

Digital Innovation and Transformation
Mba student perspectives.
- Assignments
- Assignment: Data and Analytics as…
ZARA: Achieving the “Fast” in Fast Fashion through Analytics

How does fast fashion make any business sense? Zara uses intensive data and analytics to manage a tight supply chain and give customers exactly what they want.
Introduction
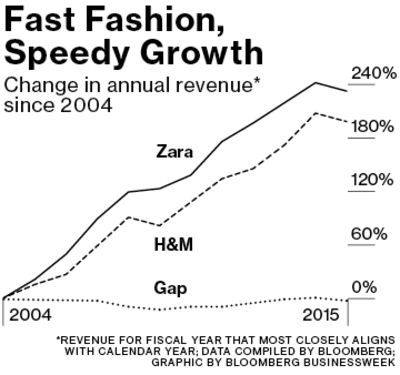
Zara’s parent company Inditex has managed to thrive in the last decade while several other fashion retailers have faced declining sales or stagnant growth. Inditex has grown over 220% in annual revenue since 2004, more than its key competitors like H&M, Gap, or Banana Republic (1).
The value of a fast fashion brand is to bring the latest designs and “trendiest trends” into the market as quickly as possible, preferably as soon as they became hot on the catwalk, and to provide these at a reasonable price. The traditional fashion industry is not well equipped to provide such value as it operates on a bi-annual or seasonal basis, with long production lead times due to outsourced manufacturing to low cost-centers. Zara has turned the industry on its head by using data and analytics to track demand on a real-time, localized basis and push new inventory in response to customer pull. This enables them to manage one of the most efficient supply chains in the fashion industry, and to create the fast fashion category as a market leader.
Pathways to a Just Digital Future
How Zara Uses Data
Inditex is a mammoth retailer, producing over 840 million garments in a year, the majority of which are sold by Zara (2). Every item of clothing is tagged with an RFID microchip before it leaves a centralized warehouse, which enables them to track that piece of inventory until it is sold to a customer (3). The data about the sale of each SKU, inventory levels in each store, and the speed at which a particular SKU moves from the shelf to the POS is sent on a real time basis to Inditex’s central data processing center (see picture below). This center is open 24 hours a day and collects information from all 6000+ Inditex stores across 80+ countries and is used by teams for inventory management, distribution, design and customer service improvements (4).

Zara’s Data Processing Center receives real-time data from around the world (4).
When the apparel arrives in store, RFID enables the stockist to determine which items need replenishing and where they are located, which has made their inventory and stock takes 80% faster than before (3). If a customer needs a particular SKU, salespeople are able to serve them better by locating it immediately in store or at a nearby location. Moreover, every Zara location receives inventory replenishments twice a week, which is tailored to that stores real-time updates on SKU-level inventory data.
The sales tracking data is critical in enabling Zara to serve its customers with trends that they actually want, and eliminate designs that don’t have customer pull. Zara’s design team is an egalitarian team of over 350 designers that use inspiration from the catwalk to design apparel on daily basis. Every morning, they dive through the sales data from stores across the world to determine what items are selling and accordingly tailor their designs that day. They also receive qualitative feedback from empowered sales employees that send in feedback and customer sentiment on a daily basis to the central HQ e.g., “customers don’t like the zipper” or “she wishes it was longer” (1).
At the start of the planning process, Zara orders very small batches of any given design from their manufacturers (even just 4-6 of a shirt per store). The majority of Zara’s factories are located proximally in Europe and North Africa, enabling them to manufacture new designs close to home and ship them to their stores within 2-3 weeks. They then test these designs in store, and if the data suggests the designs take off, Zara can quickly order more inventory in the right sizes, in the locations that demanded it. Such store-level data allows Zara to be hyper-local in serving their customer’s needs – as tastes can vary on a neighborhood level. As Inditex’s communication director told the New York Times,
“ Neighborhoods share trends more than countries do. For example, the store on Fifth Avenue in Midtown New York is more similar to the store in Ginza, Tokyo, which is an elegant area that’s also touristic. And SoHo is closer to Shibuya, which is very trendy and young.” (5)
Unlike other retailers that may order inventory based on their hypotheses about tastes at a regional level, Zara is tailors its collections based on the exact zip code and demographic that a given location serves (5).
Zara’s Results vs. Competitors
Zara sells over 11,000 distinct items per year versus its competitors that carry 2,000 to 4,000. However Zara also boasts the lowest year-end inventory levels in the fashion industry. This lean working capital management offsets their higher production costs and enables them to boast rapid sales turnover rates.
At Zara, only 15% to 25% of a line is designed ahead of the season, and over 50% of items are designed and manufactured in the middle of a season based on what becomes popular (2). This is in direct contrast to a close competitor like H&M where 80% of designs are made ahead of the season, and 20% is done in real-time during the season (6). Most other retailers commit 100% of their designs ahead of a season, and are often left with excess inventory that they then have to discount heavily at season-end. Instead, Zara’s quick replenishment cycles create a sense of scarcity which might actually generate more demand:
“With Zara, you know that if you don’t buy it, right then and there, within 11 days the entire stock will change. You buy it now or never.” (5)
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-11-23/zara-s-recipe-for-success-more-data-fewer-bosses
- http://www.digitalistmag.com/digital-supply-networks/2016/03/30/zaras-agile-supply-chain-is-source-of-competitive-advantage-04083335
- http://static.inditex.com/annual_report_2015/en/our-priorities/innovation-in-customer-services.php
- http://www.refinery29.com/2016/02/102423/zara-facts?utm_campaign=160322-zara-secrets&utm_content=everywhere&utm_medium=editorial&utm_source=email#slide-11
- http://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/11/magazine/how-zara-grew-into-the-worlds-largest-fashion-retailer.html?pagewanted=all
- https://erply.com/in-the-success-stories-of-hm-zara-ikea-and-walmart-luck-is-not-a-key-factor/
Student comments on ZARA: Achieving the “Fast” in Fast Fashion through Analytics
Great post Ravneet – I had never read about Zara’s extremely quick supply chain or hyper-local testing. I have a question for you about fast fashion in general, but especially for Zara since it produces and sells more distinct items than its competitors: it seems that many designers are not fond of the “runway-inspired” fashions sold at these stores and some have even sued stores for copying their designs. Do you think Zara and other brands like it are doing anything wrong, and if not, what recourse do designers have for “imitations” of their work?
Thanks for the post Ravneet. Zara and H&M are beacons of hope for a mostly distressed industry. Do you think Zara’s advantage could be sustained in the event of a full-on assault by the Amazons of the world?
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

- Predictive Analytics Workshops
- Corporate Strategy Workshops
- Advanced Excel for MBA
- Powerpoint Workshops
- Digital Transformation
- Competing on Business Analytics
- Aligning Analytics with Strategy
- Building & Sustaining Competitive Advantages
- Corporate Strategy
- Aligning Strategy & Sales
- Digital Marketing
- Hypothesis Testing
- Time Series Analysis
- Regression Analysis
- Machine Learning
- Marketing Strategy
- Branding & Advertising
- Risk Management
- Hedging Strategies
- Network Plotting
- Bar Charts & Time Series
- Technical Analysis of Stocks MACD
- NPV Worksheet
- ABC Analysis Worksheet
- WACC Worksheet
- Porter 5 Forces
- Porter Value Chain
- Amazing Charts
- Garnett Chart
- HBR Case Solution
- 4P Analysis
- 5C Analysis
- NPV Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
- Cost Optimization
ZARA: Fast Fashion
- Strategy & Execution / MBA EMBA Resources
Next Case Study Solutions
- Tesla Motors Case Study Solution
- Silvio Napoli at Schindler India (A) Case Study Solution
- Apple Inc. in 2012 Case Study Solution
- Nucor at a Crossroads Case Study Solution
- Yellowtail Marine, Inc. Case Study Solution
Previous Case Solutions
- DamaA? Lovina Villas: Can Eco-standards and Certification Create Competitive Advantage for a Luxury Resort? Case Study Solution
- Uncle Betty's: Toronto's Most Innovative Chef-quality Diner Case Study Solution
- Darden Restaurants: Serving Up the Future Case Study Solution
- Sustaining Customer Centricity at Chateauform', Supplement Case Study Solution
- Signalling Costs Case Study Solution

Predictive Analytics
May 3, 2024

Popular Tags
Case study solutions.

Case Study Solution | Assignment Help | Case Help
Zara: fast fashion description.
Focuses on Inditex, an apparel retailer from Spain, which has set up an extremely quick response system for its ZARA chain. Instead of predicting months before a season starts what women will want to wear, ZARA observes what's selling and what's not and continuously adjusts what it produces and merchandises on that basis. Powered by ZARA's success, Inditex has expanded into 39 countries, making it one of the most global retailers in the world. But in 2002, it faces important questions concerning its future growth.
Case Description ZARA: Fast Fashion
Strategic managment tools used in case study analysis of zara: fast fashion, step 1. problem identification in zara: fast fashion case study, step 2. external environment analysis - pestel / pest / step analysis of zara: fast fashion case study, step 3. industry specific / porter five forces analysis of zara: fast fashion case study, step 4. evaluating alternatives / swot analysis of zara: fast fashion case study, step 5. porter value chain analysis / vrio / vrin analysis zara: fast fashion case study, step 6. recommendations zara: fast fashion case study, step 7. basis of recommendations for zara: fast fashion case study, quality & on time delivery.
100% money back guarantee if the quality doesn't match the promise
100% Plagiarism Free
If the work we produce contain plagiarism then we payback 1000 USD
Paypal Secure
All your payments are secure with Paypal security.
300 Words per Page
We provide 300 words per page unlike competitors' 250 or 275
Free Title Page, Citation Page, References, Exhibits, Revision, Charts
Case study solutions are career defining. Order your custom solution now.
Case Analysis of ZARA: Fast Fashion
ZARA: Fast Fashion is a Harvard Business (HBR) Case Study on Strategy & Execution , Texas Business School provides HBR case study assignment help for just $9. Texas Business School(TBS) case study solution is based on HBR Case Study Method framework, TBS expertise & global insights. ZARA: Fast Fashion is designed and drafted in a manner to allow the HBR case study reader to analyze a real-world problem by putting reader into the position of the decision maker. ZARA: Fast Fashion case study will help professionals, MBA, EMBA, and leaders to develop a broad and clear understanding of casecategory challenges. ZARA: Fast Fashion will also provide insight into areas such as – wordlist , strategy, leadership, sales and marketing, and negotiations.
Case Study Solutions Background Work
ZARA: Fast Fashion case study solution is focused on solving the strategic and operational challenges the protagonist of the case is facing. The challenges involve – evaluation of strategic options, key role of Strategy & Execution, leadership qualities of the protagonist, and dynamics of the external environment. The challenge in front of the protagonist, of ZARA: Fast Fashion, is to not only build a competitive position of the organization but also to sustain it over a period of time.
Strategic Management Tools Used in Case Study Solution
The ZARA: Fast Fashion case study solution requires the MBA, EMBA, executive, professional to have a deep understanding of various strategic management tools such as SWOT Analysis, PESTEL Analysis / PEST Analysis / STEP Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, Go To Market Strategy, BCG Matrix Analysis, Porter Value Chain Analysis, Ansoff Matrix Analysis, VRIO / VRIN and Marketing Mix Analysis.
Texas Business School Approach to Strategy & Execution Solutions
In the Texas Business School, ZARA: Fast Fashion case study solution – following strategic tools are used - SWOT Analysis, PESTEL Analysis / PEST Analysis / STEP Analysis, Porter Five Forces Analysis, Go To Market Strategy, BCG Matrix Analysis, Porter Value Chain Analysis, Ansoff Matrix Analysis, VRIO / VRIN and Marketing Mix Analysis. We have additionally used the concept of supply chain management and leadership framework to build a comprehensive case study solution for the case – ZARA: Fast Fashion
Step 1 – Problem Identification of ZARA: Fast Fashion - Harvard Business School Case Study
The first step to solve HBR ZARA: Fast Fashion case study solution is to identify the problem present in the case. The problem statement of the case is provided in the beginning of the case where the protagonist is contemplating various options in the face of numerous challenges that Zara Inditex is facing right now. Even though the problem statement is essentially – “Strategy & Execution” challenge but it has impacted by others factors such as communication in the organization, uncertainty in the external environment, leadership in Zara Inditex, style of leadership and organization structure, marketing and sales, organizational behavior, strategy, internal politics, stakeholders priorities and more.
Step 2 – External Environment Analysis
Texas Business School approach of case study analysis – Conclusion, Reasons, Evidences - provides a framework to analyze every HBR case study. It requires conducting robust external environmental analysis to decipher evidences for the reasons presented in the ZARA: Fast Fashion. The external environment analysis of ZARA: Fast Fashion will ensure that we are keeping a tab on the macro-environment factors that are directly and indirectly impacting the business of the firm.
What is PESTEL Analysis? Briefly Explained
PESTEL stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors that impact the external environment of firm in ZARA: Fast Fashion case study. PESTEL analysis of " ZARA: Fast Fashion" can help us understand why the organization is performing badly, what are the factors in the external environment that are impacting the performance of the organization, and how the organization can either manage or mitigate the impact of these external factors.
How to do PESTEL / PEST / STEP Analysis? What are the components of PESTEL Analysis?
As mentioned above PESTEL Analysis has six elements – political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal. All the six elements are explained in context with ZARA: Fast Fashion macro-environment and how it impacts the businesses of the firm.
How to do PESTEL Analysis for ZARA: Fast Fashion
To do comprehensive PESTEL analysis of case study – ZARA: Fast Fashion , we have researched numerous components under the six factors of PESTEL analysis.
Political Factors that Impact ZARA: Fast Fashion
Political factors impact seven key decision making areas – economic environment, socio-cultural environment, rate of innovation & investment in research & development, environmental laws, legal requirements, and acceptance of new technologies.
Government policies have significant impact on the business environment of any country. The firm in “ ZARA: Fast Fashion ” needs to navigate these policy decisions to create either an edge for itself or reduce the negative impact of the policy as far as possible.
Data safety laws – The countries in which Zara Inditex is operating, firms are required to store customer data within the premises of the country. Zara Inditex needs to restructure its IT policies to accommodate these changes. In the EU countries, firms are required to make special provision for privacy issues and other laws.
Competition Regulations – Numerous countries have strong competition laws both regarding the monopoly conditions and day to day fair business practices. ZARA: Fast Fashion has numerous instances where the competition regulations aspects can be scrutinized.
Import restrictions on products – Before entering the new market, Zara Inditex in case study ZARA: Fast Fashion" should look into the import restrictions that may be present in the prospective market.
Export restrictions on products – Apart from direct product export restrictions in field of technology and agriculture, a number of countries also have capital controls. Zara Inditex in case study “ ZARA: Fast Fashion ” should look into these export restrictions policies.
Foreign Direct Investment Policies – Government policies favors local companies over international policies, Zara Inditex in case study “ ZARA: Fast Fashion ” should understand in minute details regarding the Foreign Direct Investment policies of the prospective market.
Corporate Taxes – The rate of taxes is often used by governments to lure foreign direct investments or increase domestic investment in a certain sector. Corporate taxation can be divided into two categories – taxes on profits and taxes on operations. Taxes on profits number is important for companies that already have a sustainable business model, while taxes on operations is far more significant for companies that are looking to set up new plants or operations.
Tariffs – Chekout how much tariffs the firm needs to pay in the “ ZARA: Fast Fashion ” case study. The level of tariffs will determine the viability of the business model that the firm is contemplating. If the tariffs are high then it will be extremely difficult to compete with the local competitors. But if the tariffs are between 5-10% then Zara Inditex can compete against other competitors.
Research and Development Subsidies and Policies – Governments often provide tax breaks and other incentives for companies to innovate in various sectors of priority. Managers at ZARA: Fast Fashion case study have to assess whether their business can benefit from such government assistance and subsidies.
Consumer protection – Different countries have different consumer protection laws. Managers need to clarify not only the consumer protection laws in advance but also legal implications if the firm fails to meet any of them.
Political System and Its Implications – Different political systems have different approach to free market and entrepreneurship. Managers need to assess these factors even before entering the market.
Freedom of Press is critical for fair trade and transparency. Countries where freedom of press is not prevalent there are high chances of both political and commercial corruption.
Corruption level – Zara Inditex needs to assess the level of corruptions both at the official level and at the market level, even before entering a new market. To tackle the menace of corruption – a firm should have a clear SOP that provides managers at each level what to do when they encounter instances of either systematic corruption or bureaucrats looking to take bribes from the firm.
Independence of judiciary – It is critical for fair business practices. If a country doesn’t have independent judiciary then there is no point entry into such a country for business.
Government attitude towards trade unions – Different political systems and government have different attitude towards trade unions and collective bargaining. The firm needs to assess – its comfort dealing with the unions and regulations regarding unions in a given market or industry. If both are on the same page then it makes sense to enter, otherwise it doesn’t.
Economic Factors that Impact ZARA: Fast Fashion
Social factors that impact zara: fast fashion, technological factors that impact zara: fast fashion, environmental factors that impact zara: fast fashion, legal factors that impact zara: fast fashion, step 3 – industry specific analysis, what is porter five forces analysis, step 4 – swot analysis / internal environment analysis, step 5 – porter value chain / vrio / vrin analysis, step 6 – evaluating alternatives & recommendations, step 7 – basis for recommendations, references :: zara: fast fashion case study solution.
- sales & marketing ,
- leadership ,
- corporate governance ,
- Advertising & Branding ,
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) ,
Amanda Watson
Leave your thought here

© 2019 Texas Business School. All Rights Reserved
USEFUL LINKS
Follow us on.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive news on update.

Dark Brown Leather Watch
$200.00 $180.00

Dining Chair
$300.00 $220.00

Creative Wooden Stand
$100.00 $80.00
2 x $180.00
2 x $220.00
Subtotal: $200.00
Free Shipping on All Orders Over $100!

Wooden round table
$360.00 $300.00
Hurley Dry-Fit Chino Short. Men's chino short. Outseam Length: 19 Dri-FIT Technology helps keep you dry and comfortable. Made with sweat-wicking fabric. Fitted waist with belt loops. Button waist with zip fly provides a classic look and feel .
Fern Fort University
Zara: fast fashion case study analysis & solution, harvard business case studies solutions - assignment help.
ZARA: Fast Fashion is a Harvard Business (HBR) Case Study on Strategy & Execution , Fern Fort University provides HBR case study assignment help for just $11. Our case solution is based on Case Study Method expertise & our global insights.

Strategy & Execution Case Study | Authors :: Pankaj Ghemawat, Jose Luis Nueno
Case study description.
Focuses on Inditex, an apparel retailer from Spain, which has set up an extremely quick response system for its ZARA chain. Instead of predicting months before a season starts what women will want to wear, ZARA observes what's selling and what's not and continuously adjusts what it produces and merchandises on that basis. Powered by ZARA's success, Inditex has expanded into 39 countries, making it one of the most global retailers in the world. But in 2002, it faces important questions concerning its future growth.
Competition, Globalization, Marketing, Mergers & acquisitions, Supply chain
Order a Strategy & Execution case study solution now
To Search More HBR Case Studies Solution Go to Fern Fort University Search Page
[10 Steps] Case Study Analysis & Solution
Step 1 - reading up harvard business review fundamentals on the strategy & execution.
Even before you start reading a business case study just make sure that you have brushed up the Harvard Business Review (HBR) fundamentals on the Strategy & Execution. Brushing up HBR fundamentals will provide a strong base for investigative reading. Often readers scan through the business case study without having a clear map in mind. This leads to unstructured learning process resulting in missed details and at worse wrong conclusions. Reading up the HBR fundamentals helps in sketching out business case study analysis and solution roadmap even before you start reading the case study. It also provides starting ideas as fundamentals often provide insight into some of the aspects that may not be covered in the business case study itself.
Step 2 - Reading the ZARA: Fast Fashion HBR Case Study
To write an emphatic case study analysis and provide pragmatic and actionable solutions, you must have a strong grasps of the facts and the central problem of the HBR case study. Begin slowly - underline the details and sketch out the business case study description map. In some cases you will able to find the central problem in the beginning itself while in others it may be in the end in form of questions. Business case study paragraph by paragraph mapping will help you in organizing the information correctly and provide a clear guide to go back to the case study if you need further information. My case study strategy involves -
- Marking out the protagonist and key players in the case study from the very start.
- Drawing a motivation chart of the key players and their priorities from the case study description.
- Refine the central problem the protagonist is facing in the case and how it relates to the HBR fundamentals on the topic.
- Evaluate each detail in the case study in light of the HBR case study analysis core ideas.
Step 3 - ZARA: Fast Fashion Case Study Analysis
Once you are comfortable with the details and objective of the business case study proceed forward to put some details into the analysis template. You can do business case study analysis by following Fern Fort University step by step instructions -
- Company history is provided in the first half of the case. You can use this history to draw a growth path and illustrate vision, mission and strategic objectives of the organization. Often history is provided in the case not only to provide a background to the problem but also provide the scope of the solution that you can write for the case study.
- HBR case studies provide anecdotal instances from managers and employees in the organization to give a feel of real situation on the ground. Use these instances and opinions to mark out the organization's culture, its people priorities & inhibitions.
- Make a time line of the events and issues in the case study. Time line can provide the clue for the next step in organization's journey. Time line also provides an insight into the progressive challenges the company is facing in the case study.
Step 4 - SWOT Analysis of ZARA: Fast Fashion
Once you finished the case analysis, time line of the events and other critical details. Focus on the following -
- Zero down on the central problem and two to five related problems in the case study.
- Do the SWOT analysis of the ZARA: Fast Fashion . SWOT analysis is a strategic tool to map out the strengths, weakness, opportunities and threats that a firm is facing.
- SWOT analysis and SWOT Matrix will help you to clearly mark out - Strengths Weakness Opportunities & Threats that the organization or manager is facing in the ZARA: Fast Fashion
- SWOT analysis will also provide a priority list of problem to be solved.
- You can also do a weighted SWOT analysis of ZARA: Fast Fashion HBR case study.
Step 5 - Porter 5 Forces / Strategic Analysis of Industry Analysis ZARA: Fast Fashion
In our live classes we often come across business managers who pinpoint one problem in the case and build a case study analysis and solution around that singular point. Business environments are often complex and require holistic solutions. You should try to understand not only the organization but also the industry which the business operates in. Porter Five Forces is a strategic analysis tool that will help you in understanding the relative powers of the key players in the business case study and what sort of pragmatic and actionable case study solution is viable in the light of given facts.
Step 6 - PESTEL, PEST / STEP Analysis of ZARA: Fast Fashion
Another way of understanding the external environment of the firm in ZARA: Fast Fashion is to do a PESTEL - Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental & Legal analysis of the environment the firm operates in. You should make a list of factors that have significant impact on the organization and factors that drive growth in the industry. You can even identify the source of firm's competitive advantage based on PESTEL analysis and Organization's Core Competencies.
Step 7 - Organizing & Prioritizing the Analysis into ZARA: Fast Fashion Case Study Solution
Once you have developed multipronged approach and work out various suggestions based on the strategic tools. The next step is organizing the solution based on the requirement of the case. You can use the following strategy to organize the findings and suggestions.
- Build a corporate level strategy - organizing your findings and recommendations in a way to answer the larger strategic objective of the firm. It include using the analysis to answer the company's vision, mission and key objectives , and how your suggestions will take the company to next level in achieving those goals.
- Business Unit Level Solution - The case study may put you in a position of a marketing manager of a small brand. So instead of providing recommendations for overall company you need to specify the marketing objectives of that particular brand. You have to recommend business unit level recommendations. The scope of the recommendations will be limited to the particular unit but you have to take care of the fact that your recommendations are don't directly contradict the company's overall strategy. For example you can recommend a low cost strategy but the company core competency is design differentiation.
- Case study solutions can also provide recommendation for the business manager or leader described in the business case study.
Step 8 -Implementation Framework
The goal of the business case study is not only to identify problems and recommend solutions but also to provide a framework to implement those case study solutions. Implementation framework differentiates good case study solutions from great case study solutions. If you able to provide a detailed implementation framework then you have successfully achieved the following objectives -
- Detailed understanding of the case,
- Clarity of HBR case study fundamentals,
- Analyzed case details based on those fundamentals and
- Developed an ability to prioritize recommendations based on probability of their successful implementation.
Implementation framework helps in weeding out non actionable recommendations, resulting in awesome ZARA: Fast Fashion case study solution.
Step 9 - Take a Break
Once you finished the case study implementation framework. Take a small break, grab a cup of coffee or whatever you like, go for a walk or just shoot some hoops.
Step 10 - Critically Examine ZARA: Fast Fashion case study solution
After refreshing your mind, read your case study solution critically. When we are writing case study solution we often have details on our screen as well as in our head. This leads to either missing details or poor sentence structures. Once refreshed go through the case solution again - improve sentence structures and grammar, double check the numbers provided in your analysis and question your recommendations. Be very slow with this process as rushing through it leads to missing key details. Once done it is time to hit the attach button.
Previous 5 HBR Case Study Solution
- Damaí Lovina Villas: Can Eco-standards and Certification Create Competitive Advantage for a Luxury Resort? Case Study Solution
- Uncle Betty's: Toronto's Most Innovative Chef-quality Diner Case Study Solution
- Darden Restaurants: Serving Up the Future Case Study Solution
- Sustaining Customer Centricity at Chateauform', Supplement Case Study Solution
- Signalling Costs Case Study Solution
Next 5 HBR Case Study Solution
- Tesla Motors Case Study Solution
- Silvio Napoli at Schindler India (A) Case Study Solution
- Apple Inc. in 2012 Case Study Solution
- Nucor at a Crossroads Case Study Solution
- Yellowtail Marine, Inc. Case Study Solution
Special Offers
Order custom Harvard Business Case Study Analysis & Solution. Starting just $19
Amazing Business Data Maps. Send your data or let us do the research. We make the greatest data maps.
We make beautiful, dynamic charts, heatmaps, co-relation plots, 3D plots & more.
Buy Professional PPT templates to impress your boss
Nobody get fired for buying our Business Reports Templates. They are just awesome.
- More Services
Feel free to drop us an email
- fernfortuniversity[@]gmail.com
- (000) 000-0000

Strategy & Execution

ZARA: Fast Fashion (Multimedia Case)

ZARA: Fast Fashion (Multimedia Case) ^ 131HBD
Want to buy more than 1 copy? Contact: [email protected]
Product Description
Publication Date: June 23, 2003
Focuses on Inditex, an apparel retailer from Spain, which has set up an extremely quick response system for its ZARA chain. Instead of predicting months before a season starts what women will want to wear, ZARA observes what's selling and what's not and continuously adjusts what it produces and merchandises on that basis. Powered by ZARA's success, Inditex has expanded into 39 countries, making it one of the most global retailers in the world. But in 2002, it faces important questions concerning its future growth. One year single-user license.

This Product Also Appears In
Buy together, related products.

Zara: IT for Fast Fashion

ZARA: Fast Fashion

Zara: Managing Stores for Fast Fashion
Copyright permissions.
If you'd like to share this PDF, you can purchase copyright permissions by increasing the quantity.
Order for your team and save!
Zara Across Disciplines

Leading provider of teaching materials for management education
The materials in this collection explore Zara’s early development, its operational innovations, and its current strategic challenges as new competitors enter the fast fashion space.
Background and History
Industry environment.

Sustainability and Fast Fashion
Note: Though these materials are not focused on Zara alone, they cover sustainability concepts in fast fashion as a whole and touch upon the company's role in industry sustainability.
Related Collections

Facebook, Inc. Across Disciplines
The company formerly known as Facebook, Inc. has grown phenomenally since its modest beginnings at Harvard University in 2004. These materials will acquaint students with Facebook’s revolutionary business as well as its influence in modern life, including materials on Facebook’s transformation into Meta Platforms, Inc.
Retail Management
This collection covers the opportunities and challenges retailers face in providing consumers with a seamless shopping experience across multiple retail channels.
Sustainability in the Core: Operations Management
This collection features cases and reading materials that help faculty to integrate sustainability content into their core operations management classes.
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- June 2004 (Revised September 2007)
- HBS Case Collection
Zara: IT for Fast Fashion
- Format: Print
- | Language: English
- | Pages: 23
More from the Author
- Faculty Research
Cambrian House
- December 2007
- Health Affairs
Regional Health Information Organizations: Current Activities and Financing
- October 2007
Managing in the Information Age Module Note for Students: Function IT
- Cambrian House By: Peter A. Coles, Karim R. Lakhani and Andrew P. McAfee
- Regional Health Information Organizations: Current Activities and Financing
- Managing in the Information Age Module Note for Students: Function IT

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ghemawat, Pankaj, and Jose Luis Nueno. "ZARA: Fast Fashion." Harvard Business School Case 703-497, April 2003. (Revised December 2006 ...
Focuses on Inditex, an apparel retailer from Spain, which has set up an extremely quick response system for its ZARA chain. Instead of predicting months before a season starts what women will want to wear, ZARA observes what's selling and what's not and continuously adjusts what it produces and merchandises on that basis. Powered by ZARA's success, Inditex has expanded into 39 countries ...
Source: Harvard Business School. Product #: 503050-PDF-ENG. Length: 26 page (s) Fashion retailer ZARA has achieved spectacular growth via a distinctive design-on-demand operating model. This case describes this model and outlines.
In May 2021, SHEIN overtook Amazon as the most downloaded shopping app on the US iOS and Android app stores. During the pandemic in 2020, SHEIN achieved substantial sales growth and is now catching up with the fast-fashion giant Zara. This case first briefly discusses the apparel and fast-fashion industry and the creation of the fast-fashion model by Zara. Then it covers SHEIN's historical ...
Product Description. Focuses on Inditex, an apparel retailer from Spain, which has set up an extremely quick response system for its ZARA chain. Instead of predicting months before a season starts what women will want to wear, ZARA observes what's selling and what's not and continuously adjusts what it produces and merchandises on that basis.
Zara can design, produce, and deliver a new garment to its 600-plus stores worldwide in a mere 15 days. ... Newsletters All Topics The Big Idea Data & Visuals Reading Lists Case Selections HBR ...
703-497 ZARA: Fast Fashion 2 Production Apparel production was very fragmented. On average, individual apparel manufacturing firms employed only a few dozen people, although internationally traded production, in particular, could feature tiered production chains comprising as many as hundreds of firms spread across dozens of countries.
Product Description. In May 2021, SHEIN overtook Amazon as the most downloaded shopping app on the US iOS and Android app stores. During the pandemic in 2020, SHEIN achieved substantial sales growth and is now catching up with the fast-fashion giant Zara. This case first briefly discusses the apparel and fast-fashion industry and the creation ...
Abstract. Pablo Isla, the CEO of Zara, wanted to improve operational efficiencies in managing its store network. In particular, he wanted to improve labor productivity at the stores. He considered outsourcing certain store operations to third parties, changing the way store managers were compensated, and creating formal operating procedures for ...
Learn how Zara, the fast fashion pioneer, achieved success with its unique strategy and supply chain management. Read the case study on ResearchGate.
In 2003, Zara's CIO must decide whether to upgrade the retailer's IT infrastructure and capabilities. At the time of the case, the company relies on an out-of-date operating system for its store terminals and has no full-time network in place across stores. Despite these limitations, however, Zara's parent company, Inditex, has built an extraordinarily well-performing value chain that is by ...
Zara's Results vs. Competitors. Zara sells over 11,000 distinct items per year versus its competitors that carry 2,000 to 4,000. However Zara also boasts the lowest year-end inventory levels in the fashion industry. This lean working capital management offsets their higher production costs and enables them to boast rapid sales turnover rates.
ZARA: Fast Fashion is designed and drafted in a manner to allow the HBR case study reader to analyze a real-world problem by putting reader into the position of the decision maker. ZARA: Fast Fashion case study will help professionals, MBA, EMBA, and leaders to develop a broad and clear understanding of casecategory challenges.
Step 2 - Reading the ZARA: Fast Fashion HBR Case Study. To write an emphatic case study analysis and provide pragmatic and actionable solutions, you must have a strong grasps of the facts and the central problem of the HBR case study. Begin slowly - underline the details and sketch out the business case study description map.
Ghemawat, Pankaj, and Jose Luis Nueno. "ZARA: Fast Fashion." Harvard Business School Multimedia/Video Case 703-416, May 2003. (Revised May 2009 ...
HBR On Strategy curates the best case studies and conversations with the world's top business and management experts, to help you unlock new ways of doing business. New episodes every week.
Industria de Diseño Textil, SA (Inditex), primarily through its flagship brand Zara, had grown to be the world's number-one fashion manufacturer and retailer with the introduction of what many considered a disruptive fast-fashion business model. However, Inditex's chief executive officer insisted that this term failed to describe the company's business model accurately. Like other successful ...
Powered by ZARA's success, Inditex has expanded into 39 countries, making it one of the most global retailers in the world. But in 2002, it faces important questions concerning its future growth. One year single-user license.
Her actions over the past eight years have been a case study in how to navigate workplace exclusion. ... New Perspectives on the Black Experience (Harvard Business Review Press, 2019). Post. Post ...
Harvard Business Publishing Education. Leading provider of teaching materials for management education. The materials in this collection explore Zara's early development, its operational innovations, and its current strategic challenges as new competitors enter the fast fashion space. Innovation Operations Management.
Abstract. In 2003, Zara's CIO must decide whether to upgrade the retailer's IT infrastructure and capabilities. At the time of the case, the company relies on an out-of-date operating system for its store terminals and has no full-time network in place across stores. Despite these limitations, however, Zara's parent company, Inditex, has built ...
A study of 2,400 Novartis employees around the world found that simply hearing about others' struggles can normalize accessing support at work. by Laura M. Giurge,
Each Case Flash Forward provides educators and students with a brief, 2-3 page update of key changes at a particular company covered in a related case study. It is a compilation of publicly-available content prepared by an experienced editor. This Case Flash Forward provides an update on Inditex and Zara, including significant developments, current executives, key readings, and basic financials.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks began in 2004 as a concept from the United Nations to help investors assess a company's global impact and drive corporate responsibility ...