- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file

People also looked at
Systematic review article, a systematic review of the effectiveness of online learning in higher education during the covid-19 pandemic period.

- 1 Department of Basic Education, Beihai Campus, Guilin University of Electronic Technology Beihai, Beihai, Guangxi, China
- 2 School of Sports and Arts, Harbin Sport University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 3 School of Music, Harbin Normal University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 4 School of General Education, Beihai Vocational College, Beihai, Guangxi, China
- 5 School of Economics and Management, Beihai Campus, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, Guilin, Guangxi, China
Background: The effectiveness of online learning in higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic period is a debated topic but a systematic review on this topic is absent.
Methods: The present study implemented a systematic review of 25 selected articles to comprehensively evaluate online learning effectiveness during the pandemic period and identify factors that influence such effectiveness.
Results: It was concluded that past studies failed to achieve a consensus over online learning effectiveness and research results are largely by how learning effectiveness was assessed, e.g., self-reported online learning effectiveness, longitudinal comparison, and RCT. Meanwhile, a set of factors that positively or negatively influence the effectiveness of online learning were identified, including infrastructure factors, instructional factors, the lack of social interaction, negative emotions, flexibility, and convenience.
Discussion: Although it is debated over the effectiveness of online learning during the pandemic period, it is generally believed that the pandemic brings a lot of challenges and difficulties to higher education and these challenges and difficulties are more prominent in developing countries. In addition, this review critically assesses limitations in past research, develops pedagogical implications, and proposes recommendations for future research.
1 Introduction
1.1 research background.
The COVID-19 pandemic first out broken in early 2020 has considerably shaped the higher education landscape globally. To restrain viral transmission, universities globally locked down, and teaching and learning activities were transferred to online platforms. Although online learning is a relatively mature learning model and is increasingly integrated into higher education, the sudden and unprepared transition to wholly online learning caused by the pandemic posed formidable challenges to higher education stakeholders, e.g., policymakers, instructors, and students, especially at the early stage of the pandemic ( García-Morales et al., 2021 ; Grafton-Clarke et al., 2022 ). Correspondingly, the effectiveness of online learning during the pandemic period is still questionable as online learning during this period has some unique characteristics, e.g., the lack of preparation, sudden and unprepared transition, the huge scale of implementation, and social distancing policies ( Sharma et al., 2020 ; Rahman, 2021 ; Tsang et al., 2021 ; Hollister et al., 2022 ; Zhang and Chen, 2023 ). This question is more prominent in developing or undeveloped countries because of insufficient Internet access, network problems, the lack of electronic devices, and poor network infrastructure ( Adnan and Anwar, 2020 ; Muthuprasad et al., 2021 ; Rahman, 2021 ; Chandrasiri and Weerakoon, 2022 ).
Learning effectiveness is a key consideration of education as it reflects the extent to which learning and teaching objectives are achieved and learners’ needs are satisfied ( Joy and Garcia, 2000 ; Swan, 2003 ). Online learning was generally proven to be effective within a higher education context ( Kebritchi et al., 2017 ) prior to the pandemic. ICTs have fundamentally shaped the process of learning as they allow learners to learn anywhere and anytime, interact with others efficiently and conveniently, and freely acquire a large volume of learning materials online ( Kebritchi et al., 2017 ; Choudhury and Pattnaik, 2020 ). Such benefits may be offset by the challenges brought about by the pandemic. A lot of empirical studies globally have investigated the effectiveness of online learning but there is currently a scarcity of a systematic review of these studies to comprehensively evaluate online learning effectiveness and identify factors that influence effectiveness.
At present, although the vast majority of countries have implemented opening policies to deal with the pandemic and higher education institutes have recovered offline teaching and learning, assessing the effectiveness of online learning during the pandemic period via a systematic review is still essential. First, it is necessary to summarize, learn from, and reflect on the lessons and experiences of online learning practices during the pandemic period to offer implications for future practices and research. Second, the review of online learning research carried out during the pandemic period is likely to generate interesting knowledge because of the unique research context. Third, higher education institutes still need a contingency plan for emergency online learning to deal with potential crises in the future, e.g., wars, pandemics, and natural disasters. A systematic review of research on the effectiveness of online learning during the pandemic period offers valuable knowledge for designing a contingency plan for the future.
1.2 Related concepts
1.2.1 online learning.
Online learning should not be simply understood as learning on the Internet or the integration of ICTs with learning because it is a systematic framework consisting of a set of pedagogies, technologies, implementations, and processes ( Kebritchi et al., 2017 ; Choudhury and Pattnaik, 2020). Choudhury and Pattnaik (2020; p.2) summarized prior definitions of online learning and provided a comprehensive and up-to-date definition, i.e., online learning refers to “ the transfer of knowledge and skills, in a well-designed course content that has established accreditations, through an electronic media like the Internet, Web 4.0, intranets and extranets .” Online learning differs from traditional learning because of not only technological differences, but also differences in social development and pedagogies ( Camargo et al., 2020 ). Online learning has also considerably shaped the patterns by which knowledge is stored, shared, and transferred, skills are practiced, as well as the way by which stakeholders (e.g., teachers and teachers) interact ( Desai et al., 2008 ; Anderson and Hajhashemi, 2013 ). In addition, online learning has altered educational objectives and learning requirements. Memorizing knowledge was traditionally viewed as vital to learning but it is now less important since required knowledge can be conveniently searched and acquired on the Internet while the reflection and application of knowledge becomes more important ( Gamage et al., 2023 ). Online learning also entails learners’ self-regulated learning ability more than traditional learning because the online learning environment inflicts less external regulation and provides more autonomy and flexibility ( Barnard-Brak et al., 2010 ; Wong et al., 2019 ). The above differences imply that traditional pedagogies may not apply to online learning.
There are a variety of online learning models according to the differences in learning methods, processes, outcomes, and the application of technologies ( Zeitoun, 2008 ). As ICTs can be used as either the foundation of learning or auxiliary means, online learning can be classified into assistant, blended, and wholly online models. Here, assistant online learning refers to the scenario where online learning technologies are used to supplement and support traditional learning; blended online learning refers to the integration/ mixture of online and offline methods, and; wholly online learning refers to the exclusive use of the Internet for learning ( Arkorful and Abaidoo, 2015 ). The present review focuses on wholly online learning because the review is interested in the COVID-19 pandemic context where learning activities are fully switched to online platforms.
1.2.2 Learning effectiveness
Learning effectiveness can be broadly defined as the extent to which learning and teaching objectives have been effectively and efficiently achieved via educational activities ( Swan, 2003 ) or the extent to which learners’ needs are satisfied by learning activities ( Joy and Garcia, 2000 ). It is a multi-dimensional construct because learning objectives and needs are always diversified ( Joy and Garcia, 2000 ; Swan, 2003 ). Assessing learning effectiveness is a key challenge in educational research and researchers generally use a set of subjective and objective indicators to assess learning effectiveness, e.g., examination scores, assignment performance, perceived effectiveness, student satisfaction, learning motivation, engagement in learning, and learning experience ( Rajaram and Collins, 2013 ; Noesgaard and Ørngreen, 2015 ). Prior research related to the effectiveness of online learning was diversified in terms of learning outcomes, e.g., satisfaction, perceived effectiveness, motivation, and learning engagement, and there is no consensus over which outcomes are valid indicators of learning effectiveness. The present study adopts a broad definition of learning effectiveness and considers various learning outcomes that are closely associated with learning objectives and needs.
1.3 Previous review research
Up to now, online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic period has attracted considerable attention from academia and there is a lot of related review research. Some review research analyzed the trends and major topics in related research. Pratama et al. (2020) tracked the trend of using online meeting applications in online learning during the pandemic period based on a systematic review of 12 articles. It was reported that the use of these applications kept a rising trend and this use helps promote learning and teaching processes. However, this review was descriptive and failed to identify problems related to these applications as well as the limitations of these applications. Zhang et al. (2022) implemented a bibliometric review to provide a holistic view of research on online learning in higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic period. They concluded that the majority of research focused on identifying the use of strategies and technologies, psychological impacts brought by the pandemic, and student perceptions. Meanwhile, collaborative learning, hands-on learning, discovery learning, and inquiry-based learning were the most frequently discussed instructional approaches. In addition, chemical and medical education were found to be the most investigated disciplines. This review hence offered a relatively comprehensive landscape of related research in the field. However, since it was a bibliometric review, it merely analyzed the superficial characteristics of past articles in the field without a detailed analysis of their research contributions. Bughrara et al. (2023) categorized the major research topics in the field of online medical education during the pandemic period via a scoping review. A total of 174 articles were included in the review and it was found there were seven major topics, including students’ mental health, stigma, student vaccination, use of telehealth, students’ physical health, online modifications and educational adaptations, and students’ attitudes and knowledge. Overall, the review comprehensively reveals major topics in the focused field.
Some scholars believed that online learning during the pandemic period has brought about a lot of problems while both students and teachers encounter many challenges. García-Morales et al. (2021) implemented a systematic review to identify the challenges encountered by higher education in an online learning scenario during the pandemic period. A total of seven studies were included and it was found that higher education suddenly transferred to online learning and a lot of technologies and platforms were used to support online learning. However, this transition was hasty and forced by the extreme situation. Thus, various stakeholders in learning and teaching (e.g., students, universities, and teachers) encountered difficulties in adapting to this sudden change. To deal with these challenges, universities need to utilize the potential of technologies, improve learning experience, and meet students’ expectations. The major limitation of García-Morales et al. (2021) review of the small-sized sample. Meanwhile, García-Morales et al. (2021) also failed to systematically categorize various types of challenges. Stojan et al. (2022) investigated the changes to medical education brought about by the shift to online learning in the COVID-19 pandemic context as well as the lessons and impacts of these changes via a systematic review. A total of 56 articles were included in the analysis, it was reported that small groups and didactics were the most prevalent instructional methods. Although learning engagement was always interactive, teachers majorly integrated technologies to amplify and replace, rather than transform learning. Based on this, they argued that the use of asynchronous and synchronous formats promoted online learning engagement and offered self-directed and flexible learning. The major limitation of this review is that the article is somewhat descriptive and lacks the crucial evaluation of problems of online learning.
Review research has also focused on the changes and impacts brought by online learning during the pandemic period. Camargo et al. (2020) implemented a meta-analysis on seven empirical studies regarding online learning methods during the pandemic period to evaluate feasible online learning platforms, effective online learning models, and the optimal duration of online lectures, as well as the perceptions of teachers and students in the online learning process. Overall, it was concluded that the shift from offline to online learning is feasible, and; effective online learning needs a well-trained and integrated team to identify students’ and teachers’ needs, timely respond, and support them via digital tools. In addition, the pandemic has brought more or less difficulties to online learning. An obvious limitation of this review is the overly small-sized sample ( N = 7), which offers very limited information, but the review tries to answer too many questions (four questions). Grafton-Clarke et al. (2022) investigated the innovation/adaptations implemented, their impacts, and the reasons for their selections in the shift to online learning in medical education during the pandemic period via a systematic review of 55 articles. The major adaptations implemented include the rapid shift to the virtual space, pre-recorded videos or live streaming of surgical procedures, remote adaptations for clinical visits, and multidisciplinary ward rounds and team meetings. Major challenges encountered by students and teachers include the need for technical resources, faculty time, and devices, the shortage of standardized telemedicine curricula, and the lack of personal interactions. Based on this, they criticized the quality of online medical education. Tang (2023) explored the impact of the pandemic on primary, secondary, and tertiary education in the pandemic context via a systematic review of 41 articles. It was reported that the majority of these impacts are negative, e.g., learning loss among learners, assessment and experiential learning in the virtual environment, limitations in instructions, technology-related constraints, the lack of learning materials and resources, and deteriorated psychosocial well-being. These negative impacts are amplified by the unequal distribution of resources, unfair socioeconomic status, ethnicity, gender, physical conditions, and learning ability. Overall, this review comprehensively criticizes the problems brought about by online learning during the pandemic period.
Very little review research evaluated students’ responses to online learning during the pandemic period. For instance, Salas-Pilco et al. (2022) evaluated the engagement in online learning in Latin American higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic period via a systematic review of 23 studies. They considered three dimensions of engagement, including affective, cognitive, and behavioral engagement. They described the characteristics of learning engagement and proposed suggestions for enhancing engagement, including improving Internet connectivity, providing professional training, transforming higher education, ensuring quality, and offering emotional support. A key limitation of the review is that these authors focused on describing the characteristics of engagement without identifying factors that influence engagement.
A synthesis of previous review research offers some implications. First, although learning effectiveness is an important consideration in educational research, review research is scarce on this topic and hence there is a lack of comprehensive knowledge regarding the extent to which online learning is effective during the COVID-19 pandemic period. Second, according to past review research that summarized the major topics of related research, e.g., Bughrara et al. (2023) and Zhang et al. (2022) , the effectiveness of online learning is not a major topic in prior empirical research and hence the author of this article argues that this topic has not received due attention from researchers. Third, some review research has identified a lot of problems in online learning during the pandemic period, e.g., García-Morales et al. (2021) and Stojan et al. (2022) . Many of these problems are caused by the sudden and rapid shift to online learning as well as the unique context of the pandemic. These problems may undermine the effectiveness of online learning. However, the extent to which these problems influence online learning effectiveness is still under-investigated.
1.4 Purpose of the review research
The research is carried out based on a systematic review of past empirical research to answer the following two research questions:
Q1: To what extent online learning in higher education is effective during the COVID-19 pandemic period?
Q2: What factors shape the effectiveness of online learning in higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic period?
2 Research methodology
2.1 literature review as a research methodology.
Regardless of discipline, all academic research activities should be related to and based on existing knowledge. As a result, scholars must identify related research on the topic of interest, critically assess the quality and content of existing research, and synthesize available results ( Linnenluecke et al., 2020 ). However, this task is increasingly challenging for scholars because of the exponential growth of academic knowledge, which makes it difficult to be at the forefront and keep up with state-of-the-art research ( Snyder, 2019 ). Correspondingly, literature review, as a research methodology is more relevant than previously ( Snyder, 2019 ; Linnenluecke et al., 2020 ). A well-implemented review provides a solid foundation for facilitating theory development and advancing knowledge ( Webster and Watson, 2002 ). Here, a literature review is broadly defined as a more or less systematic way of collecting and synthesizing past studies ( Tranfield et al., 2003 ). It allows researchers to integrate perspectives and results from a lot of past research and is able to address research questions unanswered by a single study ( Snyder, 2019 ).
There are generally three types of literature review, including meta-analysis, bibliometric review, and systematic review ( Snyder, 2019 ). A meta-analysis refers to a statistical technique for integrating results from a large volume of empirical research (majorly quantitative research) to compare, identify, and evaluate patterns, relationships, agreements, and disagreements generated by research on the same topic ( Davis et al., 2014 ). This study does not adopt a meta-analysis for two reasons. First, the research on the effectiveness of online learning in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic was published since 2020 and currently, there is a limited volume of empirical evidence. If the study adopts a meta-analysis, the sample size will be small, resulting in limited statistical power. Second, as mentioned above, there are a variety of indicators, e.g., motivation, satisfaction, experience, test score, and perceived effectiveness ( Rajaram and Collins, 2013 ; Noesgaard and Ørngreen, 2015 ), that reflect different aspects of online learning effectiveness. The use of diversified effectiveness indicators increases the difficulty of carrying out meta-analysis.
A bibliometric review refers to the analysis of a large volume of empirical research in terms of publication characteristics (e.g., year, journal, and citation), theories, methods, research questions, countries, and authors ( Donthu et al., 2021 ) and it is useful in tracing the trend, distribution, relationship, and general patterns of research published in a focused topic ( Wallin, 2005 ). A bibliometric review does not fit the present study for two reasons. First, at present, there are less than 4 years of history of research on online learning effectiveness. Hence the volume of relevant research is limited and the public trend is currently unclear. Second, this study is interested in the inner content and results of articles published, rather than their external characteristics.
A systematic review is a method and process of critically identifying and appraising research in a specific field based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria to test a hypothesis, answer a research question, evaluate problems in past research, identify research gaps, and/or point out the avenue for future research ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Moher et al., 2009 ). This type of review is particularly suitable to the present study as there are still a lot of unanswered questions regarding the effectiveness of online learning in the pandemic context, a need for indicating future research direction, a lack of summary of relevant research in this field, and a scarcity of critical appraisal of problems in past research.
Adopting a systematic review methodology brings multiple benefits to the present study. First, it is helpful for distinguishing what needs to be done from what has been done, identifying major contributions made by past research, finding out gaps in past research, avoiding fruitless research, and providing insights for future research in the focused field ( Linnenluecke et al., 2020 ). Second, it is also beneficial for finding out new research directions, needs for theory development, and potential solutions for limitations in past research ( Snyder, 2019 ). Third, this methodology helps scholars to efficiently gain an overview of valuable research results and theories generated by past research, which inspires their research design, ideas, and perspectives ( Callahan, 2014 ).
Commonly, a systematic review can be either author-centric or theme-centric ( Webster and Watson, 2002 ) and the present review is theme-centric. Specifically, an author-centric review focuses on works published by a certain author or a group of authors and summarizes the major contributions made by the author(s; ( Webster and Watson, 2002 ). This type of review is problematic in terms of its incompleteness of research conclusions in a specific field and descriptive nature ( Linnenluecke et al., 2020 ). A theme-centric review is more common where a researcher guides readers through reviewing themes, concepts, and interesting phenomena according to a certain logic ( Callahan, 2014 ). A theme in this review can be further structured into several related sub-themes and this type of review helps researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of relevant academic knowledge ( Papaioannou et al., 2016 ).
2.2 Research procedures
This study follows the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guideline ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) to implement a systematic review. The guideline indicates four phases of performing a systematic review, including (1) identifying possible research, (2) abstract screening, (3) assessing full-text for eligibility, and (4) qualitatively synthesizing included research. Figure 1 provides a flowchart of the process and the number of articles excluded and included in each phase.
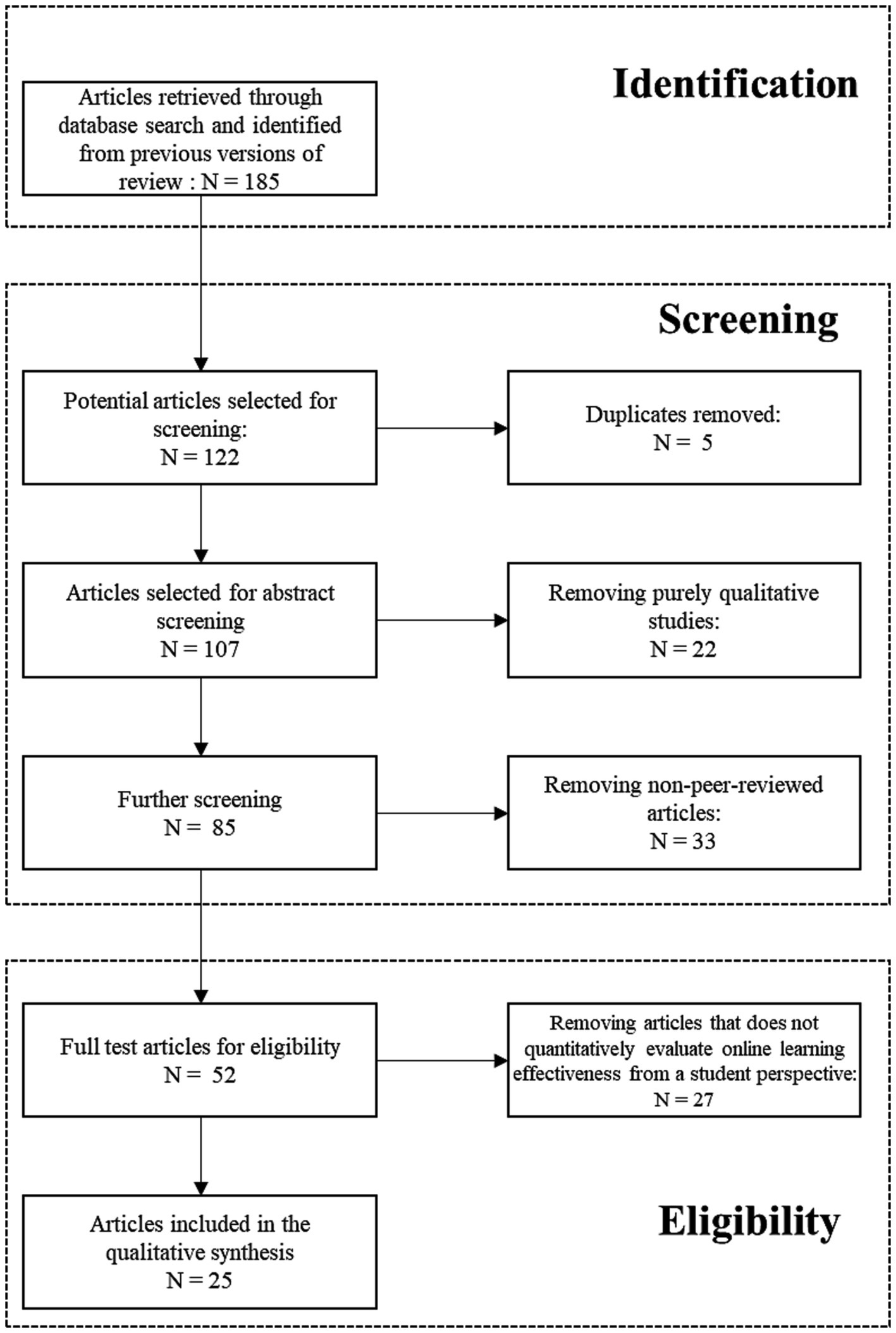
Figure 1 . PRISMA flowchart concerning the selection of articles.
This study uses multiple academic databases to identify possible research, e.g., Academic Search Complete, IGI Global, ACM Digital Library, Elsevier (SCOPUS), Emerald, IEEE Xplore, Web of Science, Science Direct, ProQuest, Wiley Online Library, Taylor and Francis, and EBSCO. Since the COVID-19 pandemic broke out in January 2020, this study limits the literature search to articles published from January 2020 to August 2023. During this period, online learning was highly prevalent in schools globally and a considerable volume of articles were published to investigate various aspects of online learning in this period. Keywords used for searching possible research include pandemic, COVID, SARS-CoV-2, 2019-nCoV, coronavirus, online learning, e-learning, electronic learning, higher education, tertiary education, universities, learning effectiveness, learning satisfaction, learning engagement, and learning motivation. Aside from searching from databases, this study also manually checks the reference lists of relevant articles and uses Google Scholar to find out other articles that have cited these articles.
2.3 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Articles included in the review must meet the following criteria. First, articles have to be written in English and published on peer-reviewed journals. The academic language being English was chosen because it is in the Q zone of the specified search engines. Second, the research must be carried out in an online learning context. Third, the research must have collected and analyzed empirical data. Fourth, the research should be implemented in a higher education context and during the pandemic period. Fifth, the outcome variable must be factors related to learning effectiveness, and included studies must have reported the quantitative results for online learning effectiveness. The outcome variable should be measured by data collected from students, rather than other individuals (e.g., instructors). For instance, the research of Rahayu and Wirza (2020) used teacher perception as a measurement of online learning effectiveness and was hence excluded from the sample. According to the above criteria, a total of 25 articles were included in the review.
2.4 Data extraction and analysis
Content analysis is performed on included articles and an inductive approach is used to answer the two research questions. First, to understand the basic characteristics of the 25 articles/studies, the researcher summarizes their types, research designs, and samples and categorizes them into several groups. The researcher carefully reads the full-text of these articles and codes valuable pieces of content. In this process, an inductive approach is used, and key themes in these studies have been extracted and summarized. Second, the researcher further categorizes these studies into different groups according to their similarities and differences in research findings. In this way, these studies are broadly categorized into three groups, i.e., (1) ineffective (2) neutral, and (3) effective. Based on this, the research answers the research question and indicates the percentage of studies that evidenced online learning as effective in a COVID-19 pandemic context. The researcher also discusses how online learning is effective by analyzing the learning outcomes brought by online learning. Third, the researcher analyzes and compares the characteristics of the three groups of studies and extracts key themes that are relevant to the conditional effectiveness of online learning from these studies. Based on this, the researcher identifies factors that influence the effectiveness of online learning in a pandemic context. In this way, the two research questions have been adequately answered.
3 Research results and discussion
3.1 study characteristics.
Table 1 shows the statistics of the 25 studies while Table 2 shows a summary of these studies. Overall, these studies varied greatly in terms of research design, research subjects, contexts, measurements of learning effectiveness, and eventually research findings. Approximately half of the studies were published in 2021 and the number of studies reduced in 2022 and 2023, which may be attributed to the fact that universities gradually implemented opening-up policies after 2020. China received the largest number of studies ( N = 5), followed by India ( N = 4) and the United States ( N = 3). The sample sizes of the majority of studies (88.0%) ranged between 101 and 500. As this review excluded qualitative studies, all studies included adopted a purely quantitative design (88.0%) or a mixed design (12.0%). The majority of the studies were cross-sectional (72%) and a few studies (2%) were experimental.
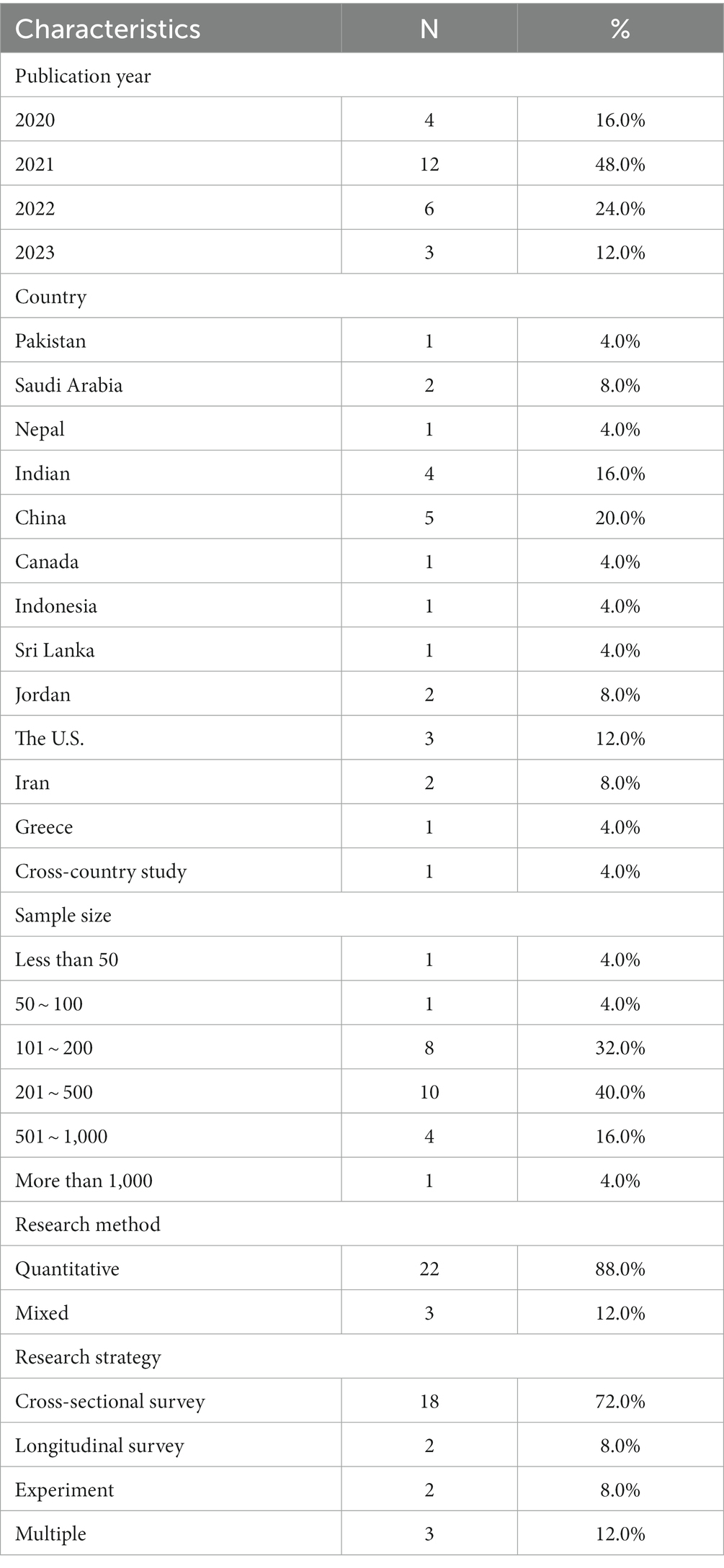
Table 1 . Statistics of studies included in the review.
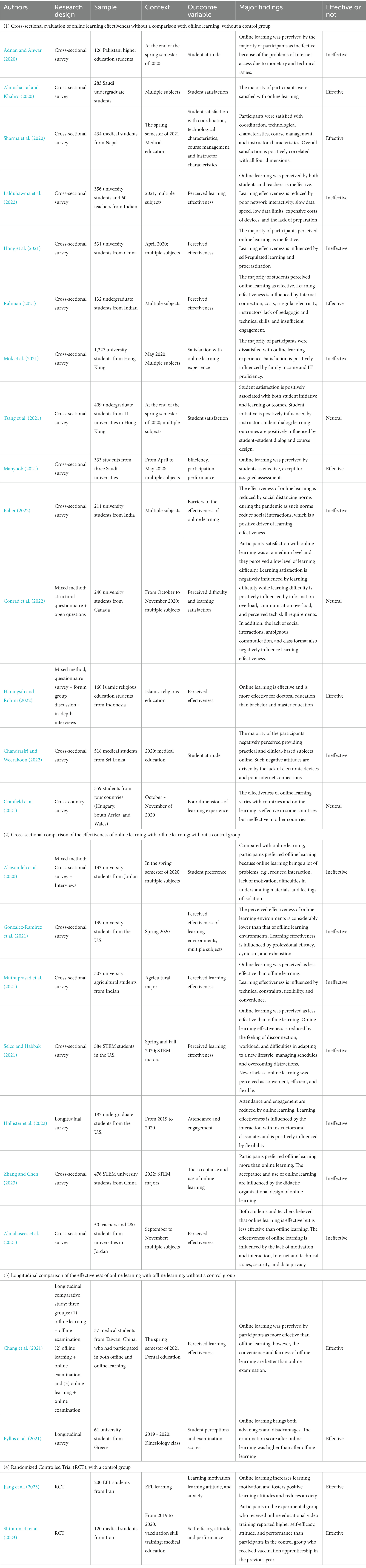
Table 2 . A summary of studies reviewed.
3.2 The effectiveness of online learning
Overall, the 25 studies generated mixed results regarding the effectiveness of online learning during the pandemic period. 9 (36%) studies reported online learning as effective; 13 (52%) studies reported online learning as ineffective, and the rest 3 (12%) studies produced neutral results. However, it should be noted that the results generated by these studies are not comparable as they used different approaches to evaluate the effectiveness of online learning. According to the approach of evaluating online learning effectiveness, these studies are categorized into four groups, including (1) Cross-sectional evaluation of online learning effectiveness without a comparison with offline learning; without a control group ( N = 14; 56%), (2) Cross-sectional comparison of the effectiveness of online learning with offline learning; without control group (7; 28%), (3) Longitudinal comparison of the effectiveness of online learning with offline learning, without a control group ( N = 2; 8%), and (4) Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT); with a control group ( N = 2; 8%).
The first group of studies asked students to report the extent to which they perceived online learning as effective, they had achieved expected learning outcomes through online learning, or they were satisfied with online learning experience or outcomes, without a comparison with offline learning. Six out of 14 studies reported online learning as ineffective, including Adnan and Anwar (2020) , Hong et al. (2021) , Mok et al. (2021) , Baber (2022) , Chandrasiri and Weerakoon (2022) , and Lalduhawma et al. (2022) . Five out of 14 studies reported online learning as effective, including Almusharraf and Khahro (2020) , Sharma et al. (2020) , Mahyoob (2021) , Rahman (2021) , and Haningsih and Rohmi (2022) . In addition, 3 out of 14 studies reported neutral results, including Cranfield et al. (2021) , Tsang et al. (2021) , and Conrad et al. (2022) . It should be noted that this measurement approach is problematic in three aspects. First, researchers used various survey instruments to measure learning effectiveness without reaching a consensus over a widely accepted instrument. As a result, these studies measured different aspects of learning effectiveness and hence their results may be incomparable. Second, these studies relied on students’ self-reports to evaluate learning effectiveness, which is subjective and inaccurate. Third, even though students perceived online learning as effective, it does not imply that online learning is more effective than offline learning because of the absence of comparables.
The second group of studies asked students to compare online learning with offline learning to evaluate learning effectiveness. Interestingly, all 7 studies, including Alawamleh et al. (2020) , Almahasees et al. (2021) , Gonzalez-Ramirez et al. (2021) , Muthuprasad et al. (2021) , Selco and Habbak (2021) , Hollister et al. (2022) , and Zhang and Chen (2023) , reported that online learning was perceived by participants as less effective than offline learning. It should be noted that these results were specific to the COVID-19 pandemic context where strict social distancing policies were implemented. Consequently, these results should be interpreted as online learning during the school lockdown period was perceived by participants as less effective than offline learning during the pre-pandemic period. A key problem of the measurement of learning effectiveness in these studies is subjectivity, i.e., students’ self-reported online learning effectiveness relative to offline learning may be subjective and influenced by a lot of factors caused by the pandemic, e.g., negative emotions (e.g., fear, loneliness, and anxiety).
Only two studies implemented a longitudinal comparison of the effectiveness of online learning with offline learning, i.e., Chang et al. (2021) and Fyllos et al. (2021) . Interestingly, both studies reported that participants perceived online learning as more effective than offline learning, which is contradicted with the second group of studies. In the two studies, the same group of students participated in offline learning and online learning successively and rated the effectiveness of the two learning approaches, respectively. The two studies were implemented by time coincidence, i.e., researchers unexpectedly encountered the pandemic and subsequently, school lockdown when they were investigating learning effectiveness. Such time coincidence enabled them to compare the effectiveness of offline and online learning. However, this research design has three key problems. First, the content of learning in the online and offline learning periods was different and hence the evaluations of learning effectiveness of the two periods are not comparable. Second, self-reported learning effectiveness is subjective. Third, students are likely to obtain better examination scores in online examinations than in offline examinations because online examinations bring a lot of cheating behaviors and are less fair than offline examinations. As reported by Fyllos et al. (2021) , the examination score after online learning was significantly higher than after offline learning. Chang et al. (2021) reported that participants generally believed that offline examinations are fairer than online examinations.
Lastly, only two studies, i.e., Jiang et al. (2023) and Shirahmadi et al. (2023) , implemented an RCT design, which is more persuasive, objective, and accurate than the above-reviewed studies. Indeed, implementing an RCT to evaluate the effectiveness of online learning was a formidable challenge during the pandemic period because of viral transmission and social distancing policies. Both studies reported that online learning is more effective than offline learning during the pandemic period. However, it is questionable about the extent to which such results are affected by health/safety-related issues. It is reasonable to infer that online learning was perceived by students as safer than offline learning during the pandemic period and such perceptions may affect learning effectiveness.
Overall, it is difficult to conclude whether online learning is effective during the pandemic period. Nevertheless, it is possible to identify factors that shape the effectiveness of online learning, which is discussed in the next section.
3.3 Factors that shape online learning effectiveness
Infrastructure factors were reported as the most salient factors that determine online learning effectiveness. It seems that research from developed countries generated more positive results for online learning than research from less developed countries. This view was confirmed by the cross-country comparative study of Cranfield et al. (2021) . Indeed, online learning entails the support of ICT infrastructure, and hence ICT related factors, e.g., Internet connectivity, technical issues, network speed, accessibility of digital devices, and digital devices, considerably influence the effectiveness of online learning ( García-Morales et al., 2021 ; Grafton-Clarke et al., 2022 ). Prior review research, e.g., Tang (2023) also suggested that the unequal distribution of resources and unfair socioeconomic status intensified the problems brought about by online learning during the pandemic period. Salas-Pilco et al. (2022) recommended that improving Internet connectivity would increase students’ engagement in online learning during the pandemic period.
Adnan and Anwar (2020) study is one of the most cited works in the focused field. They reported that online learning is ineffective in Pakistan because of the problems of Internet access due to monetary and technical issues. The above problems hinder students from implementing online learning activities, making online learning ineffective. Likewise, Lalduhawma et al. (2022) research from India indicated that online learning is ineffective because of poor network interactivity, slow data speed, low data limits, and expensive costs of devices. As a result, online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic may have expanded the education gap between developed and developing countries because of developing countries’ infrastructure disadvantages. More attention to online learning infrastructure problems in developing countries is needed.
Instructional factors, e.g., course management and design, instructor characteristics, instructor-student interaction, assignments, and assessments were found to affect online learning effectiveness ( Sharma et al., 2020 ; Rahman, 2021 ; Tsang et al., 2021 ; Hollister et al., 2022 ; Zhang and Chen, 2023 ). Although these instructional factors have been well-documented as significant drivers of learning effectiveness in traditional learning literature, these factors in the pandemic period have some unique characteristics. Both students and teachers were not well prepared for wholly online instruction and learning in 2020 and hence they encountered a lot of problems in course management and design, learning interactions, assignments, and assessments ( Stojan et al., 2022 ; Tang, 2023 ). García-Morales et al. (2021) review also suggested that various stakeholders in learning and teaching encountered difficulties in adapting to the sudden, hasty, and forced transition of offline to online learning. Consequently, these instructional factors become salient in terms of affecting online learning effectiveness.
The negative role of the lack of social interaction caused by social distancing in affecting online learning effectiveness was highlighted by a lot of studies ( Almahasees et al., 2021 ; Baber, 2022 ; Conrad et al., 2022 ; Hollister et al., 2022 ). Baber (2022) argued that people give more importance to saving lives than socializing in the online environment and hence social interactions in learning are considerably reduced by social distancing norms. The negative impact of the lack of social interaction on online learning effectiveness is reflected in two aspects. First, according to a constructivist view, interaction is an indispensable element of learning because knowledge is actively constructed by learners in social interactions ( Woo and Reeves, 2007 ). Consequently, online learning effectiveness during the pandemic period is reduced by the lack of social interaction. Second, the lack of social interaction brings a lot of negative emotions, e.g., feelings of isolation, loneliness, anxiety, and depression ( Alawamleh et al., 2020 ; Gonzalez-Ramirez et al., 2021 ; Selco and Habbak, 2021 ). Such negative emotions undermine online learning effectiveness.
Negative emotions caused by the pandemic and school lockdown were also found to be detrimental to online learning effectiveness. In this context, it was reported that many students experience a lot of negative emotions, e.g., feelings of isolation, exhaustion, loneliness, and distraction ( Alawamleh et al., 2020 ; Gonzalez-Ramirez et al., 2021 ; Selco and Habbak, 2021 ). Such negative emotions, as mentioned above, reduce online learning effectiveness.
Several factors were also found to increase online learning effectiveness during the pandemic period, e.g., convenience and flexibility ( Hong et al., 2021 ; Muthuprasad et al., 2021 ; Selco and Habbak, 2021 ). Students with strong self-regulated learning abilities gain more benefits from convenience and flexibility in online learning ( Hong et al., 2021 ).
Overall, although it is debated over the effectiveness of online learning during the pandemic period, it is generally believed that the pandemic brings a lot of challenges and difficulties to higher education. Meanwhile, the majority of students prefer offline learning to online learning. The above challenges and difficulties are more prominent in developing countries than in developed countries.
3.4 Pedagogical implications
The results generated by the systematic review offer a lot of pedagogical implications. First, online learning entails the support of ICT infrastructure, and infrastructure defects strongly undermine learning effectiveness ( García-Morales et al., 2021 ; Grafton-Clarke et al., 2022 ). Given the fact online learning is increasingly integrated into higher education ( Kebritchi et al., 2017 ) regardless of the presence of the pandemic, governments globally should increase the investment in learning-related ICT infrastructure in higher education institutes. Meanwhile, schools should consider students’ affordability of digital devices and network fees when implementing online learning activities. It is important to offer material support for those students with poor economic status. Infrastructure issues are more prominent in developing countries because of the lack of monetary resources and poor infrastructure base. Thus, international collaboration and aid are recommended to address these issues.
Second, since the lack of social interaction is a key factor that reduces online learning effectiveness, it is important to increase social interactions during the implementation of online learning activities. On the one hand, both students and instructors are encouraged to utilize network technologies to promote inter-individual interactions. On the other hand, the two parties are also encouraged to engage in offline interaction activities if the risk is acceptable.
Third, special attention should be paid to students’ emotions during the online learning process as online learning may bring a lot of negative emotions to students, which undermine learning effectiveness ( Alawamleh et al., 2020 ; Gonzalez-Ramirez et al., 2021 ; Selco and Habbak, 2021 ). In addition, higher education institutes should prepare a contingency plan for emergency online learning to deal with potential crises in the future, e.g., wars, pandemics, and natural disasters.
3.5 Limitations and suggestions for future research
There are several limitations in past research regarding online learning effectiveness during the pandemic period. The first is the lack of rigor in assessing learning effectiveness. Evidently, there is a scarcity of empirical research with an RCT design, which is considered to be accurate, objective, and rigorous in assessing pedagogical models ( Torgerson and Torgerson, 2001 ). The scarcity of ICT research leads to the difficulty in accurately assessing the effectiveness of online learning and comparing it with offline learning. Second, the widely accepted criteria for assessing learning effectiveness are absent, and past empirical studies used diversified procedures, techniques, instruments, and criteria for measuring online learning effectiveness, resulting in difficulty in comparing research results. Third, learning effectiveness is a multi-dimensional construct but its multidimensionality was largely ignored by past research. Therefore, it is difficult to evaluate which dimensions of learning effectiveness are promoted or undermined by online learning and it is also difficult to compare the results of different studies. Finally, there is very limited knowledge about the difference in online learning effectiveness between different subjects. It is likely that the subjects that depend on lab-based work (e.g., experimental physics, organic chemistry, and cell biology) are less appropriate for online learning than the subjects that depend on desk-based work (e.g., economics, psychology, and literature).
To deal with the above limitations, there are several recommendations for future research on online learning effectiveness. First, future research is encouraged to adopt an RCT design and collect a large-sized sample to objectively, rigorously, and accurately quantify the effectiveness of online learning. Second, scholars are also encouraged to develop a new framework to assess learning effectiveness comprehensively. This framework should cover multiple dimensions of learning effectiveness and have strong generalizability. Finally, it is recommended that future research could compare the effectiveness of online learning between different subjects.
4 Conclusion
This study carried out a systematic review of 25 empirical studies published between 2020 and 2023 to evaluate the effectiveness of online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic period. According to how online learning effectiveness was assessed, these 25 studies were categorized into four groups. The first group of studies employed a cross-sectional design and assessed online learning based on students’ perceptions without a control group. Less than half of these studies reported online learning as effective. The second group of studies also employed a cross-sectional design and asked students to compare the effectiveness of online learning with offline learning. All these studies reported that online learning is less effective than offline learning. The third group of studies employed a longitudinal design and compared the effectiveness of online learning with offline learning but without a control group and this group includes only 2 studies. It was reported that online learning is more effective than offline learning. The fourth group of studies employed an RCT design and this group includes only 2 studies. Both studies reported online learning as more effective than offline learning.
Overall, it is difficult to conclude whether online learning is effective during the pandemic period because of the diversified research contexts, methods, and approaches in past research. Nevertheless, the review identifies a set of factors that positively or negatively influence the effectiveness of online learning, including infrastructure factors, instructional factors, the lack of social interaction, negative emotions, flexibility, and convenience. Although it is debated over the effectiveness of online learning during the pandemic period, it is generally believed that the pandemic brings a lot of challenges and difficulties to higher education. Meanwhile, the majority of students prefer offline learning to online learning. In addition, developing countries face more challenges and difficulties in online learning because of monetary and infrastructure issues.
The findings of this review offer significant pedagogical implications for online learning in higher education institutes, including enhancing the development of ICT infrastructure, providing material support for students with poor economic status, enhancing social interactions, paying attention to students’ emotional status, and preparing a contingency plan of emergency online learning.
The review also identifies several limitations in past research regarding online learning effectiveness during the pandemic period, including the lack of rigor in assessing learning effectiveness, the absence of accepted criteria for assessing learning effectiveness, the neglect of the multidimensionality of learning effectiveness, and limited knowledge about the difference in online learning effectiveness between different subjects.
To deal with the above limitations, there are several recommendations for future research on online learning effectiveness. First, future research is encouraged to adopt an RCT design and collect a large-sized sample to objectively, rigorously, and accurately quantify the effectiveness of online learning. Second, scholars are also encouraged to develop a new framework to assess learning effectiveness comprehensively. This framework should cover multiple dimensions of learning effectiveness and have strong generalizability. Finally, it is recommended that future research could compare the effectiveness of online learning between different subjects. To fix these limitations in future research, recommendations are made.
It should be noted that this review is not free of problems. First, only studies that quantitatively measured online learning effectiveness were included in the review and hence a lot of other studies (e.g., qualitative studies) that investigated factors that influence online learning effectiveness were excluded, resulting in a relatively small-sized sample and incomplete synthesis of past research contributions. Second, since this review was qualitative, it was difficult to accurately quantify the level of online learning effectiveness.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
WM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – review & editing. NP: Writing – review & editing. XP: Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Adnan, M., and Anwar, K. (2020). Online learning amid the COVID-19 pandemic: Students' perspectives. J. Pedagogical Sociol. Psychol. 1, 45–51. doi: 10.33902/JPSP.2020261309
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Alawamleh, M., Al-Twait, L. M., and Al-Saht, G. R. (2020). The effect of online learning on communication between instructors and students during Covid-19 pandemic. Asian Educ. Develop. Stud. 11, 380–400. doi: 10.1108/AEDS-06-2020-0131
Almahasees, Z., Mohsen, K., and Amin, M. O. (2021). Faculty’s and students’ perceptions of online learning during COVID-19. Front. Educ. 6:638470. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.638470
Almusharraf, N., and Khahro, S. (2020). Students satisfaction with online learning experiences during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (iJET) 15, 246–267. doi: 10.3991/ijet.v15i21.15647
Anderson, N., and Hajhashemi, K. (2013). Online learning: from a specialized distance education paradigm to a ubiquitous element of contemporary education. In 4th international conference on e-learning and e-teaching (ICELET 2013) (pp. 91–94). IEEE.
Google Scholar
Arkorful, V., and Abaidoo, N. (2015). The role of e-learning, advantages and disadvantages of its adoption in higher education. Int. J. Instructional Technol. Distance Learn. 12, 29–42.
Baber, H. (2022). Social interaction and effectiveness of the online learning–a moderating role of maintaining social distance during the pandemic COVID-19. Asian Educ. Develop. Stud. 11, 159–171. doi: 10.1108/AEDS-09-2020-0209
Barnard-Brak, L., Paton, V. O., and Lan, W. Y. (2010). Profiles in self-regulated learning in the online learning environment. Int. Rev. Res. Open Dist. Learn. 11, 61–80. doi: 10.19173/irrodl.v11i1.769
Bughrara, M. S., Swanberg, S. M., Lucia, V. C., Schmitz, K., Jung, D., and Wunderlich-Barillas, T. (2023). Beyond COVID-19: the impact of recent pandemics on medical students and their education: a scoping review. Med. Educ. Online 28:2139657. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2022.2139657
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
Callahan, J. L. (2014). Writing literature reviews: a reprise and update. Hum. Resour. Dev. Rev. 13, 271–275. doi: 10.1177/1534484314536705
Camargo, C. P., Tempski, P. Z., Busnardo, F. F., Martins, M. D. A., and Gemperli, R. (2020). Online learning and COVID-19: a meta-synthesis analysis. Clinics 75:e2286. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2020/e2286
Choudhury, S., and Pattnaik, S. (2020). Emerging themes in e-learning: A review from the stakeholders’ perspective. Computers and Education 144, 103657. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103657
Chandrasiri, N. R., and Weerakoon, B. S. (2022). Online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: perceptions of allied health sciences undergraduates. Radiography 28, 545–549. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2021.11.008
Chang, J. Y. F., Wang, L. H., Lin, T. C., Cheng, F. C., and Chiang, C. P. (2021). Comparison of learning effectiveness between physical classroom and online learning for dental education during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Dental Sci. 16, 1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.07.016
Conrad, C., Deng, Q., Caron, I., Shkurska, O., Skerrett, P., and Sundararajan, B. (2022). How student perceptions about online learning difficulty influenced their satisfaction during Canada's Covid-19 response. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 53, 534–557. doi: 10.1111/bjet.13206
Cranfield, D. J., Tick, A., Venter, I. M., Blignaut, R. J., and Renaud, K. (2021). Higher education students’ perceptions of online learning during COVID-19—a comparative study. Educ. Sci. 11, 403–420. doi: 10.3390/educsci11080403
Desai, M. S., Hart, J., and Richards, T. C. (2008). E-learning: paradigm shift in education. Education 129, 1–20.
Davis, J., Mengersen, K., Bennett, S., and Mazerolle, L. (2014). Viewing systematic reviews and meta-analysis in social research through different lenses. SpringerPlus 3, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-511
Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., and Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research 133, 264–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070
Fyllos, A., Kanellopoulos, A., Kitixis, P., Cojocari, D. V., Markou, A., Raoulis, V., et al. (2021). University students perception of online education: is engagement enough? Acta Informatica Medica 29, 4–9. doi: 10.5455/aim.2021.29.4-9
Gamage, D., Ruipérez-Valiente, J. A., and Reich, J. (2023). A paradigm shift in designing education technology for online learning: opportunities and challenges. Front. Educ. 8:1194979. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2023.1194979
García-Morales, V. J., Garrido-Moreno, A., and Martín-Rojas, R. (2021). The transformation of higher education after the COVID disruption: emerging challenges in an online learning scenario. Front. Psychol. 12:616059. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.616059
Gonzalez-Ramirez, J., Mulqueen, K., Zealand, R., Silverstein, S., Mulqueen, C., and BuShell, S. (2021). Emergency online learning: college students' perceptions during the COVID-19 pandemic. Coll. Stud. J. 55, 29–46.
Grafton-Clarke, C., Uraiby, H., Gordon, M., Clarke, N., Rees, E., Park, S., et al. (2022). Pivot to online learning for adapting or continuing workplace-based clinical learning in medical education following the COVID-19 pandemic: a BEME systematic review: BEME guide no. 70. Med. Teach. 44, 227–243. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2021.1992372
Haningsih, S., and Rohmi, P. (2022). The pattern of hybrid learning to maintain learning effectiveness at the higher education level post-COVID-19 pandemic. Eurasian J. Educ. Res. 11, 243–257. doi: 10.12973/eu-jer.11.1.243
Hollister, B., Nair, P., Hill-Lindsay, S., and Chukoskie, L. (2022). Engagement in online learning: student attitudes and behavior during COVID-19. Front. Educ. 7:851019. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2022.851019
Hong, J. C., Lee, Y. F., and Ye, J. H. (2021). Procrastination predicts online self-regulated learning and online learning ineffectiveness during the coronavirus lockdown. Personal. Individ. Differ. 174:110673. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2021.110673
Jiang, P., Namaziandost, E., Azizi, Z., and Razmi, M. H. (2023). Exploring the effects of online learning on EFL learners’ motivation, anxiety, and attitudes during the COVID-19 pandemic: a focus on Iran. Curr. Psychol. 42, 2310–2324. doi: 10.1007/s12144-022-04013-x
Joy, E. H., and Garcia, F. E. (2000). Measuring learning effectiveness: a new look at no-significant-difference findings. JALN 4, 33–39.
Kebritchi, M., Lipschuetz, A., and Santiague, L. (2017). Issues and challenges for teaching successful online courses in higher education: a literature review. J. Educ. Technol. Syst. 46, 4–29. doi: 10.1177/0047239516661713
Lalduhawma, L. P., Thangmawia, L., and Hussain, J. (2022). Effectiveness of online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in Mizoram. J. Educ. e-Learning Res. 9, 175–183. doi: 10.20448/jeelr.v9i3.4162
Liberati, A., Altman, D. G., Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gotzsche, P. C., Ioannidis, J. P., et al. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Annals of internal medicine , 151, W-65. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00136
Linnenluecke, M. K., Marrone, M., and Singh, A. K. (2020). Conducting systematic literature reviews and bibliometric analyses. Aust. J. Manag. 45, 175–194. doi: 10.1177/0312896219877678
Mahyoob, M. (2021). Online learning effectiveness during the COVID-19 pandemic: a case study of Saudi universities. Int. J. Info. Commun. Technol. Educ. (IJICTE) 17, 1–14. doi: 10.4018/IJICTE.20211001.oa7
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, D., and Altman, G. and PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Annals of internal medicine , 151, 264–269. doi: 10.3736/jcim20090918
Mok, K. H., Xiong, W., and Bin Aedy Rahman, H. N. (2021). COVID-19 pandemic’s disruption on university teaching and learning and competence cultivation: student evaluation of online learning experiences in Hong Kong. Int. J. Chinese Educ. 10:221258682110070. doi: 10.1177/22125868211007011
Muthuprasad, T., Aiswarya, S., Aditya, K. S., and Jha, G. K. (2021). Students’ perception and preference for online education in India during COVID-19 pandemic. Soc. Sci. Humanities open 3:100101. doi: 10.1016/j.ssaho.2020.100101
Noesgaard, S. S., and Ørngreen, R. (2015). The effectiveness of e-learning: an explorative and integrative review of the definitions, methodologies and factors that promote e-learning effectiveness. Electronic J. E-learning 13, 278–290.
Papaioannou, D., Sutton, A., and Booth, A. (2016). Systematic approaches to a successful literature review. London: Sage.
Pratama, H., Azman, M. N. A., Kassymova, G. K., and Duisenbayeva, S. S. (2020). The trend in using online meeting applications for learning during the period of pandemic COVID-19: a literature review. J. Innovation in Educ. Cultural Res. 1, 58–68. doi: 10.46843/jiecr.v1i2.15
Rahayu, R. P., and Wirza, Y. (2020). Teachers’ perception of online learning during pandemic covid-19. Jurnal penelitian pendidikan 20, 392–406. doi: 10.17509/jpp.v20i3.29226
Rahman, A. (2021). Using students’ experience to derive effectiveness of COVID-19-lockdown-induced emergency online learning at undergraduate level: evidence from Assam. India. Higher Education for the Future 8, 71–89. doi: 10.1177/2347631120980549
Rajaram, K., and Collins, B. (2013). Qualitative identification of learning effectiveness indicators among mainland Chinese students in culturally dislocated study environments. J. Int. Educ. Bus. 6, 179–199. doi: 10.1108/JIEB-03-2013-0010
Salas-Pilco, S. Z., Yang, Y., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Student engagement in online learning in Latin American higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 53, 593–619. doi: 10.1111/bjet.13190
Selco, J. I., and Habbak, M. (2021). Stem students’ perceptions on emergency online learning during the covid-19 pandemic: challenges and successes. Educ. Sci. 11:799. doi: 10.3390/educsci11120799
Sharma, K., Deo, G., Timalsina, S., Joshi, A., Shrestha, N., and Neupane, H. C. (2020). Online learning in the face of COVID-19 pandemic: assessment of students’ satisfaction at Chitwan medical college of Nepal. Kathmandu Univ. Med. J. 18, 40–47. doi: 10.3126/kumj.v18i2.32943
Shirahmadi, S., Hazavehei, S. M. M., Abbasi, H., Otogara, M., Etesamifard, T., Roshanaei, G., et al. (2023). Effectiveness of online practical education on vaccination training in the students of bachelor programs during the Covid-19 pandemic. PLoS One 18:e0280312. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280312
Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 104, 333–339. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039
Stojan, J., Haas, M., Thammasitboon, S., Lander, L., Evans, S., Pawlik, C., et al. (2022). Online learning developments in undergraduate medical education in response to the COVID-19 pandemic: a BEME systematic review: BEME guide no. 69. Med. Teach. 44, 109–129. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2021.1992373
Swan, K. (2003). Learning effectiveness online: what the research tells us. Elements of quality online education, practice and direction 4, 13–47.
Tang, K. H. D. (2023). Impacts of COVID-19 on primary, secondary and tertiary education: a comprehensive review and recommendations for educational practices. Educ. Res. Policy Prac. 22, 23–61. doi: 10.1007/s10671-022-09319-y
Torgerson, C. J., and Torgerson, D. J. (2001). The need for randomised controlled trials in educational research. Br. J. Educ. Stud. 49, 316–328. doi: 10.1111/1467-8527.t01-1-00178
Tranfield, D., Denyer, D., and Smart, P. (2003). Towards a methodology for developing evidence‐informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. British journal of management , 14, 207–222. doi: 10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Tsang, J. T., So, M. K., Chong, A. C., Lam, B. S., and Chu, A. M. (2021). Higher education during the pandemic: the predictive factors of learning effectiveness in COVID-19 online learning. Educ. Sci. 11:446. doi: 10.3390/educsci11080446
Wallin, J. A. (2005). Bibliometric methods: pitfalls and possibilities. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 97, 261–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_139.x
Webster, J., and Watson, R. T. (2002). Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. MIS quarterly , 26, 13–23.
Wong, J., Baars, M., Davis, D., Van Der Zee, T., Houben, G. J., and Paas, F. (2019). Supporting self-regulated learning in online learning environments and MOOCs: a systematic review. Int. J. Human–Computer Interaction 35, 356–373. doi: 10.1080/10447318.2018.1543084
Woo, Y., and Reeves, T. C. (2007). Meaningful interaction in web-based learning: a social constructivist interpretation. Internet High. Educ. 10, 15–25. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2006.10.005
Zeitoun, H. (2008). E-learning: Concept, Issues, Application, Evaluation . Riyadh: Dar Alsolateah Publication.
Zhang, L., Carter, R. A. Jr., Qian, X., Yang, S., Rujimora, J., and Wen, S. (2022). Academia's responses to crisis: a bibliometric analysis of literature on online learning in higher education during COVID-19. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 53, 620–646. doi: 10.1111/bjet.13191
Zhang, Y., and Chen, X. (2023). Students’ perceptions of online learning in the post-COVID era: a focused case from the universities of applied sciences in China. Sustain. For. 15:946. doi: 10.3390/su15020946
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic, higher education, online learning, learning effectiveness, systematic review
Citation: Meng W, Yu L, Liu C, Pan N, Pang X and Zhu Y (2024) A systematic review of the effectiveness of online learning in higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic period. Front. Educ . 8:1334153. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2023.1334153
Received: 06 November 2023; Accepted: 27 December 2023; Published: 17 January 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Meng, Yu, Liu, Pan, Pang and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Yu, [email protected]
Advertisement
The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study
- Published: 06 September 2021
- Volume 27 , pages 429–450, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Hakan Ulum ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1398-6935 1
79k Accesses
26 Citations
11 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has been extensively used on student achievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a meta-analysis of the related studies focusing on the effect of online education on students’ academic achievement in several countries between the years 2010 and 2021 was carried out. Furthermore, this study will provide a source to assist future studies with comparing the effect of online education on academic achievement before and after the pandemic. This meta-analysis study consists of 27 studies in total. The meta-analysis involves the studies conducted in the USA, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia. The studies included in the meta-analysis are experimental studies, and the total sample size is 1772. In the study, the funnel plot, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test were utilized to determine the publication bias, which has been found to be quite low. Besides, Hedge’s g statistic was employed to measure the effect size for the difference between the means performed in accordance with the random effects model. The results of the study show that the effect size of online education on academic achievement is on a medium level. The heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Information and communication technologies have become a powerful force in transforming the educational settings around the world. The pandemic has been an important factor in transferring traditional physical classrooms settings through adopting information and communication technologies and has also accelerated the transformation. The literature supports that learning environments connected to information and communication technologies highly satisfy students. Therefore, we need to keep interest in technology-based learning environments. Clearly, technology has had a huge impact on young people's online lives. This digital revolution can synergize the educational ambitions and interests of digitally addicted students. In essence, COVID-19 has provided us with an opportunity to embrace online learning as education systems have to keep up with the rapid emergence of new technologies.
Information and communication technologies that have an effect on all spheres of life are also actively included in the education field. With the recent developments, using technology in education has become inevitable due to personal and social reasons (Usta, 2011a ). Online education may be given as an example of using information and communication technologies as a consequence of the technological developments. Also, it is crystal clear that online learning is a popular way of obtaining instruction (Demiralay et al., 2016 ; Pillay et al., 2007 ), which is defined by Horton ( 2000 ) as a way of education that is performed through a web browser or an online application without requiring an extra software or a learning source. Furthermore, online learning is described as a way of utilizing the internet to obtain the related learning sources during the learning process, to interact with the content, the teacher, and other learners, as well as to get support throughout the learning process (Ally, 2004 ). Online learning has such benefits as learning independently at any time and place (Vrasidas & MsIsaac, 2000 ), granting facility (Poole, 2000 ), flexibility (Chizmar & Walbert, 1999 ), self-regulation skills (Usta, 2011b ), learning with collaboration, and opportunity to plan self-learning process.
Even though online education practices have not been comprehensive as it is now, internet and computers have been used in education as alternative learning tools in correlation with the advances in technology. The first distance education attempt in the world was initiated by the ‘Steno Courses’ announcement published in Boston newspaper in 1728. Furthermore, in the nineteenth century, Sweden University started the “Correspondence Composition Courses” for women, and University Correspondence College was afterwards founded for the correspondence courses in 1843 (Arat & Bakan, 2011 ). Recently, distance education has been performed through computers, assisted by the facilities of the internet technologies, and soon, it has evolved into a mobile education practice that is emanating from progress in the speed of internet connection, and the development of mobile devices.
With the emergence of pandemic (Covid-19), face to face education has almost been put to a halt, and online education has gained significant importance. The Microsoft management team declared to have 750 users involved in the online education activities on the 10 th March, just before the pandemic; however, on March 24, they informed that the number of users increased significantly, reaching the number of 138,698 users (OECD, 2020 ). This event supports the view that it is better to commonly use online education rather than using it as a traditional alternative educational tool when students do not have the opportunity to have a face to face education (Geostat, 2019 ). The period of Covid-19 pandemic has emerged as a sudden state of having limited opportunities. Face to face education has stopped in this period for a long time. The global spread of Covid-19 affected more than 850 million students all around the world, and it caused the suspension of face to face education. Different countries have proposed several solutions in order to maintain the education process during the pandemic. Schools have had to change their curriculum, and many countries supported the online education practices soon after the pandemic. In other words, traditional education gave its way to online education practices. At least 96 countries have been motivated to access online libraries, TV broadcasts, instructions, sources, video lectures, and online channels (UNESCO, 2020 ). In such a painful period, educational institutions went through online education practices by the help of huge companies such as Microsoft, Google, Zoom, Skype, FaceTime, and Slack. Thus, online education has been discussed in the education agenda more intensively than ever before.
Although online education approaches were not used as comprehensively as it has been used recently, it was utilized as an alternative learning approach in education for a long time in parallel with the development of technology, internet and computers. The academic achievement of the students is often aimed to be promoted by employing online education approaches. In this regard, academicians in various countries have conducted many studies on the evaluation of online education approaches and published the related results. However, the accumulation of scientific data on online education approaches creates difficulties in keeping, organizing and synthesizing the findings. In this research area, studies are being conducted at an increasing rate making it difficult for scientists to be aware of all the research outside of their expertise. Another problem encountered in the related study area is that online education studies are repetitive. Studies often utilize slightly different methods, measures, and/or examples to avoid duplication. This erroneous approach makes it difficult to distinguish between significant differences in the related results. In other words, if there are significant differences in the results of the studies, it may be difficult to express what variety explains the differences in these results. One obvious solution to these problems is to systematically review the results of various studies and uncover the sources. One method of performing such systematic syntheses is the application of meta-analysis which is a methodological and statistical approach to draw conclusions from the literature. At this point, how effective online education applications are in increasing the academic success is an important detail. Has online education, which is likely to be encountered frequently in the continuing pandemic period, been successful in the last ten years? If successful, how much was the impact? Did different variables have an impact on this effect? Academics across the globe have carried out studies on the evaluation of online education platforms and publishing the related results (Chiao et al., 2018 ). It is quite important to evaluate the results of the studies that have been published up until now, and that will be published in the future. Has the online education been successful? If it has been, how big is the impact? Do the different variables affect this impact? What should we consider in the next coming online education practices? These questions have all motivated us to carry out this study. We have conducted a comprehensive meta-analysis study that tries to provide a discussion platform on how to develop efficient online programs for educators and policy makers by reviewing the related studies on online education, presenting the effect size, and revealing the effect of diverse variables on the general impact.
There have been many critical discussions and comprehensive studies on the differences between online and face to face learning; however, the focus of this paper is different in the sense that it clarifies the magnitude of the effect of online education and teaching process, and it represents what factors should be controlled to help increase the effect size. Indeed, the purpose here is to provide conscious decisions in the implementation of the online education process.
The general impact of online education on the academic achievement will be discovered in the study. Therefore, this will provide an opportunity to get a general overview of the online education which has been practiced and discussed intensively in the pandemic period. Moreover, the general impact of online education on academic achievement will be analyzed, considering different variables. In other words, the current study will allow to totally evaluate the study results from the related literature, and to analyze the results considering several cultures, lectures, and class levels. Considering all the related points, this study seeks to answer the following research questions:
What is the effect size of online education on academic achievement?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the country?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the class level?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the lecture?
How do the effect sizes of online education on academic achievement change according to the moderator variable of the online education approaches?
This study aims at determining the effect size of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, on students’ academic achievement in different courses by using a meta-analysis method. Meta-analysis is a synthesis method that enables gathering of several study results accurately and efficiently, and getting the total results in the end (Tsagris & Fragkos, 2018 ).
2.1 Selecting and coding the data (studies)
The required literature for the meta-analysis study was reviewed in July, 2020, and the follow-up review was conducted in September, 2020. The purpose of the follow-up review was to include the studies which were published in the conduction period of this study, and which met the related inclusion criteria. However, no study was encountered to be included in the follow-up review.
In order to access the studies in the meta-analysis, the databases of Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS were reviewed by utilizing the keywords ‘online learning and online education’. Not every database has a search engine that grants access to the studies by writing the keywords, and this obstacle was considered to be an important problem to be overcome. Therefore, a platform that has a special design was utilized by the researcher. With this purpose, through the open access system of Cukurova University Library, detailed reviews were practiced using EBSCO Information Services (EBSCO) that allow reviewing the whole collection of research through a sole searching box. Since the fundamental variables of this study are online education and online learning, the literature was systematically reviewed in the related databases (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) by referring to the keywords. Within this scope, 225 articles were accessed, and the studies were included in the coding key list formed by the researcher. The name of the researchers, the year, the database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS), the sample group and size, the lectures that the academic achievement was tested in, the country that the study was conducted in, and the class levels were all included in this coding key.
The following criteria were identified to include 225 research studies which were coded based on the theoretical basis of the meta-analysis study: (1) The studies should be published in the refereed journals between the years 2020 and 2021, (2) The studies should be experimental studies that try to determine the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement, (3) The values of the stated variables or the required statistics to calculate these values should be stated in the results of the studies, and (4) The sample group of the study should be at a primary education level. These criteria were also used as the exclusion criteria in the sense that the studies that do not meet the required criteria were not included in the present study.
After the inclusion criteria were determined, a systematic review process was conducted, following the year criterion of the study by means of EBSCO. Within this scope, 290,365 studies that analyze the effect of online education and online learning on academic achievement were accordingly accessed. The database (Web of Science, ERIC, and SCOPUS) was also used as a filter by analyzing the inclusion criteria. Hence, the number of the studies that were analyzed was 58,616. Afterwards, the keyword ‘primary education’ was used as the filter and the number of studies included in the study decreased to 3152. Lastly, the literature was reviewed by using the keyword ‘academic achievement’ and 225 studies were accessed. All the information of 225 articles was included in the coding key.
It is necessary for the coders to review the related studies accurately and control the validity, safety, and accuracy of the studies (Stewart & Kamins, 2001 ). Within this scope, the studies that were determined based on the variables used in this study were first reviewed by three researchers from primary education field, then the accessed studies were combined and processed in the coding key by the researcher. All these studies that were processed in the coding key were analyzed in accordance with the inclusion criteria by all the researchers in the meetings, and it was decided that 27 studies met the inclusion criteria (Atici & Polat, 2010 ; Carreon, 2018 ; Ceylan & Elitok Kesici, 2017 ; Chae & Shin, 2016 ; Chiang et al. 2014 ; Ercan, 2014 ; Ercan et al., 2016 ; Gwo-Jen et al., 2018 ; Hayes & Stewart, 2016 ; Hwang et al., 2012 ; Kert et al., 2017 ; Lai & Chen, 2010 ; Lai et al., 2015 ; Meyers et al., 2015 ; Ravenel et al., 2014 ; Sung et al., 2016 ; Wang & Chen, 2013 ; Yu, 2019 ; Yu & Chen, 2014 ; Yu & Pan, 2014 ; Yu et al., 2010 ; Zhong et al., 2017 ). The data from the studies meeting the inclusion criteria were independently processed in the second coding key by three researchers, and consensus meetings were arranged for further discussion. After the meetings, researchers came to an agreement that the data were coded accurately and precisely. Having identified the effect sizes and heterogeneity of the study, moderator variables that will show the differences between the effect sizes were determined. The data related to the determined moderator variables were added to the coding key by three researchers, and a new consensus meeting was arranged. After the meeting, researchers came to an agreement that moderator variables were coded accurately and precisely.
2.2 Study group
27 studies are included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies that are included in the analysis is 1772. The characteristics of the studies included are given in Table 1 .
2.3 Publication bias
Publication bias is the low capability of published studies on a research subject to represent all completed studies on the same subject (Card, 2011 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Similarly, publication bias is the state of having a relationship between the probability of the publication of a study on a subject, and the effect size and significance that it produces. Within this scope, publication bias may occur when the researchers do not want to publish the study as a result of failing to obtain the expected results, or not being approved by the scientific journals, and consequently not being included in the study synthesis (Makowski et al., 2019 ). The high possibility of publication bias in a meta-analysis study negatively affects (Pecoraro, 2018 ) the accuracy of the combined effect size, causing the average effect size to be reported differently than it should be (Borenstein et al., 2009 ). For this reason, the possibility of publication bias in the included studies was tested before determining the effect sizes of the relationships between the stated variables. The possibility of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
2.4 Selecting the model
After determining the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study, the statistical model used to calculate the effect sizes was selected. The main approaches used in the effect size calculations according to the differentiation level of inter-study variance are fixed and random effects models (Pigott, 2012 ). Fixed effects model refers to the homogeneity of the characteristics of combined studies apart from the sample sizes, while random effects model refers to the parameter diversity between the studies (Cumming, 2012 ). While calculating the average effect size in the random effects model (Deeks et al., 2008 ) that is based on the assumption that effect predictions of different studies are only the result of a similar distribution, it is necessary to consider several situations such as the effect size apart from the sample error of combined studies, characteristics of the participants, duration, scope, and pattern of the study (Littell et al., 2008 ). While deciding the model in the meta-analysis study, the assumptions on the sample characteristics of the studies included in the analysis and the inferences that the researcher aims to make should be taken into consideration. The fact that the sample characteristics of the studies conducted in the field of social sciences are affected by various parameters shows that using random effects model is more appropriate in this sense. Besides, it is stated that the inferences made with the random effects model are beyond the studies included in the meta-analysis (Field, 2003 ; Field & Gillett, 2010 ). Therefore, using random effects model also contributes to the generalization of research data. The specified criteria for the statistical model selection show that according to the nature of the meta-analysis study, the model should be selected just before the analysis (Borenstein et al., 2007 ; Littell et al., 2008 ). Within this framework, it was decided to make use of the random effects model, considering that the students who are the samples of the studies included in the meta-analysis are from different countries and cultures, the sample characteristics of the studies differ, and the patterns and scopes of the studies vary as well.
2.5 Heterogeneity
Meta-analysis facilitates analyzing the research subject with different parameters by showing the level of diversity between the included studies. Within this frame, whether there is a heterogeneous distribution between the studies included in the study or not has been evaluated in the present study. The heterogeneity of the studies combined in this meta-analysis study has been determined through Q and I 2 tests. Q test evaluates the random distribution probability of the differences between the observed results (Deeks et al., 2008 ). Q value exceeding 2 value calculated according to the degree of freedom and significance, indicates the heterogeneity of the combined effect sizes (Card, 2011 ). I 2 test, which is the complementary of the Q test, shows the heterogeneity amount of the effect sizes (Cleophas & Zwinderman, 2017 ). I 2 value being higher than 75% is explained as high level of heterogeneity.
In case of encountering heterogeneity in the studies included in the meta-analysis, the reasons of heterogeneity can be analyzed by referring to the study characteristics. The study characteristics which may be related to the heterogeneity between the included studies can be interpreted through subgroup analysis or meta-regression analysis (Deeks et al., 2008 ). While determining the moderator variables, the sufficiency of the number of variables, the relationship between the moderators, and the condition to explain the differences between the results of the studies have all been considered in the present study. Within this scope, it was predicted in this meta-analysis study that the heterogeneity can be explained with the country, class level, and lecture moderator variables of the study in terms of the effect of online education, which has been highly used since the beginning of the pandemic, and it has an impact on the students’ academic achievement in different lectures. Some subgroups were evaluated and categorized together, considering that the number of effect sizes of the sub-dimensions of the specified variables is not sufficient to perform moderator analysis (e.g. the countries where the studies were conducted).
2.6 Interpreting the effect sizes
Effect size is a factor that shows how much the independent variable affects the dependent variable positively or negatively in each included study in the meta-analysis (Dinçer, 2014 ). While interpreting the effect sizes obtained from the meta-analysis, the classifications of Cohen et al. ( 2007 ) have been utilized. The case of differentiating the specified relationships of the situation of the country, class level, and school subject variables of the study has been identified through the Q test, degree of freedom, and p significance value Fig. 1 and 2 .
3 Findings and results
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement. Before determining the effect sizes in the study, the probability of publication bias of this meta-analysis study was analyzed by using the funnel plot, Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test.
When the funnel plots are examined, it is seen that the studies included in the analysis are distributed symmetrically on both sides of the combined effect size axis, and they are generally collected in the middle and lower sections. The probability of publication bias is low according to the plots. However, since the results of the funnel scatter plots may cause subjective interpretations, they have been supported by additional analyses (Littell et al., 2008 ). Therefore, in order to provide an extra proof for the probability of publication bias, it has been analyzed through Orwin’s Safe N Analysis, Duval and Tweedie’s Trip and Fill Analysis, and Egger’s Regression Test (Table 2 ).
Table 2 consists of the results of the rates of publication bias probability before counting the effect size of online education on academic achievement. According to the table, Orwin Safe N analysis results show that it is not necessary to add new studies to the meta-analysis in order for Hedges g to reach a value outside the range of ± 0.01. The Duval and Tweedie test shows that excluding the studies that negatively affect the symmetry of the funnel scatter plots for each meta-analysis or adding their exact symmetrical equivalents does not significantly differentiate the calculated effect size. The insignificance of the Egger tests results reveals that there is no publication bias in the meta-analysis study. The results of the analysis indicate the high internal validity of the effect sizes and the adequacy of representing the studies conducted on the relevant subject.
In this study, it was aimed to determine the effect size of online education on academic achievement after testing the publication bias. In line with the first purpose of the study, the forest graph regarding the effect size of online education on academic achievement is shown in Fig. 3 , and the statistics regarding the effect size are given in Table 3 .
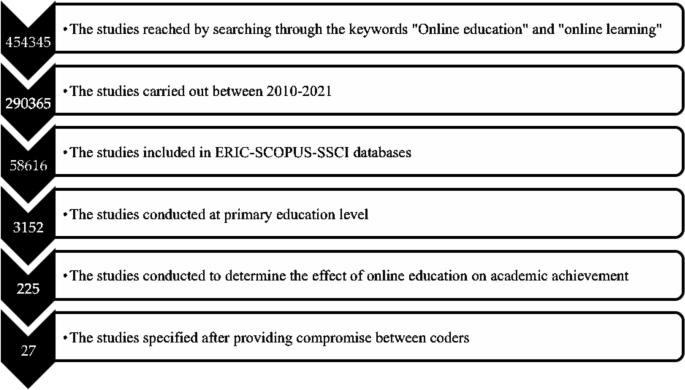
The flow chart of the scanning and selection process of the studies
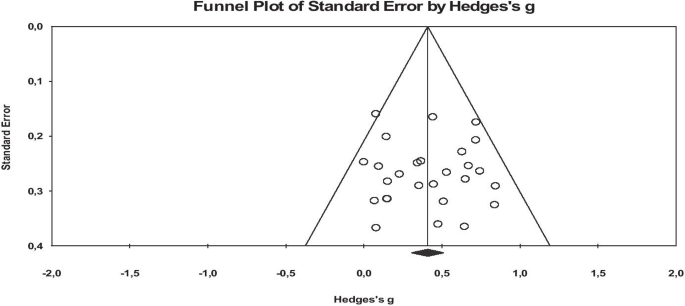
Funnel plot graphics representing the effect size of the effects of online education on academic success
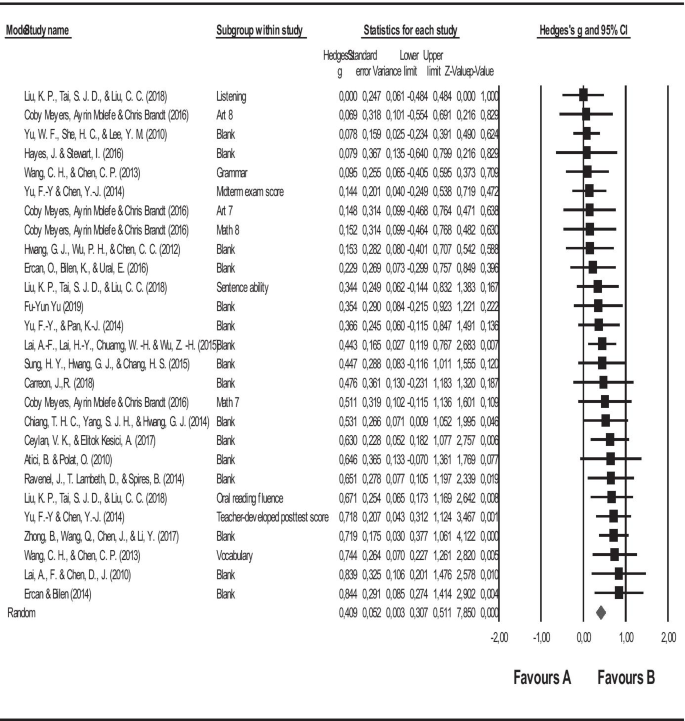
Forest graph related to the effect size of online education on academic success
The square symbols in the forest graph in Fig. 3 represent the effect sizes, while the horizontal lines show the intervals in 95% confidence of the effect sizes, and the diamond symbol shows the overall effect size. When the forest graph is analyzed, it is seen that the lower and upper limits of the combined effect sizes are generally close to each other, and the study loads are similar. This similarity in terms of study loads indicates the similarity of the contribution of the combined studies to the overall effect size.
Figure 3 clearly represents that the study of Liu and others (Liu et al., 2018 ) has the lowest, and the study of Ercan and Bilen ( 2014 ) has the highest effect sizes. The forest graph shows that all the combined studies and the overall effect are positive. Furthermore, it is simply understood from the forest graph in Fig. 3 and the effect size statistics in Table 3 that the results of the meta-analysis study conducted with 27 studies and analyzing the effect of online education on academic achievement illustrate that this relationship is on average level (= 0.409).
After the analysis of the effect size in the study, whether the studies included in the analysis are distributed heterogeneously or not has also been analyzed. The heterogeneity of the combined studies was determined through the Q and I 2 tests. As a result of the heterogeneity test, Q statistical value was calculated as 29.576. With 26 degrees of freedom at 95% significance level in the chi-square table, the critical value is accepted as 38.885. The Q statistical value (29.576) counted in this study is lower than the critical value of 38.885. The I 2 value, which is the complementary of the Q statistics, is 12.100%. This value indicates that the accurate heterogeneity or the total variability that can be attributed to variability between the studies is 12%. Besides, p value is higher than (0.285) p = 0.05. All these values [Q (26) = 29.579, p = 0.285; I2 = 12.100] indicate that there is a homogeneous distribution between the effect sizes, and fixed effects model should be used to interpret these effect sizes. However, some researchers argue that even if the heterogeneity is low, it should be evaluated based on the random effects model (Borenstein et al., 2007 ). Therefore, this study gives information about both models. The heterogeneity of the combined studies has been attempted to be explained with the characteristics of the studies included in the analysis. In this context, the final purpose of the study is to determine the effect of the country, academic level, and year variables on the findings. Accordingly, the statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the countries where the studies were conducted are given in Table 4 .
As seen in Table 4 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ significantly according to the countries where the studies were conducted in. Q test results indicate the heterogeneity of the relationships between the variables in terms of countries where the studies were conducted in. According to the table, the effect of online education on academic achievement was reported as the highest in other countries, and the lowest in the US. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table 5 .
As seen in Table 5 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the class level. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in the 4 th class. The statistics regarding the comparison of the stated relations according to the class levels are given in Table 6 .
As seen in Table 6 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to the school subjects included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in ICT subject.
The obtained effect size in the study was formed as a result of the findings attained from primary studies conducted in 7 different countries. In addition, these studies are the ones on different approaches to online education (online learning environments, social networks, blended learning, etc.). In this respect, the results may raise some questions about the validity and generalizability of the results of the study. However, the moderator analyzes, whether for the country variable or for the approaches covered by online education, did not create significant differences in terms of the effect sizes. If significant differences were to occur in terms of effect sizes, we could say that the comparisons we will make by comparing countries under the umbrella of online education would raise doubts in terms of generalizability. Moreover, no study has been found in the literature that is not based on a special approach or does not contain a specific technique conducted under the name of online education alone. For instance, one of the commonly used definitions is blended education which is defined as an educational model in which online education is combined with traditional education method (Colis & Moonen, 2001 ). Similarly, Rasmussen ( 2003 ) defines blended learning as “a distance education method that combines technology (high technology such as television, internet, or low technology such as voice e-mail, conferences) with traditional education and training.” Further, Kerres and Witt (2003) define blended learning as “combining face-to-face learning with technology-assisted learning.” As it is clearly observed, online education, which has a wider scope, includes many approaches.
As seen in Table 7 , the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ according to online education approaches included in the studies. However, the effect of online education on academic achievement is the highest in Web Based Problem Solving Approach.
4 Conclusions and discussion
Considering the developments during the pandemics, it is thought that the diversity in online education applications as an interdisciplinary pragmatist field will increase, and the learning content and processes will be enriched with the integration of new technologies into online education processes. Another prediction is that more flexible and accessible learning opportunities will be created in online education processes, and in this way, lifelong learning processes will be strengthened. As a result, it is predicted that in the near future, online education and even digital learning with a newer name will turn into the main ground of education instead of being an alternative or having a support function in face-to-face learning. The lessons learned from the early period online learning experience, which was passed with rapid adaptation due to the Covid19 epidemic, will serve to develop this method all over the world, and in the near future, online learning will become the main learning structure through increasing its functionality with the contribution of new technologies and systems. If we look at it from this point of view, there is a necessity to strengthen online education.
In this study, the effect of online learning on academic achievement is at a moderate level. To increase this effect, the implementation of online learning requires support from teachers to prepare learning materials, to design learning appropriately, and to utilize various digital-based media such as websites, software technology and various other tools to support the effectiveness of online learning (Rolisca & Achadiyah, 2014 ). According to research conducted by Rahayu et al. ( 2017 ), it has been proven that the use of various types of software increases the effectiveness and quality of online learning. Implementation of online learning can affect students' ability to adapt to technological developments in that it makes students use various learning resources on the internet to access various types of information, and enables them to get used to performing inquiry learning and active learning (Hart et al., 2019 ; Prestiadi et al., 2019 ). In addition, there may be many reasons for the low level of effect in this study. The moderator variables examined in this study could be a guide in increasing the level of practical effect. However, the effect size did not differ significantly for all moderator variables. Different moderator analyzes can be evaluated in order to increase the level of impact of online education on academic success. If confounding variables that significantly change the effect level are detected, it can be spoken more precisely in order to increase this level. In addition to the technical and financial problems, the level of impact will increase if a few other difficulties are eliminated such as students, lack of interaction with the instructor, response time, and lack of traditional classroom socialization.
In addition, COVID-19 pandemic related social distancing has posed extreme difficulties for all stakeholders to get online as they have to work in time constraints and resource constraints. Adopting the online learning environment is not just a technical issue, it is a pedagogical and instructive challenge as well. Therefore, extensive preparation of teaching materials, curriculum, and assessment is vital in online education. Technology is the delivery tool and requires close cross-collaboration between teaching, content and technology teams (CoSN, 2020 ).
Online education applications have been used for many years. However, it has come to the fore more during the pandemic process. This result of necessity has brought with it the discussion of using online education instead of traditional education methods in the future. However, with this research, it has been revealed that online education applications are moderately effective. The use of online education instead of face-to-face education applications can only be possible with an increase in the level of success. This may have been possible with the experience and knowledge gained during the pandemic process. Therefore, the meta-analysis of experimental studies conducted in the coming years will guide us. In this context, experimental studies using online education applications should be analyzed well. It would be useful to identify variables that can change the level of impacts with different moderators. Moderator analyzes are valuable in meta-analysis studies (for example, the role of moderators in Karl Pearson's typhoid vaccine studies). In this context, each analysis study sheds light on future studies. In meta-analyses to be made about online education, it would be beneficial to go beyond the moderators determined in this study. Thus, the contribution of similar studies to the field will increase more.
The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of online education on academic achievement. In line with this purpose, the studies that analyze the effect of online education approaches on academic achievement have been included in the meta-analysis. The total sample size of the studies included in the meta-analysis is 1772. While the studies included in the meta-analysis were conducted in the US, Taiwan, Turkey, China, Philippines, Ireland, and Georgia, the studies carried out in Europe could not be reached. The reason may be attributed to that there may be more use of quantitative research methods from a positivist perspective in the countries with an American academic tradition. As a result of the study, it was found out that the effect size of online education on academic achievement (g = 0.409) was moderate. In the studies included in the present research, we found that online education approaches were more effective than traditional ones. However, contrary to the present study, the analysis of comparisons between online and traditional education in some studies shows that face-to-face traditional learning is still considered effective compared to online learning (Ahmad et al., 2016 ; Hamdani & Priatna, 2020 ; Wei & Chou, 2020 ). Online education has advantages and disadvantages. The advantages of online learning compared to face-to-face learning in the classroom is the flexibility of learning time in online learning, the learning time does not include a single program, and it can be shaped according to circumstances (Lai et al., 2019 ). The next advantage is the ease of collecting assignments for students, as these can be done without having to talk to the teacher. Despite this, online education has several weaknesses, such as students having difficulty in understanding the material, teachers' inability to control students, and students’ still having difficulty interacting with teachers in case of internet network cuts (Swan, 2007 ). According to Astuti et al ( 2019 ), face-to-face education method is still considered better by students than e-learning because it is easier to understand the material and easier to interact with teachers. The results of the study illustrated that the effect size (g = 0.409) of online education on academic achievement is of medium level. Therefore, the results of the moderator analysis showed that the effect of online education on academic achievement does not differ in terms of country, lecture, class level, and online education approaches variables. After analyzing the literature, several meta-analyses on online education were published (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Machtmes & Asher, 2000 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ). Typically, these meta-analyzes also include the studies of older generation technologies such as audio, video, or satellite transmission. One of the most comprehensive studies on online education was conducted by Bernard et al. ( 2004 ). In this study, 699 independent effect sizes of 232 studies published from 1985 to 2001 were analyzed, and face-to-face education was compared to online education, with respect to success criteria and attitudes of various learners from young children to adults. In this meta-analysis, an overall effect size close to zero was found for the students' achievement (g + = 0.01).
In another meta-analysis study carried out by Zhao et al. ( 2005 ), 98 effect sizes were examined, including 51 studies on online education conducted between 1996 and 2002. According to the study of Bernard et al. ( 2004 ), this meta-analysis focuses on the activities done in online education lectures. As a result of the research, an overall effect size close to zero was found for online education utilizing more than one generation technology for students at different levels. However, the salient point of the meta-analysis study of Zhao et al. is that it takes the average of different types of results used in a study to calculate an overall effect size. This practice is problematic because the factors that develop one type of learner outcome (e.g. learner rehabilitation), particularly course characteristics and practices, may be quite different from those that develop another type of outcome (e.g. learner's achievement), and it may even cause damage to the latter outcome. While mixing the studies with different types of results, this implementation may obscure the relationship between practices and learning.
Some meta-analytical studies have focused on the effectiveness of the new generation distance learning courses accessed through the internet for specific student populations. For instance, Sitzmann and others (Sitzmann et al., 2006 ) reviewed 96 studies published from 1996 to 2005, comparing web-based education of job-related knowledge or skills with face-to-face one. The researchers found that web-based education in general was slightly more effective than face-to-face education, but it is insufficient in terms of applicability ("knowing how to apply"). In addition, Sitzmann et al. ( 2006 ) revealed that Internet-based education has a positive effect on theoretical knowledge in quasi-experimental studies; however, it positively affects face-to-face education in experimental studies performed by random assignment. This moderator analysis emphasizes the need to pay attention to the factors of designs of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The designs of the studies included in this meta-analysis study were ignored. This can be presented as a suggestion to the new studies that will be conducted.
Another meta-analysis study was conducted by Cavanaugh et al. ( 2004 ), in which they focused on online education. In this study on internet-based distance education programs for students under 12 years of age, the researchers combined 116 results from 14 studies published between 1999 and 2004 to calculate an overall effect that was not statistically different from zero. The moderator analysis carried out in this study showed that there was no significant factor affecting the students' success. This meta-analysis used multiple results of the same study, ignoring the fact that different results of the same student would not be independent from each other.
In conclusion, some meta-analytical studies analyzed the consequences of online education for a wide range of students (Bernard et al., 2004 ; Zhao et al., 2005 ), and the effect sizes were generally low in these studies. Furthermore, none of the large-scale meta-analyzes considered the moderators, database quality standards or class levels in the selection of the studies, while some of them just referred to the country and lecture moderators. Advances in internet-based learning tools, the pandemic process, and increasing popularity in different learning contexts have required a precise meta-analysis of students' learning outcomes through online learning. Previous meta-analysis studies were typically based on the studies, involving narrow range of confounding variables. In the present study, common but significant moderators such as class level and lectures during the pandemic process were discussed. For instance, the problems have been experienced especially in terms of eligibility of class levels in online education platforms during the pandemic process. It was found that there is a need to study and make suggestions on whether online education can meet the needs of teachers and students.
Besides, the main forms of online education in the past were to watch the open lectures of famous universities and educational videos of institutions. In addition, online education is mainly a classroom-based teaching implemented by teachers in their own schools during the pandemic period, which is an extension of the original school education. This meta-analysis study will stand as a source to compare the effect size of the online education forms of the past decade with what is done today, and what will be done in the future.
Lastly, the heterogeneity test results of the meta-analysis study display that the effect size does not differ in terms of class level, country, online education approaches, and lecture moderators.
*Studies included in meta-analysis
Ahmad, S., Sumardi, K., & Purnawan, P. (2016). Komparasi Peningkatan Hasil Belajar Antara Pembelajaran Menggunakan Sistem Pembelajaran Online Terpadu Dengan Pembelajaran Klasikal Pada Mata Kuliah Pneumatik Dan Hidrolik. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Education, 2 (2), 286–292.
Article Google Scholar
Ally, M. (2004). Foundations of educational theory for online learning. Theory and Practice of Online Learning, 2 , 15–44. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://eddl.tru.ca/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/01_Anderson_2008-Theory_and_Practice_of_Online_Learning.pdf
Arat, T., & Bakan, Ö. (2011). Uzaktan eğitim ve uygulamaları. Selçuk Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Meslek Yüksek Okulu Dergisi , 14 (1–2), 363–374. https://doi.org/10.29249/selcuksbmyd.540741
Astuti, C. C., Sari, H. M. K., & Azizah, N. L. (2019). Perbandingan Efektifitas Proses Pembelajaran Menggunakan Metode E-Learning dan Konvensional. Proceedings of the ICECRS, 2 (1), 35–40.
*Atici, B., & Polat, O. C. (2010). Influence of the online learning environments and tools on the student achievement and opinions. Educational Research and Reviews, 5 (8), 455–464. Retrieved on the 11th of October, 2020 from https://academicjournals.org/journal/ERR/article-full-text-pdf/4C8DD044180.pdf
Bernard, R. M., Abrami, P. C., Lou, Y., Borokhovski, E., Wade, A., Wozney, L., et al. (2004). How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A meta- analysis of the empirical literature. Review of Educational Research, 3 (74), 379–439. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543074003379
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T., & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta-analysis . Wiley.
Book Google Scholar
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L., & Rothstein, H. (2007). Meta-analysis: Fixed effect vs. random effects . UK: Wiley.
Card, N. A. (2011). Applied meta-analysis for social science research: Methodology in the social sciences . Guilford.
Google Scholar
*Carreon, J. R. (2018 ). Facebook as integrated blended learning tool in technology and livelihood education exploratory. Retrieved on the 1st of October, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1197714.pdf
Cavanaugh, C., Gillan, K. J., Kromrey, J., Hess, M., & Blomeyer, R. (2004). The effects of distance education on K-12 student outcomes: A meta-analysis. Learning Point Associates/North Central Regional Educational Laboratory (NCREL) . Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED489533.pdf
*Ceylan, V. K., & Elitok Kesici, A. (2017). Effect of blended learning to academic achievement. Journal of Human Sciences, 14 (1), 308. https://doi.org/10.14687/jhs.v14i1.4141
*Chae, S. E., & Shin, J. H. (2016). Tutoring styles that encourage learner satisfaction, academic engagement, and achievement in an online environment. Interactive Learning Environments, 24(6), 1371–1385. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2015.1009472
*Chiang, T. H. C., Yang, S. J. H., & Hwang, G. J. (2014). An augmented reality-based mobile learning system to improve students’ learning achievements and motivations in natural science inquiry activities. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (4), 352–365. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gwo_Jen_Hwang/publication/287529242_An_Augmented_Reality-based_Mobile_Learning_System_to_Improve_Students'_Learning_Achievements_and_Motivations_in_Natural_Science_Inquiry_Activities/links/57198c4808ae30c3f9f2c4ac.pdf
Chiao, H. M., Chen, Y. L., & Huang, W. H. (2018). Examining the usability of an online virtual tour-guiding platform for cultural tourism education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education, 23 (29–38), 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhlste.2018.05.002
Chizmar, J. F., & Walbert, M. S. (1999). Web-based learning environments guided by principles of good teaching practice. Journal of Economic Education, 30 (3), 248–264. https://doi.org/10.2307/1183061
Cleophas, T. J., & Zwinderman, A. H. (2017). Modern meta-analysis: Review and update of methodologies . Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-55895-0
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, K. (2007). Observation. Research Methods in Education, 6 , 396–412. Retrieved on the 11th of September, 2020 from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nabil_Ashraf2/post/How_to_get_surface_potential_Vs_Voltage_curve_from_CV_and_GV_measurements_of_MOS_capacitor/attachment/5ac6033cb53d2f63c3c405b4/AS%3A612011817844736%401522926396219/download/Very+important_C-V+characterization+Lehigh+University+thesis.pdf
Colis, B., & Moonen, J. (2001). Flexible Learning in a Digital World: Experiences and Expectations. Open & Distance Learning Series . Stylus Publishing.
CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. CoSN. (2020). COVID-19 Response: Preparing to Take School Online. Retrieved on the 3rd of September, 2021 from https://www.cosn.org/sites/default/files/COVID-19%20Member%20Exclusive_0.pdf
Cumming, G. (2012). Understanding new statistics: Effect sizes, confidence intervals, and meta-analysis. New York, USA: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203807002
Deeks, J. J., Higgins, J. P. T., & Altman, D. G. (2008). Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses . In J. P. T. Higgins & S. Green (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (pp. 243–296). Sussex: John Wiley & Sons. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470712184.ch9
Demiralay, R., Bayır, E. A., & Gelibolu, M. F. (2016). Öğrencilerin bireysel yenilikçilik özellikleri ile çevrimiçi öğrenmeye hazır bulunuşlukları ilişkisinin incelenmesi. Eğitim ve Öğretim Araştırmaları Dergisi, 5 (1), 161–168. https://doi.org/10.23891/efdyyu.2017.10
Dinçer, S. (2014). Eğitim bilimlerinde uygulamalı meta-analiz. Pegem Atıf İndeksi, 2014(1), 1–133. https://doi.org/10.14527/pegem.001
*Durak, G., Cankaya, S., Yunkul, E., & Ozturk, G. (2017). The effects of a social learning network on students’ performances and attitudes. European Journal of Education Studies, 3 (3), 312–333. 10.5281/zenodo.292951
*Ercan, O. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes . European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
Ercan, O., & Bilen, K. (2014). Effect of web assisted education supported by six thinking hats on students’ academic achievement in science and technology classes. European Journal of Educational Research, 3 (1), 9–23.
*Ercan, O., Bilen, K., & Ural, E. (2016). “Earth, sun and moon”: Computer assisted instruction in secondary school science - Achievement and attitudes. Issues in Educational Research, 26 (2), 206–224. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.3.1.9
Field, A. P. (2003). The problems in using fixed-effects models of meta-analysis on real-world data. Understanding Statistics, 2 (2), 105–124. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328031us0202_02
Field, A. P., & Gillett, R. (2010). How to do a meta-analysis. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 63 (3), 665–694. https://doi.org/10.1348/00071010x502733
Geostat. (2019). ‘Share of households with internet access’, National statistics office of Georgia . Retrieved on the 2nd September 2020 from https://www.geostat.ge/en/modules/categories/106/information-and-communication-technologies-usage-in-households
*Gwo-Jen, H., Nien-Ting, T., & Xiao-Ming, W. (2018). Creating interactive e-books through learning by design: The impacts of guided peer-feedback on students’ learning achievements and project outcomes in science courses. Journal of Educational Technology & Society., 21 (1), 25–36. Retrieved on the 2nd of October, 2020 https://ae-uploads.uoregon.edu/ISTE/ISTE2019/PROGRAM_SESSION_MODEL/HANDOUTS/112172923/CreatingInteractiveeBooksthroughLearningbyDesignArticle2018.pdf
Hamdani, A. R., & Priatna, A. (2020). Efektifitas implementasi pembelajaran daring (full online) dimasa pandemi Covid-19 pada jenjang Sekolah Dasar di Kabupaten Subang. Didaktik: Jurnal Ilmiah PGSD STKIP Subang, 6 (1), 1–9.
Hart, C. M., Berger, D., Jacob, B., Loeb, S., & Hill, M. (2019). Online learning, offline outcomes: Online course taking and high school student performance. Aera Open, 5(1).
*Hayes, J., & Stewart, I. (2016). Comparing the effects of derived relational training and computer coding on intellectual potential in school-age children. The British Journal of Educational Psychology, 86 (3), 397–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12114
Horton, W. K. (2000). Designing web-based training: How to teach anyone anything anywhere anytime (Vol. 1). Wiley Publishing.
*Hwang, G. J., Wu, P. H., & Chen, C. C. (2012). An online game approach for improving students’ learning performance in web-based problem-solving activities. Computers and Education, 59 (4), 1246–1256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.05.009
*Kert, S. B., Köşkeroğlu Büyükimdat, M., Uzun, A., & Çayiroğlu, B. (2017). Comparing active game-playing scores and academic performances of elementary school students. Education 3–13, 45 (5), 532–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2016.1140800
*Lai, A. F., & Chen, D. J. (2010). Web-based two-tier diagnostic test and remedial learning experiment. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies, 8 (1), 31–53. https://doi.org/10.4018/jdet.2010010103
*Lai, A. F., Lai, H. Y., Chuang W. H., & Wu, Z.H. (2015). Developing a mobile learning management system for outdoors nature science activities based on 5e learning cycle. Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Learning, ICEL. Proceedings of the International Association for Development of the Information Society (IADIS) International Conference on e-Learning (Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, July 21–24, 2015). Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562095.pdf
Lai, C. H., Lin, H. W., Lin, R. M., & Tho, P. D. (2019). Effect of peer interaction among online learning community on learning engagement and achievement. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies (IJDET), 17 (1), 66–77.
Littell, J. H., Corcoran, J., & Pillai, V. (2008). Systematic reviews and meta-analysis . Oxford University.
*Liu, K. P., Tai, S. J. D., & Liu, C. C. (2018). Enhancing language learning through creation: the effect of digital storytelling on student learning motivation and performance in a school English course. Educational Technology Research and Development, 66 (4), 913–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-018-9592-z
Machtmes, K., & Asher, J. W. (2000). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of telecourses in distance education. American Journal of Distance Education, 14 (1), 27–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923640009527043
Makowski, D., Piraux, F., & Brun, F. (2019). From experimental network to meta-analysis: Methods and applications with R for agronomic and environmental sciences. Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024_1696-1
* Meyers, C., Molefe, A., & Brandt, C. (2015). The Impact of the" Enhancing Missouri's Instructional Networked Teaching Strategies"(eMINTS) Program on Student Achievement, 21st-Century Skills, and Academic Engagement--Second-Year Results . Society for Research on Educational Effectiveness. Retrieved on the 14 th November, 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562508.pdf
OECD. (2020). ‘A framework to guide an education response to the COVID-19 Pandemic of 2020 ’. https://doi.org/10.26524/royal.37.6
Pecoraro, V. (2018). Appraising evidence . In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 99–114). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_9
Pigott, T. (2012). Advances in meta-analysis . Springer.
Pillay, H. , Irving, K., & Tones, M. (2007). Validation of the diagnostic tool for assessing Tertiary students’ readiness for online learning. Higher Education Research & Development, 26 (2), 217–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360701310821
Prestiadi, D., Zulkarnain, W., & Sumarsono, R. B. (2019). Visionary leadership in total quality management: efforts to improve the quality of education in the industrial revolution 4.0. In the 4th International Conference on Education and Management (COEMA 2019). Atlantis Press
Poole, D. M. (2000). Student participation in a discussion-oriented online course: a case study. Journal of Research on Computing in Education, 33 (2), 162–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/08886504.2000.10782307
Rahayu, F. S., Budiyanto, D., & Palyama, D. (2017). Analisis penerimaan e-learning menggunakan technology acceptance model (Tam)(Studi Kasus: Universitas Atma Jaya Yogyakarta). Jurnal Terapan Teknologi Informasi, 1 (2), 87–98.
Rasmussen, R. C. (2003). The quantity and quality of human interaction in a synchronous blended learning environment . Brigham Young University Press.
*Ravenel, J., T. Lambeth, D., & Spires, B. (2014). Effects of computer-based programs on mathematical achievement scores for fourth-grade students. i-manager’s Journal on School Educational Technology, 10 (1), 8–21. https://doi.org/10.26634/jsch.10.1.2830
Rolisca, R. U. C., & Achadiyah, B. N. (2014). Pengembangan media evaluasi pembelajaran dalam bentuk online berbasis e-learning menggunakan software wondershare quiz creator dalam mata pelajaran akuntansi SMA Brawijaya Smart School (BSS). Jurnal Pendidikan Akuntansi Indonesia, 12(2).
Sitzmann, T., Kraiger, K., Stewart, D., & Wisher, R. (2006). The comparative effective- ness of Web-based and classroom instruction: A meta-analysis . Personnel Psychology, 59 (3), 623–664. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.2006.00049.x
Stewart, D. W., & Kamins, M. A. (2001). Developing a coding scheme and coding study reports. In M. W. Lipsey & D. B. Wilson (Eds.), Practical metaanalysis: Applied social research methods series (Vol. 49, pp. 73–90). Sage.
Swan, K. (2007). Research on online learning. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 11 (1), 55–59.
*Sung, H. Y., Hwang, G. J., & Chang, Y. C. (2016). Development of a mobile learning system based on a collaborative problem-posing strategy. Interactive Learning Environments, 24 (3), 456–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2013.867889
Tsagris, M., & Fragkos, K. C. (2018). Meta-analyses of clinical trials versus diagnostic test accuracy studies. In G. Biondi-Zoccai (Ed.), Diagnostic meta-analysis: A useful tool for clinical decision-making (pp. 31–42). Cham, Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78966-8_4
UNESCO. (2020, Match 13). COVID-19 educational disruption and response. Retrieved on the 14 th November 2020 from https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/ coronavirus-school-closures
Usta, E. (2011a). The effect of web-based learning environments on attitudes of students regarding computer and internet. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 28 (262–269), 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2011.11.051
Usta, E. (2011b). The examination of online self-regulated learning skills in web-based learning environments in terms of different variables. Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology-TOJET, 10 (3), 278–286. Retrieved on the 14th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ944994.pdf
Vrasidas, C. & MsIsaac, M. S. (2000). Principles of pedagogy and evaluation for web-based learning. Educational Media International, 37 (2), 105–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/095239800410405
*Wang, C. H., & Chen, C. P. (2013). Effects of facebook tutoring on learning english as a second language. Proceedings of the International Conference e-Learning 2013, (2009), 135–142. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED562299.pdf
Wei, H. C., & Chou, C. (2020). Online learning performance and satisfaction: Do perceptions and readiness matter? Distance Education, 41 (1), 48–69.
*Yu, F. Y. (2019). The learning potential of online student-constructed tests with citing peer-generated questions. Interactive Learning Environments, 27 (2), 226–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2018.1458040
*Yu, F. Y., & Chen, Y. J. (2014). Effects of student-generated questions as the source of online drill-and-practice activities on learning . British Journal of Educational Technology, 45 (2), 316–329. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12036
*Yu, F. Y., & Pan, K. J. (2014). The effects of student question-generation with online prompts on learning. Educational Technology and Society, 17 (3), 267–279. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.565.643&rep=rep1&type=pdf
*Yu, W. F., She, H. C., & Lee, Y. M. (2010). The effects of web-based/non-web-based problem-solving instruction and high/low achievement on students’ problem-solving ability and biology achievement. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 47 (2), 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703291003718927
Zhao, Y., Lei, J., Yan, B, Lai, C., & Tan, S. (2005). A practical analysis of research on the effectiveness of distance education. Teachers College Record, 107 (8). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9620.2005.00544.x
*Zhong, B., Wang, Q., Chen, J., & Li, Y. (2017). Investigating the period of switching roles in pair programming in a primary school. Educational Technology and Society, 20 (3), 220–233. Retrieved on the 15th November 2020 from https://repository.nie.edu.sg/bitstream/10497/18946/1/ETS-20-3-220.pdf
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Primary Education, Ministry of Turkish National Education, Mersin, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hakan Ulum .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ulum, H. The effects of online education on academic success: A meta-analysis study. Educ Inf Technol 27 , 429–450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10740-8
Download citation
Received : 06 December 2020
Accepted : 30 August 2021
Published : 06 September 2021
Issue Date : January 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10740-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Online education
- Student achievement
- Academic success
- Meta-analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
How Effective Is Online Learning? What the Research Does and Doesn’t Tell Us

- Share article
Editor’s Note: This is part of a series on the practical takeaways from research.
The times have dictated school closings and the rapid expansion of online education. Can online lessons replace in-school time?
Clearly online time cannot provide many of the informal social interactions students have at school, but how will online courses do in terms of moving student learning forward? Research to date gives us some clues and also points us to what we could be doing to support students who are most likely to struggle in the online setting.
The use of virtual courses among K-12 students has grown rapidly in recent years. Florida, for example, requires all high school students to take at least one online course. Online learning can take a number of different forms. Often people think of Massive Open Online Courses, or MOOCs, where thousands of students watch a video online and fill out questionnaires or take exams based on those lectures.
In the online setting, students may have more distractions and less oversight, which can reduce their motivation.
Most online courses, however, particularly those serving K-12 students, have a format much more similar to in-person courses. The teacher helps to run virtual discussion among the students, assigns homework, and follows up with individual students. Sometimes these courses are synchronous (teachers and students all meet at the same time) and sometimes they are asynchronous (non-concurrent). In both cases, the teacher is supposed to provide opportunities for students to engage thoughtfully with subject matter, and students, in most cases, are required to interact with each other virtually.
Coronavirus and Schools
Online courses provide opportunities for students. Students in a school that doesn’t offer statistics classes may be able to learn statistics with virtual lessons. If students fail algebra, they may be able to catch up during evenings or summer using online classes, and not disrupt their math trajectory at school. So, almost certainly, online classes sometimes benefit students.
In comparisons of online and in-person classes, however, online classes aren’t as effective as in-person classes for most students. Only a little research has assessed the effects of online lessons for elementary and high school students, and even less has used the “gold standard” method of comparing the results for students assigned randomly to online or in-person courses. Jessica Heppen and colleagues at the American Institutes for Research and the University of Chicago Consortium on School Research randomly assigned students who had failed second semester Algebra I to either face-to-face or online credit recovery courses over the summer. Students’ credit-recovery success rates and algebra test scores were lower in the online setting. Students assigned to the online option also rated their class as more difficult than did their peers assigned to the face-to-face option.
Most of the research on online courses for K-12 students has used large-scale administrative data, looking at otherwise similar students in the two settings. One of these studies, by June Ahn of New York University and Andrew McEachin of the RAND Corp., examined Ohio charter schools; I did another with colleagues looking at Florida public school coursework. Both studies found evidence that online coursetaking was less effective.
About this series
This essay is the fifth in a series that aims to put the pieces of research together so that education decisionmakers can evaluate which policies and practices to implement.
The conveners of this project—Susanna Loeb, the director of Brown University’s Annenberg Institute for School Reform, and Harvard education professor Heather Hill—have received grant support from the Annenberg Institute for this series.
To suggest other topics for this series or join in the conversation, use #EdResearchtoPractice on Twitter.
Read the full series here .
It is not surprising that in-person courses are, on average, more effective. Being in person with teachers and other students creates social pressures and benefits that can help motivate students to engage. Some students do as well in online courses as in in-person courses, some may actually do better, but, on average, students do worse in the online setting, and this is particularly true for students with weaker academic backgrounds.
Students who struggle in in-person classes are likely to struggle even more online. While the research on virtual schools in K-12 education doesn’t address these differences directly, a study of college students that I worked on with Stanford colleagues found very little difference in learning for high-performing students in the online and in-person settings. On the other hand, lower performing students performed meaningfully worse in online courses than in in-person courses.
But just because students who struggle in in-person classes are even more likely to struggle online doesn’t mean that’s inevitable. Online teachers will need to consider the needs of less-engaged students and work to engage them. Online courses might be made to work for these students on average, even if they have not in the past.
Just like in brick-and-mortar classrooms, online courses need a strong curriculum and strong pedagogical practices. Teachers need to understand what students know and what they don’t know, as well as how to help them learn new material. What is different in the online setting is that students may have more distractions and less oversight, which can reduce their motivation. The teacher will need to set norms for engagement—such as requiring students to regularly ask questions and respond to their peers—that are different than the norms in the in-person setting.
Online courses are generally not as effective as in-person classes, but they are certainly better than no classes. A substantial research base developed by Karl Alexander at Johns Hopkins University and many others shows that students, especially students with fewer resources at home, learn less when they are not in school. Right now, virtual courses are allowing students to access lessons and exercises and interact with teachers in ways that would have been impossible if an epidemic had closed schools even a decade or two earlier. So we may be skeptical of online learning, but it is also time to embrace and improve it.
A version of this article appeared in the April 01, 2020 edition of Education Week as How Effective Is Online Learning?
Sign Up for EdWeek Tech Leader
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 09 May 2024
Looking back to move forward: comparison of instructors’ and undergraduates’ retrospection on the effectiveness of online learning using the nine-outcome influencing factors
- Yujie Su ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1444-1598 1 ,
- Xiaoshu Xu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0667-4511 1 ,
- Yunfeng Zhang 2 ,
- Xinyu Xu 1 &
- Shanshan Hao 3
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 594 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
97 Accesses
Metrics details
- Language and linguistics
This study delves into the retrospections of undergraduate students concerning their online learning experiences after the COVID-19 pandemic, using the nine key influencing factors: behavioral intention, instruction, engagement, interaction, motivation, self-efficacy, performance, satisfaction, and self-regulation. 46 Year 1 students from a comprehensive university in China were asked to maintain reflective diaries throughout an academic semester, providing first-person perspectives on the strengths and weaknesses of online learning. Meanwhile, 18 college teachers were interviewed with the same questions as the students. Using thematic analysis, the research identified 9 factors. The research revealed that instruction ranked highest among the 9 factors, followed by engagement, self-regulation, interaction, motivation, and others. Moreover, teachers and students had different attitudes toward instruction. Thirdly, teacher participants were different from student participants given self-efficacy and self-regulation due to their variant roles in online instruction. Lastly, the study reflected students were not independent learners, which explained why instruction ranked highest in their point of view. Findings offer valuable insights for educators, administrators, and policy-makers involved in higher education. Recommendations for future research include incorporating a more diverse sample, exploring relationships between the nine factors, and focusing on equipping students with skills for optimal online learning experiences.
Similar content being viewed by others
Determinants of behaviour and their efficacy as targets of behavioural change interventions

Interviews in the social sciences

Mechanisms linking social media use to adolescent mental health vulnerability
Introduction.
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on education worldwide, leading to the widescale adoption of online learning. According to the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), at the peak of the pandemic, 192 countries had implemented nationwide closures, affecting approximately 99% of the world’s student population (UNESCO 2020 a). In response, educational institutions, teachers, and students quickly adapted to online learning platforms, leveraging digital technologies to continue education amidst the crisis (Marinoni et al. 2020 ).
The rapid and unexpected shift to online learning brought about a surge in research aiming to understand its impact, effectiveness, and challenges. Researchers across the globe have been investigating various dimensions of online learning. Some focus on students’ experiences and perspectives (Aristovnik et al. 2021 ), technological aspects (Bao 2020 ), pedagogical strategies (Hodges et al. 2020 ), and the socio-emotional aspect of learning (Ali 2020 ). Tan et al. ( 2021 ) found that motivation and satisfaction were mostly positively perceived by students, and lack of interaction was perceived as an unfavorable online instruction perception. Some center on teachers’ perceptions of the benefits and challenges (Lucas and Vicente, 2023 ; Mulla et al. 2023 ), post-pandemic pedagogisation (Rapanta et al. 2021 ), and post-pandemic further education (Kohnke et al. 2023 ; Torsani et al. 2023 ). It was worth noting that elements like interaction and engagement were central to the development and maintenance of the learning community (Lucas and Vincente 2023 ),
The rise of online learning has also posed unprecedented challenges. Studies have pointed out the digital divide and accessibility issues (Crawford et al. 2020 ), students’ motivation and engagement concerns (Martin and Bolliger 2018 ), and the need for effective online instructional practices (Trust and Whalen 2020 ). The rapid transition to online learning has highlighted the need for robust research to address these challenges and understand the effectiveness of online learning in this new educational paradigm.
Despite the extensive research on online learning during and after the COVID-19 pandemic, there remains a notable gap in understanding the retrospective perspectives of both undergraduates and teachers. Much of the current literature has focused on immediate response strategies to the transition to online learning, often overlooking the detailed insights that reflective retrospection can provide (Marinoni et al. 2020 ; Bao 2020 ). In addition, while many studies have examined isolated aspects of online learning, they have not often employed a comprehensive framework, leaving undergraduates’ voices, in particular, underrepresented in the discourse (Aristovnik et al. 2021 ; Crawford et al. 2020 ). This study, situated in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic’s impetus toward online learning, seeks to fill this crucial gap. By exploring online learning from the perspectives of both instructors and undergraduates, and analyzing nine key factors that include engagement, motivation, and self-efficacy, the research contributes vital insights into the dynamics of online education (Wang and Wang 2021 ). This exploration is especially pertinent as digital learning environments become increasingly prevalent worldwide (UNESCO 2020b ). The findings of our study are pivotal for shaping future educational policies and enhancing online education strategies in this continuously evolving educational landscape (Greenhow et al. 2021 ). Thus, three research questions were raised:
Q1: How do undergraduates and teachers in China retrospectively perceive the effectiveness of online learning after the COVID-19 pandemic?
Q2: Which of the nine outcome influencing factors had the most significant impact on online learning experiences after the pandemic, and why?
Q3: What recommendations can be proposed to enhance the effectiveness of online learning in the future?
The research takes place at a comprehensive university in China, with a sample of 46 Year 1 students and 18 experienced teachers. Their reflections on the effectiveness of online learning were captured through reflective diaries guided by four questions. These questions investigated the students’ online learning states and attitudes, identified issues and insufficiencies in online learning, analyzed the reasons behind these problems, and proposed improvements. By assessing their experiences and perceptions, we seek to explore the significant factors that shaped online learning outcomes after the pandemic and the means to enhance its effectiveness.
This paper first presents a review of the existing literature, focusing on the impact of the pandemic on online learning and discussing the nine significant factors influencing online learning outcomes. Following this, the methodology utilized for this study is detailed, setting the stage for a deeper understanding of the research process. Subsequently, we delve into the results of the thematic analysis conducted based on undergraduate students and teachers’ retrospections. Finally, the paper concludes by offering meaningful implications of the findings for various stakeholders and suggesting directions for future research in this critical area.
Literature review
Online learning application and evaluation in higher education.
Online learning, also known as e-learning or distance learning, refers to education that takes place over the Internet rather than in a traditional classroom setting. It has seen substantial growth over the past decade and has been accelerated due to the COVID-19 pandemic (Trust and Whalen 2020 ). Online learning allows for a flexible learning environment, breaking the temporal and spatial boundaries of traditional classroom settings (Bozkurt and Sharma 2020 ). In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, educational institutions globally have embraced online learning at an unprecedented scale. This has led to an immense surge in research focusing on the effects of the pandemic on online learning (Crawford et al. 2020 ; Marinoni et al. 2020 ).
Researchers were divided in their attitudes toward the effects of online learning, including positive, neutral, and negative. Research by Bahasoan et al. ( 2020 ), Bernard et al. ( 2004 ), Hernández-Lara and Serradell-López ( 2018 ), and Paechter and Maier ( 2010 ) indicated the effectiveness of online learning, including improved outcomes and engagement in online formats, providing flexibility and enhancing digital skills for instance. Research, including studies by Dolan Hancock and Wareing ( 2015 ) and Means et al. ( 2010 ), indicates that under equivalent conditions and with similar levels of support, there is frequently no substantial difference in learning outcomes between traditional face-to-face courses and completely online courses.
However, online learning was not without its challenges. Research showing less favorable results for specific student groups can be referenced in Dennen ( 2014 ), etc. The common problems faced by students included underdeveloped independent learning ability, lack of motivation, difficulties in self-regulation, student engagement and technical issues (Aristovnik et al. 2021 ; Martin and Bolliger 2018 ; Song et al. 2004 ; Zheng et al. 2022 ).
Moreover, factors like instructional strategies, course design, etc. were also linked to learning outcomes and successful online learning (Ali 2020 ; Hongsuchon et al. 2022 ). Careaga-Butter et al. ( 2020 ) critically analyze online education in pandemic and post-pandemic contexts, focusing on digital tools and resources for teaching in synchronous and asynchronous learning modalities. They discuss the swift adaptation to online learning during the pandemic, highlighting the importance of technological infrastructure, pedagogical strategies, and the challenges of digital divides. The article emphasizes the need for effective online learning environments and explores trends in post-pandemic education, providing insights into future educational strategies and practices.

Determinants of online learning outcomes
Online learning outcomes in this paper refer to the measurable educational results achieved through online learning methods, including knowledge acquisition, skill development, changes in attitudes or behaviors, and performance improvements (Chang 2016 ; Panigrahi et al. 2018 ). The literature review identified key factors influencing online learning outcomes, emphasizing their significant role in academic discourse. These factors, highlighted in scholarly literature, include student engagement, instructional design, technology infrastructure, student-teacher interaction, and student self-regulation.
Student Engagement: The level of a student’s engagement significantly impacts their learning outcomes. The more actively a student is engaged with the course content and activities, the better their performance tends to be. This underscores the importance of designing engaging course content and providing opportunities for active learning in an online environment (Martin and Bolliger 2018 ).
Instructional Design: How an online course is designed can greatly affect student outcomes. Key elements such as clarity of learning objectives, organization of course materials, and the use of diverse instructional strategies significantly impact student learning (Bozkurt and Sharma 2020 ).
Technology Infrastructure: The reliability and ease of use of the learning management system (LMS) also play a significant role in online learning outcomes. When students experience technical difficulties, it can lead to frustration, reduced engagement, and lower performance (Johnson et al. 2020 ).
Student-Teacher Interaction: Interaction between students and teachers in an online learning environment is a key determinant of successful outcomes. Regular, substantive feedback from instructors can promote student learning and motivation (Boling et al. 2012 ).
Student Self-Regulation: The autonomous nature of online learning requires students to be proficient in self-regulated learning, which involves setting learning goals, self-monitoring, and self-evaluation. Students who exhibit strong self-regulation skills are more likely to succeed in online learning (Broadbent 2017 ).
While many studies have investigated individual factors affecting online learning, there is a paucity of research offering a holistic view of these factors and their interrelationships, leading to a fragmented understanding of the influences on online learning outcomes. Given the multitude of experiences and variables encompassed by online learning, a comprehensive framework like is instrumental in ensuring a thorough investigation and interpretation of the breadth of students’ experiences.
Students’ perceptions of online learning
Understanding students’ perceptions of online learning is essential for enhancing its effectiveness and student satisfaction. Studies show students appreciate online learning for its flexibility and convenience, offering personalized learning paths and resource access (Händel et al. 2020 ; Johnson et al. 2020 ). Yet, challenges persist, notably in maintaining motivation and handling technical issues (Aristovnik et al. 2021 ; Händel et al. 2020 ). Aguilera-Hermida ( 2020 ) reported mixed feelings among students during the COVID-19 pandemic, including feelings of isolation and difficulty adjusting to online environments. Boling et al. ( 2012 ) emphasized students’ preferences for interactive and communicative online learning environments. Additionally, research indicates that students seek more engaging content and innovative teaching approaches, suggesting a gap between current online offerings and student expectations (Chakraborty and Muyia Nafukho 2014 ). Students also emphasize the importance of community and peer support in online settings, underlining the need for collaborative and social learning opportunities (Lai et al. 2019 ). These findings imply that while online learning offers significant benefits, addressing its shortcomings is critical for maximizing its potential.
The pandemic prompted a reconsideration of instructional modalities, with many students favoring face-to-face instruction due to the immediacy and focus issues (Aristovnik et al. 2021 ; Trust and Whalen 2020 ). Despite valuable insights, research gaps remain, particularly in long-term undergraduate reflections and the application of nine factors of comprehensive frameworks, indicating a need for more holistic research in online learning effectiveness.
Teachers’ perceptions of online learning
The pandemic has brought attention to how teachers manage instruction in virtual learning environments. Teachers and students are divided in terms of their attitudes toward online learning. Some teachers and students looked to the convenience and flexibility of online learning (Chuenyindee et al. 2022 ; Al-Emran and Shaalan 2021 ). They conceived that online learning provided opportunities to improve educational equality as well (Tenório et al. 2016 ). Even when COVID-19 was over, the dependence on online learning was likely here to stay, for some approaches of online learning were well-received by students and teachers (Al-Rahmi et al. 2019 ; Hongsuchon et al. 2022 ).
Teachers had shown great confidence in delivering instruction in an online environment in a satisfying manner. They also agreed that the difficulty of teaching was closely associated with course structures (Gavranović and Prodanović 2021 ).
Not all were optimistic about the effects of online learning. They sought out the challenges facing teachers and students during online learning.
A mixed-method study of K-12 teachers’ feelings, experiences, and perspectives that the major challenges faced by teachers during the COVID-19 pandemic were lack of student participation and engagement, technological support for online learning, lack of face-to-face interactions with students, no work-life balance and learning new technology.
The challenges to teachers’ online instruction included instruction technology (Maatuk et al. 2022 ; Rasheed et al. 2020 ), course design (Khojasteh et al. 2023 ), and teachers’ confidence (Gavranović and Prodanović 2021 ).
Self-regulation challenges and challenges in using technology were the key challenges to students, while the use of technology for teaching was the challenge facing teachers (Rasheed et al. 2020 ).
The quality of course design was another important factor in online learning. A research revealed the competency of the instructors and their expertise in content development contributed a lot to students’ satisfaction with the quality of e-contents.
Theoretical framework
The theoretical foundation of the research is deeply rooted in multifaceted framework for online learning, which provides a comprehensive and interwoven model encompassing nine critical factors that collectively shape the educational experience in online settings. This framework is instrumental in guiding our analysis and enhances the comparability and interpretability of our results within the context of existing literature.
Central to Yu’s framework is the concept of behavioral intention, which acts as a precursor to student engagement in online learning environments. This engagement, inherently linked to the students’ intentions and motivations, is significantly influenced by the quality of instruction they receive. Instruction, therefore, emerges as a pivotal element in this model, directly impacting not only student engagement but also fostering a sense of self-efficacy among learners. Such self-efficacy is crucial as it influences both the performance of students and their overall satisfaction with the learning process.
The framework posits that engagement, a derivative of both strong behavioral intention and effective instruction, plays a vital role in enhancing student performance. This engagement is tightly interlaced with self-regulation, an indispensable skill in the autonomous and often self-directed context of online learning. Interaction, encompassing various forms such as student-teacher and peer-to-peer communications, further enriches the learning experience. It significantly contributes to the development of motivation and self-efficacy, both of which are essential for sustaining engagement and fostering self-regulated learning.
Motivation, especially when intrinsically driven, acts as a catalyst, perpetuating engagement and self-regulation, which ultimately leads to increased satisfaction with the learning experience. In this framework, self-efficacy, nurtured through effective instruction and meaningful interactions, has a positive impact on students’ performance and satisfaction, thereby creating a reinforcing cycle of learning and achievement.
Performance in this model is viewed as a tangible measure of the synergistic interplay of engagement, instructional quality, and self-efficacy, while satisfaction reflects the culmination of the learning experience, shaped by the quality of instruction, the extent and nature of interactions, and the flexibility of the learning environment. This satisfaction, in turn, influences students’ future motivation and their continued engagement with online learning.
Yu’s model thus presents a dynamic ecosystem where changes in one factor can have ripple effects across the entire spectrum of online learning. It emphasizes the need for a holistic approach in the realm of online education, considering the complex interplay of these diverse yet interconnected elements to enhance both the effectiveness and the overall experience of online learning.
The current study employed a qualitative design to explore teachers’ and undergraduates’ retrospections on the effectiveness of online learning during the first semester of the 2022–2023 school year, which is in the post-pandemic period. Data were collected using reflective diaries, and thematic analysis was applied to understand the experiences based on the nine factors.
Sample and sampling
The study involved 18 teachers and 46 first-year students from a comprehensive university in China, selected through convenience sampling to ensure diverse representation across academic disciplines. To ensure a diverse range of experiences in online learning, the participant selection process involved an initial email inquiry about their prior engagement with online education. The first author of this study received ethics approval from the department research committee, and participants were informed of the study’s objectives two weeks before via email. Only those participants who provided written informed consent were included in the study and were free to withdraw at any time. Pseudonyms were used to protect participants’ identities during the data-coding process. For direct citations, acronyms of students’ names were used, while “T+number” was used for citations from teacher participants.
The 46 students are all first-year undergraduates, 9 females and 37 males majoring in English and non-English (see Table 1 ).
The 18 teachers are all experienced instructors with at least 5 years of teaching experience, 13 females and 5 male, majoring in English and Non-English (see Table 2 ).
Data collection
Students’ data were collected through reflective diaries in class during the first semester of the 2022–2023 school year. Each participant was asked to maintain a diary over the course of one academic semester, in which they responded to four questions.
The four questions include:
What was your state and attitude toward online learning?
What were the problems and shortcomings of online learning?
What do you think are the reasons for these problems?
What measures do you think should be taken to improve online learning?
This approach provided a first-person perspective on the participants’ online teaching or learning experiences, capturing the depth and complexity of their retrospections.
Teachers were interviewed separately by responding to the four questions the same as the students. Each interview was conducted in the office or the school canteen during the semester and lasted about 20 to 30 min.
Data analysis
We utilized thematic analysis to interpret the reflective diaries, guided initially by nine factors. This method involved extensive engagement with the data, from initial coding to the final report. While Yu’s factors provided a foundational structure, we remained attentive to new themes, ensuring a comprehensive analysis. Our approach was methodical: familiarizing ourselves with the data, identifying initial codes, systematically searching and reviewing themes, and then defining and naming them. To validate our findings, we incorporated peer debriefing, and member checking, and maintained an audit trail. This analysis method was chosen for its effectiveness in extracting in-depth insights from undergraduates’ retrospections on their online learning experiences post-pandemic, aligning with our research objectives.
According to the nine factors, the interviews of 18 teachers and 46 Year 1 undergraduates were catalogued and listed in Table 3 .
Behavioral intention towards online learning post-pandemic
Since the widespread of the COVID-19 pandemic, both teachers and students have experienced online learning. However, their online teaching or learning was forced rather than planned (Baber 2021 ; Bao 2020 ). Students more easily accepted online learning when they perceived the severity of COVID-19.
When entering the post-pandemic era, traditional teaching was resumed. Students often compared online learning with traditional learning by mentioning learning interests, eye contact, face-to-face learning and learning atmosphere.
“I don’t think online learning is a good form of learning because it is hard to focus on learning.” (DSY) “In unimportant courses, I would let the computer log to the platform and at the same time do other entertains such as watching movies, listening to the music, having snacks or do the cleaning.” (XYN) “Online learning makes it impossible to have eye contact between teachers and students and unable to create a face-to-face instructional environment, which greatly influences students’ initiative and engagement in classes.” (WRX)
They noted that positive attitudes toward online learning usually generated higher behavioral intention to use online learning than those with negative attitudes, as found in the research of Zhu et al. ( 2023 ). So they put more blame on distractions in the learning environment.
“Online learning relies on computers or cell phones which easily brings many distractions. … I can’t focus on studying, shifting constantly from study and games.” (YX) “When we talk about learning online, we are hit by an idea that we can take a rest in class. It’s because everyone believes that during online classes, the teacher is unable to see or know what we are doing.” (YM) “…I am easily disturbed by external factors, and I am not very active in class.” (WZB)
Teachers reported a majority of students reluctantly turning on their cameras during online instruction and concluded the possible reason for such behavior.
“One of the reasons why some students are unwilling to turn on the camera is that they are worried about their looks and clothing at home, or that they don’t want to become the focus.” (T4)
They also noticed students’ absent-mindedness and lazy attitude during online instruction.
“As for some students who are not self-regulated, they would not take online learning as seriously as offline learning. Whenever they are logged onto the online platform, they would be unable to stay focused and keep their attention.” (T1)
Challenges and opportunities in online instruction post-pandemic
Online teaching brought new challenges and opportunities for students during and after the pandemic. The distractions at home seemed to be significantly underestimated by teachers in an online learning environment (Radmer and Goodchild 2021 ). It might be the reason why students greatly expected and heavily relied on teachers’ supervision and management.
“The biggest problem of online learning is that online courses are as imperative as traditional classes, but not managed face to face the same as the traditional ones.” (PC) “It is unable to provide some necessary supervision.” (GJX) “It is incapable of giving timely attention to every student.” (GYC) “Teachers can’t understand students’ conditions in time in most cases so teachers can’t adjust their teaching plan.” (MZY) “Some courses are unable to reach the teaching objectives due to lack of experimental conduction and practical operation.” (YZH) “Insufficient teacher-student interaction and the use of cell phones make both groups unable to engage in classes. What’s more, though online learning doesn’t put a high requirement for places, its instructional environment may be crucial due to the possible distractions.” (YCY)
Teachers also viewed online instruction as an addition to face-to-face instruction.
“Online learning cannot run as smoothly as face-to-face instruction, but it can provide an in-time supplement to the practical teaching and students’ self-learning.” (T13, T17) “Online instruction is an essential way to ensure the normal function of school work during the special periods like the pandemic” (T1, T15)
Factors influencing student engagement in online learning
Learning engagement was found to contribute to gains in the study (Paul and Diana 2006 ). It was also referred to as a state closely intertwined with the three dimensions of learning, i.e., vigor, dedication, and absorption (Schaufeli et al. 2002 ). Previous studies have found that some key factors like learning interaction, self-regulation, and social presence could influence learning engagement and learning outcomes (Lowenthal and Dunlap 2020 ; Ng 2018 ). Due to the absence of face-to-face interaction like eye contact, facial expressions and body language, both groups of interviewees agreed that the students felt it hard to keep their attention and thus remain active in online classes.
“Students are unable to engage in study due to a lack of practical learning environment of online learning.” (ZMH, T12) “Online platforms may not provide the same level of engagement and interaction as in-person classrooms, making it harder for students to ask questions or engage in discussions.” (HCK) “The Internet is cold, lack of emotional clues and practical connections, which makes it unable to reproduce face-to-face offline learning so that teachers and students are unlikely to know each other’s true feelings or thoughts. In addition, different from the real-time learning supervision in offline learning, online learning leaves students more learning autonomy.” (XGH) “Lack of teachers’ supervision and practical learning environment, students are easily distracted.” (LMA, T9)
Just as Zhu et al. ( 2023 ) pointed out, we had been too optimistic about students’ engagement in online learning, because online learning relied more on students’ autonomy and efforts to complete online learning.
Challenges in teacher-student interaction in online learning
Online learning has a notable feature, i.e., a spatial and temporal separation among teachers and students. Thus, online teacher-student interactions, fundamentals of relationship formation, have more challenges for both teachers and students. The prior studies found that online interaction affected social presence and indirectly affected learning engagement through social presence (Miao and Ma 2022 ). In the present investigation, both teachers and students noted the striking disadvantage of online interaction.
“Online learning has many problems such as indirect teacher-student communication, inactive informative communication, late response of students and their inability to reflect their problems. For example, teachers cannot evaluate correctly whether the students have mastered or not.” (YYN) “Teachers and students are separated by screens. The students cannot make prompt responses to the teachers’ questions via loudspeakers or headphones. It is not convenient for students to participate in questioning and answering. …for most of the time, the students interact with teachers via typing.” (ZJY) “While learning online, students prefer texting the questions to answering them via the loudspeaker.”(T7)
Online learning interaction was also found closely related to online learning engagement, performance, and self-efficacy.
“Teachers and students are unable to have timely and effective communication, which reduces the learning atmosphere. Students are often distracted. While doing homework, the students are unable to give feedback to teachers.” (YR) “Students are liable to be distracted by many other side matters so that they can keep their attention to online learning.” (T15)
In the online learning environment, teachers need to make efforts to build rapport and personalizing interactions with students to help them perform better and achieve greater academic success (Harper 2018 ; Ong and Quek 2023 ) Meanwhile, teachers should also motivate students’ learning by designing the lessons, giving lectures and managing the processes of student interactions (Garrison 2003 ; Ong and Quek 2023 ).
Determinants of self-efficacy in online learning
Online learning self-efficacy refers to students’ perception of their abilities to fulfill specific tasks required in online learning (Calaguas and Consunji 2022 ; Zimmerman and Kulikowich 2016 ). Online learning self-efficacy was found to be influenced by various factors including task, learner, course, and technology level, among which task level was found to be most closely related (Xu et al. 2022 ). The responses from the 46 student participants reveal a shared concern, albeit without mentioning specific tasks; they highlight critical aspects influencing online learning: learner attributes, course structure, and technological infrastructure.
One unifying theme from the student feedback is the challenge of self-regulation and environmental distractions impacting learning efficacy. For instance, participant WSX notes the necessity for students to enhance time management skills due to deficiencies in self-regulation, which is crucial for successful online learning. Participant WY expands on this by pointing out the distractions outside traditional classroom settings, coupled with limited teacher-student interaction, which hampers idea exchange and independent thought, thereby undermining educational outcomes. These insights suggest a need for strategies that bolster students’ self-discipline and interactive opportunities in virtual learning environments.
On the technological front, participants WT and YCY address different but related issues. Participant WT emphasizes the importance of up-to-date course content and learning facilities, indicating that outdated materials and tools can significantly diminish the effectiveness of online education. Participant YCY adds to this by highlighting problems with online learning applications, such as subpar functionalities that can introduce additional barriers to learning.
Teacher participants, on the other hand, shed light on objective factors predominantly related to course content and technology. Participant T5’s response underscores the heavy dependency on technological advancement in online education and points out the current inability of platforms or apps to adequately monitor student engagement and progress. Participant T9 voices concerns about course content not being updated or aligned with contemporary trends and student interests, suggesting a disconnect between educational offerings and learner needs. Meanwhile, participant T8 identifies unstable network services as a significant hindrance to online teaching, highlighting infrastructure as a critical component of online education’s success.
Teachers also believed the insufficient mastery of facilities and unfamiliarity with online instruction posed difficulty.
“Most teachers and students are not familiar with online instruction. For example, some teachers are unable to manage online courses so they cannot design the courses well. Some students lack self-regulation, which leads to their distraction or avoidance in class.” (T9)
Influences on student performance in online learning
Students’ performance during online lessons is closely associated with their satisfaction and self-efficacy. Most of the student participants reflected on their distractions, confusion, and needs, which indicates their dissatisfaction with online learning.
“During online instruction, it is convenient for the students to make use of cell phones, but instead, cell phones bring lots of distraction.” (YSC) “Due to the limits of online learning, teachers are facing the computer screen and unable to know timely students’ needs and confusion. Meanwhile, it’s inconvenient for teachers to make clear explanations of the sample questions or problems.” (HZW)
They thought their low learning efficiency in performance was caused by external factors like the learning environment.
“The most obvious disadvantage of online learning goes to low efficiency. Students find it hard to keep attention to study outside the practical classroom or in a relaxing environment.” (WY) “Teachers are not strict enough with students, which leads to ineffective learning.” (WRX)
Teacher participants conceived students’ performance as closely related to valid online supervision and students’ self-regulation.
“Online instruction is unable to create a learning environment, which helps teachers know students’ instant reaction. Only when students well regulate themselves and stay focused during online learning can they achieve successful interactions and make good accomplishments in the class.” (T11) “Some students need teachers’ supervision and high self-regulation, or they were easily distracted.” (T16)
Student satisfaction and teaching effectiveness in online learning
Online learning satisfaction was found to be significantly and positively associated with online learning self-efficacy (Al-Nasa’h et al. 2021 ; Lashley et al. 2022 ). Around 46% of student participants were unsatisfied with teachers’ ways of teaching.
“Comparatively, bloggers are more interesting than teachers’ boring and dull voices in online learning.” (DSY) “Teachers’ voice sounds dull and boring through the internet, which may cause listeners to feel sleepy, and the teaching content is not interesting enough to the students.” (MFE)
It reflected partly that some teachers were not adapted to online teaching possibly due to a lack in experience of online teaching or learning (Zhu et al. 2022 ).
“Some teachers are not well-prepared for online learning. They are particularly unready for emergent technological problems when delivering the teaching.” (T1) “One of the critical reasons lies in the fact that teachers and students are not well trained before online learning. In addition, the online platform is not unified by the college administration, which has led to chaos and difficulty of online instruction.” (T17)
Teachers recognized their inadequate preparation and mastery of online learning as one of the reasons for dissatisfaction, but student participants exaggerated the role of teachers in online learning and ignored their responsibility in planning and managing their learning behavior, as in the research of (Xu et al. 2022 ).
The role of self-regulation in online learning success
In the context of online learning, self-regulation stands out as a crucial factor, necessitating heightened levels of student self-discipline and autonomy. This aspect, as Zhu et al. ( 2023 ) suggest, grants students significant control over their learning processes, making it a vital component for successful online education.
“Online learning requires learners to be of high discipline and self-regulation. Without good self-regulation, they are less likely to be effective in online learning.” (YZJ) “Most students lack self-control, unable to control the time of using electronic products. Some even use other electronic products during online learning, which greatly reduces their efficiency in learning.” (GPY) “Students are not well developed in self-control and easily distracted. Thus they are unable to engage fully in their study, which makes them unable to keep up with others” (XYN)
Both groups of participants had a clear idea of the positive role of self-regulation in successful learning, but they also admitted that students need to strengthen their self-regulation skills and it seemed they associated with the learning environment, learning efficiency and teachers’ supervision.
“If they are self-motivated, online learning can be conducted more easily and more efficiently. However, a majority are not strong in regulating themselves. Teachers’ direct supervision in offline learning can do better in motivating them to study hard…lack of interaction makes students less active and motivated.” (LY) “Students have a low level of self-discipline. Without teachers’ supervision, they find it hard to listen attentively or even quit listening. Moreover, in class, the students seldom think actively and independently.” (T13)
The analysis of participant responses, categorized into three distinct attitude groups – positive, neutral, and negative – reveals a multifaceted view of the disadvantages of online learning, as shown in Tables 4 and 5 . This classification provides a clearer understanding of how attitudes towards online learning influence perceptions of self-regulation and other related factors.
In Table 4 , the division among students is most pronounced in terms of interaction and self-efficacy. Those with neutral attitudes highlighted interaction as a primary concern, suggesting that it is less effective in an online setting. Participants with positive attitudes noted a lack of student motivation, while those with negative views emphasized the need for better self-efficacy. Across all attitudes, instruction, engagement, self-regulation, and behavior intention were consistently identified as areas needing improvement.
Table 5 sheds light on teachers’ perspectives, revealing a consensus on the significance and challenges of instruction, motivation, and self-efficacy in online learning. Teachers’ opinions vary most significantly on self-efficacy and engagement. Those with negative attitudes point to self-efficacy and instructional quality as critical areas needing attention, while neutral attitudes focus on the role of motivation.
Discussions
Using a qualitative and quantitative analysis of the questionnaire data showed that among the 18 college teachers and 46 year 1 undergraduate students of various majors taking part in the interview, about 38.9% of teachers and about 30.4% of students supported online learning. Only two teachers were neutral about online learning, and 50% of teachers did not support virtual learning. The percentages of students who expressed positive and neutral views on online learning were the same, i.e., 34.8%. This indicates that online learning could serve as a complementary approach to traditional education, yet it is not without challenges, particularly in terms of student engagement, self-regulation, and behavioral intention, which were often attributed to distractions inherent in online environments.
In analyzing nine factors, it was evident that both teachers and students did not perceive these factors uniformly. Instruction was a significant element for both groups, as validated by findings in Tables 3 and 5 . The absence of face-to-face interactions in online learning shifted the focus to online instruction quality. Teachers cited technological challenges as a central concern, while students criticized the lack of engaging content and teaching methods. This aligns with Miao and Ma ( 2022 ), who argued that direct online interaction does not necessarily influence learner engagement, thus underscoring the need for integrated approaches encompassing interactions, self-regulation, and social presence.
Furthermore, the role of technology acceptance in shaping self-efficacy was highlighted by Xu et al. ( 2022 ), suggesting that students with higher self-efficacy tend to challenge themselves more. Chen and Hsu ( 2022 ) noted the positive influence of using emojis in online lessons, emphasizing the importance of innovative pedagogical approaches in online settings.
The study revealed distinct priorities between teachers and students in online learning: teachers emphasized effective instruction delivery, while students valued learning outcomes, self-regulation, and engagement. This divergence highlights the unique challenges each group faces. Findings by Dennen et al. ( 2007 ) corroborate this, showing instructors focusing on content and guidance, while students prioritize interpersonal communication and individualized attention. Additionally, Lee et al. ( 2011 ) found that reduced transactional distance and increased student engagement led to enhanced perceptions of learning outcomes, aligning with students’ priorities in online courses. Understanding these differing perspectives is crucial for developing comprehensive online learning strategies that address the needs of both educators and learners.
Integrating these findings with broader contextual elements such as technological infrastructure, pedagogical strategies, socio-economic backgrounds, and environmental factors (Balanskat and Bingimlas 2006 ) further enriches our understanding. The interplay between these external factors and Yu’s nine key aspects forms a complex educational ecosystem. For example, government interventions and training programs have been shown to increase teachers’ enthusiasm for ICT and its routine use in education (Balanskat and Bingimlas 2006 ). Additionally, socioeconomic factors significantly impact students’ experiences with online learning, as the digital divide in connectivity and access to computers at home influences the ICT experience, an important factor for school achievement (OECD 2015 ; Punie et al. 2006 ).
In sum, the study advocates for a holistic approach to understanding and enhancing online education, recognizing the complex interplay between internal factors and external elements that shape the educational ecosystem in the digital age.
Conclusion and future research
This study offered a comprehensive exploration into the retrospective perceptions of college teachers and undergraduate students regarding their experiences with online learning following the COVID-19 pandemic. It was guided by a framework encompassing nine key factors that influence online learning outcomes. To delve into these perspectives, the research focused on three pivotal questions. These questions aimed to uncover how both undergraduates and teachers in China view the effectiveness of online learning post-pandemic, identify which of the nine influencing factors had the most significant impact, and propose recommendations for enhancing the future effectiveness of online learning.
In addressing the first research question concerning the retrospective perceptions of online learning’s effectiveness among undergraduates and teachers in China post-COVID-19 pandemic, the thematic analysis has delineated clear divergences in attitude between the two demographics. Participants were primarily divided into three categories based on their stance toward online learning: positive, neutral, and negative. The results highlighted a pronounced variance in attitude distribution between teachers and students, with a higher percentage of teachers expressing clear-cut opinions, either favorably or unfavorably, towards the effectiveness of online learning.
Conversely, students displayed a pronounced inclination towards neutrality, revealing a more cautious or mixed stance on the effectiveness of online learning. This prevalent neutrality within the student body could be attributed to a range of underlying reasons. It might signify students’ uncertainties or varied experiences with online platforms, differences in engagement levels, gaps in digital literacy, or fluctuating quality of online materials and teaching methods. Moreover, this neutral attitude may arise from the psychological and social repercussions of the pandemic, which have potentially altered students’ approaches to and perceptions of learning in an online context.
In the exploration of the nine influential factors in online learning, it was discovered that both teachers and students overwhelmingly identified instruction as the most critical aspect. This was closely followed by engagement, interaction, motivation, and other factors, while performance and satisfaction were perceived as less influential by both groups. However, the attitudes of teachers and students towards these factors revealed notable differences, particularly about instruction. Teachers often attributed challenges in online instruction to technological issues, whereas students perceived the quality of instruction as a major influence on their learning effectiveness. This dichotomy highlights the distinct perspectives arising from their different roles within the educational process.
A further divergence was observed in views on self-efficacy and self-regulation. Teachers, with a focus on delivering content, emphasized the importance of self-efficacy, while students, grappling with the demands of online learning, prioritized self-regulation. This reflects their respective positions in the online learning environment, with teachers concerned about the efficacy of their instructional strategies and students about managing their learning process. Interestingly, the study also illuminated that students did not always perceive themselves as independent learners, which contributed to the high priority they placed on instruction quality. This insight underlines a significant area for development in online learning strategies, emphasizing the need for fostering greater learner autonomy.
Notably, both teachers and students concurred that stimulating interest was a key factor in enhancing online learning. They proposed innovative approaches such as emulating popular online personalities, enhancing interactive elements, and contextualizing content to make it more relatable to students’ lives. Additionally, practical suggestions like issuing preview tasks and conducting in-class quizzes were highlighted as methods to boost student engagement and learning efficiency. The consensus on the importance of supervisory roles underscores the necessity for a balanced approach that integrates guidance and independence in the online learning environment.
The outcomes of our study highlight the multifaceted nature of online learning, accentuated by the varied perspectives and distinct needs of teachers and students. This complexity underscores the necessity of recognizing and addressing these nuances when designing and implementing online learning strategies. Furthermore, our findings offer a comprehensive overview of both the strengths and weaknesses of online learning during an unprecedented time, offering valuable insights for educators, administrators, and policy-makers involved in higher education. Moreover, it emphasized the intricate interplay of multiple factors—behavioral intention, instruction, engagement, interaction, motivation, self-efficacy, performance, satisfaction, and self-regulation—in shaping online learning outcomes. presents some limitations, notably its reliance on a single research method and a limited sample size.
However, the exclusive use of reflective diaries and interviews restricts the range of data collection methods, which might have been enriched by incorporating additional quantitative or mixed-method approaches. Furthermore, the sample, consisting only of students and teachers from one university, may not adequately represent the diverse experiences and perceptions of online learning across different educational contexts. These limitations suggest the need for a cautious interpretation of the findings and indicate areas for future research expansion. Future research could extend this study by incorporating a larger, more diverse sample to gain a broader understanding of undergraduate students’ retrospections across different contexts and cultures. Furthermore, research could also explore how to better equip students with the skills and strategies necessary to optimize their online learning experiences, especially in terms of the self-regulated learning and motivation aspects.
Data availability
The data supporting this study is available from https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.25583664.v1 . The data consists of reflective diaries from 46 Year 1 students from a comprehensive university in China and 18 college teachers. We utilized thematic analysis to interpret the reflective diaries, guided initially by nine factors. The results highlight the critical need for tailored online learning strategies and provide insights into its advantages and challenges for stakeholders in higher education.
Aguilera-Hermida AP (2020) College students’ use and acceptance of emergency online learning due to COVID-19. Int. J. Educ. Res. Open 1:100011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2020.100011
Article Google Scholar
Al-Emran, M, & Shaalan, K (2021, October 27). E-podium technology: A medium of managing knowledge at Al Buraimi University College via M-learning. In Proceedings of the 2nd BCS International IT Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates 2014. Retrieved October 17, 2023, from https://dblp.uni-trier.de/rec/conf/bcsit/EmranS14.html
Ali W (2020) Online and remote learning in higher education institutes: A necessity in light of COVID-19 pandemic. High. Educ. Stud. 10(3):16–25. https://doi.org/10.5539/hes.v10n3p16
Al-Nasa’h M, Al-Tarawneh L, Awwad FMA, Ahmad I (2021) Estimating Students’ Online Learning Satisfaction during COVID-19: A Discriminant Analysis. Heliyon 7(12):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.helyon.2021.e08544
Al-Rahmi WM, Yahaya N, Aldraiweesh AA, Alamri MM, Aljarboa NA, Alturki U (2019) Integrating technology acceptance model with innovation diffusion theory: An empirical investigation on students’ intention to use E-learning systems. IEEE Access 7:26797–26809. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2899368
Aristovnik A, Keržič D, Ravšelj D, Tomaževič N, Umek L (2021) Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on life of higher education students: A global perspective. Sustainability 12(20):8438. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208438
Article CAS Google Scholar
Baber H (2021) Modelling the Acceptance of E-learning during the Pandemic Of COVID-19-A Study of South Korea. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 19(2):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2021.100503
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Bahasoan AN, Ayuandiani W, Mukhram M, Rahmat A (2020) Effectiveness of online learning in pandemic COVID-19. Int. J. Sci., Technol. Manag. 1(2):100–106
Google Scholar
Balanskat A, Bingimlas KA (2006) Barriers to the Successful Integration of ICT in Teaching and Learning Environments: A Review of the Literature. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 5(3):235–245. https://doi.org/10.12973/ejmste/75275
Bao W (2020) COVID-19 and Online Teaching in Higher Education: A Case Study of Peking University. Hum. Behav. Emerg. Technol. 2(2):113–115. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbe2.191
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bernard RM et al. (2004) How Does Distance Education Compare with Classroom Instruction? A Meta-Analysis of the Empirical Literature. Rev. Educ. Res. 74(3):379–439
Boling EC, Hough M, Krinsky H, Saleem H, Stevens M (2012) Cutting the distance in distance education: Perspectives on what promotes positive, online learning experiences. Internet High. Educ. 15:118–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2011.11.006
Bozkurt A, Sharma RC (2020) Emergency remote teaching in a time of global crisis due to Coronavirus pandemic. Asian J. Distance Educ. 15(1):i–vi
Broadbent J (2017) Comparing online and blended learner’s self-regulated learning strategies and academic performance. Internet High. Educ. 33:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2017.01.004
Calaguas NP, Consunji PMP (2022) A Structural Equation Model Predicting Adults’ Online Learning Self-efficacy. Educ. Inf. Technol. 27:6233–6249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10871-y
Careaga-Butter M, Quintana MGB, Fuentes-Henríquez C (2020) Critical and Prospective Analysis of Online Education in Pandemic and Post-pandemic Contexts: Digital Tools and Resources to Support Teaching in synchronous and Asynchronous Learning Modalities. Aloma: evista de. psicologia, ciències de. l’educació i de. l’esport Blanquerna 38(2):23–32
Chakraborty M, Muyia Nafukho F (2014) Strengthening Student Engagement: What do Students Want in Online Courses? Eur. J. Train. Dev. 38(9):782–802
Chang V (2016) Review and Discussion: E-learning for Academia and Industry. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 36(3):476–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2015.12.007
Chen YJ, Hsu LW (2022) Enhancing EFL Learners’ Self-efficacy Beliefs of Learning English with emoji Feedbacks in Call: Why and How. Behav. Sci. 12(7):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12070227
Chuenyindee T, Montenegro LD, Ong AKS, Prasetyo YT, Nadlifatin R, Ayuwati ID, Sittiwatethanasiri T, Robas KPE (2022) The Perceived Usability of the Learning Management System during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Integrating System Usability Scale, Technology Acceptance Model, and Task-technology Fit. Work 73(1):41–58. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-220015
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Crawford J, Butler-Henderson K, Rudolph J, Malkawi B, Glowatz M, Burton R, Lam S (2020) COVID-19: 20 countries’ higher education intra-period digital pedagogy responses. J. Appl. Teach. Learn. 3(1):120. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2020.3.1.7
Dennen VP (2014) Becoming a blogger: Trajectories, norms, and activities in a community of practice. Computers Hum. Behav. 36:350–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.03.028
Dennen VP, Darabi AA, Smith LJ (2007) Instructor–learner Interaction in Online Courses: The Relative Perceived Importance of Particular Instructor Actions on Performance and Satisfaction. Distance Educ. 28(1):65–79
Dolan E, Hancock E, Wareing A (2015) An evaluation of online learning to teach practical competencies in undergraduate health science students. Internet High. Educ. 24:21–25
Garrison DR (2003) Cognitive Presence for Effective Asynchronous Online Learning: The Role of Reflective. Inq., Self-Direction Metacognition. Elem. Qual. Online Educ.: Pract. Direction 4(10):47–58
Gavranović V, Prodanović M (2021) ESP Teachers’ Perspectives on the Online Teaching Environment Imposed in the Covid-19 Era-A Case Study. N. Educ. Rev. 2:188–197. https://doi.org/10.15804/TNER.2021.64.2.15
Greenhow C, Lewin C, Staudt Willet KB (2021) The Educational Response to Covid-19 across Two Countries: a Critical Examination of Initial Digital Pedagogy Adoption. Technol., Pedagog. Educ. 30(1):7–25
Händel M, Stephan M, Gläser-Zikuda M, Kopp B, Bedenlier S, Ziegler A (2020) Digital readiness and its effects on higher education students’ socio-emotional perceptions in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 53(2):1–13
Harper B (2018) Technology and Teacher-student Interactions: A Review of Empirical Research. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 50(3):214–225
Article ADS Google Scholar
Hernández-Lara AB, Serradell-López E (2018) Student interactions in online discussion forums: their perception on learning with business simulation games. Behav. Inf. Technol. 37(4):419–429
Hodges C, Moore S, Lockee B, Trust T, Bond A (2020) The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Educause Rev. 27:1–12
Hongsuchon T, Emary IMME, Hariguna T, Qhal EMA (2022) Assessing the Impact of Online-learning Effectiveness and Benefits in Knowledge Management, the Antecedent of Online-learning Strategies and Motivations: An Empirical Study. Sustainability 14(5):1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14052570 . (2020)
Johnson N, Veletsianos G, Seaman J (2020) US faculty and administrators’ experiences and approaches in the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic. Online Learn. 24(2):6–21
Khojasteh L, Karimian Z, Farahmandi AY, Nasiri E, Salehi N (2023) E-content Development of English Language Courses during COVID-19: A Comprehensive Analysis of Students’ Satisfaction. J. Computer Educ. 10(1):107–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40692-022-00224-0
Kohnke, L, & Foung, D (2023). Exploring Microlearning for Teacher Professional Development: Voices from Hong Kong. In Tafazoli, D, M Picard (Eds.). Handbook of CALL Teacher Education Professional Development (pp. 279-292). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd
Lai CH, Lin HW, Lin RM, Tho PD (2019) Effect of Peer Interaction among Online Learning Community on Learning Engagement and Achievement. Int. J. Distance Educ. Technol. (IJDET) 17(1):66–77
Lashley PM, Sobers NP, Campbell MH, Emmanuel MK, Greaves N, Gittens-St Hilaire M, Murphy MM, Majumder MAA (2022) Student Satisfaction and Self-Efficacy in a Novel Online Clinical Clerkship Curriculum Delivered during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Adv. Med. Educ. Pract. 13:1029–1038. https://doi.org/10.2147/AMEP.S374133
Lee SJ, Srinivasan S, Trail T, Lewis D, Lopez S (2011) Examining the Relationship among Student Perception of Support, Course Satisfaction, and Learning Outcomes in Online Learning. Internet High. Educ. 14(3):158–163
Lowenthal PR, Dunlap JC (2020) Social Presence and Online Discussions: A Mixed Method Investigation. Distance Educ. 41:490–514. https://doi.org/10.1080/01587919.2020.1821603
Lucas M, Vicente PN (2023) A Double-edged Sword: Teachers’ Perceptions of the Benefits and Challenges of Online Learning and Learning in Higher Education. Educ. Inf. Technol. 23:5083–5103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11363-3
Maatuk AM, Elberkawi EK, Aljawarneh S, Rashaideh H, Alharbi H (2022) The COVID-19 Pandemic and E-learning: Challenges and Opportunities from the Perspective of Students and Instructors. J. Comput. High. Educ. 34:21–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-021-09274-2
Marinoni G, Van’t Land H, Jensen T (2020) The Impact of Covid-19 on Higher Education around the World. IAU Glob. Surv. Rep. 23:1–17
Martin F, Bolliger DU (2018) Engagement matters: Student perceptions on the importance of engagement strategies in the online learning environment. Online Learn. 22(1):205–222
Means B, et al. (2010). Evaluation of Evidence-Based Practices in Online Learning: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Online Learning Studies. Washington, D. C.: U.S. Department of Education
Miao J, Ma L (2022) Students’ Online Interaction, Self-regulation, and Learning Engagement in Higher Education: The Importance of Social Presence to Online Learning. Front. Psychol. 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.815220
Mulla T, Munir S, Mohan V (2023) An Exploratory Study to Understand Faculty Members’ Perceptions and Challenges in Online Teaching. Int. Rev. Educ. 69:73–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11159-023-100
Ng EW (2018) Integrating Self-regulation Principles with Flipped Classroom Pedagogy for First Year University Students. Computer Educ. 126:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-011-9082-8
Ong SGT, Quek GCL (2023) Enhancing teacher–student interactions and student online engagement in an online learning environment. Learn. Environ. Res. 26:681–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-022-09447-5
Organisation for Economic Co‑operation and Development. (2015). The g20 skills strategy for developing and using skills for the 21st century. Retrieved from https://www.oecd.org/g20/topics/employment-andsocial-policy/The-G20-Skills-Strategy-for-Developing-and-Using-Skills-for-the-21st-Century.pdf
Paechter M, Maier B (2010) Online or face-to-face? Students’ experiences and preferences in e-learning. internet High. Educ. 13(4):292–297
Panigrahi R, Srivastava PR, Sharma D (2018) Online Learning: Adoption, Continuance, and Learning Outcome—A Review of Literature. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 43:1–14
Paul C, Diana M (2006) Teaching Methods and Time on Task in Junior Classrooms. Educ. Res. 30:90–97
Punie, Y, Zinnbauer, D, & Cabrera, M (2006). A review of the impact of ICT on learning. European Commission, Brussels, 6(5), 635-650
Radmer F, Goodchild S (2021) Online Mathematics Teaching and Learning during the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Perspective of Lecturers and Students. Nord. J. STEM Educ. 5(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.5324/njsteme.v5i1.3914
Rapanta C, Botturi L, Goodyear P, Guadia L, Koole M (2021) Balancing Technology, Pedagogy and the New Normal: Post-pandemic Challenges for Higher Education. Postdigital Sci. Educ. 3:715–742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42438-021-00249-1
Rasheed, RA, Kamsin, A, & Abdullah, NA (2020) Challenges in the Online Component of Blended Learning: A Systematic Review. Computers & Education, 144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103701
Schaufeli W, Salanova M, Gonzalez-Roma V (2002) The Measurement of Engagement and Burnout: A Two Sample Confirmatory Factor Analytic Approach. J. Happiness Stud. 3:71–92
Song L, Singleton ES, Hill JR, Koh MH (2004) Improving online learning: Student perceptions of useful and challenging characteristics. Internet High. Educ. 7(1):59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2003.11.003
Tan HT, Chan PP, Said NM (2021) Higher Education Students’ Online Instruction Perceptions: A Quality Virtual Learning Environment. Sustainability 13:10840. https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910840
Tenório T, Bittencourt II, Isotani S, Silva AP (2016) Does peer assessment in online learning environments work? A systematic review of the literature. Computers Hum. Behav. 64:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.06.020
Torsani, S (2023) Teacher Education in Mobile Assisted Language Learning for Adult Migrants: A Study of Provincial Centers for Adult Education in Italy. In Tafazoli, D, & M Picard (eds.). Handbook of CALL Teacher Education Professional Development (pp. 179-192). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd
Trust T, Whalen J (2020) Should teachers be trained in emergency remote teaching? Lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Technol. Teach. Educ. 28(2):189–199
UNESCO (2020a) COVID-19 Impact on education. UNESCO. Retrieved from https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse
UNESCO (2020b) Education: From Disruption to Recovery. UNESCO. Retrieved from https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse
Wang M, & Wang F (2021, August) Comparative Analysis of University Education Effect under the Traditional Teaching and Online Teaching Mode. In The Sixth International Conference on Information Management and Technology (pp. 1-6)
Xu Q, Wu J, Peng HY (2022) Chinese EFL University Students’ Self-efficacy for Online Self-regulated Learning: Dynamic Features and Influencing Factors. Front. Psychol. 13:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.912970
Zheng RK, Li F, Jiang L, Li SM (2022) Analysis of the Current Situation and Driving Factors of College Students’ Autonomous Learning in the Network Environment. Front. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2(7):44–50
Zhu XM, Gong Q, Wang Q, He YJ, Sun ZQ, Liu FF (2023) Analysis of Students’ Online Learning Engagement during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case Study of a SPOC-Based Geography Education Undergraduate Course. Sustainability 15(5):4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054544
Zhu Y, Geng G, Disney L, Pan Zihao (2023) Changes in University Students’ Behavioral intention to learn online throughout the COVID-19: Insights for Online Teaching in the Post-pandemic Era. Educ. Inf. Technol. 28:3859–3892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11320-0
Zhu YH, Xu YY, Wang XY, Yan SY, Zhao L (2022) The Selectivity and Suitability of Online Learning Resources as Predictor of the Effects of Self-efficacy on Teacher Satisfaction During the COVID-19 Lockdown. Front. Psychol. 13:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.765832
Zimmerman WA, Kulikowich JM (2016) Online Learning Self-efficacy in Students with and Without Online Learning Experience. Am. J. Distance Educ. 30(3):180–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923647.2016.1193801
Download references
Acknowledgements
The Corresponding author received the National Social Science Foundation of China for Education General Program (BGA210054) for this work.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Foreign Studies, Wenzhou University, Wenzhou, China
Yujie Su, Xiaoshu Xu & Xinyu Xu
Faculty of Languages and Translation, Macao Polytechnic University, Macao, China
Yunfeng Zhang
Faculty of Applied Sciences, Macao Polytechnic University, Macao, China
Shanshan Hao
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
XSX was responsible for conceptualization and, alongside YFZ, for data curation. YJS and XYX conducted the formal analysis. Funding acquisition was managed by YFZ. The investigation was carried out by YJS and YFZ. Methodology development was a collaboration between YJS and XSX. XSX and YJS also managed project administration, with additional resource management by SSH and XYX. YJS handled the software aspect, and supervision was overseen by XSX. SSH and XYX were responsible for validation, and visualization was managed by YJS. The original draft was written by XSX and YJS, while the review and editing were conducted by YFZ and SSH.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xiaoshu Xu .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The questionnaire and methodology for this study were approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of Wenzhou University (Ethics approval number WGY202302).
Informed consent
Informed consent was diligently obtained from all participants involved in the study, ensuring adherence to ethical standards. Detailed consent forms, outlining the study’s scope and participants’ rights, were signed by participants. Documentation of this process is well-maintained and can be provided upon request during peer review or post-publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Su, Y., Xu, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Looking back to move forward: comparison of instructors’ and undergraduates’ retrospection on the effectiveness of online learning using the nine-outcome influencing factors. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 594 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03097-z
Download citation
Received : 24 October 2023
Accepted : 17 April 2024
Published : 09 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03097-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
All About Learning Objectives for E-Learning
Most clients have a specific outcome in mind for learners when they initiate an e-learning project. So how do you make sure learners reach the desired learning destination? By creating clear objectives, or milestones, that move learners toward the goal in a specific, measurable way.
In this article we’ll look at why learning objectives are important, what makes them “good” (or “bad”), and how to craft solid e-learning objectives for your courses. Here we go!
Why Learning Objectives Are Important
Learning objectives are the cornerstone of every e-learning course. They’re the reason you’re creating the course. They guide you as you select the content and activities to include. And they help you determine whether your course has been effective.
So basically, without learning objectives you won’t know why you’re creating the course, what content to include, what activities to choose, or how to gauge the success of your course. Seems pretty important when you put it that way, doesn’t it?
What Makes Learning Objectives “Good”
Despite their importance, all too often learning objectives are vague and unclear. Say you’re creating a course for mortgage company employees on how to process FHA loans. The goal may seem clear on the surface: you want learners to understand how to process FHA loans. But how will you know if your learners have reached that goal? You won’t—because understanding isn’t something you can measure.
“Good” learning objectives are SMART objectives. They’re:
- M easurable
- A chievable
- R elevant
- T ime-related
Let’s take a closer look at how to use this simple formula to write your learning objectives.
Writing SMART Learning Objectives
How do you write SMART learning objectives? Start by taking a step back. Think about the smaller tasks that learners need to accomplish to achieve the larger goal.
Then choose a specific, measurable action verb that accurately describes what learners need to accomplish. For example, do they need to be able to recall a product name? Explain a concept? Evaluate the risks and benefits of different choices? Avoid using verbs like understand or know; they’re difficult (read: impossible) to measure. Check out Bloom’s Taxonomy for a list of verbs that work well for learning objectives.
Instead of:
At the end of the course, learners will know how to process an FHA loan
At the end of the course, learners will be able to:
- identify the documents required
- identify the credit requirements
- identify the employment requirements
Let’s check those objectives against our SMART criteria to make sure we’ve covered everything:
- Are they specific? Yes. They outline three specific requirements the learners need to be able to identify.
- Are they measurable? Yes. You could present learners with a multiple response question for each to determine whether or not they can correctly identify the requirements.
- Are they achievable? Yes. If the course explains to the learners how to identify these requirements, they should be able to do it.
- Are they relevant? Yes. Assuming the course content is focused on how to identify these requirements.
- Are they time-bound? Yes. When will the learner know how to identify these requirements? At the end of the course.
Now those are some SMART objectives! You’ll be able to use them as a guide to build a helpful course and measure its effectiveness.
The Bottom Line
Without solid learning objectives, you’ll be hard-pressed to build an effective e-learning course. After all, how can you choose relevant content and activities if you don’t know what learners need to be able to do after taking the course? And if you can’t measure whether they’ve reached those objectives, you won’t know whether your course was successful in helping them do that.
So next time you start a new e-learning project, be sure to think carefully about your learning objectives and ensure they’re SMART before you start building out your course.
Looking for more instructional design tips? Check out these helpful articles:
- An Introduction to Instructional Design
An Introduction to the ADDIE Model for Instructional Designers
- An Introduction to SAM for Instructional Designers
- An Introduction to Bloom’s Taxonomy for Instructional Designers
Subscribe to our newsletter to get the latest e-learning inspiration and insights directly in your inbox. You can also find us on LinkedIn and X (Formerly Twitter) .
Related Content
Use kpis to demonstrate the value of e-learning.
The One Thing You Need to Do to Organize Training Content: Task Analysis
Learning objectives and outcomes

How this will help:
Most of the time, when setting out on a journey, you know where you are headed and have a sense of how you’ll know when you’ve reached your destination. Learning objectives serve to define that destination for your course – it’ll be much easier for your students to engage with your course if they know where they are headed.
Most of the time, when setting out on a journey, you know where you are headed and have a sense of how you’ll know when you’ve reached your destination. Learning objectives serve to define that destination for your course – it’ll be much easier for your students to engage with your course if they know where they are headed and it will help you as you navigate the process of design.
One of the experiences many faculty new to online teaching often identify as different from their experience teaching face-to-face is engaging in an explicit design process. Most instructors teach the way they were taught, and historically, most of us were taught from a content-centric model, meaning you decide what content you want to teach, and then you teach it.
Designing a course can, in some ways, be compared to planning a road trip. A content-centric approach to course design is like deciding what tourist attractions you want to see (e.g. Niagara Falls, the Alamo, and the Vietnam War Memorial in one trip) but not defining the final destination. A backward design approach, in contrast, starts with deciding what your final destination is (e.g. your cousin’s house in Rochester, NY) and then deciding which gas stations, tourist attractions and hotels will structure your journey to make sure you get there.
When creating an online course, though, one has to think through the course design in a more detailed and explicit way (although these same design principles are useful and can be applied to face-to-face teaching). One of the common models for course design (both online and face-to-face) is the backwards design approach . Backward design, from a high level, includes three steps: identifying the desired results, determining the evidence that those results have been attained, and developing learning experiences that will help learners build that evidence. This module will focus specifically on the first step in backwards design: identifying and writing learning objectives.
What are learning objectives?
In their simplest form, learning objectives are statements describing what someone will be able to do after they engage in a learning experience. There are different schools of thought as to how much detail belongs in a learning objective, but regardless of one’s philosophy, every learning objective contains three basic elements:
- A brief description of the context in which the learning objective is relevant
- An active verb describing what a learner will know, be able to do, or value
- A brief description of the content, skill or value connected to the objective
For a first draft of a set of learning objectives, begin each objective with the phrase, “At the end of this [course, module, lesson, degree program, etc], learners will be able to…” This phrase serves as the overarching context for your learning objectives. Note that learning objectives are focused on what the learner will be able to do, not what the teacher will teach. This learner-centric approach has many advantages – the first of which is it can help you, as an instructor, begin to imagine how you’ll know whether someone has been successful in your course (or other learning experience).
The opening phrase of the objective is followed by an active verb. Many instructors, when drafting learning objectives for the very first time, default to verbs like “understand” or “know.” The learning objectives you write will be more useful to you and your learners if you push yourself at least one step further. Ask yourself, “How will I be able to tell if they understand this concept?” Do they need to verbally recall definitions? Do they need to calculate something? Do they need to critique something? What does understanding look or sound like in your discipline? The more specific you can be, the better. It isn’t very helpful to your students to hear, “I’ll know it when I see it.”
One way to find verbs more specific than “understand” and “know” is to take inspiration from a framework commonly used in education: Bloom’s revised cognitive taxonomy . Benjamin Bloom (a noted educational psychologist), in partnership with others, identified six categories of objectives: Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. Within each of these categories, instructors and education experts have identified verbs that describe activities that a learner can engage in to demonstrate their knowledge and skills. There are multiple resources online for finding verbs (e.g. this table from Fresno State or this visual from Johns Hopkins ).
The third component of a learning objective, the content or skill to be learned or demonstrated, highlights your priorities for the learning experience and can situate the experience within the larger context of the curriculum. Below are some examples of learning objectives for different kinds of learning experiences.
Example learning objectives:
Lesson or Module :
- At the end of this module, learners will be able to calculate the molecular weight of different molecules with known chemical formulas. (Chemistry)
- At the end of this module, learners will be able to identify examples of chiaroscuro in Spiderman graphic novels and describe the effect(s) of that chiaroscuro on readers. (Media Studies)
- At the end At the end of this course, learners will be able to compare and contrast different theories of human motivation. (Psychology)
- At the end of this course, learners will be able to analyze primary sources from different decades within the 19th century to understand the shift in gender roles over time. (History/Gender Studies)
Degree Program :
- Upon graduation, learners will be able to conduct independent research on social phenomena using qualitative and quantitative research methods. (Sociology)
- Upon graduation, learners will be able to place peripheral intravenous lines. (Nursing)
There are tools available to help you build your learning objectives. Arizona State and University of Central Florida host such tools. Arizona State’s tool follows the above model in which every learning objective has three component parts. The University of Central Florida tool gives users the opportunity to provide very specific assessment descriptions and proficiency levels in their learning objectives.
I have some learning objectives, now what?
When designing for online learning, generally we set our learning objectives well before we do anything with the content of the course. These learning objectives then guide every step of the design process, from which content is used to the assessments. For example, if you specify in your learning objectives that you want students to be able to evaluate a large concept critically, using a multiple choice assessment is typically not what we would recommend to demonstrate that type of learning. If you are working with an instructional designer, having some idea about what your learning objectives are can be really helpful to get the process moving more quickly. You might want to take some notes down, or use a planning worksheet .
Final thoughts on learning objectives
There’s no one answer to how many learning objectives a course should have. In general, when an instructional designer works with a faculty member to set objectives, it is typically done at a high level (more like goals) as well as at a modular level (by unit or by time). If you are in a hurry, it can be helpful to think about learning objectives in terms of what you want to have students learn during the course of a particular week.
It is important, though, to keep in mind that one of the goals of learning objectives is to help learners understand the priorities for their learning. Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe, in their book Understanding by Design, encourage instructors and course designers to differentiate between objectives around knowledge and skills that are essential for enduring understanding, important to know and do, and worth being familiar with.
Although learning objectives can help you design your course, they are also useful for your students. Sharing your learning objectives with them explicitly can help learners link the concepts in the course together and to their broader curriculum.
Practical tips
- Try to write 2-3 learning objectives for a week. You do not have to share them with students, but it will help guide your development and keep things organized.
- Write your learning objectives down. There are lots of online course design planners that can help articulate how you are teaching the course.
- University of Central Florida builder
- Arizona State University builder
University of Michigan
CRLT- Readings for course design
Other Resources
Arizona State University- Learning objective builder
University of Central Florida- Learning objective builder
Available on Amazon- Wiggins, G., & McTighe, J. (2005). Understanding by Design (2nd ed.). United States: ASCD.

IMPACT OF ONLINE EDUCATION DURING COVID 19 – A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW
- Dr. Sparsh Bansal, Dr. John Lodewijks, Dr. Priti Bakhshi Author
The online learning experience for the students’ in the initial days could have been more satisfactory(Ismaili, Y., 2021). It was because of reasons like technological constraints and older teaching methods. However, the recent pandemic has proved to be a golden opportunity to introduce the online mode of education.
The research problem of this thesis investigates - The effect of online education on students’ attendance and academics in India. A review of the research findings of more than 100 publications was done in the literature, most of which got published between 2009 and 2022. The main research objective of this study involves explaining how different aspects of online education impact students’ engagement during online classes and, after that, their performance in the assessments. The research outcomes identified through the literature review serve as a measure of how online education has impacted and affected the education system during the pandemic.
How to Cite
- Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)

- ISSN: 1539-1590
- E-ISSN: 2573-7104


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This review enabled us to identify the online learning research themes examined from 2009 to 2018. In the section below, we review the most studied research themes, engagement and learner characteristics along with implications, limitations, and directions for future research. 5.1. Most studied research themes.
The CoI model has formed the basis for a good deal of research on online learning. Most of this research. has focused on one of the three pr esences, social presence being the most frequently ...
Nashville, TN 3720 3 USA. t [email protected]. Abstract. The physical "brick and mortar" classroom is starting to lose its monopoly as the place of. learning. The Internet has made ...
BackgroundThe effectiveness of online learning in higher education during the COVID-19 pandemic period is a debated topic but a systematic review on this topic is absent.MethodsThe present study implemented a systematic review of 25 selected articles to comprehensively evaluate online learning effectiveness during the pandemic period and identify factors that influence such effectiveness ...
This systematic analysis examines effectiveness research on online and blended learning from schools, particularly relevant during the Covid-19 pandemic, and also educational games, computer-supported cooperative learning (CSCL) and computer-assisted instruction (CAI), largely used in schools but with potential for outside school.
This showed that the more effective online learning was, the more benefits and positive outcomes the student experienced. The result of this research showed that learning objectives could enable universities to increase the effectiveness of students' online learning by motivating students to join online classes and developing appropriate ...
Online learning has increased in prominence across all levels of education, despite reported learner engagement being lower online than during in-person learning. Most learner engagement research and frameworks have focused on in-person learning environments but new frameworks and strategies for online learner engagement are emerging.
Metrics. The coronavirus pandemic has forced students and educators across all levels of education to rapidly adapt to online learning. The impact of this — and the developments required to make ...
The Journal of Online Learning Research (JOLR) is a peer-reviewed journal devoted to the theoretical, empirical, and pragmatic understanding of technologies and their impact on pedagogy and policy in primary and secondary (K-12) online and blended environments. Three issues are published annually. Each submitted manuscript goes through a ...
The objective of learning analytics is to provide helpful information to optimize or improve learning designs, learning outcomes and learning environments based on the analysis results (Greller & Drachsler, 2012 ). In recent years, learning analytics has become an important issue in education, in particular, in the field of technology-enhanced ...
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has been extensively used on student achievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a meta-analysis of the related studies focusing on the effect of online education on students' academic achievement in several countries between the years 2010 and 2021 was carried out. Furthermore, this ...
1.1. Related literature. Online learning is a form of distance education which mainly involves internet‐based education where courses are offered synchronously (i.e. live sessions online) and/or asynchronously (i.e. students access course materials online in their own time, which is associated with the more traditional distance education).
There is a gap in the literature where much research similarly shows students' online learning problems [31]-[33], but the resolutions to address these drawbacks have been limited [34]. Hence, it is ... online learning methods, online learning objectives, future expectations, and other concerns; iii) Theme search: series of codes resulting ...
This review examines the transformation of educational practices to online and distance learning during the COVID-19 pandemic. It specifically focuses on the challenges, innovative approaches, and successes of this transition, emphasizing the integration of educational technology, student well-being, and teacher development. The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly transformed the educational ...
In research examining student outcomes in the context of online learning, the prevailing trend is the consistent observation that online learners often achieve less favorable results when compared ...
The spread of online learning has grown exponentially at every academic level and in many. countries in our COVID-19 world. Due to the relatively new nature of such widespread use of. online learning, little analysis or studies have been conducted on whether student performance.
Rapid developments in technology have made distance education easy (McBrien et al., 2009).). "Most of the terms (online learning, open learning, web-based learning, computer-mediated learning, blended learning, m-learning, for ex.) have in common the ability to use a computer connected to a network, that offers the possibility to learn from anywhere, anytime, in any rhythm, with any means ...
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effect of online education, which has. been extensively used on student ac hievement since the beginning of the pandemic. In line with this purpose, a ...
Online learning can take a number of different forms. Often people think of Massive Open Online Courses, or MOOCs, where thousands of students watch a video online and fill out questionnaires or ...
The research takes place at a comprehensive university in China, with a sample of 46 Year 1 students and 18 experienced teachers. Their reflections on the effectiveness of online learning were ...
Learning objectives are the cornerstone of every e-learning course. They're the reason you're creating the course. They guide you as you select the content and activities to include. And they help you determine whether your course has been effective. So basically, without learning objectives you won't know why you're creating the course ...
An active verb describing what a learner will know, be able to do, or value. A brief description of the content, skill or value connected to the objective. For a first draft of a set of learning objectives, begin each objective with the phrase, "At the end of this [course, module, lesson, degree program, etc], learners will be able to…".
This study aims to explore English for specific purposes (ESP) students' experiences during online learning, along with their concerns on learning attainment and personal adaptations. A ...
The main research objective of this study involves explaining how different aspects of online education impact students' engagement during online classes and, after that, their performance in the assessments. ... However, the recent pandemic has proved to be a golden opportunity to introduce the online mode of education. The research problem ...
With the biggest barrier to online learning being an internet connection and a device such as a phone, computer, or tablet, access to e-learning is possible for almost anyone. ... Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals ...
Objective. We describe the characteristics, content, and effectiveness of digital self-management (SM) education programs for lupus and other chronic conditions to identify gaps and inform the improvement of future programs in lupus. Methods. Three bibliographic databases were searched for articles published between May 2012 and April 2022.
In the world of education, children need to be prepared with skills that will ensure their competitive level in different fields and especially in the field of science and technology. In this research, we assume that programming is a new literacy. Literacy plays a significant role in reducing gender, race, nationality, and religious inequalities.
Research was on online learning impact on the student of higher education. and what was the impact of COVID -19 on the student education. ... The best web based learning objectives is signi fica ...
The field portions of this research were conducted under Kansas State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee protocol number 4471, for management of the bison herd, approved until 28 October 2023. No bison were handled or disturbed during this study. Objective 1: Wallow mapping and spatial characterization of abundance