
Data & Finance for Work & Life


Management Presentation: 8 Tips, Examples & a Template
In a corporate context, presenting works wonders for a career. Most professionals get exposure to presenting to informed colleagues and department managers. It’s an ideal way to get visibility and show value. But a management presentation to senior executives who aren’t familiar department nuances is a different ballgame.
A management presentation is a high-level summary to senior executive that optimizes reports to include only the details relevant to directorial decisions . They are notoriously difficult to navigate for two reasons: 1. most executives do not have working knowledge of the nuances in each department , 2. presenters rarely have time to understand executives’ preferences .
More than anything else, good management presenters learn how to strike a balance in the degree of detail: they provide enough detail so executives make informed decisions, but not so much detail that they cause confusion.
This article explores how to make a good management presentations in PowerPoint using 4 management presenting best practices , 4 management presenting techniques , providing examples for each, and finishing with a management presentation template you can apply in real life. You can use it as a jumping off point for deeper communication curriculum .
5 management presenting best practices are:
- Ask what managers prefer ahead of time.
- Have 1 message, and 1 message Only.
- The only words should be “Thought Starters.”
- Keep it short.
- Practice 7 times in advance.
4 management presenting techniques are:
- Use a CSP model – Challenge, Solution, Progress.
- Begin with a summary of exactly 3 points.
- Use only these 3 chart types: bar, line, scatter.
- Design slides with the company logo.
I will use a financial analyst perspective in this article, but everything here applies to data and business analysts as well.
Ask Executives Their Preference Ahead of Time
If you’ve ever taken a class on presentation techniques, you’ve heard the old adage “know your audience.” It’s true, the best way to deliver a great presentation is to align your message with what your audience already understands. The same applies to a management presentation.
The challenge is that, more often than not, executives are too busy for you to get to know them well. This means you hardly get the chance to understand how they like presentations. So what can you do? Well, ask them! There’s no harm in sending an email to understand better. And what’s more, once you know, you can always defer to their preferences in the future.
For a financial management presentation, common questions to ask include the following:
- Do you prefer to see raw data, or only visualizations?
- Do you prefer charts or table summaries?
- Would you like a written explanation on paper for each slide?
- Do you like averages alone, or do you prefer means, or standard deviation?
- What interests you most in a presentation?
If you gather some helpful insights, then your presentation will be that much better. That said, you may not get a response, or it may be quick and not insightful. But most senior executives will appreciate you asking .
The best part is you will be able to surprise them. Using the best practices and techniques below, in additional to any insights gathered form your email, will work wonders for you.
Have 1 Message, and 1 Message Only
The easiest mistake to make on a management presentation is trying to deliver multiple messages. Senior executives go through loads of meetings every day, and each meeting they have includes a wave of information. Your mission should be to deliver 1 essential message so they can easily understand and compartmentalize it.
This is no easy task. When I try to narrow down the focus of my management presentation message, it seems like I leave out critical information along the way. The key is to tell a story to incorporate critical information as part of a story towards the essential message.
For example, imagine you work for a wholesale watch company called Batch Watch . You want to explain a financing operation in which the company has the option of two loans to fund the initial costs of 10,000 watches. These loans have different interest rates and maturity dates. Loan A is better if the company expects to sell the watches within 3 months, while Loan B is better if the company expects to sell over more than 3 months. Each has cancellation fees and cash flow impacts.
Instead of showing the cancellation fees and cash flow impact of the each loan, all you need to say is “ we expect the company to sell them within 3 months, and we recommend loan A for that reason.” If the executives disagree on the sale timeline, they will ask for more information.
This is how you keep senior executives engaged, by integrating them in the story you tell. Ultimately, the essential message of your presentation should be how much profit the company will make from the watch funding operation. Senior executives should leave feeling like the project is in good hands with you, and they only feel that way when you tell a story around the essential message .
Whatever the Message, Use Data
Whatever message you want to send, it needs to be backed up by data. In the example above the data was financial, but it’s not always that simple. Context may require you to provide KPIs and perform extensive data analysis that culminates in a small output that your viewers can easily digest.
You need to be strong with data to deliver a good management presentation. To get started or refresh your memory, you can read AnalystAnswers’ free Intro to Data Analysis eBook .
The Only Words Should be “Thought Starters”
As a general presentation principle, you should not write many thoughts down on presentation slides. Words have two negative impacts on the audience: they demand energy from the reader, and they make the reader feel compelled to read, lest they misunderstand.
If you can avoid putting text blocks altogether, do. If you don’t need any writing at all, don’t. However, if you need guidance as you speak or want to provide reminders for a later data, use “Thought Starters.”
Thought starters are phrases of 3 words maximum that contain ideas leading to the essential message. People often call them “bullet points,” which is common for list-style thought starters. Personally, I prefer to place thought starters at different places on a slide. When I use a chart, for example, I put thought starters at relevant places on the slide.
Keep it Short
Your presentation should never consume more than 80% of the allotted timeframe. This means that if you plan a 5 minutes meeting, deliver the presentation in 4 minutes. If you’re given 30 minutes, do it in 25 minutes. If you have 1 hour, do it in 45 minutes.
By keeping the presentation short, you relieve the audience and you allow for some question buffer. Have you ever sat in a meeting planned for 1 hour, and at 45m it ends early? It’s a pleasure for everyone. Most of us feel like we’re running behind — when you put us ahead of schedule, we love you!
At the same time, senior executives may bombard you with questions throughout the presentation. If you planned to fill the whole timeframe, you won’t finish. But if you planned to finish early, you still have a chance.
And if you use the rest of these best practices and techniques, those senior executives shouldn’t need to ask too many questions!
Practice 7 Times in Advance
There’s a mix of opinions on the number of times you should rehearse a presentation before doing it live, but most people agree that it’s somewhere between 5 and 10 times. If you take nothing else from this article, take this. To deliver a good presentation, prepare excellent slides; to deliver a great presentation, practice presenting them 7 times.
To deliver a good presentation, prepare excellent slides; to deliver a great presentation, practice presenting them 7 times. AnalystAnswers.com
But just practicing isn’t enough, there are a few criteria you must meet:
- Practice in the room you will present in. There’s something about envisioning yourself live that really makes a difference. When you practice in a space other that where you’ll present, it’s good. But when you practice in the “live” room, you’re able to sensitize yourself to the environment, which calms nerves so you can focus on the message.
- Have an audience. We all behave differently when there’s stimulus of other people around. Whenever possible, get one or two people to whom you can present. In addition to getting used to having an audience, you’ll also get some feedback.
- Use the same volume of voice. When we’re not “live,” we have a tendency to hold back on our voice. This is detrimental to the presentation because you feel taken off guard by your own voice. Make sure to envision yourself in front of the senior execs when you practice.
Best Practices Recap
We’ve addressed 5 best practices — now let’s turn our attention to 4 specific techniques you can easily implement. And when you do, that work wonders for management presenting.
Use a CSP Model (Challenge, Solution, Progress)
Every presentation needs structure, but it’s easy to forget that we need to guide our audience. A great way to structure management reports is using the CSP model. CSP stands for Challenge, Solution, Progress, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.
You need to explain the challenge or goal, explain what the solution to the challenge is (or how to achieve the goal), and show where you are in the steps to completing that goal.
For example, let’s look at our Batch Watch case. Imagine you need to find funding for a new product launch — $100,000 to be exact. A sample CSP model for this would be a slide that shows:

By using the CSP model, you guide the audience. However, it’s important to note that the CSP model is not a summary . It’s an overview of the process, but a summary should always come before. Let’s talk about it now.
Begin with a Summary of Exactly 3 Points
Any good presentation begins with a summary. And a good summary communicates the essential message simply in 3 points. However, the summary is not the same thing as the CSP model. Instead, it provides an alternative view on the challenge and and solution.
For example, using our Batch Watch case of funding a new product, you could address a summary in the following way:
- Challenge, Solution, Progress
- Funding acquisition
- Project Timeline
This provides additional details that are most relevant to the project and carry added value to the CSP model.
Use only Bar Charts (aka Column Charts), Line Graphs, and Scatter Plots
Whether it’s for data, financial, and business analyst topics , management presentations should only ever have bar charts, line graphs, and scatter plots. They are common, rich in information, and well understood. Any other kind of graph is distracting more than anything else.
A bar graph is useful when you want to compare like variables. For example, if you want to show the average size of Canadian trout versus American trout. A common mistake, though, is to use bar graphs to show change over time. While it’s not incorrect to do so, line graphs are better for this purpose.
A line graph is useful when you want to show change in one variable over time (we call this time series data). For example, if you want to show the progression of revenues over time, line graphs are the perfect way to do so.
A scatter plot is best when you want to compare a set of observations of one variable to a set of observations of another. It’s the ideal way to quickly visualize the relationship between two variables. For example, if you want to see how company revenues compare to GDP, you could use a scatter plot like this:
For example, let’s look at our Batch Watch case. If we want to see how our company is performing compared to the economy as a whole, we could use this scatter plot. As you can see, we have a positive (bottom left to top right) relationship, but a weak one (points not clustered closely).

Design Slides Using the Company Logo
When you’re presenting to senior executives, you want your slides to look professional. The best way to do that is by putting your company logo on them, including any corporate design standards (colors, fonts, etc). Show through your presentation that you belong to the same company, and that you’re in it in spirit. For example, let’s add the AnalystAnswers.com logo to our CSP slide:

Techniques Recap
Here’s a sample management presentation template below. I hope you understand after reading this article that management presentation is more about your delivery than it is about the slides you prepare.
Download Management Presentation Template for Free
While the techniques we’ve discussed will help you build a good presentation, your success really depends on how well you deliver the ideas needed to help senior executives make decisions. At the end of the day, it’s all about balance.
If you only remember two things from this article, remember that great management presenters give enough detail to inform senior executive but not too much that they cause confusion, and great management presenters make sure they do so by practicing 7 times in advance. You’ll have to practice, practice, practice.
About the Author
Noah is the founder & Editor-in-Chief at AnalystAnswers. He is a transatlantic professional and entrepreneur with 5+ years of corporate finance and data analytics experience, as well as 3+ years in consumer financial products and business software. He started AnalystAnswers to provide aspiring professionals with accessible explanations of otherwise dense finance and data concepts. Noah believes everyone can benefit from an analytical mindset in growing digital world. When he's not busy at work, Noah likes to explore new European cities, exercise, and spend time with friends and family.
File available immediately.

Notice: JavaScript is required for this content.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1 Introduction to Management
Learning Objectives
The purpose of this chapter is to:
1) Give you a basic understanding of management and its importance
2) Provide a foundation of the managerial functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling
Introduction to Management
Management is not a hard science. Unlike chemistry or algebra where a right answer (often) exists, management is fluid, and subjective, and there are divergent perspectives on how to employ its principles. But what exactly is management? Most scholars have variations of the same definition that include a utilization of resources to achieve a goal. Lussier (2021) defines a manager as “the individual responsible for achieving organizational objectives through efficient and effective utilization of resources” (p. 3). The problem with this definition is that it implies that a manager has to be both efficient and effective, which eliminates the possibility of having a bad manager. Each of us can probably contradict this definition by providing an example from our personal past. However, this definition contains the basic elements of using resources to pursue goals.
An early management scholar, Mary P. Follett characterized management as “the art of getting things done through the efforts of other people” (Graham, 1995). This definition implies both pursuing goals (getting things done) and utilizing resources (predominantly through people). However, this too is missing an element, that of the organizational context. An important consideration for understanding management is that the term organization simply refers to “a collection of people working together to achieve a common purpose” (Shermerhorn, 2013, p. 11). This means an organization could be anything from your high school volleyball team to church or a corporation. Including the term “organization” in the definition leaves open the possibility that management can be practiced in each of these settings, and broadens our use of the term management. A comprehensive definition for management then, would be the pursuit of organizational goals through the use of organizational resources (Bateman & Snell, 2013). Pursuit implies a chance of failure and organizational gives us a context. This begs the question – how can we become effective at the pursuit of goals, or become more efficient in our use of organizational resources? Being good at management requires an immense focus on both of these ends, and we can achieve this through the process of the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling functions of management. These functions serve as the basis for the rest of the textbook because they are the essential tools we use to manage organizations. Most of the context and examples for this book focus on the corporate use of management. However, you should meet the concepts where you are in your professional or academic career – apply the principles to the context of your life, master the four functions for what you are doing now so that you can scale them to much bigger managerial endeavors later.
Management is not New
A broad understanding of management as resource utilization focused on a goal gives us a wide scope of situations and contexts in which to practice it. For example, the Crow Indians employed a complex strategy to harvest an entire herd of buffalo by driving them off a cliff. To funnel the herd to the lane leading up to the cliff they used a decoy (a hunter donned in a buffalo calf robe imitating a lost calf), incense to smoke them towards the lane, or rock piles to guide them to the lane (Nathan, 2018). If we apply the basic principles of management in this context we can see these hunters used resources (rocks, incense, knowledge and tradition) to pursue a goal (procurement of food, tools, and clothing the bison afforded them).

At its core, this imperial supply chain used the same approach to achieve success th at a teenager might use in a playing video games. If he rallys his friends after school in a game of Call of Duty to defeat their online opponents, he might also be considered a manager. He uses his experience and knowledge of gameplay as well as weaponry within the game to pursue his goal of competitive domination.
These examples demonstrate that management is multifarious, and not at all a recent phenomenon. Yet, when we hear the term management , most of us probably conjure an image something like that of a corporate vice president implementing a marketing strategy to meet quarterly sales goals. The irony is that the corporate manager is utilizing the same tools as those of the native hunter, Spanish fleet admiral, and sophomore gamer. Management is both universal and ubiquitous in that we all use variations of its elements.
The Four Functions of Management
The management process by which we pursue goals includes planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. These are “ the how ” a manager pursues organizational goals, and are universally known as the four functions of management. They stem from the work of a French mining administrator, Henri Fayol, who first identified management as a practice that could be improved through the use of five functions – planning, organizing, commanding, coordinating, and controlling. Since he published his work in 1916, we have decided that leading people through motivation and incentivization works much better than telling them what to do (e.g. commanding and coordinating). We use the term leading instead of these practices. Chapter 2 on the history of management will provide some insights regarding this change. Nonetheless, he gave us a place from which to start.
Even if you have never stepped foot in a corporate office, or held the title of manager at your local Dairy Queen, you have no less used the functions of management in your personal pursuits. A relevant example would be the process by which you manage your personal budget.
Reflection: Are you already a manager?
Think about your personal or family budget for a moment, and answer the following questions:
1) Do you have your budget written down somewhere, or in an excel spreadsheet?
2) What are your financial goals?
3) How much do you put in savings, charity, and monthly expenses?
4) Where does your money come from (a job, your parents, a hobby, your spouse)?
5) If you have a budget shortfall during the month, what do you do?
6) How do you keep track of expenses to ensure your bank account remains in the black?
If you answered yes to question #1, then you are already engaged in the management function of planning. You know where your money is being spent. The same holds true for your financial goals. If you want to leave college debt free, save for a down payment on a house, or go on an unforgettable spring break trip, you have defined your organizational objective! Where you put your money is a function of how you manage your resources. This organizing function is presumably in line with your financial goals. For example, if you want to save for a down payment, you need to actually allocate your resources (income) to a savings account. Moreover, where your money comes from is also the source of your organizational resources. A budget shortfall might require you to employ the leading function of management. The essence of leading is motivating other people to align with your plan. What do you do if you need to pay bills, but don’t have the money? Perhaps you ask your parents for a loan (need to sell this idea to them), or you might need to negotiate with a co-worker to let you take on extra shifts (show them what’s in it for them in return), or it might be the reality that you need to sell something to make ends meet by selling something (in which case selling requires you to inspire someone else to see value in what you are selling). Leading might also entail convincing someone else in your circle to get on board with your gameplan (like a spouse, or sibling). Finally, keeping track of your expenses to ensure solvency and pace with your goals is the core of the controlling function. Do you keep receipts and check them against your online account expenses? Do you update your spreadsheet after your bill automatically debits from your account? Do you get an email notifying you have a low balance and are in risk of overdraft charges? Each of these methods are ways to monitor your progress and decide if you need to make a change (short term or long term).
If you reflect on this example of your personal budget, or you worked to achieve a personal or team goal, you will likely conclude that you are already a manager. This wide application of managerial thinking means that if you can master its principles on your personal scale, you can then amplify its use when you need to use it on a large scale. Get good at leading your class project, organizing your club fundraiser, or helping your team win a conference championship, and you will later be able to magnify the scale to lead a marketing department, or corporate merger, and even diplomatic negotiations as a prime minister.
Mastering the four functions will allow you to apply the function of planning on a more complex stage such as evaluating the internal and external environments of your organization. Using this analysis you can create an effective game plan to formulate a sustainable competitive advantage. Developing an organizing skillset will allow you to propose a structure for your team that incorporates cross functional members and ways of thinking. It will allow you to identify and recommend resources needed to pursue your plan. Honing your leading skillset will afford you the capability to motivate your organizational stakeholders to partake in your strategy, and force you to consider the ethical implications of your actions. Finally, implementing effective controlling allows you to check progress towards your goals and to recommend changes if you need to get on track.
Planning is the systematic process of making decisions about goals and activities the organization will pursue (Bateman & Snell, 2013). To make a decision about the direction of an organization, the planning phase must begin with analyzing the environment. Without a solid understanding of the context, the manager would have no basis to provide future direction. The context gives a manager a point of reference for improvement, opportunity, and learning from past mistakes. For this reason, the planning function should begin with analysis. This analysis should consider both the internal factors such as culture, values, and performance of team members as well as the external factors such as competitive environment, legal regulations, economy, technology, social values, and demographics.
The second component of planning is to use this analysis of the environment to build goals, activities, and objectives. For a major organization this might be the vision and mission statement of the organization. For a smaller organization this could be a year end, or season end goal. Some consider planning that point in your day or month that you step away from your desk, and think about the direction of your organization. This requires you to reflect on your organization’s past, and determine how that impacts the direction going forward.

Organizing is the process of assembling and assigning the human, financial, physical, informational, and other resources needed to achieve goals (Bateman & Snell, 2013). The core of the organizing function is leveraging the resources to align with the determined goals. Organizing human resources means first of all attracting a labor force that can help you pursue your goal. Within the organization, managing the human element means assigning tasks, delegating authority, determining a structure and hierarchy. Organizing the financial resources equates to making sure your capital is being utilized to meet goals. If an organization decides they want to have a best-in-class customer service team, they better being willing to spend the money to attract people with the disposition towards serving others, and spend money on training, or a retreat to teach the agents the skillsets they need. Marshalling physical resources focuses on the effectiveness of where you place and how you use physical assets. An executive chef might re-arrange a kitchen to improve process flow, food quality, or mitigate safety risks for example. Informational resources implies a leveraging and disseminating the organization’s knowledge in meaningful ways to achieve goals. Connecting employees to how they contribute to the financial bottom line is a way of leveraging informational resources, as is using your company’s proprietary algorithm to predict stock prices or develop new products.
Leading is stimulating high performance by members of the organization (Bateman and Snell, 2013). This function is getting members of the organization on board with your plan.
Normally, this means connecting with direct reports or teammates on a personal level. Understanding what drives individuals within the team allows a manager to design strategies around motivating, incentivizing, mobilizing, and arousing a desire to contribute.
Imagine for a minute, that you analyzed the conditions of the organization, you determined a game plan to pursue and even directed resources to step in that direction. You have successfully implemented the planning and organizing functions. In this scenario, however, you did not give consideration to how your team or organization would be involved. Do they agree with your direction? Did they have input in the process? Do they feel valued as a team member? Do they understand their role in a successful outcome? All of these questions are answered by the degree to which a manager is engaged in the leading function.
Having personal conversations, designing a bonus structure, or giving a rousing speech might all be considered leading the organization.
Controlling
Control is installing processes to guide the team towards goals and monitoring performance towards goals and making changes to the plan as needed (Batemen & Snell, 2013). Control does not always mean limited what the organization can do by having a hand in everything. We might call this micro-managing, which is control in its extreme form. Healthy control processes involve putting systems in place to make sure your organization is on track to meet the goals you established in the planning process. Planning sets standards to compare against, and the control process is the dashboard that tells whether or not you are meeting the standard. For example, a grocery store might set a goal of reducing shrink (that’s product lost to shoplifting, damage). They decide that they want to reduce their shrink loss by 50%. To achieve this plan, they will have to dedicate resources (more employees to monitor, rearrange loading dock). You already recognize that step as the organizing function. We then incentivize our employees by designing a bonus structure – i.e. if we collectively meet the goal, each employee shares in the savings. If we stop there, we would have no way of knowing if we met the goal. The control process solves this for us. The last step in the grocery store manager’s managerial approach is to have each department head report their shrink loss at the end of the shift, and aggregate those in an excel spreadsheet. In this way, the manager can see if the rearrangement of the loading dock has reduced the number of damaged canned goods that was happening under the old arrangement. The manager can make changes if they see that shrink is not improving even after hiring a greeter at the entrance.
Monitoring performance is the first step in control. After see the progress towards goals, the next step is to make changes. In this way, the control process always leads a manager back to the planning phase of management. There are only two outcomes to the control process. You are making progress towards your goal, or you are digressing in your performance. If you reach your goal, you will need to set new goals, which is the planning function. If you are not progressing towards your goal, you need to analyze the environment and determine why not. In this way the management functions are related and highly dependent upon each other, especially control and planning.
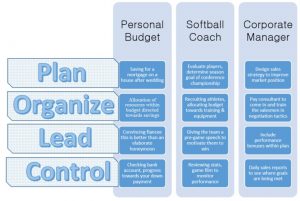
To illustrate the application of the four functions of manager, consider the various contexts in Figure 1.1. Under the personal budget, an engaged couple has decided to save for a house after getting married. The softball coach must determine how to win a conference championship, and the corporate manager is working on a strategy to improve waning sales figures.
Figure 1.1 – The Functions of Management Applied
On the Importance of Studying Management
The purpose of this textbook is to provide you with firstly, a broad exploration of what management is – its elements and origins. Secondly, the purpose of this textbook is to provide you with a managerial framework you can utilize to practice management at any level of complexity. This framework emphasizes the four basic functions – planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Most management textbooks include a wide variety of academic terms and concepts that take focus away from these four functions. Other textbooks will inundate the reader with descriptions of heuristics, focus on layers of management, or extraneous terms like the Shamrock organization that do not advance a practical understanding of management. We have designed this textbook with the four functions of management at the forefront because these elements are so critical to the foundation of everything you will do in the managerial context. This textbook provides a history of management and a chapter on ethics, but then focuses exclusively on the functions of management as the subject matter. At the completion of this textbook, you should be able to understand, recognize, and apply these four functions of management.
The four functions of management (plan, organize, lead, and control) serve as the foundation for everything else you will study in your business education. Mastering these tools at the most basic level, as well as the more sophisticated levels in classes you will take later, will best prepare you as a business professional (Dolechek et al, 2019).
Figure 1.2 – Management as the Foundation
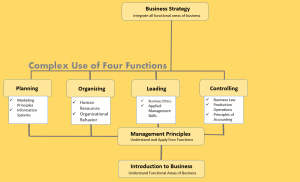
Upon completion of a management principles course, you will progress towards the applications of the four functions of management in the upper level courses. For this reason, management principles serves as a pre-requisite for most other management courses. In marketing principles you will develop an understanding of how to analyze external conditions, and a course in information systems will help you design ways to collect more information to analyze. This is the core of the planning function. In human resources and organizational behavior, you will learn the dynamics of your ever-important resource of human labor, the organizing function. In business ethics and applied management skills you work on understanding what drives people, and by association how to lead them based on that understanding. Grasping business law and production operations will give you a deeper understanding of how to monitor progress (to meet legal compliance and to test production quality for example). The entire discipline of accounting is a managerial function of control. Constructing financial statements is done for the sole purpose of determining the performance of you organization so that you can make future decisions. The capstone course of a business program is the business strategy class. In this course, students are given an opportunity to demonstrate mastery of the four functions by including all of the functional areas of business in their decision making.
A Whale of an Example
You are the city manager of a coastal Oregon city. On a quiet, rainy Tuesday, you walk into your office and put the coffee on. As you take your first sip, your administrative assistant forwards you a phone call from the parks and rec manager. “We’ve got a problem down here on the beach. The tide just left a dead humpback whale on our beach.” What do you do? What. Do. You. Do?? Now, there are several options to dealing with the dead whale. Consider the following questions:
- 1) What is your strategy for dealing with this problem? ( Plan )
- 2) What resources do you need to follow your strategy? ( Organize )
- 3) What stakeholders do you need to get on-board? ( Lead )
- 4) What steps can you take to make sure your plan is proceeding as you planned it? ( Contro l)

There are a handful of strategies we might naturally gravitate towards. The feasibility of each strategy depends on how well you employ the functions of management.
Tow the whale back to sea – A crane, tug boat, and tow cable are needed. Who might you need to include in this gameplan? The coast guard might need to be involved to discuss any pertinent regulations. A marine captain that can tell you about tides so that you can time your extraction, and insights about currents to indicate how far out you need to haul the whale once its buoyant. Should you allow a marine biologist to provide advice on what sort of ecological impact this might have (like bring in unwanted sharks or seals). How can you be sure the tow cable has enough tinsel strength to haul a bloated whale on a high friction surface like wet sand? Does the crane have the capacity to move the carcass into position to be hauled? If the whale is decaying, will the tow cable just pull through the rotten flesh?
Cut the whale up, haul it to the dump – You will need a forklift, semi-truck, and chainsaw. The first consideration here would be the logistics of pursuing this strategy. You will need to find a truck with the towing capacity to haul large chunks of the carcass off the beach. Can you ensure the weight of a loaded semi would not sink into the wet sand? How much does a semi-loaded with a whale carcass weight? You may also need to contact the county roads manager to determine if there are any bridges between the beach and the dump that have weight restrictions. What sort of protective equipment would you need for the men slicing through the whale with chainsaws? There are a few control processes that need to be put in place for this strategy to work.
Celebrate the whale – The objective of the city manager is to “deal with” the dead whale. For most, this would mean remove it somehow. For others, this might be a chance to celebrate the occasion, and establishing the experience in the culture and history of the town. To celebrate the whale, the city manager can hold a competition like car dealers do to promote their cars – have contestants place their hand on the whale and the last person to withstand touching the grotesque, slimy, and malodorous creature, somehow wins a major prize. This would require a sponsor to donate a prize (a car, a vacation) and the town can celebrate the occasion annually. If the goal is to appease the community from the existence of the whale and its stench, celebration is one strategy to pursue that end. You would need to include a biologist to determine if leaving the whale to decay after the festival would attract scavengers, and a water chemist to determine if a decaying whale creates toxicity problems for beach goers.
Blow it up! – The kid in most of us choose this option. Definitely. You might need to check with state officials to see what the protocols are on this approach. The biggest question would be how much dynamite do you need to blow up a whale, or blow it into the ocean? In Oregon, one stakeholder group you might contact is a mining company or the Oregon national guard. Both of those groups have a lot of experience calculating explosive requirements. What are the safety protocols you need in place to make sure that no one is injured? Where will you be able to source enough explosives to achieve this goal?
Use of the four functions
Each of these scenarios contain some far-fetched elements. But asking the right questions is paramount to turning any of these into a feasible strategy. You first need to decide a path, then determine your resources before getting stakeholder groups on board. For a high-risk situation like most of these solutions call for, you need to put control mechanisms in place to mitigate your risks. If you type “Oregon’s exploding whale” you can see what has become the most-watching news broadcast of all time. It shows you what happens when a city manager does not successfully navigate the situation using all four functions of management.
Critical Thinking Questions
How are the four functions of management related?
Which is the most important function of management?
Choose a historical event prior to the year 2000. Analyze the leader’s use of the four functions of management during that event.
How to Answer the Critical Thinking Questions
For each of these answers you should provide three elements.
- General Answer. Give a general response to what the question is asking, or make your argument to what the question is asking.
- Outside Resource. Provide a quotation from a source outside of this textbook. This can be an academic article, news story, or popular press. This should be something that supports your argument. Use the sandwich technique explained below and cite your source in APA in text and then a list of full text citations at the end of the homework assignment of all three sources used.
- Personal Story. Provide a personal story that illustrates the point as well. This should be a personal experience you had, and not a hypothetical. Talk about a time from your personal, professional, family, or school life. Use the sandwich technique for this as well, which is explained below.
Use the sandwich technique:
For the outside resource and the personal story you should use the sandwich technique. Good writing is not just about how to include these materials, but about how to make them flow into what you are saying and really support your argument. The sandwich technique allows us to do that. It goes like this:

Step 1: Provide a sentence that sets up your outside resource by answering who, what, when, or where this source is referring to.
Step 2: Provide the quoted material or story.
Step 3: Tell the reader why this is relevant to the argument you are making.
EXAMPLE : Let me provide an example of homework expectations using the type of question you might see in a critical thinking question at the end of the chapter. Each of the answers you provide should be this thorough.
Question: Explain why it is important to study management.
Management is important to study because it serves as the foundation for all other areas of business. The four functions can be used in other business areas such as accounting, marketing, operations management and human resources. All of the areas of business need people who know how to make a plan and allocate resources. All of the areas of business need people who know how to motivate others, and to make sure they are on track for their organization’s goals. For this reason, improving our mastery of management will make us more effective at whichever role we are in. A good example of this foundation comes from research conducted on accounting firms in Romania. Wang and Huynh (2014) found that accounting managers who embraced both managerial best practices and had the technical skills needed for accounting improved the organizational outcomes of their firms. These findings suggest that business professionals need managerial skills to supplement the day-to-day roles they have.
As I reflect on management as a foundational discipline, I remember how my high school baseball coach approached our team after a losing season. We were not a good team because we did not have fundamentals of how to grip a baseball, how to stand in the batter’s box, or how to field a ground ball. That next year, he taught us all of these fundamentals and we won a lot of games. It seems to me that learning fundamentals of management can have the same impact. Being able to execute the four functions of management allows us to get better at how we approach marketing a new product, or improving operations processes.
Wang, D., & Huynh, Q. (2014). Linkages among corporate governance, management accounting practice and organizational performance: Evidence from a Southeast Asian country. Romanian Economic and Business Review, 9(1), 63-81.
Chapter References
Aho O.W., Lloyd R.A. (2019) The Origins of Robust Supply Chain Management and Logistics in the Caribbean: Spanish Silver and Gold in the New World (1492–1700). In:
Bowden B., McMurray A. (eds) The Palgrave Handbook of Management History . Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK.
Bateman, T., & Snell, S. (2013). M: Management (3rd ed) . McGraw Hill / Irwin: New York, NY
Dolechek, R., Lippert, T., Vengrouskie, E. F., & Lloyd, R. A. (2019). Solving a whale of a problem: Introducing the four functions of management in a management principles course . International Forum of Teaching Studies, 15 (2), 29-35.
Fayol, H. (1949). General and Industrial Management . Sir Isaac Pitman & Sons Ltd: London, U.K.
Graham, P. (1995). Mary Parker Follett: Prophet of Management. Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA.
Lussier, R. (2021). Management Fundamentals: Concepts, Applications, Skill Development. (9th Ed). Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA.
Nathan, R. (2018). The Grapevine Creek Buffalo Jump Complex: Interdisciplinary Research on the Crow Reservation, Montana (Doctor of Anthropology, dissertation). Indiana University.
Shermerhorn, J. (2013). Management (12th Ed) . Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ
The Four Functions of Management Copyright © 2020 by Dr. Robert Lloyd and Dr. Wayne Aho is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Faculty Resources
Powerpoints.
This course includes PowerPoint slide decks organized by chapter and aligned to course content. The decks also include practice questions and class discussion/activity prompts, which you may use, edit, or remove according to your classroom needs.
Since the slides are openly licensed, you are welcome to retain, reuse, revise, remix, and redistribute them. They are also accessible. If you do revise them, make sure to follow these guidelines for creating accessible PowerPoints .
Download individual decks, below:
- Module 1: Role of Business
- Module 2: Economic Environment
- Module 3: Global Environment
- Module 4: Financial Markets and System
- Module 5: Legal Environment
- Module 6: Business Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility
- Module 7: Business Ownership
- Module 8: Entrepreneurship
- Module 9: Management
- Module 10: Motivating Employees
- Module 11: Teamwork and Communication
- Module 12: Managing Processes
- Module 13: Marketing Function
- Module 14: Marketing Mix
- Module 15: Human Resource Management
- Module 16: Accounting and Finance
- Module 17: Using Technology to Manage Business Information
- PowerPoints. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Projector Screen. Authored by : Denis Shumaylov. Provided by : Noun Project. Located at : https://thenounproject.com/term/projector-screen/1211212/ . License : CC BY: Attribution


Principles of Management
(18 reviews)
Copyright Year: 2015
ISBN 13: 9781946135186
Publisher: University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Nicole Englitsch, Lecturer, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 5/8/24
The material covers relevant topics that you would expect to see in a principles of management book. It is a good basic introduction to management principles. Even though it is organized well, the structure of the resource could be improved by... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The material covers relevant topics that you would expect to see in a principles of management book. It is a good basic introduction to management principles. Even though it is organized well, the structure of the resource could be improved by adapting an easier to follow structure and refer back to the big picture of POLC. Given that it was published in 2015, some cases are outdated, and instructors definitely need to add current examples and exercises.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
Text is accurate and no errors were detected. The business world has changed quite a bit from 2015, so some chapters may benefit from updating so it reflects a more accurate view.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Basics were covered well. Content could benefit from some updates but overall concepts are still relevant and will be for a long time.
Clarity rating: 4
The resource is written in a clear and concise manner. It is suited for early career college students. Some of the images/graphics could be updated to make it more visually pleasing. Some images are not extremely relevant to the text and could be omitted or replaced.
Consistency rating: 5
It follows a consistent formatting. It is consistent when it comes to terminology and the framework it uses.
Modularity rating: 5
It is easy to navigate and has a clear structure. it can easily be divided into sections and assigned accordingly.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
Even though it is organized well, the structure of the resource could be improved by adapting an easier to follow structure and refer back to the big picture of POLC. The key points at the end of each chapter were helpful and so were the references for each section (sometimes too many references and not all of great quality but students may prefer the easier to understand and quick reads). As an instructor, I would have preferred more quality references.
Interface rating: 4
No navigation problems and no interface issues. Some of the images/graphics could be updated to make it more visually appealing. Some images are not extremely relevant to the text and could be omitted or replaced. Lots of empty/white space. It is not an extremely visually appealing resource. It is not possible to easily copy & paste text from (line breaks).
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No glaring grammatical errors were noticed.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
So much is happening in the DEIB space and the text would benefit from some updates. Overall it seems relevant for mostly students in the US. The text was culturally appropriate without any bias but also did not invite for much discussion around current DEIB issues around the country and world.
This text can be a good resource and basis for a principles of management course, but instructors need to be mindful to combine it with more recent cases and discussions around current trends, best practices, and issues.
Reviewed by Anjali Chaudhry, Professor, Dominican University on 10/27/22
This open text covers all pertinent areas related to principles of management. Any core business class on management focuses on the four functions of management- planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. This material does a good job going... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
This open text covers all pertinent areas related to principles of management. Any core business class on management focuses on the four functions of management- planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. This material does a good job going over key concepts as well as terminology relevant in this area. Some of the examples may be outdated but that is understandable considering that this book was published in 2015 and the fact that the world of business has been experiencing a number of transitions. I am not too happy with the leadership chapter. Then again, in my opinion, most textbooks do a poor job with this topic.
The content is error-free, unbiased, and for the most part accurate. I specially appreciate the links for research and other sources from which the text draws support.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
Content is mostly up-to-date and therefore, I am not too concerned about the lack of editions that such a format does not offer. My recommendation is to use the book as a basic text and then use other sources such as news articles, cases, and simulations to incorporate the role of current workplace context into the study of management. What aspects of management are relevant in the modern workplace (e.g., traditional organizational designs) or how new developments such as the gig economy can be understood using the management lens can easily be taught with a few additional resources that bolster this open source book material. If and when updates are needed, I am fairly certain that these can be done in a relatively easy and straightforward manner.
Clarity rating: 5
The text is written in a clear and easy to understand style. It introduces most of the key terms and accepted jargon from the field.
Consistency rating: 4
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 4
The text has been divided in chapters and sub-sections each with its own hyperlink that makes it easy to move from one section to the next.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The logical organization and simple structure of the textbook is one of its strengths.
The text uses relevant graphs and images that I frequently use to review key points from a section. The illustrations are meaningful and well-placed.
I did not notice any glaring grammatical errors.
The text has been written to be relevant for students in the US. I am not sure whether the examples will be too applicable for those studying management in other countries. I did not find any instances where the text could be perceived as culturally insensitive or offensive to any demographics.
I have adopted this book for my core management course, and I plan to continue to use it.
Reviewed by John Strifler, Associate Adjunct, University of Indianapolis on 4/22/21
The text is appears to be an excellent text to introduce the P-O-L-C management principles, and promote the key elements of strategy, entrepreneurship, and leadership development in students. Highlights: Chapter 1 introduces the concepts... read more
The text is appears to be an excellent text to introduce the P-O-L-C management principles, and promote the key elements of strategy, entrepreneurship, and leadership development in students.
Highlights: Chapter 1 introduces the concepts thoroughly and sets the approach the rest of the book utilizes. A concise history of management thought is found in chapter 3. The summary element at end of each section ( Key Takeaway) is excellent reference for learner. With the references at the end of each section, one can pull a section out for use in a teaching setting and retain the references.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The authors are clear in the beginning that they focus performance on the triple bottom line - financial, social, and environmental - and appear faithful in maintaining this approach throughout. There are no obvious errors in examples used to illustrate principles.
Examples remain accurate and relevant in explaining the concepts, however, I would utilize additional, more recent examples - noting that the text is substantially the same as its 2010 original publication.
For example, the section 3.4 addresses contemporary principles of management addressing social movements has the latest citation in 2007. Social networks have seen a significant shift.
Level of writing is suited for early college or even college prep use. A Key term summary at the end of each section or chapter would add to its usefulness.
The textbook follows a consistent formatting, allowing for scanning through thumbnails to find illustrations or desired summaries
The way the chapters are sectioned and summarized, makes for ease of modular use. Consistently starts each new section on new page, which allows for ease of sub-dividing the material. Again, the practice of placing citations at the end of each section further adds to the modularity.
The text follows logical approach in the order of topics, similar to other management texts.
Interface rating: 5
I viewed the text in its PDF format, and found it clean to view and all images were displayed properly. Searching and navigation had no issues. Having a full feature PDF viewer will simplify the process of accessing and using sections separately.
No obvious grammatical issues
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
A variety of images used with a diversity of individuals. The examples used appear to be "globally" recognized.
Will utilize sections of this text as supplemental material to provide students additional information.
Reviewed by JOE MESSER, Professor of Entrepreneurship, Manchester University on 4/2/21
I have been a business owner for 30 years and taught business management for the last 12 years. I found this text to cover all the important areas of management. Plan, Organize, Lead, and Control, were introduced early on (page 19) and each... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
I have been a business owner for 30 years and taught business management for the last 12 years. I found this text to cover all the important areas of management. Plan, Organize, Lead, and Control, were introduced early on (page 19) and each covered in detail in their own sections in the text.
This book is well suited for an entry level course in management. Students do not need a business background before reading this text. I appreciated the current examples that were used. This will keep students engaged.
Management basics were covered very well. Examples were recent and relevant. The companies that were used as examples (SAS, Xerox, Toyota, Nucor, Google, etc. are companies that should be relevant businesses years from now.
The text was easy to read and the vocabulary was appropriate for an introductory course.
The flow and layout of the book stayed the same throughout all 16 chapters.
I found some of the sections within the chapters to be too verbose. I will cut out some of the sections (modules) in order to have time to go more in detail in other areas. For that reason the modularity is good.
The organization of the book made sense to me.
Interface rating: 2
I am still struggling trying to get access to any educational resources that go along with the book. Slides, exams, etc.
I did not run into any grammatical issues.
The text was culturally appropriate with no biases.
I intend to use this text assuming a can locate the teaching resources that go along with it. I look forward to saving my students money by using this text.
Reviewed by B'Ann Dittmar, Instructor, Clarke University on 1/7/21
Like most Principles of Management textbooks, this book has a wide breadth of topics that are covered that are relevant to the subject area. Consistent with a principles course, it does not go into great depth in most areas, as those deeper dives... read more
Like most Principles of Management textbooks, this book has a wide breadth of topics that are covered that are relevant to the subject area. Consistent with a principles course, it does not go into great depth in most areas, as those deeper dives are saved for more advanced courses. I currently use McGraw Hill's "Management: Leading & Collaborating in a Competitive World" 14th edition by authors, Thomas S. Bateman and Scott A. Snell, which is very comprehensive, and this text covers similar subject areas. The OpenStax text appears more succinct in the length of the chapters but provides adequate coverage without a lot of fluff / filler. The OpenStax text uses a couple of photo images per chapter, as well as several colorful graphics and illustrations, with adequate white space, to make it easy to read and to digest, as well as to maintain interest.
I did not see any inaccuracies within the OpenStax Principles of Management text. The text appears to remain updated with relevant examples for discussion purposes and for students to relate to.
The content provided is relevant and the examples / references to today's world provided seemed to span from 2016-2018, from what I saw. Example companies included Starbucks and Amazon, which are both relevant organizations that college students would know and have an interest in learning about. It is a contemporary text and does not feel dated. I would love to see some direct links within the text to the real-world topics that are being discussed, so students could click on them to get more information and an in-depth view, versus just a brief mention of a topic or issue. The student’s study guide contains some links like these, but it would be great to have some within the chapter, itself.
This text is easy to read, clear, and to the point. There are definitions provided for clarification, in the chapters, as well as in a list at the end of each chapter. A recommendation would be to put the chapter title and subject area on both the first page of the chapter, as well as listing it as a running head on the main window with the chapter readings. This information is currently listed along the left-hand side of the page in the table of contents, only and each chapter begins with an image and the learning outcomes on the page, but no mention of the chapter number or subject. I think this addition would provide more clarity.
Each chapter has consistency in layout and design. After each of the chapter concepts are covered, the chapter concludes with the following: • Key Terms • Summary of Learning Outcomes • Chapter Review Questions • Management Skills Application Exercises • Managerial Decision Exercises • Critical Thinking Case These resources provide a good review, as well as offering opportunities for students to synthesize / apply what they have learned. It also offers instructors the opportunity to use some of these tools for discussion.
This textbook would allow you to set up your course in a variety of modalities, as you can decide how many and which chapters you would like to use, depending on how many weeks long your course will be. It can certainly be used in a synchronous or asynchronous course, with online, hybrid, or in-person delivery. The Instructor Pack also includes several resources to take your course online and offers “cartridges” to integrate into several learning management systems, including Blackboard, Moodle, D2L Course, and Canvas.
The text appears to be well organized, overall. One chapter that could possibly be moved is the “History of Management” chapter, which is the third chapter. My current textbook addresses the history of management as an appendix to Chapter 1, which seems to make sense to me. The OpenStax text places it after Chapter 1, Managing and Performing, and after Chapter 2, Managerial Decision-Making. It may be appropriate to have Chapter 1 first, so students understand what management is, and then go into what happened in the history of management, as past events can be predictors for the future. The placement of the history chapter is not a real concern, but it just made me pause and wonder why it was placed where it was.
The interface appeared clear and functioned well. I tried it on both a laptop as well as on my iPhone. One thing I noticed as far as navigation is that when I wanted to jump to another chapter, I would click on the chapter link in the list on the left-hand tool bar, but it would not change the screen to take me there. Rather, it would open a list of drop downs for options of topics to select within that chapter. I think most people want to start at the beginning of a chapter and a click could be saved if they were taken to the beginning of the chapter when they click on the chapter title. That click could still also open the chapter options, and if they wanted to go somewhere else, they could do that.
I did not see any grammatical errors.
I appreciated that this text offered diverse images and examples that included a variety of demographics and cultural aspects. Further, you feel their commitment to diversity when you read their six-page Diversity and Representation Guidelines, which details their commitment to improving representation and diversity in OER materials. This is something that I appreciate and look for when reviewing textbook materials for use in my courses.
Overall, I believe this text is a great option for instructors and for students. I currently use the McGraw-Hill Connect access for online quizzes and exams, which include a built-in proctoring system to eliminate cheating in an online environment and would like an option for doing something similar with this open textbook. I appreciate that there are a variety of options for accessing this textbook, from an app, to a download, to viewing online, or even ordering a printed copy- all provide plenty of options for students. I also like that students can highlight within the chapters when viewing online. When I am looking to adopt a text, I am very interested in the Instructor Resources. This text offers guided lecture notes and PowerPoints as well as a test bank in Word format. Unfortunately, I found the PowerPoints to be lacking. I happen to teach Business Communications, which includes how to put together an effective PowerPoint, and typically "less is more." The PowerPoints that accompany this textbook have a plain white background with black text and no real template, so they don't look very interesting and they are inconsistent from slide to slide in their look. They also contain WAY too much text, often including full paragraphs. They should just have bullet points and save the "extra content" as lecture notes outside of the presentation slides. I did appreciate that some of the PowerPoint slides included embedded links to TED Talks and other example videos, including scenes from Apollo 13, as well as including discussion questions regarding those videos. If OpenStax: 1. Offered pre-made quiz and exam options vs. downloading a Word document with all the quiz questions and 2. They partnered with a low-cost proctoring service as an add-on solution, and 3. Updated the PowerPoint slide deck, I would be very interested in adopting this text. It offers a lot of value for an open resource.
Reviewed by Jose-Luis (Joe) Iglesias, Assistant professor of Management, USC-Beaufort on 8/25/20
I believe that the examples and cases are appropriate to demonstrate the applicability of management concepts. However, I wish that the authors could be able to update the examples and cases to a more recent world reality. Overall, the index and... read more
I believe that the examples and cases are appropriate to demonstrate the applicability of management concepts. However, I wish that the authors could be able to update the examples and cases to a more recent world reality. Overall, the index and organization works for junior students in business or someone interested in learning more about management.
I believe the content is appropriate for an introductory text in management.
The text provides the authors with the opportunity for updates.
The textbook uses an easy to understand verbatim and accessible concepts for non-business major students.
Consistency rating: 3
Terminology and frameworks are acceptable for an introduction to management. However, I would advise the authors to provide detailed information on the theories that support managerial functions.
I believe that modularity is an option. However, the instructor will need to add extra readings and complementary contents such as videos.
The sequence of managerial functions is well organized and explored in the text.
No interface issues noticed.
Grammatical Errors rating: 1
No grammatical mistakes noticed.
Cultural Relevance rating: 1
I believe that the diversity of examples and in the pictures represents a good example of inclusion.
I would consider the adoption of this textbook to an elective class in management, or management 101.
Reviewed by Linda Williamson, Program Lead, Business Administration, Klamath Community College on 3/13/19
I have reviewed numerous books related to management over the past 15 years and this text includes several components that I often need to add to the textbooks I am using. For example, there is wonderful language related to the "balanced... read more
I have reviewed numerous books related to management over the past 15 years and this text includes several components that I often need to add to the textbooks I am using. For example, there is wonderful language related to the "balanced scorecard" included in this text. I also like the depth of content related to innovation and strategic thinking that is referenced across several chapters.
I thoroughly read most chapters and carefully scanned the others; accuracy across words, figures, and exhibits appears to be strong. I did not detect any bias on the part of the authors, and in fact appreciated the wide array of business examples used to support their concepts.
The overall content in this textbook appears to be extremely relevant. Current and appropriate businesses are profiled throughout and related discussion questions seem to focus on real-world issues related to management. Chapter 2 in this text focuses on the individual student and includes substantial self-assessment; this is exactly how I teach my current Management Fundamentals course as I believe effective managers need to be aware of how they communicate with others before they can implement management tools and strategies.
This book does seem to be written in clear, concise prose, with good support and definition for new terms (and for jargon). References are provided throughout the content (including the business cases) with additional explanation for new or "involved" topics. I see consistency throughout the chapters in flow and tone, which is not always true when there are multiple authors.
This textbook appear to be consistent in the use of terminology and also in the overall framework of the content. For example, consistency in starting each chapter ("What's in it for me?"), the "Key Takeaways" at the end of each section, and the consistent reference to POLC (Planning, Organizing, Leading, Controlling) figure to consistently remind the reader how/where the new chapter content fits in to the overall role of management. Very effective!
I love the "chunks" and short chapter sections in this textbook! Each chapter has clearly defined sections (which a student can navigate directly to by using the tabs on the left of the page as soon as a "chapter" is selected) and yet the conclusion of each section and chapter still ties everything in to place. Very well designed.
The text is well organized in content, though I tend to like the "POLC" sections to be more clearly defined as "sections" of the textbook (again, the POLC figure at the start of each chapter does clear show which element the new content attaches to). There is logical flow to the content within the chapters and throughout the text overall.
I like the navigation of this textbook. Like any electronic resource, it takes a bit of getting familiar with, but it appears to be very user-friendly. When I facilitate a class using an OER, I like to have the entire textbook available in the very first module of my course in addition to having each assigned chapter available for access directly within the module that includes that specific chapter. I did not experiment to see if that would be an option with this resource.
None that I could find!
I found several examples that supported very respectful references to different cultures/people. My favorite actually involves a story of Goodwill...rather than do the traditional focus on who Goodwill serves, the authors instead focus on how the company is innovative in their strategic planning. In my opinion, that reference not only shows a different light on this company but also reminds the reader of the need for nonprofit organizations to be focused on innovation. A win-win!
I will likely select this textbook next year for my Management Fundamentals course. The authors stress upfront the necessity of determining competitive advantage and continue that theme throughout the book, which is incredibly relevant for management. The cases, discussion questions, and indepth content related to assessments (for personal growth and also for company performance such as the balanced scorecard) add a great array of materials to incorporate into this course. I really like this textbook!
Reviewed by Jeanine Parolini, Teaching Partner, Bethel University on 12/3/18
Principles of Management provides a comprehensive overview of key management and leadership principles for my professional adult undergraduate students. In our program, it is vital that we offer students a progressive big picture overview of the... read more
Principles of Management provides a comprehensive overview of key management and leadership principles for my professional adult undergraduate students. In our program, it is vital that we offer students a progressive big picture overview of the areas they need to consider in leading and managing others, and Principles of Management is that resource for our students. It is easy to access the information in this resource.
Our professional adult students need a resource that they are able to connect with and apply directly to their professional lives. Principles of Management addresses current topics that my students are dealing with in their workplaces, and it offers insights into the personal and professional management and leadership issues that pertain to most organizations today.
My adult professional undergraduate students are able to engage with the content and apply it to their personal and professional lives. The cases and examples in this resources are also relevant to students' experiences and contexts. At the same time, please keep the book up to date with considering a future revision in 2 to 5 years so that the information, examples and cases remain current.
The information is presented to my professional adult undergraduate students in a way that is engaging, practical, and accessible. The books connects well with business students and business issues.
When I engage the students in using the terminology and frameworks from Principles of Management in their papers and presentations, I am finding that students are digesting and utilizing the information properly and insightfully. They are applying it to their personal and professional lives. As I interact with students in both face to face and online venues, my experience is that students are remembering and practically using the terms and frameworks in real life applications.
Presently, I am using most of the book in my professional adult undergraduate business management course. I am able to offer several chapters in Principles of Management each week as I integrate in other articles and videos to support the week's topics. Students have commented in their evaluations that the reading is accessible, practical, interconnected with the week's topic, and a fair amount of reading for the course.
The chapters are well organized in Principles of Management and the topics in each chapter build upon each other throughout the chapter. The progression of the information in each chapter flows well and supports the practical outcomes such as discussion forums, presentations or writing assignments in my course.
For the most part the text is free from navigation issues. The one area for development is to make sure it is clear when it is a chapter subheading and when it is a figure subheading. Perhaps using a different size font or bolding or italicizing the font for one of those titles may be helpful. I have been confused at times when a figure title falls on the previous page of the actual figure, yet the chapter subheading is at the top of the figure. I have also experienced students' questions on this as well when they are being asked to assess a certain figure in the reading material and want to be sure they have the correct figure. I'd appreciate clearing this up in the next version to avoid confusion.
The text appears to be free from mechanical issues and grammatical errors. I am proud of the way the text presents itself to our professional adult undergrad students.
Cultural inclusion is important to me so I am sensitive to inclusivity of races, ethnicities and backgrounds in my approach to resources and the classroom environment. Principles of Management provides support to cultural inclusion in it's discussion of globalization and global trends, values-based leadership, and to some level related to ethics and culture. At the same time, this is a key area to keep up to date on and to realize that the globe is in our workplaces everyday with our diversity. In future revisions, I suggest taking this area to another level in helping readers to manage an innovative and diverse workplace to a greater level by being aware of cultural bias and learning through differences. I supplement the books information with additional material related to bias, insecurity and personal/cultural maturity.
Principles of Management is an engaging resource for my professional adult undergrad business students because it provides a general overview of key management and leadership topics with the opportunity for practical application through examples, cases, questions, and relevant frameworks that I can then incorporate into my weekly assignments.
Reviewed by Valerie Wallingford, Professor, Bemidji State University on 6/19/18
There should be a chapter devoted to the 4 functions of management (planning, leading, organizing & controlling) versus just one chapter covering all four primary functions of management so that is why I have ranked it a 3. read more
There should be a chapter devoted to the 4 functions of management (planning, leading, organizing & controlling) versus just one chapter covering all four primary functions of management so that is why I have ranked it a 3.
Text is accurate, case studies are outdated.
Textbook is up-to-date except cases.
The book's clarity is good as provides adequate context for terminology utilized. Easy to understand and comprehend.
Yes, the text is consistent throughout.
Yes, the text is easily readable and chapters are easily divisible into smaller reading sections which makes it nice if the professor doesn't want to cover the entire chapter just sections. There are pictures, charts, etc. that also break up the reading.
The organization/flow/structure are similar to many principles of management texts with possibly moving mission/vision chapter earlier but professor can assign chapters in the order they prefer.
The interface is good, as I had no issues with navigation, distortion, or display features.
No grammatical errors were found.
The text was not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way. It was inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
Reviewed by K Doreen MacAulay, Instructor II, University of South Florida on 3/27/18
The material covers all the basic requirements for a principles of management course. The concepts and applications are on par with what is being taught. I feel the examples are a little dated, but that is something that could easily be augmented... read more
The material covers all the basic requirements for a principles of management course. The concepts and applications are on par with what is being taught. I feel the examples are a little dated, but that is something that could easily be augmented through classroom.
The content of this book is very accurate and I did not find any errors in the delivery of the information.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
The concepts are up to date with what is important and covered in a principles of management course. The examples, although relevant to the material, could be a little more up to date. As note, however, this is something that could easily be addressed through classwork.
The concepts, theories and general knowledge delivered in this book as exactly what one would expect to find in a good Principles of Management book.
There are no consistency issues that I found throughout the reading of this book.
The segments within each of the chapters of the book made for an easy and logical flow to the material. Each segment lends itself easily to the learning process for the reader.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
The actually order of the book chapters, however, did not seem to fit a traditional model. I would not teach the chapters in the order that they are provided, however, I would use all the material provided. Example: I would have motivating after leading; the structure chapter near the end and make chapter 13 - chapter 14 and chapter 14 be chapter 13.
To me a logical concept flow goes from a general introduction, strategy and the go micro level to macro level. This book's order of chapters does not seem to have a clear path.
Some of the pictures seemed out of place because they were small. As well, there was not a uniformed look to the pictures which took away a little from the appearance, but overall the material was easy to read and that is the main point.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
Easy to read and understand.
Clearly based in a American capitalist approach to knowledge, this book is on par with most American textbooks in this area.
I look forward to incorporating this textbook into my class. I believe for a survey course like this, this work is the ideal foundation to help the students learn.
Reviewed by Debby Thomas, Assistant Professor of Management, George Fox University on 2/1/18
The text covers the basics that other Principles of Management texts do. read more
The text covers the basics that other Principles of Management texts do.
I have found this textbook to be clear and accurate. The case studies are a bit dated, but relevant.
The content of this book is organized around management concepts and principles that will not quickly go out of date. The case studies are concise, practical and relevant and should be fairly easy for the publishers to update occasionally.
This book is written in a way that the concepts are covered thoroughly without being verbose or difficult to understand. The concepts are presented in a way that is easy to comprehend and encourages application.
The terminology and framework of the text are consistent. One minor improvement would be to have a comprehensive table of contents at the beginning of the book (presently there is a table of contents of each chapter at the beginning of the chapter). This would help students follow the overall flow of the text more easily.
This text provides numbered sections for each chapter. I find this helpful and I don't always assign the whole chapter as reading for one class. I can be precise about exactly which parts of which chapters I want the students to read. The text has pictures and charts or graphs to break up the text, and the sections are generally short enough to hold a student's attention.
The topics are presented in a logical fashion. As with most Principles of Management textbooks its impossible to get through all of the content in one semester, but the set up works well to emphasize certain chapters more than others.
The book comes in multiple formats for the convenience of the reader. The PDF is usable only with the use of the built in table of contents (no clickable links to chapters in the PDF).
The text does not contain grammatical errors.
The pictures in the text include people of a variety of ethnicities. I have not found anything in the book that is insensitive or offensive in any way. It also introduces the concepts of unconscious bias early in the text.
Reviewed by Mindy Bean, Faculty, Linn-Benton Community College on 6/20/17
The Principles of Management heavily relies of the POLC method of Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling. The text was unique in covering the basics of each area within each context while tying it in with many factors that managers deal... read more
The Principles of Management heavily relies of the POLC method of Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling. The text was unique in covering the basics of each area within each context while tying it in with many factors that managers deal with. It had many concepts of most Principles of Management resources for assisting students in learning.
The books content was very accurate to the date that the sources were presented. A lot of resources were during the recession or before the recession. I feel like an OER that was adapted from 2010 should have included a few more updated examples.
The books concepts will keep for a while, when it comes to management theories there are always more being presented (fades) and there are those that keep the core concepts. I believe this book covers on the hard fundamentals of management while expressing the common trends of management in certain business industries. With technological advances and competitive nature of business, this book's relevance and longevity is based more on the subject matter.
The writing is adequate for the topics being presented. The many examples of firm situations and how they applied the concepts were well placed and had a good consistency until the end of the text. The jargon was appropriate for the subject matter.
The book carried consistent terminology and framework. The rhythm in which the reader gets used to is consistent except for two chapters toward the end in which it extended on my laptop to being about 25 pages. The way in which terms are presented are not in bold but mainly italic or overly emphasized. I believe it to be an easier read then most materials I have came across.
The book was easy and readily divisible into smaller reading sections besides the two chapters I previously mentioned towards the end. I personally would use the OER in that way due to its design to prevent good amounts of information without disruption.
The organization of the text was presented well. It was different from other materials that focus on the POLC and cover each section individually in order. I was impressed by the clear fashion that information was laid out by relating each topic outside of POLC that managers have to deal with and correlating to how it works with POLC when necessary.
The interface worked well. I pulled the book up on three different forms and systems. It was consistent, the visual aids/charts were presented well and I was able to see them all clearly. The only thing I personally didn't like was downloaded on iBooks you had to swipe versus clicking to turn the page.
The cultural relevance was accurate. I did not see any insensitive or offensive material.
I did have problems trying to get this on my Kindle.
Reviewed by Irene Seto, Faculty, Portland Community College on 6/20/17
I was involved with modifying an existing course to utilizes Open Education Resources in our introduction to Management Supervisory course. This text book is one that we selected a few chapters from for our course. I found this book covers all the... read more
I was involved with modifying an existing course to utilizes Open Education Resources in our introduction to Management Supervisory course. This text book is one that we selected a few chapters from for our course. I found this book covers all the major fundamental concepts required in a typical introduction Management course.
I did not encounter any biased or inaccurate information in the textbook.
The principles of Business be the same, but the business world and our technology is constantly changing. I would imagine minor updates of examples and case studies would be needed every 2-3 years.
I found the chapters easy to read and follow. Key terminologies were highlighted and explained well.
Each chapter's layout is consistent and created an easy to follow framework.
The chapters are well organized, similar to many introductory Management textbook. The learning objective and summary for each chapter is good.
The flow of the chapters are fine. But we did not use all of the chapters for our course. Personally, I would put Globalization and Valued Based Leadership (Chapter 3) toward the end.
The embedded links that I came across to and tested were fine. There were not many graphics.
I did not found grammatical errors.
Nothing really stood out that seem to be culturally insensitive.
Page numbers would be helpful!
Reviewed by Holly Jean Greene, Lecturer, University of Tennessee, Knoxville on 6/20/17
The textbook covers subject matter found in most management texts such as the four foundations of management - planning, organizing, leading and controlling ( P-O-L-C). In fact, each chapter links back to P-O-L-C very well. The textbook covers... read more
The textbook covers subject matter found in most management texts such as the four foundations of management - planning, organizing, leading and controlling ( P-O-L-C). In fact, each chapter links back to P-O-L-C very well.
The textbook covers organizational structure & culture, planning & goal setting, strategy & decision making, teams, leadership & motivation too. A few additional topics covered are social media and communication. One of the text strengths is in it's brevity: It covers a swath of terrain succinctly and would work well in course where an instructor wants to add additional learning tools such as videos and case studies.
I didn't find any areas of obvious inaccuracy or bias. In fact, I find the text is written without the opinion of the authors.
Each chapter includes a "case in point" story that's current or at least covers an event that's occurred within the last ten years.
I like the style in which the text is written - simple, easy to read prose. There are instances where I felt as if the text was written for an 8th grader, yet, if an instructor's goal is to use a text that simply introduces students to the foundations of management and they plan on adding additional learning tools, this is a great text to use.
I didn't see any obvious areas of inconsistency.
Using this text modularity and assigning just the sections students need is one of the text strengths. Each chapter stands on its own.
Organization of the text is clear and logical. In some instances, the text is not in the order I would assign but structuring the subject matter to an instructor's discretion is one of the advantages of using this text.
A few of the images seem small and I believe more images could have been used.
I didn't find any glaring grammatical errors.
Another one of the text strengths is its focus on helping students understand their own behavior. Each chapter contains an activity for students to complete that allows them the opportunity to learn more about their own behavior and biases.
This text in combination with additional learning materials - videos, case studies, self-assessment assignment - is a solid choice to use.
Reviewed by Paul Jacques, Associate Professor, Rhode Island College on 4/11/17
Each of the concepts that are typically covered in a Principles of Management course are included in this manuscript. The table of contents, chapter index, are helpful. Glossary of key terms is embedded within each chapter and could perhaps be... read more
Each of the concepts that are typically covered in a Principles of Management course are included in this manuscript. The table of contents, chapter index, are helpful. Glossary of key terms is embedded within each chapter and could perhaps be broken out in a separate chapter section (end of chapter?) to aid comprehension. There was no index included in this reviewer’s copy of the text.
The concepts included are presented accurately.
To be sure, each of the topics covered in this text are within the scope of the body of knowledge that an Introduction to Management student would be expected to master. The references are quite dated, however, with the bulk of the most recent references being from 2008. That said, and perhaps in the interest of providing the most updated references possible, citations from seminal work (example: NEO-PI, Costa and McCrae, 1985) are largely ignored in lieu of more recent, but relatively lightweight, work s. While major concepts are explained, the impact of these concepts on the world of work/management are given much less emphasis. To the reader, this approach can be perceived as being presented with a stream of facts, one after the other, with little attempt at anchoring the concepts to applications.
Clarity rating: 3
What’s here is good with my main concern being that there’s large sections of pure, unbroken text. I would think that the “Key takeaway” segments could be more numerous throughout the chapter. The Moreover, these takeaways would seem to benefit from several “key implications for managers” summaries throughout the chapter. As it stands now, it appears to be left to the student to pull out the relevance of the various concepts explained.
It seems apparent that there was a great deal of work involved in the preparation of the book manuscript. Each chapter’s flow and appearance are similar to that in each of the other chapters.
Each chapter appears to be designed to stand alone.
The “What’s in it for me?” chapter introductions are a useful and clever way of avoiding the more sterile term “chapter learning objectives.” The significant challenge to the student, however, is to internalize the chapter readings so that he/she sees the applicability.
Not sure if it’s a browser/printer issue, but some of the images were inordinately small (ex: figure 2.11, p. 63). Moreover, several of the figures are orphaned in the text – no reference/support afforded by surrounding paragraphs.
This reviewer observed no instances of grammatical errors which, in a work of this size (over 600 pages) is compelling evidence of polished, thoughtful preparation.
There were no examples of cultural insensitivity. To the contrary, the authors added to the reader’s understanding of the topic by presentation of findings related to the GLOBE study. Perhaps a more comprehensive treatment of the topic would have resulted had the authors presented the idea of diversity from a “levels of analysis” perspective – individual, dyad, group/collective. This approach would seem to result in a more efficient presentation of the topic and one that is applicable to all levels of management.
Overall, it seems that a strength of this text is that it encompasses a full gamut of topics that are typically included in a Principles of Management course at the undergraduate level. This reviewer found the content to be quite strong, but the interface between content and learner to be the main opportunity that exists with this title. Specifically, cases are interspersed throughout the text/chapters, but there are no questions related to any of the cases and so the cases come across more as stories than they do point of convergence/learning. In addition, the segments that are labelled “Exercises” at the end of each chapter’s segments would be more aptly referred to as simply “chapter segment questions.” The reality that there is no real deep thought required to answer the questions nor are they reflective of any experiential/active learning. The word that this reviewer keeps coming back to is “Application.” The text boasts truly excellent content, but the application portion is largely missing.
Reviewed by David Bess, Professor, University of Hawaii on 8/21/16
The text covers the major topics taught in a typical introduction to management course quite thoroughly. read more
The text covers the major topics taught in a typical introduction to management course quite thoroughly.
It read well and seemed to be quite accurate in terms of the theories/concepts and their applications.
It is up to date...other than maybe some cases.
It is easy to read; has nice summary sections; flows well./
It is consistent.
It is easy to read and has nice short sections with summaries.
The topics are presented in a logical fashion. They are offered in the rough order found in many principles texts. It is not the order in which I teach them...but it is logical and clear.
The interface is sound.
The grammar is sound.
I believe it is ;culturally relevant for most cultures.
I wish it had page numbers....it is a bit difficult to navigate.
Reviewed by Kim bishop, Adjunct Faculty, Portland Community College on 8/21/16
Yes, the subjects match up with what our school has for Course content and outcome Guides, for this course. It covers all subjects adequately. read more
Yes, the subjects match up with what our school has for Course content and outcome Guides, for this course. It covers all subjects adequately.
I did not find any errors and I did not see it as biased in any way. I guess it would depend on what you call accuracy and unbiased. For my needs, from what I have been taught and from what I have learned in the working world, I found it adequate.
The only things that would need updating would be case studies that could be more current since it was written in 2010. Having more current up to date case studies would be more interesting to the students and more engaging since it would be current or within the last couple of years at least.
very easy to read and understand. There were a couple of acronyms that were new to me, but the way they were laid out in the objectives and then addressed were helpful.
I love the way it is laid out. each chapter was easy to navigate and set up. It is the same for each objective and chapter giving you lots of options for discussion and for assigning work.
It is organized excellently. as mentioned before I like how it is laid out with learning objectives, content, key take away and exercises for each section. I like the What's in it for Me, at the beginning of the chapter so it shows students what they will get out of the chapter and then it ties in with each section. I really like how this book is laid out.
Yes, very logical and easy to read as mentioned before. Student gets to see what they will learn and how they can apply it, then each section is broken down to address the learning objectives.
There was not a lot of graphics or pictures, but the links do work that are embedded for external work.
I could not find any glaring grammatical errors.
I did not find any examples of cultural insentitivity
I really like this book and I am going to use for my course in the fall as a resource. I really like how it is laid out and the case studies the exercises, discussion points as well as the external resources like finding out what your learning style is. I like that it does not have a bunch of fluff and pictures and graphics as I will use this as a resource. It is intuitive and as current as it can be. Management concepts do not change much over time, but how they are implemented and communicated do and I feel this addresses that need for change. it was an easy read and did not feel like you were reading a textbook but interesting information about management. There are enough outside links to other information that you do not really need the textbook and the online content they have extra that you have to pay for. I would recommend the book, with some updates periodically to the case studies.
Reviewed by Brian Richardson, Adjunct Faculty, University of Hawaii at Manoa on 8/21/16
In the introduction to Principles of Management, the authors state that there are three themes in the book: strategic thinking, entrepreneurial thinking, and active management. The entrepreneurial theme is not as prevalent as their introduction... read more
In the introduction to Principles of Management, the authors state that there are three themes in the book: strategic thinking, entrepreneurial thinking, and active management. The entrepreneurial theme is not as prevalent as their introduction would suggest. There is some discussion of creativity, although references to writers and books beyond the single book by Edward De Bono would have enhanced the section. Sections that stand out as useful include the discussions of fairness, groupthink, employee performance review, and predictors of job performance. Some sub-sections and minor topics should have been separate sections with more details, such as the discussion of meetings, of interviewing, and of HR rules and policies. Finally, sections that would have useful additions to the textbook include how to write a good survey, how to deal with very difficult employees, and how to improve morale, which was referenced superficially but not focused on. The selection of management writers and level of detail provided for their positions is uneven. Maslow's hierarchy of needs is given three pages while Collins' discussion of changing good companies into great ones has two passing references and a short summary of the idea of a BAHG (big, hairy, audacious goal). Some thinkers were left out or not considered. Senge is not mentioned, even in the short section on "Learning Organizations". Likewise, academic writers and many historical thinkers, such as Max Weber, are not mentioned at all. Also lacking was a sense of how these different thinkers or ideas might disagree with each other or people outside of the management field. Instead, the text offers a series of disconnected concepts and models, which likely improved the modularity of the overall book, but at the cost of limiting the interactions between the topics and positions. As a result, there was little logical or conceptual analysis and the book relied on exposition.
Much of the textbook is made up of summaries of different concepts and models connected to management, with an emphasis on contemporary writers and psychosocial theories. There were no obvious inaccuracies in the summaries of the concepts and thinkers, although some sections could be criticized as limited, vague, superficial, or uncritical.
A textbook on management principles will become less relevant over time as updated information becomes available and new thinkers offer different concepts and models. One reference that stood out was the quote that "According to one source, there will be 11.5 million more jobs than workers in the United States by 2010." Given that this is a book last updated in 2015, the data should have been updated as well, especially given how wrong it turned out to be. Interestingly, this source is a Wired magazine article from 2007, published just before the economic crash. The examples and illustrations may become dated fairly quickly. References to specific CEOs and other leaders, for instance, will become less relevant over time. In this edition, there is a reference to and picture of Condoleeza Rice but no mention of Obama, for instance. Obama only occurs as a marginal participant in a group shot of world leaders
The clarity of the discussion is generally good, although there is some room for improvement. The photographs, for instance, do not support the text very well. A glossary would have been useful for clarifying all of terms used while an index would have helped readers access specific sections more effectively. The choice of examples is sometimes not clear. For instance, the examples used to illustrate organizations dealing with uncertain conditions, and thus needing flexible strategies were "a gang of car thieves or a construction company located in the Gaza Strip" (page 182). Both of these examples are strange and much better examples taken from businesses could have been provided and then discussed in some detail. Likewise, the example that they give of resistance to change was that people have been unwilling to adopt Dvorak keyboard and have stuck with the QWERT keyboard, despite the obvious efficiency of the Dvorak system (page 281). This is a great example of resistance to change, but one wonders why the authors could not find an example from business, such as how the railroads ignored the rise of the airplane.
While the book is generally consistent overall, it book sometimes strays from a discussion of the "principles" of management and does not adopt a consistent idea of what kinds of businesses are being talked about. The book would have been clearer if the authors had started with a classification of types of business that they are talking about (manufacturing, marketing, services, non-profits, perhaps) and be clear about what they were not covering (like government bureaucracies). For instance, I was thinking of using this textbook to support a course in Library management, and while some of it was useful, much of it would have been irrelevant or confusing. Had the book been clearer on how the different topics connected to different types of organizations, it would have been clearer which topics were relevant to specific readers or situations
The textbook is very modular, although there are times when this modularity breaks down. For instance, the discussion of data in the early part of the book was useful, but it would have been more appropriately connected to the discussion of budgeting, which occurs much later in the section on control. Another example is the discussion of globalization and intercultural issues, which occurs sporadically throughout the book and is never really brought into focus.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
The overall structure of the textbook follows Fayol's POLC model of management (Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling) with the overall narrative following the different stages in the process. Each section includes learning objectives, key takeaways, and discussion questions. These parts are very good at focusing the conversation in the larger sections. However, these additional parts are sometimes longer than the main text for that section and seem unnecessarily repetitive. The shift between institutional management and personal management is a bit strained at times, making it unclear whether the focus of the book is management or the personal growth of the manager. Each section included a list of references. In one section, there is simply a reference to the Columbia Encyclopedia, which was not helpful. Typically, however, there are a lot of references in each section. In fact, there are too many references that have minimal value. With some exceptions, the references are to short articles that could easily be retrieved by a Google search. Given that this is an introductory textbook, it would have been better to have an annotated "Further Reading" section that could lead readers to important writings and videos that expend on the different modules.
Interface rating: 3
The layout of the textbook follows standard page layout formatting. There are some things that could be improved. First, some of the text, such as some paragraph headers and keywords, are blue, which suggests that it is hyperlinked (as are the captions for pictures), but this is not the case. The full URLs in the text, also blue, are the only hyperlinks in the textbook. Another feature that could be improved is the way that the text, at least in the PDF version, has line breaks at the end of each line, which means that copying text leads to broken paragraphs that require additional editing if they are copied to another document or web page. The greatest issue with the interface, however, is the amount of white space that is included in the text. Given how short the different sections are and the way that the layout is organized, there is likely 100 pages worth of unnecessary white space in the text, which turns a 500-odd page book into over 600 pages. Added to this that the pictures and list of references are not that relevant, and the book appears to be laid out very inefficiently.
Beyond a few minor typos, the book was clearly written. The prose was a straightforward expository style, although at times it could have been more concise. The writers would often begin their paragraphs with rhetorical questions and then answer them right away, which did not help clarify the prose and typically made the writing more verbose. On page 279, the caption and the picture do not match.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
The book is focused on ideas and problems connected to American private-sector management. As a result, it is largely uncritical of large-scale organizations. Non-profits are discussed on a single page in the context of internal controls. Bureaucracy, as a term with negative connotations, is only mentioned in passing as an example of mechanistic structures, which are seen as an exception. Discrimination, likewise, is mentioned in passing three times, once in terms of how issues of discrimination have become a broader concern for "diversity management". Finally, unions are mentioned a few times in a long list of stakeholders (pages 150 and 151), even though the sample table for tracking stakeholders (page 148) does not mention them. Unions are seen as a punishment for businesses that appear to be unjust (page 529). At-will employment, on the other hand, is discussed in a focused paragraph in a way that does not consider the debate between union and at-will employment. For a textbook on industrial-focused management, the relative silence to the contrast between union and at-will employment conditions is unfortunate. When the book discusses global trends, it tends to be simplistic, taking trends such as "becoming more connected" as more important than such things as economic inequality, resource depletion, surveillance, war and terrorism, or social instability. In that sense, the book would not be very useful to people outside of the United States or to those who were actively engaged in intercultural management. At best, the book points to some of the problems that could be faced.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction to Principles of Management
- 1.1 Introduction to Principles of Management
- 1.2 Case in Point: Doing Good as a Core Business Strategy
- 1.3 Who Are Managers?
- 1.4 Leadership, Entrepreneurship, and Strategy
- 1.5 Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling
- 1.6 Economic, Social, and Environmental Performance
- 1.7 Performance of Individuals and Groups
- 1.8 Your Principles of Management Survivor's Guide
Chapter 2: Personality, Attitudes, and Work Behaviors
- 2.1 Chapter Introduction
- 2.2 Case in Point: SAS Institute Invests in Employees
- 2.3 Personality and Values
- 2.4 Perception
- 2.5 Work Attitudes
- 2.6 The Interactionist Perspective: The Role of Fit
- 2.7 Work Behaviors
- 2.8 Developing Your Positive Attitude Skills
Chapter 3: History, Globalization, and Values-Based Leadership
- 3.1 History, Globalization, and Values-Based Leadership
- 3.2 Case in Point: Hanna Andersson Corporation Changes for Good
- 3.3 Ancient History: Management Through the 1990s
- 3.4 Contemporary Principles of Management
- 3.5 Global Trends
- 3.6 Globalization and Principles of Management
- 3.7 Developing Your Values-Based Leadership Skills
Chapter 4: Developing Mission, Vision, and Values
- 4.1 Developing Mission, Vision, and Values
- 4.2 Case in Point: Xerox Motivates Employees for Success
- 4.3 The Roles of Mission, Vision, and Values
- 4.4 Mission and Vision in the P-O-L-C Framework
- 4.5 Creativity and Passion
- 4.6 Stakeholders
- 4.7 Crafting Mission and Vision Statements
- 4.8 Developing Your Personal Mission and Vision
Chapter 5: Strategizing
- 5.1 Strategizing
- 5.2 Case in Point: Unnamed Publisher Transforms Textbook Industry
- 5.3 Strategic Management in the P-O-L-C Framew
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Principles of Management teaches management principles to tomorrow's business leaders by weaving three threads through every chapter: strategy, entrepreneurship and active leadership.
Strategic — All business school teachings have some orientation toward performance and strategy and are concerned with making choices that lead to high performance. Principles of Management will frame performance using the notion of the triple bottom-line — the idea that economic performance allows individuals and organizations to perform positively in social and environmental ways as well. The triple bottom line is financial, social, and environmental performance. It is important for all students to understand the interdependence of these three facets of organizational performance.
The Entrepreneurial Manager — While the "General Management" course at Harvard Business School was historically one of its most popular and impactful courses (pioneered in the 1960s by Joe Bower), recent Harvard MBAs did not see themselves as "general managers." This course was relabeled "The Entrepreneurial Manager" in 2006, and has regained its title as one of the most popular courses. This reflects and underlying and growing trend that students, including the undergraduates this book targets, can see themselves as entrepreneurs and active change agents, but not just as managers.
By starting fresh with an entrepreneurial/change management orientation, this text provides an exciting perspective on the art of management that students can relate to. At the same time, this perspective is as relevant to existing for-profit organizations (in the form intrapreneurship) as it is to not-for-profits and new entrepreneurial ventures.
Active Leadership — Starting with the opening chapter, Principles of Management shows students how leaders and leadership are essential to personal and organizational effectiveness and effective organizational change. Students are increasingly active as leaders at an early age, and are sometimes painfully aware of the leadership failings they see in public and private organizations. It is the leader and leadership that combine the principles of management (the artist's palette, tools, and techniques) to create the art of management.
This book's modular format easily maps to a POLC (Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling) course organization, which was created by Henri Fayol (General and industrial management (1949). London: Pitman Publishing company), and suits the needs of both undergraduate and graduate course in Principles of Management.
This textbook has been used in classes at: College of Alameda, Columbia Basin College, Flagler College, Johnson County Community College, Pasadena City College, Penn State University, Renton Technical College, San Diego Mesa College, Sierra College, Yuba College.
Contribute to this Page

Introduction to Management
Apr 04, 2019
630 likes | 1.4k Views
Introduction to Management. LECTURE 3: Introduction to Management MGT 101. Introduction to Management. In lecture 2 we discussed Topics from Chapter 1: Skills Manager Require. What is an Organization ? Why Study Management ? Topics from Chapter 2 Historical Background
Share Presentation
- early examples
- system input
- entire organization
- work performance
- chester barnard managers
- skills manager require

Presentation Transcript
Introduction to Management LECTURE 3: Introduction to Management MGT 101
Introduction to Management • In lecture 2 we discussed • Topics from Chapter 1: • Skills Manager Require. • What is an Organization ? • Why Study Management ? • Topics from Chapter 2 • Historical Background • Early examples of Management • Adam Smith • Industrial Revolution
Introduction to Management • Today we will discuss • Topics from Chapter 2 • Scientific Management • General Administrative Theories • Quantitative Approach • Organizational Behavior • Systems Approach
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Chapter 2: Management History
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Scientific Management
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • Fredrick Winslow Taylor • The “father” of scientific management • Published Principles of Scientific Management (1911)
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • The theory of scientific management • Using scientific methods to define the “one best way” for a job to be done: • Putting the right person on the job with the correct tools and equipment. • Having a standardized method of doing the job. • Providing an economic incentive to the worker.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Taylor’s Principles • Develop a science for each element of an individual’s work, which will replace the old rule-of-thumb method. • Scientifically select and then train, teach, and develop the worker.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Heartily cooperate with the workers so as to ensure that all work is done in accordance with the principles of the science that has been developed. Divide work and responsibility almost equally between management and workers. Management takes over all work for which it is better fitted than the workers.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • Frank and Lillian Gilbreth • Focused on increasing worker productivity through the reduction of wasted motion • Developed the microchronometer to time worker motions and optimize work performance
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Henry Gantt
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • How Do Today’s Managers Use Scientific Management? • Use time and motion studies to increase productivity • Hire the best qualified employees • Design incentive systems based on output
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) General Administrative Theories
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • Henri Fayol • Believed that the practice of management was distinct from other organizational functions • Developed principles of management that applied to all organizational situations
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Fayol’s 14 Principles • Remuneration • Centralization • Scalar chain • Order • Equity • Stability of tenure of personnel • Initiative • Esprit de corps • Division of work • Authority • Discipline • Unity of command • Unity of direction • Subordination of individual interests to the general interest
Introduction to Management LECTURE 4: Introduction to Management MGT 101
Introduction to Management • In lecture 3 we discussed • Topics from Chapter 2: • Scientific Management. • General Administrative Theories
Introduction to Management • Today we will discuss • Topics from Chapter 2 • General Administrative Theories • Quantitative Approach • Organizational Behavior
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • Max Weber • Developed a theory of authority based on an ideal type of organization (bureaucracy) • The exercise of control on the basis of knowledge, expertise, or experience. • Emphasized rationality, predictability, impersonality, technical competence, and authoritarianism
1. Qualification-based hiring 2. Merit-based promotion 3. Chain of command 4. Division of labor 5. Impartial application of rules and procedures 6. Recorded in writing 7. Managers separate from owners Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Weber’s Bureaucracy
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Quantitative Approach
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • Also called operations research or management science • Evolved from mathematical and statistical methods developed to solve WWII military logistics and quality control problems • Focuses on improving managerial decision making by applying: • Statistics, optimization models, information models, and computer simulations
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Quality Management Intense focus on the customer Concern for continual improvement Process-focused Improvement in the quality of everything Accurate measurement Empowerment of employees
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Organizational Behavior
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2)
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Human Relations Management & Organizational Behavior • Efficiency alone is not enough to produce organizational success. • Success also depends on treating workers well.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Hawthorne Studies A series of productivity experiments conducted at Western Electric from 1924 to 1932.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • Experimental findings • Productivity unexpectedly increased under imposed adverse working conditions. • The effect of incentive plans was less than expected. • Research conclusion • Social norms, group standards and attitudes more strongly influence individual output and work behavior than do monetary incentives.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Cooperation and Acceptance of Authority: Chester Barnard Managers can gain cooperation by:Securing essential services from individuals Unifying people by clearly formulating an organization’s purpose and objectives Providing a system of effective communication
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) People will be indifferent to managerial directives if they… are understood are consistent with the purpose of the organization are compatible with the people’s personal interests can actually be carried out by those people
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Systems Approach
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • System • A set of interrelated and interdependent parts arranged in a manner that produces a unified whole.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • Basic Types of Systems • Closed systems • Are not influenced by and do not interact with their environment (all system input and output is internal). • Open systems • Dynamically interact to their environments by taking in inputs and transforming them into outputs that are distributed into their environments.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) • Implications: • Coordination of the organization’s parts is essential for proper functioning of the entire organization. • Decisions and actions taken in one area of the organization will have an effect in other areas of the organization. • Organizations are not self-contained and, therefore, must adapt to changes in their external environment.
- More by User

INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT
INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT. CHAPTER 1. Objectives of the chapter. Understanding management concepts Characteristics of management Functions of management. MANAGEMENT.
1.98k views • 34 slides

Introduction to Management. Understanding Financial Reports and Financial Ratios. How to Read A Financial Report. Goal is to understand what data is included in financial reports. Use the data to analyze the firm’s position relative to competitors, and the industry as a whole.
282 views • 14 slides

Introduction to Management. LECTURE 12: Introduction to Management MGT 101. Introduction to Management. In lecture 11 we discussed Topics from Chapter 5: Managerial Ethics Moral Development Factors that Affect Employee Ethics Ethics in International Context.
455 views • 18 slides

Introduction to Management. LECTURE 22: Introduction to Management MGT 101. Introduction to Management. In lecture 21 we discussed Topics from Chapter 10: Importance of HRM HRM Process Managing Human Resource Selection. Introduction to Management.
583 views • 28 slides

Introduction to Management. LECTURE 30: Introduction to Management MGT 101. Introduction to Management. In lecture 29 we discussed Topics from Chapter 15: Contemporary Theories in Motivation Current Issues in Motivation. Introduction to Management. Today in Chapter 16 we will discuss
421 views • 27 slides

Introduction to Management. Objectives. Identify the functions of management. Describe how the functions of management have evolved over time. Explain the nature of management at different organizational levels. Describe the needs that are needed in order to be an effective manager. .
473 views • 21 slides

Introduction to Management. Last Minute Cram. 1. Most Importantly. Tomorrow, 9.30am start, be there 9.15 In the Main Hall Bring a pen and at least a spare one Bring you id card Quiet food/water permitted. CMI Six Skills ?. Leading People Managing Change
283 views • 17 slides

Introduction to Management. LECTURE 9: Introduction to Management MGT 101. Introduction to Management. In lecture 8 we discussed Topics from Chapter 4: The Global Marketplace Regional Trade Blocks World Trade Organization. Introduction to Management. Today in Chapter 4 we will discuss
568 views • 36 slides

Chapter 1. Introduction to Management. -Bill Gates Chairman and Chief Software Architect, Microsoft.
712 views • 35 slides

Introduction to Management. Nov 15, 2010. Management Librarian in Troy. Colette Holmes Email: [email protected] Voice Mail: 518-276-8331 Folsom Library, 3 rd floor North (341A) Monday – Friday, 8:30 AM to 3:00 PM Appointments Recommended. Passwords & Tech Help.
269 views • 19 slides

Introduction to Management. LECTURE 19: Introduction to Management MGT 101. Introduction to Management. In lecture 18 we discussed Topics from Chapter 8: Corporate Strategies Competitive Strategies Strategic Management Today. Introduction to Management.
1.12k views • 31 slides

Introduction to Management. LECTURE 2: Introduction to Management MGT 101. Introduction to Management (Chapter 1). In the last lecture we discussed: What is Management ? Who is a Manager ? Types of Managers. Functions Managers perform. Managerial Roles. Skills Manager Require.
10.81k views • 31 slides
Introduction to Management. Reserved Area. LECTURE 1: Introduction to Management MGT 101. Introduction to Management. Reserved Area. Course Objectives: 1. To provide students with the theoretical background regarding Introduction to management.
861 views • 30 slides

Introduction to Management. Chapter 1. Topics. What is management? What do managers do? What challenges do managers at different levels face?. Getting work done through others. Efficiency. Effectiveness. Management is…. 1. Classical Management Functions. Updated Management Functions.
648 views • 17 slides

Chapter1 :. Introduction to Management. I-Management and Managers 1-What is Management? Efficiency: Doing the things the right way (refer to the relationship between inputs and outputs). Effectiveness: Doing the right things (goal attainment). Input -Raw material -Financial Capital
959 views • 12 slides

Introduction to Management. MT 140: Unit 1 Kaplan University. Welcome. Greetings and welcome to the Unit 1Seminar! The purpose of this seminar is to share some things with you that will help you to recognize what to expect in the course.
906 views • 30 slides

812 views • 34 slides

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT
Published by Randell Stevenson Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT"— Presentation transcript:

Introduction to Management and Organizations

Explain why managers are important to organizations

Principles of Management Session. 1 Introduction to Management &

Management and Organizations

Management: Arab World Edition Robbins, Coulter, Sidani, Jamali

MAN-3/2 Erlan Bakiev, Ph. D. IAAU Spring 2015 Management and Organizations.

Management and Organization

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1–1 Introduction to Management and Organizations Chapter 1 Management tenth edition.

Managers & Management MGT Principles of Management and Business

Topic 1: Managers and Management Objectives Understand what is meant by the term management Describes processes of management and classify different.

PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook

“It’s amazing what you can accomplish if you do not care who gets the credit” Harry Truman.

1–1 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATIONS © Prentice Hall, 2002.

Chapter 1, Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, and Nancy Langton, Fundamentals of Management, Fifth Canadian Edition 1-1 Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education.

Chapter 1, Stephen P. Robbins, Mary Coulter, and Nancy Langton, Management, Eighth Canadian Edition. Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education Canada Inc. 1 Chapter.

PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook Copyright © 2005 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 8 th edition Steven P. Robbins Mary Coulter.

Chapter 1: Foundations of Management and Organizations

Lecturer: Jude Nesa Rajah

Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall Today’s Agenda Introductions & Class Exercise Syllabus Review Who are Managers? What.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

Business Presentation Introduction Examples & Templates
Learn how to create a business presentation introduction that gets attention in the first 15 seconds. See real-life business presentation introduction examples & samples.

Dominika Krukowska
9 minute read

Short answer
What makes a good presentation introduction.
Data shows that a good presentation introduction is all about grabbing attention in the first 15 seconds.
An effective presentation introduction includes interactive design, a big idea, and a mystery to hook the audience in. A good introduction improves reader engagement and increases reading time.
You have only 15 seconds to earn your audience’s attention
Imagine a sprinter at the Olympics. They've trained for years, but a false start costs them the race. A weak introduction is the false start for your presentation, costing you your audience's attention and engagement.
But there's a way to get back on track and back in the race.
Our analysis of over 100,000 presentation sessions shows that the first 3 slides and the initial 15 seconds determine the success of your entire presentation.
These first slides and first moments decide whether a reader will give you their full attention or bounce never to look back.
In this post, we'll guide you on how to craft an introduction that ensures a strong start, keeps your audience engaged, and sets you up for a winning presentation.
Ready? Let’s dive in.
What is the purpose and goal of a presentation introduction?
The introduction in a business presentation has 4 goals: (1) to provide context by introducing the topic, (2) to build authority and trust by introducing the team (3) to manage expectations by giving a preview of the presentation content, and (4) to ignite interest by introducing a big idea.
What are the main types of presentation introductions?
8 types of presentation introductions:
- Personal intro: Unveils the speaker's background and expertise.
- Team intro: Showcases the experience and accomplishments of a team.
- Company intro: Unfolds the company's vision and values
- Topic intro: Sets the stage for the discussion topic.
- Product intro: Highlights the product's unique features and benefits.
- Project intro: Outlines the project's roadmap and expected milestones.
- Business plan intro: Provides a sneak peek into a business's strategic blueprint.
- Executive summary (Report intro): Summarizes a report's key insights and takeaways.
How to write presentation introductions that keep people reading
The introduction slide is the gateway to your presentation. Here are some tips to ensure your audience can't resist reading on:
Start with a hook: Start with a captivating bit of information - a surprising statistic, a bold statement, or a thought-provoking question.
Show relevance: Highlight why your presentation is important to your audience.
Keep it simple: Make your introduction clear and concise to avoid overwhelming your audience.
Include visuals: Incorporate relevant visuals to enhance your message.
Use interactive elements: Using running numbers to present stats or giving your audience something to play around with, like sliders or tabs to click through, is another proven way to boost engagement.
Add a personal touch: Make your introduction resonate with your specific audience by personalizing it. This can get 68% more people to read your presentation in full and increase the average reading time by 41%.
Manage expectations: Provide an estimated reading time to set clear expectations and lower your bounce rate by 24% .
How to design a presentation introduction that grabs attention?
Designing an engaging presentation introduction is a crucial step in capturing your audience's attention.
Here are some strategies you can use to create an impactful introduction:
Video introduction
A video introduction adds a personal touch to your presentation. It brings in the human element with voice, gestures, and expressions, establishing a connection with your audience. This non-verbal communication is crucial for building relatability and trust.
According to our research, presentations with a video in their cover slide have 32% more people interacting with them .
And this doesn’t just refer to the top part of your deck. By embedding any video into your presentation, you can get people to read it 37% longer and enjoy a 17% increase in the CTA click-through rate.
This can be a short clip that introduces the topic or a brief message from the presenter. Our interactive editor allows you to easily embed videos in your slides by uploading them to the media library or pasting a URL.
Here’s an example of an introduction slide with a video:

Text and image
Pairing a story with a relevant image can create a memorable connection. Whether it's a personal photo for an individual introduction, a team photo for a group introduction, or a symbolic image for a company introduction, the right image can enhance your narrative.
Our platform offers a variety of design options to help you craft this perfect pairing. You can either choose your own images or let our AI assistant take care of it for you. You can also select the placement and adjust the proportions so that it doesn’t overpower your key message.
Here’s an introduction slide sample using a mix of text and images:

Timeline (History slide)
A timeline slide can take your audience on a journey through your company's or your personal history. It allows your audience to appreciate each significant milestone individually, adding depth to your presentation and making it easier to follow.
And, on top of that, giving your readers slides they have to click through makes them 41% more likely to scroll it all the way down to the bottom and read it 21% longer.
Here's an example of a history slide:

Multiple introductions (Tabs)
Tabs offer a neat way to introduce multiple aspects within the same context. You can dedicate a tab each for the speaker, the team, leadership, partners, and the company.
This feature also allows you to tailor your introduction to different audience personas, ensuring that your content resonates with everyone. An AI text generator can reduce the time spent on these different messages.
Here’s an example of an introduction slide using tabs:

Best examples of how to write and design your presentation introduction
When it comes to creating a compelling presentation introduction, real-life examples can provide invaluable insights. Let's explore how 4 Storydoc clients have leveraged the platform's features to create impactful starts to their presentations.
Yotpo is an e-commerce marketing platform that provides solutions for managing customer reviews and loyalty programs. Their presentation starts with a dynamic variable, allowing them to personalize the experience for each viewer with just a few clicks.
The introduction slide features a video showcasing their product in action, while the third slide uses a timeline to explain how to measure the product’s impact, complete with screenshots for clarity.
This approach not only engages the viewer but also provides a comprehensive overview of the product's capabilities. And, by sharing how to use data-driven insights to make the most of the platform, it helps build trust and credibility with potential customers.
WiseStamp , an email signature manager solution, uses dynamic variables on their first slide to embed the prospect's name and their company's name.
The introduction slide visualizes what the prospect's email signature would look like if they signed up for WiseStamp. All the data, including the name, address, phone number, and website, can be pulled directly from the CRM thanks to robust integration capabilities .
And, once they’ve seen the end result, prospects can also watch a short video showing how the product works.
All this combined makes potential customers feel like the presentation was created specifically for them, when in reality it takes just a few clicks to create unlimited versions of any deck.
The end result? A completion rate of 60% and a CTA conversion rate of 10%!
Octopai , an automated data intelligence platform, also leverages the power of personalization by including a dynamic variable on the cover slide.
The introduction slide grabs the readers’ attention by using a running number to present an agonizing problem statement. The third slide uses shocking statistics to reiterate the main issue plaguing the industry, paired with relevant images.
This approach effectively highlights the problem that Octopai solves. It can easily be personalized to include the prospect’s specific pain points, either found online or mentioned during the discovery call, making them more likely to be interested in the solution.
And, it worked wonders for the Octopai team! Their salespeople could easily create several versions of the same deck using the intuitive editor, leading to more demos booked and improved sales calls.
Orbiit , a virtual networking platform, provides a link to a shorter executive summary on their first slide for prospects who don't have time to read the whole presentation. Using the analytics panel, they can easily see who clicked on it and who didn’t, and follow up accordingly.
The introduction slide uses running numbers to present statistics regarding networking benefits before moving on to the main problem statement.
This engaging approach shows the importance of solving the issue and positions Orbiit as the perfect solution provider right from the start.
If you want to see more presentation introduction samples, check out our examples section .
Business presentation introduction do’s and don’ts
To ensure your introduction hits the right notes, here are some key do's and don'ts:
✅ Ignite interest with a compelling hook, like a surprising fact or a provocative question.
✅ State the purpose of your presentation clearly. Make sure your audience understands why they should care.
✅ Enhance your introduction with strategic visuals. A picture can speak a thousand words.
✅ Tailor your introduction to your specific audience. Make them feel seen and understood.
✅ Include an estimated reading time. It helps set expectations.
❌ Flood your audience with too much information upfront. Keep it simple and intriguing.
❌ Begin with a lengthy personal introduction that doesn't directly relate to your topic.
❌ Include large blocks of text. They can be overwhelming and off-putting.
❌ Send generic introductions. They can make your audience feel disconnected.
❌ Leave your audience in the dark about how long your presentation will take.
How to write your intro based on data from previous interactions with clients
By analyzing how clients interact with your content, you can then tailor the introduction of your following presentation to their preferences and expectations.
Say the first presentation was a sales one pager, you can use the engagement data gained there to tailor the intro for your sales proposal.
You can use engagement data to answer which slides and topics they engaged with and which they skipped, or if they viewed a video, used a calculator, filled out a form, or clicked your CTA.
You can then use this information to deduce what they really care about and use that information in your next intro.
The only problem is that with traditional static presentation makers like PowerPoint or Google Slides the only information you can get is whether the email where you attached them was opened.
You’re completely blind to what happens after you hit ‘Send’, good or bad.
But if you upgrade from static PowerPoints to Storydoc’s AI business presentation maker you get out-of-the-box analytics with multi-layered engagement information down to the slide and button interactions.
You can learn more about presentation analytics here:

Advanced: How to personalize your introduction at scale?
According to our research, personalizing your presentation can greatly improve your presentation performance. For example, including a personal note in your presentation can get 68% more people to read it in full and share it internally 2.3x more often.
But personalization takes time. Time which most of us can’t afford to spend on every reader.
However, this can easily be done at scale by integrating Storydoc with your existing tech stack.
Doing this will enable you to pull customer data directly from your CRM and into your presentations with a single click (and send back engagement data to your CRM!).
All you have to do is use dynamic variables in your presentations the same way you’d use them in your email automation.
Address your readers by name, use their company logo and branding, and include a note or a video that addresses their specific pain points.
This is how it works:

Advanced: How to introduce multiple people, companies, or subjects?
When you're tasked with introducing various elements, tabs can be a game-changer. They allow you to neatly organize and present different entities such as the speaker, team, or company, each in their own dedicated space.
This way, you can customize the content to suit different audience personas.
For a more chronological approach, the timeline slide can be a great tool. It enables you to guide your audience through the history of your company or personal journey, highlighting each significant event individually.
It's a simple yet effective way to make your introduction more engaging and informative.
Make a beautiful interactive presentation introduction from a template
Creating a presentation from scratch can feel like climbing a mountain. You need to figure out the layout, the message, the story, and the visuals—it's a lot to handle!
But what if you could skip the uphill struggle and get a head start? That's where interactive introduction slide templates shine.
They offer you a ready-made design and content structure, guiding you on where to place your key points for maximum impact. It's like having a roadmap to a successful presentation.
So, why not take the shortcut? Pick a template and start building your engaging interactive presentation introduction today!

Hi, I'm Dominika, Content Specialist at Storydoc. As a creative professional with experience in fashion, I'm here to show you how to amplify your brand message through the power of storytelling and eye-catching visuals.

Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.
Create your best presentation to date
Try Storydoc interactive presentation maker for 14 days free (keep any presentation you make forever!)
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Presenting to Management? Be Prepared for the Tough Questions.
- Sabina Nawaz

Take your time, and make every word count.
We’ve often spent hours rehearsing before presenting to upper management, only to freeze when confronted with a tough question from our bosses. All our preparation and carefully curated slides go unacknowledged. It’s our botched responses in the moment that stick.
If you’re presenting to an executive audience, you clearly have credibility, expertise, and a successful track record. You know how to tackle live questions because you can fall back on your knowledge and experience. But how do you field the tough questions from management — the ones you don’t have an answer to?
Consider these tips: First, don’t be too quick to respond after an executive grills you. Pause before you speak to collect yourself. Second, have an abundance mindset to overcome any anxiety you may feel. Once you do speak, provide the bottom line first, not the steps you took to arrive at it. Then, adhere to a word diet. Budgeting your words forces you to be clear and direct.
I don’t understand. How can your numbers be so off?
- Sabina Nawaz is a global CEO coach , leadership keynote speaker, and writer working in over 26 countries. She advises C-level executives in Fortune 500 corporations, government agencies, non-profits, and academic organizations. Sabina has spoken at hundreds of seminars, events, and conferences including TEDx and has written for FastCompany.com , Inc.com , and Forbes.com , in addition to HBR.org. Follow her on Twitter .

Partner Center
Home Blog Presentation Ideas How to Start a Presentation: 5 Strong Opening Slides and 12 Tricks To Test
How to Start a Presentation: 5 Strong Opening Slides and 12 Tricks To Test

Knowing how to start a presentation is crucial: if you fail to capture the audience’s attention right off the bat, your entire presentation will flop. Few listeners will stick with you to the end and retain what you have told.
That is mildly unpleasant when you are doing an in-house presentation in front of your colleagues. But it can become utterly embarrassing when you present in front of larger audiences (e.g., at a conference) or worse – delivering a sales presentation to prospective customers.
Here is how most of us begin a presentation: give an awkward greeting, thank everyone for coming, clear our throats, tap the mic, and humbly start to mumble about our subject. The problem with such an opening performance? It effectively kills and buries even the best messages.
Table of Contents
- The Classic Trick: Open a Presentation with an Introduction
- Open a Presentation with a Hook
- Begin with a Captivating Visual
- Ask a “What if…” Question
- Use the Word “Imagine”
- Leverage The Curiosity Gap
- The Power of Silence
- Facts as Weapons of Communication
- Fact vs. Myths
- The Power of Music
- Physical Activity
- Acknowledging a Person
How to Start a PowerPoint Presentation The Right Way
Let’s say you have all of your presentation slides polished up (in case you don’t, check our quick & effective PowerPoint presentation design tips first). Your presentation has a clear storyline and agenda. Main ideas are broken into bite-sized statements for your slides and complemented with visuals. All you have left is to figure out how you begin presenting.
The best way is to appeal to and invoke certain emotions in your audience – curiosity, surprise, fear, or good old amusements. Also, it is recommended to present your main idea in the first 30 seconds of the presentation. And here’s how it’s done.
1. The Classic Trick: Open a Presentation with an Introduction

When you don’t feel like reinventing the wheel, use a classic trick from the book – start with a quick personal introduction. Don’t want to sound as boring as everyone else with your humble “Hi, I’m John, the head of the Customer Support Department”? Great, because we are all about promoting effective presentation techniques (hint: using a dull welcome slide isn’t one of them).
Here’s how to introduce yourself in a presentation the right way.
a. Use a link-back memory formula
To ace a presentation, you need to connect with your audience. The best way to do so is by throwing in a simple story showing who you are, where you came from, and why your words matter.
The human brain loves a good story, and we are more inclined to listen and retain the information told this way. Besides, when we can relate to the narrator (or story hero), we create an emotional bond with them, and, again – become more receptive, and less skeptical of the information that is about to be delivered.
So here are your presentation introduction lines:
My name is Joanne, and I’m the Head of Marketing at company XYZ. Five years ago I was working as a waitress, earning $10/hour and collecting rejection letters from editors. About ten letters every week landed to my mailbox. You see, I love words, but decent publisher thought mine were good enough. Except for the restaurant owner. I was very good at up-selling and recommending dishes to the customers. My boss even bumped my salary to $15/hour as a token of appreciation for my skill. And this made me realize: I should ditch creative writing and focus on copywriting instead. After loads of trial and error back in the day, I learned how to write persuasive copy. I was no longer getting rejection letters. I was receiving thousands of emails saying that someone just bought another product from our company. My sales copy pages generated over $1,500,000 in revenue over last year. And I want to teach you how to do the same”
b. Test the Stereotype Formula
This one’s simple and effective as well. Introduce yourself by sharing an obvious stereotype about your profession. This cue will help you connect with your audience better, make them chuckle a bit, and set a lighter mood for the speech to follow.
Here’s how you can frame your intro:
“My name is ___, and I am a lead software engineer at our platform [Your Job Title]. And yes, I’m that nerdy type who never liked presenting in front of large groups of people. I would rather stay in my den and write code all day long. [Stereotype]. But hey, since I have mustered enough courage…let’s talk today about the new product features my team is about to release….”
After sharing a quick, self-deprecating line, you transition back to your topic, reinforcing the audience’s attention . Both of these formulas help you set the “mood” for your further presentation, so try using them interchangeably on different occasions.
2. Open a Presentation with a Hook
Wow your audience straight off the bat by sharing something they would not expect to hear. This may be one of the popular first-time presentation tips but don’t rush to discard it.
Because here’s the thing: psychologically , we are more inclined to pay attention whenever presented with an unexpected cue. When we know what will happen next – someone flips the switch, and lights turn on – we don’t really pay much attention to that action.
But when we don’t know what to expect next – e.g., someone flips the switch and a bell starts ringing – we are likely to pay more attention to what will happen next. The same goes for words: everyone loves stories with unpredictable twists. So begin your presentation with a PowerPoint introduction slide or a line that no one expects to hear.
Here are a few hook examples you can swipe:
a. Open with a provocative statement
It creates an instant jolt and makes the audience intrigued to hear what you are about to say next – pedal back, continue with the provocation, or do something else that they will not expect.

“You will live seven and a half minutes longer than you would have otherwise, just because you watched this talk.”
That’s how Jane McGonigal opens one of her TED talks . Shocking and intriguing, right?
b. Ask a rhetorical, thought-provoking question
Seasoned presenters know that one good practice is to ask a question at the beginning of a presentation to increase audience engagement. Rhetorical questions have a great persuasive effect – instead of answering aloud, your audience will silently start musing over it during your presentation. They aroused curiosity and motivated the audience to remain attentive, as they did want to learn your answer to this question.
To reinforce your message throughout the presentation, you can further use the Rhetorical Triangle Concept – a rhetorical approach to building a persuasive argument based on Aristotle’s teachings.
c. Use a bold number, factor stat
A clean slide with some mind-boggling stat makes an undeniably strong impact. Here are a few opening statement examples you can use along with your slide:
- Shock them: “We are effectively wasting over $1.2 billion per year on producing clothes no one will ever purchase”
- Create empathy: “Are you among the 20% of people with undiagnosed ADHD?”
- Call to arms: “58% of marketing budgets are wasted due to poor landing page design. Let’s change this!”
- Spark curiosity: “Did you know that companies who invested in speech recognition have seen a 13% increase in ROI within just 3 years?”
3. Begin with a Captivating Visual
Compelling visuals are the ABC of presentation design – use them strategically to make an interesting statement at the beginning and throughout your presentation. Your first presentation slide can be text-free. Communicate your idea with a visual instead – a photo, a chart, an infographic, or another graphics asset.
Visuals are a powerful medium for communication as our brain needs just 13 milliseconds to render what our eyes see, whereas text comprehension requires more cognitive effort.
Relevant images add additional aesthetic appeal to your deck, bolster the audience’s imagination, and make your key message instantly more memorable.
Here’s an intro slide example. You want to make a strong presentation introduction to global pollution. Use the following slide to reinforce the statement you share:

“Seven of nine snow samples taken on land in Antarctica found chemicals known as PFAs, which are used in industrial products and can harm wildlife”
Source: Reuters
4. Ask a “What if…” Question
The “what if” combo carries massive power. It gives your audience a sense of what will happen if they choose to listen to you and follow your advice. Here are a few presentations with starting sentences + slides to illustrate this option:

Alternatively, you can work your way to this point using different questions:
- Ask the audience about their “Why.” Why are they attending this event, or why do they find this topic relevant?
- Use “How” as your question hook if you plan to introduce a potential solution to a problem.
- If your presentation has a persuasion factor associated, use “When” as a question to trigger the interest of the audience on, for example, when they are planning to take action regarding the topic being presented (if we talk about an inspirational presentation).

5. Use the Word “Imagine”
“Imagine,” “Picture This,” and “Think of” are better word choices for when you plan to begin your presentation with a quick story.
Our brain loves interacting with stories. In fact, a captivating story makes us more collaborative. Scientists have discovered that stories with tension during narrative make us:
- Pay more attention,
- Share emotions with the characters and even mimic the feelings and behaviors of those characters afterward.
That’s why good action movies often feel empowering and make us want to change the world too. By incorporating a good, persuasive story with a relatable hero, you can also create that “bond” with your audience and make them more perceptive to your pitch – donate money to support the cause; explore the solution you are offering, and so on.
6. Leverage The Curiosity Gap
The curiosity gap is another psychological trick frequently used by marketers to solicit more clicks, reads, and other interactions from the audience. In essence, it’s the trick you see behind all those clickbait, Buzzfeed-style headlines:

Not everyone is a fan of such titles. But the truth is – they do the trick and instantly capture attention. The curiosity gap sparks our desire to dig deeper into the matter. We are explicitly told that we don’t know something important, and now we crave to change that. Curiosity is an incredibly strong driving force for action – think Eve, think Pandora’s Box.
So consider incorporating these attention grabbers for your presentation speech to shock the audience. You can open with one, or strategically weave them in the middle of your presentation when you feel like your audience is getting tired and may lose their focus.
Here’s how you can use the curiosity gap during your presentation:
- Start telling a story, pause in the middle, and delay the conclusion of it.
- Withhold the key information (e.g., the best solution to the problem you have described) for a bit – but not for too long, as this can reduce the initial curiosity.
- Introduce an idea or concept and link it with an unexpected outcome or subject – this is the best opening for a presentation tip.
7. The Power of Silence
What would you do if you attended a presentation in which the speaker remains silent for 30 seconds after the presentation starts? Just the presenter, standing in front of the audience, in absolute silence.
Most likely, your mind starts racing with thoughts, expecting something of vital importance to be disclosed. The surprise factor with this effect is for us to acknowledge things we tend to take for granted.
It is a powerful resource to introduce a product or to start an inspirational presentation if followed by a fact.
8. Facts as Weapons of Communication
In some niches, using statistics as the icebreaker is the best method to retain the audience’s interest.
Say your presentation is about climate change. Why not introduce a not-so-common fact, such as the amount of wool that can be produced out of oceanic plastic waste per month? And since you have to base your introduction on facts, research manufacturers that work with Oceanic fabrics from recycled plastic bottles .
Using facts helps to build a better narrative, and also gives leverage to your presentation as you are speaking not just from emotional elements but from actually recorded data backed up by research.
9. Fact vs. Myths
Related to our previous point, we make quite an interesting speech if we contrast a fact vs. a myth in a non-conventional way: using a myth to question a well-accepted fact, then introducing a new point of view or theory, backed on sufficient research, that proves the fact wrong. This technique, when used in niches related to academia, can significantly increase the audience’s interest, and it will highlight your presentation as innovative.
Another approach is to debunk a myth using a fact. This contrast immediately piques interest because it promises to overturn commonly held beliefs, and people naturally find it compelling when their existing knowledge is put to the test. An example of this is when a nutritionist wishes to speak about how to lose weight via diet, and debunks the myth that all carbohydrates are “bad”.
10. The Power of Music
Think about a presentation that discusses the benefits of using alternative therapies to treat anxiety, reducing the need to rely on benzodiazepines. Rather than going technical and introducing facts, the presenter can play a soothing tune and invite the audience to follow an exercise that teaches how to practice breathing meditation . Perhaps, in less than 2 minutes, the presenter can accomplish the goal of exposing the advantages of this practice with a live case study fueled by the proper ambiance (due to the music played in the beginning).
11. Physical Activity
Let’s picture ourselves in an in-company presentation about workspace wellness. For this company, the sedentary lifestyle their employees engage in is a worrying factor, so they brought a personal trainer to coach the employees on a basic flexibility routine they can practice in 5 minutes after a couple of hours of desk time.
“Before we dive in, let’s all stand up for a moment.” This simple instruction breaks the ice and creates a moment of shared experience among the attendees. You could then lead them through a brief stretching routine, saying something like, “Let’s reach up high, and stretch out those muscles that get so tight sitting at our desks all day.” With this action, you’re not just talking about workplace wellness, you’re giving them a direct, personal experience of it.
This approach has several advantages. Firstly, it infuses energy into the room and increases the oxygen flow to the brain, potentially boosting the audience’s concentration and retention. Secondly, it sets a precedent that your presentation is not going to be a standard lecture, but rather an interactive experience. This can raise the level of anticipation for what’s to come, and make the presentation a topic for future conversation between coworkers.
12. Acknowledging a Person
How many times have you heard the phrase: “Before we begin, I’d like to dedicate a few words to …” . The speaker could be referring to a mentor figure, a prominent person in the local community, or a group of people who performed charity work or obtained a prize for their hard work and dedication. Whichever is the reason behind this, acknowledgment is a powerful force to use as a method of starting a presentation. It builds a connection with the audience, it speaks about your values and who you admire, and it can transmit what the conversation is going to be about based on who the acknowledged person is.
Closing Thoughts
Now you know how to start your presentation – you have the opening lines, you have the slides to use, and you can browse even more attractive PowerPoint presentation slides and templates on our website. Also, we recommend you visit our article on how to make a PowerPoint Presentation to get familiarized with the best tactics for professional presentation design and delivery, or if you need to save time preparing your presentation, we highly recommend you check our AI Presentation Maker to pair these concepts with cutting-edge slide design powered by AI.

Like this article? Please share
Curiosity Gap, Opening, Public Speaking, Rhetorical Triangle, Speech, What If Filed under Presentation Ideas
Related Articles

Filed under Presentation Ideas • September 5th, 2023
Persuasive Speech: Actionable Writing Tips and Sample Topics
Business professionals, students, and others can all benefit from learning the principles of persuasive speech. After all, the art of persuasion can be applied to any area of life where getting people to agree with you is important. In this article, we get into the basics of persuasive speaking, persuasive speech writing, and lastly persuasive speech topics.

Filed under Presentation Ideas • August 5th, 2023
How Parkinson’s Law Can Make Your Presentations Better
Sometimes even the best presenters procrastinate their work until the very last moment. And then, suddenly, they get a flow of ideas to complete their slide deck and present like they have been preparing for it for ages. However, doing so has drawbacks, as even professional presenters cannot always elude the side effects of […]

Filed under Presentation Ideas • April 29th, 2022
How to Become Great in Public Speaking: Presenting Best Practices
Public Speaking takes a lot of practice and grit, however, it also requires a method that can help you through your presentation. Explore more about this subject in this blog post.
5 Responses to “How to Start a Presentation: 5 Strong Opening Slides and 12 Tricks To Test”
I love to follow the ideas, it’s good for a freshman
Leave a Reply
Introduction to Project Management Basics
Do you feel overwhelmed with your projects? Learn the basics of project management, including tools and principles, so you can effectively and efficiently manage projects to a successful outcome. Knowing the basics of project management can also help you decide which professional certification to pursue to best meet your career goals.
On this page:
Basic Concept 1: What is a Project?
Basic concept 2: what is project management, basic concept 3: the value of project management, basic concept 4: project management phases, basic concept 5: what is a project manager.
The most basic project management concept is knowing what a project is and when work is not a project. While there are projects in every industry, there may not be formal project management or project-related job titles used. A lack of formal titles does not mean the work is not a project. The Project Management Institute (PMI) defines a project as: “ a temporary effort to create value through a unique product, service or result .” From that definition, there are four concepts to call out:
- Temporary: a project has a definitive start and end date
- Unique: a project’s work is different from the ongoing work required to maintain the business and operations
- Team, Budget, Schedule : a project has an assigned team, budget, and schedule
- Goal: a project is done when the project goals are met
All work is not a project. For example, the daily maintenance work for cleaning factory machines is part of continuous operations and, therefore, is not a project. However, if a team created a plan to upgrade those machines by a specific date and within a budget, that is a project. There is no maximum or minimum duration to be a project, but there must be a clear start and stop.
The basics of project management can be described as: “ the use of specific knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to deliver something of value to people .”
There are multiple formal project management methodologies, including Agile, Waterfall (Predictive), Scrum, Kanban, Lean, PRINCE2, and Six Sigma. Plus, some organizations have customized company names for project phases and tools. These methodologies have one or more corresponding professional organizations that set standards and provide related certifications. Companies may require the use of a specific methodology for their projects and, in some cases, what credentials are expected of project professionals.
Project management methodologies differ in tools and terminology. For example, some project management frameworks have 5 project phases while others have 7 project phases.
Also, the names and types of project roles vary by methodologies, such as a Scrum Master or Agile Coach used in an Agile project environment. But the primary purpose of project management, to guide the work for specific deliverables to occur within a set timeframe and budget, is the same.
What is management vs. project management?
Project management is the leadership of a team to complete the specific goals of a project within set deadlines and budgets. Project management is focused on a project with a finite length of time, budget, and scope.
In contrast, basic management is not limited by time or a preset amount of work. Good management is ongoing and part of business operations. Management does not have a set number of phases like a project management process, nor does it stop when the project ends.
However, management and project management have similarities. The skills commonly associated with effective management, such as fostering teamwork, conflict negotiation, and building trust, are greatly valued in project management.
In the 1960s, organizations, in both government and private manufacturing, were taking on not only more complex projects but also multiple complex projects at the same time. Project management as a formal discipline grew out of the need to standardize how complex projects could be consistently led. With the increase in project size and quantity, the fundamental challenges of:
- a lack of common terminology within teams
- ineffective resource allocation
- failure to consistently meet project goals
All of these challenges drove what would become the field of project management. As project management methodologies were developed and refined, the value of this discipline to both professionals and organizations was evident. Today there are multiple project management methodologies and certifications reflecting the diverse ways project management can be applied to a variety of industries. The value attributed to well-executed project management includes:
- increase of positive project outcomes |e.g., quality of deliverable/s, staying in/under budget, completed early/on schedule
- customer loyalty | due to consistent results and high quality
- employee retention and morale | project teams with good work experiences create high morale among employees who want to stay longer
- effective use of resources | i.e., employees with needed skills are available when a project needs them, resources are sourced appropriately and used by multiple projects
- prioritize work to fit business objectives | e.g., projects that create higher value for the organization have resource priority over optional or low-impact projects.
Companies with a strong project management culture commonly enjoy not only cost savings but also higher employee morale, deep customer loyalty, and organizational efficiencies. PMI’s white paper “ The Value of Project Management (2010)” summarizes the value of project management as follows: “ Organizations turn to project management to deliver results consistently, reduce costs, increase efficiencies and improve customer and stakeholder satisfaction .” When project management is done well, the organization can benefit in many ways.
Studying for the PMP Exam?
When applied correctly and consistently, formal project management tools and processes can increase the chances of a successful project outcome. The project management process, or project lifecycle, details what tools and actions can be completed in a recommended sequence throughout the project.
In waterfall project management, there are 5 basic phases for the progression of work. For some project management methodologies, there are 7 phases. In Agile, work is tracked through a series of increments, such as sprints or cycles. The project management process and what activities and deliverables are included in it should be tailored by industry, company, and project. For example, a project to design new software will probably not have the same project management process needs as constructing a new office building. Both should have a process, but one that supports that unique project type and needs.
Project Management Process/Project Lifecycle
For PMI’s Project Management Professional (PMP)® certification, students should understand the basic project management processes, sometimes called the project lifecycle.
• Project Initiation • Project Planning • Project Execution • Project Monitoring and Controlling • Project Closing
The Project Manager motivates the team and leads the project throughout the project phases. The project scope and the selected methodology, along with organizational requirements, will inform what documentation, tools, and reporting are needed for each phase.
Project professionals, who are ultimately responsible for the project outcome, come from various work and educational backgrounds. Regardless of their title, including but not limited to the Project Manager, Project Lead, or Project Coordinator, the project’s primary leader is responsible for ensuring the team meets as many project goals as possible.
Project Manager Responsibilities
Project management is a complex and demanding field. Successful project managers must have leadership, technical, and organizational skills to lead the team towards the project goals. Every project is unique, but every project needs the project manager to:
• Help determine the project methodology to use for the project • Ensure a project plan is developed • Recruit project staff • Support and train the project team • Manage deliverables according to the project plan • Aid in the establishment of a project schedule • Support the assignment of tasks to project team members • Communicate with stakeholders
Project Managers with a PMP certification will use the basics of project management to meet the specific needs of each project and team.
Project Team Responsibilities in Project Management
A good project outcome is more likely when the project team can:
- contribute relevant skills and knowledge to the project work
- complete individual deliverables on schedule
- provide subject matter expertise to inform project planning and decision making
- document processes, risks, decisions, and outcomes for lessons learned
- collaborate with others on the project team
- communicate in a timely and consistent manner to the project manager and other team members
Team responsibilities vary by project type, scope, and management methodology.
Project Manager Certifications
Obtaining a project management certification helps project managers demonstrate they know how to adjust to best meet the needs of each project, whether using Waterfall or Agile.
- Project Management Professional (PMP)® | overseen by Project Management Institute (PMI)®
- Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)® | overseen by Project Management Institute (PMI)®
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM)® | overseen by ScrumAlliance
- PRINCE2 Foundation/PRINCE2 Practitioner | overseen by Prince2 Foundation
There are many project management certification options beyond the four listed here, each with requirements and testing protocols. Contact a verified source, like Project Management Academy (PMA), and research verified organizations, including Project Management Institute (PMI), to inform which certification to pursue to meet your career goals.
Project Management Resources
Take advantage of the free resources available from PMA and PMI to guide your project management skill development and certification work.
- Project Management Academy | Project Management Resources and Training
- Project Management Institute | Standards and Publications
One of the exciting elements of pursuing a project management career, or even augmenting your professional skill set with project management knowledge, is its variety. Pursue training and certification in multiple project management methodologies to expand your career opportunities. After all, using Agile project management for your organization does not prevent you from learning about or obtaining PRINCE 2 certification. And the training for project management can enhance not only how projects are managed but your overall leadership and management skillset.
There are proven project management tools and principles that, when applied correctly, can increase the chances of a successful project outcome. Achieving a project management certification is one way to demonstrate your knowledge of the basics of project management, including:
- describing what a project is and is not
- knowing the difference between management and project management
- knowing the basic project management phases used to track project work
- understanding the responsibilities of a project manager
- knowing the responsibilities of a project team
Having project management skills and knowledge of project management principles will help you lead more projects to success.
Upcoming PMP Certification Training – Live & Online Classes
- Megan Bell #molongui-disabled-link What is a Project Schedule Network Diagram?
- Megan Bell #molongui-disabled-link Scheduling Methodology: Build & Control Your Project Schedule
- Megan Bell #molongui-disabled-link Schedule Baseline: How to Create, Use, and Optimize
- Megan Bell #molongui-disabled-link How to Use Agile in Project Management as a PMP® Credential Holder
Popular Courses
PMP Exam Preparation
PMI-ACP Exam Preparation
Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training
CBAP Exam Preparation
Corporate Training
Project Management Training
Agile Training
Read Our Blog
Press Release
Connect With Us
PMI, PMBOK, PMP, CAPM, PMI-ACP, PMI-RMP, PMI-SP, PMI-PBA, The PMI TALENT TRIANGLE and the PMI Talent Triangle logo, and the PMI Authorized Training Partner logo are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc. | PMI ATP Provider ID #3348 | ITIL ® is a registered trademark of AXELOS Limited. The Swirl logo™ is a trademark of AXELOS Limited | IIBA ® , BABOK ® Guide and Business Analysis Body of Knowledge ® are registered trademarks owned by International Institute of Business Analysis. CBAP ® , CCBA ® , IIBA ® -AAC, IIBA ® -CBDA, and ECBA™ are registered certification marks owned by International Institute of Business Analysis. | BRMP ® is a registered trademark of Business Relationship Management Institute.
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Health Topics A-Z
- Introduction to Prevention Effectiveness
At a glance
This course provides an overview of public health economic costs, studies, and basic economic evaluation methods applied in public health.

Learning Objectives
By the end of the course, you will be able to:
- define prevention effectiveness.
- describe the key components of prevention effectiveness studies.
- identify basic economic evaluation methods used in prevention effectiveness studies.
- identify data used in the most common types of economic evaluation methods.
Available Learning Formats
E-learning course, slide presentation.
These slide sets are in the public domain and may be downloaded and customized as needed by the user for informational or educational purposes. Permission from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is not required, but citation of the source is appreciated.
Suggested Citation:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Introduction to Public Health. In: Public Health 101 Series. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2014. Available at: /training/publichealth101/prevention-effectiveness.html .
Course Resources
- Introduction to Prevention Effectiveness Course References
Explore Careers
- See Yourself in a Public Health Career
- Careers at CDC
- CDC Steven M. Teutsch Prevention Effectiveness (PE) Fellowship
- Commissioned Corps of the U.S. Public Health Service
- Fellowships and Training Opportunities
- PublicHealthCareers.org
- National Center for State, Tribal, Local, and Territorial Public Health Infrastructure and Workforce
Public Health 101 Series
The Public Health 101 Series offers introductory courses designed for people interested in public health and public health professionals seeking a refresher.

Slides Presentation - dIMCI Smart Course Webinar - May 16, 2024

This is the slides presentation from the Introduction to a New Online Smart digital Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (Smart dIMCI) course webinar which took place on May 16, 2024.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

11 templates

20 templates

holy spirit
36 templates

9 templates

25 templates

memorial day
12 templates
Use of Fentanyl in Pain Management Breakthrough
It seems that you like this template, use of fentanyl in pain management breakthrough presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Download the Use of Fentanyl in Pain Management Breakthrough presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides.Treating diseases involves a lot of prior research and clinical trials. But whenever there’s a new discovery, a revolutionary finding that opens the door to new treatments, vaccines or ways to prevent illnesses, it’s great news. Should there be a medical breakthrough, don’t hesitate to use this Google Slides & PowerPoint template and its editable slides to share the details and the information about it. A great resource for researchers and healthcare professionals.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Seema -. This document discusses key concepts in management including: organizations achieving goals through coordinating resources like people, machinery, materials and money. It defines management as the process of using these resources to achieve organizational goals efficiently and effectively. It also outlines the functions of management ...
This course includes PowerPoint slide decks organized by chapter and aligned to course content. Since the slides are openly licensed, you are welcome to retain, reuse, revise, remix, and redistribute them.
3 LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Define organization and management. Explain the importance of management. Describe the management process or functions of P-O- L-C. Describe the levels of management, and management skills. Understand the types of managers, and describe their roles and the changing nature of their work.
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) General Administrative Theory • Max Weber • Developed a theory of authority based on an ideal type of organization (bureaucracy) • The exercise of control on the basis of knowledge, expertise, or experience. • Emphasized rationality, predictability, impersonality, technical competence, and ...
Introduction to management. Dec 17, 2014 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 3 likes • 5,164 views. Kumar. Management. Marketing. 1 of 45. Download now. Introduction to management - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
A management presentation is a high-level summary to senior executive that optimizes reports to include only the details relevant to directorial decisions.They are notoriously difficult to navigate for two reasons: 1. most executives do not have working knowledge of the nuances in each department, 2. presenters rarely have time to understand executives' preferences.
1) Give you a basic understanding of management and its importance. 2) Provide a foundation of the managerial functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Introduction to Management. Management is not a hard science. Unlike chemistry or algebra where a right answer (often) exists, management is fluid, and subjective, and there ...
This course includes PowerPoint slide decks organized by chapter and aligned to course content. The decks also include practice questions and class discussion/activity prompts, which you may use, edit, or remove according to your classroom needs.
Principles of Management teaches management principles to tomorrow's business leaders by weaving three threads through every chapter: strategy, entrepreneurship and active leadership. Strategic — All business school teachings have some orientation toward performance and strategy and are concerned with making choices that lead to high performance.
Chapter- 1 Introduction to management. 2 MEANING OF MANAGEMENT Management is getting the work done through the efforts of others and effective utilization of human and material resources to achieve the enterprise objectives. 3 The 4 M's of Management Manpower Machinery Management Materials Money. 4 Difference between Management and ...
Presentation Transcript. Chapter1: Introduction to Management I-Management and Managers 1-What is Management? Efficiency: Doing the things the right way (refer to the relationship between inputs and outputs). Effectiveness: Doing the right things (goal attainment) Input -Raw material -Financial Capital -Technology -people -Info, skill -Other ...
Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Taylor's Principles • Develop a science for each element of an individual's work, which will replace the old rule-of-thumb method. • Scientifically select and then train, teach, and develop the worker. Introduction to Management (Chapter 2) Heartily cooperate with the workers so as to ensure that ...
Subarjo Joyosumarto SE, MA, Ph.D 23 Januari 2017 Meeting 1: Introduction to Management Class Chapter 1. Foundation of Management and organization. 2 Introduction to Management Class. 3 REFERENCES The list of books are stated at page 4 CLASS PROGRAM. There will be 14 meeting and each meeting constitutes 150 minutes length List of the class ...
The introduction in a business presentation has 4 goals: (1) to provide context by introducing the topic, (2) to build authority and trust by introducing the team (3) to manage expectations by giving a preview of the presentation content, and (4) to ignite interest by introducing a big idea.
Good presentation introduction examples Here are examples for a presentation introduction following the above templates. Example 1: Basic introduction "Good morning! My name is Tasha, and I'm here today to discuss how 30% of U.S. retailers rely on CustomMax Pro for customer management.
Consider these tips: First, don't be too quick to respond after an executive grills you. Pause before you speak to collect yourself. Second, have an abundance mindset to overcome any anxiety you ...
Financial PowerPoint Template with Calculator by SlideModel. 5. Use the Word "Imagine". "Imagine," "Picture This," and "Think of" are better word choices for when you plan to begin your presentation with a quick story. Our brain loves interacting with stories. In fact, a captivating story makes us more collaborative.
Concept of management is discussed in this presentation. It explains the basics of management. It also focuses on providing fundamental knowledge about management. Read more. Education. 1 of 16. Download now. Download to read offline. Introduction to management - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Project Management Infographics. Download the "Project Management Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides to get the most out of infographics. Whether you want to organize your business budget in a table or schematically analyze your sales over the past year, this set of infographic resources will be of great help.
Quick Read. A pitch deck is a visual presentation that tells the story of a business to persuade and engage potential investors. The most common pitch deck slides are introduction, problem, solution, market size and opportunity, product, traction, team, competition, financials and use of funds. Learn from the eight real life pitch deck examples ...
Temporary: a project has a definitive start and end date. Unique: a project's work is different from the ongoing work required to maintain the business and operations. Team, Budget, Schedule: a project has an assigned team, budget, and schedule. Goal: a project is done when the project goals are met. All work is not a project.
Step 3: Add Custom Animations to Your Animated PowerPoint. Your animated PowerPoint templates and all Visme presentation templates have plenty of different styles of animation possibilities. With Visme, add all these types of animations to any element in a slide. Enter Animations. Fade in.
Step 8: Determine Follow-Up Questions and Provide Answers. At the end of your product presentation, prospects or investors are likely to have a handful of questions about your product. Typically prospective customers ask questions to know if the product is a right fit for their organization.
Introduction to Prevention Effectiveness. Slide Presentation. PowerPoint. PDF. These slide sets are in the public domain and may be downloaded and customized as needed by the user for informational or educational purposes. Permission from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is not required, but citation of the source is appreciated.
2024. Resource Type. Presentation. Languages. English. Slides Presentation - dIMCI Smart Course Webinar - May 16, 2024 23.16 MB. This is the slides presentation from the Introduction to a New Online Smart digital Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (Smart dIMCI) course webinar which took place on May 16, 2024. This is the slides ...
This position will be the fiscal business manager of the Environmental Finance section of the Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control and oversee the work product of 3 fiscal management analyst positions, 3 management analysts, 3 fiscal advisors and 1 accounting specialist. Ensures compliance with all Federal, State and agency rules, regulations, policies, and procedures ...
Download the Use of Fentanyl in Pain Management Breakthrough presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides.Treating diseases involves a lot of prior research and clinical trials. But whenever there's a new discovery, a revolutionary finding that opens the door to new treatments, vaccines or ways to prevent illnesses, it's great news. Should ...
Introduction to Management. Feb 23, 2017 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 60 likes • 44,103 views. Prakhyath Rai. The document provides an introductory glimpse of management and the history of its evolution.The document also illustrates the nature, characteristics and importance of management. Various levels of management and managerial skills ...