Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .

Neag School of Education
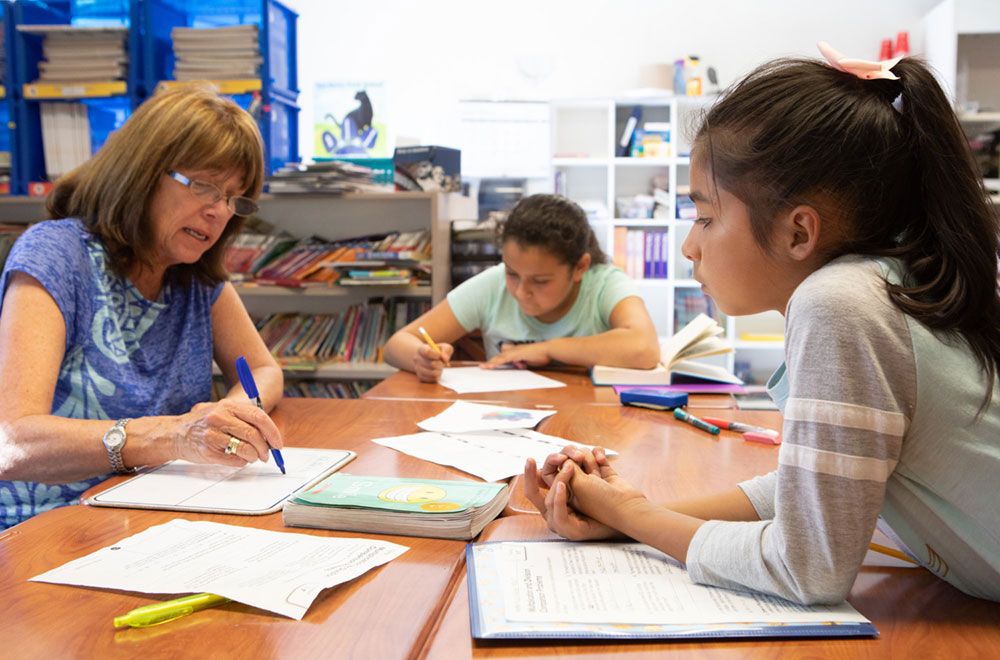
How to use homework to support student success.
- by: Sandra Chafouleas
- January 13, 2022
- Community Engagement

Editor’s Note: Board of Trustees Distinguished Professor Sandra Chafouleas shares insights on supporting students’ homework during the pandemic in the following piece, which originally appeared in Psychology Today , where she publishes a blog.
COVID has brought many changes in education. What does it mean for homework?
School assignments that a student is expected to do outside of the regular school day—that’s homework. The general guideline is 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level beginning after kindergarten. This amounts to just a few minutes for younger elementary students to up to 2 hours for high school students.
The guidance seems straightforward enough, so why is homework such a controversial topic? School disruptions, including extended periods of remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, have magnified the controversies yet also have provided an opportunity to rethink the purpose and value of homework.
Debates about the value of homework center around two primary issues: amount and inequity.
First, the amount of assigned homework may be much more than the recommended guidelines. Families report their children are stressed out over the time spent doing homework. Too much homework can challenge well-being given the restricted time available for sleep, exercise, and social connection. In a 2015 study , for example, parents reported their early elementary children received almost three times the recommended guidelines. In high school, researchers found an average of three hours of homework per night for students living in economically privileged communities.
“ Debates about the value of homework center around two primary issues: amount and inequity.”
Second, homework can perpetuate inequities. Students attending school in less economically privileged communities may receive little to no homework, or have difficulty completing it due to limited access to needed technology. This can translate into fewer opportunities to learn and may contribute to gaps in achievement.
There isn’t a ton of research on the effects of homework, and available studies certainly do not provide a simple answer. For example, a 2006 synthesis of studies suggested a positive influence between homework completion and academic achievement for middle and high school students. Supporters also point out that homework offers additional opportunities to engage in learning and that it can foster independent learning habits such as planning and a sense of responsibility. A more recent study involving 13-year-old students in Spain found higher test scores for those who were regularly assigned homework in math and science, with an optimal time around one hour—which is roughly aligned with recommendations. However, the researchers noted that ability to independently do the work, student effort, and prior achievement were more important contributors than time spent.
Opponents of homework maintain that the academic benefit does not outweigh the toll on well-being. Researchers have observed student stress, physical health problems, and lack of life balance, especially when the time spent goes over the recommended guidelines. In a survey of adolescents , over half reported the amount and type of homework they received to be a primary source of stress in their lives. In addition, vast differences exist in access and availability of supports, such as internet connection, adult assistance, or even a place to call home, as 1.5 million children experience homelessness in the United States
The COVID-19 pandemic has re-energized discussion about homework practices, with the goal to advance recommendations about how, when, and with whom it can be best used. Here’s a summary of key strategies:
Strategies for Educators
Make sure the tasks are meaningful and matched..
First, the motto “ quality over quantity ” can guide decisions about homework. Homework is not busy-work, and instead should get students excited about learning. Emphasize activities that facilitate choice and interest to extend learning, like choose your own reading adventure or math games. Second, each student should be able to complete homework independently with success. Think about Goldilocks: To be effective, assignments should be just right for each learner. One example of how do this efficiently is through online learning platforms that can efficiently adjust to skill level and can be completed in a reasonable amount of time.
Ensure access to resources for task completion.
One step toward equity is to ensure access to necessary resources such as time, space, and materials. Teach students about preparing for homework success, allocating classroom time to model and practice good study habits such as setting up their physical environment, time management, and chunking tasks. Engage in conversations with students and families to problem-solve challenges When needed, connect students with homework supports available through after-school clubs, other community supports, or even within a dedicated block during the school day.
Be open to revisiting homework policies and practices.
The days of penalizing students for not completing homework should be long gone. Homework is a tool for practicing content and learning self-management. With that in mind, provide opportunities for students to communicate needs, and respond by revising assignments or allowing them to turn in on alternative dates. Engage in adult professional learning about high-quality homework , from value (Should I assign this task?) to evaluation (How should this be graded? Did that homework assignment result in expected outcomes?). Monitor how things are going by looking at completion rates and by asking students for their feedback. Be willing to adapt the homework schedule or expectations based on what is learned.
Strategies for Families
Understand how to be a good helper..
When designed appropriately, students should be able to complete homework with independence. Limit homework wars by working to be a good helper. Hovering, micromanaging, or doing homework for them may be easiest in the moment but does not help build their independence. Be a good helper by asking guiding questions, providing hints, or checking for understanding. Focus your assistance on setting up structures for homework success, like space and time.
Use homework as a tool for communication.
Use homework as a vehicle to foster family-school communication. Families can use homework as an opportunity to open conversations about specific assignments or classes, peer relationships, or even sleep quality that may be impacting student success. For younger students, using a daily or weekly home-school notebook or planner can be one way to share information. For older students, help them practice communicating their needs and provide support as needed.
Make sure to balance wellness.
Like adults, children need a healthy work-life balance. Positive social connection and engagement in pleasurable activities are important core principles to foster well-being . Monitor the load of homework and other structured activities to make sure there is time in the daily routine for play. Play can mean different things to different children: getting outside, reading for pleasure, and yes, even gaming. Just try to ensure that activities include a mix of health-focused activities such as physical movement or mindfulness downtime.

The Council for the Accreditation of Educator Preparation (CAEP) accredits the Neag School of Education at the University of Connecticut. Read more about CAEP Accreditation, including the programs covered and the accountability measures .
Some content on this website may require the use of a plug-in, such as Adobe Acrobat Viewer .
- Support the Neag School
Neag School of Education 249 Glenbrook Road, Unit 3064 Charles B. Gentry Building Storrs, CT 06269-3064
860-486-3815 [email protected]
- 6-12th Grade Mentoring
- College Coaching
- Student Athletes
- Professional Development
- Educator Resources
- Professionals

Homework Centers
Schedule Time in the Homework Center
The homework center is our structured work environment available to students in the mentoring program. Here, they can complete assignments or study. Math and language arts support staff are available to answer questions and help keep students on task.
In-Person Homework Center (Broomfield)
In-person homework center (sport stable), remote homework center, homework center hours.
View our locations
For Broomfield and remote questions, please reach out to Sam at [email protected].
For Sport Stable questions, please reach out to Tyler at [email protected].
Let’s untap your student’s potential together.
For immediate release | November 27, 2017
A comprehensive resource to help public libraries create and manage homework centers

CHICAGO — Despite the proliferation of online homework websites and tutoring services, public libraries still have an important role to play when it comes to supporting young people’s educational needs. Public libraries that take a proactive approach—by setting up organized homework centers—have the potential to become catalysts for better performance in school, improved self-esteem, and engaged learning. Whether readers are investigating the possibility of setting up a center from scratch or are eager to revamp an existing center, Cindy Mediavilla’s “ Creating & Managing the Full-Service Homework Center ,” published by ALA Editions, shows the way forward with:
- discussion of the philosophy behind a public library homework center and its many benefits, with useful talking points for getting stakeholders on board;
- examples of model programs from across the country;
- guidance on assessing the community’s educational priorities and utilizing outcome-based planning and evaluation methods;
- pragmatic advice on how to collaborate with schools and educators to coordinate goals;
- thorough consideration of such key issues as carving out a space, setting hours, scheduling staff, and selecting and procuring educational resources;
- handy tools for a successful homework center, including sample surveys, homework helper application forms and contracts, staff and volunteer job descriptions, and focus group questions;
- advice on equipment and technology considerations; and
- methodologies for evaluation and improvement.
Mediavilla authored “Creating the Full–Service Homework Center in Your Library,” (ALA, 2001), which has been called “the quintessential guide to the practicalities of setting up a formal homework help center to provide one–to–one homework assistance to student patrons” (Intner, “Homework Help from the Library,” ix). In the early 1990s she managed a homework center, called the Friendly Stop, for the Orange (CA) Public Library, and she has been studying after–school homework programs ever since. She has published several articles on the topic and has evaluated homework programs for the Long Beach and Los Angeles public libraries. She has made presentations on homework help programs at the conferences of several major library associations, and she has also conducted many workshops on the topic.
ALA Store purchases fund advocacy, awareness and accreditation programs for library professionals worldwide. ALA Editions and ALA Neal-Schuman publishes resources used worldwide by tens of thousands of library and information professionals to improve programs, build on best practices, develop leadership, and for personal professional development. ALA authors and developers are leaders in their fields, and their content is published in a growing range of print and electronic formats. Contact ALA Editions at (800) 545-2433 ext. 5052 or [email protected].
Related Links
"Creating & Managing the Full-Service Homework Center"
"The Student’s Survival Guide to Research"
"Homework Help from the Library: In Person and Online"
Rob Christopher
Marketing Coordinator
American Library Association
ALA Publishing
(312) 280-5052
Share This Page
Featured News

May 7, 2024
ALA partners with League of Women Voters to empower voters in 2024
The American Library Association and League of Women Voters today announced a new partnership to educate and empower voters in 2024.
press release

April 17, 2024
The TRANSFORMERS Are Ready to Roll Out for Library Card Sign-Up Month
The American Library Association (ALA) is teaming up with multiplatform entertainment company Skybound Entertainment and leading toy and game company Hasbro to encourage people to roll out to their libraries with the TRANSFORMERS franchise, featuring Optimus Prime, as part of Library Card Sign-Up Month in September.

April 15, 2024
ALA launches FY 2025 #FundLibraries campaign, urges Congress to fully fund key federal programs
ALA launches FY 2025 #FundLibraries campaign, urges Congress to fully fund key federal programs.

April 10, 2024
American Library Association Launches Reader. Voter. Ready. Campaign to Equip Libraries for 2024 Elections
Today the American Library Association (ALA) kicks off its Reader. Voter. Ready. campaign, calling on advocates to sign a pledge to be registered, informed, and ready to vote in all local, state and federal elections in 2024.

April 8, 2024
ALA kicks off National Library Week revealing the annual list of Top 10 Most Challenged Books and the State of America’s Libraries Report
The American Library Association (ALA) launched National Library Week with today’s release of its highly anticipated annual list of the Top 10 Most Challenged Books of 2023 and the State of America’s Libraries Report, which highlights the ways libraries...

Pun wins 2025-2026 ALA presidency
Raymond Pun, Academic and Research Librarian at the Alder Graduate School of Education in California has been elected 2024-2025 president-elect of the American Library Association (ALA).

Creating & Managing the Full-Service Homework Center

Primary tabs
You don't need to be an ALA Member to purchase from the ALA Store, but you'll be asked to create an online account/profile during the checkout to proceed. This Web Account is for both Members and non-Members.
If you are Tax-Exempt , please verify that your account is currently set up as exempt before placing your order, as our new fulfillment center will need current documentation. Learn how to verify here.
- Description
- Table of Contents
- About the author
Read a conversation with the author now!
Despite the proliferation of online homework websites and tutoring services, public libraries still have an important role to play when it comes to supporting young people’s educational needs. Public libraries that take a proactive approach—by setting up organized homework centers—have the potential to become catalysts for better performance in school, improved self-esteem, and engaged learning. Whether readers are investigating the possibility of setting up a center from scratch or are eager to revamp an existing center, this book shows the way forward with
- discussion of the philosophy behind a public library homework center and its many benefits, with useful talking points for getting stakeholders on board;
- examples of model programs from across the country;
- guidance on assessing the community’s educational priorities and utilizing outcome-based planning and evaluation methods;
- pragmatic advice on how to collaborate with schools and educators to coordinate goals;
- thorough consideration of such key issues as carving out a space, setting hours, scheduling staff, and selecting and procuring educational resources;
- handy tools for a successful homework center, including sample surveys, homework helper application forms and contracts, staff and volunteer job descriptions, and focus group questions;
- advice on equipment and technology considerations; and
- methodologies for evaluation and improvement.
This comprehensive resource will help public libraries create and manage a vibrant homework center that effectively serves students while also building community support for the library.
Acknowledgments Introduction Chapter 1 Why Homework Centers? Chapter 2 Community Assessment Chapter 3 Service Plan Chapter 4 Staff and Volunteer Recruitment Chapter 5 Job Duties and Training Chapter 6 Funding and Partnerships Chapter 7 Collaboration with Schools Chapter 8 Space and Location Chapter 9 Service Hours Chapter 10 Programming and Corollary Services Chapter 11 Library Resources Chapter 12 Supplies and Equipment Chapter 13 Security, User Expectations, and Rules of Conduct Chapter 14 Media and Public Relations Chapter 15 Evaluation and Measuring Outcomes Appendixes
A Model Homework Programs B Community Assessment Tools C Homework Staff Recruitment Announcements D Homework Helper Application Forms E Homework Helper Contract F Homework Staff Job Descriptions G Training Modules H Staff Manual Excerpts I Letter of Intent J Teacher Letters K Registration Forms L Survey Instruments
Bibliography Index
Cindy Mediavilla
Cindy Mediavilla is an author and library consultant who recently retired from the California State Library as well as the UCLA Department of Information Studies. She is also a former public librarian. Her areas of expertise include community assessment, outcome-based planning and evaluation, after-school homework programs, library residency programs, and grant writing. Her most recent books include Libraries & Gardens: Growing Together (ALA Editions, 2019), coauthored with Carrie Banks. Cindy’s MLS and PhD are both from UCLA.
"This imaginative book offers librarians a unique opportunity to fashion creative learning centers ... The content is inspiring and offers straightforward advice for professionals interested in developing homework centers that support curriculum needs. Every librarian who strives to meet the learning needs of today’s youth needs to read this book. In addition, teachers and trainers would find this contribution to be an essential planning tool to assist in curriculum foundations." — ARBA
”A well-researched, all-inclusive guide ... The lengthy, beneficial appendix provides practical tools and details of all the steps necessary to follow the concrete examples discussed throughout the text.” — VOYA
”A solid guide for public librarians wishing to develop a homework center for students.” — School Library Journal
”If your library is considering a homework help center or if you already have one, but you wish it was more successful, you're likely to find just the help and advice you need in this book.” — Public Libraries
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
What we know about online learning and the homework gap amid the pandemic

America’s K-12 students are returning to classrooms this fall after 18 months of virtual learning at home during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some students who lacked the home internet connectivity needed to finish schoolwork during this time – an experience often called the “ homework gap ” – may continue to feel the effects this school year.
Here is what Pew Research Center surveys found about the students most likely to be affected by the homework gap and their experiences learning from home.
Children across the United States are returning to physical classrooms this fall after 18 months at home, raising questions about how digital disparities at home will affect the existing homework gap between certain groups of students.
Methodology for each Pew Research Center poll can be found at the links in the post.
With the exception of the 2018 survey, everyone who took part in the surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
The 2018 data on U.S. teens comes from a Center poll of 743 U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 conducted March 7 to April 10, 2018, using the NORC AmeriSpeak panel. AmeriSpeak is a nationally representative, probability-based panel of the U.S. household population. Randomly selected U.S. households are sampled with a known, nonzero probability of selection from the NORC National Frame, and then contacted by U.S. mail, telephone or face-to-face interviewers. Read more details about the NORC AmeriSpeak panel methodology .
Around nine-in-ten U.S. parents with K-12 children at home (93%) said their children have had some online instruction since the coronavirus outbreak began in February 2020, and 30% of these parents said it has been very or somewhat difficult for them to help their children use technology or the internet as an educational tool, according to an April 2021 Pew Research Center survey .
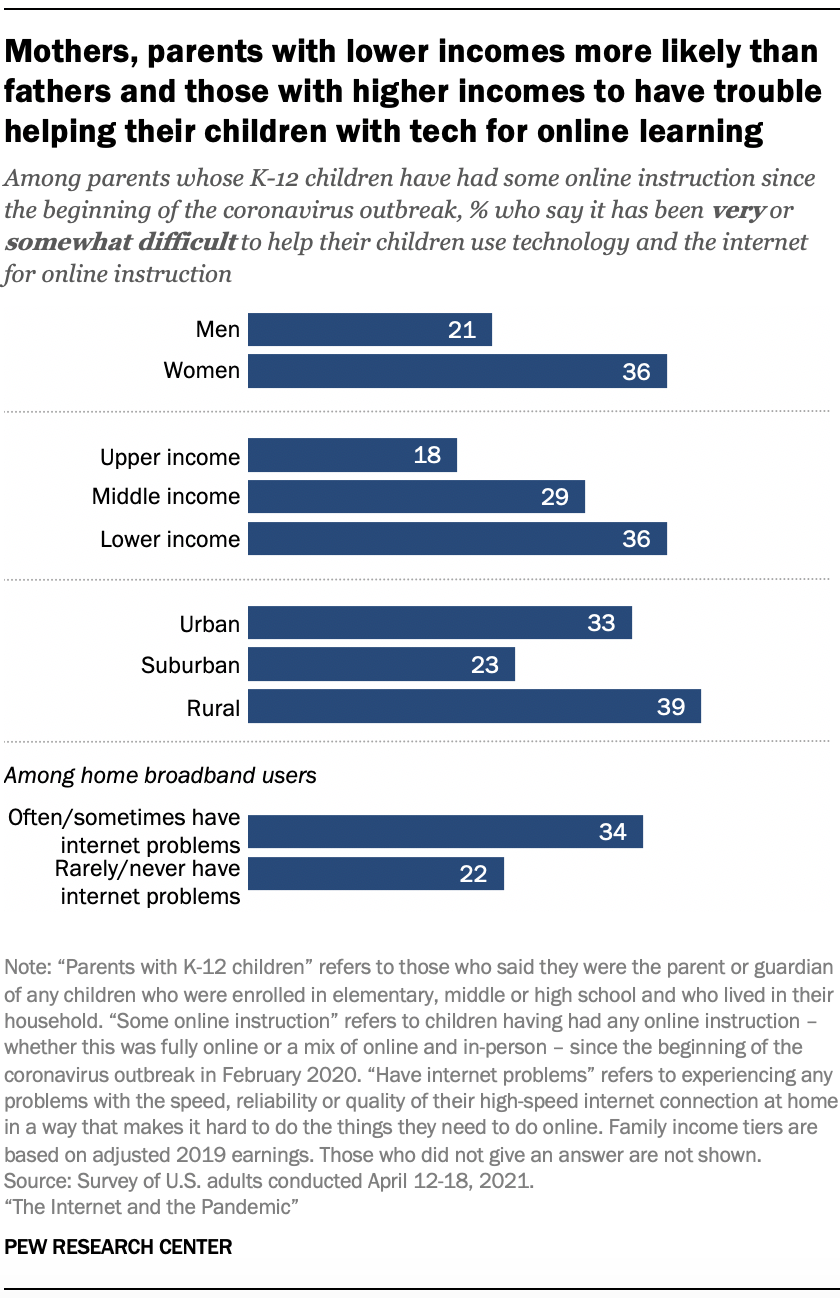
Gaps existed for certain groups of parents. For example, parents with lower and middle incomes (36% and 29%, respectively) were more likely to report that this was very or somewhat difficult, compared with just 18% of parents with higher incomes.
This challenge was also prevalent for parents in certain types of communities – 39% of rural residents and 33% of urban residents said they have had at least some difficulty, compared with 23% of suburban residents.
Around a third of parents with children whose schools were closed during the pandemic (34%) said that their child encountered at least one technology-related obstacle to completing their schoolwork during that time. In the April 2021 survey, the Center asked parents of K-12 children whose schools had closed at some point about whether their children had faced three technology-related obstacles. Around a quarter of parents (27%) said their children had to do schoolwork on a cellphone, 16% said their child was unable to complete schoolwork because of a lack of computer access at home, and another 14% said their child had to use public Wi-Fi to finish schoolwork because there was no reliable connection at home.
Parents with lower incomes whose children’s schools closed amid COVID-19 were more likely to say their children faced technology-related obstacles while learning from home. Nearly half of these parents (46%) said their child faced at least one of the three obstacles to learning asked about in the survey, compared with 31% of parents with midrange incomes and 18% of parents with higher incomes.
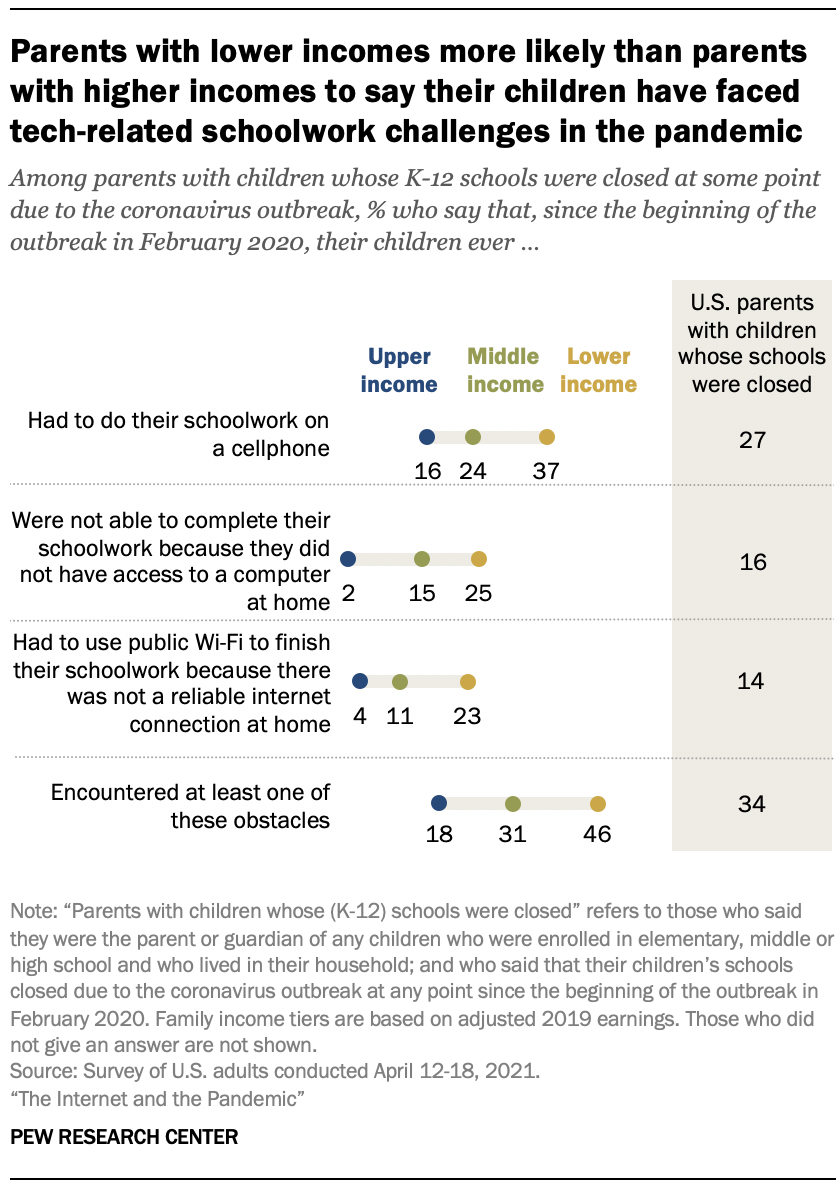
Of the three obstacles asked about in the survey, parents with lower incomes were most likely to say that their child had to do their schoolwork on a cellphone (37%). About a quarter said their child was unable to complete their schoolwork because they did not have computer access at home (25%), or that they had to use public Wi-Fi because they did not have a reliable internet connection at home (23%).
A Center survey conducted in April 2020 found that, at that time, 59% of parents with lower incomes who had children engaged in remote learning said their children would likely face at least one of the obstacles asked about in the 2021 survey.
A year into the outbreak, an increasing share of U.S. adults said that K-12 schools have a responsibility to provide all students with laptop or tablet computers in order to help them complete their schoolwork at home during the pandemic. About half of all adults (49%) said this in the spring 2021 survey, up 12 percentage points from a year earlier. An additional 37% of adults said that schools should provide these resources only to students whose families cannot afford them, and just 13% said schools do not have this responsibility.
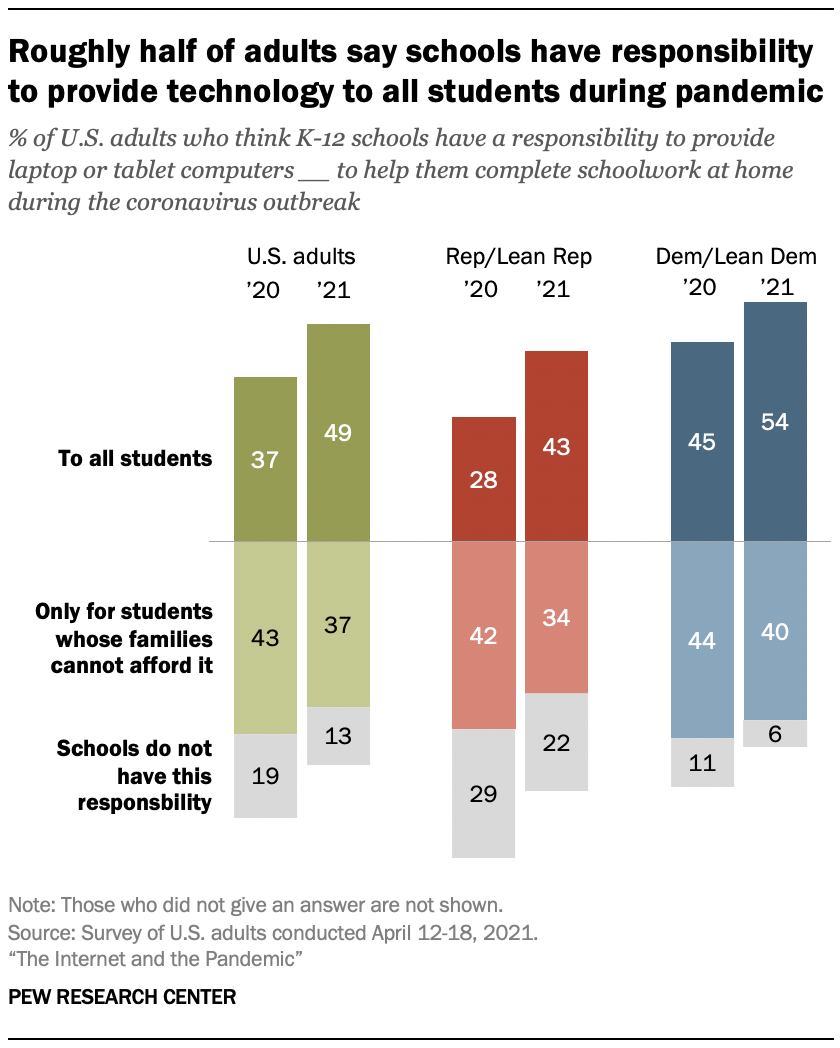
While larger shares of both political parties in April 2021 said K-12 schools have a responsibility to provide computers to all students in order to help them complete schoolwork at home, there was a 15-point change among Republicans: 43% of Republicans and those who lean to the Republican Party said K-12 schools have this responsibility, compared with 28% last April. In the 2021 survey, 22% of Republicans also said schools do not have this responsibility at all, compared with 6% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
Even before the pandemic, Black teens and those living in lower-income households were more likely than other groups to report trouble completing homework assignments because they did not have reliable technology access. Nearly one-in-five teens ages 13 to 17 (17%) said they are often or sometimes unable to complete homework assignments because they do not have reliable access to a computer or internet connection, a 2018 Center survey of U.S. teens found.
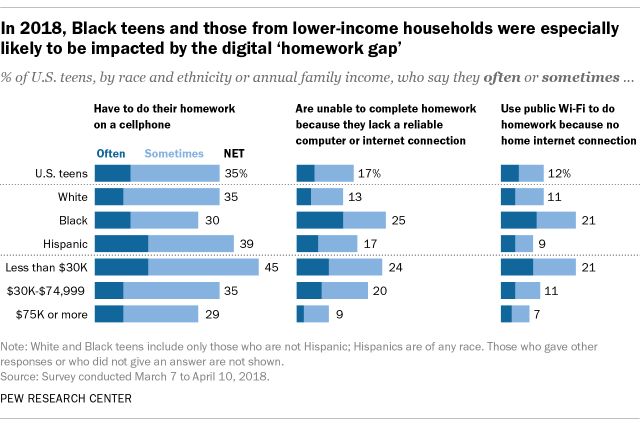
One-quarter of Black teens said they were at least sometimes unable to complete their homework due to a lack of digital access, including 13% who said this happened to them often. Just 4% of White teens and 6% of Hispanic teens said this often happened to them. (There were not enough Asian respondents in the survey sample to be broken out into a separate analysis.)
A wide gap also existed by income level: 24% of teens whose annual family income was less than $30,000 said the lack of a dependable computer or internet connection often or sometimes prohibited them from finishing their homework, but that share dropped to 9% among teens who lived in households earning $75,000 or more a year.
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- COVID-19 & Technology
- Digital Divide
- Education & Learning Online

Katherine Schaeffer is a research analyst at Pew Research Center .
How Americans View the Coronavirus, COVID-19 Vaccines Amid Declining Levels of Concern
Online religious services appeal to many americans, but going in person remains more popular, about a third of u.s. workers who can work from home now do so all the time, how the pandemic has affected attendance at u.s. religious services, mental health and the pandemic: what u.s. surveys have found, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Homework Center
- Select a Campus to Begin Get Started

- Available anytime during campus hours, 6 days a week
- Low ratio of 5 students or less per instructor
- Help available in all K-8 subjects
- Safe, supervised, and fun place for students to work, play, and make friends
- For grades K-8
- Summer Camps
- Edison Club
- Birthday Parties
- Parents Night Out Events
- Academic Enrichment
- Track Out Camps
- Into the Wild: Animal Explorers
- Summer - Lego Robotics
- Summer - STEAM Quest Galactic Missions
- Summer - STEAM Quest Superheros
- Summer - Minecraft Galaxy
- Summer - GarageBand
- Summer - 3D Printing
- Intro to Computer Science with Micro:Bit
- Summer - Intro to Scratch
- Drop and Shop
- Summer - Minecraft Physics
- Summer - App Creation
- Advanced 3D Printing
- Zane Reading
- Minecraft Industry & Production
- Online Minecraft Game Night
- Space Science
- Minecraft Game Night
- Pre-K Programs
- TestSemesters
- Minecraft Pro
- Single Day Camps
- School Break Camps
- Zaniac After-School Transportation
- Transportation
- Minecraft Engineering and Design
- Summer - STEAM Quest Harry Potter
- Summer - Intro to Circuits Activities
- Summer - Modding
- Earth Science
- Zaniac Partnerships
- Saturday Kids Club
- Coding for Parents
- Summer - Fashion Design
- Summer- Scratch Game Design
- Summer - Java
- Summer - Python
- Summer - Drones
- Young Entrepreneurs
- Zaniac At Schools
- Edison Exploration
- STEAM Summer Camps
- Summer - STEAM Quest Mario
- Summer- Computer Mastery
- Summer - Simple Machines
- Campus Events
- Scientist Earth
- Art & Design
- Engineering
- Game Based Learning
- Outreach Programs
Homework in America
- 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education
Subscribe to the Brown Center on Education Policy Newsletter
Tom loveless tom loveless former brookings expert @tomloveless99.
March 18, 2014
- 18 min read
Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education

Homework! The topic, no, just the word itself, sparks controversy. It has for a long time. In 1900, Edward Bok, editor of the Ladies Home Journal , published an impassioned article, “A National Crime at the Feet of Parents,” accusing homework of destroying American youth. Drawing on the theories of his fellow educational progressive, psychologist G. Stanley Hall (who has since been largely discredited), Bok argued that study at home interfered with children’s natural inclination towards play and free movement, threatened children’s physical and mental health, and usurped the right of parents to decide activities in the home.
The Journal was an influential magazine, especially with parents. An anti-homework campaign burst forth that grew into a national crusade. [i] School districts across the land passed restrictions on homework, culminating in a 1901 statewide prohibition of homework in California for any student under the age of 15. The crusade would remain powerful through 1913, before a world war and other concerns bumped it from the spotlight. Nevertheless, anti-homework sentiment would remain a touchstone of progressive education throughout the twentieth century. As a political force, it would lie dormant for years before bubbling up to mobilize proponents of free play and “the whole child.” Advocates would, if educators did not comply, seek to impose homework restrictions through policy making.
Our own century dawned during a surge of anti-homework sentiment. From 1998 to 2003, Newsweek , TIME , and People , all major national publications at the time, ran cover stories on the evils of homework. TIME ’s 1999 story had the most provocative title, “The Homework Ate My Family: Kids Are Dazed, Parents Are Stressed, Why Piling On Is Hurting Students.” People ’s 2003 article offered a call to arms: “Overbooked: Four Hours of Homework for a Third Grader? Exhausted Kids (and Parents) Fight Back.” Feature stories about students laboring under an onerous homework burden ran in newspapers from coast to coast. Photos of angst ridden children became a journalistic staple.
The 2003 Brown Center Report on American Education included a study investigating the homework controversy. Examining the most reliable empirical evidence at the time, the study concluded that the dramatic claims about homework were unfounded. An overwhelming majority of students, at least two-thirds, depending on age, had an hour or less of homework each night. Surprisingly, even the homework burden of college-bound high school seniors was discovered to be rather light, less than an hour per night or six hours per week. Public opinion polls also contradicted the prevailing story. Parents were not up in arms about homework. Most said their children’s homework load was about right. Parents wanting more homework out-numbered those who wanted less.
Now homework is in the news again. Several popular anti-homework books fill store shelves (whether virtual or brick and mortar). [ii] The documentary Race to Nowhere depicts homework as one aspect of an overwrought, pressure-cooker school system that constantly pushes students to perform and destroys their love of learning. The film’s website claims over 6,000 screenings in more than 30 countries. In 2011, the New York Times ran a front page article about the homework restrictions adopted by schools in Galloway, NJ, describing “a wave of districts across the nation trying to remake homework amid concerns that high stakes testing and competition for college have fueled a nightly grind that is stressing out children and depriving them of play and rest, yet doing little to raise achievement, especially in elementary grades.” In the article, Vicki Abeles, the director of Race to Nowhere , invokes the indictment of homework lodged a century ago, declaring, “The presence of homework is negatively affecting the health of our young people and the quality of family time.” [iii]
A petition for the National PTA to adopt “healthy homework guidelines” on change.org currently has 19,000 signatures. In September 2013, Atlantic featured an article, “My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me,” by a Manhattan writer who joined his middle school daughter in doing her homework for a week. Most nights the homework took more than three hours to complete.
The Current Study
A decade has passed since the last Brown Center Report study of homework, and it’s time for an update. How much homework do American students have today? Has the homework burden increased, gone down, or remained about the same? What do parents think about the homework load?
A word on why such a study is important. It’s not because the popular press is creating a fiction. The press accounts are built on the testimony of real students and real parents, people who are very unhappy with the amount of homework coming home from school. These unhappy people are real—but they also may be atypical. Their experiences, as dramatic as they are, may not represent the common experience of American households with school-age children. In the analysis below, data are analyzed from surveys that are methodologically designed to produce reliable information about the experiences of all Americans. Some of the surveys have existed long enough to illustrate meaningful trends. The question is whether strong empirical evidence confirms the anecdotes about overworked kids and outraged parents.
Data from the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) provide a good look at trends in homework for nearly the past three decades. Table 2-1 displays NAEP data from 1984-2012. The data are from the long-term trend NAEP assessment’s student questionnaire, a survey of homework practices featuring both consistently-worded questions and stable response categories. The question asks: “How much time did you spend on homework yesterday?” Responses are shown for NAEP’s three age groups: 9, 13, and 17. [iv]
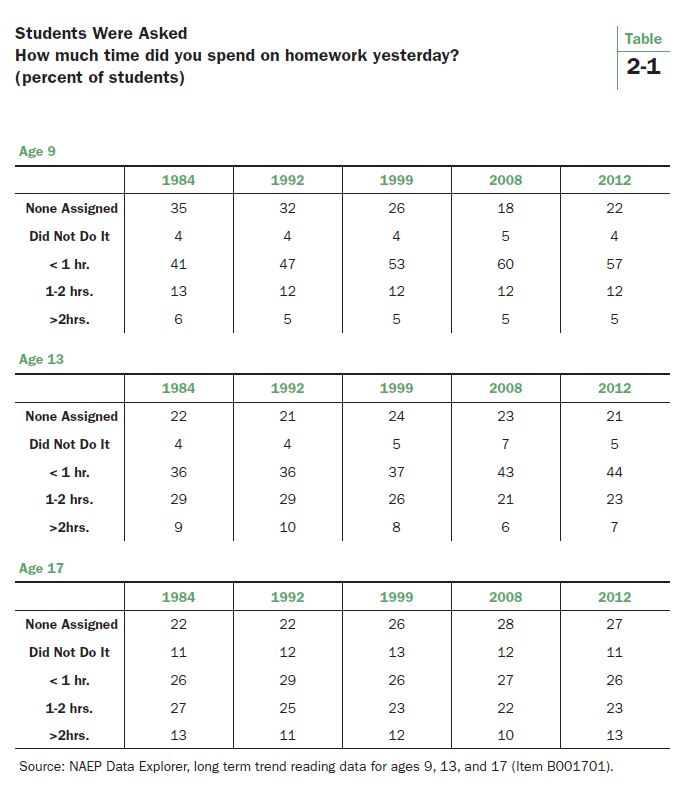
Today’s youngest students seem to have more homework than in the past. The first three rows of data for age 9 reveal a shift away from students having no homework, declining from 35% in 1984 to 22% in 2012. A slight uptick occurred from the low of 18% in 2008, however, so the trend may be abating. The decline of the “no homework” group is matched by growth in the percentage of students with less than an hour’s worth, from 41% in 1984 to 57% in 2012. The share of students with one to two hours of homework changed very little over the entire 28 years, comprising 12% of students in 2012. The group with the heaviest load, more than two hours of homework, registered at 5% in 2012. It was 6% in 1984.
The amount of homework for 13-year-olds appears to have lightened slightly. Students with one to two hours of homework declined from 29% to 23%. The next category down (in terms of homework load), students with less than an hour, increased from 36% to 44%. One can see, by combining the bottom two rows, that students with an hour or more of homework declined steadily from 1984 to 2008 (falling from 38% to 27%) and then ticked up to 30% in 2012. The proportion of students with the heaviest load, more than two hours, slipped from 9% in 1984 to 7% in 2012 and ranged between 7-10% for the entire period.
For 17-year-olds, the homework burden has not varied much. The percentage of students with no homework has increased from 22% to 27%. Most of that gain occurred in the 1990s. Also note that the percentage of 17-year-olds who had homework but did not do it was 11% in 2012, the highest for the three NAEP age groups. Adding that number in with the students who didn’t have homework in the first place means that more than one-third of seventeen year olds (38%) did no homework on the night in question in 2012. That compares with 33% in 1984. The segment of the 17-year-old population with more than two hours of homework, from which legitimate complaints of being overworked might arise, has been stuck in the 10%-13% range.
The NAEP data point to four main conclusions:
- With one exception, the homework load has remained remarkably stable since 1984.
- The exception is nine-year-olds. They have experienced an increase in homework, primarily because many students who once did not have any now have some. The percentage of nine-year-olds with no homework fell by 13 percentage points, and the percentage with less than an hour grew by 16 percentage points.
- Of the three age groups, 17-year-olds have the most bifurcated distribution of the homework burden. They have the largest percentage of kids with no homework (especially when the homework shirkers are added in) and the largest percentage with more than two hours.
- NAEP data do not support the idea that a large and growing number of students have an onerous amount of homework. For all three age groups, only a small percentage of students report more than two hours of homework. For 1984-2012, the size of the two hours or more groups ranged from 5-6% for age 9, 6-10% for age 13, and 10-13% for age 17.
Note that the item asks students how much time they spent on homework “yesterday.” That phrasing has the benefit of immediacy, asking for an estimate of precise, recent behavior rather than an estimate of general behavior for an extended, unspecified period. But misleading responses could be generated if teachers lighten the homework of NAEP participants on the night before the NAEP test is given. That’s possible. [v] Such skewing would not affect trends if it stayed about the same over time and in the same direction (teachers assigning less homework than usual on the day before NAEP). Put another way, it would affect estimates of the amount of homework at any single point in time but not changes in the amount of homework between two points in time.
A check for possible skewing is to compare the responses above with those to another homework question on the NAEP questionnaire from 1986-2004 but no longer in use. [vi] It asked students, “How much time do you usually spend on homework each day?” Most of the response categories have different boundaries from the “last night” question, making the data incomparable. But the categories asking about no homework are comparable. Responses indicating no homework on the “usual” question in 2004 were: 2% for age 9-year-olds, 5% for 13 year olds, and 12% for 17-year-olds. These figures are much less than the ones reported in Table 2-1 above. The “yesterday” data appear to overstate the proportion of students typically receiving no homework.
The story is different for the “heavy homework load” response categories. The “usual” question reported similar percentages as the “yesterday” question. The categories representing the most amount of homework were “more than one hour” for age 9 and “more than two hours” for ages 13 and 17. In 2004, 12% of 9-year-olds said they had more than one hour of daily homework, while 8% of 13-year-olds and 12% of 17-year-olds said they had more than two hours. For all three age groups, those figures declined from1986 to 2004. The decline for age 17 was quite large, falling from 17% in 1986 to 12% in 2004.
The bottom line: regardless of how the question is posed, NAEP data do not support the view that the homework burden is growing, nor do they support the belief that the proportion of students with a lot of homework has increased in recent years. The proportion of students with no homework is probably under-reported on the long-term trend NAEP. But the upper bound of students with more than two hours of daily homework appears to be about 15%–and that is for students in their final years of high school.
College Freshmen Look Back
There is another good source of information on high school students’ homework over several decades. The Higher Education Research Institute at UCLA conducts an annual survey of college freshmen that began in 1966. In 1986, the survey started asking a series of questions regarding how students spent time in the final year of high school. Figure 2-1 shows the 2012 percentages for the dominant activities. More than half of college freshmen say they spent at least six hours per week socializing with friends (66.2%) and exercising/sports (53.0%). About 40% devoted that much weekly time to paid employment.
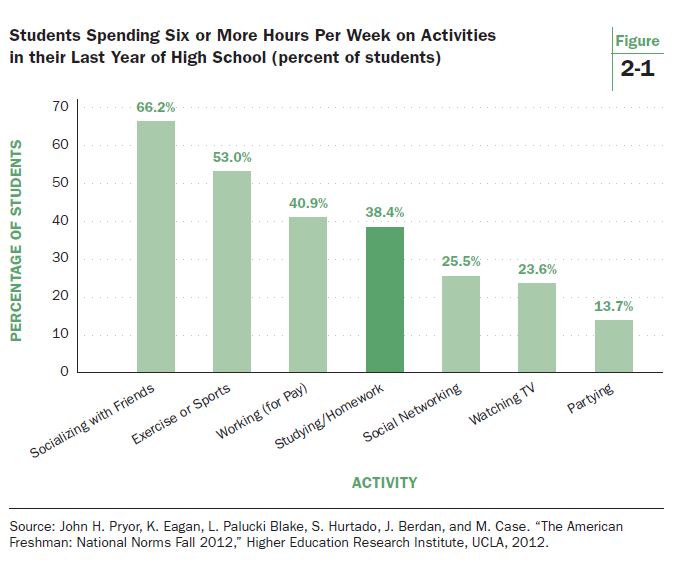
Homework comes in fourth pace. Only 38.4% of students said they spent at least six hours per week studying or doing homework. When these students were high school seniors, it was not an activity central to their out of school lives. That is quite surprising. Think about it. The survey is confined to the nation’s best students, those attending college. Gone are high school dropouts. Also not included are students who go into the military or attain full time employment immediately after high school. And yet only a little more than one-third of the sampled students, devoted more than six hours per week to homework and studying when they were on the verge of attending college.
Another notable finding from the UCLA survey is how the statistic is trending (see Figure 2-2). In 1986, 49.5% reported spending six or more hours per week studying and doing homework. By 2002, the proportion had dropped to 33.4%. In 2012, as noted in Figure 2-1, the statistic had bounced off the historical lows to reach 38.4%. It is slowly rising but still sits sharply below where it was in 1987.
What Do Parents Think?
Met Life has published an annual survey of teachers since 1984. In 1987 and 2007, the survey included questions focusing on homework and expanded to sample both parents and students on the topic. Data are broken out for secondary and elementary parents and for students in grades 3-6 and grades 7-12 (the latter not being an exact match with secondary parents because of K-8 schools).
Table 2-2 shows estimates of homework from the 2007 survey. Respondents were asked to estimate the amount of homework on a typical school day (Monday-Friday). The median estimate of each group of respondents is shaded. As displayed in the first column, the median estimate for parents of an elementary student is that their child devotes about 30 minutes to homework on the typical weekday. Slightly more than half (52%) estimate 30 minutes or less; 48% estimate 45 minutes or more. Students in grades 3-6 (third column) give a median estimate that is a bit higher than their parents’ (45 minutes), with almost two-thirds (63%) saying 45 minutes or less is the typical weekday homework load.
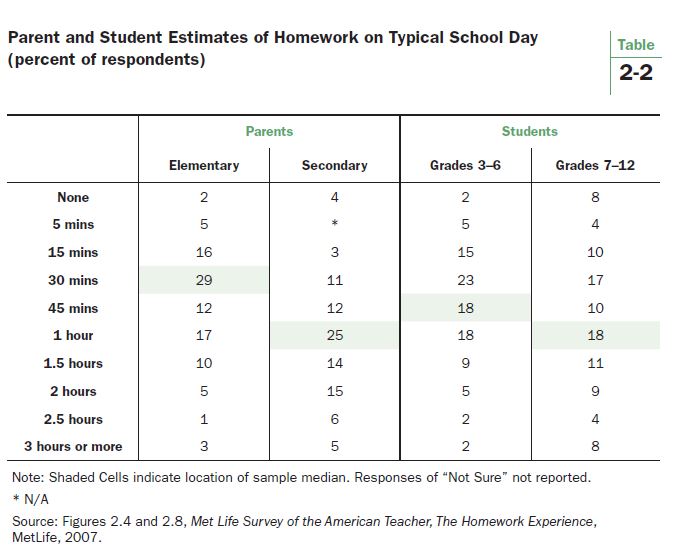
One hour of homework is the median estimate for both secondary parents and students in grade 7-12, with 55% of parents reporting an hour or less and about two-thirds (67%) of students reporting the same. As for the prevalence of the heaviest homework loads, 11% of secondary parents say their children spend more than two hours on weekday homework, and 12% is the corresponding figure for students in grades 7-12.
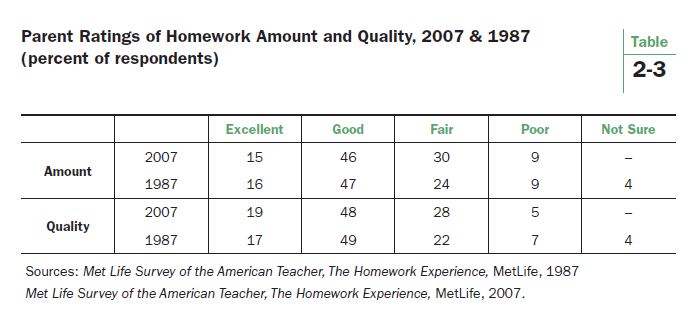
The Met Life surveys in 1987 and 2007 asked parents to evaluate the amount and quality of homework. Table 2-3 displays the results. There was little change over the two decades separating the two surveys. More than 60% of parents rate the amount of homework as good or excellent, and about two-thirds give such high ratings to the quality of the homework their children are receiving. The proportion giving poor ratings to either the quantity or quality of homework did not exceed 10% on either survey.
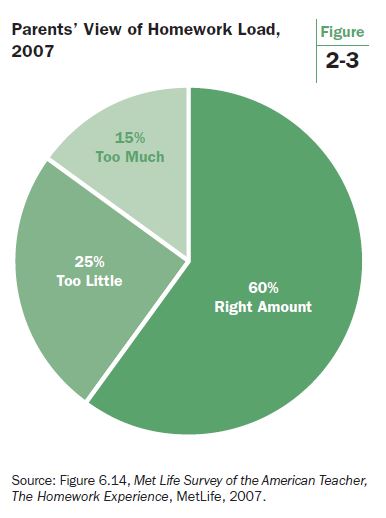
Parental dissatisfaction with homework comes in two forms: those who feel schools give too much homework and those who feel schools do not give enough. The current wave of journalism about unhappy parents is dominated by those who feel schools give too much homework. How big is this group? Not very big (see Figure 2-3). On the Met Life survey, 60% of parents felt schools were giving the right amount of homework, 25% wanted more homework, and only 15% wanted less.
National surveys on homework are infrequent, but the 2006-2007 period had more than one. A poll conducted by Public Agenda in 2006 reported similar numbers as the Met Life survey: 68% of parents describing the homework load as “about right,” 20% saying there is “too little homework,” and 11% saying there is “too much homework.” A 2006 AP-AOL poll found the highest percentage of parents reporting too much homework, 19%. But even in that poll, they were outnumbered by parents believing there is too little homework (23%), and a clear majority (57%) described the load as “about right.” A 2010 local survey of Chicago parents conducted by the Chicago Tribune reported figures similar to those reported above: approximately two-thirds of parents saying their children’s homework load is “about right,” 21% saying it’s not enough, and 12% responding that the homework load is too much.
Summary and Discussion
In recent years, the press has been filled with reports of kids over-burdened with homework and parents rebelling against their children’s oppressive workload. The data assembled above call into question whether that portrait is accurate for the typical American family. Homework typically takes an hour per night. The homework burden of students rarely exceeds two hours a night. The upper limit of students with two or more hours per night is about 15% nationally—and that is for juniors or seniors in high school. For younger children, the upper boundary is about 10% who have such a heavy load. Polls show that parents who want less homework range from 10%-20%, and that they are outnumbered—in every national poll on the homework question—by parents who want more homework, not less. The majority of parents describe their children’s homework burden as about right.
So what’s going on? Where are the homework horror stories coming from?
The Met Life survey of parents is able to give a few hints, mainly because of several questions that extend beyond homework to other aspects of schooling. The belief that homework is burdensome is more likely held by parents with a larger set of complaints and concerns. They are alienated from their child’s school. About two in five parents (19%) don’t believe homework is important. Compared to other parents, these parents are more likely to say too much homework is assigned (39% vs. 9%), that what is assigned is just busywork (57% vs. 36%), and that homework gets in the way of their family spending time together (51% vs. 15%). They are less likely to rate the quality of homework as excellent (3% vs. 23%) or to rate the availability and responsiveness of teachers as excellent (18% vs. 38%). [vii]
They can also convince themselves that their numbers are larger than they really are. Karl Taro Greenfeld, the author of the Atlantic article mentioned above, seems to fit that description. “Every parent I know in New York City comments on how much homework their children have,” Mr. Greenfeld writes. As for those parents who do not share this view? “There is always a clique of parents who are happy with the amount of homework. In fact, they would prefer more . I tend not to get along with that type of parent.” [viii]
Mr. Greenfeld’s daughter attends a selective exam school in Manhattan, known for its rigorous expectations and, yes, heavy homework load. He had also complained about homework in his daughter’s previous school in Brentwood, CA. That school was a charter school. After Mr. Greenfeld emailed several parents expressing his complaints about homework in that school, the school’s vice-principal accused Mr. Greenfeld of cyberbullying. The lesson here is that even schools of choice are not immune from complaints about homework.
The homework horror stories need to be read in a proper perspective. They seem to originate from the very personal discontents of a small group of parents. They do not reflect the experience of the average family with a school-age child. That does not diminish these stories’ power to command the attention of school officials or even the public at large. But it also suggests a limited role for policy making in settling such disputes. Policy is a blunt instrument. Educators, parents, and kids are in the best position to resolve complaints about homework on a case by case basis. Complaints about homework have existed for more than a century, and they show no signs of going away.
Part II Notes:
[i]Brian Gill and Steven Schlossman, “A Sin Against Childhood: Progressive Education and the Crusade to Abolish Homework, 1897-1941,” American Journal of Education , vol. 105, no. 1 (Nov., 1996), 27-66. Also see Brian P. Gill and Steven L. Schlossman, “Villain or Savior? The American Discourse on Homework, 1850-2003,” Theory into Practice , 43, 3 (Summer 2004), pp. 174-181.
[ii] Bennett, Sara, and Nancy Kalish. The Case Against Homework: How Homework Is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It (New York: Crown, 2006). Buell, John. Closing the Book on Homework: Enhancing Public Education and Freeing Family Time . (Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2004). Kohn, Alfie. The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing (Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, 2006). Kralovec, Etta, and John Buell. The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning (Boston: Beacon Press, 2000).
[iii] Hu, Winnie, “ New Recruit in Homework Revolt: The Principal ,” New York Times , June 15, 2011, page a1.
[iv] Data for other years are available on the NAEP Data Explorer. For Table 1, the starting point of 1984 was chosen because it is the first year all three ages were asked the homework question. The two most recent dates (2012 and 2008) were chosen to show recent changes, and the two years in the 1990s to show developments during that decade.
[v] NAEP’s sampling design lessens the probability of skewing the homework figure. Students are randomly drawn from a school population, meaning that an entire class is not tested. Teachers would have to either single out NAEP students for special homework treatment or change their established homework routine for the whole class just to shelter NAEP participants from homework. Sampling designs that draw entact classrooms for testing (such as TIMSS) would be more vulnerable to this effect. Moreover, students in middle and high school usually have several different teachers during the day, meaning that prior knowledge of a particular student’s participation in NAEP would probably be limited to one or two teachers.
[vi] NAEP Question B003801 for 9 year olds and B003901 for 13- and 17-year olds.
[vii] Met Life, Met Life Survey of the American Teacher: The Homework Experience , November 13, 2007, pp. 21-22.
[viii] Greenfeld, Karl Taro, “ My Daughter’s Homework Is Killing Me ,” The Atlantic , September 18, 2013.
Education Policy K-12 Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Katharine Meyer
May 7, 2024
Jamie Klinenberg, Jon Valant, Nicolas Zerbino
Thinley Choden
May 3, 2024
- site locations
Reimagining
Academic success, we promote confidence in our children.
Homework Central strives to create educational equity for disadvantaged elementary school students who aren’t receiving the support they need. Through lack of resources, and poor access to technology or academic assistance, too many children start to fall behind, creating an ever-widening academic gap between them and their peers.
Our mission
Our approach, what is academic success.

After-school tutoring

Family support

What’s the Purpose of Homework?
Finding the right balance between school and home..
Posted November 4, 2014 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader

Remember the days of sitting in class waiting eagerly for the bell to ring before the teacher said that dreaded word, “homework”? Sighs, rolling eyes, and grunts quickly filled the quiet classroom at the mention of that word. Well, not much has changed today except for the fact that many teachers post assignments electronically. I have yet to see a student jump for joy when the word homework is mentioned, nor have I seen students eager to get home to do their homework (maybe finish it, but not to do it). This brings up the question, “What’s the purpose of homework?”
Research shows mixed results when it comes to homework. Some research has shown that students aren’t doing any more homework than their parents did at their age. In a study, school-aged children and parents completed surveys about how much homework youth have. The results showed that the typical elementary student has 30-45 minutes of homework each night. The average high-school student has about 60 minutes per night. Interestingly, these numbers have remained consistent since 1984!
As an educator, I would like to see a replication of this study. Today's teens are taking college-level courses as early as the ninth and tenth grade. With the push of programs such as Advanced Placement, International Baccalaureate, and Dual Enrollment, it is amazing that teens are not completely burnt out. No wonder 8% of teen's age 13-18 years meet the criteria for an anxiety disorder. Too many teens are spending a lot of time on schoolwork outside of the classroom. Ask today's teen what has him/her so stressed and you'll find that about 80% of them will say school.

There are those who argue that homework does serve a purpose . For example, it helps to prepare students for national and statewide exams and tests. It helps to reinforce what’s being taught in the classroom. It enables parents to actively engage in their child’s education . Plus, it helps teach fundamental skills such as time management , organization, task completion, as well as responsibility. What’s more important is students get to demonstrate mastery of material without the assistance of a teacher.
How much homework should your child do each night? Organizations such as the National Parent Teacher Association support giving students about 10 minutes of homework each night, per grade level, starting in first grade. So a middle school student would have a full day in school and then an additional 60 minutes of homework after school. Is that too much? Are these guidelines being followed? I would recommend speaking with high-achieving teens and let them share how much of their time is consumed with homework. Many will tell you that they spend hours upon hours each night studying for tests, and preparing for papers and projects, etc.
According to Stanford University , more than a couple of hours of homework a night may be counterproductive. Researchers looked at students in high achieving communities, defined as a median household income exceeding $90,000, and 93% of the students attended post-secondary institutions. Students in these areas spent an average of three-plus hours on homework every night. So imagine a teen spending an entire day at school, going to work or extracurricular activities, then going home to do three or more hours of homework each night; only to get up the next day to do it all again.
Researchers have found that students who spend too much time on homework experience more levels of stress and physical health problems. Too much homework has also been shown to have a negative impact on students’ social lives. This is no surprise to the parents who rarely see their child because he/she is too busy working on homework, or to the parent who gets up at 12:30 A.M. to check to see if their child has made it to bed yet. Overall, high school students shouldn’t be spending over two hours on homework each night.

According to the Stanford study , too much homework leads to:
•Stress: 56% of the students surveyed considered homework a primary source of stress. Less than 1% of the students said homework was not a stressor.
•Poor health: Many students reported sleep deprivation, headaches, stomach problems, weight loss, and exhaustion.
•Less time for a social life : Students reported that spending too much time on homework led to pulling out of enjoyable activities, quitting extracurricular activities, and not spending much time with family and friends.
OK, I know not all students spend a lot of time doing homework. According to a survey by the U.S. Dept. of Education’s National Center for Education Statistics , the majority of youth spend an average of seven hours of homework outside of school each week. So while that doesn't seem like an unreasonable amount, what about the student who spends three-plus hours per night? Where is the happy medium?

There are definitely pros and cons to doing homework. I think the bigger question that educators need to address is “what’s the purpose of the assignment?” Is it merely a way to show parents and administration what's going on in the class? Is it a means to help keep the grades up? Is the homework being graded for accuracy or completion? If so, then what if the assignment is wrong? Have the necessary skills been taught so the student can master the material on his or her own? I read an article once that stated teachers underestimate the amount of homework they assign by 50%. If that's accurate then there is definitely cause for concern.
In summary, there seems to be no clear answer on the homework debate. I started the blog with a question “What’s the purpose of homework?” I’ll end with the same question. If a teacher who is assigning the homework can’t provide a clear rationale behind this question, then maybe the homework shouldn’t be assigned.
I welcome you to weigh in with your thoughts. Do you think students have too much homework? If you are a teen reading this, how much homework do you have on an average night?

Raychelle Cassada Lohman n , M.S., LPC, is the author of The Anger Workbook for Teens .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

What Is Your Homework Strategy?
by Melissa Braaten
For years, I struggled giving homework: what to give students, how much, how to grade or value it. I found I was spending a lot of time creating or searching for assignments that felt meaningful, only to have a very small portion of my students complete it outside of class. In addition, I had a lot of students with different learning challenges, who struggled with many aspects of homework: how to understand the directions, how to get started, how to keep track of the materials, and how and when to hand it in. I decided my homework strategy needed an overhaul, and I needed to start by asking myself why I was giving homework in the first place.
What is the purpose?

The majority of my learners are at earlier levels of math, and many struggle with multiple learning challenges, including executive function. They need careful scaffolding to help them to develop both academic and student skills. I am always looking for ways to get them more math learning, but I have found that having them try to learn or practice new skills outside of class (like a flipped classroom model) was usually not successful. So why give them homework at all?
Cyclical review
First of all, all of my students benefit from cyclical review of concepts they have already learned, both to reinforce and deepen their learning, and to fill in gaps created by gaps in attendance. I decided that homework would be a chance for my students to review concepts they had already worked through and mastered in class. This would make it a good use of their time, while using class time to support the exploration and learning of new concepts.
Formative assessment
How about a weekly check in of how students are doing with the content you have taught earlier in the unit? In addition to review, I decided I wanted homework to function as a consistent source of formative assessment, so I could make decisions about what skills or concepts needed revisiting in class.
Student skill development
I also decided that it was important, even for my beginning level students, that they develop the habit of completing homework, since completing independent assignments is an important contributor to long term academic success. Nevertheless, I don’t want to give adults busywork to do, so I made sure the tasks would function as both review and formative assessment.
Support for students
I wanted to keep giving homework, but I also wanted to do it in a way that would provide more scaffolding for students to be successful at completing it. In addition to making sure the homework was addressing skills and concepts most students had mastered (or close to mastered) in class, I developed a new, predictable structure to my homework.

Predictable structure
I created homework packets for each class that would last for six weeks at a time. Each week, one page would be due, always on the same day of the week. The pages were labeled by week, and students would complete the page, tear it out, and hand it in. Each week’s homework contained four problems that reviewed relevant concepts from earlier in the unit. (I created these in PowerPoint, so I ended up making one problem on each slide, and printing two slides per page, front and back.) I also find that having all the homework pages stapled together in a packet makes it much easier for students to find and not lose them (and to further facilitate this, they always get a neon-colored cover sheet with the class name, times, and my contact information).
Familiar tasks
The consistency (one page per week, always due on the same day), helped many students keep track of and begin completing homework. They could remember the expectation and it felt manageable, especially since the assignments were not long. The same type of tasks would reoccur on homework for multiple weeks, with small variations. This also made it easier for students who had a hard time understanding instructions, since once they completed homework for one week, the next week’s homework would look similar, at least in part.
Timely feedback and accountability
The short, one-page assignments were also quick for me to correct and give feedback, which meant I could usually hand it back in the next class, so students could get feedback in a timely manner, get help, and make needed corrections.
For accountability, I hand out a report every six weeks showing students which assignments they handed in, before they get a new packet.
What is sustainable for me?
Sustainability was a big concern for me. Like every teacher everywhere, I always have multiple priorities competing for my time, and I didn’t want to start a homework routine that I couldn’t keep up with. I needed a way to create and grade homework that was relevant and supportive, but also efficient.
Creating the homework packets ahead of time has worked out well, and they are not nearly as time consuming as my previous attempts at homework since they are short, and most task types are repeated. Sometimes I can purchase or find materials online that I can chop up into smaller tasks. All in all, it usually takes about one afternoon every six weeks to create a new homework packet, and then I don’t have to worry about it for a while.
The short length makes it quick to correct and give feedback, which means I can get them back to students quickly, and make decisions about upcoming classes, and which questions we should go over, or which concepts might need revisiting.
I decided not to grade homework, but to simply mark completion. That makes it easier on my end. Besides, I am using these for formative, rather than summative assessments anyway, so grading didn’t really make sense.
How is it going?
I have kept up this homework routine for the last two years, and it has worked better than any other I have tried in the past. First of all, it has been efficient and sustainable for me, and secondly, I have much higher rates of homework completion, especially in my beginner level classes. Students mostly find the homework helpful and are usually able to complete some or all of it on their own. I also get valuable formative assessment on a regular basis, which helps me make adjustments to my teaching as I go along.
Want to see an example? Click here to download a PDF of a homework packet for a beginner level (GLE 2-4, CCRSAE B) class.

Melissa Braaten is an adult education instructor at Catholic Charities Haitian Multi-Services Center in Dorchester, MA. Melissa has taught ASE and pre-ASE math and reading, as well as ABE writing, computer skills, and health classes. Melissa also is a training and curriculum development specialist for the SABES Mathematics and Adult Numeracy Curriculum & Instruction PD Center at TERC . She is the author of many articles for Math Musings, our Adult Numeracy blog.

The Liberty Champion
The official student newspaper of Liberty University
Is Homework Really Necessary?

Did you get all your homework done?
We’ve all heard that phrase one too many times before, and now it triggers your fight-or-flight response. Every waking thought is about an assignment you should be doing or that project you really should start but you just can’t bring yourself to face it. Is all this homework really necessary?
Unfortunately, it just might be. Is the homework itself the problem, or is it the amount we end up with after classes are over for the day and your bed is looking really comfy? To figure all this out we have to remember why we get homework in the first place and what school would be like without it.
In the very early 1900s, homework was actually considered unhealthy for children and was classified as child labor because it interfered with their ability to do chores around the house. The U.S. Department of Education called homework a tool for “boosting educational quality” when it was reinstated, and it became mandatory in 1986 after being rejected for so long, as recorded by the University of San Diego.
It’s always good to look at the pros and cons of something when deciding how you feel about it. So, what does homework do for us? Quite a few things actually.
First let’s address the elephant in the room. No one enjoys homework unless you’re a camp and outdoor adventure leadership (COAL) major. We all have something we would rather spend our time on; that’s just the way it is.
However, when that test rolls around, most of us are glad we stayed late at the library until we understood what we were reading. According to the University of San Diego, students only absorb 50% of what they hear in a class lecture. If that’s all you had to learn from, keeping your GPA above a 3.5 would be considered a superpower.
Whether we like it or not, homework helps us retain important information and truly grasp the concepts we are studying. Hearing about it once from your professor is great, but life as a college student is so busy that your chances of remembering everything you heard in all of your classes are next to none. Repetition is the key to retention, and other than experience training, studying the material you were given and doing your homework is how you’re going to graduate.
Then why is it such a problem? Why is it affecting people so negatively? No degree is worth your mental health; it’s time to look at the cons of homework.
I believe the real problem with homework is the amount of it. Yes, we need it to learn, but our brains can only handle so much at a time. Oftentimes the standard college workload demands that we push our minds past the limit or face a late penalty. This is what causes the exhaustion and resentment that we constantly push through for the sake of good grades and gold chords.
Studies conducted by the American Psychological Association and the U.S. Department of Health say shorter study sessions per day and more consistency over a longer period of time is the best way to retain information while not pushing yourself to your mental limit. However, there is so much to be done that studying for a mere three hours a day isn’t even practical.
Students would actually be able to study in a healthy way and retain information long term if we were not assigned and asked to complete in one week what psychological studies say should take at least two.
So, to answer the question: Yes, homework is definitely necessary. The real problem is how much we are required to process in such a short time.
As finals inch closer by the day, make a point to take care of your mind and give yourself breaks not only while studying but also from other things that can cloud your brain like social media. Coping with huge workloads is a process, so make lists, take deep breaths and get to bed on time. We’re gonna make it; I promise.
Barber is the off-campus news editor for the Liberty Champion
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Don't Miss a Post! Subscribe
- Guest Posts

- Educational AI
- Edtech Tools
- Edtech Apps
- Teacher Resources
- Special Education
- Edtech for Kids
- Buying Guides for Teachers

Educators Technology
Innovative EdTech for teachers, educators, parents, and students
Is Homework Bad? Here Is What Research Says
By Med Kharbach, PhD | Last Update: April 30, 2024

Homework is a controversial topic and the object of differing opinions among teachers, parents, and educators . While some highly value it considering it key in scholarly achievement and academic performance, others view it as a nuisance to students’ independence and a cause for unwarranted emotional and physical stress for kids.
The controversy surrounding homework does not only revolve around its value, but also around questions such as: How much homework is enough homework? How much time should be allotted to homework? How frequent should homework be assigned? Does help from others (e.g., parents or other students) undermine the value of homework? Should homework be banned? Should kids be assigned homework? and many more.
However, as the research cited in this article demonstrates, homework, controversial as it is, has some benefits for students although these benefits differ according to various factors including students age, skill and grade level, students socio-economic status, purpose behind homework, duration of the homework, among other considerations. In this article, I cover some of the key issues related to homework and provide research resources to help teachers and parents learn more about homework.
What Does Homework Mean?
According to Cooper (1989), homework is defined as “tasks assigned to students by school teachers that are meant to be carried out during non-school hours”. Cooper’s definition is similar to the one found in Cambridge Dictionary which defines homework as “work that teachers give their students to do at home” or as “studying that students do at home to prepare for school”.
There is way more to homework than what these general definitions outline. Homework assignments are not equal and there are various variables that can affect the value and effectiveness of homework.
Some of these variables, according to Blazer (2009) , include difficulty level of assigned tasks, skill and subject areas covered, completion timeframe (short or long term), degree of autonomy and individualization, social context (done independently or with the help of others), obligatory or voluntary, whether it will be submitted for grading or not, among other variables.
Is Homework Bad?
Going through the scholarly literature and regardless of the disagreement and controversies the topic of homework raises, there is a growing consensus that homework has some benefits , especially for students in middle and high school ( National Education Association ).
One of the most comprehensive research studies on homework is a meta-analysis done by professor Harris Cooper and his colleagues (2006) and published in the journal Review of Educational Research .
In this study, Cooper et al analyzed a large pool of research studies on homework conducted in the United States between between 1987 and 2003. Their findings indicate the existence of ‘a positive influence of homework on achievement’.
The influence is mainly noticed in students in grades 7-12 and less in students grades K-6. However, even though kids benefit less from homework, Cooper et al. confirm the importance of some form of homework for students of all ages.
What Is The Purpose of Homework?
There are several reasons for assigning homework. Some of these reasons according to Blazer include:
– Review and reinforce materials learned in class – Check students understanding and assess their skills and knowledge – Enhance students study skills – Provide students with learning opportunities where they can use their newly acquired skills to explore new insights. – Enable students to hone in their search skills and apply them to find resources on an assigned topic – Help students develop social emotional learning skills – Enable students to develop functional study habits and life skills. These include time management and organization skills, problem solving skills, self-discipline, accountability, self-confidence, communication skills, critical thinking skills, inquisitiveness, among others.
Drawbacks of Homework
Critics of homework argue that it has less value and can result in negative consequences. In her literature review, Blazer (2009) summarized some of these drawbacks in the following points:
– Homework can cause emotional and physical fatigue – Homework takes away from kids’ leisure time and interferes with their natural development. – Homework can drive students to develop negative attitudes towards school and learning. – Assigned homework prevents students from engaging in self-directed and independent learning. – Homework can interfere with students’ engagement in social activities including sports and community involvement. – Excessive homework can create tension and stress and lead to friction between parents and kids. – Homework may encourage a culture of cheating – Homework “can widen social inequalities. Compared to their higher income peers, students from lower income homes are more likely to work after school and less likely to have an environment conducive to studying”.

How Much Homework Should Students Have?
According to Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez and Muñiz ( 2015 ), spending 60 minutes per day doing homework is considered a reasonably effective time. However, the study also added that the amount of help and effort needed to do homework is key in this equation because “when it comes to homework”, as the authors concluded, “how is more important than how much”.
This conclusion is congruent with several other studies (e.g., Farrow et al. (1999), that emphasize the idea that when doing homework, quality is more important than quantity. When the variables of time and effort are taken into account, the question of how much homework should students have becomes statistically irrelevant.
Catty Vatterott, author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices that Support Diverse Needs , also advocates for quality over quantity when assigning homework tasks.She argues that instead of banning homework altogether, we can embrace a more open approach to homework; one that deemphasizes grading and differentiates tasks.
Along similar lines, studies have also confirmed the correlation between autonomy and positive performance. Autonomous students, that is those who can do homework on their own, are more likely to perform better academically (Fernández-Alonso, 2015; Dettmers et al.,2010, 2011; Trautwein & Lüdtke, 2007, (Xu, 2010a). Findings from these studies indicate that “students who need frequent or constant help with homework have worse academic results.” (Fernández-Alonso, 2015)
Besides the 60 minutes per day recommendation for older students, there is also the 10 minutes rule which, according to Harris Cooper , works by multiplying a kid’s grade by 10 to determine how much time they need for homework per day.
According to the 10 minute rule, first graders require 10 minutes per day of homework, second graders 20 minutes, and for each subsequent year you add another 10 minutes so that at the last year of high school, grade 12 students will have 2 hours of daily homework. As Cooper argues, “when you assign more than these levels, the law of diminishing returns or even negative effects – stress especially – begin to appear”.
The debate over homework is far from being settled and probably will never reach definitive conclusions. With that being said, l personally view homework as a heuristic for learning. It scaffolds classroom learning and helps students reinforce learned skills. For elementary students, homework should not be tied to any academic grades or achievement expectation.
In fact, kids’ homework assignments, if any, should align with the overall interests of kids in that it should support and include elements of play, fun, and exploration. Needless to mention that, once outside school, kids are to be given ample time to play, explore, and learn by doing.
As Cooper stated “A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements. If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
Research on Homework
The topic of homework has been the subject of several academic research studies. The following is a sample of some of these research studies:
- Blazer, C. (2009). Literature review: Homework. Miami, FL: Miami Dade County Public Schools.
- Cooper, H. (1989). Synthesis of research on homework. Educational Leadership, 47, 85–91.
- Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research, 76, 1– 62.
- Dettmers, S., Trautwein, U., Lüdtke, M., Kunter, M., & Baumert, J. (2010). Homework works if homework quality is high: Using multilevel modeling to predict the development of achievement in mathematics. Journal of Educational Psychology,
- Dettmers, S., Trautwein, U., & Lüdtke, O. (2009). The relationship between homework time and achievement is not universal: Evidence from multilevel analyses in 40 countries. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 20, 375– 405.
- Epstein, J. L., & van Voorhis, F. L. (2001). More than minutes: Teachers’ roles in designing homework. Educational Psychologist, 36, 181–193
- Farrow, S., Tymms, P., & Henderson, B. (1999). Homework and attainment in primary schools. British Educational Research Journal, 25, 323–341
- Goldstein, A. (1960). Does homework help? A review of research. The Elementary School Journal, 60, 212–224.
- Trautwein, U., & Köller, O. (2003). The relationship between homework and achievement: Still much of a mystery. Educational Psychology Review, 15, 115–145
- Warton, P. M. (2001). The forgotten voices in homework: Views of students. Educational Psychologist, 36, 155–165.
- Xu, J. (2013). Why do students have difficulties completing homework? The need for homework management. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 1, 98 –105.
- Zimmerman, B. J., & Kitsantas, A. (2005). Homework practices and academic achievement: The mediating role of self-efficacy and perceived responsibility beliefs. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 30, 397– 417.
- Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2001). End Homework Now. Educational Leadership, 58(7), 39-42.
- Krashen, S. (2005). The Hard Work Hypothesis: Is Doing Your Homework Enough to Overcome the Effects of Poverty? Multicultural Education, 12(4), 16-19.
- Lenard, W. (1997). The Homework Scam. Teacher Magazine, 9(1), 60-61.
- Marzano, R.J., & Pickering, D.J. (2007). The Case For and Against Homework. Educational Leadership, 64(6), 74-79.
- Skinner, D. (2004). The Homework Wars. Public Interest, 154, Winter, 49-60.
- Corno, L. (1996). Homework is a Complicated Thing. Educational Researcher, 25(8), 27-30.
- Forster, K. (2000). Homework: A Bridge Too Far? Issues in Educational Research, 10(1), 21-37.
- Hoover-Dempsey, K.V., Battiato, A.C., Walker, J.M., Reed, R.P., DeLong, J.M., & Jones, K.P. (2001). Parent Involvement in Homework. Educational Psychologist, 36(3), 195-209.
Books on Homework
Here are some interesting books that profoundly explore the concept of homework:
1. The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing , by Kohn (2006)
- 2. Rethinking Homework: Best Practices that Support Diverse Needs , by Catty Vatterot
- 3. The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning , by Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2000)
- 4. The Case Against Homework: How Homework Is Hurting Children and What Parents Can Do About It , by Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish

Join our mailing list
Never miss an EdTech beat! Subscribe now for exclusive insights and resources .

Meet Med Kharbach, PhD
Dr. Med Kharbach is an influential voice in the global educational technology landscape, with an extensive background in educational studies and a decade-long experience as a K-12 teacher. Holding a Ph.D. from Mount Saint Vincent University in Halifax, Canada, he brings a unique perspective to the educational world by integrating his profound academic knowledge with his hands-on teaching experience. Dr. Kharbach's academic pursuits encompass curriculum studies, discourse analysis, language learning/teaching, language and identity, emerging literacies, educational technology, and research methodologies. His work has been presented at numerous national and international conferences and published in various esteemed academic journals.

Join our email list for exclusive EdTech content.
Russia Travel Blog | All about Russia in English
- About our blog
- RussiaTrek.org
Sidebar →
- Architecture
- Entertainment
- RussiaTrek.org News

- Send us a tip with a message
- Support RussiaTrek.org
- Travel Guide to Ukraine
- Comments RSS
← Sidebar
Homework in Russian Education Facilities: Key Facts and Types
1 Comment · Posted by Alex Smirnov in Education
What is homework in the first place? In a nutshell, it is one of the forms of educational activities performed by students outside the classroom or in extracurricular time. This form of activity can pursue a number of goals:
- To help students assimilate and retain the material presented in the class better;
- To let students self-study certain topics or concepts that don’t require clarification from the teacher;
- To assess how well students have grasped the material. Also, to understand how well they can apply the obtained knowledge and skills for finding solutions to certain problems;
- To identify gaps in knowledge.

For decades, homework of all shapes and kinds has been an integral part of the educational process. This type of activity is used by pretty much all education facilities, regardless of the level, and all across the world. However, the essence and types of homework can vary from country to country.
Namely, due to a significant difference in the overall education system in Russia, the types of homework assigned to students in this country can be somewhat different. For example, it will be different from homework types assigned, say, in the US. As we know, here, the largest academic challenge facing students is writing, which can be delegated to make my essay service professionals. But, the situation in Russian education facilities is different.
In this article, we are going to take a closer look at the homework in Russia and discover what types of this extracurricular activity are there.
Basic Requirements for the Content and Volume of Homework
In Russia, both the volume and content of homework are regulated by law. The Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation sets very specific sanitary and epidemiological norms for the conditions and organization of training in educational institutions and closely monitors their compliance.
According to these regulations, the organization of home schoolwork has to be an integral part of the general problem of improving the educational process at school. The content, nature, and functions of homework cannot be considered in isolation from the content, nature, and methods of teaching applied in the classroom. It is during the lessons that teachers must create the right conditions for the successful completion of homework.
Many components and stages of the lesson are directly related to the subsequent completion of homework: checking homework, assigning homework lessons, students’ independent work in the lesson, etc. The combination of these components should be such that in the lesson, the student would get fully prepared for the homework and so that the lesson and subsequent independent work are a uniform process.
Currently, there are the following basic requirements for homework in Russia:
- The overall volume of the homework should not exceed 30% of the total amount of work performed in the classroom.
- The total time spent by students on homework should not exceed: 1.5 hours for 2 through 3 grade; 2 hours for 4 through 5 grade; 2.5 hours for 6 through 8 grade; and 3.5 for 9 through 11 grade.
According to stats, Russia is among the countries where students spend the most time on homework – on average, they are dealing with 9.7 hours of homework per week.
Types and Forms of Homework in Russia
Schools and higher education facilities in Russia use different types of homework assignments to ensure the integrity and efficiency of the learning process. Namely, we can distinguish the following types of assignments:
- Individual;
- Differentiated;
- One for the whole class;
- Compiling homework for a deskmate.
Now, let’s look at each type in detail.
As you can easily guess, individual homework is usually assigned to individual students and is tailored to their specific needs, the current level of knowledge, existing gaps, and other individual factors. This form of homework makes it easy for the teacher to check the level of knowledge of a particular student. Such work can be done on cards or using printed workbooks.
Group homework is also a pretty common activity. It implies that the class is being divided into smaller groups of students, and each of the groups is assigned to work on a specific task that is part of the overall classroom assignment.
Differentiated homework is shaped based on the concept of differentiated instruction, which implies distinguishing students’ differences and using them to boost the effectiveness of learning. For example, this type of homework can be characterized by the following features:
- The assignment is the same for everyone, but the method of its completion varies depending on each student’s differences.
- There can be several options in the assignment, giving students the right to choose any of them independently.
Compiling homework for a deskmate is the most innovative approach to assigning homework. It implies that students will formulate the homework tasks for their peers themselves, based on the tasks that have been performed in the classroom.
Creative assignments include academic writing, personal projects, research, etc. They are typically assigned less frequently, and teachers give students more time to complete them. For example, a typical homework can have a deadline in just a day, whereas students should be given at least a week to complete a creative assignment.
Finally, the last and the most common type of homework in Russia is one assignment for the whole class. This can include different types of activities, including reading, writing, problem-solving, testing, etc. Typically, this is the form of the task students in Russia are dealing with daily.
Tags: No tags
You might also like:

Naryan-Mar – a unique regional center in the Arctic Circle
Mountain Landscapes of the Republic of North Ossetia – Alania >>
Queen Mastropietro · April 7, 2022 at 10:57 pm
What’s up it’s me, I am also visiting this website daily, this website is really pleasant and the viewers are really sharing good thoughts
Leave a Reply
XHTML: You can use these tags: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
New Maverick mom finished homework while in labor
Thursday, May 09, 2024 • Cristal Gonzalez : contact

The journey toward baby Sarala’s arrival in September 2023 was arduous for Kelly Meek and her husband: nearly four years of fertility treatments, ultrasounds and injections to combat Meek’s diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome.
So when Sarala decided to arrive a little ahead of schedule, Meek, who was set to complete her first term in the eight-week accelerated master’s program in the College of Education at The University of Texas at Arlington, wasn’t about to let a little homework stand in her way. Her hospital “go bag” included diapers, clothes for the newborn and a laptop—so Meek could complete class assignments from the delivery room.

Now Meek is scheduled to graduate on May 10—and celebrate her first Mother’s Day as a new mom two days later.
Although entitled to excused absences and the opportunity to turn in work early or late under Title IX, Meek said she was determined to finish on time and ace her coursework.
“It was a good distraction, and I could have kept working. But when the nurses and doctors broke my water, I was in a lot of pain,” she said. “We’re always so busy, so we got used to juggling a million things. Sarala has bopped along the entire time.”
According to her husband, Chris, nothing slows down Meek, who was pursuing her master’s degree while also teaching middle school math in League City, Texas. In addition, Meek is active in her church band and even went on a 10-day trip to Alaska as a missionary, installing sheetrock and insulation for a community building—while eight months pregnant.
“She just does not give up. It’s part of what makes her an amazing partner, mother, teacher and friend,” Chris said. “I hope someone will read her story and find that it resonates with them, maybe to get started or to keep going when they think of giving up.”
- Written by Monique Bird , College of Education

Home » Travel Guides » United States » Idaho (ID) » 15 Best Things to Do in Moscow (Idaho)
15 Best Things to Do in Moscow (Idaho)
In a landscape of fertile rolling hills on the Idaho-Washington boundary, Moscow is the county seat of Latah County and the home of the University of Idaho, founded in the early 1890s.
The city has a cozy downtown with historic brick buildings from the turn of the 20th century and lots of community events, like a weekly farmers’ market spring through fall, and a bustling artwalk in June.
As you would expect, the University of Idaho plays an important role in the city’s cultural, social and sporting life, and many of the attractions in this list are connected to this institution in some way.
The surrounding Palouse landscape of rambling hills decked with wheat fields, can be explored on two paved rail trails, heading out east and west of the city.
1. University of Idaho Arboretum & Botanical Garden

The loveliest feature of the university campus’ verdant grounds is the UI Arboretum & Botanical Garden.
You’ll find it in 63 acres, just south of the President’s Residence and the university’s golf course, with undulating Palouse hills in the background.
Open to the public with free admission, the arboretum was laid out on a former hayfield in the early-1980s, although its origins go back way before, to the early 20th century.
In fact you can check out the site of the first arboretum, planted in the 1910s with majestic specimen trees, including a giant sequoia, on the north side of the President’s Residence.
As for the “new” arboretum, this counts more than 17,000 plants from over 2,400 taxa, mostly organized into geographical regions, including Europe, Asia and Eastern and Western North America.
On the south end are exquisite display gardens for xerophytes, ornamental willows, irises and heather, as well as a butterfly garden, magical in summer.
2. Latah Trail

Twelve miles long, this paved trail will take you east from Moscow all the way to the neighboring city of Troy.
The Latah Trail was completed in 2008 and is on the course of a dismantled BNSF railroad line that junctioned at Arrow, some 30 miles to the southeast.
The path is ten feet wide, allowing plenty of space for walkers and cyclists in summer, and snowshoers and cross-country skiers after snowfall in winter.
As this is a rail trail there are no difficult slopes but you’ll be guaranteed breathtaking panoramas of the Palouse, with tilled slopes interspersed with sweeps of coniferous forest.
In Moscow the Latah Trail merges seamlessly with the Paradise Path, in turn connecting with the Bill Chipman Palouse Trail, which we’ll talk about below.
3. Appaloosa Museum and Heritage Center

The Appaloosa, identified by its colorful spotted coat, is a horse breed synonymous with the Palouse region, so it’s fitting that there should be a museum for it, right on the Idaho-Washington state line.
The museum shines a light on a variety of topics, like the history of spotted horses in art and literature, Appaloosas’ various coat patterns, and the importance of Appaloosas to the native Nez Perce people.
Display cases are loaded with interesting objects, from saddles to black and white photography and Native American artifacts. There’s also a hands-on area to keep children engaged, as well as a theater and an extensive library.
4. Moscow Farmers’ Market

Taking place on Saturdays, 9 am to 1 pm, May through October, Moscow Farmers’ Market is now well into its fifth decade.
Right on Main Street, this is a celebration of the Moscow area’s farmers, artisans and musicians, giving them an opportunity to connect with the city’s residents and visitors.
For shoppers interested in food provenance the market is a chance to find out where your produce comes from and pick up tips about storage and preparation.
There’s a wide range of vendors for vegetables, fruit, plants, flowers, local grass-fed meat, pastries, honey, jams, cosmetics, home decorations, hand-forged knives and much more.
The market has live music most weeks, as well as freshly prepared food, from tacos to samosas.
5. Bill Chipman Palouse Trail

Following the right of way of the old Union Pacific Railroad, the Bill Chipman Palouse Trail runs west from Moscow, crossing the state line and taking you to Pullman, Washington.
Pullman is the home of the flagship campus for Washington State University, the second-largest institution of higher education in the state.
Seven miles long, the trail, paved all the way, carries you through bucolic Palouse scenery, parallel to State Route 270.
There’s a shallow gradient, and you’ll come across rest areas and interpretive signs along the route. And while the landscapes are gorgeous, the trail also has an important practical use as a commuter route for cyclists between the two university campuses.
6. Prichard Art Gallery

This outreach facility for the University of Idaho is located in downtown Moscow, and moved to its current location on Main Street in 1986.
The Prichard Art Gallery has a lively schedule of exhibitions, events and educational programming, receiving upwards of 17,000 visitors a year.
You can check out the creativity of members of the Idaho College of Art and Architecture, as well as temporary exhibits for local, regional, national and international artists in a whole spectrum of media.
The exhibits rotate at short intervals, so there’s always something fresh to see, while the gift shop sells unique pieces by artists and craftspeople from the area.
7. McConnell Mansion

On leafy Adams Street, a couple of blocks east of Main Street, stands the palatial W. J. McConnell House.
In a Stick/Eastlake style, this elegant residence was built in 1886 for William J. McConnell (1839-1925), who served as Governor of Idaho from 1893 to 1897, after previously representing the young state as one of its first United States Senators.
The mansion is the headquarters of the Latah County Historical Society, and you can take a look around a series of themed period rooms, featuring authentic furnishings and appliances.
The society also puts on fascinating exhibits and learning events, often in partnership with the University of Idaho and always well worth attending.
8. Colter’s Creek Winery

The rolling country south of Moscow has everything you need to make great wine, and in 2016 the Lewis-Clark Valley gained official AVA (American Viticultural Area) designation.
Colter’s Creek has a storefront and tasting room in Moscow, growing its grapes on the sunny slopes where the Potlatch flows into the Clearwater River.
Planted between the 1980s and 2010s these vineyards produce a wide variety of grapes, running the gamut from Riesling to Cabernet Sauvignon, for local handcrafted wines that have earned widespread acclaim.
The stylish Moscow tasting room is in Main Street’s Hattabaugh building, constructed in 1890, and has a choice of estate wines on tap. Wine tasting classes take place regularly, to help you tell a Sangiovese from a Tempranillo.
9. Kenworthy Performing Arts Centre

On the National Register of Historic Places, this fine old Spanish Revival cinema has a history going back to 1926, and was founded as a vaudeville stage and silent movie house.
The current tiled facade, in a pared-down Art Deco style, has been in place since 1949, and up to the late-1980s this was downtown Moscow’s main movie theater.
Since 2000, the venue has belonged to the Kenworthy Performing Arts Centre, which carried out thorough renovations in the 2010s. Come for classic, independent and foreign films, as well as a variety of community stage performances and other events.
10. Hamilton-Lowe Aquatics Center

Summers in Moscow wouldn’t be the same without this public outdoor pool, splash pad and water park, open June through September.
If you want to get your laps in, the Hamilton-Lowe Aquatics Center has a 25-yard, six-lane pool.
Meanwhile parents can bring children to the extensive play area, which features a toddler-friendly slide, tumble buckets, interactive equipment, slides for bigger kids and a small lazy river.
The center also has picnic tables, barbecues, lounge chairs and free Wi-Fi, as well as a full-service concession area, though you’re free to bring your own food.
11. Idaho Vandals

The 16,000-seater multipurpose arena, Kibbie Dome is home field for several of the University of Idaho’s sports teams, all called the Idaho Vandals.
So depending on the time of year you can catch pulsating football, basketball (men and women), soccer (women), tennis and indoor track and field at this venue.
The Kibbie Dome was completed in 1971 as an open-air stadium, and was given its barrel-vaulted roof in 1975.
The football team competes in the Big Sky Conference in the Football Championship Subdivision (FCS), returning in 2016 after 20 years bouncing around the Big West, Sun Belt and Western Athletic Conferences.
The Vandals’ golden age came between 1985 and 1995 when it reached the I-AA playoffs in ten out of 11 seasons.
If you’re wondering about the name, “Vandals”, it goes back more than a century, when UI’s feared basketball team played defense with such ferocity that they were dubbed the Vandals by the famous coach Hec Edmundson (1886-1964).
12. Ghormley Park

Bordered on the south side by Paradise Creek, Ghormley Park is the favorite destination for family fun and outdoor recreation in summer.
The park covers just over ten acres, a large section of which is in the shade of tall, mature trees.
This is where you’ll find the picnic shelter, fitted with BBQ grills, as well as a children’s playground.
Elsewhere there are amenities for baseball/softball, basketball and horseshoes. You can use the Paradise Trail, which traces the creek and connects a number of green spaces in Moscow, to get onto the Latah Trail on the east side of the city and the Bill Chipman Trail in the west.
13. Palouse Ice Rink

You can hit the ice at this popular local rink on the southeast side of town. Resembling an aircraft hangar, the Palouse Ice Rink has a temporary look about it, and when we wrote this article was making strides raising money for a permanent complex.
There are regular public skate sessions early in the day, after school and in the evening, and skate rental is reasonably priced.
Also on the schedule are casual stick-n-puck sessions, pick-up hockey, drop-in late-night curling, league curling, Palouse Adult League Hockey and much more. Check the calendar for learn-to-skate sessions.
14. Moscow Artwalk

Beginning back in 2004, the Moscow Artwalk is a landmark on the Palouse calendar. On one Friday evening in June, more than 60 businesses and 100 artists around downtown participate in a vibrant cultural and artistic event.
Moscow Artwalk brings exhibitions of a wide variety, as well as live demonstrations by artists, workshops, live music, dance performances and food vendors, on Main Street and its intersecting streets.
You can take in this cultural feast on a self-guided trail, and there’s a passport system, with six stamps making you eligible for a prize draw. And if you miss something, many of the participating businesses also have Saturday hours.
15. Fondo on the Palouse

The foundation responsible for the Latah Trail organizes this cycling event, normally staged on the last Saturday in June.
Fondo on the Palouse takes you out into the beautiful rolling Palouse landscape on a variety of group bike rides, all setting off from Moscow.
The Family Fondo is a 15-mile route from Moscow to Troy. If you want something longer but want to stay away from road traffic, there’s a 50-mile ride along the Latah and Bill Chipman Palouse Trails.
And finally the grand Moscow Fondo is a 100-mile tour of the region, passing through Troy, Deary, Princeton and Potlatch, crossing the state line to Pullman and Colfax, WA, before returning to Moscow.
15 Best Things to Do in Moscow (Idaho):
- University of Idaho Arboretum & Botanical Garden
- Latah Trail
- Appaloosa Museum and Heritage Center
- Moscow Farmers' Market
- Bill Chipman Palouse Trail
- Prichard Art Gallery
- McConnell Mansion
- Colter's Creek Winery
- Kenworthy Performing Arts Centre
- Hamilton-Lowe Aquatics Center
- Idaho Vandals
- Ghormley Park
- Palouse Ice Rink
- Moscow Artwalk
- Fondo on the Palouse

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Use homework as a tool for communication. Use homework as a vehicle to foster family-school communication. Families can use homework as an opportunity to open conversations about specific assignments or classes, peer relationships, or even sleep quality that may be impacting student success. For younger students, using a daily or weekly home ...
Homework is most impactful in math and had positive impacts on achievement in other subjects when the work assigned was NOT novel or complex (Hattie 2009, p. 235; Eren and Henderson, 2011). "Conceptual and project-based homework" had the least impact on achievement. Higher ability students gain more
Homework is a set of tasks assigned to students by their teachers to be completed at home. Common homework assignments may include required reading, ... A 2019 Pew Research Center review of Bureau of Labor Statistics' American Time Use Survey data reported that 15-, 16-, and 17-year-olds Americans, spent on average an hour a day on homework ...
The homework center is our structured work environment available to students in the mentoring program. Here, they can complete assignments or study. Math and language arts support staff are available to answer questions and help keep students on task. In-Person Homework Center (Broomfield)
Homework has been in the headlines again recently and continues to be a topic of controversy, with claims that students and families are suffering under the burden of huge amounts of homework. School board members, educators, and parents may wish to turn to the research for answers to their questions about the benefits and drawbacks of homework.
Seek out help and support from your principal, teaching colleagues, parents and school community. Here are a few tips to get you started: Decide who - Start small. Identify a small group of students who need support with completing homework. Follow the protocol for contacting parents and obtaining their permission.
Despite the proliferation of online homework websites and tutoring services, public libraries still have an important role to play when it comes to supporting young people's educational needs. Public libraries that take a proactive approach—by setting up organized homework centers—have the potential to become catalysts for better performance in school, improved self-esteem, and engaged ...
Whether readers are investigating the possibility of setting up a center from scratch or are eager to revamp an existing center, this book shows the way forward with. methodologies for evaluation and improvement. This comprehensive resource will help public libraries create and manage a vibrant homework center that effectively serves students ...
Homework skeptic Alfie Kohn has questioned the benefit of homework, arguing that its positive effects are mythical, and in fact, it can disrupt the family dynamic. 4 He questions why teachers ...
Support References The study center should include a small reference library. Supply a dictionary written at a level your child can understand. A thesaurus is a great idea as well. An atlas and a globe can also be useful for school projects and homework support.
America's K-12 students are returning to classrooms this fall after 18 months of virtual learning at home during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some students who lacked the home internet connectivity needed to finish schoolwork during this time - an experience often called the "homework gap" - may continue to feel the effects this school year. Here is what Pew Research Center surveys found ...
Homework is an important part of every child's education, but finding time to help children get their homework done can be a challenge for busy families. Homework Centres will provide a supervised and suitable learning environment in which students can complete their homework before they go home. To ease the burden on families, the Queensland ...
Homework Center gives kids the attention they need to succeed At Zaniac, we understand what a difference a little bit of extra attention can make in children's confidence in school. That's why Zaniac's trained instructors are available each day after school and on Saturdays to help your student with homework.
Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report on American Education. Homework! The topic, no, just the word itself, sparks controversy. It has for a long time. In 1900, Edward Bok, editor of the Ladies ...
Homework Center Libraries What is a Homework Center? With the support of grants and corporate/community funding, the Library has established 48 Homework Centers. These Centers provide enhanced resources, computer technology, and homework helpers to support the educational needs of students in these communities.
Homework Central strives to create educational equity for disadvantaged elementary school students who aren't receiving the support they need. Through lack of resources, and poor access to technology or academic assistance, too many children start to fall behind, creating an ever-widening academic gap between them and their peers. ...
Homework Center Libraries What is a Homework Center? With the support of grants and corporate/community funding, the Library has established 48 Homework Centers. These Centers provide enhanced resources, computer technology, and homework helpers to support the educational needs of students in these communities.
Source: Maarten/Flickr Commons. There are those who argue that homework does serve a purpose. For example, it helps to prepare students for national and statewide exams and tests. It helps to ...
Creating the homework packets ahead of time has worked out well, and they are not nearly as time consuming as my previous attempts at homework since they are short, and most task types are repeated. ... Melissa Braaten is an adult education instructor at Catholic Charities Haitian Multi-Services Center in Dorchester, MA. Melissa has taught ASE ...
In the very early 1900s, homework was actually considered unhealthy for children and was classified as child labor because it interfered with their ability to do chores around the house.
Homework is a controversial topic and the object of differing opinions among teachers, parents, and educators . While some highly value it considering it key in scholarly achievement and academic performance, others view it as a nuisance to students' independence and a cause for unwarranted emotional and physical stress for kids. The controversy surrounding homework…
Compiling homework for a deskmate is the most innovative approach to assigning homework. It implies that students will formulate the homework tasks for their peers themselves, based on the tasks that have been performed in the classroom. Creative assignments include academic writing, personal projects, research, etc.
The journey toward baby Sarala's arrival in September 2023 was arduous for Kelly Meek and her husband: nearly four years of fertility treatments, ultrasounds and injections to combat Meek's diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome. So when Sarala decided to arrive a little ahead of schedule, Meek ...
Multiple Choice question if in the short run the demand for transit by train is inelastic and in the long run the demand is elastic, then a price: a.increase will increase total revenue in the short run but decrease total revenue in the long run.
It became the major center for political and social events and today is used for big parades and public celebrations and demonstrations. At the southern end of the square is the 16th-century Cathedral of St. Basil, and at the northern end is the 19th-century State Historical Museum. ... Improved homework resources designed to support a variety ...
Moscow is the capital and largest city of Russia.The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at over 13 million residents within the city limits, over 18.8 million residents in the urban area, and over 21.5 million residents in its metropolitan area. The city covers an area of 2,511 square kilometers (970 sq mi), while the urban area covers 5,891 square ...
3. Appaloosa Museum and Heritage Center Source: Appaloosa Museum & Heritage Center / Facebook Appaloosa Museum and Heritage Center The Appaloosa, identified by its colorful spotted coat, is a horse breed synonymous with the Palouse region, so it's fitting that there should be a museum for it, right on the Idaho-Washington state line.