LITERATURE REVIEW AND HYPOTHESES
It is common to present the literature with supporting articles that are the foundation for your hypotheses—your tentative answer to the research questions stating the relationship between variables (what we already know supports what you believe your hypothesized results will be). Providing definitions of your conceptual variables is needed.
Your lit review should develop a theory. To make a contribution to the literature, your idea needs to be articulated, organized, and connected in a way that suggests new directions for researchers, fills a gap in the lit. Ideas are not a theory, regardless of how original they are. To be a theory, ideas have to be presented with a clear logic and causal relationship among the variables studied.
As stated in Chapter 6, Matching Publication Sources, be sure to match your literature review to that of your target journal. Use the same literature title heading and any subheadings commonly used in the target journal (literature review, conceptual framework, theoretical development and hypotheses, theory and hypotheses). Match paragraph lengths and writing level and format hypotheses exactly like in the target journal. The number of your references should be in the same range as other articles in your target journal, unless it is a very new topic with limited prior research. Again, cite articles from the target journal.
Here are some do’s and don’ts when writing your lit review.
- Keywords . Do use keywords when searching for the literature you will include in your review.
- Target journal . Do review and emulate the lit reviews of articles you cite, and match the target journal lit reviews. As stated, be sure to cite articles from the journal you will submit your work to.
- Hypotheses . Do format your hypotheses in the same way as the target journal articles (Chapter 6 Matching Publication Sources).
- Relevant . Do cite all the “relevant” articles that relate to your study. An article is not a dissertation, so don’t reference irrelevant articles.
The above is an excerpt of Dr. Lussier’s book, Publish Don’t Perish . More points for lit review, along with 170+ tips to get published are included.

15 Comments:
I just could not go away your site prior to suggesting that I extremely loved the usual info a person provide on your guests? Is gonna be again regularly in order to investigate cross-check new posts
Everything is very open with a really clear explanation of the issues. It was really informative. Your website is very helpful. Thank you for sharing!
Hi there,I read your new stuff named “LITERATURE REVIEW AND HYPOTHESES |” on a regular basis.Your humoristic style is awesome, keep doing what you’re doing! And you can look our website about proxy.
LITERATURE REVIEW AND HYPOTHESES | aiqsbvcnpq iqsbvcnpq http://www.g2499py76wcfvlm58936r27a36blobi5s.org/ [url=http://www.g2499py76wcfvlm58936r27a36blobi5s.org/]uiqsbvcnpq[/url]
I had a Springfield College student do an internship with me to develop the website
LITERATURE REVIEW AND HYPOTHESES | gdskmwvzgp http://www.g510m1752hjose40vwd9f300yo0q3z1os.org/ [url=http://www.g510m1752hjose40vwd9f300yo0q3z1os.org/]ugdskmwvzgp[/url] agdskmwvzgp
LITERATURE REVIEW AND HYPOTHESES | aqvhfxphfh [url=http://www.gr03x865dwpto35t0a18o1op942wog92s.org/]uqvhfxphfh[/url] qvhfxphfh http://www.gr03x865dwpto35t0a18o1op942wog92s.org/
There was no comment
Are you writing the articles in your website yourself or you outsource them? I am a blogger and having difficulty with content. Other bloggers told me I should use an AI content writer, they are actually pretty good. Here is a sample article some bloggers shared with me. Please let me know what your opinion on it and should I go ahead and use AI – https://sites.google.com/view/best-ai-content-writing-tools/home
I’m really not a good blogger. I used material from my Textbooks. Search Lussier on Amazon for my books.
If you are going for finest contents like me, only visit this web site every day because it gives feature contents, thanks
my web site tracfone special
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and site URL in my browser for next time I post a comment.

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
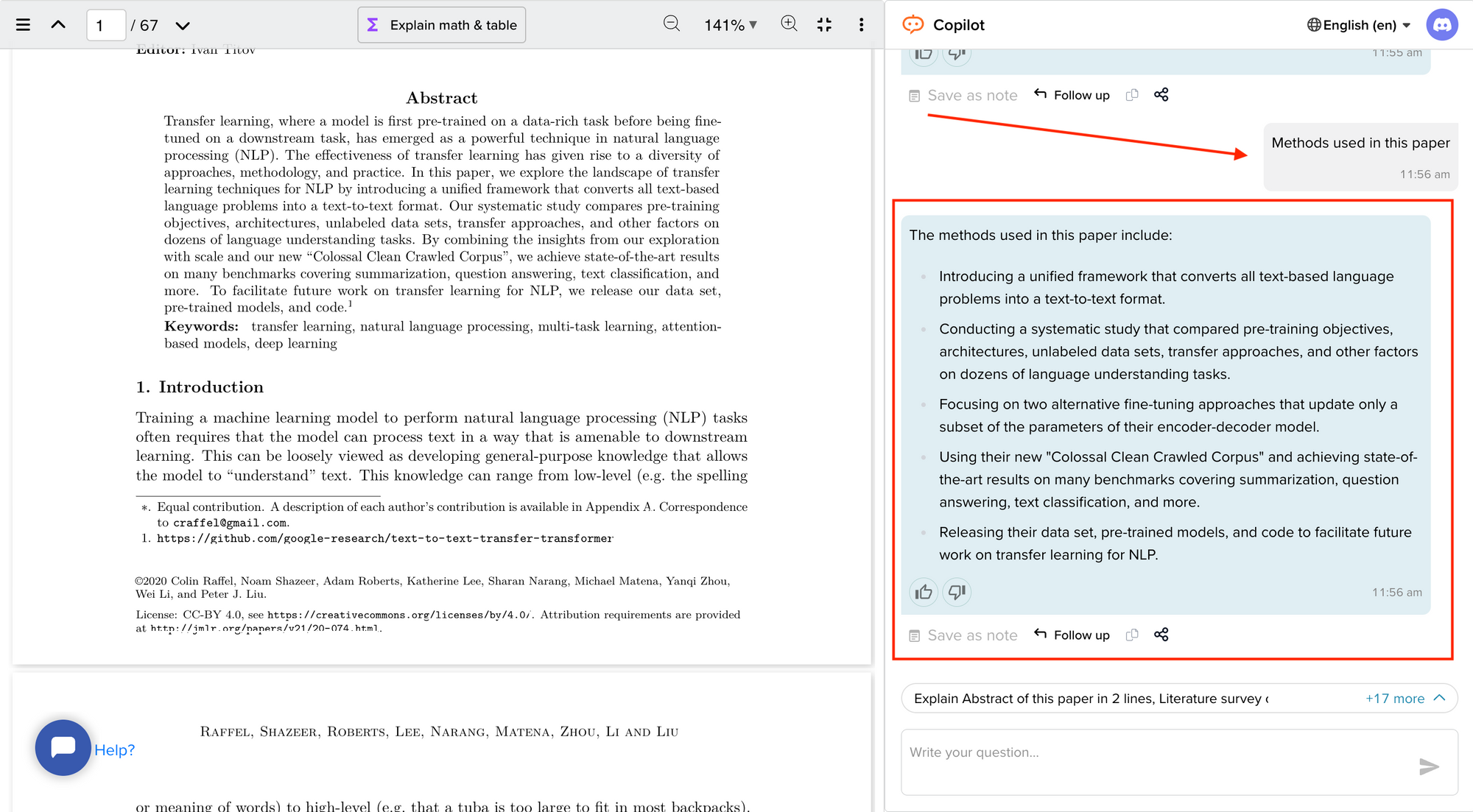
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 10:51 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Learn how to write a review of literature
What is a review of literature.
The format of a review of literature may vary from discipline to discipline and from assignment to assignment.
A review may be a self-contained unit — an end in itself — or a preface to and rationale for engaging in primary research. A review is a required part of grant and research proposals and often a chapter in theses and dissertations.
Generally, the purpose of a review is to analyze critically a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles.
Writing the introduction
In the introduction, you should:
Define or identify the general topic, issue, or area of concern, thus providing an appropriate context for reviewing the literature.
Point out overall trends in what has been published about the topic; or conflicts in theory, methodology, evidence, and conclusions; or gaps in research and scholarship; or a single problem or new perspective of immediate interest.
Establish the writer’s reason (point of view) for reviewing the literature; explain the criteria to be used in analyzing and comparing literature and the organization of the review (sequence); and, when necessary, state why certain literature is or is not included (scope).
Writing the body
In the body, you should:
Group research studies and other types of literature (reviews, theoretical articles, case studies, etc.) according to common denominators such as qualitative versus quantitative approaches, conclusions of authors, specific purpose or objective, chronology, etc.
Summarize individual studies or articles with as much or as little detail as each merits according to its comparative importance in the literature, remembering that space (length) denotes significance.
Provide the reader with strong “umbrella” sentences at beginnings of paragraphs, “signposts” throughout, and brief “so what” summary sentences at intermediate points in the review to aid in understanding comparisons and analyses.
Writing the conclusion
In the conclusion, you should:
Summarize major contributions of significant studies and articles to the body of knowledge under review, maintaining the focus established in the introduction.
Evaluate the current “state of the art” for the body of knowledge reviewed, pointing out major methodological flaws or gaps in research, inconsistencies in theory and findings, and areas or issues pertinent to future study.
Conclude by providing some insight into the relationship between the central topic of the literature review and a larger area of study such as a discipline, a scientific endeavor, or a profession.
For further information see our handouts on Writing a Critical Review of a Nonfiction Book or Article or Reading a Book to Review It .
To learn more about literature reviews, take a look at our workshop on Writing Literature Reviews of Published Research.
Sample Literature Reviews
An important strategy for learning how to compose literature reviews in your field or within a specific genre is to locate and analyze representative examples. The following collection of annotated sample literature reviews written and co-written by colleagues associated with UW-Madison showcases how these reviews can do different kind of work for different purposes. Use these successful examples as a starting point for understanding how other writers have approached the challenging and important task of situating their idea in the context of established research.
- Sample 1 (PDF) A brief literature review within a political scientists’ National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship grant
- Sample 2 (PDF) A several-page literature review at the beginning of a published, academic article about philosophy
- Sample 3 (PDF) A brief literature review at the beginning of a published, academic article about photochemistry

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.

Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students, why traditional editorial process needs an upgrade, paperpal’s new ai research finder empowers authors to..., what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., ai + human expertise – a paradigm shift..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without....
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- CBE Life Sci Educ
- v.21(3); Fall 2022
Literature Reviews, Theoretical Frameworks, and Conceptual Frameworks: An Introduction for New Biology Education Researchers
Julie a. luft.
† Department of Mathematics, Social Studies, and Science Education, Mary Frances Early College of Education, University of Georgia, Athens, GA 30602-7124
Sophia Jeong
‡ Department of Teaching & Learning, College of Education & Human Ecology, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH 43210
Robert Idsardi
§ Department of Biology, Eastern Washington University, Cheney, WA 99004
Grant Gardner
∥ Department of Biology, Middle Tennessee State University, Murfreesboro, TN 37132
Associated Data
To frame their work, biology education researchers need to consider the role of literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks as critical elements of the research and writing process. However, these elements can be confusing for scholars new to education research. This Research Methods article is designed to provide an overview of each of these elements and delineate the purpose of each in the educational research process. We describe what biology education researchers should consider as they conduct literature reviews, identify theoretical frameworks, and construct conceptual frameworks. Clarifying these different components of educational research studies can be helpful to new biology education researchers and the biology education research community at large in situating their work in the broader scholarly literature.
INTRODUCTION
Discipline-based education research (DBER) involves the purposeful and situated study of teaching and learning in specific disciplinary areas ( Singer et al. , 2012 ). Studies in DBER are guided by research questions that reflect disciplines’ priorities and worldviews. Researchers can use quantitative data, qualitative data, or both to answer these research questions through a variety of methodological traditions. Across all methodologies, there are different methods associated with planning and conducting educational research studies that include the use of surveys, interviews, observations, artifacts, or instruments. Ensuring the coherence of these elements to the discipline’s perspective also involves situating the work in the broader scholarly literature. The tools for doing this include literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks. However, the purpose and function of each of these elements is often confusing to new education researchers. The goal of this article is to introduce new biology education researchers to these three important elements important in DBER scholarship and the broader educational literature.
The first element we discuss is a review of research (literature reviews), which highlights the need for a specific research question, study problem, or topic of investigation. Literature reviews situate the relevance of the study within a topic and a field. The process may seem familiar to science researchers entering DBER fields, but new researchers may still struggle in conducting the review. Booth et al. (2016b) highlight some of the challenges novice education researchers face when conducting a review of literature. They point out that novice researchers struggle in deciding how to focus the review, determining the scope of articles needed in the review, and knowing how to be critical of the articles in the review. Overcoming these challenges (and others) can help novice researchers construct a sound literature review that can inform the design of the study and help ensure the work makes a contribution to the field.
The second and third highlighted elements are theoretical and conceptual frameworks. These guide biology education research (BER) studies, and may be less familiar to science researchers. These elements are important in shaping the construction of new knowledge. Theoretical frameworks offer a way to explain and interpret the studied phenomenon, while conceptual frameworks clarify assumptions about the studied phenomenon. Despite the importance of these constructs in educational research, biology educational researchers have noted the limited use of theoretical or conceptual frameworks in published work ( DeHaan, 2011 ; Dirks, 2011 ; Lo et al. , 2019 ). In reviewing articles published in CBE—Life Sciences Education ( LSE ) between 2015 and 2019, we found that fewer than 25% of the research articles had a theoretical or conceptual framework (see the Supplemental Information), and at times there was an inconsistent use of theoretical and conceptual frameworks. Clearly, these frameworks are challenging for published biology education researchers, which suggests the importance of providing some initial guidance to new biology education researchers.
Fortunately, educational researchers have increased their explicit use of these frameworks over time, and this is influencing educational research in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. For instance, a quick search for theoretical or conceptual frameworks in the abstracts of articles in Educational Research Complete (a common database for educational research) in STEM fields demonstrates a dramatic change over the last 20 years: from only 778 articles published between 2000 and 2010 to 5703 articles published between 2010 and 2020, a more than sevenfold increase. Greater recognition of the importance of these frameworks is contributing to DBER authors being more explicit about such frameworks in their studies.
Collectively, literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks work to guide methodological decisions and the elucidation of important findings. Each offers a different perspective on the problem of study and is an essential element in all forms of educational research. As new researchers seek to learn about these elements, they will find different resources, a variety of perspectives, and many suggestions about the construction and use of these elements. The wide range of available information can overwhelm the new researcher who just wants to learn the distinction between these elements or how to craft them adequately.
Our goal in writing this paper is not to offer specific advice about how to write these sections in scholarly work. Instead, we wanted to introduce these elements to those who are new to BER and who are interested in better distinguishing one from the other. In this paper, we share the purpose of each element in BER scholarship, along with important points on its construction. We also provide references for additional resources that may be beneficial to better understanding each element. Table 1 summarizes the key distinctions among these elements.
Comparison of literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual reviews
This article is written for the new biology education researcher who is just learning about these different elements or for scientists looking to become more involved in BER. It is a result of our own work as science education and biology education researchers, whether as graduate students and postdoctoral scholars or newly hired and established faculty members. This is the article we wish had been available as we started to learn about these elements or discussed them with new educational researchers in biology.
LITERATURE REVIEWS
Purpose of a literature review.
A literature review is foundational to any research study in education or science. In education, a well-conceptualized and well-executed review provides a summary of the research that has already been done on a specific topic and identifies questions that remain to be answered, thus illustrating the current research project’s potential contribution to the field and the reasoning behind the methodological approach selected for the study ( Maxwell, 2012 ). BER is an evolving disciplinary area that is redefining areas of conceptual emphasis as well as orientations toward teaching and learning (e.g., Labov et al. , 2010 ; American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2011 ; Nehm, 2019 ). As a result, building comprehensive, critical, purposeful, and concise literature reviews can be a challenge for new biology education researchers.
Building Literature Reviews
There are different ways to approach and construct a literature review. Booth et al. (2016a) provide an overview that includes, for example, scoping reviews, which are focused only on notable studies and use a basic method of analysis, and integrative reviews, which are the result of exhaustive literature searches across different genres. Underlying each of these different review processes are attention to the s earch process, a ppraisa l of articles, s ynthesis of the literature, and a nalysis: SALSA ( Booth et al. , 2016a ). This useful acronym can help the researcher focus on the process while building a specific type of review.
However, new educational researchers often have questions about literature reviews that are foundational to SALSA or other approaches. Common questions concern determining which literature pertains to the topic of study or the role of the literature review in the design of the study. This section addresses such questions broadly while providing general guidance for writing a narrative literature review that evaluates the most pertinent studies.
The literature review process should begin before the research is conducted. As Boote and Beile (2005 , p. 3) suggested, researchers should be “scholars before researchers.” They point out that having a good working knowledge of the proposed topic helps illuminate avenues of study. Some subject areas have a deep body of work to read and reflect upon, providing a strong foundation for developing the research question(s). For instance, the teaching and learning of evolution is an area of long-standing interest in the BER community, generating many studies (e.g., Perry et al. , 2008 ; Barnes and Brownell, 2016 ) and reviews of research (e.g., Sickel and Friedrichsen, 2013 ; Ziadie and Andrews, 2018 ). Emerging areas of BER include the affective domain, issues of transfer, and metacognition ( Singer et al. , 2012 ). Many studies in these areas are transdisciplinary and not always specific to biology education (e.g., Rodrigo-Peiris et al. , 2018 ; Kolpikova et al. , 2019 ). These newer areas may require reading outside BER; fortunately, summaries of some of these topics can be found in the Current Insights section of the LSE website.
In focusing on a specific problem within a broader research strand, a new researcher will likely need to examine research outside BER. Depending upon the area of study, the expanded reading list might involve a mix of BER, DBER, and educational research studies. Determining the scope of the reading is not always straightforward. A simple way to focus one’s reading is to create a “summary phrase” or “research nugget,” which is a very brief descriptive statement about the study. It should focus on the essence of the study, for example, “first-year nonmajor students’ understanding of evolution,” “metacognitive prompts to enhance learning during biochemistry,” or “instructors’ inquiry-based instructional practices after professional development programming.” This type of phrase should help a new researcher identify two or more areas to review that pertain to the study. Focusing on recent research in the last 5 years is a good first step. Additional studies can be identified by reading relevant works referenced in those articles. It is also important to read seminal studies that are more than 5 years old. Reading a range of studies should give the researcher the necessary command of the subject in order to suggest a research question.
Given that the research question(s) arise from the literature review, the review should also substantiate the selected methodological approach. The review and research question(s) guide the researcher in determining how to collect and analyze data. Often the methodological approach used in a study is selected to contribute knowledge that expands upon what has been published previously about the topic (see Institute of Education Sciences and National Science Foundation, 2013 ). An emerging topic of study may need an exploratory approach that allows for a description of the phenomenon and development of a potential theory. This could, but not necessarily, require a methodological approach that uses interviews, observations, surveys, or other instruments. An extensively studied topic may call for the additional understanding of specific factors or variables; this type of study would be well suited to a verification or a causal research design. These could entail a methodological approach that uses valid and reliable instruments, observations, or interviews to determine an effect in the studied event. In either of these examples, the researcher(s) may use a qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods methodological approach.
Even with a good research question, there is still more reading to be done. The complexity and focus of the research question dictates the depth and breadth of the literature to be examined. Questions that connect multiple topics can require broad literature reviews. For instance, a study that explores the impact of a biology faculty learning community on the inquiry instruction of faculty could have the following review areas: learning communities among biology faculty, inquiry instruction among biology faculty, and inquiry instruction among biology faculty as a result of professional learning. Biology education researchers need to consider whether their literature review requires studies from different disciplines within or outside DBER. For the example given, it would be fruitful to look at research focused on learning communities with faculty in STEM fields or in general education fields that result in instructional change. It is important not to be too narrow or too broad when reading. When the conclusions of articles start to sound similar or no new insights are gained, the researcher likely has a good foundation for a literature review. This level of reading should allow the researcher to demonstrate a mastery in understanding the researched topic, explain the suitability of the proposed research approach, and point to the need for the refined research question(s).
The literature review should include the researcher’s evaluation and critique of the selected studies. A researcher may have a large collection of studies, but not all of the studies will follow standards important in the reporting of empirical work in the social sciences. The American Educational Research Association ( Duran et al. , 2006 ), for example, offers a general discussion about standards for such work: an adequate review of research informing the study, the existence of sound and appropriate data collection and analysis methods, and appropriate conclusions that do not overstep or underexplore the analyzed data. The Institute of Education Sciences and National Science Foundation (2013) also offer Common Guidelines for Education Research and Development that can be used to evaluate collected studies.
Because not all journals adhere to such standards, it is important that a researcher review each study to determine the quality of published research, per the guidelines suggested earlier. In some instances, the research may be fatally flawed. Examples of such flaws include data that do not pertain to the question, a lack of discussion about the data collection, poorly constructed instruments, or an inadequate analysis. These types of errors result in studies that are incomplete, error-laden, or inaccurate and should be excluded from the review. Most studies have limitations, and the author(s) often make them explicit. For instance, there may be an instructor effect, recognized bias in the analysis, or issues with the sample population. Limitations are usually addressed by the research team in some way to ensure a sound and acceptable research process. Occasionally, the limitations associated with the study can be significant and not addressed adequately, which leaves a consequential decision in the hands of the researcher. Providing critiques of studies in the literature review process gives the reader confidence that the researcher has carefully examined relevant work in preparation for the study and, ultimately, the manuscript.
A solid literature review clearly anchors the proposed study in the field and connects the research question(s), the methodological approach, and the discussion. Reviewing extant research leads to research questions that will contribute to what is known in the field. By summarizing what is known, the literature review points to what needs to be known, which in turn guides decisions about methodology. Finally, notable findings of the new study are discussed in reference to those described in the literature review.
Within published BER studies, literature reviews can be placed in different locations in an article. When included in the introductory section of the study, the first few paragraphs of the manuscript set the stage, with the literature review following the opening paragraphs. Cooper et al. (2019) illustrate this approach in their study of course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs). An introduction discussing the potential of CURES is followed by an analysis of the existing literature relevant to the design of CUREs that allows for novel student discoveries. Within this review, the authors point out contradictory findings among research on novel student discoveries. This clarifies the need for their study, which is described and highlighted through specific research aims.
A literature reviews can also make up a separate section in a paper. For example, the introduction to Todd et al. (2019) illustrates the need for their research topic by highlighting the potential of learning progressions (LPs) and suggesting that LPs may help mitigate learning loss in genetics. At the end of the introduction, the authors state their specific research questions. The review of literature following this opening section comprises two subsections. One focuses on learning loss in general and examines a variety of studies and meta-analyses from the disciplines of medical education, mathematics, and reading. The second section focuses specifically on LPs in genetics and highlights student learning in the midst of LPs. These separate reviews provide insights into the stated research question.
Suggestions and Advice
A well-conceptualized, comprehensive, and critical literature review reveals the understanding of the topic that the researcher brings to the study. Literature reviews should not be so big that there is no clear area of focus; nor should they be so narrow that no real research question arises. The task for a researcher is to craft an efficient literature review that offers a critical analysis of published work, articulates the need for the study, guides the methodological approach to the topic of study, and provides an adequate foundation for the discussion of the findings.
In our own writing of literature reviews, there are often many drafts. An early draft may seem well suited to the study because the need for and approach to the study are well described. However, as the results of the study are analyzed and findings begin to emerge, the existing literature review may be inadequate and need revision. The need for an expanded discussion about the research area can result in the inclusion of new studies that support the explanation of a potential finding. The literature review may also prove to be too broad. Refocusing on a specific area allows for more contemplation of a finding.
It should be noted that there are different types of literature reviews, and many books and articles have been written about the different ways to embark on these types of reviews. Among these different resources, the following may be helpful in considering how to refine the review process for scholarly journals:
- Booth, A., Sutton, A., & Papaioannou, D. (2016a). Systemic approaches to a successful literature review (2nd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book addresses different types of literature reviews and offers important suggestions pertaining to defining the scope of the literature review and assessing extant studies.
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., Williams, J. M., Bizup, J., & Fitzgerald, W. T. (2016b). The craft of research (4th ed.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press. This book can help the novice consider how to make the case for an area of study. While this book is not specifically about literature reviews, it offers suggestions about making the case for your study.
- Galvan, J. L., & Galvan, M. C. (2017). Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences (7th ed.). Routledge. This book offers guidance on writing different types of literature reviews. For the novice researcher, there are useful suggestions for creating coherent literature reviews.
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORKS
Purpose of theoretical frameworks.
As new education researchers may be less familiar with theoretical frameworks than with literature reviews, this discussion begins with an analogy. Envision a biologist, chemist, and physicist examining together the dramatic effect of a fog tsunami over the ocean. A biologist gazing at this phenomenon may be concerned with the effect of fog on various species. A chemist may be interested in the chemical composition of the fog as water vapor condenses around bits of salt. A physicist may be focused on the refraction of light to make fog appear to be “sitting” above the ocean. While observing the same “objective event,” the scientists are operating under different theoretical frameworks that provide a particular perspective or “lens” for the interpretation of the phenomenon. Each of these scientists brings specialized knowledge, experiences, and values to this phenomenon, and these influence the interpretation of the phenomenon. The scientists’ theoretical frameworks influence how they design and carry out their studies and interpret their data.
Within an educational study, a theoretical framework helps to explain a phenomenon through a particular lens and challenges and extends existing knowledge within the limitations of that lens. Theoretical frameworks are explicitly stated by an educational researcher in the paper’s framework, theory, or relevant literature section. The framework shapes the types of questions asked, guides the method by which data are collected and analyzed, and informs the discussion of the results of the study. It also reveals the researcher’s subjectivities, for example, values, social experience, and viewpoint ( Allen, 2017 ). It is essential that a novice researcher learn to explicitly state a theoretical framework, because all research questions are being asked from the researcher’s implicit or explicit assumptions of a phenomenon of interest ( Schwandt, 2000 ).
Selecting Theoretical Frameworks
Theoretical frameworks are one of the most contemplated elements in our work in educational research. In this section, we share three important considerations for new scholars selecting a theoretical framework.
The first step in identifying a theoretical framework involves reflecting on the phenomenon within the study and the assumptions aligned with the phenomenon. The phenomenon involves the studied event. There are many possibilities, for example, student learning, instructional approach, or group organization. A researcher holds assumptions about how the phenomenon will be effected, influenced, changed, or portrayed. It is ultimately the researcher’s assumption(s) about the phenomenon that aligns with a theoretical framework. An example can help illustrate how a researcher’s reflection on the phenomenon and acknowledgment of assumptions can result in the identification of a theoretical framework.
In our example, a biology education researcher may be interested in exploring how students’ learning of difficult biological concepts can be supported by the interactions of group members. The phenomenon of interest is the interactions among the peers, and the researcher assumes that more knowledgeable students are important in supporting the learning of the group. As a result, the researcher may draw on Vygotsky’s (1978) sociocultural theory of learning and development that is focused on the phenomenon of student learning in a social setting. This theory posits the critical nature of interactions among students and between students and teachers in the process of building knowledge. A researcher drawing upon this framework holds the assumption that learning is a dynamic social process involving questions and explanations among students in the classroom and that more knowledgeable peers play an important part in the process of building conceptual knowledge.
It is important to state at this point that there are many different theoretical frameworks. Some frameworks focus on learning and knowing, while other theoretical frameworks focus on equity, empowerment, or discourse. Some frameworks are well articulated, and others are still being refined. For a new researcher, it can be challenging to find a theoretical framework. Two of the best ways to look for theoretical frameworks is through published works that highlight different frameworks.
When a theoretical framework is selected, it should clearly connect to all parts of the study. The framework should augment the study by adding a perspective that provides greater insights into the phenomenon. It should clearly align with the studies described in the literature review. For instance, a framework focused on learning would correspond to research that reported different learning outcomes for similar studies. The methods for data collection and analysis should also correspond to the framework. For instance, a study about instructional interventions could use a theoretical framework concerned with learning and could collect data about the effect of the intervention on what is learned. When the data are analyzed, the theoretical framework should provide added meaning to the findings, and the findings should align with the theoretical framework.
A study by Jensen and Lawson (2011) provides an example of how a theoretical framework connects different parts of the study. They compared undergraduate biology students in heterogeneous and homogeneous groups over the course of a semester. Jensen and Lawson (2011) assumed that learning involved collaboration and more knowledgeable peers, which made Vygotsky’s (1978) theory a good fit for their study. They predicted that students in heterogeneous groups would experience greater improvement in their reasoning abilities and science achievements with much of the learning guided by the more knowledgeable peers.
In the enactment of the study, they collected data about the instruction in traditional and inquiry-oriented classes, while the students worked in homogeneous or heterogeneous groups. To determine the effect of working in groups, the authors also measured students’ reasoning abilities and achievement. Each data-collection and analysis decision connected to understanding the influence of collaborative work.
Their findings highlighted aspects of Vygotsky’s (1978) theory of learning. One finding, for instance, posited that inquiry instruction, as a whole, resulted in reasoning and achievement gains. This links to Vygotsky (1978) , because inquiry instruction involves interactions among group members. A more nuanced finding was that group composition had a conditional effect. Heterogeneous groups performed better with more traditional and didactic instruction, regardless of the reasoning ability of the group members. Homogeneous groups worked better during interaction-rich activities for students with low reasoning ability. The authors attributed the variation to the different types of helping behaviors of students. High-performing students provided the answers, while students with low reasoning ability had to work collectively through the material. In terms of Vygotsky (1978) , this finding provided new insights into the learning context in which productive interactions can occur for students.
Another consideration in the selection and use of a theoretical framework pertains to its orientation to the study. This can result in the theoretical framework prioritizing individuals, institutions, and/or policies ( Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). Frameworks that connect to individuals, for instance, could contribute to understanding their actions, learning, or knowledge. Institutional frameworks, on the other hand, offer insights into how institutions, organizations, or groups can influence individuals or materials. Policy theories provide ways to understand how national or local policies can dictate an emphasis on outcomes or instructional design. These different types of frameworks highlight different aspects in an educational setting, which influences the design of the study and the collection of data. In addition, these different frameworks offer a way to make sense of the data. Aligning the data collection and analysis with the framework ensures that a study is coherent and can contribute to the field.
New understandings emerge when different theoretical frameworks are used. For instance, Ebert-May et al. (2015) prioritized the individual level within conceptual change theory (see Posner et al. , 1982 ). In this theory, an individual’s knowledge changes when it no longer fits the phenomenon. Ebert-May et al. (2015) designed a professional development program challenging biology postdoctoral scholars’ existing conceptions of teaching. The authors reported that the biology postdoctoral scholars’ teaching practices became more student-centered as they were challenged to explain their instructional decision making. According to the theory, the biology postdoctoral scholars’ dissatisfaction in their descriptions of teaching and learning initiated change in their knowledge and instruction. These results reveal how conceptual change theory can explain the learning of participants and guide the design of professional development programming.
The communities of practice (CoP) theoretical framework ( Lave, 1988 ; Wenger, 1998 ) prioritizes the institutional level , suggesting that learning occurs when individuals learn from and contribute to the communities in which they reside. Grounded in the assumption of community learning, the literature on CoP suggests that, as individuals interact regularly with the other members of their group, they learn about the rules, roles, and goals of the community ( Allee, 2000 ). A study conducted by Gehrke and Kezar (2017) used the CoP framework to understand organizational change by examining the involvement of individual faculty engaged in a cross-institutional CoP focused on changing the instructional practice of faculty at each institution. In the CoP, faculty members were involved in enhancing instructional materials within their department, which aligned with an overarching goal of instituting instruction that embraced active learning. Not surprisingly, Gehrke and Kezar (2017) revealed that faculty who perceived the community culture as important in their work cultivated institutional change. Furthermore, they found that institutional change was sustained when key leaders served as mentors and provided support for faculty, and as faculty themselves developed into leaders. This study reveals the complexity of individual roles in a COP in order to support institutional instructional change.
It is important to explicitly state the theoretical framework used in a study, but elucidating a theoretical framework can be challenging for a new educational researcher. The literature review can help to identify an applicable theoretical framework. Focal areas of the review or central terms often connect to assumptions and assertions associated with the framework that pertain to the phenomenon of interest. Another way to identify a theoretical framework is self-reflection by the researcher on personal beliefs and understandings about the nature of knowledge the researcher brings to the study ( Lysaght, 2011 ). In stating one’s beliefs and understandings related to the study (e.g., students construct their knowledge, instructional materials support learning), an orientation becomes evident that will suggest a particular theoretical framework. Theoretical frameworks are not arbitrary , but purposefully selected.
With experience, a researcher may find expanded roles for theoretical frameworks. Researchers may revise an existing framework that has limited explanatory power, or they may decide there is a need to develop a new theoretical framework. These frameworks can emerge from a current study or the need to explain a phenomenon in a new way. Researchers may also find that multiple theoretical frameworks are necessary to frame and explore a problem, as different frameworks can provide different insights into a problem.
Finally, it is important to recognize that choosing “x” theoretical framework does not necessarily mean a researcher chooses “y” methodology and so on, nor is there a clear-cut, linear process in selecting a theoretical framework for one’s study. In part, the nonlinear process of identifying a theoretical framework is what makes understanding and using theoretical frameworks challenging. For the novice scholar, contemplating and understanding theoretical frameworks is essential. Fortunately, there are articles and books that can help:
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (5th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book provides an overview of theoretical frameworks in general educational research.
- Ding, L. (2019). Theoretical perspectives of quantitative physics education research. Physical Review Physics Education Research , 15 (2), 020101-1–020101-13. This paper illustrates how a DBER field can use theoretical frameworks.
- Nehm, R. (2019). Biology education research: Building integrative frameworks for teaching and learning about living systems. Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research , 1 , ar15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-019-0017-6 . This paper articulates the need for studies in BER to explicitly state theoretical frameworks and provides examples of potential studies.
- Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Sage. This book also provides an overview of theoretical frameworks, but for both research and evaluation.
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORKS
Purpose of a conceptual framework.
A conceptual framework is a description of the way a researcher understands the factors and/or variables that are involved in the study and their relationships to one another. The purpose of a conceptual framework is to articulate the concepts under study using relevant literature ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ) and to clarify the presumed relationships among those concepts ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ; Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). Conceptual frameworks are different from theoretical frameworks in both their breadth and grounding in established findings. Whereas a theoretical framework articulates the lens through which a researcher views the work, the conceptual framework is often more mechanistic and malleable.
Conceptual frameworks are broader, encompassing both established theories (i.e., theoretical frameworks) and the researchers’ own emergent ideas. Emergent ideas, for example, may be rooted in informal and/or unpublished observations from experience. These emergent ideas would not be considered a “theory” if they are not yet tested, supported by systematically collected evidence, and peer reviewed. However, they do still play an important role in the way researchers approach their studies. The conceptual framework allows authors to clearly describe their emergent ideas so that connections among ideas in the study and the significance of the study are apparent to readers.
Constructing Conceptual Frameworks
Including a conceptual framework in a research study is important, but researchers often opt to include either a conceptual or a theoretical framework. Either may be adequate, but both provide greater insight into the research approach. For instance, a research team plans to test a novel component of an existing theory. In their study, they describe the existing theoretical framework that informs their work and then present their own conceptual framework. Within this conceptual framework, specific topics portray emergent ideas that are related to the theory. Describing both frameworks allows readers to better understand the researchers’ assumptions, orientations, and understanding of concepts being investigated. For example, Connolly et al. (2018) included a conceptual framework that described how they applied a theoretical framework of social cognitive career theory (SCCT) to their study on teaching programs for doctoral students. In their conceptual framework, the authors described SCCT, explained how it applied to the investigation, and drew upon results from previous studies to justify the proposed connections between the theory and their emergent ideas.
In some cases, authors may be able to sufficiently describe their conceptualization of the phenomenon under study in an introduction alone, without a separate conceptual framework section. However, incomplete descriptions of how the researchers conceptualize the components of the study may limit the significance of the study by making the research less intelligible to readers. This is especially problematic when studying topics in which researchers use the same terms for different constructs or different terms for similar and overlapping constructs (e.g., inquiry, teacher beliefs, pedagogical content knowledge, or active learning). Authors must describe their conceptualization of a construct if the research is to be understandable and useful.
There are some key areas to consider regarding the inclusion of a conceptual framework in a study. To begin with, it is important to recognize that conceptual frameworks are constructed by the researchers conducting the study ( Rocco and Plakhotnik, 2009 ; Maxwell, 2012 ). This is different from theoretical frameworks that are often taken from established literature. Researchers should bring together ideas from the literature, but they may be influenced by their own experiences as a student and/or instructor, the shared experiences of others, or thought experiments as they construct a description, model, or representation of their understanding of the phenomenon under study. This is an exercise in intellectual organization and clarity that often considers what is learned, known, and experienced. The conceptual framework makes these constructs explicitly visible to readers, who may have different understandings of the phenomenon based on their prior knowledge and experience. There is no single method to go about this intellectual work.
Reeves et al. (2016) is an example of an article that proposed a conceptual framework about graduate teaching assistant professional development evaluation and research. The authors used existing literature to create a novel framework that filled a gap in current research and practice related to the training of graduate teaching assistants. This conceptual framework can guide the systematic collection of data by other researchers because the framework describes the relationships among various factors that influence teaching and learning. The Reeves et al. (2016) conceptual framework may be modified as additional data are collected and analyzed by other researchers. This is not uncommon, as conceptual frameworks can serve as catalysts for concerted research efforts that systematically explore a phenomenon (e.g., Reynolds et al. , 2012 ; Brownell and Kloser, 2015 ).
Sabel et al. (2017) used a conceptual framework in their exploration of how scaffolds, an external factor, interact with internal factors to support student learning. Their conceptual framework integrated principles from two theoretical frameworks, self-regulated learning and metacognition, to illustrate how the research team conceptualized students’ use of scaffolds in their learning ( Figure 1 ). Sabel et al. (2017) created this model using their interpretations of these two frameworks in the context of their teaching.

Conceptual framework from Sabel et al. (2017) .
A conceptual framework should describe the relationship among components of the investigation ( Anfara and Mertz, 2014 ). These relationships should guide the researcher’s methods of approaching the study ( Miles et al. , 2014 ) and inform both the data to be collected and how those data should be analyzed. Explicitly describing the connections among the ideas allows the researcher to justify the importance of the study and the rigor of the research design. Just as importantly, these frameworks help readers understand why certain components of a system were not explored in the study. This is a challenge in education research, which is rooted in complex environments with many variables that are difficult to control.
For example, Sabel et al. (2017) stated: “Scaffolds, such as enhanced answer keys and reflection questions, can help students and instructors bridge the external and internal factors and support learning” (p. 3). They connected the scaffolds in the study to the three dimensions of metacognition and the eventual transformation of existing ideas into new or revised ideas. Their framework provides a rationale for focusing on how students use two different scaffolds, and not on other factors that may influence a student’s success (self-efficacy, use of active learning, exam format, etc.).
In constructing conceptual frameworks, researchers should address needed areas of study and/or contradictions discovered in literature reviews. By attending to these areas, researchers can strengthen their arguments for the importance of a study. For instance, conceptual frameworks can address how the current study will fill gaps in the research, resolve contradictions in existing literature, or suggest a new area of study. While a literature review describes what is known and not known about the phenomenon, the conceptual framework leverages these gaps in describing the current study ( Maxwell, 2012 ). In the example of Sabel et al. (2017) , the authors indicated there was a gap in the literature regarding how scaffolds engage students in metacognition to promote learning in large classes. Their study helps fill that gap by describing how scaffolds can support students in the three dimensions of metacognition: intelligibility, plausibility, and wide applicability. In another example, Lane (2016) integrated research from science identity, the ethic of care, the sense of belonging, and an expertise model of student success to form a conceptual framework that addressed the critiques of other frameworks. In a more recent example, Sbeglia et al. (2021) illustrated how a conceptual framework influences the methodological choices and inferences in studies by educational researchers.
Sometimes researchers draw upon the conceptual frameworks of other researchers. When a researcher’s conceptual framework closely aligns with an existing framework, the discussion may be brief. For example, Ghee et al. (2016) referred to portions of SCCT as their conceptual framework to explain the significance of their work on students’ self-efficacy and career interests. Because the authors’ conceptualization of this phenomenon aligned with a previously described framework, they briefly mentioned the conceptual framework and provided additional citations that provided more detail for the readers.
Within both the BER and the broader DBER communities, conceptual frameworks have been used to describe different constructs. For example, some researchers have used the term “conceptual framework” to describe students’ conceptual understandings of a biological phenomenon. This is distinct from a researcher’s conceptual framework of the educational phenomenon under investigation, which may also need to be explicitly described in the article. Other studies have presented a research logic model or flowchart of the research design as a conceptual framework. These constructions can be quite valuable in helping readers understand the data-collection and analysis process. However, a model depicting the study design does not serve the same role as a conceptual framework. Researchers need to avoid conflating these constructs by differentiating the researchers’ conceptual framework that guides the study from the research design, when applicable.
Explicitly describing conceptual frameworks is essential in depicting the focus of the study. We have found that being explicit in a conceptual framework means using accepted terminology, referencing prior work, and clearly noting connections between terms. This description can also highlight gaps in the literature or suggest potential contributions to the field of study. A well-elucidated conceptual framework can suggest additional studies that may be warranted. This can also spur other researchers to consider how they would approach the examination of a phenomenon and could result in a revised conceptual framework.
It can be challenging to create conceptual frameworks, but they are important. Below are two resources that could be helpful in constructing and presenting conceptual frameworks in educational research:
- Maxwell, J. A. (2012). Qualitative research design: An interactive approach (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. Chapter 3 in this book describes how to construct conceptual frameworks.
- Ravitch, S. M., & Riggan, M. (2016). Reason & rigor: How conceptual frameworks guide research . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. This book explains how conceptual frameworks guide the research questions, data collection, data analyses, and interpretation of results.
CONCLUDING THOUGHTS
Literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks are all important in DBER and BER. Robust literature reviews reinforce the importance of a study. Theoretical frameworks connect the study to the base of knowledge in educational theory and specify the researcher’s assumptions. Conceptual frameworks allow researchers to explicitly describe their conceptualization of the relationships among the components of the phenomenon under study. Table 1 provides a general overview of these components in order to assist biology education researchers in thinking about these elements.
It is important to emphasize that these different elements are intertwined. When these elements are aligned and complement one another, the study is coherent, and the study findings contribute to knowledge in the field. When literature reviews, theoretical frameworks, and conceptual frameworks are disconnected from one another, the study suffers. The point of the study is lost, suggested findings are unsupported, or important conclusions are invisible to the researcher. In addition, this misalignment may be costly in terms of time and money.
Conducting a literature review, selecting a theoretical framework, and building a conceptual framework are some of the most difficult elements of a research study. It takes time to understand the relevant research, identify a theoretical framework that provides important insights into the study, and formulate a conceptual framework that organizes the finding. In the research process, there is often a constant back and forth among these elements as the study evolves. With an ongoing refinement of the review of literature, clarification of the theoretical framework, and articulation of a conceptual framework, a sound study can emerge that makes a contribution to the field. This is the goal of BER and education research.
Supplementary Material
- Allee, V. (2000). Knowledge networks and communities of learning . OD Practitioner , 32 ( 4 ), 4–13. [ Google Scholar ]
- Allen, M. (2017). The Sage encyclopedia of communication research methods (Vols. 1–4 ). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. 10.4135/9781483381411 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American Association for the Advancement of Science. (2011). Vision and change in undergraduate biology education: A call to action . Washington, DC. [ Google Scholar ]
- Anfara, V. A., Mertz, N. T. (2014). Setting the stage . In Anfara, V. A., Mertz, N. T. (eds.), Theoretical frameworks in qualitative research (pp. 1–22). Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barnes, M. E., Brownell, S. E. (2016). Practices and perspectives of college instructors on addressing religious beliefs when teaching evolution . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 2 ), ar18. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.15-11-0243 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boote, D. N., Beile, P. (2005). Scholars before researchers: On the centrality of the dissertation literature review in research preparation . Educational Researcher , 34 ( 6 ), 3–15. 10.3102/0013189x034006003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Booth, A., Sutton, A., Papaioannou, D. (2016a). Systemic approaches to a successful literature review (2nd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Booth, W. C., Colomb, G. G., Williams, J. M., Bizup, J., Fitzgerald, W. T. (2016b). The craft of research (4th ed.). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brownell, S. E., Kloser, M. J. (2015). Toward a conceptual framework for measuring the effectiveness of course-based undergraduate research experiences in undergraduate biology . Studies in Higher Education , 40 ( 3 ), 525–544. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2015.1004234 [ Google Scholar ]
- Connolly, M. R., Lee, Y. G., Savoy, J. N. (2018). The effects of doctoral teaching development on early-career STEM scholars’ college teaching self-efficacy . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 1 ), ar14. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-02-0039 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cooper, K. M., Blattman, J. N., Hendrix, T., Brownell, S. E. (2019). The impact of broadly relevant novel discoveries on student project ownership in a traditional lab course turned CURE . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 4 ), ar57. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-06-0113 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (5th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- DeHaan, R. L. (2011). Education research in the biological sciences: A nine decade review (Paper commissioned by the NAS/NRC Committee on the Status, Contributions, and Future Directions of Discipline Based Education Research) . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Retrieved May 20, 2022, from www7.nationalacademies.org/bose/DBER_Mee ting2_commissioned_papers_page.html [ Google Scholar ]
- Ding, L. (2019). Theoretical perspectives of quantitative physics education research . Physical Review Physics Education Research , 15 ( 2 ), 020101. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dirks, C. (2011). The current status and future direction of biology education research . Paper presented at: Second Committee Meeting on the Status, Contributions, and Future Directions of Discipline-Based Education Research, 18–19 October (Washington, DC). Retrieved May 20, 2022, from http://sites.nationalacademies.org/DBASSE/BOSE/DBASSE_071087 [ Google Scholar ]
- Duran, R. P., Eisenhart, M. A., Erickson, F. D., Grant, C. A., Green, J. L., Hedges, L. V., Schneider, B. L. (2006). Standards for reporting on empirical social science research in AERA publications: American Educational Research Association . Educational Researcher , 35 ( 6 ), 33–40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ebert-May, D., Derting, T. L., Henkel, T. P., Middlemis Maher, J., Momsen, J. L., Arnold, B., Passmore, H. A. (2015). Breaking the cycle: Future faculty begin teaching with learner-centered strategies after professional development . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 14 ( 2 ), ar22. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.14-12-0222 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galvan, J. L., Galvan, M. C. (2017). Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences (7th ed.). New York, NY: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315229386 [ Google Scholar ]
- Gehrke, S., Kezar, A. (2017). The roles of STEM faculty communities of practice in institutional and departmental reform in higher education . American Educational Research Journal , 54 ( 5 ), 803–833. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831217706736 [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghee, M., Keels, M., Collins, D., Neal-Spence, C., Baker, E. (2016). Fine-tuning summer research programs to promote underrepresented students’ persistence in the STEM pathway . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 3 ), ar28. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-01-0046 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Institute of Education Sciences & National Science Foundation. (2013). Common guidelines for education research and development . Retrieved May 20, 2022, from www.nsf.gov/pubs/2013/nsf13126/nsf13126.pdf
- Jensen, J. L., Lawson, A. (2011). Effects of collaborative group composition and inquiry instruction on reasoning gains and achievement in undergraduate biology . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 10 ( 1 ), 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-05-0098 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kolpikova, E. P., Chen, D. C., Doherty, J. H. (2019). Does the format of preclass reading quizzes matter? An evaluation of traditional and gamified, adaptive preclass reading quizzes . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 4 ), ar52. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.19-05-0098 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Labov, J. B., Reid, A. H., Yamamoto, K. R. (2010). Integrated biology and undergraduate science education: A new biology education for the twenty-first century? CBE—Life Sciences Education , 9 ( 1 ), 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.09-12-0092 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lane, T. B. (2016). Beyond academic and social integration: Understanding the impact of a STEM enrichment program on the retention and degree attainment of underrepresented students . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 3 ), ar39. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-01-0070 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lave, J. (1988). Cognition in practice: Mind, mathematics and culture in everyday life . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lo, S. M., Gardner, G. E., Reid, J., Napoleon-Fanis, V., Carroll, P., Smith, E., Sato, B. K. (2019). Prevailing questions and methodologies in biology education research: A longitudinal analysis of research in CBE — Life Sciences Education and at the Society for the Advancement of Biology Education Research . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 18 ( 1 ), ar9. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.18-08-0164 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lysaght, Z. (2011). Epistemological and paradigmatic ecumenism in “Pasteur’s quadrant:” Tales from doctoral research . In Official Conference Proceedings of the Third Asian Conference on Education in Osaka, Japan . Retrieved May 20, 2022, from http://iafor.org/ace2011_offprint/ACE2011_offprint_0254.pdf
- Maxwell, J. A. (2012). Qualitative research design: An interactive approach (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., Saldaña, J. (2014). Qualitative data analysis (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nehm, R. (2019). Biology education research: Building integrative frameworks for teaching and learning about living systems . Disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Science Education Research , 1 , ar15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43031-019-0017-6 [ Google Scholar ]
- Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Perry, J., Meir, E., Herron, J. C., Maruca, S., Stal, D. (2008). Evaluating two approaches to helping college students understand evolutionary trees through diagramming tasks . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 7 ( 2 ), 193–201. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.07-01-0007 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Posner, G. J., Strike, K. A., Hewson, P. W., Gertzog, W. A. (1982). Accommodation of a scientific conception: Toward a theory of conceptual change . Science Education , 66 ( 2 ), 211–227. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ravitch, S. M., Riggan, M. (2016). Reason & rigor: How conceptual frameworks guide research . Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Reeves, T. D., Marbach-Ad, G., Miller, K. R., Ridgway, J., Gardner, G. E., Schussler, E. E., Wischusen, E. W. (2016). A conceptual framework for graduate teaching assistant professional development evaluation and research . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 15 ( 2 ), es2. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.15-10-0225 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reynolds, J. A., Thaiss, C., Katkin, W., Thompson, R. J. Jr. (2012). Writing-to-learn in undergraduate science education: A community-based, conceptually driven approach . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 11 ( 1 ), 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.11-08-0064 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rocco, T. S., Plakhotnik, M. S. (2009). Literature reviews, conceptual frameworks, and theoretical frameworks: Terms, functions, and distinctions . Human Resource Development Review , 8 ( 1 ), 120–130. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534484309332617 [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodrigo-Peiris, T., Xiang, L., Cassone, V. M. (2018). A low-intensity, hybrid design between a “traditional” and a “course-based” research experience yields positive outcomes for science undergraduate freshmen and shows potential for large-scale application . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 4 ), ar53. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-11-0248 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sabel, J. L., Dauer, J. T., Forbes, C. T. (2017). Introductory biology students’ use of enhanced answer keys and reflection questions to engage in metacognition and enhance understanding . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 16 ( 3 ), ar40. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.16-10-0298 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sbeglia, G. C., Goodridge, J. A., Gordon, L. H., Nehm, R. H. (2021). Are faculty changing? How reform frameworks, sampling intensities, and instrument measures impact inferences about student-centered teaching practices . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 20 ( 3 ), ar39. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.20-11-0259 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwandt, T. A. (2000). Three epistemological stances for qualitative inquiry: Interpretivism, hermeneutics, and social constructionism . In Denzin, N. K., Lincoln, Y. S. (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 189–213). Los Angeles, CA: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sickel, A. J., Friedrichsen, P. (2013). Examining the evolution education literature with a focus on teachers: Major findings, goals for teacher preparation, and directions for future research . Evolution: Education and Outreach , 6 ( 1 ), 23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1936-6434-6-23 [ Google Scholar ]
- Singer, S. R., Nielsen, N. R., Schweingruber, H. A. (2012). Discipline-based education research: Understanding and improving learning in undergraduate science and engineering . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Todd, A., Romine, W. L., Correa-Menendez, J. (2019). Modeling the transition from a phenotypic to genotypic conceptualization of genetics in a university-level introductory biology context . Research in Science Education , 49 ( 2 ), 569–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-017-9626-2 [ Google Scholar ]
- Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wenger, E. (1998). Communities of practice: Learning as a social system . Systems Thinker , 9 ( 5 ), 2–3. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ziadie, M. A., Andrews, T. C. (2018). Moving evolution education forward: A systematic analysis of literature to identify gaps in collective knowledge for teaching . CBE—Life Sciences Education , 17 ( 1 ), ar11. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.17-08-0190 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]

- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- Literature Review
- Academic Integrity
- Citing Sources
- Fair Use, Permissions, and Copyright
- Writing Resources
- Grants and Fellowships
- Last Updated: Apr 26, 2024 10:28 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
Methodology of Social Science & International Relations
6 hypothesis , research question & literature review.
Hypothesis is a potential explanation to a phenomenon, and in a much more rigorous way. It’s the core of research design, after Research Question and Literature Review. 1,Hypothesis should be used in formal logic, if XXX ,then XXX. 2,Hypothesis should have clear boundaries and testable. 3,Hypothesis should never be regarded as certain events, and it’s must be theoretical.
6.1 With Research Question
Hypothesis is the potential explanation or mechanism to the Research Question.If we try to research what result in Nagorno-Karabakh War. We need follow the steps, Research Question, Literature Review, Theoretical Framework, Hypothesis. Theoretical framework in literature is the most important resource to figure out the hypothesis.The meaning and contribution should start from existed research.

Figure 6.1: literature review & hypothesis
6.2 With Literature Review
After diving in the facts and literatures, we possiblely can have some hypotheses. Last time I introduced 3 steps of searching literatures, now we connect those with hypothesis building.
If you want to research Nagorno-Karabakh War, there are many structures we can use, like ethnic conflicts, new independent countries’ nation-buildings, or territorial conflicts. We can choose ethnic conflicts.
Inside international ethinic conflicts, then there are lots of possible hypotheses.Like ethinic diversity, regime, nationalism, economic imbalance, resource trap, cross-broder ethenic group, colonazation.The Main difference is the benchmark, that’s why firstly we need should choose problem domain. The problem domain determains our hypothesis boundary, and potential choices.

Figure 6.2: literature review & hypothesis
6.3 Rethinking Hypothesis
Should we take as much explanation as possible ? Should we call one approach is the most convincing ?
6.4 Hypothesis & Proving

Figure 6.3: circular argument
6.5 From Science
Try to introduce some explanations to obsity. 1, In evolutionary biology, in case of hunger or unstable envrionment, evolutionary selection make us to prefer high-calorie food, and feel more attractive. 2, Genomics, Ceratin genes can make our body much easier to store calorie. 3, Microbiology, Intestinal Flora affect our digestion procedures 4, Biochemistry, How stomach send the signals to our brain. 5, Neuroscience, How our brain handle incentive of food.refined/calorie 6, Medicine, Some disease can cuase obesity, like metabolism. others, like diet, sleeping, pressure
6.6 From Social Science
1, Economics, food industry’s profit-orentiation and marketing enhance our preference. 2, Political Science, Interest Group, Lobbying affect the policy 3, Psychology, Pressure and our neuro-mental mechanism 4, Sociology, social class, inequality, popoular culture, habit 5, IR, Globalisation, the expansion of global suger. 6, Reflection, How BMI, obesity is defined and interpretation.
The Use of Theories in Literature Review
Literature review is probably one of the most important chapter in a thesis. However, it should be known that the importance may be very much dependent on the type of research you intend to conduct.
If you are looking at a qualitative research, where you are ‘attempting to discover a theory’, your literature will likely be used to develop a conceptual model which will then through your research be developed into a ‘theoretical model’ for further testing. However, if you are looking at a quantitative research where you are ‘attempting to test a theory’, you literature review needs to be adequately discussed to develop a theoretical model and relevant hypothesis.
Nevertheless the important part here is the use of theories when developing your literature review
Many times as we evaluated the theories in the literature review of the thesis of students who we supervised, we find some commonality:-
- The use of wrong substantive theories to support the argument
- The mis-match of theories use
- The missing gaps between theories used
- The incomplete use of theories to support argument.
Let me try to articulate the role of theories in a literature review:-
Theories are used to justify and support your arguments, variables and the phenomena that is being studied. In developing your literature review, it will be helpful to identify an underpinning theory on which you can start developing your arguments and show the gaps of research being examined. Additional theories can be used to supplement your literature review.
Theories are formulated to explain, predict, and understand phenomena and, in many cases, to challenge and extend existing knowledge within the limits of critical bounding assumptions. The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework introduces and describes the theory that explains why the research problem under study exists.
A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study. The theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts that are relevant to the topic of your research paper and that relate to the broader areas of knowledge being considered.
The theoretical framework is most often not something readily found within the literature . You must review course readings and pertinent research studies for theories and analytic models that are relevant to the research problem you are investigating. The selection of a theory should depend on its appropriateness, ease of application, and explanatory power.
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways :
- An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically.
- The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
- Articulating the theoretical assumptions of a research study forces you to address questions of why and how. It permits you to intellectually transition from simply describing a phenomenon you have observed to generalizing about various aspects of that phenomenon.
- Having a theory helps you identify the limits to those generalizations. A theoretical framework specifies which key variables influence a phenomenon of interest and highlights the need to examine how those key variables might differ and under what circumstances.
Interested to know more?
- No 2-2, Jalan 10/18B, Sutera Damansara, 47830 Petaling Jaya, Selangor
- [email protected]
- Mon-Fri: 9am to 6pm
© 2019 Mindstorm Asia all rights reserved.
| terms and conditions.
- Open access
- Published: 19 April 2024
Person-centered care assessment tool with a focus on quality healthcare: a systematic review of psychometric properties
- Lluna Maria Bru-Luna 1 ,
- Manuel Martí-Vilar 2 ,
- César Merino-Soto 3 ,
- José Livia-Segovia 4 ,
- Juan Garduño-Espinosa 5 &
- Filiberto Toledano-Toledano 5 , 6 , 7
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 217 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
338 Accesses
Metrics details
The person-centered care (PCC) approach plays a fundamental role in ensuring quality healthcare. The Person-Centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT) is one of the shortest and simplest tools currently available for measuring PCC. The objective of this study was to conduct a systematic review of the evidence in validation studies of the P-CAT, taking the “Standards” as a frame of reference.
First, a systematic literature review was conducted following the PRISMA method. Second, a systematic descriptive literature review of validity tests was conducted following the “Standards” framework. The search strategy and information sources were obtained from the Cochrane, Web of Science (WoS), Scopus and PubMed databases. With regard to the eligibility criteria and selection process, a protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42022335866), and articles had to meet criteria for inclusion in the systematic review.
A total of seven articles were included. Empirical evidence indicates that these validations offer a high number of sources related to test content, internal structure for dimensionality and internal consistency. A moderate number of sources pertain to internal structure in terms of test-retest reliability and the relationship with other variables. There is little evidence of response processes, internal structure in measurement invariance terms, and test consequences.
The various validations of the P-CAT are not framed in a structured, valid, theory-based procedural framework like the “Standards” are. This can affect clinical practice because people’s health may depend on it. The findings of this study show that validation studies continue to focus on the types of validity traditionally studied and overlook interpretation of the scores in terms of their intended use.
Peer Review reports
Person-centered care (PCC)
Quality care for people with chronic diseases, functional limitations, or both has become one of the main objectives of medical and care services. The person-centered care (PCC) approach is an essential element not only in achieving this goal but also in providing high-quality health maintenance and medical care [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. In addition to guaranteeing human rights, PCC provides numerous benefits to both the recipient and the provider [ 4 , 5 ]. Additionally, PCC includes a set of necessary competencies for healthcare professionals to address ongoing challenges in this area [ 6 ]. PCC includes the following elements [ 7 ]: an individualized, goal-oriented care plan based on individuals’ preferences; an ongoing review of the plan and the individual’s goals; support from an interprofessional team; active coordination among all medical and care providers and support services; ongoing information exchange, education and training for providers; and quality improvement through feedback from the individual and caregivers.
There is currently a growing body of literature on the application of PCC. A good example of this is McCormack’s widely known mid-range theory [ 8 ], an internationally recognized theoretical framework for PCC and how it is operationalized in practice. This framework forms a guide for care practitioners and researchers in hospital settings. This framework is elaborated in PCC and conceived of as “an approach to practice that is established through the formation and fostering of therapeutic relationships between all care providers, service users, and others significant to them, underpinned by values of respect for persons, [the] individual right to self-determination, mutual respect, and understanding” [ 9 ].
Thus, as established by PCC, it is important to emphasize that reference to the person who is the focus of care refers not only to the recipient but also to everyone involved in a care interaction [ 10 , 11 ]. PCC ensures that professionals are trained in relevant skills and methodology since, as discussed above, carers are among the agents who have the greatest impact on the quality of life of the person in need of care [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. Furthermore, due to the high burden of caregiving, it is essential to account for caregivers’ well-being. In this regard, studies on professional caregivers are beginning to suggest that the provision of PCC can produce multiple benefits for both the care recipient and the caregiver [ 15 ].
Despite a considerable body of literature and the frequent inclusion of the term in health policy and research [ 16 ], PCC involves several complications. There is no standard consensus on the definition of this concept [ 17 ], which includes problematic areas such as efficacy assessment [ 18 , 19 ]. In addition, the difficulty of measuring the subjectivity involved in identifying the dimensions of the CPC and the infrequent use of standardized measures are acute issues [ 20 ]. These limitations and purposes motivated the creation of the Person-Centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT; [ 21 ]), which emerged from the need for a brief, economical, easily applied, versatile and comprehensive assessment instrument to provide valid and reliable measures of PCC for research purposes [ 21 ].
Person-centered care assessment tool (P-CAT)
There are several instruments that can measure PCC from different perspectives (i.e., the caregiver or the care recipient) and in different contexts (e.g., hospitals and nursing homes). However, from a practical point of view, the P-CAT is one of the shortest and simplest tools and contains all the essential elements of PCC described in the literature. It was developed in Australia to measure the approach of long-term residential settings to older people with dementia, although it is increasingly used in other healthcare settings, such as oncology units [ 22 ] and psychiatric hospitals [ 23 ].
Due to the brevity and simplicity of its application, the versatility of its use in different medical and care contexts, and its potential emic characteristics (i.e., constructs that can be cross-culturally applicable with reasonable and similar structure and interpretation; [ 24 ]), the P-CAT is one of the most widely used tests by professionals to measure PCC [ 25 , 26 ]. It has expanded to several countries with cultural and linguistic differences. Since its creation, it has been adapted in countries separated by wide cultural and linguistic differences, such as Norway [ 27 ], Sweden [ 28 ], China [ 29 ], South Korea [ 30 ], Spain [ 25 ], and Italy [ 31 ].
The P-CAT comprises 13 items rated on a 5-point ordinal scale (from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”), with high scores indicating a high degree of person-centeredness. The scale consists of three dimensions: person-centered care (7 items), organizational support (4 items) and environmental accessibility (2 items). In the original study ( n = 220; [ 21 ]), the internal consistency of the instrument yielded satisfactory values for the total scale ( α = 0.84) and good test-retest reliability ( r =.66) at one-week intervals. A reliability generalization study conducted in 2021 [ 32 ] that estimated the internal consistency of the P-CAT and analyzed possible factors that could affect the it revealed that the mean α value for the 25 meta-analysis samples (some of which were part of the validations included in this study) was 0.81, and the only variable that had a statistically significant relationship with the reliability coefficient was the mean age of the sample. With respect to internal structure validity, three factors (56% of the total variance) were obtained, and content validity was assessed by experts, literature reviews and stakeholders [ 33 ].
Although not explicitly stated, the apparent commonality between validation studies of different versions of the P-CAT may be influenced by an influential decades-old validity framework that differentiates three categories: content validity, construct validity, and criterion validity [ 34 , 35 ]. However, a reformulation of the validity of the P-CAT within a modern framework, which would provide a different definition of validity, has not been performed.
Scale validity
Traditionally, validation is a process focused on the psychometric properties of a measurement instrument [ 36 ]. In the early 20th century, with the frequent use of standardized measurement tests in education and psychology, two definitions emerged: the first defined validity as the degree to which a test measures what it intends to measure, while the second described the validity of an instrument in terms of the correlation it presents with a variable [ 35 ].
However, in the past century, validity theory has evolved, leading to the understanding that validity should be based on specific interpretations for an intended purpose. It should not be limited to empirically obtained psychometric properties but should also be supported by the theory underlying the construct measured. Thus, to speak of classical or modern validity theory suggests an evolution in the classical or modern understanding of the concept of validity. Therefore, a classical approach (called classical test theory, CTT) is specifically differentiated from a modern approach. In general, recent concepts associated with a modern view of validity are based on (a) a unitary conception of validity and (b) validity judgments based on inferences and interpretations of the scores of a measure [ 37 , 38 ]. This conceptual advance in the concept of validity led to the creation of a guiding framework to for obtaining evidence to support the use and interpretation of the scores obtained by a measure [ 39 ].
This purpose is addressed by the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing (“Standards”), a guide created by the American Educational Research Association (AERA), the American Psychological Association (APA) and the National Council on Measurement in Education (NCME) in 2014 with the aim of providing guidelines to assess the validity of the interpretations of scores of an instrument based on their intended use. Two conceptual aspects stand out in this modern view of validity: first, validity is a unitary concept centered on the construct; second, validity is defined as “the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores for proposed uses of tests” [ 37 ]. Thus, the “Standards” propose several sources that serve as a reference for assessing different aspects of validity. The five sources of valid evidence are as follows [ 37 ]: test content, response processes, internal structure, relations to other variables and consequences of testing. According to AERA et al. [ 37 ], test content validity refers to the relationship of the administration process, subject matter, wording and format of test items to the construct they are intended to measure. It is measured predominantly with qualitative methods but without excluding quantitative approaches. The validity of the responses is based on analysis of the cognitive processes and interpretation of the items by respondents and is measured with qualitative methods. Internal structure validity is based on the interrelationship between the items and the construct and is measured by quantitative methods. Validity in terms of the relationship with other variables is based on comparison between the variable that the instrument intends to measure and other theoretically relevant external variables and is measured by quantitative methods. Finally, validity based on the results of the test analyses consequences, both intended and unintended, that may be due to a source of invalidity. It is measured mainly by qualitative methods.
Thus, although validity plays a fundamental role in providing a strong scientific basis for interpretations of test scores, validation studies in the health field have traditionally focused on content validity, criterion validity and construct validity and have overlooked the interpretation and use of scores [ 34 ].
“Standards” are considered a suitable validity theory-based procedural framework for reviewing the validity of questionnaires due to its ability to analyze sources of validity from both qualitative and quantitative approaches and its evidence-based method [ 35 ]. Nevertheless, due to a lack of knowledge or the lack of a systematic description protocol, very few instruments to date have been reviewed within the framework of the “Standards” [ 39 ].
Current study
Although the P-CAT is one of the most widely used instruments by professionals and has seven validations [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 40 ], no analysis has been conducted of its validity within the framework of the “Standards”. That is, empirical evidence of the validity of the P-CAT has not been obtained in a way that helps to develop a judgment based on a synthesis of the available information.
A review of this type is critical given that some methodological issues seem to have not been resolved in the P-CAT. For example, although the multidimensionality of the P-CAT was identified in the study that introduced it, Bru-Luna et al. [ 32 ] recently stated that in adaptations of the P-CAT [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 ], the total score is used for interpretation and multidimensionality is disregarded. Thus, the multidimensionality of the original study was apparently not replicated. Bru-Luna et al. [ 32 ] also indicated that the internal structure validity of the P-CAT is usually underreported due to a lack of sufficiently rigorous approaches to establish with certainty how its scores are calculated.
The validity of the P-CAT, specifically its internal structure, appears to be unresolved. Nevertheless, substantive research and professional practice point to this measure as relevant to assessing PCC. This perception is contestable and judgment-based and may not be sufficient to assess the validity of the P-CAT from a cumulative and synthetic angle based on preceding validation studies. An adequate assessment of validity requires a model to conceptualize validity followed by a review of previous studies of the validity of the P-CAT using this model.
Therefore, the main purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic review of the evidence provided by P-CAT validation studies while taking the “Standards” as a framework.
The present study comprises two distinct but interconnected procedures. First, a systematic literature review was conducted following the PRISMA method ( [ 41 ]; Additional file 1; Additional file 2) with the aim of collecting all validations of the P-CAT that have been developed. Second, a systematic description of the validity evidence for each of the P-CAT validations found in the systematic review was developed following the “Standards” framework [ 37 ]. The work of Hawkins et al. [ 39 ], the first study to review validity sources according to the guidelines proposed by the “Standards”, was also used as a reference. Both provided conceptual and pragmatic guidance for organizing and classifying validity evidence for the P-CAT.
The procedure conducted in the systematic review is described below, followed by the procedure for examining the validity studies.
Systematic review
Search strategy and information sources.
Initially, the Cochrane database was searched with the aim of identifying systematic reviews of the P-CAT. When no such reviews were found, subsequent preliminary searches were performed in the Web of Science (WoS), Scopus and PubMed databases. These databases play a fundamental role in recent scientific literature since they are the main sources of published articles that undergo high-quality content and editorial review processes [ 42 ]. The search formula was as follows. The original P-CAT article [ 21 ] was located, after which all articles that cited it through 2021 were identified and analyzed. This approach ensured the inclusion of all validations. No articles were excluded on the basis of language to avoid language bias [ 43 ]. Moreover, to reduce the effects of publication bias, a complementary search in Google Scholar was also performed to allow the inclusion of “gray” literature [ 44 ]. Finally, a manual search was performed through a review of the references of the included articles to identify other articles that met the search criteria but were not present in any of the aforementioned databases.
This process was conducted by one of the authors and corroborated by another using the Covidence tool [ 45 ]. A third author was consulted in case of doubt.
Eligibility criteria and selection process
The protocol was registered in PROSPERO, and the search was conducted according to these criteria. The identification code is CRD42022335866.
The articles had to meet the following criteria for inclusion in the systematic review: (a) a methodological approach to P-CAT validations, (b) an experimental or quasiexperimental studies, (c) studies with any type of sample, and (d) studies in any language. We discarded studies that met at least one of the following exclusion criteria: (a) systematic reviews or bibliometric reviews of the instrument or meta-analyses or (b) studies published after 2021.
Data collection process
After the articles were selected, the most relevant information was extracted from each article. Fundamental data were recorded in an Excel spreadsheet for each of the sections: introduction, methodology, results and discussion. Information was also recorded about the limitations mentioned in each article as well as the practical implications and suggestions for future research.
Given the aim of the study, information was collected about the sources of validity of each study, including test content (judges’ evaluation, literature review and translation), response processes, internal structure (factor analysis, design, estimator, factor extraction method, factors and items, interfactor R, internal replication, effect of the method, and factor loadings), and relationships with other variables (convergent, divergent, concurrent and predictive validity) and consequences of measurement.
Description of the validity study
To assess the validity of the studies, an Excel table was used. Information was recorded for the seven articles included in the systematic review. The data were extracted directly from the texts of the articles and included information about the authors, the year of publication, the country where each P-CAT validation was produced and each of the five standards proposed in the “Standards” [ 37 ].
The validity source related to internal structure was divided into three sections to record information about dimensionality (e.g., factor analysis, design, estimator, factor extraction method, factors and items, interfactor R, internal replication, effect of the method, and factor loadings), reliability expression (i.e., internal consistency and test-retest) and the study of factorial invariance according to the groups into which it was divided (e.g., sex, age, profession) and the level of study (i.e., metric, intercepts). This approach allowed much more information to be obtained than relying solely on source validity based on internal structure. This division was performed by the same researcher who performed the previous processes.
Study selection and study characteristics
The systematic review process was developed according to the PRISMA methodology [ 41 ].
The WoS, Scopus, PubMed and Google Scholar databases were searched on February 12, 2022 and yielded a total of 485 articles. Of these, 111 were found in WoS, 114 in Scopus, 43 in PubMed and 217 in Google Scholar. In the first phase, the title and abstracts of all the articles were read. In this first screening, 457 articles were eliminated because they did not include studies with a methodological approach to P-CAT validation and one article was excluded because it was the original P-CAT article. This resulted in a total of 27 articles, 19 of which were duplicated in different databases and, in the case of Google Scholar, within the same database. This process yielded a total of eight articles that were evaluated for eligibility by a complete reading of the text. In this step, one of the articles was excluded due to a lack of access to the full text of the study [ 31 ] (although the original manuscript was found, it was impossible to access the complete content; in addition, the authors of the manuscript were contacted, but no reply was received). Finally, a manual search was performed by reviewing the references of the seven studies, but none were considered suitable for inclusion. Thus, the review was conducted with a total of seven articles.
Of the seven studies, six were original validations in other languages. These included Norwegian [ 27 ], Swedish [ 28 ], Chinese (which has two validations [ 29 , 40 ]), Spanish [ 25 ], and Korean [ 30 ]. The study by Selan et al. [ 46 ] included a modification of the Swedish version of the P-CAT and explored the psychometric properties of both versions (i.e., the original Swedish version and the modified version).
The item selection and screening process are illustrated in detail in Fig. 1 .
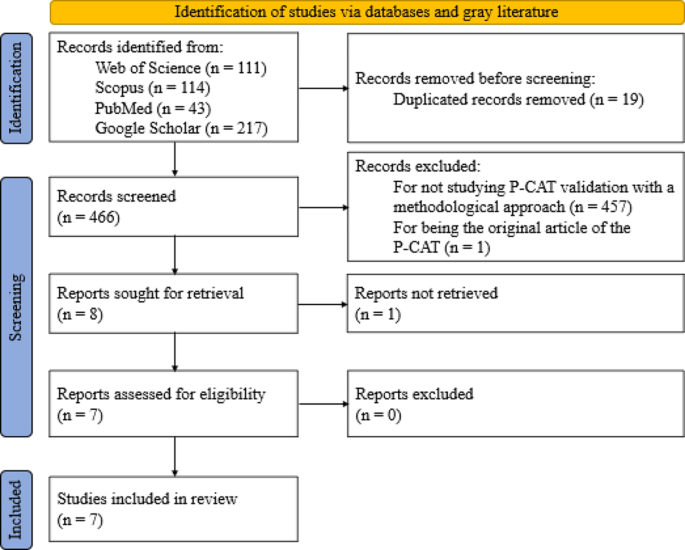
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic reviews including database searches
Validity analysis
To provide a clear overview of the validity analyses, Table 1 descriptively shows the percentages of items that provide information about the five standards proposed by the “Standards” guide [ 37 ].
The table shows a high number of validity sources related to test content and internal structure in relation to dimensionality and internal consistency, followed by a moderate number of sources for test-retest and relationship with other variables. A rate of 0% is observed for validity sources related to response processes, invariance and test consequences. Below, different sections related to each of the standards are shown, and the information is presented in more detail.
Evidence based on test content
The first standard, which focused on test content, was met for all items (100%). Translation, which refers to the equivalence of content between the original language and the target language, was met in the six articles that conducted validation in another language and/or culture. These studies reported that the validations were translated by bilingual experts and/or experts in the area of care. In addition, three studies [ 25 , 29 , 40 ] reported that the translation process followed International Test Commission guidelines, such as those of Beaton et al. [ 47 ], Guillemin [ 48 ], Hambleton et al. [ 49 ], and Muñiz et al. [ 50 ]. Evaluation by judges, who referred to the relevance, clarity and importance of the content, was divided into two categories: expert evaluation (a panel of expert judges for each of the areas to consider in the evaluation instrument) and experiential evaluation (potential participants testing the test). The first type of evaluation occurred in three of the articles [ 28 , 29 , 46 ], while the other occurred in two [ 25 , 40 ]. Only one of the items [ 29 ] reported that the scale contained items that reflected the dimension described in the literature. The validity evidence related to the test content presented in each article can be found in Table 2 .
Evidence based on response processes
The second standard, related to the validity of the response process, was obtained according to the “Standards” from the analysis of individual responses: “questioning test takers about their performance strategies or response to particular items (…), maintaining records that monitor the development of a response to a writing task (…), documentation of other aspects of performance, like eye movement or response times…” [ 37 ] (p. 15). According to the analysis of the validity of the response processes, none of the articles complied with this evidence.
Evidence based on internal structure
The third standard, validity related to internal structure, was divided into three sections. First, the dimensionality of each study was examined in terms of factor analysis, design, estimator, factor extraction method, factors and items, interfactor R, internal replication, effect of the method, and factor loadings. Le et al. [ 40 ] conducted an exploratory-confirmatory design while Sjögren et al. [ 28 ] conducted a confirmatory-exploratory design to assess construct validity using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and investigated it further using exploratory factor analysis (EFA). The remaining articles employed only a single form of factor analysis: three employed EFA, and two employed CFA. Regarding the next point, only three of the articles reported the factor extraction method used, including Kaiser’s eigenvalue, criterion, scree plot test, parallel analysis and Velicer’s MAP test. Instrument validations yielded a total of two factors in five of the seven articles, while one yielded a single dimension [ 25 ] and the other yielded three dimensions [ 29 ], as in the original instrument. The interfactor R was reported only in the study by Zhong and Lou [ 29 ], whereas in the study by Martínez et al. [ 25 ], it could be easily obtained since it consisted of only one dimension. Internal replication was also calculated in the Spanish validation by randomly splitting the sample into two to test the correlations between factors. The effectiveness of the method was not reported in any of the articles. This information is presented in Table 3 in addition to a summary of the factor loadings.
The second section examined reliability. All the studies presented measures of internal consistency conducted in their entirety with Cronbach’s α coefficient for both the total scale and the subscales. The ω coefficient of McDonald was not used in any case. Four of the seven articles performed a test-retest test. Martínez et al. [ 25 ] conducted a test-retest after a period of seven days, while Le et al. [ 40 ] and Rokstad et al. [ 27 ] performed it between one and two weeks later and Sjögren et al. [ 28 ] allowed approximately two weeks to pass after the initial test.
The third section analyzes the calculation of invariance, which was not reported in any of the studies.
Evidence based on relationships with other variables
In the fourth standard, based on validity according to the relationship with other variables, the articles that reported it used only convergent validity (i.e., it was hypothesized that the variables related to the construct measured by the test—in this case, person-centeredness—were positively or negatively related to another construct). Discriminant validity hypothesizes that the variables related to the PCC construct are not correlated in any way with any other variable studied. No article (0%) measured discriminant evidence, while four (57%) measured convergent evidence [ 25 , 29 , 30 , 46 ]. Convergent validity was obtained through comparisons with instruments such as the Person-Centered Climate Questionnaire–Staff Version (PCQ-S), the Staff-Based Measures of Individualized Care for Institutionalized Persons with Dementia (IC), the Caregiver Psychological Elder Abuse Behavior Scale (CPEAB), the Organizational Climate (CLIOR) and the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI). In the case of Selan et al. [ 46 ], convergent validity was assessed on two items considered by the authors as “crude measures of person-centered care (i.e., external constructs) giving an indication of the instruments’ ability to measure PCC” (p. 4). Concurrent validity, which measures the degree to which the results of one test are or are not similar to those of another test conducted at more or less the same time with the same participants, and predictive validity, which allows predictions to be established regarding behavior based on comparison between the values of the instrument and the criterion, were not reported in any of the studies.
Evidence based on the consequences of testing
The fifth and final standard was related to the consequences of the test. It analyzed the consequences, both intended and unintended, of applying the test to a given sample. None of the articles presented explicit or implicit evidence of this.
The last two sources of validity can be seen in Table 4 .
Table 5 shows the results of the set of validity tests for each study according to the described standards.
The main purpose of this article is to analyze the evidence of validity in different validation studies of the P-CAT. To gather all existing validations, a systematic review of all literature citing this instrument was conducted.
The publication of validation studies of the P-CAT has been constant over the years. Since the publication of the original instrument in 2010, seven validations have been published in other languages (taking into account the Italian version by Brugnolli et al. [ 31 ], which could not be included in this study) as well as a modification of one of these versions. The very unequal distribution of validations between languages and countries is striking. A recent systematic review [ 51 ] revealed that in Europe, the countries where the PCC approach is most widely used are the United Kingdom, Sweden, the Netherlands, Northern Ireland, and Norway. It has also been shown that the neighboring countries seem to exert an influence on each other due to proximity [ 52 ] such that they tend to organize healthcare in a similar way, as is the case for Scandinavian countries. This favors the expansion of PCC and explains the numerous validations we found in this geographical area.
Although this approach is conceived as an essential element of healthcare for most governments [ 53 ], PCC varies according to the different definitions and interpretations attributed to it, which can cause confusion in its application (e.g., between Norway and the United Kingdom [ 54 ]). Moreover, facilitators of or barriers to implementation depend on the context and level of development of each country, and financial support remains one of the main factors in this regard [ 53 ]. This fact explains why PCC is not globally widespread among all territories. In countries where access to healthcare for all remains out of reach for economic reasons, the application of this approach takes a back seat, as does the validation of its assessment tools. In contrast, in a large part of Europe or in countries such as China or South Korea that have experienced decades of rapid economic development, patients are willing to be involved in their medical treatment and enjoy more satisfying and efficient medical experiences and environments [ 55 ], which facilitates the expansion of validations of instruments such as the P-CAT.
Regarding validity testing, the guidelines proposed by the “Standards” [ 37 ] were followed. According to the analysis of the different validations of the P-CAT instrument, none of the studies used a structured validity theory-based procedural framework for conducting validation. The most frequently reported validity tests were on the content of the test and two of the sections into which the internal structure was divided (i.e., dimensionality and internal consistency).
In the present article, the most cited source of validity in the studies was the content of the test because most of the articles were validations of the P-CAT in other languages, and the authors reported that the translation procedure was conducted by experts in all cases. In addition, several of the studies employed International Test Commission guidelines, such as those by Beaton et al. [ 47 ], Guillemin [ 48 ], Hambleton et al. [ 49 ], and Muñiz et al. [ 50 ]. Several studies also assessed the relevance, clarity and importance of the content.
The third source of validity, internal structure, was the next most often reported, although it appeared unevenly among the three sections into which this evidence was divided. Dimensionality and internal consistency were reported in all studies, followed by test-retest consistency. In relation to the first section, factor analysis, a total of five EFAs and four CFAs were presented in the validations. Traditionally, EFA has been used in research to assess dimensionality and identify key psychological constructs, although this approach involves a number of inconveniences, such as difficulty testing measurement invariance and incorporating latent factors into subsequent analyses [ 56 ] or the major problem of factor loading matrix rotation [ 57 ]. Studies eventually began to employ CFA, a technique that overcame some of these obstacles [ 56 ] but had other drawbacks; for example, the strict requirement of zero cross-loadings often does not fit the data well, and misspecification of zero loadings tends to produce distorted factors [ 57 ]. Recently, exploratory structural equation modeling (ESEM) has been proposed. This technique is widely recommended both conceptually and empirically to assess the internal structure of psychological tools [ 58 ] since it overcomes the limitations of EFA and CFA in estimating their parameters [ 56 , 57 ].
The next section, reliability, reports the total number of items according to Cronbach’s α reliability coefficient. Reliability is defined as a combination of systematic and random influences that determine the observed scores on a psychological test. Reporting the reliability measure ensures that item-based scores are consistent, that the tool’s responses are replicable and that they are not modified solely by random noise [ 59 , 60 ]. Currently, the most commonly employed reliability coefficient in studies with a multi-item measurement scale (MIMS) is Cronbach’s α [ 60 , 61 ].
Cronbach’s α [ 62 ] is based on numerous strict assumptions (e.g., the test must be unidimensional, factor loadings must be equal for all items and item errors should not covary) to estimate internal consistency. These assumptions are difficult to meet, and their violation may produce small reliability estimates [ 60 ]. One of the alternative measures to α that is increasingly recommended by the scientific literature is McDonald’s ω [ 63 ], a composite reliability measure. This coefficient is recommended for congeneric scales in which tau equivalence is not assumed. It has several advantages. For example, estimates of ω are usually robust when the estimated model contains more factors than the true model, even with small samples, or when skewness in univariate item distributions produces lower biases than those found when using α [ 59 ].
The test-retest method was the next most commonly reported internal structure section in these studies. This type of reliability considers the consistency of the scores of a test between two measurements separated by a period [ 64 ]. It is striking that test-retest consistency does not have a prevalence similar to that of internal consistency since, unlike internal consistency, test-retest consistency can be assessed for practically all types of patient-reported outcomes. It is even considered by some measurement experts to report reliability with greater relevance than internal consistency since it plays a fundamental role in the calculation of parameters for health measures [ 64 ]. However, the literature provides little guidance regarding the assessment of this type of reliability.
The internal structure section that was least frequently reported in the studies in this review was invariance. A lack of invariance refers to a difference between scores on a test that is not explained by group differences in the structure it is intended to measure [ 65 ]. The invariance of the measure should be emphasized as a prerequisite in comparisons between groups since “if scale invariance is not examined, item bias may not be fully recognized and this may lead to a distorted interpretation of the bias in a particular psychological measure” [ 65 ].
Evidence related to other variables was the next most reported source of validity in the studies included in this review. Specifically, the four studies that reported this evidence did so according to convergent validity and cited several instruments. None of the studies included evidence of discriminant validity, although this may be because there are currently several obstacles related to the measurement of this type of validity [ 66 ]. On the one hand, different definitions are used in the applied literature, which makes its evaluation difficult; on the other hand, the literature on discriminant validity focuses on techniques that require the use of multiple measurement methods, which often seem to have been introduced without sufficient evidence or are applied randomly.
Validity related to response processes was not reported by any of the studies. There are several methods to analyze this validity. These methods can be divided into two groups: “those that directly access the psychological processes or cognitive operations (think aloud, focus group, and interviews), compared to those which provide indirect indicators which in turn require additional inference (eye tracking and response times)” [ 38 ]. However, this validity evidence has traditionally been reported less frequently than others in most studies, perhaps because there are fewer clear and accepted practices on how to design or report these studies [ 67 ].
Finally, the consequences of testing were not reported in any of the studies. There is debate regarding this source of validity, with two main opposing streams of thought. On the one hand [ 68 , 69 ]) suggests that consequences that appear after the application of a test should not derive from any source of test invalidity and that “adverse consequences only undermine the validity of an assessment if they can be attributed to a problem of fit between the test and the construct” (p. 6). In contrast, Cronbach [ 69 , 70 ] notes that adverse social consequences that may result from the application of a test may call into question the validity of the test. However, the potential risks that may arise from the application of a test should be minimized in any case, especially in regard to health assessments. To this end, it is essential that this aspect be assessed by instrument developers and that the experiences of respondents be protected through the development of comprehensive and informed practices [ 39 ].
This work is not without limitations. First, not all published validation studies of the P-CAT, such as the Italian version by Brugnolli et al. [ 31 ], were available. These studies could have provided relevant information. Second, many sources of validity could not be analyzed because the studies provided scant or no data, such as response processes [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ], relationships with other variables [ 27 , 28 , 40 ], consequences of testing [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ], or invariance [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ] in the case of internal structure and interfactor R [ 27 , 28 , 30 , 40 , 46 ], internal replication [ 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ] or the effect of the method [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ] in the case of dimensionality. In the future, it is hoped that authors will become aware of the importance of validity, as shown in this article and many others, and provide data on unreported sources so that comprehensive validity studies can be performed.
The present work also has several strengths. The search was extensive, and many studies were obtained using three different databases, including WoS, one of the most widely used and authoritative databases in the world. This database includes a large number and variety of articles and is not fully automated due to its human team [ 71 , 72 , 73 ]. In addition, to prevent publication bias, gray literature search engines such as Google Scholar were used to avoid the exclusion of unpublished research [ 44 ]. Finally, linguistic bias was prevented by not limiting the search to articles published in only one or two languages, thus avoiding the overrepresentation of studies in one language and underrepresentation in others [ 43 ].
Conclusions
Validity is understood as the degree to which tests and theory support the interpretations of instrument scores for their intended use [ 37 ]. From this perspective, the various validations of the P-CAT are not presented in a structured, valid, theory-based procedural framework like the “Standards” are. After integration and analysis of the results, it was observed that these validation reports offer a high number of sources of validity related to test content, internal structure in dimensionality and internal consistency, a moderate number of sources for internal structure in terms of test-retest reliability and the relationship with other variables, and a very low number of sources for response processes, internal structure in terms of invariance, and test consequences.
Validity plays a fundamental role in ensuring a sound scientific basis for test interpretations because it provides evidence of the extent to which the data provided by the test are valid for the intended purpose. This can affect clinical practice as people’s health may depend on it. In this sense, the “Standards” are considered a suitable and valid theory-based procedural framework for studying this modern conception of questionnaire validity, which should be taken into account in future research in this area.
Although the P-CAT is one of the most widely used instruments for assessing PCC, as shown in this study, PCC has rarely been studied. The developers of measurement tests applied to the health care setting, on which the health and quality of life of many people may depend, should use this validity framework to reflect the clear purpose of the measurement. This approach is important because the equity of decision making by healthcare professionals in daily clinical practice may depend on the source of validity. Through a more extensive study of validity that includes the interpretation of scores in terms of their intended use, the applicability of the P-CAT, an instrument that was initially developed for long-term care homes for elderly people, could be expanded to other care settings. However, the findings of this study show that validation studies continue to focus on traditionally studied types of validity and overlook the interpretation of scores in terms of their intended use.
Data availability
All data relevant to the study were included in the article or uploaded as additional files. Additional template data extraction forms are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
American Educational Research Association
American Psychological Association
Confirmatory factor analysis
Organizational Climate
Caregiver Psychological Elder Abuse Behavior Scale
Exploratory factor analysis
Exploratory structural equation modeling
Staff-based Measures of Individualized Care for Institutionalized Persons with Dementia
Maslach Burnout Inventory
Multi-item measurement scale
Maximum likelihood
National Council on Measurement in Education
Person-Centered Care Assessment Tool
- Person-centered care
Person-Centered Climate Questionnaire–Staff Version
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
International Register of Systematic Review Protocols
Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing
weighted least square mean and variance adjusted
Web of Science
Institute of Medicine. Crossing the quality chasm: a new health system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: National Academy; 2001.
Google Scholar
International Alliance of Patients’ Organizations. What is patient-centred healthcare? A review of definitions and principles. 2nd ed. London, UK: International Alliance of Patients’ Organizations; 2007.
World Health Organization. WHO global strategy on people-centred and integrated health services: interim report. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2015.
Britten N, Ekman I, Naldemirci Ö, Javinger M, Hedman H, Wolf A. Learning from Gothenburg model of person centred healthcare. BMJ. 2020;370:m2738.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Van Diepen C, Fors A, Ekman I, Hensing G. Association between person-centred care and healthcare providers’ job satisfaction and work-related health: a scoping review. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e042658.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ekman N, Taft C, Moons P, Mäkitalo Å, Boström E, Fors A. A state-of-the-art review of direct observation tools for assessing competency in person-centred care. Int J Nurs Stud. 2020;109:103634.
American Geriatrics Society Expert Panel on Person-Centered Care. Person-centered care: a definition and essential elements. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016;64:15–8.
Article Google Scholar
McCormack B, McCance TV. Development of a framework for person-centred nursing. J Adv Nurs. 2006;56:472–9.
McCormack B, McCance T. Person-centred practice in nursing and health care: theory and practice. Chichester, England: Wiley; 2016.
Nolan MR, Davies S, Brown J, Keady J, Nolan J. Beyond person-centred care: a new vision for gerontological nursing. J Clin Nurs. 2004;13:45–53.
McCormack B, McCance T. Person-centred nursing: theory, models and methods. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010.
Book Google Scholar
Abraha I, Rimland JM, Trotta FM, Dell’Aquila G, Cruz-Jentoft A, Petrovic M, et al. Systematic review of systematic reviews of non-pharmacological interventions to treat behavioural disturbances in older patients with dementia. The SENATOR-OnTop series. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e012759.
Anderson K, Blair A. Why we need to care about the care: a longitudinal study linking the quality of residential dementia care to residents’ quality of life. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2020;91:104226.
Bauer M, Fetherstonhaugh D, Haesler E, Beattie E, Hill KD, Poulos CJ. The impact of nurse and care staff education on the functional ability and quality of life of people living with dementia in aged care: a systematic review. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;67:27–45.
Smythe A, Jenkins C, Galant-Miecznikowska M, Dyer J, Downs M, Bentham P, et al. A qualitative study exploring nursing home nurses’ experiences of training in person centred dementia care on burnout. Nurse Educ Pract. 2020;44:102745.
McCormack B, Borg M, Cardiff S, Dewing J, Jacobs G, Janes N, et al. Person-centredness– the ‘state’ of the art. Int Pract Dev J. 2015;5:1–15.
Wilberforce M, Challis D, Davies L, Kelly MP, Roberts C, Loynes N. Person-centredness in the care of older adults: a systematic review of questionnaire-based scales and their measurement properties. BMC Geriatr. 2016;16:63.
Rathert C, Wyrwich MD, Boren SA. Patient-centered care and outcomes: a systematic review of the literature. Med Care Res Rev. 2013;70:351–79.
Sharma T, Bamford M, Dodman D. Person-centred care: an overview of reviews. Contemp Nurse. 2016;51:107–20.
Ahmed S, Djurkovic A, Manalili K, Sahota B, Santana MJ. A qualitative study on measuring patient-centered care: perspectives from clinician-scientists and quality improvement experts. Health Sci Rep. 2019;2:e140.
Edvardsson D, Fetherstonhaugh D, Nay R, Gibson S. Development and initial testing of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT). Int Psychogeriatr. 2010;22:101–8.
Tamagawa R, Groff S, Anderson J, Champ S, Deiure A, Looyis J, et al. Effects of a provincial-wide implementation of screening for distress on healthcare professionals’ confidence and understanding of person-centered care in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016;14:1259–66.
Degl’ Innocenti A, Wijk H, Kullgren A, Alexiou E. The influence of evidence-based design on staff perceptions of a supportive environment for person-centered care in forensic psychiatry. J Forensic Nurs. 2020;16:E23–30.
Hulin CL. A psychometric theory of evaluations of item and scale translations: fidelity across languages. J Cross Cult Psychol. 1987;18:115–42.
Martínez T, Suárez-Álvarez J, Yanguas J, Muñiz J. Spanish validation of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT). Aging Ment Health. 2016;20:550–8.
Martínez T, Martínez-Loredo V, Cuesta M, Muñiz J. Assessment of person-centered care in gerontology services: a new tool for healthcare professionals. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2020;20:62–70.
Rokstad AM, Engedal K, Edvardsson D, Selbaek G. Psychometric evaluation of the Norwegian version of the person-centred Care Assessment Tool. Int J Nurs Pract. 2012;18:99–105.
Sjögren K, Lindkvist M, Sandman PO, Zingmark K, Edvardsson D. Psychometric evaluation of the Swedish version of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT). Int Psychogeriatr. 2012;24:406–15.
Zhong XB, Lou VW. Person-centered care in Chinese residential care facilities: a preliminary measure. Aging Ment Health. 2013;17:952–8.
Tak YR, Woo HY, You SY, Kim JH. Validity and reliability of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool in long-term care facilities in Korea. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2015;45:412–9.
Brugnolli A, Debiasi M, Zenere A, Zanolin ME, Baggia M. The person-centered Care Assessment Tool in nursing homes: psychometric evaluation of the Italian version. J Nurs Meas. 2020;28:555–63.
Bru-Luna LM, Martí-Vilar M, Merino-Soto C, Livia J. Reliability generalization study of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool. Front Psychol. 2021;12:712582.
Edvardsson D, Innes A. Measuring person-centered care: a critical comparative review of published tools. Gerontologist. 2010;50:834–46.
Hawkins M, Elsworth GR, Nolte S, Osborne RH. Validity arguments for patient-reported outcomes: justifying the intended interpretation and use of data. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2021;5:64.
Sireci SG. On the validity of useless tests. Assess Educ Princ Policy Pract. 2016;23:226–35.
Hawkins M, Elsworth GR, Osborne RH. Questionnaire validation practice: a protocol for a systematic descriptive literature review of health literacy assessments. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e030753.
American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association. National Council on Measurement in Education. Standards for educational and psychological testing. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association; 2014.
Padilla JL, Benítez I. Validity evidence based on response processes. Psicothema. 2014;26:136–44.
PubMed Google Scholar
Hawkins M, Elsworth GR, Hoban E, Osborne RH. Questionnaire validation practice within a theoretical framework: a systematic descriptive literature review of health literacy assessments. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e035974.
Le C, Ma K, Tang P, Edvardsson D, Behm L, Zhang J, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the person-centred Care Assessment Tool. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e031580.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. 2021;88:105906.
Falagas ME, Pitsouni EI, Malietzis GA, Pappas G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of Science, and Google Scholar: strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008;22:338–42.
Grégoire G, Derderian F, Le Lorier J. Selecting the language of the publications included in a meta-analysis: is there a tower of Babel bias? J Clin Epidemiol. 1995;48:159–63.
Arias MM. Aspectos metodológicos Del metaanálisis (1). Pediatr Aten Primaria. 2018;20:297–302.
Covidence. Covidence systematic review software. Veritas Health Innovation, Australia. 2014. https://www.covidence.org/ . Accessed 28 Feb 2022.
Selan D, Jakobsson U, Condelius A. The Swedish P-CAT: modification and exploration of psychometric properties of two different versions. Scand J Caring Sci. 2017;31:527–35.
Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25:3186–91.
Guillemin F. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of health status measures. Scand J Rheumatol. 1995;24:61–3.
Hambleton R, Merenda P, Spielberger C. Adapting educational and psychological tests for cross-cultural assessment. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2005.
Muñiz J, Elosua P, Hambleton RK. International test commission guidelines for test translation and adaptation: second edition. Psicothema. 2013;25:151–7.
Rosengren K, Brannefors P, Carlstrom E. Adoption of the concept of person-centred care into discourse in Europe: a systematic literature review. J Health Organ Manag. 2021;35:265–80.
Alharbi T, Olsson LE, Ekman I, Carlström E. The impact of organizational culture on the outcome of hospital care: after the implementation of person-centred care. Scand J Public Health. 2014;42:104–10.
Bensbih S, Souadka A, Diez AG, Bouksour O. Patient centered care: focus on low and middle income countries and proposition of new conceptual model. J Med Surg Res. 2020;7:755–63.
Stranz A, Sörensdotter R. Interpretations of person-centered dementia care: same rhetoric, different practices? A comparative study of nursing homes in England and Sweden. J Aging Stud. 2016;38:70–80.
Zhou LM, Xu RH, Xu YH, Chang JH, Wang D. Inpatients’ perception of patient-centered care in Guangdong province, China: a cross-sectional study. Inquiry. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/00469580211059482 .
Marsh HW, Morin AJ, Parker PD, Kaur G. Exploratory structural equation modeling: an integration of the best features of exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2014;10:85–110.
Asparouhov T, Muthén B. Exploratory structural equation modeling. Struct Equ Model Multidiscip J. 2009;16:397–438.
Cabedo-Peris J, Martí-Vilar M, Merino-Soto C, Ortiz-Morán M. Basic empathy scale: a systematic review and reliability generalization meta-analysis. Healthc (Basel). 2022;10:29–62.
Flora DB. Your coefficient alpha is probably wrong, but which coefficient omega is right? A tutorial on using R to obtain better reliability estimates. Adv Methods Pract Psychol Sci. 2020;3:484–501.
McNeish D. Thanks coefficient alpha, we’ll take it from here. Psychol Methods. 2018;23:412–33.
Hayes AF, Coutts JJ. Use omega rather than Cronbach’s alpha for estimating reliability. But… Commun Methods Meas. 2020;14:1–24.
Cronbach LJ. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika. 1951;16:297–334.
McDonald R. Test theory: a unified approach. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum; 1999.
Polit DF. Getting serious about test-retest reliability: a critique of retest research and some recommendations. Qual Life Res. 2014;23:1713–20.
Ceylan D, Çizel B, Karakaş H. Testing destination image scale invariance for intergroup comparison. Tour Anal. 2020;25:239–51.
Rönkkö M, Cho E. An updated guideline for assessing discriminant validity. Organ Res Methods. 2022;25:6–14.
Hubley A, Zumbo B. Response processes in the context of validity: setting the stage. In: Zumbo B, Hubley A, editors. Understanding and investigating response processes in validation research. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2017. pp. 1–12.
Messick S. Validity of performance assessments. In: Philips G, editor. Technical issues in large-scale performance assessment. Washington, DC: Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics; 1996. pp. 1–18.
Moss PA. The role of consequences in validity theory. Educ Meas Issues Pract. 1998;17:6–12.
Cronbach L. Five perspectives on validity argument. In: Wainer H, editor. Test validity. Hillsdale, MI: Erlbaum; 1988. pp. 3–17.
Birkle C, Pendlebury DA, Schnell J, Adams J. Web of Science as a data source for research on scientific and scholarly activity. Quant Sci Stud. 2020;1:363–76.
Bramer WM, Rethlefsen ML, Kleijnen J, Franco OH. Optimal database combinations for literature searches in systematic reviews: a prospective exploratory study. Syst Rev. 2017;6:245.
Web of Science Group. Editorial selection process. Clarivate. 2024. https://clarivate.com/webofsciencegroup/solutions/%20editorial-selection-process/ . Accessed 12 Sept 2022.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the casual helpers for their aid in information processing and searching.
This work is one of the results of research project HIM/2015/017/SSA.1207, “Effects of mindfulness training on psychological distress and quality of life of the family caregiver”. Main researcher: Filiberto Toledano-Toledano Ph.D. The present research was funded by federal funds for health research and was approved by the Commissions of Research, Ethics and Biosafety (Comisiones de Investigación, Ética y Bioseguridad), Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez, National Institute of Health. The source of federal funds did not control the study design, data collection, analysis, or interpretation, or decisions regarding publication.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Departamento de Educación, Facultad de Ciencias Sociales, Universidad Europea de Valencia, 46010, Valencia, Spain
Lluna Maria Bru-Luna
Departamento de Psicología Básica, Universitat de València, Blasco Ibáñez Avenue, 21, 46010, Valencia, Spain
Manuel Martí-Vilar
Departamento de Psicología, Instituto de Investigación de Psicología, Universidad de San Martín de Porres, Tomás Marsano Avenue 242, Lima 34, Perú
César Merino-Soto
Instituto Central de Gestión de la Investigación, Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal, Carlos Gonzalez Avenue 285, 15088, San Miguel, Perú
José Livia-Segovia
Unidad de Investigación en Medicina Basada en Evidencias, Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez Instituto Nacional de Salud, Dr. Márquez 162, 06720, Doctores, Cuauhtémoc, Mexico
Juan Garduño-Espinosa & Filiberto Toledano-Toledano
Unidad de Investigación Multidisciplinaria en Salud, Instituto Nacional de Rehabilitación Luis Guillermo Ibarra Ibarra, México-Xochimilco 289, Arenal de Guadalupe, 14389, Tlalpan, Mexico City, Mexico
Filiberto Toledano-Toledano
Dirección de Investigación y Diseminación del Conocimiento, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias e Innovación para la Formación de Comunidad Científica, INDEHUS, Periférico Sur 4860, Arenal de Guadalupe, 14389, Tlalpan, Mexico City, Mexico
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
L.M.B.L. conceptualized the study, collected the data, performed the formal anal- ysis, wrote the original draft, and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. M.M.V. collected the data and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. C.M.S. collected the data, performed the formal analysis, wrote the original draft, and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. J.L.S. collected the data, wrote the original draft, and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. J.G.E. collected the data and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. F.T.T. conceptualized the study and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. L.M.B.L. conceptualized the study and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. M.M.V. conceptualized the study and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. C.M.S. reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. J.G.E. reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. F.T.T. conceptualized the study; provided resources, software, and supervision; wrote the original draft; and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Filiberto Toledano-Toledano .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Commissions of Research, Ethics and Biosafety (Comisiones de Investigación, Ética y Bioseguridad), Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez, National Institute of Health. HIM/2015/017/SSA.1207, “Effects of mindfulness training on psychological distress and quality of life of the family caregiver”.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bru-Luna, L.M., Martí-Vilar, M., Merino-Soto, C. et al. Person-centered care assessment tool with a focus on quality healthcare: a systematic review of psychometric properties. BMC Psychol 12 , 217 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01716-7
Download citation
Received : 17 May 2023
Accepted : 07 April 2024
Published : 19 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01716-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Person-centered care assessment tool
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Rethinking cluster under coopetition strategy: an integrative literature review and research agenda
- Open access
- Published: 24 April 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7685-2718 1 , 2 ,
- Rosana L. Coelho Fernandes ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0007-6026-7857 2 &
- Jefferson Marlon Monticelli ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1605-7090 3
22 Accesses
Explore all metrics
This study aimed to integrate the dimensions and elements of intra-cluster coopetition, identify the emergence of a complementary theoretical perspective to cluster theory and create an integrative research agenda to support the rethinking cluster approach based on coopetition. It is an integrative Systematic Literature Review that generates insights to move the topic forward. Results showed coopetition as context, process, or outcome. The research focus was grouped into six dimensions of intra-cluster coopetition: Strategic Adjustment, Perceived Benefits, Mediated Coopetition, Social Interaction, Coopetitive Orientation, and Temporality of Coopetition. Four hundred eighty-six elements used by scholars created a second-order coding to represent the variables of coopetition in clusters. From the integrative literature overview, a theoretical framework emerges with four dimensions: Conditional factors, Policies, Market commonality, and Formal supporting structure. These dimensions act as drivers, markets, or intensifiers of the intra-cluster coopetition strategy. At the same time, the dimensions suffer the influence of external, internal, and ecosystem contexts. Our literature review builds theory to advance cluster coopetition research and complement the Porterian perspective. The framework suggests the main elements to manage clusters under the coopetition strategy. These findings rethink cluster theory and deliver the business co-evolution perspective, considering the cluster as a business ecosystem with an open system based on coopetition. Findings offer an inductive-deductive pattern system to further research that represents the evolutionary trend of the topic itself.
Similar content being viewed by others

Co-opetition Reloaded: Rethinking the Role of Globalization, Supply Chains, and Mechanism Design Theory

Business Model Design and Value Co-creation: Looking for a New Pattern

New Business Models: Examining the Role of Principles Relating to Transactions and Interactions
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Coopetition is the interplay among organizations that complement each other through partnerships while competing for competitive advantage and market share (Bengtsson and Kock 2014 ). Studies highlighted several benefits of coopetition for organizations mainly result from the ability to obtain scarce resources, stimulate innovation, reduce costs, provide opportunities for technological growth, and increase innovation, competitiveness and sustainability (Estrada et al. 2016 ; Crick et al. 2020 ; Ferasso et al. 2022 ; Ramjaun et al. 2023 ). On the other hand, there is also research on threats, risks, and disadvantages of coopetition (Cygler and Sroka 2017 ; Estrada et al. 2016 ; Mantovani and Ruiz-Aliseda 2012 ; Ritala et al. 2008 ).
Scholars point out that coopetition is a paradigm to update competitiveness theories and a strategy subfield directed to shared goals (Yami et al. 2010 ; Köseoğlu et al. 2019 ). Theoretical Roots of coopetition are diverse but predominately of Game Theory, Resource-Based View (RBV), and Network Theory (Klimas et al. 2023 ). Coopetition emerges from a strategic relational view (Minà and Dagnino 2016 ), which means it is aligned with the Extended-RBV proposed by Barney ( 2018 ) that considers the relationships as a strategic resource to achieve sustainable competitive advantage. Köseoğlu et al. ( 2019 ) suggested that process and strategy are coopetition components used in strategic and tactical dimensions.
Coopetition has a multidimensional and multifaceted nature, which can be horizontal, that is, between direct competitors; vertical, for example, among the firm and its providers; or mixed, i.e., along a value chain (Czakon and Sołtysik 2016 ). Sometimes, coopetition is a deliberate strategy purposely designed with formal agreements structured by the players. Other times, it is a response to a market circumstance as an emerging behavior, an unintentional strategy (Czakon et al. 2020a , b ; Bengtsson and Kock 2014 ). Some contexts are more favorable to coopetition since it is an intrinsic behavior, such as the tourism destination (Della and Aria 2016 ; Kylanen and Mariani 2012 ), business ecosystems or innovation ecosystems (Lehtonen et al. 2020 ) and local productive arrangements or clusters (Dana et al. 2013 ).
1.1 Why coopetition and cluster?
According to Dana et al. ( 2013 ), coopetitive relationships between partners evolve inside clusters, helping clustered firms leverage sustainable coopetitive advantage. Porter ( 1998 ) defines clusters as geographic concentrations of interrelated companies that compete but cooperate, linked by common and complementary elements, such as suppliers, service providers, companies from related sectors, and even institutions, such as universities, trade associations, think tanks, government, etc. The cluster Porterian concept confirms that coopetition is an inherent behavior of clusters. Although the coopetition perspective was not a theoretical background of Porter’s theory ( 1998 ), he highlighted the interplay of competition and cooperation along cluster dimensions and among different participants within the productive arrangements that positively affect the partners’ productivity.
Porterian Theories are the main background of the cluster theory despite many underlying perspectives and theories supporting the intra and inter-cluster strategies. According to Porter ( 1998 ), the complementarity between the support institutions and the clusterized firms defines the cluster boundaries. That means the network defines the cluster. Stead and Stead ( 2019 ) suggested that the Porterian paradigm had an invaluable contribution to the strategic management field but needs to evolve to explain the current business environment. In this sense, scholars have been rethinking the cluster approach, for example, Harris ( 2021 ), Lazzeretti et al. ( 2019 ), and Tracey and Clark ( 2003 ).
Among the assumptions of the Rethinking Cluster approach, coopetition is pointed out as the strategy to foster economic advantage, allowing shared information, knowledge, markets, and marketing intelligence networks, as well as supply and distribution chains (Ferasso et al. 2022 ; Sellitto and Luchese 2018 ; Dana et al. 2013 ). The coopetition networks assume an essential role in constructing social capital that facilitates inter-organizational behavior typically characterized by competition. Coopetition provides forces which balance in symbiotic intra-cluster management, whose interplay requires a proactive attitude towards cooperation, building trust, and commitment (Felzensztein et al. 2018 ).
Coopetition in clusters is a spotlight topic among scholars due to the growing use of this strategy in various industries (Feraso et al. 2022 ), besides the importance of clusters for regional economic and social development (Porter 1998 ). Most studies analyzed coopetition at the individual, intra-organizational, inter-organizational, and inter-network levels (Czakon et al. 2020a , b ) or the level of society (Oliveira-Ribeiro et al. 2022 ). However, in the cluster, coopetition occurs at the intra and inter-cluster levels with particular conditions that can provide a complementary view to the Cluster theory (Porter 1991 ). This complementarity can help to build the Rethinking Cluster approach, but it is necessary to identify the status of intra-cluster coopetition knowledge and create a research agenda.
1.2 Rethinking cluster from coopetition theoretical lens: a critical integrative review
We developed an integrative systematic integrative literature review (SLR) on cluster coopetition to answer three research questions:
(Q1) What dimensions and elements of intra-cluster coopetition? (Q2) What complementary framework emerges from the cluster coopetition to cluster theory? (Q3) What dynamics of the research agenda can help the rethinking cluster from a coopetition perspective?
Our article has a twofold purpose. Firstly, the study aims to integrate the dimensions and elements of intra-cluster coopetition to identify the emergence of a complementary theoretical perspective to cluster theory. Second, this study seeks to create an integrative research agenda to support the rethinking cluster approach based on relational strategies based on coopetition.
Systematic reviews are essential for summarizing evidence accurately and reliably, providing information about the theory and practice for any discipline, and leading to a research agenda (Liberati et al. 2009 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ). Our research reduces one literature gap and contributes to advancing cluster and coopetition theories. Systematic Literature Reviews (SLR) exist on coopetition but do not focus on clusters. For example, the literature review of Gernsheimer et al. ( 2021 ) focuses on antecedents, execution, interaction, results, and coopetition levels. Boucken et al. (2015) examined innovation strategy, supply chains, management, and the benefits and risks of coopetition. Dorn et al. ( 2016 ) organized the literature according to the nature of competition, governance and management, the results, and the characteristics of players and environments. Bengtsson and Raza-Ullah ( 2016 ) compared different conceptualizations of coopetition and levels and schools of thought. They reviewed the literature according to drivers, processes, and outcome structures. Devece et al. ( 2019 ) classified coopetition studies by theory, methods, and objectives. They identified two independent research trends: mathematical modeling studies using game theory and case study research on coopetition tension. Yadav et al. ( 2022 ) published a bibliometric review that updated the list of primary areas and dynamics of coopetition studies. Klimas et al. ( 2023 ) provided an integrative overview of the theoretical roots of competition, showing ten theories mainly related to strategic thinking.
Our SLR complements the previous systematic reviews and goes beyond. The study’s originality lies in (1) we focus on cluster coopetition to highlight the overlap of cluster and coopetition theoretical perspectives; (2) we identify drivers of intra-cluster coopetition to rethink cluster strategies; (3) We build theory to advance cluster coopetition research revisiting the Porterian perspective; (4) we provide an integrative research agenda to support the development of intra-cluster coopetition strategic management research.
2 Review method and literature screening
Our Integrative Systematic Literature Review (SLR) performed a process of identification, selection, and structured evaluation with a transparent and reproducible evidence assessment, as Tranfield et al. ( 2003 ) indicated. The search process followed the PRISMA and SPIDER protocols. PRISMA items guide the Identification, Screening, Eligibility, and Inclusion stages in SLR (Moher et al. 2009 ). In turn, the SPIDER method is a search strategy that comprises a Sample, Phenomenon of Interest, Project, Design, Evaluation, and type of Research (Cooke et al. 2012 ). Searches occurred in Jun/2023 and Dec/2023 in the Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus databases, the two largest world databases of social sciences research. We performed two searches to identify articles published in English between 1996 and December 2023 covering the emergence of the coopetition perspective. Including articles in Early Access, 102 were extracted from Scopus and 113 from Web of Science. However, there were 61 overlaps and 154 articles in the screening phase. Figure 1 shows the results of the searches and exclusions due to overlaps and other criteria.
Two researchers independently evaluated all articles to define their relevance to the final sample to ensure greater rigor and reliability in the screening process. In the case of different choices, we established a consensus. This procedure led to the exclusion of 97 articles, as they studied: statistical clusters (15 articles), virtual clusters (1), sectorial analysis (20), network analysis or group of firms (14), cooperatives (2), productive or supply chains (5), ecosystems or tourism destinations (6), not related with coopetition (24), literature reviews (12), and one article was not available. Finally, 54 articles remained since they fit the SLR scope. Following the SPIDER protocol, we previously defined the variables of the Content analyses in the articles, namely the study’s objectives, level of analysis, methodological design, coopetition variables, main results, contributions, and future research pointed out by the authors (Fig. 1 ).
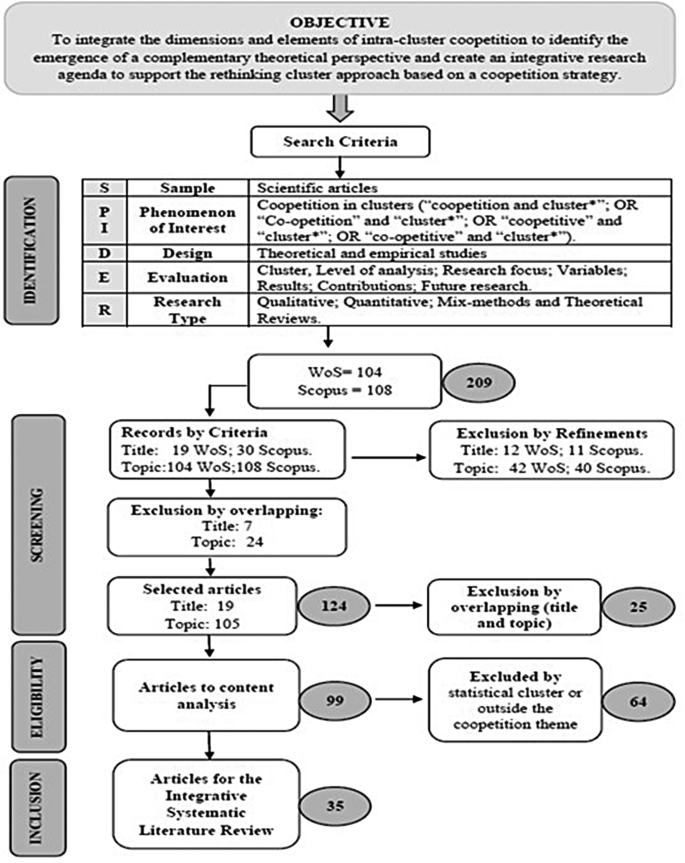
Methodological design based on PRISMA and SPIDER protocols. Source : Elaborated by the authors based on Cooke et al. ( 2012 ) and Moher et al. ( 2009 )
3 Review results
3.1 an overview of studies on coopetition in clusters.
Table 1 indicated that cluster coopetition studies started in 2003, although coopetition literature emerged in 1996. That means a gap of seven years to crossline both perspectives: coopetition and the Porterian cluster. Until 2012, there was only one article for most of the years. Since 2013, the annual production has grown. However, the timeline confirmed that cluster coopetition is a theme that is still understudied.
The authors with more articles published on cluster coopetition are Crick (Crick et al. 2020 ; Crick and Crick 2021 , 2022 ), Dana (Dana and Granata 2013 ; Dana et al. 2013 ), and Felzensztein (Felzensztein et al. 2018 , 2019 ). Dana and Felzensztein published articles with the words ‘coopetition and cluster’ in the title, which indicates a direct focus on the subject. The first publication of Dana was in 2013, focusing more on clusters than coopetition, while Felzensztein started in 2018 and explored coopetition more. In turn, Crick focuses more on coopetition, specifically in wine clusters. The top four countries with more clusters studied on the coopetition lens were Brazil (9), New Zealand (8), Germany (4) and France (4). Regarding the affiliations’ authors, the Top most productive countries in cluster coopetition studies were Brazil (8), France (8), the UK (7), and New Zealand (6). Italy and the United States had surprising results. Even though Italy is the birthplace of the geographic concentration of companies as a business success factor, the country has only one publication on coopetition in a cluster (See Maso and Lattanzi 2014 ). In turn, the United States, despite being the country of the cluster concept creator, had only one article examining USA Clusters (see Crick and Crick 2021 ) and two published by USA researchers together with Singapore and Turkey (See Yuan et al. 2021 ; Harmancioglu and Tellis 2018 ).
Brazil and New Zealand have many clusters studied and researchers studying the topic. New Zealand is probably due to a research program analyzing the country’s clusters. According to Molina and Yoong ( 2003 ), this Program is part of the public policy to promote regional economic growth. The Pilot Program of Business Clusters was created in 2000 to assist firms in internationalization through collaborative networks. This program was a branch of the “New Zealand Updating Competitive Advantage Project” started in 1991 and was headed by Michael Porter, and for that reason, it became known as “Project Porter.” It pointed to the need for a new competitive economic order worldwide but in harmony with the country’s social aspirations (Molina and Yoong 2003 ). In Brazil, the reason for spotlighting the country in publications on coopetition in clusters with 25% of the sample papers is similar to New Zealand. The Brazilian government, since 2004, has a public policy that created a Permanent Working Group for Local Productive Arrangements, coordinated by the Ministry of Industry, Foreign Trade, and Services. The Brazilian public policy of clusters is toward achieving economic and regional development to reduce social and regional inequalities.
Different journals published these 54 articles on cluster coopetition covering management, knowledge, innovation, social networks, organization, business, commerce, service, research, agribusiness, marketing, entrepreneurship, and tourism. Empirical studies are predominant, with approximately 92% of publications and only five theoretical studies from Min et al. ( 2008 ), Hu and He ( 2013 ), Ketchen et al. ( 2004 ), M’Chirgui ( 2005 ), and Poisson-de-Haro and Myard ( 2018 ). Table 1 also showed a diversification of studied clusters using a wide range of research techniques with a prevalence of qualitative methodology. Only 28% are quantitative research. The topic follows the same research path on coopetition, which started with case studies as a more frequent technique (Gernsheimer et al. 2021 ).
The empirical papers analyzing clusters of the wine industry have more publications (8 articles), with multiple and longitudinal case studies in Argentina, Chile, France, and, mainly, New Zealand (Molina and Yoong 2003 ; Dana and Granata 2013 ; Dana et al. 2013 ; Granata et al. 2017 ; Felzensztein et al. 2019 ; Crick et al. 2020 ; Crick and Crick 2021 , 2022 ). Another high number of publications on cluster coopetition was in maritime activities (7 articles), including oil and marine services in Norway (Smiljic 2020 ), knowledge-intensive service activities on inducing innovation in maritime cluster in Portugal (Monteiro 2016 ), yacht industry in an emerging economy in Taiwan (Chung and Cheng 2019 ); salmon industry at Chile (Felzensztein et al. 2018 ); shipbroking industry in Denmark (Nowińska 2019 ), nautical tourism in Portugal (Monteiro et al. 2017 ), and nautical industry in Italy (Maso and Lattanzi 2014 ).
The furniture cluster in Brazil (Barros et al. 2016 ; Sellitto and Lucchese 2018) and Indonesia (Hartono and Sobari 2016 ) comes third in the research with three publications. Scholars preferred to analyze the intra-cluster level of analysis (87% of publications). Three articles performed an analysis inter-cluster (Harmancioglu and Tellis 2018 ; Cusin and Loubaresse 2018 ; Wolff et al. 2020 ), probably due to the difficulty of analyzing various clusters that are usually in different stages of development. Due to multi-dimensional studies, the literature on cluster coopetition has a high dispersion of variables, elements, and contributions.
3.2 Theoretical roots of cluster coopetition
Before the emergence of coopetition as a significant business strategy, firms relied on the separate concepts of competition and cooperation to characterize their relationships (M’Chirgui 2005 ). Until the mid-1980s, the analysis of inter-organizational relations predominantly focused on competition influenced by economic theories. In the latter half of the 1980s, some researchers began delving into studying cooperation between firms. In the 1990s, the first attempts were made to explore the interplay between cooperation and competition strategies. These strategies, namely cooperation and coopetition, go beyond the traditional competitive paradigm, giving rise to novel forms of intra-organizational governance and broadening the range of options for inter-organizational collaborations (Brandenburger and Nalebuff 1995 ; Padula and Dagnino 2007 ).
The neologism “coopetition”, coined from the fusion of cooperation and competition, first surfaced in literature through Cherington ( 1913 ) to explain the discourse of the Sealshipt Oyster System CEO. In describing the intricate network involving 35,000 oyster dealers, Pickett emphasized that they were not in direct competition but engaged in cooperative efforts to enhance business collectively. The concept gained early mention but garnered significant attention in later years, with its resurgence attributed to managerial practices (Cherington, 1976 ). R. Hunt published the idea again in the Los Angeles Times in 1937 but did not receive notoriety (Yami et al. 2010 ). However, the term became popular only decades later through managerial practices.
The managerial genesis of the term “coopetition” is often attributed to Ray Noords, the founder and CEO of Novell, who introduced it in the 1980s. Noords highlighted the need to compete and cooperate simultaneously, emphasizing the evolving dynamics of markets and firm configurations (Bengtsson and Kock, 2000 ). In the subsequent decade, “coopetition” transitioned from managerial discourse to an academic concept, becoming a subject of theoretical exploration. Brandenburger and Nalebuff ( 1995 ), in their influential article, employed game theory as a theoretical foundation to support the notion of “Sleeping with the enemy”—encouraging firms to learn how to collaborate with their rivals (Coy 2006 ).
Several theories can explain the theoretical roots of cluster coopetition. Based on our Integrative Literature Review, we classified these theories according to two criteria that follow theoretical perspectives: first, related to coopetition dynamics, i.e. coopetition as a process, context, or result; second, related to geographical coverage considering external, internal, and regional ecosystem conditions (Fig. 2 ). The relationship between coopetition dynamics and the geographical coverage of clusters is relevant to understanding the firm interplay coexisting in a particular territory.
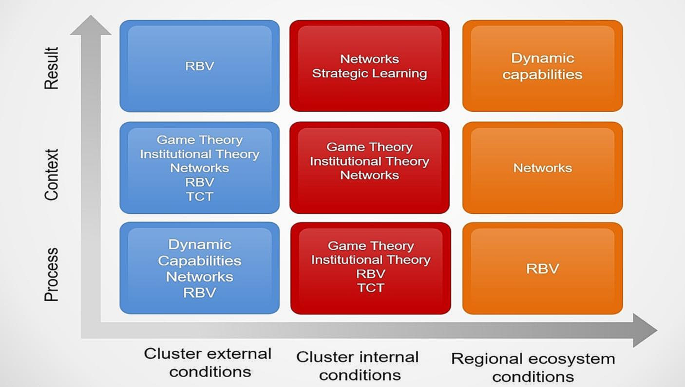
Theoretical roots of cluster coopetition. Source : Elaborated by the authors
First, considering coopetition as a process related to cluster external conditions, we identified articles that used dynamic capabilities, networks, and resource-based view (RBV) to present different cases. For instance, dynamic capabilities have been used to explain how coopetition promotes collective purchases, shared distribution expenses, shared production, and education of consumers and other beer producers in microbreweries in Brazil (da Silva et al., 2023 ). Networks form the foundation for cultivating competitive advantages by elucidating the means to access and expand knowledge and resources beyond the confines of the firm through coopetitive strategies. For example, Chaudhry et al. ( 2023 ) explore the coopetition within networks of competing micro-sized, independent, family restaurants owned by entrepreneurs from ethnic minorities. RBV has a broad application in the literature on coopetition. Examining coopetition as a process within the external conditions of the cluster, RBV enabled the investigation of intercluster dynamics among rival global clusters, focusing on monthly counts of patents, startups, and new product commercialization (Harmancioglu and Tellis 2018 ).
Second, when regarding coopetition as a process tied to internal cluster conditions, we identified four theoretical perspectives: game theory, institutional theory, RBV and transaction-cost theory (TCT). From the game theory standpoint, scholars examine coopetition as a win-win game, exploring the equilibrium between value creation (targeting shared benefits) and value appropriation (aiming for individual gains). For instance, Ramjaun et al. ( 2023 ) analyzed the United Kingdom craft brewing sector. They discussed how competing small enterprises can reduce their material supply costs through increased efficiencies, bargaining power and economies of scale. Xu et al. ( 2023 ) developed research focused on institutional support’s moderating role in promoting interfirm coopetition on firm innovativeness within a cluster. Dana and Granata ( 2013 ) explored the Waipara case study in New Zealand to comprehend the evolution of wine production clusters over time, focusing specifically on the coopetition dynamics among cluster members. Barros et al. ( 2016 ) analyzed the relationship between firms in the furniture production cluster in Brazil. They found opportunistic behaviour and a lack of trust among participants. At the same time, firms know the benefits of cooperation, such as access to information and improvement of products, but do not apply in the cluster.
Third, relating coopetition as a process in regional ecosystem conditions, RBV is the prevailing theoretical perspective because it allows mobilizing resources and technologies as resources that can become the basis for creating a competitive advantage (Quintana-Garcia and Benavídes-Velasco, 2004 ). For example, Ge and Liu ( 2022 ) explored how actors of the industrial innovation ecosystem focused on China’s solar photovoltaic industry can catch up so rapidly without radical technological innovation through resource orchestration.
Fourth, approaching coopetition as a context, five theoretical perspectives guide most studies focused on the cluster external conditions: game theory, institutional theory, networks, RBV, and transaction-cost theory (TCT). Li and Jiang ( 2012 ) analyzed the mechanism of coopetition evolution based on Game theory. They identified that the cooperation strategy promotes a better equilibrium for the oligopolies among industrial clusters. König ( 2023 ) examined co-located industrial clusters and identified that changes in the institutional setting (for example, the regulatory environment) lead to more collaboration between competitors. Andrey ( 2013 ) studied entrepreneurial coopetition related to interpersonal relations and territorial embeddedness. The results clarified spatial networking boundaries considering different spatial, temporal, social, and cognitive factors. Crick et al. ( 2020 ) examined New Zealand wine producers participating in diverse value co-creation activities, encompassing wine hospitality and tourism, such as accommodation and restaurants, extending to wine sales, including those at cellar doors. Their findings revealed that competing businesses in the product markets necessitate the management of complementary resources both within and across clusters. TCT centres on a highly precarious business scenario, as competitors operate based on individual business incentives that could give rise to opportunistic behaviour, bounded rationality, and a restricted pool of potential partners. For instance, Cusin and Loubaresse ( 2018 ) researched a French cluster called Inno’vin. They underscore the significance of competition within the intercluster context and delineate the primary challenges associated with inter-cluster coopetition, explicitly focusing on the role of asymmetry.
Fifth, detailing the cluster internal conditions in coopetition viewed as a context, we identified four prominent theoretical streams: game theory, institutional theory, and networks. Mucha-Kus et al. ( 2021 ) researched Energy Communities in Poland, including energy clusters and cooperatives. These authors observed that members collaborate concurrently within a competitive environment to attain shared benefits. Ralandison ( 2021 ) observed two clusters of small and medium-sized enterprises involved in the essential oil industry in Madagascar. They proposed a model of paradox management inside and between the organizations to deal with integrated coopetition. Networks are the foundation for cultivating competitive advantages, elucidating how to access and expand knowledge and resources beyond the firm through coopetitive relationships. For instance, Chai and Yang ( 2011 ) evaluated the impact of social networks on building control mechanisms of a Chinese service cluster. They developed a framework to explain how social networks “Guanxi” could be encouraged by the cluster’s geographical proximity and the government’s intervention.
Sixth, we identified studies focused on coopetition as a context that explores regional ecosystem conditions. In this line, Hückstädt ( 2022 ) recognized that for cluster researchers to accomplish their shared research objectives, fulfil their overarching role in integrative knowledge production, and ensure the sustainability of their collaboration, they must engage in close cooperation. Simultaneously, they compete with each other for scientific recognition or third-party funding.
Seventh, RBV has consolidated studies that address cluster external conditions and coopetition as a result. For example, Ferasso et al. ( 2022 ) explained how strategies and knowledge are used within a medium-low-tech industrial cluster to achieve competitive advantages. Eight, networks and strategic learning have discussed cluster internal conditions. Darbi and Knott ( 2023 ) discussed strategy as a practice in a cluster of small informal businesses in Ghana. They demonstrated how extensive cooperation among competing firms evolved into a normalized practice within the cluster, embedded as a cultural assumption. Monteiro ( 2016 ) researched activities centered around knowledge-intensive business services that promote co-opetition dynamics capable of catalyzing innovation within the maritime cluster in Algarve, Portugal.
Finally, a few articles related to cluster coopetition consider regional ecosystem conditions as a result. Shen and Liu ( 2023 ) focused on an open innovation business ecosystem composed of 20 industry clusters in the Yangtze River Delta region to investigate the direct impact of partner matches on different business model innovations. The results showed the demand to develop dynamic capabilities between firms that cover a broad spectrum of cross-organizational innovation capacities. This includes strengthening organizational learning capabilities, creating interactive network platforms to enhance coordination capabilities, and participating in integrative activities to cultivate a collective mindset. As a result of the interplay between cooperative and competitive strategies, research typically differentiates between dyadic coopetition and network coopetition. However, cluster coopetition studies have disregarded regional ecosystem conditions, making this approach incomplete.
3.3 Coopetition dynamics
We synthesized the literature contributions in three groups: related to coopetition as context, process, or result. The immediate focus on coopetition results does not necessarily indicate appropriation of competitive advantages. Analysis of the context and process is also necessary to provide a better understanding of the cluster coopetition perspective.
3.3.1 Coopetition as a context
Coopetition is a context-dependent strategy (Czakon et al. 2020a , b ) that involves firms providing learning opportunities to stakeholders such as suppliers, clients, and others (Ritala and Hurmelinna-Laukkanen 2009 ). Coopetiton positioned as a network contributing value through environmental interaction is presented within a broader chain that adds value to the firm, incorporating elements like customers, suppliers, substitutes, and complements referred to as “The Value Net” (Brandenburger and Nalebuff 2011 ; Lado et al. 1997 ). This strategic approach relies on the ability of firms to collaboratively create and capture value to individually secure a significant share of that value (Gnyawali and Park 2011 ).
Some analyses of coopetition focused on the interplay among firms considering the context, i.e., an environment capable of adding value to companies (Monticelli et al. 2019 ). From this analysis perspective, the scholars revealed many assumptions of coopetition in clusters. For instance, gender and education affect coopetition (Santos et al. 2021 ); the micro-foundations of dynamic capabilities (da Silva et al. 2023 ); insight into coopetition in the entertainment industry (Yuan et al. 2021 ); expanding the coopetition theoretical framework in functional areas (Sellitto and Luchese 2018 ); understanding of coopetition embedded as a cultural context (Darbi and Knott 2023 ); confirming propositions about the effects of the internal and external environment of small and medium-sized companies on coopetition (Monticelli et al. 2018 ); analyze the relationships between actors and benefits in attracting customers (Barros et al. 2016 ); demonstrate the importance of local authorities supporting for interplay with foreign competitors (Maso and Lattanzi 2014 ); geographical proximity as a non-prerequisite for coopetition (Nowińska 2019 ); confirming synergies of coopetition in wine clusters and its context (Dana et al. 2013 ); indicating public and private policies to accelerate growth from coopetition (Leite et al. 2009 ); game model to supply chains (Min et al. 2008 ); and the influence of regulatory and support institutional contexts on the intracluster coopetition relationship (Xu et al. 2023 ; König 2023 ).
3.3.2 Coopetition as a process
Coopetition encompasses the simultaneous application of competitive and cooperative strategies among rival firms operating across various domains and levels of interaction (Ann Peng et al. 2018 ; Monticelli et al. 2019 ). The process is characterized as the dynamic progression of change that defines the equilibrium and intensity of cooperative and competitive interactions (Dahl 2014 ). Environmental shifts have the potential to either undermine firms or prompt varied behaviours and responses to a firm’s strategy, influencing the effectiveness of a coopetitive approach (Padula and Dagnino 2007 ). The optimization of coopetition is often contingent on the levels of market commonality and resource asymmetry between firms. Market commonality tends to be more pertinent to competitive dynamics, while resource asymmetry is typically more relevant to cooperative aspects (Hung and Chang 2012 ).
Articles analyzing the coopetition process provided significant learning. This group of studies has more contributions, indicating coopetition relationships, their main formative factors, dynamics, network management, the influence of time, and its orientation towards knowledge sharing, R&D projects, and innovation. Under this perspective of coopetition as a process, the literature presented contributions related to the dynamics of interaction, strategy, and knowledge sharing in medium-low technology clusters (Ferasso et al. 2022 ); understanding of coopetition relationships (Wolff et al. 2020 ), their causality (Bispo et al. 2020 ) analysis of how coopetition happens in clusters (Hoetoro 2014 ); the effects on coopetition networks under the leans of club‑theoretical perspective (Hückstädt 2022 ) and the management of coopetition intrinsic conflict in clusters (Mathews 2018 ). Coopetition is a dynamic process, so under this perspective, scholars’ contributions showed the mutability of clusters over time and their influence on coopetition relationships (Felzensztein et al. 2018 ).
Also, the insertion of the concept of coopetition into the initial model by Kim and Wicks (Chin et al. 2017 ); stages driven by specific environmental factors and it is facilitated by the social capital (Granata et al. 2017 ); potential elements to guide the process of coopetition in RandD projects (Nemeh and Yami 2016 ); main factors in the formation of coopetition involving complex systems (Hartono and Sobari 2016 ); construction of a benign competitive mechanism to promote innovation (Hu and He 2013 ); evolution of coopetition through equilibrium in the price competition game based on the Cournot model identifying the best strategy for oligopolies in the industrial cluster (Li et al. 2012 ); control mechanisms, and which reputation on the social network is crucial for intra-cluster coopetition (Chai and Yang 2011 ); knowledge sharing in clusters during the initiation and incubation stage (Molina and Yoong 2003 ); process of collaborative procurement among craft beer producers (Ramjaun et al. 2023 ); management of complementary relationships within and across clusters to enhance value co-creation activities (Crick et al. 2020 ); and dynamic co-opetition of industrial cluster evolution (Itoga et al. 2014 ).
3.3.3 Coopetition as a result
Coopetition is a strategy to maximize outcomes through joint efforts (Ann Peng et al. 2018 ; Monticelli et al. 2019 ). Both coopetition and collaboration stem from shared interests, prioritizing collective benefits over maximizing individual gains. However, it’s important to note that the resulting gains may be distributed unevenly between the involved parties (Padula and Dagnino 2007 ). Instances of disagreement can emerge, particularly regarding the allocation of outcomes. The returns from the relationship may not always align proportionally with the investments made by participants, considering factors such as learning and the bargaining power within the strategic relationship (Gnyawali and Ryan Charleton 2018 ).
Coopetition is a strategy to maximize outcomes through joint efforts (Ann Peng et al. 2018 ; Monticelli et al. 2019 ). Gernsheimer et al. ( 2021 ) highlighted that coopetition from the results perspective had been investigated mainly concerning innovation, firm performance, and, more recently, organizational learning and sustainability. We confirmed Gernsheimer’s et al. ( 2021 ) findings in studies on cluster coopetition but included results related to internationalization, public policies, and leadership. In clusters, scholars studied the positive relationship between absorptive capacity and coopetition level (Begnini et al. 2022 ); the integrative view of coopetition to R&D projects (Smiljic 2020 ); improvements of internationalization by coopetition (Felzensztein et al. 2019 ); benefits of coopetition strategy to the performance (Chung and Cheng 2019 ); coopetition dynamics for marketing products and startups (Harmancioglu and Tellis 2018 ); reduction of the uncertainty of the innovation process, public policies to sustainability, visibility of the sector and its stakeholders (Poisson-de-Haro and Myard 2018 ); advantages of inter-cluster coopetition and the intervention by public and private players (Cusin and Loubaresse 2018 ); coopetitive advantages to productivity and innovation (Monteiro 2016 ).
Some authors focused on the effects on performance from coopetition producing internal knowledge, innovation capacity and performance of Knowledge Intensive Business Services (Monteiro 2016 ), coopetition and leadership for differentiation and internationalization (Dana and Granata 2013 ). Also, the negative effect of cluster coopetition was studied as a result. For instance, the damage to extremely novel revolutionary innovation (Bouncken and Kraus 2013 ) and the negative impacts of coopetition on store performance in the retail and service clusters (Teller et al. 2016 ).
3.4 Dimensions and elements of coopetition in clusters
We use an open coding procedure, hence an inductive analytical approach (Mosonyi et al. 2020 ). In the articles, we identified the research focus. Results showed 45 different focuses in the 54 articles. We aggregated them into six dimensions based on a consensus among three coopetition scholars to reduce the subjective nature of the grouping process. In the sequence, we extracted 486 elements related to cluster coopetition used in the articles. Aggregating elements in previously defined dimensions followed a deductive pattern, generating second-order coding. They represent the variables of coopetition in clusters. Some elements are synonymous or have the same purpose; thus, we grouped them. Other times, the same element is in more than one category, depending on the perspective used by the author. This finding confirmed the complex, fragmented and multidimensional nature of the coopetition highlighted, for instance, by Gernsheimer et al. ( 2021 ).
Figure 3 summarizes the research dimensions derived from the focus on coopetition addressed by the authors: Strategic Fit, Perceived Benefits, Mediated Coopetition, Social Interaction, Coopetitive Orientation, and the Temporality of Coopetition. Also, we synthesize the themes that were studied more and their respective authors in each dimension (Fig. 3 ). The Strategic Fit dimension was the biggest, encompassing 18 research focuses. Followed by Perceived Benefits and Social Interactions, each with eight research focuses. Our results revealed a gap in studies focusing on the risks of coopetition in clusters. Coopetitive relationships trigger tensions, distrust, and opportunism, which are challenges to ensuring coopetition results (Gernsheimer et al. 2021 ). The agenda of scholars in coopetition included these challenges but not the agenda of scholars in cluster coopetition. Also, the mediate coopetition needs more studies since cluster governance is a type of mediation among cauterized firms.
3.4.1 Strategic fit dimension
Strategic Fit Dimension is the alignment of objectives among competitors who collaborate in certain areas with shared goals seeking to capture the benefits of coopetition (Czakon et al. 2020a , b ). The literature pointed out that it is necessary to establish previous guidelines to minimize collaboration problems between competitors (Min et al. 2008 ; Hu and He 2013 ; Nemeh and Yami 2016 ; Ferasso et al. 2022 ). The main variables to study the Strategic Fit at clusters in the coopetition studies were networks, shared information, multilevel interdependencies, R&D investment, innovation projects, support agencies, macrodynamic capabilities, patent collaborations, co-production, and co-commercialization.
3.4.2 Perceived benefits dimension
The final goal of collaboration between competitors is the perceived benefits of this relationship, understood as the results of coopetition (Chim-Miki and Batista-Canino 2016; Czakon et al. 2020a , b ). The RSL of Gernsheimer et al. ( 2021 ) found that such benefits were mainly investigated related to innovation and firm performance, but recent studies also focused on organizational learning and sustainability. We identified that the benefits of coopetition in clusters are perceived in access to capital, government support, strengthening the productive arrangement and its firms (Barros et al. 2016 ), the opportunity for joint activities, training management, and human resources, innovation performance (Poisson-de-Haro and Myard 2018 ; Nemeh and Yami 2016 ), improvement in production and market activities (Yuan et al. 2021 ). Therefore, the investigation of the perceived benefits of coopetition in clusters has some differences in the direction of research on coopetition, as pointed out by Gernsheimer et al. ( 2021 ). Innovation and performance are benefits also pursued by clustered firms, but the joint actions are aimed at strengthening the entire productive arrangement and sustainable regional growth besides the firms. The cluster is a way to achieve sustainability, as it can reduce economic asymmetries (Chung and Cheng 2019 ). Our results also suggested that organizational learning as a perceived benefit of cluster coopetition is a gap in the literature.
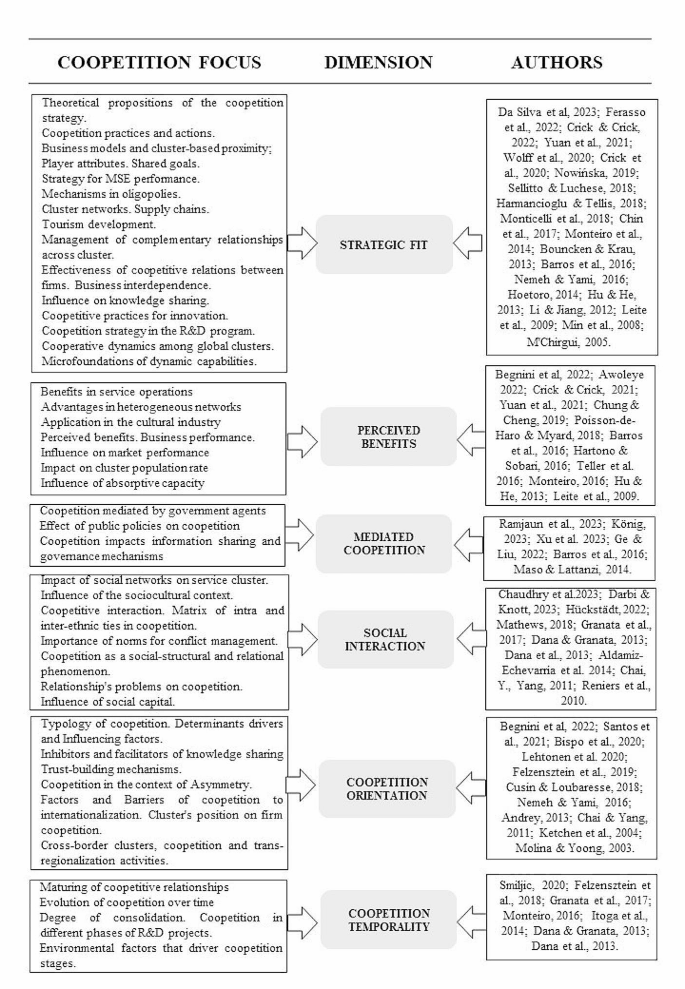
Research dimensions according to the addressed focus of coopetition. Source : Elaborated by the authors
3.4.3 Mediated coopetition dimension
Mediated coopetition is the intermediation performed by a third party to build trust, structure, and facilitate collaboration among competitors (Hidalgo et al. 2022 ; Gernsheimer et al. 2021 ; Dana and Granata 2013 ). In articles published on cluster coopetition, mediated coopetition occurs through a public agency or a public policy (Barros et al. 2016 ; Maso and Lattanzi 2014 ). The main elements used to study cluster-mediated coopetition were governance, the culture of cooperation, crise management, workforce quality (Barros et al. 2016 ), training programs, communication, consultancy, financial management, public policy, fiscal policies, investment opportunities, media network (Maso and Lattanzi 2014 ). Cluster-mediated coopetition is an underexplored theme. Only two published articles address the topic, focusing on coopetition mediated by a public agent. Therefore, there is a literature gap regarding coopetition mediation by a private agent, although many clusters have an independent and private outsourced manager, as highlighted by Dana and Granata ( 2013 ). This manager is not directly involved in the competitive relationship between members, which helps minimize the tension while overseeing the interests of the clusterized firms and cluster (Dana and Granata 2013 ; Monticelli et al., 2018 ).
3.4.4 Social interaction dimension
The social interaction dimension is characterized by two types of relationships: internal, among the clustered firms to promote integration among players and their objectives, and external, among the clustered firms and other institutions to stimulate its growth and the capture of competitive advantages (Dana and Granata 2013 ; Dana et al. 2013 ). It is a social network influenced by the sociocultural cluster (Chai and Yang 2011 ) and becomes a social-structural phenomenon (Darbi and Knott 2023 ). Understanding what the environment is like and how the various actors interact has been recognized as the critical element to stimulate co-competitive relationships, minimize the risks and natural mistrust of the dichotomy of collaboration between competitors and the differential to accelerate the positive results arising from this relationship (Dana and Granata 2013 ; Dana et al. 2013 ; Czakon et al. 2020a , b ). The critical point for social interaction is local solid norms, which facilitate both the integration of coopetitive strategies by company managers and conflict management (Mathews 2018 ) since managing coopetition is seen as tension management (Czakon et al. 2020a , b ). Darbi and Knott ( 2023 ) suggested immersive cooperation among clusterized firms became a usual practice embedded as a culture. Scholars used diverse elements associated with the social interaction dimension of intra-cluster coopetition, such as the cluster environment and its advantages (Hu and He 2013 ); coopetitive relationships (Hoetoro 2014 ); strategy, including internationalization; and management and human resources (Leite et al. 2009 ; Dana and Granata 2013 ; Dana et al. 2013 ; Hu and He 2013 ; Mathews 2018 ).
3.4.5 Coopetitive orientation dimension
Coopetitive orientation is intrinsic motivation or the ability to collaborate with rivals (Czakon et al. 2020a , b ). The coopetitive orientation focuses on balancing collaboration and competition, coopetition challenges, and trust-generating mechanisms in cluster studies. The article by Cusin and Loubaresse ( 2018 ) analyzes the coopetitive orientation at intra-cluster in a context of asymmetry, addressing elements of coverage area, cluster expansion, differentiation, regional identity (Felzensztein et al. 2019 ), attractiveness, visibility (Cusin and Loubaresse 2018 ); cluster life cycle (Hartono and Sobari 2016 ); cluster integration; number, satisfaction, and loyalty of clusterized firms; joint projects and actions (Nemeh and Yami 2016 ; Smiljic 2020 ); complementarity (Sellitto et al. 2018); stability of the management team, and relational proximity (Mathews 2018 ). At the intra-cluster level, this dimension represents factors that form and influence coopetition but can also include inhibitors.
3.4.6 Coopetition temporality dimension
The dimension temporality of coopetition focuses on the dynamics of inter-organizational relationships that continually reconfigure the relational interdependencies as partnerships evolve (Kylanen and Mariani 2012 ; Chim-Miki and Batista-Canino 2017 ). In cluster studies, scholars associated the temporality of coopetition with the evolution, maturation, and degree of consolidation of cooperative relationships over time (Dana et al. 2013 ; Dana and Granata 2013 ; Granata et al. 2017 ). For instance, Felzensztein et al. ( 2018 ) demonstrated that clusters change over time, and inter-collaboration and social networks are determined by internal conditions (degree of competition, for example) and external conditions (economic crisis, for example). These set of effects generate changes in intra-cluster collaboration as a cluster matures. Monteiro ( 2016 ) highlighted that coopetition relationships should be built and managed over time by improving the strategies toward innovations and technological diversity.
Indeed, the coopetitive orientation, social interaction, and mediated coopetition lead companies to develop a strategic fit to achieve the perceived benefits of coopetition in clusters, but the existence of risks of opportunism, conflicts of interest, and perception of injustice in the division of gains (Raza-Ullah et al. 2014 ; Bouncken et al. 2018 ; Crick 2020 ), for example, can prevent the achievement of positive results. All these relationship dynamics can also suffer from the influence of time.
4 A framework and research agenda to develop intra-cluster coopetition
4.1 building theory from the review: advancing cluster coopetition research.
To provide a framework from the literature-systematized and integrative overview of the main intra-cluster coopetition elements (Fig. 4 ). We created subgroups (macro dimensions) according to the authors’ approach: Factors, conditions, Policies, Market commonality, and Formal supporting structure. Figure 3 confirms coopetition as the ‘cluster glue.’ It is the intrinsic behavior and primary strategy since they are interrelated and concentrated firms that must cooperate despite their individual interests.
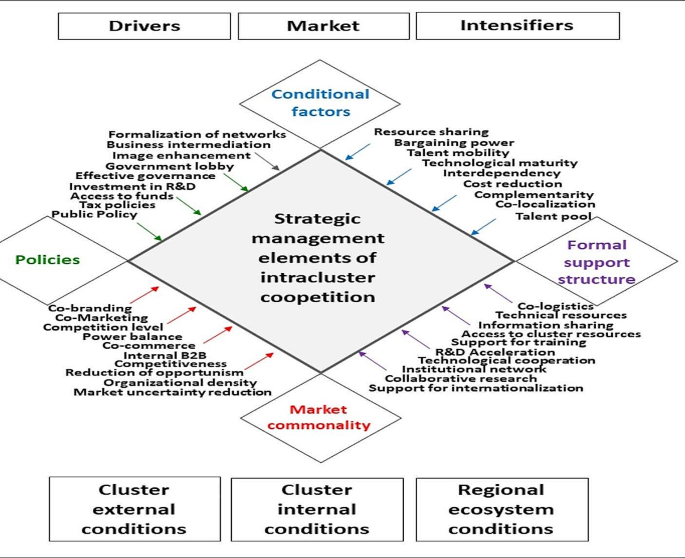
Framework of the coopetition strategy at the intra-cluster level
The Policy dimension included driver elements for the intra-cluster coopetition strategy (Fig. 4 ). They are external cluster conditions, such as public policies to promote regional development based on clusters, tax policies, governance models, intermediation of external businesses, and partnership programs. In contrast, the dimensions of conditional factors and market commonality are internal cluster conditions. The degree of complementarity and interdependence of the clusterized firms, the ability to share resources, reduce costs and take advantage of co-location synergy to improve their bargaining power, and talent retention are conditioning elements of intra-cluster coopetition. The market commonality indicates competition among clusterized firms related to customers, suppliers, and resources, such as capital, human talents, technology support, etc. The balance of market commonality impacts the creation of networks for joint market-oriented strategies, such as co-marketing, co-branding, co-commerce, and internal business (B2B). Also, it can reduce adverse effects, such as opportunism or market uncertainty. Finally, the intensifying elements of the intra-cluster coopetition strategy are the conditions of the regional ecosystem of the cluster. This dimension represents the formal cluster’s support organizations that enhance innovation networks, training, technological and information sharing, and collaborative research networks.
The cluster coopetition framework can be seen as a revisited Porterian theory (Table 2 ). The sum of intra-cluster coopetition strategy elements pointed out by the literature complements Porterian theory showing common and complementary factors and institutions, governance, and public policies (Porter 1998 ). The determinants of regional advantage according to the Diamond Model are (1) firm strategy, structure and rivalry; (2) demand conditions; (3) factor conditions; and (4) related and supporting industries. In turn, the determinants of cluster coopetitive advantage are (1) Market commonality, (2) Policies, (3) Factors conditions, and (4) Formal supporting structure. However, for Porter, “chance” and “government” are two factors that influence the four determinants of the Diamond model. In the evolutionary framework of this Porterian reinterpretation from the perspective of coopetition in clusters, the factors that influence it are contextual, internal, and external to the cluster and the ecosystem in which it is inserted. Both chance and government are present in the contextual cluster factors.
The coopetition networks define the cluster boundaries from the business and organizational links. The clusters’ organisational structure minimises competition problems without imposing vertical or formal networks (Porter 1998 ). They promote alliances, shared goals, and the coexistence of competition and cooperation. Therefore, coopetition is a core behaviour of clusters, and it is their strategic management.
4.2 Research agenda: a set of future approaches to intra-cluster coopetition perspective
Our literature review followed Post et al. ( 2020 ) indications: integrative theorizing and creating a research agenda to advance the field. In the reviewed articles, we identified 35 future research questions suggested by the authors, which still need to be answered according to our analysis. We label the questions according to the focus on public policy or management practices representing the internal and external cluster context (Table 3 ).
Besides the indications of the research questions, a research agenda can be shaped for intra-cluster coopetition considering the relationships between the six identified dimensions. A set of future approaches to the intra-cluster coopetition perspective guides the re-thinking cluster toward an integrated perspective on the dynamics of coopetition (Fig. 5 ).
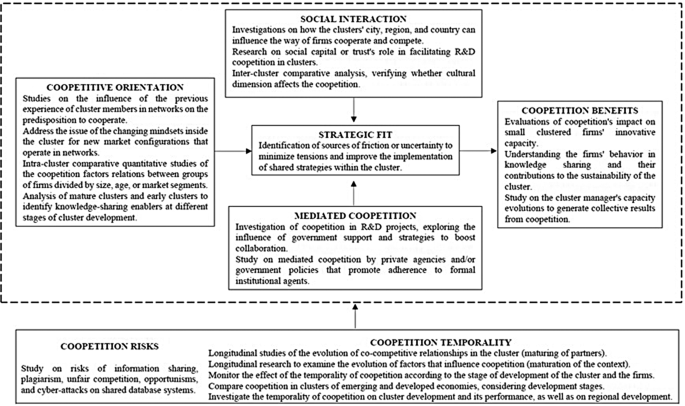
Conceptual map for future research on intra-cluster coopetition perspective.
Source : Elaborated by the authors
Coopetition is a multidimensional and multilevel phenomenon. Its dimensions should be considered together (Köseoğlu et al. 2019 ), as the context, process, and result are inseparable. From the literature review, considering the previous studies and the trends, a set of future approaches to deepen the intra-cluster coopetition perspective emerges. Figure 5 indicates a connected research framework to generate an evolution of intra-cluster coopetition based on its dynamics. The strategic fit is the core of intra-cluster coopetition relationships. It is part but goes beyond what Porter ( 1998 ) highlighted as the complementarity between the support institutions and the clusterized firms that define the cluster boundaries. Nevertheless, most cluster studies have focused on the sources of strategic fit, leaving knowledge gaps on the factors that reduce the coupling among clusterized firms and between the firms and the cluster.
Coopetitive orientation is an antecedent behavior that facilitates strategic fit (Czakon et al. 2020a , b ). The willingness or predisposition to cooperate should be studied from various angles, such as the firm’s previous experience in alliances and the background of cluster managers in joint projects or networks (Cusin and Loubaresse 2018 ). The level of coopetition willingness across the cluster cycle-of-life phases and in different sectors also needs more understanding to create adequate strategies for each context.
Social interaction is a dimension that gains status at the intra-cluster level, but it has been little studied in all coopetition levels. Some studies suggest a positive effect of social ties on the consolidation of coopetition networks and the generation of mutual trust (Felzensztein et al. 2018 ). In coopetition, social ties can be related to belonging to a place or group, cultural similarity, or local behavior (Oliveira-Ribeiro et al. 2022 ; Chaudhry et al. 2023 ). Thus, it is necessary for more studies on the influence of the city, country, culture, and local social capital on intra-cluster coopetition networks to improve the strategic fit for joint projects and cooperative R&D.
Just as the strategic fic is the core, the mediated coopetition is the intra-cluster management model. It can be generated by the regulatory environment and institutional configuration (König 2023 ), by some firms that act as central nodes in the coopetition networks (Ge and Liu 2022 ) or by the cluster governance mechanisms (Ramjaun et al. 2023 ). Besides, a cluster assumes the existence of governance (Porter 1998 ). In the evolution of strategic management suggested by Stead and Stead ( 2019 ), which also complements Porterian theory, coopetition becomes an ecosystem behavior and extends across multisectoral and multistakeholder relationships. However, to obtain competitive advantages for the cluster and clusterized firms, it is necessary to manage this open system properly to minimize the intrinsic tension of coopetition (Dana and Granata 2013 ). Therefore, more studies are needed on the role of government, business associations, public policies, and other formal institutions constituting the mediation mechanisms of intra-cluster coopetition.
The benefits are the outputs and the competitive advantages of the coopetition strategy. It is the primary motivator for firms to cooperate (Leite et al. 2009 ; Sellitto and Luchese 2018 ). The literature still needs studies with models or tools for monitoring coopetition results. It is necessary to verify the positive effects at the cluster and firm level, including mechanisms that consider the different firm’s sizes since they have different levels of value created and appropriated (Ritala et al. 2008 ). Also, it is necessary to understand how the benefits of coopetition contribute to cluster sustainability, which includes studies on innovative capacity and knowledge generation intra-cluster.
The temporality of the coopetition and the risks are two dimensions that influence the entire intra-cluster strategy. Studies need to identify risks and create mechanisms to minimize them. Few studies addressed coopetition risks in the literature. In some conditions, the cluster network consolidation tends to grow over time (Dana et al. 2013 ; Dana and Granata 2013 ) and improve coopetition outputs (Monteiro 2016 ). However, only some longitudinal studies provide insights into understanding the coopetition strategies along the cluster cycle life. Three aspects can mature over time: the partners, the cluster management, and the regional context where the cluster is part. Studies need to verify these dynamics and their influence on intra-cluster coopetition.
5 Conclusions and contributions
Thus, as the second contribution, we proposed a theoretical framework from the literature-systematized and integrative overview with our dimensions: Conditional factors, Policies, Market commonality, and Formal supporting structure. These dimensions act as drivers, markets, or intensifiers of the intra-cluster coopetition strategy. At the same time, the dimensions suffer the influence of external, internal, and ecosystem contexts (Fig. 3 ). The framework suggests the main elements to manage clusters under the coopetition strategy. These findings rethinking cluster theory (Porter 1998 ) and build the business co-evolution perspective of Stead and Stead ( 2019 ). The cluster is a business ecosystem with an open system based on coopetition. Nevertheless, Porter ( 1998 ) states that the complementarity among clusterized firms and supporting institutions can provide cluster boundaries; in the rethinking cluster, there are no boundaries. Cluster coopetition is multilevel and multi-stakeholders, so it is impossible to establish boundaries; however, it is essential to develop a mechanism to manage the network, mediated coopetition, and monitor the outputs as feedback to engage the players and improve the strategy fit.
Our third contribution is to open new paths to rethinking clusters from a coopetition perspective from a dynamic viewpoint. We suggest a set of approaches to advancing the intra-cluster coopetition perspective. The systematization of this SLR, based on six coopetition dimensions, captured the dynamics among them, orienting the frameworks towards an integrated perspective on intra-cluster coopetition issues. Coopetitive orientation, social interaction, and mediated coopetition lead companies to develop a strategic fit to achieve the perceived benefits of coopetition. However, it is necessary to advance research on Coopetition Risks and temporality of coopetition. The research agenda of cluster scholars barely pointed out particular coopetition risks despite the dark side of coopetition being discussed in strategy studies. The categories were created based on studied themes plus emerging trends extracted from indications for future research. Thus, it was an inductive-deductive pattern system that represented the evolutionary trend of the topic itself.
Our research had limitations; although it was an in-depth analysis, it focused on articles published on the Web of Science and Scopus, not including doctoral thesis and other scientific bases. We suggest an additional literature review covering more databases. Also, complement the theoretical review with empirical approaches that consider the view from within the cluster, that is, clustered firms and cluster managers, to identify the elements of intra-cluster coopetition. Cluster coopetition is an essential strategy for the sustainable development of firms, regions, and countries. It is necessary to study how coopetition influences the new re-shoring strategies and new industrial policies. For this, the theme needs more research to develop a coopetition strategy to support the development of public policies, the cluster digital transformation, and management practices toward rethinking clusters.
Andrey MS (2013) Case study on the structural transformation of an international cluster: European perspective. Mod Appl Sci 7(12):1–8. https://doi.org/10.5539/mas.v7n12p1
Article Google Scholar
Andrey MS (2013) Features of the triple helix model in cross-border clusters. World Appl Sci J 21(12):1734–1738. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2013.21.12.180
Ann Peng TJ, Yen MH, Bourne M (2018) How rival partners compete based on cooperation? Long Range Plann 51(2):351–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2017.10.003
Awoleye OM (2022) Knowledge spillover, human capital and agglomeration dynamics in Nigeria’s ICT clusters. Int J Bus Innov Res 27(3):352–382. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBIR.2022.121695
Barney JB (2018) Why resource-based theory’s model of profit appropriation must incorporate a stakeholder perspective. Strateg Manag J 39(13):3305–3325. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.2949
Barros LEV, de Castro CC, Kalil JPA, Antonialli LM, Santos AC (2016) Competition, coopetition and cooperation in a cluster: the furniture sector case in the county of Santa Cruz De Minas (MG). Revista Espacios 37(30):4–20
Google Scholar
Begnini S, Simi SS, Carvalho CE (2022) The influence of the absorptive capacity and the position of the firm in the cluster on coopetition. Int J Econ Bus Res 24(4):533–554. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEBR.2022.126438
Bengtsson M, Kock S (2000) “Coopetition” in business networks—to cooperate and compete simultaneously. Ind Mark Manag 29(5):411–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0019-8501(99)00067-X
Bengtsson M, Kock S (2014) Coopetition—Quo Vadis? Past accomplishments and future challenges. Ind Mark Manage 43(2):180–188
Bengtsson M, Raza-Ullah T (2016) A systematic review of research on coopetition: toward a multilevel understanding. Ind Mark Manage 57:23–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.05.003
Bispo E, de Silva S, Santos RS, dos JM, Nascimento EA (2020) do Relações Entre Pequenos Feirantes de um Aglomerado de Varejo em Aracaju-SE. Gestão e Desenvolvimento 17(3):56–78
Bouncken RB, Kraus S (2013) Innovation in knowledge-intensive industries: the double-edged sword of coopetition. J Bus Res 66(10):2060–2070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2013.02.032
Bouncken RB, Fredrich V, Ritala P, Kraus S (2018) Coopetition in New Product Development Alliances: advantages and tensions for Incremental and Radical Innovation. Br J Manag 29(3):391–410. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.12213
Brandenburger AM, Nalebuff BJ (1995) The right game: use game theory to shape strategy, vol 76. Harvard Business Review, Chicago, pp 57–71
Brandenburger AM, Nalebuff BJ (2011) Co-opetition . Currency
Chai Y, Yang F (2011) Risk control of coopetition relationship: an exploratory case study on social networks ‘Guanxi’ in a Chinese logistics services cluster. Int J Interdisciplinary Social Sci 6(3):29–39
Chaudhry S, Crick D, Crick JM (2023) I’ll be there for you: coopetition and competitor-oriented activities among south Asian restaurants in two UK regional clusters. Int J Entrepreneurial Behav Res 29(9/10):1973–2004. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-08-2022-0694
Cherington PT (1913) Advertising as a business force. Doubleday, Page for the associated advertising clubs of America
Cherington PT (1976) Advertising as a business force: a compilation of experiences, reissue edn. Manchester, NH: Ayer Co Pub.
Chim-Miki AF, Batista-Canino RM (2017) Tourism coopetition: an introduction to the subject and a research agenda. Int Bus Rev 26(6):1208–1217
Chin WL, Haddock-Fraser J, Hampton MP (2017) Destination competitiveness: evidence from Bali. Curr Issues Tourism 20(12):1265–1289. https://doi.org/10.1080/13683500.2015.1111315
Chung HM, Cheng LH (2019) Coopetition and firm survival in a cluster: insights from the population ecology on the yacht industry in an emerging economy 1957–2010. Manage Organ Rev 15(4):837–856. https://doi.org/10.1017/mor.2018.60
Cooke A, Smith D, Booth A (2012) Beyond PICO: the SPIDER Tool for qualitative evidence synthesis. Qual Health Res 22(10):1435–1443. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732312452938
Coy P (2006) Sleeping with the enemy. Bus Week 21(28):96–97
Crick J (2020) The dark side of coopetition: when collaborating with competitors is harmful for company performance. J Bus Industrial Mark 35(2):318–337. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-01-2019-0057
Crick JM, Crick D (2021) Coopetition and family-owned wine producers. J Bus Res 135:319–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.06.046
Crick JM, Crick D (2022) Coopetition and international entrepreneurship: the influence of a competitor orientation. Int J Entrepreneurial Behav Res 28(3):801–828. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-06-2021-0519
Crick JM, Crick D, Tebbett N (2020) Competitor orientation and value co-creation in sustaining rural New Zealand wine producers. J Rural Stud 73:122–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2019.10.019
Cusin J, Loubaresse E (2018) Inter-cluster relations in a coopetition context: the case of inno’vin. J Small Bus Entrepreneurship 30(1):27–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/08276331.2017.1356158
Cygler J, Sroka W (2017) Coopetition disadvantages: the case of the high tech companies. Eng Econ 28(5):494–504. https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.ee.28.5.16421
Czakon WMK, Sołtysik M (2016) Coopetition strategy—what is in it for all? A study of common benefits in the Polish energy balancing market. Int Stud Manage Organ 46(2–3):80–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/00208825.2015.1093792
Czakon W, Klimas P, Mariani M (2020a) Behavioral antecedents of coopetition: a synthesis and measurement scale. Long Range Plann 53(1):101875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2019.03.001
Czakon W, Srivastava MK, Le Roy F, Gnyawali D (2020b) Coopetition strategies: a critical issues and research directions. Long Range Plann 53(1):1019148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2019.101948
da Silva LM, da Silveira AB, Monticelli JM, Kretschmer C (2023) Microfoundations of dynamic coopetition capabilities in firms from a microbrewery cluster. Revista De Gestão 30(2):190–206. https://doi.org/10.1108/REGE-04-2021-0064
Dahl J (2014) Conceptualizing coopetition as a process: an outline of change in cooperative and competitive interactions. Ind Mark Manage 43(2):272–279
Dana LP, Granata J (2013) Evolution de la coopétition dans un cluster: le cas de waipara dans le secteur du vin. J Small Bus Entrepreneurship 26(4):429–442. https://doi.org/10.1080/08276331.2013.822144
Dana LP, Granata J, Lasch F, Carnaby A (2013) The evolution of co-opetition in the Waipara wine cluster of New Zealand. Wine Econ Policy 2(1):42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wep.2013.05.001
Darbi WPK, Knott P (2023) Coopetition strategy as naturalised practice in a cluster of informal businesses. Int Small Bus J 41(1):88–114. https://doi.org/10.1177/02662426221079728
Della Corte V, Aria M (2016) Coopetition and sustainable competitive advantage. The case of tourist destinations. Tour Manag 54:524–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2015.12.009
Devece C, Ribeiro-Soriano DE, Palacios-Marqués D (2019) Coopetition as the new trend in inter-firm alliances: literature review and research patterns. RMS 13:207–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-017-0245-0
Dorn S, Schweiger B, Albers S (2016) Levels, phases and themes of coopetition: a systematic literature review and research agenda. Eur Manag J 34(5):484–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2016.02.009
dos Santos OB, Olave MEL, Rocha R, Nogueira ADSDS (2021) Cooperação, competição e coopetição em clusters. Revista Gestão Tecnologia 21(2):132–155
Echevarría CA, Aguirre MS, Aparicio MG (2014) Orígenes, elementos determinantes y resultados de un exitoso proceso de colaboración entre competidores y otros agentes: El Cluster De La Alta Cocina Vasca. Cuad De Gestión 14(2):51–72. https://doi.org/10.5295/cdg.120385ca
Estrada I, Faems D, de Faria P (2016) Coopetition and product innovation performance: the role of internal knowledge sharing mechanisms and formal knowledge protection mechanisms. Ind Mark Manage 53:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.11.013
Felzensztein C, Gimmon E, Deans KR (2018) Coopetition in regional clusters: keep calm and expect unexpected changes. Ind Mark Manage 69:116–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2018.01.013
Felzensztein C, Deans KR, Dana LP (2019) Small firms in Regional clusters: local networks and internationalization in the Southern Hemisphere. J Small Bus Manage 57(2):496–516. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsbm.12388
Ferasso M, Sulich A, Durán-Romero G, Sztando A (2022) The interplay of strategies and knowledge for competitive advantages in a medium low-tech industrial cluster located in an emerging country. Int J Knowl Manage Stud 13(1):33–54. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJKMS.2022.119259
Ge S, Liu X (2022) Catch-up in solar PV industry of China: a perspective of industrial innovation ecosystem. Int J Innov Technol Manag. 19(06):2250016. https://doi.org/10.1142/S021987702250016X
Gernsheimer O, Kanbach DK, Gast J (2021) Coopetition research - A systematic literature review on recent accomplishments and trajectories. Ind Mark Manage 96:113–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2021.05.001
Gnyawali DR, Park BJR (2011) Co-opetition between giants: collaboration with competitors for technological innovation. Res Policy 40(5):650–663
Gnyawali DR, Ryan Charleton T (2018) Nuances in the interplay of competition and cooperation: towards a theory of coopetition. J Manag 44(7):2511–2534
Granata J, Géraudel M, Nicolosi A, Garcia K (2017) Understanding the evolution of coopetition among SMEs in a wine cluster: a social capital approach. Int J Entrepreneurship Small Bus 31(1):67–84. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJESB.2017.083846
Harmancioglu N, Tellis GJ (2018) Silicon envy: how global innovation clusters hurt or stimulate each other across developed and emerging markets. J Int Bus Stud 49(7):902–918. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41267-018-0162-8
Harris JL (2021) Rethinking cluster evolution: actors, institutional configurations, and new path development. Prog Hum Geogr 45(3):436–454. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309132520926587
Hartono S, Sobari A (2016) The role of cluster cycle and pattern of interaction to competition strategy. Probl Perspect Manage 14(2):74–83. https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.14(2).2016.08
Hidalgo G, Monticelli JM, Pedroso J, Verschoore JR, de Matos CA (2022) The influence of formal Institution agents on Coopetition in the OrgaFood Industry. J Agricultural Food Industrial Organ 20(2):61–74. https://doi.org/10.1515/jafio-2019-0009
Hoetoro A (2014) Cooperation and competition among clustered MSEs in East Java. Gadjah Mada Int J Bus 16(3):275–293. https://doi.org/10.22146/gamaijb.5660
Hu Y-C, He X-L (2013) Research on the Coopetition Relationship of Cluster enterprises based on the Network View-taking central-satellite type industry cluster as Example. J Appl Sci 13(8):1332–1338
Hückstädt M (2022) Coopetition between frenemies–interrelations and effects of seven collaboration problems in research clusters. Scientometrics 127(9):5191–5224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-022-04472-w
Hung SW, Chang CC (2012) A co-opetition perspective of technology alliance governance modes. Technol Anal Strateg Manag 24(7):679–696
Itoga H, Grace TR, Yang FCH, Joseph ZS (2014) Dynamics of industrial cluster scenarios. Revista de Cercetare si Interventie Sociala 47:233
Ketchen DJ Jr, Snow CC, Hoover VL (2004) Research on competitive dynamics: recent accomplishments and future challenges. J Manag 30(6):779–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jm.2004.06.002
Klimas P, Ahmadian AA, Soltani M, Shahbazi M, Hamidizadeh A (2023) Coopetition, where do you come from? Identification, categorization, and configuration of theoretical roots of coopetition. SAGE Open 13(1):21582440221085003. https://doi.org/10.1177/21582440221085003
König T (2023) Between collaboration and competition: co-located clusters of different industries in one region—the context of Tuttlingen’s medical engineering and metal processing industries. Reg Sci Policy Pract 15(2):288–325. https://doi.org/10.1111/rsp3.12581
Köseoğlu MA, Yildiz M, Okumus F, Barca M (2019) The intellectual structure of coopetition: past, present and future. J Strategy Manage 12(1):2–29. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSMA-07-2018-0073
Kylanen M, Mariani MM (2012) Unpacking the temporal dimension of coopetition in tourism destinations: evidence from Finnish and Italian theme parks. Anatolia 23(1):61–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/13032917.2011.653632
Lado AA, Boyd NG, Hanlon SC (1997) Competition, cooperation, and the search for economic rents: a syncretic model. Acad Manage Rev 22(1):110–141
Lazzeretti L, Capone F, Caloffi A, Sedita SR (2019) Rethinking clusters. Towards a new research agenda for cluster research. Eur Plan Stud 27(10):1879–1903. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654313.2019.1650899
Lehtonen MJ, Ainamo A, Harviainen J (2020) The four faces of creative industries: visualising the game industry ecosystem in Helsinki and Tokyo. Ind Innovat 27(9):1062–1087. https://doi.org/10.1080/13662716.2019.1676704
Leite RS, Garcia Lopes HE, Duarte Silva SA (2009) A estratégia em relacionamentos coopetitivos: urn estudo do arranjo produtivo de Nova Serrana. Revista Brasileira De Gestao De Negocios 11(30):65–78. https://doi.org/10.7819/rbgn.v11i30.439
Li H, Wang Y, Yin R, Kull TJ, Choi TY (2012) Target pricing: demand-side versus supply-side approaches. Int J Prod Econ 136(1):172–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2011.10.002
Li M, Jiang X (2012) Co-opetition pricing game of industrial clusters based on incomplete information cournot model. Int J Advancements Comput Technol 4(18):424–432
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, Moher D (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ (Clinical Res Ed) 339. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
M’Chirgui Z (2005) The economics of the smart card industry: towards coopetitive strategies. Econ Innov New Technol 14(6):455–477
Mantovani A, Ruiz-Aliseda F (2016) Equilibrium innovation ecosystems: the dark side of collaborating with complementors. Manage Sci 62(2):534–549. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2050969
Maso LD, Lattanzi N (2014) Local firms’ strategies and cluster coopetition in Tuscany: the case of Toscana Promozione Agency. Probl Perspect Manage 12(1):132–142
Mathews M (2018) Managing local supplier networks: conflict or compromise? Reg Stud 52(7):890–900. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2017.1360479
Min Z, Feiqi D, Sai W (2008) Coordination game model of co-opetition relationship on cluster supply chains. J Syst Eng Electron 19(3):499–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1004-4132(08)60113-9
Minà A, Dagnino GB (2016) In search of coopetition consensus: shaping the collective identity of a relevant strategic management community. Int J Technol Manage 71(1–2):123–154. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJTM.2016.077981
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Altman D, Antes G, Atkins D, Barbour V, Barrowman N, Berlin JA, Clark J, Clarke M, Cook D, D’Amico R, Deeks JJ, Devereaux PJ, Dickersin K, Egger M, Ernst E, Tugw P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement (Chinese edition). J Chin Integr Med 7(9):889–896. https://doi.org/10.3736/jcim20090918
Molina M, Yoong P (2003) Knowledge sharing in a co-opetitive environment: the case of business clusters. J Inform Knowl Manage 2(4):321–341. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219649203000528
Monteiro PV (2016) The role of knowledge-intensive service activities on inducing innovation in co-opetition strategies: lessons from the maritime cluster of the Algarve region. Int J Manage Enterp Dev 15(1):78–95. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMED.2016.075876
Monteiro PV, Salvador R, Soares CG (2017) A microcluster approach applied to the case of the nautical tourism sector of the Algarve region (Portugal). Tourism Mar Environ 12(2):105–124. https://doi.org/10.3727/154427317X14890156492368
Monticelli JM, Da Silveira AB, Da Silva LM (2018) The process of coopetitive strategy: A case study of microbreweries in Porto Alegre. In Revista de Administracao Mackenzie 19. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-6971/eRAMR180012
Monticelli JM, Garrido IL, Vasconcellos SL (2019) Coopetition in internationalization of wineries in southern Brazil with the support of formal institutions. Rev Adm UFSM 12(4):679–700. https://doi.org/10.5902/19834659
Mosonyi S, Empson L, Gond JP (2020) Management consulting: towards an integrative framework of knowledge, identity, and power. Int J Manage Reviews 22(2):120–149. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12218
Mucha-Kuś K, Sołtysik M, Zamasz K, Szczepańska-Woszczyna K (2021) Coopetitive nature of energy communities—the energy transition context. Energies 2021:14;931. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14040931
Nemeh A, Yami S (2016) The determinants of the emergence of Coopetition Strategy in RandD. Int Stud Manage Organ 46(2–3):159–178. https://doi.org/10.1080/00208825.2016.1112151
Nowińska A (2019) Ships and relationships: competition, geographical proximity, and relations in the shipping industry. J Bus Res 101:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.04.021
Oliveira-Ribeiro R, Chim-Miki AF, de Araújo Machado P (2022) Coopetition at Society Level: a scale validation. Int J Bus Adm 13(4). https://doi.org/10.5430/ijba.v13n4p19
Padula G, Dagnino GB (2007) Untangling the rise of coopetition: the intrusion of competition in a cooperative game structure. Int Stud Manage Organ 37(2):32–52
Poisson-de-Haro S, Myard A (2018) Cultural Cluster coopetition: a look at the Montreal circus world. Can J Administrative Sci 35(3):390–402. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjas.1448
Porter ME (1991) Towards a dynamic theory of strategy. Strateg Manag J 12(S2):95–117. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.4250121008
Porter ME (1998) Clusters and the new economics of competition. Harvard Business Rev 76(6):77–90
Post C, Sarala R, Gatrell C, Prescott JE (2020) Advancing theory with review articles. J Manag Stud 57(2):351–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12549
Quintana-Garcia C, Benavides-Velasco CA (2004) Cooperation, competition, and innovative capability: a panel data of European dedicated biotechnology firms. Technovation 24(12):927–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4972(03)00060-9
Ralandison T (2021) Exploring corporation-cooperative arrangements in agricultural value chains: the case of Madagascar vanilla. Jpn J Agric Econ 23:113–118. https://doi.org/10.18480/jjae.23.0_113
Ramjaun TI, Pullman M, Kumar M, Sanchez Rodrigues V (2023) Strength in numbers: collaborative procurement and competitiveness of craft breweries. Int J Oper Prod Manage 4(3):643–665. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-08-2022-0503
Raza-Ullah T, Bengtsson M, Kock S (2014) The coopetition paradox and tension in coopetition at multiple levels. Ind Mark Manage 43(2):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2013.11.001
Reniers G, Dullaert W, Visser L (2010) Empirically based development of a framework for advancing and stimulating collaboration in the chemical industry (ASC): creating sustainable chemical industrial parks. J Clean Prod 18(16–17):1587–1597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2010.07.013
Ritala P, Hurmelinna-Laukkanen P (2009) What’s in it for me? Creating and appropriating value in innovation-related coopetition. Technovation 29(12):819–828
Ritala P, Hallikas J, Sissonen H (2008) The Effect of Strategic Alliances between Key competitors on firm performance. Manage Research: J Iberoamerican Acad Manage 6(3):179–187. https://doi.org/10.2753/jmr1536-5433060302
Sellitto MA, Luchese J (2018) Systemic Cooperative actions among competitors: the case of a Furniture Cluster in Brazil. J Ind Competition Trade 18(4):513–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10842-018-0272-9
Shen L, Liu Y (2023) Exploring the impact of partner match on business model innovation: the mediating role of interfirm dynamic capabilities-based on ecosystem orchestration perspective. Kybernetes Vol ahead–of–print. https://doi.org/10.1108/K-03-2023-0382
Smiljic S (2020) Beyond the dyad: role of non-competitive partners in coopetitive RandD projects. Int J Innov Manag 24(8):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1142/S136391962040006X
Stead JG, Stead WE (2019) Why Porter is not enough: economic foundations of sustainable strategic management. Rethinking Strategic Management: Sustainable Strategizing Posit Impact 67–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06014-5_4
Teller C, Alexander A, Floh A (2016) The impact of competition and cooperation on the performance of a retail agglomeration and its stores. Ind Mark Manage 52:6–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2015.07.010
Tracey P, Clark GL (2003) Alliances, networks and competitive strategy: rethinking clusters of innovation. Growth Change 34(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-2257.00196
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic Review* introduction: the need for an evidence- informed approach. Br J Manag 14:207–222
Wolff G, Wältermann M, Rank ON (2020) The embeddedness of social relations in inter-firm competitive structures. Social Networks 62:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socnet.2020.03.001
Xu R, Zhu X, Wang Y, Gu J, Felzensztein C (2023) Inter-firm coopetition and innovation in industrial clusters: the role of institutional support. J Bus Industrial Mark. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-07-2022-0339 . No. ahead-of-print
Yadav N, Kumar R, Malik A (2022) Global developments in coopetition research: a bibliometric analysis of research articles published between 2010 and 2020. J Bus Res 145:495–508
Yami S, Castaldo S, Dagnino GB, Frédéric LR (2010) Coopetition: Winning Strategies for the 21st Century (E. Elgar, Ed.)
Yuan X, Dai T, Chen LG, Gavirneni S (2021) Co-opetition in service clusters with waiting-area entertainment. Manuf Service Oper Manage 23(1):116–122. https://doi.org/10.1287/MSOM.2019.0815
Download references
This work was supported by a Productivity Grant of the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development CNPq 307536/2021-1.
Open access funding provided by FCT|FCCN (b-on).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Degeit, Research Unit on Governance, Competitiveness and Public Policies (GOVCOOP), Universidade de Aveiro, Campus Santiago, Aveiro, 3810-193, Portugal
Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki
Federal University of Campina Grande, Aprigio Veloso Street, 882, Campina Grande, Paraíba, 58429-900, Brazil
Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki & Rosana L. Coelho Fernandes
Business and Management School, Unisinos University, Unisinos Avenue, 950 - Cristo Rei, São Leopoldo, RS, 93022-000, Brazil
Jefferson Marlon Monticelli
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki and Rosana Lacerda Coelho Fernandes; Methodology: Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki and Rosana Lacerda Coelho Fernandes; Formal analysis and investigation: Rosana Lacerda Coelho Fernandes, Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki, and Jefferson Marlon Monticelli; Writing - original draft preparation: Rosana Lacerda Coelho Fernandes and Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki; Writing - review and editing: Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki and Jefferson Marlon Monticelli; Funding acquisition: Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki; Resources: Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki; Supervision: Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki and Jefferson Marlon Monticelli.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Adriana Fumi Chim-Miki .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare they have no financial and no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Chim-Miki, A.F., Fernandes, R.L.C. & Monticelli, J.M. Rethinking cluster under coopetition strategy: an integrative literature review and research agenda. Manag Rev Q (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-024-00434-z
Download citation
Received : 05 August 2023
Accepted : 31 March 2024
Published : 24 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-024-00434-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coopetition
- Research agenda
- Rethinking cluster
- Integrative systematic literature review
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
admin September 9, 2016 Blog, Literature Review and Hypotheses. A literature review shows the cumulative knowledge which is the conceptual framework your study is based. It gives an overview of prior research identifying the details of the need for your study stated in your introduction section. It is common to present the literature with ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
The key here is to focus first on the literature relevant to the puzzle. In this example, the tokenism literature sets up a puzzle derived from a theory and contradictory empirical evidence. Let's consider what each of these means... The literature(s) from which you develop the theoretical/empirical puzzle that drives your research question.
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
With a proper and thorough review of the literature, one will become an expert in the subject matter. With this expertise, an original and relevant hypothesis is most likely to be developed. Developing a Hypothesis With a thorough review of the literature accomplished, one may reasonably develop original and relevant (i.e., meaningful) hypotheses.
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims: To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory; To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic; Identify a problem in a field of research ; Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature ...
Integrated Literature Review, Research Question/Hypothesis. Before writing your integrated literature review, you should have searched the research literature and written summaries of each of the articles. You may want to use Table 4.2 from the text, "Anatomy of a Research Article and Comparison of Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches to ...
hypothesis testing in order to show that a change in one variable is associated (what we fre-quently statistically call "correlated") with a change in a second variable, but they do not ... literature, called a literature review, which I will discuss in more detail in the next section. For our purposes now, however, I will say that a ...
A review is a required part of grant and research proposals and often a chapter in theses and dissertations. Generally, the purpose of a review is to analyze critically a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles.
A thorough review of the literature is essential on your topic of interest. With this accomplished, one may reasonably develop original and relevant (i.e., meaningful) hypotheses. Not all original and relevant hypotheses, however, are feasible (i.e., testable). Once an original, relevant, and feasible hypothesis has been developed, an optimal ...
Literature review is an essential feature of academic research. Fundamentally, knowledge advancement must be built on prior existing work. To push the knowledge frontier, we must know where the frontier is. By reviewing relevant literature, we understand the breadth and depth of the existing body of work and identify gaps to explore.
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the "literature review" or "background" section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses (Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013).
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing ...
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
A literature review should connect to the study question, guide the study methodology, and be central in the discussion by indicating how the analyzed data advances what is known in the field. ... Theoretical frameworks are explicitly stated by an educational researcher in the paper's framework, theory, or relevant literature section. The ...
Literature Review; Write and Cite. This guide offers information on writing resources, citation style guides, and academic writing expectations and best practices, as well as information on resources related to copyright, fair use, permissions, and open access. Table of Contents .
6 Hypothesis , Research Question & Literature Review. Hypothesis is a potential explanation to a phenomenon, and in a much more rigorous way. It's the core of research design, after Research Question and Literature Review. 1,Hypothesis should be used in formal logic, if XXX ,then XXX. 2,Hypothesis should have clear boundaries and testable.
Theories are used to justify and support your arguments, variables and the phenomena that is being studied. In developing your literature review, it will be helpful to identify an underpinning theory on which you can start developing your arguments and show the gaps of research being examined. Additional theories can be used to supplement your ...
The literature, and consequently the literature review, heavily pulls from Kolb's Experiential Learning model and Mayer's Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning. We find a general trend suggesting the efficacy of creating experiential learning-based lessons and the efficacy of multimedia learning formats.
A systematic literature review design was used in this study following the guidelines of Paul and Criado (Citation 2020). There are various types of systematic literature reviews, including structured reviews, framework-based reviews, bibliometric reviews, and meta-analysis reviews. ... Business: Theory and Practice, 23, 1-13. https://doi.org ...
The present study comprises two distinct but interconnected procedures. First, a systematic literature review was conducted following the PRISMA method ( []; Additional file 1; Additional file 2) with the aim of collecting all validations of the P-CAT that have been developed.Second, a systematic description of the validity evidence for each of the P-CAT validations found in the systematic ...
This review study aims to critically review these theoretical foundations and associated empirical studies to examine their potential for addressing the complex and evolving notions of fairness in classroom assessment contexts. This study also builds on fairness and justice literature in social sciences and broader educational discourses to ...
The promotion and development of healthy cities are vital for enhancing human habitats and fostering sustainable economic growth. Based on the core databases of Web of Science, PubMed, Google Scholar, and PsycINFO, and the knowledge graph software, this paper presents a quantitative analysis of the literature related to attention recovery abroad. It is found that in recent years, the research ...
This study aimed to integrate the dimensions and elements of intra-cluster coopetition, identify the emergence of a complementary theoretical perspective to cluster theory and create an integrative research agenda to support the rethinking cluster approach based on coopetition. It is an integrative Systematic Literature Review that generates insights to move the topic forward. Results showed ...