

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 13 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Question 1:
An electric motor is a rotating device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy electric motors are used as an important component in electric fans, refrigerators, mixer, washing machines, computers, MP3 players etc. Motor Works on the principle that when a rectangular coil is placed in a magnetic field and current is passed through it, a force acts on the coil which rotates it continuously. When the coil rotates the shaft attached to it also rotates. In this way the electrical energy supplied to the motor is converted into the mechanical energy of rotation.
1.1) When the current is switched on, an electric fan converts : (a) electrical energy into mechanical energy (b) chemical energy into mechanical energy (c) electrical energy into mechanical energy (d) mechanical energy into electrical energy
Answer: (c) electrical energy into mechanical energy
1.2) In an electric motor, the direction of current in the coil changes once in each (a) two rotations (b) one rotation (c) half rotation (d) one-fourth rotation
Answer: (c) half rotation
1.3) An electron beam enters a magnetic field at right angles to it. The direction of force acting on the electron beam will be : (a) to the right (b) to the left (c) into the page (d) out of the page
Answer: (c) into the page
1.4) A magnetic field exerts no force on : (a) an unmagnetised iron bar (b) a stationary electric charge (c) a magnet (d) an electric charge moving perpendicular to its direction
Answer: (b) a stationary electric charge
1.5) Which of the following has no effect on the size of the turning effect on the coil of an electric motor? (a) The amount of the current in the coil. (b) The number of turns in the coil. (c) The direction of the current in the coil. (d) The strength of the magnetic field.
Answer: (c) The direction of the current in the coil
Question 2:
An insulated copper wire wound on a cylindrical cardboard tube such that its length is greater than its diameter is called a solenoid. When an electric current is passed through the solenoid, it produces a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. The strong magnetic field produced inside a current-carrying solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of a magnetic material like soft iron when placed inside the solenoid. The strength of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is directly proportional to the number of turns and strength of the current in the solenoid.
(i) The strength of magnetic field inside a long current-carrying straight solenoid is (a) more at the ends than at the centre (b) minimum in the middle (c) same at all points (d) found to increase from one end to the other.
Answer: (c) same at all points
(ii) The north-south polarities of an electromagnet can be found easily by using
Answer: (c) Clock face rule
(iii) For a current in a long straight solenoid N-and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is (a) The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid. (b) The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material like soft iron, when placed inside the coil. (c) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet. (d) The N- and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed.
Answer: (c) The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
(iv) A long solenoid carrying a current produces a magnetic field B along its axis. If the current is double and the number of turns per cm is halved, then new value of magnetic field is
Answer: (a) B
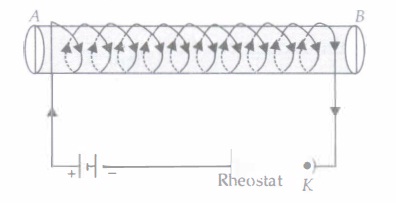
Answer: (a) N-pole
Question 3:
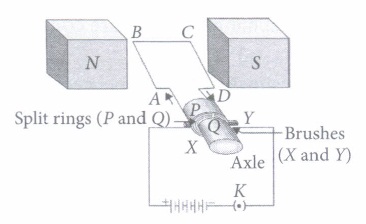
(i) Choose incorrect statement from the following regarding split rings. (a) Split rings are used to reverse the direction of current in coil. (b) Split rings are also known as commutator. (c) Split ring ii a discontinuous or a broken ring. (d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
(ii) Which of the following has no effect on the size of the turning effect on the coil of an electric motor?
Answer: (b) The direction of the current in the coil.
(iii) When current is switched ON, an electric fan converts
Answer: (b) electrical energy to mechanical energy
(iv) In an electric motor, device that makes contact with the rotating rings and through them to supply current to coil is
Answer:(b) brushes
(v) In an electric motor, the direction of current in the coil changes once in each
Answer:(c) half rotation
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries of CBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

Class 10 Science MCQ Online Test Free Chapter-wise
Cbse class 10 social science previous year question(pyq) chapterwise download pdf: last year sst class 10 questions.

Download Pearson Complete Guide to NTSE Class 10 – Best Book for NTSE
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
Please refer to Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current
Case/Passage – 1 A solenoid is a long helical coil of wire through which a current is run in order to create a magnetic field. The magnetic field of the solenoid is the superposition of the fields due to the current through each coil. It is nearly uniform inside the solenoid and close to zero outside and is similar to the field of a bar magnet having a north pole at one end and a south pole at the other depending upon the direction of current flow. The magnetic field produced in the solenoid is dependent on a few factors such as, the current in the coil, number of turns per unit length etc. The following graph is obtained by a researcher while doing an experiment to see the variation of the magnetic fieldwith respect to the current in the solenoid. The unit of magnetic field as given in the graph attached is in milli-Tesla (mT) and the current is given in Ampere.

Question: What will happen if a soft iron bar is placed inside the solenoid? (a) The bar will be electrocuted resulting in shortcircuit. (b) The bar will be magnetised as long as there is current in the circuit. (c) The bar will be magnetised permanently. (d) The bar will not be affected by any means.
Question: From the graph deduce which of the following statements is correct. (a) For a current of 0.8A the magnetic field is 13 mT (b) For larger currents, the magnetic field increases nonlinearly. (c) For a current of 0.8A the magnetic field is 1.3 mT (d) There is not enough information to find the magnetic field corresponding to 0.8A current.
Question: The magnetic field lines produced inside the solenoid are similar to that of … (a) a bar magnet 10 (b) a straight current carrying conductor (c) a circular current carrying loop (d) electromagnet of any shape
Question: What type of energy conversion is observed in a linear solenoid? (a) Mechanical to Magnetic (b) Electrical to Magnetic (c) Electrical to Mechanical (d) Magnetic to Mechanical
Question: After analysing the graph a student writes the following statements. I. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is inversely proportional to the current. II. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is directly proportional to the current. III. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is directly proportional to square of the current. IV. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is independent of the current. Choose from the following which of the following would be the correct statement(s). (a) Only IV (b) I and III and IV (c) I and II (d) Only II
Case/Passage – 2 For a conductor of length L carrying a current of I in a field B the force experienced by the conductor F → = I L → x → B If the current-carrying conductor in the form of a loop of any arbitrary shape is placed in a uniform field, then, F → =0 i.e., the net magnetic force on a current loop in a uniform magnetic field is always zero. Here it must be kept in mind that in this situation different parts of the loop may experience elemental force due to which the loop may be under tension or may experience a torque. Direction of force can be determined by fleming’s left hand rule, right hand palm rule or screw rule.
Question: An electron moving with uniform velocity in x-direction enters a region of uniform magnetic field along y-direction. Which of the following physical quantity(ies) is (are) non-zero and remain constant?
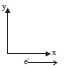
I. Velocity of the electron II. Magnitude of the momentum of the electron. III. Force on the electron. IV. The kinetic energy of electron. (a) Only I andII. (b) Only III and IV. (c) All four (d) Only II and IV.
Question: A wire is lying horizontally in the north-south direction and there is a horizontal magnetic field pointing towards and the east. Some positive charges in the wire move north and an equal number of negative charges move south. The direction of force on the wire will be

(a) east (b) down, into the page (c) up, out of the page (d) west
Question: Which of the following can produce a magnetic field? (a) Electric charges at rest (b) Electric charges in motion (c) Only by permanent magnets (d) Electric charges whether at rest or in motion
Question: The direction of induced current is obtained by (a) Fleming’s left hand rule (b) Maxwell’s cork-screw rule (c) Ampere’s rule (d) Fleming’s right hand rule
Question: Four situations are given below- I. An infinitely long wire carrying current II. A rectangular loop carrying current III. A solenoid of finite length carrying current IV. A circular loop carrying current. In which of the above cases will the magnetic field produced be like that of a bar magnet? (a) I (b) I and III (c) Only III (d) Only IV
Case/Passage – 3
The strength of the magnetic field produced by a currentcarrying circular coil (or circular wire) depends on (i) Current flowing through the coil. (ii) Radius of the circular coil. (iii) Number of turns of wire in the circular coil.
Question: What type of curve we get, between magnetic field and distance along the axis of a current carrying circular coil? (a) Straight (b) Circular (c) Parabolic (d) None of these
Question:A long horizontal power line is carrying a current of 100 A in the east-west direction. The direction of magnetic field at a point 1.0 m below it is (a) south to north (b) north to south (c) east to west (d) west to east
Question: If a current carrying straight conductor is placed is east-west direction, then the direction of the force experienced by the conductor due to earth’s magnetic field is: (a) downward (b) upward (c) east-west (d) west east
Case/Passage – 4
Study this table related to wattage of home appliances and answer the questions that follow.
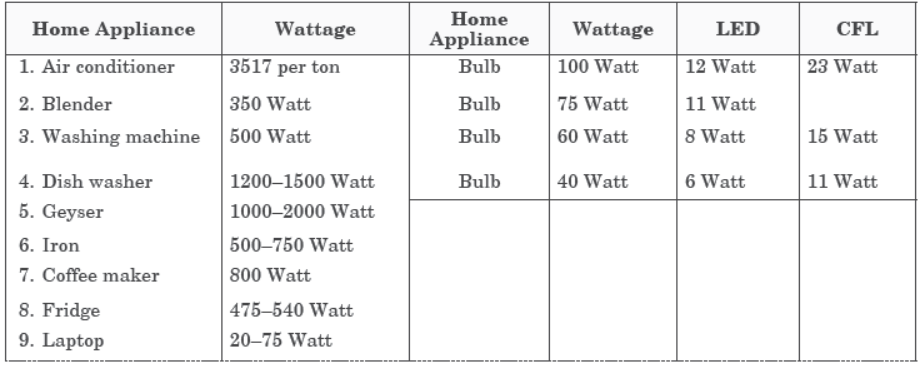
Question. Which of the following will to consume least power? (a) Laptop (b) Desktop (c) Printer (d) Blender
Question. Many appliance works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. The role which depicts the direction of induced current is as (a) Faraday’s rule (b) Henery’s rule (c) Fleming’s rule (d) Maxwell’s rule
Question. Which of the following home applicance is not based on magnetic effect of current? (a) Ceiling fan (b) Blender (c) Geyser (d) Washing Machine
Question. Which of the following will consume maximum power? (a) Fridge (b) Iron (c) Air conditioner (d) Coffee maker
Question. Which of the following lighting device is best to use in terms of power consumption? (a) Bulb (b) CFL (c) Tube light (d) LED
Case/Passage – 5
A magnetic stripe card, also referred to as a swipe card or magstripe, is a plastic card with a magnetic strip attached on its surface. This stripe is made of tiny iron-based components whose magnetism can be modified and can therefore be used to store information. A magstripe is quite similar to a magnetic recording tape, which you might find in videotape or a music cassette. The magnetic strip on a card can be ‘written’ or encoded with information because the tiny iron-based particles that make up the strip can be magnetised in different directions by a device that produces a strong magnetic field. This device is a ‘solenoid’, which is basically a coil wound into a tightly packed helix. The wire is wound around a highpermeable, metallic core that produces a strong magnetic field when a current is passed through it. This device encodes the required information onto the stripe, which is then pasted on a plastic card. When a card with a magnetic strip is moved back and forth over the ‘reader head’ , a voltage is induced in the coils of the card reader device. A card reader consists of solenoid too – the same component that is used to write information in the magnetic strip. This voltage can be amplified and recorded electronically, which is finally read by a computer (or a processor installed within the reader) to authenticate a user (in the case of identity cards) or a transaction (in the case of credit/debit cards).
Question. The force on a wire inside a magnetic field increase when (a) The current is increased (b) Strength of magnetic field increases (c) Length of wire is increased (d) All of above
Question. The factors on which one magnetic field strength produced by current carrying solenoids depends are (a) Magnitude of current (b) Number of turns (c) Heat produced (d) Both (a) and (b)
Question. Which of the following are the devices that uses magnetic theory to record data (a) The hotel key cards (b) Audio tapes (c) CD’s (d) All of the above
Question. The information of users which are read by the ATM machines are stored on (a) Magnetic box on card (b) Magnetic strip on card (c) Inside ATM machine (d) None of above
Question. Name the scientist who gave the principle of electromagnetic field (a) Oersted (b) Faraday (c) Bohr (d) Ampere

Related Posts

Resources and Development Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

Political Parties Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

Case Study Chapter 9 Heredity And Evolution
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Ap inter results.
- AP Board Results 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions
Chapter wise important case study questions cbse class 10 science: cbse class 10 science board exam 2024 is just around the corner and students are working hard to score maximum marks. check these case study questions from class 10 science to ace your examination this year also download the solutions from the pdf attached towards the end. .

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions: While the CBSE Board exam for Class 10 students are ongoing, the CBSE Class 10 Science board exam 2024 is to be held on March 2, 2024. With the exams just a few days away, CBSE Class 10th Board exam candidates are rushing to prepare the remaining syllabus, practising their weak portions, trying to revise the important questions from the past year papers, practise questions, etc.
Why are CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions Important?
- Section A : 20 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B : 6 Very Short Answer type questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C : 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D : 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E : 3 Case Based/ Source Based units of assessment (4 marks each) with sub-parts.
How to solve case study questions in CBSE Class 10 Science?
- Read the case given and the associated questions carefully.
- Read the questions attentively and analyse what they are asking.
- Apply your subject knowledge and theories in the given case to decide what the correct answers should be.
1.A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the
(a) combination reaction
(b) decomposition reaction
(c) displacement reaction
(d) double displacement reaction
(ii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of
(a) lead nitrate
(b) nitrogen oxide
(c) lead oxide
(d) oxygen gas
(iii) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction?
(a) CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2 (aq)
(b) CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2(g)
(c) Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
(d) 2FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3 (s) +SO2(g) + SO3(g)
(iv) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y.
Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction.
Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction.
(a)X-Combination,Y-Decomposition
(b)X-Decomposition,Y-Combination
(c)X-Combination,Y-Displacement
(d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
2.The earlier concept of oxidation and reduction is based on the addition or removal of oxygen or hydrogen elements so, in terms of oxygen and hydrogen, oxidation is addition of oxygen to a substance and removal of hydrogen from a substance. On the other hand, reduction is addition of hydrogen to a substance and removal of oxygen from a substance. The substance which gives oxygen to another substance or removes hydrogen from another substance in an oxidation reaction is known as oxidising agent, while the substance which gives hydrogen to another substance or removes oxygen from another substance in a reduction reaction is known as reducing agent. For example,
(i) A redox reaction is one in which
(a) both the substances are reduced
(b) both the substances are oxidised
(c) an acid is neutralised by the base
(d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
(ii) In the reaction, H2S+Cl2⟶S+2HCl
(a) H2S is the reducing agent.
(b) HCl is the oxidising agent.
(c) H2S is the oxidising agent.
(d) Cl2 is the reducing agent.
(iii) Which of the following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) Formation of slaked lime from quicklime.
(b) Heating mercuric oxide.
(c) Formation of manganese chloride from manganese oxide (MnO2).
(d) Formation of zinc from zinc blende.
(iv) Mg+CuO⟶MgO+Cu
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
(a) CuO gets reduced
(b) Mg gets oxidised.
(c) CuO gets oxidised.
(d) It is a redox reaction.
3.A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lemon on the vessel, the surface is cleaned, and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that which reacts with the acid present in lemon to form a salt which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
1.Which of the following acids is present in lemon?
(a) Formic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
2.The nature of copper oxide is
d) amphoteric
3.Name the salt formed in the above reaction
a) copper carbonate
b) copper chloride
c)copper citrate
d) copper citrate
4.The phenomenon of copper getting tarnished is
a) corrosion
b) rancidity
c) displacement
d)none of these
4.Metals as we know, are very useful in all fields, industries in particular. Non-metals are no less in any way. Oxygen present in air is essential for breathing as well as for combustion. Non-metals form a large number of compounds which are extremely useful, e.g., ammonia, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, etc. Non-metals are found to exist in three states of matter. Only solid non-metals are expected to be hard however, they have low density and are brittle. They usually have low melting and boiling points and are poor conductors of electricity.
i.____________ is a non-metal but is lustrous
A.Phosphorus
ii.Which of the following is known as 'King of chemicals'?
C. Sulphuric acid
D. Nitric acid
iii.Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
iv.Hydrogen is used
A.for the synthesis of ammonia
B. for the synthesis of methyl alcohol
C.nitrogenous fertilizers
D. all of these
5.Nisha observed that the bottoms of cooking utensils were turning black in colour while the flame of her stove was yellow in colour. Her daughter suggested cleaning the air holes of the stove to get a clean, blue flame. She also told her mother that this would prevent the fuel from getting wasted.
a) Identify the reasons behind the sooty flame arising from the stove.
b) Can you distinguish between saturated and unsaturated compounds by burning them? Justify your answer.
c) Why do you think the colour of the flame turns blue once the air holes of the stove are cleaned?
6.Blood transport food, Oxygen and waste materials in our bodies. It consists of plasma as a fluid medium. A pumping organ [heart] is required to push the blood around the body. The blood flows through the chambers of the heart in a specific manner and direction. While flowing throughout the body, blood exerts a pressure against the wall or a vessel.
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Very narrow and have high resistance
- Much wide and have low resistance
- Very narrow and have low resistance
- Much wide and have high resistance
- It is a hollow muscular organ
- It is four chambered having three auricles and one ventricle.
- It has different chambers to prevent O2 rich blood from mixing with the blood containing CO2
- Both A & C
- Blood = Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets
- Plasma = Blood – RBC
- Lymph = Plasma + RBC
- Serum = Plasma + RBC + WBC
7.A brain is displayed at the Allen Institute for Brain Science. The human brain is a 3-pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it's the most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
1)Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It's packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
- b) Learning
3)Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter
b) Cerebrospinal fluid
d) Grey matter
4.Ram was studying in his room. Suddenly he smells something burning and sees smoke in the room. He rushes out of the room immediately. Was Ram’s action voluntary or involuntary? Why?
8.Preeti is very fond of gardening. She has different flowering plants in her garden. One day a few naughty children entered her garden and plucked many leaves of Bryophyllum plant and threw them here and there in the garden. After few days, Preeti observed that new Bryophyllum plants were coming out from the leaves which fell on the ground.
1.What does the incident sited in the paragraph indicate?
(a). Bryophyllum leaves have special buds that germinate to give rise to new plant.
(b). Bryophyllum can propagate vegetatively through leaves.
(c). Bryophyllum is a flowering plant that reproduces only asexually
(d). Both (a) and (b).
2.Which of the following plants can propagate vegetatively through leaves like Bryophyllum?
3.Do you think any other vegetative part of Bryophyllum can help in propagation? If yes, then which part?
(c) Flowers
4.Which of the following plant is artificially propagated (vegetatively) by stem cuttings in horticultural practices?
(b)Snakeplant
(d)Water hyacinth
9.The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of the population.
1) What are common signs of sexual maturation in boys?
a) Broadening of shoulders
b) Development of mammary glands
c) Broadening of waist
d) High pitch of voice
2) Common sign of sexual maturation in girls is
a) Low pitch voice
b) Appearance of moustache and beard
c) Development of mammary glands
d) Broadening of shoulders
3) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body?
b) Diaphragms
c) Oral pills
d) Both a) and b)
4) What should be maintained for healthy society?
a) Rate of birth and death rate
b) Male and female sex ratio
c) Child sex ratio
d) None of these
10.Pea plants can have smooth seeds or wrinkled seeds. One of the phenotypes is completely dominant over the other. A farmer decides to pollinate one flower of a plant with smooth seeds using pollen from a plant with wrinkled seeds. The resulting pea pod has all smooth seeds.
i) Which of the following conclusions can be drawn?
(1) The allele for smooth seeds is dominated over that of wrinkled seeds.
(2) The plant with smooth seeds is heterozygous.
(3) The plant with wrinkled seeds is homozygous.
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ii) Which of the following crosses will give smooth and wrinkled seeds in same proportion?
(a) RR X rr
(b) Rr X rr
(d) rr X rr
iii) Which of the following cross can be used to determine the genotype of a plant with dominant phenotype?
(a) RR X RR
(b) Rr X Rr
(c) Rr X RR
(d) RR X rr
iv) On crossing of two heterozygous smooth seeded plants (Rr), a total of 1000 plants were obtained in F1 generation. What will be the respective number of smooth and wrinkled seeds obtained in F1 generation?
(a) 750, 250
(b) 500, 500
(C) 800, 200
(d) 950, 50
11.Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases.The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers.Primary producers or autotrophs,can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds,whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis,most life could not exist if the sun disappeared.Even so,it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life,chemotrophs,that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents,thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
1.If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem,what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy?
(d)It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant
2.Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
(a)Energy is by directional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(b)Energy is repeatedly circulating and matter is unidirectional
(c)Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(d)Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional
3.Raj is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
(a)First trophic level
(b)Second trophic level
(c)Third trophic level
(d)Fourth trophic level
4.Which of the following, limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain
(a)Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(b)Less availability of food
(c)Polluted air
5.The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers
(a) Act at every trophic level at the food chain
(b) Do not breakdown organic compounds
(c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms
(d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
12.Shyam participated in a group discussion in his inter school competition on the practical application of light and was very happy to win an award for his school. That very evening his father gave treat to celebrate Shyam’s win. Shyam while sitting saw an image of a person sitting at his backside in his curved plate and could see that person’s mobile drop in the flower bed. Person was not aware until Shyam went and informed him. He thanked Shyam for his clever move.
a)From which side of his plate Shyam observed the incident –
i)outward curved
ii)inward curved
iii)plane surface
b)Part of plate from which Shyam observed the incident acted like a-
i)concave mirror
ii)convex mirror
iii)plane mirror
c)The nature of the size of the image formed in above situation is –
i)real, inverted and magnified
ii)same size , laterally inverted
iii)virtual, erect and diminished
iv)real , inverted and diminished
d)Magnification of the image formed by convex mirror is –
more than 1
iii)equal to 1
iv)less than 1
- The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(a) at focus
(c) at optical center
- When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
(a)real and smaller
(b) virtual and smaller
(c) virtual and inverted
- The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus ofconvex lens is
(a) highly magnified
(b) point in size
- When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(b) between F and optical center
(c) at infinity
(d) none of the above
14.One of the wires in domestic circuits supply, usually with a red insulation cover, is called live wire. with black insulation is called neutral wire. The earth wire, which has insulation of green colour, is usually connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near the house appliances that has a metallic body. Overloading contact, in such a situation the current in the circuit abruptly increases. circuit prevents damage to the appliances and the circuit due to overloading.
1 When do we say that an electrical appliance
2 Mention the function of earth wire in electrical line
3 How is an electric fuse connected in a domestic circuit?
4 When overloading and short circuiting are said to occur?
5 What is a live wire?
15.Light of all the colours travel at the same speed in vacuum for all wavelengths. But in any transparent medium(glass or water), the light of different colours travels at different speeds for different wavelengths, which means that the refractive index of a particular medium is different for different wavelengths. As there is a difference in their speeds, the light of different colours bend through different angles. The speed of violet colour is maximum and the speed of red colour is minimum in glass so, the red light deviates least and violet colour deviates most. Hence, higher the wavelength of a colour of light, smaller the refractive index and less is the bending of light.
(i)Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of Light of different colours of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
(ii)Which of the following is the correct order of wavelength?
(a) Red> Green> Yellow
(b) Red> Violet> Green
(c) Yellow> Green> Violet
(d) Red> Yellow> Orange
(iii)Which of the following is the correct order of speed of light in glass?
(a) Red> Green> Blue
(b) Blue> Green> Red
(c) Violet> Red> Green
(d) Green> Red> Blue
(iv)Which colour has maximum frequency?
16.The region around a magnet where magnetism acts is represented by the magnetic field.The force of magnetism is due to moving charge or some magnetic material. Like stationary charges produce an electric field proportional to the magnitude of charge, moving charges produce magnetic fields proportional to the current. In other words, a current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. The subatomic particles in the conductor, like the electrons moving in atomic orbitals, are responsible for the production of magnetic fields. The magnetic field lines around a straight conductor (straight wire) carrying current are concentric circles whose centres lie on the wire.
1)The magnetic field associated with a current carrying straight conductor is in anti- clockwise direction. If the conductor was held horizontally along east west direction,what is the direction of current through it?
2)Name and state the rule applied to determine the direction of magnetic field in a straight current carrying conductor.
3)Ramus performs an experiment to study the magnetic effect of current around a current carrying straight conductor with the help of a magnetic compass. He reports that
a)The degree of deflection of magnetic compass increases when the compass is moved away from the conductor.
b)The degree of deflection of the magnetic compass increases when the current through the conductor is increased.
Which of the above observations of the student appears to be wrong and why?
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science CBSE Chapter Wise PDF
Related resources to prepare for cbse 10th science board exam 2024.
- CBSE class 10 Science syllabus 2024
- NCERT Book for Class 10th Science 2023-2024 (PDF)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science sample paper
- Previous Year Questions of CBSE Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Biology Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Topper Answer Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Practice Paper 2023 with Answers
- Class 10 CBSE Admit Card 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet 2023
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2023 - 2024
- CBSE Class 10 DELETED Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10th Sample Paper 2022-23: Download Sample Question Papers and Marking Scheme
- CBSE Class 10 Previous Year Question Papers for 2022-23
- CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers for 2023-24 of ALL Chapters
- CBSE Class 10 Practice Papers: All Subjects
- CBSE Topper Answer Sheet Class 10: Model Answer Paper Download PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Mock Tests: All Subjects
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- NDA Admit Card 2024
- TNPSC Group 1 Hall Ticket 2024
- APPSC Group 1 Result 2024
- AIASL Executive Recruitment 2024
- NTA NITTT Result 2024
- APPSC Group 2 Result 2024
- CUET PG Answer Key 2024
- TN SET Application Form 2024
- BPSC Head Master 2024 Last Date Extended
- UGC NET Notification 2024
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
Latest Education News
Today’s IPL Match (7 April) - MI vs DC: Team Squad, Match Time, Where to Watch Live and Stadium
Today’s IPL Match (7 April) - GT vs LSG: Team Squad, Match Time, Where to Watch Live and Stadium
Who Won Yesterday IPL Match: RR vs RCB, Match 19, Check All Details and Latest Points Table
[Current] Orange Cap and Purple Cap Holders in IPL 2024
[Today] IPL 2024 Points Table: Team Rankings and Net Run Rate
[Updated] Most Centuries in IPL History: List of 100 (Hundreds) Made by Players
KSDNB Revaluation GNM Result 2024 at ksdneb.org: Check Latest Updates
Test Your IQ: Only Geniuses Can Find The Missing Number In 60 Seconds!
Grahan 2024: इस साल कब-कब लगेंगे सूर्य और चंद्र ग्रहण? देखें सही टाइम
Surya Grahan 2024: मोबाइल पर ऐसे देखें साल के पहले सूर्यग्रहण की LIVE स्ट्रीमिंग, चेक करें सही टाइम
World Health Day 2024 Theme: What is the meaning of My Health, My Right? Check Details by WHO
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Use Your Sports Vision To Spot A Racket In 12 Seconds!
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Use Your Eagle Vision To Spot A Measuring Scale In 12 Seconds!
JEE Main Analysis 2024 (April 6) Shift 1, 2: Check Subject-Wise Paper Analysis, Difficulty Level, Questions Asked
JEE Main Session 2 (April 6) Aakash Answer Key 2024: Download Shift 1 and Shift 2 Answer Key FREE PDF
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: You Are Highly Attentive If You Can Spot The Pencil In 12 Seconds!
Optical Illusion IQ Test: You Have Eyes Of A Hunter If You Can Spot A Button In 12 Seconds!
MUHS Result 2024 OUT at muhs.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet PDF
Rayalaseema University Result 2024 OUT at ruk.ac.in: Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
JEE Main Session 2 Question Paper 2024 Memory Based: Check Question Paper with Solutions April 6
myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
2 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 2023-24

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-13 Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download
The important questions for class 10 science chapter 13 - Magnetic effects of electric current is made available to the students of class 10 herein. The committee of expert science teachers here have made sure that they cover every topic of chapter 13 while preparing the important questions and answers. All the answers of chapter 13 science class 10 important questions are explained thoroughly so that the students grasp the concept at one go. This will help them to formulate a proper strategy during the science exam preparation. The students can now download the free PDF of Magnetic effect of electric current class 10 important questions from the website of Vedantu easily.
Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. You can download class 10 maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2023-24 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for other chapters:

Related Chapters
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Important Questions - Free PDF Available
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Magnetic field lines determine
The shape of magnetic field
Only the direction of magnetic field
Only the relative strength of the magnetic field
Both the direction and the relative strength of magnetic field
Ans: (d) Both the direction and the relative strength of magnetic field
2. A device for producing electric current is called a
Galvanometer
Ans: (c) Generator
3. At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit
vary continuously
reduced considerably
increases heavily
does not change
Ans: (c) increases heavily
4. Figure shows the magnetic field lines between the two faces A and B of two magnets.
Both faces A and B of two bar magnets are North pole.
Both faces A and B of two bar magnets are South pole.
Face A is south pole while face B is north pole.
None of the above.
Ans: (d) None of the above.
5. The magnetic field near a long straight wire is described by
Straight field lines parallel to the wire.
Straight field lines perpendicular to the wire.
Connective circle centred on the wire.
Radial field lines starting from the wire.
Ans: (c) Connective circle centred on the wire.
6. A current carrying conductor placed in magnetic field experiences a force. The displacement of the conductor in magnetic field can be increased by
Decreasing the magnetic field.
Decreasing the current in the conductor.
Increasing the magnetic field.
Ans: (c) Increasing the magnetic field.
7. A positively charged particle say an alpha particle projected towards west is deflected toward north by a magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field is
towards south
towards east
Ans: (a) upward
8. Which of the following properties of a proton can change when it moves freely in a magnetic field?
Ans: (c) velocity and (d) momentum
9. The direction of the magnetic field at a point P above the wire carrying current as shown in the figure is
down the page
up the page
into the page
out of the page
Ans: (d) out of the page
10. Concentric circles with arrows centred at the wire AB are shown in figure.
no current in AB
current flows from B to A
current – flows from A to B
none of these
Ans: (b) current flows from B to A
11. Electric motor converts
Mechanical energy into electrical energy
Mechanical energy into heat energy
Electrical energy into heat energy
Electrical energy into mechanical energy
Ans: (d) Electrical energy into mechanical energy
12. Potential difference between a live wire and a neutral wire is
Ans: (d) 220 volt.
13. The most important safety device method used for protecting electrical appliances from short circuiting or overloading is
use of stabilizer
use of electric meter
Ans: (d) fuse
14. Forces acting on a stationary charge of in the magnetic field B is
Ans: (d) zero
15. The rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of induced current change once in each
one revolution
one fourth revolution
half revolution
two revolutions
Ans: (c) half revolution
16. Choose the correct option:
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid-carrying current is zero.
Decrease as we move towards its end.
Increase as we move towards it end.
Is the same all points.
Ans: (d) Is the same at all points.
17. Name some sources of direct current.
Ans: A cell, a battery, and a D.C. generator are all examples of direct current sources.
18. The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
the process of charging a body.
the process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil.
producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
the process of rotating a coil at an electric motor.
Ans: (c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
19. The essential difference between A.C. generator and a D.C. generator is that
A.C. generator has an electromagnet while a D.C. generator has permanent magnet.
D.C. generator will generate a higher voltage
A.C. generator will generate a higher voltage
A.C. generator has slip rings while the D.C. generator has commentator.
Ans: (d) A.C. generator has slip rings while the D.C. generator has commentator.
20. In which position the force on conductor is maximum when it uniform magnetic field? is placed in
Ans: When the conductor is parallel to the field
21. How can it be shown that magnetic field exist around a wire carrying current?
Ans: By using a magnetic compass that displays deflection.
22. How can a solenoid be used to magnet a steel bar?
Ans: By placing a steel bar into the solenoid and turning on the electricity.
23. Why can’t two magnetic field lines ever intersect?
Ans: If this is the case, there will be two separate magnetic field directions at the site of intersection, which is not feasible.
24. Can 5A fuse be used in wire carrying 15 A current? Why?
Ans: Because they'd both be useless at managing the quantity of current flowing if that happened.
25. Give the factors that affect strength of magnetic field at a point due to a straight conductor carrying current.
Ans: Perpendicular distance between that point and the conductor, magnitude of electric content.
26. Where do we connect a fuse: with live wire or with neutral wire?
Ans: It is always wired with live electricity.
27. Name any two devices which use permanent magnets.
Ans: Loudspeaker, Motor, Galvanometer, voltmeter.
28. Draw the magnetic field lines representing uniform magnetic field.
29. If the frequency of A.C. is 50 Hz. Then how many times it is changing its direction in 1 second
Ans: 100 Times will be changing its direction in a second.
30. What is the pattern of the magnetic field lines around a straight conductor carrying current?
Ans: Concentric circles
31. If the current is flowing in the direction of advancement of screw, then what is the direction of magnetic field lines?
Ans: Magnetic field will be directed inwards .
32. How can you say that the magnetic field is uniform inside the solenoid?
Ans: Because the field lines inside the solenoid are parallel.
33. Which property of a proton will change while it moves freely in a magnetic field?
Ans: Momentum or Velocity.
34. According to Flemings right hand rule, which part of right hand indicate the movement of conductor?
35. If the no. of turns of a circular current carrying coil are doubled, then how will the magnetic field produced by it changes?
Ans: Doubled
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. State two properties of magnetic lines of force?
Ans: The two properties of magnetic lines of force are-
i. The strength of the magnetic field is proportional to the closeness of the lines.
ii. They can never cross i.e. the field is unique at any point in space.
2. Why does a compass needle deflect when brought near a bar magnet?
Ans: A compass needle deflected when brought near a bar magnet due to the magnetic field of the bar magnet.
3. The magnetic field lines in a given region are uniform. Draw a diagram to represent.
Ans: The magnetic field lines in a given region are uniform when they are represented in the same direction.
4. Write two ways to induce current in a coil?
Ans: The two ways to induce current in a coil are-
i. By moving a bar magnet toward or away from the coil current is induced.
ii. By moving a coil rapidly between the two poles of a horseshoe magnet.
5. Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet? Give one point of difference between uniform and non- uniform magnetic field.
Ans: The magnetic field lines around a bar magnet is as follows:
Uniform magnetic field lines are parallel but non- uniform magnetic field lines are non-parallel.
6. Why do not two magnetic field lines intersect each other?
Ans: If two magnetic field lines intersect each other then there will be two directions of magnetic field, which is not possible. Thus, they do not intersect each other.
7. Name and state rule used to determine the direction of magnetic field produced around a straight conductor carrying current?
Ans: Right hand thumb rule is used to determine the direction of magnetic field produced around a straight conductor carrying current. It states that if we hold the current-carrying conductor in our right hand such that the thumb points the direction of the current, then the direction in which the fingers encircle, gives the direction of magnetic lines.
8. What is electric fuse? Where is it connected in a circuit?
Ans: Electric fuse is a safety device which is used to limit the current in an electric circuit which is made up of a wire made of copper or aluminium or a tin lead alloy. It is always connected in series at the beginning of the circuit.
9. State the factors on which strength of magnetic field at a point due to a current carrying conductor depends?
Ans: The factors on which strength of magnetic field at a point due to a current carrying conductor depends are-
i. It is directly proportional to the amount of current (I) flowing through the conductor.
ii. It is inversely proportional to the distance (r) from the current carrying conductor.
10. What is an electromagnet? Write two uses of an electromagnet?
Ans: They are the type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current i.e. when current is passed through a solenoid it behaves as a magnet and is called an electromagnet.
The two uses of an electromagnet are-
i. Used in electrical devices like motors, generators etc.
ii. Used to lift heavy iron pieces.
11. State and define S.I unit of magnetic field?
Ans: The S.I unit of magnetic field is Tesla (T). It states that 1meter long conductor carrying 1 ampere current experiences 1 Newton force, when placed perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field then the magnetic field strength is 1 Tesla.
12. A current carrying conductor is placed perpendicular to the uniform magnetic field. What happens to displacement of the conductor if
i. strength of current increases
Ans: The displacement of the conductor will increase on increasing the strength of current.
ii. If horseshoe magnet is replaced by a weak horse shoe magnet.
Ans: The displacement of the conductor will decrease on using a weak horseshoe magnet.
13. Draw magnetic field around a bar magnet.
Ans: The magnetic field around a bar magnet is as follows:
14. Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
15. Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.
Ans: According to the right-hand rule inside the loop, the magnetic field lines are directed perpendicular to the plane of paper in the inward direction while outside the loop magnetic field lines are directed out of the plane paper.
16. What is the role of the split ring in an electric motor?
Ans: Split ring is used for reversing the direction of current in the coil. It acts as a commutator i.e., the direction of current flowing in the motor coil reverses after half turn, giving rise to a continuous rotation of the coil and the axle.
17. State the principle of an electric generator.
Ans: The principle of an electric generator is electromagnetic induction i.e., When a rectangular coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field, an induced emf is generated between the ends of the coil.
18. Which sources produce alternating current?
Ans: The sources that produce alternating current are-
House generators
Car alternators
Bicycle dynamos
Hydroelectric Power Plants
Thermal power generators
Nuclear power generators,
AC generators etc.
19. Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
Ans: The two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances are-
use of earth wire and proper earthing.
use of fuse or MCB.
20. State whether the following statements are true or false.
a. An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
b. An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
c. The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight line
d. A wire with green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply.
21. When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in magnetic field largest?
Ans: When the conductor is placed with its length in a direction perpendicular to that of the magnetic field then the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in the magnetic field largest.
22. Name some devices in which electric motors are used.
Ans: Electric motors are used in all devices where we want to convert electrical energy into Mechanical energy. Some devices in which electric motors are used are-
Water pumps
Washing machines etc
23. When does an electric short circuit occur?
Ans: An electric short circuit occurs when the current in the circuit rises rapidly and the electrical connection draws an excessive amount of current from the supply it is because if either the insulation of wires used in an electric circuit is damaged or there is a fault in the appliances, live wire and neutral wire may come in direct contact.
24. Why is the earth pin thicker and longer than the live and the neutral pins?
Ans: The earth pin is made longer so that even by mistake it cannot be inserted into the hole for the live or neutral connection of the socket or it gets connected to the earth terminal earlier than the live and neutral pins and it is made thicker so that it does not enter into the live or neutral sockets.
25. A current-carrying straight conductor is placed in the east-west direction. What will be the direction of the force experienced by this conductor due to earth’s magnetic field? How will this force get affected?
a. reversing the direction of flow of current
Ans: The direction of earth’s magnetic field is from south to north and if current is from west to east. Therefore, force is vertically upwards. By reversing the direction of current, the direction of force will be reversed i.e., vertically downwards.
b. doubling the magnitude of current
Ans: The direction of earth’s magnetic field is from south to north and if current is from west to east. Therefore, force is vertically upwards. By doubling the magnitude of current the magnitude of the force is doubled.
26. Give two uses of electromagnets.
Ans: The two uses of electromagnets are-
27. A straight wire carrying electric current is moving out of plane of paper and is perpendicular to it. What is the direction and type of induced magnetic field?
Ans: If a straight wire carrying electric current is moving out of the plane of paper and is perpendicular to it then the induced magnetic field will be in the form of concentric circles in the plane of paper.
28. Why does the bulk of iron filings stick to the ends of a bar magnet and not at its centre?
Ans: Since at the ends magnetic strength is maximum and at canters magnetic strength is least. Therefore, the bulk of iron filings slick to the ends of a bar magnet and not at its centre.
29. A student draws three magnetic field lines 1,2 and 3 of a bar magnet with the help of a compass needle as shown in figure.
a. Is this configuration possible?
Ans: No, this configuration is not possible.
b. If not, what is
Ans: Because two field lines cannot intersect, and the direction of some field lines are wrong.
30. Suppose you are sifting in a room facing one of the wall. An electron beam moving horizontally from your back goes towards the wall in front you deflected to our left, what is the direction of magnetic field in the room?
Ans: The direction of the magnetic field in the room will be vertically upward.
31. A current through a horizontal power line flows in north to south direction. What is the direction of magnetic field directly above it?
i. at a point directly below it and
Ans: The direction of the magnetic field is West to East.
ii. at a point
Ans: The direction of the magnetic field is East to West.
32. Electric appliances like electric -press, toaster, fans etc are connected to electric mains through three-pin plug. Why?
Ans: Electric appliances are connected to three pin plugs because heavy appliances require earth wire to prevent short circuiting and to prevent users from getting shock in case of leakage of any current.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic casing of electric appliances?
Ans: The earth wire is used for the safety measures that have green insulation and is connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near our houses. Appliances like the electric press, toaster, table fan, refrigerator, etc have the metallic body that needs to connect to the earth wire this will provide a low resistance path for the. Thus, if any leakage of current occurs to the metallic body of the appliance it keeps potential to that of the earth, and this may prevent the severe electric shock.
2. We know a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experience a force due to which the conductor moves. How do we think the rod displaces if
(a) current in the rod is increased
Ans: Force acting on the current-carrying conductor depends on the strength of the magnetic field, amount of current flowing in the conductor, and length of the conductor. Therefore, when the current in the rod increase then the force also increases hence displacement of the rod increases.
(b) a stronger horseshoe is inserted
Ans: Force acting on the current-carrying conductor depends on the strength of the magnetic field, amount of current flowing in the conductor, and length of the conductor. Therefore, when a stronger horseshoe magnet is inserted, the magnetic field increases. So, force increase. Hence displacement increases.
(c) length of the rod is increased
Ans: Force acting on the current-carrying conductor depends on the strength of the magnetic field, amount of current flowing in the conductor, and length of the conductor. Therefore, when the length of the rod increase, force increases, and hence displacement increases.
3. What is the principle of electric motor?
Ans: Electric motor is a rotating device that can convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Which works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor placed perpendicular to a magnetic field experience a force.
State the function of,
(i) split ring
Ans: It acts as a commutator. The split ring reverses the direction of current through the coil after every half rotation and thus the direction of force is also reserved. As a result, the dc motor continues to rotate in the same direction.
(ii) field magnet used in the electric motor.
Ans: Field magnet used in the electric motor provided a strong magnetic field.
4. State three factors on which magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid depends.
Ans: The three factors on which the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid depends are the strength of the current flowing through the solenoid, the number of turns of the wire of the solenoid, and the nature of the material inside the solenoid.
5. What is a solenoid? Draw magnetic field lines showing the magnetic field inside and outside the current-carrying solenoid?
Ans: A solenoid is a coil that has many circular turns of insulated copper wire, which are arranged closely in the shape of a cylinder.
(a) Name four appliances wherein an electric motor is used as an important component. In what respect is it different from a generator?
Ans: The four appliances which have electric motor inside them are Mixers, washing machines, refrigerators, and blenders. In electric motor electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy whereas, in an electric generator mechanical energy is used to produce electricity.
(b) Define the terms used in the generator
(i) armature
Ans: Armature is a coil of a large number of turns of insulated copper wire wound over a soft iron core.
(ii) slip rings
Ans: Rings made up of brass that rotates along with the coil and helps in reversal of the direction of the current.
(iii) brushes
Ans: Brushes are made up of carbon which is pressed against the slip rings and are connected to an external circuit where output is obtained.
(a) What is the standard colour code followed for
(ii) neutral and
(iii) earth wires used in electric circuits?
(b) Which part of an electric appliance is earthed and why?
Ans: The metallic case of an electrical appliance is earthed because metals are good conductors of electricity and in case of current leakage i.e. live wire touches the metallic case of an appliance and then due to proper earthing all the excess amount of current flows down to the earth and thus, we can prevent ourselves from an electric shock.
(a) What is short-circuiting?
Ans: Overloading occurs when live and neutral wires come into direct contact, in that case, the current in the circuit increases abruptly. This is called short-circuiting.
(b) What is overloading? How can you avoid overloading?
Ans: Overloading means a huge amount of current flows in the circuit. It can occur when live and neutral wires come into direct contact. It can be avoided by not using too many appliances in a single socket and by using a fuse in the circuit which can prevent damage to the appliances and the circuit.
9. Define electromagnetic induction? Two circular coils A and B are placed close to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Explain.
Ans: Electromagnetic induction is a process by which the production of induced current in a conductor due to the change in the magnetic field in another conductor. When the current in first coil A is changed, the magnetic field associated with coil A also changes. Thus, the magnetic field lines around the secondary coil B will also change. Hence the change in magnetic field lines associated with the secondary coil B will induce electric current in it.
10. Why does a current carrying conductor keep in a magnetic field experience force? What is the direction of force acting on the conductor?
Ans: A current-carrying conductor is kept in a magnetic field experience force. This is because the electric current that flows through a conductor, produces this magnetic field. A force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction is exerted by this magnetic field.
(a) Distinguish between A.C and D.C?
Ans: The difference between AC and DC is listed below:
(b) Which source produces alternating current?
Ans: The sources that produce alternating current are AC generators, hydroelectric power plants, nuclear power generators, and thermal power generators.
(a) Define the term current rating of an electric fuse?
Ans: The maximum amount of current that can be passed through the fuse wire without melting it.
(b) Name the material used to make an electric fuse?
Ans: Alloy of Lead and Tin is used to make an electric fuse.
(c) Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances?
Ans: Electric fuses and earth wire.
13. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
Ans: The compass needle is a small bar magnet. When a compass needle is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact with that of the compass needle. Then due to repulsive force between like poles and attraction between unlike poles, the compass needle is deflected.
14. List the properties of magnetic lines of force.
Ans: Properties of magnetic field lines of force are as follows:
i. Outside a magnet, the field lines are directed from the N-pole of the magnet towards the S-pole, and inside the magnet, lines are directed from S-pole to N-pole.
ii. Magnetic field lines are closed curves.
iii. No two magnetic field lines intersect each other.
iv. The density of magnetic lines decreases, when the distance between the poles increases.
15. In activity 13.7, how do we think the displacement of rod AB will be affected if
(i) current is rod AB is increased,
Ans: If the current in rod AB is increased then its displacement will also increase.
(ii) a stronger horseshoe magnet is used, and
Ans: If a stronger horseshoe magnet is used then the displacement of rod AB will also increase.
(iii) length of the rod AB is increased?
Ans: If the length of the rod AB is increased, the force acting on it will increase hence, displacement of the rod also increases.
16. State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Ans: Fleming’s left-hand rule states that stretch the forefinger, the central finger, and the thumb of your left hand in a way they mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger shows the direction of the magnetic field and the central finger that of the current, then the thumb will point towards the direction of motion of the conductor or the force acting.
17. What is the principle of an electric motor?
Ans: Electric motor is a rotating device that can convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. An electric motor is based on the principle that the current-carrying conductor experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field. The direction of the force is given by Fleming’s left-hand rule, if the direction of the magnetic field and that of the current are mutually perpendicular.
18. Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
Ans: If a coil is moved rapidly between the south and north poles of a horseshoe magnet, relative to a coil the magnet is moved, and By keeping the coil still and rotating a magnet inside it are the different ways to induce a current in a coil.
19. An electric oven of \[2\] kW power rating is operated in a domestic electric circuit ( \[220\] V) that has a current rating of \[5\] A. What result do you expect? Explain.
Ans: The power rating of the electric oven (P) \[=2\text{ }kW\text{ }\]
\[\Rightarrow 2\times 1000=2000W\]
Current drawn \[(I)=\dfrac{P}{V}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{2000}{220}=9.09A\]
The current rating of the domestic electric circuit is given as $5$ A and the oven draws a current of \[9.09A\]. Which is more than the current rating; hence the circuit will be damaged due to overheating or overloading.
20. What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading of the domestic electric circuit?
Ans: Two separate circuits should be used for domestic purposes, one of 5A current rating of bulbs, fans, tubes, etc., and the other 15 A current rating for appliances with a higher current rating such as geysers, air coolers, electric iron, and stoves, etc. Too many appliances should never be connected to a single socket. A fuse of appropriate current rating should be used with the electric circuit for proper safety. These are the precautions we should take to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits.
21. List three methods of producing a magnetic field.
Ans: Three methods of producing magnetic fields are as follows,
Using permanent magnets or horse-shoe magnets at the place where the magnetic field is required.
By using electromagnets
Using current-carrying conductors or a current-carrying coil.
22. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a current-carrying solenoid with the help of a bar magnet? Explain.
Ans: The solenoid has a soft iron core with insulated copper wire over it so it can behave like a magnet. A strong and uniform magnetic field is produced around the solenoid when a current is passed through it. which is similar to that of the magnetic field of a bar magnet.
Solenoid behaves like a strong bar magnet. We can determine the poles of magnets formed by solenoids. The solenoid repels if the north pole of a bar magnet is brought near the negative terminal of the battery, the same for the south pole. As we know, poles repel each other.
23. Imagine that you are sitting in chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
Ans: From the problem, it is clear that an electron beam moving horizontally from the back wall towards the front wall is equivalent to a current flowing in the opposite direction. The deflection of the electron beam as seen by the observer is to his right side. Then by applying Fleming’s left-hand rule we find that the magnetic field is acting in a vertically downward direction.
24. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is
(i) pushed into the coil.
Ans: When a bar magnet is pushed into the coil of insulated copper wire connected to a galvanometer, the galvanometer gives a deflection towards the left direction.
(ii) withdrawn from inside the coil
Ans: When the bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil, then an induced current is set in the coil that deflects the galvanometer in the right direction.
(iii) held stationary inside the coil?
Ans: If the bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil, then there won’t be any induced current so the galvanometer does not show any deflection.
25. Two circular coils A and B are placed close to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
Ans: Yes, If the current in coil A is changed, then some current will be induced in coil B.
As the two circular coils, A and B are placed close to each other. When the current in coil A is changed, the magnetic field associated with it also changes. As coil B is placed near coil A, the magnetic field lines around coil B also change. Due to changes in magnetic field lines associated with coil B, a current is induced in coil B.
26. State the rule to determine the direction of a
(i) magnetic field produced around a straight current carrying conductor
Ans: The direction of the magnetic field produced around a straight conductor can be determined from the “Right-hand thumb Rule”.
(ii) force experienced by a current carrying straight conductor
Ans: To find the direction of force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field we make use of “Fleming’s left-hand rule”.
(iii) current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
Ans: For finding the direction of current induced in a coil we use “Fleming’s right-hand rule”.
27. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
Ans: The earth wires function as a safety measure, especially for those appliances like heater, electric, press, room cooler, etc that have a metallic body. The metallic body of the appliance is connected to the earth wire, which provides a low resistance conducting path for electric current. It ensures that any leakage of current to the metallic body of an appliance keeps its potential the same as of earth. As a result, the user is safe from severe electric shock, even if a user touches the body of the appliance.
28. An electron enters a magnetic field at right angles to it as shown in fig. The direction of the force acting on the electron will be:
to the right (b) to the left (c) out of the page (d) into the page
Ans: An electron enters a magnetic field at right angles to it so the direction of the force acting on the electron will be into the page.
When a conductor carrying current is placed perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, then the direction is given by Fleming’s left-hand rule. According to Fleming's Left-Hand rule, we know that the direction of force is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field and current. Here, the direction of current can be taken as the opposite to the direction of motion of electrons. The force acting on an electron is opposite to that. Therefore, in this case, it is into the page.
29. Consider a circular wire lying in the plane of the table and the direction current in it is antilock wise.
(i) Draw the magnetic field lines produced around it.
(ii) Why does magnetic field at the center of current carrying circular loop appear straight? Explain with diagram.
Ans: Because of the large curvature of magnetic field lines at centre.
30. If we place a compass needle near straight conductor carrying current
(a) What happens to the deflection of the compass needle if the direction of current reversed.
Ans: If we place a compass needle near a straight conductor carrying current then the deflection of the compass needle will reverse if the direction of current is reversed.
(b) What change will you notice in the compass needle if it is moved away from conductor but the current through the conductor remains the same?
Ans: If we place a compass needle near a straight conductor carrying current Deflection will decrease in the compass needle if it is moved away from the conductor but the current through the conductor remains the same.
31. A magnet is moving towards a coil as shown in figure.
(1) Which phenomenon is shown in figure.
Ans: Electromagnetic induction
(2) Which physical quantity is between magnet and coil? set up in the coil when there is a relative motion
Ans: Induced current
(3) What may be the cause of the production of that physical quantity?
Ans: Change in magnetic lines of forces through the coil
32. Suppose your science teacher asks you to demonstrate the phenomena of EMI with following materials:
(a) Two different coils land 2 of copper wire having large no. of turns 50 and 100 respectively.
(b) A non-conducting cylinder
(c) A battery
(d) A plug key
(e) A galvanometer
(i) Draw a labeled diagram of your demonstration setup.
(ii) How will you prove the phenomena of EMI.
Ans: When the key is closed, there is deflection in the galvanometer.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. Current- time graph from two different sources are shown in the figure.
(i) Name the type of current shown by graph (A) and (B)?
Ans: Graph A represents direct current and graph B represents alternating current.
(ii) Name any one source of shown by (A) and (B)?
Ans: Source of (A) can be dry cell and Source of (B) can be AC generator.
(iii) What is frequency of current in case (B)?
Ans: As graph B represents the alternating current the frequency is given by, $f=\dfrac{1}{T}$
$\Rightarrow f=\dfrac{1}{0.02}=50Hz$
(iv) Write two differences between current shown by (A) and (B)?
Ans: The differences between AC and DC is listed below
2. Explain the principle, construction and working of an electric motor with the help of a labeled diagram?
Principle: The electric motor is a rotating device that can convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. An electric motor is based on the principle that the current-carrying conductor experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field. The direction of the force is given by Fleming’s left-hand rule if the direction of the magnetic field and that of the current are mutually perpendicular.
Construction:
(i) Armature or coil- It consists of an insulated copper wire wound on a soft iron core.
(ii) Strong field magnet- two pole pieces of a strong magnet that can provide a strong magnetic field.
(iii) Split ring – split ring acts as a commutator which has two halves (R 1 and R 2 ) of a metallic ring that reverses the direction of the current in a coil.
(iv) Brushes- two carbon brushes touch the commutator (split ring).
(v) Battery – a battery is connected across the brushes.
Working : From the figure, ABCD is a rectangular coil of insulated copper wire and this coil is placed between the south and north poles of a magnetic field in such a way that the AB and CD are perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. The ends of the coil are connected to the two halves of a split ring, say P and Q. The external conducting edges of P and Q can touch two conducting stationary brushes X and Y.
Let the current in the coil ABCD of motor enters from the source battery through the conducting brush X, flow along ABCD, and finally flows back to the battery through brush Y. On applying Fleming’s left-hand rule we find that force acting on arm AB due to magnetic field pushes it downwards. But the force acting on the arm CD pushes it upwards. Thus, the coil and the axle rotate anticlockwise. Due to the action of split rings, P and Q change their contacts with brushes. Now, P makes contact with Y and Q with X. As a result, the current begins to flow in coil along DCBA. The arms are pushed in opposite directions and the coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
3. Draw a labeled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working. What is the function of split ring in an electric motor?
Ans: Electric motor labeled diagram of an electric motor is as follows:
Principle: The electric motor is a rotating device that can convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. An electric motor is based on the principle that the current-carrying conductor experiences a force when placed in a magnetic field. The direction of the force is given by Fleming’s left-hand rule if the direction of the magnetic field and that of the current are mutually perpendicular. Due to this force, the conductor begins to move, if it is free to rotate.
Working : Let the current in the coil ABCD of motor enters from the source battery through the conducting brush X, flow along ABCD, and finally flows back to the battery through brush Y. On applying Fleming’s left-hand rule we find that force acting on arm AB due to magnetic field pushes it downwards. But the force acting on the arm CD pushes it upwards. Thus, the coil and the axle rotate anticlockwise. Due to the action of split rings, P and Q change their contacts with brushes. Now, P makes contact with Y and Q with X. As a result, the current begins to flow in coil along DCBA. The arms are pushed in opposite directions and the coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
Split ring : It acts as a commutator. The split ring reverses the direction of current through the coil after every half rotation and thus the direction of force is also reserved. As a result, the dc motor continues to rotate in the same direction.
4. Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labeled diagram. What is the function of brushes?
Ans: Electric generator labeled diagram is given as follows:
Principle: An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
Working: In an electric generator, a rotating rectangular coil ABCD is placed between the south and north poles of a permanent magnet. As shown in the figure the two ends of this coil are connected to the two rings R1 and R2. Let the, in the beginning, brushes B1 and B2 are kept pressed separately on rings R1 and R2 respectively. The two rings are internally attached to an axle which may be mechanically rotated from outside for the rotation of the coil inside the magnetic field. To show the flow of current in the given external circuit, the outer ends of the two brushes are connected to the galvanometer. The arm AB moves upwards and the arm CD moves downwards when the axle attached to the two rings R1 and R2 is rotated then the magnetic field is produced by the permanent magnet. By applying the induced currents are in these arms along the directions AB and CD by Fleming’s right-hand rule. Thus, in the direction of ABCD an induced current flows. The current in the external circuit flows from B2 to B1.
After half rotation, arm AB moves downward and arms CD upward to change the direction opposite to the first case. Thus, after every half rotation current changes its direction and an alternate current is obtained in the generator. Brushes B1 and B2 are kept pressed on the two slip rings R1 and R2 separately. The outer ends of the brushes are connected to the galvanometer. Thus, brushes help to show the flow of current in the given external circuit.
A magnet is a material that has two poles namely a north pole and a south pole.
2. Magnetic Field and Magnetic Field Lines
A magnetic field is a phenomenon that is found in the area around a magnet or an electric current that creates a magnetic force on the object placed near it.
(Image will be Uploaded soon)
Magnetic field visually lines represent a magnetic field.
A magnetic field possesses both magnitude and direction.
The effect of the magnetic field is always maximum near the magnet and it decreases as the distance increases.
A compass needle also acts as a bar magnet.
The shape of the magnetic field around a current-carrying straight wire is in the form of concentric circles.
3. Right-Hand Thumb Rule or Maxwell’s Corkscrew Rule
The direction of the magnetic field around a current carrying-conductor is detected with the help of right-hand thumb rule.
Maxwell’s corkscrew rule is another method for detecting the direction of magnetic field lines around a straight current-carrying conductor.
If a straight wire is bent into a circle, the direction of the magnetic field of the circular wire can be found at each part of the wire with the application of right-hand thumb rule.
The shape of the magnetic field lines is in the form of straight lines towards the centre of the circular current-carrying wire due to decrease in strength.
4. Solenoid
A solenoid is a cylindrical shaped coil of wire whose one end acts as a magnetic north pole and the other end acts as a magnetic south pole similar to that of a bar magnet and the magnetic field is uniform inside it.
An electromagnet can be made when a piece of magnetic material is placed inside the solenoid.
5. Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule
When a current-carrying conductor and a magnet are placed near, they produce an equal and opposite force on each other that becomes maximum when the direction of the magnetic field and electric current is at 90°.
The direction of the force is found out with the application of Fleming's left-hand rule where the thumb represents the direction of the force and the index finger and middle finger represents the magnetic field and current respectively. The three fingers are perpendicular to each other.
6. Electric Motor
The electrical energy can be converted into mechanical energy with the help of an electric motor.
The presence of the electric current in a circuit is detected with the help of a galvanometer.
7. Electromagnetic Induction
When a magnet is moved near an electric coil attached to a galvanometer, it produces a potential difference that creates an induced current in the coil. This process is called electromagnetic induction.
The direction of the induced current can be found out with the application of Fleming's right-hand rule.
8. Electric Generator
The device in which mechanical energy is used to rotate a conductor inside a magnetic field to produce electric current is called an electric generator.
The electric current is of two types - Direct current and Alternating current.
When the electric current alters direction at equal intervals, it is called alternating current. The device that produces alternating current is called an AC generator.
When the electric current does not change direction with time, it is called direct current. The device that produces direct current is called a DC generator.
9. Electric Fuse
An electric fuse stops the flow of high electric current during overloading or short-circuiting occurs in our home.
The students are advised to refer to the above-given summary before attempting the important questions for class 10 science chapter 13. The students can download the Vedantu app on mobile and tablets also to access the PDF of chapter 13 science class 10 important questions . Apart from the NCERT question, the students must have a look at the class 10 science chapter 13 extra questions provided by Vedantu to hone their knowledge regarding the magnetic effects of electric current.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Science

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current 2023-24
Q1. What are the properties of magnetic field lines according to Chapter 13 of Class 10 Science?
Ans: Magnetic field lines refer to imaginary lines that are drawn around a magnet. The line's density generally tests the magnitude of a magnetic field. Magnetic field lines consist of many properties. Some of them include:
Magnetic field lines cannot traverse between each other
Magnetic field lines can emerge from the north pole but terminate from the south pole.
The direction of magnetic fields inside a magnet is from the south pole to the north pole.
Q2. Define Fleming's left-hand rule according to Chapter 13 of Class 10 Science.
Ans: With the help of Fleming's left-hand rule, one can determine the direction of the magnetic field. According to this rule, if you put your middle finger, forefinger, and thumb of your left hand at right angles perpendicular to the same of your right hand then the direction to which the thumb is pointing detects the direction of the magnetic force. Whereas the middle finger and the forefinger will determine the direction in which the magnetic field moves.
Q3. What are the important concepts in Chapter 13 of Class 10 Science?
Ans: Magnetic Effects of Electric current is an important chapter for Class 8 Science from the examination point of view. There are many important concepts that Students must learn and understand in this chapter. Some of these concepts include a definition of the magnet, magnetic field and magnetic field lines, Maxwell's Corkscrew rule, solenoid, Fleming's left-hand rule, electric motor, electromagnetic induction, electric generator, and electric fuse. There are many important questions that are taken from these important concepts.
Q4. What is the cause of the magnetic effect of current as explained in Chapter 13 of Class 10 Science?
Ans: It is known that electric current has the capacity to produce magnetic effects. This magnetic effect of electric current is popularly known as the electromagnetic effect. For example, a solenoid behaves like a magnetic bar when electric current passes through it. Similarly, When a compass is brought close to an electric current conductor, then the needle of the compass gets deflected. This mainly happens because of the flow of electricity in the conductor. This observation proves that electric current does produce a magnetic effect.
Q5. Are there any Numerical in the magnetic effect of electric current topic of Chapter 13 of Class 10 Science?
Ans: Yes, there are numericals available in Chapter 8 of Class 8 Science. The magnetic effect of electric current is an important chapter for Students to learn from the examination point of view. There are many important questions that are asked in this chapter. Out of which, the numerical questions are the most important ones. The main formulas in the chapter help to calculate the electric flow. Vedantu provides students with a simple explanation of all numerical questions.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- DK Goel Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
- STATE WISE BOOKS
- ENGINEERING EXAM
- SCHOLARSHIP OLYMPIAD
- STATE BOOKS
CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ Questions
CBSE Term 1 exam is not so far and surely you have begun the preparation for the board exam. Therefore we have dedicated this page to help you out in your preparation. This year for the first time the board has introduced the Case based Questions which will be asked in the Term 1 exam that is likely to be held in November-December.
Therefore, we have brought you the CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ on this page. The questions are given in objective types. Such types of questions are solved by reading the given scenario in the paragraph.
All these science case study questions are developed as per the new CBSE Pattern. The team of subject matter experts have crafted the given MCQs. The Case Based Questions that we are providing here are worthy to solve and practice because class 10th syllabus has been taken into consideration while preparing the problems.
CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study, Assertion & Reasoning, MCQ
The Class tenth CBSE Science Case Study, Assertion & Reasoning, MCQs are very helpful in practicing and getting a deep understanding in the topics of science. However, a comprehensible knowledge of NCERT Science Book is a must to be able to solve these types of problems.
The PDF that is available here to download contains the problems in three different variants; One is general objective types of questions that is MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions), second one is Assertion and Reasoning and the last one is Case-Based Questions.
If you Download PDF CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study from the given links, then you will be able to get the quick revision for each chapter that will help you to recall your learnings and give you information about some important Chemicals Formulas and reactions.
What are Assertion & Reasoning Questions?
Assertion & Reasoning questions are basically a type of multiple-choice question that is solved by reading the given statement and the reason. The question typically consists of one statement followed by its reason. Students' duty is to verify both statements and reason whether they are correct or not and if they are correct then it is time to look at whether the given statement truly satisfies the reason or not.
These questions should not be difficult to solve but you have to have rigorous and extensive practice. The Assertion & Reasoning questions along with the solutions are given in the CBSE Class 10 Science case study 2021-2022 PDF that is available here.
Class 10th has very basic and important chapters that are necessary to solve. A few chapters that are available in the beginning of the science books are Chemical Reactions and Equations, Acids, Bases and Salts, Metals and Non-metals, Carbon and Its Compounds, Periodic Classification of Elements, Life Processes, etc.
Since you are here to find out the CBSE Class 10 Science MCQ Based Questions, the possibilities are you need CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions too.
FAQs on CBSE Class 10th Science Case Study Questions

Case Study Questions are based on the data which are given in the form of passage. These types of questions generally consist of real life examples. Usually it contains upto 4 or 5 questions.
To prepare for Class 10 Science MCQ Be thorough with the concepts, Practice the questions regularly, Attempt online tests as much as you can. To do all these things visit the Selfstudys.com. They are providing everything for free of cost.
In class 10 Science Based Questions you will be asked to answer the questions that are explained in the standard Xth Science Syllabus. However, the problems will be related to real world examples.
To find Class 10 Science Chapter wise Assertion and Reason Questions you simply need to reach at the Selfstudys website. It provides all the study resources for free of cost. You will be able to download the assertion reason with solutions as well.
No, CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ Question is not difficult, if you pay a good attention to the given paragraph. It is important to be able to find the tiny details in the passage to answer the Case Based questions.

CBSE Class 10 Exams Finish, When Can You Expect Results? Details Here

CBSE Board Class 10 Information Technology Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

CBSE Board Class 10 Computer Applications Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

CBSE Class 10 Information Technology Exam 2024 : Most Important Questions Answers for Last-Minute Revision


CBSE Class 10 Computer Applications Exam 2024 : Most Important Questions Answers for Last-Minute Revision

CBSE Board Class 10 Maths Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Case Based Questions - Our Environment
Case study - 1.
All organisms such as plants, animals, microorganisms and human beings as well as the physical surroundings interact with each other and maintain a balance in nature. All the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem. Thus, an ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals.
Q1: What is natural ecosystem? Ans: An environment where living organism and non- living interact with each other freely in nature is called as natural ecosystem. Q2: what are the examples of artificial ecosystem? Ans: Gardens, crop- fields Q3: What are consumers? Ans: Organism which consume food either directly or indirectly by feeding on one another animals are called as consumers. Q4: What are the type of consumers? Ans: They are herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites. Q5: What are producers? Ans: The green plants and some bacteria which make their food by using sunlight i.e photosynthesis are called as producers.
Case Study - 2
The food we eat acts as a fuel to provide us energy to do work. Thus the interactions among various components of the environment involves flow of energy from one component of the system to another. As we have studied, the autotrophs capture the energy present in sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. This energy supports all the activities of the living world. From autotrophs, the energy goes to the heterotrophs and decomposers.
Q1: What is food chain? Ans: A series of organism feeding on one another and taking part in various biotic levels is called food chain. Q2: Give a example of one terrestrial food chain. Ans: Sunlight ⇒ plants (producers) ⇒ Goat/ Deer (herbivores) ⇒ Tiger (carnivores) Q3: What are the feature of food chain? Ans: It is unidirectional The energy available at each level gets diminished due to loss at each level. Q4: What do you meant by biological magnification? Ans: The gradual increase in the concentration of any substance ( generally toxic) in trophic levels is called as biological magnification. Q5: What is the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaching the next level of consumers? Ans: 10%
Case Study - 3
In our daily activities, we generate a lot of material that are thrown away. What are some of these waste materials? What happens after we throw them away? Let us perform an activity to find answers to these questions.
- Collect waste material from your homes. This could include all the waste generated during a day, like kitchen waste (spoilt food, vegetable peels, used tea leaves, milk packets and empty cartons), waste paper, empty medicine bottles/strips/bubble packs, old and torn clothes and broken footwear.
- Bury this material in a pit in the school garden or if there is no space available, you can collect the material in an old bucket/ flower pot and cover with at least 15 cm of soil.
- Keep this material moist and observe at 15-day intervals.
- What are the materials that remain unchanged over long periods of time?
- What are the materials which change their form and structure over time?
- Of these materials that are changed, which ones change the fastest?
We have seen in the chapter on ‘Life Processes’ that the food we eat is digested by various enzymes in our body. Have you ever wondered why the same enzyme does not break-down everything we eat? Enzymes are specific in their action, specific enzymes are needed for the break-down of a particular substance. That is why we will not get any energy if we try to eat coal! Because of this, many human-made materials like plastics will not be broken down by the action of bacteria or other saprophytes. These materials will be acted upon by physical processes like heat and pressure, but under the ambient conditions found in our environment, these persist for a long time.
Q1: What is biodegradable substances? Ans: The substances that are broken down by biological process are called as biodegradable substances. Example: Vegetables waste materials. Q2: What are the examples of non- biodegradable substances? Ans: Plastic, rubber, foam, batteries etc. Q3: What are the ways through which we can reduce pollution especially the non- biodegradable waste? Ans:
- We can use RRR methods i.e reduce, reuse and recycle.
- Reduce the use of plastic.
Q4: What are the effects of biodegradable substances on our environment? Ans:
- Release green house gases.
- They are breeding ground for mosquitoes and houseflies causing various disease.
Q5: What are the non- biodegradable on environment? Ans:
- causes soil pollution and sometimes air pollution when burnt in air.
- death of cattles due to ingestion of these waste.
- choking of drainage system.
Case Study - 4
We are an integral part of the environment. Changes in the environment affect us and our activities change the environment around us Ozone (O3 ) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. While O2 , which we normally refer to as oxygen, is essential for all aerobic forms of life. Ozone, is a deadly poison. However, at the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
Q1: How does ozone is formed? Ans: The UV radiations coming from the sun split the molecular oxygen into nascent oxygen. When these nascent oxygen combined to molecular oxygen, it forms ozone(O3). Q2: In which layer of atmosphere does ozone is present? Ans: The ozone is present in the stratosphere layer of atmosphere just above troposphere. Q3: What are the causes for ozone depletion? Ans: The synthetic chemicals like CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) which used as refrigerants amd in the fire extinguisher. Q4: Write the chemical reaction for the formation of ozone? Ans: O2 ⇒ [O] + [O] [O] + O2 ⇒ O3 (ozone) Q5: What are the effects of UV radiations? Ans: It causes different types of cancer in human beings.
Case study – 5
In Kunjpura village, located in Karnal district, Haryana, Aditya Aggarwal and his older brother Amit Aggarwal run Tee Cee Industries, a steel plant set up by their ancestors in 1984. Along with this, they also run a gaushala that houses 1,200 cows that can no longer produce milk. The cow shelter was manageable but running the steel plant was turning out to be expensive because they spent a whopping Rs 5 lakh every month on electricity. The brothers struck upon an idea. Why not run the factory with the biogas produced from cow dung from the shelter and other gaushalas, along with bio and agri led Aditya and Amit to start Amrit Fertilizers, a biogas project, in 2014, without any government support.
Q1: Raw material used in bio gas plant is (a) Animal dung (b) Crop residue (c) Food waste (d) All of the above Ans: (d) Explanation: Biogas is produced through a process called anaerobic digestion, in which organic materials are broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen. Various organic materials can be used as raw materials in a biogas plant, including animal dung, crop residues, and food waste. All of these materials are rich in organic matter, which serves as a source of energy for the microorganisms to produce biogas. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) All of the above. Q2: Biogas is a better fuel than animal dung cake because (i) Biogas has lower calorific value. (ii) Animal dung cake has higher calorific value. (iii) Biogas has high heating capacity. (iv) Biogas burns without smoke. (a) (i) only (b) (ii) only (c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i) and (ii) Ans: (c) Explanation: Biogas is a better fuel than animal dung cake for several reasons. Biogas has a higher calorific value compared to animal dung cake, meaning it releases more energy when burned. Additionally, biogas burns without producing smoke, making it a cleaner fuel option. The statements (iii) and (iv) are correct, as biogas indeed has a high heating capacity and burns without smoke. Therefore, the correct answer is (c) (iii) and (iv). Q3: Biogas is formed in the (a) presence of air only. (b) presence of water only. (c) absence of air only. (d) presence of water and absence of air. Ans: (d) Explanation: Biogas is formed through the process of anaerobic digestion, which occurs in the absence of air (oxygen). The microorganisms that produce biogas thrive in an oxygen-free environment. However, the presence of water is also important for the process to take place. Water helps maintain the right conditions for the microorganisms to break down organic materials and produce biogas. Therefore, the correct answer is (d) presence of water and absence of air. Q4: Biogas is a mixture of the following gases. (a) Ethane, Carbon monoxide, Nitrogen and Butane (b) Methane, Hydrogen, Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen (c) Butane, Carbon monoxide, Propane and Hydrogen (d) Carbon monoxide, Sulphur dioxide and Hydrogen Ans: (b) Explanation: Biogas is primarily composed of methane (CH4), which is the main combustible component and provides the energy content. It also contains smaller amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), some traces of hydrogen (H2), and in some cases, small quantities of nitrogen (N2) and other gases. The option (b) correctly lists the main components of biogas, which are methane, hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. Therefore, the correct answer is (b) Methane, Hydrogen, Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen.
Case Study – 6
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases. The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers. Primary producers, or autotrophs, can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds, whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis, most life could not exist if the sun disappeared. Even so, it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life, chemotrophs, that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents, thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
Q1: If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy? (a) 10,000 J (b) 100 J (c) 1000 J (d) It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant Ans: (b) Explanation: The efficiency of energy conversion from solar energy to food energy in plants is generally low. Only a small fraction of the solar energy is converted through photosynthesis into food energy (organic matter). It's estimated that, on average, about 1% to 3% of the solar energy is converted into chemical energy in plants. Therefore, in this case, if 10,000 J of solar energy falls on green plants, approximately 100 J (1% of 10,000 J) would be converted into food energy. The correct answer is (b) 100 J. Q2: Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of (a) Energy is bidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. (b) Energy is repeatedly circulation and matter is unidirectional. (c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. (d) Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional. Ans: (c) Explanation: In an ecosystem, energy flows in a unidirectional manner, usually from the Sun through producers (plants), consumers, and ultimately decomposers. Matter, on the other hand, circulates within the ecosystem through various biogeochemical cycles (such as the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, etc.), which involve the uptake, use, and recycling of elements like carbon, nitrogen, and other nutrients. Therefore, the correct answer is (c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating. Q3: Mr. X is eating curd/yogurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying (a) First trophic level (b) Second trophic level (c) Third trophic level (d) Fourth trophic level Ans: (c) Explanation: When Mr. X eats curd/yogurt, he is consuming a product derived from milk, which is obtained from animals such as cows. Since he is consuming a product derived from primary consumers (herbivores), he should be considered as occupying the third trophic level in the food chain. The primary producers (plants) form the first trophic level, the herbivores (consumers that eat plants) form the second trophic level, and the carnivores or omnivores that eat herbivores occupy higher trophic levels. Therefore, the correct answer is (c) Third trophic level. Q4: Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain? (a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels (b) Less availability of food (c) Polluted air (d) Water Ans: (a) Explanation: The decrease in energy at higher trophic levels is a key factor that limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain. As energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next, there is a significant loss of energy, usually in the form of heat, due to metabolic processes and inefficiencies in energy conversion. This decrease in available energy limits the amount of energy that can sustain organisms at higher trophic levels. As a result, there is typically a decrease in the number of trophic levels in a food chain, with fewer organisms occupying higher trophic levels. Therefore, the correct answer is (a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels. Q5: The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers: (a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain (b) Do not breakdown organic compounds (c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms (d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms Ans: (a) Explanation: The decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients in ecosystems. However, they do not occupy specific trophic levels in a linear food chain like producers and consumers do. Instead, decomposers act at every trophic level of the food chain and ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter and returning nutrients to the soil, which are then taken up by plants. This cycling of nutrients is essential for the functioning of ecosystems but does not fit into the traditional linear structure of a food chain. Therefore, the correct reason is (a) Decomposers act at every trophic level of the food chain.
Top Courses for Class 10
Extra questions, video lectures, sample paper, previous year questions with solutions, practice quizzes, study material, objective type questions, viva questions, important questions, shortcuts and tricks, mock tests for examination, past year papers, semester notes.

Case Based Questions: Our Environment Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: our environment, case based questions: our environment notes, case based questions: our environment class 10, study case based questions: our environment on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions Download Free PDF
If you are looking for the CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions in PDF, then you are in the right place. CBSE 10th Class Case Study for the Science Subject is available here. These Case studies can help the students to solve the different types of questions that are based on the case study.

CBSE Board will be asking case study questions based on Science subjects in the upcoming board exams. Thus, it becomes an essential resource to study.
The Science Subject case study for class 10th covers a wide range of chapters from the Science. Students willing to score good marks in their board exams can use it. The questions are highly interactive and it allows students to use their thoughts and skills to solve such kinds of questions.
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning . Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of elements
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 How do organisms reproduce?
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Light reflection and refraction
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Human eye and colorful world
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Electricity
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Magnetic effects of current
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Our Environment
The above Case studies for CBSE Class 10 Science will help you to score good marks in the Case Study questions that have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study have been developed by experts of cbseexperts.com for benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 10 Science Assertion and Reason Questions
Case Study Type Questions in Science Class 10
Case Study Type Questions in Science Class 10 include the information or data. Students willing to solve them are required to read the passage carefully and then solve them. While solving the paragraph the ideal way is to highlight the key information or given data.
Because later it will ease them to write the final answers. Science Case study type questions consist of 4 to 5 questions that should be answered in an MCQ manner.
While reading the paragraph students will get the clue in between about the possible answer of the question. They should definitely highlight those questions. This is the best way to solve such kind of Case study Type Questions.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Case Study Questions
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Redox reactions are those reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur Simultaneously. A redox reaction is made up of two half reactions. In the first half reaction, oxidation takes place and in second half reaction, reduction occurs. Oxidation is a process in which a substance loses electrons and in reduction, a substance gains electrons. The substance which gains electrons is reduced and acts as an oxidising agent. On the other hand, a substance which loses electrons is oxidised and acts as a reducing agent. (i) Which of the following is a redox reaction?
(ii) Identify the reaction in which H2 02 is acting as a reducing agent.
(iii) For the following reactions, identify the one in which H 2 S acts as a reducing agent.
(iv) For the following reaction, identify the correct statement. \(\mathrm{ZnO}+\mathrm{CO} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\)
(v) In the following reaction, which substance is reduced? \(\mathrm{PbS}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbSO}_{4}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
(ii) If the pH of a solution is 8, then its [H + ] ion is
(iii) In terms of acidic strength, which one of the following is in the correct increasing order?
(iv) Which of the following compounds does not give H + ions in aqueous solution?
(v) Four solutions labelled as P, Q, Rand Shave pH values 1, 9, 3 and 13 respectively. Which of the following statements about the given solutions is incorrect?
Baking powder produces carbon dioxide on heating, so it is used in cooking to make the batter spongy. Although, baking soda also produces CO 2 on heating, but it is not used in cooking because on heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate along with carbon dioxide. Sodium carbonate, thus, produced, makes the taste bitter. Baking powder is the mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid. Generally, tartaric acid is mixed with baking soda to make baking powder. When baking powder is heated, NaHCO 3 decomposes to give CO 2 which makes bread and cake fluffy. Tartaric acid helps to remove bitter taste due to formation of sodium tartrate. \(2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+ \ \ \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{6} \mathrm{O}_{6} \quad \longrightarrow \quad 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{4} \mathrm{O}_{6}\) Baking soda Tartaric acid Carbon dioxide Sodium tartrate (i) On passing excess CO 2 gas in aqueous solution of sodium carbonate, the substance obtained is
(ii) When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to acetic acid, it evolves a gas. Which of the following statements are true about the gas evolved? (I) It turns lime water milky (II) It extinguishes a burning splinter (III) It dissolves in a solution of sodium hydroxide (IV) It has a pungent odour
(iii) Select the correct statement regarding sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(iv) Acetic acid was added to a solid X kept in a test tube. A colourless and odourless gas was evolved. The gas was passed through lime water which turned milky. It was concluded that
(v) Which of the following statements are correct regarding baking soda? (I) Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (II) On heating, baking soda gives sodium carbonate (III) It is used for manufacture of soap (IV) It is an ingredient of baking powder
The chemical reactivity of an element depends upon its electronic configuration. All elements having less than eight electrons in the outermost shell show chemical reactivity. During chemical reactions, atoms of all elements tend to achieve a completely filled valence shell. Metals are electropositive in nature. They have tendency to lose one or more electrons present in the valence shell of their atoms to form cations and achieve nearest noble gas configuration. The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from one element to other are known as ionic or electrovalent compounds. (i) The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are: X : 2 Y: 2, 8, 7 Z : 2, 8, 2 Which of the following is correct regarding these elements?
(ii) Element X reacts with element Y to form a compound Z. During the formation of compound Z, atoms of X lose one electron each whereas atoms of Y gain one electron each. Which of the following properties is not shown by compound Z?
(iii) Which of the following is correct representation of formation of magnesium chloride?
(iv) The electronic configuration of sodium ion is
(v)Which of the following represents an electropositive element?
A hydrocarbon (P) has the molecular formula C 10 H 22 .A hydrocarbon (Q) has two carbon atoms less than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. A hydrocarbon (R) has two carbon atoms more than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. (i) What is the molecular formula of (Q) ?
(ii) To which homologous series do the compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong?
(iii) What is the molecular formula of (R) ?
(iv) Identify the correct statement about compounds (P), (Q) and (R) .
(v) Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are
The recurrence of properties of the elements after a certain regular intervals, when they are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic numbers, is called periodicity. There are a number of physical properties such as atomic size, metallic and non -metallic character, etc. which show periodic variation. In periodic table, various properties vary differently from moving left to right in a period and going down in a group. In a period, properties vary because from moving left to right in a period, number of shells remain same but valence electron increases by one number hence nuclear charge increases. In a group, on going down, number of valence shells increases while number of valence electrons remains same. (i) From top to bottom in a group of the periodic table, the electropositive character of the element
(ii) Which element has the largest size in the second period?
(iii) Which of the following elements has three valence electrons?
(iv) In the periodic table, the metallic character of elements (a) decreases from left to right and decreases down the group (b) decreases from left to right and increases down the group (c) increases from left to right and increases down the group (d) increases from left to right and decreases down the group (v) Which of the following increases along the period?
The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal. It is a narrow tube of about 6 metres which lies coiled in the abdomen. The length of small intestine varies in different animals depending on the type of food they eat. (i) Humans are not able to digest cellulose whereas they are able to digest starch due to
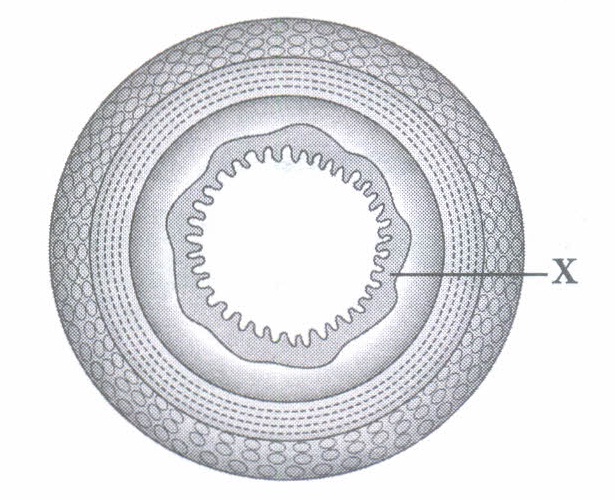
(iii) Butter cannot be digested in the stomach as lipase and bile are(a) released in small intestine
(iv) Which of the following is a correct statement? (a) Herbivores have shorter small intestine as they eat grasses (b) Carnivores have larger small intestine as they eat meat (c) Herbivores have larger small intestine as they eat grasses (d) None of these (v) Various types of movements are generated by the ______ layer of the small intestine.
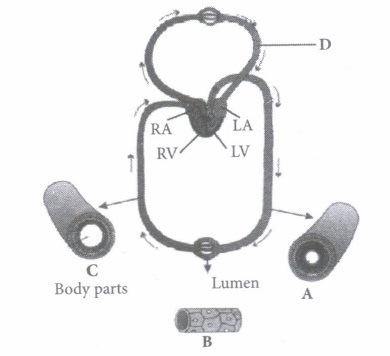
(iii) Which of the following animals shows double circulatory pathway?
(v) Select the option which properly represents pulmonary circulation in humans. \(\text { (a) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \text { Right ventricle }\) \(\text { (b) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Right ventricle }\) \(\text { (c) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \rightarrow \text { Left auricle }\) \(\text { (d) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}>\text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \gg \text { Left auricle }\)
Spore formation, method of asexual reproduction is used by unicellular as well as multicellular organisms.Spores are microscopic units which could be air borne or are present in soil, etc. (i) A slice of bread kept in open for sometime shows growing white cottony mass which later turns black. This happens because (a) bacterial spores present in air germinate on the surface of bread slice (b) fungal spores present in air germinate on the surface of bread slice (c) protozoan microbes start feeding on bread slice (d) none ef these. (ii) Spore formation can be seen in
(iii) Bulb like structure at top of erect hyphae where spores are produced is
Gregor Mendel conducted hybridisation experiments on garden peas for seven years and proposed the laws of inheritance in living organisms. He investigated characters in the garden pea plant that were manifested as two opposing traits, e.g., tall or dwarf plants, yellow and green seeds, etc. (i) Among the seven pairs of contrasting traits in pea plant as studied by Mendel, the number of traits related to flower, pod and seed respectively were
(ii) The colour based contrasting traits in seven contrasting pairs, studied by Mendel in pea plant were
(iii) Refer to the given table of contrasting traits in pea plants studied by Mendel.
Which of the given traits is correctly placed? (a) (i), (ii) and (iii) only (b) (ii), (iii) and (iv) only (c) (ii) and (iii) only (d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) (iv) Some of the dominant traits studied by Mendel were (a) round seed shape, green seed colour and axial flower position (b) terminal flower position, green pod colour and inflated pod shape (c) violet flower colour, green pod colour and round seed shape (d) wrinkled seed shape, yellow pod colour and axial flower position. (v) Which of the following characters was not chosen by Mendel?
(ii) The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called
(iii) When a ray is refracted through a prism, then
(iv) The angle of deviation depends on
(v) The rectangular surfaces of a prism are known as
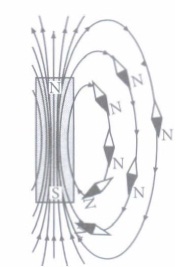
Some harmful non-biodegradable chemicals, i.e., pesticides (e.g., DDT) and heavy metals (e.g., mercury, arsenic cadmium, etc.) enter the bodies of organism through the food chain and go on concentrating at each trophic level. This phenomenon is called bio-magnification or biological magnification. (i) Refer to the given food chain Phytoplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Zooplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Small fish \(\longrightarrow\) Large fish \(\longrightarrow\) Fish eating birds If concentration of DDT in small fish is estimated to be 0.5 ppm, then amount of DDT in zooplankton and large fish would respectively be
(ii) Refer to the given table.
According to the given data. The correct order in a food chain will be
(iv) Higher amount of DDT disturb calcium metabolism of birds. This results in
(v) When animals are sprayed with poisons, they may die immediately, but their bodies still contain the poison. The poison in their bodies will then be passed on to the animals which eat them. What would be the consequence of a mass poisoning of the rabbit population in a grazing food chain and why? (a) Plants would die quickly as they are eaten by rabbits (b) Grasshopper would die quickly as all the animals in the food web would be affected (c) Western rattlesnakes would quickly become poisoned as they eat rabbits (d) Hawk would become poisoned as they feed on rabbits
(v) Greenhouse effect is due to
Energy flow is the key function of an ecosystem. It is determined by the two basic laws of thermodynamics. Flow of energy in our ecosystem is unidirectional. Green plants capture approximately about 1% of the solar energy incident on the earth to carry out the process of photosynthesis. In an ecosystem, transfer of energy follows 10 percent law, i.e., only 10% energy is transferred from one trophic level to another and remaining 90% of energy is lost in respiration. (i) Read the given statements and select the incorrect one(s). I. At each trophic level organisms utilise energy in respiration. II. Only 10 percent of the solar radiations that fall on earth is used by green plants. III. Green plants are the ultimate source of entire energy as most of the food chain begin with them. IV. A food chain usually consist of 3-4 trophic levels.
(ii) Refer to the given flow chart. Plants \(\rightarrow\) Rat \(\rightarrow\) Snake 20 units 2 units 0.2 unit The given flow chart states that (a) flow of energy in an ecosystem is unidirectional (b) as we move along in a food chain the number of individuals at each trophic level decreases (c) only 10% of the total energy becomes available to next trophic level (d) both (a) and (c). (iii) Nearly 90% of the energy is wasted while moving from one trophic level to other. This energy is used in
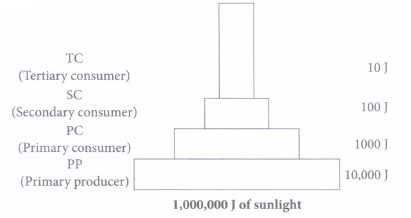
(v) Which of the following correctly states the processes involved in energy transfer between the trophic levels?
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject case study questions answer keys.
(I) (b) : H 2 is oxidised to HCI while Cl 2 is reduced to HCl. (ii) (c) \((iii) (c): 2 \mathrm{Fe} \mathrm{Cl}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{s}\) H 2 Sitself gets oxidised to Sand reduces FeCl 3 to FeCI 2 (iv) (a ): ZnO is reduced to Zn and CO is oxidised to CO 2 (v) (b) : H 2 O 2 is reduced to water by removal of oxygen.
(i) (c): As the pH value increases from 7 to 14, it represents decrease in H+ ion concentration in the solution. (ii) (c) : pH = -log l0 [H + ] = 8 log l0 [H + ] =-8 [H + ] = 10 - 8 mol/L (iii) (a) (iv) (b): C 2 H 5 OH is not an ionic compound, it is a covalent compound and hence does not give H + ions in aqueous solution. (v) (c) : (a) Lower the pH of the solution, more acidic is the solution and higher is the [H + ] ions Thus, solution P (pH = 1) has higher [H + ] ions than solution R (pH = 3). (b) Higher the pH of the solution, more basic is the solution and higher is the [OH - ] ions Thus, solution Q (pH = 9) has lower [OH - ] ions than solution S (pH = l3). (c) Solution P (pH = 1) is acidic which turns blue litmus solution red whereas solution Q (pH = 9) is basic which turns red litmus solution blue. (d) Solution P (pH = 1) is highly acidic while solution S (pH = l3) is highly basic and solution Q (pH = 9) is weakly basic.
\({ (i) }(\mathrm{b}): \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}\) (ii) (b) : \(\mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COONa}\) \(+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \uparrow+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) Carbon dioxide gas is evolved which turns limewater milky. It extinguishes a burning splinter since it is not a supporter of combustion. It dissolves in sodium hydroxide solution and it is an odourless gas. \({ (iii) }(\mathrm{c}): 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3} \stackrel{\text { Heat }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) NaHCO 3 is soluble in water. \({ (iv) }(\mathbf{b}): \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \longrightarrow\) \(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COONa}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) (v) (c): It is not used in manufacture of soap .
(i) (d) (Ii) (b): '2' is an ionic compound \({ (iii) }(\mathrm{a}): \mathrm{Mg} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}+2 e^{-}\) \(\mathrm{Cl}+e^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\) \(\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_{2}\) 2,8,2 2,8 2,8,7 2,8,8 \((\text { iv })(\mathrm{d}): \mathrm{Na} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{+}+e^{-}\) 2,8,1 2,8 (v) (c): (a) and (d) represent electronegative elements and (b) represents a noble gas.
(i) (c) : Molecular formula of (Q) is CSH1Sas it has two carbon atoms less than (P). (ii) (c): Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are alkanes having general formula C n H 2n+2 . (iii) (a): Molecular formula of (R) is C 12 H 26 as it has two carbon atoms more than (P) (iv) (b): Compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong to same homologous series so they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties. They have same general formula C n H 2n+2 .They . differ by 2 carbon atoms and 4 hydrogen atoms. (v) (a)
(i) (a): As the size of the atom increases down the group, electropositive character increases. (ii) (c): Li is the first element of the second period. As the size decreases in the period from left to right, therefore, Li is the largest atom in the period. (iii) (c): Al (Z = 13) : 2, 8, 3 (iv) (b): Metallic character of elements decreases from left to right and increases down the group. (v) (a): As we move from left to right along a period, the number of valence electrons increases from 1 to 8.
(i) (a): In human, cellulose is indigestible as it cannot be broken into smaller molecules due to absence of cellulase enzyme. (ii) (b): Finger-like projections that come out from mucosa of intestine form villi. Cells lining the villi produce numerous microscopic projections called microvilli giving a brush border appearance which increase the surface area for absorption enormously. Villi has a good supply of capillaries and a large lymph vessel for absorption of nutrients. If the inner lining of the small intestine will be smooth, the surface for absorption will be reduced. (iii) (a) (iv) (c) (v) (b)
(i) (c): A- Artery: Carries blood from heart to different body parts. It is thick-walled and elastic. It acts as a "pressure reservoir" for maintaining the blood flow. B - Capillary : Nutrients, hormones, gases, etc. can diffuse into tissue cells through capillaries and vice versa. It is thin-walled, and only one cell layer thick resting on basement membrane. C - Vein: Brings blood from different body parts to the heart. It is thin-walled and act as low-resistance conduct for blood flow. D - Pulmonary vein: Two pulmonary veins from each lung transport the oxygenated blood to the left atrium. (ii) (d): In amphibians, the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the gills/lungs/skin and the right atrium gets the deoxygenated blood from other body parts. However, they get mixed up in the single ventricle which pumps out mixed blood i.e., incomplete double circulation (iii) (d): Whale is a mammal and in mammals, two separate circulatory pathways are found - systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation. Oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods received by the left and right atria respectively pass on to the left and right ventricles. Thus, oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods are not mixed. This is referred to as double circulation. (iv) (a) (v) (c): Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood between heart and lungs. During this pathway deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium, moves into the right ventricle. From here it moves through the pulmonary arch into the lungs for oxygenation. Then from lungs the oxygenated blood moves into the left atrium through pulmonary veins.
(i) (b): The tiny spores of bread mould (Rhizopus) are always present in air. On coming in contact with moist surface of bread slice they settle on it and germinate to form new fungal hyphae which first look like white cottony mass and later turns black. (ii) (a): Mucor (fungus) reproduces asexually through spore formation. (iii) (d) (iv) (c) : Bacteria produce endospore which is a dormant and tough structure that enables bacteria to remain dormant for extended periods under unfavorable conditions. (v) (d)
(i) (a) : Characters studied by Mendel are as follows:
(i) (a): The angle between the two refracting surfaces of a prism is called angle of prism. (ii) (b): The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called angle of deviation. (iii) (d): As the ray of light enters from rarer medium (air) to denser medium (glass), the angle of incidence is more than angle of refraction. (iv) (c): More be the refractive index, more be the angle of deviation and it also depends on the refractive index of prism. (v) (c): The refraction of light takes place through rectangular surfaces.
(i) (c): No two magnetic field lines are found to cross each other. If two field lines crossed each other, it would mean that at the point of intersection, the compass needle would point in two directions at the same time, which is not possible. (ii) (d): The magnetic field and hence the magnetic line of force exist in all the planes all around the magnet. (iii) (d): The relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines and the direction of the magnetic field is obtained by tangent to the field lines at the point of intersect. (iv) (d): The magnetic field lines due to a bar magnet are closed continuous curves directed from N to S outside the magnet and directed from S to N inside the magnet. Hence option (d) is correct. v) (d): Inside a bar magnet, the direction of field lines is from south pole to north pole
(i) (a): Due to bio-rnagnification, the concentration of DDT will always be less in zooplanktons than large fish (ii) (c) (iii) (b) : Due to bio-rnagnification the nonbio-degradable chemicals such as DDT accumulate and go on concentrating at each trophic level. (iv) (d) : Higher amounts of DDT disturb calcium metabolism of birds resulting in thinning of egg shells and their prematllre breaking that kills the embryos. (v) (d)
( i) (b) : In the given pie chart, gases P, Q, Rand S respectively are CO 2 , CH 4 , CFCs and N 2 O. Methane is produced by incomplete combustion of biomass. (ii) (c): Methane (gas Q) is produced by incomplete biomass combustion and incomplete decomposition mostly by anaerobic methanogens. Flooded paddy fields, marshes and cattles are the major source of this gas. (iii) (c) : CO 2 is the principal greenhouse gas that helps to keep the earth warm. (iv) (d) (v) (c)
(i) (b): 1% of solar radiation is captured by plants. Sun is the ultimate source of all energy. (ii) (d) (iii) (d) (iv) (d): The given pyramid is pyramid of energy that shows the two basic laws of thermodynamics. (v) (c): Light energy from the sun is converted to chemical energy in producers via photosynthesis. This chemical energy is then transferred to primary consumer, then subsequently to secondary consumer via feeding.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Free PDF Download
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 13 – magnetic effects of electric current.
Toppr.com is one of the leading online tutoring company in India. Through this article, we will provide the free PDF for NCERT solutions for class 10 Science chapter 13, which is Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. Also, the solutions for the Magnetic Effects of Electric Current have been solved by our Physics subject experts. All the exercise questions given in chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current are there for you to revise the whole syllabus and score higher marks.
Also, Toppr provides online coaching for NEET, IIT JEE, medical and engineering entrance examinations. So, you can register anytime for coaching through an online website or through application and have the benefits of learning with the experts. Download the Toppr learning app to get access to live classes, free PDFs, and online test for various classes.
Toppr provides free study materials, 1000+ hours of video lectures, and last 10 years question papers for free. Download Toppr for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Download NCERT Solutions for other subjects here.
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All chapters here.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NCERT Solutions
NCERT Class 10 science chapter 13, comes under the theme of how things work. Our subject matter experts made solutions for chapter 13, the magnetic effects of electric current for this chapter. Also, these solutions will help you score higher in the exam.

Furthermore, the topic magnetic field due to a current-carrying conductor includes the magnetic field due to a current through a straight conductor. Also, the right-hand thumb rule described here is with the help of descriptive diagrams and practical activities and practice-based questions.
Additionally, the solutions provided for the questions helps in understanding the electric current through a metallic conductor that produces a magnetic field around it. Also, the topics in this chapter include Magnetic field due to current in solenoid, magnetic field due to current running through a circular loop, etc.
Thus, the solutions and practical activities here in the chapter help the learners understand the magnetic field and right-hand thumb rule a solenoid and circular loop.
Sub-topics covered under NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13
Ex 13.1 – Magnetic Field and Field Lines
Ex 13.2 – Magnetic Field Due to a Current-carrying Conductor
- 13.2.1 – Magnetic Field Due to a Current Through a Straight Conductor
- 13.2.2 – Right-hand Thumb Rule
- 13.2.3 – Magnetic Field Due to a Current Through a Circular Loop
- 13.2.4 – Magnetic Field Due to a Current in a Solenoid
Ex 13.3 – Force on a Current-carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
Ex 13.4 – Electric Motor
13.5 – Electromagnetic Induction
Ex 13.6 – Electric Generator
Ex 13.7 – Domestic Electric Circuits.
Furthermore, the topic focuses on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field. Also, it is important to understand how the magnetic field produces a force. This exerts force on the magnet placed in the vicinity of the conductor.
Also, there are solved numerical problems, explanatory diagrams, and solutions for the questions. This shall strengthen the learner’s knowledge related to the topics involved. The comprehensive, simple, and lucid solutions given for the topics like electromagnetic induction, electric motor, domestic electric circuits, and the electric generator will help students master these topics.
You can download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 by clicking on the download button below

Download Toppr – Best Learning App for Class 5 to 12
On Toppr, you will get features like online classes, adaptive practice, mock tests, live doubts session, and lives classes. Through these features, you will definitely be able to score the desired marks at the comfort of your home.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 6 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 1 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 2 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 4 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 5 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 7 Free PDF Download
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Chapter 8 Free PDF Download
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Class 10 Science
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects Electric Current
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 13 – cbse free pdf download.
* According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 12.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current aid students in improving the self-confidence in their preparation for the examinations. It is the best reference material to build a foundation for Science subjects for both board and other entrance examinations. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science, Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current are generally used by every student during their exam preparations. Our subject experts have explained all the questions effectively, as provided in the NCERT textbooks. These NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science are prepared by our team of highly experienced subject experts after thorough research. They are available in a simple language so that students can learn and understand the entire concept at a deeper level.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 10 Science Chapter – 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Download most important questions for class 10 science chapter – 13 magnetic effects of electric current.
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 The Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
carouselExampleControls112

Previous Next
Access Answers of Science NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
In text 13.1 page:224.
1. Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
The compass needle is a small magnet. When the compass needle is brought close to a bar magnet, the magnetic field lines of the compass needle interact with the magnetic field lines of the bar magnet, which causes the compass needle to deflect.
In text 13.2.2 Page:228
1. Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
Magnetic field lines of a bar magnet emerge from the North Pole and terminate at the South Pole, as shown in the figure below.

2. List the properties of magnetic field lines.
The properties of magnetic field lines are as follows:
- Magnetic field lines do not intersect with each other.
- They emerge from the North Pole and terminate at the South Pole.
- Inside the magnet, the direction of the field lines is from the South Pole to the North Pole.
3. Why don’t two magnetic field lines intersect each other?
If two magnetic field lines intersect, then at the point of intersection, the compass needle shows two different directions, which is not possible. Hence they do not intersect with each other.
In text 13.2.4 Page:229
1. Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.

For the downward direction of the current, the direction of the magnetic field will be as if emerging from the table outside the loop and merging with the table inside the loop. Similarly, for current flowing in an upward direction, the direction of the magnetic field will be as if they are emerging from the table outside the loop and merging with the table inside the loop, as shown in the figure.
2. The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.

3. Choose the correct option.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid-carrying current
- decreases as we move towards its end.
- increases as we move towards its end.
- is the same at all points.
d. is the same at all points
The magnetic field inside a long straight current-carrying solenoid is uniform. Therefore, it is the same at all points.
In text 13.3 Page:231
1. Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
(c) and (d)
When a proton enters the region of a magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force. Due to this, the path of the proton becomes circular. As a result, the velocity and the momentum change.
2. In Activity 13.7, how do we think the displacement of rod AB will be affected if (i) current in rod AB is increased; (ii) a stronger horse-shoe magnet is used; and (iii) length of the rod AB is increased?
A current-carrying conductor, when placed in a magnetic field, experiences force. The magnitude of this force will increase with the increase in the amount of current, the length of the conductor and the strength of the magnetic field. Hence, the strength of the magnetic force exerted on the rod AB and its displacement will increase if
- The current in rod AB is increased
- A stronger horseshoe magnet is used
- When the length of the rod AB increases
3. A positively-charged particle (alpha-particle) projected towards the west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field is
- towards south
- towards east
The direction of the magnetic field can be determined using Fleming’s Left-hand rule. According to the rule, if we arrange our thumb, forefinger and the middle finger of the left hand right perpendicular to each other, then the thumb points towards the direction of the magnetic force, the middle finger the direction of current and the forefinger the direction of magnetic field. Since the direction of the positively charged particle is towards the west, the direction of the current will also be towards the west. The direction of the magnetic force is towards the north. Hence the direction of the magnetic field will be upward according to Fleming’s Left-hand rule.
In text 13.4 Page:233
1. State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Fleming’s Left-hand rule states that if we arrange our thumb, forefinger and middle finger of the left hand at right angles to each other, then the thumb points towards the direction of the magnetic force, the forefinger points towards the direction of the magnetic field and the middle finger points towards the direction of the current.
2. What is the principle of an electric motor?
The working principle of an electric motor is based on the magnetic effect of current. A current-carrying conductor, when placed in a magnetic field, experiences force and rotates. The direction of the rotation of the conductor can be determined by Fleming’s Left-hand rule.
3. What is the role of split ring in an electric motor?
The split ring plays the role of a commutator in an electric motor. The commutator reverses the direction of the current flowing through the coil after each half-rotation of the coil. Due to this reversal of current, the coil continues to rotate in the same direction.
In text 13.5 Page:236
1. Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
Following are the different ways to induce a current in a coil:
- If the coil is moved rapidly between the two poles of a horseshoe magnet, an electric current is induced in the coil.
- When a magnet is moved relative to the coil, an electric current is induced in the coil.
In text 13.6 Page:237
1. State the principle of an electric generator.
An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. In a generator, electricity is generated by rotating a coil in the magnetic field.
2. Name some sources of direct current.
DC generators and cells are some sources of direct current.
3. Which sources produce alternating current?
Power plants and AC generators are some of the sources that produce alternating current.
4. Choose the correct option.
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each
- two revolutions
- one revolution
- half revolution
- one-fourth revolution
c. half revolution
When a rectangular coil is rotated in a magnetic field, the direction of the induced current changes once in a half revolution; as a result, the direction of the current in the coil remains the same.
In text 13.7 Page:238
1. Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
The safety measures commonly used in electric circuits are as follows:
Each circuit should be connected to a fuse because a fuse prevents the flow of excessive current through the circuit. When the current in the circuit exceeds the maximum limit of the fuse element, the fuse melts to stop the flow of current protecting the appliance connected to the circuit.
Earthing protects the user from electric shocks. Any leakage of current in an appliance is transferred to the ground by earthing, and the people using the appliance are prevented from getting electrocuted.
2. An electric oven of 2 kW power rating is operated in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you expect? Explain.
The current drawn by the electric oven can be calculated using the formula
Substituting the values, we get
I = 2000 W/220 V = 9.09 A
The current drawn by the electric oven is 9.09 A which exceeds the safe limit of the circuit. This causes the fuse to melt and break the circuit.
3 . What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits?
A few of the precautions to be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits are as follows:
- Connecting too many devices to a single socket should be avoided
- Using too many appliances at the same time should be avoided
- Faulty appliances should not be connected to the circuit
Exercises Page:240
1. Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
- The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
- The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
- The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
- The field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire.
4. The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire.
The magnetic field near a long straight wire is concentric circles. Their centres lie on the wire.
2. The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
- the process of charging a body.
- the process of generating a magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil.
- producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
- the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor.
3. producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
The phenomenon of inducing current in a coil due to the relative motion between the coil and the magnet is known as electromagnetic induction.
3. The device used for producing electric current is called a
- galvanometer
a. generator
The device used for producing electric current is known as a generator. The generator converts mechanical energy to electric energy.
4. The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that
- AC generator has an electromagnet while a DC generator has permanent magnet.
- DC generator will generate a higher voltage.
- AC generator will generate a higher voltage.
- AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
4. AC generator has slip rings, while the DC generator has a commutator.
AC generators have two rings known as the slip rings, while DC generators have two half rings known as the commutator. This is the main difference between AC generator and DC generator.
5. At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit
- reduces substantially.
- does not change.
- increases heavily.
- vary continuously.
3. increases heavily
When two naked wires in the circuit come in contact with each other, the amount of current flowing in the circuit increase abruptly resulting in short circuit.
6. State whether the following statements are true or false.
- An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
- The field at the center of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
- A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply.
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
An electric generator is a device that generates electricity by rotating a coil in a magnetic field.
A long circular coil is a solenoid. The magnetic field lines inside a solenoid are parallel straight lines.
Live wires have red insulation cover, while the earth wire has green insulation.
7. List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
Following are the methods of producing magnetic fields:
- By using a permanent magnet, we can produce a magnetic field, and it can be visualized by spreading iron fillings on white paper and keeping a magnet beneath the paper.
- A current-carrying straight conductor produces magnetic field.
- Different types of conductors, such as solenoid and circular loops, can be used to see the presence of a magnetic field.
8. How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a current–carrying solenoid with the help of a bar magnet? Explain.
A solenoid is a long coil of circular loops of insulated copper wire. The magnetic field produced around the solenoid when the current is passed through it is similar to the magnetic field produced around the bar magnet when a current is passed through it. The figure shown below shows the arrangement of magnetic fields produced around the solenoid when current is passed through it.

When the north pole of the bar magnet is brought close to the end connected to the negative terminal of the battery, the solenoid repels the battery. As like poles repel each other, we can infer that the end connected to the negative terminal behaves as a north pole while the end connected to the positive terminal behaves as a south pole.
9. When is the force experienced by a current–carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
When the direction of the current is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, the force experienced is the largest.
10. Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
The direction of the magnetic field can be determined using Fleming’s Left-hand rule. The direction of the magnetic field will be perpendicular to the direction of the current and the direction of deflection, i.e., either upward or downward. The direction of the current is from the front wall to the back wall because negatively charged electrons move from the back wall to the front wall. The direction of the magnetic force is rightward. Hence, using Fleming’s left-hand rule, it can be concluded that the direction of the magnetic field inside the chamber is downward.
11. Draw a labelled diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and working. What is the function of a split ring in an electric motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. It works on the principle of the magnetic effect of current. The figure listed below shows a simple electric motor.

When current is made to flow through the coil MNST by closing the switch, the coil starts to rotate in the anticlockwise direction. This is due to the downward force acting on the length MN and simultaneously an upward force acting along the length ST. As a result of which, the coil rotates in the anticlockwise direction. Current in the length MN flows from M to N, and the magnetic fields act from left to right normal to the length MN. According to Fleming’s Left-Hand rule, a downward force acts along the length MN. Similarly, the current along the length ST flows from S to T and the magnetic field acts from left to right. Therefore, an upward force acts along the length ST. These two forces together cause the coil to rotate anti-clockwise. After half a rotation, the position of MN and ST interchange. The half-ring C comes in contact with brush B and the half-ring D comes in contact with rush C. Hence the direction of current in the coil MNST gets reversed.
12. Name some devices in which electric motors are used.
A few devices in which electric motors are used are:
- Electric fans
- Water pumps
- Washing machines
13. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is (i) pushed into the coil, (ii) withdrawn from inside the coil, (iii) held stationary inside the coil?
(i) When a bar magnet is pushed into the coil, a current is induced in the coil momentarily. As a result, the galvanometer deflects in a particular direction momentarily.
(ii) When the bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil, a current is induced momentarily but in the opposite direction, and the galvanometer deflects in the opposite direction momentarily.
(iii) When the bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil, no current will be induced. As a result, there will be no deflection in the galvanometer.
14. Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
When the current in coil A changes, the magnetic field associated with it also changes. As a result, the magnetic field around coil B undergoes change. The change in the magnetic field of coil B induces a current in it.
15. State the rule to determine the direction of a (i) magnetic field produced around a straight conductor-carrying current, (ii) force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it, and (iii) current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
(i) The rule used to determine the direction of the magnetic field produced around a straight conductor-carrying current is Maxwell’s right-hand thumb rule.
(ii) The rule used to determine the force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it is the Fleming’s left hand rule.
(iii) The rule used to determine the current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field is Fleming’s right-hand rule.
16. Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labelled diagram. What is the function of brushes?
The electric generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The working principle of the electric generator is electromagnetic induction. It generates electricity by rotating a coil in the magnetic field. The figure below shows the construction of a simple AC generator.

In the diagram,
A and B are brushes.
C and D are slip rings.
X is the axle.
G is the galvanometer.
When the axle X is rotated clockwise, MN moves upwards while ST moves downward. The movement of MN and ST in the magnetic field results in the production of electric current due to electromagnetic induction. MN moves upwards, and the magnetic fields act from left to right. Therefore, according to Fleming’s right hand rule, the direction of the induced current will be from M to N along the length MN. Similarly, the direction of the induced current will be from S to T along the length ST. The direction of the current in the coil is MNST. Hence, the galvanometer shows a deflection in a particular direction.
After half a rotation, length MN starts moving downwards while the length ST starts moving upwards. Now, the direction of the induced current reverses to TSNM. Since the direction of the induced current reverses every half rotation, the current induced is known as alternating current.
Function of Brushes
Brushes are kept pressed onto two slip rings separately. The outer ends of the brushes are connected to the galvanometer. Thus, brushes help in transferring current from the coil to the external circuit.
- When does an electric short circuit occur?
Listed below are two instances of when a short-circuit can occur:
1) When too many appliances are connected to a single socket or when high power rating appliances are connected to a light circuit, the resistance of the circuit becomes low. As a result, the current flowing through the circuit becomes very high. This condition results in a short circuit.
2) When live wires whose insulation has worn off come in contact with each other, the current flowing in the circuit increases abruptly, which results in a short circuit.
18. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
The metallic body of electric appliances is earthed by means of an earth wire. Any leakage of electric wire is transferred to the ground by means of the earth wire. This prevents the user of the electric appliance from getting electric shocks. This is the reason why it is important for metallic appliances to be earthed.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
As per the updated marking scheme, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current is one of the important topics, and the expected weightage is 10 marks. In this chapter, students learn more in detail about Electric Current, Magnetic fields, magnetic field lines, compass, electromagnetic induction, Effects of Electric Current and so on. Oersted’s law and his Experiment is the most important 5-mark question, which has been the most frequently asked in the previous year papers.
List of Exercises
13.1 Magnetic Field and Field Lines
13.2 Magnetic Field due to a Current-Carrying Conductor
13.3 Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
13.4 Electric Motor
13.5 Electromagnetic Induction
13.6 Electric Generator
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current are also known as the electromagnetic effect. It is the branch of physics which mainly deals with the study of the electromagnetic force, electrically charged particles, electric fields and magnetic fields. In this topic, students can learn more interesting concepts related to Magnetic fields and Electric Current, along with a few interesting experiments. Other interesting topics explained in this chapter include:
- Properties of the magnet – 2 Questions (1 short, 1 MCQ)
- How does magnetic effect work -1 Question (1 MCQ)
- Clock Face Rule-1 Question (1 short)
- Fleming’s left-hand rule-1 Question (1 long)
- Maxwell’s Right Hand Thumb Rule and its Application -1 Question (1 long)
Key Features of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current:
- Provides solved solutions to all the questions in the respective NCERT textbooks.
- The language used in these NCERT Solutions is easy and simple to understand for the students.
- These solutions are prepared by our subject experts after extensive research on every topic in order to provide appropriate and genuine information to the students.
- These solutions will be useful for Olympiads, CBSE exams and other competitive exams.
- Detailed answers are provided to all the questions to help students in their preparations.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13
How to determine the direction of a magnetic field in chapter 13 of ncert solutions for class 10 science, how many questions are present under each topic in chapter 13 magnetic effects of electric current of ncert solutions for class 10 science, why are ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 13 beneficial for the students, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Our Environment
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 15 our environment.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Our Environment. Term 2 Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Our Environment.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 15 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Our Environment
Case Study – 1
1.) Waste management is essential in today’s society. Due to an increase in population, the generation of waste is getting doubled day by day. Moreover, the increase in waste is affecting the lives of many people. Waste management is the managing of waste by disposal and recycling of it. Moreover, waste management needs proper techniques keeping in mind the environmental situations. For instance, there are various methods and techniques by which the waste is disposed of. You must have come across 5 R’s to save the environment: refuse, reduce, reuse, repurpose and recycle.
[ CBSE Academic Question Paper ]
1) Recycling of paper is a good practice but recycled paper should not be used as food packaging because
a) recycled papers take lots of space b) recycled papers can’t cover food properly c) recycled papers can cause infection d) recycled papers are costly
Answer – c) recycled papers can cause infection
2) Effective segregation of wastes at the point of generation is very important. Select the appropriate statements giving the importance of waste segregation.
- i) less waste goes to the landfills
- ii) better for public health and the environment
- iii) help in reducing the waste
- iv) resulting in deterioration of a waste picker’s health
a) both i) and ii) b) both i) and iii) c) both ii) and iii) d) both i) and iv)
Answer – a) both i) and ii)
Case Study – 2
1.) Food chains are very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases. The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers. Primary producers, or autotrophs, can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds, whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis, most life could not exist if the sun disappeared. Even so, it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life, chemotrophs, that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents, thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
1) If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy?
- a) 10,000 J
- d) It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant.
Answer – b) 100 J
2) Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
- a) Energy is bidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating.
- b) Energy is repeatedly circulation and matter is unidirectional.
- c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating.
- d) Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional.
Answer – c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating
3) Mr. X is eating curd/yogurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
- a) First trophic level
- b) Second trophic level
- c) Third trophic level
- d) Fourth trophic level
Answer – c) Third Trophic level
4 Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
- a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
- b) Less availability of food
- c) Polluted air
Answer – a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic level
5) The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers:
- a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain
- b) Do not breakdown organic compounds
- c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms
- d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
Answer – a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain
Case Study – 3
Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.

1) Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
Answer – a) Decrease in energy at higher trophic level
2) If Ravi is consuming curd/yogurt for lunch , which trophic level in a food chain he should be considered as occupying ?
Answer – c) Third Trophic level
3) Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
Answer – c) Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating.
4) If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem, what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy ?
Answer – a) Act at every trophic level of the food chain
Case study – 4
In Kunjpura village, located in Karnal district, Haryana, Aditya Aggarwal and his older brother Amit Aggarwal run Tee Cee Industries, a steel plant set up by their ancestors in 1984. Along with this, they also run a gaushala that houses 1,200 cows that can no longer produce milk. The cow shelter was manageable but running the steel plant was turning out to be expensive because they spent a whopping Rs 5 lakh every month on electricity. The brothers struck upon an idea. Why not run the factory with the biogas produced from cow dung from the shelter and other gaushalas, along with bio and agri led Aditya and Amit to start Amrit Fertilizers, a biogas project, in 2014, without any government support.
1) Raw material used in bio gas plant is
- (a) Animal dung
- (b) crop residue
- (c) Food waste
- (d) All of the above
Answer – (d) All of the above
2) Biogas is a better fuel than animal dung cake because
- (i) Biogas has lower calorific value.
- (ii) Animal dung cake has higher calorific value.
- (iii) Biogas has high heating capacity.
- (iv) Biogas burns without smoke.
(a) (i) only
(b) (ii) only
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Answer – (c) (iii) and (iv)
3) Biogas is formed in the
(a) presence of air only.
(b) presence of water only.
(c) absence of air only.
(d) presence of water and absence of air.
Answer – (d) presence of water and absence of air.
4) Biogas is a mixture of the following gases.
(a) Ethane,Carbon monoxide, Nitrogen and Butane
(b) Methane,Hydrogen,Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen
(c) Butane,Carbon monoxide,Propane and Hydrogen
(d) Carbon monoxide,Sulphur dioxide and Hydrogen
Answer – (b) Methane, Hydrogen, Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen
CASE STUDY : 5
We are an integral part of the environment. Changes in the environment affect us and our activities change the environment around us
Ozone (O3 ) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. While O2 , which we normally refer to as oxygen, is essential for all aerobic forms of life. Ozone, is a deadly poison. However, at the higher levels of the atmosphere, ozone performs an essential function. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
i) How does ozone is formed?
Ans: The UV radiations coming from the sun split the molecular oxygen into nascent oxygen. When these nascent oxygen combined to molecular oxygen, it forms ozone(O3).
ii) In which layer of atmosphere does ozone is present?
Ans: The ozone is present in the stratosphere layer of atmosphere just above troposphere.
iii) What are the causes for ozone depletion?
Ans: The synthetic chemicals like CFCs ( chlorofluorocarbons) which used as refrigerants amd in the fire extinguisher
iv) Write the chemical reaction for the formation of ozone?
Ans: O2 👉 [O] + [O]
[O] + O2 👉 O3 (ozone)
v) What are the effects of UV radiations?
Ans: It causes different types of cancer in human beings.
CASE STUDY : 6
In our daily activities, we generate a lot of material that are thrown away. What are some of these waste materials? What happens after we throw them away? Let us perform an activity to find answers to these questions.
- Collect waste material from your homes. This could include all the waste generated during a day, like kitchen waste (spoilt food, vegetable peels, used tea leaves, milk packets and empty cartons), waste paper, empty medicine bottles/strips/bubble packs, old and torn clothes and broken footwear.
- Bury this material in a pit in the school garden or if there is no space available, you can collect the material in an old bucket/ flower pot and cover with at least 15 cm of soil.
- Keep this material moist and observe at 15-day intervals.
- What are the materials that remain unchanged over long periods of time?
- What are the materials which change their form and structure over time?
- Of these materials that are changed, which ones change the fastest?
We have seen in the chapter on ‘Life Processes’ that the food we eat is digested by various enzymes in our body. Have you ever wondered why the same enzyme does not break-down everything we eat? Enzymes are specific in their action, specific enzymes are needed for the break-down of a particular substance. That is why we will not get any energy if we try to eat coal! Because of this, many human-made materials like plastics will not be broken down by the action of bacteria or other saprophytes. These materials will be acted upon by physical processes like heat and pressure, but under the ambient conditions found in our environment, these persist for a long time.
i) What is biodegradable substances?
Ans: The substances that are broken down by biological process are called as biodegradable substances.
Eg: Vegetables waste materials.
ii) What are the examples of non- biodegradable substances?
Ans: Plastic, rubber, foam, batteries etc.
iii) what are the ways through which we can reduce pollution especially the non- biodegradable waste?
Ans: •We can use RRR methods i.e reduce, reuse and recycle.
Reduce the use of plastic
iv) What are the effects of biodegradable substances on our environment?
Ans: • Release green house gases.
They are breeding ground for mosquitoes and houseflies causing various disease.
v) What are the non- biodegradable on environment?
Ans: • causes soil pollution and sometimes air pollution when burnt in air.
- death of cattles due to ingestion of these waste.
- choking of drainage system
CASE STUDY : 7
The food we eat acts as a fuel to provide us energy to do work. Thus the interactions among various components of the environment involves flow of energy from one component of the system to another. As we have studied, the autotrophs capture the energy present in sunlight and convert it into chemical energy. This energy supports all the activities of the living world. From autotrophs, the energy goes to the heterotrophs and decomposers.
i) What is food chain?
Ans: A series of organism feeding on one another and taking part in various biotic levels is called food chain.
ii) Give a example of one terrestrial food chain.
Ans: Sunlight 👉 plants (producers) 👉 Goat/ Deer (herbivores) 👉 Tiger (carnivores)
iii) What are the feature of food chain?
Ans: •It is unidirectional
The energy available at each level gets diminished due to loss at each level.
iv) What do you meant by biological magnification?
Ans: The gradual increase in the concentration of any substance ( generally toxic) in trophic levels is called as biological magnification.
v) What is the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaching the next level of consumers?
CASE STUDY : 8
All organisms such as plants, animals, microorganisms and human beings as well as the physical surroundings interact with each other and maintain a balance in nature. All the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem. Thus, an ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals.
i) What is natural ecosystem?
Ans: An environment where living organism and non- living interact with each other freely in nature is called as natural ecosystem.
ii) what are the examples of artificial ecosystem?
Ans: Gardens, crop- fields
iii) what are consumers?
Ans: Organism which consume food either directly or indirectly by feeding on one another animals are called as consumers.
iv) What are the type of consumers?
Ans: They are herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites.
v) What are producers?
Ans: The green plants and some bacteria which make their food by using sunlight i.e photosynthesis are called as producers
We hope that above case study questions will help you for your upcoming exams. To see more click below –
- Class 10 Assertion & Reason
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- Important Difference between Class 10 Biology
- Important Difference between Class 10 Physics
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 10 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction .
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual.
A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole. the image formed is virtual and erect.
A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as doctor’s head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified image of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirrors in automobiles because it can form an small and erect image of an object.
(i) When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is (a) larger than the object (b) smaller than the object (c) same size as that of the object (d) highly enlarged.
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be (a) plane (b) concave (c) convex (d) either plane or convex.
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top. (a) Plane, convex and concave (b) Convex, concave and plane (c) Concave, plane and convex (d) Convex, plane and concave
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror (d) a plane mirror.
(v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen. (b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these.
Question 2:
The lenses forms different types of images when object placed at different locations. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.
When a ray goes through the optical centre of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between focus and optical center of the convex lens, erect and magnified image is formed.
As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also the size of image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted.
A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective to the position of the object.
(i) The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is (a) at focus (b) at 2F (c) at optical center (d) between Fand 2F
(ii) When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is (a) real and smaller (b) virtual and inverted (c) virtual and smaller (d) real and erect
(iii) The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is (a) small (b) point in size (c) highly magnified (d) same as that of object
(iv) When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is (a) at F (b) at 2 F on the other side (c) at infinity (d) between F and optical center
(v) At which location of object in front of concave lens, the image between focus and optical centre is formed (a) anywhere between centre and infinity (b) at F (c) at 2F (d) infinity
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
3 thoughts on “ Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction ”
Thank you so much bruh you are God
- Pingback: CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions – ebookpublisher.in
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Question 1: An electric motor is a rotating device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy electric motors are used as an important component in electric fans ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. Case Study - 1. Andre Marie Ampere suggested that a magnet must exert an equal and opposite force on a current carrying conductor, which was experimentally found to be true. But we know that current is due to charges in motion.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Question 1: A student wants to study the working of electric motor. He used a model of DC motor for electromagnetism as shown in figure. He fixed the two ends of the coil to a pair of curved elastic metal strips. … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect of ...
Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations. Case Study Questions Chapter 13 Magnetic Effect Of Electric Current. Case/Passage - 1 A solenoid is a long helical coil of wire through which a current is run in order to create a magnetic field. The magnetic field of the solenoid ...
The Chapter wise Important case study based questions with their solved answers in CBSE Class 10 Science can be accessed from the table below: CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions ...
Accurate answers of all the Case-based questions given in the PDF. Case Study class 10 Science solutions are prepared by subject experts referring to the CBSE Syllabus of class 10. Free to download in Portable Document Format (PDF) so that students can study without having access to the internet.
Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions. Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App. There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph ...
Multiple Choice Questions. 1) The strength of magnetic field inside a long current carrying straight solenoid is. 2) Which instrument is used to determine the presence of magnetic field? 3) In India the potential difference between live wire and neutral wire is. Students are provided with Important Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 13 ...
Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Chapter-wise: Chapter 1. Chemical reactions and equations. Chapter 9. Heredity and Evolution. Chapter 2. Acids, bases and salt. Chapter 10. Light Reflection and Refraction.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Important Questions - Free PDF Available. Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark) 1. Magnetic field lines determine. The shape of magnetic field. Only the direction of magnetic field. Only the relative strength of the magnetic field. Both the direction and the relative strength ...
Such types of questions are solved by reading the given scenario in the paragraph. CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Case Study. Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions & Equations Case Study. Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases & Salts Case Study. Science Chapter 3 Metals & Non-Metals Case Study. Science Chapter 4 Carbon & Its Compounds Case Study.
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations. Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs.
This cycling of nutrients is essential for the functioning of ecosystems but does not fit into the traditional linear structure of a food chain. Therefore, the correct reason is (a) Decomposers act at every trophic level of the food chain. The document Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Case Based Questions - Our Environment is a part of the Class 10 ...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science. In board exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . ... (Z = 13) : 2, 8, 3 (iv) (b): Metallic character of elements decreases from left to right and increases down the group. ... CBSE 10th Science Metals And Non Metals Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All chapters here. CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NCERT Solutions. NCERT Class 10 science chapter 13, comes under the theme of how things work. Our subject matter experts made solutions for chapter 13, the magnetic effects of electric current for this chapter.
Physics Chapters for Case Study Questions. Light - Reflection and Refraction. The Human Eye and The Colourful World. Electricity. Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Science students. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 - CBSE Free PDF Download *According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 12. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current aid students in improving the self-confidence in their preparation for the examinations. It is the best reference material to build a foundation ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Our Environment. Case Study - 1. 1.) Waste management is essential in today's society. Due to an increase in population, the generation of waste is getting doubled day by day. Moreover, the increase in waste is affecting the lives of many people. Waste management is the managing of waste by ...
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 ...