

What is Hypothesis? Definition, Meaning, Characteristics, Sources
- Post last modified: 10 January 2022
- Reading time: 18 mins read
- Post category: Research Methodology

- What is Hypothesis?
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
As an example, if we want to explore whether using a specific teaching method at school will result in better school marks (research question), the hypothesis could be that the mean school marks of students being taught with that specific teaching method will be higher than of those being taught using other methods.
In this example, we stated a hypothesis about the expected differences between groups. Other hypotheses may refer to correlations between variables.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Hypothesis?
- 2 Hypothesis Definition
- 3 Meaning of Hypothesis
- 4.1 Conceptual Clarity
- 4.2 Need of empirical referents
- 4.3 Hypothesis should be specific
- 4.4 Hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques
- 4.5 Hypothesis should be consistent with the theory
- 4.6 Hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events
- 4.7 Hypothesis should be simple
- 5.1 Observation
- 5.2 Analogies
- 5.4 State of Knowledge
- 5.5 Culture
- 5.6 Continuity of Research
- 6.1 Null Hypothesis
- 6.2 Alternative Hypothesis
Thus, to formulate a hypothesis, we need to refer to the descriptive statistics (such as the mean final marks), and specify a set of conditions about these statistics (such as a difference between the means, or in a different example, a positive or negative correlation). The hypothesis we formulate applies to the population of interest.
The null hypothesis makes a statement that no difference exists (see Pyrczak, 1995, pp. 75-84).
Hypothesis Definition
A hypothesis is ‘a guess or supposition as to the existence of some fact or law which will serve to explain a connection of facts already known to exist.’ – J. E. Creighton & H. R. Smart
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition not known to be definitely true or false, examined for the sake of determining the consequences which would follow from its truth.’ – Max Black
Hypothesis is ‘a proposition which can be put to a test to determine validity and is useful for further research.’ – W. J. Goode and P. K. Hatt
A hypothesis is a proposition, condition or principle which is assumed, perhaps without belief, in order to draw out its logical consequences and by this method to test its accord with facts which are known or may be determined. – Webster’s New International Dictionary of the English Language (1956)
Meaning of Hypothesis
From the above mentioned definitions of hypothesis, its meaning can be explained in the following ways.
- At the primary level, a hypothesis is the possible and probable explanation of the sequence of happenings or data.
- Sometimes, hypothesis may emerge from an imagination, common sense or a sudden event.
- Hypothesis can be a probable answer to the research problem undertaken for study. 4. Hypothesis may not always be true. It can get disproven. In other words, hypothesis need not always be a true proposition.
- Hypothesis, in a sense, is an attempt to present the interrelations that exist in the available data or information.
- Hypothesis is not an individual opinion or community thought. Instead, it is a philosophical means which is to be used for research purpose. Hypothesis is not to be considered as the ultimate objective; rather it is to be taken as the means of explaining scientifically the prevailing situation.
The concept of hypothesis can further be explained with the help of some examples. Lord Keynes, in his theory of national income determination, made a hypothesis about the consumption function. He stated that the consumption expenditure of an individual or an economy as a whole is dependent on the level of income and changes in a certain proportion.
Later, this proposition was proved in the statistical research carried out by Prof. Simon Kuznets. Matthus, while studying the population, formulated a hypothesis that population increases faster than the supply of food grains. Population studies of several countries revealed that this hypothesis is true.
Validation of the Malthus’ hypothesis turned it into a theory and when it was tested in many other countries it became the famous Malthus’ Law of Population. It thus emerges that when a hypothesis is tested and proven, it becomes a theory. The theory, when found true in different times and at different places, becomes the law. Having understood the concept of hypothesis, few hypotheses can be formulated in the areas of commerce and economics.
- Population growth moderates with the rise in per capita income.
- Sales growth is positively linked with the availability of credit.
- Commerce education increases the employability of the graduate students.
- High rates of direct taxes prompt people to evade taxes.
- Good working conditions improve the productivity of employees.
- Advertising is the most effecting way of promoting sales than any other scheme.
- Higher Debt-Equity Ratio increases the probability of insolvency.
- Economic reforms in India have made the public sector banks more efficient and competent.
- Foreign direct investment in India has moved in those sectors which offer higher rate of profit.
- There is no significant association between credit rating and investment of fund.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Not all the hypotheses are good and useful from the point of view of research. It is only a few hypotheses satisfying certain criteria that are good, useful and directive in the research work undertaken. The characteristics of such a useful hypothesis can be listed as below:
Conceptual Clarity
Need of empirical referents, hypothesis should be specific, hypothesis should be within the ambit of the available research techniques, hypothesis should be consistent with the theory, hypothesis should be concerned with observable facts and empirical events, hypothesis should be simple.
The concepts used while framing hypothesis should be crystal clear and unambiguous. Such concepts must be clearly defined so that they become lucid and acceptable to everyone. How are the newly developed concepts interrelated and how are they linked with the old one is to be very clear so that the hypothesis framed on their basis also carries the same clarity.
A hypothesis embodying unclear and ambiguous concepts can to a great extent undermine the successful completion of the research work.
A hypothesis can be useful in the research work undertaken only when it has links with some empirical referents. Hypothesis based on moral values and ideals are useless as they cannot be tested. Similarly, hypothesis containing opinions as good and bad or expectation with respect to something are not testable and therefore useless.
For example, ‘current account deficit can be lowered if people change their attitude towards gold’ is a hypothesis encompassing expectation. In case of such a hypothesis, the attitude towards gold is something which cannot clearly be described and therefore a hypothesis which embodies such an unclean thing cannot be tested and proved or disproved. In short, the hypothesis should be linked with some testable referents.
For the successful conduction of research, it is necessary that the hypothesis is specific and presented in a precise manner. Hypothesis which is general, too ambitious and grandiose in scope is not to be made as such hypothesis cannot be easily put to test. A hypothesis is to be based on such concepts which are precise and empirical in nature. A hypothesis should give a clear idea about the indicators which are to be used.
For example, a hypothesis that economic power is increasingly getting concentrated in a few hands in India should enable us to define the concept of economic power. It should be explicated in terms of measurable indicator like income, wealth, etc. Such specificity in the formulation of a hypothesis ensures that the research is practicable and significant.
While framing the hypothesis, the researcher should be aware of the available research techniques and should see that the hypothesis framed is testable on the basis of them. In other words, a hypothesis should be researchable and for this it is important that a due thought has been given to the methods and techniques which can be used to measure the concepts and variables embodied in the hypothesis.
It does not however mean that hypotheses which are not testable with the available techniques of research are not to be made. If the problem is too significant and therefore the hypothesis framed becomes too ambitious and complex, it’s testing becomes possible with the development of new research techniques or the hypothesis itself leads to the development of new research techniques.
A hypothesis must be related to the existing theory or should have a theoretical orientation. The growth of knowledge takes place in the sequence of facts, hypothesis, theory and law or principles. It means the hypothesis should have a correspondence with the existing facts and theory.
If the hypothesis is related to some theory, the research work will enable us to support, modify or refute the existing theory. Theoretical orientation of the hypothesis ensures that it becomes scientifically useful. According to Prof. Goode and Prof. Hatt, research work can contribute to the existing knowledge only when the hypothesis is related with some theory.
This enables us to explain the observed facts and situations and also verify the framed hypothesis. In the words of Prof. Cohen and Prof. Nagel, “hypothesis must be formulated in such a manner that deduction can be made from it and that consequently a decision can be reached as to whether it does or does not explain the facts considered.”
If the research work based on a hypothesis is to be successful, it is necessary that the later is as simple and easy as possible. An ambition of finding out something new may lead the researcher to frame an unrealistic and unclear hypothesis. Such a temptation is to be avoided. Framing a simple, easy and testable hypothesis requires that the researcher is well acquainted with the related concepts.
Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can be derived from various sources. Some of the sources is given below:
Observation
State of knowledge, continuity of research.
Hypotheses can be derived from observation from the observation of price behavior in a market. For example the relationship between the price and demand for an article is hypothesized.
Analogies are another source of useful hypotheses. Julian Huxley has pointed out that casual observations in nature or in the framework of another science may be a fertile source of hypotheses. For example, the hypotheses that similar human types or activities may be found in similar geophysical regions come from plant ecology.
This is one of the main sources of hypotheses. It gives direction to research by stating what is known logical deduction from theory lead to new hypotheses. For example, profit / wealth maximization is considered as the goal of private enterprises. From this assumption various hypotheses are derived’.
An important source of hypotheses is the state of knowledge in any particular science where formal theories exist hypotheses can be deduced. If the hypotheses are rejected theories are scarce hypotheses are generated from conception frameworks.
Another source of hypotheses is the culture on which the researcher was nurtured. Western culture has induced the emergence of sociology as an academic discipline over the past decade, a large part of the hypotheses on American society examined by researchers were connected with violence. This interest is related to the considerable increase in the level of violence in America.
The continuity of research in a field itself constitutes an important source of hypotheses. The rejection of some hypotheses leads to the formulation of new ones capable of explaining dependent variables in subsequent research on the same subject.
Null and Alternative Hypothesis
Null hypothesis.
The hypothesis that are proposed with the intent of receiving a rejection for them are called Null Hypothesis . This requires that we hypothesize the opposite of what is desired to be proved. For example, if we want to show that sales and advertisement expenditure are related, we formulate the null hypothesis that they are not related.
Similarly, if we want to conclude that the new sales training programme is effective, we formulate the null hypothesis that the new training programme is not effective, and if we want to prove that the average wages of skilled workers in town 1 is greater than that of town 2, we formulate the null hypotheses that there is no difference in the average wages of the skilled workers in both the towns.
Since we hypothesize that sales and advertisement are not related, new training programme is not effective and the average wages of skilled workers in both the towns are equal, we call such hypotheses null hypotheses and denote them as H 0 .
Alternative Hypothesis
Rejection of null hypotheses leads to the acceptance of alternative hypothesis . The rejection of null hypothesis indicates that the relationship between variables (e.g., sales and advertisement expenditure) or the difference between means (e.g., wages of skilled workers in town 1 and town 2) or the difference between proportions have statistical significance and the acceptance of the null hypotheses indicates that these differences are due to chance.
As already mentioned, the alternative hypotheses specify that values/relation which the researcher believes hold true. The alternative hypotheses can cover a whole range of values rather than a single point. The alternative hypotheses are denoted by H 1 .
Business Ethics
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Theories of CSR
- Arguments Against CSR
- Business Case for CSR
- Importance of CSR in India
- Drivers of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Developing a CSR Strategy
- Implement CSR Commitments
- CSR Marketplace
- CSR at Workplace
- Environmental CSR
- CSR with Communities and in Supply Chain
- Community Interventions
- CSR Monitoring
- CSR Reporting
- Voluntary Codes in CSR
- What is Corporate Ethics?
Lean Six Sigma
- What is Six Sigma?
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Value and Waste in Lean Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Team
- MAIC Six Sigma
- Six Sigma in Supply Chains
- What is Binomial, Poisson, Normal Distribution?
- What is Sigma Level?
- What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
- What is DMADV in Six Sigma?
- Six Sigma Project Charter
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
- Research Methodology
- What is Research?
- Sampling Method
Research Methods
- Data Collection in Research
Methods of Collecting Data
- Application of Business Research
- Levels of Measurement
- What is Sampling?
- Hypothesis Testing
- Research Report
- What is Management?
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- What is Controlling?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Staffing?
- Organization Structure
- What is Departmentation?
- Span of Control
- What is Authority?
- Centralization vs Decentralization
- Organizing in Management
- Schools of Management Thought
- Classical Management Approach
- Is Management an Art or Science?
- Who is a Manager?
Operations Research
- What is Operations Research?
- Operation Research Models
- Linear Programming
- Linear Programming Graphic Solution
- Linear Programming Simplex Method
- Linear Programming Artificial Variable Technique
- Duality in Linear Programming
- Transportation Problem Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- Transportation Problem Finding Optimal Solution
- Project Network Analysis with Critical Path Method
- Project Network Analysis Methods
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Simulation in Operation Research
- Replacement Models in Operation Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
- What is Service?
- What is Service Operations Management?
- What is Service Design?
- Service Design Process
- Service Delivery
- What is Service Quality?
- Gap Model of Service Quality
- Juran Trilogy
- Service Performance Measurement
- Service Decoupling
- IT Service Operation
- Service Operations Management in Different Sector
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Supply Chain Planning and Measuring Strategy Performance
- What is Warehousing?
- What is Packaging?
- What is Inventory Management?
- What is Material Handling?
- What is Order Picking?
- Receiving and Dispatch, Processes
- What is Warehouse Design?
- What is Warehousing Costs?
You Might Also Like
Sampling process and characteristics of good sample design, what is research problem components, identifying, formulating,, data analysis in research, cross-sectional and longitudinal research, what is measurement scales, types, criteria and developing measurement tools, what is parametric tests types: z-test, t-test, f-test, what is experiments variables, types, lab, field, data processing in research, types of hypotheses, primary data and secondary data, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal growth.

Development
- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation.
Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments and the collection and analysis of data. It is an essential element of the scientific method, as it allows researchers to make predictions about the outcome of their experiments and to test those predictions to determine their accuracy.
Types of Hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis are as follows:
Research Hypothesis
A research hypothesis is a statement that predicts a relationship between variables. It is usually formulated as a specific statement that can be tested through research, and it is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is no significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as a starting point for testing the research hypothesis, and if the results of the study reject the null hypothesis, it suggests that there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Alternative Hypothesis
An alternative hypothesis is a statement that assumes there is a significant difference or relationship between variables. It is often used as an alternative to the null hypothesis and is tested against the null hypothesis to determine which statement is more accurate.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the direction of the relationship between variables. For example, a researcher might predict that increasing the amount of exercise will result in a decrease in body weight.
Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis is a statement that predicts the relationship between variables but does not specify the direction. For example, a researcher might predict that there is a relationship between the amount of exercise and body weight, but they do not specify whether increasing or decreasing exercise will affect body weight.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement that assumes a particular statistical model or distribution for the data. It is often used in statistical analysis to test the significance of a particular result.
Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis is a statement that assumes more than one condition or outcome. It can be divided into several sub-hypotheses, each of which represents a different possible outcome.
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement that is based on observed phenomena or data. It is often used in scientific research to develop theories or models that explain the observed phenomena.
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement that assumes only one outcome or condition. It is often used in scientific research to test a single variable or factor.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is a statement that assumes multiple outcomes or conditions. It is often used in scientific research to test the effects of multiple variables or factors on a particular outcome.
Applications of Hypothesis
Hypotheses are used in various fields to guide research and make predictions about the outcomes of experiments or observations. Here are some examples of how hypotheses are applied in different fields:
- Science : In scientific research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain natural phenomena. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular variable on a natural system, such as the effects of climate change on an ecosystem.
- Medicine : In medical research, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of treatments and therapies for specific conditions. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new drug on a particular disease.
- Psychology : In psychology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of human behavior and cognition. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a particular stimulus on the brain or behavior.
- Sociology : In sociology, hypotheses are used to test theories and models of social phenomena, such as the effects of social structures or institutions on human behavior. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of income inequality on crime rates.
- Business : In business research, hypotheses are used to test the validity of theories and models that explain business phenomena, such as consumer behavior or market trends. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the effects of a new marketing campaign on consumer buying behavior.
- Engineering : In engineering, hypotheses are used to test the effectiveness of new technologies or designs. For example, a hypothesis might be formulated to test the efficiency of a new solar panel design.
How to write a Hypothesis
Here are the steps to follow when writing a hypothesis:
Identify the Research Question
The first step is to identify the research question that you want to answer through your study. This question should be clear, specific, and focused. It should be something that can be investigated empirically and that has some relevance or significance in the field.
Conduct a Literature Review
Before writing your hypothesis, it’s essential to conduct a thorough literature review to understand what is already known about the topic. This will help you to identify the research gap and formulate a hypothesis that builds on existing knowledge.
Determine the Variables
The next step is to identify the variables involved in the research question. A variable is any characteristic or factor that can vary or change. There are two types of variables: independent and dependent. The independent variable is the one that is manipulated or changed by the researcher, while the dependent variable is the one that is measured or observed as a result of the independent variable.
Formulate the Hypothesis
Based on the research question and the variables involved, you can now formulate your hypothesis. A hypothesis should be a clear and concise statement that predicts the relationship between the variables. It should be testable through empirical research and based on existing theory or evidence.
Write the Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is the opposite of the alternative hypothesis, which is the hypothesis that you are testing. The null hypothesis states that there is no significant difference or relationship between the variables. It is important to write the null hypothesis because it allows you to compare your results with what would be expected by chance.
Refine the Hypothesis
After formulating the hypothesis, it’s important to refine it and make it more precise. This may involve clarifying the variables, specifying the direction of the relationship, or making the hypothesis more testable.
Examples of Hypothesis
Here are a few examples of hypotheses in different fields:
- Psychology : “Increased exposure to violent video games leads to increased aggressive behavior in adolescents.”
- Biology : “Higher levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere will lead to increased plant growth.”
- Sociology : “Individuals who grow up in households with higher socioeconomic status will have higher levels of education and income as adults.”
- Education : “Implementing a new teaching method will result in higher student achievement scores.”
- Marketing : “Customers who receive a personalized email will be more likely to make a purchase than those who receive a generic email.”
- Physics : “An increase in temperature will cause an increase in the volume of a gas, assuming all other variables remain constant.”
- Medicine : “Consuming a diet high in saturated fats will increase the risk of developing heart disease.”
Purpose of Hypothesis
The purpose of a hypothesis is to provide a testable explanation for an observed phenomenon or a prediction of a future outcome based on existing knowledge or theories. A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to design experiments or studies to gather evidence and data that can support or refute the proposed explanation or prediction.
The formulation of a hypothesis is based on existing knowledge, observations, and theories, and it should be specific, testable, and falsifiable. A specific hypothesis helps to define the research question, which is important in the research process as it guides the selection of an appropriate research design and methodology. Testability of the hypothesis means that it can be proven or disproven through empirical data collection and analysis. Falsifiability means that the hypothesis should be formulated in such a way that it can be proven wrong if it is incorrect.
In addition to guiding the research process, the testing of hypotheses can lead to new discoveries and advancements in scientific knowledge. When a hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be used to develop new theories or models to explain the observed phenomenon. When a hypothesis is not supported by the data, it can help to refine existing theories or prompt the development of new hypotheses to explain the phenomenon.
When to use Hypothesis
Here are some common situations in which hypotheses are used:
- In scientific research , hypotheses are used to guide the design of experiments and to help researchers make predictions about the outcomes of those experiments.
- In social science research , hypotheses are used to test theories about human behavior, social relationships, and other phenomena.
- I n business , hypotheses can be used to guide decisions about marketing, product development, and other areas. For example, a hypothesis might be that a new product will sell well in a particular market, and this hypothesis can be tested through market research.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some common characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable : A hypothesis must be able to be tested through observation or experimentation. This means that it must be possible to collect data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
- Falsifiable : A hypothesis must be able to be proven false if it is not supported by the data. If a hypothesis cannot be falsified, then it is not a scientific hypothesis.
- Clear and concise : A hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner so that it can be easily understood and tested.
- Based on existing knowledge : A hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and research in the field. It should not be based on personal beliefs or opinions.
- Specific : A hypothesis should be specific in terms of the variables being tested and the predicted outcome. This will help to ensure that the research is focused and well-designed.
- Tentative: A hypothesis is a tentative statement or assumption that requires further testing and evidence to be confirmed or refuted. It is not a final conclusion or assertion.
- Relevant : A hypothesis should be relevant to the research question or problem being studied. It should address a gap in knowledge or provide a new perspective on the issue.
Advantages of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have several advantages in scientific research and experimentation:
- Guides research: A hypothesis provides a clear and specific direction for research. It helps to focus the research question, select appropriate methods and variables, and interpret the results.
- Predictive powe r: A hypothesis makes predictions about the outcome of research, which can be tested through experimentation. This allows researchers to evaluate the validity of the hypothesis and make new discoveries.
- Facilitates communication: A hypothesis provides a common language and framework for scientists to communicate with one another about their research. This helps to facilitate the exchange of ideas and promotes collaboration.
- Efficient use of resources: A hypothesis helps researchers to use their time, resources, and funding efficiently by directing them towards specific research questions and methods that are most likely to yield results.
- Provides a basis for further research: A hypothesis that is supported by data provides a basis for further research and exploration. It can lead to new hypotheses, theories, and discoveries.
- Increases objectivity: A hypothesis can help to increase objectivity in research by providing a clear and specific framework for testing and interpreting results. This can reduce bias and increase the reliability of research findings.
Limitations of Hypothesis
Some Limitations of the Hypothesis are as follows:
- Limited to observable phenomena: Hypotheses are limited to observable phenomena and cannot account for unobservable or intangible factors. This means that some research questions may not be amenable to hypothesis testing.
- May be inaccurate or incomplete: Hypotheses are based on existing knowledge and research, which may be incomplete or inaccurate. This can lead to flawed hypotheses and erroneous conclusions.
- May be biased: Hypotheses may be biased by the researcher’s own beliefs, values, or assumptions. This can lead to selective interpretation of data and a lack of objectivity in research.
- Cannot prove causation: A hypothesis can only show a correlation between variables, but it cannot prove causation. This requires further experimentation and analysis.
- Limited to specific contexts: Hypotheses are limited to specific contexts and may not be generalizable to other situations or populations. This means that results may not be applicable in other contexts or may require further testing.
- May be affected by chance : Hypotheses may be affected by chance or random variation, which can obscure or distort the true relationship between variables.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Great Hypothesis
Hypothesis Definition, Format, Examples, and Tips
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Verywell / Alex Dos Diaz
- The Scientific Method
Hypothesis Format
Falsifiability of a hypothesis.
- Operationalization
Hypothesis Types
Hypotheses examples.
- Collecting Data
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process.
Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test performance. The hypothesis might be: "This study is designed to assess the hypothesis that sleep-deprived people will perform worse on a test than individuals who are not sleep-deprived."
At a Glance
A hypothesis is crucial to scientific research because it offers a clear direction for what the researchers are looking to find. This allows them to design experiments to test their predictions and add to our scientific knowledge about the world. This article explores how a hypothesis is used in psychology research, how to write a good hypothesis, and the different types of hypotheses you might use.
The Hypothesis in the Scientific Method
In the scientific method , whether it involves research in psychology, biology, or some other area, a hypothesis represents what the researchers think will happen in an experiment. The scientific method involves the following steps:
- Forming a question
- Performing background research
- Creating a hypothesis
- Designing an experiment
- Collecting data
- Analyzing the results
- Drawing conclusions
- Communicating the results
The hypothesis is a prediction, but it involves more than a guess. Most of the time, the hypothesis begins with a question which is then explored through background research. At this point, researchers then begin to develop a testable hypothesis.
Unless you are creating an exploratory study, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen.
In a study exploring the effects of a particular drug, the hypothesis might be that researchers expect the drug to have some type of effect on the symptoms of a specific illness. In psychology, the hypothesis might focus on how a certain aspect of the environment might influence a particular behavior.
Remember, a hypothesis does not have to be correct. While the hypothesis predicts what the researchers expect to see, the goal of the research is to determine whether this guess is right or wrong. When conducting an experiment, researchers might explore numerous factors to determine which ones might contribute to the ultimate outcome.
In many cases, researchers may find that the results of an experiment do not support the original hypothesis. When writing up these results, the researchers might suggest other options that should be explored in future studies.
In many cases, researchers might draw a hypothesis from a specific theory or build on previous research. For example, prior research has shown that stress can impact the immune system. So a researcher might hypothesize: "People with high-stress levels will be more likely to contract a common cold after being exposed to the virus than people who have low-stress levels."
In other instances, researchers might look at commonly held beliefs or folk wisdom. "Birds of a feather flock together" is one example of folk adage that a psychologist might try to investigate. The researcher might pose a specific hypothesis that "People tend to select romantic partners who are similar to them in interests and educational level."
Elements of a Good Hypothesis
So how do you write a good hypothesis? When trying to come up with a hypothesis for your research or experiments, ask yourself the following questions:
- Is your hypothesis based on your research on a topic?
- Can your hypothesis be tested?
- Does your hypothesis include independent and dependent variables?
Before you come up with a specific hypothesis, spend some time doing background research. Once you have completed a literature review, start thinking about potential questions you still have. Pay attention to the discussion section in the journal articles you read . Many authors will suggest questions that still need to be explored.
How to Formulate a Good Hypothesis
To form a hypothesis, you should take these steps:
- Collect as many observations about a topic or problem as you can.
- Evaluate these observations and look for possible causes of the problem.
- Create a list of possible explanations that you might want to explore.
- After you have developed some possible hypotheses, think of ways that you could confirm or disprove each hypothesis through experimentation. This is known as falsifiability.
In the scientific method , falsifiability is an important part of any valid hypothesis. In order to test a claim scientifically, it must be possible that the claim could be proven false.
Students sometimes confuse the idea of falsifiability with the idea that it means that something is false, which is not the case. What falsifiability means is that if something was false, then it is possible to demonstrate that it is false.
One of the hallmarks of pseudoscience is that it makes claims that cannot be refuted or proven false.
The Importance of Operational Definitions
A variable is a factor or element that can be changed and manipulated in ways that are observable and measurable. However, the researcher must also define how the variable will be manipulated and measured in the study.
Operational definitions are specific definitions for all relevant factors in a study. This process helps make vague or ambiguous concepts detailed and measurable.
For example, a researcher might operationally define the variable " test anxiety " as the results of a self-report measure of anxiety experienced during an exam. A "study habits" variable might be defined by the amount of studying that actually occurs as measured by time.
These precise descriptions are important because many things can be measured in various ways. Clearly defining these variables and how they are measured helps ensure that other researchers can replicate your results.
Replicability
One of the basic principles of any type of scientific research is that the results must be replicable.
Replication means repeating an experiment in the same way to produce the same results. By clearly detailing the specifics of how the variables were measured and manipulated, other researchers can better understand the results and repeat the study if needed.
Some variables are more difficult than others to define. For example, how would you operationally define a variable such as aggression ? For obvious ethical reasons, researchers cannot create a situation in which a person behaves aggressively toward others.
To measure this variable, the researcher must devise a measurement that assesses aggressive behavior without harming others. The researcher might utilize a simulated task to measure aggressiveness in this situation.
Hypothesis Checklist
- Does your hypothesis focus on something that you can actually test?
- Does your hypothesis include both an independent and dependent variable?
- Can you manipulate the variables?
- Can your hypothesis be tested without violating ethical standards?
The hypothesis you use will depend on what you are investigating and hoping to find. Some of the main types of hypotheses that you might use include:
- Simple hypothesis : This type of hypothesis suggests there is a relationship between one independent variable and one dependent variable.
- Complex hypothesis : This type suggests a relationship between three or more variables, such as two independent and dependent variables.
- Null hypothesis : This hypothesis suggests no relationship exists between two or more variables.
- Alternative hypothesis : This hypothesis states the opposite of the null hypothesis.
- Statistical hypothesis : This hypothesis uses statistical analysis to evaluate a representative population sample and then generalizes the findings to the larger group.
- Logical hypothesis : This hypothesis assumes a relationship between variables without collecting data or evidence.
A hypothesis often follows a basic format of "If {this happens} then {this will happen}." One way to structure your hypothesis is to describe what will happen to the dependent variable if you change the independent variable .
The basic format might be: "If {these changes are made to a certain independent variable}, then we will observe {a change in a specific dependent variable}."
A few examples of simple hypotheses:
- "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast."
- "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
- "Motorists who talk on the phone while driving will be more likely to make errors on a driving course than those who do not talk on the phone."
- "Children who receive a new reading intervention will have higher reading scores than students who do not receive the intervention."
Examples of a complex hypothesis include:
- "People with high-sugar diets and sedentary activity levels are more likely to develop depression."
- "Younger people who are regularly exposed to green, outdoor areas have better subjective well-being than older adults who have limited exposure to green spaces."
Examples of a null hypothesis include:
- "There is no difference in anxiety levels between people who take St. John's wort supplements and those who do not."
- "There is no difference in scores on a memory recall task between children and adults."
- "There is no difference in aggression levels between children who play first-person shooter games and those who do not."
Examples of an alternative hypothesis:
- "People who take St. John's wort supplements will have less anxiety than those who do not."
- "Adults will perform better on a memory task than children."
- "Children who play first-person shooter games will show higher levels of aggression than children who do not."
Collecting Data on Your Hypothesis
Once a researcher has formed a testable hypothesis, the next step is to select a research design and start collecting data. The research method depends largely on exactly what they are studying. There are two basic types of research methods: descriptive research and experimental research.
Descriptive Research Methods
Descriptive research such as case studies , naturalistic observations , and surveys are often used when conducting an experiment is difficult or impossible. These methods are best used to describe different aspects of a behavior or psychological phenomenon.
Once a researcher has collected data using descriptive methods, a correlational study can examine how the variables are related. This research method might be used to investigate a hypothesis that is difficult to test experimentally.
Experimental Research Methods
Experimental methods are used to demonstrate causal relationships between variables. In an experiment, the researcher systematically manipulates a variable of interest (known as the independent variable) and measures the effect on another variable (known as the dependent variable).
Unlike correlational studies, which can only be used to determine if there is a relationship between two variables, experimental methods can be used to determine the actual nature of the relationship—whether changes in one variable actually cause another to change.
The hypothesis is a critical part of any scientific exploration. It represents what researchers expect to find in a study or experiment. In situations where the hypothesis is unsupported by the research, the research still has value. Such research helps us better understand how different aspects of the natural world relate to one another. It also helps us develop new hypotheses that can then be tested in the future.
Thompson WH, Skau S. On the scope of scientific hypotheses . R Soc Open Sci . 2023;10(8):230607. doi:10.1098/rsos.230607
Taran S, Adhikari NKJ, Fan E. Falsifiability in medicine: what clinicians can learn from Karl Popper [published correction appears in Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jun 17;:]. Intensive Care Med . 2021;47(9):1054-1056. doi:10.1007/s00134-021-06432-z
Eyler AA. Research Methods for Public Health . 1st ed. Springer Publishing Company; 2020. doi:10.1891/9780826182067.0004
Nosek BA, Errington TM. What is replication ? PLoS Biol . 2020;18(3):e3000691. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000691
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P. Study designs: Part 2 - Descriptive studies . Perspect Clin Res . 2019;10(1):34-36. doi:10.4103/picr.PICR_154_18
Nevid J. Psychology: Concepts and Applications. Wadworth, 2013.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
What Is A Research (Scientific) Hypothesis? A plain-language explainer + examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
If you’re new to the world of research, or it’s your first time writing a dissertation or thesis, you’re probably noticing that the words “research hypothesis” and “scientific hypothesis” are used quite a bit, and you’re wondering what they mean in a research context .
“Hypothesis” is one of those words that people use loosely, thinking they understand what it means. However, it has a very specific meaning within academic research. So, it’s important to understand the exact meaning before you start hypothesizing.
Research Hypothesis 101
- What is a hypothesis ?
- What is a research hypothesis (scientific hypothesis)?
- Requirements for a research hypothesis
- Definition of a research hypothesis
- The null hypothesis
What is a hypothesis?
Let’s start with the general definition of a hypothesis (not a research hypothesis or scientific hypothesis), according to the Cambridge Dictionary:
Hypothesis: an idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved.
In other words, it’s a statement that provides an explanation for why or how something works, based on facts (or some reasonable assumptions), but that has not yet been specifically tested . For example, a hypothesis might look something like this:
Hypothesis: sleep impacts academic performance.
This statement predicts that academic performance will be influenced by the amount and/or quality of sleep a student engages in – sounds reasonable, right? It’s based on reasonable assumptions , underpinned by what we currently know about sleep and health (from the existing literature). So, loosely speaking, we could call it a hypothesis, at least by the dictionary definition.
But that’s not good enough…
Unfortunately, that’s not quite sophisticated enough to describe a research hypothesis (also sometimes called a scientific hypothesis), and it wouldn’t be acceptable in a dissertation, thesis or research paper . In the world of academic research, a statement needs a few more criteria to constitute a true research hypothesis .
What is a research hypothesis?
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes – specificity , clarity and testability .
Let’s take a look at these more closely.
Need a helping hand?
Hypothesis Essential #1: Specificity & Clarity
A good research hypothesis needs to be extremely clear and articulate about both what’ s being assessed (who or what variables are involved ) and the expected outcome (for example, a difference between groups, a relationship between variables, etc.).
Let’s stick with our sleepy students example and look at how this statement could be more specific and clear.
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
As you can see, the statement is very specific as it identifies the variables involved (sleep hours and test grades), the parties involved (two groups of students), as well as the predicted relationship type (a positive relationship). There’s no ambiguity or uncertainty about who or what is involved in the statement, and the expected outcome is clear.
Contrast that to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – and you can see the difference. “Sleep” and “academic performance” are both comparatively vague , and there’s no indication of what the expected relationship direction is (more sleep or less sleep). As you can see, specificity and clarity are key.

Hypothesis Essential #2: Testability (Provability)
A statement must be testable to qualify as a research hypothesis. In other words, there needs to be a way to prove (or disprove) the statement. If it’s not testable, it’s not a hypothesis – simple as that.
For example, consider the hypothesis we mentioned earlier:
Hypothesis: Students who sleep at least 8 hours per night will, on average, achieve higher grades in standardised tests than students who sleep less than 8 hours a night.
We could test this statement by undertaking a quantitative study involving two groups of students, one that gets 8 or more hours of sleep per night for a fixed period, and one that gets less. We could then compare the standardised test results for both groups to see if there’s a statistically significant difference.
Again, if you compare this to the original hypothesis we looked at – “Sleep impacts academic performance” – you can see that it would be quite difficult to test that statement, primarily because it isn’t specific enough. How much sleep? By who? What type of academic performance?
So, remember the mantra – if you can’t test it, it’s not a hypothesis 🙂

Defining A Research Hypothesis
You’re still with us? Great! Let’s recap and pin down a clear definition of a hypothesis.
A research hypothesis (or scientific hypothesis) is a statement about an expected relationship between variables, or explanation of an occurrence, that is clear, specific and testable.
So, when you write up hypotheses for your dissertation or thesis, make sure that they meet all these criteria. If you do, you’ll not only have rock-solid hypotheses but you’ll also ensure a clear focus for your entire research project.
What about the null hypothesis?
You may have also heard the terms null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis, or H-zero thrown around. At a simple level, the null hypothesis is the counter-proposal to the original hypothesis.
For example, if the hypothesis predicts that there is a relationship between two variables (for example, sleep and academic performance), the null hypothesis would predict that there is no relationship between those variables.
At a more technical level, the null hypothesis proposes that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations and that any differences are due to chance alone.
And there you have it – hypotheses in a nutshell.
If you have any questions, be sure to leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to help you. If you need hands-on help developing and testing your hypotheses, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research journey.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

16 Comments
Very useful information. I benefit more from getting more information in this regard.
Very great insight,educative and informative. Please give meet deep critics on many research data of public international Law like human rights, environment, natural resources, law of the sea etc
In a book I read a distinction is made between null, research, and alternative hypothesis. As far as I understand, alternative and research hypotheses are the same. Can you please elaborate? Best Afshin
This is a self explanatory, easy going site. I will recommend this to my friends and colleagues.
Very good definition. How can I cite your definition in my thesis? Thank you. Is nul hypothesis compulsory in a research?
It’s a counter-proposal to be proven as a rejection
Please what is the difference between alternate hypothesis and research hypothesis?
It is a very good explanation. However, it limits hypotheses to statistically tasteable ideas. What about for qualitative researches or other researches that involve quantitative data that don’t need statistical tests?
In qualitative research, one typically uses propositions, not hypotheses.
could you please elaborate it more
I’ve benefited greatly from these notes, thank you.
This is very helpful
well articulated ideas are presented here, thank you for being reliable sources of information
Excellent. Thanks for being clear and sound about the research methodology and hypothesis (quantitative research)
I have only a simple question regarding the null hypothesis. – Is the null hypothesis (Ho) known as the reversible hypothesis of the alternative hypothesis (H1? – How to test it in academic research?
this is very important note help me much more
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is Research Methodology? Simple Definition (With Examples) - Grad Coach - […] Contrasted to this, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research aims and objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example,…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of hypothesis
Did you know.
The Difference Between Hypothesis and Theory
A hypothesis is an assumption, an idea that is proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
In the scientific method, the hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done, apart from a basic background review. You ask a question, read up on what has been studied before, and then form a hypothesis.
A hypothesis is usually tentative; it's an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
A theory , in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory . Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, it is understood to be more likely to be true than a hypothesis is.
In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch, with theory being the more common choice.
Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theory are prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories.
The most common occurrence is when theory is interpreted—and sometimes even gleefully seized upon—to mean something having less truth value than other scientific principles. (The word law applies to principles so firmly established that they are almost never questioned, such as the law of gravity.)
This mistake is one of projection: since we use theory in general to mean something lightly speculated, then it's implied that scientists must be talking about the same level of uncertainty when they use theory to refer to their well-tested and reasoned principles.
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said , a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
- proposition
- supposition
hypothesis , theory , law mean a formula derived by inference from scientific data that explains a principle operating in nature.
hypothesis implies insufficient evidence to provide more than a tentative explanation.
theory implies a greater range of evidence and greater likelihood of truth.
law implies a statement of order and relation in nature that has been found to be invariable under the same conditions.
Examples of hypothesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'hypothesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
Greek, from hypotithenai to put under, suppose, from hypo- + tithenai to put — more at do
1641, in the meaning defined at sense 1a
Phrases Containing hypothesis
- counter - hypothesis
- nebular hypothesis
- null hypothesis
- planetesimal hypothesis
- Whorfian hypothesis
Articles Related to hypothesis

This is the Difference Between a...
This is the Difference Between a Hypothesis and a Theory
In scientific reasoning, they're two completely different things
Dictionary Entries Near hypothesis
hypothermia
hypothesize
Cite this Entry
“Hypothesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/hypothesis. Accessed 1 May. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of hypothesis, medical definition, medical definition of hypothesis, more from merriam-webster on hypothesis.
Nglish: Translation of hypothesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of hypothesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about hypothesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, commonly misspelled words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, how to use accents and diacritical marks, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 26, 9 superb owl words, 'gaslighting,' 'woke,' 'democracy,' and other top lookups, 10 words for lesser-known games and sports, your favorite band is in the dictionary, games & quizzes.

- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

The Craft of Writing a Strong Hypothesis

Table of Contents
Writing a hypothesis is one of the essential elements of a scientific research paper. It needs to be to the point, clearly communicating what your research is trying to accomplish. A blurry, drawn-out, or complexly-structured hypothesis can confuse your readers. Or worse, the editor and peer reviewers.
A captivating hypothesis is not too intricate. This blog will take you through the process so that, by the end of it, you have a better idea of how to convey your research paper's intent in just one sentence.
What is a Hypothesis?
The first step in your scientific endeavor, a hypothesis, is a strong, concise statement that forms the basis of your research. It is not the same as a thesis statement , which is a brief summary of your research paper .
The sole purpose of a hypothesis is to predict your paper's findings, data, and conclusion. It comes from a place of curiosity and intuition . When you write a hypothesis, you're essentially making an educated guess based on scientific prejudices and evidence, which is further proven or disproven through the scientific method.
The reason for undertaking research is to observe a specific phenomenon. A hypothesis, therefore, lays out what the said phenomenon is. And it does so through two variables, an independent and dependent variable.
The independent variable is the cause behind the observation, while the dependent variable is the effect of the cause. A good example of this is “mixing red and blue forms purple.” In this hypothesis, mixing red and blue is the independent variable as you're combining the two colors at your own will. The formation of purple is the dependent variable as, in this case, it is conditional to the independent variable.
Different Types of Hypotheses

Types of hypotheses
Some would stand by the notion that there are only two types of hypotheses: a Null hypothesis and an Alternative hypothesis. While that may have some truth to it, it would be better to fully distinguish the most common forms as these terms come up so often, which might leave you out of context.
Apart from Null and Alternative, there are Complex, Simple, Directional, Non-Directional, Statistical, and Associative and casual hypotheses. They don't necessarily have to be exclusive, as one hypothesis can tick many boxes, but knowing the distinctions between them will make it easier for you to construct your own.
1. Null hypothesis
A null hypothesis proposes no relationship between two variables. Denoted by H 0 , it is a negative statement like “Attending physiotherapy sessions does not affect athletes' on-field performance.” Here, the author claims physiotherapy sessions have no effect on on-field performances. Even if there is, it's only a coincidence.
2. Alternative hypothesis
Considered to be the opposite of a null hypothesis, an alternative hypothesis is donated as H1 or Ha. It explicitly states that the dependent variable affects the independent variable. A good alternative hypothesis example is “Attending physiotherapy sessions improves athletes' on-field performance.” or “Water evaporates at 100 °C. ” The alternative hypothesis further branches into directional and non-directional.
- Directional hypothesis: A hypothesis that states the result would be either positive or negative is called directional hypothesis. It accompanies H1 with either the ‘<' or ‘>' sign.
- Non-directional hypothesis: A non-directional hypothesis only claims an effect on the dependent variable. It does not clarify whether the result would be positive or negative. The sign for a non-directional hypothesis is ‘≠.'
3. Simple hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, “Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking.
4. Complex hypothesis
In contrast to a simple hypothesis, a complex hypothesis implies the relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. For instance, “Individuals who eat more fruits tend to have higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.” The independent variable is eating more fruits, while the dependent variables are higher immunity, lesser cholesterol, and high metabolism.
5. Associative and casual hypothesis
Associative and casual hypotheses don't exhibit how many variables there will be. They define the relationship between the variables. In an associative hypothesis, changing any one variable, dependent or independent, affects others. In a casual hypothesis, the independent variable directly affects the dependent.
6. Empirical hypothesis
Also referred to as the working hypothesis, an empirical hypothesis claims a theory's validation via experiments and observation. This way, the statement appears justifiable and different from a wild guess.
Say, the hypothesis is “Women who take iron tablets face a lesser risk of anemia than those who take vitamin B12.” This is an example of an empirical hypothesis where the researcher the statement after assessing a group of women who take iron tablets and charting the findings.
7. Statistical hypothesis
The point of a statistical hypothesis is to test an already existing hypothesis by studying a population sample. Hypothesis like “44% of the Indian population belong in the age group of 22-27.” leverage evidence to prove or disprove a particular statement.
Characteristics of a Good Hypothesis
Writing a hypothesis is essential as it can make or break your research for you. That includes your chances of getting published in a journal. So when you're designing one, keep an eye out for these pointers:
- A research hypothesis has to be simple yet clear to look justifiable enough.
- It has to be testable — your research would be rendered pointless if too far-fetched into reality or limited by technology.
- It has to be precise about the results —what you are trying to do and achieve through it should come out in your hypothesis.
- A research hypothesis should be self-explanatory, leaving no doubt in the reader's mind.
- If you are developing a relational hypothesis, you need to include the variables and establish an appropriate relationship among them.
- A hypothesis must keep and reflect the scope for further investigations and experiments.
Separating a Hypothesis from a Prediction
Outside of academia, hypothesis and prediction are often used interchangeably. In research writing, this is not only confusing but also incorrect. And although a hypothesis and prediction are guesses at their core, there are many differences between them.
A hypothesis is an educated guess or even a testable prediction validated through research. It aims to analyze the gathered evidence and facts to define a relationship between variables and put forth a logical explanation behind the nature of events.
Predictions are assumptions or expected outcomes made without any backing evidence. They are more fictionally inclined regardless of where they originate from.
For this reason, a hypothesis holds much more weight than a prediction. It sticks to the scientific method rather than pure guesswork. "Planets revolve around the Sun." is an example of a hypothesis as it is previous knowledge and observed trends. Additionally, we can test it through the scientific method.
Whereas "COVID-19 will be eradicated by 2030." is a prediction. Even though it results from past trends, we can't prove or disprove it. So, the only way this gets validated is to wait and watch if COVID-19 cases end by 2030.
Finally, How to Write a Hypothesis

Quick tips on writing a hypothesis
1. Be clear about your research question
A hypothesis should instantly address the research question or the problem statement. To do so, you need to ask a question. Understand the constraints of your undertaken research topic and then formulate a simple and topic-centric problem. Only after that can you develop a hypothesis and further test for evidence.
2. Carry out a recce
Once you have your research's foundation laid out, it would be best to conduct preliminary research. Go through previous theories, academic papers, data, and experiments before you start curating your research hypothesis. It will give you an idea of your hypothesis's viability or originality.
Making use of references from relevant research papers helps draft a good research hypothesis. SciSpace Discover offers a repository of over 270 million research papers to browse through and gain a deeper understanding of related studies on a particular topic. Additionally, you can use SciSpace Copilot , your AI research assistant, for reading any lengthy research paper and getting a more summarized context of it. A hypothesis can be formed after evaluating many such summarized research papers. Copilot also offers explanations for theories and equations, explains paper in simplified version, allows you to highlight any text in the paper or clip math equations and tables and provides a deeper, clear understanding of what is being said. This can improve the hypothesis by helping you identify potential research gaps.
3. Create a 3-dimensional hypothesis
Variables are an essential part of any reasonable hypothesis. So, identify your independent and dependent variable(s) and form a correlation between them. The ideal way to do this is to write the hypothetical assumption in the ‘if-then' form. If you use this form, make sure that you state the predefined relationship between the variables.
In another way, you can choose to present your hypothesis as a comparison between two variables. Here, you must specify the difference you expect to observe in the results.
4. Write the first draft
Now that everything is in place, it's time to write your hypothesis. For starters, create the first draft. In this version, write what you expect to find from your research.
Clearly separate your independent and dependent variables and the link between them. Don't fixate on syntax at this stage. The goal is to ensure your hypothesis addresses the issue.
5. Proof your hypothesis
After preparing the first draft of your hypothesis, you need to inspect it thoroughly. It should tick all the boxes, like being concise, straightforward, relevant, and accurate. Your final hypothesis has to be well-structured as well.
Research projects are an exciting and crucial part of being a scholar. And once you have your research question, you need a great hypothesis to begin conducting research. Thus, knowing how to write a hypothesis is very important.
Now that you have a firmer grasp on what a good hypothesis constitutes, the different kinds there are, and what process to follow, you will find it much easier to write your hypothesis, which ultimately helps your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace Discover . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
It includes everything you need, including a repository of over 270 million research papers across disciplines, SEO-optimized summaries and public profiles to show your expertise and experience.
If you found these tips on writing a research hypothesis useful, head over to our blog on Statistical Hypothesis Testing to learn about the top researchers, papers, and institutions in this domain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what is the definition of hypothesis.
According to the Oxford dictionary, a hypothesis is defined as “An idea or explanation of something that is based on a few known facts, but that has not yet been proved to be true or correct”.
2. What is an example of hypothesis?
The hypothesis is a statement that proposes a relationship between two or more variables. An example: "If we increase the number of new users who join our platform by 25%, then we will see an increase in revenue."
3. What is an example of null hypothesis?
A null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between two variables. The null hypothesis is written as H0. The null hypothesis states that there is no effect. For example, if you're studying whether or not a particular type of exercise increases strength, your null hypothesis will be "there is no difference in strength between people who exercise and people who don't."
4. What are the types of research?
• Fundamental research
• Applied research
• Qualitative research
• Quantitative research
• Mixed research
• Exploratory research
• Longitudinal research
• Cross-sectional research
• Field research
• Laboratory research
• Fixed research
• Flexible research
• Action research
• Policy research
• Classification research
• Comparative research
• Causal research
• Inductive research
• Deductive research
5. How to write a hypothesis?
• Your hypothesis should be able to predict the relationship and outcome.
• Avoid wordiness by keeping it simple and brief.
• Your hypothesis should contain observable and testable outcomes.
• Your hypothesis should be relevant to the research question.
6. What are the 2 types of hypothesis?
• Null hypotheses are used to test the claim that "there is no difference between two groups of data".
• Alternative hypotheses test the claim that "there is a difference between two data groups".
7. Difference between research question and research hypothesis?
A research question is a broad, open-ended question you will try to answer through your research. A hypothesis is a statement based on prior research or theory that you expect to be true due to your study. Example - Research question: What are the factors that influence the adoption of the new technology? Research hypothesis: There is a positive relationship between age, education and income level with the adoption of the new technology.
8. What is plural for hypothesis?
The plural of hypothesis is hypotheses. Here's an example of how it would be used in a statement, "Numerous well-considered hypotheses are presented in this part, and they are supported by tables and figures that are well-illustrated."
9. What is the red queen hypothesis?
The red queen hypothesis in evolutionary biology states that species must constantly evolve to avoid extinction because if they don't, they will be outcompeted by other species that are evolving. Leigh Van Valen first proposed it in 1973; since then, it has been tested and substantiated many times.
10. Who is known as the father of null hypothesis?
The father of the null hypothesis is Sir Ronald Fisher. He published a paper in 1925 that introduced the concept of null hypothesis testing, and he was also the first to use the term itself.
11. When to reject null hypothesis?
You need to find a significant difference between your two populations to reject the null hypothesis. You can determine that by running statistical tests such as an independent sample t-test or a dependent sample t-test. You should reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than 0.05.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Research Hypothesis In Psychology: Types, & Examples
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
A research hypothesis, in its plural form “hypotheses,” is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method .
Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding
Some key points about hypotheses:
- A hypothesis expresses an expected pattern or relationship. It connects the variables under investigation.
- It is stated in clear, precise terms before any data collection or analysis occurs. This makes the hypothesis testable.
- A hypothesis must be falsifiable. It should be possible, even if unlikely in practice, to collect data that disconfirms rather than supports the hypothesis.
- Hypotheses guide research. Scientists design studies to explicitly evaluate hypotheses about how nature works.
- For a hypothesis to be valid, it must be testable against empirical evidence. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
- Hypotheses are informed by background knowledge and observation, but go beyond what is already known to propose an explanation of how or why something occurs.
Predictions typically arise from a thorough knowledge of the research literature, curiosity about real-world problems or implications, and integrating this to advance theory. They build on existing literature while providing new insight.
Types of Research Hypotheses
Alternative hypothesis.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative or experimental hypothesis in experimental research.
It typically suggests a potential relationship between two key variables: the independent variable, which the researcher manipulates, and the dependent variable, which is measured based on those changes.
The alternative hypothesis states a relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable affects the other).
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a key component of the scientific method. Some key points about hypotheses:
- Important hypotheses lead to predictions that can be tested empirically. The evidence can then confirm or disprove the testable predictions.
In summary, a hypothesis is a precise, testable statement of what researchers expect to happen in a study and why. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
An experimental hypothesis predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and are significant in supporting the theory being investigated.
The alternative hypothesis can be directional, indicating a specific direction of the effect, or non-directional, suggesting a difference without specifying its nature. It’s what researchers aim to support or demonstrate through their study.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states no relationship exists between the two variables being studied (one variable does not affect the other). There will be no changes in the dependent variable due to manipulating the independent variable.
It states results are due to chance and are not significant in supporting the idea being investigated.
The null hypothesis, positing no effect or relationship, is a foundational contrast to the research hypothesis in scientific inquiry. It establishes a baseline for statistical testing, promoting objectivity by initiating research from a neutral stance.
Many statistical methods are tailored to test the null hypothesis, determining the likelihood of observed results if no true effect exists.
This dual-hypothesis approach provides clarity, ensuring that research intentions are explicit, and fosters consistency across scientific studies, enhancing the standardization and interpretability of research outcomes.
Nondirectional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis, also known as a two-tailed hypothesis, predicts that there is a difference or relationship between two variables but does not specify the direction of this relationship.
It merely indicates that a change or effect will occur without predicting which group will have higher or lower values.
For example, “There is a difference in performance between Group A and Group B” is a non-directional hypothesis.
Directional Hypothesis
A directional (one-tailed) hypothesis predicts the nature of the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. It predicts in which direction the change will take place. (i.e., greater, smaller, less, more)
It specifies whether one variable is greater, lesser, or different from another, rather than just indicating that there’s a difference without specifying its nature.
For example, “Exercise increases weight loss” is a directional hypothesis.
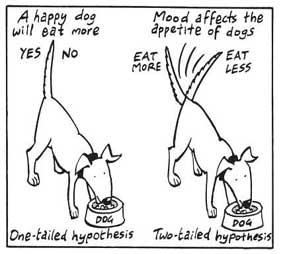
Falsifiability
The Falsification Principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory or hypothesis to be considered scientific, it must be testable and irrefutable.
Falsifiability emphasizes that scientific claims shouldn’t just be confirmable but should also have the potential to be proven wrong.
It means that there should exist some potential evidence or experiment that could prove the proposition false.
However many confirming instances exist for a theory, it only takes one counter observation to falsify it. For example, the hypothesis that “all swans are white,” can be falsified by observing a black swan.
For Popper, science should attempt to disprove a theory rather than attempt to continually provide evidence to support a research hypothesis.
Can a Hypothesis be Proven?
Hypotheses make probabilistic predictions. They state the expected outcome if a particular relationship exists. However, a study result supporting a hypothesis does not definitively prove it is true.
All studies have limitations. There may be unknown confounding factors or issues that limit the certainty of conclusions. Additional studies may yield different results.
In science, hypotheses can realistically only be supported with some degree of confidence, not proven. The process of science is to incrementally accumulate evidence for and against hypothesized relationships in an ongoing pursuit of better models and explanations that best fit the empirical data. But hypotheses remain open to revision and rejection if that is where the evidence leads.
- Disproving a hypothesis is definitive. Solid disconfirmatory evidence will falsify a hypothesis and require altering or discarding it based on the evidence.
- However, confirming evidence is always open to revision. Other explanations may account for the same results, and additional or contradictory evidence may emerge over time.
We can never 100% prove the alternative hypothesis. Instead, we see if we can disprove, or reject the null hypothesis.
If we reject the null hypothesis, this doesn’t mean that our alternative hypothesis is correct but does support the alternative/experimental hypothesis.
Upon analysis of the results, an alternative hypothesis can be rejected or supported, but it can never be proven to be correct. We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist which could refute a theory.
How to Write a Hypothesis
- Identify variables . The researcher manipulates the independent variable and the dependent variable is the measured outcome.
- Operationalized the variables being investigated . Operationalization of a hypothesis refers to the process of making the variables physically measurable or testable, e.g. if you are about to study aggression, you might count the number of punches given by participants.
- Decide on a direction for your prediction . If there is evidence in the literature to support a specific effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a directional (one-tailed) hypothesis. If there are limited or ambiguous findings in the literature regarding the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable, write a non-directional (two-tailed) hypothesis.
- Make it Testable : Ensure your hypothesis can be tested through experimentation or observation. It should be possible to prove it false (principle of falsifiability).
- Clear & concise language . A strong hypothesis is concise (typically one to two sentences long), and formulated using clear and straightforward language, ensuring it’s easily understood and testable.
Consider a hypothesis many teachers might subscribe to: students work better on Monday morning than on Friday afternoon (IV=Day, DV= Standard of work).
Now, if we decide to study this by giving the same group of students a lesson on a Monday morning and a Friday afternoon and then measuring their immediate recall of the material covered in each session, we would end up with the following:
- The alternative hypothesis states that students will recall significantly more information on a Monday morning than on a Friday afternoon.
- The null hypothesis states that there will be no significant difference in the amount recalled on a Monday morning compared to a Friday afternoon. Any difference will be due to chance or confounding factors.
More Examples
- Memory : Participants exposed to classical music during study sessions will recall more items from a list than those who studied in silence.
- Social Psychology : Individuals who frequently engage in social media use will report higher levels of perceived social isolation compared to those who use it infrequently.
- Developmental Psychology : Children who engage in regular imaginative play have better problem-solving skills than those who don’t.
- Clinical Psychology : Cognitive-behavioral therapy will be more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety over a 6-month period compared to traditional talk therapy.
- Cognitive Psychology : Individuals who multitask between various electronic devices will have shorter attention spans on focused tasks than those who single-task.
- Health Psychology : Patients who practice mindfulness meditation will experience lower levels of chronic pain compared to those who don’t meditate.
- Organizational Psychology : Employees in open-plan offices will report higher levels of stress than those in private offices.
- Behavioral Psychology : Rats rewarded with food after pressing a lever will press it more frequently than rats who receive no reward.
- Maths Notes Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- RD Sharma Solutions Class 12
- Maths Formulas Class 12
- Maths Previous Year Paper Class 12
- Class 12 Syllabus
- Class 12 Revision Notes
- Physics Notes Class 12
- Chemistry Notes Class 12
- Biology Notes Class 12
- Null Hypothesis
- Hypothesis Testing Formula
- Difference Between Hypothesis And Theory
- Real-life Applications of Hypothesis Testing
- Permutation Hypothesis Test in R Programming
- Bayes' Theorem
- Hypothesis in Machine Learning
- Current Best Hypothesis Search
- Understanding Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis Testing in R Programming
- Jobathon | Stats | Question 10
- Jobathon | Stats | Question 17
- Testing | Question 1
- Difference between Null and Alternate Hypothesis
- ML | Find S Algorithm
- Python - Pearson's Chi-Square Test
- Libraries in Python
- How to Connect Python with SQL Database?
- Reading Rows from a CSV File in Python
- Data Communication - Definition, Components, Types, Channels
- Logic Gates - Definition, Types, Uses
- What is an IP Address?
- SQL HAVING Clause with Examples
- Business Studies
- Sorting Algorithms in Python
Hypothesis is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables. Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion. Hypothesis creates a structure that guides the search for knowledge.
In this article, we will learn what is hypothesis, its characteristics, types, and examples. We will also learn how hypothesis helps in scientific research.

What is Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a suggested idea or plan that has little proof, meant to lead to more study. It’s mainly a smart guess or suggested answer to a problem that can be checked through study and trial. In science work, we make guesses called hypotheses to try and figure out what will happen in tests or watching. These are not sure things but rather ideas that can be proved or disproved based on real-life proofs. A good theory is clear and can be tested and found wrong if the proof doesn’t support it.
Hypothesis Meaning
A hypothesis is a proposed statement that is testable and is given for something that happens or observed.
- It is made using what we already know and have seen, and it’s the basis for scientific research.
- A clear guess tells us what we think will happen in an experiment or study.
- It’s a testable clue that can be proven true or wrong with real-life facts and checking it out carefully.
- It usually looks like a “if-then” rule, showing the expected cause and effect relationship between what’s being studied.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Here are some key characteristics of a hypothesis:
- Testable: An idea (hypothesis) should be made so it can be tested and proven true through doing experiments or watching. It should show a clear connection between things.
- Specific: It needs to be easy and on target, talking about a certain part or connection between things in a study.
- Falsifiable: A good guess should be able to show it’s wrong. This means there must be a chance for proof or seeing something that goes against the guess.
- Logical and Rational: It should be based on things we know now or have seen, giving a reasonable reason that fits with what we already know.
- Predictive: A guess often tells what to expect from an experiment or observation. It gives a guide for what someone might see if the guess is right.
- Concise: It should be short and clear, showing the suggested link or explanation simply without extra confusion.
- Grounded in Research: A guess is usually made from before studies, ideas or watching things. It comes from a deep understanding of what is already known in that area.
- Flexible: A guess helps in the research but it needs to change or fix when new information comes up.
- Relevant: It should be related to the question or problem being studied, helping to direct what the research is about.
- Empirical: Hypotheses come from observations and can be tested using methods based on real-world experiences.

Sources of Hypothesis
Hypotheses can come from different places based on what you’re studying and the kind of research. Here are some common sources from which hypotheses may originate:
- Existing Theories: Often, guesses come from well-known science ideas. These ideas may show connections between things or occurrences that scientists can look into more.
- Observation and Experience: Watching something happen or having personal experiences can lead to guesses. We notice odd things or repeat events in everyday life and experiments. This can make us think of guesses called hypotheses.
- Previous Research: Using old studies or discoveries can help come up with new ideas. Scientists might try to expand or question current findings, making guesses that further study old results.
- Literature Review: Looking at books and research in a subject can help make guesses. Noticing missing parts or mismatches in previous studies might make researchers think up guesses to deal with these spots.
- Problem Statement or Research Question: Often, ideas come from questions or problems in the study. Making clear what needs to be looked into can help create ideas that tackle certain parts of the issue.
- Analogies or Comparisons: Making comparisons between similar things or finding connections from related areas can lead to theories. Understanding from other fields could create new guesses in a different situation.
- Hunches and Speculation: Sometimes, scientists might get a gut feeling or make guesses that help create ideas to test. Though these may not have proof at first, they can be a beginning for looking deeper.
- Technology and Innovations: New technology or tools might make guesses by letting us look at things that were hard to study before.
- Personal Interest and Curiosity: People’s curiosity and personal interests in a topic can help create guesses. Scientists could make guesses based on their own likes or love for a subject.
Types of Hypothesis
Here are some common types of hypotheses:
Simple Hypothesis
Complex hypothesis, directional hypothesis.
- Non-directional Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis (H0)
Alternative hypothesis (h1 or ha), statistical hypothesis, research hypothesis, associative hypothesis, causal hypothesis.
Simple Hypothesis guesses a connection between two things. It says that there is a connection or difference between variables, but it doesn’t tell us which way the relationship goes.
Complex Hypothesis tells us what will happen when more than two things are connected. It looks at how different things interact and may be linked together.
Directional Hypothesis says how one thing is related to another. For example, it guesses that one thing will help or hurt another thing.
Non-Directional Hypothesis
Non-Directional Hypothesis are the one that don’t say how the relationship between things will be. They just say that there is a connection, without telling which way it goes.
Null hypothesis is a statement that says there’s no connection or difference between different things. It implies that any seen impacts are because of luck or random changes in the information.
Alternative Hypothesis is different from the null hypothesis and shows that there’s a big connection or gap between variables. Scientists want to say no to the null hypothesis and choose the alternative one.
Statistical Hypotheis are used in math testing and include making ideas about what groups or bits of them look like. You aim to get information or test certain things using these top-level, common words only.
Research Hypothesis comes from the research question and tells what link is expected between things or factors. It leads the study and chooses where to look more closely.
Associative Hypotheis guesses that there is a link or connection between things without really saying it caused them. It means that when one thing changes, it is connected to another thing changing.
Causal Hypothesis are different from other ideas because they say that one thing causes another. This means there’s a cause and effect relationship between variables involved in the situation. They say that when one thing changes, it directly makes another thing change.
Hypothesis Examples
Following are the examples of hypotheses based on their types:
Simple Hypothesis Example
- Studying more can help you do better on tests.
- Getting more sun makes people have higher amounts of vitamin D.
Complex Hypothesis Example
- How rich you are, how easy it is to get education and healthcare greatly affects the number of years people live.
- A new medicine’s success relies on the amount used, how old a person is who takes it and their genes.
Directional Hypothesis Example
- Drinking more sweet drinks is linked to a higher body weight score.
- Too much stress makes people less productive at work.
Non-directional Hypothesis Example
- Drinking caffeine can affect how well you sleep.
- People often like different kinds of music based on their gender.
- The average test scores of Group A and Group B are not much different.
- There is no connection between using a certain fertilizer and how much it helps crops grow.
Alternative Hypothesis (Ha)
- Patients on Diet A have much different cholesterol levels than those following Diet B.
- Exposure to a certain type of light can change how plants grow compared to normal sunlight.
- The average smarts score of kids in a certain school area is 100.
- The usual time it takes to finish a job using Method A is the same as with Method B.
- Having more kids go to early learning classes helps them do better in school when they get older.
- Using specific ways of talking affects how much customers get involved in marketing activities.
- Regular exercise helps to lower the chances of heart disease.
- Going to school more can help people make more money.
- Playing violent video games makes teens more likely to act aggressively.
- Less clean air directly impacts breathing health in city populations.
Functions of Hypothesis
Hypotheses have many important jobs in the process of scientific research. Here are the key functions of hypotheses:
- Guiding Research: Hypotheses give a clear and exact way for research. They act like guides, showing the predicted connections or results that scientists want to study.
- Formulating Research Questions: Research questions often create guesses. They assist in changing big questions into particular, checkable things. They guide what the study should be focused on.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by saying what connections between variables should be found. They set the targets that scientists try to reach with their studies.
- Testing Predictions: Theories guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By doing tests in a planned way, scientists can check if what they see matches the guesses made by their ideas.
- Providing Structure: Theories give structure to the study process by arranging thoughts and ideas. They aid scientists in thinking about connections between things and plan experiments to match.
- Focusing Investigations: Hypotheses help scientists focus on certain parts of their study question by clearly saying what they expect links or results to be. This focus makes the study work better.
- Facilitating Communication: Theories help scientists talk to each other effectively. Clearly made guesses help scientists to tell others what they plan, how they will do it and the results expected. This explains things well with colleagues in a wide range of audiences.
- Generating Testable Statements: A good guess can be checked, which means it can be looked at carefully or tested by doing experiments. This feature makes sure that guesses add to the real information used in science knowledge.
- Promoting Objectivity: Guesses give a clear reason for study that helps guide the process while reducing personal bias. They motivate scientists to use facts and data as proofs or disprovals for their proposed answers.
- Driving Scientific Progress: Making, trying out and adjusting ideas is a cycle. Even if a guess is proven right or wrong, the information learned helps to grow knowledge in one specific area.
How Hypothesis help in Scientific Research?
Researchers use hypotheses to put down their thoughts directing how the experiment would take place. Following are the steps that are involved in the scientific method:
- Initiating Investigations: Hypotheses are the beginning of science research. They come from watching, knowing what’s already known or asking questions. This makes scientists make certain explanations that need to be checked with tests.
- Formulating Research Questions: Ideas usually come from bigger questions in study. They help scientists make these questions more exact and testable, guiding the study’s main point.
- Setting Clear Objectives: Hypotheses set the goals of a study by stating what we think will happen between different things. They set the goals that scientists want to reach by doing their studies.
- Designing Experiments and Studies: Assumptions help plan experiments and watchful studies. They assist scientists in knowing what factors to measure, the techniques they will use and gather data for a proposed reason.
- Testing Predictions: Ideas guess what will happen in experiments or observations. By checking these guesses carefully, scientists can see if the seen results match up with what was predicted in each hypothesis.
- Analysis and Interpretation of Data: Hypotheses give us a way to study and make sense of information. Researchers look at what they found and see if it matches the guesses made in their theories. They decide if the proof backs up or disagrees with these suggested reasons why things are happening as expected.
- Encouraging Objectivity: Hypotheses help make things fair by making sure scientists use facts and information to either agree or disagree with their suggested reasons. They lessen personal preferences by needing proof from experience.
- Iterative Process: People either agree or disagree with guesses, but they still help the ongoing process of science. Findings from testing ideas make us ask new questions, improve those ideas and do more tests. It keeps going on in the work of science to keep learning things.
People Also View:
Mathematics Maths Formulas Branches of Mathematics
Summary – Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a testable statement serving as an initial explanation for phenomena, based on observations, theories, or existing knowledge. It acts as a guiding light for scientific research, proposing potential relationships between variables that can be empirically tested through experiments and observations. The hypothesis must be specific, testable, falsifiable, and grounded in prior research or observation, laying out a predictive, if-then scenario that details a cause-and-effect relationship. It originates from various sources including existing theories, observations, previous research, and even personal curiosity, leading to different types, such as simple, complex, directional, non-directional, null, and alternative hypotheses, each serving distinct roles in research methodology. The hypothesis not only guides the research process by shaping objectives and designing experiments but also facilitates objective analysis and interpretation of data, ultimately driving scientific progress through a cycle of testing, validation, and refinement.
FAQs on Hypothesis
What is a hypothesis.
A guess is a possible explanation or forecast that can be checked by doing research and experiments.
What are Components of a Hypothesis?
The components of a Hypothesis are Independent Variable, Dependent Variable, Relationship between Variables, Directionality etc.
What makes a Good Hypothesis?
Testability, Falsifiability, Clarity and Precision, Relevance are some parameters that makes a Good Hypothesis
Can a Hypothesis be Proven True?
You cannot prove conclusively that most hypotheses are true because it’s generally impossible to examine all possible cases for exceptions that would disprove them.
How are Hypotheses Tested?
Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data
Can Hypotheses change during Research?
Yes, you can change or improve your ideas based on new information discovered during the research process.
What is the Role of a Hypothesis in Scientific Research?
Hypotheses are used to support scientific research and bring about advancements in knowledge.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.

- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Maths-Class-12
- Geeks Premier League
- Mathematics
- School Learning

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Open Education Sociology Dictionary
Table of Contents
Definition of Hypothesis
( noun ) A proposed and testable explanation between two or more variables that predicts an outcome or explains a phenomenon.
Examples of Hypothesis
- Note : The variables are the students, the time spent studying, and the test grades. To test the hypothesis, collect information from each student about how much time they spent studying prior to the test and compare that to the the testing outcomes.
- Sapir-Whorf hypothesis
Types of Hypothesis
- asymmetry hypothesis
- null hypothesis
- substantive hypothesis
Hypothesis Pronunciation
Pronunciation Usage Guide
Syllabification : hy·poth·e·sis
Audio Pronunciation
Phonetic Spelling
- American English – /hie-pAHth-uh-suhs/
- British English – /hie-pOth-i-sis/
International Phonetic Alphabet
- American English – /haɪˈpɑθəsəs/
- British English – /hʌɪˈpɒθᵻsᵻs/
Usage Notes
- Plural: hypotheses
- A hypothesis must have the capacity to be disconfirmed or proven false to have meaning. For example, “criminals” commit more crimes than “non-criminals” cannot be proven wrong.
- A hypothesis can either come from theory ( deduction ) or lead to theory ( induction ).
- A working hypothesis refers to a hypothesis that has not been thoroughly tested and verified.
- Hypothesis testing is the process of testing a hypothesis in a scientific manner that requires a link between the concepts or variables under investigation and rigorous testing methodology .
- An ( noun ) hypothesist ( verb ) hypothesizes ( adverb ) hypothetically about social issues to create an ( adjective ) hypothetical explanation.
Related Videos
Additional Information
- Quantitative Research Resources – Books, Journals, and Helpful Links
- Word origin of “hypothesis” – Online Etymology Dictionary: etymonline.com
- Gauch, Hugh G., Jr. 2003. Scientific Method in Practice . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Lehmann, E. L., and Joseph P. Romano. 2010. Testing Statistical Hypotheses . 3rd ed. New York: Springer.
- Poletiek, Fenna. 2001. Hypothesis-testing Behaviour . Philadelphia: Psychology.
- Popper, Karl R. 1959. The Logic of Scientific Discovery . New York: Basic Books.
Related Terms
- correlation
- dependent variable
- hypothetico-deductive model
- independent variable
- inferential statistics
- statistical analysis
Contributor: C. E. Seaman
Works Consulted
Andersen, Margaret L., and Howard Francis Taylor. 2011. Sociology: The Essentials . 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Babbie, Earl. 2013. The Practice of Social Research . 13th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Bilton, Tony, Kevin Bonnett, Pip Jones, David Skinner, Michelle Stanworth, and Andrew Webster. 1996. Introductory Sociology . 3rd ed. London: Macmillan.
Branscombe, Nyla R., and Robert A. Baron. 2017. Social Psychology . 14th ed. Harlow, England: Pearson.
Brinkerhoff, David, Lynn White, Suzanne Ortega, and Rose Weitz. 2011. Essentials of Sociology . 8th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Brym, Robert J., and John Lie. 2007. Sociology: Your Compass for a New World . 3rd ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Bryman, Alan. 2012. Social Research Methods . 4th ed. New York: Oxford University Press.
Burdess, Neil. 2010. Starting Statistics: A Short, Clear Guide . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Cramer, Duncan, and Dennis Howitt. 2004. The SAGE Dictionary of Statistics: A Practical Resource for Students in the Social Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Farlex. (N.d.) TheFreeDictionary.com: Dictionary, Encyclopedia and Thesaurus . Farlex. ( http://www.thefreedictionary.com/ ).
Ferrante, Joan. 2011a. Seeing Sociology: An Introduction . Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Ferrante, Joan. 2011b. Sociology: A Global Perspective . 7th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Ferris, Kerry, and Jill Stein. 2010. The Real World: An Introduction to Sociology . 2nd ed. New York: Norton.
Fioramonti, Lorenzo. 2014. How Numbers Rule the World: The Use and Abuse of Statistics in Global Politics . London: Zed Books.
Griffiths, Heather, Nathan Keirns, Eric Strayer, Susan Cody-Rydzewski, Gail Scaramuzzo, Tommy Sadler, Sally Vyain, Jeff Bry, Faye Jones. 2016. Introduction to Sociology 2e . Houston, TX: OpenStax.
Henslin, James M. 2012. Sociology: A Down-to-Earth Approach . 10th ed. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Hughes, Michael, and Carolyn J. Kroehler. 2011. Sociology: The Core . 10th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Kendall, Diana. 2011. Sociology in Our Times . 8th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Kimmel, Michael S., and Amy Aronson. 2012. Sociology Now . Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Kornblum, William. 2008. Sociology in a Changing World . 8th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Larson, Ron, and Elizabeth Farber. 2015. Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World . 6th ed. Boston: Pearson.
Macionis, John. 2012. Sociology . 14th ed. Boston: Pearson.
Macionis, John, and Kenneth Plummer. 2012. Sociology: A Global Introduction . 4th ed. Harlow, England: Pearson Education.
O’Leary, Zina. 2007. The Social Science Jargon Buster: The Key Terms You Need to Know . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Oxford University Press. (N.d.) Oxford Dictionaries . ( https://www.oxforddictionaries.com/ ).
Ravelli, Bruce, and Michelle Webber. 2016. Exploring Sociology: A Canadian Perspective . 3rd ed. Toronto: Pearson.
Salkind, Neil J., ed. 2007. Encyclopedia of Measurement and Statistics . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
Schaefer, Richard. 2013. Sociology: A Brief Introduction . 10th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Shepard, Jon M. 2010. Sociology . 11th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Shepard, Jon M., and Robert W. Greene. 2003. Sociology and You . New York: Glencoe.
Stolley, Kathy S. 2005. The Basics of Sociology . Westport, CT: Greenwood Press.
Taylor & Francis. (N.d.) Routledge Handbooks Online . ( https://www.routledgehandbooks.com/ ).
Thompson, William E., and Joseph V. Hickey. 2012. Society in Focus: An Introduction to Sociology . 7th ed. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Tischler, Henry L. 2011. Introduction to Sociology . 10th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Weinstein, Jay A. 2010. Applying Social Statistics: An Introduction to Quantitative Reasoning in Sociology . Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield.
Wikipedia contributors. (N.d.) Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia . Wikimedia Foundation. ( https://en.wikipedia.org/ ).
Wikipedia contributors. (N.d.) Wiktionary, The Free Dictionary . Wikimedia Foundation. ( http://en.wiktionary.org ).
Wiley. (N.d.) Wiley Online Library . ( http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/ ).
Cite the Definition of Hypothesis
ASA – American Sociological Association (5th edition)
Seaman, C. E. 2015. “hypothesis.” In Open Education Sociology Dictionary , edited by Kenton Bell. Retrieved May 1, 2024 ( https://sociologydictionary.org/hypothesis/ ).
APA – American Psychological Association (6th edition)
Seaman, C. E. (2015). hypothesis. In K. Bell (Ed.), Open education sociology dictionary . Retrieved from https://sociologydictionary.org/hypothesis/
Chicago/Turabian: Author-Date – Chicago Manual of Style (16th edition)
Seaman, C. E. 2015. “hypothesis.” In Open Education Sociology Dictionary , edited by Kenton Bell. Accessed May 1, 2024. https://sociologydictionary.org/hypothesis/ .
MLA – Modern Language Association (7th edition)
Seaman, C. E. “hypothesis.” Open Education Sociology Dictionary . Ed. Kenton Bell. 2015. Web. 1 May. 2024. < https://sociologydictionary.org/hypothesis/ >.
A hypothesis (plural hypothesis) is a proposed clarification for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be logical speculation. These are the logical strategy necessitate that one can test it. Researchers for the most part base logical hypothesis on past perceptions that can’t sufficiently be clarified with the accessible logical hypothesis.
Despite the fact that the word “hypothesis” is regularly in use. Equivalently, a logical hypothesis isn’t equivalent to a scientific hypothesis. A working hypothesis is a temporarily acknowledged hypothesis proposed for additional exploration, in a cycle starting with an informed estimate or thought.

Hypothesis
In its antiquated utilization, hypothesis alluded to an outline of the plot of an old-style dramatization. The English word hypothesis comes from the antiquated Greek word hypothesis. Its exacting or etymological sense is “putting or setting under”. Henceforth in broad use has numerous different implications including “assumption”.
In Common Utilization
In common utilization, a hypothesis alludes to a temporary thought whose legitimacy requires assessment. For legitimate assessment, the composer of a hypothesis needs to characterize particulars in operational terms. A hypothesis requires more work by the scientist to either affirm or negate it. At the appointed time, an affirmed hypothesis may turn out to be important for a hypothesis. At times may develop to turn into a hypothesis itself.
Regularly, a logical hypothesis has the type of numerical model. Sometimes, however not generally, one can likewise plan them as existential proclamations. Expressing that some specific case of the phenomenon under assessment has some trademark and causal clarifications. This has the overall type of explanations, expressing that each case of the specific trademark.
In Innovative Science
In innovative science, a hypothesis is useful to define temporary thoughts inside a business setting. The figured hypothesis is then assessed where either the hypothesis is demonstrated to be “valid” or “bogus”. It is through an undeniable nature or falsifiability-arranged test.
Any valuable hypothesis will empower forecasts by thinking (counting deductive thinking). It may foresee the result of an analysis in a research centre setting or the perception of wonder in nature. The forecast may likewise conjure measurements and just discussion about probabilities. Karl Popper, following others, has contended that a hypothesis must be falsifiable. One can’t view a suggestion or hypothesis as logical on the off chance that it doesn’t concede the chance of being indicated bogus. Different thinkers of science have dismissed the model of falsifiability or enhanced it with other measures.
For example, undeniable nature for e.g., verificationism or soundness like affirmation comprehensive quality. The logical technique includes experimentation, to test the capacity of some hypothesis to satisfactorily address the inquiry under scrutiny. Conversely, liberated perception isn’t as liable to bring up unexplained issues or open issues in science. As it would the plan of a pivotal trial to test the hypothesis. A psychological test may likewise be utilized to test the hypothesis too.
In outlining a hypothesis, the examiner must not right now know the result of a test. It remains sensibly under proceeding with examination. Just in such cases does the analysis, test or study conceivably increment the likelihood of indicating the reality of a hypothesis.
If the specialist definitely knows the result, it considers an “outcome”. The scientist ought to have just thought about this while detailing the hypothesis. On the off chance that one can’t survey the expectations by perception or by experience. The hypothesis should be tried by others giving perceptions. For instance, another innovation or hypothesis may make the essential trials practical.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis:
- The theory ought to be clear and exact to believe it to be solid.
- If the hypothesis is a social theory, at that point it ought to express the connection between factors.
- The theory must be explicit and ought to have scope for leading more tests.
- The method of clarification of the theory must be basic and it should likewise be perceived that the straightforwardness of the hypothesis isn’t identified with its essentialness.
Sources of Hypothesis
Following are the sources of the hypothesis:
- The likeness between the wonder.
- Observations from past investigations, present-day encounters and from the contenders.
- Scientific hypothesis.
- General designs that impact the considering cycle individuals.
Types of Hypothesis
There are six forms of the hypothesis and they are:
- Simple hypothesis
- Complex hypothesis
- Directional hypothesis
- Non-directional hypothesis
- Null hypothesis
- Associative and casual hypothesis
Simple Hypothesis
It shows a connection between one ward variable and a solitary autonomous variable. For instance, If you eat more vegetables, you will get in shape quicker. Here, eating more vegetables is a free factor, while getting more fit is the needy variable.
Complex Hypothesis
It shows the connection between at least two ward factors and at least two autonomous factors. Eating more vegetables and natural products prompts weight reduction. May be sparkling skin, diminishes the danger of numerous infections, for example, coronary illness, hypertension and a few diseases.
Directional Hypothesis
It shows how an analyst is scholarly and focused on a specific result. The connection between the factors can likewise foresee its inclination. For instance, kids matured four years eating appropriate food over a five-year time frame are having higher IQ levels than youngsters not having a legitimate dinner. This shows the impact and course of impact.
Non-directional Hypothesis
It is utilized when there is no theory included. It is an explanation that a relationship exists between two factors, without foreseeing the specific nature (course) of the relationship.
Null Hypothesis
It gives the explanation which is in opposition to the theory. It’s a negative assertion, and there is no connection between autonomous and subordinate factors. The image is indicated by “HO”.
Associative and Causal Hypothesis
Acquainted hypothesis happens when there is an adjustment in one variable bringing about an adjustment in the other variable. Though, the causal hypothesis proposes a circumstances and logical results connection between at least two factors.
Examples of Hypothesis
Following are the examples of the hypothesis according to their types:
- Consumption of sweet beverages consistently prompts weight is a case of a straightforward theory.
- All lilies have a similar number of petals is a case of an invalid hypothesis.
- If an individual gets 7 hours of rest, at that point he will feel less weakness than if he dozens less.
FAQs about Hypothesis
Q.1. Write a short note on the term hypothesis.
Answer: A hypothesis (plural hypothesis) is a proposed clarification for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be logical speculation. The logical strategy necessitates that one can test it. Researchers for the most part base logical hypothesis on past perceptions that can’t sufficiently be clarified with the accessible logical hypotheses. Despite the fact that the words “hypothesis” and “hypothesis” are regularly utilized equivalently, a logical hypothesis isn’t equivalent to a scientific hypothesis.
Q.2. What are the functions of the Hypothesis?
Answer: Following are the functions performed by the hypothesis:
- Hypothesis helps in mentioning an objective fact and tests conceivable.
- It turns into the beginning point for the formal examination.
- Hypothesis helps in checking the perceptions.
- It helps in coordinating the requests in the correct ways.
Q.3. How will Hypothesis help in Scientific Method?
Answer: Scientists use theory to put down their considerations coordinating how the test would happen. Following are the means that are engaged with the logical strategy:
- Formation of inquiry
- Doing foundation research
- Creation of hypothesis
- Designing an investigation
- Collection of information
- Result examination
- Summarizing the trial
- Communicating the outcomes
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Statistical Physics
- Physics Diagrams
- Constants In Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Electron Spin
- Bridge Construction
- Physics Symbols
- Murphy’s Law
- Difference Between in Physics
2 responses to “Difference Between in Physics”
I want to prepare for nda
I want to prepare physics for x group exam
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Define Hypothesis: Unveiling the First Step in Scientific Inquiry
Master Scientific Data Visualization. Learn how to make data easier, unlock insights and captivate audiences effectively.
Welcome to the world of research, where you’ll journey through a universe brimming with questions and curiosity. In this cosmos, a hypothesis is one celestial object you can’t miss! Today’s expedition invites you on board an exploration to ‘Define Hypothesis.’ Hop in; it wouldn’t be hyperbole to state we’re about to unlock the nucleus behind every ever scientific theory and inquiry!
Definition of Hypothesis
Introduction to the concept of hypothesis.
Picture yourself as a detective solving a case. Right from inspecting clues, formulating potential theories on whodunit, putting these theories under rigorous tests until finally reaching that elusive conclusive evidence – exciting, isn’t it?
Now replace detective with researcher and voila – here comes our heavyweight term: Hypothesis. Much like how any plausible theory drives detectives’ investigations, scientific hypotheses are vital navigational compasses guiding researchers in their quest for scientific evolutions.
Explanation of What a Hypothesis Is in The Context of Research and Scientific Inquiry
A hypothesis – popularly known as an educated guess or predictive statement – represents an initial supposition or proposed explanation made on limited information but founded on validation-grounded knowledge. It forms the basis for preliminary exploration into a specific set of circumstances or natural phenomena beyond.
Formulated prior to conducting research, scientists employ hypotheses as testable conjectures to explain an observed behavior or event. Confused? Fret not. To put it simply and by example: “If I increase the frequency of watering my plants twice daily (instead of solely relying upon weather conditions), then they will grow faster.” Now that’s what we call an everyday-life hypothesis!
Remember, hypotheses are not wild guesses plucked out of thin air but rather preconceived assertions open to empirical verification. They mark the inception point for any scientific investigation and serve as cornerstones for further experiments.
Characteristics and Components of a Hypothesis
Key characteristics of a hypothesis.
Before plunging into the deep end to define a hypothesis, let’s brush up on the features that contribute to effective hypotheses. For starters, a strong hypothesis is testable. This means it must be possible for empirical evidence to either support the word hypothesis or contradict it. The proposal should also be logically consistent and grounded firmly in existing knowledge.
Further down the line, another salient feature is specificity. Good hypotheses are not broad statements but instead focus on a specific aspect or phenomenon within the intended research field. Moreover, they are typically succinct and easily understandable ensuring information isn’t lost in translation among researchers.
Moreover, any well-structured hypothesis connects the independent and dependent variables together – typically, there’s at least one independent and one dependent variable involved. These elements form a relationship where changes instigated in the independent variable affect the values observed for the dependent variable.
Lastly but importantly, a solid hypothesis often carries potential implications for future research areas and can potentially lead to further tests and studies if verified.
Elements that make up a well-formulated hypothesis
Delving deeper into what shapes up a robust hypothesis, we realize that certain crucial components determine its effectiveness.
Firstly, every good hypothesis or test has clear variables which essentially refer to specific aspects of the study subject matter being measured or manipulated during research. These aspects are segregated as:
- Independent Variable (IV): This component relates directly to what you have control over in your study.
- Dependent Variable (DV): This component consists of outcomes affected by alterations made in IV
Next comes ‘Predicted Outcome’ – what you anticipate happening as repercussions due to modification of two or more variables under scrutiny.
The ‘Testability’ factor also holds veritable importance comprising experimental procedures capable enough to refute or accept your claims.
The last element circles the argument around presenting a capacity called ‘Relationship’ correlating IV with DV believed to either causing some effect or showcasing an association.
Hence, these prime facets further accentuate your endeavor to adequately define the hypothesis.
Importance and Purpose of a Hypothesis
Understanding the Role of a Hypothesis in Research
First, let’s delve into the overarching role that hypothesis plays within research scenarios. As we define the hypothesis, you should view this as an underlying pillar or guiding star for your investigation. A well-articulated hypothesis steers your exploration by providing clarity on what specifically you aim to examine.
A meaningful analogy would be considering a hypothesis as a compass during a voyage. If research is the vast ocean where confusing whirlpools of data and evidence abound, then it can guide us in our direction rather than letting us drift aimlessly. Furthermore, the formulation of a quality hypothesis inherently demands clarity about your objectives upfront – this essentially sets your research vessel on course bearing towards effective outcomes.
Exploring Why Formulating A Hypothesis is Crucial in Scientific Investigations
So why precisely is nurturing such a detailed forecast vital?
- Structural Advantage: By proposing potential answers to posed questions via hypotheses, researchers streamline their methods and techniques. The approach undertaken depends significantly on what the suggested outcome or phenomenon might be.
- Generate Preliminary Expectations: Even if they’re proven wrong, making observations and developing models based on hypotheses often lead to more interesting inquiries or turn up unexpected findings.
- Quantifiable Predictions: More than simple conjectures, strong hypotheses are testable; they propose results expressed in measurable terms.
In essence, remember that formulating hypotheses smoothes the path towards solid conclusions by being the architect’s blueprints of robust investigations. Never underestimate the forward thrust they provide for progress within scientific inquiry!
Types of Hypotheses
Once we understand to define a hypothesis, we’ll find that hypotheses come in several types. Different classifications of plural hypotheses depend on their formulations and the nature of predictions or assumptions they lead towards – simple, complex, directional, non-directional, null, associative and causal. Let’s explore some of these.
Simple Hypothesis: Definition and Examples
A simple hypothesis is a type of prediction or an educated guess that carries one independent variable and one dependent variable. In essence, it creates a relationship between two singular entities; for instance, ‘Exercise improves memory.’ This suggests that there’s an impact (of improvement) on the ‘memory’ (dependent variable) by ‘exercise’ (independent variable).
Complex Hypothesis: Definition and Examples
On the contrary to its name mate – a simple hypothesis – a complex hypothesis involves more than just two variables. It points out multiple variables and how they interlink with each other. The effects aren’t just limited to cause-and-effect but can be interactive or combined impact-dependent variables too – for instance,’Diet and exercise affect weight loss and heart health.’ Here, diet and exercise are your independent factors influencing multifold aspects like weight loss (a dependent variable) alongside heart health(another dependent variable).
Directional Hypothesis: Definition and Examples
One might argue that the path laid by a directional hypothesis is less twisted as it predicts the directionality of an effect – whether one variable will increase or decrease another variable. An example here could be “Cutting down on alcohol will reduce liver disorders.” Here a reduction in ‘drinking alcohol’ implicitly identifies fewer occurrences of ‘liver disorders.’
Non-directional Hypothesis: Definition and Examples
Sometimes science requires open-ended answers; henceforth comes into play our non-directional hypothesis which merely stipulates that there’s going to be an impact without specifying its course – good, bad or otherwise. For example, “Exposure to secondhand smoke influences lung health.” It infers that there’s an effect on ‘lung health’ due to ‘secondhand smoke,’ without indicating if it’s an improvement or deterioration.
Null Hypothesis: Definition and Examples
The null hypothesis, often symbolized as H0, makes things pretty straight with assumptions; basically, it purports no existence of a relationship between the variables. Researchers utilize this hypothesis chiefly for statistical testing. In lay terms – “Smoking is not linked to lung cancer.” Here a nonexistence of association is suggested between ‘smoking’ and ‘lung cancer.’
Associative and Causal Hypothesis: Explanation and Examples
Now leaving the train station named Null-ville we enter into quite associative terrain where the associative hypothesis foretells ‘relationships’ but are shy when it comes to cause-effects. An instance could be “Students scoring high also tend to play chess.” These fellows here don’t claim that playing chess outrightly shoots up scores yet suggests a specific pattern.
On another spectrum brightful cause-effect claims jump in bravely shouting out not just relationships but boldly stating their causes too – “Consumption of fast food leads to obesity” is being so certain about fast food consumption (cause) escalating obesity levels(effect).
Navigating through these alternative hypotheses and variants allows us to step into researchers’ shoes better while also helps defining complex constructions bit by bit, making them simple outcomes anyone can interpret.
Developing and Testing a Hypothesis
In the world of research, it’s not uncommon to hear someone say “Let’s define hypothesis!” This term may seem complex at first glance, but its essence falls within our natural instinct to question and learn. To give structure to this innate curiosity, we form hypotheses and navigate through the rigorous process of testing them.
Process of Formulating a Hypothesis
Forming an effective hypothesis is both an art and a science. It involves finding a perfect blend between creativity and logical reasoning. Here are some simple yet essential steps you’d want to follow:
- Identify Your Research Question – The first step towards formulating a hypothesis is defining your research question based on preliminary observations or literature review.
- Conduct Thorough Literature Review – Once your question is in place, an extensive read about what has already been studied can help refine it further.
- Create Tentative Explanation – Develop a preliminary answer based on your knowledge and understanding which will serve as your tentative explanation or hypothesis.
- Refine Your Hypothesis : Refine this initial guess considering available resources for empirical testing, ethical implications, and potential outcomes.
Remember that the key is formation clarity in statement-making; overly complex language might obscure rather than clarify your central idea.
Importance of Testing a Hypothesis Through Empirical Research Methods

Testing a hypothesis isn’t simply about proving it right or wrong; it’s much more refined than that – it’s about validation and advancement of human knowledge. By applying empirical methods such as observation or experimentation, logic meets practice in real-world scenarios.
These hands-on approaches afford us precious insights into how our theories hold up under scrutiny outside the confines of abstract thought alone.
- Validity Confirmation : Empirical testing helps confirm if our predictions were correct or not, providing validation for our presumptions.
- Understanding Relationships : Testing allows us to assess the relational dynamics between variables under investigation.
- Promotes Scientific Inquiry : Empirical testing encourages a systematic and objective approach to understanding phenomena, which lies at the heart of scientific inquiry.
Consider this: hypotheses are our best-educated guesses – smart hunches rooted in what we know so far. To move beyond guessing and into knowledgeable assertion, we define hypothesis structure as one that can be empirically tested. Only then do we truly start to shape our understanding with any level of certainty.
Examples of Hypotheses in Different Fields
Indeed, it’s fundamental to understand that hypotheses are not confined to a single discipline but span across numerous fields. To better illuminate this, let’s delve into various examples.
Examples of Hypotheses in Scientific Research Studies
In the realm of scientific research studies, hypotheses play a pivotal role in shaping the basis for investigations research hypotheses and experiments. Let’s consider an elementary example: studying plant growth. A researcher might formulate the hypothesis – “If a specific type of fertilizer is used, then plants will grow more rapidly.” This hypothesis aims to validate or refute the assumption that given fertilizer perceptibly affects plant growth rate.
Another common example arises from investigating causal relationships between physical activity and heart health. The scientist may hypothesize that “Regular aerobic exercise decreases the risk of heart disease.”
Examples of Hypotheses in Social Sciences
When we transition towards social sciences, which deals with human behavior and its relation to societal constructs, our formative definitions undergo a change as well.
Imagine researchers examining how socioeconomic status influences educational attainment rates. They could pose a hypothesis saying, “High socioeconomic status positively correlates with higher levels of formal education.” This hypothesis attempts to tie economic background directly to education outcomes.
The correlation between gender diversity within workplace teams and improved business performance presents another illustration. A possible hypothesis could be – “Teams comprising diverse genders exhibit superior business performance than homogenous teams.”
Examples of Hypotheses in Psychology
Within psychology – the study dedicated to how individuals think, feel, and behave; clearly stated hypotheses serve as essential stepping stones for meaningful findings and insights.
Take, for instance, predicting performance under pressure: psychologists may propose an assumption like – “Stress triggers increased errors on complex tasks”. Or when researching cognitive development in children – they may hypothesize – “Language acquisition accelerates once children start attending school”.
Examples of Hypotheses in Medical Research
Lastly but importantly, in medical research, well-articulated hypotheses help probe pressing healthcare questions and identify effective treatments.
For instance: “Patients receiving chemotherapy experience significant weight loss”. Or regarding disease transmission during pandemics – they might propose “Regular hand sanitation reduces the risk of COVID-19 infection.”
In conclusion, these examples hopefully underline the importance and versatility of a hypothesis in scientific inquiry. Irrespective of its utilization within various research fields, a scientific hypothesis still essentially remains an educated assumption that offers direction and purpose to the investigation. Interestingly enough, each study’s defined hypothesis sets forth a path leading towards a better comprehension of our world and life within it.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Formulating a Hypothesis
Identifying errors that researchers often make when developing a hypothesis.
Many researchers, especially those new in the field, may sometimes falter while crafting their hypotheses. Here are some frequently observed mistakes:
- Framing Vague Hypotheses : Clarity is vital when defining your hypothesis. A common pitfall involves creating an ambiguous statement which leaves room for multiple interpretations. This hinders precise data collection and analysis.
- Formulating Unfalsifiable Hypotheses : These are statements that cannot be proven false because they don’t connect to observable or measurable variables.
- Targeting Unachievable Results : Often, there is an inclination to develop complex hypotheses expecting groundbreaking findings. However, it’s crucial to limit the scope according to practical constraints and possibilities.
- Ignoring Null Hypothesis : The null hypothesis provides a means of contradiction to the alternative hypothesis being tested, making it essential for any research study.
Tips for avoiding these mistakes
After identifying the commonly made errors when forming a hypothesis, let’s now consider some proactive measures you can adopt:
- Crystallize Your Thoughts : Before you articulate your hypothesis, refine and clarify your ideas first. Define the parameters of your study clearly and ensure your proposition directly aligns with them.
- Keep It Simple : Stick with simplicity as much as possible in describing expected relationships or patterns in your research subject area. Remember: A simpler hypothesis often leads to effective testing.
- Embrace Falsifiability . To avoid making unfalsifiable claims, learn how to craft ‘If – Then’ statements articulately in your define hypothesis process.
- Remember the Null Hypothesis : Always formulate and account for a null hypothesis—a statement that negates the relationship between variables—for robust results validation.
In truth, it takes practice to strike the right balance and formulate a solid, practical hypothesis for your research. With these tips in mind, you’re better equipped to avoid common pitfalls that can compromise the quality of your investigation as they guide your approach when you define hypotheses.
Evaluating and Refining a Hypothesis
Laying out a hypothesis is merely the first stage of an intricate journey. Testing and refining this conjecture is equally pivotal in perfecting your next scientific method of undertaking. This pathway comprises evaluation for validity, and relevance, followed by refinement through research findings.
Methods for Assessing the Validity and Relevance of a Hypothesis
To define a hypothesis of meticulosity, we need to subject it to rigorous scrutiny. Utilizing statistical tests enables you to judge the validity of your hypothesis. Here’s a brief look at some key methods that can assist in assessing your theory:
- Empirical Testing : Conduct experiments or surveys as per the requirements of your study.
- Consistency Check : The hypothesis should remain consistent with other established theories and laws within its field.
- Falsifiability principle : Proposed by Karl Popper, a valid hypothesis must be capable of being proven wrong.
Let me reemphasize here, that relevance plays an integral part too especially when defining hypotheses linked with pragmatics like social sciences or business studies.
A relevant hypothesis will hold significance to not just existing knowledge but also pave the way for future work within the particular area of expertise. It should address gaps in current scientific theories while shedding light on possible solutions.
Ways to Refine and Modify a Hypothesis Based on Research Findings
Our job doesn’t end up on developing an initial proposition; it’s crucial to use findings from our research to refine that preliminary conception further. This essential process breathes life into what was once purely speculative.
While refining your conjecture can sound daunting initially, I assure you it’s nothing more complicated than diagnosing any missing links between your original theory and novel evidence you’ve discovered along this research journey.
If H0 (null hypothesis) contradicts your empirical results, then getting back onto the drafting board becomes necessary for crafting H1 (alternative hypothesis). This scientific cycle of formulating, testing then reformulating the hypotheses can continue till we eventually reach statistically significant results.
Remember, it’s important to be open-minded and responsive towards indications from your research findings. They will guide you intuitively in tweaking your working hypothesis in sync with your target goals.
Hence we must embrace this intricate art of defining a hypothesis while simultaneously embracing its dynamic nature which requires periodic refinement based upon insightful feedback from meticulous research.
Summarizing the Key Points About the Definition and Characteristics of a Hypothesis
Having delved into the concept extensively, we can confidently define a hypothesis as an informed and testable guess or prediction that acts as a guiding light in research studies and scientific investigations. When formulated correctly, it comprises two essential elements: clarity and specificity. It should be free from ambiguity, allowing other researchers to easily understand its proposed idea and the direction the study is heading.
In addition, a robust hypothesis exhibits predictability. As a researcher, you’re not only stating what you think will happen but also defining the variables in your experiment – your assumption confines your investigation’s parameters to make it manageable. Lastly, remember that any meaningful hypothesis must be verifiable — capable of being supported or refuted through data collection and analysis.
Reiterating the Importance of Hypotheses in Scientific Inquiry and Research
This discourse wouldn’t be complete without reaffirming how indispensable hypotheses are within scientific explorations and research inquiries. A conceptualized hypothesis serves as a foundational block upon which every aspect of a research project is built. It directs your observations along assumed patterns, thereby saving time during investigations.
We also need to note that formulating hypotheses promotes critical thinking skills among researchers because they require logical reasoning backed by empirical evidence rather than just empty conjectures.
Henceforth, whether you’re treading through unchartered waters of complex scientific endeavors or conducting social science research with less strict rules for predictions – keeping these insights on “define hypothesis” at hand would surely enhance your journey towards revealing valuable truths.
In essence, cultivating a comprehensive understanding of what constitutes a well-formed hypothesis not only lends credibility to our investigative ventures but also enables us to bring precision, focus, and relevance to our chosen field of exploration. The power lies in its simplistic yet profound ability to guide us from uncertainty towards concrete evidential findings – truly embodying scientific inquiry’s spirit!
Unlock the Power of Visualization with Mind the Graph: Elevate Your Hypothesis to New Heights
As a scientist, your hypothesis is the cornerstone of your research journey. But what if you could take it beyond mere words and equations, and transform it into a visual masterpiece that captivates your audience? Enter Mind the Graph , your ultimate ally in scientific visualization. With our intuitive platform, you can seamlessly translate complex hypotheses into stunning graphs, charts, and illustrations that speak volumes. Whether you are presenting at a conference, publishing a paper, or simply sharing your findings with the world, Mind the Graph empowers you to convey your hypotheses with clarity, precision, and undeniable impact. Join the scientific revolution today and let your hypotheses shine like never before with Mind the Graph.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Fabricio Pamplona
Fabricio Pamplona is the founder of Mind the Graph - a tool used by over 400K users in 60 countries. He has a Ph.D. and solid scientific background in Psychopharmacology and experience as a Guest Researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry (Germany) and Researcher in D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR, Brazil). Fabricio holds over 2500 citations in Google Scholar. He has 10 years of experience in small innovative businesses, with relevant experience in product design and innovation management. Connect with him on LinkedIn - Fabricio Pamplona .
Content tags

Hypothesis: Functions, Problems, Types, Characteristics, Examples
Basic Elements of the Scientific Method: Hypotheses
The Function of the Hypotheses
A hypothesis states what one is looking for in an experiment. When facts are assembled, ordered, and seen in a relationship, they build up to become a theory. This theory needs to be deduced for further confirmation of the facts, this formulation of the deductions constitutes of a hypothesis. As a theory states a logical relationship between facts and from this, the propositions which are deduced should be true. Hence, these deduced prepositions are called hypotheses.
Problems in Formulating the Hypothesis
As difficult as the process may be, it is very essential to understand the need of a hypothesis. The research would be much unfocused and a random empirical wandering without it. The hypothesis provides a necessary link between the theory and investigation which often leads to the discovery of additions to knowledge.
There are three major difficulties in the formulation of a hypothesis, they are as follows:
- Absence of a clear theoretical framework
- Lack of ability to utilize that theoretical framework logically
- Failure to be acquainted with available research techniques so as to phrase the hypothesis properly.
Sometimes the deduction of a hypothesis may be difficult as there would be many variables and the necessity to take them all into consideration becomes a challenge. For instance, observing two cases:
- Principle: A socially recognized relationship with built-in strains also governed by the institutional controls has to ensure conformity of the participants with implicit or explicit norms.
Deduction: This situation holds much more sense to the people who are in professions such as psychotherapy, psychiatry and law to some extent. They possess a very intimate relationship with their clients, thus are more susceptible to issues regarding emotional strains in the client-practitioner relationship and more implicit and explicit controls over both participants in comparison to other professions.
The above-mentioned case has variable hypotheses, so the need is to break them down into sub hypotheses, they are as follows:
- Specification of the degree of difference
- Specification of profession and problem
- Specification of kinds of controls.
2. Principle: Extensive but relatively systematized data show the correlation between members of the upper occupational class and less unhappiness and worry. Also, they are subjected to more formal controls than members of the lower strata.
Deduction: There can numerous ways to approach this principle, one could go with the comparison applying to martial relationships of the members and further argue that such differential pressures could be observed through divorce rates. This hypothesis would show inverse correlations between class position and divorce rates. There would be a very strong need to define the terms carefully to show the deduction from the principle problem.
The reference of these examples showcases a major issue in the hypothesis formulations procedures. One needs to keep the lines set for the deductions and one should be focusing on having a hypothesis at the beginning of the experiment, that hypothesis may be subject to change in the later stages and it is referred to as a „working hypothesis. Hence, the devising and utilization of a hypothesis is essential for the success of the experiment.
Types of Hypothesis
There are many ways to classify hypotheses, but it seems adequate to distinguish to separate them on the basis of their level of abstraction. They can be divided into three broad levels which will be increasing in abstractness.
- The existence of empirical uniformities : These hypotheses are made from problems which usually have a very high percentage of representing scientific examination of common–sense proportions. These studies may show a variety of things such as the distribution of business establishments in a city, behavior patterns of specific groups, etc. and they tend to show no irregularities in their data collection or review. There have been arguments which say that these aren’t hypothesis as they represent what everyone knows. This can be counter argued on the basis of two things that, “what everyone knows” isn’t always in coherence with the framework of science and it may also be incorrect. Hence, testing these hypotheses is necessary too.
- Complex ideal types: These hypotheses aim at testing the existence of logically derived relationships between empirical uniformities. This can be understood with an example, to observe ecology one should take in many factors and see the relationship between and how they affect the greater issue. A theory by Ernest W. Burgess gave out the statement that concentric growth circles are the one which characterize the city. Hence, all issues such as land values, industrial growth, ethnic groups, etc. are needed to be analyzed for forming a correct and reasonable hypothesis.
- Relations of analytic variables: These hypotheses are a bit more complex as they focus on they lead to the formulation of a relationship between the changes in one property with respect to another. For instance, taking the example of human fertility in diverse regions, religions, wealth gap, etc. may not always affect the end result but it doesn’t mean that the variables need not be accounted for. This level of hypothesizing is one of the most effective and sophisticated and thus is only limited by theory itself.
Science and Hypothesis
“The general culture in which a science develops furnishes many of its basic hypotheses” holds true as science has developed more in the West and is no accident that it is a function of culture itself. This is quite evident with the culture of the West as they read for morals, science and happiness. After the examination of a bunch of variables, it is quite easy to say that the cultural emphasis upon happiness has been productive of an almost limitless range.
The hypotheses originate from science; a key example in the form of “socialization” may be taken. The socialization process in learning science involves a feedback mechanism between the scientist and the student. The student learns from the scientist and then tests for results with his own experience, and the scientist in turn has to do the same with his colleagues.
Analogies are a source of useful hypotheses but not without its dangers as all variables may not be accounted for it as no civilization has a perfect system.
Hypotheses are also the consequence of personal, idiosyncratic experience as the manner in which the individual reacts to the hypotheses is also important and should be accounted for in the experiment.
The Characteristics for Usable Hypotheses
The criteria for judging a hypothesis as mentioned below:
- Complete Clarity : A good hypothesis should have two main elements, the concepts should be clearly defined and they should be definitions which are communicable and accepted by a larger section of the public. A lot of sources may be used and fellow associates may be used to help with the cause.
- Empirical Referents : A great hypothesis should have scientific concepts with the ultimate empirical referent. It can‟t be based on moral judgment though it can explore them but the goal should be separated from moral preachment and the acceptance of values. A good start could be analyzing the concepts which express attitudes rather than describing or referring to empirical phenomena.
- Specific Goal : The goal and procedure of the hypothesis should be tangible as grand experiments are harder to carry out. All operations and predictions should be mapped and in turn the possibility of testing the hypothesis increases. This not only enables the conceptual clarity but also the description of any indexes used. These indexes are used as variables for testing hypotheses on a larger scale. A general prediction isn’t as reliable as a specific prediction as the specific prediction provides a better result.
- Relation to Available Techniques : The technique with which a hypothesis is tested is of the utmost importance and so thorough research should be carried out before the experiment in order to find the best possible way to go about it. The example of Karl Marx may be given regarding his renowned theories; he formulated his hypothesis by observing individuals and thus proving his hypothesis. So, finding the right technique may be the key to a successful test.
- Relation to a Body of Theory: Theories on social relations can never be developed in isolation but they are a further extension of already developed or developing theories. For instance, if the “intelligence quotient” of a member of the society is to be measured, certain variables such as caste, ethnicity, nationality, etc. are chosen thus deductions are made from time to time to eventually find out what is the factor that influences intelligence.
The Conclusion
The formulation of a hypothesis is probably the most necessary step in good research practice and it is very essential to get the thought process started. It helps the researcher to have a specific goal in mind and deduce the end result of an experiment with ease and efficiency. History is evident that asking the right questions always works out fine.
Also Read: Research Methods – Basics
Goode, W. E. and P. K. Hatt. 1952. Methods in Social Research.New York: McGraw Hill. Chapters 5 and 6. Pp. 41-73
Kartik is studying BA in International Relations at Amity and Dropped out of engineering from NIT Hamirpur and he lived in over 5 different countries.

- Current Affairs & GK
- Data Analysis
- Environment
- How to / Tips
- Human Resource Management
- Marketing Management
- Mathematics and Statistics
- Research Methodology
- Information Technology
- Libre Office
- Affiliated Post
- Data Science
- Ecology, Evolution, Behaviour And Systematics
- Food Science

What is Hypothesis? What are its types and characteristics?
“Hypothesis may be defined as a proposition or a set of propositions set forth as an explanation for the occurrence of some specified group of phenomena either asserted merely as a provisional conjecture to guide some investigation in the light of established facts” (Kothari, 1988).
A research hypothesis is quite often a predictive statement, which is capable of being tested using scientific methods that involve an independent and some dependent variables. For instance, the following statements may be considered:
- “Drinking sugary drinks daily leads to obesity” or,
- “The female students perform as well as the male students”.
These two statements are hypotheses that can be objectively verified and tested. Thus, they indicate that a hypothesis states what one is looking for. Besides, it is a proposition that can be put to test in order to examine its validity.
Types of hypothesis
Hypotheses are of two types,
Null hypothesis
Alternative hypothesis.
When two methods A and B are compared on their relative superiority, and
- It is assumed that both the methods are equally good, then such a statement is known as the null hypothesis . A null hypothesis exists when a researcher believes there is no relationship between the two variables, or there is a lack of information to state a scientific hypothesis. This is something to attempt to disprove or discredit.
- On the other hand, if method A is considered relatively superior to method B, or vice-versa, then such a statement is known as an alternative hypothesis . In an attempt to disprove a null hypothesis, researchers will seek to discover an alternative hypothesis.
The null hypothesis is expressed as H 0 , while the alternative hypothesis is expressed as H 1 .
Characteristics
A hypothesis should have the following characteristic features
- It must be precise and clear. If it is not precise and clear, then the inferences drawn on its basis would not be reliable.
- A hypothesis must be capable of being put to test. Quite often, the research programmes fail owing to its incapability of being subject to testing for validity. Therefore, some prior study may be conducted by the researcher in order to make a hypothesis testable. A hypothesis “is tested if other deductions can be made from it, which in turn can be confirmed or disproved by observation” (Kothari, 1988).
- It must state the relationship between two variables, in the case of relational hypotheses.
- It must be specific and limited in scope. This is because a simpler hypothesis generally would be easier to test for the researcher. And therefore, he/she must formulate such hypotheses.
- As far as possible, a hypothesis must be stated in the simplest language, so as to make it understood by all concerned. However, it should be noted that the simplicity of a hypothesis is not related to its significance.
- It must be consistent and derived from the most known facts. In other words, it should be consistent with a substantial body of established facts. That is, it must be in the form of a statement which is most likely to occur.
- It must be amenable to testing within a stipulated or reasonable period of time. No matter how excellent a hypothesis, a researcher should not use it if it cannot be tested within a given period of time, as no one can afford to spend a lifetime on collecting data to test it.
- A hypothesis should state the facts that give rise to the necessity of looking for an explanation. This is to say that by using the hypothesis, and other known and accepted generalizations, a researcher must be able to derive the original problem condition. Therefore, a hypothesis should explain what it actually wants to explain, and for this, it should also have an empirical reference.
Share and Subscribe SAR Publisher. Leave your queries in the comment section below.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Tips to make unique assignments, what is hypothesis testing, how to write a methodology for a research paper.
- Privacy Policy
- Payment information
Top 10 Finance journals
Information from correspondents – methods of primary data collection.
- Math Article
Hypothesis Definition
In Statistics, the determination of the variation between the group of data due to true variation is done by hypothesis testing. The sample data are taken from the population parameter based on the assumptions. The hypothesis can be classified into various types. In this article, let us discuss the hypothesis definition, various types of hypothesis and the significance of hypothesis testing, which are explained in detail.
Hypothesis Definition in Statistics
In Statistics, a hypothesis is defined as a formal statement, which gives the explanation about the relationship between the two or more variables of the specified population. It helps the researcher to translate the given problem to a clear explanation for the outcome of the study. It clearly explains and predicts the expected outcome. It indicates the types of experimental design and directs the study of the research process.
Types of Hypothesis
The hypothesis can be broadly classified into different types. They are:
Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis is a hypothesis that there exists a relationship between two variables. One is called a dependent variable, and the other is called an independent variable.
Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is used when there is a relationship between the existing variables. In this hypothesis, the dependent and independent variables are more than two.
Null Hypothesis
In the null hypothesis, there is no significant difference between the populations specified in the experiments, due to any experimental or sampling error. The null hypothesis is denoted by H 0 .
Alternative Hypothesis
In an alternative hypothesis, the simple observations are easily influenced by some random cause. It is denoted by the H a or H 1 .
Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is formed by the experiments and based on the evidence.
Statistical Hypothesis
In a statistical hypothesis, the statement should be logical or illogical, and the hypothesis is verified statistically.
Apart from these types of hypothesis, some other hypotheses are directional and non-directional hypothesis, associated hypothesis, casual hypothesis.
Characteristics of Hypothesis
The important characteristics of the hypothesis are:
- The hypothesis should be short and precise
- It should be specific
- A hypothesis must be related to the existing body of knowledge
- It should be capable of verification
To learn more Maths definitions, register with BYJU’S – The Learning App.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- CBSE Class 10th
CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Answer Key
- SRMJEEE Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- JEE Advanced Registration
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Predictors & Articles
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- NID DAT Syllabus 2025
- NID DAT 2025
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Interior Design Colleges in India
- Top Graphic Designing Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Top Interior Design Colleges in Bangalore
- NIFT Result 2024
- NIFT Fees Structure
- NIFT Syllabus 2025
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission 2024
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- LPU NEST 2024
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Admit card 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET Courses List 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Hypothesis - Definition, Characteristics, Sources, Types, Examples, Functions, FAQs
- What is a Hypothesis?
Hypothesis Definition: Hypothesis is a starting of any investigation. It explains what is going to happen further and how the investigation will go through. It consists of variables, a population, and the relationship between the variables. Hypothesis in research is a theory used to test the relationship between two or more variables.
Latest: JEE Main: high scoring chapters | Past 10 year's papers
Don't Miss: Most scoring concepts for NEET | NEET papers with solutions
New: Aakash iACST Scholarship Test. Up to 90% Scholarship. Register Now
Characteristics of Hypothesis
Sources of hypothesis, types of hypothesis, hypothesis examples, functions of hypothesis.
A Hypothesis should have the following characteristics in order to be complete and good.
- It must come into direct contact with observable objects. It should not be based on fake belief , but rather on observation. Those things and objects that we cannot observe in order to formulate that hypothesis.
- A Hypothesis should be understandable to everyone including laymen. It should not contain scientific terms or definitions which are complex and difficult to anyone.
- A Hypothesis has to be specific and to the point. It should not roam around the topic or contain extra irrelevant information.
- It should also be able to provide new ideas and suggestions to the investigation.
Also read -
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for All Subjects
There are several sources of hypothesis but some of the important ones are given as follows :
- Previous study ? Previous knowledge and information regarding the topic of hypothesis will be extremely helpful to create a concrete hypothesis.
- Personal experience ? If one has a personal experience regarding the topic of investigation, he/she can use that information in the hypothesis to make it more complete and good quality.
- Thinking and imagination ? A researcher's creative thinking and imagination can sometimes aid in the formulation of a good hypothesis. A researcher's personal ideas and thinking abilities would result in a greater number of hypothesis formulations as well as control over the problem.
- Scientific theory ? It would be extremely helpful to use scientific theories in hypothesis because it is capable of explaining all the facts related to the investigation.
NCERT Physics Notes:
- NCERT Notes Class 11th Physics
- NCERT Notes Class 12th Physics
- NCERT Notes For All Subjects
There are basically several types of Hypothesis but some of the common and important type of formulation of Hypothesis are explained below:
- Simple hypothesis ? It is also known as a basic hypothesis. It depicts the relationship between two variables, one of which is known as the independent variable or ‘cause' and the other as the dependent variable or ‘effect.'
- Complex hypothesis ? A complex hypothesis is one that has multiple dependent and independent variables.
- Null hypothesis ? It contradicts the empirical hypothesis because it asserts that there is no relationship between the dependent and independent variables. It basically says that the data and variables being tested do not exist.
- Alternative hypothesis ? It is also referred to as a sustained hypothesis or a research hypothesis. To begin, numerous hypothesis are proposed. The most efficient one is then chosen from among them. Alternative hypothesis are further classified into four main types
- Point alternative hypothesis
- Non-directional alternative hypothesis
- One-tailed directional hypothesis
Two-tailed directional hypothesis
- Logical hypothesis ? It is logically verified, as the name implies. The verification process entails the following steps:
- Disagreement
- Different points of view
- Empirical hypothesis ? It is also known as a 'working hypothesis.' During the formulation phase, it is only an assumption, but once tested, it is no longer just an idea or notion. It is actually changing in relation to those independent variables.
- Statistical hypothesis ? The statement could be logical or illogical, but if statistical evidence validates it, it becomes a statistical hypothesis.
To understand the concept of hypothesis more clearly and completely, here are the examples of each type of hypothesis :
- Simple hypothesis :
Icebergs melt as a result of global warming.
The cause in this case is global warming, and the effect is melting icebergs.
- Complex hypothesis :
Global warming causes icebergs to melt which leads to significant changes in weather patterns.
The cause in this case is global warming but the effect is melting icebergs along with changing weather.
- Null hypothesis :
Water has no effect on plant growth.
Read must :
- NCERT notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Physical world
- NCERT solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Physical world
Logical hypothesis :
An animal cannot survive in the absence of water.
This is correct because all living things require water.
- Empirical hypothesis :
Cotton clothing is preferable to velvet clothing in the summer.
- Statistical hypothesis :
Vitamin C is beneficial to the skin.
To validate this hypothesis, you would need to test it on a group of people. This is a statistical approach to verifying the statement.
There are several functions of hypothesis. Some of them are given below:
- Hypothesis facilitates observation and experimentation.
- It serves as the investigation’s starting point.
- The hypothesis aids in the verification of the observations.
- It aids in steering inquiries in the right direction.
Also check-
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11th Physics Solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12th Physics Solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for All Subjects
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
A hypothesis is an assumption made on the basis of evidence. This is the starting point for any investigation in which the research questions are translated into a prediction.
There are total 7 main types of hypothesis
Simple hypothesis
Complex hypothesis
Null hypothesis
Alternative hypothesis
Logical hypothesis
Empirical hypothesis
Statistical hypothesis
The four main sources of hypothesis are:
Previous study
Personal experience
Thinking and imagination
Scientific theory
A simple hypothesis is a type of hypothesis in which there are two variables one of which is independent variable and other one is dependent variable. It is also known as basic hypothesis.
Alternative hypothesis are further classified into four main types
Point alternative hypothesis
Non-directional alternative hypothesis
One-tailed directional hypothesis
Apr 27, 2022 - 12:42 p.m. IST ---STATIC
- Latest Articles
- Popular Articles
Applications for Admissions are open.

JEE Main Important Physics formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Physics formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

UPES School of Liberal Studies
Ranked #52 Among Universities in India by NIRF | Up to 30% Merit-based Scholarships | Lifetime placement assistance | Last Date to Apply - 30th April

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd
Enrol in PACE IIT & Medical, Financial District, Hyd for JEE/NEET preparation

ALLEN JEE Exam Prep
Start your JEE preparation with ALLEN
Explore on Careers360
- Board Exams
- Navodaya Vidyalaya
- Top Schools
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6
NCERT Exemplars
- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Books for class 6
- NCERT Books for class 7
- NCERT Books for class 8
- NCERT Books for class 9
- NCERT Books for Class 10
- NCERT Books for Class 11
- NCERT Books for Class 12
- NCERT Notes for Class 9
- NCERT Notes for Class 10
- NCERT Notes for Class 11
- NCERT Notes for Class 12
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 6
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 7
- NCERT Syllabus for class 8
- NCERT Syllabus for class 9
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 10
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 11
- NCERT Syllabus for Class 12
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Admit Card
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Result Name and State Wise
- CBSE Passing Marks
CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Board Class 10th
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE 10th Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 10 Answer Key
- CBSE 10th Admit Card
- CBSE 10th Result
- CBSE 10th Toppers
- CBSE Board Class 12th
- CBSE Class 12 Date Sheet
- CBSE Class 12 Admit Card
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 12 Exam Pattern
- CBSE Class 12 Answer Key
- CBSE 12th Result
- CBSE Class 12 Toppers
CISCE Board 10th
- ICSE 10th time table
- ICSE 10th Syllabus
- ICSE 10th exam pattern
- ICSE 10th Question Papers
- ICSE 10th Result
- ICSE 10th Toppers
- ISC 12th Board
- ISC 12th Time Table
- ISC Syllabus
- ISC 12th Question Papers
- ISC 12th Result
- IMO Syllabus
- IMO Sample Papers
- IMO Answer Key
- IEO Syllabus
- IEO Answer Key
- NSO Syllabus
- NSO Sample Papers
- NSO Answer Key
- NMMS Application form
- NMMS Scholarship
- NMMS Eligibility
- NMMS Exam Pattern
- NMMS Admit Card
- NMMS Question Paper
- NMMS Answer Key
- NMMS Syllabus
- NMMS Result
- NTSE Application Form
- NTSE Eligibility Criteria
- NTSE Exam Pattern
- NTSE Admit Card
- NTSE Syllabus
- NTSE Question Papers
- NTSE Answer Key
- NTSE Cutoff
- NTSE Result
- NVS Admit Card
- Navodaya Result
- Navodaya Exam Date
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission Class 6
- JNVST admit card for class 6
- JNVST class 6 answer key
- JNVST class 6 Result
- JNVST Class 6 Exam Pattern
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission
- JNVST class 9 exam pattern
- JNVST class 9 answer key
- JNVST class 9 Result
Schools By Medium
- Malayalam Medium Schools in India
- Urdu Medium Schools in India
- Telugu Medium Schools in India
- Karnataka Board PUE Schools in India
- Bengali Medium Schools in India
- Marathi Medium Schools in India
By Ownership
- Central Government Schools in India
- Private Schools in India
- Schools in Delhi
- Schools in Lucknow
- Schools in Kolkata
- Schools in Pune
- Schools in Bangalore
- Schools in Chennai
- Schools in Mumbai
- Schools in Hyderabad
- Schools in Gurgaon
- Schools in Ahmedabad
- Schools in Uttar Pradesh
- Schools in Maharashtra
- Schools in Karnataka
- Schools in Haryana
- Schools in Punjab
- Schools in Andhra Pradesh
- Schools in Madhya Pradesh
- Schools in Rajasthan
- Schools in Tamil Nadu
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Certifications
We Appeared in

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Hypothesis is a prediction of the outcome of a study. Hypotheses are drawn from theories and research questions or from direct observations. In fact, a research problem can be formulated as a hypothesis. To test the hypothesis we need to formulate it in terms that can actually be analysed with statistical tools.
Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis: The hypothesis should be clear and precise to consider it to be reliable. If the hypothesis is a relational hypothesis, then it should be stating the relationship between variables. The hypothesis must be specific and should have scope for conducting more tests.
Definition: Hypothesis is an educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, based on some initial observations or data. It is a tentative statement that can be tested and potentially proven or disproven through further investigation and experimentation. Hypothesis is often used in scientific research to guide the design of experiments ...
The hypothesis of Andreas Cellarius, showing the planetary motions in eccentric and epicyclical orbits.. A hypothesis (pl.: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon.For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous observations that cannot satisfactorily be explained ...
A hypothesis is a tentative statement about the relationship between two or more variables. It is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in a study. It is a preliminary answer to your question that helps guide the research process. Consider a study designed to examine the relationship between sleep deprivation and test ...
The Royal Society - On the scope of scientific hypotheses (Apr. 24, 2024) scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world. The two primary features of a scientific hypothesis are falsifiability and testability, which are reflected in an "If ...
hypothesis, something supposed or taken for granted, with the object of following out its consequences (Greek hypothesis, "a putting under," the Latin equivalent being suppositio ). Discussion with Kara Rogers of how the scientific model is used to test a hypothesis or represent a theory. Kara Rogers, senior biomedical sciences editor of ...
5. Phrase your hypothesis in three ways. To identify the variables, you can write a simple prediction in if…then form. The first part of the sentence states the independent variable and the second part states the dependent variable. If a first-year student starts attending more lectures, then their exam scores will improve.
A research hypothesis (also called a scientific hypothesis) is a statement about the expected outcome of a study (for example, a dissertation or thesis). To constitute a quality hypothesis, the statement needs to have three attributes - specificity, clarity and testability. Let's take a look at these more closely.
hypothesis: [noun] an assumption or concession made for the sake of argument. an interpretation of a practical situation or condition taken as the ground for action.
Simple hypothesis. A simple hypothesis is a statement made to reflect the relation between exactly two variables. One independent and one dependent. Consider the example, "Smoking is a prominent cause of lung cancer." The dependent variable, lung cancer, is dependent on the independent variable, smoking. 4.
It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis. 7.
A hypothesis is a supposition or tentative explanation for (a group of) phenomena, (a set of) facts, or a scientific inquiry that may be tested, verified or answered by further investigation or methodological experiment. It is like a scientific guess. It's an idea or prediction that scientists make before they do experiments.
Examples. A research hypothesis, in its plural form "hypotheses," is a specific, testable prediction about the anticipated results of a study, established at its outset. It is a key component of the scientific method. Hypotheses connect theory to data and guide the research process towards expanding scientific understanding.
Hypothesis. Hypothesis is a testable statement that explains what is happening or observed. It proposes the relation between the various participating variables. Hypothesis is also called Theory, Thesis, Guess, Assumption, or Suggestion. Hypothesis creates a structure that guides the search for knowledge.
Definition of Hypothesis (noun) A proposed and testable explanation between two or more variables that predicts an outcome or explains a phenomenon.Examples of Hypothesis "I think the more time students spend studying prior to a test the higher their grade will be.". Note: The variables are the students, the time spent studying, and the test grades. . To test the hypothesis, collect ...
Characteristics of Hypothesis. Following are the characteristics of the hypothesis: The theory ought to be clear and exact to believe it to be solid. If the hypothesis is a social theory, at that point it ought to express the connection between factors. The theory must be explicit and ought to have scope for leading more tests.
Summarizing the Key Points About the Definition and Characteristics of a Hypothesis. Having delved into the concept extensively, we can confidently define a hypothesis as an informed and testable guess or prediction that acts as a guiding light in research studies and scientific investigations.
The Function of the Hypotheses. A hypothesis states what one is looking for in an experiment. When facts are assembled, ordered, and seen in a relationship, they build up to become a theory. This theory needs to be deduced for further confirmation of the facts, this formulation of the deductions constitutes of a hypothesis.
A hypothesis should have the following characteristic features. It must be precise and clear. If it is not precise and clear, then the inferences drawn on its basis would not be reliable. A hypothesis must be capable of being put to test. Quite often, the research programmes fail owing to its incapability of being subject to testing for validity.
The various types of Hypothesis are-. 1. Simple Hypothesis. Simple Hypothesis defines the relation between the two variables such as independent and dependent variables. For example - If you exercise, you will lose weight faster. Here, exercising is an independent variable, while losing weight is the dependent variable. 2.
In a statistical hypothesis, the statement should be logical or illogical, and the hypothesis is verified statistically. Apart from these types of hypothesis, some other hypotheses are directional and non-directional hypothesis, associated hypothesis, casual hypothesis. Characteristics of Hypothesis. The important characteristics of the ...
Hypothesis Definition: Hypothesis is a starting of any investigation. It explains what is going to happen further and how the investigation will go through. It consists of variables, a population, and the relationship between the variables. ... Characteristics of Hypothesis. A Hypothesis should have the following characteristics in order to be ...