102 Intercultural Communication Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best intercultural communication topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on intercultural communication, 📌 most interesting intercultural communication topics to write about, ❓ questions about intercultural communication.
- 6 Barriers of Intercultural Communication Essay Cross cultural or intercultural communication is a part of the interaction of different people from different backgrounds and heritages. In this way, prejudice is inevitable blockage of cross-cultural communication as it is a source to […]
- Reasons for Not Appreciating Different Cultural Point of View One of the reasons why people may not appreciate the cultural point of view of others is because of the differences in cultural values.
- Diverse Contexts and Intercultural Communication at Work As the world moves to the global environment, the modern workplace becomes more and more diverse. When individuals are educated about intercultural differences are more likely to alter their communication styles to suit the needs […]
- The Role of Ethnocentrism in Intercultural Communication The only way to control ethnocentrism is to avoid biases as we find better ways to understand other people’s point of view.
- Ways to Improve Intercultural Communication There may be lack of understanding between the two parties because information may be misunderstood because of the preconceived beliefs about members of one’s cultural background which may not apply to the individual involved in […]
- Intercultural Communication Led by UNESCO The organization aspires to achieve universal respect for justice, the rule of law, human rights, and freedom for all the communities in the world.
- Intercultural Communication Patterns in the U.S. and UK Additionally, the concept of equality is notable in the American culture. Contrastingly, in the American culture, people are more casual and less formal compared to Britons.
- Efficient Intercultural Interaction and Communication This way, they will be able to learn the different languages and this is important for communication and good co-existence in the societies. The kind or number of affiliations that a person may have with […]
- Challenges of Effective Intercultural Communication Inter-cultural communications professionals work with global firms to play down the aforementioned results of poor inter-cultural understanding. Lingual acquaintance serves to bridge the cultural bridges and evening lines of communication.
- The Effect of Global Technology on Intercultural Communication Global technology allows for open access to a wealth of information, resources, and influence that can encourage change in cultures and societies.
- Interpersonal and Intercultural Communication in the UAE Since the business and cultural links established between the UAE and other states are crucial for the process of the states’ development, it is highly required that the root causes of intercultural and intracultural conflicts […]
- Intercultural Communication Barriers There is absolutely no way through which one is able to learn all the norms of every culture and their sub-culture all in a bid to understand the various barriers to intercultural communication.
- Franco-Italian Intercultural Communication As a result, collective approaches to the problems created by their uprooting and by the necessity of adjusting to the new society tend to be organized along village lines, or at best on the basis […]
- Intercultural Communication Perspectives These include the definition of intercultural communication and an overview of the contents involved in teaching it; it also provides a brief overview of personal experience as a teacher in an intercultural learning institution.
- Fundamentals of Intercultural Communication This education is one that derived from the cultural point of view of the society and hence the early childhood education strove to inculcate this sense in the young minds.
- Religion in Intercultural Communication The main political message in the scripture explains God’s role as the creator and master of everything in the universe. The excerpt is generally acknowledged as one of the most important verses in the sacred […]
- Personal Worldview and Intercultural Communications God sacrificed Jesus to wash the sins of people and get rid of the iniquities and curses on the earth. From a Christian worldview, I could easily identify topics and teachings of the Christian religion […]
- Effects of the Language Barrier on Intercultural Communication This paper will argue for some of the major problems of language barriers in the context of intercultural communication, highlighting the severity of the issue and its effect on the practice.
- Face Concept in Chinese Culture: A Complication to Intercultural Communication One of the concepts of face in Chinese culture is that of losing face. This paper set out to argue that the concept of face in Chinese culture complicates intercultural communication.
- Intercultural and International Differences in Professional Communication On the other hand, the Americans communication culture is comprised of verbal communication. In this case, the Taiwanese culture is the high context culture while Americans is the low context culture.
- Inter-Cultural Communication Skills in Career Goal at the Contemporary Workplace It will be necessary for me to use emotional intelligence, for example in a scenario where the customer was mean or rude to one of my graphic designers’ due to dissatisfaction, it will be imperative […]
- Intercultural Communication in Contexts: Chapters Review As it is clear in this chapter, one of the ways by which the two differ from each other is that; nonverbal communication which includes the use of facial expressions, gestures, and proxemics among other […]
- Intercultural Communication in Business For an organization to be successful in the global market, leaders must conduct extensive research and fully understand the cultural and social values of the foreign country.
- Intercultural Communication: Self-Awareness’ Importance However, to understand it, a person must be able to connect to the lives of others and to observe these processes in other people.
- Intercultural Communication Principles In other words, if good interpersonal and international relationships are not managed through intercultural communication, there is no possibility of gaining benefits from all other areas.
- Australian Education and Intercultural Communication Australian education is among the best globally, offering quality education that has led to the growth and development of the nation socially, culturally, and economically.
- The Engagement of Christian Intercultural Communication Therefore, the text generally provides the comparison between the Christian Intercultural Communication in the missionaries and theologians concerning the intercultural Communication and its impact on the fulfillment of the great commission.
- Understanding Intercultural Communication by Ting-Toomey and Leeva Christianity in the North American and European tradition has a hard-hitting history of Christian colonialism, when the faith was imposed on the inhabitants of the territories of the occupied countries, with the belittling of the […]
- Intercultural Communication in Chinese Business Despite the accelerating processes of globalization, the diversity of cultures still obliges people to be familiar with values and customs in advance to create the best and most delicate communication channel.
- Importance of Understanding Intercultural Communication Therefore, understanding the customs and culture of the people you engage with is crucial for effective communication. In conclusion, it is vital to learn the customs of other nations because it ensures effective communication.
- The Importance of Intercultural Communication Engaging in dual perspectives is among the concepts I would apply to improve communication of my ideas and needs to the Chinese friend.
- Local Community and Intercultural Communication: Helping Immigrants I will organize community events and invite both local members of the church and the immigrants in order to create a safe environment for them to meet.
- Limitations in Intercultural Communication The main barriers that reduce the effectiveness of interactions are the differences in cognitive schemes used by representatives of different cultures 1.
- Intercultural Communication and Healthcare Delivery: Cranford Population The racial composition of the Cranford population shows that it comprises of different races, which implies that cultural communication is essential in the delivery of healthcare services.
- Relationship Between Ethnocentrism and Intercultural Communication The scaling for the questions administered ranged from 1 to 5; a score with a mean of 1 showed a low level of ethnocentrism, while a score with a mean of 5 showed a higher […]
- Intercultural Communication Campaign: Asian Students’ Reticence Issues The given communication campaign will primarily focus on the issues of reticence among Asian international students through the socio-centric and non-argumentative approaches.
- Intercultural and Cross-Cultural Communication It examines Agar’s specific approach to the notion of culture, the preconditions for intercultural breakdowns, and the appropriate solution to prevent them.
- Effective Intercultural Communication Culture is collective programming, a system of meanings and notions, which are shared between the members of one culture group and are used to construe the world around them.
- Intercultural Communication, Culture Shock and Immigration in Literature Westerners on the other hand believe in individualism so much that they forget that harmonious living is important for personal and society’s development.
- Intercultural Communication Attitudes It’s important to take into account cultural differences to make intercultural teams effective. It’s also necessary to pay attention to gender, age, and socioeconomic status.
- Intercultural Communication: Aspects In order to fulfill my interests, I always ensure that I make good use of every opportunity I get by interacting a lot with the people I meet.
- Intercultural Communication in the Workplace For this to happen, both men and women do not have to be in a relationship as it happens in many cases. In business matters, it is very significant to appreciate the morals and customs […]
- Intercultural Communication in the Global Workplace This intercultural communication can be defined as the process which involves a combination of various skills, knowledge plus the combination of theoretical insights in trying to exchange meaningful and unambiguous information across the cultural boundaries […]
- Personal Worldview and Intercultural Communication Since I believe that living according to the word is the only right thing to do, I tend to disregard other people’s cultures because, in my view, my culture is right and other people’s cultures […]
- Reducing Intercultural Communication Barriers To reduce the above challenges, I must be aware of the barriers, be empathetic, pay careful attention to communication cues, and always verify with the receiver that I have understood his or her response. Academically, […]
- Intercultural Communication as Practiced in the US There are certain patterns of nonverbal behavior disclosing a particular communicative idea, but there are cases when it is impossible to display those patterns successfully. Therefore, it is much harder to conceal nonverbal signals that […]
- Intercultural Communication in the Arabian Gulf Region The concept of intercultural communication is particularly important to the countries in the Arabian Gulf where the rate of cultural diversity is at an all time high.
- Intercultural Communication Sensitivity Against Ethnocentrism While examining the ethnocentric limitations of the humanistic theory, it is necessary to consider the theoretical concept of ethnocentrism in detail.
- Intercultural Communication in the Series “Tyrant” Caught up in the middle of a revolt against the ruling family, he loses his father, who died during the coup, and is forced to help his brother and the new president to overcome the […]
- Intercultural Business Communication Approaches This section assesses Hofstede’s research and arguments in support of the validity and reliability of his research. Hofstede’s research on culture is the most extensive and widely referenced.
- Business and Intercultural Communication The ability to communicate in a business environment might be hindered by the following factors that are not typical for less formal communication: workforce diversity, the pervasiveness of technology, the complexity of the organizational structures, […]
- Culture Shock and Intercultural Communication The challenges of mistreatment of women and religious orientations can be addressed by conducting workshops and trainings aimed at assisting expatriate employees to develop adequate cultural competence on how to deal with culturally diverse others […]
- Intercultural Communication in Contexts: Fifth Edition Review Another aspect of language to consider is the evolvement of technology in the digital age and the emergence of online communication.
- Intercultural Communication: Identity and Relationships The other position is the relativist, which provides that the language, which a person speaks, determines the perception of that particular person on different issues in life.
- Intercultural Communication in the Business World In the context of the case study, one of the mistakes Clyde made was the failure to take time to learn about the culture of Senseyans before interacting with them.
- Intercultural Communication in “Gran Torino” Movie However, it is also quite peculiar that the scene in question allows viewing the issue of the culture clash on so many different levels; specifically, the fact that the conflict occurs not only between an […]
- Intercultural Communication: Different Aspects Discussing the main aspects of the inter-cultural communication, Carol Myers-Scotton focuses on the role of globalisation in the process, on differences between collectivistic and individualistic cultures which influence the particular features of the representatives’ communication, […]
- Intercultural Communication: Workers From Diverse Backgrounds Verderber and Verderber allege that communication is quite intricate in multinational organizations due to a diverse body of workers with distinct educational, cultural, and social backgrounds.
- Computer Mediated Interpersonal and Intercultural Communication Despite the fact that social media clearly poses a tangible threat to the culture of live communication and, therefore, will contribute to the shriveling of people’s social skills, computer mediated interpersonal and intercultural communication will […]
- Intercultural Communication: Stereotypes and Perspectives Finally, it is possible to say that being a rather complicated issue; communication also has a great number of different prejudices connected with the culture of people and their behavior.
- International and Intercultural Communication On the masculinity and femininity dimension, the scores of the two countries are 62 for the United States and 40 for Tanzania.
- Intercultural Interaction and Communication Plan: Merced, CA The documents help to inform the school and students about the changes in education and ensure communities and parents participate in the process of learning.
- Intercultural Communication and Success at Work Such people have limited abilities to consider alternative behaviours in processes of interpersonal communications that involve different cultures. Such forms of cross-cultural communications are difficult and may lead to interpersonal conflicts in communications.
- Intercultural Communication in Management The managers should, therefore, ensure that the process of communication satisfies these different needs to ensure that they are all aware of their role in the organization and in the implementation of the new strategy.
- Interpersonal and Intercultural Communication at the Workplace The interview was explained to the reasons of the interview and the need for the specific information being searched for. The key concept to retain in communication, is that no one component of communication – […]
- Kinesics and Proxemics in Intercultural Negotiations There are a myriad of kinesics and it will be hard for the US Company to learn all of the applicable kinesics when relating to the Japanese people.
- Intercultural Communication in Society Unlike other people in New Jersey, Alexander Mathew has a friendly attitude towards tourists, as he likes sharing his cultural beliefs and traditions with different people.
- Intercultural Communication Experiences: Interview With an Immigrant Sheik Omar is an immigrant to the United States and lives in the Atlantic City, New Jersey. The writer thought that Sheik Omar has adopted American culture since he has lived in the United States […]
- Language and Culture: Language Acquisition The process of the first language acquisition is considered to be a psycholinguistic process, while the second language acquisition is the area for study for linguists.
- Martin and Nakayama: Intercultural Communication in Contexts In their book, the authors reveal to the readers that there are two types of nonverbal communication. To this end, they state that motivation, knowledge, attitude and behavior are the major components for facilitating intercultural […]
- Intercultural Communication in Various Contexts Code switching practices have led countries to declare the official languages in a country in order to promote the assimilation of the people in the country.
- Fundamentals of Intercultural Communication Unlike other minority groups in Europe, the Jews face more segregation owing to the stereotype created about them in reference to the past association with the communities there, particularly, Germany and Austria, countries that were […]
- “Intercultural Communication in Business Ventures” Article Study Upon determining the market potential in the international market, it is critical for firms’ management teams to evaluate the various factors that would be necessary in the exploitation of the market opportunities.
- Islamic Living: Effective Cross-Cultural Communication It is not possible to separate Islam as a religion and the way one who professes the faith lives because it has been said to be a way of life.
- Intercultural Business and Legal Communication Additionally, the scholarly critique shall attempt to identify the goals of the article and the key theories and concepts used and whether are not these theories and concepts achieved the goals of the article. The […]
- Cross Cultural Communications in the Globalized World Among the cultures that have always been in conflict are the Islamic culture and the American culture. Assimilation in the American and Islamic cultures is desirable if effective communication is to occur between adherents of […]
- What Are Some Examples of Intercultural Communication?
- How Can Barriers to Intercultural Communication Be Overcome?
- What Are the Types of Intercultural Communication?
- How Does Poor Intercultural Communication Affect International Commerce and Foreign Policy?
- How Do We Deal With Intercultural Communication?
- What Are Some Intercultural Communication Problems?
- What Are Intercultural Communication Skills?
- What Is Intercultural Communication and Examples?
- What Makes Intercultural Communication Essential in the Process of Globalization?
- What Is Intercultural Communication, and Why Is It Important?
- Why Is It Important to Think Beyond Ourselves as Individuals in Intercultural Interaction?
- How Does Poor Intercultural Communication Affects International?
- What Are the Four Forms of Intercultural Communication?
- What Is the Other Name for Intercultural Communication?
- What Is the Role of Intercultural Communication in Work-Life?
- What Are the Three Challenges of Intercultural Communication?
- Why Do We Need to Understand Intercultural Communication?
- How Important Is Intercultural Communication to Our Society?
- What Makes for Good Intercultural Communication?
- What Are the Four Elements of Intercultural Communication?
- What Role Does Intercultural Communication Play in Achieving Effective Communication?
- What Is the Difference Between Cultural and Intercultural?
- What Are the Six Dichotomies of Intercultural Communication?
- What Are the Challenges of Intercultural Communication?
- What Is the Meaning of Intercultural?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 28). 102 Intercultural Communication Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/
"102 Intercultural Communication Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 28 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '102 Intercultural Communication Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 28 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "102 Intercultural Communication Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "102 Intercultural Communication Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "102 Intercultural Communication Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." February 28, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/.
- Bilingual Education Essay Ideas
- Immigration Titles
- Cross-Cultural Management Research Topics
- Globalization Essay Topics
- Corporate Communication Questions
- International Studies Ideas
- Ethnocentrism Topics
- Information Management Paper Topics

Research Topics in Intercultural Interaction
Cite this chapter.

- Helen Spencer-Oatey 3 &
- Peter Franklin 4
Part of the book series: Research and Practice in Applied Linguistics ((RPAL))
923 Accesses
This chapter and the next focus on research into intercultural interaction. In this chapter, we outline some key research topics, and sample studies, associated with the various issues explored in Parts 1 and 2. In the next chapter, we explore the steps involved in carrying out a research project, and discuss the ways in which cultural factors need to be taken into consideration in relation to each of them.
A sense of curiosity is nature’s original school of education. Smiley Blanton
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Warwick, UK
Helen Spencer-Oatey
HTWG Konstanz University of Applied Sciences, Germany
Peter Franklin
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Copyright information
© 2009 Helen Spencer-Oatey and Peter Franklin
About this chapter
Spencer-Oatey, H., Franklin, P. (2009). Research Topics in Intercultural Interaction. In: Intercultural Interaction. Research and Practice in Applied Linguistics. Palgrave Macmillan, London. https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230244511_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230244511_10
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, London
Print ISBN : 978-1-4039-8631-3
Online ISBN : 978-0-230-24451-1
eBook Packages : Palgrave Language & Linguistics Collection Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Frontiers in Communication
- Culture and Communication
- Research Topics
Intercultural Communication and International Students
Total Downloads
Total Views and Downloads
About this Research Topic
With internationalization high on the agenda of education providers worldwide, the complex relationship between intercultural communication and the international student phenomenon deserves close study. Being an international student is a great opportunity to be exposed to a new language and culture ...
Keywords : international students, student experience, teaching and learning, intercultural interaction, internationalization, empowement
Important Note : All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review.
Topic Editors
Topic coordinators, recent articles, submission deadlines, participating journals.
Manuscripts can be submitted to this Research Topic via the following journals:
total views
- Demographics
No records found
total views article views downloads topic views
Top countries
Top referring sites, about frontiers research topics.
With their unique mixes of varied contributions from Original Research to Review Articles, Research Topics unify the most influential researchers, the latest key findings and historical advances in a hot research area! Find out more on how to host your own Frontiers Research Topic or contribute to one as an author.
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
Pathways of intercultural communication research. How different research communities of communication scholars deal with the topic of intercultural communication
The following article deals with intercultural communication research as a (potential) subfield of communication studies. The broader aim is to contribute to the history as well as to the systematization of the field of intercultural communication research. The author is mapping three very different national research communities: Germany, France and the US. The main question is: Why, in each of the countries under comparison, do communication studies deal so differently with the subject of intercultural communication as a research topic and/or field? The methodology is comparative and focuses on the differences and similarities in the three national communities of communication studies and research. Both the German and the French communication researchers look closely (but again differently and completely in ignorance of each other) at US research. It appears that research traditions and general trends of mainstreaming in communication studies are highly influential as gatekeepers or barriers to intercultural communication research as a subfield of communication studies.
©2013 Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin Boston
- X / Twitter
Supplementary Materials
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.
Journal and Issue
Articles in the same issue.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8.3 Intercultural Communication
Learning objectives.
- Define intercultural communication.
- List and summarize the six dialectics of intercultural communication.
- Discuss how intercultural communication affects interpersonal relationships.
It is through intercultural communication that we come to create, understand, and transform culture and identity. Intercultural communication is communication between people with differing cultural identities. One reason we should study intercultural communication is to foster greater self-awareness (Martin & Nakayama, 2010). Our thought process regarding culture is often “other focused,” meaning that the culture of the other person or group is what stands out in our perception. However, the old adage “know thyself” is appropriate, as we become more aware of our own culture by better understanding other cultures and perspectives. Intercultural communication can allow us to step outside of our comfortable, usual frame of reference and see our culture through a different lens. Additionally, as we become more self-aware, we may also become more ethical communicators as we challenge our ethnocentrism , or our tendency to view our own culture as superior to other cultures.
As was noted earlier, difference matters, and studying intercultural communication can help us better negotiate our changing world. Changing economies and technologies intersect with culture in meaningful ways (Martin & Nakayama). As was noted earlier, technology has created for some a global village where vast distances are now much shorter due to new technology that make travel and communication more accessible and convenient (McLuhan, 1967). However, as the following “Getting Plugged In” box indicates, there is also a digital divide , which refers to the unequal access to technology and related skills that exists in much of the world. People in most fields will be more successful if they are prepared to work in a globalized world. Obviously, the global market sets up the need to have intercultural competence for employees who travel between locations of a multinational corporation. Perhaps less obvious may be the need for teachers to work with students who do not speak English as their first language and for police officers, lawyers, managers, and medical personnel to be able to work with people who have various cultural identities.
“Getting Plugged In”
The Digital Divide
Many people who are now college age struggle to imagine a time without cell phones and the Internet. As “digital natives” it is probably also surprising to realize the number of people who do not have access to certain technologies. The digital divide was a term that initially referred to gaps in access to computers. The term expanded to include access to the Internet since it exploded onto the technology scene and is now connected to virtually all computing (van Deursen & van Dijk, 2010). Approximately two billion people around the world now access the Internet regularly, and those who don’t face several disadvantages (Smith, 2011). Discussions of the digital divide are now turning more specifically to high-speed Internet access, and the discussion is moving beyond the physical access divide to include the skills divide, the economic opportunity divide, and the democratic divide. This divide doesn’t just exist in developing countries; it has become an increasing concern in the United States. This is relevant to cultural identities because there are already inequalities in terms of access to technology based on age, race, and class (Sylvester & McGlynn, 2010). Scholars argue that these continued gaps will only serve to exacerbate existing cultural and social inequalities. From an international perspective, the United States is falling behind other countries in terms of access to high-speed Internet. South Korea, Japan, Sweden, and Germany now all have faster average connection speeds than the United States (Smith, 2011). And Finland in 2010 became the first country in the world to declare that all its citizens have a legal right to broadband Internet access (ben-Aaron, 2010). People in rural areas in the United States are especially disconnected from broadband service, with about 11 million rural Americans unable to get the service at home. As so much of our daily lives go online, it puts those who aren’t connected at a disadvantage. From paying bills online, to interacting with government services, to applying for jobs, to taking online college classes, to researching and participating in political and social causes, the Internet connects to education, money, and politics.
- What do you think of Finland’s inclusion of broadband access as a legal right? Is this something that should be done in other countries? Why or why not?
- How does the digital divide affect the notion of the global village?
- How might limited access to technology negatively affect various nondominant groups?
Intercultural Communication: A Dialectical Approach
Intercultural communication is complicated, messy, and at times contradictory. Therefore it is not always easy to conceptualize or study. Taking a dialectical approach allows us to capture the dynamism of intercultural communication. A dialectic is a relationship between two opposing concepts that constantly push and pull one another (Martin & Nakayama, 2010). To put it another way, thinking dialectically helps us realize that our experiences often occur in between two different phenomena. This perspective is especially useful for interpersonal and intercultural communication, because when we think dialectically, we think relationally. This means we look at the relationship between aspects of intercultural communication rather than viewing them in isolation. Intercultural communication occurs as a dynamic in-betweenness that, while connected to the individuals in an encounter, goes beyond the individuals, creating something unique. Holding a dialectical perspective may be challenging for some Westerners, as it asks us to hold two contradictory ideas simultaneously, which goes against much of what we are taught in our formal education. Thinking dialectically helps us see the complexity in culture and identity because it doesn’t allow for dichotomies. Dichotomies are dualistic ways of thinking that highlight opposites, reducing the ability to see gradations that exist in between concepts. Dichotomies such as good/evil, wrong/right, objective/subjective, male/female, in-group/out-group, black/white, and so on form the basis of much of our thoughts on ethics, culture, and general philosophy, but this isn’t the only way of thinking (Marin & Nakayama, 1999). Many Eastern cultures acknowledge that the world isn’t dualistic. Rather, they accept as part of their reality that things that seem opposite are actually interdependent and complement each other. I argue that a dialectical approach is useful in studying intercultural communication because it gets us out of our comfortable and familiar ways of thinking. Since so much of understanding culture and identity is understanding ourselves, having an unfamiliar lens through which to view culture can offer us insights that our familiar lenses will not. Specifically, we can better understand intercultural communication by examining six dialectics (see Figure 8.1 “Dialectics of Intercultural Communication” ) (Martin & Nakayama, 1999).
Figure 8.1 Dialectics of Intercultural Communication
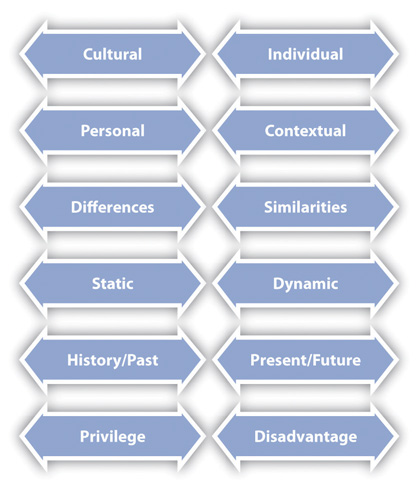
Source: Adapted from Judith N. Martin and Thomas K. Nakayama, “Thinking Dialectically about Culture and Communication,” Communication Theory 9, no. 1 (1999): 1–25.
The cultural-individual dialectic captures the interplay between patterned behaviors learned from a cultural group and individual behaviors that may be variations on or counter to those of the larger culture. This dialectic is useful because it helps us account for exceptions to cultural norms. For example, earlier we learned that the United States is said to be a low-context culture, which means that we value verbal communication as our primary, meaning-rich form of communication. Conversely, Japan is said to be a high-context culture, which means they often look for nonverbal clues like tone, silence, or what is not said for meaning. However, you can find people in the United States who intentionally put much meaning into how they say things, perhaps because they are not as comfortable speaking directly what’s on their mind. We often do this in situations where we may hurt someone’s feelings or damage a relationship. Does that mean we come from a high-context culture? Does the Japanese man who speaks more than is socially acceptable come from a low-context culture? The answer to both questions is no. Neither the behaviors of a small percentage of individuals nor occasional situational choices constitute a cultural pattern.
The personal-contextual dialectic highlights the connection between our personal patterns of and preferences for communicating and how various contexts influence the personal. In some cases, our communication patterns and preferences will stay the same across many contexts. In other cases, a context shift may lead us to alter our communication and adapt. For example, an American businesswoman may prefer to communicate with her employees in an informal and laid-back manner. When she is promoted to manage a department in her company’s office in Malaysia, she may again prefer to communicate with her new Malaysian employees the same way she did with those in the United States. In the United States, we know that there are some accepted norms that communication in work contexts is more formal than in personal contexts. However, we also know that individual managers often adapt these expectations to suit their own personal tastes. This type of managerial discretion would likely not go over as well in Malaysia where there is a greater emphasis put on power distance (Hofstede, 1991). So while the American manager may not know to adapt to the new context unless she has a high degree of intercultural communication competence, Malaysian managers would realize that this is an instance where the context likely influences communication more than personal preferences.
The differences-similarities dialectic allows us to examine how we are simultaneously similar to and different from others. As was noted earlier, it’s easy to fall into a view of intercultural communication as “other oriented” and set up dichotomies between “us” and “them.” When we overfocus on differences, we can end up polarizing groups that actually have things in common. When we overfocus on similarities, we essentialize , or reduce/overlook important variations within a group. This tendency is evident in most of the popular, and some of the academic, conversations regarding “gender differences.” The book Men Are from Mars and Women Are from Venus makes it seem like men and women aren’t even species that hail from the same planet. The media is quick to include a blurb from a research study indicating again how men and women are “wired” to communicate differently. However, the overwhelming majority of current research on gender and communication finds that while there are differences between how men and women communicate, there are far more similarities (Allen, 2011). Even the language we use to describe the genders sets up dichotomies. That’s why I suggest that my students use the term other gender instead of the commonly used opposite sex . I have a mom, a sister, and plenty of female friends, and I don’t feel like any of them are the opposite of me. Perhaps a better title for a book would be Women and Men Are Both from Earth .
The static-dynamic dialectic suggests that culture and communication change over time yet often appear to be and are experienced as stable. Although it is true that our cultural beliefs and practices are rooted in the past, we have already discussed how cultural categories that most of us assume to be stable, like race and gender, have changed dramatically in just the past fifty years. Some cultural values remain relatively consistent over time, which allows us to make some generalizations about a culture. For example, cultures have different orientations to time. The Chinese have a longer-term orientation to time than do Europeans (Lustig & Koester, 2006). This is evidenced in something that dates back as far as astrology. The Chinese zodiac is done annually (The Year of the Monkey, etc.), while European astrology was organized by month (Taurus, etc.). While this cultural orientation to time has been around for generations, as China becomes more Westernized in terms of technology, business, and commerce, it could also adopt some views on time that are more short term.
The history/past-present/future dialectic reminds us to understand that while current cultural conditions are important and that our actions now will inevitably affect our future, those conditions are not without a history. We always view history through the lens of the present. Perhaps no example is more entrenched in our past and avoided in our present as the history of slavery in the United States. Where I grew up in the Southern United States, race was something that came up frequently. The high school I attended was 30 percent minorities (mostly African American) and also had a noticeable number of white teens (mostly male) who proudly displayed Confederate flags on their clothing or vehicles.
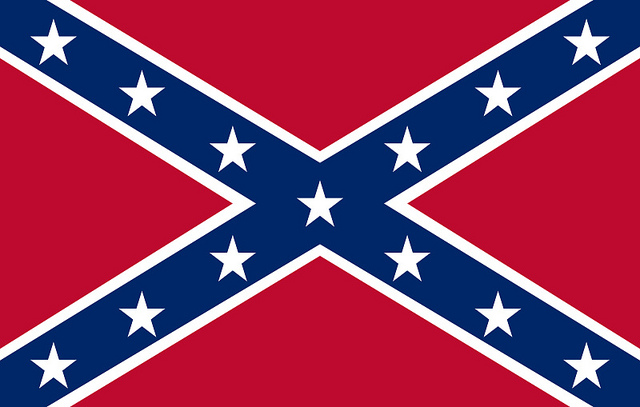

There has been controversy over whether the Confederate flag is a symbol of hatred or a historical symbol that acknowledges the time of the Civil War.
Jim Surkamp – Confederate Rebel Flag – CC BY-NC 2.0.
I remember an instance in a history class where we were discussing slavery and the subject of repatriation, or compensation for descendants of slaves, came up. A white male student in the class proclaimed, “I’ve never owned slaves. Why should I have to care about this now?” While his statement about not owning slaves is valid, it doesn’t acknowledge that effects of slavery still linger today and that the repercussions of such a long and unjust period of our history don’t disappear over the course of a few generations.
The privileges-disadvantages dialectic captures the complex interrelation of unearned, systemic advantages and disadvantages that operate among our various identities. As was discussed earlier, our society consists of dominant and nondominant groups. Our cultures and identities have certain privileges and/or disadvantages. To understand this dialectic, we must view culture and identity through a lens of intersectionality , which asks us to acknowledge that we each have multiple cultures and identities that intersect with each other. Because our identities are complex, no one is completely privileged and no one is completely disadvantaged. For example, while we may think of a white, heterosexual male as being very privileged, he may also have a disability that leaves him without the able-bodied privilege that a Latina woman has. This is often a difficult dialectic for my students to understand, because they are quick to point out exceptions that they think challenge this notion. For example, many people like to point out Oprah Winfrey as a powerful African American woman. While she is definitely now quite privileged despite her disadvantaged identities, her trajectory isn’t the norm. When we view privilege and disadvantage at the cultural level, we cannot let individual exceptions distract from the systemic and institutionalized ways in which some people in our society are disadvantaged while others are privileged.
As these dialectics reiterate, culture and communication are complex systems that intersect with and diverge from many contexts. A better understanding of all these dialectics helps us be more critical thinkers and competent communicators in a changing world.
“Getting Critical”
Immigration, Laws, and Religion
France, like the United States, has a constitutional separation between church and state. As many countries in Europe, including France, Belgium, Germany, the Netherlands, and Sweden, have experienced influxes of immigrants, many of them Muslim, there have been growing tensions among immigration, laws, and religion. In 2011, France passed a law banning the wearing of a niqab (pronounced knee-cobb ), which is an Islamic facial covering worn by some women that only exposes the eyes. This law was aimed at “assimilating its Muslim population” of more than five million people and “defending French values and women’s rights” (De La Baume & Goodman, 2011). Women found wearing the veil can now be cited and fined $150 euros. Although the law went into effect in April of 2011, the first fines were issued in late September of 2011. Hind Ahmas, a woman who was fined, says she welcomes the punishment because she wants to challenge the law in the European Court of Human Rights. She also stated that she respects French laws but cannot abide by this one. Her choice to wear the veil has been met with more than a fine. She recounts how she has been denied access to banks and other public buildings and was verbally harassed by a woman on the street and then punched in the face by the woman’s husband. Another Muslim woman named Kenza Drider, who can be seen in Video Clip 8.2, announced that she will run for the presidency of France in order to challenge the law. The bill that contained the law was broadly supported by politicians and the public in France, and similar laws are already in place in Belgium and are being proposed in Italy, Austria, the Netherlands, and Switzerland (Fraser, 2011).
- Some people who support the law argue that part of integrating into Western society is showing your face. Do you agree or disagree? Why?
- Part of the argument for the law is to aid in the assimilation of Muslim immigrants into French society. What are some positives and negatives of this type of assimilation?
- Identify which of the previously discussed dialectics can be seen in this case. How do these dialectics capture the tensions involved?
Video Clip 8.2
Veiled Woman Eyes French Presidency
(click to see video)
Intercultural Communication and Relationships
Intercultural relationships are formed between people with different cultural identities and include friends, romantic partners, family, and coworkers. Intercultural relationships have benefits and drawbacks. Some of the benefits include increasing cultural knowledge, challenging previously held stereotypes, and learning new skills (Martin & Nakayama, 2010). For example, I learned about the Vietnamese New Year celebration Tet from a friend I made in graduate school. This same friend also taught me how to make some delicious Vietnamese foods that I continue to cook today. I likely would not have gained this cultural knowledge or skill without the benefits of my intercultural friendship. Intercultural relationships also present challenges, however.
The dialectics discussed earlier affect our intercultural relationships. The similarities-differences dialectic in particular may present challenges to relationship formation (Martin & Nakayama, 2010). While differences between people’s cultural identities may be obvious, it takes some effort to uncover commonalities that can form the basis of a relationship. Perceived differences in general also create anxiety and uncertainty that is not as present in intracultural relationships. Once some similarities are found, the tension within the dialectic begins to balance out and uncertainty and anxiety lessen. Negative stereotypes may also hinder progress toward relational development, especially if the individuals are not open to adjusting their preexisting beliefs. Intercultural relationships may also take more work to nurture and maintain. The benefit of increased cultural awareness is often achieved, because the relational partners explain their cultures to each other. This type of explaining requires time, effort, and patience and may be an extra burden that some are not willing to carry. Last, engaging in intercultural relationships can lead to questioning or even backlash from one’s own group. I experienced this type of backlash from my white classmates in middle school who teased me for hanging out with the African American kids on my bus. While these challenges range from mild inconveniences to more serious repercussions, they are important to be aware of. As noted earlier, intercultural relationships can take many forms. The focus of this section is on friendships and romantic relationships, but much of the following discussion can be extended to other relationship types.
Intercultural Friendships
Even within the United States, views of friendship vary based on cultural identities. Research on friendship has shown that Latinos/as value relational support and positive feedback, Asian Americans emphasize exchanges of ideas like offering feedback or asking for guidance, African Americans value respect and mutual acceptance, and European Americans value recognition of each other as individuals (Coller, 1996). Despite the differences in emphasis, research also shows that the overall definition of a close friend is similar across cultures. A close friend is thought of as someone who is helpful and nonjudgmental, who you enjoy spending time with but can also be independent, and who shares similar interests and personality traits (Lee, 2006).
Intercultural friendship formation may face challenges that other friendships do not. Prior intercultural experience and overcoming language barriers increase the likelihood of intercultural friendship formation (Sias et al., 2008). In some cases, previous intercultural experience, like studying abroad in college or living in a diverse place, may motivate someone to pursue intercultural friendships once they are no longer in that context. When friendships cross nationality, it may be necessary to invest more time in common understanding, due to language barriers. With sufficient motivation and language skills, communication exchanges through self-disclosure can then further relational formation. Research has shown that individuals from different countries in intercultural friendships differ in terms of the topics and depth of self-disclosure, but that as the friendship progresses, self-disclosure increases in depth and breadth (Chen & Nakazawa, 2009). Further, as people overcome initial challenges to initiating an intercultural friendship and move toward mutual self-disclosure, the relationship becomes more intimate, which helps friends work through and move beyond their cultural differences to focus on maintaining their relationship. In this sense, intercultural friendships can be just as strong and enduring as other friendships (Lee, 2006).
The potential for broadening one’s perspective and learning more about cultural identities is not always balanced, however. In some instances, members of a dominant culture may be more interested in sharing their culture with their intercultural friend than they are in learning about their friend’s culture, which illustrates how context and power influence friendships (Lee, 2006). A research study found a similar power dynamic, as European Americans in intercultural friendships stated they were open to exploring everyone’s culture but also communicated that culture wasn’t a big part of their intercultural friendships, as they just saw their friends as people. As the researcher states, “These types of responses may demonstrate that it is easiest for the group with the most socioeconomic and socio-cultural power to ignore the rules, assume they have the power as individuals to change the rules, or assume that no rules exist, since others are adapting to them rather than vice versa” (Collier, 1996). Again, intercultural friendships illustrate the complexity of culture and the importance of remaining mindful of your communication and the contexts in which it occurs.
Culture and Romantic Relationships
Romantic relationships are influenced by society and culture, and still today some people face discrimination based on who they love. Specifically, sexual orientation and race affect societal views of romantic relationships. Although the United States, as a whole, is becoming more accepting of gay and lesbian relationships, there is still a climate of prejudice and discrimination that individuals in same-gender romantic relationships must face. Despite some physical and virtual meeting places for gay and lesbian people, there are challenges for meeting and starting romantic relationships that are not experienced for most heterosexual people (Peplau & Spalding, 2000).
As we’ve already discussed, romantic relationships are likely to begin due to merely being exposed to another person at work, through a friend, and so on. But some gay and lesbian people may feel pressured into or just feel more comfortable not disclosing or displaying their sexual orientation at work or perhaps even to some family and friends, which closes off important social networks through which most romantic relationships begin. This pressure to refrain from disclosing one’s gay or lesbian sexual orientation in the workplace is not unfounded, as it is still legal in twenty-nine states (as of November 2012) to fire someone for being gay or lesbian (Human Rights Campaign, 2012). There are also some challenges faced by gay and lesbian partners regarding relationship termination. Gay and lesbian couples do not have the same legal and societal resources to manage their relationships as heterosexual couples; for example, gay and lesbian relationships are not legally recognized in most states, it is more difficult for a gay or lesbian couple to jointly own property or share custody of children than heterosexual couples, and there is little public funding for relationship counseling or couples therapy for gay and lesbian couples.
While this lack of barriers may make it easier for gay and lesbian partners to break out of an unhappy or unhealthy relationship, it could also lead couples to termination who may have been helped by the sociolegal support systems available to heterosexuals (Peplau & Spalding, 2000).
Despite these challenges, relationships between gay and lesbian people are similar in other ways to those between heterosexuals. Gay, lesbian, and heterosexual people seek similar qualities in a potential mate, and once relationships are established, all these groups experience similar degrees of relational satisfaction (Peplau & Spalding, 2000). Despite the myth that one person plays the man and one plays the woman in a relationship, gay and lesbian partners do not have set preferences in terms of gender role. In fact, research shows that while women in heterosexual relationships tend to do more of the housework, gay and lesbian couples were more likely to divide tasks so that each person has an equal share of responsibility (Peplau & Spalding, 2000). A gay or lesbian couple doesn’t necessarily constitute an intercultural relationship, but as we have already discussed, sexuality is an important part of an individual’s identity and connects to larger social and cultural systems. Keeping in mind that identity and culture are complex, we can see that gay and lesbian relationships can also be intercultural if the partners are of different racial or ethnic backgrounds.
While interracial relationships have occurred throughout history, there have been more historical taboos in the United States regarding relationships between African Americans and white people than other racial groups. Antimiscegenation laws were common in states and made it illegal for people of different racial/ethnic groups to marry. It wasn’t until 1967 that the Supreme Court ruled in the case of Loving versus Virginia , declaring these laws to be unconstitutional (Pratt, 1995). It wasn’t until 1998 and 2000, however, that South Carolina and Alabama removed such language from their state constitutions (Lovingday.org, 2011). The organization and website lovingday.org commemorates the landmark case and works to end racial prejudice through education.
Even after these changes, there were more Asian-white and Latino/a-white relationships than there were African American–white relationships (Gaines Jr. & Brennan, 2011). Having already discussed the importance of similarity in attraction to mates, it’s important to note that partners in an interracial relationship, although culturally different, tend to be similar in occupation and income. This can likely be explained by the situational influences on our relationship formation we discussed earlier—namely, that work tends to be a starting ground for many of our relationships, and we usually work with people who have similar backgrounds to us.
There has been much research on interracial couples that counters the popular notion that partners may be less satisfied in their relationships due to cultural differences. In fact, relational satisfaction isn’t significantly different for interracial partners, although the challenges they may face in finding acceptance from other people could lead to stressors that are not as strong for intracultural partners (Gaines Jr. & Brennan, 2011). Although partners in interracial relationships certainly face challenges, there are positives. For example, some mention that they’ve experienced personal growth by learning about their partner’s cultural background, which helps them gain alternative perspectives. Specifically, white people in interracial relationships have cited an awareness of and empathy for racism that still exists, which they may not have been aware of before (Gaines Jr. & Liu, 2000).
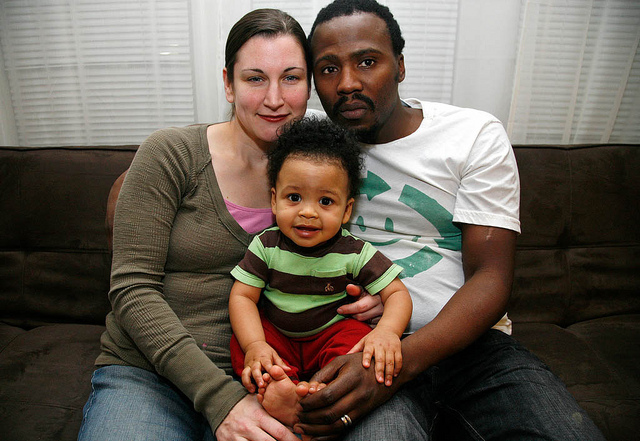

The Supreme Court ruled in the 1967 Loving v. Virginia case that states could not enforce laws banning interracial marriages.
Bahai.us – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Key Takeaways
- Studying intercultural communication, communication between people with differing cultural identities, can help us gain more self-awareness and be better able to communicate in a world with changing demographics and technologies.
- A dialectical approach to studying intercultural communication is useful because it allows us to think about culture and identity in complex ways, avoiding dichotomies and acknowledging the tensions that must be negotiated.
- Intercultural relationships face some challenges in negotiating the dialectic between similarities and differences but can also produce rewards in terms of fostering self- and other awareness.
- Why is the phrase “Know thyself” relevant to the study of intercultural communication?
- Apply at least one of the six dialectics to a recent intercultural interaction that you had. How does this dialectic help you understand or analyze the situation?
- Do some research on your state’s laws by answering the following questions: Did your state have antimiscegenation laws? If so, when were they repealed? Does your state legally recognize gay and lesbian relationships? If so, how?
Allen, B. J., Difference Matters: Communicating Social Identity , 2nd ed. (Long Grove, IL: Waveland, 2011), 55.
ben-Aaron, D., “Bringing Broadband to Finland’s Bookdocks,” Bloomberg Businessweek , July 19, 2010, 42.
Chen, Y. and Masato Nakazawa, “Influences of Culture on Self-Disclosure as Relationally Situated in Intercultural and Interracial Friendships from a Social Penetration Perspective,” Journal of Intercultural Communication Research 38, no. 2 (2009): 94. doi:10.1080/17475750903395408.
Coller, M. J., “Communication Competence Problematics in Ethnic Friendships,” Communication Monographs 63, no. 4 (1996): 324–25.
De La Baume, M. and J. David Goodman, “First Fines over Wearing Veils in France,” The New York Times ( The Lede: Blogging the News ), September 22, 2011, accessed October 10, 2011, http://thelede.blogs.nytimes.com/2011/09/22/first-fines-over -wearing-full-veils-in-france .
Fraser, C., “The Women Defying France’s Fall-Face Veil Ban,” BBC News , September 22, 2011, accessed October 10, 2011, http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-15023308 .
Gaines Jr. S. O., and Kelly A. Brennan, “Establishing and Maintaining Satisfaction in Multicultural Relationships,” in Close Romantic Relationships: Maintenance and Enhancement , eds. John Harvey and Amy Wenzel (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum, 2011), 239.
Stanley O. Gaines Jr., S. O., and James H. Liu, “Multicultural/Multiracial Relationships,” in Close Relationships: A Sourcebook , eds. Clyde Hendrick and Susan S. Hendrick (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000), 105.
Hofstede, G., Cultures and Organizations: Softwares of the Mind (London: McGraw-Hill, 1991), 26.
Human Rights Campaign, “Pass ENDA NOW”, accessed November 5, 2012, http://www.hrc.org/campaigns/employment-non-discrimination-act .
Lee, P., “Bridging Cultures: Understanding the Construction of Relational Identity in Intercultural Friendships,” Journal of Intercultural Communication Research 35, no. 1 (2006): 11. doi:10.1080/17475740600739156.
Loving Day, “The Last Laws to Go,” Lovingday.org , accessed October 11, 2011, http://lovingday.org/last-laws-to-go .
Lustig, M. W., and Jolene Koester, Intercultural Competence: Interpersonal Communication across Cultures , 2nd ed. (Boston, MA: Pearson, 2006), 128–29.
Martin, J. N., and Thomas K. Nakayama, Intercultural Communication in Contexts , 5th ed. (Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill, 2010), 4.
Martin, J. N., and Thomas K. Nakayama, “Thinking Dialectically about Culture and Communication,” Communication Theory 9, no. 1 (1999): 14.
McLuhan, M., The Medium Is the Message (New York: Bantam Books, 1967).
Peplau, L. A. and Leah R. Spalding, “The Close Relationships of Lesbians, Gay Men, and Bisexuals,” in Close Relationships: A Sourcebook , eds. Clyde Hendrick and Susan S. Hendrick (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000), 113.
Pratt, R. A., “Crossing the Color Line: A Historical Assessment and Personal Narrative of Loving v. Virginia ,” Howard Law Journal 41, no. 2 (1995): 229–36.
Sias, P. M., Jolanta A. Drzewiecka, Mary Meares, Rhiannon Bent, Yoko Konomi, Maria Ortega, and Colene White, “Intercultural Friendship Development,” Communication Reports 21, no. 1 (2008): 9. doi:10.1080/08934210701643750.
Smith, P., “The Digital Divide,” New York Times Upfront , May 9, 2011, 6.
Sylvester, D. E., and Adam J. McGlynn, “The Digital Divide, Political Participation, and Place,” Social Science Computer Review 28, no. 1 (2010): 64–65. doi:10.1177/0894439309335148.
van Deursen, A. and Jan van Dijk, “Internet Skills and the Digital Divide,” New Media and Society 13, no. 6 (2010): 893. doi:10.1177/1461444810386774.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Communication and Culture
- Communication and Social Change
- Communication and Technology
- Communication Theory
- Critical/Cultural Studies
- Gender (Gay, Lesbian, Bisexual and Transgender Studies)
- Health and Risk Communication
- Intergroup Communication
- International/Global Communication
- Interpersonal Communication
- Journalism Studies
- Language and Social Interaction
- Mass Communication
- Media and Communication Policy
- Organizational Communication
- Political Communication
- Rhetorical Theory
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Intercultural competence.
- Lily A. Arasaratnam Lily A. Arasaratnam Director of Research, Department of Communication, Alphacrucis College
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190228613.013.68
- Published online: 03 February 2016
The phrase “intercultural competence” typically describes one’s effective and appropriate engagement with cultural differences. Intercultural competence has been studied as residing within a person (i.e., encompassing cognitive, affective, and behavioral capabilities of a person) and as a product of a context (i.e., co-created by the people and contextual factors involved in a particular situation). Definitions of intercultural competence are as varied. There is, however, sufficient consensus amongst these variations to conclude that there is at least some collective understanding of what intercultural competence is. In “Conceptualizing Intercultural Competence,” Spitzberg and Chagnon define intercultural competence as, “the appropriate and effective management of interaction between people who, to some degree or another, represent different or divergent affective, cognitive, and behavioral orientations to the world” (p. 7). In the discipline of communication, intercultural communication competence (ICC) has been a subject of study for more than five decades. Over this time, many have identified a number of variables that contribute to ICC, theoretical models of ICC, and quantitative instruments to measure ICC. While research in the discipline of communication has made a significant contribution to our understanding of ICC, a well-rounded discussion of intercultural competence cannot ignore the contribution of other disciplines to this subject. Our present understanding of intercultural competence comes from a number of disciplines, such as communication, cross-cultural psychology, social psychology, linguistics, anthropology, and education, to name a few.
- intercultural competence
- intercultural communication
- appropriate
A Brief Introduction
With increasing global diversity, intercultural competence is a topic of immediate relevance. While some would question the use of the term “competence” as a Western concept, the ability to understand and interact with people of different cultures in authentic and positive ways is a topic worth discussing. Though several parts of the world do remain culturally homogenous, many major cities across the world have undergone significant transformation in their cultural and demographic landscape due to immigration. Advances in communication technologies have also facilitated intercultural communication without the prerequisite of geographic proximity. Hence educational, business, and other projects involving culturally diverse workgroups have become increasingly common. In such contexts the success of a group in accomplishing its goals might not depend only on the group members’ expertise in a particular topic or ability to work in a virtual environment but also on their intercultural competence (Zakaria, Amelinckx, & Wilemon, 2004 ). Cultural diversity in populations continues to keep intercultural competence (or cultural competence, as it is known in some disciplines) on the agenda of research in applied disciplines such as medicine (Bow, Woodward, Flynn, & Stevens, 2013 ; Charles, Hendrika, Abrams, Shea, Brand, & Nicol, 2014 ) and education (Blight, 2012 ; Tangen, Mercer, Spooner-Lane, & Hepple, 2011 ), for example.
As noted in the historiography section, early research in intercultural competence can be traced back to acculturation/adaptation studies. Labels such as cross-cultural adaptation and cross-cultural adjustment/effectiveness were used to describe what we now call intercultural competence, though adaptation and adjustment continue to remain unique concepts in the study of migrants. It is fair to say that today’s researchers would agree that, while intercultural competence is an important part of adapting to a new culture, it is conceptually distinct.
Although our current understanding of intercultural competence is (and continues to be) shaped by research in many disciplines, communication researchers can lay claim to the nomenclature of the phrase, particularly intercultural communication competence (ICC). Intercultural competence is defined by Spitzberg and Chagnon ( 2009 ) as “the appropriate and effective management of interaction between people who, to some degree or another, represent different or divergent affective, cognitive, and behavioral orientations to the world” (p. 7), which touches on a long history of intercultural competence being associated with effectiveness and appropriateness. This is echoed in several models of intercultural competence as well. The prevalent characterization of effectiveness as the successful achievement of one’s goals in a particular communication exchange is notably individualistic in its orientation. Appropriateness, however, views the communication exchange from the other person’s point of view, as to whether the communicator has communicated in a manner that is (contextually) expected and accepted.
Generally speaking, research findings support the view that intercultural competence is a combination of one’s personal abilities (such as flexibility, empathy, open-mindedness, self-awareness, adaptability, language skills, cultural knowledge, etc.) as well as relevant contextual variables (such as shared goals, incentives, perceptions of equality, perceptions of agency, etc.). In an early discussion of interpersonal competence, Argyris ( 1965 ) proposed that competence increases as “one’s awareness of relevant factors increases,” when one can solve problems with permanence, in a manner that has “minimal deterioration of the problem-solving process” (p. 59). This view of competence places it entirely on the abilities of the individual. Kim’s ( 2009 ) definition of intercultural competence as “an individual’s overall capacity to engage in behaviors and activities that foster cooperative relationships in all types of social and cultural contexts in which culturally or ethnically dissimilar others interface” (p. 62) further highlights the emphasis on the individual. Others, however, suggest that intercultural competence has an element of social judgment, to be assessed by others with whom one is interacting (Koester, Wiseman, & Sanders, 1993 ). A combination of self and other assessment is logical, given that the definition of intercultural competence encompasses effective (from self’s perspective) and appropriate (from other’s perspective) communication.
Before delving further into intercultural competence, some limitations to our current understanding of intercultural competence must be acknowledged. First, our present understanding of intercultural competence is strongly influenced by research emerging from economically developed parts of the world, such as the United States and parts of Europe and Oceania. Interpretivists would suggest that the (cultural) perspectives from which the topic is approached inevitably influence the outcomes of research. Second, there is a strong social scientific bias to the cumulative body of research in intercultural competence so far; as such, the findings are subject to the strengths and weaknesses of this epistemology. Third, because many of the current models of intercultural competence (or intercultural communication competence) focus on the individual, and because individual cultural identities are arguably becoming more blended in multicultural societies, we may be quickly approaching a point where traditional definitions of intercultural communication (and by association, intercultural competence) need to be refined. While this is not an exhaustive list of limitations, it identifies some of the parameters within which current conceptualizations of intercultural competence must be viewed.
The following sections discuss intercultural competence, as we know it, starting with what it is and what it is not . A brief discussion of well-known theories of ICC follows, then some of the variables associated with ICC are identified. One of the topics of repeated query is whether ICC is culture-general or culture-specific. This is addressed in the section following the discussion of variables associated with ICC, followed by a section on assessment of ICC. Finally, before delving into research directions for the future and a historiography of research in ICC over the years, the question of whether ICC can be learned is addressed.
Clarification of Nomenclature
As noted in the summary section, one of the most helpful definitions of intercultural competence is provided by Spitzberg and Chagnon ( 2009 ), who define it as “the appropriate and effective management of interaction between people who, to some degree or another, represent different or divergent affective, cognitive, and behavioral orientations to the world” (p. 7). However, addressing what intercultural competence is not is just as important as explaining what it is, in a discussion such as this. Conceptually, intercultural competence is not equivalent to acculturation, multiculturalism, biculturalism, or global citizenship—although intercultural competence is a significant aspect of them all. Semantically, intercultural efficiency, cultural competence, intercultural sensitivity, intercultural communication competence, cross-cultural competence, and global competence are some of the labels with which students of intercultural competence might be familiar.
The multiplicity in nomenclature of intercultural competence has been one of the factors that have irked researchers who seek conceptual clarity. In a meta-analysis of studies in intercultural communication competence, Bradford, Allen, and Beisser ( 2000 ) attempted to synthesize the multiple labels used in research; they concluded that intercultural effectiveness is conceptually equivalent to intercultural communication competence. Others have proposed that intercultural sensitivity is conceptually distinct from intercultural competence (Chen & Starosta, 2000 ). Others have demonstrated that, while there are multiple labels in use, there is general consensus as to what intercultural competence is (Deardorff, 2006 ).
In communication literature, it is fair to note that intercultural competence and intercultural communication competence are used interchangeably. In literature in other disciplines, such as medicine and health sciences, cultural competence is the label with which intercultural competence is described. Some have also proposed the phrase cultural humility as a deliberate alternative to cultural competence, suggesting that cultural humility involves life-long learning through self-awareness and critical reflection (Tervalon & Murray-Garcia, 1998 ).
The nature of an abstract concept is such that its reality is defined by the labels assigned to it. Unlike some concepts that have been defined and developed over many years within the parameters of a single discipline, intercultural competence is of great interest to researchers in multiple disciplines. As such, researchers from different disciplines have ventured to study it, without necessarily building on findings from other disciplines. This is one factor that has contributed to the multiple labels by which intercultural competence is known. This issue might not be resolved in the near future. However, those seeking conceptual clarity could look for the operationalization of what is being studied, rather than going by the name by which it is called. In other words, if what is being studied is effectiveness and appropriateness in intercultural communication (each of these terms in turn need to be unpacked to check for conceptual equivalency), then one can conclude that it is a study of intercultural competence, regardless of what it is called.
Theories of Intercultural Competence
Many theories of intercultural (communication) competence have been proposed over the years. While it is fair to say that there is no single leading theory of intercultural competence, some of the well-known theories are worth noting.
There are a couple of theories of ICC that are identified as covering laws theories (Wiseman, 2002 ), namely Anxiety Uncertainty Management (AUM) theory and Face Negotiation theory. Finding its origins in Berger and Calabrese ( 1975 ), AUM theory (Gudykunst, 1993 , 2005 ) proposes that the ability to be mindful and the effective management of anxiety caused by the uncertainty in intercultural interactions are key factors in achieving ICC. Gudykunst conceptualizes ICC as intercultural communication that has the least amount of misunderstandings. While AUM theory is not without its critics (for example, Yoshitake, 2002 ), it has been used in a number of empirical studies over the years (examples include Duronto, Nishida, & Nakayama, 2005 ; Ni & Wang, 2011 ), including studies that have extended the theory further (see Neuliep, 2012 ).
Though primarily focused on intercultural conflict rather than intercultural competence, Face Negotiation theory (Ting-Toomey, 1988 ) proposes that all people try to maintain a favorable social self-image and engage in a number of communicative behaviours designed to achieve this goal. Competence is identified as being part of the concept of “face,” and it is achieved through the integration of knowledge, mindfulness, and skills in communication (relevant to managing one’s own face as well as that of others). Face Negotiation theory has been used predominantly in intercultural conflict studies (see Oetzel, Meares, Myers, & Lara, 2003 ). As previously noted, it is not primarily a theory of intercultural competence, but it does address competence in intercultural settings.
From a systems point of view, Spitzberg’s ( 2000 ) model of ICC and Kim’s ( 1995 ) cultural adaptation theory are also well-known. Spitzberg identifies three levels of analysis that must be considered in ICC, namely the individual system, the episodic system, and the relational system. The factors that contribute to competence are delineated in terms of characteristics that belong to an individual (individual system), features that are particular to a specific interaction (episodic system), and variables that contribute to one’s competence across interactions with multiple others (relational system). Kim’s cultural adaptation theory recognizes ICC as an internal capacity within an individual; it proposes that each individual (being an open system) has the goal of adapting to one’s environment and identifies cognitive, affective, and behavioral dimensions of ICC.
Wiseman’s ( 2002 ) chapter on intercultural communication competence, in the Handbook of International and Intercultural Communication provides further descriptions of theories in ICC. While there have been several models of ICC developed since then, well-formed and widely tested theories of ICC remain few.
Variables Associated with Intercultural Competence
A number of variables have been identified as contributors to intercultural competence. Among these are mindfulness (Gudykunst, 1993 ), self and other awareness (Deardorff, 2006 ), listening skills (Ting-Toomey & Kurogi, 1998 ), positive attitude toward other cultures, and empathy (Arasaratnam & Doerfel, 2005 ), to name a few. Further, flexibility, tolerance for ambiguity, capacity for complexity, and language proficiency are also relevant. There is evidence to suggest that personal spiritual wellbeing plays a positive role in intercultural competence (Sandage & Jankowski, 2013 ). Additionally, there is an interesting link between intercultural competence and a biological variable, namely sensation seeking. Evidence suggests that, in the presence of a positive attitude towards other cultures and motivation to interact with people from other cultures, there is a positive relationship between sensation seeking and intercultural competence (Arasaratnam & Banerjee, 2011 ). Sensation seeking has also been associated with intercultural friendships (Morgan & Arasaratnam, 2003 ; Smith & Downs, 2004 ).
Cognitive complexity has also been identified with intercultural competence (Gudykunst & Kim, 2003 ). Cognitive complexity refers to an individual’s ability to form multiple nuanced perceptual categories (Bieri, 1955 ). A cognitively complex person relies less on stereotypical generalizations and is more perceptive to subtle racism (Reid & Foels, 2010 ). Gudykunst ( 1995 ) proposed that cognitive complexity is directly related to effective management of uncertainty and anxiety in intercultural communication, which in turn leads to ICC (according to AUM theory).
Not all variables are positively associated with intercultural competence. One of the variables that notably hinder intercultural competence is ethnocentrism. Neuliep ( 2002 ) characterizes ethnocentrism as, “an individual psychological disposition where the values, attitudes, and behaviors of one’s ingroup are used as the standard for judging and evaluating another group’s values, attitudes, and behaviors” (p. 201). Arasaratnam and Banerjee ( 2011 ) found that introducing ethnocentrism into a model of ICC weakened all positive relationships between the variables that otherwise contribute to ICC. Neuliep ( 2012 ) further discovered that ethnocentrism and intercultural communication apprehension debilitate intercultural communication. As Neuliep observed, ethnocentrism hinders mindfulness because a mindful communicator is receptive to new information, while the worldview of an ethnocentric person is rigidly centered on his or her own culture.
This is, by no means, an exhaustive list of variables that influence intercultural competence, but it is representative of the many individual-centered variables that influence the extent to which one is effective and appropriate in intercultural communication. Contextual variables, as noted in the next section, also play a role in ICC. It must further be noted that many of the ICC models do not identify language proficiency as a key variable; however, the importance of language proficiency has not been ignored (Fantini, 2009 ). Various models of intercultural competence portray the way in which (and, in some cases, the extent to which) these variables contribute to intercultural competence. For an expansive discussion of models of intercultural competence, see Spitzberg and Chagnoun ( 2009 ).
If one were to broadly summarize what we know thus far about an interculturally competent person, one could say that she or he is mindful, empathetic, motivated to interact with people of other cultures, open to new schemata, adaptable, flexible, able to cope with complexity and ambiguity. Language skills and culture-specific knowledge undoubtedly serve as assets to such an individual. Further, she or he is neither ethnocentric nor defined by cultural prejudices. This description does not, however, take into account the contextual variables that influence intercultural competence; highlighting the fact that the majority of intercultural competence research has been focused on the individual.
The identification of variables associated with intercultural competence raises a number of further questions. For example, is intercultural competence culture-general or culture-specific; can it be measured; and can it be taught or learned? These questions merit further exploration.
Culture General or Culture Specific
A person who is an effective and appropriate intercultural communicator in one context might not be so in another cultural context. The pertinent question is whether there are variables that facilitate intercultural competence across multiple cultural contexts. There is evidence to suggest that there are indeed culture-general variables that contribute to intercultural competence. This means there are variables that, regardless of cultural perspective, contribute to perception of intercultural competence. Arasaratnam and Doerfel ( 2005 ), for example, identified five such variables, namely empathy, experience, motivation, positive attitude toward other cultures, and listening. The rationale behind their approach is to look for commonalities in emic descriptions of intercultural competence by participants who represent a variety of cultural perspectives. Some of the variables identified by Arasaratnam and Doerfel’s research are replicated in others’ findings. For example, empathy has been found to be a contributor to intercultural competence in a number of other studies (Gibson & Zhong, 2005 ; Nesdale, De Vries Robbé, & Van Oudenhoven, 2012 ). This does not mean, however, that context has no role to play in perception of ICC. Contextual variables, such as the relationship between the interactants, the values of the cultural context in which the interaction unfolds, the emotional state of the interactants, and a number of other such variables no doubt influence effectiveness and appropriateness. Perception of competence in a particular situation is arguably a combination of culture-general and contextual variables. However, the aforementioned “culture-general” variables have been consistently associated with perceived ICC by people of different cultures. Hence they are noteworthy. The culture-general nature of some of the variables that contribute to intercultural competence provides an optimistic perspective that, even in the absence of culture-specific knowledge, it is possible for one to engage in effective and appropriate intercultural communication. Witteborn ( 2003 ) observed that the majority of models of intercultural competence take a culture-general approach. What is lacking at present, however, is extensive testing of these models to verify their culture-general nature.
The extent to which the culture-general nature of intercultural competence can be empirically verified depends on our ability to assess the variables identified in these models, and assessing intercultural competence itself. To this end, a discussion of assessment is warranted.
Assessing Intercultural Competence
Researchers have employed both quantitative and qualitative techniques in the assessment of intercultural competence. Deardorff ( 2006 ) proposed that intercultural competence should be measured progressively (at different points in time, over a period of time) and using multiple methods.
In terms of quantitative assessment, the nature of intercultural competence is such that any measure of this concept has to be one that (conceptually) translates across different cultures. Van de Vijver and Leung ( 1997 ) identified three biases that must be considered when using a quantitative instrument across cultures. First, there is potential for construct biases where cultural interpretations of a particular construct might vary. For example, “personal success” might be defined in terms of affluence, job prestige, etc., in an individualistic culture that favors capitalism, while the same construct could be defined in terms of sense of personal contribution and family validation in a collectivistic culture (Arasaratnam, 2007 ). Second, a method bias could be introduced by the very choice of the use of a quantitative instrument in a culture that might not be familiar with quantifying abstract concepts. Third, the presence of an item that is irrelevant to a particular cultural group could introduce an item bias when that instrument is used in research involving participants from multiple cultural groups. For a more detailed account of equivalence and biases that must be considered in intercultural research, see Van de Vijver and Leung ( 2011 ).
Over the years, many attempts have been made to develop quantitative measures of intercultural competence. There are a number of instruments that have been designed to measure intercultural competence or closely related concepts. A few of the more frequently used ones are worth noting.
Based on the Developmental Model of Intercultural Sensitivity (DMIS) (Bennett, 1986 ), the Intercultural Development Inventory (IDI) measures three ethnocentric and three ethno-relative levels of orientation toward cultural differences, as identified in the DMIS model (Hammer, Bennett, & Wiseman, 2003 ). This instrument is widely used in intercultural research, in several disciplines. Some examples of empirical studies that use IDI include Greenholtz ( 2000 ), Sample ( 2013 ), and Wang ( 2013 ).
The Intercultural Sensitivity Inventory (ICSI) is another known instrument that approaches intercultural competence from the perspective of a person’s ability to appropriately modify his or her behavior when confronted with cultural differences, specifically as they pertain to individualistic and collectivistic cultures (Bhawuk & Brislin, 1992 ). It must be noted, however, that intercultural sensitivity is not necessarily equivalent to intercultural competence. Chen and Starosta ( 2000 ), for example, argued that intercultural sensitivity is a pre-requisite for intercultural competence rather than its conceptual equivalent. As such, Chen and Starosta’s Intercultural Sensitivity scale should be viewed within the same parameters. The authors view intercultural sensitivity as the affective dimension of intercultural competence (Chen & Starosta, 1997 ).
Although not specifically designed to measure intercultural competence, the Multicultural Personality Questionnaire (MPQ) measures five dimensions, namely open mindedness, emotional stability, cultural empathy, social initiative, and flexibility (Van Oudenhoven & Van der Zee, 2002 ), all of which have been found to be directly related to intercultural competence, in other research (see Matsumoto & Hwang, 2013 ).
Quantitative measures of intercultural competence almost exclusively rely on self-ratings. As such, they bear the strengths and weaknesses of any self-report (for a detailed discussion of self-knowledge, see Bauer & Baumeister, 2013 ). There is some question as to whether Likert-type scales favor individuals with higher cognitive complexity because such persons have a greater capacity for differentiating between constructs (Bowler, Bowler, & Cope, 2012 ). Researchers have also used other methods such as portfolios, reflective journals, responses to hypothetical scenarios, and interviews. There continues to be a need for fine-tuned methods of assessing intercultural competence that utilize others’ perceptions in addition to self-reports.
Can Intercultural Competence Be Learned?
If competence is the holy grail of intercultural communication, then the question is whether it can be learned. On the one hand, many researchers suggest that the process of learning intercultural competence is developmental (Beamer, 1992 ; Bennett, 1986 ; Hammer, Bennett, & Wiseman, 2003 ). Which means that over time, experiences, and deliberate reflection, people can learn things that cumulatively contribute to intercultural competence. Evidence also suggests that collaborative learning facilitates the development of intercultural competence (Helm, 2009 ; Zhang, 2012 ). On the other hand, given research shows that there are many personality variables that contribute to intercultural competence; one could question whether these are innate or learned. Further, many causal models of intercultural competence show that intercultural competence is the product of interactions between many variables. If some of these can be learned and others are innate, then it stands to reason that, given equal learning opportunities, there would still be variations in the extent to which one “achieves” competence. There is also evidence to suggest that there are certain variables, such as ethnocentrism, that debilitate intercultural competence. Thus, it is fair to conclude that, while there is the potential for one to improve one’s intercultural competence through learning, not all can or will.
The aforementioned observation has implications for intercultural training, particularly training that relies heavily on dissemination of knowledge alone. In other words, just because someone knows facts about intercultural competence, it does not necessarily make them an expert at effective and appropriate communication. Developmental models of intercultural competence suggest that the learning process is progressive over time, based on one’s reaction to various experiences and one’s ability to reflect on new knowledge (Saunders, Haskins, & Vasquez et al., 2015 ). Further, research shows that negative attitudes and attitudes that are socially reinforced are the hardest to change (Bodenhausen & Gawronski, 2013 ). Hence people with negative prejudices toward other cultures, for example, may not necessarily be affected by an intercultural training workshop. While many organizations have implemented intercultural competency training in employee education as a nod to embracing diversity, the effectiveness of short, skilled-based training bears further scrutiny. For more on intercultural training, see the Handbook of Intercultural Training by Landis, Bennett, and Bennett ( 2004 ).
Research Directions
In a review of ICC research between 2003 and 2013 , Arasaratnam ( 2014 ) observed that there is little cross-disciplinary dialogue when it comes to intercultural competence research. Even though intercultural competence is a topic of interest to researchers in multiple disciplines, the findings from within a discipline appear to have limited external disciplinary reach. This is something that needs to be addressed. While the field of communication has played a significant role in contributing to current knowledge of intercultural competence, findings from other disciplines not only add to this knowledge but also potentially address gaps in research that are inevitable from a single disciplinary point of view. As previously observed, one of the reasons for lack of cross-disciplinary referencing (apart from lack of familiarity with work outside of one’s own discipline) could be the use of different labels to describe intercultural competence. Hence, students and scholars would do well to include these variations in labels when looking for research in intercultural competence. This would facilitate consolidation of inter-disciplinary knowledge in future research.
New and robust theories of intercultural competence that are empirically tested in multiple cultural groups are needed. As previously observed, the majority of existing theories in intercultural communication competence stem from the United States, and as such are influenced by a particular worldview. Theories from other parts of the world would enrich our current understanding of intercultural competence.
Thus far, the majority of research in intercultural communication has been done with the fundamental assumption that participants in a dyadic intercultural interaction arrive at it from two distinct cultural perspectives. This assumption might not be valid in all interactions that could still be classified as intercultural. With increasing global mobility, there are more opportunities for people to internalize more than one culture, thus becoming bicultural or blended in their cultural identity. This adds a measure of complexity to the study of intercultural competence because there is evidence to show that there are cultural differences in a range of socio-cognitive functions such as categorization, attribution, and reasoning (Miyamoto & Wilken, 2013 ), and these functions play important roles in how we perceive others, which in turn influences effective and appropriate communication (Moskowitz & Gill, 2013 ).
The concept of competence itself merits further reflection. Because the majority of voices that contribute to ongoing discussions on intercultural competence arise from developed parts of the world, it is fair to say that these discussions are not comprehensively representative of multiple cultural views. Further, the main mechanisms of academic publishing favor a peer-review system which can be self-perpetuating because the reviewers themselves are often the vocal contributors to the existing body of knowledge. For a more well rounded reflection of what it means to engage in authentic and affirming intercultural communication, sources of knowledge other than academic publications need to be considered. These may include the work done by international aid agencies and not-for-profit organizations for example, which engage with expressions of intercultural communication that are different from those that are observed among international students, expatriates, or medical, teaching, or business professionals, who inform a significant amount of intercultural competence research in academia.

Historiography: Research in Intercultural Competence over the Years
The concept of “competence” is not recent. For example, in an early use of the term, psychologist Robert W. White ( 1959 ) characterized competence as “an organism’s capacity to interact effectively with its environment” (p. 297) and proposed that effectance motivation (which results in feelings of efficacy) is an integral part of competence. Today’s research in intercultural competence has been informed by the work of researchers in a number of disciplines, over several decades.
In the field of communication, some of the pioneers of ICC research are Mary Jane Collier ( 1986 ), Norman G. Dinges ( 1983 ), William B. Gudykunst ( 1988 ), Mitchell R. Hammer ( 1987 ), T. Todd Imohari (Imohari & Lanigan, 1989 ), Daniel J. Kealey ( 1989 ), Young Yun Kim ( 1991 ), Jolene Koester (Koester & Olebe, 1988 ), Judith N. Martin ( 1987 ), Hiroko Nishida ( 1985 ), Brent D. Ruben ( 1976 ), Brian H. Spitzberg ( 1983 ), Stella Ting-Toomey ( 1988 ), and Richard L. Wiseman (Wiseman & Abe, 1986 ).
While much of the momentum in communication research started in the late 1970s, a conservative (and by no means comprehensive) glance at history traces back some of the early works in intercultural competence to the 1960s, where researchers identified essential characteristics for intercultural communication. This research was based on service personnel and Americans travelling overseas for work (Gardner, 1962 ; Guthrie & Zetrick, 1967 ; Smith, 1966 ). The characteristics they identified include flexibility, stability, curiosity, openness to other perspectives, and sensitivity, to name a few, and these characteristics were studied in the context of adaptation to a new culture.
In the 1970s, researchers built on early work to further identify key variables in intercultural “effectiveness” or “cross-cultural” competency. Researchers in communication worked toward not only identifying but also assessing these variables (Hammer, Gudykunst, & Wiseman, 1978 ; Ruben & Kealey, 1979 ), primarily using quantitative methods. Ruben, Askling, and Kealey ( 1977 ) provided a detailed account of “facets of cross-cultural effectiveness” identified by various researchers.
In the 1980s, research in ICC continued to gain momentum, with a special issue of the International Journal of Intercultural Relations dedicated to this topic. ICC was still approached from the point of view of two specific cultures interacting with each other, similar to the acculturation approach in the previous decade. Many of the conceptualizations of ICC were derived from (interpersonal) communication competence, extending this to intercultural contexts. For example, Spitzberg and Cupach’s ( 1984 ) conceptualization of communication competence as effective and appropriate communication has been foundational to later work in ICC.
Researchers in the 1990s built on the work of others before them. Chen ( 1990 ) presented eleven propositions and fifteen theorems in regards to the components of ICC, building from a discussion of Dinges’ ( 1983 ) six approaches to studying effective and appropriate communication in intercultural contexts. Chen went on to propose that competence is both inherent and learned. The 1993 volume of the International and Intercultural Communication Annual was dedicated to ICC, introducing some of the theories that later become influential in intercultural research, such as Gudykunst’s ( 1993 ) Anxiety/Uncertainty Management (AUM) theory, Cupach and Imahori’s ( 1993 ) Identity Management theory, and Ting-Toomey’s ( 1993 ) Identity Negotiation theory. Contributions to intercultural competence theory came from other disciplines as well, such as a learning model for becoming interculturally competent (Taylor, 1994 ) and an instructional model of intercultural strategic competence (Milhouse, 1996 ), for example. The formation of the International Academy for Intercultural Research, in 1997 , marked a significant step toward interdisciplinary collaboration in intercultural research. Research in the 1990s contributed to the strides made in the 2000s.
In a meta-review of ICC, Bradford, Allen, and Beisser ( 2000 ) observed that ICC and intercultural communication effectiveness have been used (conceptually) interchangeably in previous research. Despite the different labels under which this topic has been studied, Arasaratnam and Doerfel ( 2005 ) made the case for the culture-general nature of ICC, and Deardorff ( 2006 ) demonstrated that there is consensus amongst experts as to what ICC is. The publication of the SAGE Handbook of Intercultural Competence (Deardorff, 2009 ) and Spitzberg and Chagnon’s ( 2009 ) comprehensive introductory chapter on conceptualizing intercultural competence are other noteworthy contributions to literature in intercultural competence. In 2015 , the publication of another special issue on intercultural competence by the International Journal of Intercultural Relations (some 25 years after the 1989 special issue) signals that intercultural competence continues to be a topic of interest amongst researchers in communication and other disciplines. As discussed in the Research Directions section, the areas that are yet to be explored would hopefully be addressed in future research.
Further Reading
- Arasaratnam, L. A. (2014). Ten years of research in intercultural communication competence (2003–2013): A retrospective. Journal of Intercultural Communication , 35 .
- Arasaratnam, L. A. , & Deardorff, D. K. (Eds.). (2015). Intercultural competence [Special issue]. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 48 .
- Bennett, J. M. (2015). The SAGE encyclopedia of intercultural competence . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Bradford, L. , Allen, M. , & Beisser, K. R. (2000). An evaluation and meta-analysis of intercultural communication competence research. World Communication , 29 (1), 28–51.
- Deardorff, D. K. (2009). The SAGE handbook of intercultural competence . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Martin, J. N. (Ed.). (1989). Intercultural communication competence [Special issue]. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 13 (3).
- Wiseman, R. L. (2002). Intercultural communication competence. In W. B. Gudykunst & B. Moody (Eds.), Handbook of international and intercultural communication (pp. 207–224). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Wiseman, R. L. , & Koester, J. (1993). Intercultural communication competence . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Arasaratnam, L. A. (2007). Empirical research in intercultural communication competence: A review and recommendation. Australian Journal of Communication , 34 , 105–117.
- Arasaratnam, L. A. , & Banerjee, S. C. (2011). Sensation seeking and intercultural communication competence: A model test. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 35 , 226–233.
- Arasaratnam, L. A. , & Doerfel, M. L. (2005). Intercultural communication competence: Identifying key components from multicultural perspectives. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 29 , 137–163.
- Argyris, C. (1965). Explorations in interpersonal competence-I. Journal of Applied Behavioral Science , 1 , 58–83.
- Bauer, I. M. , & Baumeister, R. F. (2013). Self-knowledge. In D. Reisberg (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of cognitive psychology [online publication]. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Beamer, L. (1992). Learning intercultural competence. International Journal of Business Communication , 29 (3), 285–303.
- Bennett, M. J. (1986). A developmental approach to training for intercultural sensitivity. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 10 , 179–196.
- Berger, C. R. , & Calabrese, R. J. (1975). Some explorations in initial interaction and beyond: Toward a developmental theory of interpersonal communication. Human Communication Theory , 1 , 99–112.
- Bhawuk, D. P. S. , & Brislin, R. W. (1992). The measurement of intercultural sensitivity using the concepts of individualism and collectivism. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 16 (4), 413–436.
- Bieri, J. (1955). Cognitive complexity-simplicity and predictive behaviour. Journal of Abnormal & Social Psychology , 51 , 263–268.
- Blight, M. (2012). Cultures education in the primary years: Promoting active global citizenship in a changing world. Journal of Student Engagement: Educational Matters , 2 (1), 49–53.
- Bodenhausen, G. V. , & Gawronski, B. (2013). Attitude change. In D. Reisberg (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of cognitive psychology [online publication]. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Bow, C. , Woodward, R. , Flynn, E. , & Stevens, M. (2013). Can I ask you something about your personal life? Sensitive questioning in intercultural doctor-patient interviews. Focus on Health Professional Education , 15 (2), 67–77.
- Bowler, M. C. , Bowler, J. L. , & Cope, J. G. (2012). Further evidence of the impact of cognitive complexity on the five-factor model. Social Behaviour and Personality , 40 (7), 1083–1098.
- Bradford, L. , Allen, M. , & Beisser, K. R. (2000). Meta-analysis of intercultural communication competence research. World Communication , 29 (1), 28–51.
- Charles, L. , Hendrika, M. , Abrams, S. , Shea, J. , Brand, G. , & Nicol, P. (2014). Expanding worldview: Australian nursing students’ experience of cultural immersion in India. Contemporary Nurse: A Journal for the Australian Nursing Profession , 48 (1), 67–75.
- Chen, G. M. (1990). Intercultural communication competence: Some perspectives of research. The Howard Journal of Communications , 2 (3), 243–261.
- Chen, G. M. , & Starosta, W. J. (1997). A review of the concept of intercultural sensitivity. Human Communication , 1 , 1–16.
- Chen, G. M. , & Starosta, W. J. (2000). The development and validation of the intercultural communication sensitivity scale. Human Communication , 3 , 1–15.
- Collier, M. J. (1986). Culture and gender: Effects on assertive behavior and communication competence. In M. McLaughlin (Ed.), Communication yearbook 9 (pp. 576–592). Beverly Hills, CA: SAGE.
- Cupach, W. R. , & Imahori, T. T. (1993). Identity management theory: Communication competence in intercultural episodes and relationships. In R. L Wiseman & J. Koester (Eds.), Intercultural communication competence (pp. 112–131). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Deardorff, D. K. (2006). Identification and assessment of intercultural competence as a student outcome of internationalization. Journal of Studies in Intercultural Education , 10 , 241–266.
- Dinges, N. (1983). Intercultural competence. In D. Landis & R. W. Brislin (Eds.), Handbook of intercultural training (Vol. 1) : Issues in theory and design (pp. 176–202). New York: Pergamon.
- Duronto, P. M. , Nishida, T. , & Nakayama, S. I. (2005). Uncertainty, anxiety, and avoidance in communication with strangers. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 29 (5), 549–560.
- Fantini, A. E. (2009). Assessing intercultural competence. In D. K. Deardorff (Ed.), The SAGE Handbook of Intercultural Competence (pp. 456–476). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Gardner, G. H. (1962). Cross-cultural communication. Journal of Social Psychology , 58 , 241–256.
- Gibson, D. W. , & Zhong, M. (2005). Intercultural communication competence in the healthcare context. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 29 , 621–634.
- Greenholtz, J. (2000). Assessing cross-cultural competence in transnational education: The intercultural development inventory. Higher Education in Europe , 25 (3), 411–416.
- Gudykunst, W. B. (1988). Uncertainty and anxiety. In Y. Kim & W. Gudykunst (Eds.), Theories in intercultural communication (pp. 123–156). Newbury Park, CA: SAGE.
- Gudykunst, W. B. (1993). Toward a theory of effective interpersonal and intergroup communication: An anxiety/uncertainty management (AUM) perspective. In R. L Wiseman & J. Koester (Eds.), Intercultural communication competence (pp. 33–71). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Gudykunst, W. B. (1995). Anxiety/uncertainty management (AUM) theory. In R. Wiseman (Ed.), Intercultural communication theory (pp. 8–58). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Gudykunst, W. B. (2005). An anxiety/uncertainty management (AUM) theory of effective communication: Making the mesh of the net finer. In W. B. Gudykunst (Ed.), Theorizing about intercultural communication (pp. 281–322). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Gudykunst, W. B. , & Kim, Y. (2003). Communicating with strangers: An approach to intercultural communication . New York: McGraw Hill.
- Guthrie, G. M. , & Zetrick, I. N. (1967). Predicting performance in the Peace Corps. Journal of Social Psychology , 71 , 11–21.
- Hammer, M. R. (1987). Behavioral dimensions of intercultural effectiveness: A replication and extension. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 11 , 65–88.
- Hammer, M. R. , Bennett, M. J. , & Wiseman, R. L. (2003). Measuring intercultural sensitivity: The intercultural development inventory. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 27 , 421–443.
- Hammer, M. R. , Gudykunst, W. B. , & Wiseman, R. L. (1978). Dimensions of intercultural effectiveness: An exploratory study. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 2 (4), 382–393.
- Helm, F. (2009). Language and culture in an online context: What can learner diaries tell us about intercultural competence? Language & Intercultural Communication , 9 , 91–104.
- Imohari, T. , & Lanigan, M. (1989). Relational model of intercultural communication competence. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 13 (3), 269–289.
- Kealey, D. J. (1989). A study of cross-cultural effectiveness: Theoretical issues, practical applications. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 13 (3), 397–428.
- Koester, J. , & Olebe, M. (1988). The behavioral assessment scale for intercultural communication effectiveness. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 12 , 233–246.
- Kim, Y. (1991). Intercultural communication competence. In S. Ting-Toomey & F. Korzennt (Eds.), Cross-cultural personal communication (pp. 259–275). Newbury Park, CA: SAGE.
- Kim, Y. (1995). Cross-cultural adaptation: An integrative theory. In R. L. Wiseman (Ed.), Intercultural communication theory (pp. 170–193). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Kim, Y. (2009). The identity factor in intercultural competence. In D. K. Deardorff (Ed.), The SAGE Handbook of Intercultural Competence (pp. 53–65). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Koester, J. , Wiseman, R. L. , & Sanders, J. A. (1993). Multiple perspectives of intercultural communication competence. In R. L Wiseman & J. Koester (Eds.), Intercultural communication competence (pp. 3–15). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Landis, D. , Bennett, J. , & Bennett, M. (2004). Handbook of intercultural training . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Martin, J. N. (1987). The relationship between student sojourner perceptions of intercultural competencies and previous sojourn experience. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 11 , 337–355.
- Matsumoto, D. , & Hwang, H. C. (2013). Assessing cross-cultural competence: A review of available tests. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology , 44 (6), 849–873.
- Milhouse, V. H. (1996). Intercultural strategic competence: An effective tool collectivist and individualist students can use to better understand each other. Journal of Instructional Psychology , 23 (1), 45–52.
- Miyamoto, Y. , & Wilken, B. (2013). Cultural differences and their mechanisms. In D. Reisberg (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of cognitive psychology [online publication]. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Morgan, S. E. , & Arasaratnam, L. A. (2003). Intercultural friendships as social excitation: Sensation seeking as a predictor of intercultural friendship seeking behavior. Journal of Intercultural Communication Research , 32 , 175–186.
- Moskowitz, G. B. , & Gill, M. J. (2013). Person perception. In D. Reisberg (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of cognitive psychology [online publication]. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Nesdale, D. , De Vries Robbé, M. , & Van Oudenhoven, J. P. (2012). Intercultural effectiveness, authoritarianism, and ethnic prejudice. Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 42 , 1173–1191.
- Neuliep, J. W. (2002). Assessing the reliability and validity of the generalized ethnocentrism scale. Journal of Intercultural Communication Research , 31 (4), 201–215.
- Neuliep, J. W. (2012). The relationship among intercultural communication apprehension, ethnocentrism, uncertainty reduction, and communication satisfaction during initial intercultural interaction: An extension of Anxiety Uncertainty Management (AUM) theory. Journal of Intercultural Communication Research , 41 (1), 1–16.
- Ni, L. , & Wang, Q. (2011). Anxiety and uncertainty management in an intercultural setting: The impact on organization-public relationships. Journal of Public Relations , 23 (3), 269–301.
- Nishida, H. (1985). Japanese intercultural communication competence and cross-cultural adjustment. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 9 (3), 247–269.
- Oetzel, J. , Meares, M. , Myers, K. K. , & Lara, E. (2003). Interpersonal conflict in organizations: Explaining conflict styles via face-negotiation theory. Communication Research Reports , 20 (2), 106–115.
- Reid, L. D. , & Foels, R. (2010). Cognitive complexity and the perception of subtle racism. Basic and Applied Social Psychology , 32 , 291–301.
- Ruben, B. D. (1976). Assessing communication competency for intercultural adaptation. Group and Organization Studies , 1 , 334–354.
- Ruben, B. D. , Askling, L. R. , & Kealey, D. J. (1977). Cross-cultural effectiveness. In D. S. Hoopes , P. B. Pedersen , and G. Renwick (Eds.), Overview of intercultural education, training, and research . (Vol. I): Theory (pp. 92–105). Washington, DC: Society for Intercultural Education, Training, and Research.
- Ruben, B. D. , & Kealey, D. J. (1979). Behavioral assessment of communication competency and the prediction of cross-cultural adaptation. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 3 (1), 15–47.
- Sample, S. G. (2013). Developing intercultural learners through the international curriculum. Journal of Studies in International Education , 17 (5), 554–572.
- Sandage, S. J. , & Jankowski, P. J. (2013). Spirituality, social justice, and intercultural competence: Mediator effects for differentiation of self. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 37 , 366–374.
- Smith, M. B. (1966). Explorations in competence: A study of Peace Corps teachers in Ghana. American Psychologist , 21 , 555–566.
- Smith, R. A. , & Downs, E. (2004). Flying across cultural divides: Sensation seeking and engagement in intercultural communication. Journal of Intercultural Communication Research , 33 (3), 223–230.
- Spitzberg, B. H. (1983). Communication competence as knowledge, skill, and impression. Communication Education , 32 , 323–329.
- Spitzberg, B. H. (2000). A model of intercultural communication competence. In L. Samovar & R. Porter (Eds.), Intercultural communication: A reader (pp. 375–387). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
- Spitzberg, B. H. , & Chagnon, G. (2009). Conceptualizing intercultural competence. In D. K. Deardorff (Ed.), The SAGE Handbook of Intercultural Competence (pp. 2–52). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Spitzberg, B. H. , & Cupach, W. R. (1984). Interpersonal communication competence . Beverly Hills, CA: SAGE.
- Saunders, J. A. , Haskins, M. , & Vasquez, M. (2015). Cultural competence: A journey to an elusive goal. Journal of Social Work Education , 51 , 19–34.
- Tangen, D. , Mercer, K. L. , Spooner-Lane, R. , & Hepple, E. (2011). Exploring intercultural competence: A service-learning approach. Australian Journal of Teacher Education , 36 (11), 62–72.
- Taylor, E. W. (1994). A learning model for becoming interculturally competent. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 18 (3), 389–408.
- Tervalon, M. , & Murray-Garcia, J. (1998). Cultural humility versus cultural competence: A critical distinction in identifying physician training outcomes in multicultural education. Journal of Health Care for the Poor and Undeserved , 9 (2), 117–125.
- Ting-Toomey, S. (1988). Intercultural conflicts: A face-negotiation theory. In Y. Y. Kim and W. B. Gudykunst (Eds.), Theories in intercultural communication (pp. 213–235). Newbury Park, CA: SAGE.
- Ting-Toomey, S. (1993). Communicative resourcefulness: An identity negotiation perspective. In R. L Wiseman & J. Koester (Eds.), Intercultural communication competence (pp. 72–111). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Ting-Toomey, S. , & Kurogi, A. (1998). Facework competence in intercultural conflict: An updated face-negotiation theory. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 22 , 187–225.
- Van de Vijver, F. J. R. , & Leung, K. (1997). Methods and data analysis for cross-cultural research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Van de Vijver, F. J. R. , & Leung, K. (2011). Equivalence and bias: A review of concepts, models, and data analytic procedures. In D. Matsumoto & F. J. R. Van de Vijver (Eds.), Cross-cultural research methods in psychology (pp. 17–45). New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Van Oudenhoven, J. P. , & Van der Zee, K. (2002). Predicting multicultural effectiveness of international students: The multicultural personality questionnaire. International Journal of Intercultural Relations , 26 , 679–694.
- Wang, J. (2013). Moving towards ethnorelativism: A framework for measuring and meeting students’ needs in cross-cultural business and technical communication. Journal of Technical Writing & Communication , 43 (2), 201–218.
- White, R. W. (1959). Motivation reconsidered: The concept of competence. Psychological Review , 66 (5), 297–333.
- Wiseman, R. L. (2002). Intercultural communication competence. In W. B. Gudykunst and B. Moody (Eds.), Handbook of international and intercultural communication (pp. 207–224). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Wiseman, R. L. , & Abe, H. (1986). Cognitive complexity and intercultural effectiveness. In M. McLaughlin (Ed.), Communication yearbook 9 (pp. 611–624). Beverly Hills, CA: SAGE.
- Witteborn, S. (2003). Communicative competence revisited: An emic approach to studying intercultural communicative competence. Journal of Intercultural Communication Research , 32 , 187–203.
- Yoshitake, M. (2002). Anxiety/uncertainty management (AUM) theory: A critical examination of an intercultural communication theory. Intercultural Communication Studies , 11 , 177–193.
- Zakaria, N. , Amelinckx, A. , & Wilemon, D. (2004). Working together apart? Building a knowledge-sharing culture for global virtual teams. Creativity and Innovation Management , 13 (1), 15–29.
- Zhang, H. (2012). Collaborative learning as a pedagogical tool to develop intercultural competence in a multicultural class. China Media Research , 8 , 107–111.
Related Articles
- Women Entrepreneurs, Global Microfinance, and Development 2.0
- Movements and Resistance in the United States, 1800 to the Present
- Rhetorical Construction of Bodies
- Intercultural Friendships
- A Culture-Centered Approach to Health and Risk Communication
- Race, Nationalism, and Transnationalism
- Methods for Intercultural Communication Research
- Globalizing and Changing Culture
- Communication Skill and Competence
- Intercultural Conflict
- Anxiety, Uncertainty, and Intercultural Communication
- Bella Figura: Understanding Italian Communication in Local and Transatlantic Contexts
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Communication. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 10 May 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.66.14.236]
- 185.66.14.236
Character limit 500 /500
113 Intercultural Communication Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on intercultural communication, 👍 good intercultural communication research topics & essay examples, 🎓 most interesting intercultural communication research titles, 💡 simple intercultural communication essay ideas, ❓ intercultural communication questions.
- Importance of Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication in Intercultural Communication
- Barna’s Intercultural Communication Stumbling Blocks: Summary and Response
- Intercultural Communication in the Workplace
- Intercultural Communication: Dimensions of Bengali Culture
- Improving Intercultural Communication Skills
- Intercultural Relationships and Communication
- Intercultural Communication in Business
- A Review of “Understanding Intercultural Communication” The book “Understanding Intercultural Communication” is excellent reading for all people wanting to fulfill the Great Commission abroad.
- Exploring Intercultural Communication by Grothe The most interesting concepts from Exploring Intercultural Communication by Grothe are the interrelation between ascribed and avowed identities and ability as a cultural identity.
- Intercultural Communication in TV Shows The paper discusses filmmaking that used various television series and movies to examine the question of intercultural communication.
- Intercultural Communication: Interfaith Marriages Nowadays rapidly changing the world sets new opportunities and challenges in the field of intercultural communication. One of them is a growing number of interfaith marriages.
- Intercultural Communication Competence The characteristics of people’s personalities have a beneficial effect on the development of intercultural communication.
- The U-Curve Model of Intercultural Communication The U-Curve Model provides a fast and effective way of channeling the intercultural communication process toward reconciliation and collaboration.
- Intercultural Communication in Business, Education, and Healthcare The rules of communication vary depending on different contexts; that’s why this paper aims to discuss intercultural communication in business, education, and healthcare.
- Appropriate and Effective Christian Intercultural Communication The current paper can help people understand the ability to communicate even with different views on life and different cultural customs.
- Intercultural Communication: Autoethnographic Reflection The basic tenets of intercultural communication competence constitute attitudes, knowledge, and skills and are complemented by personal values held as part of a social group.
- Intercultural Communication: the Product Names and Logos When doing business globally, it is crucial to take into consideration the meanings and sounding of the product names and logos into the languages of the cultures a product target.
- Stereotypes and Prejudices in Intercultural Communication The aim is to study modern contacts between representatives of different cultures, arising within the same and different states, and whether they carry problems in communication.
- Verbal Processes in Intercultural Communication Proficiency in more than one language is necessary because of where people live. In addition to culture, the context of communication depends on the relationship between individuals
- Digital Media and Intercultural Communication The role of digital media in globalization’s growing speed could not be underestimated as it made people in all countries immensely interconnected.
- Intercultural Communication: Problems and Benefits In the article, the author examines the issues of intercultural communication and briefly discusses the problems that may arise in this case.
- Intercultural Communication thru Literature Customs and traditions become a law of social order determining communication patterns and interaction between people, their destinies and life paths.
- Indian Greeting Traditions: Intercultural Communication Study in India Different countries have different traditions and customs when it comes to greeting or addressing others. Many nuances depend on the culture of a nation and its history.
- Intercultural Business Communication in Brazil This study is designed to explore the particularities of intercultural business communication for proper company product selling in Brazil.
- Diversity and Intercultural Communication in the Workplace The article argues society must ensure comfortable and humane coexistence for all individuals, regardless of their belonging to other social or cultural groups.
- Intercultural Business Communication in Japan The purpose of this paper is to introduce readers to Japan, a country steeped in cultural tradition which has influenced the development of its business culture to a considerable degree.
- The U-Curve Model: Managing Intercultural Communication The U-Curve Model can be used as a framework for managing intercultural communication and minimizing the threat and impact of cross-cultural conflicts.
- Intercultural Communication in Real Life Situations Intercultural communication is essential in the era of globalization, as it strengthens society and ensures acceptance for each individual.
- Deep Dive Reading and Intercultural Communication The paper suggests a textual analysis of some of the most crucial intercultural communication papers over the last five years.
- Intercultural Conflict Communication Style There are various approaches to characterize conflict resolution styles, and one of them is the Intercultural Conflict Style Inventory.
- Barriers to Intercultural Communications Grothe (2020) identifies individual and institutional levels. Still, overall, this article presents a superficial review of the possible barrier.
- Diversity and Intercultural Communication in Business The paper explores some literature regarding the benefits of integration of diversity in the workplace and its importance.
- The Problems and Rules of Intercultural Communication Communication with people is a complex and multi-layered task to engage in for people because interaction or comes as second nature or presents a significant challenge.
- Workplace Diversity and Intercultural Communication The research mainly focuses on intercultural communication experiences between non-native English-speaking women and native English speakers.
- Intercultural Communication in Traditional Educational Setting Intercultural education should not be limited only to school subjects since more direct contact with other cultures is crucial.
- Vision Bank’s Intercultural Communication: Problems and Recommendations The selected company for this report is Vision Bank. It provides banking, loans, financial advice, and consultancy services to customers in different regions.
- Intercultural Communication: Cultural Relativity Principles This paper considers the intercultural communication question, exploring Vicki Marie’s essay about Samoan culture, Davidson’s essay on Australian aborigines, and some photographs.
- Intercultural Encounter and Communication Barriers The experience involved interaction with an African American person. The purpose of the interaction was to enquire direction to a certain place.
- Intercultural Business Communication in China The purpose of this paper is to introduce you, the reader, to the business culture, customs and tradition that comes with working in China.
- American and Chinese Intercultural Communication
- Poor Intercultural Communication That Significantly Affected International Commerce or Foreign Policy
- Business and Intercultural Communication Issues: Three Contributions to Various Aspects of Business Communication
- Intercultural Communication and How to Develop It
- Effective Intercultural Communication and Cultural Values
- The Power for Successful Business: Intercultural Communication and Competence
- Intercultural Communication Among Black/African American Women
- How Poor Intercultural Communication Affects International Commerce and Foreign Policy
- Intercultural Communication Between People From Different Cultures
- Inarritu’s “Babel” and the Exploration of Intercultural Communication Barriers
- Chinua Achebe’s “Things Fall Apart” and Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication and Cross-Cultural Man
- Joel Zwick’s “Big Fat Greek Wedding”: A Look at the Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication and Identity in Health Care
- Major Issues and Ways of Preventing Intercultural Communication Problems
- Intercultural Communication Between China and America
- Problematic Issues Arising With Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication and Negotiation in Indochina (Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam)
- Meaning, Causes, and Consequences of Racist Communication in Malaysia: How Not to Be Racist in Intercultural Communication in Malaysia
- Intercultural Communication Challenges for an American Company That Moves Production
- Peace, Economic, Technological and Demographic Imperatives of Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication: How Danone Adapted Its Products
- Cultural Differences and Intercultural Communication
- Improving Intercultural Communication Skills by Learning
- Men-Women and Japanese-American Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication and Business Practice
- Non-Verbal and Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication and the Contemporary World
- Culture, Communication, and Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication Bridges the Gap Between Global Performance and National Interests
- Popular Culture and Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication: Advantages and Disadvantages
- The Importance of Intercultural Communication Training to the Global Workforce
- Internet: Bridging Intercultural Communication
- Understanding Intercultural Communication in Business
- Intercultural Communication and International Business
- The Benefits and Problems of the Intercultural Communication at Campus
- Intercultural Communication Business Practices of Italy
- Physical and Cultural Context of Intercultural Communication
- Intercultural Communication: Comparing Sydney Suburbs Double Bay and Auburn
- Understanding the Intercultural Communication Gap
- Intercultural Communication: Cultures That Lead to Miscommunication
- The Cultural Differences and Their Impact on Intercultural Communication in the Film and Literature
- Intercultural Communication: Probing Cultural Stereotypes
- What Are the Barriers to Effective Intercultural Communication?
- How Can Intercultural Communication Cause Disruption in the Workplace?
- What Is the Essence of Intercultural Communication?
- How Are Intercultural Communication and Intracultural Communication Similar?
- How Does Identity Influence Intercultural Communication?
- What Is the Purpose of Intercultural Communication?
- What Is Intercultural Communication Apprehension?
- What Are the Most Critical Elements of Intercultural Communication Competence?
- Why Does Intercultural Communication Have the Potential for Increased Noise?
- Does Globalization Affect Intercultural Communication?
- What Role Might Religion Play in an Intercultural Communication Encounter?
- What Are the Basic Components of Intercultural Communication Competence?
- What Are the Problems in Intercultural Communication?
- How Do Board Games Improve Intercultural Communication Skills?
- What Skills Are Most Important for the Development of Intercultural Communication?
- What Are Cultural Spaces in Intercultural Communications?
- What Is Perception in Intercultural Communication?
- How Do Stereotypes Affect Intercultural Communication?
- How Does Gender Affect Intercultural Communication?
- How Do Commercials Influence Intercultural Communication?
- What Links Are There Between Intercultural Communication and Interpersonal Communication?
- What Are the Advantages of Intercultural Communication?
- How Is Intercultural Communication Important in Business?
- What Is the Importance of Cultural Intelligence for Intercultural Communication?
- Why Should We Learn Intercultural Communication?
- What Role Do Non-verbal Behaviors Have In Intercultural Communication?
- What Is the Role of Values in Intercultural Communication?
- How Does Social Media Affect Intercultural Communication?
- Why Is Symbolic Convergence Theory Important to Intercultural Communication?
- How Important Is Intercultural Communication in Our Society?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, October 26). 113 Intercultural Communication Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/
"113 Intercultural Communication Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 26 Oct. 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '113 Intercultural Communication Essay Topics'. 26 October.
1. StudyCorgi . "113 Intercultural Communication Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "113 Intercultural Communication Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "113 Intercultural Communication Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/intercultural-communication-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Intercultural Communication were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 8, 2024 .
Intercultural and Intergroup Communication Research Paper Topics

Origins of the Theories ICC has been studied for over 50 years (see Leeds- Hurwitz 1990) and developed to focus on how different cultures are distinguished from one another through their management of behaviors such as personal space and gestures. Particular attention has been devoted to understanding the cultural values that underpin different cultures’ communicative practices, including individualism– collectivism, high–low contexts, and so forth (Watson 2012). From the ICC perspective, when an individual recognizes that he is engaged in an intercultural interaction, the focus remains on competent interpersonal communication.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
- Acculturation Processes and Communication
- African Communication Modes
- Anxiety Uncertainty Management Theory
- Asian Communication Modes
- Bi- and Multilingualism
- Collective Action and Communication
- Cultural Patterns and Communication
- Disability and Communication
- Diversity in the Workplace
- Ethnic Media and their Influence
- Ethnographic Perspectives on Culture and Communication
- Ethnolinguistic Vitality and Communication
- Hate Speech and Ethnophaulisms
- Hispanic Communication Modes
- Intercultural Communication in Health-Care
- Intercultural Communication Training
- Intercultural Conflict Styles and Facework
- Intercultural Norms
- Interethnic Relationships in Families
- Intergroup Accommodative Processes
- Intergroup Communication and Discursive Psychology
- Intergroup Contact and Communication
- Intergroup Dimensions of Organizational Life
- Language Attitudes in Intergroup Contexts
- Marginality, Stigma, and Communication
- Media and Group Representations
- Migration and Immigration
- Muslim Communication Modes
- Nonverbal Communication and Culture
- Power in Intergroup Settings
- Prejudiced and Discriminatory Communication
- Social Stereotyping and Communication
- Western Communication Modes
In contrast to ICC, the IGC approach came out of social identity theory (SIT: Tajfel 1978) which states that individuals categorize themselves and others into social groups and have a need to compare themselves with others, as a way of attaining a positive self-concept. We seek to favor our own groups (ingroups) compared to groups to which we do not belong (outgroups) and, communicatively act in accord with these social identities (Giles & Giles 2012). To join an outgroup, as, for instance, with immigrants wishing to acculturate into a host community, we communicate with members in ways akin to them so that we may gain membership to that group (Giles et al. 2012). SIT is not a communication theory but, rather, represents a theory of intergroup behavior and cognitions. Communication theories such as communication accommodation theory explain how and why individuals engage in specific communication strategies when they interact with representatives of salient ingroups and outgroups.
Intercultural and Intergroup Communication Applications
Wiseman (2002) detailed the applications of ICC competence to assist individuals from differing cultures to communicate effectively with one another. The ICC literature embraces a skills training approach, the premises of which are that individuals must have knowledge of the culture with which they engage, the motivation to effectively communicate (including intercultural sensitivity and empathy), and appropriate communication skills. Interactions are viewed as activities that occur at the interpersonal level.
In contrast, the main focus in IGC is on interactants implicitly (and sometimes explicitly) taking on the role of being representatives of their respective cultures. This explicit acknowledgment that at times our intergroup identities take precedence has important implications for any interaction. Individuals who perceive that their personal identity is salient may engage in different communications strategies from those who believe they are representative of a particular group. Whether individual or group identities, or both, are made salient will shape the communication process in different ways which, in turn, can reconstruct the very nature of those identities (Dragojevic & Giles in press).
The way a group or culture expresses its unique identity through a dialect, specialized jargon, or nonverbal demeanor, is fundamental to a healthy social identity, and to one (under differing conditions) that group members can vigorously and creatively sustain and proliferate. Intercultural communication is not subsumed under, or even a special case of, intergroup communication, but rather the two are parallel traditions capable of significant coalescence (Gudykunst 2002).
Assumptions of Both Theories
There are assumptions within ICC theories that are not held in IGC (Brabant et al. 2007). These are: that strangers to a new culture will take on an ethno-relativist position; they need to be educated in the new culture’s values and norms; and when strangers possess knowledge of the culture and use expedient communication skills, effective communication will prevail. However, there is no extension within ICC theories to predict and explain when misunderstanding could in some cases be inevitable, despite any one individual’s excellent skills and cultural knowledge. Sociopsychological theories that emphasize the intergroup nature of intercultural communication, rather than only its interpersonal aspects, directly address miscommunication and related issues of prejudice and intercultural tensions.
IGC is highly cognizant of how status and power differentials impact communication behavior. Power is, arguably, not a key consideration in ICC and the implicit overarching assumption is that competent communication is the main communication goal. However, when two individuals from different cultures with a history of power differentials and consequent perceived injustices come together, effective and competent communication may not be their mutual goal. A training and skills focus on achieving effective communication does not take account of the fact that culturally-salient power differentials may dictate what is appropriate communication for any particular encounter.
ICC as well as IGC – beyond the study of national and ethnic groups – can truly embrace an array of different categories including older people, homosexuals, bisexuals, or academicians from different disciplines, as well as those embedded in for example, religious, or organizational cultures (Giles 2012). Importantly, their members may view themselves as belonging to a group that owns specific characteristics and traits that set them apart from others. IGC theories distinguish between “me” in an interaction as an individual and “us” as a virtual representative of a group. While intercultural as well as intergroup perspectives have sometimes been infused into studies in such contexts, there is much more room for invoking each other’s positions. The challenge is to move toward bringing these two theoretical viewpoints together in order to explain and predict the variables that determine effective and ineffective interactions (Kim, forthcoming).
References:
- Brabant, M., Watson, B. M., & Gallois, C. (2007). Psychological perspectives: Social psychology, language and intercultural communication. In H. Kotthoff & H. Spencer-Oatey (eds.), Handbook of intercultural communication. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter, pp. 55–75.
- Dragojevic, M. & Giles, H. (in press). Language and interpersonal communication: Their intergroup dynamics. In C. R. Berger (ed.), Handbook of interpersonal communication. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton.
- Giles, H. (ed.) (2012). The handbook of intergroup communication. London: Routledge.
- Giles, H., Bonilla, D., & Speer, R. (2012). Acculturating intergroup vitalities, accommodation and contact. In J. Jackson (ed.), Routledge handbook of intercultural communication. London: Routledge, pp. 244–259.
- Giles, H. & Giles, J. L. (2012). Ingroups and outgroups communicating. In A. Kuyulo (ed.), Inter/cultural communication: Representation and construction of culture in everyday interaction. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, pp. 141–162.
- Gudykunst, W. B. (2002). Intercultural communication theories. In W. B. Gudykunst & B. Mody (eds.), Handbook of international and intercultural communication, 2nd edn. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, pp. 183–205.
- Kim, Y. Y. (ed.) (forthcoming). The international encyclopedia of intercultural communication. New York: Wiley Blackwell.
- Leeds-Hurwitz, W. (1990). Notes on the history of intercultural communication: The Foreign Service Institute and the mandate for intercultural training. Quarterly Journal of Speech, 76, 262–281.
- Tajfel, H. (ed.) (1978). Differentiation between social groups: Studies in the social psychology of intergroup relations. New York: Academic Press.
- Watson, B. M. (2012). Intercultural and cross-cultural communication. In A. Kurylo (ed.), Inter/cultural communication. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, pp. 25–46.
- Wiseman, R. L. (2002). Intercultural communication competence In W. B. Gudykunst & B. Mody (eds.), Handbook of international and intercultural communication, 2nd edn. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, pp. 207–224.
Back to Communication Research Paper Topics .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Introductory Guide to Research in Intercultural Communication

Intercultural communication is the process by which meaning and messages are shared and interpreted between cultures. The study of intercultural communication is focused on how variance in cultural symbols, values, and behaviors affects communication interactions across cultures. It is a misnomer that intercultural communication means communication between different nations. While this is one type of cultural difference, it is important to recognize that individual nations are made up of co-cultures and there are many cases of intercultural communication that happen within a single nation and even within smaller, more local communities.
Defining Intercultural Communication
In order to define intercultural communication, it is important to first define culture and communication. Culture is how a group of people create a system of shared symbols, values, and behaviors over time in an effort to maintain social cohesion, survive, and instruct future generations. Communication is the process of sharing and interpreting meaning and information using symbols and behavior. Intercultural communication, then, involves understanding symbols, values, and behaviors as they vary by culture and how they impact communication interactions.
Historically, and especially in a generally ethnocentric American society, the need for intercultural understanding and intercultural communication had to be justified. However, in an increasingly globalized world, the study of intercultural communication by scholars, businesses, and individuals hardly requires justification — its need is nearly self-evident. Globalization makes competent intercultural communication an imperative for many individuals and businesses, resulting in an ever-growing demand for intercultural communication experts and the study of intercultural communication.
Outside this capitalistic view, the import of intercultural communication continues to be realized as well. The free exchange of ideas, concepts of liberty and human rights, and communicating our shared humanity ultimately relies upon the principles studied by scholars of intercultural communication. Additionally, with the Internet’s rise and the relative ease of travel, there is a desire to learn, to seek out information about other cultures.
It is important to note that intercultural communication is not necessarily international communication. Scholars find great interest in studying co-cultures that reside within national boundaries. For example, individuals living in the southern United States have a distinctly different culture from those living in New England. Likewise, individuals in the deaf community have a distinct culture from those who are part of hearing culture. As a final example, individuals living in rural and urban areas have noticeably different cultures. Clearly, intercultural communication applies when individuals in these examples communicate, regardless of their shared national borders and language.
As individuals study intercultural communication, the goal is to become a competent communicator in cross-cultural communication situations. This involves an understanding of each culture’s communication norms, and the ability to view the world with cultural relativism (i.e., evaluate others’ actions not by one’s own societal standards, but by the standards of that culture). To illustrate, review the following questions:
- Imagine the first business meeting between two individuals. Should they ask each other about their families? Should they immediately discuss business? How would an age difference between each individual impact this meeting? Where should this meeting take place?
- If Bob and John are friends, and Bob sees John’s wife out to dinner with a man other than John, is this something that Bob should mention to John?
- How close should two people stand when having a conversation?
- In the event of a marriage between two people who come from families with different ethnic, geographical, and/or political cultures, how are the inter-family dynamics and politics to be negotiated?
Regardless of how these questions are answered, the answers are heavily influenced by the norms of one’s own culture. In each situation, an intercultural expert is interested in the norms of each culture, where the interaction is taking place, how differences in cultural norms might affect the interaction, and much more.
Overarching Intercultural Communication Theories and Constructs
Scholars have built various theories to describe, explain, and predict intercultural communication. Over time, scholars continue to go through a process of theory building, which involves reevaluating, advancing, and refining existing theories while building new theories. The following list illustrates some of the most common theories or topics discussed in the area of intercultural communication.
Social Identity Theory : This theory is used to understand intercultural communication behaviors based on the perception of one’s membership status within a culture and the relative status of that cultural group. This theory is also used to understand the stability of one’s cultural group, cultural group status, and the ability to move between cultural groups.
Intercultural Workgroup Communication Theory : This theory discusses how cultural diversity influences workgroup communication and how that communication will affect the success of a group in achieving its goals. This theory states that factors like group composition (i.e., heterogeneous or homogeneous), cultural differences, and individual characteristics will ultimately affect the quality of the communication within the group. In turn, communication quality will impact the group’s outcome.
Cross-Cultural Adaptation Theory : As one might imagine, immigration offers a ripe opportunity for research and intercultural understanding. Cross-Cultural Adaptation Theory is used to describe, predict, and explain behaviors of immigrants as they adapt to their host culture. This theory is specifically interested in how individuals adapt to new cultures over time.
Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions : Nearly every student who takes a basic intercultural communication course will be introduced to Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions. Geert Hofstede developed six dimensions by which we can understand societal values. One of these dimensions is the power distance dimension. Power distance is the extent to which a member of a society expects that, within groups, there will be relative equality or inequality between more and less powerful members. For example, in some societies there is high power distance between a son and father, or a supervisor and supervisee. One might ask, “In my society, do I have the ability to suggest that my parent, teacher, or supervisor might be wrong?” If the answer is yes, that person is probably in a low power distance society. In a high power distance society, this would rarely be acceptable.
As a second example, another dimension is the individualism vs. collectivism dimension. This is the extent to which a society values the individual over the group or vice-versa. As one might imagine, the United States is a highly individualistic society where individual needs and achievement are often more important than the needs of the group. On the contrary, Japan is a highly collectivistic society in which the needs of the group and the achievement of the group is much more important than any individual’s needs or achievement.
Together, Hofstede’s six dimensions give some insight into how cultures work. It is important to note that Hofstede’s dimensions have been heavily criticized due to the fact that they were developed through studying participants who were mostly educated, mostly upper-class, and mostly men. Furthermore, there is some criticism that national cultures often have such important intracultural differences that Hofstede’s dimensions can hardly be applied with accuracy to individuals or subgroups. Regardless, these dimensions are commonly taught in intercultural communication courses and are regularly used in intercultural communication research.
Linguistic Relativity (The Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis) : Simply put, linguistic relativity states that the language an individual speaks affects their world view. Essentially, this theory suggests that one’s understanding of the world is socially constructed, in part, by the language that individual speaks. For example, research has supported the hypothesis that when someone speaks a language without a future tense, they are more likely to save money and take care of their health. The basis for this effect is that, without future tense, people begin to see the future and the present to have a much closer relationship, which motivates behavior in the present that will positively affect one’s future.
Approaching Intercultural Communication from a Critical Perspective
As mentioned above, intercultural communication also involves the study of cultures that exist within a larger culture and how that communication is managed, negotiated, and contested. Oftentimes, this facet of intercultural communication requires a critical lens in examining the power dynamics that exist between a culture that is reliant upon the hegemonic power structure and a culture that challenges that power structure.
In other words, scholars that employ a critical cultural perspective in intercultural communication bring to the fore the ways in which groups in power maintain a cultural hierarchy, thereby subjugating any that oppose it. Additionally, scholars also look at how marginalized groups challenge the hierarchy and maintain their culture through communication. Good examples of this perspective in action come from scholars examining white nationalist rhetoric, Black Lives Matter, the white backlash to Black Lives Matter, and the communicative practices of recent immigrant groups. The following are theories and concepts that stem from this critical perspective.
Critical Race Theory : Broadly speaking, Critical Race Theory relates to racism and how it functions in modern society. This theory posits that racism is an ordinary and common component of everyday life that is rarely overt, which makes it quite difficult to resolve or address. This theory also suggests that, because racism and racist policies support the dominant group’s advancement, few members of the dominant group are actually interested in eliminating racism and racist policies from a culture.
Co-Cultural Theory : As previously discussed, cultural groups are not always separated by national borders or languages. Co-cultural theory is used to understand conversations between members of marginalized groups and members of dominant social groups. For example, a researcher may be interested in how grade school age children who speak English as a second language navigate their relationships with teachers and fellow students who speak English as a primary language within the context of an English dominant society like the United States. Co-cultural theory could help to predict and explain the actions of this underrepresented group.
Studying Intercultural Communication
Students interested in studying intercultural communication should review individual programs to gain insight into how each program addresses the topic. In some cases, programs are highly theoretical, focusing on social-scientific research as it relates to intercultural communication. Students who graduate from a theoretical program in intercultural communication often advance to Ph.D. programs, during which time they develop social-scientific research and teach undergraduate students about the topic.
Other programs are more concerned with how intercultural communication skills can be developed for the workforce. In these programs, students will examine common business practices across cultures. It is not unusual for these programs to involve seminars abroad, which allow students to become immersed in a different culture or cultures. Intercultural communication is also an important component of both internal and external facing strategic communications for organizations, and is highly relevant to fields such as politics and diplomacy, marketing and public relations, and corporate communication/human resources. As a result, intercultural communication courses are often included in applied programs in strategic communication, global strategic communication, political communication, integrated marketing communications, and organizational communication.
Additional Resources
Prospective students who are interested in learning more about intercultural communication can review the following resources:
- Cross-Cultural Adaptation – Young Yun Kim
- Intercultural Communication – Inc.
- Intercultural Communication Skills – Skills You Need
- Social Identity Theory – SimplyPsychology
- The 6-Dimensions Model of National Culture – Geert Hofstede
- The Effect of Language on Economic Behavior: Evidence from Savings Rates, Health Behaviors, and Retirement Assets – Keith Chen
- What is Critical Race Theory – UCLA School of Public Affairs
- What You Need to Know About: Effective Intercultural Workgroup Communication Theory – Binus University

- Information Technology
- Commuter Services
- Human Resources
- Campus Safety
When in Rome: Intercultural Business Communication – w/ Miriam Bandala

Bringing her culinary skills abroad, Miriam Bandala collaborated with a local restaurant during her visit to the Study Abroad Program in Rome. She enjoys sharing experiences through cuisines with others and learning about cultural connections within languages.
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Science communication competition brings research into the real world
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
Laurence Willemet remembers countless family dinners where curious faces turned to her with shades of the same question: “What is it, exactly, that you do with robots?”
It’s a familiar scenario for MIT students exploring topics outside of their family’s scope of knowledge — distilling complex concepts without slides or jargon, plumbing the depths with nothing but lay terms. “It was during these moments,” Willemet says, “that I realized the importance of clear communication and the power of storytelling.”
Participating in the MIT Research Slam, then, felt like one of her family dinners.
The finalists in the 2024 MIT Research Slam competition met head-to-head on Wednesday, April 17 at a live, in-person showcase event. Four PhD candidates and four postdoc finalists demonstrated their topic mastery and storytelling skills by conveying complex ideas in only 180 seconds to an educated audience unfamiliar with the field or project at hand.
The Research Slam follows the format of the 3-Minute Thesis competition, which takes place annually at over 200 universities around the world. Both an exciting competition and a rigorous professional development training opportunity, the event serves an opportunity to learn for everyone involved.
One of this year’s competitors, Bhavish Dinakar, explains it this way: “Participating in the Research Slam was a fantastic opportunity to bring my research from the lab into the real world. In addition to being a helpful exercise in public speaking and communication, the three-minute time limit forces us to learn the art of distilling years of detailed experiments into a digestible story that non-experts can understand.”
Leading up to the event, participants joined training workshops on pitch content and delivery, and had the opportunity to work one-on-one with educators from the Writing and Communication Center, English Language Studies, Career Advising and Professional Development, and the Engineering Communication Labs, all of which co-sponsored and co-produced the event. This interdepartmental team offered support for the full arc of the competition, from early story development to one-on-one practice sessions.
The showcase was jovially emceed by Eric Grunwald, director of English language learning. He shared his thoughts on the night: “I was thrilled with the enthusiasm and skill shown by all the presenters in sharing their work in this context. I was also delighted by the crowd’s enthusiasm and their many insightful questions. All in all, another very successful slam.”
A panel of accomplished judges with distinct perspectives on research communication gave feedback after each of the talks: Deborah Blum, director of the Knight Science Journalism Program at MIT; Denzil Streete, senior associate dean and director of graduate education; and Emma Yee, scientific editor at the journal Cell .
Deborah Blum aptly summed up her experience: “It was a pleasure as a science journalist to be a judge and to listen to this smart group of MIT grad students and postdocs explain their research with such style, humor, and intelligence. It was a reminder of the importance the university places on the value of scientists who communicate. And this matters. We need more scientists who can explain their work clearly, explain science to the public, and help us build a science-literate world.”
After all the talks, the judges provided constructive and substantive feedback for the contestants. It was a close competition, but in the end, Bhavish Dinakar was the judges’ choice for first place, and the audience agreed, awarding him the Audience Choice award. Omar Rutledge’s strong performance earned him the runner-up position. Among the postdoc competitors, Laurence Willemet won first place and Audience Choice, with Most Kaniz Moriam earning the runner-up award.
Postdoc Kaniz Mariam noted that she felt privileged to participate in the showcase. “This experience has enhanced my ability to communicate research effectively and boosted my confidence in sharing my work with a broader audience. I am eager to apply the lessons learned from this enriching experience to future endeavors and continue contributing to MIT's dynamic research community. The MIT Research Slam Showcase wasn't just about winning; it was about the thrill of sharing knowledge and inspiring others. Special thanks to Chris Featherman and Elena Kallestinova from the MIT Communication Lab for their guidance in practical communication skills. ”
Double winner Laurence Willemet related the competition to experiences in her daily life. Her interest in the Research Slam was rooted in countless family dinners filled with curiosity. “‘What is it exactly that you do with robots?’ they would ask, prompting me to unravel the complexities of my research in layman’s terms. Each time, I found myself grappling with the task of distilling intricate concepts into digestible nuggets of information, relying solely on words to convey the depth of my work. It was during these moments, stripped of slides and scientific jargon, that I realized the importance of clear communication and the power of storytelling. And so, when the opportunity arose to participate in the Research Slam, it felt akin to one of those family dinners for me.”
The first place finishers received a $600 cash prize, while the runners-up and audience choice winners each received $300.
Last year’s winner in the PhD category, Neha Bokil, candidate in biology working on her dissertation in the lab of David Page, is set to represent MIT at the Three Minute Thesis Northeast Regional Competition later this month, which is organized by the Northeastern Association of Graduate Schools.
A full list of slam finalists and the titles of their talks is below.
PhD Contestants:
- Pradeep Natarajan, Chemical Engineering (ChemE), “What can coffee-brewing teach us about brain disease?”
- Omar Rutledge, Brain and Cognitive Sciences, “Investigating the effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on social anxiety disorder”
- Bhavish Dinakar, ChemE, “A boost from batteries: making chemical reactions faster”
- Sydney Dolan, Aeronautics and Astronautics, “Creating traffic signals for space”
Postdocs:
- Augusto Gandia, Architecture and Planning, “Cyber modeling — computational morphogenesis via ‘smart’ models”
- Laurence Willemet, Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, “Remote touch for teleoperation”
- Most Kaniz Moriam, Mechanical Engineering, “Improving recyclability of cellulose-based textile wastes”
- Mohammed Aatif Shahab, ChemE, “Eye-based human engineering for enhanced industrial safety”
Research Slam organizers included Diana Chien, director of MIT School of Engineering Communication Lab ; Elena Kallestinova, director of MIT Writing and Communication Center ; Alexis Boyer, assistant director, Graduate Career Services, Career Advising and Professional Development (CAPD); Amanda Cornwall, associate director, Graduate Student Professional Development, CAPD; and Eric Grunwald, director of English Language Studies. This event was sponsored by the Office of Graduate Education, the Office of Postdoctoral Services, the Writing and Communication Center, MIT Career Advising and Professional Development , English Language Studies, and the MIT School of Engineering Communication Labs.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- MIT Research Slam
- Research Slam YouTube channel
- MIT Career Advising and Professional Development (CAPD)
- Graduate Student Professional Development
- Writing and Communication Center
- MIT School of Engineering Communication Lab
- MIT English Language Studies
Related Topics
- Contests and academic competitions
- Science communications
- Graduate, postdoctoral
- Technology and society
- Science writing
- Career Advising and Professional Development
Related Articles

Third annual MIT Research Slam showcase highlights PhD and postdoc communication skills

MIT Research Slam showcases postdoc and PhD communication skills

Third annual Science Slam becomes first virtual Research Slam
Previous item Next item
More MIT News
A better way to control shape-shifting soft robots
Read full story →

From steel engineering to ovarian tumor research

Professor Emeritus David Lanning, nuclear engineer and key contributor to the MIT Reactor, dies at 96

Discovering community and cultural connections

MIT Supply Chain Management Program earns top honors in three 2024 rankings
New treatment could reverse hair loss caused by an autoimmune skin disease
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research on intercultural communication is conducted using primarily three different methodological approaches: social scientific, interpretive, and critical. ... The interviews can focus on narratives, topics, perspectives, and opinions and often are conducted in a semi-structured manner (although unstructured interviews are sometimes ...
The Journal of Intercultural Communication Research (JICR) is a publication of the World Communication Association.JICR seeks submissions exploring the dynamic interplay between culture and communication and the symbolic facets of cultural interaction in direct or mediated contexts using a broad spectrum of methodological perspectives.JICR is deeply committed to contributing to the culture and ...
However, intercultural communication is a challenging type of human communication and the lack of ICC, especially the lack of communication engagement, interpersonal skills, and team effectiveness are the main barriers to conducting helpful intercultural communication (Chen & Starosta, 2007; Sarwari & Abdul Wahab, 2017).
The purpose of this review is to critically analyze the state of intercultural communication literature. This review has three purposes. First, this review summarizes where the discipline has been, paying close attention to the discipline's history and some key areas of research. Second, this review discusses where the discipline is going ...
SLR findings can provide strong conceptual foundations for future research directions on the topic reviewed. Current research on all things 'intercultural' indicates persisting conceptual imprecision regarding the exact meanings and definitions of the intercultural notion as embodied in the concepts of IC and ICD (Modood, Citation 2017).
978-1-108-42969-6 — The Cambridge Handbook of Intercultural Communication Edited by Guido Rings , Sebastian Rasinger Frontmatter ... contemporary research in critical intercultural communication and post-colonial studies. ... encompass the most important issues and topics within each subject, offering a coherent picture of the latest theories and
Fred Dervin is Professor of Multicultural Education at the University of Helsinki (Finland). He also holds several associate professorships around the world. specializes in language and intercultural education, the sociology of multicultural-ism, and linguistics for intercultural communication and education.
Research Topics in Intercultural Interaction A sense of curiosity is nature's original school of education. Smiley Blanton Chapter outline 10.1 Researching intercultural interaction competence 10.2 Researching understanding and rapport in intercultural interaction 10.3 Researching disadvantage and domination in intercultural interaction
Intercultural communication is concerned with how people from different cultural backgrounds interact and negotiate cultural or linguistic differences. A paradigm is the overarching constructive framework and meta-thinking behind a piece of research.
Research Methods in Intercultural Communication introduces and contextualizes the most important methodological issues in the field for upper-level undergraduate and graduate students. Examples of these issues are which paradigms and how to research multilingually, interculturally and ethnically. Provides the first dedicated and most comprehensive volume on research methods in intercultural ...
Challenges of Effective Intercultural Communication. Inter-cultural communications professionals work with global firms to play down the aforementioned results of poor inter-cultural understanding. Lingual acquaintance serves to bridge the cultural bridges and evening lines of communication.
Moreover, common topics in CCM are intercultural communication (Adler and Gunderson, 2008; ... This study systematically examines research topics, paradigms, and methodical approaches of CCM over time in two leading academic journals of the research field: CCSM and IJCCM. The study resulted from the need to draw a landscape of the research ...
Abstract. This chapter and the next focus on research into intercultural interaction. In this chapter, we outline some key research topics, and sample studies, associated with the various issues explored in Parts 1 and 2. In the next chapter, we explore the steps involved in carrying out a research project, and discuss the ways in which ...
The combination of intercultural communication and international students is a broad and fascinating topic of research. Extant research on the topic has mainly focused on the following areas: international students' perceptions of intercultural communication, the difficulties faced by international students, and the correlations between ...
The following article deals with intercultural communication research as a (potential) subfield of communication studies. The broader aim is to contribute to the history as well as to the systematization of the field of intercultural communication research. The author is mapping three very different national research communities: Germany, France and the US. The main question is: Why, in each ...
Intercultural communication is communication between people with differing cultural identities. One reason we should study intercultural communication is to foster greater self-awareness (Martin & Nakayama, 2010). Our thought process regarding culture is often "other focused," meaning that the culture of the other person or group is what ...
Even though intercultural competence is a topic of interest to researchers in multiple disciplines, the findings from within a discipline appear to have limited external disciplinary reach. This is something that needs to be addressed. ... Journal of Intercultural Communication Research, 41(1), 1-16. Ni, L., & Wang, Q. (2011). Anxiety and ...
Intercultural Communication Interaction Among the Local and International ELS Postgraduate Students: A Case Study of International Universities in Malaysia. Popoola Kareem Hamed, Daud Abdul Quadir Elega, Salawudeen Olayiwola Khalid & Koussoube Issa. Pages: 629-645. Published online: 08 Dec 2023.
This paper considers the intercultural communication question, exploring Vicki Marie's essay about Samoan culture, Davidson's essay on Australian aborigines, and some photographs. Intercultural Encounter and Communication Barriers. The experience involved interaction with an African American person.
See our list of intercultural and intergroup communication research paper topics.. Social groups, such as adolescents and ethnic groups, very often have their own distinctive cultures that include specialized foods, customs and rituals, literature, music, while other intergroup situations (e.g., artificially constructed laboratory groups) constitute social categories that cannot claim such ...
Communication is the process of sharing and interpreting meaning and information using symbols and behavior. Intercultural communication, then, involves understanding symbols, values, and behaviors as they vary by culture and how they impact communication interactions. Historically, and especially in a generally ethnocentric American society ...
Bringing her culinary skills abroad, Miriam Bandala collaborated with a local restaurant during her visit to the Study Abroad Program in Rome. She enjoys sharing experiences through cuisines with others and learning about cultural connections within languages.
researchers: identity, intercultural communication competence, and adaptation. Within each of these areas of research we identify and describe key theories that have shaped intercultural communication. Intercultural communication and identity There are two ways to approach identity in intercultural communication: the traditional
Four PhD candidates and four postdoc finalists demonstrated their topic mastery and storytelling skills by conveying complex ideas in only 180 seconds to an educated audience unfamiliar with the field or project at hand. ... A panel of accomplished judges with distinct perspectives on research communication gave feedback after each of the talks ...
Debate topics included disaster preparedness, diagnostic disclosure, appropriate pandemic response, racial health disparities, abortion access, public health measures, and incorporation of artificial intelligence in health-care settings. ... Supported by course readings on both our subject matter and principles of intercultural exchange ...
Data analysis in this research suggests that gender plays an important role in intercultural communication between patients and health professionals on sexual health-related topics. Gender segregation due to cultural traditions and religious beliefs can create huge barriers between female patients and male health professionals.