- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

KnowledgeManagement →
No results found in working knowledge.
- Were any results found in one of the other content buckets on the left?
- Try removing some search filters.
- Use different search filters.
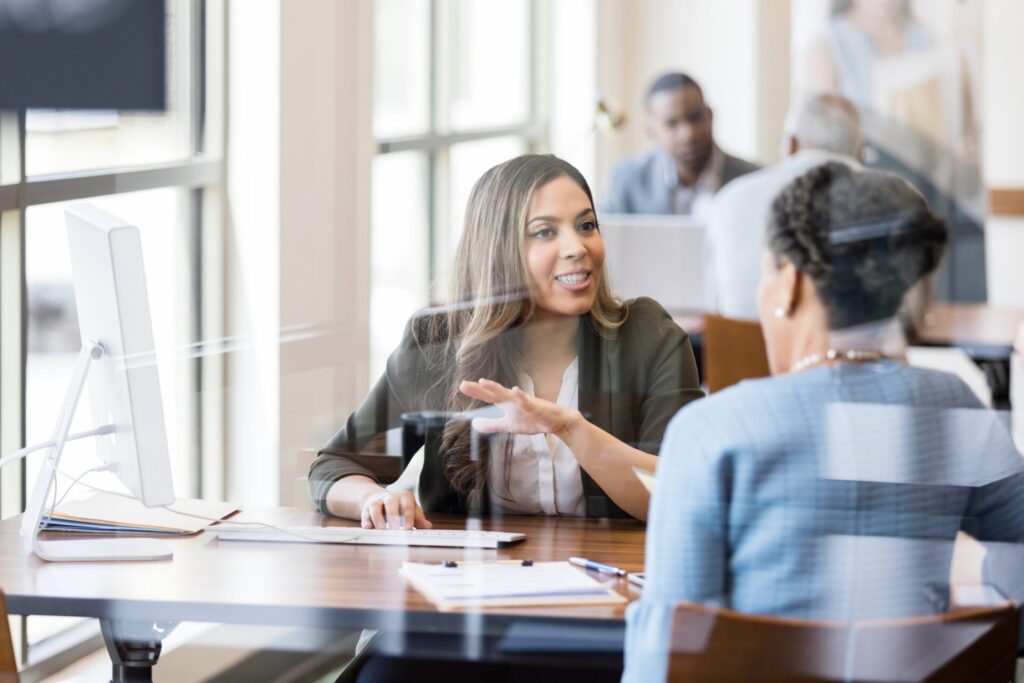
Knowledge Management with M365 – A Case Study
by Matt DiPasquale | Oct 6, 2021 | Microsoft , Office 365 , The Bamboo Team Blog

Effective solutions can be quick and easy. As an example, adding Bamboo’s Tree View to replicate the familiar Windows Folder navigation for your document library. More complex solutions may include creating a custom approval process with Power Automate integrated with Microsoft Teams.
Bamboo Solution’s first case study shows how the Bamboo Consulting team addressed a large and growing company’s knowledge management issues by leveraging the power of M365. Files and information stored across multiple repositories were consolidated into SharePoint Online. This solution included the creation of a corporate portal. A review/inventory of the existing document repositories, and the development of a migration plan. This plan addressed security and controls as well as the addition of metadata to simplify data searches.
SharePoint Online
The cloud parts are functional components that extend your SharePoint Online environment in Microsoft 365.
Supports Classic and Modern sites for SharePoint Online/Microsoft 365
Small Business Pricing and Discounts
Top sharepoint online products.
Experience greater power and savings by bundling our SharePoint apps and cloud parts.
Calendar Plus
Employee Directory Plus
Org Chart Plus
Simple Search
On-Premises Only
These web parts extend SharePoint beyond its out-of-the-box capabilities by tailoring it to your requirements with Bamboo Solution’s growing portfolio of SharePoint Web Parts.
SharePoint 2016, 2019, 2022 – Classic Pages Only
Top On-Premises Only Products
Experience greater power and savings by bundling our SharePoint apps and web parts.
Data Viewer
Password Change
Password Expiration
Password Reset
Our team of Microsoft 365 Technology Consultants helps you get the most out of your Microsoft technology, we have the best Microsoft 365 talent to streamline your organization.
Consulting to Streamline Your Department
Managed Services
Microsoft 365
Human Resources
Information Technology
Marketing Campaigns
Our Consultants Have What You Need
Federal contractors.
Microsoft 365 Enablement
Migration to Microsoft 365
Microsoft Teams
Power Automate
Blog Categories
- Cyber Security (6)
- data migration services (11)
- Employee Spotlight (33)
- Events (158)
- In the News (62)
- Microsoft (42)
- Microsoft AppSource Product Update (2)
- Microsoft SharePoint Bloggers (15)
- Midshare (1)
- Office 365 (55)
- PowerApps (5)
- Press Release (72)
- Product Updates (129)
- Products (320)
- SharePoint 2010 (173)
- SharePoint 2013 (257)
- SharePoint Blank (47)
- SharePoint Experts (196)
- SharePoint for Administrators (22)
- SharePoint for Project Management (16)
- SharePoint Solutions (250)
- SharePoint Term Store (3)
- SharePointXperts (188)
- The Bamboo Team Blog (1,385)
- The Bottom-Line PM: A Realist’s Guide to Using SharePoint and Microsoft Project for Project Management (25)
- The Business of SharePoint (24)
- Year-End Review (2)
- About Bamboo Solutions
- Request a Trial
Corporate Headquarters
Bamboo Solutions 12110 Sunset Hills Road, #600 Reston, VA 20190 USA Get Directions
Toll Free: +1 877.226.2662 Tel: +1 703.964.2002
Connect With Us
Sales inquiries.
Toll Free: +1 877.226.2662 Email: Bamboo Solutions Sales
U.S. General Services Administration

Contract #: GS-35F-291DA Schedule: Standard Form 1449
See how the world’s leading brands are using Bloomfire
We know that Bloomfire is a powerful tool for sharing and discovering information, but don’t just take our word for it. See what our customers have to say.

Echo Improves the Transportation of Insights and Analyses with Bloomfire

Asure Software Empowers Sales, Services, and Support Teams With Bloomfire

Bloomfire Speeds Employee Onboarding for Research & Consulting Firm

Dexcom Opens Its Insights Vault to Better Understand the Customer and Increase Efficiency

ICF Uses Bloomfire for Real Time Q&A

PennyMac Delivers Digestible Customer Service Knowledge

UT Health Strengthens Employee Experience with Bloomfire
Case studies.

How Bloomfire Helped Easy Ice Create Competitive Advantage and Improve Their Service Offering

Giltner Logistics Slashes Onboarding Time and Aligns Distributed Teams

Topline Strategy Group Scales Growth with Efficient Knowledge Sharing

Dime Equips Employees with the Knowledge They Need to Make Informed Decisions

King’s Hawaiian Answers Consumer Research Questions Faster with Bloomfire

DraftKings Centralizes Insights and Increases Research Buy-In With Bloomfire

ActiveProspect Empowers Employees and Customers with Centralized Knowledge

Midan Marketing Strengthens Position as Innovative Agency With Bloomfire

Olive Tames Information Sprawl and Centralizes Knowledge with Bloomfire

Unlock the full potential of your business with exclusive strategies and data-driven insights curated by Knowledge Management experts.
Start working smarter with Bloomfire
See how Bloomfire helps companies find information, create insights, and maximize value of their most important knowledge.

Take a self guided Tour
See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge.
Designed for Contact Centers by people who understand Contact Centers
Unleash the potential of your contact center with the market leading AI Knowledge Management solution
Provide your customers with answers – not long documents to read and interpret. livepro delivers answers
Deliver answers by livepro, through any of your trusted Customer Service or Collaboration apps.
Implementation
We have a near perfect success rate because we adjust our Implementation plan to your environment
Deliver answers through nearly any App using livepro simple API
We work hard to keep your system safe. See how.
FEATURED RESOURCES

livepro Launches LightspeedAI: Transformative Generative AI for Effortless Document Migration in Contact Centers
19 February 2024 — livepro a leading provider

Why Your CX Strategy Must Use Customer-Centric Knowledge Management
A common myth in our business is that

The AI Wave is Coming: Is Your Knowledge Management System Ready?
Your AI Model is Only as Good as
- See your ROI
- All features
LivePro for…
Featured resources
19 February 2024 — livepro a leading provider of Knowledge
A common myth in our business is that any knowledge
Your AI Model is Only as Good as the Data
- Case Studies
browse resource topics
Townsville Council
Case studies .
See for yourself how the leading single source of truth creates happier customers and staff while cutting costs.

Avant Mutual's onboarding time slashed from three months to two weeks with livepro
Almost immediately, new starters using livepro performed significantly better than existing staff using our old system.
Andrea Pepper-Edwards,
Change Specialist at Avant Mutual
Finally, we have a Knowledge Management platform that provides us with everything we need to improve the efficiency of the contact center as well as reducing customer effort. We have seen a reduction in repeat calls and an 80% reduction in SME support needed. Quality scores have increased and the engagement from the team has been brilliant. It was great to work with the livepro team who were so passionate and hands on from day 1 to completion.”
Chris Nugent
Contact Center Manager at MAS National

ME Bank cuts AHT by 40% and Achieves Exciting Staff Engagement
We couldn’t be happier with livepro. It’s an essential tool that underpins our commitment to great customer service.”
Sean McGinn,
General Manager at ME Bank

It was such a relief to work with a company that would listen and learn about our unique product, rather than dictate what they think we need.
Quality, Improvement & Assist team at Remserv
All case studies

November 17, 2023

Townsville Council
December 12, 2022

Hornsby Shire Council

Liverpool City Council

Lockyer Valley Regional Council

Goulburn Mulwaree Council

October 6, 2022

Avant mutual
October 5, 2022
Stay in the loop
Subscribe to have the latest updates, insights, and more delivered straight to your inbox.
Delight customers with fast, correct answers in any channel from one knowledge base
Let us help you deliver the answers to your customers and your agents through any user interface. livepro’s speed brings answers through any channel.
See what your ROI will be by using livepro to cut contact center costs.
livepro for

Cookie Notice
Privacy overview.
Common searches
KM, contact center, training

- Predictive Analytics Workshops
- Corporate Strategy Workshops
- Advanced Excel for MBA
- Powerpoint Workshops
- Digital Transformation
- Competing on Business Analytics
- Aligning Analytics with Strategy
- Building & Sustaining Competitive Advantages
- Corporate Strategy
- Aligning Strategy & Sales
- Digital Marketing
- Hypothesis Testing
- Time Series Analysis
- Regression Analysis
- Machine Learning
- Marketing Strategy
- Branding & Advertising
- Risk Management
- Hedging Strategies
- Network Plotting
- Bar Charts & Time Series
- Technical Analysis of Stocks MACD
- NPV Worksheet
- ABC Analysis Worksheet
- WACC Worksheet
- Porter 5 Forces
- Porter Value Chain
- Amazing Charts
- Garnett Chart
- HBR Case Solution
- 4P Analysis
- 5C Analysis
- NPV Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
- Cost Optimization
Knowledge Management at Accenture
- Technology & Operations / MBA EMBA Resources
Next Case Study Solutions
- Government E-Procurement: Electronic Tendering System in the Hong Kong SAR Case Study Solution
- H.E. Butt Grocery Co.: The New Digital Strategy (A) Case Study Solution
- General Motors: Building a Digital Loyalty Network Through Demand and Supply Chain Integration Case Study Solution
- Jardines: Tapping the Asian E-Commerce Market Case Study Solution
- E-Commerce at Williams-Sonoma Case Study Solution
Previous Case Solutions
- First Virtual Holdings, Inc. (A) Case Study Solution
- Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management Case Study Solution
- Lucent Technologies: Optical Networking Group Case Study Solution
- Pilkington Float Glass--1955 Case Study Solution
- Silicon Graphics, Inc. (B) Case Study Solution

Predictive Analytics
April 11, 2024

Popular Tags
Case study solutions.

Case Study Solution | Assignment Help | Case Help
Knowledge management at accenture description.
Accenture has long been seen as a leader in knowledge management, having received awards for many years. Over the years though, islands of knowledge have developed throughout the organization and the delivery infrastructure has become progressively more expensive. In 2004, the global knowledge management lead has been given the mandate to lead a revitalization of knowledge management. Outlines governance challenges in the global firm, the transition to a new IT infrastructure, and the strategic challenges and opportunities facing knowledge management within Accenture.
Case Description Knowledge Management at Accenture
Strategic managment tools used in case study analysis of knowledge management at accenture, step 1. problem identification in knowledge management at accenture case study, step 2. external environment analysis - pestel / pest / step analysis of knowledge management at accenture case study, step 3. industry specific / porter five forces analysis of knowledge management at accenture case study, step 4. evaluating alternatives / swot analysis of knowledge management at accenture case study, step 5. porter value chain analysis / vrio / vrin analysis knowledge management at accenture case study, step 6. recommendations knowledge management at accenture case study, step 7. basis of recommendations for knowledge management at accenture case study, quality & on time delivery.
100% money back guarantee if the quality doesn't match the promise
100% Plagiarism Free
If the work we produce contain plagiarism then we payback 1000 USD
Paypal Secure
All your payments are secure with Paypal security.
300 Words per Page
We provide 300 words per page unlike competitors' 250 or 275
Free Title Page, Citation Page, References, Exhibits, Revision, Charts
Case study solutions are career defining. Order your custom solution now.
Case Analysis of Knowledge Management at Accenture
Knowledge Management at Accenture is a Harvard Business (HBR) Case Study on Technology & Operations , Texas Business School provides HBR case study assignment help for just $9. Texas Business School(TBS) case study solution is based on HBR Case Study Method framework, TBS expertise & global insights. Knowledge Management at Accenture is designed and drafted in a manner to allow the HBR case study reader to analyze a real-world problem by putting reader into the position of the decision maker. Knowledge Management at Accenture case study will help professionals, MBA, EMBA, and leaders to develop a broad and clear understanding of casecategory challenges. Knowledge Management at Accenture will also provide insight into areas such as – wordlist , strategy, leadership, sales and marketing, and negotiations.
Case Study Solutions Background Work
Knowledge Management at Accenture case study solution is focused on solving the strategic and operational challenges the protagonist of the case is facing. The challenges involve – evaluation of strategic options, key role of Technology & Operations, leadership qualities of the protagonist, and dynamics of the external environment. The challenge in front of the protagonist, of Knowledge Management at Accenture, is to not only build a competitive position of the organization but also to sustain it over a period of time.
Strategic Management Tools Used in Case Study Solution
The Knowledge Management at Accenture case study solution requires the MBA, EMBA, executive, professional to have a deep understanding of various strategic management tools such as SWOT Analysis, PESTEL Analysis / PEST Analysis / STEP Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, Go To Market Strategy, BCG Matrix Analysis, Porter Value Chain Analysis, Ansoff Matrix Analysis, VRIO / VRIN and Marketing Mix Analysis.
Texas Business School Approach to Technology & Operations Solutions
In the Texas Business School, Knowledge Management at Accenture case study solution – following strategic tools are used - SWOT Analysis, PESTEL Analysis / PEST Analysis / STEP Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, Go To Market Strategy, BCG Matrix Analysis, Porter Value Chain Analysis, Ansoff Matrix Analysis, VRIO / VRIN and Marketing Mix Analysis. We have additionally used the concept of supply chain management and leadership framework to build a comprehensive case study solution for the case – Knowledge Management at Accenture
Step 1 – Problem Identification of Knowledge Management at Accenture - Harvard Business School Case Study
The first step to solve HBR Knowledge Management at Accenture case study solution is to identify the problem present in the case. The problem statement of the case is provided in the beginning of the case where the protagonist is contemplating various options in the face of numerous challenges that Knowledge Accenture is facing right now. Even though the problem statement is essentially – “Technology & Operations” challenge but it has impacted by others factors such as communication in the organization, uncertainty in the external environment, leadership in Knowledge Accenture, style of leadership and organization structure, marketing and sales, organizational behavior, strategy, internal politics, stakeholders priorities and more.
Step 2 – External Environment Analysis
Texas Business School approach of case study analysis – Conclusion, Reasons, Evidences - provides a framework to analyze every HBR case study. It requires conducting robust external environmental analysis to decipher evidences for the reasons presented in the Knowledge Management at Accenture. The external environment analysis of Knowledge Management at Accenture will ensure that we are keeping a tab on the macro-environment factors that are directly and indirectly impacting the business of the firm.
What is PESTEL Analysis? Briefly Explained
PESTEL stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors that impact the external environment of firm in Knowledge Management at Accenture case study. PESTEL analysis of " Knowledge Management at Accenture" can help us understand why the organization is performing badly, what are the factors in the external environment that are impacting the performance of the organization, and how the organization can either manage or mitigate the impact of these external factors.
How to do PESTEL / PEST / STEP Analysis? What are the components of PESTEL Analysis?
As mentioned above PESTEL Analysis has six elements – political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal. All the six elements are explained in context with Knowledge Management at Accenture macro-environment and how it impacts the businesses of the firm.
How to do PESTEL Analysis for Knowledge Management at Accenture
To do comprehensive PESTEL analysis of case study – Knowledge Management at Accenture , we have researched numerous components under the six factors of PESTEL analysis.
Political Factors that Impact Knowledge Management at Accenture
Political factors impact seven key decision making areas – economic environment, socio-cultural environment, rate of innovation & investment in research & development, environmental laws, legal requirements, and acceptance of new technologies.
Government policies have significant impact on the business environment of any country. The firm in “ Knowledge Management at Accenture ” needs to navigate these policy decisions to create either an edge for itself or reduce the negative impact of the policy as far as possible.
Data safety laws – The countries in which Knowledge Accenture is operating, firms are required to store customer data within the premises of the country. Knowledge Accenture needs to restructure its IT policies to accommodate these changes. In the EU countries, firms are required to make special provision for privacy issues and other laws.
Competition Regulations – Numerous countries have strong competition laws both regarding the monopoly conditions and day to day fair business practices. Knowledge Management at Accenture has numerous instances where the competition regulations aspects can be scrutinized.
Import restrictions on products – Before entering the new market, Knowledge Accenture in case study Knowledge Management at Accenture" should look into the import restrictions that may be present in the prospective market.
Export restrictions on products – Apart from direct product export restrictions in field of technology and agriculture, a number of countries also have capital controls. Knowledge Accenture in case study “ Knowledge Management at Accenture ” should look into these export restrictions policies.
Foreign Direct Investment Policies – Government policies favors local companies over international policies, Knowledge Accenture in case study “ Knowledge Management at Accenture ” should understand in minute details regarding the Foreign Direct Investment policies of the prospective market.
Corporate Taxes – The rate of taxes is often used by governments to lure foreign direct investments or increase domestic investment in a certain sector. Corporate taxation can be divided into two categories – taxes on profits and taxes on operations. Taxes on profits number is important for companies that already have a sustainable business model, while taxes on operations is far more significant for companies that are looking to set up new plants or operations.
Tariffs – Chekout how much tariffs the firm needs to pay in the “ Knowledge Management at Accenture ” case study. The level of tariffs will determine the viability of the business model that the firm is contemplating. If the tariffs are high then it will be extremely difficult to compete with the local competitors. But if the tariffs are between 5-10% then Knowledge Accenture can compete against other competitors.
Research and Development Subsidies and Policies – Governments often provide tax breaks and other incentives for companies to innovate in various sectors of priority. Managers at Knowledge Management at Accenture case study have to assess whether their business can benefit from such government assistance and subsidies.
Consumer protection – Different countries have different consumer protection laws. Managers need to clarify not only the consumer protection laws in advance but also legal implications if the firm fails to meet any of them.
Political System and Its Implications – Different political systems have different approach to free market and entrepreneurship. Managers need to assess these factors even before entering the market.
Freedom of Press is critical for fair trade and transparency. Countries where freedom of press is not prevalent there are high chances of both political and commercial corruption.
Corruption level – Knowledge Accenture needs to assess the level of corruptions both at the official level and at the market level, even before entering a new market. To tackle the menace of corruption – a firm should have a clear SOP that provides managers at each level what to do when they encounter instances of either systematic corruption or bureaucrats looking to take bribes from the firm.
Independence of judiciary – It is critical for fair business practices. If a country doesn’t have independent judiciary then there is no point entry into such a country for business.
Government attitude towards trade unions – Different political systems and government have different attitude towards trade unions and collective bargaining. The firm needs to assess – its comfort dealing with the unions and regulations regarding unions in a given market or industry. If both are on the same page then it makes sense to enter, otherwise it doesn’t.
Economic Factors that Impact Knowledge Management at Accenture
Social factors that impact knowledge management at accenture, technological factors that impact knowledge management at accenture, environmental factors that impact knowledge management at accenture, legal factors that impact knowledge management at accenture, step 3 – industry specific analysis, what is porter five forces analysis, step 4 – swot analysis / internal environment analysis, step 5 – porter value chain / vrio / vrin analysis, step 6 – evaluating alternatives & recommendations, step 7 – basis for recommendations, references :: knowledge management at accenture case study solution.
- sales & marketing ,
- leadership ,
- corporate governance ,
- Advertising & Branding ,
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) ,
Amanda Watson
Leave your thought here

© 2019 Texas Business School. All Rights Reserved
USEFUL LINKS
Follow us on.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive news on update.

Dark Brown Leather Watch
$200.00 $180.00

Dining Chair
$300.00 $220.00

Creative Wooden Stand
$100.00 $80.00
2 x $180.00
2 x $220.00
Subtotal: $200.00
Free Shipping on All Orders Over $100!

Wooden round table
$360.00 $300.00
Hurley Dry-Fit Chino Short. Men's chino short. Outseam Length: 19 Dri-FIT Technology helps keep you dry and comfortable. Made with sweat-wicking fabric. Fitted waist with belt loops. Button waist with zip fly provides a classic look and feel .
Artificial intelligence is disrupting many different areas of business. The technology’s potential is particularly apparent in customer service, talent, and application modernization. According to IBM’s Institute of Business Value (IBV) , AI can contain contact center cases, enhancing customer experience by 70%. Additionally, AI can increase productivity in HR by 40% and in application modernization by 30%. One example of this is reducing labor burdens by automating ticket assistance through IT operations. Although, while these numbers indicate transformation opportunities for enterprises, scaling and operationalizing AI has historically been challenging for organizations.
There’s no AI, without IA
AI is only as good as the data that informs it, and the need for the right data foundation has never been greater. According to IDC, stored data is expected to grow up to 250% over the next 5 years .
With data stored across clouds and on-premises environments, it becomes difficult to access it while managing governance and controlling costs. Further complicating matters, the uses of data have become more varied, and companies are faced with managing complex or poor-quality data.
Precisely conducted a study that found that within enterprises, data scientists spend 80% of their time cleaning, integrating and preparing data , dealing with many formats, including documents, images, and videos. Overall placing emphasis on establishing a trusted and integrated data platform for AI.
Trust, AI and effective knowledge management
With access to the right data, it is easier to democratize AI for all users by using the power of foundation models to support a wide range of tasks. However, it’s important to factor in the opportunities and risks of foundation models—in particular, the trustworthiness of models to deploying AI at scale.
Trust is a leading factor in preventing stakeholders from implementing AI. In fact, IBV found that 67% of executives are concerned about potential liabilities of AI . Existing responsible AI tooling lacks technical ability and is restricted to specific environments, meaning customers are unable to use the tools to govern models on other platforms. This is alarming, considering how generative models often produce output containing toxic language—including hate, abuse, and profanity (HAP)—or leak personal identifiable information (PII). Companies are increasingly receiving negative press for AI usage, damaging their reputation. Data quality strongly impacts the quality and usefulness of content produced by an AI model, underscoring the significance of addressing data challenges.

Increasing user productivity: Knowledge management use cases
An emerging generative AI application is knowledge management . With the power of AI, enterprises can use knowledge management tools to collect, create, access and share relevant data for organizational insights. Knowledge management software applications are often implemented into a centralized system, or knowledge base, to support business domains and tasks—including talent, customer service and application modernization.
HR, talent and AI
HR departments can put AI to work through tasks like content generation, retrieval augmented generation (RAG) and classification. Content generation can be utilized to quickly create the description for a role. Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) can help with identifying the skills needed for a role based on internal HR documents. Classification can help with determining whether the applicant is a good fit for the enterprise given their application. These tasks streamline the processing time from when a person applies to receiving a decision on their application.
Customer service and AI
Customer service divisions can take advantage of AI by using RAG, summarization and classification. For example, enterprises can incorporate a customer service chatbot on their website that would use generative AI to be more conversational and context specific. Retrieval augmented generation can be used to search through internal documents of organizational knowledge to answer the customer’s inquiry and generate a tailored output. Summarization can help employees by providing them a brief of the customer’s problem and previous interactions with the company. Text classification can be utilized to classify the customer’s sentiment. These tasks can reduce manual labor while improving customer support and, hopefully, customer satisfaction and retention.
Application modernization and AI
App modernization can also be achieved with the help of summarization and content generation tasks. With a summary of the company’s knowledge and business objectives, developers can spend less time learning this necessary information and more time coding. IT workers can also create a summary ticket request to quickly address and prioritize issues found in a support ticket. Another way developers can use generative AI is by communicating with large language models (LLMs) in human language and asking the model to generate code. This can help the developer translate code languages, solve bugs and reduce time spent coding, allowing for more creative ideation.
Powering a knowledge management system with a data lakehouse
Organizations need a data lakehouse to target data challenges that come with deploying an AI-powered knowledge management system. It provides the combination of data lake flexibility and data warehouse performance to help to scale AI. A data lakehouse is a fit-for-purpose data store.
To prepare data for AI, data engineers need the ability to access any type of data across vast amounts of sources and hybrid cloud environments from a single point of entry. A data lakehouse with multiple query engines and storage can allow team members to share data in open formats. Additionally, engineers can cleanse, transform and standardize data for AI/ML modeling without duplicating or building additional pipelines. Moreover, enterprises should consider lakehouse solutions that incorporate generative AI to help data engineers and non-technical users easily discover, augment and enrich data with natural language. Data lakehouses improve the efficiency of deploying AI and the generation of data pipelines.
AI-powered knowledge management systems hold sensitive data, including HR email automations, marketing video translations and call center transcript analytics. When it comes to this sensitive information, having access to secure data becomes increasingly important. Customers need a data lakehouse that offers built-in centralized governance and local automated policy enforcement, supported by data cataloging, access controls, security and transparency in data lineage.
Through these data foundations set by a data lakehouse solution, data scientists can confidently use governed data to build, train, tune and deploy AI models, ensuring trust and confidence.
Ensure responsible, transparent and explainable knowledge management systems
As previously mentioned, chatbots are a popular form of generative AI-powered knowledge management system used for customer experience. This application can produce value for an enterprise, but it also poses risk.
For instance, a chatbot for a healthcare company can reduce nurse workloads and improve customer service by answering questions about treatments using known details from previous interactions. However, if data quality is poor or if bias was injected into the model during the fine-tuning or prompt tuning , the model is likely to be untrustworthy. As a result, the chatbot may offer a response to a patient that includes inappropriate language or leaks another patient’s PII.
To prevent this situation from happening, organizations need proactive detection and mitigation of bias and drift when deploying AI models. Having an automatic content filtering capability to detect HAP and PII leakage would reduce the model validators burden of manually validating models to ensure they avoid toxic content.
Turn possibility into reality with watsonx
As stated, a knowledge management strategy refers to the collection, creation and sharing of knowledge within an organization. It is often implemented into a knowledge sharing system that can be shared with stakeholders to learn and leverage existing collective knowledge and organizational insights. For instance, a RAG AI task can help with identifying the skills needed for a job role based on internal HR documents or support a customer service chatbot to search through internal documents to answer a customer’s inquiry and generate a tailored output.
When looking to deploy generative AI models, businesses should join forces with a trusted partner that has created or sourced quality models from quality data—one that allows customization with enterprise data and goals.
To help our clients solve for knowledge mangement, we offer IBM watsonx.ai . As part of the IBM watsonx platform that brings together new generative AI capabilities, watsonx.ai is powered by foundation models and traditional machine learning into a powerful studio spanning the AI lifecycle. With watsonx.ai , you can train, validate, tune and deploy generative AI, foundation models and machine learning capabilities with ease and build AI applications in a fraction of the time with a fraction of the data.
More from Artificial intelligence
How the masters uses watsonx to manage its ai lifecycle.
5 min read - At the Masters®, storied tradition meets state-of-the-art technology. Through a partnership spanning more than 25 years, IBM has helped the Augusta National Golf Club capture, analyze, distribute and use data to bring fans closer to the action, culminating in the AI-powered Masters digital experience and mobile app. Now, whether they’re lining the fairways or watching from home, fans can more fully appreciate the performance of the world’s best golfers at the sport’s most prestigious tournament. In a continuous design thinking…
IBM Tech Now: April 8, 2024
< 1 min read - Welcome IBM Tech Now, our video web series featuring the latest and greatest news and announcements in the world of technology. Make sure you subscribe to our YouTube channel to be notified every time a new IBM Tech Now video is published. IBM Tech Now: Episode 96 On this episode, we're covering the following topics: IBM Cloud Logs A collaboration with IBM watsonx.ai and Anaconda IBM offerings in the G2 Spring Reports Stay plugged in You can check out the…
Bakstage.AI integrates IBM watsonx.ai to help businesses unlock the full potential of their online sales
2 min read - There is an ongoing discussion as to whether consumers prefer interacting either with chatbots or with people. With the proliferation of AI, this conversation is not going away any time soon. However, at Bakstage.AI, we don’t believe that it should be an either/or proposition. Instead, we think AI should be used to empower sales specialists and customer service professionals with insights in real-time and post-conversations, so that every interaction can be extremely personalized and tailored to each customer. That’s why…
IBM Newsletters

- Call Center
- Self Service
- Branches & Stores
- Tech Support
- Virtual Assistants
- Knowledge Portal
- Distributed Workforce
- Salesforce Integration
- Zendesk Integration
- Freshworks Integration
- Hospitality & Travel
- Case Studies
- Resources Center
- Lighthouse University
- ROI Calculator
- News & Events
You’re in good company
See how our customers use Lighthouse to enhance customer experience

Case studies
Companies across a wide array of industries have successfully implemented Lighthouse to transform their customers’ experience. We have a growing base of case studies that demonstrate how we help our customers identify the issues, integrate the solutions, and realize highly improved business processes. Read through any or all of these case studies to learn how effectively KMS Lighthouse serves the needs of our customers.

Accessibility Toolbar
- Powered with favorite Love by Codenroll
Knowledge Management: A Case Study of CeedOman company, Issues and Solutions
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
- Administración
Knowledge Management. Case studies
- A Angel L. Arboníes, Jon Landeta y Olga Rivera
- 13 minutos de lectura
Case studies are used by the Knowledge Management Society (KMS) as a tool in promoting the dissemination of Knowledge management to other agents.
To begin with, case studies are used in teaching. Here the relationship between university and firm facilitates the externalization of tacit Knowledge. What is new is that these case studies relate to Basque firms, are mainly SMEs. This is an important point, since the managerial practice in question is described in its proper context. Moreover, the purpose of these case studies, from the point of view of the Knowledge Management Society, is to promote new Knowledge on the basis of the socialization, internalization, and combination of knowledge through such agents as consultancies, universities, and management-related institutions and other firms.
MANAGEMENT AND CONTEXT
Ideas about management need to be proved useful in practice. Managers and other professionals refer constantly to what works and what does not. The problem is less a scientific one than one of social acceptance. Social acceptance is a cultural phenomenon in which social agents must modify ideas for adaptation to the requirements of the local culture.
There is a system in which agents and institutions interact in this process. No one has control over management. Rather managers, politicians, and consultants are value creators, forming part of the national skill formation system [Mohr, 1982].
EXTERNAL FORCES
- Economic and political circumstances
NECESSARY CONDITIONS
- Teachers in business administration
- Politicians
- Business groups
INTERACTION
- Interaction between the groups
NEW KNOWLEDGE
TABLE 1. Adapted from Mohr (1982)
This theory of social context would appear to run counter to globalization. One of the most important topics dealt with in the area of globalization is that of business knowledge, which has emerged in full force over the last few years. Here knowledge has grown exponentially, as can be seen in the literature regarding management structures and their various types.
The term globalization generally connotes a world that is becoming more uniform, one in which Western capitalism is imposing standardization on technological, commercial, and cultural phenomena. However, recent studies suggest that each region establishes its own characteristics. And this can indeed be seen in managerial practice. With Withley we assert that «management is more social- and context-dependent than other so-called sciences.»
On the other hand there is a tendency, in transferring managerial Knowledge, to concentrate on the context at source rather than on the context within which the transfer will be received. Thus a lot of managerial Knowledge is concentrated within large firms. In large firms there is no problem in acquiring such Knowledge, while a mere reduction in scale may not be the way to adapt it to the needs of SMEs. For one thing the management of the smaller firm in industry is not necessarily less complex than that of the large one.
Newel, Robertson, and Swan have shown that the professional associations have a major role to play in the diffusion of Knowledge by providing a forum for the setting up of networks between organizations.
The Knowledge Management Society in the Basque Country is a network of universities, business schools, consultants, firms, agencies, and public bodies, engaged in producing and disseminating business Knowledge. In the era of post-bureaucratic organizations, knowledge theory has come to endorse change and creativity, and some consultants are developing products aimed at the diffusion of management Knowledge. In particular, Knowledge Management Society is concerned first with creation, adaptation, diffusion, and implementation, and secondly with the institutional conditions for the social acceptance of ideas in management. Knowledge and action, theory and practice follow one another.
The Knowledge Management Society is put into practice in accordance with the concept of the KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT VALUE CHAIN
…………………………. Creation ……… Adaptation ……. Dissemination ……. Action
TABLE 2. Knowledge Management Value Chain
Managerial culture in the Basque Country is technically oriented, with an emphasis on SMEs, and with an incipient but strong commitment of working with public bodies. The Basque Country has emerged from an industrial crisis but many companies have been transformed and have become leaders. Accordingly we suspect that there is a lot of implicit knowledge to be disseminated.
Case studies are a powerful tool, useful as an aid not only to teaching but also to making knowledge available to others and thus to enhancing the performance of firms in a given region. Where the objective is to introduce new, advanced practices into firms less aware of developments, the credibility of the company or manager supplying the case history must greatly bear on the effectiveness of dissemination, since many managers are looking for knowledge that can be translated into action. A detailed case history will help managers by affording lessons for learning, especially if it is chosen in light of the geographical and cultural conditions in question.
THE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT VALUE : CIRCULAR PERSPECTIVE
In a linear perspective the agents chiefly concerned with creating fresh management knowledge are to be found in the academic community. The fruit of their research must be converted into tools and methods so that firms can apply it. This conversion is the task of consulting firms. Academics, consultants, publishers, pioneer firms, and so on publicize the new advances. The process comes to an end when the knowledge is adopted by firms in general. Their role is passive to the extent that they simply take aboard the new knowledge coming from the external agents.
The foregoing might be regarded as a linear view of the matter. A circular view is closer to Schumpeter’s theory of the firm. Here it is recognized that knowledge can be created by firms as well, even if their means differ from those of academics and consultants. The theoretical work of Tackeuchi & Nonaka in regard to the mechanisms used by firms to create Knowledge is truly insightful:
- A given firm, or individuals within it, can receive knowledge from external agents or from other members of the organization, but the process in one case is different from that in the other.
- A given firm, or individuals within it, can create vast stores of tacit knowledge, but this must become explicit if it is to be shared by other agents, or by other individuals in the firm.
Where the question is how they should relate to one another, this new perspective represents a challenge for the various agents involved in the management Knowledge value chain. The status quo is no longer good enough.
CASE STUDIES AS A TOOL USED IN UNCOVERING AND DISSEMINATING MANAGERIAL KNOWLEDGE
Using written case studies to externalize knowledge.
If we take a circular view of the Knowledge value chain, and note the importance of the firm as creating agent, then we are designing instruments that make it possible to pick up the knowledge generated and accumulated in company organizations. This is the first step in the process leading to its dissemination.
Managerial Knowledge is basically tacit, so that it must be drawn out, arranged, and externalized. The methods used must enable the investigator to understand the circumstances in which the Knowledge has come into being and in which he finds its effective application. This means making a major effort to understand the business context in question, as well as the history behind it.
The methods already developed for the writing up of cases1, and in a broader framework for social research, may prove a valuable aid toward achievement of the objective. Where these research methods are not known, and, as often happen in a business environment, time is not as abundant as it might be, external specialists should be involved. These will include researchers, consultants, and students.
Naturally, any research method employed in uncovering tacit knowledge should ascribe major importance to the members of the organization in question. The researcher must observe and delimit the circumstances, formulate hypotheses and test them, get information, arrange it and write it up, and so on, but the Knowledge and the guidelines that might be used in getting at it are inside the members of the firm. Interviews with important people in the organization and in its environment are the most appropriate aid to picking up that information in its entirety. It is useful to consult the written and graphic material available (brochures, memos, web pages, accounting data, questionnaires mailed in by executives), but this is not enough.
CASES AS AN INSTRUMENT IN THE DISSEMINATION OF MANAGERIAL KNOWLEDGE
When the Knowledge has been externalized, then the risk of its loss, from the point of view of the firm or of society, is naturally lessened2. Its attractive and faithful exposition in the form of company cases will facilitate its diffusion.
On the one hand, it may in this form be easily conveyed to the actual members of the organization in question. It will be an interesting instrument for use in communicating and educating, for use along with other means of dissemination employed inside the firm3.
On the other hand, knowledge may be conveyed to individuals outside the firm. Here we are concerned with the use of cases in external diffusion and management training.
Executives generally wish to acquire knowledge that can be related to what they already know, that will find practical application in real situations, and that will help them in the work they already do. The learning undertaken should be suited to these particularities. In addition, it should entail experimentation and reflection4.
If we take for reference the classification proposed by Ausubel, learning may range from rote to significant, the aim in the latter case being to raise the quality and intensity of the links established between the new material and the old. Or it may range from learning by reception, i.e. where the teacher is the main transmitter, to learning by independent discovery, i.e. discovery with external aid. Somewhere in between we find guided discovery (See Table 4)
Learning via cases is thus significant, or it may be tantamount to learning by discovery (independently, or, more probably, under guidance).
Depending on the manner in which it is carried out, it shares a field of operation with teaching methods that seek basically to develop skills, such as guided discussion, role-playing, structured exercises, business games, group undertakings, seminars, or even reading. Without doubt, however, it exhibits different characteristics. (See Table 5)
The case method makes it possible to move appropriately and directly from theory to practice, to the acquisition of information regarding life as it really is for executives in the firm, with a look at team work, the taking of decisions, the summing up of information, the exercise of creativity, and oral reasoning.
The Knowledge and skills here referred to can be dealt with in various ways. There may be variations in the method of case study, e.g. the Kogan method [García del Junco and Castellanos, 1997], the situation method [García del Junco and Castellanos, 1998] and the critical incident method [García del Junco and Castellanos, 1997].
These achievements are of particular interest in higher-level business courses, i.e. when there is already a theoretical basis on which to undertake significant learning, as well as continuous and postgraduate training. In this latter case the student’s experience may conduce to more active participation, as well as to more efficient use of class time, with assimilation and swifter application of the proposals that have arisen.5
In whichever case, the didactic value of this method like that of any other, derives more from the context in which it is used than from its intrinsic qualities. The context is what gives it real value and allows one to adjust the objectives and mechanics of each exercise and training method to the interests and potentialities of the students, trainers, and firms.
Thus the one case, on paper, may be used in very different ways. It may be used as a basis for taking business decisions in a group or in the classroom, whether or not the students have experience. It may be used as an example of corporate strategies within the framework of a teacher’s exposition. Or it may be used as reading material in relation to outstanding practices and events in a business, suitable for the interested student or as a vehicle for conveying executive Knowledge, cultural values, or any other information of interest to the members of the organization in question.
TABLE 4. Types of learning (Ausubel)
TABLE 5. Teaching methods (based on Ausubel)
CASE STUDIES AT THE KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT SOCIETY
The Knowledge Management Society in the Basque Country is using case studies as an aid not only to teaching but also to collaboration between agents of the management system, the final aim being to make people aware of new ideas in management.
- The most traditional way to use the case method is focused on the learning process of students or practitioners in formation and educational programs. From the point of view of learning process is a way to internalize the explicit knowledge transferred at the formal educational program, by the assumption of the manager role at the case study
- Our experience shows that the case method can also be used inside the firm on which the case study in being based, to achieve a process of externalization of the tacit knowledge created by the firm through their experience.
- Once this process of externalization has been accomplished, the results are not only useful for the firm but also can be diffused and adapted by other firms and agents of the Knowledge Value Chain.
A relation of this sort between the academic and business worlds makes it possible to rectify one of the most serious deficiencies where the creation of new knowledge by practitioners is concerned, as well as one of the major restrictions on the process of learning through experience. It provides the time needed to reflect in a structured way on decisions and initiatives taken in the past.
METHODOLOGY
The principal distinguishing feature in our method is that cases are closed and finished. In a given case there is no first part, devoted to exposition, followed by a reply. And the student is in no way put in the place of the decision-makers.
A case adheres to the following rules, which in this way contribute to the achievement of the objectives described in the course of the present paper:
Selection of Cases
- Firms with growth rates above average in the sector, associated with the generation of employment, and enjoying a certain social prestige. The key to success should lie largely in changes undertaken in management.
- They act as driving forces, providing encouragement to firms that are reluctant to use advanced management tools.
Real and Nearby Data
- Names and other data are real.
- Better credibility.
- Concentration is on Basque industry, specifically industrial SMEs.
- Use of the cases in different situations between the university, the firm, consultants, etc.
The Expressions Are Respected
- The writers are university professors of the highest level, but they do not write up reality as they would like it to be, or from a critical point of view. Their aim is to get the facts, sum them up, and arrange them in organized fashion.
- The teacher learns in the process.
- There is no repetition of theoretical schemata already set forth in books on management. Rather the approach is to adapt this knowledge to particular circumstances.
- Real tacit knowledge is conveyed.
Cases Are Not Classified
- They do not belong to any area, e.g. Marketing, Human Resources, and Finance.
Advantages
- They make it possible to take a closer look at corporate circumstances and at how knowledge is applied in management, as executives know it.
A Work Nucleus, Various Derivatives
- A work nucleus is considered that has inspired the management of the firm and hypothetically has contributed to its success.
- In the notes for the teacher there are other themes suggested for discussion and use.
- They can be used with absolute flexibility in various areas.
- Overall it is demonstrated that there are many routes to success.
The Teacher’s Notes Are Not A Solution for the Case
- No solution is proposed. The teacher does not have control of the case. Advantages
- They are useful especially for open discussions, examinations, group work, comparative work, etc.
- They can be used on a visit to the firm or on executives’ visits.
CONCLUSIONS
The Knowledge Management Society at the Basque Country (Spain) is using case studies using a wide scope, thus is to convert tacit knowledge embedded in firms into explicit knowledge. The writing and teaching of case studies is used in a process of knowledge management conversion.
1To include a reference or two consulted in preparing the methodology employed in the study of advanced- management firms in the Basque Country.
2 The chance that Knowledge will be lost through the disappearance of its possessors is reduced, but there is a greater possibility that it will be shared, and this may be an aid to the enhancement of operations within the company in question, in other companies, and in society generally. There is, however, the chance that competitive advantage will be lost. The firm will therefore wish to determine how much diffusion is wanted, and what its scope should be. See Grant, R.M. (1991), «The Resource-Based Theory of Competitive Advantage: Implications for Strategic Formulation», California Management Review, 33, pp. 114-135. And also Grant, R.M. (1996), «Toward a Knowledge-Based Theory of the Firm», Strategic Management Journal, vol. 17, pp. 109-122.
3For a closer look at the types and mechanisms of internal Knowledge diffusion, see the following:
Fernández, E. (1996): Innovación, tecnología y alianzas estratégicas. Factores clave de la competencia. Cívitas, Madrid.
Grant, R.M. (1996), «Toward a Knowledge-Based Theory of the Firm», op. cit.
Nonaka, I. and Takeuchi, H. (1995), The Knowledge Creating Company: How Japanese Companies Create the Dynamics of Innovation, Oxford University Press, New York.
4Mintzberg, H. (1983): La naturaleza del trabajo directivo, Airel, Barcelona. «Learning is most effective when the student develops a skill in as realistic a situation as possible and later examines explicitly what he has done…. He should put skills into practice and examine the results, and he should study the critical comments of someone versed in the matter.» (p. 246)
5Snow (1976), cited by Díez de Castro and others (1989, p. 164), observed that low-order managerial achievements, such as the identification or description of object or subject, are more easily attained to via more passive methods, methods more controlled by the instructor, e.g. exposition, reading, debates. On the other hand, managerial objectives at higher level, e.g. the acquisition of skills for the resolution of complex problems, call for methods in which the student’s contribution is more active (cases, experiments, simulations, etc.).
Ausubel, D.P. Psicología educativa. Un punto de vista cognitivo. (Ed. Trillas, Mexico, 1976)
Díez de Castro, E.; Leal, A.; and Martín, F., «La enseñanza de administración de empresas», Revista de Economía y
Empresa, (1989), vol. X. no. 24.25, pp. 159-176.
García del Junco, J. and Castellanos Verdugo, M, «El método de las situaciones: herramientas de diagnóstico y decisión», Dirección y Organización, (1998) 19, pp. 95-115.
García de Junco, J. and Castellanos Verdugo, M., «La formación de directivos a través del estudio de incidentes», Capital Humano, (1997) 102, pp.25-31
García del Junco, J. and others, Casos prácticos de Economía de la Empresa. (Pirámide, Madrid, 1998) García del Junco, J. and others, Casos prácticos de Economía de la Empresa. (Pirámide, Madrid, 1998) Gimeno, J., Teoría de la enseñanza y desarrollo del currículo, (Anaya, Salamanca, 1985)
Mohr, Laurence, Explaining Organizational Behaviour: The limits and possibilities of Theory and Research. (San Francisco CA: Jossey Bass, 1982)
Mucchielli, R., La Méthode des cas, L’Enterprise Moderne, (Paris, 1968)
Newell, S., Robertson, M. and Swan, J., Proffessional Associations as Brokers, Facilitating Networking and the Diffusion of new Ideas, in The Diffusion and Comsuption of Business Knowledge (Alvarez, J.L, McMillan Press Ltd, 1998)
Withley, Richard, European Business Systems (London: Sage, 1992)
Cita esta página
Escrito por:.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Knowledge Management Case Study

The goal of this article is to understand better the knowledge management sides, the author examined two case studies that observed two distinctive knowledge management's issue; the author showed and enumerated the essential organizational issues objectives that were solved when the implementation of knowledge management took place. The author also probed about the obstacles that were faced, in addition, he gave many outlets to overcome these issues. The author also discussed the knowledge management issue in Eureka system that raised by Cox. Then, he identified the difficulties relate to Eureka system with photocopier's repairmen and the management, and then he gauged the degree of the problem inside the organization. Eventually, he derived a couple of solutions and aspects for a successful Knowledge Management implementation
Related Papers
Prof. Peyman Akhavan
International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Research Technology
Ijesrt Journal
Every organization and institute is facing the savior problem of generating the knowledge on the basis of their assets. Knowledge management is very indispensable for any organization. We discuss about the knowledge management through this paper. This paper provide an outline of knowledge management and how knowledge management is useful to improve the quality of the educational institute. With the help of knowledge management system we can manage any information. We can define knowledge management such as it is a gathering of interesting and useful information. Knowledge management is not a technology but knowledge management is a collection of process that manage information.
International Journal of Knowledge Management
Dr Suraj Kumar Mukti
Over of the past several years, there have been rigorous discussions about the significance of knowledge management (KM) within the organization and the society. The management of knowledge is endorsed as a significant and essential factor for organizational existence and maintenance of ambitious strength. This article provides an in-depth knowledge of factors affecting KM. Literatures from 1992 to 2018 are covered in this article, 169 research papers have been explored which are related to classification of knowledge, factors affecting KM, KM tools and its planning & application. Various frameworks related to the successful implementation of KM and KM implementation tools proposed by previous authors are presented in this research article. KM is defined, classification of KM is presented, factors affecting KM are shown and its implementation strategies & tools are elucidated in available literatures in discrete manner.
maryam hassanzadeh
Information Impact: Journal of Information and Knowledge Management
Hamad Bin Malik
Recent years have witnessed a growing interest on the part of the business sector to adopt the notion of knowledge management (KM), and it has become a very important and influential factor in the success or failure of an organization. As a result, the literature about this management concept has grown in its quantity and quality. According to Magd and Hamza (2012), basic economic resources are comprised not only of capital, or natural resources, or workers, but also of knowledge, which will be the main engine of activities leading to wealth and the production of new projects; hence, many researchers have studied the principles of knowledge management and the ways to implement them within organizations. This paper explains some principles of knowledge management. First, it presents several definitions of the term ‘principle.’ Then, it highlights the background of knowledge management. Finally, it discusses three principles of knowledge management: the expensive of knowledge management (unintelligent concept), the importance of managers, and the fact that improving knowledge means sharing.
Desidoc Journal of Library Information Technology
Anjali Gulati
ABSTRACT Knowledge management describes the way in which organisations are attempting to capture, enhance, and use the knowledge necessary for their survival. In this paper, the author discusses about concept of knowledge management, contribution of ...
Dr. Elijah Clark
Dr Mostafa Jafari
Jesilin Manjula
RELATED PAPERS
Cahiers de Biologie Marine
Michał Majsterek
Manuel/Magnesium
Uri Vainberg
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences
chakravarthy thejesh
Dmitriy Palatnik
Biomedical Research and Therapy
Nguyen Van Thuan
2016 IEEE International Conference on Automatica (ICA-ACCA)
Usman Nasir
BMC Research Notes
Johanna Lönn
Hemşirelikte Eğitim ve Araştırma Dergisi
Sibel Yolcu
erwin hidayatulloh
Izabela Augustyniak
Victor Hugo Salazar Ortiz
Journal of Enterprising Communities: People and Places in the Global Economy
MOHAMMAD IMTIAZ HOSSAIN , Mohammad Nurul Alam
Optical Review
Taehyung Park
Environmental Science and Pollution Research
GANEZ REGAN
Ganatubuuka Regan
Interdisciplinary Journal of Research and Development
Kamila Karaj
Peace Psychology Book Series
Klaus Boehnke
Church History
George Keiser
Physical review
Gary Goldstein
ACS Synthetic Biology
Andrew Garst
Indo Nordic Author's Collective
Dr. Uday Dokras
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology
Hoda Mohamed
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Privacy Policy
Knowledge Management Case Study With Solution
Managing knowledge and information systems explained with knowledge management case study., introduction.
Knowledge management is an important aspect of every organization. This is because, in a knowledge-based setting, organizations usually encounter problems as they seek to diversify their processes and manage knowledge. Consequently, the need to identify the causes of the problems they face arises, and thus, proffering solutions to this problems become one of the major challenges. This is exemplary in the case study of this paper. TPMT is faced with some challenges that require a high level of knowledge management to solve. In order to address some of these problems, web 2.0 technologies would be needed and applicable, especially when the need to develop customer relationship arises. And since web 2.0 is a technology trend that fascinates perfect information sharing, increased collaboration, and improved functionality of a website, it can further address the major problem under study.
The Key Knowledge Management (KM) Business Problems in TPMT
The flow of communication is absolutely imperative to business success and performance. Especially, when the business is operated in different countries, it is very important to maintain an excellent level of communication and motivation across all branches, with the agents, customers, and offices. Although, different countries have their specific unique business environments, the growth of any business is based on the cooperation of all staff working as part of a particular organisation. (“Nibusiness n.d”)
Additionally, there are various means of communication which include formal and informal communication. The absence of any of these communication means could lead to a serious low productivity within an organization. (“Reference for Business”) In order to create or establish a strong relationship with customers for their premium satisfaction, it becomes necessary to provide a means whereby customers can easily interact with the organization at any level so that the integrity and the name the organization is building or protecting can remain successful. Furthermore, it is also a known fact that customer service is imperative for business success. However, to many organizations, customer service is one of the most difficult and challenging aspect of their management, including those that are provided with modern call-centres. (“businessballs n.d”) To many customers, the quality of customer service determines whether they can confide in an organization to buy, and most importantly to remain a customer or become a repeat buyer to an organization. (“businessballs n.d”)
Moreover, business communication encompasses other important issues, such as brand management, corporate communication, customer relations, community engagement, interpersonal communication, reputation management, employee engagement, and marketing communication. (“Business Dictionary n.d: Wikipedia”) When any of these is lacking between the management of an organization and its consumer or customers, it may deter the productivity of that organization. Employing interpersonal communication with customers also helps develop a strong relationship with them. This can be achieved using several methods of business communication including the web-based communication which provides a better and enhanced communication, anytime and anywhere, video conferencing which permits people in various locations to hold any interactive meetings, reports which helps in documenting the activities of the department of an organisation, presentations which gives an audio-visual relationship with customers, telephone conversation for long distance communication, face-to-face meetings which allows interpersonal conversation and succeeded by a written follow-up, (Newman et al. 2013: Wikipedia)
Also Study: Pillars of Knowledge Management Examples in Organizations
Therefore, in the case of TPMT, these are the major challenges being faced. The management at headquarter in the UK finds it difficult to maintain an excellent relationship with the customers in other parts of the country in which they are operated in. In the countries that are provided with agents, the agents are supposed to develop a high level of communication with the customers. However, TPMT should also ensure there is a direct link customers can reach them directly from any part of the countries in which they operate through any of the above-listed communication mediums. On the other hand, for countries that are not provided with agents, but have to be contacted when they are needed, there are more indications that the organization may not be successfully run since they are not operating a full-time operation. Therefore, customers still have to be linked with TPMT directly based on any of the above-listed communication tools. Thus, building a mutual relationship with the customer to improve and support sales as required.
An Overview of the Characteristics of Web 2.0 Technologies
Web 2.0 technologies have so many descriptions attached to it. But, it can be simply described as the representation of an important shift based on the way digital information is created, stored, shared, administered, distributed, collaborated, and manipulated. (Wolcott 2007) Basically, one of the major features of this technologies is the fact that it had led to the development of hosted services and Web-based communities, such as the social-networking sites (that is, Facebook, MySpace, Twitter, etc), video sharing websites (that is, YouTube), blogs, wiki, etc. This is because it is the changing trends in the utilization of World Wide Web (WWW) technology and Web design targeted at enhancing its main function of creating and securing information sharing. (Stern n.d) Some of the key features of Web 2.0 technologies include:
- User control: In the traditional web, the content provided on a website is done by the site owner, and the user always receives it, thus making the information model One Way. However, Web 2.0 user can contribute to the content through evaluation, commenting, and reviewing. (“WebAppRater 2010”)
- Network as a platform: This is applicable in the delivering of information and applications completely through a web browser. For example, Google Docs and Spreadsheets. (“usf.edu 2011”)
- Social network features: With this, users can freely share information with one another. Most of the web 2.0 websites offers the accessibility to build a network of other users for sharing resources that could have been stored online. For example, del.icious a social bookmarking website that allows the storage of bookmarks on the Internet and sharing them with other del.icio.us users. (“usf.edu 2011”)
- An architecture of participation encouraging users to put together value to the application the moment it is used. For example, a website that performs the responsibility of tracking popular news stories and any other blog posts using users to vote on the. (“usf.edu 2011”)
- Folksonomy: Web 2.0 does not have to stick to existing framework of categories, but allows a user to create free arrangement/classification of information. (“WebAppRater 2010”)
- A rich, interactive, and user-friendly interface: Many of interactive website on the Internet are map services. For instance, Google Maps or Yahoo Maps. Additionally, Web 2.0 makes use of Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript with XML) offering dynamic and rich user experience to the users. (Levy 2010)
The Benefits and Challenges of Applying Web 2.0 Technologies
Every tool or technology will be developed comes with amazing features that could either offer awesome benefit to its application for the user or pose a challenge when using it for a particular purpose. Consequently, different organizations benefit from Web 2.0 and this could be used to address TPMT’s problems, however, using these technologies to solve TPMT’s problem may come along with some challenges.
Benefits of Web 2.0 Technologies to Solving TPMT’s Problem
Web 2.0 offers a high level of socialization. Web users now experience a level of customization and interactivity in the sites they visit. (Kooser 2007) Business owners can only provide this through social networking. In the case of TPMT, the barrier between the Director and the customers can be eradicated with the use of Web 2.0 technology when integrated into the social networks. Since this is majorly the problem even with those countries that still have agents, there is need for strong communication to build an effective relationship.
Furthermore, integrating an interactive community in which users (TPMT customers) through which they can communicate with the directors can help gather feedbacks, allowing the customers to provide suggestions and also provide input for developments. Although, achieving this has to be constructively carried out. (Hinchcliffe 2007: Kooser 2007) When TPMT employs this integration into the social networks, they will achieve a lowered support cost, and thus earn more customer satisfaction. (Quarterly 2009) The need for this in TPMT is necessary since it is a networked company that has to interact with other countries. Thus, an internal integration of the Web 2.0 technologies tools among the agents will strengthen the company ties with even the external stakeholders who are the customers and business partners (Quarterly 2009) of TPMT.
Additionally, Web 2.0 offers the benefits of expanding opportunities for collaboration and also allowing the spread of knowledge more effectively. This provides the capability of the director to put powerful collaboration tools in the hands of the employees, agents, and the customers, this is where the chain of command begins to look similar to a spider web. The director can integrate a hosted online collaboration service based in the UK that mixes with wikis, group calendars, blogs, and file sharing. (Kooser 2007) These tools are basically popular among consumers too. For example, organization who made use of these tools have cited that many RSS, blogs, and social networks are very important in the exchange of knowledge. Some other companies reported to use web videos too since they are easier to produce and disseminate within and outside of the organizations. (Quarterly 2007)
Challenges of Web 2.0 Technologies to Solving TPMT’s Problem
The risks of the information security must be considered. This is related to the protection of intellectual property, personally identifiable information, trade secrets, or any other sensitive information. Putting information with the agents or customers is certainly not uncommon. But having to monitor shared information on the Internet requires strict and close security controls. This is because many of the Web 2.0 applications do not contain provision for the monitoring of content or traffic to make sure that sensitive information is not being aired inappropriately. (Cunningham 2009)
Furthermore, infrastructure duplication is one of the major challenges while implementing Web 2.0 technologies. As much as many organizations find the use of Web 2.0 applications very easily in meeting their daily needs, many other organization still needs to retain their e-mail infrastructure and licenses to only commercial off-the-shelf software. TPMT would have to spend more to ensure this is successful. From helping the agents understand the processes as well as the customers. Thereby, defeating the aspect of cost savings as well as the infrastructure management promised by the Web 2.0 technologies. (Cunningham 2009)
Moreover, being very smart is necessary while implementing the Web 2.0 technologies. The public nature of many of the Web 2.0 technologies invites users to share information about themselves. One factor to consider is the blurring lines between personal details and business details. However, many organizations have some challenges with some employees who leak out information about their company in their personal spaces on the Internet. The more the adoption of Web 2.0 tools are considered, the more it is necessary to take great care to clearly define what belongs to the organization and what should belong to the individual. (Cunningham 2009) In TPMT, some agents work part-time only when they are needed, and even those full-time workers who work for 2 years get more information about the company that they could use it elsewhere. So implementing Web 2.0 in this regard can be very risky.
Recommendations
TPMT is assumed to be a small organization with temporary employees and agents in other countries. In order for TPMT’s Directors to be able to have their employees maintain good relationships with the buyers or customers so they can place future orders, TPMT Directors have to develop an innovative strategy to implement Web 2.0 in order to reap the benefits of better web interactivity, collaboration tools, and customization.
This can be implemented with knowledge management practices ensuring active participation of users. An instance this could be functional is using the social networks or blogs where users or TPMT knowledge can be shared and preserved. This knowledge depends on the users and without them, these activities cannot occur. When customers, who are the active users participate through comments and suggestions on contents placed via blogs or the social media, the Directors can see and understand the market value of their product as well as the rate of success of their business and would also motivate the employees to work knowing too well that the Directors are seeing comments made by customers which could be detrimental to their jobs. Additionally, when the customers’ participation is encouraged by the agents and employees, the need to add contents will arise and convincing people to comment and also add contents would arise as well. This implies that the contents have to be very simple, accessible, and also appealing. Basically, direct communication with customers through the agents is the major focus to build the relationship for a great revenue. This can also be integrated into the existing system through the need for building an effective RSS where customers are alerted on what’s new in the organization website and also ensuring the customers have a way of commenting or reviewing the products.
References:
- Business communication. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/business_communication
- BusinessBalls. customer service. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://www.businessballs.com/customer_service.htm
- Communication in Organizations. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://www.referenceforbusiness.com/encyclopedia/clo-con/communication-in-organizations.html
- Cunningham, P. (2009). Web 2.0: Issues & Risks. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://content.arma.org/imm/janfeb09/walk_in_the_cloud/web_2.0_issues_risks.aspx
- Face-to-Face Communication: The Trust That Helps Build a Business. (2012). Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://www.healio.com/orthotics-prosthetics/human-resources/news/print/o-and-p-news/{ab5bdfed-6cea-47d6-b2bb-9b57d79c406a}/face-to-face-communication-the-trust-that-helps-build-a-business
- Kooser, A. C. (2007). What Can Web 2.0 Do for Your Business? Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/173496
- Levy, M. (2009). WEB 2.0 implications on knowledge management. J Of Knowledge Management Journal of Knowledge Management , 13 (1), 120–134. https://doi.org/10.1108/13673270910931215
- Maintaining good communications between branches. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://www.nibusinessinfo.co.uk/content/maintaining-good-communications-between-branches
- Stern, J. Introduction to Web 2.0 Technologies , 1–9. Retrieved from https://www.wlac.edu/online/documents/web_2.0 v.02.pdf
- Quarterly, M. K. (2009). How companies are benefiting from Web 2.0: McKinsey Global Survey results. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/business-technology/our-insights/how-companies-are-benefiting-from-web-20-mckinsey-global-survey-results
- WebbAppRater Admin. (2010). 7 key features of web 2.0. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://webapprater.com/general/7-key-features-of-web-2-0.html
- What is effective communication? definition and meaning. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/effective-communication.html
- What is web 2.0. Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://etc.usf.edu/techease/win/internet/what-is-web-2-0/
- Wolcott, M. (2007). What Is Web 2.0? Retrieved April 22, 2016, from https://www.cbsnews.com/news/what-is-web-20/
Related Posts
A case study on sustainable building, suspicious behaviors of malware in android, how epa links with the superfund in new..., nokia case study analysis, importance of public spaces in a neighbourhood of..., community based tourism in uganda and tanzania, mount st. helens hazardous simulations, the contradiction of homosexuality, walmart cross-cultural issues case study analysis, case study on leadership and management, leave a comment cancel reply.
Please enter an answer in digits: 13 + seven =
Marketing Process Analysis
Segmentation, targeting, positioning, marketing strategic planning, marketing 5 concepts analysis, swot analysis & matrix, porter five forces analysis, pestel / pest / step analysis, cage distance analysis international marketing analysis leadership, organizational resilience analysis, bcg matrix / growth share matrix analysis, block chain supply chain management, paei management roles, leadership with empathy & compassion, triple bottom line analysis, mckinsey 7s analysis, smart analysis, vuca analysis ai ethics analysis analytics, hill & knowlton: knowledge management case study solution & analysis / mba resources.
- Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management
- Technology & Operations / MBA Resources
Introduction to case study solution
EMBA Pro case study solution for Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management case study
At EMBA PRO , we provide corporate level professional case study solution. Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management case study is a Harvard Business School (HBR) case study written by Darren Meister, Ken Mark. The Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management (referred as “Knowlton Hill” from here on) case study provides evaluation & decision scenario in field of Technology & Operations. It also touches upon business topics such as - Value proposition, IT, Knowledge management. Our immersive learning methodology from – case study discussions to simulations tools help MBA and EMBA professionals to - gain new insight, deepen their knowledge of the Technology & Operations field, and broaden their skill set.
Urgent - 12Hr
- 100% Plagiarism Free
- On Time Delivery | 27x7
- PayPal Secure
- 300 Words / Page
Case Description of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management Case Study
Hill & Knowlton is a division of one of the world's largest communication services group. Tagging e-mail communications to support knowledge management codification and connection strategies is an important issue for managers. Issues related to privacy and performance need to be considered. The worldwide director of knowledge management at Hill & Knowlton must assess the degree to which tagging should be enforced in a communication services organization that supports numerous clients around the world.
Case Authors : Darren Meister, Ken Mark
Topic : technology & operations, related areas : it, knowledge management, what is the case study method how can you use it to write case solution for hill & knowlton: knowledge management case study.
Almost all of the case studies contain well defined situations. MBA and EMBA professional can take advantage of these situations to - apply theoretical framework, recommend new processes, and use quantitative methods to suggest course of action. Awareness of the common situations can help MBA & EMBA professionals read the case study more efficiently, discuss it more effectively among the team members, narrow down the options, and write cogently.
Case Study Solution Approaches
Three Step Approach to Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management Case Study Solution
The three step case study solution approach comprises – Conclusions – MBA & EMBA professionals should state their conclusions at the very start. It helps in communicating the points directly and the direction one took. Reasons – At the second stage provide the reasons for the conclusions. Why you choose one course of action over the other. For example why the change effort failed in the case and what can be done to rectify it. Or how the marketing budget can be better spent using social media rather than traditional media. Evidences – Finally you should provide evidences to support your reasons. It has to come from the data provided within the case study rather than data from outside world. Evidences should be both compelling and consistent. In case study method there is ‘no right’ answer, just how effectively you analyzed the situation based on incomplete information and multiple scenarios.
Case Study Solution of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management
We write Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management case study solution using Harvard Business Review case writing framework & HBR Technology & Operations learning notes. We try to cover all the bases in the field of Technology & Operations, IT, Knowledge management and other related areas.
Objectives of using various frameworks in Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management case study solution
By using the above frameworks for Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management case study solutions, you can clearly draw conclusions on the following areas – What are the strength and weaknesses of Knowlton Hill (SWOT Analysis) What are external factors that are impacting the business environment (PESTEL Analysis) Should Knowlton Hill enter new market or launch new product (Opportunities & Threats from SWOT Analysis) What will be the expected profitability of the new products or services (Porter Five Forces Analysis) How it can improve the profitability in a given industry (Porter Value Chain Analysis) What are the resources needed to increase profitability (VRIO Analysis) Finally which business to continue, where to invest further and from which to get out (BCG Growth Share Analysis)
SWOT Analysis of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management
SWOT analysis stands for – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. Strengths and Weaknesses are result of Knowlton Hill internal factors, while opportunities and threats arise from developments in external environment in which Knowlton Hill operates. SWOT analysis will help us in not only getting a better insight into Knowlton Hill present competitive advantage but also help us in how things have to evolve to maintain and consolidate the competitive advantage.
- High customer loyalty & repeat purchase among existing customers – Knowlton Hill old customers are still loyal to the firm even though it has limited success with millennial. I believe that Knowlton Hill can make a transition even by keeping these people on board.
- Strong Balance Sheet – The financial statement of Knowlton Hill looks strong and will help the company going forward.
- Little experience of international market – Even though it is a major player in local market, Knowlton Hill has little experience in international market. According to Darren Meister, Ken Mark , Knowlton Hill needs international talent to penetrate into developing markets.
- Low profitability which can hamper new project investment – Even though Knowlton Hill financial statement is stable, but going forward Knowlton Hill 5-7% profitability can lead to shortage of funds to invest into new projects.
Opportunities
- E-Commerce and Social Media Oriented Business Models – E-commerce business model can help Knowlton Hill to tie up with local suppliers and logistics provider in international market. Social media growth can help Knowlton Hill to reduce the cost of entering new market and reaching to customers at a significantly lower marketing budget.
- Lucrative Opportunities in International Markets – Globalization has led to opportunities in the international market. Knowlton Hill is in prime position to tap on those opportunities and grow the market share.
- Home market marketing technique won’t work in new markets such as India and China where scale is prized over profitability.
- Customers are moving toward mobile first environment which can hamper the growth as Knowlton Hill still hasn’t got a comprehensive mobile strategy.
Once all the factors mentioned in the Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management case study are organized based on SWOT analysis, just remove the non essential factors. This will help you in building a weighted SWOT analysis which reflects the real importance of factors rather than just tabulation of all the factors mentioned in the case.
What is PESTEL Analysis
PESTEL /PEST / STEP Analysis of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management Case Study
PESTEL stands for – Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors that impact the macro environment in which Knowlton Hill operates in. Darren Meister, Ken Mark provides extensive information about PESTEL factors in Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management case study.
Political Factors
- Little dangers of armed conflict – Based on the research done by international foreign policy institutions, it is safe to conclude that there is very little probability of country entering into an armed conflict with another state.
- Political consensus among various parties regarding taxation rate and investment policies. Over the years the country has progressively worked to lower the entry of barrier and streamline the tax structure.
Economic Factors
- Inflation rate is one of the key criteria to consider for Knowlton Hill before entering into a new market.
- Foreign Exchange movement is also an indicator of economic stability. Knowlton Hill should closely consider the forex inflow and outflow. A number of Knowlton Hill competitors have lost money in countries such as Brazil, Argentina, and Venezuela due to volatile forex market.
Social Factors
- Demographic shifts in the economy are also a good social indicator for Knowlton Hill to predict not only overall trend in market but also demand for Knowlton Hill product among its core customer segments.
- Consumer buying behavior and consumer buying process – Knowlton Hill should closely follow the dynamics of why and how the consumers are buying the products both in existing categories and in segments that Knowlton Hill wants to enter.
Technological Factors
- 5G has potential to transform the business environment especially in terms of marketing and promotion for Knowlton Hill.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning will give rise to importance of speed over planning. Knowlton Hill needs to build strategies to operate in such an environment.
Environmental Factors
- Environmental regulations can impact the cost structure of Knowlton Hill. It can further impact the cost of doing business in certain markets.
- Consumer activism is significantly impacting Knowlton Hill branding, marketing and corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives.
Legal Factors
- Property rights are also an area of concern for Knowlton Hill as it needs to make significant IT, Knowledge management infrastructure investment just to enter new market.
- Intellectual property rights are one area where Knowlton Hill can face legal threats in some of the markets it is operating in.
What are Porter Five Forces
Porter Five Forces Analysis of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management
Competition among existing players, bargaining power of suppliers, bargaining power of buyers, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
What is VRIO Analysis
VRIO Analysis of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management
VRIO stands for – Value of the resource that Knowlton Hill possess, Rareness of those resource, Imitation Risk that competitors pose, and Organizational Competence of Knowlton Hill. VRIO and VRIN analysis can help the firm.
What is Porter Value Chain
Porter Value Chain Analysis of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management
As the name suggests Value Chain framework is developed by Michael Porter in 1980’s and it is primarily used for analyzing Knowlton Hill relative cost and value structure. Managers can use Porter Value Chain framework to disaggregate various processes and their relative costs in the Knowlton Hill. This will help in answering – the related costs and various sources of competitive advantages of Knowlton Hill in the markets it operates in. The process can also be done to competitors to understand their competitive advantages and competitive strategies. According to Michael Porter – Competitive Advantage is a relative term and has to be understood in the context of rivalry within an industry. So Value Chain competitive benchmarking should be done based on industry structure and bottlenecks.
What is BCG Growth Share Matrix
BCG Growth Share Matrix of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management
BCG Growth Share Matrix is very valuable tool to analyze Knowlton Hill strategic positioning in various sectors that it operates in and strategic options that are available to it. Product Market segmentation in BCG Growth Share matrix should be done with great care as there can be a scenario where Knowlton Hill can be market leader in the industry without being a dominant player or segment leader in any of the segment. BCG analysis should comprise not only growth share of industry & Knowlton Hill business unit but also Knowlton Hill - overall profitability, level of debt, debt paying capacity, growth potential, expansion expertise, dividend requirements from shareholders, and overall competitive strength. Two key considerations while using BCG Growth Share Matrix for Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management case study solution - How to calculate Weighted Average Market Share using BCG Growth Share Matrix Relative Weighted Average Market Share Vs Largest Competitor
5C Marketing Analysis of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management
4p marketing analysis of hill & knowlton: knowledge management, porter five forces analysis and solution of hill & knowlton: knowledge management, porter value chain analysis and solution of hill & knowlton: knowledge management, case memo & recommendation memo of hill & knowlton: knowledge management, blue ocean analysis and solution of hill & knowlton: knowledge management, marketing strategy and analysis hill & knowlton: knowledge management, vrio /vrin analysis & solution of hill & knowlton: knowledge management, pestel / step / pest analysis of hill & knowlton: knowledge management, swot analysis and solution of hill & knowlton: knowledge management, references & further readings.
Darren Meister, Ken Mark (2018) , "Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management Harvard Business Review Case Study. Published by HBR Publications.
Case Study Solution & Analysis
- First Virtual Holdings, Inc. (A) Case Study Solution & Analysis
- Knowledge Management at Accenture Case Study Solution & Analysis
- Government E-Procurement: Electronic Tendering System in the Hong Kong SAR Case Study Solution & Analysis
- H.E. Butt Grocery Co.: The New Digital Strategy (A) Case Study Solution & Analysis
- General Motors: Building a Digital Loyalty Network Through Demand and Supply Chain Integration Case Study Solution & Analysis
- Lucent Technologies: Optical Networking Group Case Study Solution & Analysis
- Pilkington Float Glass--1955 Case Study Solution & Analysis
- Silicon Graphics, Inc. (B) Case Study Solution & Analysis
- Baker Precision Instruments, Inc. Case Study Solution & Analysis
- Air Products and Chemicals, Inc.: MIS Reorganization (A) Case Study Solution & Analysis
Explore More
Feel free to connect with us if you need business research.
You can download Excel Template of Case Study Solution & Analysis of Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Knowledge Management (KM) is presently experiencing a rebirth, with greater executive interest and organizational commitment. ... Use Case #1: Knowledge Sharing and Retention. ... This solution allowed them to realize an array of Artificial Intelligence capabilities, including an intelligent chatbot, a recommendation engine, and an application ...
An organization's captured (and codified) knowledge--white papers, case studies, documented processes--should help project teams perform better, but does it? Existing research has not answered the question, even as U.S. companies alone spend billions annually on knowledge management programs.
Abstract. Sumario: The cases described here provide detailed examples focus on information-technology-based tools for KM, these cases pay close attention to people management and organisational ...
The study contributes to this literature and presents a case in which KM is a potential solution to enhance collaboration among the test labs' members of the Dutch railway infrastructure manager. Specifically, the evaluation shows a statistically significant reduction in file search time of the developed interface design compared to the ...
Knowledge Management Case Studies Volume II DIGITAL VERSION AVAILABLE A digital version of this CALL publication is available to view or download from the ... domains to provide a solution. Case study three is an example of a predominately civilian organization, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE), embarking on a deliberate change ...
Bamboo Solution's first case study shows how the Bamboo Consulting team addressed a large and growing company's knowledge management issues by leveraging the power of M365. Files and information stored across multiple repositories were consolidated into SharePoint Online. This solution included the creation of a corporate portal.
Purpose of the study: This study aims to gain an understanding of how (and if) the InterContinental Hotels Group (IHG) manages knowledge to create value. Methodology: Publicly available data about the IHG were assessed using Pawlowski and Bick's (2015) Global Knowledge Management Framework (GKMFW) to determine the extent to which the IHG is ...
Take a self guided Tour. See Bloomfire in action across several potential configurations. Imagine the potential of your team when they stop searching and start finding critical knowledge. Take a Test Drive. Discover how Bloomfire has helped companies successfully implement knowledge management systems and best practices using our solution.
Knowledge management (KM) is the process of identifying, organizing, storing and disseminating information within an organization. When knowledge is not easily accessible within an organization, it can be incredibly costly to a business as valuable time is spent seeking out relevant information versus completing outcome-focused tasks.
Let us help you deliver the answers to your customers and your agents through any user interface. livepro's speed brings answers through any channel. See what your ROI will be by using livepro to cut contact center costs. Discover the real-world impact of knowledge management with Livepro's case studies.
The latest edition of Deloitte's Global Human Capital Trends study ranks 'knowledge management' as one of the top three issues influencing company success, yet only 9 per cent of surveyed organisations feel ready to address it. 1 The transfer of knowledge has become even more essential as COVID-19 has scattered staff among homes and different work sites.
Knowledge Management at Accenture case study solution is focused on solving the strategic and operational challenges the protagonist of the case is facing. The challenges involve - evaluation of strategic options, key role of Technology & Operations, leadership qualities of the protagonist, and dynamics of the external environment.
According to IBM's Institute of Business Value (IBV), AI can contain contact center cases, enhancing customer experience by 70%. Additionally, AI can increase productivity in HR by 40% and in application modernization by 30%. One example of this is reducing labor burdens by automating ticket assistance through IT operations.
See how our customers use Lighthouse to enhance customer experience. Time savings gain of 60% for content management. Succinct 1 hour training to onboard all customer facing employees. Increased employee productivity by 150%. " KMS lighthouse has dramatically reduced our call center operational costs and agents' training time.
Knowledge has long been recognized as competitive tool and currency of the 21st century of organizations. The awareness has been increased about knowledge management in the organizations through specific knowledge management processes. Many organization concentrate to implement the best practice in managing the knowledge within the organization. This paper provides a holistic clarification ...
Journal of Education and Social Sciences, Vol. 6, Issue 2, (February) ISSN 2289-1552 2017 132 In the start of the existence of such a process Davenport (1994) made the following statement: "knowledge management is the process of capturing, distributing, and effectively using knowledge", being a clear and straightforward statement and point of view
Summary. Knowledge management is an essential practice but is difficult to achieve sustainably. This Solution Path guides application technical professionals through the process of establishing, growing and maturing an effective KM practice, and defines a maturity model for assessing progress.
Abstract Case studies are used by the Knowledge Management Society (KMS) as a tool in promoting the dissemination of Knowledge management to other agents. To begin with, case studies are used in teaching. Here the relationship between university and firm facilitates the externalization of tacit Knowledge. What is new is that these case studies relate […]
The first case study examines the efforts to implement and use a KM system at a tax firm, and the challenges encountered that defied resolution, leading to the KM system's demise. The second case study examines the building of a customer service solution that is based on a Knowledge Management system.
This case is about the knowledge management (KM) practices at Whirlpool Corporation (Whirlpool). In 1999, the then CEO of Whirlpool, David R. Whitwam (Whitwam), launched a worldwide effort to embed innovation as a core competency across the organization. He felt that Whirlpool could gain sustainable competitive advantage by focusing on innovation.
Dr. Momen Nachar. The goal of this article is to understand better the knowledge management sides, the author examined two case studies that observed two distinctive knowledge management's issue; the author showed and enumerated the essential organizational issues objectives that were solved when the implementation of knowledge management took ...
Knowledge management is an important aspect of every organization. This is because, in a knowledge-based setting, organizations usually encounter problems as they seek to diversify their processes and manage knowledge. Consequently, the need to identify the causes of the problems they face arises, and thus, proffering solutions to this problems ...
Three Step Approach to Hill & Knowlton: Knowledge Management Case Study Solution. Conclusions - MBA & EMBA professionals should state their conclusions at the very start. It helps in communicating the points directly and the direction one took. Reasons - At the second stage provide the reasons for the conclusions.