Essay On Sustainable Development
500 words essay on sustainable development.
Sustainable development is basically an action plan which helps us to achieve sustainability in any activity which makes use of the resource. Moreover, it also demands immediate and intergenerational replication. Through essay on sustainable development, we will help you understand the concept and its advantages.
Through sustainable development, we formulate organising principles which help to sustain the limited resources essential to provide for the needs of our future generations. As a result, they will be able to lead a content life on the planet .


What is Sustainable Development?
The World Commission on Environment and Development popularized this concept in 1987. Their report defines the idea as a “development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs.”
In other words, they aimed to prevent the stripping the natural world of resources which the future generations will require. As we all know that usually, one particular need drives development. Consequently, the wider future impacts are not considered.
As a result, a lot of damage happens due to this type of approach. Thus, the longer we continue to pursue unsustainable development, the more severe will the consequences be. One of the most common is climate change which is being debated widely worldwide.
In fact, climate change is already wreaking havoc on our surroundings. So, the need of the hour is sustainable development. We must ask ourselves, must we leave a scorched planet with an ailing environment for our future generations?
In order to undo the mess created by us, we must follow sustainable development. This will help us promote a more social, environmental and economical thinking. Most importantly, it is not that difficult to attain this.
We must see that world as a system which connects space, and time. Basically, it helps you understand that water pollution in South Africa will ultimately impact water quality in India. Similarly, it is the case for other things as well.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Measures to Practice Sustainable Development
There are many measures to take up for practising sustainable development. To begin with, it is important to ensure clean and hygienic living and working conditions for the people.
Next, sponsoring research on environmental issues which pertains to regions. Further, ensuring safety against known and proven industrial hazards. It is also important to find economical methods to salvage dangerous industrial wastes.
Most importantly, we must encourage afforestation . Including environmental education as part of the school and college curriculum will also help. Similarly, it is essential to socialize and humanize all environmental issues.
Further, we must encourage uses of non-conventional sources of energy, especially solar energy. Looking for substitutes for proven dangerous materials on the basis of local resources and needs will help. Likewise, we must produce environment-friendly products.
It is also essential to popularize the use of organic fertilizers and other biotechniques. Finally, the key is environmental management which must be monitored and ensure accountability.
Conclusion of Essay on Sustainable Development
To sum it up, sustainable development continuously seeks to achieve social and economic progress in ways which will not exhaust the Earth’s finite natural resources. Thus, we must all develop ways to meet these needs so that our future generations can inherit a healthier and greener planet.
FAQ on Essay on Sustainable Development
Question 1: State two measures we can take for sustainable development.
Answer 1: The first measure we can take is by finding economical methods for salvaging hazardous industrial wastes. Next, we must encourage afforestation.
Question 2: What is the aim of sustainable development?
Answer 2 : The aim of sustainable development is to maximise human well-being or quality of life without having to risk the life support system.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Essay on Sustainable Development: Samples in 250, 300 and 500 Words
- Updated on
- Nov 18, 2023

On 3rd August 2023, the Indian Government released its Net zero emissions target policy to reduce its carbon footprints. To achieve the sustainable development goals (SDG) , as specified by the UN, India is determined for its long-term low-carbon development strategy. Selfishly pursuing modernization, humans have frequently compromised with the requirements of a more sustainable environment.
As a result, the increased environmental depletion is evident with the prevalence of deforestation, pollution, greenhouse gases, climate change etc. To combat these challenges, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change launched the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) in 2019. The objective was to improve air quality in 131 cities in 24 States/UTs by engaging multiple stakeholders.
‘Development is not real until and unless it is sustainable development.’ – Ban Ki-Moon
The concept of Sustainable Development in India has even greater relevance due to the controversy surrounding the big dams and mega projects and related long-term growth. Since it is quite a frequently asked topic in school tests as well as competitive exams , we are here to help you understand what this concept means as well as the mantras to drafting a well-written essay on Sustainable Development with format and examples.
This Blog Includes:
What is sustainable development, 250-300 words essay on sustainable development, 300 words essay on sustainable development, 500 words essay on sustainable development, introduction, conclusion of sustainable development essay, importance of sustainable development, examples of sustainable development.
As the term simply explains, Sustainable Development aims to bring a balance between meeting the requirements of what the present demands while not overlooking the needs of future generations. It acknowledges nature’s requirements along with the human’s aim to work towards the development of different aspects of the world. It aims to efficiently utilise resources while also meticulously planning the accomplishment of immediate as well as long-term goals for human beings, the planet as well and future generations. In the present time, the need for Sustainable Development is not only for the survival of mankind but also for its future protection.
Looking for ideas to incorporate in your Essay on Sustainable Development? Read our blog on Energy Management – Find Your Sustainable Career Path and find out!
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 250-300 words:
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 300 + words:

Must Read: Article Writing
To give you an idea of the way to deliver a well-written essay, we have curated a sample on sustainable development below, with 500 + words:

Essay Format
Before drafting an essay on Sustainable Development, students need to get familiarised with the format of essay writing, to know how to structure the essay on a given topic. Take a look at the following pointers which elaborate upon the format of a 300-350 word essay.
Introduction (50-60 words) In the introduction, students must introduce or provide an overview of the given topic, i.e. highlighting and adding recent instances and questions related to sustainable development. Body of Content (100-150 words) The area of the content after the introduction can be explained in detail about why sustainable development is important, its objectives and highlighting the efforts made by the government and various institutions towards it. Conclusion (30-40 words) In the essay on Sustainable Development, you must add a conclusion wrapping up the content in about 2-3 lines, either with an optimistic touch to it or just summarizing what has been talked about above.
How to write the introduction of a sustainable development essay? To begin with your essay on sustainable development, you must mention the following points:
- What is sustainable development?
- What does sustainable development focus on?
- Why is it useful for the environment?
How to write the conclusion of a sustainable development essay? To conclude your essay on sustainable development, mention why it has become the need of the hour. Wrap up all the key points you have mentioned in your essay and provide some important suggestions to implement sustainable development.
The importance of sustainable development is that it meets the needs of the present generations without compromising on the needs of the coming future generations. Sustainable development teaches us to use our resources in the correct manner. Listed below are some points which tell us the importance of sustainable development.
- Focuses on Sustainable Agricultural Methods – Sustainable development is important because it takes care of the needs of future generations and makes sure that the increasing population does not put a burden on Mother Earth. It promotes agricultural techniques such as crop rotation and effective seeding techniques.
- Manages Stabilizing the Climate – We are facing the problem of climate change due to the excessive use of fossil fuels and the killing of the natural habitat of animals. Sustainable development plays a major role in preventing climate change by developing practices that are sustainable. It promotes reducing the use of fossil fuels which release greenhouse gases that destroy the atmosphere.
- Provides Important Human Needs – Sustainable development promotes the idea of saving for future generations and making sure that resources are allocated to everybody. It is based on the principle of developing an infrastructure that is can be sustained for a long period of time.
- Sustain Biodiversity – If the process of sustainable development is followed, the home and habitat of all other living animals will not be depleted. As sustainable development focuses on preserving the ecosystem it automatically helps in sustaining and preserving biodiversity.
- Financial Stability – As sustainable development promises steady development the economies of countries can become stronger by using renewable sources of energy as compared to using fossil fuels, of which there is only a particular amount on our planet.
Mentioned below are some important examples of sustainable development. Have a look:
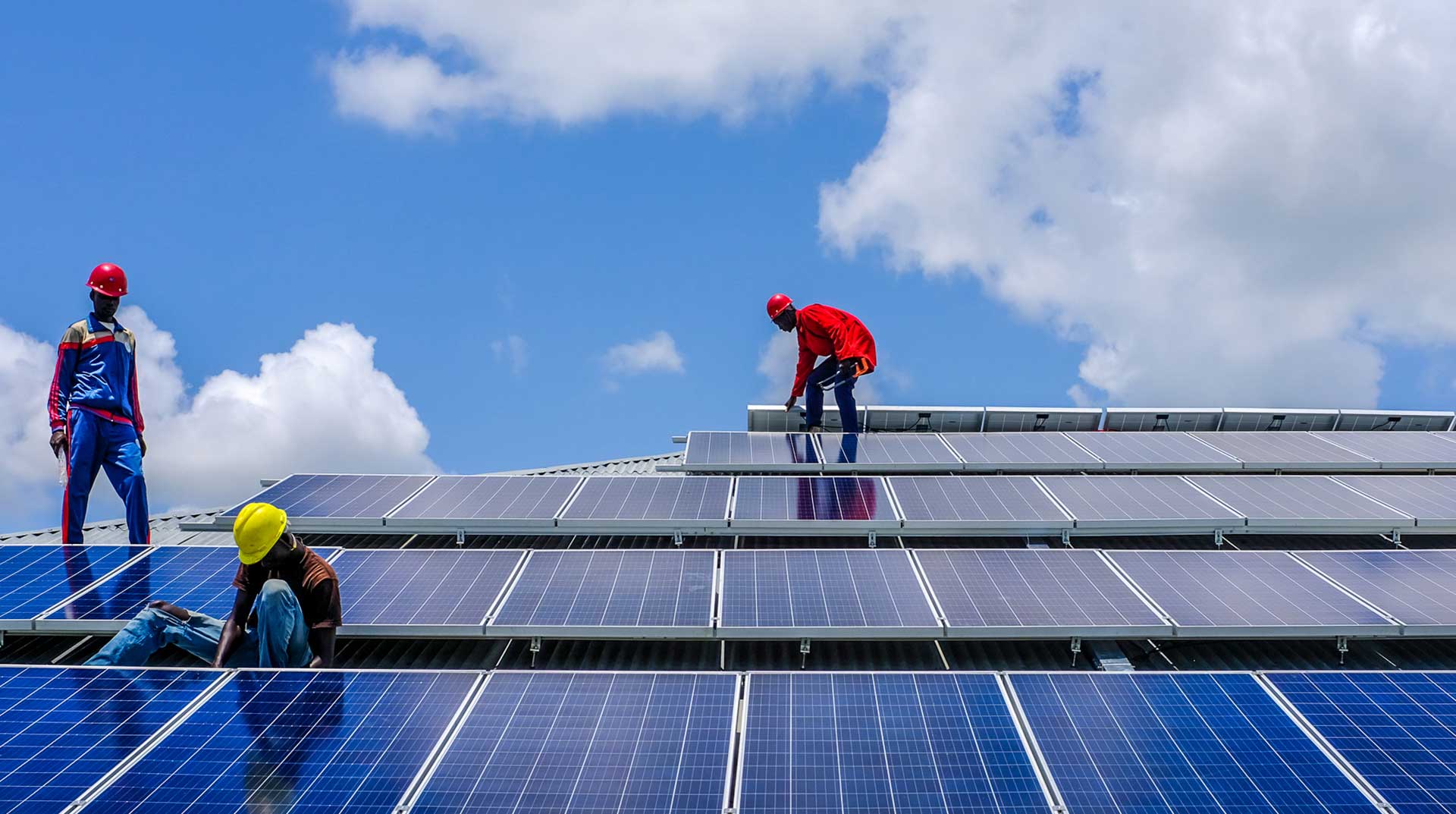
- Wind Energy – Wind energy is an easily available resource. It is also a free resource. It is a renewable source of energy and the energy which can be produced by harnessing the power of wind will be beneficial for everyone. Windmills can produce energy which can be used to our benefit. It can be a helpful source of reducing the cost of grid power and is a fine example of sustainable development.
- Solar Energy – Solar energy is also a source of energy which is readily available and there is no limit to it. Solar energy is being used to replace and do many things which were first being done by using non-renewable sources of energy. Solar water heaters are a good example. It is cost-effective and sustainable at the same time.
- Crop Rotation – To increase the potential of growth of gardening land, crop rotation is an ideal and sustainable way. It is rid of any chemicals and reduces the chances of disease in the soil. This form of sustainable development is beneficial to both commercial farmers and home gardeners.
- Efficient Water Fixtures – The installation of hand and head showers in our toilets which are efficient and do not waste or leak water is a method of conserving water. Water is essential for us and conserving every drop is important. Spending less time under the shower is also a way of sustainable development and conserving water.
- Sustainable Forestry – This is an amazing way of sustainable development where the timber trees that are cut by factories are replaced by another tree. A new tree is planted in place of the one which was cut down. This way, soil erosion is prevented and we have hope of having a better, greener future.
Related Articles
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015. These include: No Poverty Zero Hunger Good Health and Well-being Quality Education Gender Equality Clean Water and Sanitation Affordable and Clean Energy Decent Work and Economic Growth Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure Reduced Inequality Sustainable Cities and Communities Responsible Consumption and Production Climate Action Life Below Water Life on Land Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions Partnerships for the Goals
The SDGs are designed to address a wide range of global challenges, such as eradicating extreme poverty globally, achieving food security, focusing on promoting good health and well-being, inclusive and equitable quality education, etc.
India is ranked #111 in the Sustainable Development Goal Index 2023 with a score of 63.45.
Hence, we hope that this blog helped you understand the key features of an essay on sustainable development. If you are interested in Environmental studies and planning to pursue sustainable tourism courses , take the assistance of Leverage Edu ’s AI-based tool to browse through a plethora of programs available in this specialised field across the globe and find the best course and university combination that fits your interests, preferences and aspirations. Call us immediately at 1800 57 2000 for a free 30-minute counselling session
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Thanks a lot for this important essay.
NICELY AND WRITTEN WITH CLARITY TO CONCEIVE THE CONCEPTS BEHIND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY.
Thankyou so much!

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals were adopted by the United Nations in 2015 as a call-to-action for people worldwide to address five critical areas of importance by 2030: people, planet, prosperity, peace, and partnership.
Biology, Health, Conservation, Geography, Human Geography, Social Studies, Civics
Set forward by the United Nations (UN) in 2015, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) are a collection of 17 global goals aimed at improving the planet and the quality of human life around the world by the year 2030.
Image courtesy of the United Nations

In 2015, the 193 countries that make up the United Nations (UN) agreed to adopt the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The historic agenda lays out 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and targets for dignity, peace, and prosperity for the planet and humankind, to be completed by the year 2030. The agenda targets multiple areas for action, such as poverty and sanitation , and plans to build up local economies while addressing people's social needs.
In short, the 17 SDGs are:
Goal 1: No Poverty: End poverty in all its forms everywhere.
Goal 2: Zero Hunger: End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture.
Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Goal 4: Quality Education: Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
Goal 5: Gender Equality : Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls.
Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation: Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all.
Goal 7: Affordable and Clean Energy: Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all.
Goal 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth: Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all.
Goal 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation.
Goal 10: Reduced Inequality : Reduce in equality within and among countries.
Goal 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities: Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.
Goal 12: Responsible Consumption and Production: Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns.
Goal 13: Climate Action: Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
Goal 14: Life Below Water: Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development.
Goal 15: Life on Land: Protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss.
Goal 16: Peace, Justice , and Strong Institutions: Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions at all levels.
Goal 17: Partnerships to Achieve the Goal: Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development.
The SDGs build on over a decade of work by participating countries. In essence, the SDGs are a continuation of the eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), which began in the year 2000 and ended in 2015. The MDGs helped to lift nearly one billion people out of extreme poverty, combat hunger, and allow more girls to attend school. The MDGs, specifically goal seven, helped to protect the planet by practically eliminating global consumption of ozone-depleting substances; planting trees to offset the loss of forests; and increasing the percent of total land and coastal marine areas worldwide. The SDGs carry on the momentum generated by the MDGs with an ambitious post-2015 development agenda that may cost over $4 trillion each year. The SDGs were a result of the 2012 Rio+20 Earth Summit, which demanded the creation of an open working group to develop a draft agenda for 2015 and onward.
Unlike the MDGs, which relied exclusively on funding from governments and nonprofit organizations, the SDGs also rely on the private business sector to make contributions that change impractical and unsustainable consumption and production patterns. Novozymes, a purported world leader in biological solutions, is just one example of a business that has aligned its goals with the SDGs. Novozymes has prioritized development of technology that reduces the amount of water required for waste treatment. However, the UN must find more ways to meaningfully engage the private sector to reach the goals, and more businesses need to step up to the plate to address these goals.
Overall, limited progress has been made with the SDGs. According to the UN, many people are living healthier lives now compared to the start of the millennium, representing one area of progress made by the MDGs and SDGs. For example, the UN reported that between 2012 and 2017, 80 percent of live births worldwide had assistance from a skilled health professional—an improvement from 62 percent between 2000 and 2005.
While some progress has been made, representatives who attended sustainable development meetings claimed that the SDGs are not being accomplished at the speed, or with the appropriate momentum, needed to meet the 2030 deadline. On some measures of poverty, only slight improvements have been made: The 2018 SDGs Report states that 9.2 percent of the world's workers who live with family members made less than $1.90 per person per day in 2017, representing less than a 1 percent improvement from 2015. Another issue is the recent rise in world hunger. Rates had been steadily declining, but the 2018 SDGs Report stated that over 800 million people were undernourished worldwide in 2016, which is up from 777 million people in 2015.
Another area of the SDGs that lacks progress is gender equality. Multiple news outlets have recently reported that no country is on track to achieve gender equality by 2030 based on the SDG gender index. On a scale of zero to 100, where a score of 100 means equality has been achieved, Denmark was the top performing country out of 129 countries with score slightly under 90. A score of 90 or above means a country is making excellent progress in achieving the goals, and 59 or less is considered poor headway. Countries were scored against SDGs targets that particularly affect women, such as access to safe water or the Internet. The majority of the top 20 countries with a good ranking were European countries, while sub-Saharan Africa had some of the lowest-ranking countries. The overall average score of all countries is a poor score of 65.7.
In fall of 2019, heads of state and government will convene at the United Nations Headquarters in New York to assess the progress in the 17 SDGs. The following year—2020—marks the deadline for 21 of the 169 SDG targets. At this time, UN member states will meet to make a decision to update these targets.
In addition to global efforts to achieve the SDGs, according to the UN, there are ways that an individual can contribute to progress: save on electricity while home by unplugging appliances when not in use; go online and opt in for paperless statements instead of having bills mailed to the house; and report bullying online when seen in a chat room or on social media.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction of Sustainability, Sustainable Development, and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
What is sustainability.
Sustainability is a well-known and frequently used term of the 21st century. How often do you see or hear the word? Have you ever stopped to really think about what exactly does sustainability mean and where did the term originate from?
A quick Google search for ‘what is sustainability’ yields over 1.9 billion results. Sustainability is widely defined as ‘the ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level’. Embedded in most definitions of sustainability are concerns for the environment, social equity, and economic prosperity(1). Most definitions look to avoid the depletion of natural resources to maintain an ecological balance. Sustainability in the context of the environment looks at the activities required to balance social, economic, and environmental needs to maintain ecosystem services at a suitable level. It is generally accepted, the goals of sustainability are related to the need for the conservation of natural capital and ecosystem services, with a shift to a less resource-intensive future [1] .
While to most, the concept of sustainability is a relatively new idea, sustainability has a long history of use and meaning. The practice of sustainability has been utilized by various cultures for thousands of years, with the term sustainability first used in the 1700’s. Sustainability comes from the practice of nachhaltigkeit , translated to mean ‘sustained yield’ in English, a term coined in 1713 by German foresters [2] . Sustained yield refers to the practice of taking only enough trees to allow forests to naturally regenerate well into the future. The concept of sustained yield broadened to include the conservation of plants, animals, and other food necessities, eventually moving beyond the forestry discourse but still mainly confined to research and science.
It was not until the 1970’s that the concept of sustainability became more widely used. In January 1972, the journal the Ecologist published the Blueprint for Survival , a series of science papers calling for better management of natural resources and modification of consumptive lifestyles of western civilizations. That same year, a global think-tank published the report Limits to Growth , where a definition was given to the term sustainable. For the first time in the literature, sustainable was defined to mean without sudden and uncontrolled collapse and capable of satisfying the basic material requirements of all its people (2). Then later that year the United Nations (UN) world conference on human environment was held Stockholm, Sweden to address the global the growing environmental crisis. The term sustainable development was introduced into the discourse. As evidenced at the UN Conference, the environment was being neglected and not in balance with economic development.
Through the 1980’s, the concept of sustainability became more mainstream. In 1987, former Norwegian Prime Minister Gro Harlem Brundtland, as chairwoman of what was then the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) released a Report, widely known as the Brundtland’s Commission, Our Common Future . The report emphasized the importance that development should consider social, environmental, and economic aspects to ensure the sustainability of all human societies. Her main concern was that development had to meet “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” [3] . This concept went on to become the most widely used definition of sustainability although in the context of sustainable development.
Although sustainability and sustainable development both consider the environment, society, and economies with a future timeframe, the two terms have very different meanings and should not be used interchangeably. Sustainability looks at the activities required to protect the environment as our base for survival while balancing social, cultural, and economic needs. It is generally accepted that the goals of sustainability are related to the need to conserve our natural world with a shift away from the resource-intensive current way of living 1 .
What is Sustainable Development?
We learned that sustainability is the process of living within the limits of available physical, natural, and social resources in ways that allow all living things, not only humans to thrive well into the future.
Sustainable development is a process that creates growth and progress through the addition of physical, economic, environmental, and social components to improve quality of life without damaging the resources of the environment. Simply put, sustainable development is a way for people to use resources without the resources running out 3 .
As previously discussed, the concept of sustainable development arrived in 1987 by the Brundtland Commission “Our Common Future”, the document that defined sustainable development as an approach designed to meet the needs of the present [generation] without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs 3 . This definition incorporated the understanding that economic growth is required to provide societies with the necessities of life such as clean water and food, while acknowledging the dilemma of environmental degradation that often coincides with economic development.
In 1992 the UN conference on the environment and development, informally known as the Earth Summit, or the Rio Conference took place in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The conference promoted the idea of ecological sustainable development and in order to achieve it you had to consider social development (communities). From the mid 1990’s, different strategies were developed to try to work out what sustainability means in practice, how do we get that middle area where the environment, economics, and social development are achieved at the same time. Governments alone can not achieve sustainable development. Governments can set regulations and determine infrastructure needs but they don’t tend to have long-term goals in mind, they tend to focus on election cycles which are typically about 4 to 8 years. The market economies (goods and services) timeframe is usually only about 4 months to a year. Sustainability is about long-term solutions. The market economies and governments can not effectively do this. If the community is not driving the will for a better more sustainable future, sustainable development will be difficult to achieve. As we previously discussed, the Brundtland Commission’s definition has become a widely used definition for sustainable development and sustainability and has therefore come with many challenges, including confusion over meaning, interpretations, and misinformation.
Recognizing some of the key challenges with the implementation of sustainable development and the quest for achieving a balance between the environment and economies, the role of people and societies were formally added into the equation for sustainable development in 2005 at the UN World Summit on Social Development. The three pillars of sustainability became widely known and currently used today:
(Click on the “?” icons below for more information):
This updated model for sustainable development recognizes that in order to meet the needs of current and future generations you have to consider the three pillars or the 3P’s (people, planet, prosperity), and they all need to be working together at the same. The key being all at the same time, or simultaneously.
Integrating the short-term and long-term needs with a focus on future generations, will require social development, environmental protection, and economic prosperity working in unison. Being able to incorporate sustainability into your day to day activities, this is what will create change.
The United Nations and the Path to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
History of the un.
Direct Source
The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945 after the Second World War by 51 countries committed to maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations, and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights.
Due to its unique international character, and the powers vested in its founding Charter, the Organization can take action on a wide range of issues and provide a forum for its 193 Member States to express their views, through the General Assembly, the Security Council, the Economic and Social Council and other bodies and committees.
The work of the United Nations reaches every corner of the globe. Although best known for peacekeeping, peace-building, conflict prevention and humanitarian assistance, there are many other ways the United Nations and its System (specialized agencies, funds, and programmes) affect our lives and make the world a better place. The Organization works on a broad range of fundamental issues, from sustainable development, environment and refugees protection, disaster relief, counter terrorism, disarmament and non-proliferation, to promoting democracy, human rights, gender equality and the advancement of women, governance, economic and social development and international health, clearing landmines, expanding food production, and more, in order to achieve its goals and coordinate efforts for a safer world for this and future generations.
The UN has 4 main purposes:
- To keep peace throughout the world;
- To develop friendly relations among nations;
- To help nations work together to improve the lives of poor people, to conquer hunger, disease, and illiteracy, and to encourage respect for each other’s rights and freedoms;
- To be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations to achieve these goals
Pathway to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
In 2015, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development was adopted by 193 United Nations (UN) Member States. The 2030 Agenda is centered on the 17 SDGs which are underpinned by the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). The MDGs were developed in 2000 to end poverty and hunger, fight inequality and injustice, advance climate change action, create sustainable consumption and production, and promote peace and prosperity for all. One major change between the MDGs versus the SDGs is that for the SDGs, all countries are now involved. The MDGs only applied to developing countries. Another difference is that each country has set their own goals and priorities for achieving the SDGs. International collaboration to advance the SDG Agenda remains a critical component. The 17 SD goals, with their 169 targets, and over 230 indicators work together at the local and international level to help promote a shared global framework to achieve a fair, equitable, and sustainable future for all. Currently, all countries and international organizations are working on the achievement of the UN 2030 Agenda serving as the basis for better economic development that is environmentally low impact, socially just, and economically efficient and fair.
Pathway to the SDGs
Comprehension Questions
Recommended reading.
- Sustainable Development Solutions Network. (2021). Sustainable Development Report 2021: The Decade of Action for the Sustainable Development Goals .
Additional Readings
- Brundtland G, Khalid M. 1987. UN Brundtland commission report. Our Common Future . 41-59.
- Kidd C. V. 1992. The evolution of sustainability . Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Ethics , 5(1), 1-26.
- Baker, J., Dupont, D., & Vasseur, L. (2021). Exploring Canadian Ramsar Sites Ecosystem Governance and Sustainability. Wetlands, 41(1), 1-11. ↵
- Grober, U. (2007). Deep roots-a conceptual history of sustainable development (Nachhaltigkeit) . ↵
- United Nations. (2021). 1987 Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future (page 41) . ↵
Introduction to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Copyright © by Jocelyn Baker is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Get involved

THE SDGS IN ACTION.
What are the sustainable development goals.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), also known as the Global Goals, were adopted by the United Nations in 2015 as a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that by 2030 all people enjoy peace and prosperity.
The 17 SDGs are integrated—they recognize that action in one area will affect outcomes in others, and that development must balance social, economic and environmental sustainability.
Countries have committed to prioritize progress for those who're furthest behind. The SDGs are designed to end poverty, hunger, AIDS, and discrimination against women and girls.
The creativity, knowhow, technology and financial resources from all of society is necessary to achieve the SDGs in every context.

Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015, too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs.
As of 2015, about 736 million people still lived on less than US$1.90 a day; many lack food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid growth in countries such as China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to be poor than men because they have less paid work, education, and own less property.
Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty.
The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started, and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing basic resources and services, and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.

736 million people still live in extreme poverty.
10 percent of the world’s population live in extreme poverty, down from 36 percent in 1990.
Some 1.3 billion people live in multidimensional poverty.
Half of all people living in poverty are under 18.
One person in every 10 is extremely poor.
Goal targets
- By 2030, reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions according to national definitions
- Implement nationally appropriate social protection systems and measures for all, including floors, and by 2030 achieve substantial coverage of the poor and the vulnerable
- By 2030, ensure that all men and women, in particular the poor and the vulnerable, have equal rights to economic resources, as well as access to basic services, ownership and control over land and other forms of property, inheritance, natural resources, appropriate new technology and financial services, including microfinance
- By 2030, build the resilience of the poor and those in vulnerable situations and reduce their exposure and vulnerability to climate-related extreme events and other economic, social and environmental shocks and disasters
- Ensure significant mobilization of resources from a variety of sources, including through enhanced development cooperation, in order to provide adequate and predictable means for developing countries, in particular least developed countries, to implement programmes and policies to end poverty in all its dimensions
- Create sound policy frameworks at the national, regional and international levels, based on pro-poor and gender-sensitive development strategies, to support accelerated investment in poverty eradication actions
SDGs in Action

UNDP’s Engagement at Financing...

Voices of youth in the lead up...

Building a new, secure climate...
Publications.

Accelerating the Green Transit...

Localizing Multidimensional Po...

Mapping Essential Life Support...
Zero hunger.

Zero Hunger
The number of undernourished people has dropped by almost half in the past two decades because of rapid economic growth and increased agricultural productivity. Many developing countries that used to suffer from famine and hunger can now meet their nutritional needs. Central and East Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean have all made huge progress in eradicating extreme hunger.
Unfortunately, extreme hunger and malnutrition remain a huge barrier to development in many countries. There are 821 million people estimated to be chronically undernourished as of 2017, often as a direct consequence of environmental degradation, drought and biodiversity loss. Over 90 million children under five are dangerously underweight. Undernourishment and severe food insecurity appear to be increasing in almost all regions of Africa, as well as in South America.
The SDGs aim to end all forms of hunger and malnutrition by 2030, making sure all people–especially children–have sufficient and nutritious food all year. This involves promoting sustainable agricultural, supporting small-scale farmers and equal access to land, technology and markets. It also requires international cooperation to ensure investment in infrastructure and technology to improve agricultural productivity.

The number of undernourished people reached 821 million in 2017.
In 2017 Asia accounted for nearly two thirds, 63 percent, of the world’s hungry.
Nearly 151 million children under five, 22 percent, were still stunted in 2017.
More than 1 in 8 adults is obese.
1 in 3 women of reproductive age is anemic.
26 percent of workers are employed in agriculture.
- By 2030, end all forms of malnutrition, including achieving, by 2025, the internationally agreed targets on stunting and wasting in children under 5 years of age, and address the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women and older persons
- By 2030, double the agricultural productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers, in particular women, indigenous peoples, family farmers, pastoralists and fishers, including through secure and equal access to land, other productive resources and inputs, knowledge, financial services, markets and opportunities for value addition and non-farm employment
- By 2030, ensure sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agricultural practices that increase productivity and production, that help maintain ecosystems, that strengthen capacity for adaptation to climate change, extreme weather, drought, flooding and other disasters and that progressively improve land and soil quality
- By 2020, maintain the genetic diversity of seeds, cultivated plants and farmed and domesticated animals and their related wild species, including through soundly managed and diversified seed and plant banks at the national, regional and international levels, and promote access to and fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources and associated traditional knowledge, as internationally agreed
- Increase investment, including through enhanced international cooperation, in rural infrastructure, agricultural research and extension services, technology development and plant and livestock gene banks in order to enhance agricultural productive capacity in developing countries, in particular least developed countries
- Correct and prevent trade restrictions and distortions in world agricultural markets, including through the parallel elimination of all forms of agricultural export subsidies and all export measures with equivalent effect, in accordance with the mandate of the Doha Development Round
- Adopt measures to ensure the proper functioning of food commodity markets and their derivatives and facilitate timely access to market information, including on food reserves, in order to help limit extreme food price volatility.

One year into war, much remain...

UNDP at the 4th International ...

UNDP at the UN ECOSOC Youth Fo...

"We felt very welcome and acce...
Good health and well-being.

We have made great progress against several leading causes of death and disease. Life expectancy has increased dramatically; infant and maternal mortality rates have declined, we’ve turned the tide on HIV and malaria deaths have halved.
Good health is essential to sustainable development and the 2030 Agenda reflects the complexity and interconnectedness of the two. It takes into account widening economic and social inequalities, rapid urbanization, threats to the climate and the environment, the continuing burden of HIV and other infectious diseases, and emerging challenges such as noncommunicable diseases. Universal health coverage will be integral to achieving SDG 3, ending poverty and reducing inequalities. Emerging global health priorities not explicitly included in the SDGs, including antimicrobial resistance, also demand action.
But the world is off-track to achieve the health-related SDGs. Progress has been uneven, both between and within countries. There’s a 31-year gap between the countries with the shortest and longest life expectancies. And while some countries have made impressive gains, national averages hide that many are being left behind. Multisectoral, rights-based and gender-sensitive approaches are essential to address inequalities and to build good health for all.

At least 400 million people have no basic healthcare, and 40 percent lack social protection.
More than 1.6 billion people live in fragile settings where protracted crises, combined with weak national capacity to deliver basic health services, present a significant challenge to global health.
By the end of 2017, 21.7 million people living with HIV were receiving antiretroviral therapy. Yet more than 15 million people are still waiting for treatment.
Every 2 seconds someone aged 30 to 70 years dies prematurely from noncommunicable diseases - cardiovascular disease, chronic respiratory disease, diabetes or cancer.
7 million people die every year from exposure to fine particles in polluted air.
More than one of every three women have experienced either physical or sexual violence at some point in their life resulting in both short- and long-term consequences for their physical, mental, and sexual and reproductive health.
- By 2030, reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births
- By 2030, end preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age, with all countries aiming to reduce neonatal mortality to at least as low as 12 per 1,000 live births and under-5 mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births
- By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases and combat hepatitis, water-borne diseases and other communicable diseases
- By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being
- Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse, including narcotic drug abuse and harmful use of alcohol
- By 2020, halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents
- By 2030, ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services, including for family planning, information and education, and the integration of reproductive health into national strategies and programmes
- Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection, access to quality essential health-care services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines and vaccines for all
- By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination
- Strengthen the implementation of the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in all countries, as appropriate
- Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and noncommunicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights regarding flexibilities to protect public health, and, in particular, provide access to medicines for all
- Substantially increase health financing and the recruitment, development, training and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, especially in least developed countries and small island developing States
- Strengthen the capacity of all countries, in particular developing countries, for early warning, risk reduction and management of national and global health risks

HIV and Health Annual Report 2...

Bridging Gender Gaps with a Su...

How Do Investments in Human Ca...
Quality education.

Since 2000, there has been enormous progress in achieving the target of universal primary education. The total enrollment rate in developing regions reached 91 percent in 2015, and the worldwide number of children out of school has dropped by almost half. There has also been a dramatic increase in literacy rates, and many more girls are in school than ever before. These are all remarkable successes.
Progress has also been tough in some developing regions due to high levels of poverty, armed conflicts and other emergencies. In Western Asia and North Africa, ongoing armed conflict has seen an increase in the number of children out of school. This is a worrying trend. While Sub-Saharan Africa made the greatest progress in primary school enrollment among all developing regions – from 52 percent in 1990, up to 78 percent in 2012 – large disparities still remain. Children from the poorest households are up to four times more likely to be out of school than those of the richest households. Disparities between rural and urban areas also remain high.
Achieving inclusive and quality education for all reaffirms the belief that education is one of the most powerful and proven vehicles for sustainable development. This goal ensures that all girls and boys complete free primary and secondary schooling by 2030. It also aims to provide equal access to affordable vocational training, to eliminate gender and wealth disparities, and achieve universal access to a quality higher education.

Enrollment in primary education in developing countries has reached 91 percent.
Still, 57 million primary-aged children remain out of school, more than half of them in sub-Saharan Africa.
In developing countries, one in four girls is not in school.
About half of all out-of-school children of primary school age live in conflict-affected areas.
103 million youth worldwide lack basic literacy skills, and more than 60 percent of them are women.
6 out of 10 children and adolescents are not achieving a minimum level of proficiency in reading and math.
- By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys complete free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education leading to relevant and Goal-4 effective learning outcomes
- By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys have access to quality early childhood development, care and preprimary education so that they are ready for primary education
- By 2030, ensure equal access for all women and men to affordable and quality technical, vocational and tertiary education, including university
- By 2030, substantially increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs and entrepreneurship
- By 2030, eliminate gender disparities in education and ensure equal access to all levels of education and vocational training for the vulnerable, including persons with disabilities, indigenous peoples and children in vulnerable situations
- By 2030, ensure that all youth and a substantial proportion of adults, both men and women, achieve literacy and numeracy
- By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including, among others, through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship and appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture’s contribution to sustainable development
- Build and upgrade education facilities that are child, disability and gender sensitive and provide safe, nonviolent, inclusive and effective learning environments for all
- By 2020, substantially expand globally the number of scholarships available to developing countries, in particular least developed countries, small island developing States and African countries, for enrolment in higher education, including vocational training and information and communications technology, technical, engineering and scientific programmes, in developed countries and other developing countries
- By 2030, substantially increase the supply of qualified teachers, including through international cooperation for teacher training in developing countries, especially least developed countries and small island developing states

Using technology to support ne...

The future of education

A brighter future: Lillian
Gender equality.

Gender Equality
Ending all discrimination against women and girls is not only a basic human right, it’s crucial for sustainable future; it’s proven that empowering women and girls helps economic growth and development.
UNDP has made gender equality central to its work and we’ve seen remarkable progress in the past 20 years. There are more girls in school now compared to 15 years ago, and most regions have reached gender parity in primary education.
But although there are more women than ever in the labour market, there are still large inequalities in some regions, with women systematically denied the same work rights as men. Sexual violence and exploitation, the unequal division of unpaid care and domestic work, and discrimination in public office all remain huge barriers. Climate change and disasters continue to have a disproportionate effect on women and children, as do conflict and migration.
It is vital to give women equal rights land and property, sexual and reproductive health, and to technology and the internet. Today there are more women in public office than ever before, but encouraging more women leaders will help achieve greater gender equality.

Women earn only 77 cents for every dollar that men get for the same work.
35 percent of women have experienced physical and/or sexual violence.
Women represent just 13 percent of agricultural landholders.
Almost 750 million women and girls alive today were married before their 18th birthday.
Two thirds of developing countries have achieved gender parity in primary education.
Only 24 percent of national parliamentarians were women as of November 2018, a small increase from 11.3 percent in 1995.
- End all forms of discrimination against all women and girls everywhere
- Eliminate all forms of violence against all women and girls in the public and private spheres, including trafficking and sexual and other types of exploitation
- Eliminate all harmful practices, such as child, early and forced marriage and female genital mutilation
- Recognize and value unpaid care and domestic work through the provision of public services, infrastructure and social protection policies and the promotion of shared responsibility within the household and the family as nationally appropriate
- Ensure women’s full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decisionmaking in political, economic and public life
- Ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights as agreed in accordance with the Programme of Action of the International Conference on Population and Development and the Beijing Platform for Action and the outcome documents of their review conferences
- Undertake reforms to give women equal rights to economic resources, as well as access to ownership and control over land and other forms of property, financial services, inheritance and natural resources, in accordance with national laws
- Enhance the use of enabling technology, in particular information and communications technology, to promote the empowerment of women
- Adopt and strengthen sound policies and enforceable legislation for the promotion of gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls at all levels

SDG Push through Social Protec...

Climate governance, adaptation...
Clean water and sanitation.

Water scarcity affects more than 40 percent of people, an alarming figure that is projected to rise as temperatures do. Although 2.1 billion people have improved water sanitation since 1990, dwindling drinking water supplies are affecting every continent.
More and more countries are experiencing water stress, and increasing drought and desertification is already worsening these trends. By 2050, it is projected that at least one in four people will suffer recurring water shortages.
Safe and affordable drinking water for all by 2030 requires we invest in adequate infrastructure, provide sanitation facilities, and encourage hygiene. Protecting and restoring water-related ecosystems is essential.
Ensuring universal safe and affordable drinking water involves reaching over 800 million people who lack basic services and improving accessibility and safety of services for over two billion.
In 2015, 4.5 billion people lacked safely managed sanitation services (with adequately disposed or treated excreta) and 2.3 billion lacked even basic sanitation.

71 percent of the global population, 5.2 billion people, had safely-managed drinking water in 2015, but 844 million people still lacked even basic drinking water.
39 percent of the global population, 2.9 billion people, had safe sanitation in 2015, but 2.3 billion people still lacked basic sanitation. 892 million people practiced open defecation.
80 percent of wastewater goes into waterways without adequate treatment.
Water stress affects more than 2 billion people, with this figure projected to increase.
80 percent of countries have laid the foundations for integrated water resources management.
The world has lost 70 percent of its natural wetlands over the last century.
- By 2030, achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all
- By 2030, achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all and end open defecation, paying special attention to the needs of women and girls and those in vulnerable situations
- By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally
- By 2030, substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity and substantially reduce the number of people suffering from water scarcity
- By 2030, implement integrated water resources management at all levels, including through transboundary cooperation as appropriate
- By 2020, protect and restore water-related ecosystems, including mountains, forests, wetlands, rivers, aquifers and lakes
- By 2030, expand international cooperation and capacity-building support to developing countries in water- and sanitation-related activities and programmes, including water harvesting, desalination, water efficiency, wastewater treatment, recycling and reuse technologies
- Support and strengthen the participation of local communities in improving water and sanitation management

The challenges facing Sudan

Navigating the crossroads of c...
Affordable and clean energy.

Between 2000 and 2018, the number of people with electricity increased from 78 to 90 percent, and the numbers without electricity dipped to 789 million.
Yet as the population continues to grow, so will the demand for cheap energy, and an economy reliant on fossil fuels is creating drastic changes to our climate.
Investing in solar, wind and thermal power, improving energy productivity, and ensuring energy for all is vital if we are to achieve SDG 7 by 2030.
Expanding infrastructure and upgrading technology to provide clean and more efficient energy in all countries will encourage growth and help the environment.

One out of 10 people still lacks electricity, and most live in rural areas of the developing world. More than half are in sub-Saharan Africa.
Energy is by far the main contributor to climate change. It accounts for 73 percent of human-caused greenhouse gases.
Energy efficiency is key; the right efficiency policies could enable the world to achieve more than 40 percent of the emissions cuts needed to reach its climate goals without new technology.
Almost a third of the world’s population—2.8 billion—rely on polluting and unhealthy fuels for cooking.
As of 2017, 17.5 percent of power was generated through renewable sources.
The renewable energy sector employed a record 11.5 million people in 2019. The changes needed in energy production and uses to achieve the Paris Agreement target of limiting the rise in temperature to below 2C can create 18 million jobs.
- By 2030, ensure universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services
- By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix
- By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency
- By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology
- By 2030, expand infrastructure and upgrade technology for supplying modern and sustainable energy services for all in developing countries, in particular least developed countries, small island developing States, and land-locked developing coun

The big switch

Targeted and Inclusive Approac...

Breaking the cycle of poverty ...
Decent work and economic growth.

Over the past 25 years the number of workers living in extreme poverty has declined dramatically, despite the lasting impact of the 2008 economic crisis and global recession. In developing countries, the middle class now makes up more than 34 percent of total employment – a number that has almost tripled between 1991 and 2015.
However, as the global economy continues to recover we are seeing slower growth, widening inequalities, and not enough jobs to keep up with a growing labour force. According to the International Labour Organization, more than 204 million people were unemployed in 2015.
The SDGs promote sustained economic growth, higher levels of productivity and technological innovation. Encouraging entrepreneurship and job creation are key to this, as are effective measures to eradicate forced labour, slavery and human trafficking. With these targets in mind, the goal is to achieve full and productive employment, and decent work, for all women and men by 2030.

An estimated 172 million people worldwide were without work in 2018 - an unemployment rate of 5 percent.
As a result of an expanding labour force, the number of unemployed is projected to increase by 1 million every year and reach 174 million by 2020.
Some 700 million workers lived in extreme or moderate poverty in 2018, with less than US$3.20 per day.
Women’s participation in the labour force stood at 48 per cent in 2018, compared with 75 percent for men. Around 3 in 5 of the 3.5 billion people in the labour force in 2018 were men.
Overall, 2 billion workers were in informal employment in 2016, accounting for 61 per cent of the world’s workforce.
Many more women than men are underutilized in the labour force—85 million compared to 55 million.
- Sustain per capita economic growth in accordance with national circumstances and, in particular, at least 7 per cent gross domestic product growth per annum in the least developed countries
- Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labour-intensive sectors
- Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation, and encourage the formalization and growth of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises, including through access to financial services
- Improve progressively, through 2030, global resource efficiency in consumption and production and endeavour to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation, in accordance with the 10-year framework of programmes on sustainable consumption and production, with developed countries taking the lead
- By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including for young people and persons with disabilities, and equal pay for work of equal value
- By 2020, substantially reduce the proportion of youth not in employment, education or training
- Take immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labour, end modern slavery and human trafficking and secure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour, including recruitment and use of child soldiers, and by 2025 end child labour in all its forms
- Protect labour rights and promote safe and secure working environments for all workers, including migrant workers, in particular women migrants, and those in precarious employment
- By 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products
- Strengthen the capacity of domestic financial institutions to encourage and expand access to banking, insurance and financial services for all
- Increase Aid for Trade support for developing countries, in particular least developed countries, including through the Enhanced Integrated Framework for Trade-Related Technical Assistance to Least Developed Countries
- By 2020, develop and operationalize a global strategy for youth employment and implement the Global Jobs Pact of the International Labour Organization

Preparing Cities for Climate D...
Industry, innovation and infrastructure.

Investment in infrastructure and innovation are crucial drivers of economic growth and development. With over half the world population now living in cities, mass transport and renewable energy are becoming ever more important, as are the growth of new industries and information and communication technologies.
Technological progress is also key to finding lasting solutions to both economic and environmental challenges, such as providing new jobs and promoting energy efficiency. Promoting sustainable industries, and investing in scientific research and innovation, are all important ways to facilitate sustainable development.
More than 4 billion people still do not have access to the Internet, and 90 percent are from the developing world. Bridging this digital divide is crucial to ensure equal access to information and knowledge, as well as foster innovation and entrepreneurship.

Worldwide, 2.3 billion people lack access to basic sanitation.
In some low-income African countries, infrastructure constraints cut businesses’ productivity by around 40 percent.
2.6 billion people in developing countries do not have access to constant electricity.
More than 4 billion people still do not have access to the Internet; 90 percent of them are in the developing world.
The renewable energy sectors currently employ more than 2.3 million people; the number could reach 20 million by 2030.
In developing countries, barely 30 percent of agricultural products undergo industrial processing, compared to 98 percent high-income countries.
- Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all
- Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and, by 2030, significantly raise industry’s share of employment and gross domestic product, in line with national circumstances, and double its share in least developed countries
- Increase the access of small-scale industrial and other enterprises, in particular in developing countries, to financial services, including affordable credit, and their integration into value chains and markets
- By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes, with all countries taking action in accordance with their respective capabilities
- Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries, in particular developing countries, including, by 2030, encouraging innovation and substantially increasing the number of research and development workers per 1 million people and public and private research and development spending
- Facilitate sustainable and resilient infrastructure development in developing countries through enhanced financial, technological and technical support to African countries, least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing States 18
- Support domestic technology development, research and innovation in developing countries, including by ensuring a conducive policy environment for, inter alia, industrial diversification and value addition to commodities
- Significantly increase access to information and communications technology and strive to provide universal and affordable access to the Internet in least developed countries by 2020
How Digital is Transforming th...

Popping the bottle

Small Island Digital States: H...
Reduced inequalities.

Income inequality is on the rise—the richest 10 percent have up to 40 percent of global income whereas the poorest 10 percent earn only between 2 to 7 percent. If we take into account population growth inequality in developing countries, inequality has increased by 11 percent.
Income inequality has increased in nearly everywhere in recent decades, but at different speeds. It’s lowest in Europe and highest in the Middle East.
These widening disparities require sound policies to empower lower income earners, and promote economic inclusion of all regardless of sex, race or ethnicity.
Income inequality requires global solutions. This involves improving the regulation and monitoring of financial markets and institutions, encouraging development assistance and foreign direct investment to regions where the need is greatest. Facilitating the safe migration and mobility of people is also key to bridging the widening divide.

In 2016, 22 percent of global income was received by the top 1 percent compared with 10 percent of income for the bottom 50 percent.
In 1980, the top one percent had 16 percent of global income. The bottom 50 percent had 8 percent of income.
Economic inequality is largely driven by the unequal ownership of capital. Since 1980, very large transfers of public to private wealth occurred in nearly all countries. The global wealth share of the top 1 percent was 33 percent in 2016.
Under "business as usual", the top 1 percent global wealth will reach 39 percent by 2050.
Women spend, on average, twice as much time on unpaid housework as men.
Women have as much access to financial services as men in just 60 percent of the countries assessed and to land ownership in just 42 percent of the countries assessed.
- By 2030, progressively achieve and sustain income growth of the bottom 40 per cent of the population at a rate higher than the national average
- By 2030, empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all, irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion or economic or other status
- Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities of outcome, including by eliminating discriminatory laws, policies and practices and promoting appropriate legislation, policies and action in this regard
- Adopt policies, especially fiscal, wage and social protection policies, and progressively achieve greater equality
- Improve the regulation and monitoring of global financial markets and institutions and strengthen the implementation of such regulations
- Ensure enhanced representation and voice for developing countries in decision-making in global international economic and financial institutions in order to deliver more effective, credible, accountable and legitimate institutions
- Facilitate orderly, safe, regular and responsible migration and mobility of people, including through the implementation of planned and well-managed migration policies
- Implement the principle of special and differential treatment for developing countries, in particular least developed countries, in accordance with World Trade Organization agreements
- Encourage official development assistance and financial flows, including foreign direct investment, to States where the need is greatest, in particular least developed countries, African countries, small island developing States and landlocked developing countries, in accordance with their national plans and programmes
- By 2030, reduce to less than 3 per cent the transaction costs of migrant remittances and eliminate remittance corridors with costs higher than 5 per cent
Sustainable cities and communities

More than half of us live in cities. By 2050, two-thirds of all humanity—6.5 billion people—will be urban. Sustainable development cannot be achieved without significantly transforming the way we build and manage our urban spaces.
The rapid growth of cities—a result of rising populations and increasing migration—has led to a boom in mega-cities, especially in the developing world, and slums are becoming a more significant feature of urban life.
Making cities sustainable means creating career and business opportunities, safe and affordable housing, and building resilient societies and economies. It involves investment in public transport, creating green public spaces, and improving urban planning and management in participatory and inclusive ways.

In 2018, 4.2 billion people, 55 percent of the world’s population, lived in cities. By 2050, the urban population is expected to reach 6.5 billion.
Cities occupy just 3 percent of the Earth’s land but account for 60 to 80 percent of energy consumption and at least 70 percent of carbon emissions.
828 million people are estimated to live in slums, and the number is rising.
In 1990, there were 10 cities with 10 million people or more; by 2014, the number of mega-cities rose to 28, and was expected to reach 33 by 2018. In the future, 9 out of 10 mega-cities will be in the developing world.
In the coming decades, 90 percent of urban expansion will be in the developing world.
The economic role of cities is significant. They generate about 80 percent of the global GDP.
- By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services and upgrade slums
- By 2030, provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all, improving road safety, notably by expanding public transport, with special attention to the needs of those in vulnerable situations, women, children, persons with disabilities and older persons
- By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries
- Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage
- By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease the direct economic losses relative to global gross domestic product caused by disasters, including water-related disasters, with a focus on protecting the poor and people in vulnerable situations
- By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management
- By 2030, provide universal access to safe, inclusive and accessible, green and public spaces, in particular for women and children, older persons and persons with disabilities
- Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening national and regional development planning
- By 2020, substantially increase the number of cities and human settlements adopting and implementing integrated policies and plans towards inclusion, resource efficiency, mitigation and adaptation to climate change, resilience to disasters, and develop and implement, in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030, holistic disaster risk management at all levels
- Support least developed countries, including through financial and technical assistance, in building sustainable and resilient buildings utilizing local materials

Unlocking barriers to a sustai...

The beginning of the end for p...
Responsible consumption and production.

Achieving economic growth and sustainable development requires that we urgently reduce our ecological footprint by changing the way we produce and consume goods and resources. Agriculture is the biggest user of water worldwide, and irrigation now claims close to 70 percent of all freshwater for human use.
The efficient management of our shared natural resources, and the way we dispose of toxic waste and pollutants, are important targets to achieve this goal. Encouraging industries, businesses and consumers to recycle and reduce waste is equally important, as is supporting developing countries to move towards more sustainable patterns of consumption by 2030.
A large share of the world population is still consuming far too little to meet even their basic needs. Halving the per capita of global food waste at the retailer and consumer levels is also important for creating more efficient production and supply chains. This can help with food security, and shift us towards a more resource efficient economy.

1.3 billion tonnes of food is wasted every year, while almost 2 billion people go hungry or undernourished.
The food sector accounts for around 22 percent of total greenhouse gas emissions, largely from the conversion of forests into farmland.
Globally, 2 billion people are overweight or obese.
Only 3 percent of the world’s water is fresh (drinkable), and humans are using it faster than nature can replenish it.
If people everywhere switched to energy efficient lightbulbs, the world would save US$120 billion annually.
One-fifth of the world’s final energy consumption in 2013 was from renewable sources.
- Implement the 10-year framework of programmes on sustainable consumption and production, all countries taking action, with developed countries taking the lead, taking into account the development and capabilities of developing countries
- By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources
- By 2030, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses
- By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle, in accordance with agreed international frameworks, and significantly reduce their release to air, water and soil in order to minimize their adverse impacts on human health and the environment
- By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse
- Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle
- Promote public procurement practices that are sustainable, in accordance with national policies and priorities
- By 2030, ensure that people everywhere have the relevant information and awareness for sustainable development and lifestyles in harmony with nature
- Support developing countries to strengthen their scientific and technological capacity to move towards more sustainable patterns of consumption and production
- Develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products
- Rationalize inefficient fossil-fuel subsidies that encourage wasteful consumption by removing market distortions, in accordance with national circumstances, including by restructuring taxation and phasing out those harmful subsidies, where they exist, to reflect their environmental impacts, taking fully into account the specific needs and conditions of developing countries and minimizing the possible adverse impacts on their development in a manner that protects the poor and the affected communities
Generic web page
Popping the bottle.

Preserving the laboratory of e...

Unsung heroes: Four things pol...
Climate action.

There is no country that is not experiencing the drastic effects of climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions are more than 50 percent higher than in 1990. Global warming is causing long-lasting changes to our climate system, which threatens irreversible consequences if we do not act.
The annual average economic losses from climate-related disasters are in the hundreds of billions of dollars. This is not to mention the human impact of geo-physical disasters, which are 91 percent climate-related, and which between 1998 and 2017 killed 1.3 million people, and left 4.4 billion injured. The goal aims to mobilize US$100 billion annually by 2020 to address the needs of developing countries to both adapt to climate change and invest in low-carbon development.
Supporting vulnerable regions will directly contribute not only to Goal 13 but also to the other SDGs. These actions must also go hand in hand with efforts to integrate disaster risk measures, sustainable natural resource management, and human security into national development strategies. It is still possible, with strong political will, increased investment, and using existing technology, to limit the increase in global mean temperature to two degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, aiming at 1.5 ° C, but this requires urgent and ambitious collective action.

As of 2017 humans are estimated to have caused approximately 1.0°C of global warming above pre-industrial levels.
Sea levels have risen by about 20 cm (8 inches) since 1880 and are projected to rise another 30–122 cm (1 to 4 feet) by 2100.
To limit warming to 1.5C, global net CO2 emissions must drop by 45% between 2010 and 2030, and reach net zero around 2050.
Climate pledges under The Paris Agreement cover only one third of the emissions reductions needed to keep the world below 2°C.
Bold climate action could trigger at least US$26 trillion in economic benefits by 2030.
The energy sector alone will create around 18 million more jobs by 2030, focused specifically on sustainable energy.
- Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries
- Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning
- Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning
- Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to a goal of mobilizing jointly $100 billion annually by 2020 from all sources to address the needs of developing countries in the context of meaningful mitigation actions and transparency on implementation and fully operationalize the Green Climate Fund through its capitalization as soon as possible
- Promote mechanisms for raising capacity for effective climate change-related planning and management in least developed countries and small island developing States, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities
Life Below Water
The world’s oceans – their temperature, chemistry, currents and life – drive global systems that make the Earth habitable for humankind. How we manage this vital resource is essential for humanity as a whole, and to counterbalance the effects of climate change.
Over three billion people depend on marine and coastal biodiversity for their livelihoods. However, today we are seeing 30 percent of the world’s fish stocks overexploited, reaching below the level at which they can produce sustainable yields.
Oceans also absorb about 30 percent of the carbon dioxide produced by humans, and we are seeing a 26 percent rise in ocean acidification since the beginning of the industrial revolution. Marine pollution, an overwhelming majority of which comes from land-based sources, is reaching alarming levels, with an average of 13,000 pieces of plastic litter to be found on every square kilometre of ocean.
The SDGs aim to sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems from pollution, as well as address the impacts of ocean acidification. Enhancing conservation and the sustainable use of ocean-based resources through international law will also help mitigate some of the challenges facing our oceans.

The ocean covers three quarters of the Earth’s surface and represents 99 percent of the living space on the planet by volume.
The ocean contains nearly 200,000 identified species, but actual numbers may lie in the millions.
As much as 40 percent of the ocean is heavily affected by pollution, depleted fisheries, loss of coastal habitats and other human activities.
The ocean absorbs about 30 percent of carbon dioxide produced by humans, buffering the impacts of global warming.
More than 3 billion people depend on marine and coastal biodiversity for their livelihoods.
The market value of marine and coastal resources and industries is estimated at US$3 trillion per year, about 5 percent of global GDP.
- By 2025, prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, in particular from land-based activities, including marine debris and nutrient pollution
- By 2020, sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems to avoid significant adverse impacts, including by strengthening their resilience, and take action for their restoration in order to achieve healthy and productive oceans
- Minimize and address the impacts of ocean acidification, including through enhanced scientific cooperation at all levels
- By 2020, effectively regulate harvesting and end overfishing, illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing and destructive fishing practices and implement science-based management plans, in order to restore fish stocks in the shortest time feasible, at least to levels that can produce maximum sustainable yield as determined by their biological characteristics
- By 2020, conserve at least 10 per cent of coastal and marine areas, consistent with national and international law and based on the best available scientific information
- By 2020, prohibit certain forms of fisheries subsidies which contribute to overcapacity and overfishing, eliminate subsidies that contribute to illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing and refrain from introducing new such subsidies, recognizing that appropriate and effective special and differential treatment for developing and least developed countries should be an integral part of the World Trade Organization fisheries subsidies negotiation
- By 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries from the sustainable use of marine resources, including through sustainable management of fisheries, aquaculture and tourism
- Increase scientific knowledge, develop research capacity and transfer marine technology, taking into account the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission Criteria and Guidelines on the Transfer of Marine Technology, in order to improve ocean health and to enhance the contribution of marine biodiversity to the development of developing countries, in particular small island developing States and least developed countries
- Provide access for small-scale artisanal fishers to marine resources and markets
- Enhance the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and their resources by implementing international law as reflected in UNCLOS, which provides the legal framework for the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and their resources, as recalled in paragraph 158 of The Future We Want

Investing in SIDS and LLDCs is...
Small island developing states and pathways t..., life on land.

Human life depends on the earth as much as the ocean for our sustenance and livelihoods. Plant life provides 80 percent of the human diet, and we rely on agriculture as an important economic resources. Forests cover 30 percent of the Earth’s surface, provide vital habitats for millions of species, and important sources for clean air and water, as well as being crucial for combating climate change.
Every year, 13 million hectares of forests are lost, while the persistent degradation of drylands has led to the desertification of 3.6 billion hectares, disproportionately affecting poor communities.
While 15 percent of land is protected, biodiversity is still at risk. Nearly 7,000 species of animals and plants have been illegally traded. Wildlife trafficking not only erodes biodiversity, but creates insecurity, fuels conflict, and feeds corruption.
Urgent action must be taken to reduce the loss of natural habitats and biodiversity which are part of our common heritage and support global food and water security, climate change mitigation and adaptation, and peace and security.

Around 1.6 billion people depend on forests for their livelihoods.
Forests are home to more than 80 percent of all terrestrial species of animals, plants and insects.
2.6 billion people depend directly on agriculture for a living.
Nature-based climate solutions can contribute about a third of CO2 reductions by 2030.
The value of ecosystems to human livelihoods and well-being is $US125 trillion per year.v
Mountain regions provide 60-80 percent of the Earth's fresh water.
- By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements
- By 2020, promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally
- By 2030, combat desertification, restore degraded land and soil, including land affected by desertification, drought and floods, and strive to achieve a land degradation-neutral world
- By 2030, ensure the conservation of mountain ecosystems, including their biodiversity, in order to enhance their capacity to provide benefits that are essential for sustainable development
- Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity and, by 2020, protect and prevent the extinction of threatened species
- Promote fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources and promote appropriate access to such resources, as internationally agreed
- Take urgent action to end poaching and trafficking of protected species of flora and fauna and address both demand and supply of illegal wildlife products
- By 2020, introduce measures to prevent the introduction and significantly reduce the impact of invasive alien species on land and water ecosystems and control or eradicate the priority species
- By 2020, integrate ecosystem and biodiversity values into national and local planning, development processes, poverty reduction strategies and accounts
- Mobilize and significantly increase financial resources from all sources to conserve and sustainably use biodiversity and ecosystems
- Mobilize significant resources from all sources and at all levels to finance sustainable forest management and provide adequate incentives to developing countries to advance such management, including for conservation and reforestation
- Enhance global support for efforts to combat poaching and trafficking of protected species, including by increasing the capacity of local communities to pursue sustainable livelihood opportunities
Peace, justice and strong institutions

We cannot hope for sustainable development without peace, stability, human rights and effective governance, based on the rule of law. Yet our world is increasingly divided. Some regions enjoy peace, security and prosperity, while others fall into seemingly endless cycles of conflict and violence. This is not inevitable and must be addressed.
Armed violence and insecurity have a destructive impact on a country’s development, affecting economic growth, and often resulting in grievances that last for generations. Sexual violence, crime, exploitation and torture are also prevalent where there is conflict, or no rule of law, and countries must take measures to protect those who are most at risk
The SDGs aim to significantly reduce all forms of violence, and work with governments and communities to end conflict and insecurity. Promoting the rule of law and human rights are key to this process, as is reducing the flow of illicit arms and strengthening the participation of developing countries in the institutions of global governance.

By the end of 2017, 68.5 million people had been forcibly displaced as a result of persecution, conflict, violence or human rights violations.
There are at least 10 million stateless people who have been denied nationality and its related rights.
Corruption, bribery, theft and tax evasion cost developing countries US$1.26 trillion per year.
49 countries lack laws protecting women from domestic violence.
In 46 countries, women now hold more than 30 percent of seats in at least one chamber of national parliament.
1 billion people are legally ‘invisible’ because they cannot prove who they are. This includes an estimated 625 million children under 14 whose births were never registered.
- Significantly reduce all forms of violence and related death rates everywhere
- End abuse, exploitation, trafficking and all forms of violence against and torture of children
- Promote the rule of law at the national and international levels and ensure equal access to justice for all
- By 2030, significantly reduce illicit financial and arms flows, strengthen the recovery and return of stolen assets and combat all forms of organized crime
- Substantially reduce corruption and bribery in all their forms
- Develop effective, accountable and transparent institutions at all levels
- Ensure responsive, inclusive, participatory and representative decision-making at all levels
- Broaden and strengthen the participation of developing countries in the institutions of global governance
- By 2030, provide legal identity for all, including birth registration
- Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements
- Strengthen relevant national institutions, including through international cooperation, for building capacity at all levels, in particular in developing countries, to prevent violence and combat terrorism and crime
- Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development

How Likely Are We to Achieve t...


Identifying Key Priorities and...
Partnerships for the goals.

The SDGs can only be realized with strong global partnerships and cooperation. Official Development Assistance remained steady but below target, at US$147 billion in 2017. While humanitarian crises brought on by conflict or natural disasters continue to demand more financial resources and aid. Many countries also require Official Development Assistance to encourage growth and trade.
The world is more interconnected than ever. Improving access to technology and knowledge is an important way to share ideas and foster innovation. Coordinating policies to help developing countries manage their debt, as well as promoting investment for the least developed, is vital for sustainable growth and development.
The goals aim to enhance North-South and South-South cooperation by supporting national plans to achieve all the targets. Promoting international trade, and helping developing countries increase their exports is all part of achieving a universal rules-based and equitable trading system that is fair and open and benefits all.

The UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) says achieving SDGs will require US$5 trillion to $7 trillion in annual investment.
Total official development assistance reached US$147.2 billion in 2017.
In 2017, international remittances totaled US$613 billion; 76 percent of it went to developing countries.
In 2016, 6 countries met the international target to keep official development assistance at or above 0.7 percent of gross national income.
Sustainable and responsible investments represent high-potential sources of capital for SDGs. As of 2016, US$18.2 trillion was invested in this asset class.
The bond market for sustainable business is growing. In 2018 global green bonds reached US$155.5billion, up 78 percent from previous year.
- Strengthen domestic resource mobilization, including through international support to developing countries, to improve domestic capacity for tax and other revenue collection
- Developed countries to implement fully their official development assistance commitments, including the commitment by many developed countries to achieve the target of 0.7 per cent of ODA/GNI to developing countries and 0.15 to 0.20 per cent of ODA/GNI to least developed countries ODA providers are encouraged to consider setting a target to provide at least 0.20 per cent of ODA/GNI to least developed countries
- Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries from multiple sources
- Assist developing countries in attaining long-term debt sustainability through coordinated policies aimed at fostering debt financing, debt relief and debt restructuring, as appropriate, and address the external debt of highly indebted poor countries to reduce debt distress
- Adopt and implement investment promotion regimes for least developed countries
- Enhance North-South, South-South and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology and innovation and enhance knowledge sharing on mutually agreed terms, including through improved coordination among existing mechanisms, in particular at the United Nations level, and through a global technology facilitation mechanism
- Promote the development, transfer, dissemination and diffusion of environmentally sound technologies to developing countries on favourable terms, including on concessional and preferential terms, as mutually agreed
- Fully operationalize the technology bank and science, technology and innovation capacity-building mechanism for least developed countries by 2017 and enhance the use of enabling technology, in particular information and communications technology
Capacity building
- Enhance international support for implementing effective and targeted capacity-building in developing countries to support national plans to implement all the sustainable development goals, including through North-South, South-South and triangular cooperation
- Promote a universal, rules-based, open, non-discriminatory and equitable multilateral trading system under the World Trade Organization, including through the conclusion of negotiations under its Doha Development Agenda
- Significantly increase the exports of developing countries, in particular with a view to doubling the least developed countries’ share of global exports by 2020
- Realize timely implementation of duty-free and quota-free market access on a lasting basis for all least developed countries, consistent with World Trade Organization decisions, including by ensuring that preferential rules of origin applicable to imports from least developed countries are transparent and simple, and contribute to facilitating market access
Systemic issues
Policy and institutional coherence
- Enhance global macroeconomic stability, including through policy coordination and policy coherence
- Enhance policy coherence for sustainable development
- Respect each country’s policy space and leadership to establish and implement policies for poverty eradication and sustainable development
Multi-stakeholder partnerships
- Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources, to support the achievement of the sustainable development goals in all countries, in particular developing countries
- Encourage and promote effective public, public-private and civil society partnerships, building on the experience and resourcing strategies of partnerships
Data, monitoring and accountability
- By 2020, enhance capacity-building support to developing countries, including for least developed countries and small island developing States, to increase significantly the availability of high-quality, timely and reliable data disaggregated by income, gender, age, race, ethnicity, migratory status, disability, geographic location and other characteristics relevant in national contexts
- By 2030, build on existing initiatives to develop measurements of progress on sustainable development that complement gross domestic product, and support statistical capacity-building in developing countries

Return-on-Investment in Nation...

SDG Budget Tagging: A proposal...

Sustainable Development Goals Integration
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
- Climate Change
- Policy & Economics
- Biodiversity
- Conservation
Get focused newsletters especially designed to be concise and easy to digest
- ESSENTIAL BRIEFING 3 times weekly
- TOP STORY ROUNDUP Once a week
- MONTHLY OVERVIEW Once a month
- Enter your email *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Explainer: What Is Sustainability and Why Is It Important?
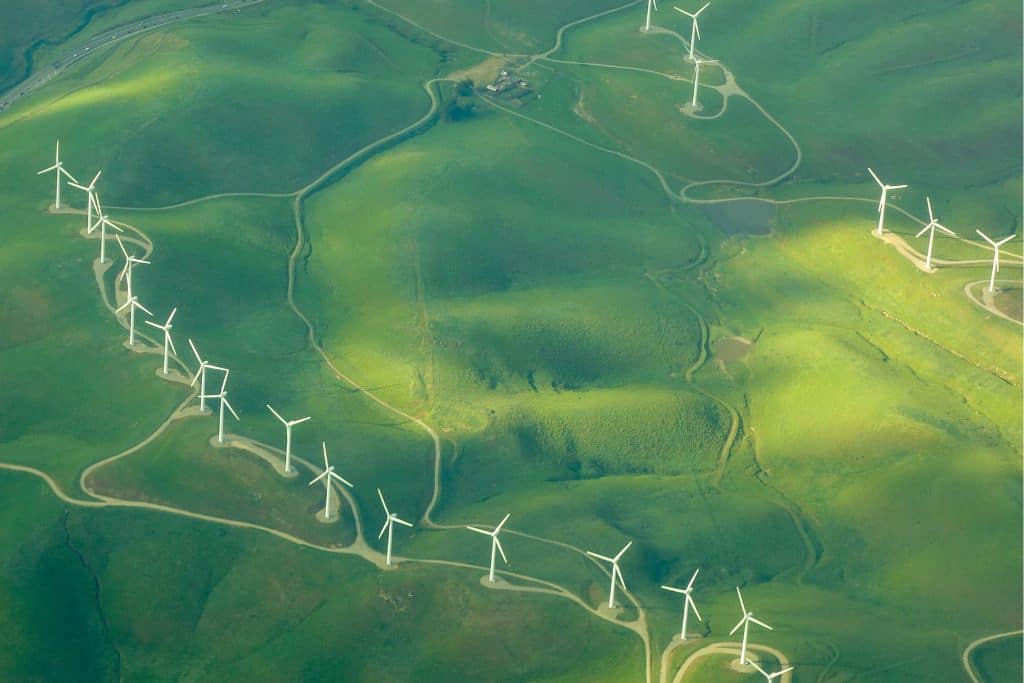

It seems like nowadays, the term ‘sustainable’ is used all around us – from food packaging to clothing companies and even tourism. In fact, ‘sustainability’ was one of the most-searched terms in fashion in 2019, and Google searches for the term have been on the rise, illustrating the public’s growing interest in the topic. But what is sustainability exactly and why is it so important?
What Is Sustainability
The go-to definition when discussing sustainability is “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”. And though you may have heard this before, many people do not know the origins of this definition in particular. In 1987, the United Nations Brundtland Commission published this particular definition of sustainability in the Brundtland report , which called for a strategy that united development and the environment. Over the years, alternative definitions have emerged, but the Brundtland report’s 1980s take on the explanation is still commonly used.
The ‘ Three Pillars of Sustainability’ is another popular framework used to describe what sustainable development is. This tool conveys that sustainability consists of environmental, social, and economic factors that are vital when discussing the topic:
- Environmental sustainability is perhaps the most obvious of the three pillars, as it symbolises the importance of things like natural resources and biodiversity to support life on Earth.
- Social sustainability places importance on social structures, well-being, and harmony; all factors that poverty, wars, and injustices can affect.
- Economic sustainability describes the ability of an economy to grow. This is especially important in today’s societies, at a time when many sustainable initiatives require financing and a strong economic rationale.
In order to find solutions to ongoing sustainability issues, it is imperative that we consider all three pillars.
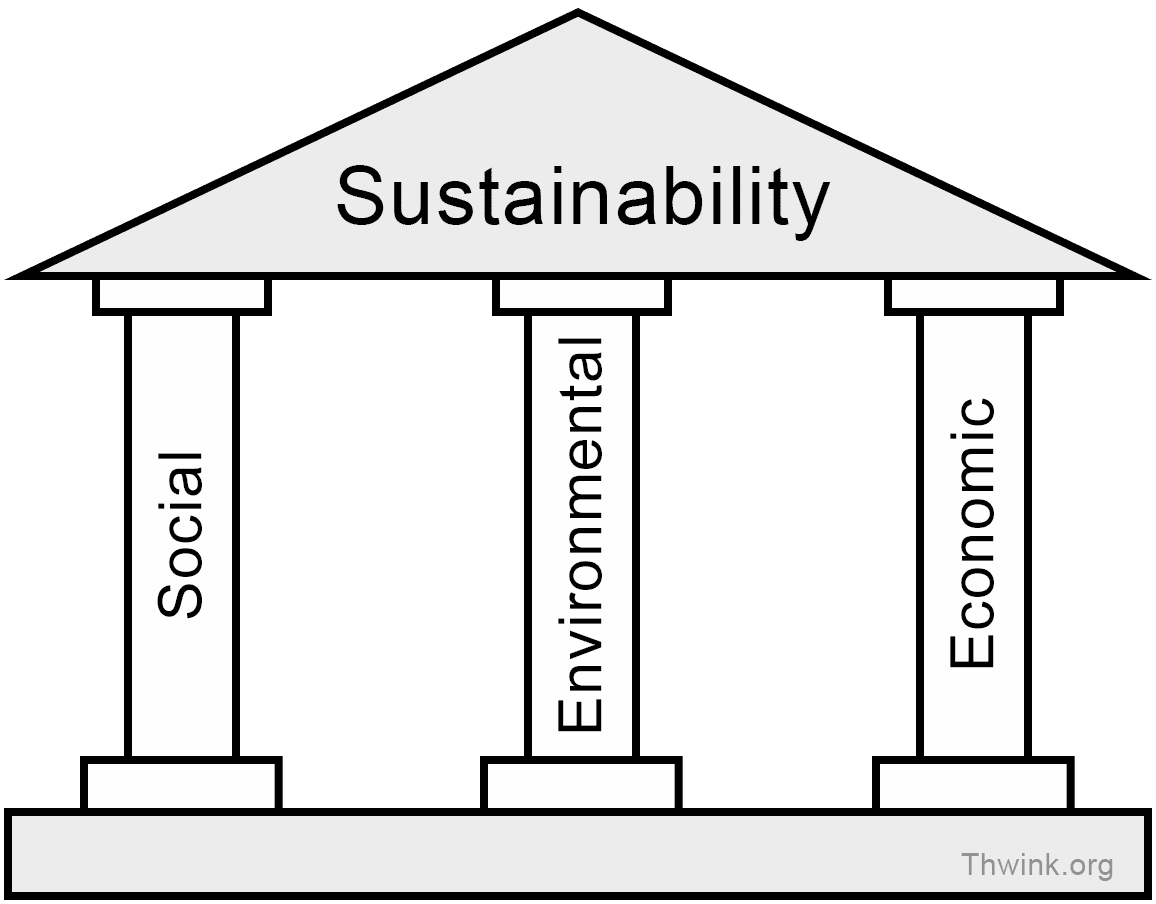
You might also like: We Need Sustainable Food Packaging Now. Here’s Why.
What Are the Planetary Boundaries And How Do They Relate to Sustainability?
The concept of planetary boundaries (PB) is focussed on nine aspects that humanity needs in order to thrive in the future. This idea was developed in 2009 by the Stockholm Resilience Centre and other groups: “ We propose a new approach to global sustainability in which we define planetary boundaries within which we expect that humanity can operate safely. Transgressing one or more […] may be deleterious or even catastrophic due to the risk of crossing .”
At the time when this new concept was introduced, scientists believed that humanity had already transgressed three boundaries, and was rapidly approaching several others. In 2022, a re-assessment of the PBs by fourteen scientists concluded that humanity had transgressed additional boundaries, relating to freshwater and environmental pollutants in particular.

The PBs have been widely cited in sustainability literature over the last decade, and provide an illustrative tool to track and evaluate how we are depleting the Earth’s valuable ecosystem services and precious systems. Though the tool is mainly environmentally focused, it has informed various policies and practices, including the World Business Council on Sustainable Development’s Action 2020 Strategy. In turn, this has had a knock-on effect on social and economic aspects of global policy and governance, including “financial investment, food, textiles, building, technology and household goods sectors”.
You might also like: Sustainable Alternatives to Fast Fashion
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
In 2015, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development was adopted by the UN Member States. One of the most well-known elements of this were the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) which set out various goals that the international community must work together to achieve – ranging from environmental and social to economic issues.

We cannot discuss the SDGs without first acknowledging their predecessor – the eight Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) – set out in September 2000. These goals ranged from halving extreme poverty to halting the spread of HIV/AIDS. By the end of the 15-year cycle of the MDGs in 2015, the UN established an even more ambitious set of goals – the SDGs – to enter into force on 1 January 2016. While not all of the MDGs were met globally, significant progress was made in several areas.
The SDGs have been continually monitored and provide key benchmarks for us to understand how sustainability is being achieved worldwide. Overview reports are regularly published and comment on the nuances that significant events bring to achieving the SDGs (like the COVID-19 pandemic, for example). You can read the 2022 SDG Report here .
You might also like: Why the Sustainable Development Goals for 2030 Are More Important Than Ever
Why Is Sustainability Important?
So far, we’ve discussed the different ways that sustainability is defined and the tools and metrics we have developed on a global scale to measure our impact on the environment, societies, and economies worldwide. But why is sustainability important?
Here are a few reasons, although the list could go on for a lot longer:
- Sustainability joins social, environmental, and economic issues together throughout global discussions, ensuring that key elements do not get left behind. Focusing on aspects other than the environment alone ensures a fairer, more equitable discussion (as long as a diverse range of players is at the table).
- Sustainability opens up new conversations between a range of people with diverse skills and thought processes – for example scientists, sociologists, and economists all have key skills to enable humanity to thrive and sustain the Earth.
- The SDGs are an impactful way to evaluate our progress and have encouraged key ideas and strategies to flourish while remaining realistic about the next steps and improvements.
This story is funded by readers like you
Our non-profit newsroom provides climate coverage free of charge and advertising. Your one-off or monthly donations play a crucial role in supporting our operations, expanding our reach, and maintaining our editorial independence.
About EO | Mission Statement | Impact & Reach | Write for us

Top 7 Smart Cities in the World in 2024

The Green Dilemma: Can AI Fulfil Its Potential Without Harming the Environment?

How Does Overpopulation Affect Sustainability? Challenges and Solutions
Hand-picked stories weekly or monthly. We promise, no spam!
Boost this article By donating us $100, $50 or subscribe to Boosting $10/month – we can get this article and others in front of tens of thousands of specially targeted readers. This targeted Boosting – helps us to reach wider audiences – aiming to convince the unconvinced, to inform the uninformed, to enlighten the dogmatic.

The Sustainable Development Agenda

17 Goals for People, for Planet
World leaders came together in 2015 and made a historic promise to secure the rights and well-being of everyone on a healthy, thriving planet when they adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and its 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) .
The Agenda remains the world’s roadmap for ending poverty, protecting the planet and tackling inequalities. The 17 SDGs, the cornerstone of the Agenda, offer the most practical and effective pathway to tackle the causes of violent conflict, human rights abuses, climate change and environmental degradation and aim to ensure that no one will be left behind. The SDGs reflect an understanding that sustainable development everywhere must integrate economic growth, social well-being and environmental protection.
Keeping the Promise
While a fragile global economy, rising conflicts and the climate emergency have placed the promise of the Goals in peril, we can still turn things around in the remaining seven years. Notably, there has been some SDG success since 2015 with improvements in key areas, including poverty reduction, child mortality, electricity access and the battle against certain diseases.
Countries continue to supercharge efforts to achieve the SDGs. We see this at the annual High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development — the central platform for reviewing progress on the SDGs — where for the last eight years, countries, civil society and businesses have gathered to showcase the bold actions they are taking to achieve the SDGs.

Every four years, the High-Level Political Forum meets under the auspices of the UN General Assembly, known as the SDG Summit . In 2023, the second SDG Summit took place on September 18-19, bringing together Heads of State and Government to catalyze renewed efforts towards accelerating progress on the SDGs. The Summit culminated in the adoption of a political declaration to accelerate action to achieve the 17 goals.
A Decade of Action

The UN Secretary-General called on all sectors of society to mobilize for a decade of action on three levels: global action to secure greater leadership, more resources and smarter solutions for the Sustainable Development Goals; local action embedding the needed transitions in the policies, budgets, institutions and regulatory frameworks of governments, cities and local authorities; and people action , including by youth, civil society, the media, the private sector, unions, academia and other stakeholders, to generate an unstoppable movement pushing for the required transformations.
Numerous civil society leaders and organizations have also called for a “super year of activism” to accelerate progress on the Sustainable Development Goals, urging world leaders to redouble efforts to reach the people furthest behind, support local action and innovation, strengthen data systems and institutions, rebalance the relationship between people and nature, and unlock more financing for sustainable development.
At the core of the 2020-2030 decade is the need for action to tackle growing poverty , empower women and girls , and address the climate emergency .
More people around the world are living better lives compared to just a decade ago. More people have access to better healthcare, decent work, and education than ever before. But inequalities and climate change are threatening to undo the gains. Investment in inclusive and sustainable economies can unleash significant opportunities for shared prosperity. And the political, technological and financial solutions are within reach. But much greater leadership and rapid, unprecedented changes are needed to align these levers of change with sustainable development objectives. #ForPeopleForPlanet
SDG Report 2023

The annual SDG reports provide an overview of the world’s implementation efforts to date, highlighting areas of progress and where more action needs to be taken. They are prepared by the UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs, with input from international and regional organizations and the United Nations system of agencies, funds and programmes. Several national statisticians, experts from civil society and academia also contribute to the reports.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is sustainable development?
- Sustainable development has been defined as development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
- Sustainable development calls for concerted efforts towards building an inclusive, sustainable and resilient future for people and planet.
- For sustainable development to be achieved, it is crucial to harmonize three core elements: economic growth, social inclusion and environmental protection. These elements are interconnected and all are crucial for the well-being of individuals and societies.
- Eradicating poverty in all its forms and dimensions is an indispensable requirement for sustainable development. To this end, there must be promotion of sustainable, inclusive and equitable economic growth, creating greater opportunities for all, reducing inequalities, raising basic standards of living, fostering equitable social development and inclusion, and promoting integrated and sustainable management of natural resources and ecosystems.
How will the Sustainable Development Goals be implemented?
- The Addis Ababa Action Agenda that came out of the Third International Conference on Financing for Development provided concrete policies and actions to support the implementation of the new agenda.
- Implementation and success will rely on countries’ own sustainable development policies, plans and programmes, and will be led by countries. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) will be a compass for aligning countries’ plans with their global commitments.
- Nationally owned and country-led sustainable development strategies will require resource mobilization and financing strategies.
- All stakeholders: governments, civil society, the private sector, and others, are expected to contribute to the realisation of the new agenda.
- A revitalized global partnership at the global level is needed to support national efforts. This is recognized in the 2030 Agenda.
- Multi-stakeholder partnerships have been recognized as an important component of strategies that seek to mobilize all stakeholders around the new agenda.
How will the Sustainable Development Goals be monitored?
- At the global level, the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and 169 targets of the new agenda will be monitored and reviewed using a set of global indicators. The global indicator framework for Sustainable Development Goals was developed by the Inter-Agency and Expert Group on SDG Indicators (IAEG-SDGs) and agreed upon at the 48 th session of the United Nations Statistical Commission held in March 2017.
- Governments will also develop their own national indicators to assist in monitoring progress made on the goals and targets.
- Chief statisticians from Member States are working on the identification of the targets with the aim to have 2 indicators for each target. There will be approximately 300 indicators for all the targets. Where the targets cover cross-cutting issues, however, the number of indicators may be reduced.
- The follow-up and review process will be informed by an annual SDG Progress Report to be prepared by the Secretary-General.
- The annual meetings of the High-level Political Forum on sustainable development will play a central role in reviewing progress towards the SDGs at the global level. The means of implementation of the SDGs will be monitored and reviewed as outlined in the Addis Ababa Action Agenda, the outcome document of the Third International Conference on Financing for Development, to ensure that financial resources are effectively mobilized to support the new sustainable development agenda.
How much will the implementation of this sustainable development agenda cost?
- To achieve the Sustainable Development Goals, annual investment requirements across all sectors have been estimated at around $5-7 trillion. Current investment levels are far from the scale needed. With global financial assets estimated at over $200 trillion, financing is available, but most of these resources are not being channeled towards sustainable development at the scale and speed necessary to achieve the SDGs and objectives of the Paris Agreement on climate change.
- Interest and investment in the Sustainable Development Goals are growing and investment in the Goals makes economic sense. Achieving the SDGs could open up US$12 trillion of market opportunities and create 380 million new jobs by 2030.
- The Global Investors for Sustainable Development Alliance , a UN-supported coalition of 30 business leaders announced in October 2019, works to provide decisive leadership in mobilizing resources for sustainable development and identifying incentives for long-term sustainable investments.Net Official Development Assistance totaled $149 billion in 2018, down by 2.7% in real terms from 2017.
How does climate change relate to sustainable development?
- Climate change is already impacting public health, food and water security, migration, peace and security. Climate change, left unchecked, will roll back the development gains we have made over the last decades and will make further gains impossible.
- Investments in sustainable development will help address climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and building climate resilience.
- Conversely, action on climate change will drive sustainable development.
- Tackling climate change and fostering sustainable development are two mutually reinforcing sides of the same coin; sustainable development cannot be achieved without climate action. Conversely, many of the SDGs are addressing the core drivers of climate change.
Are the Sustainable Development Goals legally binding?
- No. The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are not legally binding.
- Nevertheless, countries are expected to take ownership and establish a national framework for achieving the 17 Goals.
- Implementation and success will rely on countries’ own sustainable development policies, plans and programmes.
- Countries have the primary responsibility for follow-up and review, at the national, regional and global levels, with regard to the progress made in implementing the Goals and targets by 2030.
- Actions at the national level to monitor progress will require quality, accessible and timely data collection and regional follow-up and review.
How are the Sustainable Development Goals different from the MDGs?
- The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) with 169 targets are broader in scope and go further than the MDGs by addressing the root causes of poverty and the universal need for development that works for all people. The goals cover the three dimensions of sustainable development: economic growth, social inclusion and environmental protection.
- Building on the success and momentum of the MDGs, the new goals cover more ground, with ambitions to address inequalities, economic growth, decent jobs, cities and human settlements, industrialization, oceans, ecosystems, energy, climate change, sustainable consumption and production, peace and justice.
- The new Goals are universal and apply to all countries, whereas the MDGs were intended for action in developing countries only.
- A core feature of the SDGs is their strong focus on means of implementation—the mobilization of financial resources—capacity-building and technology, as well as data and institutions.
- The new Goals recognize that tackling climate change is essential for sustainable development and poverty eradication. SDG 13 aims to promote urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 29 June 2022
The importance of the Sustainable Development Goals to students of environmental and sustainability studies—a global survey in 41 countries
- Matthias Winfried Kleespies ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8413-879X 1 &
- Paul Wilhelm Dierkes ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6046-6406 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 9 , Article number: 218 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
33k Accesses
12 Citations
44 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental studies
To fight the global problems of humanity, the United Nations has adopted 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). To achieve these goals, it is necessary that future decision-makers and stakeholders in society consider these goals to be important. Therefore, in this study, we examined how important students in 41 countries directly related to the environmental sector rated each of the 17 SDGs. Based on the analysis of these ratings, it was possible to categorize the SDGs into three higher-level factors that reflect the three pillars of sustainability (social, economic, environmental). These three pillars are considered to be of varying importance in different countries. We also correlated the ratings of these higher-level factors with country-specific indicators, such as the Human Development Index. The correlations between the indicators and the higher-level factors revealed that in countries with higher indices, the SDGs are rated as less important compared to in countries with lower indices. These results provide stakeholders with important guidance on how the SDGs should be promoted in their country.
Similar content being viewed by others
Worldwide divergence of values
Joshua Conrad Jackson & Danila Medvedev

Interviews in the social sciences
Eleanor Knott, Aliya Hamid Rao, … Chana Teeger
The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals
Ricardo Vinuesa, Hossein Azizpour, … Francesco Fuso Nerini
Introduction
Currently, humanity is facing major environmental, social and economic problems worldwide. To address these global issues on an international cross-border level and to create a more sustainable and better future for all, the United Nations adopted the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015 (United Nations, 2015 ). Each of the SDGs has indicators that are used to measure progress towards achieving the goals (United Nations, 2017 ). The individual goals do not stand alone but rather influence each other and are closely linked (Bali Swain and Yang-Wallentin, 2020 ; Nilsson et al., 2016 ; Pham‐Truffert et al., 2020 ; Pradhan et al., 2017 ); each goal addresses environmental, social and economic problems (Elder and Olsen, 2019 ).
It is particularly important how the SDGs are perceived, accepted and evaluated by people worldwide. In this context, there have been several surveys conducted in recent years, some with varying results. While awareness of the SDGs has increased globally compared to their predecessor, i.e., the Millennium Development Goals (GlobeScan, 2016 ), 63% of the respondents in a survey of 28 European countries said they had never heard of the SDGs. Globally, awareness of the SDGs is approximately 50% (Theresa et al., 2020 ); however, only 1% of people say they are very well informed about the SDGs (Lampert and Papadongonas, 2016 ). There are also regional differences in the assessment of the individual goals. Globally, ‘climate action’, ‘good health’ and ‘well-being and quality education’ are considered particularly important (Theresa et al., 2020 ). In another survey, ‘zero hunger’, ‘clean water and sanitation’ and ‘no poverty’ were selected as the most important SDGs (Lampert and Papadongonas, 2016 ). Young people in particular are more likely to have heard of the SDGs, and for them, quality education is particularly important (Youth Speak Survey, 2020 ). In general, people around the world have a high level of acceptance about the content of the SDGs (Ipsos, 2015 ).
The education system has an important role in raising awareness of the SDGs and in teaching skills and values that lead to more sustainable behaviour. Therefore, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) has developed learning objectives for the SDGs to support teachers and learners (UNESCO, 2017 ). Tertiary educational institutions are particularly important in this regard, as they educate the next generation of decision-makers who will have a critical impact on the future of the planet (Yuriev and Sierra‐Barón, 2020 ). Universities, through their education and influence, contribute directly to the achievement of a whole range of SDGs (Kioupi and Voulvoulis, 2020 ). In recent years, there has been a strong increase in sustainability programmes at universities, with a particular focus on student attitudes (Rodríguez-García et al., 2019 ); however, there is wide divergence between programmes (O’Byrne et al., 2015 ). Despite the recent surge of sustainability in higher education, students generally have limited knowledge of the SDGs (Zamora-Polo et al., 2019 ). Higher education institutes, such as universities, have a special responsibility worldwide because they shape future leaders (Alshuwaikhat and Abubakar, 2008 ; Bellou et al., 2017 ), decision-makers (Alshuwaikhat and Abubakar, 2008 ; Lozano et al., 2013 ), professionals (Kioupi and Voulvoulis, 2020 ) and intellectuals in various academic fields (Lozano, 2006 ).
In addition to educating the next generation of decision-makers, which is most likely the most important factor, universities also make an important contribution to achieving the SDGs through research, public engagement or university policy (Kestin et al., 2017 ). They can influence politicians and industry leaders with their clear and unbiased information (Stephens et al., 2008 ) and reach a wide audience in the general population (Kioupi and Voulvoulis, 2020 ).
While elite positions in society can be reached independently of having a university education, universities provide knowledge and technical skills that significantly increase the likelihood that a person will achieve such a socially relevant position (Frank and Meyer, 2007 ; Vicente-Molina et al., 2013 ). Therefore, students, as potential future decision-makers of society, contribute greatly to the achievement of the SDGs and have an impact on the major problems of humanity and thus on the future of the planet. Until now, however, there has been a lack of valid international research that examines the perspective of students in the natural and sustainable sciences on the various SDGs. This study is an attempt to reduce the international research gap and examine the views of environmental students in different countries regarding the SDGs. The aim is to determine how important students in each country consider the SDGs to be. In this context, statistical methods will be used to check whether the individual SDGs can be assigned to higher-order groups on the basis of the students’ evaluation. To identify patterns and differences between the countries, these higher-ranking groups were compared among the individual countries and correlated with country-specific indicators. The results are intended to provide guidance for action for today’s decision-makers in individual countries.
Therefore, in our study, we asked more than 4000 university students in 41 countries whose course of study is directly related to sustainability to rate the 17 SDGs on a scale of 1–5 (important to unimportant). In the first step of the analysis, an exploratory factor analysis was used to investigate the extent to which the SDGs can be categorized into higher-level factors based on the participants’ ratings. In a second step, we examined how these higher ranking factors differed among the 41 countries studied. In the final step, we analysed the relationship between these higher-ranking factors and various country-specific indicators (GDP per capita, the Human Development Index, the Education Index, the Environment Performance Index and the SDG Index).
Data collection procedure
The survey was conducted using an online questionnaire. To guarantee a high level of data protection and the anonymity of the participants, the survey software that is also applied for evaluation at Goethe University in Frankfurt was used. Students were shown the labels and descriptions of each SDG (Table 1 ) and asked to rate them on a scale of 1 to 5 (unimportant to important). The survey was conducted in one of the official languages of the respective countries. The translation of the questionnaires was performed by a native-speaking translator and always checked by an additional person. The translations of the SDGs were taken from the official website of the UN (United Nations, 2016 ). If no translation was available, the SDGs were translated by a translator following the same principle. The English version of the questionnaire can be found in Supplementary Fig. 1 . To collect the data, professors and scientists worldwide were contacted and asked for their help. The scientists were asked to distribute the questionnaire among their students. An English cover letter was provided to participants and described the content and background of the study. In addition, a short introductory text at the beginning of the questionnaire explained the research project to the participants. Only people from natural science courses directly related to sustainability (e.g., biology, environmental sciences, ecology and conservation, natural resources management, etc.) were contacted.
A total of 4305 students (34.3% male, 63.6% female, 0.8% divers, 1.2% no answer) participated in the survey. The participants were on average 22.59 (±0.495) years old and in the 4.29th (±2.744) semester of study. The number of participants broken down by country is shown in Supplementary Table 2 . The survey period was September 2020–July 2021.
The study was reviewed by the ethics committee of the science didactic institutes and departments of the Goethe University Frankfurt am Main under approval number 15-WLSD-2104. If a university required a local ethics vote, that vote was also conducted prior to the survey.
An exploratory factor analysis was conducted to examine the relationship between the individual SDGs and to assign the SDGs to higher ranking factors based on the students’ ratings. This is a structure-simplifying procedure that is used to assign individual variables or items to higher-order factors and thus simplify the interpretation of the data (Yong and Pearce, 2013 ). In simple terms, a factor analysis generates a correlation matrix ( R -matrix) for all items used. Items that correlate particularly well and separate themselves from other item clusters are assigned to a higher ranking factor (Field, 2013 ). The rotation method chosen was varimax, which is considered the most reliable orthogonal rotation method (Fabrigar et al., 1999 ). To check whether the data were at all suitable for this type of analysis, Bartlett’s test of sphericity and the Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin measure of sampling adequacy were performed (Dziuban and Shirkey, 1974 ). The number of factors was determined by the Kaiser criterion, which takes into account all factors that have an eigenvalue larger than 1 (Kaiser, 1960 ). To examine whether the values of the three higher-level factors found by the factor analysis differed within countries or whether the factors were perceived to be of similar importance, the (two-tailed) Friedman test was used (Field, 2013 ). For significant results, a pairwise comparison was performed using the (two-tailed) Dunn–Bonferroni test (Dunn, 1964 ). The effect size was calculated using the following formula: r = \(\frac{Z}{{\sqrt N }}\) (Fritz et al., 2012 ).
To investigate whether there is a linear relationship between the factors found through factor analysis and the indices of each country (e.g., the Human Development Index and the Education Index), the Spearman rank correlation was calculated. The Spearman rank correlation was selected because the data were ordinally scaled and not normally distributed (Field, 2013 ; Schober et al., 2018 ).
Selected indices
The following five country-specific indices were selected:
Gross domestic product per capita (GDP per capita, 2021): GDP per capita is a value calculated by organizations such as the international monetary fund (International Monetary Fund, 2021 ). It is often used as an indicator of the standard of living, even though some weaknesses in this interpretation are currently known (Goossens, 2007 ).
Human Development Index (HDI from 2020): The HDI is an indicator of the United Nations (Conceição et al., 2020 ) that consists of life expectancy, the average number of years of schooling, and the standard of living (United Nations Development Programme, 2020b ).
Education Index (EI from 2020): The EI is a United Nations indicator that consists of the number of years of schooling that an adult person has attended on average and the expected years of schooling that a child will attend (United Nations Development Programme, 2020a ).
Environment Performance Index (EPI from 2020): The EPI is an index that assesses environmental health and ecosystem vitality using 32 performance indicators (Wendling et al., 2020 ).
SDG Index (SDGI from 2021): The SDGI is an indicator of the Bertelsmann Foundation that attempts to calculate the progress of the SDGs in percent based on various indicators. For example, if a country has an SDGI of 85.9, then approximately 86% of the SDGs have been achieved by that country (Sachs et al., 2021 ).
Both the Bartlett test ( p < 0.001) and the KMO criterion (KMO = 0.924) confirmed the applicability of an exploratory factor analysis for the 17 SDGs. The analysis revealed three factors with an eigenvalue > 1, indicating that the SDGs can be attributed to three higher-order factors (social, economic, environmental), which together can explain 53.48% of the variance. Overall, there was a clear assignment of items to the factors, and only a few cross-loadings were observed (Table 1 ).
The comparison of the three sustainability factors within the tested countries showed that the countries rated the individual dimensions of the SDGs differently. For example, in some countries, all three sustainability factors were rated as being equally important (Fig. 1a ); thus, there was no significant difference between the factors. In a number of countries, the environmental component was rated higher than the economic component, but no difference was found between the social and environmental components or between the social and economic components (Fig. 1b ). In the third group, the economic factor was rated as slightly less important than the environmental and social factors (Fig. 1c ). In some countries, the environmental factor was rated significantly higher than the other factors (Fig. 1d ). For better clarity, the individual significance levels are not marked in Fig. 1 but can be found along with the effect sizes in Supplementary Table 1 .
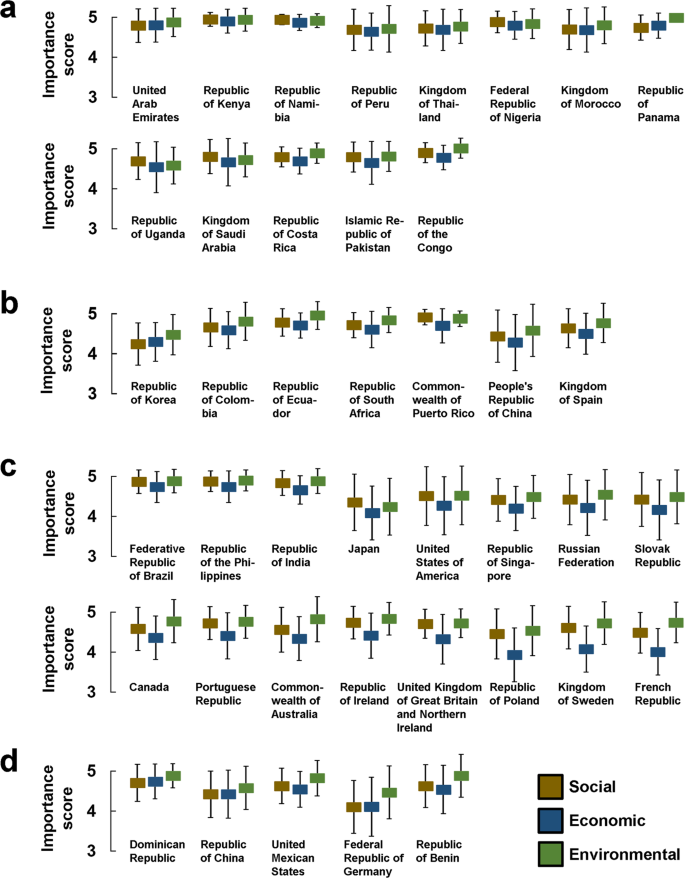
In group ( a ), there are no significant differences between the three factors within the countries. In group ( b ), the environmental factor is rated higher than the economic factor but not higher than the social factor. In group ( c ), the economic factor is rated lower than the other two factors. In group ( d ), the environmental factor is rated significantly higher than both the economic and environmental factors. For clarity, the significance levels are not marked with asterisks in the figure. Exact significance levels and effect sizes can be found in Supplementary Table 1 . The boxes represent the mean of the components; the error bars represent the standard deviation.
The three higher-level sustainability factors show significant correlations with all five selected country-specific global development indices ( p < 0.001). The correlations are shown in Table 2 .
All correlations are in the high range according to the common interpretation (Field, 2013 ). It is noteworthy that there is a negative correlation for all the global development indices examined. It follows that students in countries with higher indices rate the SDGs as less important than do students in countries with lower indices. For all the global development indices tested, a higher score means a higher standard. In other words, students in countries with, for example, a higher standard of education or higher income per person consider the SDGs to be less important compared to their counterparts.
The correlations between the three sustainability factors found and the individual indices are shown in Fig. 2 . The importance score refers to the mean values of the individual sustainability factors for the different countries. The dashed lines represent the linear trend.
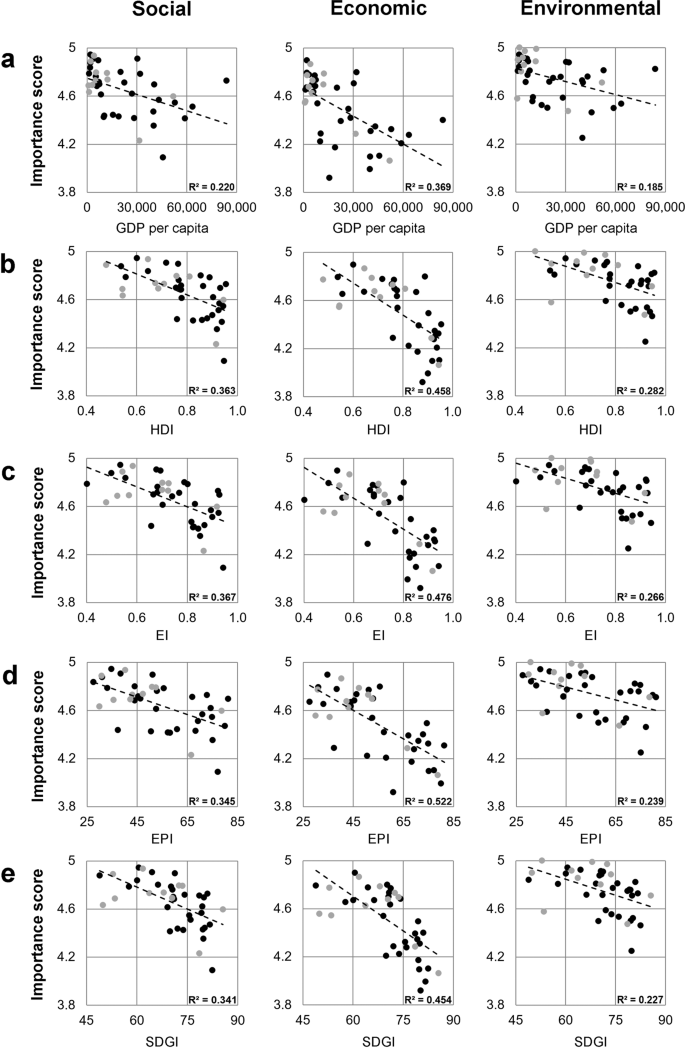
Each point represents one country. Countries with fewer than 50 respondents are shown in grey, and countries with more than 50 respondents are shown in black. a Gross domestic product per capita in US dollars, b Human Development Index, c Education Index, d Environment Performance Index, and e SDG Index.
The results of this study provide important information on how students in the environmental field worldwide perceive and evaluate the 17 SDGs. Based on the rating of the importance of the individual SDGs, it was possible to assign them to three higher-level factors in the factor analysis. Although each of the 17 SDGs contains all three pillars of sustainability (social, economic and environmental (Purvis et al., 2019 )) and the different levels of sustainability build on each other (Sachs, 2012 ; United Nations, 2015 ), it has also been shown in previous studies that people assign the SDGs to individual pillars to varying degrees (Bain et al., 2019 ; Dalampira and Nastis, 2020 ; Elder and Olsen, 2019 ). Reviewing the three higher-level factors, it can be assumed that our data also reflect such a classification. When considering only the labels and short descriptions, Factor 1 includes the SDGs that are primarily considered social, Factor 2 includes the SDGs that are considered economic, and Factor 3 includes the SDGs that are considered environmental (Elder and Olsen, 2019 ). While in previous studies, respondents were often asked directly to assign the SDGs to the three pillars of sustainability, in this study, the classification was solely based on the different ratings of the importance of each SDG.
The clear separation of the SDGs into these three groups and the low cross-loading values suggest that environmental students worldwide make this categorization and assign different importance to the SDGs in the three groups, potentially subconsciously. It can be concluded that the students consider ecological, economic and social challenges to be of varying importance. This finding provides an essential starting point for decision-makers in tertiary education institutions. In addition to the current increasing number of courses with a focus on sustainability (O’Byrne et al., 2015 ; Rodríguez-García et al., 2019 ), more emphasis should be placed on the interconnectedness of the individual layers of the various SDGs. For each SDG, attention should be given to highlighting social, environmental and economic components and to underlining the close relationship between these pillars. In this way, the importance of all three components of each SDG can be taken into account for current issues. Fisheries, for example, have important elements of the social and economic components, in addition to the environmental component, and all of these elements are closely linked (Asche et al., 2018 ). These connections should be addressed and highlighted in environmental education courses.
When comparing these three factors within the countries, different patterns emerge. In approximately two-thirds of the countries, the three factors are not rated as equally important. A noticeable pattern, which is particularly evident in a number of industrialized countries, is that the gap between the economic factor and the other two factors is particularly large. This could well be explained to some extent by the attitudes of people in industrialized countries; i.e., environmental issues, such as fighting climate change, are seen as particularly important aims in North America and Europe (Theresa et al., 2020 ). When considering problems in developing counties, people in Europe often rate issues belonging to the social component (such as peace and security) as particularly important (European Commission. Directorate General for International Cooperation and Development. et al., 2016 ). This potentially leads to the assessment that the environmental and social factors are particularly important, while the economic SDGs are perceived as less important, as they do not fall into either category.
Another pattern that repeatedly emerges is that the environmental component is rated as being more important than one or both of the other components. In no country was the environmental component rated significantly worse than the two other factors. These results are very positive, as environmental problems are currently more relevant than ever before. The boundaries of our planet are being increasingly exhausted, and there is an urgent need for action at the global level (Steffen et al., 2015 ). The high rating of environmental factors also shows a particularly positive trend in all countries. In the past, many governments and experts prioritized economic growth and considered environmental damage as a trade-off (Elder and Olsen, 2019 ). The common approach has been to accept pollution as a consequence of economic growth and to deal with the related environmental problems that arise later (Azadi et al., 2011 ). This view is not reflected in our study of environmental students. In the current study, environmental concerns are considered to be at least as important, and in some countries even more important, than social and economic factors.
The differences identified between countries can serve as a possible guide to action for local decision-makers who can incorporate specific promotion of the importance of different SDGs into the curriculum. In this way, country-specific actions can be implemented that specifically address the economic, ecological or environmental awareness of each of the SDGs. These results can also be seen as a call to those countries in which the gap between the three factors is particularly large. Especially in these countries, political or educational actions, such as emphasizing the global importance of the economic SDGs in the educational context, would be particularly important.
The comparison of the country-specific indicators with the rating of the importance of the higher-level factors shows a similar picture for all indicators. In countries with higher indices (higher GDP per capita, higher health index, etc.), the SDGs are generally rated as being less important than in countries with lower indices. In this context, it does not matter whether the SDGs are perceived as social, economic or environmental. This result is surprising, since in previous international studies, it was often found that people in wealthier countries, i.e., countries with a higher GDP per capita, have a more positive attitude towards, for example, environmental problems, than do people in countries with a lower GDP per capita (Franzen, 2003 ; Franzen and Meyer, 2010 ; Franzen and Vogl, 2013 ). The research of and theory put forth by Inglehart is often used as a basis for explanation. He found that in countries where postmaterialist values dominate, people have a more positive attitude towards environmental protection than they do in countries with more materialist values. Thus, postmaterialist values are more likely to be found in advanced industrial societies (Inglehart, 1995 ). However, postmaterialist values do not necessarily lead to higher support for the SDGs (Guan et al., 2019 ). Our study also supports this assumption. The results show that, on average, people in societies with higher indices (usually industrialized societies) rate the SDGs as being less important than do people in countries with lower indices. This provides important insights for politicians, stakeholders and decision-makers; i.e., in wealthier countries that have already made great progress in implementing the SDGs, the relevance of the SDGs must be communicated at different levels. Particular attention must be paid to higher educational institutions. The fact that the SDGs are rated lower on average in wealthier countries with a higher Education Index outcome shows that it is especially in these countries that there is a need to improve the related knowledge and that the focus of higher education institutions should be placed specifically on content related to the SDGs. In this context, it is not sufficient to teach only basic scientific knowledge (Frick et al., 2004 ); rather, other factors, such as attitudes (Gifford and Sussman, 2012 ) or values (Steg and Groot, 2012 ), should also be a particular focus of education. The importance of the SDGs should be considered not only for specific countries but also in an international and global context. Thus, these topics could be integrated into the curricula of universities and schools to enable students, as future decision-makers in society, to act as multipliers and pass on the relevance and importance of the SDGs in society.
Limitations
Although the study was conducted with great care, some limitations must be addressed. For example, the study surveyed a very select group of students in environmental and sustainability science courses. It can be assumed that people in these courses are more interested in environmental issues than the general population. However, because a similar group of students was surveyed in each country, cross-country comparison is possible. Nevertheless, it must be assumed that the results cannot be generalized to other courses of study or to the general population. Further international studies are necessary to investigate relationships in other groups.
Another limitation of the study is that the survey was conducted by e-mail on a voluntary basis. This could possibly lead to self-selection; i.e., people who were already interested in the topic of the SDGs were more likely to participate in the survey.
It should also be mentioned that the sample size differs in part between the individual countries. While in some countries, several hundred people could be surveyed, in other countries, only a sample size in the two-digit range was possible. This result could potentially have had an influence on the comparison between the countries.
When evaluating the individual SDGs, it cannot be ruled out that the students did not rate each SGD independently but rather related their importance to each other. As a result, some SDGs may have been rated differently than they would have been without such a direct comparison. However, since this effect was equally possible in all countries, the results remain comparable, and the conclusions remain valid.
The current research was able to show that the importance of the SDGs, regardless of the pillar of sustainability (social, economic, environmental), is considered important by students in environmental and sustainability science courses in different countries. However, there are variations between the countries in how important the individual pillars for sustainability are considered to be. This result offers the opportunity to specifically promote individual pillars for sustainability in those countries in which a pillar was perceived as being less important. Another important finding of the study is that especially in countries with high global development indices, the SDGs are rated as less important compared to the ratings in countries with lower global development indices. Therefore, our research is a call to countries with higher indices, where the SDGs have already been implemented to a higher extent, to actively improve the view and acceptance of students regarding the SDGs. This can help to further achieve the SDGs both in individual countries and at the global level.
Data availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors to any qualified researcher.
Alshuwaikhat HM, Abubakar I (2008) An integrated approach to achieving campus sustainability: assessment of the current campus environmental management practices. J Cleaner Prod 16(16):1777–1785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2007.12.002
Asche F et al. (2018) Three pillars of sustainability in fisheries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(44):11221–11225. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1807677115
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Azadi H, Verheijke G, Witlox F (2011) Pollute first, clean up later? Global Planet Change 78(3-4):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2011.05.006
Article ADS Google Scholar
Bain PG et al. (2019) Public views of the Sustainable Development Goals across countries. Nat Sustain 2(9):819–825. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-019-0365-4
Article Google Scholar
Bali Swain R, Yang-Wallentin F (2020) Achieving sustainable development goals: predicaments and strategies. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 27(2):96–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2019.1692316
Bellou C, Petreniti V, Skanavis C (2017) Greening the campus intentions: a study of the University of the Aegean nonacademic staff. Int J Sust Higher Ed 18(4):520–532. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSHE-05-2015-0102
Conceição P et al. (2020) Human development report 2020: the next frontier. Human development and the Anthropocene. United Nations Development Programme, New York
Google Scholar
Dalampira ES, Nastis SA (2020) Back to the future: simplifying Sustainable Development Goals based on three pillars of sustainability. Int J Sustain Agric Manag Inf 6(3):226. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSAMI.2020.10034327
Dunn OJ (1964) Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 6(3):241. https://doi.org/10.2307/1266041
Dziuban CD, Shirkey EC (1974) When is a correlation matrix appropriate for factor analysis? Some decision rules. Psychol Bull 81(6):358–361. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0036316
Elder M, Olsen SH (2019) The design of environmental priorities in the SDGs. Glob Policy 10(S1):70–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-5899.12596
European Commission. Directorate General for International Cooperation and Development, TNS Opinion & Social, European Commission. Directorate General for Communication (2016) Special Eurobarometer 441: The European year for development: citizens’s view on development, cooperation and aid. Publications Office
Fabrigar LR, Wegener DT, MacCallum RC, Strahan EJ (1999) Evaluating the use of exploratory factor analysis in psychological research. Psychol Methods 4(3):272–299. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.4.3.272
Field A (2013) Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics: and sex and drugs and rock ‘n’ roll, 4th edn. Sage, Los Angeles, London, New Delhi, Singapore, Washington, DC
Frank DJ, Meyer JW (2007) University expansion and the knowledge society. Theor Soc 36(4):287–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11186-007-9035-z
Franzen A (2003) Environmental attitudes in international comparison: an analysis of the ISSP surveys 1993 and 2000 *. Soc Sci Q 84(2):297–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/1540-6237.8402005
Franzen A, Meyer R (2010) Environmental attitudes in cross-national perspective: A multilevel analysis of the ISSP 1993 and 2000. Eur. Sociol. Rev. 26(2):219–234. https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcp018
Franzen A, Vogl D (2013) Two decades of measuring environmental attitudes: a comparative analysis of 33 countries. Global Environ Change 23(5):1001–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2013.03.009
Frick J, Kaiser FG, Wilson M (2004) Environmental knowledge and conservation behavior: exploring prevalence and structure in a representative sample. Personal Individ Differ 37(8):1597–1613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2004.02.015
Fritz CO, Morris PE, Richler JJ (2012) Effect size estimates: current use, calculations, and interpretation. J Exp Psychol Gen 141(1):2–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024338
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Gifford R, Sussman R (2012) Environmental attitudes. In: Clayton SD (ed) The Oxford handbook of environmental and conservation psychology. Oxford library of psychology. Oxford University Press, New York, Oxford, pp 65–80
GlobeScan (2016) Awareness of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) vs. Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). https://globescan.com/awareness-of-sustainable-development-goals-sdgs-vs-millennium-development-goals-mdgs/
Goossens Y (2007) Alternative progress indicators to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) as a means towards sustainable development. European Parliament
Guan T, Meng K, Liu W, Xue L (2019) Public attitudes toward Sustainable Development Goals: evidence from five Chinese cities. Sustainability 11(20):5793. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205793
Inglehart R (1995) Public support for environmental protection: objective problems and subjective values in 43 societies. Political Sci Politics 28(1):57. https://doi.org/10.2307/420583
International Monetary Fund (2021) World Economic Outlook: managing divergent recoveries. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2021/April
Ipsos (2015) Ipsos public affairs findings from a global poll on the Sustainable Development Goals. https://www.ipsos.com/en-us/17-country-study-foreign-aid-and-sustainable-development-goals
Kaiser HF (1960) The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas 20(1):141–151. https://doi.org/10.1177/001316446002000116
Kestin T et al. (2017) Getting started with the SDGs in universities: a guide for universities, higher education institutions, and the academic sector. Sustainable Development Solutions Network, Melbourne
Kioupi V, Voulvoulis N (2020) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): assessing the contribution of higher education programmes. Sustainability 12(17):6701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12176701
Lampert M, Papadongonas P (2016) Towards 2030 Without Poverty: increasing knowledge of progress made and opportunities for engaging frontrunners in the world population with the global goals. https://oxfamsol.be/sites/default/files/documents/towards_2030_without_poverty-glocalities2016-2-new.pdf
Lozano R (2006) Incorporation and institutionalization of SD into universities: breaking through barriers to change. J Cleaner Prod 14(9–11):787–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2005.12.010
Lozano R et al (2013) Declarations for sustainability in higher education: becoming better leaders, through addressing the university system. J Cleaner Prod 48:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.10.006
Nilsson M, Griggs D, Visbeck M (2016) Policy: map the interactions between Sustainable Development Goals. Nature 534(7607):320–322. https://doi.org/10.1038/534320a
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
O’Byrne D, Dripps W, Nicholas KA (2015) Teaching and learning sustainability: an assessment of the curriculum content and structure of sustainability degree programs in higher education. Sustain Sci 10(1):43–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-014-0251-y
Pham‐Truffert M et al. (2020) Interactions among Sustainable Development Goals: Knowledge for identifying multipliers and virtuous cycles. Sustain Dev 28(5):1236–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2073
Pradhan P et al. (2017) A systematic study of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interactions. Earth’s Future 5(11):1169–1179. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017EF000632
Purvis B, Mao Y, Robinson D (2019) Three pillars of sustainability: in search of conceptual origins. Sustain Sci 14(3):681–695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-018-0627-5
Rodríguez-García A-M, López Belmonte J, Agreda Montoro M, Moreno-Guerrero A-J (2019) Productive, structural and dynamic study of the concept of sustainability in the educational field. Sustainability 11(20):5613. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11205613
Sachs JD (2012) From millennium development goals to Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet 379(9832):2206–2211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60685-0
Sachs JD et al. (2021) Sustainable Development Report 2021: the decade of action for the Sustainable Development Goals. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Book Google Scholar
Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA (2018) Correlation coefficients: appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth Analg 126(5):1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000002864
Steffen W et al. (2015) Planetary boundaries: guiding human development on a changing planet. Sustain Sci 347(6223):1259855. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1259855
Article CAS Google Scholar
Steg L, Groot JIMde (2012) Environmental Values. In: Clayton SD (ed.) The Oxford handbook of environmental and conservation psychology. Oxford library of psychology. Oxford University Press, New York, Oxford, pp 81–92
Stephens JC et al. (2008) Higher education as a change agent for sustainability in different cultures and contexts. Int J Sust Higher Ed 9(3):317–338. https://doi.org/10.1108/14676370810885916
Theresa F, Joachim S, Todd C (2020) Report of results global survey on sustainability and the SDGs: awareness, priorities, need for action. Schlange & Co. GmbH, Hamburg
UNESCO (2017) Education for sustainable development goals: learning objectives. UNESCO, Paris
United Nations (2015) Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development: A/RES/71/1. https://undocs.org/A/RES/71/1
United Nations (2016) The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in your language. https://unric.org/en/sdgs-in-your-language/
United Nations (2017) Global indicator framework for the Sustainable Development Goals and targets of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development: A/RES/71/313. https://undocs.org/A/RES/71/313
United Nations Development Programme (2020a) Human development reports: education index. http://hdr.undp.org/en/indicators/103706
United Nations Development Programme (2020b) Technical notes: calculating the human development indices—graphical presentation. http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr2020_technical_notes.pdf
Vicente-Molina MA, Fernández-Sáinz A, Izagirre-Olaizola J (2013) Environmental knowledge and other variables affecting pro-environmental behaviour: comparison of university students from emerging and advanced countries. J Clean Prod 61:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.05.015
Wendling ZA et al. (2020) 2020 Environmental Performance Index. https://epi.yale.edu/
Yong AG, Pearce S (2013) A beginner’s guide to factor analysis: focusing on exploratory factor analysis. Tutor Quant Methods Psychol 9(2):79–94. https://doi.org/10.20982/tqmp.09.2.p079
Youth Speak Survey (2020) Global report 2020. https://www.youthforesight.org/resource-details/Publications/858
Yuriev A, Sierra‐Barón W (2020) Exploring sustainability cross‐culturally: employees’ beliefs on green behaviors. Sustain Dev 28(5):1199–1207. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2069
Zamora-Polo F, Sánchez-Martín J, Corrales-Serrano M, Espejo-Antúnez L (2019) What do university students know about Sustainable Development Goals? A realistic approach to the reception of this UN program amongst the youth population. Sustainability 11(13):3533. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133533
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank all study participants and the more than 300 researchers and universities that shared our questionnaires. This study was partly supported by the Opel-Zoo foundation professorship in zoo biology from the “von Opel Hessische Zoostiftung”.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Bioscience Education and Zoo Biology, Goethe University Frankfurt, Frankfurt, Germany
Matthias Winfried Kleespies & Paul Wilhelm Dierkes
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: MWK and PWD; data collection: MWK; methodology: MWK and PWD; validation, formal analysis, investigation: MWK and PWD; figures: PWD and MWK; writing—original: MWK; writing—review and editing: MWK and PWD, funding acquisition: PWD. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Matthias Winfried Kleespies .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the science didactic institutes and Departments of the Goethe University Frankfurt am Main under approval number 15-WLSD-2104.
Informed consent
Participants were informed in writing before the start of the online survey about the voluntary character of participation, data protection and the aims of the study. After this information, participation in the study was considered informed consent. Participants could withdraw from the study at any time by closing the browser. It is not possible to identify individuals from the anonymously obtained data, and only persons of legal age were surveyed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplemental file, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kleespies, M.W., Dierkes, P.W. The importance of the Sustainable Development Goals to students of environmental and sustainability studies—a global survey in 41 countries. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 9 , 218 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01242-0
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2021
Accepted : 16 June 2022
Published : 29 June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01242-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Understanding the role of green finance and renewable energy consumption for sustainable development in aci economies.
- Muhammad Awais Baloch
- Zubeyde Senturk Ulucak
Climatic Change (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
What you need to know about education for sustainable development
What is education for sustainable development .
Education for sustainable development (ESD) gives learners of all ages the knowledge, skills, values and agency to address interconnected global challenges including climate change, loss of biodiversity, unsustainable use of resources, and inequality. It empowers learners of all ages to make informed decisions and take individual and collective action to change society and care for the planet. ESD is a lifelong learning process and an integral part of quality education. It enhances the cognitive, socio-emotional and behavioural dimensions of learning and encompasses learning content and outcomes, pedagogy and the learning environment itself.
How does UNESCO work on this theme?
UNESCO is the United Nations leading agency for ESD and is responsible for the implementation of ESD for 2030 , the current global framework for ESD which takes up and continues the work of the United Nations Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (2005-2014) and the Global Action Programme (GAP) on ESD (2015-2019).
UNESCO’s work on ESD focuses on five main areas:
- Advancing policy
- Transforming learning environments
- Building capacities of educators
- Empowering and mobilizing youth
- Accelerating local level action
UNESCO supports countries to develop and expand educational activities that focus on sustainability issues such as climate change, biodiversity, disaster risk reduction, water, the oceans, sustainable urbanisation and sustainable lifestyles through ESD. UNESCO leads and advocates globally on ESD and provides guidance and standards. It also provides data on the status of ESD and monitors progress on SDG Indicator 4.7.1, on the extent to which global citizenship education and ESD are mainstreamed in national education policies, curricula, teacher education and student assessment.
How does UNESCO mobilize education to address climate change?
Climate change education is the main thematic focus of ESD as it helps people understand and address the impacts of the climate crisis, empowering them with the knowledge, skills, values and attitudes needed to act as agents of change. The importance of education and training to address climate change is recognized in the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change , the Paris Agreement and the associated Action for Climate Empowerment agenda which all call on governments to educate, empower and engage all stakeholders and major groups on policies and actions relating to climate change. Through its ESD programme, UNESCO works to make education a more central and visible part of the international response to climate change. It produces and shares knowledge, provides policy guidance and technical support to countries, and implements projects on the ground.
UNESCO encourages Member States to develop and implement their country initiative to mainstream education for sustainable development.
What is the Greening Education Partnership?
To coordinate actions and efforts in the field of climate change education the Greening Education Partnership was launched in 2022 during the UN Secretary General's Summit on Transforming Education. This partnership, coordinated by a UNESCO Secretariat, is driving a global movement to get every learner climate-ready. The Partnership addresses four key areas of transformative education: greening schools, curricula, teachers training and education system's capacities, and communities.
How can I get involved?
Every single person can take action in many different ways every day to protect the planet. To complement the ESD for 2030 roadmap , UNESCO has developed the ESD for 2030 toolbox to provide an evolving set of selected resources to support Member States, regional and global stakeholders to develop activities in the five priority action areas and activities in support of the six key areas of implementation.
UNESCO also launched the Trash Hack campaign in response to the 2 billion tons of waste that the world produces every year, waste which clog up the oceans, fill the streets and litter huge areas. Trash Hacks are small changes everyone can make every day to reduce waste in their lives, their communities and the world.
Related items
- Education for sustainable development
- Environmental education
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Sustainable development goal 11: sustainable cities and communities.
Sustainable Development Goal 11, one of 17 goals that make up the United Nation’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, provides targets and guidance for urban planning to support cities with growing populations.
Anthropology, Sociology, Biology, Health, Conservation, Social Studies, Civics
The Tower Bridge
The tower bridge is a symbol of the city to many locals and foreigners alike. The tower bridge was built in 1886 and crosses over the River Thames.
Photograph by Robert Bye

Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 11 is about making “cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable.” It is one of the 17 SDGs in the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development .
In 2015, the United Nations (UN) adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development , a plan to promote peace and sustainable growth worldwide. One of the goals within the plan is SDG 11, which addresses urban development. The goal says cities should ensure access to safe and affordable housing, public transportation, and public green spaces. It states that cities should be resilient to natural disasters and protect those in vulnerable situations while also minimizing economic loss.
One sustainability target that is often overlooked is social sustainability and civic engagement . This includes actions individuals can take, like voting for measures that increase sustainability in their own city or for politicians who support these measures. People can also attend their city’s public forums to give feedback on sustainability initiatives. Taken as a whole, SDG 11 is a comprehensive and complex goal: creating sustainable cities that can withstand both climate change and unprecedented growth.
The Agenda for Sustainable Development , and the goals contained within it, are important because nations are facing new challenges as their cities grow in size and in population. The 2019 progress review of SDG 11 stated: “Globally, urban areas are expanding at a faster rate than their populations. Between 2000 and 2014, areas occupied by cities grew 1.28 times faster than their populations.” This means that cities are sprawling and becoming less dense. This leaves some urban residents without access to necessary infrastructure , like public transportation.
Environmental concerns are heightened in areas of urban growth as well. Air quality is worse in urban areas, and cities account for 70 percent of greenhouse gas emissions . Cities are also extremely vulnerable to the impacts of climate change , as a high number of urban areas lie along coastlines, which are prone to climate change –related natural disasters.
Many cities have already implemented sustainability efforts to meet SDG 11. Cities such as London, England, and New York City, New York, have passed legislation for congestion pricing to reduce air pollution. Congestion pricing is used to discourage people from driving by charging drivers higher tolls if they travel during rush hour or in certain high-traffic areas. Drivers of electric cars are sometimes allowed to travel for free in order to encourage environmentally conscious travel. Individuals can participate in this effort by choosing an electric car as their next vehicle or opting to walk or bike more frequently.
Though SDG 11 is primarily focused on government action, the initiatives need community buy-in from individual citizens as well as community leaders. For example, individuals can take actions such as fixing up their local parks, creating rooftop gardens, or participating in community composting programs to improve the quality of greenspaces and create additional ones in new spots. People can make small steps in their own neighborhoods to support sustainable cities on a world-wide level.
Articles & Profiles
Media credits.
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Manager
Program specialists, specialist, content production, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
- List of Commerce Articles
- Meaning And Features Of Sustainable Development
What is Sustainable Development?
Sustainable development can be defined as an approach to the economic development of a country without compromising with the quality of the environment for future generations. In the name of economic development, the price of environmental damage is paid in the form of land degradation, soil erosion, air and water pollution, deforestation, etc. This damage may surpass the advantages of having more quality output of goods and services.
Sustainable Development Goals
- To promote the kind of development that minimises environmental problems.
- To meet the needs of the existing generation without compromising with the quality of the environment for future generations.
Also check: Important Questions for Environment and Sustainable Development
Achieving Sustainable Development
Sustainable development can be achieved if we follow the following points:
- It can be achieved by restricting human activities.
- Technological development should be input effective and not input utilising.
- The rate of consumption should not surpass the rate of salvation.
- For renewable resources, the rate of consumption should not surpass the rate of production of renewable substitutes.
- All types of pollution should be minimised.
- It can be achieved by sensible use of natural resources.
Examples of Sustainable Development
- Wind energy
- Solar energy
- Crop rotation
- Sustainable construction
- Efficient water fixtures
- Green space
- Sustainable forestry
What is Environmental Crisis?
Environmental crisis refers to a situation when an environment fails to perform its vital function of life sustenance. The environment becomes suitable as soon as the following happens:
- Resource extraction remains below the rate of resource generation.
- Generation of waste remains within the absorption capacity of the environment.
Reasons for Environmental Crisis
(1) Population explosion
- The high rate of growth of population adversely affects the environment.
- It increases the demand for environmental resources, but their supply is limited.
- This results in overuse and misuse of resources.
(2) Rise in economic activity
- The rise in economic growth results in affluent consumption and production of goods and services.
- It generates wastes that are beyond the absorptive capacity of the environment.
(3) Rapid industrialisation
- Rapid industrialisation has led to deforestation, and depletion of natural resources.
- It leads to contamination of water [3] due to the accumulation of increasing quantity of toxic substances and industrial wastes in the water bodies.
(4) Urbanisation
- A large migration of population from rural to urban areas results in the fast growth of slum areas.
- It leads to the excess burden on the existing infrastructural activities.
(5) Deforestation
- Deforestation refers to cutting down of trees, clearing forest, etc.
- It adversely affects the environment and causes other problems.
(6) Increased use of insecticides, pesticides, and chemical fertilisers
- Farmers and workers suffer health problems due to the increased use of poisonous insecticides, pesticides, and chemical fertilisers.
- The crop generated also contains chemical elements in it.
Short Questions
Q.1: What is the opportunity cost of a negative environment?
Ans: It is the cost incurred by a society from the impact of a negative environment on the society.
Q.2: What is global warming?
Ans: It is a situation of the gradual but consistent rise in the atmospheric temperature.
Q.3: What is ozone depletion?
Ans: Ozone depletion refers to the destruction of the ozone layer due to the presence of chlorine and bromine from man-made CFC (Chlorofluorocarbon) and other gases.
Q.4: What is land degradation?
Ans: It refers to a decline in the quality of soil, water, or vegetation conditions.
Multiple Choice Questions:
For more data on Economics Class 11 Syllabus, Commerce notifications and sample papers for Class 11 Commerce, stay tuned to BYJU’S.
Frequently Asked Questions on Sustainable Development
What is the main goal of sustainable development.
Sustainable development is to achieve a better and more sustainable future for everyone. It is a collection of 17 SDG’s or Sustainable development goals.
What are the three types of sustainable development?
The three types of sustainable development are:
- Economic viability
- Environmental protection
- Social equity
Give 2 Examples of Sustainable Development.
The two examples of sustainable development are:
1.Solar energy: Harnessing the solar energy to reduce pollution in the environment.
2.Crop Rotation : Planting different types of crops on the same land on a rotational basis for improving soil fertility.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It is very helpful for making projects and for learning also
The best website
BYJU’S is the best website
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sustainable development is basically an action plan which helps us to achieve sustainability in any activity which makes use of the resource. Moreover, it also demands immediate and intergenerational replication. Through essay on sustainable development, we will help you understand the concept and its advantages.
Essay on Sustainable Development: Samples in 250, 300 and 500 Words. On 3rd August 2023, the Indian Government released its Net zero emissions target policy to reduce its carbon footprints. To achieve the sustainable development goals (SDG), as specified by the UN, India is determined for its long-term low-carbon development strategy.
Sarah E. Boslaugh. Sustainable development, approach to social, economic, and environmental planning that attempts to balance the social and economic needs of present and future human generations with the imperative of preserving, or preventing undue damage to, the natural environment. Sustainable development lacks a.
500+ Words Essay on Sustainable Development. Sustainable development is a central concept. It is a way of understanding the world and a method for solving global problems. The world population continues to rise rapidly. This increasing population needs basic essential things for their survival such as food, safe water, health care and shelter.
Sustainable development requires six central capacities. Sustainable development is an organizing principle that aims to meet human development goals while also enabling natural systems to provide necessary natural resources and ecosystem services to humans. The desired result is a society where living conditions and resources meet human needs without undermining the planetary integrity and ...
Therefore, sustainable development requires the elimination of fragmentation; that is, environmental, social, and economic concerns must be integrated throughout decision making processes in order to move towards development that is truly sustainable. References Brodhag, C., & Taliere, S. (2006). Sustainable development strategies: Tools for ...
The term "sustainable development" is often used in business, government, and non-profit spaces to refer to the processes and pathways required to balance economic growth, environmental stewardship, and social inclusion. Sustainability is considered a paradigm for thinking about balancing environmental, economic, and social needs for the ...
In short, the 17 SDGs are: Goal 1: No Poverty: End poverty in all its forms everywhere. Goal 2: Zero Hunger: End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture. Goal 3: Good Health and Well-being: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
Sustainable development is a process that creates growth and progress through the addition of physical, economic, environmental, and social components to improve quality of life without damaging the resources of the environment. Simply put, sustainable development is a way for people to use resources without the resources running out 3.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) make a bold commitment to end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and other communicable diseases by 2030. The aim is to achieve universal health ...
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), also known as the Global Goals, were adopted by the United Nations in 2015 as a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that by 2030 all people enjoy peace and prosperity. The 17 SDGs are integrated—they recognize that action in one area will affect outcomes in others ...
It seems like nowadays, the term 'sustainable' is used all around us - from food packaging to clothing companies and even tourism. In fact, 'sustainability' was one of the most-searched terms in fashion in 2019, and Google searches for the term have been on the rise, illustrating the public's growing interest in the topic. But what is sustainability exactly and why is it so important?
ticular the emergence of "sustainable development" discourse over a relatively short period of time, in a context of sharp differences of views to what it might mean, as well as still evolving practices of applying the concept. (Sands 2003: 289) One essential problem in defining the substance of "sustainable development", as I suggest in
The 17 SDGs, the cornerstone of the Agenda, offer the most practical and effective pathway to tackle the causes of violent conflict, human rights abuses, climate change and environmental ...
To fight the global problems of humanity, the United Nations has adopted 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). To achieve these goals, it is necessary that future decision-makers and ...
Sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the future. (Foto: CC0 Public Domain / pexels - pixabay) Sustainable development is an approach to development that balances different needs against an awareness of the environmental, social and economic limitations we face as a society.
For my short essay topic, I wanted to look through UN's Sustainable Development Goals' data. What I had came across while going through different analysis were quite interesting.
Education for sustainable development (ESD) gives learners of all ages the knowledge, skills, values and agency to address interconnected global challenges including climate change, loss of biodiversity, unsustainable use of resources, and inequality. It empowers learners of all ages to make informed decisions and take individual and collective ...
Sustainable development is broadly defined as: 'development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs'. The drive for economic growth has resulted in problems such as environmental degradation and social disparities. Sustainable development prescribes for a more ...
These goals include a focus on ending poverty, tackling climate change, and maintaining high standards of resources. SDG 6 focuses on ensuring a clean and stable water supply and effective water sanitation for all people by the year 2030. The goal is a reaction to the fact that many people throughout the world lack these basic services.
Sustainable development aims for "sustainable development" for rich countries to achieve continuous reductions in the levels of energy consumption and natural resources, which reach many times in the rich countries compared to the poor countries. For example, energy consumption from oil, gas, and coal in the United States reaches a higher ...
Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 11 is about making "cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable." It is one of the 17 SDGs in the 2030 Agenda for . Sustainable Development.. In 2015, the United Nations (UN) adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, a plan to promote peace and sustainable growth worldwide.One of the goals within the plan is SDG 11 ...
Sustainable development can be defined as an approach to the economic development of a country without compromising with the quality of the environment for future generations. In the name of economic development, the price of environmental damage is paid in the form of land degradation, soil erosion, air and water pollution, deforestation, etc.