Entrepreneurship Thesis (13 Great Tips)
- 5 month(s) ago


Table of Contents
I. introduction, ii. crafting the perfect entrepreneurship thesis statement, iii. choosing the right entrepreneurship thesis topic, iv. conducting a literature review, v. methodology selection, vii. data collection, vii. data analysis, viii. results presentation, ix. discussion of findings, x. conclusion, xi. frequently asked questions (faqs), xii. peer review and feedback, xiii. formatting and style guidelines, xiv. finalizing your entrepreneurship thesis.
A. Definition of Entrepreneurship in the Academic Context

In the academic context, entrepreneurship is a multifaceted concept that extends beyond the traditional understanding of business ventures and profit-making. It encompasses the identification and exploitation of opportunities, the allocation of resources, and the creation of value in various sectors. Within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, the definition of entrepreneurship underscores the importance of innovation, risk-taking, and proactive problem-solving. It goes beyond the mere act of starting a business and delves into the entrepreneurial mindset, emphasizing the capacity to envision and implement novel ideas.
In this academic exploration, entrepreneurship is viewed as a dynamic force that drives economic development, fosters job creation, and catalyzes societal change. A nuanced understanding of entrepreneurship in the academic context is crucial for students crafting their theses, as it provides a solid foundation for research that goes beyond the surface level, delving into the intricate interplay of factors that contribute to entrepreneurial success.
B. Importance of Crafting a Strong Entrepreneurship Thesis
The importance of crafting a strong entrepreneurship thesis cannot be overstated within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work. A robust thesis serves as the intellectual backbone of a student’s academic endeavor, providing a clear roadmap for research and analysis. A well-constructed thesis not only demonstrates a student’s mastery of the subject matter but also showcases their ability to formulate a research problem, design a methodological approach, and contribute meaningfully to the existing body of knowledge in entrepreneurship. It serves as a testament to the student’s critical thinking skills and research acumen, playing a pivotal role in academic evaluation.
Furthermore, a strong entrepreneurship thesis contributes to the broader academic discourse by shedding light on emerging trends, addressing gaps in current knowledge, and offering valuable insights for both scholars and practitioners in the field. As students embark on the journey of crafting their entrepreneurship theses, recognizing the significance of this foundational document becomes essential for achieving academic excellence and making a meaningful impact in the realm of entrepreneurship research.
C. Overview of the Article Sections
The comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work unfolds across several key sections, each meticulously designed to provide aspiring scholars with a structured pathway for their academic exploration. The guide kicks off with an insightful introduction, offering a precise definition of entrepreneurship within the academic context and highlighting the pivotal role a strong thesis plays in this domain. The subsequent section delves into the historical evolution of entrepreneurship, elucidating key characteristics that define successful entrepreneurs and examining the role of entrepreneurship in modern economies.
Moving forward, the guide navigates through the intricacies of crafting an impactful thesis statement and aids students in selecting a pertinent topic by exploring the process of narrowing down focus and aligning personal interests with current trends. The guide further leads students through crucial steps such as conducting a literature review, selecting an appropriate methodology, and addressing challenges in entrepreneurship research. The comprehensive nature of this guide ensures that students are equipped with the essential tools and insights needed at each stage of their entrepreneurship thesis journey.
A. Importance of a Well-Defined Thesis Statement
The significance of a well-defined thesis statement in crafting the perfect entrepreneurship thesis cannot be overstated within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work. The thesis statement serves as the compass that guides the entire research endeavor, providing a concise and clear expression of the central argument and purpose of the study. A robust thesis statement not only informs the reader about the scope and direction of the research but also crystallizes the researcher’s focus, ensuring a cohesive and purposeful exploration of the chosen topic.
In the guide, emphasis is placed on the importance of formulating a thesis statement that is not only specific and debatable but also relevant to the broader field of entrepreneurship. It sets the tone for the entire thesis, influencing the research questions, methodology, and overall structure. Recognizing the pivotal role of a well-crafted thesis statement is fundamental for students embarking on the journey of entrepreneurship research, as it lays the foundation for a compelling and academically rigorous thesis.
B. Identifying the Scope and Purpose
In the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, the process of crafting the perfect entrepreneurship thesis statement involves a meticulous examination of the scope and purpose of the research. Identifying the scope is crucial as it delineates the boundaries within which the study will unfold, ensuring a focused and manageable investigation. This section of the guide emphasizes the importance of clearly defining what the thesis will cover, helping students avoid the pitfalls of a thesis that is either too broad or too narrow.
Simultaneously, understanding the purpose of the research statement is equally paramount. It requires students to reflect on the overarching goal of their study, whether it be contributing new knowledge to the field, addressing a specific problem, or testing a hypothesis. By navigating through the intricacies of scope and purpose, students are equipped with the tools to shape a thesis statement that not only encapsulates the essence of their research but also resonates with academic rigor and relevance in the realm of entrepreneurship.
C. Examples of Effective Entrepreneurship Thesis Statements
Within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a pivotal aspect of crafting the perfect entrepreneurship thesis statement involves examining examples of effective statements. These exemplars serve as instructive models, showcasing the qualities that make a thesis statement impactful and resonant. The guide illustrates how an effective thesis statement in entrepreneurship should not only clearly articulate the research’s central argument but also demonstrate a level of specificity that piques the reader’s interest. It emphasizes the importance of avoiding vague or overly broad statements, urging students to tailor their thesis statements to the unique nuances of their research.
By providing concrete examples, the guide aims to inspire students, offering them a practical understanding of how to distill the essence of their study into a concise and compelling thesis statement that will captivate both academic and non-specialist audiences alike.
A. Narrowing Down Your Focus
In the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a crucial step in the thesis development process is the art of narrowing down one’s focus when selecting the right entrepreneurship thesis topic. This section underscores the importance of specificity and clarity in defining the research parameters, urging students to hone in on particular aspects or dimensions within the vast field of entrepreneurship.
By encouraging a focused approach, the guide helps students avoid the pitfalls of overly broad or generic topics, facilitating a more in-depth exploration of a chosen subject. It emphasizes that a well-defined and narrow focus not only makes the research more manageable but also enhances the depth and precision of the ensuing study. This section serves as a navigational tool, empowering students to strategically narrow their focus and align their research interests with the nuances of the ever-evolving landscape of entrepreneurship.
B. Identifying Your Personal Interests and Strengths
In the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, the process of choosing the right entrepreneurship thesis topic is intricately linked with identifying personal interests and strengths. This crucial step recognizes that a student’s passion and strengths play a pivotal role in sustaining motivation and commitment throughout the research journey. The guide encourages students to introspectively assess their own interests within the broad field of entrepreneurship, considering areas that genuinely captivate their curiosity and enthusiasm.
Simultaneously, it emphasizes recognizing individual strengths and skills, as leveraging these attributes can enhance the quality and depth of the research. By aligning the chosen thesis topic with personal interests and strengths, students not only make the research process more engaging but also position themselves to contribute meaningfully to the academic discourse in entrepreneurship. This section of the guide serves as a compass, guiding students toward a research path that resonates with their intrinsic motivations and capabilities.
C. Researching Current Trends in Entrepreneurship
In the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, an integral step in choosing the right entrepreneurship thesis topic involves researching current trends in the field. This section underscores the dynamic nature of entrepreneurship and encourages students to stay abreast of the latest developments, innovations, and challenges within the entrepreneurial landscape. By engaging with current trends, students gain valuable insights into emerging topics, pressing issues, and areas where gaps in knowledge exist.
The guide emphasizes the importance of aligning one’s thesis topic with these contemporary dynamics, ensuring that the research remains relevant and contributes to the ongoing discourse in entrepreneurship. Through a thorough exploration of current trends, students are empowered to make informed choices, selecting topics that not only resonate with their academic interests but also address the evolving needs and interests of the entrepreneurial community.
A. Understanding the Significance of a Literature Review
Within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a pivotal section highlights the significance of understanding the literature review in the broader context of academic research. Here, the guide emphasizes that a literature review is not merely a perfunctory task but a critical component that lays the groundwork for the entire thesis. It serves as a comprehensive survey of existing knowledge, theories, and research related to the chosen entrepreneurship topic. By understanding the significance of a literature review, students recognize its role in identifying gaps in current knowledge, framing research questions, and contextualizing the importance of their study within the broader academic landscape.
The guide underscores the value of a well-crafted literature review in demonstrating a student’s familiarity with relevant scholarship and in setting the stage for a rigorous, informed, and impactful research endeavor. Understanding the weight and purpose of the literature review is crucial for students as they embark on the journey of conducting a literature review for their entrepreneurship thesis.
B. Identifying Relevant Studies and Research Papers
In the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a key stage in conducting a literature review involves the meticulous process of identifying relevant studies and research papers. This section underscores the importance of a systematic and thorough approach to literature searching, guiding students on how to navigate academic databases, libraries, and reputable journals to locate pertinent literature.
By emphasizing the need for precision in identifying studies that directly contribute to the chosen entrepreneurship thesis topic, the guide enables students to build a strong foundation for their research. It encourages the exploration of diverse perspectives, methodologies, and findings to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter. This step not only aids in synthesizing existing knowledge but also positions students to critically evaluate and integrate the insights garnered from a spectrum of relevant studies, ultimately enhancing the depth and scholarly merit of their literature review.
C. Analyzing and Synthesizing Existing Knowledge
In the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, the pivotal phase of conducting a literature review involves the intricate processes of analyzing and synthesizing existing knowledge. This section underscores the active engagement required in evaluating and making sense of the diverse array of studies and research papers identified. The guide emphasizes the importance of critically assessing the methodologies, findings, and theoretical frameworks of each source, enabling students to discern patterns, contradictions, and gaps in the existing literature.
Furthermore, it guides students on how to synthesize this wealth of information into a coherent narrative, connecting various threads of research to form a nuanced understanding of the chosen entrepreneurship topic. By highlighting the significance of both analysis and synthesis, the guide empowers students to not only showcase their mastery of existing knowledge but also lay the groundwork for their own original contributions to the field of entrepreneurship.
A. Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research Methods
Within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, the section on methodology selection delves into the critical decision between qualitative and quantitative research methods. This stage recognizes that the choice between these approaches significantly shapes the research design and outcomes. The guide elucidates the distinctions between qualitative and quantitative methods, highlighting that qualitative methods, such as interviews, focus groups, and case studies, delve into the depth and richness of experiences, while quantitative methods, involving surveys and statistical analyses, aim for numerical precision and generalizability. It underscores that the selection should align with the research questions and objectives.
The guide assists students in navigating this decision-making process by providing insights into the strengths and limitations of each approach, ensuring a methodological choice that not only suits the nature of the research but also contributes to the robustness and validity of the entrepreneurship thesis.
B. Case Studies and Their Application in Entrepreneurship Thesis

In the methodology selection section of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a particular focus is placed on the significance of case studies and their application. This methodological choice is elucidated as a powerful means of gaining in-depth insights into real-world entrepreneurial phenomena. The guide underscores that case studies, whether single or multiple, allow researchers to explore intricate details, contexts, and dynamics surrounding entrepreneurial endeavors. It emphasizes how this approach can provide a holistic understanding of the complexities and nuances inherent in the chosen entrepreneurship topic.
By delving into the unique experiences and challenges faced by entrepreneurs, case studies offer a valuable qualitative lens for researchers. The guide guides students on leveraging case studies effectively, ensuring that this methodological choice aligns seamlessly with the research objectives, contributing to a comprehensive and nuanced exploration in their entrepreneurship thesis.
C. Choosing the Right Methodology for Your Research Question
In the methodology selection segment of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, an essential emphasis is placed on the strategic process of choosing the right methodology tailored to the research question at hand. This section recognizes the dynamic interplay between research questions and the most suitable methodological approach. The guide underscores the importance of aligning the chosen methodology with the nature of the research inquiry, whether it involves exploring phenomena qualitatively through in-depth interviews, employing statistical analyses for quantitative data, or employing a mixed-methods approach for a more comprehensive understanding.
By offering guidance on this critical decision-making process, the guide ensures that students are equipped to select a methodology that not only addresses their specific research questions but also enhances the overall rigor and validity of their entrepreneurship thesis. This strategic alignment between research questions and methodology serves as a cornerstone for a well-executed and impactful research endeavor.
A. Surveys and Questionnaires
In the data collection phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a crucial aspect is the effective utilization of surveys and questionnaires. This section underscores the versatility and efficiency of these tools in gathering quantitative data from a targeted sample. The guide emphasizes that surveys and questionnaires are invaluable instruments for obtaining a broad understanding of entrepreneurial trends, attitudes, and behaviors.
It provides insights into how to design these instruments effectively, ensuring clarity, relevance, and reliability in the collected data. By guiding students through the intricacies of survey construction, the guide ensures that the data collected aligns closely with the research objectives, facilitating a robust analysis in the subsequent stages of the entrepreneurship thesis. The section recognizes the role of surveys and questionnaires as powerful tools in eliciting quantifiable responses, enabling students to contribute valuable empirical evidence to the academic discourse on entrepreneurship.
B. Interviews with Entrepreneurs
In the data collection phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a critical dimension involves conducting interviews with entrepreneurs. This section acknowledges the unique insights and contextual depth that interviews can provide in understanding the lived experiences of entrepreneurs. The guide underscores the significance of designing structured yet flexible interview protocols that allow for in-depth exploration of the chosen entrepreneurship topic. It guides students on how to formulate open-ended questions that elicit rich narratives, experiences, and perspectives from entrepreneurs.
By providing insights into the art of effective interviewing, the guide ensures that students can navigate this qualitative data collection method with skill and sensitivity. Interviews with entrepreneurs emerge as a valuable means to uncover nuanced details, motivations, and challenges, enriching the depth and authenticity of the data collected for the entrepreneurship thesis.
C. Utilizing Secondary Data Sources

In the data collection phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, the utilization of secondary data sources is explored as a strategic approach. This section acknowledges the wealth of existing information available through various secondary sources, including academic journals, reports, and databases. The guide emphasizes the importance of leveraging these sources to complement primary data, offering additional context, and validating findings. It provides insights into effective methods of retrieving, evaluating, and synthesizing secondary data, ensuring that students can harness the breadth of existing knowledge to enhance the robustness of their entrepreneurship thesis.
By guiding students on the judicious use of secondary data sources, the comprehensive guide aims to instill a nuanced understanding of how these resources can contribute to a well-rounded and evidence-based exploration of the chosen entrepreneurship topic.
A. Statistical Analysis Techniques
In the data analysis phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a pivotal aspect is the application of statistical analysis techniques. This section recognizes the significance of employing quantitative methods to interpret and derive meaningful insights from collected data. The guide emphasizes the importance of choosing the appropriate statistical techniques based on the nature of the research questions and the type of data gathered, whether through surveys, questionnaires, or other quantitative methods. It provides insights into commonly used statistical analyses such as regression analysis, chi-square tests, and ANOVA, guiding students on their application to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends within the entrepreneurial data.
By offering a comprehensive overview of statistical analysis techniques, the guide ensures that students can navigate this complex aspect of data analysis with precision, contributing to the credibility and validity of their entrepreneurship thesis.
B. Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
In the data analysis phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a significant focus is placed on qualitative data analysis methods. This section recognizes the richness and complexity of qualitative data gathered from interviews, case studies, and other narrative sources.
The guide emphasizes the importance of systematic approaches to analyze and interpret this qualitative information, such as thematic analysis, content analysis, and grounded theory. It provides insights into the nuanced process of coding, categorizing, and identifying patterns within qualitative data, enabling students to derive meaningful and contextually relevant findings. By guiding students through the intricacies of qualitative data analysis methods, the comprehensive guide ensures that they can uncover the depth and intricacies inherent in qualitative data, contributing to a more comprehensive and textured understanding of the chosen entrepreneurship topic.
C. Interpreting Results and Drawing Conclusions
In the data analysis phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a critical step involves interpreting results and drawing conclusions from the gathered data. This section recognizes that the ultimate goal of data analysis is to derive meaningful insights that contribute to the overarching research objectives.
The guide emphasizes the importance of systematically interpreting both quantitative and qualitative findings, linking them back to the research questions and hypotheses posed at the outset of the thesis. It provides insights into the art of drawing valid and well-supported conclusions, avoiding overgeneralization and ensuring that the interpretations align with the evidence presented. By guiding students through this crucial analytical process, the comprehensive guide ensures that they can distill key findings, highlight patterns, and offer insightful interpretations, contributing to a robust and credible entrepreneurship thesis.
A. Effectively Communicating Your Findings

In the results presentation phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a paramount focus lies on effectively communicating the findings. This section recognizes that the value of insightful research is inherently tied to how well it is conveyed to the intended audience. The guide emphasizes the importance of clarity, coherence, and precision in presenting both quantitative and qualitative results. It provides insights into structuring the presentation to tell a compelling narrative, utilizing visuals, charts, and graphs judiciously for enhanced comprehension.
By guiding students on effective communication strategies, the comprehensive guide ensures that they can convey their findings in a manner that not only engages the reader but also allows for a nuanced understanding of the contributions made by the research to the field of entrepreneurship. Effective communication of findings is fundamental to showcasing the rigor and significance of the research conducted throughout the entrepreneurship thesis.
B. Utilizing Visual Aids for Clarity
In the results presentation phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a pivotal emphasis is placed on utilizing visual aids for clarity. This section recognizes the power of visual elements in enhancing the comprehension and impact of research findings. The guide emphasizes the strategic use of charts, graphs, tables, and other visual representations to succinctly convey complex data patterns. It provides insights into the art of designing visuals that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also serve as effective tools for communication. By guiding students on how to thoughtfully incorporate visual aids, the comprehensive guide ensures that their entrepreneurship thesis benefits from enhanced clarity and accessibility.
Visual aids not only simplify the understanding of intricate results but also elevate the overall presentation, contributing to a more compelling and informative research narrative.
C. Highlighting Key Discoveries and Patterns
In the results presentation phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a crucial focus is placed on highlighting key discoveries and patterns. This section underscores the importance of distilling complex findings into clear and impactful messages for the audience. The guide emphasizes the identification and emphasis on significant trends, correlations, and novel insights gleaned from the data analysis. It provides insights into how to articulate these key discoveries cohesively, ensuring that readers can readily grasp the essence of the research outcomes.
By guiding students on effective highlighting strategies, the comprehensive guide ensures that their entrepreneurship thesis not only presents comprehensive results but also directs attention to the most crucial and illuminating aspects of the research, contributing to a nuanced understanding of the entrepreneurial phenomena under investigation.
A. Interpreting Results in the Context of Existing Literature
In the discussion of findings phase within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a critical step involves interpreting results in the context of existing literature. This section recognizes the interconnectedness of new discoveries with established knowledge in the field. The guide underscores the importance of not only presenting raw results but also contextualizing them within the broader academic discourse. It provides insights into how students can critically analyze their findings in relation to existing research, identifying points of agreement, contradiction, or expansion.
By guiding students through this interpretative process, the comprehensive guide ensures that the discussion of findings not only contributes to the existing body of knowledge but also serves to advance and refine theoretical frameworks within entrepreneurship research. This approach enriches the academic conversation by placing new insights in dialogue with established literature, fostering a deeper understanding of the complexities inherent in the chosen entrepreneurship topic.
B. Addressing Implications for Future Research

In the discussion of findings phase within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, an essential aspect is addressing implications for future research. This section recognizes that every study, while contributing valuable insights, opens new avenues for exploration. The guide emphasizes the importance of students reflecting on the broader implications of their findings and suggesting directions for future research in entrepreneurship. It provides insights into how to identify unexplored aspects, potential extensions of the study, or avenues where further investigation could deepen understanding.
By guiding students through this forward-looking perspective, the comprehensive guide ensures that their entrepreneurship thesis not only serves as a contribution to the existing knowledge base but also sparks inspiration for subsequent scholars to continue advancing the field. Addressing implications for future research is a vital component in sustaining the momentum of academic inquiry and promoting a continual evolution of entrepreneurship scholarship.
C. Offering Practical Applications for Entrepreneurs
In the discussion of findings phase within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a crucial dimension is the emphasis on offering practical applications for entrepreneurs. This section recognizes the significance of bridging academic research with real-world implications. The guide underscores the importance of students translating their research findings into actionable insights for entrepreneurs, highlighting how the study’s outcomes can inform decision-making, strategy development, or problem-solving in entrepreneurial endeavors. It provides insights into effectively communicating these practical applications, ensuring that the entrepreneurship thesis not only contributes to theoretical understanding but also serves as a valuable resource for practitioners.
By guiding students on articulating tangible benefits and applications, the comprehensive guide ensures that their research becomes a catalyst for positive change in the entrepreneurial landscape, fostering a dynamic relationship between academia and practical entrepreneurship.
A. Summarizing Key Findings
In the concluding section of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a pivotal focus lies on summarizing key findings. This phase recognizes the culmination of the research journey and underscores the importance of succinctly presenting the core discoveries. The guide emphasizes the need for a concise yet comprehensive summary that encapsulates the main insights derived from the study. It provides insights into how students can distill complex results into clear and digestible points, ensuring that the reader grasps the essence of the research.
By guiding students on effective summarization strategies, the comprehensive guide ensures that the conclusion not only reinforces the significance of the study but also leaves a lasting impression, emphasizing the enduring impact of the entrepreneurship thesis within the academic and practical realms.
B. Emphasizing the Contribution to Entrepreneurship Knowledge
In the conclusion section of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a critical emphasis is placed on highlighting the contribution to entrepreneurship knowledge. This phase recognizes the scholarly significance of the research conducted and underscores the importance of explicitly stating how the study adds value to the existing body of entrepreneurship literature.
The guide encourages students to reflect on the novel insights, unique perspectives, or methodological advancements introduced in their thesis. It provides insights into articulating the specific ways in which the research expands, refines, or challenges current understanding within the field. By guiding students in emphasizing their contribution, the comprehensive guide ensures that the conclusion serves as a capstone, reinforcing the academic merit and broader relevance of the entrepreneurship thesis within the scholarly discourse.
C. Encouraging Further Exploration in the Field
In the conclusion section of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a forward-looking perspective is cultivated by encouraging further exploration in the field. This phase acknowledges that the culmination of one thesis represents not the end but a continuation of the scholarly conversation in entrepreneurship. The guide underscores the importance of inspiring future researchers to build upon the current study, suggesting unexplored avenues, additional dimensions, or new questions that merit investigation. It provides insights into crafting a conclusion that sparks intellectual curiosity, fostering a sense of ongoing inquiry within the entrepreneurship domain.
By guiding students to express the potential for further exploration, the comprehensive guide ensures that the conclusion not only serves as a reflective endpoint but also as a launchpad for future scholarship, contributing to the continuous evolution of knowledge within the field of entrepreneurship.

A. What is the significance of entrepreneurship in academia?
B. How do I choose a relevant and engaging thesis topic?
C. What are the common challenges in entrepreneurship research?
D. How can I ensure the ethical conduct of my research?
E. What are some examples of successful entrepreneurship thesis statements?
A. Seeking Feedback from Advisors and Mentors
In the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, the section on peer review and feedback places a significant emphasis on seeking feedback from advisors and mentors. This phase recognizes the instrumental role that constructive feedback plays in refining and enhancing the quality of the thesis. The guide encourages students to actively engage with their advisors and mentors, presenting drafts of their work to solicit valuable insights. It provides insights into how to navigate this feedback-seeking process effectively, ensuring that students are receptive to suggestions, critical observations, and guidance.
By guiding students through the importance of this collaborative feedback loop, the comprehensive guide aims to foster a culture of continuous improvement, where the thesis evolves through iterative refinement. Seeking feedback from advisors and mentors not only enhances the academic rigor of the entrepreneurship thesis but also contributes to the personal and intellectual growth of the researcher.
B. Incorporating Constructive Criticism
Within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, the segment on peer review and feedback underscores the significance of incorporating constructive criticism. This phase recognizes that the journey of refining a thesis is inherently collaborative, involving the valuable input of peers, advisors, and mentors. The guide encourages students to view constructive criticism as an opportunity for growth, emphasizing the importance of remaining open-minded and receptive to diverse perspectives. It provides insights into how to sift through feedback, discerning actionable insights that can elevate the quality of the thesis.
By guiding students through this process, the comprehensive guide ensures that they not only welcome constructive criticism but also use it as a catalyst for strengthening arguments, clarifying concepts, and fortifying the overall coherence of the entrepreneurship thesis. Incorporating constructive criticism becomes a pivotal step in the iterative refinement process, contributing to the scholarly robustness and excellence of the final research output.
A. Following the Preferred Citation Style
In the formatting and style guidelines section of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a crucial emphasis is placed on following the preferred citation style. This phase recognizes that adherence to a specific citation style is not merely a matter of aesthetic uniformity but a fundamental aspect of scholarly integrity. The guide underscores the importance of consistency in citing sources, whether it be APA, MLA, Chicago, or any other designated style. It provides insights into the intricacies of proper citation, covering aspects like in-text citations, bibliography, and reference lists.
By guiding students on following the preferred citation style meticulously, the comprehensive guide ensures that the entrepreneurship thesis not only meets academic standards but also pays due respect to the intellectual contributions of the sources used, fostering a scholarly ethos in the presentation of research.
B. Structuring Your Thesis According to Academic Standards
In the formatting and style guidelines section of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a fundamental focus is directed towards structuring the thesis according to academic standards. This phase acknowledges that a well-organized and coherent structure not only enhances the readability of the thesis but also aligns with established academic conventions. The guide emphasizes the importance of adhering to a clear and logical sequence in presenting the introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. It provides insights into the nuanced aspects of formatting, such as heading hierarchy, page layout, and proper citation placement.
By guiding students through the intricacies of structuring their thesis, the comprehensive guide ensures that the research is not only academically rigorous but also presented in a manner that facilitates comprehension and engagement for readers. Following academic standards in structuring the thesis becomes a cornerstone for effective communication and scholarly presentation within the field of entrepreneurship.
A. Conducting a Comprehensive Proofread
In the finalizing phase of the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work, a paramount emphasis is placed on conducting a comprehensive proofread. This stage recognizes that meticulous proofreading is an integral component of presenting a polished and professional thesis.
The guide underscores the importance of scrutinizing the entire document for grammatical errors, typographical mistakes, and formatting inconsistencies. It provides insights into effective proofreading strategies, such as reading the thesis aloud, using grammar-check tools, and seeking feedback from peers. By guiding students through this meticulous proofreading process, the comprehensive guide ensures that the entrepreneurship thesis is free from distracting errors, allowing the quality of the research and the scholar’s proficiency to shine through. Conducting a comprehensive proofread becomes a crucial step in delivering a refined and academically rigorous final product that meets the highest standards of scholarly excellence.

Place a Quick Order
We have qualified Experts in all fields
Latest Articles
Financial Presentation Essays (9 Top Tips) 21 hours ago
Money Market Assignments (9 Great Tips) 21 hours ago
Cost Accounting Essays ( 6 Best Tips) 2 days ago
Sales Forecasting Reports (7 Best Hints) 3 days ago
Marketing Campaign Dissertations (12 Top Tips) 3 days ago
Managerial Accounting Reports (9 Top Tips) 4 days ago
VRIO Analysis ( Student’s Guide) 4 days ago
Negotiation Essays (9 Top Writing Tips) 5 days ago
Outsourcing Summaries (12 Major Points) 5 days ago
Supplier Selection Essays ( 5 Writing Tips) 8 days ago

Radio Active Tutors is a freelance academic writing assistance company. We provide our assistance to the numerous clients looking for a professional writing service.
Need academic writing assistance ? Order Now
The impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and its determinants: a systematic review
- Open access
- Published: 04 August 2020
- Volume 71 , pages 553–584, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Thomas Neumann ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7189-8159 1
87k Accesses
Explore all metrics
This paper presents a systematic review of (a) the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and (b) the factors determining this impact. Research over the past 25 years shows that entrepreneurship is one cause of macroeconomic development, but that the relationship between entrepreneurship and welfare is very complex. The literature emphasizes that the generally positive impact of entrepreneurship depends on a variety of associated determinants which affect the degree of this impact. This paper seeks to contribute to the literature in three ways. First, it updates and extends existing literature reviews with the recently emerged research stream on developing countries, and incorporates studies analysing not only the impact of entrepreneurship on economic growth and welfare but also on social and environmental welfare. Second, it identifies and structures the current knowledge on the determinants of this impact. And third, it provides a roadmap for future research which targets the shortcomings of the existing empirical literature on this topic. The review of 102 publications reveals that the literature generally lacks research which (a) goes beyond the common measures of economic welfare, (b) examines the long-term impact of entrepreneurship and (c) focuses on emerging and developing countries. Regarding the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship, the results highlight the need for empirical research which addresses both already investigated determinants which require more attention (e.g. survival, internationalisation, qualifications) and those which are currently only suspected of shaping the impact of entrepreneurship (e.g. firm performance, the entrepreneur’s socio-cultural background and motivations).
Similar content being viewed by others
Economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on entrepreneurship and small businesses

Artificial Intelligence and Economic Development: An Evolutionary Investigation and Systematic Review

Entrepreneurship in China
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Entrepreneurship and its possible impact on the economy have been studied extensively during the past two decades but the research field still continues to develop and grow. The majority of studies from a variety of scientific disciplines have found empirical evidence for a significant positive macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship (e.g. Atems and Shand 2018 ; Audretsch and Keilbach 2004a ; Fritsch and Mueller 2004 , 2008 ). However, several empirical studies show that the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship can also be negative under certain conditions (e.g. Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Andersson and Noseleit 2011 ; Fritsch and Mueller 2004 , 2008 ). Potential explanations for these contradictory results are to be found in the complex relationship between entrepreneurship and economic growth. Already some of the very first empirical studies on the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship showed that factors such as industrial affiliation (Fritsch 1996 ), the country’s level of development and the local density of business owners (Carree et al. 2002 ) significantly determine the impact of entrepreneurship. With more entrepreneurship datasets becoming available, researchers found evidence that only a small number of new firms such as particularly innovative new firms and firms with high-growth expectations create economic value and initiate Schumpeter’s process of ‘creative destruction’ (e.g. Szerb et al. 2018 ; Valliere and Peterson 2009 ; van Oort and Bosma 2013 ; Wong et al. 2005 ). However, over the past decade, researchers have identified a multitude of other relevant determinants (e.g. survival rates of new firms, institutional and cultural settings, motivations and qualifications of the entrepreneur), thereby drawing an increasingly complex web of interrelated determinants around the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship. This complexity combined with the fact that the research on determinants is scattered and mostly based on separate analyses of determinants leads to a number of hitherto unidentified research opportunities. In order to detect these opportunities and to exploit them in a targeted manner, a structured overview of the current knowledge on the determinants of the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship is required. In this context, a structured overview is not only essential for the scientific entrepreneurship community but also for politicians all over the world who need detailed information on the impact of entrepreneurship to promote the right types of entrepreneurship in the right situations.
To ensure that this information prepared for policy makers are truly comprehensive, it is essential that state-of-the-art research considers not only economic outcomes of entrepreneurship but also its social and environmental effects. This demand for a more holistic impact analyses is based on the call of economists who have been emphasizing since the 1970’s that economic development may is a significant part of welfare, but that social and environmental dimensions need to be considered as well (Daly et al. 1994 ; Meadows et al. 1972 ; Nordhaus and Tobin 1972 ). Tietenberg and Lewis ( 2012 , p. 553) summarised the economic, social and environmental effects in a holistic welfare definition and state that a “true measure of development would increase whenever we, as a nation or as a world, were better off and decrease whenever we were worse off”. This understatement is in line with many authors who recently highlighted the importance of entrepreneurship for social and environmental welfare (e.g. Alvarez and Barney 2014 ; Dhahri and Omri 2018 ; McMullen 2011 ). Entrepreneurship research has come to see entrepreneurs as a solution for social inequality and environmental degradation rather than a possible cause of them (Gast et al. 2017 ; Munoz and Cohen 2018 ; Terán-Yépez et al. 2020 ). This scientific consent of the past 50 years clearly illustrates how important it is that econometric research on entrepreneurship incorporates research on the economic as well as on the social and environmental impact of entrepreneurship. Footnote 1
Considering that the research on the macroeconomic impacts of entrepreneurship has been gaining increasing recognition over the last two decades and across a wide range of disciplines (Urbano et al. 2019a ), literature reviews must be conducted periodically to synthesize and reflect recent progress and to stimulate future research. Several high-quality reviews have already summarized the significant amount of research on the impact of entrepreneurship on the economy. Wennekers and Thurik ( 1999 ) were the first who discussed the link between entrepreneurship and economic growth in a narrative literature analysis. With their summary of the theoretical knowledge of that time and the first framework of the entrepreneurial impact the authors laid the groundwork for the following decade of empirical research on that matter. van Praag and Versloot ( 2007 ), extended that first review by systematically reviewing and evaluating the empirical findings of 57 articles published between 1995 and 2007. More precisely, the authors evaluated the various economic contributions of entrepreneurial firms, which have been defined by the authors as either employing fewer than 100 employees, being younger than 7 years or being new entrants into the market, relative to their counterparts. van Praag and Versloot ( 2007 ) thus made the first systematic attempt to distinguish the few new firms which are of economic relevance from the majority of meaningless new firms. Fritsch ( 2013 ), in a non-systematic monograph, exhaustively surveyed and assessed the then available knowledge on how new firms particularly effect regional development over time. Within this review, the author has established the term ‘determinants’ in the field of research on the impact of entrepreneurship and developed first suggestions on which factors may determine the impact of new firms. However, the author has not provided any empirical evidence for the effect of his proposed determinants. In contrast to these three literature reviews, the three most recent reviews also incorporated the latest findings from international studies and on developing countries. However, the three latest reviews all have a narrowly defined research focus. While Block et al. ( 2017 ; systematic literature review of 102 studies published between 2000 and 2015) analysed antecedents, behaviour and consequences of innovative entrepreneurship, Bjørnskov and Foss ( 2016 ; systematic literature review of 28 studies) and Urbano et al. ( 2019a ; systematic literature review of 104 studies published between 1992 and 2016) focused on the relationship between the institutional context, entrepreneurship and economic growth. Accordingly, all the existing reviews are either (1) already outdated, (2) mostly on highly developed countries or (3) focused on specific topics. Furthermore, none of these reviews provided (4) a structured overview on the empirical knowledge on the impact of entrepreneurship on the economy or (5) included research on the social and environmental impact of entrepreneurship.
This paper addresses these five shortcomings through a comprehensive and systematic review of empirical research into the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, Footnote 2 social and environmental welfare. The methodology of the review is based on the current knowledge of systematic reviews (e.g. Fayolle and Wright 2014 ; Fisch and Block 2018 ; Jones and Gatrell 2014 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ), on narrative synthesis (e.g. Dixon-Woods et al. 2005 ; Jones and Gatrell 2014 ; Popay et al. 2006 ) and on recent examples of best practice (e.g. Jones et al. 2011 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ; van Praag and Versloot 2007 ). Using this approach, this paper aims to contribute to the literature on the impact of entrepreneurship on welfare in three ways. First, it updates and extends the existing literature reviews. More specifically, it follows recent research recommendations (e.g. Block et al. 2017 ; Fritsch 2013 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ) by incorporating the recent empirical stream of research on the impact of entrepreneurship in developing countries and research that goes beyond measures of common economic welfare. In practical terms, this means that this review not only considers measures of economic welfare (e.g. GDP, employment rates, innovative capacity), but also for social welfare (e.g. life expectancy, literacy rates, income inequality), for environmental welfare (e.g. CO 2 emissions, water pollution, soil quality) and for indicators which incorporate all three welfare dimensions (e.g. Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare, Genuine Progress Indicator). Second, this paper, as demanded in previous reviews (Fritsch 2013 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ), aims to provide a descriptive analysis of the factors determining the entrepreneurial impact by critically assessing (a) which determinants of the entrepreneurial impact have (b) what impact on (c) which measures of economic welfare. This paper thus represents the first comprehensive attempt to summarize and structure the empirical knowledge on the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship. Finally, to encourage future research, this paper indicates shortcomings in the empirical research not only on the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare, but also on the described and structured determinants of this impact. It concludes with suggestions for future research avenues to close these research gaps.
To achieve these objectives, this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 describes the methodological approach of the review. Sections 3.1 and 3.2 report the available empirical research into the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare. Section 3.3 summarizes the determinants of this impact and Sect. 4 presents a roadmap for future research. Section 5 discusses the limitations of this paper and provides a conclusion.
2 Methodology
In order to clarify not only the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare but also the determinants of this impact, this paper provides a broad-ranging systematic, evidence-based literature review including a narrative synthesis. According to Mulrow ( 1994 ), systematic reviews are particularly useful in identifying and evaluating a large volume of evidence published over a long period of time and have been frequently applied in recent state-of-the-art literature reviews (e.g. Li et al. 2020 ; Mochkabadi and Volkmann 2020 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ). The systematic literature review conducted in this paper employs a rather broad empirical definition of entrepreneurship which covers both the entrepreneur, who creates or discovers new businesses (Kirzner 1973 ; Schumpeter 1942 ) and the entrepreneurial firm itself. Entrepreneurship is understood here as new business activity, which includes entrepreneurs in the process of new firm creation as well as recently founded firms. Furthermore, although not necessarily associated with the formation of new firms, self-employed individuals and owner-managers are defined here as entrepreneurs as well. This general definition is consistent with the majority of empirical studies (e.g. Bosma et al. 2011 ; Fritsch and Schindele 2011 ; Mueller et al. 2008 ). The review process comprises three major steps, namely (1) data collection, (2) the selection of relevant studies and (3) data synthesis.
2.1 Data collection
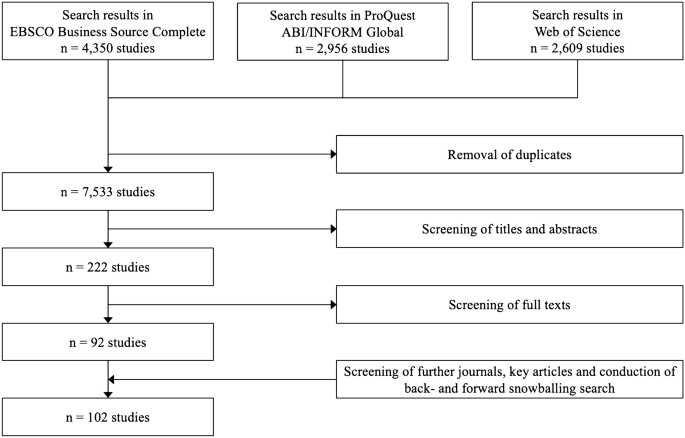
As a first step, to reduce bias and maintain objectivity in all stages of the review, a review panel was set up. The panel consists of the author, a professor and two doctoral students knowledgeable in this field of research. In order to obtain the most relevant terms for the systematic search, the suggestions of Tranfield et al. ( 2003 ) were followed and a number of scoping studies based on combinations of keywords related to the topic were performed. The insights from this initial search phase were used to further develop relevant search terms resulting in the Boolean search string presented in the online appendix. The number of selected search terms was intentionally rather broad to avoid overlooking potentially valuable studies. It included the most common terms and measures of entrepreneurship and of economic, social and environmental welfare. This search string was subsequently used to scan titles, abstracts, and enclosed keywords of studies in the electronic databases EBSCO Business Source Complete, ProQuest ABI/INFORM Global and Web of Science. These databases were selected, because they allow the application of complex search strings and cover an extensive range of scientific journals from a variety of different disciplines. In order to provide a quality threshold, only peer-reviewed journal articles were scanned, since they are considered as validated knowledge (Podsakoff et al. 2005 ; Ordanini et al. 2008 ). Unpublished papers, books, book chapters, conference papers and dissertations were omitted in the initial search. Furthermore, the search was restricted to studies written in English. The main search was conducted in May 2019 and updated once in December 2019. It yielded, after the removal of duplicates, an initial data set of n = 7533 studies.
In addition to the main search, three more steps were conducted to create an exhaustive sample. First, five journals of particular relevance for the discussion were manually searched. Footnote 3 Second, meta-studies and literature reviews on related topics were screened for additional studies. Footnote 4 And finally, based on the guidelines of Wohlin ( 2014 ), an iterative back- and forward snowballing approach was conducted. The whole process of data collection and selection and its results are summarized in Fig. 1 .
Systematic process of data collection and selection
2.2 Data selection and quality assessment
The studies collected during the main search were carefully reviewed to determine whether they were suitable for the objective of this paper. Titles, abstracts and, in doubtful cases, whole studies were checked against the following set of selection criteria.
Studies must analyse the macroeconomic impact of entrepreneurship by applying at least one economic, social or environmental welfare measure on an aggregated regional, national or global level.
Studies must employ definitions of entrepreneurship as discussed in the introduction of Sect. 2 . Studies that solely analysed the impact of small firms, intrapreneurship, corporate-entrepreneurship, institutional entrepreneurship, or entrepreneurial capital were excluded.
Studies must apply adequate quantitative methods to measure the impact of entrepreneurship. Studies that only discuss this matter theoretically, that follow a qualitative approach or that do not go beyond simple correlation techniques were excluded.
Studies must analyse spatial units, as they seem to be considerably better suited to analysing the impact of entrepreneurship (Fritsch 2013 ). Studies that are based on the analysis of industry units were excluded.
Studies must analyse long-term panel data or data on an adequately aggregated level to account for demographic, political and economic events. Studies that analysed single spatial units over a short period of time were excluded.
Due to the broadness of the search string, the main search yielded many studies which solely dealt with the microeconomic performance of new firms or which analyse how the local level of development determines the number of new firms. Studies which were not related to the research questions or did not meet all five selection criteria, were manually removed. This process of selection in the main search led to a total of n = 92 studies. The three additional search steps increased this number by n = 10, resulting in a final data set of n = 102 studies, including two high-quality book chapters which present empirical results of particular relevance to the paper’s objective (namely Stam et al. 2011 ; Verheul and van Stel 2010 ). When comparing the sample size with that of related literature reviews, it appears to be appropriate. Hence, even if the selected sample is not exhaustive, it is very likely to be representative of the relevant literature.
2.3 Data analysis
Given that research in this area employs a variety of measures of entrepreneurship and of economic welfare and is methodologically diverse, it was unfeasible to perform a meta-analysis. Instead, an integrative and evidence-driven narrative synthesis based on the guidelines established by Popay et al. ( 2006 ) was chosen to aggregate, combine and summarise the diverse set of studies. Narrative synthesis is considered particularly useful when, as in this case, research area is characterised by heterogeneous methods, samples, theories, etc. (Fayolle and Wright 2014 ).
Once the final set of studies had been identified, the characteristics and study findings were extracted by carefully reading the methods and results sections. To reduce research bias, a review-specific data-extraction form was employed. The extraction-form is based on the suggestions of Tranfield et al. ( 2003 ) and Higgins and Green ( 2008 ) and contains general information, details about the analysed samples, the applied measures of entrepreneurship and economic welfare, the applied econometric techniques as well as short summaries of the relevant findings and the identified microeconomic impact factors.
3 Results of the literature review
The main results of the literature review regarding the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and the determinants of this impact are presented in Table 5 (see online appendix). The large number of gathered studies on impact of entrepreneurship (n = 102) as well as on its determinants (n = 51) attest to the fact that this field of research has already been studied in great detail. Most of the identified studies were published in high-quality management, economics, social science and environmental science journals. Table 1 illustrates that the main part of the cross-disciplinary scientific discussion, however, took place in the Journals Small Business Economics (24%) and Regional Studies (7%). The number of empirical studies published per year has increased over the last decade, indicating the topicality of the research field and the need for an updated review of the new knowledge.
Figure 2 summarizes the statistics of the large amount of data gathered in Table 5 (see appendix) and illustrates the complexity of the research field. The left-hand-side lists the measures of entrepreneurship used in the analysed studies and shows how often they were applied. The most frequently applied measure of entrepreneurship is new firm formations either (a) per work force (labour market approach), (b) per number of existing firms (ecological approach) or (c) per capita. Another frequently applied measure of entrepreneurship is total early-stage entrepreneurial activity (TEA) based on data from the Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (Reynolds et al. 2003 ) or its subgroups: necessity-driven entrepreneurial activity (NEA), opportunity-driven entrepreneurial activity (OEA), innovative entrepreneurial activity (IEA) and high-growth expectation entrepreneurial activity (HEA). Other authors estimated regional entrepreneurship using self-employment or business ownership rates. The Kauffman Foundation Index for entrepreneurial activity is used less frequently, as it is a specific measure of entrepreneurship for US regions.
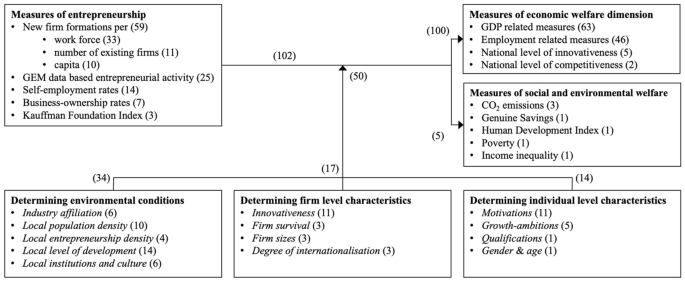
Overview of applied measures of entrepreneurship and welfare, and analysed determinants. Note : the numbers in brackets represent the numbers of associated empirical studies
Regarding the right-hand-side of Fig. 2 , it is noticeable that the majority of authors analysed the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare, primarily on GDP, growth and employment-related measures. Far fewer studies analysed the impact on the economic measures of national competitiveness or innovativeness, e.g. the number of patent applications. In contrast to the clear research focus on economic welfare, only five studies were found which analysed the impact of entrepreneurship on environmental or social welfare. Although many common measures of social and environmental welfare (e.g. crime rates or ecological footprint) were explicitly included in the search string (see online Appendix), no studies could be found that analyse the impact of entrepreneurship on them.
Independent of the measures of entrepreneurship and welfare used, the reviewed studies test their relationship by applying a very heterogenous set of methods. With the availability of more and more cross-sectional data covering longer and high-frequency time-series, authors started to apply new econometric approaches such as pooled and panel data regressions, fixed effect models, and subsequently, dynamic panel data models. Most authors based their analyses on rather straightforward regression techniques.
Sections 3.1 and 3.2 discuss empirical knowledge relating to the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare as well as on social and environmental welfare. Section 3.3 deals with the empirical evidence on the factors which determine this impact of entrepreneurship (see the lower part of Fig. 2 ).
3.1 Impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare
The analysed literature predominantly confirms the results of previous literature reviews and gives empirical evidence that new firm formations have a generally positive effect on regional development and economic performance. The relationship holds for all tested measures of entrepreneurship and is robust across a broad range of spatial and cultural contexts.
The impact does, however, differ over time. Fritsch and Mueller ( 2004 ) studied the time-lag structure of the impact of entrepreneurship by applying an Almon lag model of different polynomial orders in their study of 326 West German regions. Their results revealed that the impact of entrepreneurship follows a typical time-sequence: an S- or wave-shaped pattern which can be structured into three phases. Phase I is defined by a positive immediate increase of employment (direct effects of new capacities). After approximately 1 year, in phase II, this positive short-term impact becomes smaller, insignificant or even negative (displacement effects and market selection). Around year five, this medium-term impact becomes positive again and reaches a peak in year eight (supply-side and spill-over effects). This positive long-term effect of entrepreneurship on employment, which defines phase III, diminishes after a period of 10 years.
Table 2 presents the findings of all reviewed studies which analysed the impact of new firm formations on employment and GDP in one, two or all three phases. It shows that the findings regarding the impact of entrepreneurship on employment are largely consistent with the wave-pattern theory. The existence of the wave-pattern could be confirmed on different regional levels for Great Britain (Mueller et al. 2008 ), for the United States (Acs and Mueller 2008 ; Henderson and Weiler 2009 ), for Portugal (Baptista et al. 2008 ; Baptista and Preto 2010 , 2011 ), for West Germany (Fritsch and Mueller 2008 ; Fritsch and Noseleit 2013a ), for the Netherlands (van Stel and Suddle 2008 ; Koster 2011 ; Delfmann and Koster 2016 ), for Sweden (Andersson and Noseleit 2011 ), for China (Rho and Gao 2012 ) for Canada (Matejovsky et al. 2014 ) as well as in several cross-country studies on OECD countries (Audretsch et al. 2015 ; Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Koellinger and Thurik 2012 ; Thurik et al. 2008 ). Furthermore, the reviewed studies reveal that this relationship not only holds for new firm formations as a measure of entrepreneurship but also for self-employment (e.g. Matejovsky et al. 2014 ; Rho and Gao 2012 ; Thurik et al. 2008 ) and business ownership (e.g. Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Henderson and Weiler 2009 ; Koellinger and Thurik 2012 ). The latter two measures of entrepreneurship, however, seem to have a less pronounced impact (Acs and Armington 2004 ; Rho and Gao 2012 ; Dvouletý 2017 ). Empirical evidence suggests a similar wave-pattern for the impact of entrepreneurship on GDP. Studies on GDP analysing all three phases confirm the positive short- and long-term peaks. However, in contrast to the results on employment, they find the medium-term impact to be less pronounced and positive (Audretsch et al. 2015 ; Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Koellinger and Thurik 2012 ; Matejovsky et al. 2014 ). The few empirical results displayed in Table 2 , which contradict the wave-pattern theory (e.g. findings of a negative short-term impact of entrepreneurship on GDP), can largely be explained by certain determining factors such as a differing impact in developing countries (see Sect. 3.3.4 ) or of necessity-driven entrepreneurship (see Sect. 3.3.9 ).
The results for other measures of economic welfare are scarce and contradictory. Ferreira et al. ( 2017 ) analysed the short-term impact of entrepreneurship on different measures of competitiveness and found that TEA and IEA positively related to competitiveness. However, they found no significant relationship between OEA and competitiveness. On the contrary, a study by Mrozewski and Kratzer ( 2017 ) found a positive relationship between OEA and competitiveness, but not between TEA and competitiveness.
The empirical results regarding the impact of entrepreneurship on innovativeness are also inconclusive. Acs and Varga ( 2005 ) and Draghici and Albulescu ( 2014 ) found that OEA has a positive impact on patent applications and innovation indices, but that TEA and NEA do not have any significant impact on them. Anokhin and Wincent ( 2012 ) found a positive impact of TEA on innovativeness but a more recent study from Albulescu and Draghici ( 2016 ) found that neither TEA nor OEA have a significant relationship to innovativeness. Similarly, Cumming et al. ( 2014 ) found new firm formations based on the labour market approach have a positive short-term impact on patent applications, but new firm formations based on the ecological approach and business ownership rates do not.
3.2 The impact of entrepreneurship on social and environmental welfare
Contrary to the well-researched impact of entrepreneurship on employment and GDP, little is known about the impact on social and environmental welfare. Three independent studies recently found empirical evidence that entrepreneurship positively affects measures of social welfare. Rupasingha and Goetz ( 2013 ) found that in the short-term self-employment reduces poverty in rural and urban U.S. counties, Atems and Shand ( 2018 ) found that in the medium-term self-employment decreases income inequality in U.S. states and, finally, Dhahri and Omri ( 2018 ) found new firm formations to increase the national modified Human Development Index (MHDI) in developing countries.
The empirical research on the impact of new firm formations on environmental welfare, however, illustrates that entrepreneurship may also come with major drawbacks. Omri ( 2017 ) as well as Dhahri and Omri ( 2018 ) and Ben Youssef et al. ( 2018 ) found that new firms significantly increase the amount of national CO 2 -emissions. According to Ben Youssef et al. ( 2018 ), this unfortunate impact on CO 2 -emissions is in fact so great that, despite the positive impact on GDP, new firms decrease Genuine Savings (also known as adjusted net saving) in African countries. They also found that the impact is more pronounced for informal new firm formations. This finding matches the results of Omri ( 2017 ), who detected the impact on CO 2 -emissions to be lower in developed countries which generally have lower rates of informal entrepreneurship (Williams and Lansky 2013 ). Furthermore, Omri ( 2017 ) discovered that the relationship between new firm formations and CO 2 -emissions is not linear but can be described as exhibiting an inverted U-shape. Thus, at an already high level of entrepreneurship, new firm formations may result in a decrease in CO 2 -emissions.
3.3 Determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship
So far, the empirical results suggest, in many cases, a clear causal macroeconomic impact of new firm formations on economic measures of welfare. However, this topic is reasonably complex, and the complexity increases further when determining factors of this impact are considered. The lower part of Fig. 2 presents an overview of the empirical knowledge on these determinants. A key finding of this review, namely that all of the found analyses of determinants focus exclusively on the economic effects of entrepreneurship, is, however, not illustrated in Fig. 2 . The review revealed that, although they are strongly interdependent, the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship can generally be categorized into external environmental conditions, firm level characteristics and individual characteristics of the entrepreneurs themselves. Figure 2 illustrates that most empirical research has been conducted on the determining environmental conditions and on the firm level characteristic innovativeness and on the individual level characteristic motivations . In fact, some of the determinants presented have already been thoroughly investigated in highly recommendable earlier literature reviews, namely: industry affiliation (Fritsch 2013 ), regional population - and entrepreneurship density (Fritsch 2013 ), institutions and culture (Bjørnskov and Foss 2016 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ), innovativeness (Block et al. 2017 ). The review for this paper confirms these findings and briefly summarizes the key learnings in the Sects. 3.3.1 to 3.3.3 and 3.3.5 . However, except for a recently emerged empirical research stream on innovativeness , no new insights could be gained on the already reviewed determinants. Therefore, the focus of this section is primarily on the empirical evidence which has not yet been systematically investigated.
3.3.1 Industry affiliation
Fritsch ( 1996 ) was one of the first to analyse how entrepreneurial impact differs between industries. He focused on the impact of new firm formations on employment in West Germany and found it to be significantly higher in the manufacturing sector than in the service sector. Several authors confirmed this finding for the Netherlands (van Stel and Suddle 2008 ), for West-Germany (Fritsch and Mueller 2004 ) and for Sweden (Andersson and Noseleit 2011 ). Other studies, however, found the impact of new firms on economic welfare measures to be higher in the service sector (Bosma et al. 2011 ; Koster and van Stel 2014 ). Fritsch ( 2013 ) reasoned that these contradicting results may be due to considerable differences between the industries in different regions or countries and thus an analysis at the industry level might be not appropriate at all. For more information on the industrial perspective of the entrepreneurial impact on the economy, Fritsch ( 2013 ) provides a comprehensive overview including policy implications and avenues for further research.
3.3.2 Regional population- and entrepreneurship density
In a second wave of literature, researchers analysed how the impact of entrepreneurship differs between regions. They found clear evidence that the magnitude of the entrepreneurial impact is positively related to the population density (Baptista and Preto 2011 ; Fritsch and Mueller 2004 , 2008 ; Fritsch and Schroeter 2011 ; Henderson and Weiler 2009 ; Lee 2017 ; Li et al. 2011 ; van Stel and Suddle 2008 ). In urban regions and agglomerations, new firms have a more pronounced and more positive impact on employment (Baptista and Preto 2011 ; Henderson and Weiler 2009 ; van Stel and Suddle 2008 ) and GDP (Audretsch et al. 2015 ; Belitski and Desai 2016 ) throughout all three previously described phases (see Sect. 3.1 ). On the contrary, in rural and less agglomerated regions, the entrepreneurial impact is weak and often negative (Fritsch and Mueller 2004 , 2008 ).
While the economic relevance of new firm formations seems to increase with the population density, empirical evidence suggests that this is not the case for the relation between firm formations and regional entrepreneurship density. On the contrary, several authors found that the economic effect of another new firm becomes lower the more entrepreneurs are already on the market and even zero for regions with high entrepreneurship rates close to equilibrium rate (e.g. Carree et al. 2002 , 2007 ; Mueller et al. 2008 ). These empirical insights identify entrepreneurship as a regional phenomenon and illustrate that macroeconomic effects of new firms are shaped by local conditions. An in-depth discussion of regional differences in the macroeconomic impact of new firms can be found in the monograph by Fritsch ( 2013 ).
3.3.3 Institutions and culture
To shed light on the complex interactions between institutions, entrepreneurship and economic growth, Urbano et al. ( 2019a ) and Bjørnskov and Foss ( 2016 ) recently conducted thorough literature reviews. The empirical evidence identified in the present paper (Aparicio et al. 2016 ; Audretsch and Keilbach 2004a , b , c ; Bjørnskov and Foss 2016 ) is in line with the findings of these two reviews which suggest that institutions affect the economy indirectly through endogenous factors like entrepreneurship. This holds true for formal institutions like (academic) support systems for new firms, procedures and costs to create a business, property rights or political structures as well as for informal institutions like social norms, cultures or belief systems (Urbano et al. 2019a ). However, in contrast to Bjørnskov and Foss ( 2016 ), Urbano et al. ( 2019a ) suggest that formal and informal institutions are not of equal importance, but that social norms and cultures have higher and more positive effects on the relation between entrepreneurship and economic growth.
3.3.4 Local level of development
While Sect. 3.1 illustrates that the impact of entrepreneurship in developed countries follows a typical wave-pattern, until now, no studies have analysed this time-pattern in developing countries. In general, the empirical evidence on the impact in developing countries is contradictory: some studies found a positive impact of entrepreneurship (Ben Youssef et al. 2018 ; Dhahri and Omri 2018 ; Feki and Mnif 2016 ; Stam et al. 2011 ), others found no or even a negative impact (Anokhin and Wincent, 2012 ; Ferreira et al. 2017 ; Verheul and van Stel 2010 ). However, studies which compared countries in different development stages found that the magnitude of the impact of entrepreneurship depends on the national welfare level and is generally higher in more developed countries (Anokhin and Wincent 2012 ; Carree et al. 2002 , 2007 ; Crnogaj et al. 2015 ; Hessels and van Stel 2011 ; Urbano and Aparicio 2016 ; Valliere and Peterson 2009 ; van Stel et al. 2005 ; Verheul and van Stel 2010 ). Furthermore, little is known on the mechanisms behind the impact of entrepreneurship in developing countries. Most of the few studies which specifically deal with developing countries (n = 19) analysed the impact on a national level (n = 16) based on GEM data (n = 12), focused on the impact on GDP related measures (n = 17), or solely analysed the short- or medium-term impact (n = 16).
3.3.5 Innovativeness
According to the knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship, new knowledge results in business opportunities and entrepreneurs exploit these opportunities by turning the new knowledge into innovative products (Acs et al. 2009 , 2013 ; Audretsch and Keilbach 2005 ). Recent studies confirm this theory and provide empirical evidence that entrepreneurship moderates the transformation of new knowledge into innovations (Block et al. 2013 ) and that innovative regions with higher levels of entrepreneurship perform economically better (González-Pernía et al. 2012 ). Accordingly, it is reasonable to assume that particularly innovative new firms are more important to economic welfare than their non-innovative counterparts. These considerations coincide with those presented in the literature review on innovative entrepreneurship by Block et al. ( 2017 ). However, the present systematic literature review extends the review of Block et al. ( 2017 ) by including previously unconsidered as well as recently emerged empirical evidence on the macroeconomic impact of innovative entrepreneurship. The identified empirical studies do indeed confirm the presumed positive impact of innovativeness. Crnogaj et al. ( 2015 ) as well as Du and O’Connor ( 2017 ) and Szerb et al. ( 2018 ) used GEM data to compare the impact of founders who stated their products or services to be new or at least unfamiliar to their customers. All of the previously mentioned authors found that innovative founders have a higher impact on GDP, economic efficiency, gross value added (GVA) and employment than less innovative founders. Furthermore, earlier studies attest to new firms which are in innovative, knowledge- or technology-intensive industries a higher than average impact on both GDP (Audretsch and Keilbach 2004a , b , 2005 , Mueller 2007 ) and employment (Baptista and Preto 2010 , 2011 ).
3.3.6 Firm survival
Empirical evidence suggests that a particularly important determinant of the impact of entrepreneurship is whether new firms are able to survive the first years. Falck ( 2007 ) was the first to find empirical evidence of a positive relationship between new firms which survive for at least 5 years and efficiency of the industry in which they are in. On the contrary, he could not find any significant relationship to industry level efficiency growth for firms which did not survive the first 5 years. Brixy ( 2014 ), Fritsch and Noseleit ( 2013b ) and Fritsch and Schindele ( 2011 ) have confirmed that Falck’s ( 2007 ) findings not only hold for the relationship between entrepreneurship and GDP but also for the relationship between entrepreneurship and employment.
3.3.7 Firm size
Baptista and Preto ( 2010 ) found that new firms of a larger than average initial size have a strong impact on employment and that this impact follows a pronounced wave-shaped time-lag structure (see Sect. 3.1 ). New firm formations which are smaller than average, on the other hand, only have a small impact. Acs and Mueller ( 2008 ) confirmed this finding and show that small new firms have a positive but declining direct impact on employment. The impact of medium and large new firms, however, is much higher and increases till it peaks in year five. Very large new firms (> 499 employees), however, decrease employment in the short- and medium-term, probably due to restructuring processes of incumbents. This empirical evidence suggests that up to a threshold, large new firms have a larger impact on employment.
3.3.8 Degree of internationalization
A less studied but yet empirically significant determinant is a firm’s degree of internationalization. Baptista and Preto ( 2010 ) analyzed 30 Portuguese regions and found that new firms which were, at least, partially owned by foreign investors had a much higher and more pronounced medium- and long-term impact on employment. A second measure of the positive impact of internationally active new firms is the export-orientation of new firms. Hessels and van Stel ( 2011 ) compared the impact of total-entrepreneurial activity and export-driven entrepreneurial activity on GDP per capita in 34 developed and developing countries. They found evidence that new firms for which the share of customers living abroad is above 26% have a more positive impact on GDP—but only in developed countries. González-Pernía and Peña-Legazkue ( 2015 ) confirmed their finding on a regional level by comparing OEA and export-oriented OEA in 17 Spanish regions. Besides a generally higher impact of export-oriented new firms, González-Pernía and Peña-Legazkue ( 2015 ) found that the impact increases with higher shares of foreign customers up to a threshold level. An earlier study by Fryges and Wagner ( 2008 ), who found a positive relationship between firm-level productivity and export-sales ratio, supports the evidence for a more positive impact of internationally active new firms.
3.3.9 Motivation
The literature review conducted for this paper provided eleven studies which empirically tested the macroeconomic importance of the entrepreneur’s motivations. All of these studies applied GEM-based data and definitions for opportunity-driven entrepreneurial activity (OEA) and necessity-driven entrepreneurial activity (NEA). Although four of these studies could not find a significant economic impact of OEA or NEA (Albulescu and Draghici 2016 ; Ferreira et al. 2017 ; Valliere and Peterson 2009 ; Wong et al. 2005 ), the other seven studies found evidence that OEA significantly increases national innovativeness (Acs and Varga 2005 ; Draghici and Albulescu 2014 ), competitiveness (Mrozewski and Kratzer 2017 ) and productivity (Du and O’Connor 2017 ; González-Pernía and Peña-Legazkue 2015 ; Ivanovic-Ðukic et al. 2018 ; Urbano and Aparicio 2016 ). Moreover, six of these seven studies confirmed that the impact of OEA is higher compared to NEA and TEA. Mrozewski and Kratzer ( 2017 ) even found NEA to decrease the national competitiveness.
3.3.10 Growth-ambitions
There are some entrepreneurs who not only seek to exploit a business-opportunity but also have high growth - ambitions for their new firms. All five empirical studies selected for this paper take GEM data on high-growth expectation entrepreneurship (HEA) as a measure of the entrepreneur’s growth - ambitions and found that it has a significantly positive impact on GDP-related measures of welfare. Furthermore, the impact of HEA seems to be more positive compared to TEA, to NEA and even to OEA (Ivanović-Đukić et al. 2018 ; Stam et al. 2011 ; Valliere and Peterson 2009 ; Wong et al. 2005 ). Generally, this macroeconomic impact of HEA seems to increase with the level of growth-aspiration (van Oort and Bosma 2013 ). The positive impact of HEA on economic welfare could be confirmed on the regional- and national-level as well as for developed countries. For less-developed countries, however, the empirical evidence is contradicting. On the one hand, Valliere and Peterson ( 2009 ) only found a significant impact of HEA on GDP for 25 developed countries, but not for the 18 emerging countries. On the other hand, Stam et al. ( 2011 ) found the impact of HEA on GDP in eight analysed lower-income to upper-middle-income economies (World Bank 2002 classification) even higher compared to the impact in the 22 analysed high-income economies.
3.3.11 Qualification
While many microeconomic studies have highlighted that an entrepreneur’s qualifications in terms of education (e.g. Kangasharju and Pekkala 2002 ), skills and experience (e.g. Brüderl et al. 1992 ; Baum et al. 2001 ; Unger et al. 2011 ) play a significant part in the success of new firms, only one of the studies empirically investigated the macroeconomic impact of education. This is an analysis of 3702 German firms conducted by Engel and Metzger ( 2006 ). It suggests that new firms founded by people with an academic degree may have a more positive direct employment effect, than firms founded by people without an academic degree. This finding is, however, based on an old dataset (1990–1993) and a simple descriptive comparison and the authors did not apply control variables such as the regional density of more educated people.
3.3.12 Gender and age
Only one study could be found which empirically analysed the economic impact of the entrepreneur’s gender and age . This study was conducted by Verheul and van Stel ( 2010 ) and was based on a dataset of 36 developed and developing countries. Their results show that there is a positive relationship between young opportunity-driven entrepreneurs between the ages of 18 and 24 and national GDP growth in developed countries, while in developing countries there is only a significant positive relationship between entrepreneurs aged between 45 and 64 and GDP growth (Verheul and van Stel 2010 ). Contrary to the microeconomic literature (e.g. Cliff 1998 ; Kalleberg and Leicht 1991 ; Rosa et al. 1996 ), Verheul and van Stel ( 2010 ) could not find any significant gender differences on the macroscale.
4 Roadmap for further research
The major scientific value and contribution of this paper lies in the groundwork for future research. Despite the extant of the reviewed existing research, many questions still remain unanswered. The following two sections therefore highlight the shortcomings of current research and make suggestions on how to address them. Section 4.1 discusses how remaining gaps in empirical research into the impact of entrepreneurship can be addressed and Sect. 4.2 presents fruitful research avenues on the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship.
4.1 Implications for future research on the impact of entrepreneurship
4.1.1 more variety in the measures of entrepreneurship.
A high variety of measures of entrepreneurship is required to test the robustness of results but international comparative studies, in particular, are mainly based on just two entrepreneurship datasets: Comparative Entrepreneurship Data for International Analysis (COMPENDIA) based on OECD statistics and data from the GEM research project. The use of a high variety of entrepreneurship definitions and measures of entrepreneurship across studies makes it difficult to compare the results of these studies. While some studies simply estimate entrepreneurship based on self-employment rates or business-ownership rates, others measure entrepreneurship by counting new firm formations and firm exits or use holistic measures based on, e.g., Schumpeter’s understanding of entrepreneurship.
In order to test the robustness of the results and, at the same time, to allow for comparability between different studies, researchers should employ not one but multiple common measures of entrepreneurship in future studies. To make this possible, policy makers need to encourage the creation of internationally harmonized entrepreneurship databases. Furthermore, due to the limited availability of entrepreneurship data, only a few empirical studies have made a distinction between different types of entrepreneurship. That is why, as recommended by many researchers before (e.g. Baptista and Preto 2011 ; Fritsch and Schroeter 2011 ; Urbano et al. 2019a ), this study calls for more diversity in the application of measures of entrepreneurship.
4.1.2 Implementation of measures of social and environmental welfare
Section 3.1 revealed that 95.1% of the examined empirical studies only analysed the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare. Politicians who have no information on the impact of entrepreneurship on social and environmental welfare and thus solely rely on this economic information, however, may implement unsustainable development strategies (Tietenberg and Lewis 2012 ). Indeed, the few empirical studies (n = 5) which go beyond a traditional economic analysis indicate that entrepreneurship also has a significant contribution to measures of social and environmental welfare such as HDI, CO 2 emissions or poverty, which must not be neglected by politicians and researchers alike. To fill the immense gap in research on the impact of entrepreneurship on social and environmental welfare, two simultaneous approaches are proposed. First, as mentioned before, future research should generally include a variety of dependent welfare variables—social and environmental as well as economic ones. Second, future research should adopt research designs that have already proved effective in the macroeconomic impact analysis to answer novel research questions that address the impact of entrepreneurship on social and environmental welfare. The required methods for such analyses have been tested many times and, at least at national level, data availability poses no problem. Most countries have not only been collecting specific social and environmental welfare data for many years, but also established more holistic measures of welfare such as the Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare. Accordingly, it is up to the research community to break with traditions and expand the field of research by analysing social and environmental welfare rather than just economic welfare.
4.1.3 More research on developing countries
Section 3.3.4 illustrated that the local level of development is a relevant determinant of the impact of entrepreneurship. Nevertheless, most of the research reviewed for this paper focused solely on developed countries. This can partly be explained by the fact that most of the authors of these studies are based in Europe and the US, as well as by the lack of adequate long-term data for developing countries. However, this has begun to change. In the past 5 years, the number of empirical studies on developing countries has more than doubled to n = 30. Nevertheless, regional-level studies as well as long-term studies for developing countries remain scarce. Because of the growing importance of developing and particularly BRICS countries, it is important to increase the knowledge on how the impact of entrepreneurship manifests in these countries.
4.1.4 More studies on the lag-structure of the impact of entrepreneurship
Section 3.1 illustrates that although the important indirect impact of entrepreneurship requires 5 or more years to unfold, most empirical research focuses on the direct short-term impact. Neglecting the long-term effects of entrepreneurship therefore results in an incomplete picture. Furthermore, the analysis of longitudinal data is required to conduct relevant causality tests. So far, the bottleneck for national-level long-term studies has been the lack of longitudinal data. But, due to more than 20 years of worldwide data collection for the GEM, there is now at least one sufficiently large entrepreneurship database. In line with other authors who have recognised this issue (e.g. Baptista et al. 2008 ; Carree and Thurik 2008 ; Fritsch 2013 ), this paper recommends that all future research should analyse not only the short-term but also the medium- and long-term impact of entrepreneurship.
4.2 Implications for future research on determinants
Table 3 summarizes key statistics for the determinants in the research reviewed for this paper. Comparing the last two rows, it seems that the studies analysing the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship are a representative share of all reviewed studies. For this reason, the previously presented suggestions for future research also apply to literature on the determinants. On closer examination, however, Table 3 reveals further and more precise research gaps. These include, inter alia, the need to study particularly the environmental and firm level determinants in developing countries, and the analysis of individual level determinants in combination with the lag-structure of the impact of entrepreneurship. The requirement for more long-term studies is further highlighted here. This finding further specifies the previous call for more long-term studies. The following subsections present further research and research implications.
4.2.1 More variety in measures of entrepreneurship
Table 3 shows that research on environmental and firm level determinants are mainly based on new firm formations as a measure of entrepreneurship, and research on individual level determinants almost solely measures entrepreneurship using GEM data.
The only exceptions are studies on the determinants local level of development —which are comparing the entrepreneurial impact across countries and thus are also mostly based on GEM data—and on innovativeness . None of the studies on the determinants apply self-employment (for the sake of clarity not presented in Table 3 ) to estimate entrepreneurship. This illustrates that the research on all individual determinants, except for innovativeness , considerably lacks variety when it comes to the applied measures of entrepreneurship.
4.2.2 More variety in measures of welfare
In addition to the fact that there are no studies examining the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship on social or environmental welfare, there is also a lack of variety in the studies of measures of economic welfare. Studies on all individual level determinants and particularly on the determinant local level of development almost exclusively analyse the impact of entrepreneurship on GDP-related measures of welfare. Studies on the determinants industry affiliation , population density , firm survival and firm size mainly analyse employment effects of entrepreneurship. Other common measures of economic welfare, such as innovativeness or competitiveness, are rarely studied and need further investigation.
4.2.3 Further research on determinants
Table 3 illustrates that the existing research is imbalanced and that it pays varying degrees of attention to individual determinants. Determinants such as innovativeness , motivations and most environmental level determinants have so far received a great deal of attention, while others have only been analysed in very few studies. However, some of these poorly researched factors promise to be relevant determinants. More specific, the few existing empirical results analysing firm survival , degree of internationalisation and growth - ambitions suggest that these determinants have a comparatively high effect on the relationship between entrepreneurship and economic welfare. Furthermore, these determinants as well as the largely unexplored determinant qualifications are of considerable practical and political relevance. More empirical research on these determinants and their moderating role is required to improve incentives and support programs for entrepreneurs.
4.2.4 New research focus on determinants not yet empirically investigated
Table 4 provides a short overview of determinants which are likely to shape the entrepreneurial macroeconomic impact, but which have not yet been empirically investigated. They are a selection of indicators which are believed to determine the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare or which are empirically related to the success and survival of new firms and thus are also likely to be of macroeconomic importance. The overview is based on a non-systematic scan of the microeconomic literature and makes no claim to completeness. Due to their particularly high microeconomic relevance highlighted by the authors listed in Table 4 , this paper specifically proposes additional research on how firm performance, organisational structure and strategies, networking activities and motivations (beyond necessity and opportunity entrepreneurship) determine the impact of entrepreneurship.

4.2.5 Methodological recommendations
Many of the determinants discussed here are highly interdependent, which makes it very difficult to extract and examine their separate effects. Individual level characteristics and environmental conditions are especially likely to affect the impact of entrepreneurship mainly indirectly through firm performance. The complexity is increased further as determinants may be indicators for other macroeconomically relevant effects. For instance, the numbers of highly innovative new firms and of highly qualified entrepreneurs may be positively correlated with the excellence of the regional educational infrastructure. This in turn could mean that the excellence of educational infrastructure is the true reason for economic growth and innovative new firms and highly qualified entrepreneurs have little or no economic impact but are merely indicators for the educational infrastructure. However, little is currently known about such interdependencies and research is required which particularly studies the path dependencies behind the impact of entrepreneurship. This is why future empirical research should examine determinants which are supposed to be interdependent as well as external effects which may be related to the determinants of interest.
5 Limitations and conclusion
This paper has shed light on the impact of entrepreneurship on economic welfare and the determinants of this impact, but it is not without limitations. First, this paper seeks to give a comprehensive overview of the empirical research, but the search was limited by a variety of in- and exclusion criteria as well as by the terms used in the search string. Although the exclusive focus on peer-reviewed articles is common practice in systematic literature reviews, this may have led to the systematic exclusion of potentially relevant research outcomes, e.g. from dissertation, book chapters, conference contributions or working papers. Furthermore, it is possible that individual studies were not identified by the automated search for the search string in keywords, titles and abstracts. These limitations were necessary to reduce the search results to a manageable level and to ensure a certain quality of the results. The additional screening of key journals, meta-studies and reviews as well as the applied back- and forward snowballing approach, however, weaken the effects of these limitations. Second, this paper only deals with empirical studies. The inclusion of qualitative studies might have revealed further studies dealing with the impact of entrepreneurship on environmental and social welfare. Additionally, the exclusion of qualitative studies limits the analytical depth within the discussion of the determinants. Third, the paper focused on research on a few selected measures of entrepreneurship. In doing so, intrapreneurship, entrepreneurship culture or diverse composed entrepreneurial activity measures of entrepreneurship were excluded. Fourth, it needs to be stated that large parts of the data selection and synthesis were only conducted by the author. Although the chosen procedure and the frequent consultation with the research panel reduced the likelihood of biases, the chance remains that the review is burdened with subjectivity and selection biases. Finally, the scope of this paper was to provide a first descriptive summary of the determinants analysed in the empirical literature and to derive research recommendation. Due to this clear focus this paper does not comprise extensive bibliometric- or meta-analyses that describe in detail the general literature on the impact of entrepreneurship.
The systematic review presented in this paper was conducted for three main reasons. First, to summarize the current state of empirical research on the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare. Second, to identify the determinants of this impact and third, to develop a roadmap for future research. Due to the application of a broad entrepreneurship definition and due to the incorporation of economic, social and environmental welfare, this paper presents the most comprehensive overview, summary and synthesis of empirical research on this topic to date. The results confirm the findings and theories of previous literature reviews on the impact of entrepreneurship, provide an update and extension to the current knowledge and finally, represent a first attempt to structure the determinants of the impact of entrepreneurship. The new determinants-driven perspective on the research field reveals several shortcomings that would otherwise have gone unnoticed. The developed roadmap for future research—combined with a higher variety of applied measures of entrepreneurship and with an increased awareness of causality and interdependency issues—will allow future researchers to unravel the complex relationship between entrepreneurship and welfare and therewith to provide politicians the comprehensive information they need to promote the right types of entrepreneurship in the right situations.
For purposes of this study, the three welfare dimensions refer to the widely used definition of the three pillars of sustainable development (economic growth, social equality protection, environmental protection) of the Brundtland Report (World Development Commission on Environment and Development 1987 ). However, the reader should note that later sustainability models like the ‘prism model’ or the ‘concentric circles model’ illustrate that the three pillars of sustainable development (resp. the three welfare dimensions) are interlinked and not always clearly separable from one another.
Although the author is fully aware of their different meanings, for simplicity, the more general term ‘economic welfare’ is used throughout this paper as synonymous with the terms ‘economic growth’ and ‘economic development’.
Namely: Regional Studies , Entrepreneurship & Regional Development , The Annals of Regional Science , Economic Development Quarterly , Technological Forecasting and Social Change .
Namely: Bjørnskov and Foss ( 2016 ), Block et al. ( 2017 ), Fritsch ( 2013 ), Sutter et al. (2018), Urbano et al. ( 2019a ), van Praag and Versloot ( 2007 ), Wennekers and Thurik ( 1999 ).
Abdesselam R, Bonnet J, Renou-Maissant P (2014) Typology of the French regional development: revealing the refugee versus Schumpeter effects in new-firm start-ups. Appl Econ 46:3437–3451. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2014.931920
Article Google Scholar
Acs ZJ, Armington C (2004) Employment growth and entrepreneurial activity in cities. Reg Stud 38:911–927. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280938
Acs ZJ, Mueller P (2008) Employment effects of business dynamics: mice, gazelles and elephants. Small Bus Econ 30:85–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9052-3
Acs ZJ, Varga A (2005) Entrepreneurship, agglomeration and technological change. Small Bus Econ 24:323–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-005-1998-4
Acs ZJ, Braunerhjelm P, Audretsch DB, Carlsson B (2009) The knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship. Small Bus Econ 32:15–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-008-9157-3
Acs ZJ, Audretsch DB, Braunerhjelm P, Carlsson B (2012) Growth and entrepreneurship. Small Bus Econ 39:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-010-9307-2
Acs ZJ, Audretsch DB, Lehmann EE (2013) The knowledge spillover theory of entrepreneurship. Small Bus Econ 41:757–774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-013-9505-9
Adusei M (2016) Does entrepreneurship promote economic growth in Africa? Afr Dev Rev 28:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8268.12190
Albulescu CT, Draghici A (2016) Entrepreneurial activity and national innovative capacity in selected European countries. Int J Entrep Innov 17:155–172. https://doi.org/10.1177/1465750316655902
Alvarez SA, Barney JB (2014) Entrepreneurial opportunities and poverty alleviation. Entrep Theory Pract 38:159–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12078
Andersson M, Noseleit F (2011) Start-ups and employment dynamics within and across sectors. Small Bus Econ 36:461–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9252-0
Andersson M, Braunerhjelm P, Thulin P (2012) Creative destruction and productivity: entrepreneurship by type, sector and sequence. J Entrep Public Policy 1:125–146. https://doi.org/10.1108/20452101211261417
Anokhin S, Wincent J (2012) Start-up rates and innovation: a cross-country examination. J Int Bus Stud 43:41–60. https://doi.org/10.1057/jibs.2011.47
Aparicio S, Urbano D, Audretsch D (2016) Institutional factors, opportunity entrepreneurship and economic growth: panel data evidence. Technol Forecast Soc Change 102:45–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2015.04.006
Apergis N, Payne JE (2016) An empirical note on entrepreneurship and unemployment: further evidence from U.S. states. J Entrep Public Policy 5:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEPP-10-2015-0029
Arribas I, Vila JE (2007) Human capital determinants of the survival of entrepreneurial service firms in Spain. Int Entrep Manag J 3:309–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-007-0038-z
Ashcroft B, Love JH (1996) Firm births and employment change in the British counties: 1981–89. Pap Reg Sci 75:483–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1435-5597.1996.tb00675.x
Atems B, Shand G (2018) An empirical analysis of the relationship between entrepreneurship and income inequality. Small Bus Econ 51:905–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-017-9984-1
Audretsch DB, Fritsch M (2003) Linking entrepreneurship to growth: the case of West Germany. Ind Innov 10:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/1366271032000068104
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2004a) Entrepreneurship capital and economic performance. Reg Stud 38:949–959. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280956
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2004b) Entrepreneurship and regional growth: an evolutionary interpretation. J Evol Econ 14:605–616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-004-0228-6
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2004c) Does entrepreneurship capital matter? Entrep Theory Pract 28:419–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6520.2004.00055.x
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2005) Entrepreneurship capital and regional growth. Ann Reg Sci 39:457–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-005-0246-9
Audretsch DB, Keilbach M (2008) Resolving the knowledge paradox: knowledge-spillover entrepreneurship and economic growth. Res Policy 37:1697–1705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2008.08.008
Audretsch DB, Boente W, Keilbach M (2008) Entrepreneurship capital and its impact on knowledge diffusion and economic performance. J Bus Ventur 23:687–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2008.01.006
Audretsch DB, Belitski M, Desai S (2015) Entrepreneurship and economic development in cities. Ann Reg Sci 55:33–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-015-0685-x
Banerji D, Reimer T (2019) Startup founders and their LinkedIn connections: are well-connected entrepreneurs more successful? Comput Hum Behav 90:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.08.033
Baptista R, Preto MT (2010) Long-term effects of new firm formation by type of start-up. Int J Entrep Small Bus 11:382–402. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJESB.2010.036293
Baptista R, Preto MT (2011) New firm formation and employment growth: regional and business dynamics. Small Bus Econ 36:419–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9254-y
Baptista R, Escária V, Madruga P (2008) Entrepreneurship, regional development and job creation: the case of Portugal. Small Bus Econ 30:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9055-0
Bashir S, Gebremedhin T (2011) An analysis of the relationship between new firm formation and economic development in the northeast region of the United States. J Dev Entrep 16:289–306. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1084946711001859
Baum JR, Smith KG, Locke EA (2001) A multidimensional model of venture growth. Acad Manag J 44:292–303. https://doi.org/10.2307/3069456
Belitski M, Desai S (2016) Creativity, entrepreneurship and economic development: city-level evidence on creativity spillover of entrepreneurship. J Technol Transf 41:1354–1376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-015-9446-3
Ben Youssef A, Boubaker S, Omri A (2018) Entrepreneurship and sustainability: the need for innovative and institutional solutions. Technol Forecast Soc Change 129:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.11.003
Bjørnskov C, Foss N (2013) How strategic entrepreneurship and the institutional context drive economic growth. Strateg Entrep J 7:50–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/sej.1148
Bjørnskov C, Foss NJ (2016) Institutions, entrepreneurship, and economic growth: what do we know and what do we still need to know? Acad Manag Perspect 30:292–315
Block J, Thurik R, Zhou H (2013) What turns knowledge into innovative products? The role of entrepreneurship and knowledge spillovers. J Evol Econ 23:693–718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-012-0265-5
Block JH, Fisch CO, van Praag M (2017) The Schumpeterian entrepreneur: a review of the empirical evidence on the antecedents, behaviour and consequences of innovative entrepreneurship. Ind Innov 24:61–95. https://doi.org/10.1080/13662716.2016.1216397
Bosma N, Stam E, Schutjens V (2011) Creative destruction and regional productivity growth: evidence from the Dutch manufacturing and services industries. Small Bus Econ 36:401–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9257-8
Braunerhjelm P, Borgman B (2004) Geographical concentration, entrepreneurship and regional growth: evidence from regional data in Sweden, 1975–99. Reg Stud 38:929–947. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280947
Braunerhjelm P, Acs ZJ, Audretsch DB, Carlsson B (2010) The missing link: knowledge diffusion and entrepreneurship in endogenous growth. Small Bus Econ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9235-1
Brixy U (2014) The significance of entry and exit for regional productivity growth. Reg Stud 48:1051–1070. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2014.895804
Brüderl J, Preisendörfer P, Ziegler R (1992) Survival chances of newly founded business organizations. Am Sociological Rev 57:227. https://doi.org/10.2307/2096207
Carree MA, Thurik RA (2008) The lag structure of the impact of business ownership on economic performance in OECD countries. Small Bus Econ 30:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-006-9007-0
Carree M, van Stel A, Thurik R, Wennekers S (2002) Economic development and business ownership: an analysis using data of 23 OECD countries in the period 1976–1996. Small Bus Econ 19:271–290. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019604426387
Carree M, van Stel A, Thurik R, Wennekers S (2007) The relationship between economic development and business ownership revisited. Entrep Reg Dev 19:281–291. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985620701296318
Carree M, Congregado E, Golpe A, van Stel A (2015) Self-employment and job generation in metropolitan areas, 1969–2009. Entrep Reg Dev 27:181–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985626.2015.1025860
Chen CC (2014) Entrepreneurship economic growth and employment: a case study of Taiwan. Hitotsubashi J Econ 55:71–88. https://doi.org/10.15057/26817
Chrisman JJ, Bauerschmidt A, Hofer CW (1998) The determinants of new venture performance: an extended model. Entrep Theory Pract 23:5–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/104225879802300101
Cliff JE (1998) Does one size fit all? Exploring the relationship between attitudes towards growth, gender, and business size. J Bus Ventur 13:523–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-9026(97)00071-2
Cole IM (2018) Unemployment and entrepreneurship in the Mid-Atlantic Region of the United States: a spatial panel data analysis. Rev Reg Stud 48:347–375
Google Scholar
Criscuolo C, Gal PN, Menon C (2017) Do micro start-ups fuel job creation? Cross-country evidence from the DynEmp Express database. Small Bus Econ 48:393–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-016-9778-x
Crnogaj K, Rebernik M, Hojnik BB (2015) Supporting economic growth with innovation-oriented entrepreneurship. Ekonomický časopis 63:395–409
Cumming D, Johan S, Zhang M (2014) The economic impact of entrepreneurship: comparing international datasets. Corp Gov Int Rev 22:162–178. https://doi.org/10.1111/corg.12058
Daly HE, Cobb JB, Cobb CW (1994) For the common good: redirecting the economy toward community, the environment, and a sustainable future/Herman E. Daly and John B. Cobb, Jr.; with contributions by Clifford W. Cobb, 2nd ed., updated and expanded. Beacon Press, Boston
Delfmann H, Koster S (2016) The effect of new business creation on employment growth in regions facing population decline. Ann Reg Sci 56:33–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-015-0738-1
Dhahri S, Omri A (2018) Entrepreneurship contribution to the three pillars of sustainable development: what does the evidence really say? World Dev 106:64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.01.008
Dixon-Woods M, Agarwal S, Jones D, Young B, Sutton A (2005) Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. J Health Serv Res Policy 10:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1258/1355819052801804
Doran J, McCarthy N, O’Connor M (2016) Entrepreneurship and employment growth across European regions. Reg Stud Reg Sci 3:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681376.2015.1135406
Draghici A, Albulescu CT (2014) Does the entrepreneurial activity enhance the national innovative capacity? Procedia Soc Behav Sci 124:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.02.500
Du K, O’Connor A (2017) Entrepreneurship and advancing national level economic efficiency. Small Bus Econ 50:91–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-017-9904-4
Dvouletý O (2017) Can policy makers count with positive impact of entrepreneurship on economic development of the Czech regions? J Entrep Emerg Econ 9:286. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEEE-11-2016-0052
Engel D, Metzger G (2006) Direct employment effects of new firms. In: Fritsch M, Schmude J (eds) Entrepreneurship in the region, vol 49. Springer, Boston, pp 75–93
Chapter Google Scholar
Eraydin A, Tasan-Kok T, Vranken J (2010) Diversity matters: immigrant entrepreneurship and contribution of different forms of social integration in economic performance of cities. Eur Plan Stud 18:521–543. https://doi.org/10.1080/09654311003593556
Erken H, Donselaar P, Thurik R (2018) Total factor productivity and the role of entrepreneurship. J Technol Transf 43:1493–1521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-016-9504-5
Falck O (2007) Mayflies and long-distance runners: the effects of new business formation on industry growth. Appl Econ Lett 14:919–922. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504850600705877
Fayolle A, Wright M (2014) How to get published in the best entrepreneurship journals: a guide to steer your academic career/edited by Alain Fayolle and Mike Wright. Edward Elgar, Cheltenham
Book Google Scholar
Feki C, Mnif S (2016) Entrepreneurship, technological innovation, and economic growth: empirical analysis of panel data. J Knowl Econ 7:984–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-016-0413-5
Ferreira JJ, Fayolle A, Fernandes C, Raposo M (2017) Effects of Schumpeterian and Kirznerian entrepreneurship on economic growth: panel data evidence. Entrep Reg Dev 29:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985626.2016.1255431
Fisch C, Block J (2018) Six tips for your (systematic) literature review in business and management research. Manag Rev Q 68:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-018-0142-x
Fölster S (2000) Do entrepreneurs create jobs? Small Bus Econ 14:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008141516160
Frenken K, Cefis E, Stam E (2014) Industrial dynamics and clusters: a survey. Reg Stud 49:10–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2014.904505
Fritsch M (1996) Turbulence and growth in West Germany: a comparison of evidence by regions and industries. Rev Ind Organ 11:231–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157669
Fritsch M (2013) New business formation and regional development: a survey and assessment of the evidence. Found Trends Entrep 9:249–364. https://doi.org/10.1561/0300000043
Fritsch M, Mueller P (2004) Effects of new business formation on regional development over time. Reg Stud 38:961–975. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280965
Fritsch M, Mueller P (2008) The effect of new business formation on regional development over time: the case of Germany. Small Bus Econ 30:15–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9067-9
Fritsch M, Noseleit F (2013a) Investigating the anatomy of the employment effect of new business formation. Camb J Econ. https://doi.org/10.1093/cje/bes030
Fritsch M, Noseleit F (2013b) Start-ups, long- and short-term survivors, and their contribution to employment growth. J Evol Econ 23:719–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-012-0301-5
Fritsch M, Schindele Y (2011) The contribution of new businesses to regional employment—an empirical analysis. Econ Geogr 87:153–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1944-8287.2011.01113.x
Fritsch M, Schroeter A (2011) Why does the effect of new business formation differ across regions? Small Bus Econ 36:383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9256-9
Fryges H, Wagner J (2008) Exports and productivity growth: first evidence from a continuous treatment approach. Rev World Econ 144:695–722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10290-008-0166-8
Gast J, Gundolf K, Cesinger B (2017) Doing business in a green way: a systematic review of the ecological sustainability entrepreneurship literature and future research directions. J Clean Prod 147:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.065
Gilbert BA, McDougall PP, Audretsch DB (2006) New venture growth: a review and extension. J Manag 32:926–950. https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206306293860
Gilbert BA, McDougall PP, Audretsch DB (2008) Clusters, knowledge spillovers and new venture performance: an empirical examination. J Bus Ventur 23:405–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2007.04.003
Gittell R, Sohl J, Tebaldi E (2014) Do entrepreneurship and high-tech concentration create jobs? Exploring the growth in employment in U.S. metropolitan areas from 1991 to 2007. Econ Dev Q 28:244–253. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891242414530467
González-Pernía J, Peña-Legazkue I (2015) Export-oriented entrepreneurship and regional economic growth. Small Bus Econ 45:505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-015-9657-x
González-Pernía J, Peña-Legazkue I, Vendrell-Herrero F (2012) Innovation, entrepreneurial activity and competitiveness at a sub-national level. Small Bus Econ 39:561–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-011-9330-y
Hafer RW (2013) Entrepreneurship and state economic growth. J Entrep Public Policy. https://doi.org/10.1108/20452101311318684
Hamdan AMM (2019) Entrepreneurship and economic growth: an Emirati perspective. J Dev Areas 53:65–78. https://doi.org/10.1353/jda.2019.0004
Harmina A (2016) The role of entrepreneurship in explaining the real gross domestic product per capita: regression model selection. Croat Rev Econ Bus Soc Stat 2:297. https://doi.org/10.1515/crebss-2016-0007
Henderson J, Weiler S (2009) Entrepreneurs and job growth: probing the boundaries of time and space. Econ Dev Q 24:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891242409350917
Hessels J, van Stel A (2011) Entrepreneurship, export orientation, and economic growth. Small Bus Econ 37:255–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9233-3
Higgins JPT, Green S (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Wiley, Chichester
Hoang H, Yi A (2015) Network-based Research in entrepreneurship: a decade in review. Found Trends Entrep 11:1–54. https://doi.org/10.1561/0300000052
Irastorza N, Pena-Legazkue I (2018) Immigrant entrepreneurship and business survival during recession: evidence from a local economy. J Entrep 27:243–257. https://doi.org/10.1177/0971355718781248
Ivanović-Đukić M, Lepojevi V, Stefanovic S, van Stel A, Petrovic J (2018) Contribution of entrepreneurship to economic growth: a comparative analysis of south-east transition and developed European countries. Int Rev Entrep 16:257–276
Jones O, Gatrell C (2014) Editorial: The future of writing and reviewing for IJMR. Int J Manag Rev 16:249–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12038
Jones MV, Coviello N, Tang YK (2011) International entrepreneurship research (1989–2009): a domain ontology and thematic analysis. J Bus Ventur 26:632–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2011.04.001
Kalleberg AL, Leicht KT (1991) Gender and organizational performance: determinants of small business survival and success. Acad Manag J 34:136–161. https://doi.org/10.5465/256305
Kangasharju A, Pekkala S (2002) The role of education in self-employment success in Finland. Growth Change 33:216–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/0017-4815.00188
Kasseeah H (2016) Investigating the impact of entrepreneurship on economic development: a regional analysis. J Small Bus Enterp Dev. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-09-2015-0130
Kessler A, Korunka C, Frank H, Lueger M (2012) Predicting founding success and new venture survival: a longitudinal nascent entrepreneurship approach. J Enterp Cult 20:25–55. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218495812500021
Kirzner IM (1973) Competition and entrepreneurship. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Koellinger PD, Thurik RA (2012) Entrepreneurship and the business cycle. Rev Econ Stat 94:1143–1156. https://doi.org/10.1162/REST_a_00224
Koster S (2011) Individual foundings and organizational foundings: their effect on employment growth in The Netherlands. Small Bus Econ 36:485–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-009-9253-z
Koster S, van Stel A (2014) The relationship between start-ups, market mobility and employment growth: an empirical analysis for Dutch regions. Pap Reg Sci 93:203–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/pirs.12000
Lee YS (2017) Entrepreneurship, small businesses and economic growth in cities. J Econ Geogr 17:311–343. https://doi.org/10.1093/jeg/lbw021
Li H, Cheng S, Haynes KE (2011) The employment effects of new business formation: a regional perspective. Econ Dev Q 25:282–292. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891242411407310
Li H, Yang Z, Yao X, Zhang H, Zhang J (2012) Entrepreneurship, private economy and growth: evidence from China. China Econ Rev 23:948–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2012.04.015
Li H, Terjesen S, Umans T (2020) Corporate governance in entrepreneurial firms: a systematic review and research agenda. Small Bus Econ 54:43–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-018-0118-1
Liargovas P, Repousis S (2013) Development paths in the knowledge economy: innovation and entrepreneurship in Greece. J Knowl Econ 6:1063–1077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-013-0176-1
Matejovsky L, Mohapatra S, Steiner B (2014) The dynamic effects of entrepreneurship on regional economic growth: evidence from Canada. Growth Change 45:611–639. https://doi.org/10.1111/grow.12055
McMullen JS (2011) Delineating the domain of development entrepreneurship: a market-based approach to facilitating inclusive economic growth: ET&P ET&P. Entrep Theory Pract 35:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6520.2010.00428.x
Meadows DH, Meadows DL, Randers J, Behrens WW III (1972) The limits to growth: a report for the Club of Rome’s project on the predicament of mankind/Donella H. Meadows … [et al.]. Universe Books, New York
Meyer N, Meyer DF (2017) An econometric analysis of entrepreneurial activity, economic growth and employment: the case of the BRICS countries. Int J Econ Perspect 11:429–441
Mochkabadi K, Volkmann CK (2020) Equity crowdfunding: a systematic review of the literature. Small Bus Econ 54:75–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-018-0081-x
Mrozewski M, Kratzer J (2017) Entrepreneurship and country-level innovation: investigating the role of entrepreneurial opportunities. J Technol Transf 42:1125–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-016-9479-2
Mueller P (2007) Exploiting entrepreneurial opportunities: the impact of entrepreneurship on growth. Small Bus Econ 28:355–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-006-9035-9
Mueller P, van Stel A, Storey DJ (2008) The effects of new firm formation on regional development over time: the case of Great Britain. Small Bus Econ 30:59–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11187-007-9056-Z
Mulrow CD (1994) Rationale for systematic reviews. BMJ 309:597–599. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.309.6954.597
Munoz P, Cohen B (2018) Sustainable entrepreneurship research: taking stock and looking ahead. Bus Strateg Environ 27:300–322. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2000
Nafziger EW, Terrell D (1996) Entrepreneurial human capital and the long-run survival of firms in India. World Dev 24:689–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-750X(95)00161-5
Naudé W, Siegel M, Marchand K (2017) Migration, entrepreneurship and development: critical questions. IZA J Migration 6:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40176-016-0077-8
Nissan E, Galindo Martin M-A, Mendez Picazo M-T (2011) Relationship between organizations, institutions, entrepreneurship and economic growth process. Int Entrep Manag J 7:311–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-011-0191-2
Nordhaus W, Tobin J (1972) Is growth obsolete? Econ Res 5:1–80
North DC (2012) Institutions, institutional change and economic performance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Noseleit F (2013) Entrepreneurship, structural change, and economic growth. J Evol Econ 23:735–766. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00191-012-0291-3
Omri A (2017) Entrepreneurship, sectoral outputs and environmental improvement: international evidence. Technol Forecast Soc Change. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.10.016
Ordanini A, Rubera G, DeFillippi R (2008) The many moods of inter-organizational imitation: a critical review. Int J Manag Rev 10:375–398. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2370.2008.00233.x
Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Bachrach DG, Podsakoff NP (2005) The influence of management journals in the 1980s and 1990s. Strateg Manag J 26:473–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.454
Popay J, Roberts H, Sowden A, Petticrew M, Arai L, Rodgers M, Britten N, Roen K, Duffy S (2006) Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews: a product from the ESRC Methods Programme. Lancaster University, Lancaster
Prieger JE, Bampoky C, Blanco LR, Liu A (2016) Economic growth and the optimal level of entrepreneurship. World Dev 82:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2016.01.013
Raz O, Gloor PA (2007) Size really matters-new insights for start-ups’ survival. Manag Sci 53:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.1060.0609
Reynolds PD, Bygrave WD, Autio E (2003) Global entrepreneurship Monitor: 2003 executive report. http://www.gemconsortium.org/report/47102 . Accessed 27 Dec 2017
Rho S, Gao J (2012) Employment effect of entrepreneurial activity in China’s private economy. Seoul J Econ 25:177–206
Rosa P, Carter S, Hamilton D (1996) Gender as a determinant of small business performance: insights from a British study. Small Bus Econ 8:463–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390031
Rupasingha A, Goetz SJ (2013) Self-employment and local economic performance: evidence from US counties. Pap Reg Sci 92:141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1435-5957.2011.00396.x
Sabella A, Farraj W, Burbar M, Qaimary D (2014) Entrepreneurship and economic growth in West Bank, Palestine. J Dev Entrep 19:1. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1084946714500034
Salgado Banda H (2007) Entrepreneurship and economic growth: an empirical analysis. J Dev Entrep 12:3–29. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1084946707000538
Schumpeter JA (1942) Capitalism, socialism and democracy, [Reprint]. Harper colophon, Harper Perennial, New York
Semrau T, Werner A (2014) How exactly do network relationships pay off? The effects of network size and relationship quality on access to start-up resources. Entrep Theory Pract 38:501–525. https://doi.org/10.1111/etap.12011
Stam E, Hartog C, van Stel A, Thurik R (2011) Ambitious entrepreneurship, high-growth firms, and macroeconomic growth. In: Minniti M (ed) The dynamics of entrepreneurship. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Szerb L, Lafuente E, Horváth K, Páger B (2018) The relevance of quantity and quality entrepreneurship for regional performance: the moderating role of the entrepreneurial ecosystem. Reg Stud. https://doi.org/10.1080/00343404.2018.1510481
Tang J, Tang Z (2007) The relationship of achievement motivation and risk-taking propensity to new venture performance: a test of the moderating effect of entrepreneurial munificence. Int J Entrep Small Bus 4:450. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJESB.2007.013691
Terán-Yépez E, Marín-Carrillo GM, Casado-Belmonte MP, Capobianco-Uriarte MM (2020) Sustainable entrepreneurship: review of its evolution and new trends. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119742
Thurik RA, Carree MA, van Stel A, Audretsch DB (2008) Does self-employment reduce unemployment? J Bus Ventur 23:673–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2008.01.007
Tietenberg TH, Lewis L (2012) Environmental & natural resource economics. Pearson series in economics, 9th edn. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14:207–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Unger JM, Rauch A, Frese M, Rosenbusch N (2011) Human capital and entrepreneurial success: a meta-analytical review. J Bus Ventur 26:341–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2009.09.004
Urbano D, Aparicio S (2016) Entrepreneurship capital types and economic growth: International evidence. Technol Forecast Soc Change 102:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2015.02.018
Urbano D, Aparicio S, Audretsch D (2019a) Twenty-five years of research on institutions, entrepreneurship, and economic growth: what has been learned? Small Bus Econ 53:21–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-018-0038-0
Urbano D, Audretsch D, Aparicio S, Noguera M (2019b) Does entrepreneurial activity matter for economic growth in developing countries? The role of the institutional environment. Int Entrep Manag J 6:875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-019-00621-5
Valliere D, Peterson R (2009) Entrepreneurship and economic growth: evidence from emerging and developed countries. Entrep Reg Dev 21:459–480. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985620802332723
van Oort FG, Bosma NS (2013) Agglomeration economies, inventors and entrepreneurs as engines of European regional economic development. Ann Reg Sci 51:213–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00168-012-0547-8
van Praag CM, Versloot PH (2007) What is the value of entrepreneurship? A review of recent research. Small Bus Econ 29:351–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9074-x
van Praag CM, Wit GD, Bosma N (2005) Initial capital constraints hinder entrepreneurial venture performance. J Priv Equity 9:36–44. https://doi.org/10.3905/jpe.2005.605369
van Stel A, Storey D (2004) The link between firm births and job creation: is there a Upas Tree effect? Reg Stud 38:893–909. https://doi.org/10.1080/0034340042000280929
van Stel A, Suddle K (2008) The impact of new firm formation on regional development in the Netherlands. Small Bus Econ 30:31–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-007-9054-1
van Stel A, Carree M, Thurik R (2005) The effect of entrepreneurial activity on national economic growth. Small Bus Econ 24:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-005-1996-6
Vázquez-Rozas E, Gómes S, Viera E (2010) Entrepreneurship and economic growth in Spanish and Portuguese regions. Reg Sect Econ Stud 10:109–126
Verheul I, van Stel A (2010) Entrepreneurial diversity and economic growth. In: van Auken H, Bonnet J, García Pérez De Lima D (eds) The entrepreneurial society. Edward Elgar Publishing, Cheltenham
Watson J (2007) Modeling the relationship between networking and firm performance. J Bus Ventur 22:852–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusvent.2006.08.001
Wennberg K, Lindqvist G (2010) The effect of clusters on the survival and performance of new firms. Small Bus Econ 34:221–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-008-9123-0
Wennekers S, Thurik R (1999) Linking entrepreneurship and economic growth. Small Bus Econ 13:27. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008063200484
Williams CC, Lansky MA (2013) Informal employment in developed and developing economies: perspectives and policy responses. Int Labour Rev 152:355–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1564-913X.2013.00196.x
Wohlin C (2014) Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In: Shepperd M, Hall T, Myrtveit I (eds) Proceedings of the 18th international conference on evaluation and assessment in software engineering—EASE ‘14. ACM Press, New York, pp 1–10
Wong PK, Ho YP, Autio E (2005) Entrepreneurship, innovation and economic growth: evidence from GEM data. Small Bus Econ 24:335–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-005-2000-1
World Commission on Environment and Development (1987) Brundtland report: our common future. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Zhao S (2018) Entrepreneurship and economic growth during china’s economic transformation, 1978–2008. Seoul J Econ 31:307–331
Download references
Acknowledgements
Open Access funding provided by Projekt DEAL. I like to thank Dirk Ludewig, of the Flensburg University of Applied Sciences and Olav Hohmeyer, of the Europa-Universität Flensburg, for their useful and valuable feedback on previous versions of this paper. Furthermore, I would like to express my appreciation to the participants of the G-Forum conference in Wien, Austria (September, 2019) and of the paper development workshop of the FGF e.V. working group on sustainable entrepreneurship in Flensburg, Germany (March, 2020), where earlier versions of the paper were discussed.
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of economics, Flensburg University of Applied Sciences, Kanzleistraße 91-93, Flensburg, Germany
Thomas Neumann
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Thomas Neumann .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 109 kb)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Neumann, T. The impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and its determinants: a systematic review. Manag Rev Q 71 , 553–584 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00193-7
Download citation
Received : 21 May 2020
Accepted : 19 July 2020
Published : 04 August 2020
Issue Date : July 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00193-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Entrepreneurship
- Economic development
- Sustainable development
- Developing countries
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- How it works
Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Entrepreneurship Dissertation Topics
Published by Carmen Troy at January 4th, 2023 , Revised On August 15, 2023
Choosing the right topic for your dissertation is extremely important. For both an undergraduate and postgraduate degree, the dissertation is worth a large number of credits. Your dissertation project is going to take a lot of time to complete. This is why it’s best to choose a topic that’s both interesting and unique.
The structure is extremely important in a dissertation . Each sentence should be relevant and contribute to the research argument. It should be a high-quality piece of academic work. That’s why, when choosing the right topic, it’s important not to be vague. Broad topics make it harder for you to draw brief and relevant conclusions.
Similarly, being too narrow with your topic will make it hard for you to expand on your arguments. Conclusively, your dissertation topic should be as objective as possible with a realistic scope. It’s best to think about the subject matter from an outside perspective to better grasp the strength of your topic. Discussing the topic with your tutor and other knowledgeable people can also help you get more insight into the matter.
Research is your biggest ally and will help you ensure that the topic you are choosing is the right one.
How to choose an Entrepreneurship Dissertation Topic?
The process of launching and developing a new business is called entrepreneurship. While it starts out as a small venture, when successful, it can grow to become a huge corporate firm. For an entrepreneur, there are a lot of risks involved before they can reap the benefits.
Entrepreneurship is a vast field that includes many aspects. It has also become a widely popular field of interest as many aspire to become an entrepreneur nowadays. The fact that this area encompasses so much may be the reason why students often find doing a dissertation on entrepreneurship a daunting task.
However, there are a lot of interesting topics that can be covered! After all, what does being an entrepreneur truly entail? Are entrepreneurs born or made? These questions are all very engrossing and can make interesting dissertation topics.
Students often review successful business organizations and even outsource for new ideas. For many entrepreneurs, kick-starting and operating a business alone is not what the job means. There are various other aspects involved. For example: persuading investors, making other people believe in your idea, and demonstrating that you have taken all the necessary measures for success.
All in all, if you are covering entrepreneurship for your dissertation, it’s important to produce a tightly written piece that truly reflects the essence of the field.
Here are twenty excellent entrepreneurship dissertation topics that you can work on:
Want to know what essay structure and style will work best for your assignment?
Problem fixed! We can write any type of essay in any referencing style. We ensure every essay written is beyond your expectations.

2022 Entrepreneurship Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: a study on the increasing trend of entrepreneurship: a solution for poverty alleviation in the uk..
Research Aim: The research aims to describe the ongoing and increasing trend of entrepreneurship in the UK and the way it is alleviating poverty in the country.
Objectives:
- To examine the increasing trend of entrepreneurship in the UK.
- To interpret how entrepreneurship is being a solution for alleviating poverty in the UK.
- To recommend strategies to entrepreneurs in the UK about how they can contribute to alleviate poverty.
Topic 2: Investigating the impacts of the growing number of entrepreneurs in the UK economy – a case study of the Global Entrepreneur Program of the government
Research Aim: The research aim investigates how the growing number of entrepreneurs is impacting the UK economy. The role of the UK government’s Global Entrepreneur Program will also be analysed.
- To investigate the impacts and roles of the increasing number of entrepreneurs in the UK economy.
- To analyse the role of the UK government’s Global Entrepreneur Program for supporting entrepreneurs.
- To suggest strategies about how entrepreneurs can be benefitted in the best possible way with the help of the UK government’s Global Entrepreneur Program.
Topic 3: Exploring the impacts of using cloud technology on quality control and cost saving by the entrepreneurs in the UK.
Research Aim: The research aims to explore the impacts of using cloud technologies by entrepreneurs in the UK for the purposes like cost saving and quality control.
- To analyse the benefits of using cloud technologies in an organisation.
- To shed light on how the UK entrepreneurs are embracing cloud technologies for quality control and saving costs.
- To recommend strategies about how cloud technologies can be improved by the UK entrepreneurs to enhance cost saving and quality control.
Topic 4: Examining the increasing scope of entrepreneurship in the UK and implications in driving competition and productivity.
Research Aim: The aim examines the expanding scope of entrepreneurship in the UK and how this is affecting and accelerating competition and productivity.
- To shed light on the context of the increasing scope of entrepreneurship in the UK.
- To investigate how growth in entrepreneurship affects and drives competition and productivity.
- To suggest strategies for driving entrepreneurship in the UK thereby driving competition and productivity.
Topic 5: A study on the role of effective leadership of entrepreneurs in small businesses in the UK while driving performance efficiency and teamwork.
Research Aim: The aim is to critically analyse the role of effective leadership of entrepreneurs in small businesses in the UK that can drive teamwork and performance efficiency.
- To interpret the significance of effective leadership of entrepreneurs in small businesses in the UK.
- To analyse how effective leadership of entrepreneurs in the UK small businesses drives teamwork and performance efficiency.
- To recommend effective strategies for nurturing leadership practices by the entrepreneurs in the UK small businesses to improve teamwork and performance efficiency for a better outcome.
Topic 1: An investigation on the effects of technological advancement on entrepreneurship in a company
Research Aim: The goal of the research will be to see if technology improvements have an impact on the sector of entrepreneurship. The study will also highlight some of the technical tools that have a favorable impact on an organization’s entrepreneurship levels.
Topic 2: A case study to see how gender affects the development of entrepreneurial skills
Research Aim: The goal of this research is to see if gender difference has an impact on the development of entrepreneurial abilities. It will be feasible to discover which of the two genders has greater entrepreneurship skills by doing this study.
Topic 3: An analysis of the impact of government policies on entrepreneurship in a specific country
Research Aim: The goal of this research is to see if government policies in a certain country have an impact on entrepreneurial activity in that country. Some policies that may have an impact on entrepreneurship will be identified as a result of this research.
Topic 4: An examination of the role of entrepreneurship in a country's economic development
Research Aim: The research aims to investigate whether entrepreneurship has a hand in determining and evaluating a country’s economic progress. Following the completion of this study, it will be possible to establish how entrepreneurship influences a country’s economic development.
Topic 5: An investigation on the factors that influence entrepreneurial creativity in a company
Research Aim: This research will aid in identifying some of the characteristics that influence entrepreneurial innovation in a company. It will be feasible to discover how each of the factors operates as a determinant of entrepreneurial innovation in an organization by doing this study.
Topic 6: An investigation into the impact of entrepreneurship education in schools on the development of entrepreneurial abilities
Research Aim: The goal of this research is to see if adding entrepreneurship in schools helps students acquire entrepreneurship abilities. Following this research, the influence of include this study in the promotion of entrepreneurship in the country will be determined.
Topic 7: Public Support for Technology-Based Ventures (Entrepreneurship Policy)
Research Aim: This thesis is on entrepreneurship policy, with a focus on public assistance plans for early-stage technology-based ventures. It argues that a comprehensive perspective should be taken on the types of entrepreneurship policies that aim to support the ability of supported businesses to connect to their surrounding innovation system, allowing them to secure access to critical external resources.
Topic 8: Research on Small Business Growth and Performance
Research Aim: Why do some small businesses thrive and develop while others do not? Is there a role for entrepreneurship in this process? These are the two main concerns that can be raised in this essay. Variables boosting and constraining small company growth and performances can be identified based on a thorough literature study.
Topic 9: Study on How Small Businesses Operate in an Unstable Environment
Research Aim: This thesis examines how small businesses, particularly their CEOs, deal with high levels of environmental turbulence. Their performance and their CEO’s self-awareness and obscurity, several different companies, can be chosen for the empirical investigation.
How Can ResearchProspect Help?
ResearchProspect writers can send several custom topic ideas to your email address. Once you have chosen a topic that suits your needs and interests, you can order for our dissertation outline service which will include a brief introduction to the topic, research questions , literature review , methodology , expected results , and conclusion . The dissertation outline will enable you to review the quality of our work before placing the order for our full dissertation writing service !
Topic 10: Entrepreneurship's effects on business designs and models
Research Aim: This research intends to investigate how digital innovation has caused small and medium enterprises to further analyze and perform experimentation on their business models and how this affects their innovativeness and the way they perform.
- How global technology innovation has impacted small-business entrepreneurship on a broad scale.
- Identifying entrepreneurship as a separate social force
- Studying how the social characteristics of a given culture might help you understand entrepreneurship
- How entrepreneurship helps isolated groups of people develop their capabilities.
- The impact of entrepreneurship on the company model
- The use of design as a mediator to bring management theory and practice together.
- Distinguish between the five types of entrepreneurs
- Is it true that all people are born with entrepreneurial tendencies, or can these traits be learned?
- Donald Trump is one of the most well-known businessmen in the world. He is, however, well-known for his demeanor and a variety of other characteristics that do not garner widespread adoration. Discuss how a person’s success as an entrepreneur can cause them to lose touch with their humanity.
- Discuss some of the difficulties that entrepreneurs experience when they first start their companies. At the same time, offer some answers to these problems, emphasizing how technological advancements have made it simpler for individuals to overcome them.
Choosing Your Dissertation Topic:
When deciding on your topic, consider the message you want to send with your title. It’s not just a catch-all phrase for calling your study. It also serves as a concise summary of your complete body of work. It should be able to express the most important aspects of your research and provide a clear picture of what’s to come.
Choose your words and phrases with care. Each word must be significant. Your title should be a fair length to convey your point while remaining concise and unobtrusive. Clarity is necessary. Each character in the title has a place and has a purpose, with no extraneous words.
It’s possible that you’ll have to follow academic rules. Some subjects of study, for example, may enable compound titles or primary and subtitles. Maintain your concentration. The title should be brief but informative. It should state the purpose of your study.
Stick to the format given by your school of choice. In a title for a work of this grade, there is usually no room for humor. Save the humor for another occasion. A tight write-up that is information-based, accurate, perfectly reflects your topic, and coherently explains your aim of the research is best for a dissertation.
For most students, coming up with a dissertation topic in entrepreneurship might be a difficult process. Fortunately, students can gain ideas and inspiration by looking at outsourcing, evaluating corporate enterprises, nation-state aggressiveness, or asking whether entrepreneurs are born or made. As can be seen above, there are a plethora of fascinating topics that center around being an entrepreneur and running a firm.
Using these topic ideas in a broad sense will help you build a title that complements your content for your unique topic. They are just intended to be used as a guideline and should not be used in their entirety. As they say, experience is the best teacher, so use these samples to practice molding your words into engaging and effective titles.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find entrepreneurship dissertation topics.
To discover entrepreneurship dissertation topics:
- Study emerging business trends.
- Investigate startup challenges.
- Analyze success factors.
- Examine niche markets.
- Explore innovation and technology.
- Opt for topics resonating with your passion and expertise.
You May Also Like
Need interesting and manageable HRM dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending HRM dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
Need interesting computing engineering dissertation topics? Here are the trending Computing engineering dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
Need interesting and manageable Mental Health dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending Mental Health dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

PhD THESIS - SOCIAL ENTREPRENEURSHIP: SOCIALITY, ETHICS AND POLITICS

Related Papers
carolina bandinelli
This article adds to contemporary studies of neoliberalism by offering an empirical investigation of the production of subjectivity in the context of coworking spaces' sociality. Coworking spaces are exemplary milieux where to explore the organisation and significance of work. Drawing on the life history of a creative worker and member of a leading coworking space, I unveil the ethical labour that is required to access coworking's sociality. Using a Foucauldian framework, I conceptualise this process as a process of subjectivation and concentrate on its ambivalent character, signalling the inherent intertwinement of self-commodification and self-improvement. This article contributes to the scholarly debates on the organisation and significance of work in two key ways. Firstly, it expands our understanding of how the production of subjectivity is experienced at the level of the self. Secondly, it argues that coworking spaces function as apparatuses for the production of subjectivities in neoliberal culture industries.
Alberto Cossu
Freelancers, social entrepreneurs and artists have intervened in the social fabric by operating in peculiar, but somewhat analogous ways, blending collaboration, entrepreneurship and creative practice in an original manner. Each from their own standpoint, they now reclaim a central role in an urban collaborative scene that they commonly consider the space for the enactment of their creative, (self)entrepreneurial endeavours. Their subjectivity, as we are about to observe, is similarly characterised by a political attitude towards change and an ideological disposition to ‘newness’, that is made explicit in the attempt to combine economic with what may be seen as forms of ‘aest-ethical’ action – and is nonetheless frustrated in the capacity to coalesce as a collective subject within and beyond the fragmented scene they inhabit. By operating in a milieu largely determined by a market economy, yet nonetheless experimenting with forms of commons-based peer production, we argue that freelancers, social entrepreneurs and artists are manifestations, in their own peculiar ways, of that process of ‘re-embeddedness’ of the economic into the social (Pais and Provasi, 2015) that seems to characterise the current socio-economic conjuncture.
carolina bandinelli , Alberto Cossu
More than a decade after the enthusiastic call for the rise of a 'creative class' (Florida, 2002), the conditions of today's creative economy appear to be quite different from the expectations that accompanied its acclaimed surge as a propeller of economic development in the late 1990s and early 2000s. The frenzy around creativity that has characterised cultural economies as a whole since then has evolved into a context that is now largely animated by a casualisation and entrepreneurialisation of work, with project-based employment rising to an unprecedented scale (McRobbie, 2015).
Dissertation
Seung Cheol Lee
Etnološka tribina 41
Miha Kozorog
This paper is about the young entrepreneur as an emerging social agent in contemporary Slovenia. Young entrepreneurs are affected by both an ideal sociality of entrepreneurial ecosystems and the small scale of their environment. This paper argues that while the former is promoted as a tool for strengthening local communities and a means of moving toward a prosperous future, the later prevents its actualization but provides security for young people. Family and other established social relationships are of considerable importance for maintaining young entrepreneurs' careers.
This chapter reflects on the relationship between coworking spaces as a type of creative hub, and the practices of networking that are often described as typical of the creative economy. Elaborating on ethnographic research conducted by the authors in the UK and Italy, we argue that coworking spaces can be seen as heterotopic spaces (Foucault, 1986) in which a certain vision of the world is produced and reproduced. This vision acts as a symbolic dimension that expands the practices of 'network sociality' (Wittel, 2001) by adding to them an imaginary communitarian element. This is characterised by the enactment of a specific disposition that we call 'collaborative individualism'. With this term we want to capture the ambivalence of coworkers' sociality and point at the compresence of an entrepreneurialised and individualised conduct with an ethics of sharing and collaborating.
Pascal Dey , Chris Steyaert
This article identifies power, subjectivity, and practices of freedom as neglected but significant elements for understanding the ethics of social entrepreneurship. While the ethics of social entrepreneurship is typically conceptualized in conjunction with innate properties or moral commitments of the individual, we problematize this view based on its presupposition of an essentialist conception of the authentic subject. We offer, based on Foucault’s ethical oeuvre, a practice-based alternative which sees ethics as being exercised through a critical and creative dealing with the limits imposed by power, notably as they pertain to the conditioning of the neoliberal subject. To this end, we first draw on prior research which looks at how practitioners of social enterprises engage with government policies that demand that they should act and think more like prototypical entrepreneurs. Instead of simply endorsing the kind of entrepreneurial subjectivity implied in prevailing policies, our results indicate that practitioners are mostly reluctant to identify themselves with the invocation of governmental power, often rejecting the subjectivity offered to them by discourse. Conceiving these acts of resistance as emblematic of how social entrepreneurs practice ethics by retaining a skeptical attitude toward attempts that seek to determine who they should be and how they should live, we introduce three vignettes that illustrate how practices of freedom relate to critique, the care for others, and reflected choice. We conclude that a practice-based approach of ethics can advance our understanding of how social entrepreneurs actively produce conditions of freedom for themselves as well as for others without supposing a ‘true self’ or a utopian space of liberty beyond power.
Constellations
Niklas Angebauer
Understanding neoliberalism remains a crucial task for critical theories of the present. While Marxist approaches such as David Harvey's tend to underestimate its novelty and struggle to explain its pervasiveness, Foucauldian perspectives are better equipped to understand neoliberalism in its singularity. These perspectives culminate in the diagnosis of the emergence of a specifically neoliberal subject, the entrepreneurial self. One implication of this diagnosis that has not received nearly enough attention is neoliberal's implicit subscription to the doctrine of self-ownership: The entrepreneurial self is necessarily self-owning, even if that often remains implicit in neoliberal theory. Starting with a discussion of liberal self-ownership (Levellers, Locke), the article shows that neoliberal rationality is premised on self-ownership, discussing human capital theory and Income Share Agreements. The focus on neoliberal self-ownership and its consequences, it is argued, can be used for an immanent critique of neoliberal rationality.
Daniel G Cockayne
In this paper I examine entrepreneurial work in San Francisco's digital media sector to consider how affect and desire are invested in sites of neoliberal production. Drawing on recent writing on affect, I treat affect as ambivalent and coextensive with the mode of production, suggesting an approach that looks beyond the investment of value in commodities, to how desire is produced and directly located in economic infrastructures. Entrepreneurial affect functions through the embodiment of work as a site of personal ''satisfaction,'' the development of passionate attachments to that work, and the production of working subjectivities characterized by their ''compulsory sociality.'' I argue that affect functions through entrepreneurial forms of digital media work to produce and reproduce attachments to precarious working conditions. Drawing on recent debates on precariousness and precarity, I reflect on the possible consequences of affective attachments to entrepreneurial work as a primary site for the justification of precarious work practices and neoliberal modes of governance in general.
RELATED PAPERS
Dana N Johnson
Jason Weidner
The 11th International Critical Management Conference – CMS 2019
Lorayne Finol Romero
Environment and Planning A: Economy and Space
Andrea Pollio
Critical Perspectives on Social Entrepreneurship
Angela M Eikenberry
James Reveley
Adam Arvidsson , carolina bandinelli
Christos Petritzis
Tomas Marttila
Eeva Houtbeckers
Debats. Revista de cultura, poder i societat , María Inés Landa
wanda vrasti
Dr. Susan Gill
Sami Moisio , Ugo Rossi
American Ethnologist
Tomas Matza
Creative Hubs in Question Place, Space and Work in the Creative Economy
RAE-Revista de Administração de Empresas (Journal of Business Management)
Oriana Bernasconi
Ephemera: theory & politics in organization
Janet Merkel
June Wang , Tan Yujing
Entrepreneurship Education and Pedagogy
Michał Zawadzki , Anna Pluszyńska
Johan Fornäs
Milena A Melo
Benjamin Matthews
EPA: Economy and Space
Adam Arvidsson , Alessandro Caliandro , Alberto Cossu , Maitrayee Deka , Vincenzo Luise
Cuadernos de Bioética. 2018; 29(96): 193-201
Alessio Musio
Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Basel
… Communities: People and Places in the …
Billie Sandberg
Gender, Work and Organization
Adriana Kemp , Nitza Berkovitch
Revistas de Estudos e Pesquisas sobre as Américas
Vladimir Ferrari Puzone , Eduardo Altheman Camargo Santos
Marnie Holborow
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ABSTRACT OF THESIS ENTREPRENEURSHIP, INFORMATION, AND ECONOMIC GROWTH ... entrepreneur is an individual who takes an idea and turns it into economic knowledge. For example, the requisite pieces to produce a modern automobile were known prior to their mass production: carriages provided the basic form, gear-turning engines already ...
Essays on Entrepreneurship and Innovation Abstract These essays investigate the role of entrepreneurial human capital as a driver of innovation and growth. In the first chapter, I estimate the effect of manager education on firm employment growth using administrative panel data on the universe of firms in Portugal between 1995 and 2009.
Name of thesis THE ROLE OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP AS THE DRIVER OF ECONOMIC GROWTH Instructor Eija Torkinlampi Pages 40 + 4 Supervisor ... The write-up was inspired by a statement from the finance minister of Nigeria after National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) disclosed Nigeria economy was in a recession. Kemi Adeosun said the country was in "its worst
Entrepreneurship has three dimensions: the organizational, the environmental and the individual (Doll-inger 1995, 10-11). In this thesis, all the research aims to concentrate on the personality characteristics of an entrepreneur, so the focus of the research is going to be on the entrepreneur as an individual.
Master Thesis-Corporate Entrepreneurship and Innovation. Toma Martinkute Kian Skandarioon Page 11 Hereinafter we presented all these five factors that were described by different scholars to give general understanding how important these factors are in order to encourage higher level of EC of organization. 1.
A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirement of Staffordshire University for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Economics ... entrepreneurship and economic performance, the evidence is still not conclusive. Given the heterogeneity of results, methodological approaches and study
The significance of a well-defined thesis statement in crafting the perfect entrepreneurship thesis cannot be overstated within the comprehensive guide for entrepreneurship thesis for school work. The thesis statement serves as the compass that guides the entire research endeavor, providing a concise and clear expression of the central argument ...
Writing your Thesis in Strategic Entrepreneurship This version: March 8, 2016 . There are two ways to write your final thesis in Strategic Entrepreneurship. First, we regularly advertise topics on the website of the TUM Entrepreneurship Research Institute (TUM-ERI). Second, you may apply directly with us to write on your own topic.
AN ANALYSIS OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP EDUCATION (BIRMINGHAM BUSINESS SCHOOL 2007-2009) by Zacharias Prodromou A thesis submitted to The University of Birmingham ... Any use made of information contained in this thesis/dissertation must be in accordance with that legislation and must be properly acknowledged. Further
This paper presents a systematic review of (a) the impact of entrepreneurship on economic, social and environmental welfare and (b) the factors determining this impact. Research over the past 25 years shows that entrepreneurship is one cause of macroeconomic development, but that the relationship between entrepreneurship and welfare is very complex. The literature emphasizes that the generally ...
The theses are ordered into four groups on ontology (1&2), process (3, 4 & 5), learning (6, 7 & 8) and education (9, 10 & 11). The paper is deliberately short, as the 11 theses by themselves constitute the body text of the paper. For each of the theses a short argumentation is given in a footnote. The paper can be read in two ways.
Jean-Baptiste Say Institute for Entrepreneurship Chair of Entrepreneurship and Digital Innovation Prof. Dr. René Mauer ESCP Europe Berlin 1 Entrepreneurship Topics for Theses of Bachelor in Management Students April 2019 Supervisor Contact Thesis Topic Short Description of Topic Language Introductory Literature Professor René Mauer
Entrepreneurship, and Economic Development, I argue that the economic basis of entrepreneurship can be explained in the process of innovative production, in which individual entrepreneurs play a pivotal role in initializing the exchange of information and knowledge, thus, the reallocation of resources. In this theoretically orientated essay,
1.1 Background of the thesis. This thesis topic emerged from the author's own personal interest to make sense of the wide amount of entrepreneurship literature, concentrating especially on the studies of the entrepreneur as an individual. The author is interested in becoming an entrepreneur herself in the near future and the studies linked to ...
Jean-Baptiste Say Institute for Entrepreneurship Chair of Entrepreneurship and Digital Innovation Prof. Dr. René Mauer ESCP Europe Berlin 1 Entrepreneurship Topics for Master Programs´ Theses April 2019 Supervisor Contact Thesis Topic Short Description of Topic Language Introductory Literature Comment Program MiM MBA MISM SUSTM Professor ...
This thesis is concerned with how entrepreneurs' performance - the act of impression (Goffman, 1959a), is accomplished through emotion management - the work that an individual does to manage and display situation-appropriate feelings (Hochschild, 1983). There is literature that suggests that understanding entrepreneurs' emotion management ...
reducing the rate of unemployment. "Entrepreneurship education consists of three ingredients: creativity—creating all kinds of ideas; innovation—find value in selected ideas; and. entrepreneurship—develop a business from the innovative idea." (Nwekeaku, 2013, p. 53).
Abstract. This paper investigates whether national and entrepreneurial framework conditions positively affect economic growth via its effects on entrepreneurial activity more significantly than via its effects on technological innovation intensity1. The revised GEM conceptual model is tested for a sample of Nordic countries (Norway, Finland ...
Entrepreneurship Dissertation Topics. Topic 1: An investigation on the effects of technological advancement on entrepreneurship in a company. Topic 2: A case study to see how gender affects the development of entrepreneurial skills. Topic 3: An analysis of the impact of government policies on entrepreneurship in a specific country.
through entrepreneurship education programs to be proactive in defining professional projects [68-71]. In regions with low levels of entrepreneurship, high levels of poverty are found [72-74]. Moreover, these indexes justify an increasingly intense and collective commitment to promoting the spirit of initiative, entrepreneurial culture ...
E-mail: [email protected]. unanimously accepted definition of the entrepreneur or of the entrepreneurship process, the specialists agree over their importance in the economic development (Nagy et al., 2010). This study is aimed at identifying relevant concepts from literature relating to entrepreneurship and entrepre-neur.
Young entrepreneurs are affected by both an ideal sociality of entrepreneurial ecosystems and the small scale of their environment. This paper argues that while the former is promoted as a tool for strengthening local communities and a means of moving toward a prosperous future, the later prevents its actualization but provides security for ...
entrepreneurship, blurring sector boundaries, for-profit social enterprise, scaling social innovations, developing earned-income strategies, and the process of social entrepreneurship. She has also supervised, researched, written and edited several cases on social entrepreneurship and philanthropy. She received her M.B.A from Stanford
In this paper, the results of ten-year research on youth entrepreneurship are reviewed. In. this study 5670 participants - high school students, and university students from the Republic of ...