, a testament to the depth of our connection and the love that binds us.
I love your quirks and imperfections. Your true essence shines through these unique aspects! Your little traits make me smile and remind me of the beautiful individual you are. I love how you wrinkle your nose when you laugh, become lost in thought when reading a book, and even sing off-key in the shower. These imperfections make you human, relatable, and utterly lovable.
I love the future we envision together. We support each other’s goals, cheering one another on as we navigate the path toward our dreams. The thought of building a life together, creating a home filled with love and shared experiences, fills my heart with anticipation and excitement. The future we imagine is one that I am eager to explore with you by my side.
In conclusion, the reasons why I love you are as vast and varied as the universe itself. It is a love that defies logic and surpasses the limitations of language. From the depths of my being, I love you for the person you are, the way you make me feel, the memories we cherish, your quirks and imperfections, and the future we envision together. My love for you is boundless, unconditional, and everlasting.
A 5-paragraph essay about love

I’ve gathered all the samples (and a few bonus ones) in one PDF. It’s free to download. So, you can keep it at hand when the time comes to write a love essay.

Ready to Write Your Essay About Love?
Now that you know the definition of a love essay and have many topic ideas, it’s time to write your A-worthy paper! Here go the steps:
- Check all the examples of what is love essay from this post.
- Choose the topic and angle that fits your prompt best.
- Write your original and inspiring story.
Any questions left? Our writers are all ears. Please don’t hesitate to ask!
- Essay samples
- Essay writing
- Writing tips
Recent Posts
- Writing the “Why Should Abortion Be Made Legal” Essay: Sample and Tips
- 3 Examples of Enduring Issue Essays to Write Yours Like a Pro
- Writing Essay on Friendship: 3 Samples to Get Inspired
- How to Structure a Leadership Essay (Samples to Consider)
- What Is Nursing Essay, and How to Write It Like a Pro
University of Notre Dame
Notre Dame Philosophical Reviews
- Home ›
- Reviews ›
Thinking about Love: Essays in Contemporary Continental Philosophy

Diane Enns and Antonio Calcagno (eds.), Thinking about Love: Essays in Contemporary Continental Philosophy, Pennsylvania State University Press, 2015, 262pp., $84.95 (hbk), ISBN 9780271070964.
Reviewed by Helen A. Fielding, The University of Western Ontario
This collection addresses a lacuna in contemporary continental philosophy: thinking about love. As the editors explain, Western philosophers tend to avoid addressing love since it is associated more closely with the body and emotion, instead attending to what is deemed to be the business of philosophy, delimiting reason. The matter of love has been left to poets and musicians. But as they further point out, "love is not beyond thinking." Love both motivates and transforms us, and is thus part of the human condition (1). While a few philosophers in the Anglo-American philosophical tradition have explicitly addressed love, within the continental tradition, philosophical meditation on love has generally been linked to theology. This means there is a need for attention from continental philosophers on this theme since they raise different kinds of questions concerning love, questions about subjectivity, identity and the ways we relate to one another. As such, this collection provides a much-needed intervention on the intertwinings of thinking and love. To this end, the book is thematically organized: divided into five parts it addresses the limits of love, love's intersection with the divine, with politics and with phenomenological experience as well as the stories love allows us to tell.
In the first section, "Human Vulnerability and the Limits of Love," three philosophers explore what defines love as love, and their conclusions vary widely, provoking the question of whether it's even possible to find agreement about what constitutes love. Perhaps it is precisely the varied possibilities for defining love's limits -- possibilities that cannot be discovered through reason -- that make it so difficult to thematize and yet provide the other side to reason that makes it human. For Todd May, the limit of love is our mortality. That we will die is what guarantees its intensity. Exploring the ways in which love has been taken up in the analytic tradition, he concludes that the one common element is that romantic love entails an intensity of engagement (23). Because romantic love between two people "occurs not only for but also with the other," it requires that the relationship be between equals who also "consider each other to be equals" (24). In his reading of the film Ground Hog Day (1993), where one day is repeated over and over again, he further concludes that a relationship between equals not governed by the limit of death would lose its intensity, and similarly, watching our lover age reminds us of the limit of the time we will be together, of its ephemerality.
Diane Enns' lyrical essay, "Love's Limit", takes a completely different turn. Countering the liberal perspective that champions love between equal and sovereign selves who enjoy a love that endures and "is not supposed to fail" (33), she defends love between imperfect individuals, where there is jealously, obsessiveness, and abandonment of the self. It is love that is more often referred to as "masochism, repetition compulsion, fantasy, an unhealthy attachment" (34). In dialogue with Beauvoir she suggests we consider the limit of love from the "perspective of the loving self". This shift in focus from autonomy to vulnerability entails openness and risk: "For there is no love without abandoning one's position and 'crossing' over an abyss like an acrobat" (36-37). To love imperfectly is human, and "failed relationships do not necessitate failed love" (41). Thus to love is to open ourselves to the other's vulnerabilities and weaknesses, to open our selves to being transformed by love. Accordingly, the limit of love for Enns is when the lover's "capacity for love is harmed." For "lovers cannot endure all things." What must be preserved are the conditions of love that allow for a spacing and "movement of love between two" (43). It is the question of whether it's even possible to love in our contemporary world that John Caruana explores. Drawing on the work of Julia Kristeva, he explores the symbolic and semiotic aspects of love, arguing that contemporary phenomena of self-harm ranging from cutting to the ISIS terrorist "prepared to maim and kill innocents" point towards "an unparalleled crisis in subjectivity, an inability to love" (47). What are required are narratives and images to support psychic renewal, and the ability to believe again in the world, "a secular symbolic discourse that would promote flourishing subjects" (59).
The four essays in part two, "Love, Desire, and the Divine," focus on love as transcendence. In this section, we see consistency amongst the authors who all seem to conclude in some way that transcendence can be found in the particularity of love, in its erotic articulations rather than the universality of love as general and passionless. Christina M. Gschwandtner turns critically to the work of contemporary continental philosophers of religion who are inspired by theological affirmations of Christ's "kenotic" love, which she describes as one of devotion and self-sacrifice. It is the exclusivity of kenotic love that is problematic for Gschwandtner, in that applied to our everyday lives it can provide justification for the kind of self-sacrificing love often demanded of women, or that provides justifications for all kinds of abuse (75). Kenotic love does have place in philosophy, but only as a religious phenomenon rather than a "general phenomenological account of all loving relations". Mélanie Walton, drawing on Lyotard, privileges eros over caritas or charity. The problem with caritas , the Christian narrative of love, is that it ultimately produces a closed system, "a universal, circular, and conditional logic" with a "meaning that has been given in advance," and that "necessitates one's free commitment". As a universal love it does not recognize the particularities of love: "the subject marching under this banner does not actually have the freedom to choose and enact love toward another subject." (103) Erotic desire on the other hand, because it is unpredictable, provides for an open system from which change, and justice can be effected.
Felix Ó Murchadha also comes out on the side of erotic love, arguing against the duality of self that separates the responsible self from passion in the philosophical tradition. Ó Murchadha observes that though there is always the danger of losing oneself in love, ultimately we become fully ourselves only through being in love; thus privileging the autonomous thinking subject is to forget that the self emerges from "the between space of being in love" (96). While Ó Murchadha, focusing on the emergence of the self, concludes that "to be a person is to be in love," Antonio Calcagno turns his attention to the way that desire motivates the mind in its engagement with the world (90). Focusing critically on the work of Hannah Arendt, Calcagno argues her account of the life of the mind requires a "more robust understanding of desire." As he points out, the object of desire, which lies outside the self, is precisely that which moves us to "to desire to think, judge, and will" (114). Indeed, thinking, judging and willing as described by Arendt entail a "kind of passivity or receptivity," which opens the mind to that which is other than the self. The mind's activity is accordingly "solicited by desire" for that which lies beyond the self, and this desire needs to be taken into account in our theorizing about the life of the mind.
While the thematic arrangement of the essays does work, any such arrangement sets up particular conversations. The two essays on love and politics, for example, consider how change can emerge when love is considered as a social phenomenon. Sophie Bourgault considers the role of love in politics by turning to the seemingly disparate perspectives of Arendt and Simone Weil. There is no place for love and compassion in politics according to Arendt, while for Weil, compassion is precisely what is called for. For Arendt, politics is characterized by speech and action, but Weil's concern is that those who are most disadvantaged have no voice. But as Bourgault points out, the two thinkers do come together in their agreement that what is needed in our modern world is "more thoughtfulness and (empathetic) attention" (165). Rethought as attention, love has a place in the social and political world. This is not insignificant, as Christian Lotz reminds us. For, within the context of recent left political philosophy developed by thinkers such as Hardt, Negri, and Badiou, love seems to be granted a metaphysical status. Lotz reminds us, however, of the Marxist critique of essentialist conceptions of love which "tend to overlook the material, historical, and social form that love takes on in real individuals" shaped by class (131). Also connecting the particular to the general, Lotz points out that "What we can see, feel hear is not sensual in an abstract sense; rather, it is the result of concrete historical forms of how we are related to one another, and of how the sensual world is itself reproduced through labor" (133). In other words, love allows us to engage in particular and concrete relations in a world that is shaped through material relations. Lotz concludes that rather than thinking about love "in terms of a truth procedure (Badiou) or an ontological event (Negri)," it is the social aspect of love, and the ways in which it is produced to which we should turn our attention (147).
Dorothea Olkowski, whose essay completes the fourth part on the phenomenological experience of love, is also concerned with forms of love, in particular in light of recent neurophysiological explanations of love that cannot account for intentionality. In working through her ontology of love, she draws on Merleau-Ponty, in particular his early work "on the interplay of the organism and the phenomenal field" (202). Like Lotz, Olkowski thinks through sensory perception drawing on form. In this case the "sensory value of each element is determined by its function in the whole and varies with it. Every action undertaken modifies the field where it occurs and establishes lines of force within which action unfolds and alters the phenomenal field" (207). This means that sensory input alone is not sufficient for explaining why we respond in certain ways. Instead, what is needed is an account of intentionality, of consciousness of certain objects and the ways we take them up, consciousness of the actions we take, of the words we speak, and the ways in which these "consciously constitute the intention(s) in which they are involved" (207). Consciousness and the world are intertwined. Relations are motivated and not causal in one direction, and "there is a 'network of significative intentions,' more or less clear, lived rather than known" (208). So desire cannot be mere instinct or drive. Instincts are part of an entire organism or structure, which means that they cannot be separated out from perception, intelligence and emotions. Physical events do not equate with situations, which are the lived interpretation of what takes place.
Also drawing on Merleau-Ponty and our intertwinement with the world, Fiona Utley explores the ways in which the loving bonds we create in the world not only anchor us there but also provide us with "another self who shares and knows the intimate structures of our world" (169). This means for Utley that to love we must trust. Thus, the trust that sustains this love must be central to human existence. Utley picks up here on a theme others in this volume have explored, namely that loving makes us vulnerable. It opens us to the risk of heartbreak, of "violence, cruelty and death" (175). Marguerite La Caze explores this close relation between love and hate through the work of Beauvoir. Supporting Utley's findings, she concludes that love allows for both reciprocal and ambiguous relations that belong to being human. Hate, however, is not relational as such. It stresses the "material, object status of the hated offender."
The final two essays are thematized as love stories. Dawne McCance writes eloquently about Derrida as a philosopher who did not practice "philosophical detachment" when he wrote about love. Coming back to the opening theme that any binary of reason and emotion is doomed from the start, she explains how Derrida's "deconstruction is not only about acknowledging difference", but "is also about being open to being altered in one's encounter" with it (222). It is about changing how we think as well as what we think about. Alphonso Lingis puts this into practice, dwelling on practices of loving and living that shape the ways we think about ourselves and our relations to nature.
This collection opens up an overdue discussion of the intersections of love and thinking within the continental tradition. Some of the observations were ones I anticipated; others were surprising. My only real criticism is that there is no mention of the work of Luce Irigaray, a contemporary continental philosopher for whom love is at the center of her work. Nonetheless, it is easy to fault a work for what it has not done. In the end it must be judged by what it has accomplished, and that by all measures is much.
Essay on Love for Students and Children
500+ words essay on love.
Love is the most significant thing in human’s life. Each science and every single literature masterwork will tell you about it. Humans are also social animals. We lived for centuries with this way of life, we were depended on one another to tell us how our clothes fit us, how our body is whether healthy or emaciated. All these we get the honest opinions of those who love us, those who care for us and makes our happiness paramount.

What is Love?
Love is a set of emotions, behaviors, and beliefs with strong feelings of affection. So, for example, a person might say he or she loves his or her dog, loves freedom, or loves God. The concept of love may become an unimaginable thing and also it may happen to each person in a particular way.
Love has a variety of feelings, emotions, and attitude. For someone love is more than just being interested physically in another one, rather it is an emotional attachment. We can say love is more of a feeling that a person feels for another person. Therefore, the basic meaning of love is to feel more than liking towards someone.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Need of Love
We know that the desire to love and care for others is a hard-wired and deep-hearted because the fulfillment of this wish increases the happiness level. Expressing love for others benefits not just the recipient of affection, but also the person who delivers it. The need to be loved can be considered as one of our most basic and fundamental needs.
One of the forms that this need can take is contact comfort. It is the desire to be held and touched. So there are many experiments showing that babies who are not having contact comfort, especially during the first six months, grow up to be psychologically damaged.
Significance of Love
Love is as critical for the mind and body of a human being as oxygen. Therefore, the more connected you are, the healthier you will be physically as well as emotionally. It is also true that the less love you have, the level of depression will be more in your life. So, we can say that love is probably the best antidepressant.
It is also a fact that the most depressed people don’t love themselves and they do not feel loved by others. They also become self-focused and hence making themselves less attractive to others.
Society and Love
It is a scientific fact that society functions better when there is a certain sense of community. Compassion and love are the glue for society. Hence without it, there is no feeling of togetherness for further evolution and progress. Love , compassion, trust and caring we can say that these are the building blocks of relationships and society.
Relationship and Love
A relationship is comprised of many things such as friendship , sexual attraction , intellectual compatibility, and finally love. Love is the binding element that keeps a relationship strong and solid. But how do you know if you are in love in true sense? Here are some symptoms that the emotion you are feeling is healthy, life-enhancing love.
Love is the Greatest Wealth in Life
Love is the greatest wealth in life because we buy things we love for our happiness. For example, we build our dream house and purchase a favorite car to attract love. Being loved in a remote environment is a better experience than been hated even in the most advanced environment.
Love or Money
Love should be given more importance than money as love is always everlasting. Money is important to live, but having a true companion you can always trust should come before that. If you love each other, you will both work hard to help each other live an amazing life together.
Love has been a vital reason we do most things in our life. Before we could know ourselves, we got showered by it from our close relatives like mothers , fathers , siblings, etc. Thus love is a unique gift for shaping us and our life. Therefore, we can say that love is a basic need of life. It plays a vital role in our life, society, and relation. It gives us energy and motivation in a difficult time. Finally, we can say that it is greater than any other thing in life.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Feb 20, 2023
250-500 Word Example Essays About Love and Romance
Got an Essay assignment about Love and Romance? Let us help you out with these inspiring Examples!
Love, an emotion that has captivated the hearts and minds of poets, authors, and artists throughout history, remains a profound and multi-faceted subject. While the depth and complexity of this emotion can make it a daunting topic to explore in an essay, the right resources can turn this challenge into a rewarding endeavor. For those looking to capture the essence of love and romance in their writing, our essay writer can be a beacon of inspiration and assistance. This tool, powered by Jenni.ai, offers a seamless journey through the essay-writing process, from brainstorming ideas to refining the final draft.
Whether you're delving into argumentative, persuasive , or reflective essays about love, Jenni.ai ensures clarity, coherence, and a touch of elegance in your prose. It's a trusted companion for students, educators, and seasoned writers alike, simplifying the writing journey every step of the way.
1. The Evolution of Love: A Study of the Changing Nature of Romance throughout History
Introduction.
Love is one of humanity's most complicated and mysterious emotions. People have strived to comprehend and define Love throughout history, resulting in many works of literature, art, and music dedicated to the subject. Despite its universal appeal, the nature of Love has evolved significantly throughout time, reflecting evolving cultural, social, and economic situations. In this essay, we will look at the evolution of Love, from ancient times to the present.
Ancient Love
A. Greek and Roman Love
Love was viewed as a complex and varied feeling in ancient Greece and Rome, comprising characteristics of desire, friendship, and awe. Love was frequently represented as a tremendous force in ancient civilizations, capable of both propelling individuals to high heights of success and bringing them down into the depths of sorrow. This was especially true of romantic Love, which was glorified in epic poems like the Iliad and Odyssey , as well as works of art and literature depicting the hardships and sufferings of star-crossed lovers.
B. Medieval Love
A chivalric code known as courtly Love emerged in medieval Europe. Its core tenants were the importance of Love, honour, and devotion. During this time, romantic Love was typically portrayed as an unrequited emotion, with the lover pining for the affections of a faraway and unreachable beloved. Medieval poets and troubadours mirrored this romanticised picture of Love in their works by singing and writing about the highs and lows of passionate Love.
Modern Love
A. The Renaissance
The idealized picture of Love that had ruled for centuries was called into question by artists and intellectuals during the Renaissance, marking a turning point in the development of romantic relationships. During this time, romantic Love was portrayed as more tactile and visceral. Shakespeare, for instance, reflected the shifting beliefs of his day by exploring the nuanced and often tragic nature of Love in his works.
B. The Enlightenment
The concepts of reason and individuality began to gain root during the Enlightenment, and with that came a shift in how people saw Love. Political marriages and alliances were often formed based on Love, which was now considered a more sensible and practical feeling. Thinkers from the Enlightenment period, including Voltaire and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, shared this perspective on Love as a tool for bettering society and the individual.
C. The Modern Era
Today, the word "love" is most often used to describe a feeling one has when they are in a committed relationship or when one has achieved their own goals. Love has become a consumable good thanks to the spread of consumerism and the worship of the individual. The media and arts reflect this conception of Love by depicting it as a means to one's fulfillment and contentment.
The changing cultural, social, and economic conditions of each historical epoch are reflected in the history of Love. The essence of Love has changed dramatically throughout the years, from its idealised image in ancient Greece and Rome to its depiction as a spiritual tie in mediaeval Europe to its current identification with romantic relationships and personal fulfilment. Despite these changes, Love remains a strong and enduring force in human existence, inspiring numerous works of art, literature, and music and affecting how we live and interact with one another.
2. The Power of Love: Examining the Impact of Love on Our Lives and Relationships
Love is a strong feeling that may dramatically alter our life and the bonds we form with others. love, whether romantic, familial, or platonic, can unite us and improve our lives in countless ways., the benefits of love.
A. Improved Physical Health
Love has been demonstrated to improve physical health by decreasing stress, lowering blood pressure, and increasing immunity. The hormone oxytocin, which is released in response to social bonding and has been demonstrated to reduce physiological responses to stress, is thought to be at play here.
B. Enhanced Mental Health
In addition to its physical benefits, Love has been shown to have a beneficial effect on our mental health, lowering stress and anxiety levels and boosting our general sense of happiness. The protective powers of Love against the negative consequences of stress and other difficulties in life are well accepted.
C. Strengthened Relationships
A stronger tie may be formed between two people via the power of Love. Relationships of all kinds, whether romantic, familial, or platonic, may benefit from the strengthening effects of Love by increasing their levels of closeness, trust, and mutual understanding.
The Challenges of Love
A. Love can be painful
Sometimes Love hurts, as when a relationship ends or when we can't find the one we're looking for. One of life's most trying events is losing someone we care about, which may leave us feeling isolated, discouraged, and empty.
The Power of Love to Overcome Challenges
Despite these difficulties, Love may help us overcome them and grow closer to one another. The strength of Love is that it may help us learn and grow, both as people and as a community, via its many forms, such as forgiveness, compromise, and the willingness to persevere through adversity.
Finally, Love is a strong and transformational force that may profoundly influence our lives and relationships. Love may provide us joy, comfort, and a feeling of purpose, whether between friends, family, or romantic partners. Despite its numerous advantages, Love may also bring with it difficulties such as heartbreak and strife. Nonetheless, never underestimate the power of Love.
It has the potential to draw people together and form deep, long-lasting bonds. Love has the power to make the world a better place, whether through acts of kindness, selflessness, or simply being there for one another. So, let us embrace Love in all of its manifestations and harness its potential to improve our lives and the lives of those around us.
3. The Science of Love: Understanding the Biology and Psychology Behind Love and Attraction
For millennia, people have been drawn and intrigued by the intricate and intriguing feeling of Love. Despite its enormous global significance, the science of Love is now being thoroughly investigated. This paper will investigate the biology and psychology of Love and attraction, delving into the different elements that impact these powerful emotions and how they form our relationships.
The Biology of Love
A. Hormone Function
Love is a biological process controlled by chemicals such as dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin. These hormones influence our sensations of attraction, enthusiasm, and enjoyment and boost sentiments of trust and closeness.
B. The Influence of Genetics
Genetics also has an impact on Love and attraction, with some personality qualities and physical characteristics that are considered to be appealing to potential spouses being handed down from generation to generation. This suggests that particular preferences for specific sorts of people are hardwired into our genetics, influencing our romantic and sexual attraction patterns.
The Psychology of Love
A. The Role of Attachment Styles
Our attachment types, which we acquire from our early connections with our caretakers, also affect our Love. These attachment types can significantly influence our later relationships, influencing how we build and keep deep attachments with others.
B. The Impact of Social Norms and Values
Cultural Values
Social conventions and cultural ideas also impact Love and attraction, with societal expectations and values impacting our romantic and sexual impulses. These social conventions and cultural ideas influence everything from who we are attracted to and how we approach and pursue relationships.
The Meeting of Biology and
Love Psychology
The biology and psychology of Love are inextricably linked and interdependent, with one having a complicated and subtle impact on the other. This suggests that, while biology influences our sentiments of attraction and Love, our psychological experiences and beliefs may equally shape these emotions.
To summarise, love science is a complicated and intriguing discipline that encompasses the biology and psychology of this strong and transformational emotion. By investigating the elements that impact Love and attraction, we may gain a deeper understanding of the systems that underpin these feelings and how they shape our lives and relationships. The study of Love is a vital and beneficial effort, whether we seek Love, attempt to preserve Love, or wonder about the science underlying this feeling.
4. The Fine Line Between Love and Obsession: Exploring the Dark Side of Love
Love is a powerful and transformative emotion that can bring immense joy and fulfilment to our lives. But Love can also turn dark and dangerous when it crosses the line into obsession. This essay will examine the fine line between Love and obsession, exploring how Love can become unhealthy and dangerous.
The Characteristics of Obsessive Love
A. Unhealthy Attachment
Obsessive Love is characterized by an unhealthy attachment to another person, with the obsessed person becoming overly dependent on their partner for emotional fulfilment. This can lead to feelings of possessiveness and jealousy, as well as a need for constant attention and validation.
B. Control and Manipulation
Obsessive Love can also involve control and manipulation, with the obsessed person trying to control every aspect of their partner's life and behaviour. This can range from minor acts of manipulation, such as trying to dictate what their partner wears or who they spend time with, to more serious forms of control, such as physical abuse or stalking.
The Dark Side of Love
A. Stalking and Harassment
The dark side of Love can take many forms, with stalking and harassment being among the most extreme and dangerous forms of obsessive behaviour. Stalking and harassment can have serious and long-lasting consequences for the victim, causing fear, stress, and trauma that can impact their mental and physical well-being.
B. Domestic Violence
Domestic violence is another form of the dark side of Love, with physical, sexual, and psychological abuse being used as a means of control and domination. Domestic violence can have devastating consequences for the victim, often leading to serious injury or even death.
The Roots of Obsessive Love
A. Psychological Issues
Obsessive Love can have its roots in psychological issues, including depression, anxiety, and borderline personality disorder. These conditions can lead to feelings of insecurity and low self-esteem, making it difficult for individuals to form healthy relationships.
B. Cultural and Social Factors
Cultural and social factors can also play a role in the development of obsessive Love, with certain societal beliefs and norms promoting possessiveness and control in relationships. This can include gender roles, expectations, and cultural beliefs about Love and relationships.
In conclusion, the fine line between Love and obsession is delicate and dangerous, with Love crossing over into unhealthy and dangerous territory when it becomes obsessive. By understanding the characteristics of obsessive Love and how it can take dark and dangerous forms, we can better protect ourselves and our loved ones from the negative consequences of this powerful emotion.
5. The Concept of Unconditional Love: An Analysis of the Ideal of Selfless Love
All kinds of different things count as Love since it's such a complicated and diverse feeling. Unconditional Love is frequently depicted as altruistic, all-encompassing, and unshakable, making it one of the most romanticized types. In this essay, I'd discuss the idea of unconditional Love, defining it and contrasting it with other types of affection.
An Explanation of Selfless Love
A. Selfless Love
The term "unconditional love" is commonly used to describe a type of Love that puts the other person's needs before its own. In this kind of Love, one person cares for another without any thought of return or compensation.
B. Love that encompasses everything
Many people use the term "all-encompassing" to express how unconditional Love embraces a person regardless of who they are or what they've done in their lives. A love like this doesn't depend on the other person changing or improving in any way; rather, it's an unconditional embrace of the person as they are.
The Ideal of Unconditional Love
A. Love Without Conditions
Unconditional Love is a romantic ideal in which the lover places no restrictions on the object of his affection. Since it involves so much giving of oneself, this kind of Love is typically held up as the pinnacle of romantic relationships.
B. Putting the Feeling into Action
However, since we are all flawed human beings, practising unconditional Love can be challenging in daily life. Although this may be the case, the ideal of unconditional Love is still significant since it motivates us to improve our Love and compassion towards others.
The Advantages of Unconditional Love
A. Stronger Connections
Unconditional Love has the potential to improve our connections with others, leading to deeper and more meaningful bonds. This kind of Love creates a non-judgmental and welcoming attitude towards people, which can assist to lessen conflict and improve understanding.
B. More Joy and Satisfaction
As a result of the more profound relationships it fosters, unconditional Love may also increase a person's sense of well-being and contentment. Finding Love like this may give our life new meaning and make us feel whole.
In conclusion, many of us hold unconditional Love as a relationship goal. Even if it's not always possible, the ideal of unconditional Love is worthwhile since it motivates us to increase our Love and compassion. The concept of unconditional Love may lead us to a more meaningful and happy lifestyle, whether our goal is to better our relationships or to find more pleasure and contentment in general.
6. The Importance of Communication in Love Relationships: A Study of the Role of Communication in Maintaining Love
Love relationships, like all others, benefit greatly from open lines of communication between partners. Connecting with one another on a regular basis, whether it's to chat about the day, express emotions, or problem-solve, is crucial to keeping the Love alive between you. This essay will discuss the significance of communication in romantic relationships, specifically how it helps couples stay together and grow closer over time.
Advantages of good communication
Increased Compatibility and Mutual Understanding
Love partnerships benefit significantly from open lines of communication that facilitate mutual understanding and closeness. Sharing our innermost ideas, emotions, and experiences with our partners via direct and honest communication strengthens our bonds with them.
Reduced Conflict
As we can better address difficulties and find positive solutions to differences when communicating effectively, we experience less conflict in our relationships. Relationships may be stronger and more loving by talking through differences and finding common ground.
The Difficulties in Expressing Your Feelings in a Romantic Relationship
A. Confusing Messages and Confused Intents
Good communication can sometimes be difficult, especially in romantic partnerships, despite its many advantages. Conflict, anger and a lack of trust may all result from poor communication and misunderstandings in relationships.
B. Vulnerability and Emotional Safety
Likewise, it takes courage and trust to open up and talk about your feelings with the person you love. It may be nerve-wracking to communicate our innermost thoughts and feelings with a partner because of the risk of being judged harshly or rejected.
The Importance of Active Listening
What is Active Listening?
Maintaining positive connections with others requires not just good talkers but also good listeners. Paying close attention to the other person as they speak and making an effort to get their viewpoint and requirements is an essential component of active listening.
The Benefits of Active Listening
The ability to listen attentively and process information can have a significant influence on interpersonal bonds. You may show your spouse how much you value their opinion and the commitment you have to the relationship by listening attentively to what they have to say.
Finally, it's important to note that communication is a cornerstone of successful, loving partnerships. Communication is crucial for developing and maintaining healthy relationships , whether it is via problem-solving, venting, or just listening. Your relationship may grow stronger and become more rewarding and loving if you put an emphasis on communicating well with one another.
Final Words
Love is a complicated and varied theme that has inspired numerous works of art, literature, and music. Whether it is the science of Love, the power of Love, or the development of Love, there is a great deal to learn and comprehend about this universal feeling.
Students now have access to a potent tool that may assist them in writing essays about Love with ease and assurance thanks to Jenni.ai. From giving ideas and recommendations to leading you through the writing process, Jenni.ai is the ideal option for anyone who wants to write about Love and relationships. Why then wait? Sign up for a free trial of Jenni.ai today and explore its numerous writing perks!
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back
- Home
- University Colleges
- SUNY College at New Paltz
- SUNY New Paltz Undergraduate Honors Thesis Collection
Campus Communities in SOAR
Exploring love languages: the key to building and maintaining healthy relationships.

Average rating
Cast your vote you can rate an item by clicking the amount of stars they wish to award to this item. when enough users have cast their vote on this item, the average rating will also be shown. star rating, date published, collections.
The following license files are associated with this item:
- Creative Commons
entitlement

Export search results
The export option will allow you to export the current search results of the entered query to a file. Different formats are available for download. To export the items, click on the button corresponding with the preferred download format.
By default, clicking on the export buttons will result in a download of the allowed maximum amount of items.
To select a subset of the search results, click "Selective Export" button and make a selection of the items you want to export. The amount of items that can be exported at once is similarly restricted as the full export.
After making a selection, click one of the export format buttons. The amount of items that will be exported is indicated in the bubble next to export format.
The New York Times
The upshot | the words men and women use when they write about love.
Advertisement
- Visit The Upshot on Facebook
- Visit The Upshot on Twitter
- Follow The Upshot via RSS
Get the Upshot in your Inbox
The Words Men and Women Use When They Write About Love
By JOSH KATZ , CLAIRE CAIN MILLER and KATHLEEN A. FLYNN NOV. 7, 2017

How Certain We Are That A Word Was ...
When writing about love, men are more likely to write about sex, and women about marriage. Women write more about feelings, men about actions.
Even as gender roles have merged and same-sex romance has become more accepted, men and women still speak different languages when they talk about love — at least, if Modern Love essays submitted to The New York Times are any indication.
We examined the last four years of essay submissions and charted the words along two dimensions: whether the essay was published and the author’s gender.
Words toward the top of the chart above are more likely in published essays, and those on the bottom are more likely in rejected ones; words on the right of the chart are more likely in essays submitted by women, while those on the left are more likely in essays by men. We found overlap in both dimensions, represented by words in purplish circles near the center of the chart. But there were striking differences, too.
First, between men and women: When men wrote about family, they used words like “father,” “dad” and “son,” while women used “mother,” “mom” and “daughter.” (And we checked — in these essays, the writers were almost always referring to their own or their partner’s family members, not themselves.)
Words used by men and women when talking about family
Of course, these essays represent a highly unrepresentative sample. Yet many of the patterns are backed up by research.
Parents report feeling a closer relationship to a child of the same sex even before babies are born, some studies have shown. They tend to spend more time with children of the same sex and are more likely to say they want a child of their sex. And children often look to parents of the same sex as role models for relationships.
Other studies have shown that females are more likely to talk about emotions than males are, and parents are more likely to use a larger emotional vocabulary with girls and to tell boys not to cry. Boys are generally taught to express anger ; girls are advised the opposite.
That pattern shows up in these charts, too. Men’s words tended to be more active: “bomb,” “hit,” “strike,” “punch,” “battle.” Women were more likely to describe feelings: “resentment,” “furious,” “agony,” “hurt;” they were also significantly more likely to use the word “feel.” Men, meanwhile, didn’t write about different emotions than women – they just mentioned fewer of them.
Notable differences between male and female authors
And regarding sex versus love, men and women want both, said William Doherty , a couples counselor and professor of family science at the University of Minnesota. But sexual chemistry is more often an initial filter for men entering a relationship, while closeness is for women.
Still, the line between male and female behavior — emotional, romantic and otherwise — is blurring, said Robin Lakoff , professor emeritus of linguistics at the University of California, Berkeley.
“Back in the 50s, men could show anger, rivalry and hostility, so they could swear,” she said. “Women could show fear, sorrow and love, and so they could cry.”
Today, she said, “it’s probably best to say we are somewhat confused about gender roles and stereotypes.”
Differences in published and rejected essays
Our analysis also offered hints about what kind of essays are published versus those that are rejected.
For example, what’s telling about many of the nouns near the top of the chart is how concrete they are. They suggest specific characters who might stride through a story — one’s father, doctor, children, mother, boyfriend or therapist — as well as where it might unfold: at a party, in an apartment, on the couch, at dinner, in bed, on a futon, at the altar, in the hospital. That specificity appears to have caught an editor’s attention and made for engaging reading.
It’s also worth noting how many more adjectives there are near the bottom of the chart — for example, “familiar,” “digital,” “beautiful,” “excited,” “proud” and “endless” — compared with top, which included “fine,” “mysterious” and “sexual.” As E.B. White put it in “The Elements of Style”: “There is nothing wrong, really, with any word — all are good, but some are better than others.”
Selected adjectives

Modern Love at 13: Awkward and Amazing

Recognizing What They Had, 20 Years Too Late

Mom: ‘Is He Jewish?’ Me: ‘No.’ Mom: ‘Is He Smart?’

Modern Love: We Were in Our 20s and We Didn’t Have a Clue
The word choices that explain why jane austen endures.
There’s a way to measure the acute emotional intelligence that has never gone out of style.
Subscribe to our newsletter
50 great articles and essays about love and relationships, love and life, masters of love by emily esfahani smith, this is emo by chuck klosterman, how to pick your life partner by tim urban, my superpower is being alone forever by joe berkowitz and joanna neborsky, it's not them, it's you by jen doll, together alone by michael hobbes, liking is for cowards by jonathan franzen, 30 more essays about life, relationships, in relationships, be deliberate by emily esfahani smith and galena rhoades, endless love by aaron ben-ze’ev, does a more equal marriage mean less sex by lori gottlieb, deeply, truly (but not physically) in love by lauren slater, is an open marriage a happier marriage by susan dominus, the breakup museum by leslie jamison, tinder and the dawn of the "dating apocalypse" by nancy jo sales, dating online by emily witt, love me tinder by emily witt, tinder hearted by allison p. davis, a million first dates by dan slater, mormons, orthodox jews and the dating crisis by jon birger, dating by numbers by kevin poulsen, why we cheat by lisa taddeo, why women stray by david buss, the adultery arms race by michelle cottle, the cuckold by james harms, why we love by helen fisher, essays in love by alain de botton, all about love by bell hooks, a general theory of love by thomas lewis, fari amini and richard lannon, 100 more great nonfiction books, see also..., 50 great psychology articles, 50 great essays about life, 20 great articles about happiness.

The Psychology of Love
Love by lauren slater, the science of love by barbara fredrickson, the biology of attraction by helen e. fisher, love is like cocaine by helen fisher, the rejection lab by alison kinney, there's no such thing as everlasting love by emily esfahani smith, 50 more articles about psychology, men, women, sex and darwin by natalie angier, 12 revelations about sex by alain de botton, safe-sex lies by meghan daum, why my wife won't sleep with me by sean elder, women who want to want by daniel bergner, 50 more articles about sex, kids these days, no labels, no drama, right by jordana narin, why developing serious relationships in your 20s matters by elizabeth spiers, like. flirt. ghost. by mary h. k. choi, friends without benefits by nancy jo sales, boys on the side by hanna rosin, 50 more articles about growing up, the limits of friendship by maria konnikova, the type of love that makes people happiest by arthur c. brooks, how friendships change in adulthood by julie beck, it’s your friends who break your heart by jennifer senior, friends of a certain age by alex williams, a guide to friendship, schmoozing, and social advancement by glenn o'brien, the man date by jennifer 8. lee.
About The Electric Typewriter We search the net to bring you the best nonfiction, articles, essays and journalism
The enchanted vision. An invitation to read about love Mark Vernon - Talks and Thoughts
- Religion & Spirituality
To read the essay, go to Aeon magazine's website, or https://aeon.co/essays/in-the-beginning-there-was-love-we-can-move-with-its-power
- More Episodes
- © 2024 Mark Vernon - Talks and Thoughts
Top Podcasts In Religion & Spirituality


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Brian Rea. By Ada Calhoun. It's unrealistic to expect your spouse to forever remain the same person you fell in love with. 13. After 264 Haircuts, a Marriage Ends. Brian Rea. By William Dameron ...
romantic love is the valuing of the qualities had by our partners as well as the appreciation of a. relationship from the perspective of the participants in that relationship, and the valuing of one's. beloved. Later in we worked to get clearer on the ideal of stability. Stability is the ideal that we.
Love and forgiveness: How its power heals wounds and strengthens bonds. Love Essay Examples: Choose Your Sample for Inspiration. Essays about love are usually standard, 5-paragraph papers students write in college: One paragraph is for an introduction, with a hook and a thesis statement; Three are for a body, with arguments or descriptions
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement About Love. Conduct the first research. You can write a thesis statement about love from different angles: this could be romantic, platonic, love between family, love as a sacrifice, etc. Whichever angle you choose to write from, make sure to read previously written works on the subject first. Write a proposal.
Introduction. The concept of true love is based on the belief that to truly love someone you have to accept them for who they are (including their shortcoming and faults), put their happiness above your own (even if your heart is broken in the process) and that you will always love them even if they are not by your side. We will write a custom ...
Cognisant being must be involved in all aspects and movements involving love. (Vacek, 1996) Thesis Statement. This paper is a critical analysis over the characteristics associate with the definition of love. It firmly takes the notion, "Falling in love entails spiritually nurturing personal and populace growth". Relation of love and stress
Love. First published Fri Apr 8, 2005; substantive revision Wed Sep 1, 2021. This essay focuses on personal love, or the love of particular persons as such. Part of the philosophical task in understanding personal love is to distinguish the various kinds of personal love. For example, the way in which I love my wife is seemingly very different ...
The Oxford Handbook of Philosophy of Love offers a wide array of original essays on the nature and value of love. The editors, Christopher Grau and Aaron Smuts, have assembled an esteemed group of thinkers, including both established scholars and younger voices. The volume contains thirty-three essays addressing both issues about love as well ...
For more information, please contact [email protected]. Running head: LOVE. Love: A biological, psychological and philosophical study. Heather Chapman. University of Rhode Island Dedication. This paper is dedicated to the love of my life. Jason Matthew Nye. October 4,1973 - January 26, 2011 Abstract.
New philosophical essays on love by a diverse group of international scholars. Topics include contributions to the ongoing debate on whether love is arational or if there are reasons for love, and if so what kind; the kinds of love there may be (between humans and artificial intelligences, between non-human animals and humans); whether love can explain the difference between nationalism and ...
It could even be your love story. As you analyze and explain the love story, talk about the highs and lows of love. Showcase the hard and great parts of this love story, then end the essay by talking about what real love looks like (outside the flowers and chocolates). 3. What True Love Looks Like.
The concept of love: an exploratory study with a. sample of young Brazilians. 1. Thiago de Almeida, José Fernando Bittencourt Lo mônaco. Department of Psychology of Learning, Development and ...
The essays focus on the contradictions and limits of love, manifested in such phenomena as trust, abuse, grief, death, violence, politics, and desire. An erudite examination of the many facets of love, this book fills a lacuna in the philosophy of this richly complicated topic.
5 Essay Examples. 1. Love and Marriage by Kannamma Shanmugasundaram. "In successful love marriages, couples have to learn to look past these imperfections and remember the reasons why they married each other in the first place. They must be able to accept the fact that neither one of them is perfect.
Good writing about love features the same virtues that define a good relationship: honesty, generosity, open-mindedness, curiosity, humor and self-deprecation. Bad writing about love suffers from ...
Essays about love are usually standard, 5-paragraph papers students write in college: One paragraph is for an introduction, with a hook and a thesis statement; Three are for a body, with arguments or descriptions; One last passage is for a conclusion, with a thesis restatement and final thoughts;
The two essays on love and politics, for example, consider how change can emerge when love is considered as a social phenomenon. Sophie Bourgault considers the role of love in politics by turning to the seemingly disparate perspectives of Arendt and Simone Weil. There is no place for love and compassion in politics according to Arendt, while ...
500+ Words Essay on Love. Love is the most significant thing in human's life. Each science and every single literature masterwork will tell you about it. Humans are also social animals. We lived for centuries with this way of life, we were depended on one another to tell us how our clothes fit us, how our body is whether healthy or emaciated.
Here are some essay topics and thesis ideas about the romantic movement from a retired British Literature teacher. With these tips and ideas, your essay will come together in no time! ... Sir Walter Scott, and Thomas Love Peacock. Romantic novels you might be familiar with are Frankenstein (Mary Shelley), Ivanhoe (Sir Walter Scott), ...
Introduction. Love is a powerful and transformative emotion that can bring immense joy and fulfilment to our lives. But Love can also turn dark and dangerous when it crosses the line into obsession. This essay will examine the fine line between Love and obsession, exploring how Love can become unhealthy and dangerous.
Through a series of interviews, the paper explores five "love languages" developed by Dr Gary Chapman used to communicate emotional fulfillment. The paper challenges the idea that time is a key component to the development of the five love languages. The research demonstrates that over time individuals discover their love language and that ...
That pattern shows up in these charts, too. Men's words tended to be more active: "bomb," "hit," "strike," "punch," "battle.". Women were more likely to describe feelings ...
Why We Love by Helen Fisher "The Nature and Chemistry of Romantic Love" Essays in Love by Alain De Botton Charting a relationship, from the first blush to the final heartbreak All About Love by Bell Hooks A critical examination of love in the modern world A General Theory of Love by Thomas Lewis, Fari Amini and Richard Lannon The science of love
Show Mark Vernon - Talks and Thoughts, Ep The enchanted vision. An invitation to read about love - Apr 19, 2024
751 likes, 31 comments - thesisyouneed on April 30, 2024: "Sis you blocking your own blessing!! #faith #reels #reelsinstagram #prayer #prophet #jesus #jesuschrist # ...
Govardhan (Vijay Deverakonda), a devoted architect from Hyderabad, juggles supporting his extended family while seeking a partner who understands his commitments. When he discovers Indu (Mrunal Thakur) thesis on his family, he challenges her, leading to unexpected twists as they navigate misunderstandings and eventually find love amidst sacrifice and understanding
Investors love nothing more than their thesis on a stock playing out. Journalists sometimes get to enjoy the feeling too. Shares in Royal Philips [jumped nearly 30% in European trading Monday ...