Structure & Function of Water
Function of water.
Water is a major component of cells and makes up 60-70% of the human body. Life evolved in an environment where water was abundant. It has several properties that are important in biology.


Importance of water
- As a reactant in cells (e.g. photosynthesis, hydrolysis).
- Provides structural support in cells.
- Keeps organisms cool to maintain an optimum body temperature.

Properties of water
- Metabolic importance.
- High heat capacity.
- Heat of vaporization.
- Cohesive properties.
- Useful as a solvent.
The Structure of Water
The structure of a water molecule helps us to understand hydrogen bonding and the function of water.
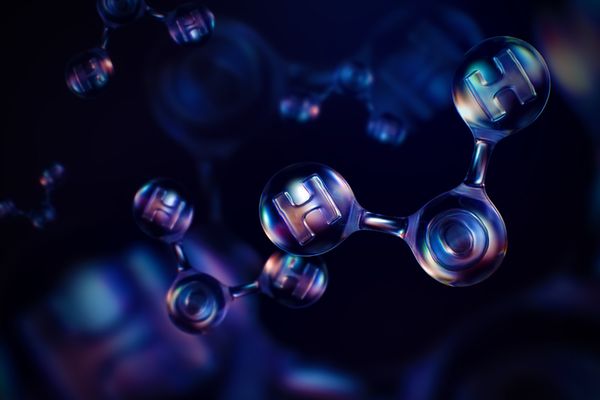

Contents of a water molecule
- One oxygen atom.
- Two hydrogen atoms.

- The oxygen atoms in water are slightly negatively charged.
- The hydrogen atoms in water are slightly positively charged.

Hydrogen bonding
- The polarity of water molecules means that a hydrogen atom on one water molecule is attracted to the oxygen atom on another water molecule.
- This attraction is called hydrogen bonding.
Useful Properties of Water
Water is a major component of cells and is essential to life as we know it (60–70% of the human body is made up of water). The properties of water that make it such a useful substance are:

Good metabolite
- A bond is broken and a water molecule is used up and so this is a hydrolysis reaction.
- A new bond is formed and a water molecule is released and so this is a condensation reaction.

High heat of vaporisation
- The specific latent heat of vaporisation is the amount of energy needed to change 1 kg of a liquid substance to a gas.
- When water evaporates, energy is used up - this cools the environment where the evaporation is taking place.
- This is why sweating helps with body temperature regulation.

High heat capacity
- Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat one gram of a substance must absorb or lose to change its temperature by 1 o C.
- The specific heat capacity of water is much larger than sand. This is why land cools faster than the sea.
- Water is used by warm blooded animals to more evenly disperse heat in their bodies.
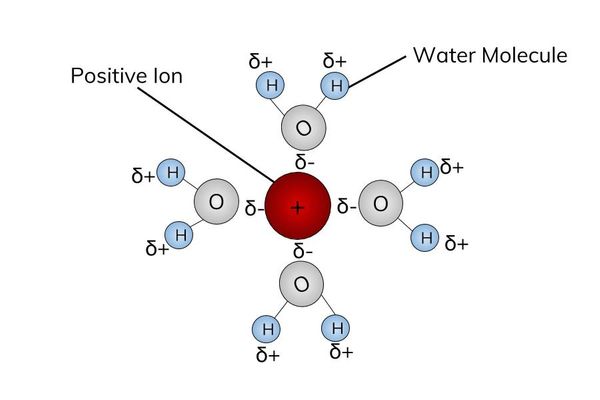
Good solvent
- Water is a good solvent because ions and polar molecules can easily dissolve in it.
- Water is a polar molecule. This means that the positive end of the water molecule attracts negative ions and the negative end will attract positive ions.
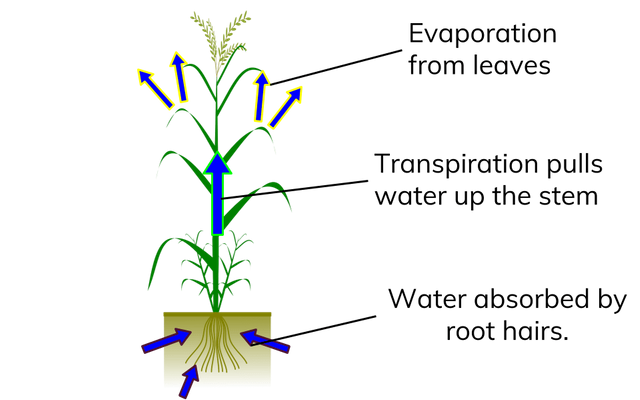
Cohesive properties
- The strong attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonds is called cohesion.
- This is why water forms droplets when placed on a dry surface rather than being flattened out by gravity.
- Plants use this natural phenomenon to help transport water from their roots to their leaves.
1 Biological Molecules
1.1 Monomers & Polymers
1.1.1 Monomers & Polymers
1.1.2 Condensation & Hydrolysis Reactions
1.2 Carbohydrates
1.2.1 Structure of Carbohydrates
1.2.2 Types of Polysaccharides
1.2.3 End of Topic Test - Monomers, Polymers and Carbs
1.2.4 Exam-Style Question - Carbohydrates
1.2.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Carbohydrates
1.3.1 Triglycerides & Phospholipids
1.3.2 Types of Fatty Acids
1.3.3 Testing for Lipids
1.3.4 Exam-Style Question - Fats
1.3.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Lipids
1.4 Proteins
1.4.1 The Peptide Chain
1.4.2 Investigating Proteins
1.4.3 Primary & Secondary Protein Structure
1.4.4 Tertiary & Quaternary Protein Structure
1.4.5 Enzymes
1.4.6 Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
1.4.7 Enzyme-Controlled Reactions
1.4.8 End of Topic Test - Lipids & Proteins
1.4.9 A-A* (AO3/4) - Enzymes
1.4.10 A-A* (AO3/4) - Proteins
1.5 Nucleic Acids
1.5.1 DNA & RNA
1.5.2 Polynucleotides
1.5.3 DNA Replication
1.5.4 Exam-Style Question - Nucleic Acids
1.5.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Nucleic Acids
1.6.1 Structure of ATP
1.6.2 End of Topic Test - Nucleic Acids & ATP
1.7.1 Structure & Function of Water
1.7.2 A-A* (AO3/4) - Water
1.8 Inorganic Ions
1.8.1 Inorganic Ions
1.8.2 End of Topic Test - Water & Inorganic Ions
2.1 Cell Structure
2.1.1 Introduction to Cells
2.1.2 Eukaryotic Cells & Organelles
2.1.3 Eukaryotic Cells & Organelles 2
2.1.4 Prokaryotes
2.1.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Organelles
2.1.6 Methods of Studying Cells
2.1.7 Microscopes
2.1.8 End of Topic Test - Cell Structure
2.1.9 Exam-Style Question - Cells
2.1.10 A-A* (AO3/4) - Cells
2.2 Mitosis & Cancer
2.2.1 Mitosis
2.2.2 Investigating Mitosis
2.2.3 Cancer
2.2.4 A-A* (AO3/4) - The Cell Cycle
2.3 Transport Across Cell Membrane
2.3.1 Cell Membrane Structure
2.3.2 A-A* (AO3/4) - Membrane Structure
2.3.3 Diffusion
2.3.4 Osmosis
2.3.5 Active Transport
2.3.6 End of Topic Test - Mitosis, Cancer & Transport
2.3.7 Exam-Style Question - Membranes
2.3.8 A-A* (AO3/4) - Membranes & Transport
2.3.9 A-A*- Mitosis, Cancer & Transport
2.4 Cell Recognition & the Immune System
2.4.1 Immune System
2.4.2 The Immune Response
2.4.3 Antibodies
2.4.4 Primary & Secondary Response
2.4.5 Vaccines
2.4.7 Ethical Issues
2.4.8 End of Topic Test - Immune System
2.4.9 Exam-Style Question - Immune System
2.4.10 A-A* (AO3/4) - Immune System
3 Substance Exchange
3.1 Surface Area to Volume Ratio
3.1.1 Size & Surface Area
3.1.2 A-A* (AO3/4) - Cell Size
3.2 Gas Exchange
3.2.1 Single-Celled Organisms
3.2.2 Multicellular Organisms
3.2.3 Control of Water Loss
3.2.4 Human Gas Exchange
3.2.5 Ventilation
3.2.6 Dissection
3.2.7 Measuring Gas Exchange
3.2.8 Lung Disease
3.2.9 Lung Disease Data
3.2.10 End of Topic Test - Gas Exchange
3.2.11 A-A* (AO3/4) - Gas Exchange
3.3 Digestion & Absorption
3.3.1 Overview of Digestion
3.3.2 Digestion in Mammals
3.3.3 Absorption
3.3.4 End of Topic Test - Substance Exchange & Digestion
3.3.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Substance Ex & Digestion
3.4 Mass Transport
3.4.1 Haemoglobin
3.4.2 Oxygen Transport
3.4.3 The Circulatory System
3.4.4 The Heart
3.4.5 Blood Vessels
3.4.6 Cardiovascular Disease
3.4.7 Heart Dissection
3.4.8 Xylem
3.4.9 Phloem
3.4.10 Investigating Plant Transport
3.4.11 End of Topic Test - Mass Transport
3.4.12 A-A* (AO3/4) - Mass Transport
4 Genetic Information & Variation
4.1 DNA, Genes & Chromosomes
4.1.2 Genes
4.1.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - DNA
4.2 DNA & Protein Synthesis
4.2.1 Protein Synthesis
4.2.2 Transcription & Translation
4.2.3 End of Topic Test - DNA, Genes & Protein Synthesis
4.2.4 Exam-Style Question - Protein Synthesis
4.2.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Coronavirus Translation
4.2.6 A-A* (AO3/4) - Transcription
4.2.7 A-A* (AO3/4) - Translation
4.3 Mutations & Meiosis
4.3.1 Mutations
4.3.2 Meiosis
4.3.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - Meiosis
4.3.4 Meiosis vs Mitosis
4.3.5 End of Topic Test - Mutations, Meiosis
4.3.6 A-A* (AO3/4) - DNA,Genes, CellDiv & ProtSynth
4.4 Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.4.1 Genetic Diversity
4.4.2 Natural Selection
4.4.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - Natural Selection
4.4.4 Adaptations
4.4.5 Investigating Natural Selection
4.4.6 End of Topic Test - Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.4.7 A-A* (AO3/4) - Genetic Diversity & Adaptation
4.5 Species & Taxonomy
4.5.1 Classification
4.5.2 DNA Technology
4.5.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - Species & Taxonomy
4.6 Biodiversity Within a Community
4.6.1 Biodiversity
4.6.2 Agriculture
4.6.3 End of Topic Test - Species,Taxonomy& Biodiversity
4.6.4 A-A* (AO3/4) - Species,Taxon&Biodiversity
4.7 Investigating Diversity
4.7.1 Genetic Diversity
4.7.2 Quantitative Investigation
5 Energy Transfers (A2 only)
5.1 Photosynthesis
5.1.1 Overview of Photosynthesis
5.1.2 Light-Dependent Reaction
5.1.3 Light-Independent Reaction
5.1.4 A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis Reactions
5.1.5 Limiting Factors
5.1.6 Photosynthesis Experiments
5.1.7 End of Topic Test - Photosynthesis
5.1.8 A-A* (AO3/4) - Photosynthesis
5.2 Respiration
5.2.1 Overview of Respiration
5.2.2 Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.3 A-A* (AO3/4) - Anaerobic Respiration
5.2.4 Aerobic Respiration
5.2.5 Respiration Experiments
5.2.6 End of Topic Test - Respiration
5.2.7 A-A* (AO3/4) - Respiration
5.3 Energy & Ecosystems
5.3.1 Biomass
5.3.2 Production & Productivity
5.3.3 Agricultural Practices
5.4 Nutrient Cycles
5.4.1 Nitrogen Cycle
5.4.2 Phosphorous Cycle
5.4.3 Fertilisers & Eutrophication
5.4.4 End of Topic Test - Nutrient Cycles
5.4.5 A-A* (AO3/4) - Energy,Ecosystems&NutrientCycles
6 Responding to Change (A2 only)
6.1 Nervous Communication
6.1.1 Survival
6.1.2 Plant Responses
6.1.3 Animal Responses
6.1.4 Reflexes
6.1.5 End of Topic Test - Reflexes, Responses & Survival
6.1.6 Receptors
6.1.7 The Human Retina
6.1.8 Control of Heart Rate
6.1.9 End of Topic Test - Receptors, Retina & Heart Rate
6.2 Nervous Coordination
6.2.1 Neurones
6.2.2 Action Potentials
6.2.3 Speed of Transmission
6.2.4 End of Topic Test - Neurones & Action Potentials
6.2.5 Synapses
6.2.6 Types of Synapse
6.2.7 Medical Application
6.2.8 End of Topic Test - Synapses
6.2.9 A-A* (AO3/4) - Nervous Comm&Coord
6.3 Muscle Contraction
6.3.1 Skeletal Muscle
6.3.2 Sliding Filament Theory
6.3.3 Contraction
6.3.4 Slow & Fast Twitch Fibres
6.3.5 End of Topic Test - Muscles
6.3.6 A-A* (AO3/4) - Muscle Contraction
6.4 Homeostasis
6.4.1 Overview of Homeostasis
6.4.2 Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.3 Controlling Blood Glucose Concentration
6.4.4 End of Topic Test - Blood Glucose
6.4.5 Primary & Secondary Messengers
6.4.6 Diabetes Mellitus
6.4.7 Measuring Glucose Concentration
6.4.8 Osmoregulation
6.4.9 Controlling Blood Water Potential
6.4.11 End of Topic Test - Diabetes & Osmoregulation
6.4.12 A-A* (AO3/4) - Homeostasis
7 Genetics & Ecosystems (A2 only)
7.1 Genetics
7.1.1 Key Terms in Genetics
7.1.2 Inheritance
7.1.3 Linkage
7.1.4 Multiple Alleles & Epistasis
7.1.5 Chi-Squared Test
7.1.6 End of Topic Test - Genetics
7.1.7 A-A* (AO3/4) - Genetics
7.2 Populations
7.2.1 Populations
7.2.2 Hardy-Weinberg Principle
7.3 Evolution
7.3.1 Variation
7.3.2 Natural Selection & Evolution
7.3.3 End of Topic Test - Populations & Evolution
7.3.4 Types of Selection
7.3.5 Types of Selection Summary
7.3.6 Overview of Speciation
7.3.7 Causes of Speciation
7.3.8 Diversity
7.3.9 End of Topic Test - Selection & Speciation
7.3.10 A-A* (AO3/4) - Populations & Evolution
7.4 Populations in Ecosystems
7.4.1 Overview of Ecosystems
7.4.2 Niche
7.4.3 Population Size
7.4.4 Investigating Population Size
7.4.5 End of Topic Test - Ecosystems & Population Size
7.4.6 Succession
7.4.7 Conservation
7.4.8 End of Topic Test - Succession & Conservation
7.4.9 A-A* (AO3/4) - Ecosystems
8 The Control of Gene Expression (A2 only)
8.1 Mutation
8.1.1 Mutations
8.1.2 Effects of Mutations
8.1.3 Causes of Mutations
8.2 Gene Expression
8.2.1 Stem Cells
8.2.2 Stem Cells in Disease
8.2.3 End of Topic Test - Mutation & Gene Epression
8.2.4 A-A* (AO3/4) - Mutation & Stem Cells
8.2.5 Regulating Transcription
8.2.6 Epigenetics
8.2.7 Epigenetics & Disease
8.2.8 Regulating Translation
8.2.9 Experimental Data
8.2.10 End of Topic Test - Transcription & Translation
8.2.11 Tumours
8.2.12 Correlations & Causes
8.2.13 Prevention & Treatment
8.2.14 End of Topic Test - Cancer
8.2.15 A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Expression & Cancer
8.3 Genome Projects
8.3.1 Using Genome Projects
8.4 Gene Technology
8.4.1 Recombinant DNA
8.4.2 Producing Fragments
8.4.3 Amplification
8.4.4 End of Topic Test - Genome Project & Amplification
8.4.5 Using Recombinant DNA
8.4.6 Medical Diagnosis
8.4.7 Genetic Fingerprinting
8.4.8 End of Topic Test - Gene Technologies
8.4.9 A-A* (AO3/4) - Gene Technology
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
End of Topic Test - Nucleic Acids & ATP
A-A* (AO3/4) - Water
Skip to content

Get Revising
Join get revising, already a member, essay 14: the biological importance of water.
- Created by: bethanythomas101
- Created on: 10-04-18 15:21
The biological importance of water:
- Structure (Dipolar, Hydrogen bonds)
- Solvent (Hydrophobic/phillic interactions, proteins, nucleic acids, diffusion of molecules, dilution of toxic compunds- urea)
- Osmosis and turgidity (Effect on plants)
- Transport medium (Xylem, phloem, blood, lymph, secretion, excretion)
- High heat capacity (Temperature regulation)
- High heat of vapourisation (Cooling effect- sweating…
- Whole Syllabus
No comments have yet been made
Similar Biology resources:
AQA Biology Unit 5 - Synoptic essay titles 0.0 / 5
ESSAYS - AQA A Level Biology 0.0 / 5
AQA SYNOPTIC ESSAY PLAN 0.0 / 5
All previous essay titles 0.0 / 5
Survival and response, Nerve impulses, Synaptic transmission, Receptors and Control of heart rate AQA A2 Biology - EXAM QUESTIONS 0.0 / 5
Biology - Topic 1 Biological Molecules - Carbohydrates 1 0.0 / 5
1.1 Chemical elements and biological compounds 0.0 / 5
Module 2: Section 2 - Biological Molecules 0.0 / 5
Core Concepts; Chemical elements and biological compounds 0.0 / 5
2.2 Biological Molecules 0.0 / 5
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Paper 3 AQA a Level biology »
- AQA Biology essay »
- Tips for A Level »
- AQA A-Level Biology Paper 3 [21st June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Should I do a science essay competition for my personal statement? »
- 25 mark essay question »
- Paper 3 BIO essay question »
- GCSE English spoken language endorsement »
- Ib ee research question on pyschology maybe? »
- 25 marker essay biology »
This website works best with JavaScript switched on. Please enable JavaScript
- Centre Services
- Associate Extranet
- All About Maths
AS and A-level Biology
- Specification
- Planning resources
- Teaching resources
- Assessment resources
- Introduction
- Specification at a glance
- 3.1 Biological molecules
- 3.3 Organisms exchange substances with their environment
- 3.4 Genetic information, variation and relationships between organisms
- 3.5 Energy transfers in and between organisms (A-level only)
- 3.6 Organisms respond to changes in their internal and external environments (A-level only)
- 3.7 Genetics, populations, evolution and ecosystems (A-level only)
- 3.8 The control of gene expression (A-level only)
- Scheme of assessment
- General administration
- Mathematical requirements and exemplifications
- AS practical assessment
- A-level practical assessment

3.1.7 Water
NEW Create SEO-optimized articles of any YouTube video with our free tool.
Mastering aqa biology essays: strategies for a-level success.
Article created from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5lGejJiPHY

Introduction
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on how to excel in AQA Biology A-Level essays, a component that accounts for a significant portion of your final grade. Preparing for these essays can seem daunting, but with the right approach and understanding, you can significantly enhance your performance and boost your overall grade.
The Importance of the AQA Biology Essay
The AQA A-Level Biology essay, particularly in Paper 3, is worth almost 10% of the total grade, making it a critical area for scoring high marks. Through detailed analysis of past essay titles across different specifications, we identify common themes and patterns to help students prepare effectively. While predictions of exact essay titles are not possible, focusing on recurring themes can guide your revision strategy.
Disclaimer on Essay Predictions
It's crucial to note that while this guide offers insights into potential essay titles based on past patterns, these are not predictions. Relying solely on these suggestions without a broader study could be misleading. The aim is to use these titles as a basis for practice and revision.
Key Essay Titles to Consider
Let's delve into three challenging essay titles that could enhance your revision efforts:
The Importance of Responses to Internal and External Environments in Organisms : This essay title focuses on how organisms adjust to changes in their environments, requiring a deep understanding of homeostasis, osmoregulation, and blood glucose control. For example, discussing the role of insulin in lowering blood glucose levels illustrates the complexity of internal environment responses.
The Importance of Energy Transfers Between and Within Organisms : Here, the focus shifts to energy transfer processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and food chains. Students should emphasize the efficiency of energy transfers and the significance of energy loss at different trophic levels, applying A-Level concepts to demonstrate understanding beyond GCSE knowledge.
The Importance of the Control of Processes in Organisms : This title invites discussion on regulatory mechanisms within organisms, such as the role of spindle fibers in mitosis, transcription factors in gene expression, and ADH in osmoregulation. Highlighting the importance of these control processes is crucial to scoring high marks.
Strategies for Essay Success
- Understand the Mark Scheme : Familiarize yourself with the AQA mark scheme and examiner reports to grasp what distinguishes a high-scoring essay from a mediocre one.
- Practice with Purpose : Regularly practice writing essays on these themes, focusing on structuring your arguments coherently and including relevant A-Level content.
- Revise Broadly : While these essay titles are valuable for focused revision, ensure you cover the entire AQA Biology specification to prepare for any curveballs in the exam.
Essay Boot Camp
For students seeking additional support, consider enrolling in an essay boot camp course. These courses offer detailed guidance on essay writing skills, topic mastery, and techniques to maximize marks.
Mastering the AQA Biology essay requires a strategic approach to revision, an understanding of key themes, and practice. By focusing on the areas highlighted in this guide, you can approach your A-Level Biology exam with confidence, ready to tackle essays that showcase your knowledge and analytical skills.
For more detailed insights into each essay title and further resources, including the essay boot camp, check out the video linked below.
Watch the full video here
Ready to automate your customer support with AI?
Join over 150+ businesses, websites and startups automating their customer support with a custom trained GPT chatbot.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Biology is detailed and comprehensive A-level content, uses appropriate terminology, and is very well written and always clearly explained. No significant errors or irrelevant material. For top marks in the band, the answer shows evidence of reading beyond specification requirements. 16-20. Relational.
The importance of shapes fitting together in cells and organisms. 1) Enzyme properties and digestion. 2) Protein structure. 3) Plasma membrane structure and cell transport. 4) Antigens, antibodies, B cells & T cells. 5) Vaccines. 6) Structure of DNA. 7) DNA Replication (not PCR) 8) Transcription & translation.
The importance of ions in biology. Click the card to flip 👆. 1.) Na+ ions in cotransport of glucose. - importance: Na+ ion concentration gradient is what drives the movement of glucose into cell - utilising energy efficiently. 2.) Na+ ions in osmoregulation. - Loop of Henle - maintains Na+ ion gradient. - importance: ensures water can leave ...
An example AQA Biology A-Level synoptic essay for the title "The ways in which water and the regulation of water content are important in organisms" Top band standard (25/25). Intended to be used as an example essay for inspiration and not to be copied under any circumstances.
Join now →. The biological importance of water is due to its unique properties, such as its high polarity, ability to form hydrogen bonds, and high heat capacity, which make it essential for a variety of biological processes, including maintaining cellular structure, regulating temperature, and facilitating metabolic reactions.
Water is of great biological importance. It is the medium in which all metabolic reactions take place in cells. Between 70% to 95% of the mass of a cell is water. Water is composed of atoms of hydrogen and oxygen. One atom of oxygen combines with two atoms of hydrogen by sharing electrons ( covalent bonding) This separation of charge due to the ...
the essay (e.g. importance) at A-level standard. The ways in which water and the regulation of water content are important to organisms. In order to fully address the question and reach the highest mark bands students must also include at least five topics in their answer, to demonstrate a synoptic approach to the essay. Specification reference
AQA A-Level Biology alevelbiology.co.uk 3.1.7 Water SPECIFICATION Water is a major component of cells. It has several properties that are important in biology. In particular, water: ‒ is a metabolite in many metabolic reactions, including condensation and hydrolysis reactions ‒ is an important solvent in which metabolic reactions occur has a
Cohesion produces surface tension where water meets air. This is why water forms droplets when placed on a dry surface rather than being flattened out by gravity. Plants use this natural phenomenon to help transport water from their roots to their leaves. Water is a major component of cells and makes up 60-70% of the human body.
The biological importance of water: Structure (Dipolar, Hydrogen bonds) Solvent (Hydrophobic/phillic interactions, proteins, nucleic acids, diffusion of molecules, dilution of toxic compunds- urea) Osmosis and turgidity (Effect on plants) ... Paper 3 AQA a Level biology » AQA Biology essay » ...
5. Water is a metabolite in metabolic reactions (condensation, hydrolysis) 6. Water stabilises external temperatures. 7. Water important in cooling internal temperature of organisms. Most substances contract when they cool. Water is unusual, as it freezes, it expands and becomes lighter. Suggest why water becomes lighter as it expands.
Water is a major component of cells. It has several properties that are important in biology. In particular, water: is a metabolite in many metabolic reactions, including condensation and hydrolysis reactions. is an important solvent in which metabolic reactions occur. has a relatively high heat capacity, buffering changes in temperature.
Throughout the development of the current 7402 A-level Biology specification, AQA spoke to teachers and university experts about the biology essay. It was clear that that extended writing was seen as an important skill that biology students should be developing. 'Level of response' mark
Water is an essential biological molecule. In this video, I explain how water's dipole structure and hydrogen bonds lead to it having these 5 key features:1...
44 essay titles and indiciative mark schemes for AQA A level biology Paper 3 25 mark essay question. contents essay mark schemes general guidance. Skip to document. ... A-level biology notes on water, 354658960 Kahulugan at Kalikasan Ng Akademikong Pagsulat; ... Not addressing the biological theme of the essay (e. importance) at A-level ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Explain five properties that make water important for organisms, State and explain the property of water that helps to prevent temperature increase in a cell, State and explain the property of water that can help to buffer changes in temperature and more.
The Importance of the AQA Biology Essay. The AQA A-Level Biology essay, particularly in Paper 3, is worth almost 10% of the total grade, making it a critical area for scoring high marks. Through detailed analysis of past essay titles across different specifications, we identify common themes and patterns to help students prepare effectively.
AQA A Level Biology - 25 Mark Essays. 23 terms. biotig. Preview. ... Haematopoiesis and lymph organogenesis . 14 terms. Fkerr2003. Preview. Importance of cycles in biology essay*** 20+/25. 29 terms. hjungbluth. Preview. Biology essay plans. 14 terms. Emily_Storer. Preview. Biology- 3.4 Food production. 20 terms. ... Importance of water and ...
Solvent. As water is a polar molecule many ions, e.g. sodium and chloride ions, and covalently bonded polar substances, e.g. glucose, will dissolve in it . Water molecules surround charged particles; the positive parts of water are attracted to negatively charged particles and the negative parts of water are attracted to positively charged particles ...
AQA A level Biology Essay. The importance of responses to changes in the internal and external environment of an organism. Click the card to flip 👆. Control of heart rate (changes in pH and pressure) Control of blood glucose (glucagon and insulin) Osmoregulation (water potential changes) Action potentials/ pacinian corpuscles (stimulus)
AmySutherland103. Preview. Biology Exam 4 (Energy) 47 terms. shortie__2. Preview. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The importance of responses to changes in the internal and external environment of an organism., The importance of diffusion in organisms., The functions of enzymes and their importance in organisms ...