Suggestions or feedback?

MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Sustainability
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
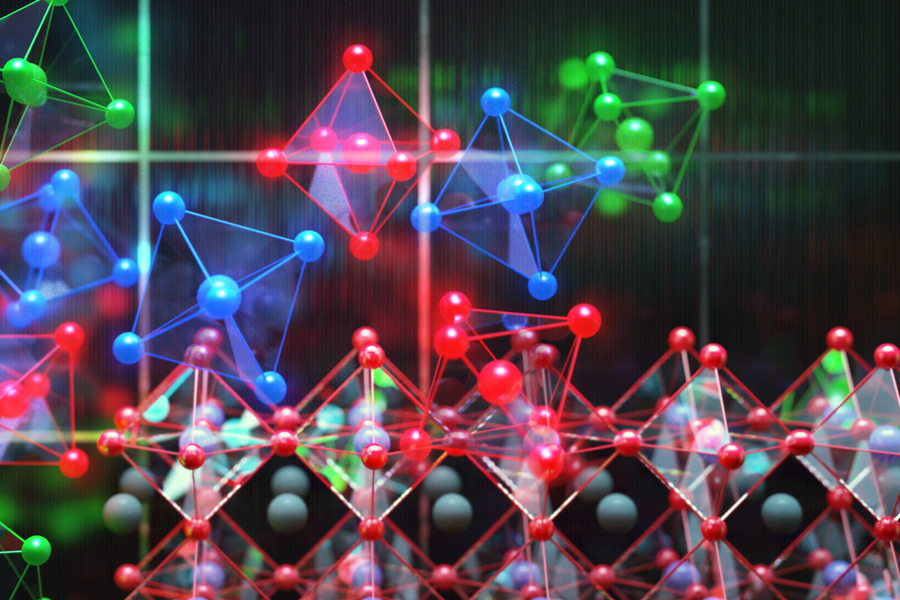
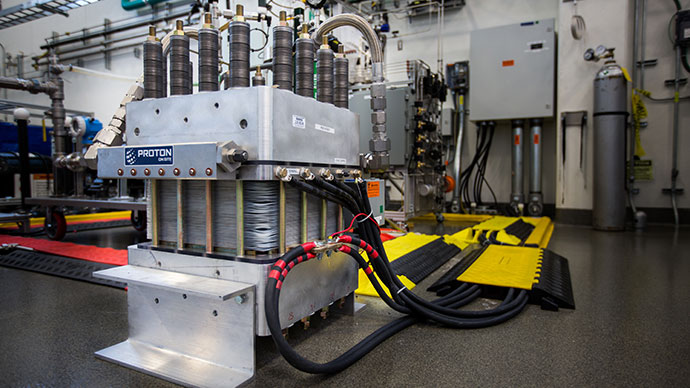
Researchers improve efficiency of next-generation solar cell material
Press contact :, media download.
*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."
Previous image Next image
Perovskites are a leading candidate for eventually replacing silicon as the material of choice for solar panels. They offer the potential for low-cost, low-temperature manufacturing of ultrathin, lightweight flexible cells, but so far their efficiency at converting sunlight to electricity has lagged behind that of silicon and some other alternatives.
Now, a new approach to the design of perovskite cells has pushed the material to match or exceed the efficiency of today’s typical silicon cell, which generally ranges from 20 to 22 percent, laying the groundwork for further improvements.
By adding a specially treated conductive layer of tin dioxide bonded to the perovskite material, which provides an improved path for the charge carriers in the cell, and by modifying the perovskite formula, researchers have boosted its overall efficiency as a solar cell to 25.2 percent — a near-record for such materials, which eclipses the efficiency of many existing solar panels. (Perovskites still lag significantly in longevity compared to silicon, however, a challenge being worked on by teams around the world.)
The findings are described in a paper in the journal Nature by recent MIT graduate Jason Yoo PhD ’20, professor of chemistry and Lester Wolfe Professor Moungi Bawendi, professor of electrical engineering and computer science and Fariborz Maseeh Professor in Emerging Technology Vladimir Bulović, and 11 others at MIT, in South Korea, and in Georgia.
Perovskites are a broad class of materials defined by the fact that they have a particular kind of molecular arrangement, or lattice, that resembles that of the naturally occurring mineral perovskite. There are vast numbers of possible chemical combinations that can make perovskites, and Yoo explains that these materials have attracted worldwide interest because “at least on paper, they could be made much more cheaply than silicon or gallium arsenide,” one of the other leading contenders. That’s partly because of the much simpler processing and manufacturing processes, which for silicon or gallium arsenide requires sustained heat of over 1,000 degrees Celsius. In contrast, perovskites can be processed at less than 200 C, either in solution or by vapor deposition.
The other major advantage of perovskite over silicon or many other candidate replacements is that it forms extremely thin layers while still efficiently capturing solar energy. “Perovskite cells have the potential to be lightweight compared to silicon, by orders of magnitude,” Bawendi says.
Perovskites have a higher bandgap than silicon, which means they absorb a different part of the light spectrum and thus can complement silicon cells to provide even greater combined efficiencies. But even using only perovskite, Yoo says, “what we’re demonstrating is that even with a single active layer, we can make efficiencies that threaten silicon, and hopefully within punching distance of gallium arsenide. And both of those technologies have been around for much longer than perovskites have.”
One of the keys to the team’s improvement of the material’s efficiency, Bawendi explains, was in the precise engineering of one layer of the sandwich that makes up a perovskite solar cell — the electron transport layer. The perovskite itself is layered with a transparent conductive layer used to carry an electric current from the cell out to where it can be used. However, if the conductive layer is directly attached to the perovskite itself, the electrons and their counterparts, called holes, simply recombine on the spot and no current flows. In the researchers’ design, the perovskite and the conductive layer are separated by an improved type of intermediate layer that can let the electrons through while preventing the recombination.
This middle electron transport layer, and especially the interfaces where it connects to the layers on each side of it, tend to be where inefficiencies occur. By studying these mechanisms and designing a layer, consisting of tin oxide, that more perfectly conforms with those adjacent to it, the researchers were able to greatly reduce the losses.
The method they use is called chemical bath deposition. “It’s like slow cooking in a Crock-Pot,” Bawendi says. With a bath at 90 degrees Celsius, precursor chemicals slowly decompose to form the layer of tin dioxide in place. “The team realized that if we understood the decomposition mechanisms of these precursors, then we’d have a better understanding of how these films form. We were able to find the right window in which the electron transport layer with ideal properties can be synthesized.”
After a series of controlled experiments, they found that different mixtures of intermediate compounds would form, depending on the acidity of the precursor solution. They also identified a sweet spot of precursor compositions that allowed the reaction to produce a much more effective film.
The researchers combined these steps with an optimization of the perovskite layer itself. They used a set of additives to the perovskite recipe to improve its stability, which had been tried before but had an undesired effect on the material’s bandgap, making it a less efficient light absorber. The team found that by adding much smaller amounts of these additives — less than 1 percent — they could still get the beneficial effects without altering the bandgap.
The resulting improvement in efficiency has already driven the material to over 80 percent of the theoretical maximum efficiency that such materials could have, Yoo says.
While these high efficiencies were demonstrated in tiny lab-scale devices, Bawendi says that “the kind of insights we provide in this paper, and some of the tricks we provide, could potentially be applied to the methods that people are now developing for large-scale, manufacturable perovskite cells, and therefore boost those efficiencies.”
In pursuing the research further, there are two important avenues, he says: to continue pushing the limits on better efficiency, and to focus on increasing the material’s long-term stability, which currently is measured in months, compared to decades for silicon cells. But for some purposes, Bawendi points out, longevity may not be so essential. Many electronic devices such as cellphones, for example, tend to be replaced within a few years anyway, so there may be some useful applications even for relatively short-lived solar cells.
“I don’t think we’re there yet with these cells, even for these kind of shorter-term applications,” he says. “But people are getting close, so combining our ideas in this paper with ideas that other people have with increasing stability could lead to something really interesting.”
Robert Hoye, a lecturer in materials at Imperial College London, who was not part of the study, says, “This is excellent work by an international team.” He adds, “This could lead to greater reproducibility and the excellent device efficiencies achieved in the lab translating to commercialized modules. In terms of scientific milestones, not only do they achieve an efficiency that was the certified record for perovskite solar cells for much of last year, they also achieve open-circuit voltages up to 97 percent of the radiative limit. This is an astonishing achievement for solar cells grown from solution.”
The team included researchers at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology, the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, and Georgia Tech. The work was supported by MIT’s Institute for Soldier Nanotechnology, NASA, the Italian company Eni SpA through the MIT Energy Initiative, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the National Research Council of Science and Technology.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Moungi Bawendi
- Vladimir Bulović
- Bawendi Group
- Department of Chemistry
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Related Topics
- Photovoltaics
- Electronics
- Nanoscience and nanotechnology
- Renewable energy
- Electrical engineering and computer science (EECS)
Related Articles
Experiments show dramatic increase in solar cell output

Quantum dots can spit out clone-like photons

Unleashing perovskites’ potential for solar cells

Nanoparticles open new window for biological imaging

Cheap, flexible solar
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Helping robots zero in on the objects that matter
Read full story →

Where flood policy helps most — and where it could do more

MIT launches new Music Technology and Computation Graduate Program

New security protocol shields data from attackers during cloud-based computation

How social structure influences the way people share money

Mars’ missing atmosphere could be hiding in plain sight
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
- Newsletters
Super-efficient solar cells: 10 Breakthrough Technologies 2024
Solar cells that combine traditional silicon with cutting-edge perovskites could push the efficiency of solar panels to new heights.
- Emma Foehringer Merchant archive page

Beyond Silicon, Caelux, First Solar, Hanwha Q Cells, Oxford PV, Swift Solar, Tandem PV
3 to 5 years
In November 2023, a buzzy solar technology broke yet another world record for efficiency. The previous record had existed for only about five months—and it likely won’t be long before it too is obsolete. This astonishing acceleration in efficiency gains comes from a special breed of next-generation solar technology: perovskite tandem solar cells. These cells layer the traditional silicon with materials that share a unique crystal structure.
In the decade that scientists have been toying with perovskite solar technology , it has continued to best its own efficiency records, which measure how much of the sunlight that hits the cell is converted into electricity. Perovskites absorb different wavelengths of light from those absorbed by silicon cells, which account for 95% of the solar market today. When silicon and perovskites work together in tandem solar cells, they can utilize more of the solar spectrum, producing more electricity per cell.
Technical efficiency levels for silicon-based cells top out below 30%, while perovskite-only cells have reached experimental efficiencies of around 26%. But perovskite tandem cells have already exceeded 33% efficiency in the lab. That is the technology’s tantalizing promise: if deployed on a significant scale, perovskite tandem cells could produce more electricity than the legacy solar cells at a lower cost.
But perovskites have stumbled when it comes to actual deployment. Silicon solar cells can last for decades. Few perovskite tandem panels have even been tested outside.
The electrochemical makeup of perovskites means they’re sensitive to sucking up water and degrading in heat, though researchers have been working to create better barriers around panels and shifting to more stable perovskite compounds.
In May, UK-based Oxford PV said it had reached an efficiency of 28.6% for a commercial-size perovskite tandem cell, which is significantly larger than those used to test the materials in the lab, and it plans to deliver its first panels and ramp up manufacturing in 2024. Other companies could unveil products later this decade.
Climate change and energy

Your future air conditioner might act like a battery
New technologies store cooling power for when it’s needed most.
- Casey Crownhart archive page

This rare earth metal shows us the future of our planet’s resources
The story of neodymium reveals many of the challenges we’ll likely face across the supply chain in the coming century and beyond.

Why Microsoft made a deal to help restart Three Mile Island
A once-shuttered nuclear plant could soon return to the grid.

Andrew Ng’s new model lets you play around with solar geoengineering to see what would happen
The climate emulator invites you to explore the controversial climate intervention. I gave it a whirl.
- James Temple archive page
Stay connected
Get the latest updates from mit technology review.
Discover special offers, top stories, upcoming events, and more.
Thank you for submitting your email!
It looks like something went wrong.
We’re having trouble saving your preferences. Try refreshing this page and updating them one more time. If you continue to get this message, reach out to us at [email protected] with a list of newsletters you’d like to receive.
New solar cell breaks records for efficiency and voltage
- Nanotechnology
- Weinberg College
In the race to make solar energy more practical amidst soaring gas prices and threats of climate catastrophe, a team of researchers is taking steps toward a more efficient, higher-voltage solar cell.
Now, a Northwestern University, University of Toronto and the University of Toledo team is introducing in a new type of solar cell produced without silicon. Not only does the new cell have extremely high efficiency and record-setting voltage, it also bypasses the need for silicon, which is energetically costly to produce and purify.
In a new paper published this week in Nature , the international team of researchers used two different layers of perovskites — a type of nanocrystal dispersed in a liquid and coated onto a surface using low-cost, well-established techniques. The researchers then tuned each perovskite layer to a different part of the solar spectrum, producing a tandem solar cell.
The team’s prototype solar cell measures one square centimeter in area and produces an open-circuit voltage of 2.19 electron volts, a record for all-perovskite tandem solar cells. Its power-conversion efficiency reached 27.4%, which also breaks the current record for traditional silicon solar cells .
“Further improvements in the efficiency of solar cells are crucial for the ongoing decarbonization of our economy,” said corresponding author Ted Sargent. “While silicon solar cells have undergone impressive advances in recent years, there are inherent limitations to their efficiency and cost, arising from material properties. Perovskite technology can overcome these limitations, but, until now, it had performed below its full potential. Our latest study identifies a key reason for this and points a way forward.”
Sargent joined Northwestern this fall as the Lynn Hopton Davis and Greg Davis Professor of Chemistry at the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences and a professor of electrical and computer engineering in the McCormick School of Engineering.
By adjusting the thickness and chemical composition of the perovskite crystal films, manufacturers can selectively “tune” which wavelengths of light are absorbed and converted into electricity. This is a beneficial contrast to silicon, which always absorbs the same limited section of the solar spectrum.
“In our cell, the top perovskite layer absorbs well in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum, as well as some visible light,” said Chongwen Li, a postdoctoral researcher in Sargent’s lab and one of five co-first authors of the new paper. “The bottom layer has a narrow band gap, which is tuned more toward the infrared part of the spectrum. Between the two, we cover more of the spectrum than would be possible with silicon.”
The tandem design enables the cell to produce a very high open-circuit voltage, which in turn improves its efficiency. But the key innovation came when the team analyzed the touchpoints between the perovskite layer, where light is absorbed and transformed into excited electrons, and the adjacent layer, known as the electron transport layer.
“What we found is that the electric field across the surface of the perovskite layer — we call it the surface potential — was not uniform,” co-lead author and Ph.D. student Aidan Maxwell said. “The effect of this was that in some places, excited electrons were moving easily into the electron transport layer, but, in others, electrons were being lost to the circuit.”
To address this challenge, the team coated the surface of the perovskite layer with a substance known as 1,3-propanediammonium (PDA).
“PDA has a positive charge, and it is able to even out the surface potential,” postdoctoral fellow Hao Chen said. “When we added the coating, we got much better energetic alignment of the perovskite layer with the electron transport layer, and that led to a big improvement in our overall efficiency.”
The cell was independently certified at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Colorado, delivering an efficiency of 26.3%. The team used industry standard methods to measure the stability of the new cell and found that it maintained 86% of its initial efficiency after 500 hours of continuous operation.
"Continuing to advance the efficiency and stability of next-generation solar cells is a crucial priority for decarbonizing the electricity supply,” said Professor Alberto Salleo, chair of the department of materials science and engineering at Stanford University, who was not involved in the study. “The team developed a deep chemical understanding of what was limiting a crucial interface in perovskite solar cells. These insights from basic science, acted on with innovative materials engineering strategies, will continue to drive the field forward.”
Next, the team hopes to scale their production for commercial use, further enhance the tandem cell’s efficiency and improve its stability.
“In this work, we’ve focused on the interface between the perovskite layer and the electron transport layer, but there is another important layer that extracts the ‘holes’ those electrons leave behind,” Sargent said. “One of the intriguing things in my experience with this field is that learning to master one interface doesn't necessarily teach you the rules for mastering the other interfaces. I think there's lots more discovery to be done.”
Maxwell said that the ability of perovskite technology to hold its own against silicon, even though the latter has had a multi-decade head start, is encouraging. The industry’s ability to incorporate new materials and diversify the products it offers will accelerate the economy toward decarbonization.
“In the last 10 years, perovskite technology has come almost as far as silicon has in the last 40,” Maxwell said. “Just imagine what it will be able to do in another 10 years.”
Additional reporting by Tyler Irving / University of Toronto Engineering.
Editor’s Picks

Northwestern faculty to speak at TEDxChicago
New biomaterial regrows damaged cartilage in joints, chronicling chicago, one column at a time, related stories.

Researchers move closer to green hydrogen via water electrolysis
Deep-ocean floor produces its own ‘dark oxygen’, northwestern to lead midwestern carbon-capture hub.
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- The Big Story
- Newsletters
- Steven Levy's Plaintext Column
- WIRED Classics from the Archive
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
These Record-Breaking New Solar Panels Produce 60 Percent More Electricity

If you buy something using links in our stories, we may earn a commission. This helps support our journalism. Learn more . Please also consider subscribing to WIRED
THIS ARTICLE IS republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license .
The sight of solar panels installed on rooftops and large energy farms has become commonplace in many regions around the world. Even in the gray and rainy UK, solar power is becoming a major player in electricity generation.
This surge in solar is fueled by two key developments. First, scientists, engineers, and those in industry are learning how to make solar panels by the billions. Every fabrication step is meticulously optimized to produce them very cheaply. The second and most significant is the relentless increase in the panels’ power conversion efficiency—a measure of how much sunlight can be transformed into electricity.
The higher the efficiency of solar panels , the cheaper the electricity. This might make you wonder: Just how efficient can we expect solar energy to become? And will it make a dent in our energy bills?
Commercially available solar panels today convert about 20 to 22 percent of sunlight into electrical power. However, new research published in Nature has shown that future solar panels could reach efficiencies as high as 34 percent by exploiting a new technology called tandem solar cells. The research demonstrates a record power-conversion efficiency for tandem solar cells.
What Are Tandem Solar Cells?
Traditional solar cells are made using a single material to absorb sunlight. Currently, almost all solar panels are made from silicon—the same material at the core of microchips. While silicon is a mature and reliable material, its efficiency is limited to about 29 percent.
To overcome this limit, scientists have turned to tandem solar cells, which stack two solar materials on top of each other to capture more of the sun’s energy.
In the new Nature paper, a team of researchers at the energy giant LONGi has reported a new tandem solar cell that combines silicon and perovskite materials. Thanks to their improved sunlight harvesting, the new perovskite-silicon tandem has achieved a world record 33.89 percent efficiency.
Perovskite solar materials, which were discovered less than two decades ago , have emerged as the ideal complement to the established silicon technology. The secret lies in their light absorption tunability . Perovskite materials can capture high-energy blue light more efficiently than silicon.
In this way, energy losses are avoided and the total tandem efficiency increases. Other materials, called III-V semiconductors, have also been used in tandem cells and achieved higher efficiencies. The problem is they are hard to produce and expensive, so only small solar cells can be made in combination with focused light.
The scientific community is putting tremendous effort into perovskite solar cells. They have kept a phenomenal pace of development with efficiencies (for a single cell in the lab) rising from 14 percent to 26 percent in only 10 years. Such advances enabled their integration into ultra-high-efficiency tandem solar cells, demonstrating a pathway to scale photovoltaic technology to the trillions of watts the world needs to decarbonize our energy production.
The Cost of Solar Electricity
The new record-breaking tandem cells can capture an additional 60 percent of solar energy. This means fewer panels are needed to produce the same energy, reducing installation costs and the land (or roof area) required for solar farms.
It also means that power plant operators will generate solar energy at a higher profit. However, due to the way that electricity prices are set in the UK , consumers may never notice a difference in their electricity bills. The real difference comes when you consider rooftop solar installations where the area is constrained and the space has to be exploited effectively.
The price of rooftop solar power is calculated based on two key measures: first, the total cost to install solar panels on your roof, and second, how much electricity they will generate over 25 years of operation. While the installation cost is easy to obtain, the savings from generating solar electricity at home are a bit more nuanced. You can save money by using less energy from the grid, especially in periods when it is costly, and you can also sell some of your surplus electricity back to the grid. However, grid operators pay a very small price for this electricity, so sometimes it is more advantageous to use a battery and store the energy for use at night.
Using average considerations for a typical British household, I have calculated the cash savings to consumers using rooftop solar panels. If we can improve panel efficiency from 22 percent to 34 percent without increasing the installation cost, savings in electricity bills will rise from £558ְ ($747) per year up to £709 ($950) per year. A 27 percent bump in cash savings that would make solar rooftops extremely attractive, even in gray and cloudy Britain.
Tandem solar panels may become standard in the future—but scaling up production of these cells will be challenging.
So When Can We Buy These New Solar Panels?
As research continues, considerable efforts are being made to scale up this technology and ensure its long-term durability. The record-breaking tandem cells are made in laboratories and are smaller than a postage stamp. Translating such high performance to meter-square areas remains a vast challenge.
Yet we are making progress. Earlier this month, Oxford PV, a solar manufacturer at the forefront of perovskite technology, announced the first sale of its newly developed tandem solar panels. They have successfully tackled the challenges of integrating two solar materials and making durable and reliable panels. While they are still far from 34 percent efficiency, their work shows a promising route for next-generation solar cells.
Another consideration is the sustainability of the materials used in tandem solar panels. Extracting and processing some of the minerals in solar panels can be hugely energy-intensive . Besides silicon, perovskite solar cells require the elements lead, carbon, iodine, and bromine as components to make them work properly. Connecting perovskite and silicon also requires scarce materials containing an element called indium , so there is plenty of research still required to address these difficulties.
Despite the challenges, the scientific and industrial communities remains committed to developing tandem solar devices that could be integrated into almost anything—cars, buildings, and planes.
The recent developments toward high-efficiency perovskite-silicon tandem cells indicate a bright future for solar power, ensuring that solar continues to play a more prominent role in the global transition to renewable energy.
You Might Also Like …
In your inbox: The best and weirdest stories from WIRED’s archive
Elon Musk is a national security risk
Interview: Meredith Whittaker is out to prove capitalism wrong
How do you solve a problem like Polestar ?
Event: Join us for The Big Interview on December 3 in San Francisco
Recent advances in organic solar cells: materials, design, and performance
- Research Article
- Published: 12 July 2023
- Volume 53 , pages 1403–1419, ( 2024 )
Cite this article

- Ahmed Salih Mahdi 1 ,
- Lina M. Shaker 1 &
- Ahmed Alamiery ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1033-4904 2 nAff3
1442 Accesses
7 Citations
Explore all metrics
Organic solar cells have emerged as promising alternatives to traditional inorganic solar cells due to their low cost, flexibility, and tunable properties. This mini review introduces a novel perspective on recent advancements in organic solar cells, providing an overview of the latest developments in materials, device architecture, and performance optimization. In contrast to existing literature, this review places a strong emphasis on the role of molecular engineering in achieving high power conversion efficiencies. It delves into the latest materials used in organic solar cells, including novel polymers and small molecules, showcasing their unique properties and potential for improved performance. Furthermore, the review explores cutting-edge device architectures, specifically tandem and multi-junction cells, which offer unprecedented opportunities for achieving higher efficiencies. The discussion on these advanced architectures highlights their potential and paves the way for future advancements in the field of organic solar cells. To maximize the performance of organic solar cells, this review also presents recent strategies for performance optimization, focusing on interface engineering, morphological control, and stability enhancement. By providing a comprehensive analysis of these strategies, the review enables readers to gain a deeper understanding of the underlying principles and techniques driving the improvement in device performance. By introducing this novel perspective on recent developments, this mini review offers researchers and practitioners a valuable resource for staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in organic solar cells. It not only presents the current state of the field but also identifies future directions and challenges, fostering further research and innovation in this rapidly evolving field.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Recent progress in organic solar cells (Part II device engineering)

A Review on “Designs and Fabrication” for the Next Generation of Organic Solar Cells Technology

Introduction to Organic Solar Cells
Explore related subjects.
Y. Zhang, L. Zuo, L. Ding, H. Wu, Organic solar cells based on small molecules. J. Mater. Chem. A 9 (9), 4942–4956 (2021)
Google Scholar
C.J. Brabec, S. Gowrisanker, J.J. Halls, D. Laird, S. Jia, S.P. Williams, Polymer–fullerene bulk-heterojunction solar cells. Adv. Mater. 22 (34), 3839–3856 (2010)
Article Google Scholar
P. Chaudhary, P. Kumar, P. Kumar, I. Kaur, Organic solar cells: a review on recent advances and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 139 , 110686 (2021)
G. Li, R. Zhu, Y. Yang, Polymer solar cells. Nat. Photonics 6 (3), 153–161 (2012)
Article ADS Google Scholar
F.C. Krebs, Fabrication and processing of polymer solar cells: a review of printing and coating techniques. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 93 (4), 394–412 (2009)
Z. He, B. Xiao, F. Liu, H. Wu, Y. Yang, S. Xiao, Y. Cao, single-junction polymer solar cells exceeding 10% power conversion efficiency. Adv. Mater. 27 (6), 1035–1041 (2015)
Y. Chang, C. Chu, Y. Yang, X. Gong, Recent advances in roll-to-roll fabrication of polymer solar cells. Adv. Mater. 26 (36), 6342–6363 (2014)
Y. Liang, Z. Xu, J. Xia, S.T. Tsai, Y. Wu, G. Li, Y. Yang, For the bright future-bulk heterojunction polymer solar cells with power conversion efficiency of 7.4%. Adv. Mater. 22 (20), E135–E138 (2010)
J. Hou, O. Inganäs, R.H. Friend, F. Gao, Organic solar cells based on non-fullerene acceptors. Nat. Mater. 17 (2), 119–128 (2018)
X. Chen, X. Guo, S. Zhang, Y. Li, F. Liu, L. Huo, Y. Yang, Ladder-type polymer PT-TQBD enables efficient solar cells with a very low energy loss. Nat. Energy 3 (5), 422–427 (2018)
ADS Google Scholar
W. Zhao, S. Li, H. Yao, S. Zhang, Y. Zhang, B. Yang, J. Hou, Molecular optimization enables over 13% efficiency in organic solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 (21), 7148–7151 (2017)
G. Li, Y. Yang, P. Smith, High-efficiency solution processable polymer photovoltaic cells by self-organization of polymer blends. Nat. Mater. 4 (11), 864–868 (2005)
L. Ye, Y. Xiong, W. Li, S. Li, Y. Wu, J. Hou, High-performance multiple-donor bulk heterojunction solar cells. Nat. Photonics 9 (10), 662–667 (2015)
J. Kim, S. Hong, K. Lee, H. Kang, H. Kim, T.W. Lee, Versatile non-fullerene acceptors for organic photovoltaics. Nat. Commun. 9 (1), 1–11 (2018)
B. Kan, H. Feng, X. Wan, X. Liu, W. Ni, S. Yang, Y. Wang, C. Li, L. Feng, Y. Chen et al., A series of simple oligomer-like small molecules based on diketopyrrolopyrrole for solution-processed solar cells with high efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136 (42), 15529–15532 (2014)
L. Mao, Z. Xie, L. Wang, F. Xie, H. Chen, Zinc phthalocyanine/C60 bilayer heterojunction photovoltaic devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 (9), 093504 (2006)
Y. Li, L. Ye, W. Zhao, S. Li, S. Zhang, S. Mukherjee, H. Ade, J. Hou, A molecular nematic liquid crystalline material for high-performance organic photovoltaics. Nat. Commun. 9 (1), 1–9 (2018)
Z. He, C. Zhong, S. Su, M. Xu, H. Wu, Y. Cao, Enhanced power-conversion efficiency in polymer solar cells using an inverted device structure. Nat. Photonics 6 , 591–595 (2012)
Y. Liu, Y. Chang, C. Chao, C. Wang, W. Lee, H. Chen, A.J. Heeger, A high-mobility electron-transporting polymer for printed transistors. Nature 466 , 622–626 (2010)
Y. Lin, F. Zhao, Y. Wu, K. Jiang, J. Zhu, H. Ade, H. Yan, A chlorinated acceptor for high-efficiency organic photovoltaics. Nat. Energy 3 , 748–754 (2018)
F. Liu, M. Zhang, Y. Yang et al., Aggregation and morphology control enables multiple cases of high-efficiency polymer solar cells. Nat. Commun. 10 , 1095 (2019)
Y. Zhang, X. Zhan, Non-fullerene acceptors for organic solar cells. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2 , 190838 (2019)
N. Gasparini, T. Näreoja, D. Pankov et al., 3D molecular ordering of a high-performance solution-processed small-molecule organic semiconductor. Nat. Mater. 15 , 999–1005 (2016)
C. Yan, S. Barlow, Z. Wang et al., Non-fullerene acceptor with low energy loss for organic solar cells with efficiency over 16%. Nat. Commun. 9 , 5357 (2018)
G. Li, V. Shrotriya, J. Huang et al., High-efficiency solution processable polymer photovoltaic cells by self-organization of polymer blends. Nat. Mater. 4 , 864–868 (2005)
Y. Yang, Z. Zhang, H. Bin et al., Over 16% efficiency organic photovoltaic cells enabled by a chlorinated acceptor with increased open-circuit voltages. Nat. Commun. 7 , 13751 (2016)
S. Zhang, L. Ye, J. Hou, A wide bandgap polymer with a deep HOMO level enables 14.2% efficiency in polymer solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 139 , 2387–2390 (2017)
Y. Lin, X. Zhan, Y. Yang, Non-fullerene acceptors for organic solar cells. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3 , 18003 (2018)
M. Zhang, Y. Wang, T. Zhang, Z. Ling, J. Liu, L. Feng, X. Guo, Z. Wei, W. Ma, A non-fullerene acceptor with superior properties: wide-bandgap, low-LUMO, and high mobility. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57 , 14717–14721 (2018)
C.J. Brabec, S. Gowrisanker, J.J.M. Halls, D. Laird, S. Jia, S.P. Williams, Polymer-fullerene bulk-heterojunction solar cells. Adv. Mater. 22 , 3839–3856 (2010)
C.J. Brabec, N.S. Sariciftci, J.C. Hummelen, Plastic solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 11 , 15–26 (2001)
M.A. Green, K. Emery, D.L. King, S. Igari, W. Warta, Solar cell efficiency tables (version 37). Prog. Photovolt. 19 , 84–107 (2011)
Z. He, C. Zhong, S. Su, M. Xu, H. Wu, W. Cao, Y. Huang, Enhanced power-conversion efficiency in polymer solar cells using an inverted device structure. Adv. Mater. 24 , 1740–1743 (2012)
L. Hu, M. Wu, G. Wang, X. Zhou, Y. Liu, Y. Ma, X. Yang, Y. Cao, Polymeric photovoltaic cells based on conjugated polymers incorporating palladium or platinum complex units. Adv. Mater. 23 , 1482–1486 (2011)
Y. Cui, H. Yao, T. Zhang, Y. Wang, K. Xian, Y. Xu, L. Hong, J. Wei, C. An, J. Hou, Y. Li, Y. Chen, High-performance tandem organic solar cells with complementary absorption bands. Nat. Commun. 9 , 2572 (2018)
S. Chen, E. Mosconi, Y. Fang, M. Xiao, H. Wang, Y. Zhou, Y. Zhao, Y. Gao, J. Huang, Perovskite/perovskite tandem solar cells. Nat. Mater. 17 , 703–709 (2018)
X. Yang, P. Cheng, L. Wang, G. Zhou, W. Ma, J. Zhao, H. Ade, H. Yan, F. Gao, Triple-junction polymer solar cells incorporating both fluorescence and phosphorescence. Adv. Energy Mater. 9 , 1900808 (2019)
H. Yao, Y. Chen, Design and synthesis of a low-bandgap small molecule acceptor for efficient polymer solar cells with high open-circuit voltage. Energy Environ. Sci. 11 , 1898–1904 (2018)
M.A. Green, A. Ho-Baillie, Tandem solar cells: review of design principles and roadmap to commercialization. npj Flex Electron. 1 , 1–12 (2017)
S. Albrecht, C.J. Brabec, Tandem solar cells: the frontier of crystalline silicon photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 29 , 1606480 (2017)
J.F. Geisz, D.J. Friedman, J.S. Ward, W. Olavarria, I. Garcia, M.A. Steiner, T. Moriarty, J.T. Kiehl, M.J. Romero, Progress toward 50% efficiency for mechanically stacked multijunction solar cells. IEEE J. Photovolt. 7 (6), 1487–1494 (2017)
U. Würfel, S. Rein, Tandem Solar Cells: Fundamentals, Design, and Applications (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2015)
O.D. Miller, C. Xu, G.J. Rey, P. Ireland, D. Johnstone, E.C. Warmann, M.L. Lee, M.A. Green, K.R. Catchpole, Cost-effective four-terminal perovskite-silicon tandem solar cells enabling ultrahigh efficiency. Joule 4 , 510–522 (2020)
M. Dupuis, E.E. Looney, Multi-junction and tandem solar cells for space applications, in 2019 IEEE Aerospace Conference , IEEE, pp 1–16 ( 2019)
W. Li, A. Furlan, K.H. Hendriks, Material science of organic solar cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 6 (20), 1600377 (2016)
P. Cheng, X. Zhan, Y. Wu, Interface engineering for organic electronics. Adv. Mater. 30 (39), 1707005 (2018)
N. Li, C.J. Brabec, Air-stable and efficient tandem organic solar cells based on zinc phthalocyanine and a fullerene derivative. Adv. Energy Mater. 9 (5), 1802989 (2019)
S. Li, F. Liu, T.P. Russell, Solution-processed semiconducting polymer bulk heterojunctions: from morphology control to improved electronic performance. Acc. Chem. Res. 49 (11), 2199–2207 (2016)
F. De Rossi, A. Giuri, V. D’Innocenzo, A. Luzio, G. Grancini, A. Petrozza, Light management in organic solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49 (13), 4533–4553 (2020)
A. Facchetti, π-Conjugated polymers for organic electronics and photovoltaic cell applications. Chem. Mater. 23 (3), 733–758 (2011)
I. Salzmann, G. Heimel, Interface engineering in organic field-effect transistors. Chem. Rev. 116 (23), 13714–13751 (2016)
S. Liu, S. Wang, H. Zhou, Interface engineering of metal oxide electrodes for high-performance energy storage devices. Energy Storage Mater. 21 , 291–308 (2019)
Z. Li, J. Song, M. Sun, X. Hu, W. Zhu, Morphology control of organic solar cells by mixed solvent towards high performance. Org. Electron. 64 , 44–51 (2019)
L. Zhou, K. Zhou, J. Wang, W. Ma, H. Zhang, Polymer additives for efficient organic solar cells: recent developments and future prospects. Adv. Mater. 30 (42), 1802102 (2018)
N. Li, F. Zhang, C. Liu, X. Zhan, Efficient and stable polymer solar cells based on a polymer encapsulation strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10 (3), 2433–2440 (2018)
C. Cui, C. Li, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, Z. Liu, Y. Li et al., Enhancing stability and efficiency of organic solar cells through the molecular engineering of an alkylated indacenodithienothiophene-based donor. J. Mater. Chem. A 8 (3), 1423–1431 (2020)
Z. Li, Y. Lin, W. Li, P. Cheng, F. Liu, X. Hu et al., A chlorinated acceptor with improved electron mobility and stability for high-performance organic solar cells. Adv. Mater. 29 (19), 1605658 (2017)
Y. Zhou, C. Fuentes-Hernandez, T.M. Khan, J. Liu, J. Hsu, J. Shim et al., Efficient and stable large-area perovskite solar cells with inorganic charge extraction layers. Science 363 (6422), 265–270 (2019)
Y. Li, Z. Zhao, H. Li, J. Fang, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang et al., Spray-coating fabrication of efficient organic solar cells with enhanced uniformity and reproducibility. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 209 , 110464 (2020)
W. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Zhao, Interface engineering for organic electronics. Adv. Mater. 29 (7), 1602546 (2017)
Z. Li et al., A star-shaped electron acceptor with alkylthio side chains for efficient organic solar cells with reduced energy loss. J. Mater. Chem. A 7 (28), 16843–16849 (2019)
W. Liu et al., Efficient and stable organic solar cells based on an n-type small molecule acceptor with a high electron mobility. J. Mater. Chem. A 8 (29), 14402–14410 (2020)
G. Zhang et al., Polymer acceptors with minimized absorption overlap for efficient organic solar cells with high stability. Energy Environ. Sci. 14 (2), 1113–1123 (2021)
H. Zhou et al., A polymer tandem solar cell with 10.6% power conversion efficiency. Nat. Commun. 5 , 1–8 (2014)
M. Saliba et al., Cesium-containing triple cation perovskite solar cells: improved stability, reproducibility and high efficiency. Energy Environ. Sci. 9 (6), 1989–1997 (2016)
A. Abate, T. Leijtens, S. Pathak, H.J. Snaith, Tandem solar cells: advances and challenges. Nat. Energy 5 (7), 596–605 (2020)
P. Pandit, A. Chandak, P. Shrivastava, Environmental effects on the performance of solar photovoltaic systems: a review. Energy Convers. Manage. 233 , 113758 (2021)
L.M. Shaker, A.A. Al-Amiery, W.K. Al-Azzawi, A clearer vision: a mini-review on contact lenses. J. Opt. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01222-w
L.M. Shaker, W.K. Al-Azzawi, A. Al-Amiery, M.S. Takriff, W.N.R. Wan Isahak, Highly transparent antibacterial hydrogel-polymeric contact lenses doped with silver nanoparticles. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/vnl.21995
L.M. Shaker, S. Abdulhadi, W.K. Al-Azzawi, A. Alamiery, M.S. Takriff, W.N.R.W. Isahak, Colorless poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) hydrogel contact lenses synergized with silver nanoparticles. J. Opt. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01176-z
L.M. Shaker, A.A. Alamiery, M. Takriff, W.N.R. Wan Isahak, Nano-titanium oxide in polymeric contact lenses. Nanomanufacturing 2 (3), 71–81 (2022)
L.M. Shaker, A. Alamiery, M. Takriff, W.N.R. Wan Isahak, Novel Blue-wavelength-blocking contact lens with Er 3+ /TiO 2 NPs: manufacture and characterization. Nanomaterials 11 (9), 2190 (2022)
L.M. Shaker, A. Al-Adili, A.A. Al-Amiery, Human eye response to the iris diameter variation at polychromatic light programmatically. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 1795 (1), 012025 (2021)
S.L.M. Shaker, S. Osamah, A.A. Al-Amiery, ingle-mode optical fibers coupling: study of the field of view. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 1045 (1), 012009 (2021)
L.M. Shaker, A.A. Al-Amiery, A.A.H. Kadhum, M.S. Takriff, Manufacture of contact lens of nanoparticle-doped polymer complemented with zemax. Nanomaterials 10 (10), 2028 (2020)
L.M. Shaker, A.H. Al-Hamdani, A.A. Al-Amiery, Vision improvement using titanium dioxide nanoparticles-doped PMMA for contact lenses. Eng. Technol. J. 38 (5), 681–689 (2020)
L.M. Shaker, A.H. Al-Hamdani, A.A. Al-Amiery, Nano-particle doped polymers to improve contact lenses optical quality. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 13 (1), 1–12 (2020)
L.M. Shaker, A.H. Al-Hamdani, A.A. Al-Amiery, A comparative study of optical quality for different polymeric contact lenses. J. Phys: Conf. Ser. 1234 (1), 012042 (2020)
L.M. Shaker, A.H. Al-Hamdani, A.A. Al-Amiery, Plastic materials for modifying the refractive index of contact lens overview. Res. Dev. Mater. Sci. 11 , 2–1 (2019)
Download references
Author information
Ahmed Alamiery
Present address: Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Built Environment, University Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM), P.O. Box 43000, Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
Authors and Affiliations
Research Energy Department, Training and Research Office, Baghdad, 10001, Iraq
Ahmed Salih Mahdi & Lina M. Shaker
Energy and Renewable Energies Technology Center, University of Technology, Baghdad, 10001, Iraq
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ahmed Alamiery .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Mahdi, A.S., Shaker, L.M. & Alamiery, A. Recent advances in organic solar cells: materials, design, and performance. J Opt 53 , 1403–1419 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01262-2
Download citation
Received : 12 May 2023
Accepted : 03 June 2023
Published : 12 July 2023
Issue Date : April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12596-023-01262-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Organic solar cells
- Optimization
- Roll-to-roll printing
- Spray-coating
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Journal Proposal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Photovoltaic solar cells: a review.

1. Introduction
2. solar cells, 2.1. the working principle of pv cells.
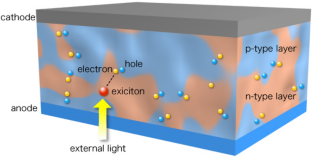
- Absorption of photons in a p-n junction electronic semiconductor to generate the charge carriers (electron-hole pairs). The absorption of a photon with energy (E = hυ) higher than the gap energy ‘E g ’ of the doped semiconductor material means that its energy is used to excite an electron from the valence band ‘Eυ’ to the conduction band ‘E c ’ leaving a void (hole) at the valance level. Additional kinetic energy is given to the electron or hole by the excess photon energy (hυ–hυ 0 ). ‘hυ 0 ′ is the minimum energy or work function of the semiconductor required to generate an electron-hole pair. The work function here represents the energy gap. The excess energy is dissipated as heat in the semiconductor [ 21 , 22 ].
- Consequent separation of the light-generated charge carriers. In an external solar circuit, the holes can flow away from the junction through the p-region, and electrons can flow out across the n-region and pass through the circuit before they recombine with the holes.
- Finally, the separated electrons can be used to drive an electric circuit. After the electrons passed through the circuit, they will recombine with the holes.
2.2. Solar Cell Panels
2.3. components of solar power system, 2.4. p-n junction solar cell, 2.4.1. formation of the depletion region, 2.4.2. p-n junction solar cell under applied voltage, 2.4.3. pv cell under illumination.
- The net flow of the electrons and holes in a p-n junction semiconductor under equilibrium conditions will generate two currents: ‘ I diff ’ and ‘ I drift ’. These currents balance and cancel each other at the equilibrium state.
- If an external source is deployed to the p-n junction, the generated current is the diode current ‘ I d ’.
- Under illumination, the p-n junction will present another current called light or photocurrent ‘ I ph ’.
2.5. I-V and P-V Characteristics
- Short-circuit current density ‘ Isc ’ occurs at (R = 0 and V = 0)
- Open-circuit voltage ‘ Voc ’ (no-load, I = 0 and R = ∞)
- Fill factor ‘ FF ’ that represents the ratio of ‘ Pmax ’ to the electrical output of ‘ Voc ’ and ‘ Isc ’
2.6. Design Considerations
2.7. materials employed in pv cells, 2.7.1. iii-v pv gallium arsenide, 2.7.2. future trends, 2.8. challenges in solar cells, 3. simulation of solar cells and modules, 3.1. simulation of solar cells by matlab/simulink, 3.2. simulation of solar cells by comsol/multiphysics.
- Creating a user-defined, spatially dependent variable for the generation rate, using an integral expression involving the solar radiation ‘ F ( λ )’, which is used to find the rate of photon generation ‘ ϕ ( λ )’.
Share and Cite
Al-Ezzi, A.S.; Ansari, M.N.M. Photovoltaic Solar Cells: A Review. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022 , 5 , 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi5040067
Al-Ezzi AS, Ansari MNM. Photovoltaic Solar Cells: A Review. Applied System Innovation . 2022; 5(4):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi5040067
Al-Ezzi, Athil S., and Mohamed Nainar M. Ansari. 2022. "Photovoltaic Solar Cells: A Review" Applied System Innovation 5, no. 4: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi5040067
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Journal of Materials Chemistry A
Advanced research trends in dye-sensitized solar cells.

* Corresponding authors
a Microelectronics Research Unit, Faculty of Information Technology & Electrical Engineering, University of Oulu, P. O. Box 4500, Finland E-mail: [email protected]
b Nano and Molecular Systems Research Unit, University of Oulu, Finland
c Optoelectronics and Measurement Techniques Research Unit, Faculty of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland
d Center for Ubiquitous Computing, Department of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering, University of Oulu, Finland
e New Energy Technologies Research Group, Department of Applied Physics, Aalto University, P.O. Box 15100, Aalto, Finland
f BCMaterials-Basque Center for Materials, Applications and Nanostructures, UPV/EHU Science Park, Leioa, Spain
g IKERBASQUE, Basque Foundation for Science, Bilbao, Spain
h Department of Chemistry, Ångström Laboratory, Uppsala University, P. O. Box 523, 75120 Uppsala, Sweden
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) are an efficient photovoltaic technology for powering electronic applications such as wireless sensors with indoor light. Their low cost and abundant materials, as well as their capability to be manufactured as thin and light-weight flexible solar modules highlight their potential for economic indoor photovoltaics. However, their fabrication methods must be scaled to industrial manufacturing with high photovoltaic efficiency and performance stability under typical indoor conditions. This paper reviews the recent progress in DSSC research towards this goal through the development of new device structures, alternative redox shuttles, solid-state hole conductors, TiO 2 photoelectrodes, catalyst materials, and sealing techniques. We discuss how each functional component of a DSSC has been improved with these new materials and fabrication techniques. In addition, we propose a scalable cell fabrication process that integrates these developments to a new monolithic cell design based on several features including inkjet and screen printing of the dye, a solid state hole conductor, PEDOT contact, compact TiO 2 , mesoporous TiO 2 , carbon nanotubes counter electrode, epoxy encapsulation layers and silver conductors. Finally, we discuss the need to design new stability testing protocols to assess the probable deployment of DSSCs in portable electronics and internet-of-things devices.

- This article is part of the themed collections: Journal of Materials Chemistry A Recent Review Articles , Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers and 2021 Journal of Materials Chemistry A most popular articles
Article information
Download Citation
Permissions.
M. Kokkonen, P. Talebi, J. Zhou, S. Asgari, S. A. Soomro, F. Elsehrawy, J. Halme, S. Ahmad, A. Hagfeldt and S. G. Hashmi, J. Mater. Chem. A , 2021, 9 , 10527 DOI: 10.1039/D1TA00690H
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence . You can use material from this article in other publications without requesting further permissions from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author, advertisements.
IEEE Account
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents

Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

How NASA Uses and Improves Solar Power
The sun is the most energetic object in our solar system ..
Humans have been finding creative ways to harness the Sun's heat and light for thousands of years. But the practice of converting the Sun’s energy into electricity — what we now call solar power — is less than 200 years old. Yet in that short time, solar power has revealed the Sun’s limitless potential to power an increasingly technological society. Since the 1950s, NASA has harnessed the energy of the Sun to power spacecraft and drive scientific discovery across our solar system. Today, NASA continues to advance solar panel technology and test new innovations. Video credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Lacey Young
A Brief History of Solar Power

Even before the light bulb, scientists had inklings of the power locked up in a ray of sunlight.
In 1839, French scientist Alexandre Edmond Becquerel (who was 19 at the time) was working in his father’s laboratory, experimenting with two metal sheets placed in an electricity-conducting liquid. As he shined light on the device, he detected a weak electric current — what we now know to be a flow of electrons through the material. This phenomenon was the first demonstration that light could generate electricity, known today as the photovoltaic effect.

In 1872, scientists discovered the first solid material — selenium — that could pass an electrical current.
By 1884 selenium had been incorporated in the world’s first solar array, which was installed on a New York City rooftop. Scientists continued to develop and experiment with selenium and other photovoltaic materials for the next 70 years, but practical applications were limited by their low efficiency – only about 1% of light energy could be converted to electricity.

A breakthrough came in 1954.
That's when scientists at Bell Labs used an abundant material called silicon to create the first solar cell that achieved 6% efficiency. Solar panels today use this same basic design, with adjustments that have allowed industrial and commercial solar panels to achieve between 15% and 23% efficiency.
How Solar Panels Work
Silicon is an abundant material used in many technological applications because it is a very good “semiconductor,” or material whose ability to carry electric current can be easily manipulated by adding energy. In typical solar cells, silicon is layered in three thin sheets. A middle layer is made of pure silicon. The outer two silicon layers are injected with other elements (typically phosphorous on one side, and boron on the other) that differ in their capacity to “donate” or “accept” electrons. As light strikes the pure silicon layer, it energizes the silicon’s electrons, which then begin to move within the material. Those electrons are attracted to the silicon layer designed to “accept” electrons, leading to a buildup of negative and positive charges in the outer layers. These two sides are then connected with wires to form a circuit that facilitates the flow of electrons from one side to the other, generating usable power.
Silicon-based solar cells power many of NASA’s spacecraft, including the James Webb Space Telescope. Learn more about why this abundant material is used in solar panels in this excerpt from NASA’s Elements of Webb video series.
Solar Power in Space

A mere four years after the first viable solar cells were created, they made their way to space.
The Soviet Union kicked off the space race with the launch of Sputnik on Oct. 4, 1957, quickly followed by the United States’ Explorer 1 on Jan. 31, 1958. But as both satellites ran exclusively on battery power, they were dead within a few weeks. In March 1958, the United States launched the first solar-powered spacecraft, Vanguard 1 (pictured at right), which transmitted data for the next six years.

Solar cells became the de facto way to power spacecraft, and remain so today.
Some missions, such as NASA’s Parker Solar Probe, require specialized solar panels that can operate in extreme environments. Flying on an elliptical orbit into the Sun’s hot outer atmosphere, Parker Solar Probe uses solar panels angled away and partially shaded from the Sun. It also uses a special cooling system to ensure the system isn’t overwhelmed by heat and was designed to be extra robust to deal with the intense ultraviolet rays it receives when close to the Sun, which can degrade materials rapidly. The spacecraft’s elliptical orbit also takes it far from the Sun, even beyond Venus. Engineers designed the solar array to compensate for how the light changes at different distances to the Sun, which alters the color and intensity of the sunlight it receives.

But sunlight drops dramatically with distance.
At Jupiter, which receives 25 times less light than Earth, the Juno spacecraft (pictured at right) needs three 30-foot-long panels to generate 500 watts of energy — about how much a typical refrigerator uses. Its orbit around Jupiter also helps keep the solar panels almost constantly exposed to sunlight to maximize power generation. Solar power becomes less viable for missions that venture even farther, where there’s not even enough light to charge a battery. Deep space missions like NASA’s Voyager 1 and 2 rely instead on energy from the radioactive decay of plutonium-238 to keep them running well into interstellar space.
How NASA is Improving Solar Power
Perovskites for improved efficiency.
NASA scientists and other researchers around the world are working to improve the efficiency and durability of solar panels. In addition to using silicon, scientists have discovered that adding a layer of minerals known as perovskites can dramatically improve panel efficiency. Perovskites help capture bluer visible wavelengths, complimenting silicon’s redder wavelength coverage and allowing a solar cell to capture more light. In 2023, several independent research teams created small perovskite-silicon solar cells that exceeded 30% efficiency, and the best experimental cells today are approaching 50% efficiency.

ROSAs for Flexibility
NASA is also developing technology for flexible and rollable solar panels that can improve their use in constrained spaces. Using different materials for the base layer of a solar panel can make a panel lighter and more flexible — essential attributes for space missions that need to be packed into a small space in a rocket. The first two sets of solar arrays used by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope in the 1990s and 2000s were designed with solar cells mounted to a flexible blanket-like material so they could be rolled up and stowed to fit inside the space shuttle cargo bay for launch. In 2009, NASA and its partners started working on the next iteration of flexible solar panels called roll-out solar arrays (ROSAs). These arrays, which unfurl like a roll of paper towels, are even lighter and more affordable than previous arrays. They have been used on NASA’s DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Test) mission, on commercial geostationary satellites, and on the International Space Station to augment its traditional solar array. NASA plans to include ROSAs on Gateway, an orbiting outpost crucial to NASA’s Artemis campaign.
Vertical Arrays for Lunar Applications

NASA is also involved with envisioning the next generation of solar power usage in space. To advance the Artemis campaign, NASA tasked three companies with developing and building prototypes of vertical deployable solar array systems to power human and robotic exploration of the Moon. Most space solar array structures are designed to be used horizontally, but on the Moon, vertically oriented structures atop tall masts will be needed to maximize sunlight collection at the lunar poles, where the Sun stays close to the horizon. Scientists are also investigating the feasibility of space-based solar power, which would collect sunlight from space and beam the energy back to Earth, potentially serving remote locations across the planet to supplement power transmission infrastructure on the ground.
The Future of Solar Power in Space
Sailing with the sun.
Along with working to improve the efficiency of solar panels, NASA is also looking beyond photovoltaics to an old technology: sails. Humans have crossed open waters by sail for thousands of years. And now, NASA is working on a system to traverse space using solar sails. Unlike photovoltaics, which work by capturing the energy of light, solar sails use the pressure of light. When a photon, or individual particle of light, bounces off a reflective solar sail, it imparts a small push. With enough photons, these tiny nudges can move an entire spacecraft, much like how traditional sails harness the multitude of tiny air molecules that make up the wind. In the future, solar sails could replace heavy propulsion systems and enable longer-duration and lower-cost missions.
The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System
In 2024, the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System, a microwave-sized spacecraft, launched to test a new composite boom — a sail’s framework — made from materials that are stiffer and lighter than previous boom designs. The spacecraft has a solar sail measuring about 860 square feet — about the size of six parking spots. The seven-meter-long boom that holds out the solar sail can collapse into a bundle that would fit in your hand, which allowed it to fit compactly inside the spacecraft. The mission demonstrated the boom’s deployment and is now testing the sail’s performance using a series of maneuvers to adjust the spacecraft orbit using the sail angle. The technology could eventually allow for future sails up to half the size of a soccer field, enabling travel to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.

Explore NASA's Sun-related stories and download high-resolution images of the solar system, agency missions, and more.

Advanced Composite Solar Sail System (ACS3)
Just as a sailboat is powered by wind in a sail, solar sails employ the pressure of sunlight for propulsion, eliminating the need for conventional rocket propellant.

Oct. 2 Annular Solar Eclipse
On Oct. 2, 2024, the Moon will pass in front of the Sun, casting its shadow across parts of Earth.

Our closest star is so much more than meets the eye.
Related Terms
- Heliophysics
- Heliophysics Division
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Solar energy articles from across Nature Portfolio
Related subjects.
- Artificial photosynthesis
- Photovoltaics
- Solar fuels
- Solar thermal energy
- Thermophotovoltaics
Latest Research and Reviews
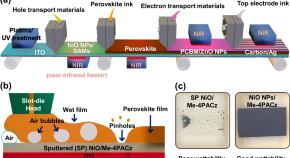
Influence of interfacial roughness on slot-die coatings for scaling-up high-performance perovskite solar cells
Slot-die coating is promising for the large-scale and low-cost manufacture of perovskite solar cells. Here, the effect of wettability of the hole transport layer is investigated, finding that increased surface roughness improves wettability and prevents pinhole formation, favoring solar cell efficiency.
- Sushil Shivaji Sangale
- Dilpreet Singh Mann
Impurity-healing interface engineering for efficient perovskite submodules
- Haifei Wang
- Shuojian Su
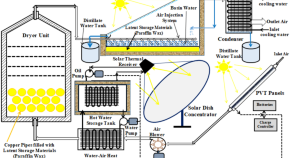
Integrated solar dryer and distillation system with PCM and injection, powered by PVT panels and solar concentrator
- Reda S. Salama
- Habib Ben Bacha
- Abd Elnaby Kabeel
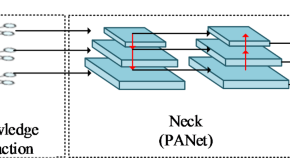
A photovoltaic cell defect detection model capable of topological knowledge extraction
- Zhaoyang Qu
- Lingcong Li
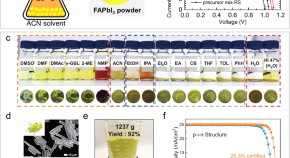
Materials and methods for cost-effective fabrication of perovskite photovoltaic devices
The scalable and cost-effective synthesis of perovskite solar cells is dependent on materials chemistry and the synthesis technique. This Review discusses these considerations, including selecting a suitable perovskite pre-cursor, additive engineering, and the deposition process.
- Chunyang Zhang
- Nam-Gyu Park

The real-time shadow detection of the PV module by computer vision based on histogram matching and gamma transformation method
News and Comment
Combining photovoltaic elements.
- Giulia Tregnago
Testing in the real world
- James Gallagher
Transforming wearable technology with advanced ultra-flexible energy harvesting and storage solutions
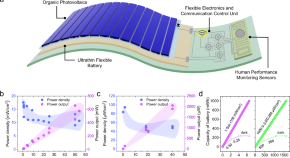
Flexible organic photovoltaics and energy storage systems have profound implications for future wearable electronics. Here, the authors discuss the transformative potential and challenges associated with the integrative design of these systems for energy harvesting.
- Muhammad Jahandar
- Dong Chan Lim
Top performance whatever the doping
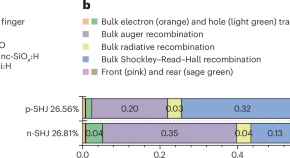
The highest power conversion efficiencies for silicon heterojunction solar cells have been achieved on devices based on n-type doped silicon wafers, yet these wafers are usually more expensive than p-type ones. Now, researchers reduce charge recombination in the bulk of p-type silicon, demonstrating comparable efficiency to devices based on n-type silicon.
- Bernd Stannowski
Chirality for stable interfaces
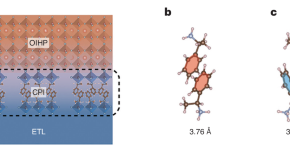
Interfacial engineering is key to ensure the long-term stability of perovskite solar cells. Research now shows that chiral molecules can both improve the mechanical stability of the interfaces and afford passivation of defects at the perovskite surface, making solar cells more tolerant to thermal cycling stress.
- Juan-Pablo Correa-Baena
Smoothing down interfaces
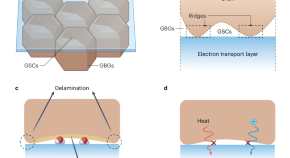
The surfaces of polycrystalline perovskite films impact the long-term performance of perovskite solar cells, yet their microstructure is not well understood. Research now reveals the existence of concave grain structures at the surface of the perovskite layer facing the electron transport layer, and their detrimental effect on the stability of the interface and eventually the devices.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Notification: View the latest site access restrictions, updates, and resources related to the coronavirus (COVID-19) »
Publications
NREL solar researchers actively publish their latest scientific findings and breakthroughs in a newsletter, journal articles, conference papers, technical reports, and presentations.
Solar Newsletter
Read the newsletter . Also, subscribe to receive the newsletter and see the archives .
Featured Publications

Complementary Interface Formation Toward High-Efficiency All-Back-Contact Perovskite Solar Cells , Cell Reports Physical Science (2021)
Steady-State Off-Design Modeling of the Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Recompression Cycle for Concentrating Solar Power Applications With Two-Tank Sensible-Heat Storage , Solar Energy (2020)

Solar Photovoltaic Module Recycling: A Survey of U.S. Policies and Initiatives , NREL Technical Report (2021)
By Research Area
Concentrating solar power
Photovoltaic research
Grid modernization
NREL Publications Database
Find solar research publications in the NREL publications database.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Materials (Basel)

Photovoltaic Cell Generations and Current Research Directions for Their Development
Associated data.
Not applicable.
The purpose of this paper is to discuss the different generations of photovoltaic cells and current research directions focusing on their development and manufacturing technologies. The introduction describes the importance of photovoltaics in the context of environmental protection, as well as the elimination of fossil sources. It then focuses on presenting the known generations of photovoltaic cells to date, mainly in terms of the achievable solar-to-electric conversion efficiencies, as well as the technology for their manufacture. In particular, the third generation of photovoltaic cells and recent trends in its field, including multi-junction cells and cells with intermediate energy levels in the forbidden band of silicon, are discussed. We also present the latest developments in photovoltaic cell manufacturing technology, using the fourth-generation graphene-based photovoltaic cells as an example. An extensive review of the world literature led us to the conclusion that, despite the appearance of newer types of photovoltaic cells, silicon cells still have the largest market share, and research into ways to improve their efficiency is still relevant.
1. Introduction
Concerns about climate change and the increase in demand for electricity due to, among other things, an ever-growing population, necessitate efforts to move away from conventional methods of energy production. Rising carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere caused by the use of fossil fuels is one of the factors causing ongoing climate change. Switching to renewable energy will produce energy with a smaller environmental footprint compared to fossil fuel sources. We are able to harness the full potential of sunlight energy to develop the best possible energy harvesting technologies capable of converting solar energy into electricity [ 1 ].
The currently used solar energy is very marginal—0.015% is used for electricity production, 0.3% for heating, and 11% is used in the natural photosynthesis of biomass. In contrast, about 80–85% of global energy needs are met by fossil fuels. The difficulty with fossil fuels is that their resources are limited and hostile to the environment due to their CO 2 emissions. For instance, for every ton of coal burned, one ton of carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere. This emitted carbon dioxide is toxic to the environment and is a primary cause of global warming, the greenhouse effect, climate change, and ozone depletion [ 2 ].
The necessity of finding new renewable energy forms is extremely relevant and urgent today. That is why mankind must find alternative sources of energy to provide a clean and sustainable future. Within this context, solar energy is the best option among all alternative renewable energy sources due to its widespread accessibility, universality, and eco-friendly nature [ 3 ].
The most common metric used to evaluate the performance of photovoltaic technologies is conversion efficiency, which expresses the ratio of solar energy input to electrical energy output. The efficiency combines multiple component characteristics of the system, such as short-circuit current, open-circuit voltage, and fill factor, which in turn are dependent upon basic material features and manufacturing defects [ 4 ].
The cost-effectiveness of making a photovoltaic cell and its efficiency depend on the material from which it is made. Much research in this field has been carried out to find the material that is the most efficient and cost-effective for building photovoltaic cells. The specifications for an ideal material for PV solar cells include the following [ 5 ]:
- The cells are expected to have a band gap between 1.1 and 1.7 eV;
- Should have a direct band structure;
- Need to be easily accessible and non-toxic; and
- Should have high photovoltaic conversion efficiency [ 5 ].
A key problem in the area of photovoltaic cell development is the development of methods to achieve the highest possible efficiency at the lowest possible production cost. Improving the efficiency of solar cells is possible by using effective ways to reduce the internal losses of the cell. There are three basic types of losses: optical, quantum, and electrical, which have different sources of origin. Reducing losses of any kind requires different, often advanced, methods of cell manufacturing and photovoltaic module production. An upper efficiency limit for commercially accessible technologies is determined by the well-known Shockley–Queisser (SQ) limit, taking into account the balance between photogeneration and radiative recombination [ 6 ].
However, the greatest potential lies in the ability to reduce quantum losses, as they are intimately connected with the material properties and internal structure of the cell. Relevant here is the concept of band gap, which defines the minimum required energy of a photon incident onto the cell surface for it to take part in the photovoltaic conversion process. There is a relationship between the efficiency of the cell and the value of the band gap, which in turn is highly dependent on the material from which the photovoltaic cell is made. The basic, commonly used material for solar cells is silicon, which has a band gap value of about 1.12 eV, but by introducing modifications in its crystal structure, the physical properties of the material, especially the band gap width, can be affected [ 7 ].
The dominant loss mechanisms in conventional photovoltaic cells are the inability to absorb photons below the band gap and the thermalization of solar photons with energies above the band gap energy. Third-generation solar cell concepts have been proposed to address these two loss mechanisms in an attempt to improve solar cell performance. These solutions aim to exploit the entire spectrum by incorporating novel mechanisms to create new electron–hole pairs [ 8 ].
Major development potential among these concepts for improving the power generation efficiency of solar cells made of silicon is shown by the idea of cells whose basic feature is an additional intermediate band in the band gap model of silicon. It is located between the conduction band and the valence band, and its function is to allow the absorption of photons with energies below the width of the energy gap, resulting in higher quantum efficiency (a higher number of excited electrons in relation to the number of photons incident onto the surface of the cell) [ 9 ]. Currently, many directions of research development on the introduction of intermediate bands in semiconductors can be identified. One of them is the use of ion implantation, where two methods can be distinguished: introduction of dopants with extremely high concentrations to the substrate of the semiconductor, and implantation of the layer of silicon with high-dose metal ions [ 10 ].
The improvement of solar cell efficiency involves reducing various types of losses affecting the resultant cell efficiency. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) runs a compilation of the highest verified research cell conversion efficiencies for different photovoltaic technologies, compiled from 1976 to the present ( Figure 1 ). Cell efficiency results are given for each semiconductor family: multi-junction cells; gallium arsenide single-junction cells; crystalline silicon cells; thin film technologies; emerging photovoltaic technologies. The latest world record for an individual technology is indicated by a flag across the right edge containing the efficiency and technology symbol [ 11 ].

NREL Best Research-Cell Efficiencies chart [ 11 ].
Photovoltaic cells can be categorized by four main generations: first, second, third, and fourth generation. The details of each are discussed in the next section.
2. Photovoltaic Cell Generations
In the past decade, photovoltaics have become a major contributor to the ongoing energy transition. Advances relating to materials and manufacturing methods have had a significant role behind that development. However, there are still numerous challenges before photovoltaics can provide cleaner and low-cost energy. Research in this direction is focused on efficient photovoltaic devices such as multi-junction cells, graphene or intermediate band gap cells, and printable solar cell materials such as quantum dots [ 12 ].
The primary role of a photovoltaic cell is to receive solar radiation as pure light and transform it into electrical energy in a conversion process called the photovoltaic effect. There are several technologies involved with the manufacturing process of photovoltaic cells, using material modification with different photoelectric conversion efficiencies in the cell components. Due to the emergence of many non-conventional manufacturing methods for fabricating functioning solar cells, photovoltaic technologies can be divided into four major generations, which is shown in Figure 2 [ 13 ].

Various solar cell types and current developments within this field [ 14 ].
The generations of various photovoltaic cells essentially tell the story of the stages of their past evolution. There are four main categories that are described as the generations of photovoltaic technology for the last few decades, since the invention of solar cells [ 15 ]:
- First Generation: This category includes photovoltaic cell technologies based on monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon and gallium arsenide (GaAs).
- Second Generation: This generation includes the development of first-generation photovoltaic cell technology, as well as the development of thin film photovoltaic cell technology from “microcrystalline silicon (µc-Si) and amorphous silicon (a-Si), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) and cadmium telluride/cadmium sulfide (CdTe/CdS) photovoltaic cells”.
- Third Generation: This generation counts photovoltaic technologies that are based on more recent chemical compounds. In addition, technologies using nanocrystalline “films,” quantum dots, dye-sensitized solar cells, solar cells based on organic polymers, etc., also belong to this generation.
- Fourth Generation: This generation includes the low flexibility or low cost of thin film polymers along with the durability of “innovative inorganic nanostructures such as metal oxides and metal nanoparticles or organic-based nanomaterials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes and graphene derivatives” [ 15 ].
Examples of solar cell types for each generation along with average efficiencies are shown in Figure 3 .

Examples of photovoltaic cell efficiencies [ 16 ].
2.1. First Generation of Photovoltaic Cells
Silicon-based PV cells were the first sector of photovoltaics to enter the market, using processing information and raw materials supplied by the industry of microelectronics. Solar cells based on silicon now comprise more than 80% of the world’s installed capacity and have a 90% market share. Due to their relatively high efficiency, they are the most commonly used cells. The first generation of photovoltaic cells includes materials based on thick crystalline layers composed of Si silicon. This generation is based on mono-, poly-, and multicrystalline silicon, as well as single III-V junctions (GaAs) [ 17 , 18 ].
Comparison of first-generation photovoltaic cells [ 18 ]:
- Solar cells based on monocrystalline silicon (m-si)
Efficiency : 15 ÷ 24%; Band gap : ~1.1 eV; Life span : 25 years; Advantages : Stability, high performance, long service life; Restrictions : High manufacturing cost, more temperature sensitivity, absorption problem, material loss.
- Solar cells based on polycrystalline silicon (p-si)
Efficiency : 10 ÷ 18%; Band gap : ~1.7 eV; Life span : 14 years; Advantages : Manufacturing procedure is simple, profitable, decreases the waste of silicon, higher absorption compared to m-si; Restrictions : Lower efficiency, higher temperature sensitivity.
- Solar cells based on GaAs
Efficiency : 28 ÷ 30%; Band gap : ~1.43 eV; Life span : 18 years; Advantages : High stability, lower temperature sensitivity, better absorption than m-si, high efficiency; Restrictions : Extremely expensive [ 18 ].
The first generation concerns p-n junction-based photovoltaic cells, which are mainly represented by mono- or polycrystalline wafer-based silicon photovoltaic cells. Monocrystalline silicon solar cells involve growing Si blocks from small monocrystalline silicon seeds and then cutting them to form monocrystalline silicon wafers, which are fabricated using the Czochralski process ( Figure 4 a). Monocrystalline material is widely used due to its high efficiency compared to multicrystalline material. Key technological challenges associated with monocrystalline silicon include stringent requirements for material purity, high material consumption during cell production, cell manufacturing processes, and limited module sizes composed of these cells [ 19 ].

A picture showing ( a ) the Czochralski process for monocrystalline blocks and ( b ) the process of directional solidification for multicrystalline blocks [ 21 ].
Multicrystalline silicon blocks are produced through melting high-purity silicon and crystallizing it in a big crucible by directional solidification process ( Figure 4 b). There is no reference crystal orientation in this process, as in the Czochralski process, and therefore, silicon material with different orientations is produced. The most commonly used base material for solar cells are p-type Si substrates doped with boron. The n-type silicon substrates are also used for the fabrication of high-efficiency solar cells, but they present additional technical challenges, such as achieving uniform doping along the silicon block in comparison to p-type substrates [ 20 ].
In the production of crystalline solar cells, six or more steps need to be carried out sequentially. These typically include surface texturing, doping, diffusion, oxide removal, anti-reflective coating, metallization, and firing. At the end of the process, the cell efficiency and other parameters are measured (under standard test conditions). The efficiency of photovoltaic cells is determined by the material quality that is used in their manufacture [ 21 ].
The theoretical efficiency threshold for first-generation PV cells appears to have been estimated at 29.4%, and a sufficiently close value was reached as early as two decades ago. At the laboratory scale, reaching 25% efficiency was recorded as early as 1999, and since then, very minimal improvements in efficiency values have been achieved. Since the appearance of crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells, their efficiency has increased by 20.1%, from 6% when they were first discovered to the current record of 26.1% efficiency. There are factors that limit cell efficiency, such as volume defects. Breakthroughs in the production of these cells include the introduction of an aluminum back surface field (Al-BSF) to reduce the recombination rate on the back surface, or the development of Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) technology to further reduce the recombination rate on the back surface [ 22 ].
2.1.1. Al-BSF Photovoltaic Cells
Silicon solar cells with distributed p-n junctions were invented as early as the 1950s, soon after the first semiconductor diodes. Originally, boron diffusion in arsenic-doped wafers was used to form p-n junctions, but now, the industry standard is phosphor diffusion in boron-doped wafers. After the transition in the 1960s from n-type wafers to p-type wafers, the implementation of an aluminum back-surface field (Al-BSF) by fusing the back contact to the substrate made it possible to reduce recombination on the back side ( Figure 5 ). This fairly simple contact screen printing design held a dominant position, with 70–90% of the market share for the past several decades [ 23 ].

Silicon solar cell structure: Al-BSF [ 1 ].
Standard aluminum back surface field (Al-BSF) technology is one of the most widely used solar cell technologies due to its relatively simple manufacturing process. It is based on depositing Al entirely on the full rear-side (RS) in a screen-printing process and forming a p+ BSF, which helps repel electrons from the rear-side of the p-type substrate and improves the cell performance. The process flow of Al-BSF solar cell fabrication is shown in Figure 6 . Standard commercial solar cell design consists of a front side with a grid and a rear-side with full area contacts [ 24 ].

Al-BSF solar cell manufacturing process [ 21 ].
2.1.2. PERC Photovoltaic Cells
The efficiency of the industrial Al-BSF cell, however, reached about 20% around 2013. It has therefore become attractive to replace the fully contacted Al-BSF cell with a PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) structure with local back contacts to achieve enhanced electrical and optical properties ( Figure 7 ). The passivated emitter and rear contact (PERC) solar cell improves the Al-BSF architecture by the addition of a passivation layer on the rear side to improve passivation and internal reflection. Aluminum oxide has been found to be a suitable material for rear side passivation [ 25 ].

Silicon solar cell structure: PERC [ 1 ].
The capability of this cell structure was demonstrated as early as the 1980s, although it was limited to laboratory processing because of its high cost relative to the yield gain. Moving the PERC technology into mass industrial production in theory involved a comparatively small industry threshold, as only two steps needed to be added to the Al-BSF process, i.e., passivation of the back surface and precise calibration of local back contacts. Nevertheless, decades passed before a profitable PERC process could be developed. A number of reasons led to the implementation of PERC in low-cost, high-volume production, and the increase in productivity to levels ranging from 22% to 23.4% [ 26 ]:
- Introduction of aluminum oxide back surface passivation by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) and formation of local back surface field (BSF) by laser ablation of back passivation layer and Al alloy;
- Introduction of a selective emitter process in low-cost manufacturing, a “back-etching” process, or through a laser doping process;
- Reducing the width of front metallization fingers from about 100 μm to less than 30 μm in high-volume production while reducing contact resistance for lightly phosphorus-doped silicon;
- Adding a low-cost hydrogenation step at the end of the cell formation process to passivate volume defects and inactivate boron–oxygen complexes responsible for light-induced degradation (LID); and
- Reappearance of monocrystalline silicon wafers as a result of cost reduction in silicon ingot production by the Czochralski method and the introduction of diamond wire cutting [ 27 ].
2.1.3. SHJ-Type Photovoltaic Cells
In parallel with PERC cells, other high-performance cell designs such as interdigitated back contact (IBC) solar cells and heterojunction solar cells (SHJ) have been introduced to mass production. Silicon heterojunction solar cells (SHJ), otherwise referred to as HIT cells, use passivating contacts based on a stack of layers of intrinsic and doped amorphous silicon ( Figure 8 ). Among the major technological challenges associated with this promising cell structure is that once the amorphous silicon layer is deposited, processes above 200 °C cannot be used. This rules out the well-known burned-in screen-printed metal contacts, and thus demands alternative methods using low-temperature pastes or galvanic contacts [ 28 ].

Silicon solar cell structures: heterojunction (SHJ) in rear junction configuration [ 1 ].
There are currently intensive efforts to develop high-capacity production lines that could be competitive with present production standard lines. For SHJ technology to become widespread, there will be a need to overcome the challenges of increased cost of cell manufacturing tools, reducing the use of silver or replacing it with copper by developing Cu electroplating technology, as well as reducing the use of indium in the transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layer [ 29 ].
Moreover, as shown in Figure 9 , the HIT solar cell has a symmetric structure, which has two advantages. One is that the cell can be used in what is known as a bifacial module, which can generate more electricity than a regular module, and the other is that the structure is less stressed, which is important when processing thinner wafers [ 30 ].

Structure of an HIT solar cell [ 30 ].
2.1.4. Photovoltaic Cells Based on Single III-V Junctions
GaAs-based single III-V junctions are reviewed at the end of this section. The III-V materials give the greatest photovoltaic conversion efficiency, achieving 29.1% with a GaAs single junction under single sunlight and 47.1% for a six-junction device under concentrated sunlight. These devices are also thinner (absorption layers typically being 2 to 5 µm thick) and thus could be fabricated as lightweight, flexible devices capable of being placed on curved surfaces. The III-V devices have high stability and have a history of high performance for challenging applications such as space [ 31 ].
The dominant III-V layer deposition process, metal–organic vapor phase epitaxy (MOVPE), holds the responsibility behind practically every performance record for III-V devices. Yet, historically, this process has been considered as a costly growth technique because of the high cost of precursors, the comparatively low usage of these precursors, and batch growth cycles that require many hours to be completed. Latest studies have significantly improved the growth rate and demonstrated much greater use of precursor chemicals using both MOVPE and hydrogen vapor phase epitaxy (HVPE) techniques, with HVPE also solving the precursor cost problem. Finishing currently includes a great number of labor-intensive, high-priced, and comparatively inefficient process steps, involving photolithography, manual application of spin coating, contact alignment, and metal evaporation and lifting [ 32 ].
2.2. Second Generation of Photovoltaic Cells
The thin film photovoltaic cells based on CdTe, gallium selenide, and copper (CIGS) or amorphous silicon have been designed to be a lower-cost replacement for crystalline silicon cells. They offer improved mechanical properties that are ideal for flexible applications, but this comes with the risk of reduced efficiency. Whereas the first generation of solar cells was an example of microelectronics, the evolution of thin films required new methods of growing and opened the sector up to other areas, including electrochemistry [ 33 ].
The second-generation photovoltaic cell comparison [ 18 ]:
- Solar cells based on amorphous silicon (a-si)
Efficiency : 5 ÷ 12%; Band gap : ~1.7 eV; Life span : 15 years; Advantages : Less expensive, available in large quantities, non-toxic, high absorption coefficient; Restrictions : Lower efficiency, difficulty in selecting dopant materials, poor minority carrier lifetime.
- Solar cells based on cadium telluride/cadium sulfide (CdTe/CdS)
Efficiency : 15 ÷ 16%; Band gap : ~1.45 eV; Life span : 20 years; Advantages : High absorption rate, less material required for production; Restrictions : Lower efficiency, Cd being extremely toxic, Te being limited, more temperature-sensitive.
- Solar cells based on copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS)
Efficiency : 20%; Band gap : ~1.7 eV; Life span : 12 years; Advantages : Less material required for production; Restrictions : Very high-priced, not stable, more temperature-sensitive, highly unreliable [ 18 ].
2.2.1. CIGS Photovoltaic Cells
A key aspect that needed improvement was reducing the high dependence on semiconductor materials. This was the driving force that led to the emergence of the second generation of thin film photovoltaic cells, which include CIGS. In terms of efficiency, the record value for CIGS is 23.4%, which is comparable to the best silicon cell efficiencies. It should be noted, however, that the efficiency of the research cells does not directly translate to industrially achievable efficiency due to the nature of large-scale processing. Nevertheless, module efficiencies above 20% are already a reality. There has been a significant increase in the efficiency of CIGS cells in recent years and further increases are expected, for example, as a result of further research into alkaline treatment after deposition [ 34 ].
Group I-III-VI semiconducting chalcopyrite alloys (Ag,Cu)(In,Ga)(S,Se) 2 , commonly known as CIGS, are particularly favorable absorber materials for solar cells. They have direct band gaps ranging from ~1 to 2.6 eV, high absorption coefficients, and favorable internal defect parameters that allow high minority carrier lifetimes, and solar cells made from them are inherently stable in operation. The first recorded yield was 12% in a monocrystalline device in the mid-1970s. Subsequently, CIGS thin film absorbers, processing, and contacts were greatly improved, resulting in thin film cells with a small area and an efficiency of 23.4%. Current record module efficiencies are 17.6% on glass and 18.6% on flexible steel [ 35 ].
CIGS solar cells have been developed in a standard substrate configuration; however, deposition of CIGS at comparatively low temperatures on metal or polymer substrates to form flexible solar products is also possible. CIGS thin films are mainly being deposited by co-evaporation/devaporation or sputtering, and to a minor extent by electrochemical deposition as well as ion beam-assisted deposition. Since these are quaternary compounds, it is critical to control the stoichiometry of the thin film during fabrication. Work is also underway to produce fully or partially solution-deposited CIGS solar cells, and some predict that they could be the ultimate path to ultra-thin, coiled, and flexible PV modules [ 36 ].
The steps to improve the efficiency of CIGS cells may be described in the following way: (1) evaporation of CIS compound; (2) reactive elemental bilayer deposition; (3) selenization of sputtered metal precursors; (4) chemical bath deposition of CdS with ZnO:Al as emitter; (5) gallium alloying; (6) sodium alkali incorporation; (7) three-step co-deposition; (8) post-deposition treatment involving heavy alkali ion exchange; and (9) sulfurization after selenization (SAS). Progress is far from linear, with the complete potential for the optimization of the complex interactions between those techniques, along with others under development (e.g., silver alloys), yet to be achieved. A large number of scientists who specialize in CIGS think that efficiencies of 25% can be reached [ 37 ].
CIGS is a versatile material that can be produced by many processes and used in a variety of forms. There are currently four main categories of depositing methods used to fabricate CIGS films: (1) metal precursor deposition followed by sulfo-selenization; (2) reactive co-deposition; (3) electrodeposition; and (4) solution processing. All recent world records and the greatest commercial successes have been achieved by two-step sulfo-selenization of metal precursors or reactive co-deposition. CIGS can be deposited on a variety of substrates, including glass, metal films, and polymers. Glass is suitable for making rigid modules, while metal and polymer films allow applications that require lighter or flexible modules. With the evolution of global energy markets toward an appreciation of greenhouse gas reduction and circular economy aspects, the comparatively benign environmental impact of CIGS (especially without CdS) in comparison to different photovoltaic technologies is becoming the next competitive advantage [ 38 ].
Photovoltaic cells based on CIGS technology are composed of a pile of thin films deposited on a glass substrate by magnetron sputtering: a bottom molybdenum (Mo) electrode, a CIGS absorbing layer, a CdS buffer layer, and a zinc-doped oxide (ZnO:Al) top electrode. The co-evaporation and CdS buffer layer deposit the CIGS active layer by means of a chemical bath in a regular procedure ( Figure 10 ) [ 38 ].

Demonstration of the CIGS-based standard solar cell stack [ 38 ].
2.2.2. CdTe Photovoltaic Cells
Second-generation photovoltaic cells also include CdTe-based solar cells. An interesting property of CdTe is the reduction in cell size—due to its high spectral efficiency, the absorber thickness can be reduced to about 1 μm without much loss in efficiency, although further work is needed ( Figure 11 ). Super-thin cells are particularly attractive for flexible applications, particularly in building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) due to their lighter weight, and transparent photovoltaic panels with CdTe can be developed due to the choice of transparent coating. Their transparency varies from about 10% to 50%, with the disadvantage that an increase in transparency necessarily decreases efficiency. Still, the transparent panels could replace window panels in buildings, not only generating electricity that could be used to power itself, but also contributing to noise reduction and thermal insulation, since most panels are encased in double glass [ 39 ].

Schematic of a CdTe solar cell [ 1 ].
The technology of CdTe solar cells has developed considerably with the passage of time. In the 1980s, the efficiency of certified cells reached 10%, and in the 1990s, the efficiency was above 15% with the use of a glass/SnO 2 /CdS/CdTe layer structure and annealing in a CdCl 2 environment, and subsequent Cu diffusion. By the 2000s, efficiency of the cells hit 16.7% using sputtered Cd 2 SnO 4 and Zn 2 SnO 4 as transparent conductive oxide (TCO) layers. Over the past decade, new cell efficiency records have reached 22.1%. CdTe technology is increasingly used in rooftop systems and building-integrated photovoltaics [ 40 ].
In 2001, NREL produced a cell with an efficiency of 16.5%, which remained the benchmark for about 10 years. The record efficiency has been improved several times in the past 2 years by First Solar and GE Global Research. Currently, CdTe thin films account for less than 10% of the global PV market, with capacity expected to increase. Most of the commercial CdTe cells are manufactured by First Solar, which has achieved record cell efficiencies of 22.1% and average commercial module efficiencies of 17.5–18% [ 41 ].
The history of research and development and production of CdTe-based PV cells begins several decades beyond the first studies conducted by Bell Labs (Murray Hill, NJ, USA) in the 1950s on Si crystalline cells. The leading companies have been working on the commercialization of the underlying technology: Matsushita (Kadoma, Osaka, Japan), BP Solar (Madrid, Spain), Solar Cells Inc.—predecessor to First Solar (Tempe, AZ, USA), Abound Solar (Loveland, CO, USA) and GE PrimeStar (Denver, CO, USA). The top manufacturer of thin film CdTe PV is currently First Solar Solar (Tempe, AZ, USA), having fabricated 25 GW of PV modules since 2002 [ 42 ].
A range of comparatively easy and inexpensive approaches have been used to produce solar cells with 10–16% efficiency. Examples of several promising cheap deposition techniques include (1) close-space sublimation, (2) spray deposition, (3) electrodeposition, (4) screen printing, and (5) sputtering [ 43 ].
Recently, a record efficiency of 16% was reported in a CdS (0.4 μm)/CdTe (3.5 μm) thin film solar cell in which CdS and CdTe layers are deposited using metal–organic CVD (MOCVD) and CSS deposition techniques, respectively. Most of the high-performance solar cells use a device configuration of the superstrate type, where CdTe is deposited on a window layer of CdS. Typically, the structure of the device is composed of glass/CdS/CdTe/Cu-C/Ag. Most of the time, post-deposition heat treatment of the CdTe layer in the presence of CdCl 2 is necessary to optimize device performance [ 44 ].
The recent increase in efficiency is due partly to almost maximum photocurrent by optimizing the optical properties of the cell, deleting parasitically absorbing CdS and introducing CdSe x Te 1−x with a lower band gap. CdSe x Te 1-x extends the bandwidth of the absorber from ~1.4 to 1.5 eV and increases the carrier lifetime, thus improving photocurrent collection with no proportional loss of photocurrent. The use of ZnTe in the rear contact also improves the contact ohmicity significantly, and thus the efficiency [ 45 ].
2.2.3. Kesterite Photovoltaic Cells
In recent years, kesterite thin film materials have attracted more interest than CdTe and CIGS chalcogenide materials. Cu 2 ZnSnS x Se 4−x (CZTSSe) thin film photovoltaic material is attracting worldwide attention for its exceptional efficiency and composition derived from the Earth. A lot of research is being conducted on material engineering or designing new architecture to achieve high-performance CZTSSe thin film solar cells. Until recently, the most advanced thin film CZTSSe solar cells have been limited to 11.1% power conversion efficiency (PCE), with these efficiency levels reached using the hydrazine suspension method. Further vacuum and non-vacuum deposition techniques also proved effective in producing CZTSSe solar cells that had a PCE above 8%. Yet still, even record equipment with a PCE of 11% is significantly below the physical limit, generally referred to as the Shockley–Queisser (SQ) limit, which is around 31% efficiency under the Earth’s conditions [ 46 ].
A hydrazine-based pure solution method is used to prepare CZTSSe layers, and a Cu-poor and Zn-rich stoichiometry is adopted in the starting solution (Cu/(Zn + Sn) = 0.8 and Zn/Sn = 1.1). Multiple layers of components are spin-coated onto Mo-coated soda-lime glass and annealed at temperatures above 500 °C. Regarding the fabrication of devices, CZTSSe layers are deposited on Mo-coated glass substrates, then 25 nm CdS is deposited in a standard chemical bath and sputtered with 10 nm ZnO/50 nm ITO. A 2 μm thick Ni/Al top metal contact and 110 nm MgF 2 should be deposited on top of the devices by electron beam evaporation. The area of the device should be determined by mechanical scribing [ 47 ].
2.2.4. Photovoltaic Cells Based on Amorphous Silicon
The last type of cells classified as second-generation are devices that use amorphous silicon. Amorphous silicon (a-Si) solar cells are by far the most common thin film technology, whose efficiency is between 5% and 7%, rising to 8–10% for double and triple junction structures. Some varieties of amorphous silicon (a-Si) are amorphous silicon carbide (a-SiC), amorphous germanium silicon (a-SiGe), microcrystalline silicon (μ-Si), and amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiN). Hydrogen is required to dope the material, leading to hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H). The gas phase deposition technique is typically used to form a-Si photovoltaic cells with metal or gas as the substrate material [ 48 ].
A typical manufacturing process for a-Si:H cells is the roll-to-roll process. First, a cylindrical sheet, usually stainless steel, is rolled out to be used as a deposition surface. The sheet is washed, cut to the desired size, and coated with an insulating layer. Next, a-Si:H is applied to the reflector, after which a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) is deposited on the silicon layer. Finally, laser cuts are made to join the different layers and the module is closed [ 49 ].
Amorphous silicon is usually deposited by plasma-enhanced vapor phase deposition (PECVD) at comparatively low substrate temperatures of 150–300 °C. A 300 nm thick a-Si:H layer is capable of absorbing about 90% of photons above the passband in a single pass, allowing the fabrication of lighter and more flexible solar cells [ 2 ].
Figure 12 shows the step-by-step fabrication process of an a-Si-based photovoltaic cell. Photovoltaic cells based on thin films are cheaper, thinner, and more flexible compared to first generation photovoltaic cells. The thickness of the light absorbing layer, which was 200–300 µm in first-generation photovoltaic cells, is 10 µm in second-generation cells. Semiconductor materials ranging from “micromorphic and amorphous silicon” to quaternary or binary semiconductors such as “cadmium telluride (CdTe) and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS)” are used in thin films of photovoltaic cells [ 50 ].

Manufacturing process of a-Si-based solar PV cell [ 2 ].
2.3. Third Generation of Photovoltaic Cells
The third generation of solar cells (including tandem, perovskite, dye-sensitized, organic, and emerging concepts) represent a wide range of approaches, from inexpensive low-efficiency systems (dye-sensitized, organic solar cells) to expensive high-efficiency systems (III-V multi-junction cells) for applications that range from building integration to space applications. Third-generation photovoltaic cells are sometimes referred to as “emerging concepts” because of their poor market penetration, even though some of these have been studied for more than 25 years [ 51 ].
The latest trends in silicon photovoltaic cell development are methods involving the generation of additional levels of energy in the semiconductor’s band structure. The most advanced studies of manufacturing technology and efficiency improvements are now concentrated on third-generation solar cells.
One of the current methods to increase the efficiency of PV cells is the introduction of additional energy levels in the semiconductor’s band gap (IBSC and IPV cells) and the increasing use of ion implantation in the manufacturing process. Other innovative third-generation cells that are lesser-known commercial “emerging” technologies include [ 52 ]:
- Organic materials (OSC) photovoltaic cells;
- Perovskites (PSC) photovoltaic cells;
- Dye-sensitized (DSSC) photovoltaic cells;
- Quantum dots (QD) photovoltaic cells; and
- Multi-junction photovoltaic cells [ 52 ].
Third-generation photovoltaic cell comparison [ 18 ]:
- Solar cells based on dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells
Efficiency : 5 ÷ 20%; Advantages : Lower cost, low light and wider angle operation, lower internal temperature operation, robustness, and extended lifetime; Restrictions : Problems with temperature stability, poisonous and volatile substances.
- Solar cells based on quantum dots
Efficiency : 11 ÷ 17%; Advantages : Low production cost, low energy consumption; Restrictions : High toxicity in nature, degradation.
- Solar cells based on organic and polymeric photovoltaic cells
Efficiency : 9 ÷ 11%; Advantages : Low processing cost, lighter weight, flexibility, thermal stability; Restrictions : Low efficiency.
- Solar cells based on perovskite
Efficiency : 21%; Advantages : Low-cost and simplified structure, light weight, flexibility, high efficiency, low manufacturing cost; Restrictions : Unstable.
- Multi-junction solar cells
Efficiency : 36% and higher; Advantages : High performance; Restrictions : Complex, expensive [ 18 ].
2.3.1. Organic and Polymeric Materials Photovoltaic Cells (OSC)
Organic solar cells (OSCs) are beneficial in applications related to solar energy since they have the potential to be used in a variety of prospects on the basis of the unique benefits of organic semiconductors, including their ability to be processed in solution, light weight, low cost, flexibility, semi-transparency, and applicability to large-scale roll-to-roll processing. Solution-processed organic solar cells (OSCs) that absorb near-infrared (NIR) radiation have been studied worldwide for their potential to be donor:acceptor bulk heterojunction (BHJ) compounds. In addition, NIR-absorbing OSCs have attracted attention as high-end equipment in next-generation optoelectronic devices, such as translucent solar cells and NIR photodetectors, because of their potential for industrial applications. With the introduction of non-fullerene acceptors (NFAs) that absorb light in the NIR range, the value of OSC is increasing, while organic donor materials capable of absorbing light in the NIR range have not yet been actively studied compared to acceptor materials that absorb light in the NIR range [ 53 ].
The most advanced BHJ structure by combining organic donor and acceptor materials showed tremendous hope for low-cost and lightweight organic solar cells. Over the past decade, enormous progress was made, with power conversion efficiencies reaching more than 14% for a single-junction device and more than 17% for a tandem device through the design of new NIR photoactive materials with low bandwidth. Compared to wide-band organic photovoltaic materials, low-band donor and non-fullerene acceptor materials with wide-range solar coverage extended to the NIR region typically exhibit more tightly superimposed electronic orbitals, easier delocalization of π electrons, higher dielectric constant, stronger dipole moment, and lower exciton binding energy. These properties make low-bandwidth photovoltaic materials play an important role in high-performance organic solar cells, including single-junction and tandem devices [ 54 ].
A clever strategy in active layer design could be summed up as optimizing the weight ratio of donor to acceptor materials, using ultra-low band gap materials as a third component to improve NIR light utilization efficiency, and adjusting the thickness of the active layer to achieve a compromise between photon collection and charge accumulation. Much effort has gone into optimizing the translucent top electrode: well-balanced conductivity and transmittance in the visible light range, increased reflectance in the NIR or ultraviolet (UV) light range, and better compatibility with active layers. In terms of device engineering, photon crystal, anti-reflection coating, optical microcavity, and dielectric/metal/dielectric (DMD) structures have been placed to realize selective transmission and reflection for simultaneous improvement of power conversion efficiency and average transmission of translucent OSC visible light [ 55 ].
2.3.2. Dye-Sensitized Photovoltaic Cells (DSSC)
Conjugated polymers and organic semiconductors have been successful in flat panel displays and LEDs, so they are considered advanced materials in the current generation of photovoltaic cells. A schematic representation of dye-sensitized organic photovoltaic cells (DSSCs) is shown in Figure 13 . Polymer/organic photovoltaic cells can also be divided into dye-sensitized organic photovoltaic cells (DSSCs), photoelectrochemical photovoltaic cells, and plastic (polymer) and organic photovoltaic devices (OPVDs), differing in mechanism of operation [ 56 ].

Schematic representation of a DSSCs [ 2 ].
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) represent one of the best nanotechnology materials for energy harvesting in photovoltaic technologies. It is a hybrid organic–inorganic structure where a highly porous, nanocrystalline layer of titanium dioxide (TiO 2 ) is used as a conductor of electrons in contact with an electrolyte solution also containing organic dyes that absorb light near the interfaces. A charge transfer occurs at the interface, resulting in the transport of holes in the electrolyte. The power conversion efficiency has been shown to be about 11%, and commercialization of dye-sensitized photovoltaic modules is underway. A novel feature in DSSC solar cells is the photosensitization of nanosized TiO 2 coatings in combination with optically active dyes, which increases their efficiency to more than 10% [ 57 ].
DSSCs hold promise as photovoltaic devices because of their simple fabrication, low material costs, and their benefits in transparence, color capability, and mechanical flexibility. The main challenges in commercializing DSSCs are poor photoelectric conversion efficiency and cell stability. The highest attainable theoretical energy conversion efficiency was estimated at 32% for DSSCs; however, the highest efficiency reported to date is only 13%. Intensive work is underway to understand the parameters governing the DSSC to improve its efficiency. Numerous attempts have been made to optimize the redox pair and absorbance of the dye, modify a wide band gap semiconductor as a working electrode, and develop a counter electrode (CE). In addition to increasing the efficiency of DSSC, the cost of materials is another major issue that needs to be solved in future work [ 58 ].
2.3.3. Perovskite Photovoltaic Cells
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are a revolutionary new photovoltaic cell concept that relies on metal halide perovskites (MHPs), e.g., methylammonium iodide as well as formamidine lead iodide (MAPbI 3 or FAPbI 3 , respectively). MHPs integrate a number of features favored in photovoltaic absorbers, including a direct band gap with a high absorption coefficient, long carrier lifetime and diffusion length, low defect density, and ease of tuning the composition and band gap. In the year 2009, MHP was first described as a sensitizer in a dye cell based on liquid electrolyte conducting holes. In 2012, MHP demonstrating ~10% efficiency of PSCs based on a solid-state hole conductor sparked an explosion of PSC studies. In about a decade of research, the efficiency of a single PSC junction increased to a certified level of 25.2% [ 59 ].
The development of PSCs has been heavily influenced by the improvement of material quality through a broad range of synthetic methods designed under the guidance of a fundamental understanding of MHP growth mechanisms. Comprehension of the complex and correlated processes of perovskite growth (e.g., nucleation, grain growth, as well as microstructure evolution) has aided in the development of a broad range of high-efficiency growth modes (for example, single-step growth, sequential growth, dissolution process, vapor process, post-deposition processing, non-stoichiometric growth, additive-assisted growth, and fine-tuning of structure dimensions). The latest efforts were concentrated on interface engineering, focusing on reducing open-circuit voltage losses and improving stability, particularly by introducing a two-dimensional perovskite surface layer. With progress in synthetic control, the perovskite composition is becoming simpler, mainly toward FAPbI 3 . This will undoubtedly contribute to the simplification of scale deposition methods and a basic understanding of the properties of these cells [ 60 ].
2.3.4. Quantum Dots Photovoltaic Cells
Solar cells made from these materials are called quantum dots (QDs) and are also known as nanocrystalline solar cells. They are fabricated by epitaxial growth on a substrate crystal. Quantum dots are surrounded by high potential barriers in a three-dimensional shape, and the electrons and electron holes in a quantum dot become discrete energy because they are confined in a small space ( Figure 14 ). Consequently, the ground state energy of electrons and electron holes in a quantum dot depends on the size of the quantum dot [ 61 ].

( a ) A scheme of a solar cell based on quantum dots, ( b ) solar cell band diagram [ 64 ].
Nanocrystalline cells have relatively high absorption coefficients. Four consecutive processes occur in a solar cell: (1) light absorption and exciton formation, (2) exciton diffusion, (3) charge separation, and (4) charge transport. Due to the poor mobility and short lifetime of excitons in conducting polymers, organic compounds are characterized by small exciton diffusion lengths (10–20 nm). In other words, excitons that form far from the electrode or carrier transport layer recombine and the conversion efficiency drops [ 62 ].
The development of thin film solar cells with metal halide perovskites has led to intensive attention to the corresponding nanocrystals (NCs) or quantum dots (QDs). Today, the record efficiency of QD solar cells was improved to 16.6% using mixed colloidal QDs with perovskites. The universality of these new nanomaterials regarding ease of fabrication and the ability to tune the band gap and control the surface chemistry allows a variety of possibilities for photovoltaics, such as single-junction, elastic, translucent, controlled cells with heterostructures and multi-junction tandem solar cells which would push the field even further. However, a narrower size distribution has the potential to enhance the performance of QD solar cells through more ways than one. Firstly, electron transport might be better in smaller QDs, as larger QDs function as a band tail or shallow trap that makes transport more difficult. Secondly, the open-circuit voltage (V OC ) of QD solar cells could be limited by the smallest band gap (largest size) QD near the contacts. Enhancing the homogeneity and uniformity of QD size would also improve PV performance by the minimization of such losses. Although controlled experiments such as these have not yet been reported, it is possible that more controlled synthesis might provide benefits to QD cells [ 63 ].
2.3.5. Multi-Junction Photovoltaic Cells
Multi-junction (MJ) solar cells consist of plural p-n junctions fabricated from various semiconductor materials, with each junction producing an electric current in response to light of a different wavelength, thereby improving the conversion of incident sunlight into electricity and the efficiency of the device. The concept to use various materials with different band gaps has been suggested to utilize the maximum possible number of photons and is known as a tandem solar cell. An entire cell could be fabricated from the same or different materials, giving a broad spectrum of possible designs [ 65 ].
Usually, the cells are integrated monolithically and connected in series through a tunnel junction, and current matching between cells is obtained through adjusting each cell’s band gap and thickness. The theoretical feasibility of using multiple band gaps was examined and was found to be 44% for two band gaps, 49% for three band gaps, 54% for four band gaps, and 66% for an infinite number of gaps. Figure 15 illustrates a scheme of an InGaP/(In)GaAs/Ge triple solar cell and presents crucial technologies to enhance efficiency of conversion [ 66 ].

Schematic illustration of a triple-junction cell and approaches for improving efficiency of the cell [ 65 ].
Grid-matched InGaP/(In)GaAs/Ge triple solar cells have been widely used in space photovoltaics and have achieved the highest true efficiency of over 36%. Heavy radiation bombardment of various energetic particles in the space environment inevitably damages solar cells and causes the formation of additional non-radiative recombination centers, which reduces the diffusion length of minority carriers and leads to a reduction in solar cell efficiency. The sub-cells in multi-junction solar cells are connected in series; the sub-cell with the greatest radiation degradation degrades the efficiency of the multi-junction solar cell. To improve the radiation resistance of (In)GaAs sub-cells, measures such as reducing the dopant concentration, decreasing the thickness of the base region, etc., can be used [ 66 ].
2.3.6. Photovoltaic Cells with Additional Intermediate Band
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) estimates that multi-junction and IBSC photovoltaic cells have the highest efficiency under experimental conditions (47.1%). The main feature of these cells is precisely the additional intermediate band in the band gap of silicon. Currently, two types of these cells are specified in the world literature: IBSC (Intermediate Band Solar Cells) and IPV (Impurity Photovoltaic Effect) [ 67 ].
Impurity Photovoltaic Effect (IPV) is one of the solutions used to increase the infrared response of PV cells and thus increase the solar-to-electric energy conversion efficiency. The idea of the IPV effect is based on the introduction of deep radiation defects in the structure of the semiconductor crystal structure. These defects ensure a multi-step absorption mechanism for photons with energies below the band gap width. The addition of IPV dopants into silicon solar cell structure, under certain conditions, increases the spectral response, short circuit current density, and conversion efficiency [ 68 ].
A major direction of study with great potential for development is Intermediate Band Solar Cells (IBSCs). They represent a third-generation solar cell concept and involve not only silicon, but also other materials. The idea behind the intermediate band gap solar cell (IBSC) concept is to absorb photons with an energy corresponding to the sub-band width in the cell structure. These photons are absorbed by a semiconductor-like material that, in addition to the conduction and valence bands, has an intermediate band (IB) in the conventional semiconductor’s band gap ( Figure 16 ). In IBSCs, the silicon layers are implanted with very high doses of metal ions to create an additional energy level [ 69 ].

Energy band diagram of an intermediate band solar cell (IBSC) [ 69 ].
Based on the research conducted on the effect of defects introduced into the silicon structure, a model was developed according to which introducing selected deep defects into the charge carrier capture region results in improved PV cell efficiency. Of particular interest are defects that facilitate the transport of majority carriers and defects that counteract the accumulation of minority carriers. This contributes significantly to reducing the recombination process at the charge carrier capture site. Finally, by introducing defects into the structure of the silicon underlying the solar cell, we combine effective surface passivation with simultaneous reduction in optical losses [ 70 ].
The introduction of intermediate bands in semiconductors, using ion implantation, can be executed using two methods: by introducing dopants of very high concentration into the semiconductor substrate, or by implanting the silicon layer with high-dose metal ions. The increasing use of ion implantation in the photovoltaic cell manufacturing process has the potential to reduce the cost of deployment and increase the cost-effectiveness of silicon cells by increasing their efficiency. The use of ion implantation technology provides increased precision of silicon layer doping and generation of additional levels of energy in the band gap, as well as shortening the individual stages of cell fabrication, which ultimately translates into improved quality and lower production costs [ 71 ].
Lately, the technique of ion implantation is gaining popularity in the solar industry, gradually displacing the diffusion technique that has been used for many years. As can be seen in Figure 17 , cell performance is expected to continue to improve as the technology evolves toward higher efficiencies. In addition to local and reference doping, the major benefits of this technology involve high precision control of the amount and distribution of dopant doses, which results in high uniformity, repeatability, and increased efficiency (above 19%), with a significantly narrower distribution of cell performance [ 72 ].

Stabilized cell efficiency trend curves [ 72 ].
In the method of ion implantation, chosen ions with the required impurity are inserted into the semiconductor by accelerating the impurity ions to a high energy level and implanting the ions into the semiconductor. The energy given to the impurity ions defines the depth of ion implantation. Contrary to the diffusion technology (where the impurity ion dose is introduced only at the surface), in the ion implantation technique, a controllable dose of impurity ions can be placed deeply into the semiconductor [ 73 ].
2.4. Fourth Generation of Photovoltaic Cells
Fourth-generation photovoltaic cells are also known as hybrid inorganic cells because they combine the low cost and flexibility of polymer thin films, with the stability of organic nanostructures such as metal nanoparticles and metal oxides, carbon nanotubes, graphene, and their derivatives. These devices, often referred to as “nanophotovoltaics”, could become the promising future of photovoltaics [ 74 ].
Graphene-Based Photovoltaic Cells
By using thin polymer layers and metal nanoparticles, as well as various metal oxides, carbon nanotubes, graphene, and their derivatives, the fourth generation provides excellent affordability and flexibility. Particular emphasis was placed on graphene because it is considered a nanomaterial of the future. Due to their unique properties, such as high carrier mobility, low resistivity and transmittance, and 2D lattice packing, graphene-based materials are being considered for use in PV devices instead of existing conventional materials. However, to achieve adequate device performance, the key to its practical applications is the synthesis of graphene materials with appropriate structure and properties [ 75 ].
Since the properties of graphene are fundamentally related to its fabrication process, a judicious choice of methods is essential for targeted applications. In particular, highly conductive graphene is suitable for use in flexible photovoltaic devices, and its high compatibility with metal oxides, metallic compounds, and conductive polymers makes it suitable for use as a selective charge-taking element and electrode interlayer material [ 76 ].
In the past two decades, graphene has been combined with the concept of photovoltaic material and is showing a significant role as a transparent electrode, hole/electron transport material, and interfacial buffer layer in solar cell devices. We can distinguish several types of graphene-based solar cells, including organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ) cells, dye-sensitized cells, and perovskite cells. The energy conversion efficiency exceeded 20.3% for graphene-based perovskite solar cells and reached 10% for BHJ organic solar cells. In addition to its function of extracting and transporting charge to the electrodes, graphene plays another unique role—it protects the device from environmental degradation through its packed 2D lattice structure and ensures the long-term environmental stability of photovoltaic devices [ 77 ].
Semi-metallic graphene having a zero band gap creates Schottky junction solar cells with silicon semiconductors. Even though graphene was discovered for the first time in 2004, the first graphene–silicon solar cell was not characterized as an n-silicon cell until 2010. Figure 18 schematically shows a graphene–silicon solar cell with a Schottky junction. Graphene sheets (GS), cultured by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on nickel films, were wet deposited on pre-patterned Si/SiO 2 substrates with an effective area of 0.1–0.5 cm 2 . The graphene sheet forms a coating on the exposed n-Si substrate, creating a Schottky junction. The graphene sheet was contacted using Au electrodes [ 78 ].

Graphene–silicon Schottky junction solar cell. ( a ) Cross-sectional view, ( b ) schematic illustration of the device configuration [ 75 ].
Graphene synthesis uses mainly two methodologies, which are the bottom-up and top-down methods. In the top-down approach, graphite is the starting material, and the goal is to intercalate and exfoliate it into graphene sheets by solid, liquid, or electrochemical exfoliation. Another approach under this categorization is the exfoliation of graphite oxide into graphene oxide (GO), after which chemical or thermal reduction takes place. A bottom-up approach is to produce graphene from molecular precursors by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or epitaxial growth. The structure, morphology, and attributes of the resulting graphene, including the layer numbers, level of defects, electrical and thermal conductivity, solubility, and hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity, are dependent on the manufacturing process [ 78 , 79 ].
Graphene can absorb 2.3% of incident white light even though it is only one atom thick. Incorporating graphene into a silicon solar cell is a promising platform since graphene has a strong interaction with light, fulfilling both the optical (high transmittance) and electrical (low layer resistance) requirements of a typical transparent conductive electrode. It is important to note that both the layer resistance and the transmittance of graphene change with the number of layers. As the layer resistance decreases as the number of graphene layers increases, the optical transparency decreases as well [ 80 ].
For PV technology, graphene offers a lot more because of its flexibility, environmental stability, low electrical resistivity, and photocatalytic features, while having to be carefully and deliberately designed for the targeted applications and specific requirements [ 78 , 80 ].
One problem for graphene application is the absence of a simpler, more reliable way to deposit a well-ordered monolayer with low-cost flakes on target substrates having various surface properties. The other problem is the adhesion of the deposited graphene thin film, a subject that has not yet been studied properly. Large-area continuous graphene layers with high optical transparency and electrical conductivity may be fabricated by CVD. As an anode in organic photovoltaic devices, graphene holds great promise as a replacement for indium tin oxide (ITO) because of its inherently low-cost manufacturing process and excellent conductivity and transparency properties [ 81 ].
Graphene’s major disadvantage is its poor hydrophilicity, which negatively affects the design of devices processed in solution, but that fact may be overcome through modifying the surface by non-covalent chemical functionalization. Given graphene’s mechanical strength and flexibility, as well as its excellent conductivity properties, it can be anticipated that new applications in plastic electronics and optoelectronics will soon emerge involving this new class of CVD graphene materials. The discovery paves the way for low-cost graphene layers to replace ITO in photovoltaic and electroluminescent devices [ 82 ].
3. Prospects and Research Directions
Since the beginning of photovoltaic cells, crystalline silicon-based photovoltaic technology has played a dominant role in the market, with crystalline PV modules accounting for about 90% of the market share in 2020. In recent years, there has been a rapid development of thin film solar cells (such as cadmium telluride (CdTe) and indium–gallium selenium compounds (CIGS) cells) and new solar cells (such as dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs), perovskite solar cells (PSCs), quantum dot solar cells (QDSCs), etc.) [ 83 ].
The growing interest in BIPV systems has contributed to the overall development of photovoltaic technology, which has led to lower costs, increasing the feasibility of investment. Most of the standard second-generation technologies show efficiencies of 20–25%, and while they are expensive, the cost of silicon cells has come down and it is the improvement of silicon technologies that is now one of the key research directions [ 84 ].
Graphene and its derivatives are a promising area of research as they are in the early stages of research and development. The goal of using carbon nanostructures is to produce energy-efficient products that combine transport, active, and electrode layers. Many researchers in contemporary graphene research are now focusing on new graphene derivatives and their novel applications in manufacturing devices [ 85 ].
Nevertheless, the technologies used for third- and fourth-generation cells are still in the prototyping stage. Production-scale prototypes have also been built and have been successful (10–17% efficiency). In contrast, third-generation multi-junction cells are already commercially available and have achieved exceptional conversion factors (from 40% to over 50%) that place this alternative as the best [ 85 ]. Considering the market trends of increasing use of intermediate energy levels in PV cell production, it makes perfect sense to conduct research in this direction, which is exactly what our research team is doing.
The practical realization of the idea of energy-efficient IBSC-type silicon solar cells with intermediate energy levels in the band gap of the semiconductor, produced by ion implantation, needs more studies directed at the search for the optimal implantation parameters, which is the energy, type, and dose of ions, adjusted to the substrate material properties, particularly the level and type of dopant [ 86 ].
It appears that implantation can also lead to a reduction in the optical losses present in the cell. Impurities and defects introduced into the silicon crystal lattice under the right conditions can create additional intermediate band gaps, which realistically contributes to the reduction in the energy gap width. As a result, some photons with energies lower than the band gap value cause the formation of additional electron–hole pairs. The existence of this additional energy band contributes to the increase in the value of the photoelectric current, which results from the absorption of photons not previously involved in the photovoltaic conversion process. The range of absorbed light radiation increases toward the infrared, and after absorbing a photon from this range, the electron goes first to the intermediate band and then to the conduction band [ 87 ].
Our long-standing studies on changing the electrical parameters of silicon through the use of neon ion implantation have resulted in the development of the authorial methodology for the generation and identification of additional levels of energy in the silicon band structure, improving the efficiency of photovoltaic cells made based on it [ 88 ].
The research has been directed at determining the effect of the degree and type of silicon defect in terms of the possibility of producing intermediate energy levels in the semiconductor’s band gap, thereby increasing the efficiency of solar cells by enabling a multi-step transition of electrons from the valence band to the intermediate band and then to the conduction band.
The object of our research is a method of producing intermediate energy levels in the band gap of n- and p-type silicon, with a specific resistivity ρ ranging from 0.25 Ω·cm to 10 Ω·cm, by generating deep radiation defects in the crystal structure of the semiconductor by implantation of Ne + neon ions. The research material is doped with elements such as boron, phosphorus, and antimony.
Neon ions were chosen because the ions primarily produce point defects, the deliberate introduction of which into the crystalline lattice of silicon in the process of implantation makes it possible to alter its fundamental electrical parameters, including energy gap width and resistivity. The parameters significantly affect internal losses in photovoltaic cells [ 89 ]. Experimental studies were conducted to provide details for determination of the optimal dose of implanted neon ions because of their ability to generate intermediate energy levels in the semiconductor band gap.
The Results of the Author’s Research
The silicon samples were implanted with neon ions of energy E = 100 keV and different doses D using a UNIMAS 79 ion implanter and then isochronically annealed at 598 K for 15 min in a resistance furnace. The electrical parameters of the silicon samples were tested using a Discovery DY600C climate chamber using the proprietary PV Cells Meter computer program and the Winkratos software. A GW Instek LCR-8110G Series LCR meter was used to measure capacitance and conductance values, while sample temperature values were measured using Fluke 289 and Lutron TM-917 multimeters ( Figure 19 ).

Silicon samples laboratory stand. ( a ) Schematic diagram of the laboratory stand: 1—solar cell, 2—supporting construction, 3—temperature sensor, 4—pyranometer, 5—light source, V1—Fluke 289, V2—The LCR-8110G Series LCR meter, RC—shunt resistor, RL—adjustable load. ( b ) Special measuring holders inside the climate chamber to hold silicon samples. ( c ) Discovery DY600C climate chamber [ 90 ].
The resulting capacitance and conductance measurements allowed us to determine the position values of the additional energy levels in the band gap. Two methods were used for this purpose. The first is the Thermal Admittance Spectroscopy (TAS) method, by which it was possible to determine the e t ( T p ) rate that determines the thermal emission, followed by the Arrhenius curves. By using the Arrhenius equation, it was possible to determine the activation energies of the deep energy levels by approximating the experimental data with a linear function [ 86 ]. An example of the results obtained by the TAS method is shown in Figure 20 a.

The Arrhenius law approximation ranges for silicon implanted with neon Ne + ions of energy E = 100 keV ( a ) P-type silicon doped with boron, ρ = 0.4 Ω·cm, D = 2.2 × 10 14 cm −2 , Δ E = 0.46 eV. ( b ) N-type silicon doped with phosphorus, ρ = 10 Ω·cm, D = 4.0 × 10 14 cm −2 , Δ E = 0.23 eV [ 86 , 87 ].
Another method of determining the activation energy is the approximation of selected parts of the course C p = f(1000/ T p ) with the function of the equation ln(y) = Ax + B, where C p is the unit capacitance of the tested sample, and T p is the temperature of the sample during the measurements performed at the frequency of the measuring signal f = 100 kHz. This in turn allowed the calculation of the conduction activation energy Δ E , which determines the depth of the additional intermediate energy level [ 87 ]. An example of the results obtained by the Arrhenius curve approximation method is shown in Figure 20 b.
On the basis of the conducted research, it was possible to identify radiation defects that create additional energy levels in the silicon band gap, with corresponding activation energies, where the results are shown in Table 1 . Our research proved that the implantation of Ne+ ions results in generating radiation defects in the crystal lattice of silicon as a photovoltaic cell base material and enables the generation of intermediate levels of energy in the band gap, improving the efficiency of photovoltaic cells made on its basis.
Determination of intermediate energy levels for boron and phosphorus doped silicon samples implanted with Ne + ions and energy E = 100 keV, isochronically annealed at 598 K [ 86 , 87 ].
| Sample | Label | Resistivity | Dose | Activation Energy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Si+B | = 0.4 Ω·cm | = 4.0 × 10 cm | Δ = 0.34 eV |
| | Si+B | = 0.4 Ω·cm | = 2.2 × 10 cm | Δ = 0.46 eV |
| | Si+B | = 0.4 Ω·cm | = 4.0 × 10 cm | Δ = 0.32 eV |
| | Si+P | = 10 Ω·cm | = 4.0 × 10 cm | Δ = 0.19 eV |
| | Si+P | = 10 Ω·cm | = 4.0 × 10 cm | Δ = 0.23 eV |
4. Conclusions
Solar energy is one of the most demanding renewable sources of electricity. Electricity production using photovoltaic technology not only helps meet the growing demand for energy, but also contributes to mitigating global climate change by reducing dependence on fossil fuels. The level of competitiveness of innovative next-generation solar cells is increasing due to the efforts of researchers and scientists related to the development of new materials, particularly nanomaterials and nanotechnology.
It is noted that the solar cell market is dominated by monocrystalline silicon cells due to their high efficiency. About two decades ago, the efficiency of crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells reached the 25% threshold at the laboratory scale. Despite technological advances since then, peak efficiency has now increased very slightly to 26.6%. As the efficiency of crystalline silicon technology approaches the saturation curve, researchers around the world are exploring alternative materials and manufacturing processes to further increase this efficiency. Polycrystalline and amorphous thin film silicon cells are seen as a serious competitor to monocrystalline silicon cells. However, their disadvantage is their disordered nature which results in low efficiency.
In this paper is a comprehensive overview of various PV technologies that are currently available or will be available in the near future on a commercial scale. A comparative analysis in terms of efficiency and the technological processes used is presented. Over the past few decades, many new materials have emerged that provide an efficient source of power generation to meet future demands while being cost-effective. This paper is a comprehensive study covering the generations of photovoltaic cells and the properties that characterize these cells. Photovoltaic cell materials of different generations have been compared based on their fabrication methods, properties, and photoelectric conversion efficiency.
First-generation solar cells are conventional and based on silicon wafers. The second generation of solar cells involves thin film technologies. The third generation of solar cells includes new technologies, including solar cells made of organic materials, cells made of perovskites, dye-sensitized cells, quantum dot cells, or multi-junction cells. With advances in technology, the drawbacks of previous generations have been eliminated in fourth-generation graphene-based solar cells. The popularity of photovoltaics depends on three aspects—cost, raw material availability, and efficiency. Third-generation solar cells are the latest and most promising technology in photovoltaics. Research on these is still in progress. This review pays special attention to the new generation of solar cells: multi-junction cells and photovoltaic cells with an additional intermediate band.
Recent advances in multi-junction solar cells based on n-type silicon and functional nanomaterials such as graphene offer a promising alternative to low-cost, high-efficiency cells. Currently, multi-junction cells, which benefit from advances enabled by nanotechnology, are breaking efficiency records. They are still quite expensive and represent a complex system, but there are simpler alternatives that may eventually provide a path to the competitiveness of the highest efficiency devices. Another significant advance is being made in the generation of additional energy levels in the band structure of silicon. In both cases, more research evidence, policies, and technology are needed to make them accessible. Therefore, it remains crucial to develop silicon-based technologies. The use of these new solar cell architectures would provide a new direction toward achieving commercial goals. Multi-junction based solar cells and new photovoltaic cells with an additional intermediate energy level are expected to provide extremely high efficiency. The research in this case focuses on a low-cost manufacturing process. Therefore, commercialization of these cells requires further work and exploration.
Nanotechnology and newly developed multifunctional nanomaterials can help overcome current performance barriers and significantly improve solar energy generation and conversion through photovoltaic techniques. Many physical phenomena have been identified at the nanoscale that can improve solar energy generation and conversion. However, the challenges associated with these technologies continue to be an issue when they are incorporated into PV manufacturing. Thanks to initial successes in recent years, nanomaterials are one of the most promising energy technologies of the future and are expected to significantly reform the future energy market. Carbon nanoparticles and their allotropic forms, such as graphene, are expected to offer high efficiency compared to conventional silicon cells in the near future and thus contribute to new prospects for the solar energy market.
Funding Statement
This research was funded by the Lublin University of Technology, grant number FD-20/EE-2/708.
Author Contributions
P.W. proposed a study on photovoltaic cell generations and current research directions for their development and guided the work. J.P. conducted a literature review and wrote the paper. J.P. and P.W. described further prospects and research directions and outlined conclusions based on the collected literature. P.W. reviewed and edited the work. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research now shows that chiral molecules can both improve the mechanical stability of the interfaces and afford passivation of defects at the perovskite surface, making solar cells more tolerant ...
Commercial silicon cells are typically larger than an A5 sheet of paper, and these are assembled into 2-metre-long modules — the building blocks of larger panels and arrays — that have an ...
Solar cells based on CdTe 7,8, quantum dot sensitized-based solar cells 9, CIGS 10,11, organic photo cells 12 and perovskite-based solar cells 13 have also been explored by researchers.
Popular Science reporter Andrew Paul writes that MIT researchers have developed a new ultra-thin solar cell that is one-hundredth the weight of conventional panels and could transform almost any surface into a power generator. The new material could potentially generate, "18 times more power-per-kilogram compared to traditional solar technology," writes Paul.
Perovskite/organic tandem solar cells. Organic solar cells (OSCs) are an attractive option for next-generation photovoltaics due to their low-cost, tunable optical properties, solution ...
A groundbreaking research breakthrough in solar energy has propelled the development of the world's most efficient quantum dot (QD) solar cell, marking a significant leap towards the ...
By adding a specially treated conductive layer of tin dioxide bonded to the perovskite material, which provides an improved path for the charge carriers in the cell, and by modifying the perovskite formula, researchers have boosted its overall efficiency as a solar cell to 25.2 percent — a near-record for such materials, which eclipses the ...
Solar technology refers to technology that uses solar radiation to generate electricity or utilize thermal energy. Solar energy is environmentally friendly, renewable, noiseless, and pollution-free and does not require fuel, making it a form of renewable energy. A solar cell (SC) comprises multiple thin layers of semiconductor materials. When sunlight shines on an SC, photons excite electrons ...
In May, UK-based Oxford PV said it had reached an efficiency of 28.6% for a commercial-size perovskite tandem cell, which is significantly larger than those used to test the materials in the lab ...
The team's prototype solar cell measures one square centimeter in area and produces an open-circuit voltage of 2.19 electron volts, a record for all-perovskite tandem solar cells. Its power-conversion efficiency reached 27.4%, which also breaks the current record for traditional silicon solar cells. "Further improvements in the efficiency ...
However, new research published in Nature has shown that future solar panels could reach efficiencies as high as 34 percent by exploiting a new technology called tandem solar cells. The research ...
Organic solar cells have emerged as promising alternatives to traditional inorganic solar cells due to their low cost, flexibility, and tunable properties. This mini review introduces a novel perspective on recent advancements in organic solar cells, providing an overview of the latest developments in materials, device architecture, and performance optimization. In contrast to existing ...
Accordingly, the air processed perovskite solar cells based on compact-In 2 O 3 film exhibits high PCE of 13.97% whereas pristine In 2 O 3 -film shows the PCE of 9.81%. Along with high PCE the proposed indium-based perovskite solar cell shows long term stability and retains 94% of its PCE even after 31 days of storage.
Solar energy. Organic solar cells (OSCs) have been recognized to have tremendous potential as alternatives to their inorganic counterparts, with devices that are low-cost, lightweight, and easily processed and have less environmental impact. Challenges for OSCs to be utilized commercially on a large scale have been highlighted by their ...
Employing sunlight to produce electrical energy has been demonstrated to be one of the most promising solutions to the world's energy crisis. The device to convert solar energy to electrical energy, a solar cell, must be reliable and cost-effective to compete with traditional resources. This paper reviews many basics of photovoltaic (PV) cells, such as the working principle of the PV cell ...
This c-Si solar cell had an area of 4 cm 2 and was based on the so-called passivated emitter and rear locally diffused (PERL) solar cell technology (Fig. 4a). However, this cell suffered from ...
An International Journal Devoted to Photovoltaic, Photothermal, and Photochemical Solar Energy Conversion. Solar Energy Materials & Solar Cells is intended as a vehicle for the dissemination of research results on materials science and technology related to photovoltaic, photothermal and photoelectrochemical solar energy conversion.Materials science is taken in the broadest possible sense and ...
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) are an efficient photovoltaic technology for powering electronic applications such as wireless sensors with indoor light. Their low cost and abundant materials, as well as their capability to be manufactured as thin and light-weight flexible solar modules highlight their po Journal of Materials Chemistry A Recent Review Articles Journal of Materials Chemistry ...
Solar cells have been a cost-effective technology of producing a sustainable electricity using renewable sun energy. In this paper we have focused our research on an innovative yet simple approach including concentrated PV (Photovoltaic) cells using Fresnel lens. In our findings we tried to expound the refracting properties of the Fresnel lens to concentrate the solar spectrum on to a ...
The global installed solar capacity over the past ten years and the contributions of the top fourteen countries are depicted in Table 1, Table 2 (IRENA, 2023). Table 1 shows a tremendous increase of approximately 22% in solar energy installed capacity between 2021 and 2022. While China, the US, and Japan are the top three installers, China's relative contribution accounts for nearly 37% of the ...
Perovskites help capture bluer visible wavelengths, complimenting silicon's redder wavelength coverage and allowing a solar cell to capture more light. In 2023, several independent research teams created small perovskite-silicon solar cells that exceeded 30% efficiency, and the best experimental cells today are approaching 50% efficiency.
Perovskite solar cells and have shown great promise on the lab scale, but work is needed to scale-up their fabrication. Here, blade coating is used to fabricate 15 cm×15 cm perovskite modules ...
Low-Energy Process for High-Performance Solar Cells. May 7, 2024 — Finding reliable, eco-friendly power sources is crucial as our world grapples with increasing energy needs and the urgent call ...
NREL solar researchers actively publish their latest scientific findings and breakthroughs in a newsletter, journal articles, conference papers, technical reports, and presentations. ... Complementary Interface Formation Toward High-Efficiency All-Back-Contact Perovskite Solar Cells, Cell Reports Physical Science (2021 ... Find solar research ...
Abstract. The purpose of this paper is to discuss the different generations of photovoltaic cells and current research directions focusing on their development and manufacturing technologies. The introduction describes the importance of photovoltaics in the context of environmental protection, as well as the elimination of fossil sources.