The Advantages and Limitations of Single Case Study Analysis

As Andrew Bennett and Colin Elman have recently noted, qualitative research methods presently enjoy “an almost unprecedented popularity and vitality… in the international relations sub-field”, such that they are now “indisputably prominent, if not pre-eminent” (2010: 499). This is, they suggest, due in no small part to the considerable advantages that case study methods in particular have to offer in studying the “complex and relatively unstructured and infrequent phenomena that lie at the heart of the subfield” (Bennett and Elman, 2007: 171). Using selected examples from within the International Relations literature[1], this paper aims to provide a brief overview of the main principles and distinctive advantages and limitations of single case study analysis. Divided into three inter-related sections, the paper therefore begins by first identifying the underlying principles that serve to constitute the case study as a particular research strategy, noting the somewhat contested nature of the approach in ontological, epistemological, and methodological terms. The second part then looks to the principal single case study types and their associated advantages, including those from within the recent ‘third generation’ of qualitative International Relations (IR) research. The final section of the paper then discusses the most commonly articulated limitations of single case studies; while accepting their susceptibility to criticism, it is however suggested that such weaknesses are somewhat exaggerated. The paper concludes that single case study analysis has a great deal to offer as a means of both understanding and explaining contemporary international relations.
The term ‘case study’, John Gerring has suggested, is “a definitional morass… Evidently, researchers have many different things in mind when they talk about case study research” (2006a: 17). It is possible, however, to distil some of the more commonly-agreed principles. One of the most prominent advocates of case study research, Robert Yin (2009: 14) defines it as “an empirical enquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon in depth and within its real-life context, especially when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident”. What this definition usefully captures is that case studies are intended – unlike more superficial and generalising methods – to provide a level of detail and understanding, similar to the ethnographer Clifford Geertz’s (1973) notion of ‘thick description’, that allows for the thorough analysis of the complex and particularistic nature of distinct phenomena. Another frequently cited proponent of the approach, Robert Stake, notes that as a form of research the case study “is defined by interest in an individual case, not by the methods of inquiry used”, and that “the object of study is a specific, unique, bounded system” (2008: 443, 445). As such, three key points can be derived from this – respectively concerning issues of ontology, epistemology, and methodology – that are central to the principles of single case study research.
First, the vital notion of ‘boundedness’ when it comes to the particular unit of analysis means that defining principles should incorporate both the synchronic (spatial) and diachronic (temporal) elements of any so-called ‘case’. As Gerring puts it, a case study should be “an intensive study of a single unit… a spatially bounded phenomenon – e.g. a nation-state, revolution, political party, election, or person – observed at a single point in time or over some delimited period of time” (2004: 342). It is important to note, however, that – whereas Gerring refers to a single unit of analysis – it may be that attention also necessarily be given to particular sub-units. This points to the important difference between what Yin refers to as an ‘holistic’ case design, with a single unit of analysis, and an ’embedded’ case design with multiple units of analysis (Yin, 2009: 50-52). The former, for example, would examine only the overall nature of an international organization, whereas the latter would also look to specific departments, programmes, or policies etc.
Secondly, as Tim May notes of the case study approach, “even the most fervent advocates acknowledge that the term has entered into understandings with little specification or discussion of purpose and process” (2011: 220). One of the principal reasons for this, he argues, is the relationship between the use of case studies in social research and the differing epistemological traditions – positivist, interpretivist, and others – within which it has been utilised. Philosophy of science concerns are obviously a complex issue, and beyond the scope of much of this paper. That said, the issue of how it is that we know what we know – of whether or not a single independent reality exists of which we as researchers can seek to provide explanation – does lead us to an important distinction to be made between so-called idiographic and nomothetic case studies (Gerring, 2006b). The former refers to those which purport to explain only a single case, are concerned with particularisation, and hence are typically (although not exclusively) associated with more interpretivist approaches. The latter are those focused studies that reflect upon a larger population and are more concerned with generalisation, as is often so with more positivist approaches[2]. The importance of this distinction, and its relation to the advantages and limitations of single case study analysis, is returned to below.
Thirdly, in methodological terms, given that the case study has often been seen as more of an interpretivist and idiographic tool, it has also been associated with a distinctly qualitative approach (Bryman, 2009: 67-68). However, as Yin notes, case studies can – like all forms of social science research – be exploratory, descriptive, and/or explanatory in nature. It is “a common misconception”, he notes, “that the various research methods should be arrayed hierarchically… many social scientists still deeply believe that case studies are only appropriate for the exploratory phase of an investigation” (Yin, 2009: 6). If case studies can reliably perform any or all three of these roles – and given that their in-depth approach may also require multiple sources of data and the within-case triangulation of methods – then it becomes readily apparent that they should not be limited to only one research paradigm. Exploratory and descriptive studies usually tend toward the qualitative and inductive, whereas explanatory studies are more often quantitative and deductive (David and Sutton, 2011: 165-166). As such, the association of case study analysis with a qualitative approach is a “methodological affinity, not a definitional requirement” (Gerring, 2006a: 36). It is perhaps better to think of case studies as transparadigmatic; it is mistaken to assume single case study analysis to adhere exclusively to a qualitative methodology (or an interpretivist epistemology) even if it – or rather, practitioners of it – may be so inclined. By extension, this also implies that single case study analysis therefore remains an option for a multitude of IR theories and issue areas; it is how this can be put to researchers’ advantage that is the subject of the next section.
Having elucidated the defining principles of the single case study approach, the paper now turns to an overview of its main benefits. As noted above, a lack of consensus still exists within the wider social science literature on the principles and purposes – and by extension the advantages and limitations – of case study research. Given that this paper is directed towards the particular sub-field of International Relations, it suggests Bennett and Elman’s (2010) more discipline-specific understanding of contemporary case study methods as an analytical framework. It begins however, by discussing Harry Eckstein’s seminal (1975) contribution to the potential advantages of the case study approach within the wider social sciences.
Eckstein proposed a taxonomy which usefully identified what he considered to be the five most relevant types of case study. Firstly were so-called configurative-idiographic studies, distinctly interpretivist in orientation and predicated on the assumption that “one cannot attain prediction and control in the natural science sense, but only understanding ( verstehen )… subjective values and modes of cognition are crucial” (1975: 132). Eckstein’s own sceptical view was that any interpreter ‘simply’ considers a body of observations that are not self-explanatory and “without hard rules of interpretation, may discern in them any number of patterns that are more or less equally plausible” (1975: 134). Those of a more post-modernist bent, of course – sharing an “incredulity towards meta-narratives”, in Lyotard’s (1994: xxiv) evocative phrase – would instead suggest that this more free-form approach actually be advantageous in delving into the subtleties and particularities of individual cases.
Eckstein’s four other types of case study, meanwhile, promote a more nomothetic (and positivist) usage. As described, disciplined-configurative studies were essentially about the use of pre-existing general theories, with a case acting “passively, in the main, as a receptacle for putting theories to work” (Eckstein, 1975: 136). As opposed to the opportunity this presented primarily for theory application, Eckstein identified heuristic case studies as explicit theoretical stimulants – thus having instead the intended advantage of theory-building. So-called p lausibility probes entailed preliminary attempts to determine whether initial hypotheses should be considered sound enough to warrant more rigorous and extensive testing. Finally, and perhaps most notably, Eckstein then outlined the idea of crucial case studies , within which he also included the idea of ‘most-likely’ and ‘least-likely’ cases; the essential characteristic of crucial cases being their specific theory-testing function.
Whilst Eckstein’s was an early contribution to refining the case study approach, Yin’s (2009: 47-52) more recent delineation of possible single case designs similarly assigns them roles in the applying, testing, or building of theory, as well as in the study of unique cases[3]. As a subset of the latter, however, Jack Levy (2008) notes that the advantages of idiographic cases are actually twofold. Firstly, as inductive/descriptive cases – akin to Eckstein’s configurative-idiographic cases – whereby they are highly descriptive, lacking in an explicit theoretical framework and therefore taking the form of “total history”. Secondly, they can operate as theory-guided case studies, but ones that seek only to explain or interpret a single historical episode rather than generalise beyond the case. Not only does this therefore incorporate ‘single-outcome’ studies concerned with establishing causal inference (Gerring, 2006b), it also provides room for the more postmodern approaches within IR theory, such as discourse analysis, that may have developed a distinct methodology but do not seek traditional social scientific forms of explanation.
Applying specifically to the state of the field in contemporary IR, Bennett and Elman identify a ‘third generation’ of mainstream qualitative scholars – rooted in a pragmatic scientific realist epistemology and advocating a pluralistic approach to methodology – that have, over the last fifteen years, “revised or added to essentially every aspect of traditional case study research methods” (2010: 502). They identify ‘process tracing’ as having emerged from this as a central method of within-case analysis. As Bennett and Checkel observe, this carries the advantage of offering a methodologically rigorous “analysis of evidence on processes, sequences, and conjunctures of events within a case, for the purposes of either developing or testing hypotheses about causal mechanisms that might causally explain the case” (2012: 10).
Harnessing various methods, process tracing may entail the inductive use of evidence from within a case to develop explanatory hypotheses, and deductive examination of the observable implications of hypothesised causal mechanisms to test their explanatory capability[4]. It involves providing not only a coherent explanation of the key sequential steps in a hypothesised process, but also sensitivity to alternative explanations as well as potential biases in the available evidence (Bennett and Elman 2010: 503-504). John Owen (1994), for example, demonstrates the advantages of process tracing in analysing whether the causal factors underpinning democratic peace theory are – as liberalism suggests – not epiphenomenal, but variously normative, institutional, or some given combination of the two or other unexplained mechanism inherent to liberal states. Within-case process tracing has also been identified as advantageous in addressing the complexity of path-dependent explanations and critical junctures – as for example with the development of political regime types – and their constituent elements of causal possibility, contingency, closure, and constraint (Bennett and Elman, 2006b).
Bennett and Elman (2010: 505-506) also identify the advantages of single case studies that are implicitly comparative: deviant, most-likely, least-likely, and crucial cases. Of these, so-called deviant cases are those whose outcome does not fit with prior theoretical expectations or wider empirical patterns – again, the use of inductive process tracing has the advantage of potentially generating new hypotheses from these, either particular to that individual case or potentially generalisable to a broader population. A classic example here is that of post-independence India as an outlier to the standard modernisation theory of democratisation, which holds that higher levels of socio-economic development are typically required for the transition to, and consolidation of, democratic rule (Lipset, 1959; Diamond, 1992). Absent these factors, MacMillan’s single case study analysis (2008) suggests the particularistic importance of the British colonial heritage, the ideology and leadership of the Indian National Congress, and the size and heterogeneity of the federal state.
Most-likely cases, as per Eckstein above, are those in which a theory is to be considered likely to provide a good explanation if it is to have any application at all, whereas least-likely cases are ‘tough test’ ones in which the posited theory is unlikely to provide good explanation (Bennett and Elman, 2010: 505). Levy (2008) neatly refers to the inferential logic of the least-likely case as the ‘Sinatra inference’ – if a theory can make it here, it can make it anywhere. Conversely, if a theory cannot pass a most-likely case, it is seriously impugned. Single case analysis can therefore be valuable for the testing of theoretical propositions, provided that predictions are relatively precise and measurement error is low (Levy, 2008: 12-13). As Gerring rightly observes of this potential for falsification:
“a positivist orientation toward the work of social science militates toward a greater appreciation of the case study format, not a denigration of that format, as is usually supposed” (Gerring, 2007: 247, emphasis added).
In summary, the various forms of single case study analysis can – through the application of multiple qualitative and/or quantitative research methods – provide a nuanced, empirically-rich, holistic account of specific phenomena. This may be particularly appropriate for those phenomena that are simply less amenable to more superficial measures and tests (or indeed any substantive form of quantification) as well as those for which our reasons for understanding and/or explaining them are irreducibly subjective – as, for example, with many of the normative and ethical issues associated with the practice of international relations. From various epistemological and analytical standpoints, single case study analysis can incorporate both idiographic sui generis cases and, where the potential for generalisation may exist, nomothetic case studies suitable for the testing and building of causal hypotheses. Finally, it should not be ignored that a signal advantage of the case study – with particular relevance to international relations – also exists at a more practical rather than theoretical level. This is, as Eckstein noted, “that it is economical for all resources: money, manpower, time, effort… especially important, of course, if studies are inherently costly, as they are if units are complex collective individuals ” (1975: 149-150, emphasis added).
Limitations
Single case study analysis has, however, been subject to a number of criticisms, the most common of which concern the inter-related issues of methodological rigour, researcher subjectivity, and external validity. With regard to the first point, the prototypical view here is that of Zeev Maoz (2002: 164-165), who suggests that “the use of the case study absolves the author from any kind of methodological considerations. Case studies have become in many cases a synonym for freeform research where anything goes”. The absence of systematic procedures for case study research is something that Yin (2009: 14-15) sees as traditionally the greatest concern due to a relative absence of methodological guidelines. As the previous section suggests, this critique seems somewhat unfair; many contemporary case study practitioners – and representing various strands of IR theory – have increasingly sought to clarify and develop their methodological techniques and epistemological grounding (Bennett and Elman, 2010: 499-500).
A second issue, again also incorporating issues of construct validity, concerns that of the reliability and replicability of various forms of single case study analysis. This is usually tied to a broader critique of qualitative research methods as a whole. However, whereas the latter obviously tend toward an explicitly-acknowledged interpretive basis for meanings, reasons, and understandings:
“quantitative measures appear objective, but only so long as we don’t ask questions about where and how the data were produced… pure objectivity is not a meaningful concept if the goal is to measure intangibles [as] these concepts only exist because we can interpret them” (Berg and Lune, 2010: 340).
The question of researcher subjectivity is a valid one, and it may be intended only as a methodological critique of what are obviously less formalised and researcher-independent methods (Verschuren, 2003). Owen (1994) and Layne’s (1994) contradictory process tracing results of interdemocratic war-avoidance during the Anglo-American crisis of 1861 to 1863 – from liberal and realist standpoints respectively – are a useful example. However, it does also rest on certain assumptions that can raise deeper and potentially irreconcilable ontological and epistemological issues. There are, regardless, plenty such as Bent Flyvbjerg (2006: 237) who suggest that the case study contains no greater bias toward verification than other methods of inquiry, and that “on the contrary, experience indicates that the case study contains a greater bias toward falsification of preconceived notions than toward verification”.
The third and arguably most prominent critique of single case study analysis is the issue of external validity or generalisability. How is it that one case can reliably offer anything beyond the particular? “We always do better (or, in the extreme, no worse) with more observation as the basis of our generalization”, as King et al write; “in all social science research and all prediction, it is important that we be as explicit as possible about the degree of uncertainty that accompanies out prediction” (1994: 212). This is an unavoidably valid criticism. It may be that theories which pass a single crucial case study test, for example, require rare antecedent conditions and therefore actually have little explanatory range. These conditions may emerge more clearly, as Van Evera (1997: 51-54) notes, from large-N studies in which cases that lack them present themselves as outliers exhibiting a theory’s cause but without its predicted outcome. As with the case of Indian democratisation above, it would logically be preferable to conduct large-N analysis beforehand to identify that state’s non-representative nature in relation to the broader population.
There are, however, three important qualifiers to the argument about generalisation that deserve particular mention here. The first is that with regard to an idiographic single-outcome case study, as Eckstein notes, the criticism is “mitigated by the fact that its capability to do so [is] never claimed by its exponents; in fact it is often explicitly repudiated” (1975: 134). Criticism of generalisability is of little relevance when the intention is one of particularisation. A second qualifier relates to the difference between statistical and analytical generalisation; single case studies are clearly less appropriate for the former but arguably retain significant utility for the latter – the difference also between explanatory and exploratory, or theory-testing and theory-building, as discussed above. As Gerring puts it, “theory confirmation/disconfirmation is not the case study’s strong suit” (2004: 350). A third qualification relates to the issue of case selection. As Seawright and Gerring (2008) note, the generalisability of case studies can be increased by the strategic selection of cases. Representative or random samples may not be the most appropriate, given that they may not provide the richest insight (or indeed, that a random and unknown deviant case may appear). Instead, and properly used , atypical or extreme cases “often reveal more information because they activate more actors… and more basic mechanisms in the situation studied” (Flyvbjerg, 2006). Of course, this also points to the very serious limitation, as hinted at with the case of India above, that poor case selection may alternatively lead to overgeneralisation and/or grievous misunderstandings of the relationship between variables or processes (Bennett and Elman, 2006a: 460-463).
As Tim May (2011: 226) notes, “the goal for many proponents of case studies […] is to overcome dichotomies between generalizing and particularizing, quantitative and qualitative, deductive and inductive techniques”. Research aims should drive methodological choices, rather than narrow and dogmatic preconceived approaches. As demonstrated above, there are various advantages to both idiographic and nomothetic single case study analyses – notably the empirically-rich, context-specific, holistic accounts that they have to offer, and their contribution to theory-building and, to a lesser extent, that of theory-testing. Furthermore, while they do possess clear limitations, any research method involves necessary trade-offs; the inherent weaknesses of any one method, however, can potentially be offset by situating them within a broader, pluralistic mixed-method research strategy. Whether or not single case studies are used in this fashion, they clearly have a great deal to offer.
References
Bennett, A. and Checkel, J. T. (2012) ‘Process Tracing: From Philosophical Roots to Best Practice’, Simons Papers in Security and Development, No. 21/2012, School for International Studies, Simon Fraser University: Vancouver.
Bennett, A. and Elman, C. (2006a) ‘Qualitative Research: Recent Developments in Case Study Methods’, Annual Review of Political Science , 9, 455-476.
Bennett, A. and Elman, C. (2006b) ‘Complex Causal Relations and Case Study Methods: The Example of Path Dependence’, Political Analysis , 14, 3, 250-267.
Bennett, A. and Elman, C. (2007) ‘Case Study Methods in the International Relations Subfield’, Comparative Political Studies , 40, 2, 170-195.
Bennett, A. and Elman, C. (2010) Case Study Methods. In C. Reus-Smit and D. Snidal (eds) The Oxford Handbook of International Relations . Oxford University Press: Oxford. Ch. 29.
Berg, B. and Lune, H. (2012) Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences . Pearson: London.
Bryman, A. (2012) Social Research Methods . Oxford University Press: Oxford.
David, M. and Sutton, C. D. (2011) Social Research: An Introduction . SAGE Publications Ltd: London.
Diamond, J. (1992) ‘Economic development and democracy reconsidered’, American Behavioral Scientist , 35, 4/5, 450-499.
Eckstein, H. (1975) Case Study and Theory in Political Science. In R. Gomm, M. Hammersley, and P. Foster (eds) Case Study Method . SAGE Publications Ltd: London.
Flyvbjerg, B. (2006) ‘Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research’, Qualitative Inquiry , 12, 2, 219-245.
Geertz, C. (1973) The Interpretation of Cultures: Selected Essays by Clifford Geertz . Basic Books Inc: New York.
Gerring, J. (2004) ‘What is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?’, American Political Science Review , 98, 2, 341-354.
Gerring, J. (2006a) Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . Cambridge University Press: Cambridge.
Gerring, J. (2006b) ‘Single-Outcome Studies: A Methodological Primer’, International Sociology , 21, 5, 707-734.
Gerring, J. (2007) ‘Is There a (Viable) Crucial-Case Method?’, Comparative Political Studies , 40, 3, 231-253.
King, G., Keohane, R. O. and Verba, S. (1994) Designing Social Inquiry: Scientific Inference in Qualitative Research . Princeton University Press: Chichester.
Layne, C. (1994) ‘Kant or Cant: The Myth of the Democratic Peace’, International Security , 19, 2, 5-49.
Levy, J. S. (2008) ‘Case Studies: Types, Designs, and Logics of Inference’, Conflict Management and Peace Science , 25, 1-18.
Lipset, S. M. (1959) ‘Some Social Requisites of Democracy: Economic Development and Political Legitimacy’, The American Political Science Review , 53, 1, 69-105.
Lyotard, J-F. (1984) The Postmodern Condition: A Report on Knowledge . University of Minnesota Press: Minneapolis.
MacMillan, A. (2008) ‘Deviant Democratization in India’, Democratization , 15, 4, 733-749.
Maoz, Z. (2002) Case study methodology in international studies: from storytelling to hypothesis testing. In F. P. Harvey and M. Brecher (eds) Evaluating Methodology in International Studies . University of Michigan Press: Ann Arbor.
May, T. (2011) Social Research: Issues, Methods and Process . Open University Press: Maidenhead.
Owen, J. M. (1994) ‘How Liberalism Produces Democratic Peace’, International Security , 19, 2, 87-125.
Seawright, J. and Gerring, J. (2008) ‘Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research: A Menu of Qualitative and Quantitative Options’, Political Research Quarterly , 61, 2, 294-308.
Stake, R. E. (2008) Qualitative Case Studies. In N. K. Denzin and Y. S. Lincoln (eds) Strategies of Qualitative Inquiry . Sage Publications: Los Angeles. Ch. 17.
Van Evera, S. (1997) Guide to Methods for Students of Political Science . Cornell University Press: Ithaca.
Verschuren, P. J. M. (2003) ‘Case study as a research strategy: some ambiguities and opportunities’, International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 6, 2, 121-139.
Yin, R. K. (2009) Case Study Research: Design and Methods . SAGE Publications Ltd: London.
[1] The paper follows convention by differentiating between ‘International Relations’ as the academic discipline and ‘international relations’ as the subject of study.
[2] There is some similarity here with Stake’s (2008: 445-447) notion of intrinsic cases, those undertaken for a better understanding of the particular case, and instrumental ones that provide insight for the purposes of a wider external interest.
[3] These may be unique in the idiographic sense, or in nomothetic terms as an exception to the generalising suppositions of either probabilistic or deterministic theories (as per deviant cases, below).
[4] Although there are “philosophical hurdles to mount”, according to Bennett and Checkel, there exists no a priori reason as to why process tracing (as typically grounded in scientific realism) is fundamentally incompatible with various strands of positivism or interpretivism (2012: 18-19). By extension, it can therefore be incorporated by a range of contemporary mainstream IR theories.
— Written by: Ben Willis Written at: University of Plymouth Written for: David Brockington Date written: January 2013

Further Reading on E-International Relations
- Identity in International Conflicts: A Case Study of the Cuban Missile Crisis
- Imperialism’s Legacy in the Study of Contemporary Politics: The Case of Hegemonic Stability Theory
- Recreating a Nation’s Identity Through Symbolism: A Chinese Case Study
- Ontological Insecurity: A Case Study on Israeli-Palestinian Conflict in Jerusalem
- Terrorists or Freedom Fighters: A Case Study of ETA
- A Critical Assessment of Eco-Marxism: A Ghanaian Case Study
Please Consider Donating
Before you download your free e-book, please consider donating to support open access publishing.
E-IR is an independent non-profit publisher run by an all volunteer team. Your donations allow us to invest in new open access titles and pay our bandwidth bills to ensure we keep our existing titles free to view. Any amount, in any currency, is appreciated. Many thanks!
Donations are voluntary and not required to download the e-book - your link to download is below.
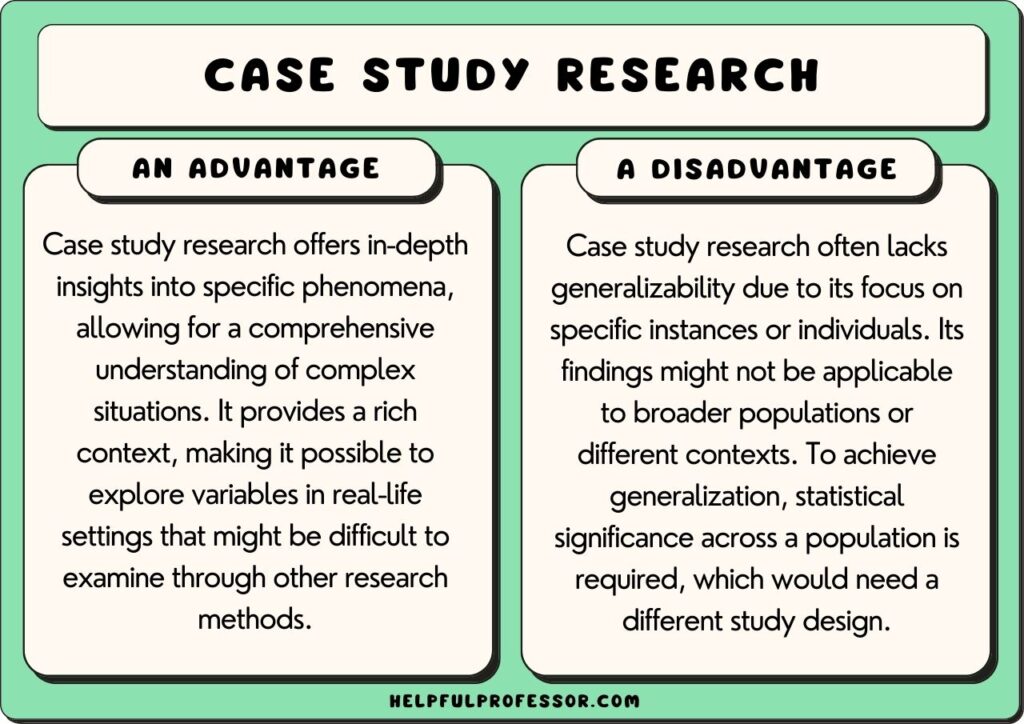
10 Case Study Advantages and Disadvantages

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
A case study in academic research is a detailed and in-depth examination of a specific instance or event, generally conducted through a qualitative approach to data.
The most common case study definition that I come across is is Robert K. Yin’s (2003, p. 13) quote provided below:
“An empirical inquiry that investigates a contemporary phenomenon within its real-life context, especially when the boundaries between phenomenon and context are not clearly evident.”
Researchers conduct case studies for a number of reasons, such as to explore complex phenomena within their real-life context, to look at a particularly interesting instance of a situation, or to dig deeper into something of interest identified in a wider-scale project.
While case studies render extremely interesting data, they have many limitations and are not suitable for all studies. One key limitation is that a case study’s findings are not usually generalizable to broader populations because one instance cannot be used to infer trends across populations.
Case Study Advantages and Disadvantages
1. in-depth analysis of complex phenomena.
Case study design allows researchers to delve deeply into intricate issues and situations.
By focusing on a specific instance or event, researchers can uncover nuanced details and layers of understanding that might be missed with other research methods, especially large-scale survey studies.
As Lee and Saunders (2017) argue,
“It allows that particular event to be studies in detail so that its unique qualities may be identified.”
This depth of analysis can provide rich insights into the underlying factors and dynamics of the studied phenomenon.
2. Holistic Understanding
Building on the above point, case studies can help us to understand a topic holistically and from multiple angles.
This means the researcher isn’t restricted to just examining a topic by using a pre-determined set of questions, as with questionnaires. Instead, researchers can use qualitative methods to delve into the many different angles, perspectives, and contextual factors related to the case study.
We can turn to Lee and Saunders (2017) again, who notes that case study researchers “develop a deep, holistic understanding of a particular phenomenon” with the intent of deeply understanding the phenomenon.
3. Examination of rare and Unusual Phenomena
We need to use case study methods when we stumble upon “rare and unusual” (Lee & Saunders, 2017) phenomena that would tend to be seen as mere outliers in population studies.
Take, for example, a child genius. A population study of all children of that child’s age would merely see this child as an outlier in the dataset, and this child may even be removed in order to predict overall trends.
So, to truly come to an understanding of this child and get insights into the environmental conditions that led to this child’s remarkable cognitive development, we need to do an in-depth study of this child specifically – so, we’d use a case study.
4. Helps Reveal the Experiences of Marginalzied Groups
Just as rare and unsual cases can be overlooked in population studies, so too can the experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of marginalized groups.
As Lee and Saunders (2017) argue, “case studies are also extremely useful in helping the expression of the voices of people whose interests are often ignored.”
Take, for example, the experiences of minority populations as they navigate healthcare systems. This was for many years a “hidden” phenomenon, not examined by researchers. It took case study designs to truly reveal this phenomenon, which helped to raise practitioners’ awareness of the importance of cultural sensitivity in medicine.
5. Ideal in Situations where Researchers cannot Control the Variables
Experimental designs – where a study takes place in a lab or controlled environment – are excellent for determining cause and effect . But not all studies can take place in controlled environments (Tetnowski, 2015).
When we’re out in the field doing observational studies or similar fieldwork, we don’t have the freedom to isolate dependent and independent variables. We need to use alternate methods.
Case studies are ideal in such situations.
A case study design will allow researchers to deeply immerse themselves in a setting (potentially combining it with methods such as ethnography or researcher observation) in order to see how phenomena take place in real-life settings.
6. Supports the generation of new theories or hypotheses
While large-scale quantitative studies such as cross-sectional designs and population surveys are excellent at testing theories and hypotheses on a large scale, they need a hypothesis to start off with!
This is where case studies – in the form of grounded research – come in. Often, a case study doesn’t start with a hypothesis. Instead, it ends with a hypothesis based upon the findings within a singular setting.
The deep analysis allows for hypotheses to emerge, which can then be taken to larger-scale studies in order to conduct further, more generalizable, testing of the hypothesis or theory.
7. Reveals the Unexpected
When a largescale quantitative research project has a clear hypothesis that it will test, it often becomes very rigid and has tunnel-vision on just exploring the hypothesis.
Of course, a structured scientific examination of the effects of specific interventions targeted at specific variables is extermely valuable.
But narrowly-focused studies often fail to shine a spotlight on unexpected and emergent data. Here, case studies come in very useful. Oftentimes, researchers set their eyes on a phenomenon and, when examining it closely with case studies, identify data and come to conclusions that are unprecedented, unforeseen, and outright surprising.
As Lars Meier (2009, p. 975) marvels, “where else can we become a part of foreign social worlds and have the chance to become aware of the unexpected?”
Disadvantages
1. not usually generalizable.
Case studies are not generalizable because they tend not to look at a broad enough corpus of data to be able to infer that there is a trend across a population.
As Yang (2022) argues, “by definition, case studies can make no claims to be typical.”
Case studies focus on one specific instance of a phenomenon. They explore the context, nuances, and situational factors that have come to bear on the case study. This is really useful for bringing to light important, new, and surprising information, as I’ve already covered.
But , it’s not often useful for generating data that has validity beyond the specific case study being examined.
2. Subjectivity in interpretation
Case studies usually (but not always) use qualitative data which helps to get deep into a topic and explain it in human terms, finding insights unattainable by quantitative data.
But qualitative data in case studies relies heavily on researcher interpretation. While researchers can be trained and work hard to focus on minimizing subjectivity (through methods like triangulation), it often emerges – some might argue it’s innevitable in qualitative studies.
So, a criticism of case studies could be that they’re more prone to subjectivity – and researchers need to take strides to address this in their studies.
3. Difficulty in replicating results
Case study research is often non-replicable because the study takes place in complex real-world settings where variables are not controlled.
So, when returning to a setting to re-do or attempt to replicate a study, we often find that the variables have changed to such an extent that replication is difficult. Furthermore, new researchers (with new subjective eyes) may catch things that the other readers overlooked.
Replication is even harder when researchers attempt to replicate a case study design in a new setting or with different participants.
Comprehension Quiz for Students
Question 1: What benefit do case studies offer when exploring the experiences of marginalized groups?
a) They provide generalizable data. b) They help express the voices of often-ignored individuals. c) They control all variables for the study. d) They always start with a clear hypothesis.
Question 2: Why might case studies be considered ideal for situations where researchers cannot control all variables?
a) They provide a structured scientific examination. b) They allow for generalizability across populations. c) They focus on one specific instance of a phenomenon. d) They allow for deep immersion in real-life settings.
Question 3: What is a primary disadvantage of case studies in terms of data applicability?
a) They always focus on the unexpected. b) They are not usually generalizable. c) They support the generation of new theories. d) They provide a holistic understanding.
Question 4: Why might case studies be considered more prone to subjectivity?
a) They always use quantitative data. b) They heavily rely on researcher interpretation, especially with qualitative data. c) They are always replicable. d) They look at a broad corpus of data.
Question 5: In what situations are experimental designs, such as those conducted in labs, most valuable?
a) When there’s a need to study rare and unusual phenomena. b) When a holistic understanding is required. c) When determining cause-and-effect relationships. d) When the study focuses on marginalized groups.
Question 6: Why is replication challenging in case study research?
a) Because they always use qualitative data. b) Because they tend to focus on a broad corpus of data. c) Due to the changing variables in complex real-world settings. d) Because they always start with a hypothesis.
Lee, B., & Saunders, M. N. K. (2017). Conducting Case Study Research for Business and Management Students. SAGE Publications.
Meir, L. (2009). Feasting on the Benefits of Case Study Research. In Mills, A. J., Wiebe, E., & Durepos, G. (Eds.). Encyclopedia of Case Study Research (Vol. 2). London: SAGE Publications.
Tetnowski, J. (2015). Qualitative case study research design. Perspectives on fluency and fluency disorders , 25 (1), 39-45. ( Source )
Yang, S. L. (2022). The War on Corruption in China: Local Reform and Innovation . Taylor & Francis.
Yin, R. (2003). Case Study research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 19 Top Cognitive Psychology Theories (Explained)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

Transformative Design – Methods, Types, Guide

Experimental Design – Types, Methods, Guide

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Mixed Methods Research – Types & Analysis

Triangulation in Research – Types, Methods and...
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

The Strengths and Limitations of Case Study Research

Related Papers
Ilse Schrittesser
International studies provide evidence that effective teachers are essential to students' learning success. Research on teacher effectiveness in the United States began in the 1980's, and valid and reliable methods for assessing teacher effectiveness have been developed in its context, research on this topic is still relatively new in German-speaking countries. While effective teaching is a highly complex construct which includes a whole repertoire of skills, there seems evidence that some of these skills play a particularly significant role for effective teaching. The present article will take a close look at these skills from the perspective of two mostly separate discourses: expertise research and the qualities of expert teachers, which are usually discussed in the Anglo-American context, and theories of teacher professionalism which is highly influential in the German speaking countries. The two concepts are explained and it is argued that-interestingly enough-research r...
Anju Chhetri
This article presents the case study as a type of qualitative research. Its aim is to give a detailed description of a case study-its definition, some classifications, and several advantages and disadvantages-in order to provide a better understanding of this widely used type of qualitative approac h. In comparison to other types of qualitative research, case studies have been little understood both from a methodological point of view, where disagreements exist about whether case studies should be considered a research method or a research type, and from a content point of view, where there are ambiguities regarding what should be considered a case or research subject. A great emphasis is placed on the disadvantages of case studies, where we try to refute some of the criticisms concerning case studies, particularly in comparison to quantitative research approaches.
Cambridge Journal of Education
ethiopia-ed.net
Kathleen Armour
Bedrettin Yazan
Case study methodology has long been a contested terrain in social sciences research which is characterized by varying, sometimes opposing, approaches espoused by many research methodologists. Despite being one of the most frequently used qualitative research methodologies in educational research, the methodologists do not have a full consensus on the design and implementation of case study, which hampers its full evolution. Focusing on the landmark works of three prominent methodologists, namely Robert Yin, Sharan Merriam, Robert Stake, I attempt to scrutinize the areas where their perspectives diverge, converge and complement one another in varying dimensions of case study research. I aim to help the emerging researchers in the field of education familiarize themselves with the diverse views regarding case study that lead to a vast array of techniques and strategies, out of which they can come up with a combined perspective which best serves their research purpose.
Nina Oktavia
Case study is believed as the widely used kind of research to view phenomena, despite of some critics on it concerning mostly on its data reliability, validity and subjectivity. This article therefore discusses some aspects of case study which are considered important to be recognized by novice researchers, especially about the way how to design and how to make sure the quality and reliability of the case. In addition, the case studying educational research also becomes the focus to be discussed, completed with some examples, to be able to open our mind to the plenty opportunities for case study in education.
Professional Development in Education
Lars Petter Storm Torjussen
Higher Education Pedagogies
Frances O'Brien
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
International Journal of Lifelong Education
Irfan Ahmed Rind
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MANAGEMENT & INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Damber Kharka
Waleed Alabri
Journal of Music Teacher Education
Daniel Fasko
Proceedings of the International Conference on Trends and Innovations in Language Teaching - TILT2014
Cherry M Philipose
Paula Dawidowicz
Eva Thaller
James Underwood , Nicola Moksa , David Jarvis , David Cousens , Bryn James , Deshnee Moodley , Rachael Rudge , Mari Chikvaidze
Suzanne Wilson
Journal of Curriculum Studies
Lee Shulman
Journal of College Science Teaching
Clare Kilbane
Ignatius Odongo , Felix Oyejide Omotosho PhD
Brenda Leibowitz
Teaching and Teacher Education
Mary Lundeberg
South African Journal of Higher Education
Peter Rule , Robert J Balfour
Bartın Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi
Nur Ütkür Güllühan
Faculty of Science and Technology
Tony Jewels
Case methods in teacher education
Angela Izuagba
European Journal of Education
Marco Kools
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- First Online: 27 October 2022
Cite this chapter

- R. M. Channaveer 4 &
- Rajendra Baikady 5
2750 Accesses
1 Citations
This chapter reviews the strengths and limitations of case study as a research method in social sciences. It provides an account of an evidence base to justify why a case study is best suitable for some research questions and why not for some other research questions. Case study designing around the research context, defining the structure and modality, conducting the study, collecting the data through triangulation mode, analysing the data, and interpreting the data and theory building at the end give a holistic view of it. In addition, the chapter also focuses on the types of case study and when and where to use case study as a research method in social science research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Case Study Research

Ang, C. S., Lee, K. F., & Dipolog-Ubanan, G. F. (2019). Determinants of first-year student identity and satisfaction in higher education: A quantitative case study. SAGE Open, 9 (2), 215824401984668. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244019846689
Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2015). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report . Published. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/2008.1573
Bhatta, T. P. (2018). Case study research, philosophical position and theory building: A methodological discussion. Dhaulagiri Journal of Sociology and Anthropology, 12 , 72–79. https://doi.org/10.3126/dsaj.v12i0.22182
Article Google Scholar
Bromley, P. D. (1990). Academic contributions to psychological counselling. A philosophy of science for the study of individual cases. Counselling Psychology Quarterly , 3 (3), 299–307.
Google Scholar
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 11 (1), 1–9.
Grässel, E., & Schirmer, B. (2006). The use of volunteers to support family carers of dementia patients: Results of a prospective longitudinal study investigating expectations towards and experience with training and professional support. Zeitschrift Fur Gerontologie Und Geriatrie, 39 (3), 217–226.
Greenwood, D., & Lowenthal, D. (2005). Case study as a means of researching social work and improving practitioner education. Journal of Social Work Practice, 19 (2), 181–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/02650530500144782
Gülseçen, S., & Kubat, A. (2006). Teaching ICT to teacher candidates using PBL: A qualitative and quantitative evaluation. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 9 (2), 96–106.
Gomm, R., Hammersley, M., & Foster, P. (2000). Case study and generalization. Case study method , 98–115.
Hamera, J., Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). Performance ethnography . SAGE.
Hayes, N. (2000). Doing psychological research (p. 133). Open University Press.
Harrison, H., Birks, M., Franklin, R., & Mills, J. (2017). Case study research: Foundations and methodological orientations. In Forum qualitative sozialforschung/forum: Qualitative social research (Vol. 18, No. 1).
Iwakabe, S., & Gazzola, N. (2009). From single-case studies to practice-based knowledge: Aggregating and synthesizing case studies. Psychotherapy Research, 19 (4–5), 601–611. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503300802688494
Johnson, M. P. (2006). Decision models for the location of community corrections centers. Environment and Planning b: Planning and Design, 33 (3), 393–412. https://doi.org/10.1068/b3125
Kaarbo, J., & Beasley, R. K. (1999). A practical guide to the comparative case study method in political psychology. Political Psychology, 20 (2), 369–391. https://doi.org/10.1111/0162-895x.00149
Lovell, G. I. (2006). Justice excused: The deployment of law in everyday political encounters. Law Society Review, 40 (2), 283–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5893.2006.00265.x
McDonough, S., & McDonough, S. (1997). Research methods as part of English language teacher education. English Language Teacher Education and Development, 3 (1), 84–96.
Meredith, J. (1998). Building operations management theory through case and field research. Journal of Operations Management, 16 (4), 441–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-6963(98)00023-0
Mills, A. J., Durepos, G., & Wiebe, E. (Eds.). (2009). Encyclopedia of case study research . Sage Publications.
Ochieng, P. A. (2009). An analysis of the strengths and limitation of qualitative and quantitative research paradigms. Problems of Education in the 21st Century , 13 , 13.
Page, E. B., Webb, E. J., Campell, D. T., Schwart, R. D., & Sechrest, L. (1966). Unobtrusive measures: Nonreactive research in the social sciences. American Educational Research Journal, 3 (4), 317. https://doi.org/10.2307/1162043
Rashid, Y., Rashid, A., Warraich, M. A., Sabir, S. S., & Waseem, A. (2019). Case study method: A step-by-step guide for business researchers. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 18 , 160940691986242. https://doi.org/10.1177/1609406919862424
Ridder, H. G. (2017). The theory contribution of case study research designs. Business Research, 10 (2), 281–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40685-017-0045-z
Sadeghi Moghadam, M. R., Ghasemnia Arabi, N., & Khoshsima, G. (2021). A Review of case study method in operations management research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 20 , 160940692110100. https://doi.org/10.1177/16094069211010088
Sommer, B. B., & Sommer, R. (1997). A practical guide to behavioral research: Tools and techniques . Oxford University Press.
Stake, R. E. (2010). Qualitative research: Studying how things work .
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research . Sage Publications.
Stoecker, R. (1991). Evaluating and rethinking the case study. The Sociological Review, 39 (1), 88–112.
Suryani, A. (2013). Comparing case study and ethnography as qualitative research approaches .
Taylor, S., & Berridge, V. (2006). Medicinal plants and malaria: An historical case study of research at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine in the twentieth century. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 100 (8), 707–714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2005.11.017
Tellis, W. (1997). Introduction to case study. The Qualitative Report . Published. https://doi.org/10.46743/2160-3715/1997.2024
Towne, L., & Shavelson, R. J. (2002). Scientific research in education . National Academy Press Publications Sales Office.
Widdowson, M. D. J. (2011). Case study research methodology. International Journal of Transactional Analysis Research, 2 (1), 25–34.
Yin, R. K. (2004). The case study anthology . Sage.
Yin, R. K. (2003). Design and methods. Case Study Research , 3 (9.2).
Yin, R. K. (1994). Case study research: Design and methods (2nd ed.). Sage Publishing.
Yin, R. (1984). Case study research: Design and methods . Sage Publications Beverly Hills.
Yin, R. (1993). Applications of case study research . Sage Publishing.
Zainal, Z. (2003). An investigation into the effects of discipline-specific knowledge, proficiency and genre on reading comprehension and strategies of Malaysia ESP Students. Unpublished Ph. D. Thesis. University of Reading , 1 (1).
Zeisel, J. (1984). Inquiry by design: Tools for environment-behaviour research (No. 5). CUP archive.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Social Work, Central University of Karnataka, Kadaganchi, India
R. M. Channaveer
Department of Social Work, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Rajendra Baikady
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to R. M. Channaveer .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Centre for Family and Child Studies, Research Institute of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates
M. Rezaul Islam
Department of Development Studies, University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Niaz Ahmed Khan
Department of Social Work, School of Humanities, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Channaveer, R.M., Baikady, R. (2022). Case Study. In: Islam, M.R., Khan, N.A., Baikady, R. (eds) Principles of Social Research Methodology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_21
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_21
Published : 27 October 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-5219-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-5441-2
eBook Packages : Social Sciences
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 27 June 2011
The case study approach
- Sarah Crowe 1 ,
- Kathrin Cresswell 2 ,
- Ann Robertson 2 ,
- Guro Huby 3 ,
- Anthony Avery 1 &
- Aziz Sheikh 2
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 11 , Article number: 100 ( 2011 ) Cite this article
787k Accesses
1061 Citations
37 Altmetric
Metrics details
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables 1 , 2 , 3 and 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 – 7 ].
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables 2 , 3 and 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 – 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].
What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables 2 and 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 – 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table 8 )[ 8 , 18 – 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table 9 )[ 8 ].
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Yin RK: Case study research, design and method. 2009, London: Sage Publications Ltd., 4
Google Scholar
Keen J, Packwood T: Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995, 311: 444-446.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J, et al: Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009, 6 (10): 1-11.
Article Google Scholar
Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, et al: The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO). 2008, [ http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf ]
Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T, et al: Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010, 41: c4564-
Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P, the Patient Safety Education Study Group: Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010, 15: 4-10. 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA: The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002, 60 (1): 17-37. 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7.
Stake RE: The art of case study research. 1995, London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R: Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002, 52 (482): 746-51.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
King G, Keohane R, Verba S: Designing Social Inquiry. 1996, Princeton: Princeton University Press
Doolin B: Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998, 13: 301-311. 10.1057/jit.1998.8.
George AL, Bennett A: Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. 2005, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press
Eccles M, the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG): Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006, 1: 1-8. 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A: Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005, 365 (9456): 312-7.
Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G: Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004, 59 (7): 634-
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U: 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005, 4: 7-22. 10.1177/1471301205049188.
Som CV: Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005, 18: 463-477. 10.1108/09513550510608903.
Lincoln Y, Guba E: Naturalistic inquiry. 1985, Newbury Park: Sage Publications
Barbour RS: Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?. BMJ. 2001, 322: 1115-1117. 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115.
Mays N, Pope C: Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000, 320: 50-52. 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50.
Mason J: Qualitative researching. 2002, London: Sage
Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V: Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008, 7: 5-17. 10.1177/1534735407313395.
Miles MB, Huberman M: Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 1994, CA: Sage Publications Inc., 2
Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N: Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000, 320: 114-116. 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114.
Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A: Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010, 10 (1): 67-10.1186/1472-6947-10-67.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malterud K: Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001, 358: 483-488. 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Yin R: Case study research: design and methods. 1994, Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing, 2
Yin R: Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999, 34: 1209-1224.
Green J, Thorogood N: Qualitative methods for health research. 2009, Los Angeles: Sage, 2
Howcroft D, Trauth E: Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. 2005, Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar
Book Google Scholar
Blakie N: Approaches to Social Enquiry. 1993, Cambridge: Polity Press
Doolin B: Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004, 14: 343-362. 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x.
Bloomfield BP, Best A: Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992, 40: 533-560.
Shanks G, Parr A: Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. 2003, Naples
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Sarah Crowe & Anthony Avery
Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Kathrin Cresswell, Ann Robertson & Aziz Sheikh
School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sarah Crowe .
Additional information
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A. et al. The case study approach. BMC Med Res Methodol 11 , 100 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Download citation
Received : 29 November 2010
Accepted : 27 June 2011
Published : 27 June 2011
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Case Study Approach
- Electronic Health Record System
- Case Study Design
- Case Study Site
- Case Study Report
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Strengths and Weaknesses of Case Studies
There is no doubt that case studies are a valuable and important form of research for all of the industries and fields that use them. However, along with all their advantages, they also have some disadvantages. In this article we are going to look at both.
Advantages of Case Studies
Intensive Study
Case study method is responsible for intensive study of a unit. It is the investigation and exploration of an event thoroughly and deeply. You get a very detailed and in-depth study of a person or event. This is especially the case with subjects that cannot be physically or ethically recreated.
This is one of the biggest advantages of the Genie case. You cannot lock up a child for 13 years and deprive them of everything. That would be morally and ethically wrong in every single way. So when the opportunity presented itself, researchers could not look away. It was a once in a lifetime opportunity to learn about feral children.
Genie was a feral child. She was raised in completed isolation, with little human contact. Because of the abuse she withstood, she was unable to develop cognitively. From infancy she was strapped to a potty chair, and therefore never acquired the physicality needed for walking, running and jumping.
If Genie made a noise, her father beat her. Therefore, she learned to not make a noise. Once she was found, researchers studied her language skills, and attempted to find ways to get her to communicate. They were successful. While she never gained the ability to speak, she did develop other ways to communicate. However, the public soon lost interest in her case, and with that, the funds to conduct the study.
However, her case was extremely important to child development psychology and linguistic theory. Because of her, we know that mental stimulation is needed for proper development. We also now know that there is a "critical period" for the learning of language.
Developing New Research
Case studies are one of the best ways to stimulate new research. A case study can be completed, and if the findings are valuable, they can lead to new and advanced research in the field. There has been a great deal of research done that wouldn't have been possible without case studies.
An example of this is the sociological study Nickel and Dimed. Nickel and Dimed is a book and study done by Barbara Ehrenreich. She wanted to study poverty in America, and did so by living and working as a person living on minimum wage.
Through her experiment, she discovered that poverty was almost inescapable. As soon as she saved a little money, she was hit with a crisis. She might get sick, or her car might break down, all occurrences that can be destructive when a person doesn't have a safety net to fall back on.
It didn't matter where she lived or what she did. Working a minimum wage job gave her no chances for advancement or improvement whatsoever. And she did the experiment as a woman with no children to support.
This study opened a lot of eyes to the problem of the working poor in America. By living and working as the experiment, Ehrenreich was able to show first-hand data regarding the issues surrounding poverty. The book didn't end with any solutions, just suggestions for the reader and points for them to think about.
Using this case study information, new studies could be organized to learn better ways to help people who are fighting poverty, or better ways to help the working poor.
Contradicting Established Ideas or Theories
Oftentimes there are theories that may be questioned with case studies. For example, in the John/John case study, it was believed that gender and sexual identity were a construct of nurture, not nature.
John-John focused on a set of twin boys, both of whom were circumcised at the age of 6 months. One of the twin's circumcisions failed, causing irreparable damage to the penis. His parents were concerned about the sexual health of their son, so they contacted Dr. John Money for a solution.
Dr. Money believed that sexuality came from nurture, not nature, and that the injured baby, Bruce, could be raised as a girl. His penis was removed and he was sexually reassigned to become a girl. Bruce's name was changed to Brenda, and his parents decided to raise him as a girl.
In this case, Dr. Money was dishonest. He believed that gender could be changed, which has since been proven false. Brenda's parents were also dishonest, stating that the surgery was a success, when in fact that wasn't the case.
As Brenda grew up, she always acted masculine and was teased for it at school. She did not socialize as a girl, and did not identify as a female. When Brenda was 13 she learned the truth, and was incredibly relieved. She changed her name to David, and lived the rest of her life as a male.
This case proved that the general theory was wrong, and is still valuable, even though the study author was dishonest.
Giving New Insight
Case studies have the ability to give insight into phenomena that cannot be learned in any other way. An example of this is the case study about Sidney Bradford. Bradford was blind from the age of 10 months old, and regained his sight at the age of 52 from a corneal transplant.
This unique situation allowed researchers to better learn how perception and motion changes when suddenly given sight. They were able to better understand how colors and dimensions affect the human process. For what it is worth, Bradford continued to live and work with his eyes closed, as he found sight too stimulating.
Another famous study was the sociological study of Milgram.
Stanley Milgram did a study from 1960 to 1974 in which he studied the effects of social pressure. The study was set up as an independent laboratory. A random person would walk in, and agree to be a part of the study. He was told to act as a teacher, and ask questions to another volunteer, who was the learner.
The teacher would ask the learner questions, and whenever he answered incorrectly, the teacher was instructed to give the learner an electric shock. Each time the learner was wrong, the shock would be increased by 15 volts. What the teacher didn't know was that the learner was a part of the experiment, and that no shocks were being given. However, the learner did act as if they were being shocked.
If the teachers tried to quit, they were strongly pushed to continue. The goal of the experiment was to see whether or not any of the teachers would go up to the highest voltage. As it turned out, 65% of the teachers did.
This study opened eyes when it comes to social pressure. If someone tells you it is okay to hurt someone, at what point will the person back off and say "this is not ok!" And in this study, the results were the same, regardless of income, race, gender or ethnicity.
This study opened up the sociological world of understanding the divide between social pressure and morality.
Disadvantages of Case Studies
Inability to Replicate
As demonstrated with the Genie case study, many studies cannot be replicated, and therefore, cannot be corroborated. Because the studies cannot be replicated, it means the data and results are only valid for that one person. Now, one could infer that that results of the Genie study would be the same with other feral children, without additional studies we can never be 100% certain.
Also, Genie was a white, American female. We do not know whether someone with a different gender, race or ethnicity would have a different result.
Key Term! Hawthorne Effect
The effect in which people change their behavior when they are aware they are being observed.
Researcher Bias
When conducting a case study, it is very possible for the author to form a bias. This bias can be for the subject; the form of data collection, or the way the data is interpreted. This is very common, since it is normal for humans to be subjective. It is well known that Sigmund Freud, the father of psychology, was often biased in his case histories and interpretations.
The researcher can become close to a study participant, or may learn to identify with the subject. When this happens the researcher loses their perspective as an outsider.
No Classification
Any classification is not possible due to studying a small unit. This generalization of results is limited, since the study is only focusing on one small group. However, this isn't always a problem, especially if generalization is not one of the study's goals.
Time Intensive
Case studies can be very time consuming. The data collection process can be very intensive and long, and this is something new researchers are not familiar with. It takes a long period of time to develop a case study, and develop a detailed analysis.
Many studies also require the authors to immerse themselves in the case. For example, in the Genie case, the lead researchers spent an abnormal amount of time with Genie, since so few people knew how to handle her. David Rigler, one of the lead researchers, actually had Genie live with him and his family for years. Because of this attachment, many questioned the veracity of the study data.
Possibility of Errors
Case study method may have errors of memory or judgment. Since reconstructing case history is based on memory, this can lead to errors. Also, how one person perceived the past could be different for another person, and this can and does lead to errors.
When considering various aspects of their lives, people tend to focus on issues that they find most important. This allows them to form a prejudice and can make them unaware of other possible options.
Ethical Issues
With small studies, there is always the question of ethics. At what point does a study become unethical? The Genie case was riddled with accusations of being unethical, and people still debate about it today.
Was it ethical to study Genie as deeply as she was studied?
Did Genie deserve to live out her life unbothered by researchers and academics trying to use her case to potentially further their careers?
At what point does the pursuit of scientific knowledge outweigh the right to a life free from research?
Also, because the researchers became so invested in the study, people questioned whether a researcher would report unethical behavior if they witnessed it.
Advantages and Disadvantages in Real-Life Studies
Two of these case studies are the Tylenol Scandal and the Genie language study.
Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of these two studies.
Genie – Advantages
Uniqueness of study – Being able to study a feral child is a rare occurrence.
Genie – Disadvantages
Ethics - The lead researcher David Rigler provided a home for Genie, and was paid for being a foster parent. This is often seen as unethical, since Rigler had a financial interest in Genie and her case.
Tylenol – Advantages
Uniqueness of study – What happened to Tylenol was very unique and rare. While companies face crisis all the time, a public health crisis of this magnitude is very unique.
Tylenol – Disadvantages

- Course Catalog
- Group Discounts
- Gift Certificates
- For Libraries
- CEU Verification
- Medical Terminology
- Accounting Course
- Writing Basics
- QuickBooks Training
- Proofreading Class
- Sensitivity Training
- Excel Certificate
- Teach Online
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy

Case Study Research Method | Benefits, Limitations
Case study research is a type of qualitative research that helps understand an individual case or a specific situation in detail.
A case study can be written as a final report or it can be presented as an article in a journal or conference proceedings. Before you begin your next case study, you must know about its scope and limitations.
Table of Contents
What is a Case Study?
Case studies concentrate on gathering data about a particular object, event, or activity, like a certain business unit or organization. The person, group, organization, event, or circumstance that the researcher is interested in is the case in a case study.
Most importantly, a case study helps you understand the reasons for the occurrence or failure of a specific event. Case studies are common in business and management research . They can be qualitative or quantitative in nature. Researchers explore a single case, typically a business-related event or experiment.
Researchers document findings as case studies and present them with the help of visuals such as
Case Study- Example
This might be stated as a case study of a nearby school that encourages active learning.
When to do a case study?
Step by step guide for conducting case study research, define the problem, create a research plan, conduct field research.
Once you have a research plan, start your field research . You can use a variety of methods to conduct field research in a case study. You can use observation, interviews, or document analysis to collect data related to your case study.
Analyze data
Organize data, present case findings.
Once you have organized data and summarized it, it’s time to present your case findings. You can write a case study report or present it in the form of an article in a journal or conference proceedings.
Benefits of Case Study Research
Multiple case studies are frequently more robust and trustworthy than single case studies. Studies with multiple cases enable the formation of theories and a more thorough investigation of research problems .
Limitations of Case Study Research
Bottom line, other articles.
Please read through some of our other articles with examples and explanations if you’d like to learn more about research methodology.
Related Posts
Alternative hypothesis: types and examples, causal research: examples, benefits, and practical tips, 7 types of observational studies | examples, writing an introduction for a research paper: a guide (with examples), clinical research design: elements and importance, dependent variable in research: examples, what is an independent variable, how to write a high-quality conference paper, what are scholarly sources and where can you find them, how to write a conclusion for research paper | examples.

What are the limitations of case studies?
Case studies are in-depth analyses of a particular person, group, circumstance, or civilization. Data is frequently obtained from several sources and in various methods (e.g. observations & interviews). The patient’s medical history or personal case study is where the case study research methodology started, and case studies frequently look into one person in their investigations.
The content is mostly biographical and pertains to noteworthy events in the person’s past (i.e., retrospective) and current events in their day-to-day lives. The case study is not a research method in and of itself; rather, researchers select methods for data collection and analysis that will result in case study-worthy data.

Limitations of Case Studies
- There is insufficient scientific rigour and no basis for extending findings to a broader population.
- The researchers could inject their personal opinions into the case study (researcher bias).
- It is challenging to repeat.
- It’s expensive and time-consuming.
- The amount of analysis done with the instruments was constrained by the data and the time limits imposed.
It is hard to determine whether a case study represents a larger body of “similar” events because it only examines one individual, event, or group. As a result, the findings drawn in one instance might not apply in another. Since case studies are based on qualitative (descriptive) data, the psychologist’s interpretation is essential.
Author’s Update: Keep up to date on industry advancements, support, and training.
Pubrica Connect: Read articles about research, technology, and health communities daily.
Researcher Academy: Improve your manuscript by learning academic writing skills.
Language editing by Pubrica Author Services: Before submitting your work, double-check that it is written in proper English.
Translation by Pubrica Author Services: Translate your work into English professionally.
Search engine optimization (SEO): Make your article more visible by using SEO.
Your paper, your way: Save time by making your first submission simple.

The why and how of presenting research limitations: A case study
Results & Discussion
Kakoli Majumder

Case: An author approached Editage Insights seeking advice on a dilemma that she was faced with. She was the first author for a manuscript that she had co-authored with a colleague from her lab. While conducting the research, they discovered a flaw in the research design that might question the validity of the results. However, they decided to go ahead with the flawed design as they had already collected a significant amount of data.
In the final stages of the manuscript preparation, however, the co-author suggested that these flaws should not be discussed in the study limitations as it could lead to rejection. He even suggested that some of the percentages in charts and other figures be changed to make the results stronger. When the first author expressed her disagreement to manipulate the data and hide the limitations, the co-author refused to give his approval for submission of the manuscript. At this point, the first author approached us seeking advice on what could be done in this matter and whether it was advisable to hide the study limitations.
Action: Our publication experts strongly advised against tampering with the data in any way. We explained that data manipulation is a serious form of academic misconduct. We also advised that the flaw in research design should be included in the study limitations. If peer reviewers detected the flaw, they would definitely point it out in their comments, and this might lead to rejection. On the other hand, if the problem in the study design was acknowledged in the manuscript, this would demonstrate that the authors have a thorough understanding of the research process, population, methodology, and scope of the findings.
Additionally, we also explained that the study limitations should be written in such a way as to not undermine the impact of the research. This could be done by framing the limitations is a positive light. We guided the author on how to do this: one way was to briefly explain each limitation and then discuss why the results were important in spite of the limitation, and how it could provide direction for future research. If each limitation was systematically addressed in this way, it would in fact, give more rigor and validity to the study. In addition, the limitations should be followed by a summary of the study as a whole, thus reiterating the significance and value of the study. If approached in this way, the limitations could be expressed without undermining the impact of the study.

When the first author explained this to her co-author, he was convinced and agreed to make the changes suggested. He also gave his approval for submission, and the paper was finally submitted.
Summary: No study is expected to be flawless. Research is like building blocks and each new study is rooted in a limitation that existed in a previous study. It is important to communicate the limitations to your readers as they provide direction for future research.
Hiding the limitations only draws more attention to them and additionally gives the impression that the research process was not rigorous enough and that the authors did not have adequate understanding of the process and its applicability. Being self-critical and acknowledging the study’s limitations will give the impression that you are aware of what the study was not able to cover. Moreover, it would prevent the peer reviewer from pointing them out.
Do remember not to use an apologetic tone while stating the limitations. Rather, make each limitation clear while at the same time explaining how the study is still relevant and how this specific limitation opens up scope for further research. If expressed in this way, the study limitations will add to the overall credibility of your research and value in terms of validity and rigor of the research process.

Do you want to learn more about presenting limitations in your study? These posts will be helpful:
- What are the limitations of a study and how to write them?
- HANDBOOK: Write a convincing discussion section – The key to journal acceptance

Be the first to clap
for this article
Published on: Jun 19, 2019
- Discussion Section
You're looking to give wings to your academic career and publication journey. We like that!
Why don't we give you complete access! Create a free account and get unlimited access to all resources & a vibrant researcher community.
One click sign-in with your social accounts

Sign up via email
1536 visitors saw this today and 1210 signed up.
Subscribe to Manuscript Writing
Translate your research into a publication-worthy manuscript by understanding the nuances of academic writing. Subscribe and get curated reads that will help you write an excellent manuscript.
Confirm that you would also like to sign up for free personalized email coaching for this stage.
Related Reading

Planning to Write
Manuscript structure: How to convey your most important ideas through…

Study Background & Introduction
Tips for writing the perfect IMRAD manuscript

The secret to writing the Results and Discussion sections of a…
The why and how of presenting research limitations: A case study 4 min read
50 Motivational quotes and tips, 1 for each week of 2019 37 min read
Help your publisher help you: 6 Short tips to make the road to publication smoother 13 min read
Why is there resistance to considering AI for manuscript evaluation? An interview with Alessandro Checco 8 min read
What can journals do to increase researcher trust in peer review? An expert opinion 6 min read
Trending Searches
- Statement of the problem
- Background of study
- Scope of the study
- Types of qualitative research
- Rationale of the study
- Concept paper
- Literature review
- Introduction in research
- Under "Editor Evaluation"
- Ethics in research
Recent Searches
- Review paper
- Responding to reviewer comments
- Predatory publishers
- Scope and delimitations
- Open access
- Plagiarism in research
- Journal selection tips
- Editor assigned
- Types of articles
- "Reject and Resubmit" status
- Decision in process
- Conflict of interest

Home » Pros and Cons » 12 Case Study Method Advantages and Disadvantages
12 Case Study Method Advantages and Disadvantages
A case study is an investigation into an individual circumstance. The investigation may be of a single person, business, event, or group. The investigation involves collecting in-depth data about the individual entity through the use of several collection methods. Interviews and observation are two of the most common forms of data collection used.
The case study method was originally developed in the field of clinical medicine. It has expanded since to other industries to examine key results, either positive or negative, that were received through a specific set of decisions. This allows for the topic to be researched with great detail, allowing others to glean knowledge from the information presented.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of using the case study method.
List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method
1. it turns client observations into useable data..
Case studies offer verifiable data from direct observations of the individual entity involved. These observations provide information about input processes. It can show the path taken which led to specific results being generated. Those observations make it possible for others, in similar circumstances, to potentially replicate the results discovered by the case study method.
2. It turns opinion into fact.
Case studies provide facts to study because you’re looking at data which was generated in real-time. It is a way for researchers to turn their opinions into information that can be verified as fact because there is a proven path of positive or negative development. Singling out a specific incident also provides in-depth details about the path of development, which gives it extra credibility to the outside observer.
3. It is relevant to all parties involved.
Case studies that are chosen well will be relevant to everyone who is participating in the process. Because there is such a high level of relevance involved, researchers are able to stay actively engaged in the data collection process. Participants are able to further their knowledge growth because there is interest in the outcome of the case study. Most importantly, the case study method essentially forces people to make a decision about the question being studied, then defend their position through the use of facts.
4. It uses a number of different research methodologies.
The case study method involves more than just interviews and direct observation. Case histories from a records database can be used with this method. Questionnaires can be distributed to participants in the entity being studies. Individuals who have kept diaries and journals about the entity being studied can be included. Even certain experimental tasks, such as a memory test, can be part of this research process.
5. It can be done remotely.
Researchers do not need to be present at a specific location or facility to utilize the case study method. Research can be obtained over the phone, through email, and other forms of remote communication. Even interviews can be conducted over the phone. That means this method is good for formative research that is exploratory in nature, even if it must be completed from a remote location.
6. It is inexpensive.
Compared to other methods of research, the case study method is rather inexpensive. The costs associated with this method involve accessing data, which can often be done for free. Even when there are in-person interviews or other on-site duties involved, the costs of reviewing the data are minimal.
7. It is very accessible to readers.
The case study method puts data into a usable format for those who read the data and note its outcome. Although there may be perspectives of the researcher included in the outcome, the goal of this method is to help the reader be able to identify specific concepts to which they also relate. That allows them to discover unusual features within the data, examine outliers that may be present, or draw conclusions from their own experiences.
List of the Disadvantages of the Case Study Method
1. it can have influence factors within the data..
Every person has their own unconscious bias. Although the case study method is designed to limit the influence of this bias by collecting fact-based data, it is the collector of the data who gets to define what is a “fact” and what is not. That means the real-time data being collected may be based on the results the researcher wants to see from the entity instead. By controlling how facts are collected, a research can control the results this method generates.
2. It takes longer to analyze the data.
The information collection process through the case study method takes much longer to collect than other research options. That is because there is an enormous amount of data which must be sifted through. It’s not just the researchers who can influence the outcome in this type of research method. Participants can also influence outcomes by given inaccurate or incomplete answers to questions they are asked. Researchers must verify the information presented to ensure its accuracy, and that takes time to complete.
3. It can be an inefficient process.
Case study methods require the participation of the individuals or entities involved for it to be a successful process. That means the skills of the researcher will help to determine the quality of information that is being received. Some participants may be quiet, unwilling to answer even basic questions about what is being studied. Others may be overly talkative, exploring tangents which have nothing to do with the case study at all. If researchers are unsure of how to manage this process, then incomplete data is often collected.

4. It requires a small sample size to be effective.
The case study method requires a small sample size for it to yield an effective amount of data to be analyzed. If there are different demographics involved with the entity, or there are different needs which must be examined, then the case study method becomes very inefficient.
5. It is a labor-intensive method of data collection.
The case study method requires researchers to have a high level of language skills to be successful with data collection. Researchers must be personally involved in every aspect of collecting the data as well. From reviewing files or entries personally to conducting personal interviews, the concepts and themes of this process are heavily reliant on the amount of work each researcher is willing to put into things.
These case study method advantages and disadvantages offer a look at the effectiveness of this research option. With the right skill set, it can be used as an effective tool to gather rich, detailed information about specific entities. Without the right skill set, the case study method becomes inefficient and inaccurate.
Related Posts:
- 25 Best Ways to Overcome the Fear of Failure
- Monroe's Motivated Sequence Explained [with Examples]
- 21 Most Effective Bundle Pricing Strategies with Examples
- Force Field Analysis Explained with Examples

- About This Site
- What is social theory?
- Habermas/Parsons
- Frankfurt School
- Inequalities
- Research Students
- Dirty Looks
- Latest Posts
- Pedagogy & Curriculum
- Contributors
- Publications
Select Page
What are the benefits and drawbacks of case study research?
Posted by Mark Murphy | May 24, 2014 | Method , Research Students | 0

There should be no doubt that with case studies what you gain in depth you lose in breadth – this is the unavoidable compromise that needs to be understood from the beginning of the research process. So this is neither an advantage nor a disadvantage as one aspect cancels out the benefits/drawbacks of the other – there are other benefits and drawbacks that need attention however …
- Their flexibility: case studies are popular for a number of reasons, one being that they can be conducted at various points in the research process. Researchers are known to favour them as a way to develop ideas for more extensive research in the future – pilot studies often take the form of case studies. They are also effective conduits for a broad range of research methods; in that sense they are non-prejudicial against any particular type of research – focus groups are just as welcome in case study research as are questionnaires or participant observation.
- Capturing reality: One of their key benefits is their ability to capture what Hodkinson and Hodkinson call ‘lived reality’ (2001: 3). As they put it, case studies have the potential, when applied successfully, to ‘retain more of the “noise” of real life than many other types of research’ (Hodkinson and Hodkinson, 2001: 3). The importance of ‘noise’ and its place in research is especially important in contexts such as education, for example in schools where background noise is unavoidable. Educational contexts are always complex, and as a result it is difficult to exclude other unwanted variables, ‘some of which may only have real significance for one of their students’ (Hodkinson and Hodkinson, 2001, 4).
- The challenge of generality: At the same time, given their specificity, care needs to be taken when attempting to generalise from the findings. While there’s no inherent flaw in case study design that precludes its broader application, it is preferable that researchers choose their case study sites carefully, while also basing their analysis within existing research findings that have been generated via other research designs. No design is infallible but so often has the claim against case studies been made, that some of the criticism (unwarranted and unfair in many cases) has stuck.
- Suspicion of amateurism: Less partisan researchers might wonder whether the case study offers the time and finance-strapped researcher a convenient and pragmatic source of data, providing findings and recommendations that, given the nature of case studies, can neither be confirmed nor denied, in terms of utility or veracity. Who is to say that case studies offer anything more than a story to tell, and nothing more than that?
- But alongside this suspicion is another more insiduous one – a notion that ‘stories’ are not what social science research is about. This can be a concern for those who favour case study research, as the political consequences can be hard to ignore. That said, so much research is based either on peoples’ lives or the impact of other issues (poverty, institutional policy) on their lives, so the stories of what actually occurs in their lives or in professional environments tend to be an invaluable source of evidence. The fact is that stories (individual, collective, institutional) have a vital role to play in the world of research. And to play the specific v. general card against case study design suggests a tendency towards forms of research fundamentalism as opposed to any kind of rational and objective take on case study’s strengths and limitations.
- Preciousness: Having said that, researchers should not fall into the trap (surprising how often this happens) of assuming that case study data speaks for itself – rarely is this ever the case, an assumption that is as patronising to research subjects as it is false. The role of the researcher is both to describe social phenomena and also to explain – i.e., interpret. Without interpretation the research findings lack meaningful presentation – they present themselves as fact when of course the reality of ‘facts’ is one of the reasons why such research is carried out.
- Conflation of political/research objectives: Another trap that case study researchers sometimes fall into is presenting research findings as if they were self-evidently true, as if the stories were beyond criticism. This is often accompanied by a vague attachment to the notion that research is a political process – one that is performed as a form of liberation against for example policies that seek to ignore the stories of those who ‘suffer’ at the hands of overbearing political or economic imperatives. Case study design should not be viewed as a mechanism for providing a ‘local’ bulwark against the ‘global’ – bur rather as a mechanism for checking the veracity of universalist claims (at least one of its objectives). The valorisation of particularism can only get you so far in social research.
[This post is adapted from material in ‘Research and Education’ (Curtis, Murphy and Shields , Routledge 2014), pp. 80-82].
Reference: Hodkinson, P. and H. Hodkinson (2001). The strengths and limitations of case study research. Paper presented to the Learning and Skills Development Agency conference, Making an impact on policy and practice , Cambridge, 5-7 December 2001, downloaded from h ttp://education.exeter.ac.uk/tlc/docs/publications/LE_PH_PUB_05.12.01.rtf.26.01.2013
About The Author
Mark Murphy
Mark Murphy is a Reader in Education and Public Policy at the University of Glasgow. He previously worked as an academic at King’s College, London, University of Chester, University of Stirling, National University of Ireland, Maynooth, University College Dublin and Northern Illinois University. Mark is an active researcher in the fields of education and public policy. His research interests include educational sociology, critical theory, accountability in higher education, and public sector reform.
Related Posts

New Bloomsbury book series: Social theory and methodology in education research
April 28, 2016

Finding your writing flow
July 15, 2015

Using Bourdieu in my PhD on Parental Influence: Irene Kleanthous Writes
January 31, 2013

I am moving to Norway
August 14, 2013
Recent Posts


The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.

Case Study Method – 18 Advantages and Disadvantages
The case study method uses investigatory research as a way to collect data about specific demographics. This approach can apply to individuals, businesses, groups, or events. Each participant receives an equal amount of participation, offering information for collection that can then find new insights into specific trends, ideas, of hypotheses.
Interviews and research observation are the two standard methods of data collection used when following the case study method.
Researchers initially developed the case study method to develop and support hypotheses in clinical medicine. The benefits found in these efforts led the approach to transition to other industries, allowing for the examination of results through proposed decisions, processes, or outcomes. Its unique approach to information makes it possible for others to glean specific points of wisdom that encourage growth.
Several case study method advantages and disadvantages can appear when researchers take this approach.
List of the Advantages of the Case Study Method
1. It requires an intensive study of a specific unit. Researchers must document verifiable data from direct observations when using the case study method. This work offers information about the input processes that go into the hypothesis under consideration. A casual approach to data-gathering work is not effective if a definitive outcome is desired. Each behavior, choice, or comment is a critical component that can verify or dispute the ideas being considered.
Intensive programs can require a significant amount of work for researchers, but it can also promote an improvement in the data collected. That means a hypothesis can receive immediate verification in some situations.
2. No sampling is required when following the case study method. This research method studies social units in their entire perspective instead of pulling individual data points out to analyze them. That means there is no sampling work required when using the case study method. The hypothesis under consideration receives support because it works to turn opinions into facts, verifying or denying the proposals that outside observers can use in the future.
Although researchers might pay attention to specific incidents or outcomes based on generalized behaviors or ideas, the study itself won’t sample those situations. It takes a look at the “bigger vision” instead.
3. This method offers a continuous analysis of the facts. The case study method will look at the facts continuously for the social group being studied by researchers. That means there aren’t interruptions in the process that could limit the validity of the data being collected through this work. This advantage reduces the need to use assumptions when drawing conclusions from the information, adding validity to the outcome of the study over time. That means the outcome becomes relevant to both sides of the equation as it can prove specific suppositions or invalidate a hypothesis under consideration.
This advantage can lead to inefficiencies because of the amount of data being studied by researchers. It is up to the individuals involved in the process to sort out what is useful and meaningful and what is not.
4. It is a useful approach to take when formulating a hypothesis. Researchers will use the case study method advantages to verify a hypothesis under consideration. It is not unusual for the collected data to lead people toward the formulation of new ideas after completing this work. This process encourages further study because it allows concepts to evolve as people do in social or physical environments. That means a complete data set can be gathered based on the skills of the researcher and the honesty of the individuals involved in the study itself.
Although this approach won’t develop a societal-level evaluation of a hypothesis, it can look at how specific groups will react in various circumstances. That information can lead to a better decision-making process in the future for everyone involved.
5. It provides an increase in knowledge. The case study method provides everyone with analytical power to increase knowledge. This advantage is possible because it uses a variety of methodologies to collect information while evaluating a hypothesis. Researchers prefer to use direct observation and interviews to complete their work, but it can also advantage through the use of questionnaires. Participants might need to fill out a journal or diary about their experiences that can be used to study behaviors or choices.
Some researchers incorporate memory tests and experimental tasks to determine how social groups will interact or respond in specific situations. All of this data then works to verify the possibilities that a hypothesis proposes.
6. The case study method allows for comparisons. The human experience is one that is built on individual observations from group situations. Specific demographics might think, act, or respond in particular ways to stimuli, but each person in that group will also contribute a small part to the whole. You could say that people are sponges that collect data from one another every day to create individual outcomes.
The case study method allows researchers to take the information from each demographic for comparison purposes. This information can then lead to proposals that support a hypothesis or lead to its disruption.
7. Data generalization is possible using the case study method. The case study method provides a foundation for data generalization, allowing researches to illustrate their statistical findings in meaningful ways. It puts the information into a usable format that almost anyone can use if they have the need to evaluate the hypothesis under consideration. This process makes it easier to discover unusual features, unique outcomes, or find conclusions that wouldn’t be available without this method. It does an excellent job of identifying specific concepts that relate to the proposed ideas that researchers were verifying through their work.
Generalization does not apply to a larger population group with the case study method. What researchers can do with this information is to suggest a predictable outcome when similar groups are placed in an equal situation.
8. It offers a comprehensive approach to research. Nothing gets ignored when using the case study method to collect information. Every person, place, or thing involved in the research receives the complete attention of those seeking data. The interactions are equal, which means the data is comprehensive and directly reflective of the group being observed.
This advantage means that there are fewer outliers to worry about when researching an idea, leading to a higher level of accuracy in the conclusions drawn by the researchers.
9. The identification of deviant cases is possible with this method. The case study method of research makes it easier to identify deviant cases that occur in each social group. These incidents are units (people) that behave in ways that go against the hypothesis under consideration. Instead of ignoring them like other options do when collecting data, this approach incorporates the “rogue” behavior to understand why it exists in the first place.
This advantage makes the eventual data and conclusions gathered more reliable because it incorporates the “alternative opinion” that exists. One might say that the case study method places as much emphasis on the yin as it does the yang so that the whole picture becomes available to the outside observer.
10. Questionnaire development is possible with the case study method. Interviews and direct observation are the preferred methods of implementing the case study method because it is cheap and done remotely. The information gathered by researchers can also lead to farming questionnaires that can farm additional data from those being studied. When all of the data resources come together, it is easier to formulate a conclusion that accurately reflects the demographics.
Some people in the case study method may try to manipulate the results for personal reasons, but this advantage makes it possible to identify this information readily. Then researchers can look into the thinking that goes into the dishonest behaviors observed.
List of the Disadvantages of the Case Study Method
1. The case study method offers limited representation. The usefulness of the case study method is limited to a specific group of representatives. Researchers are looking at a specific demographic when using this option. That means it is impossible to create any generalization that applies to the rest of society, an organization, or a larger community with this work. The findings can only apply to other groups caught in similar circumstances with the same experiences.
It is useful to use the case study method when attempting to discover the specific reasons why some people behave in a specific way. If researchers need something more generalized, then a different method must be used.
2. No classification is possible with the case study method. This disadvantage is also due to the sample size in the case study method. No classification is possible because researchers are studying such a small unit, group, or demographic. It can be an inefficient process since the skills of the researcher help to determine the quality of the data being collected to verify the validity of a hypothesis. Some participants may be unwilling to answer or participate, while others might try to guess at the outcome to support it.
Researchers can get trapped in a place where they explore more tangents than the actual hypothesis with this option. Classification can occur within the units being studied, but this data cannot extrapolate to other demographics.
3. The case study method still offers the possibility of errors. Each person has an unconscious bias that influences their behaviors and choices. The case study method can find outliers that oppose a hypothesis fairly easily thanks to its emphasis on finding facts, but it is up to the researchers to determine what information qualifies for this designation. If the results from the case study method are surprising or go against the opinion of participating individuals, then there is still the possibility that the information will not be 100% accurate.
Researchers must have controls in place that dictate how data gathering work occurs. Without this limitation in place, the results of the study cannot be guaranteed because of the presence of bias.
4. It is a subjective method to use for research. Although the purpose of the case study method of research is to gather facts, the foundation of what gets gathered is still based on opinion. It uses the subjective method instead of the objective one when evaluating data, which means there can be another layer of errors in the information to consider.
Imagine that a researcher interprets someone’s response as “angry” when performing direct observation, but the individual was feeling “shame” because of a decision they made. The difference between those two emotions is profound, and it could lead to information disruptions that could be problematic to the eventual work of hypothesis verification.
5. The processes required by the case study method are not useful for everyone. The case study method uses a person’s memories, explanations, and records from photographs and diaries to identify interactions on influences on psychological processes. People are given the chance to describe what happens in the world around them as a way for researchers to gather data. This process can be an advantage in some industries, but it can also be a worthless approach to some groups.
If the social group under study doesn’t have the information, knowledge, or wisdom to provide meaningful data, then the processes are no longer useful. Researchers must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of the case study method before starting their work to determine if the possibility of value exists. If it does not, then a different method may be necessary.
6. It is possible for bias to form in the data. It’s not just an unconscious bias that can form in the data when using the case study method. The narrow study approach can lead to outright discrimination in the data. Researchers can decide to ignore outliers or any other information that doesn’t support their hypothesis when using this method. The subjective nature of this approach makes it difficult to challenge the conclusions that get drawn from this work, and the limited pool of units (people) means that duplication is almost impossible.
That means unethical people can manipulate the results gathered by the case study method to their own advantage without much accountability in the process.
7. This method has no fixed limits to it. This method of research is highly dependent on situational circumstances rather than overarching societal or corporate truths. That means the researcher has no fixed limits of investigation. Even when controls are in place to limit bias or recommend specific activities, the case study method has enough flexibility built into its structures to allow for additional exploration. That means it is possible for this work to continue indefinitely, gathering data that never becomes useful.
Scientists began to track the health of 268 sophomores at Harvard in 1938. The Great Depression was in its final years at that point, so the study hoped to reveal clues that lead to happy and healthy lives. It continues still today, now incorporating the children of the original participants, providing over 80 years of information to sort through for conclusions.
8. The case study method is time-consuming and expensive. The case study method can be affordable in some situations, but the lack of fixed limits and the ability to pursue tangents can make it a costly process in most situations. It takes time to gather the data in the first place, and then researchers must interpret the information received so that they can use it for hypothesis evaluation. There are other methods of data collection that can be less expensive and provide results faster.
That doesn’t mean the case study method is useless. The individualization of results can help the decision-making process advance in a variety of industries successfully. It just takes more time to reach the appropriate conclusion, and that might be a resource that isn’t available.
The advantages and disadvantages of the case study method suggest that the helpfulness of this research option depends on the specific hypothesis under consideration. When researchers have the correct skills and mindset to gather data accurately, then it can lead to supportive data that can verify ideas with tremendous accuracy.
This research method can also be used unethically to produce specific results that can be difficult to challenge.
When bias enters into the structure of the case study method, the processes become inefficient, inaccurate, and harmful to the hypothesis. That’s why great care must be taken when designing a study with this approach. It might be a labor-intensive way to develop conclusions, but the outcomes are often worth the investments needed.
How to Write Limitations of the Study (with examples)
This blog emphasizes the importance of recognizing and effectively writing about limitations in research. It discusses the types of limitations, their significance, and provides guidelines for writing about them, highlighting their role in advancing scholarly research.
Updated on August 24, 2023

No matter how well thought out, every research endeavor encounters challenges. There is simply no way to predict all possible variances throughout the process.
These uncharted boundaries and abrupt constraints are known as limitations in research . Identifying and acknowledging limitations is crucial for conducting rigorous studies. Limitations provide context and shed light on gaps in the prevailing inquiry and literature.
This article explores the importance of recognizing limitations and discusses how to write them effectively. By interpreting limitations in research and considering prevalent examples, we aim to reframe the perception from shameful mistakes to respectable revelations.
What are limitations in research?
In the clearest terms, research limitations are the practical or theoretical shortcomings of a study that are often outside of the researcher’s control . While these weaknesses limit the generalizability of a study’s conclusions, they also present a foundation for future research.
Sometimes limitations arise from tangible circumstances like time and funding constraints, or equipment and participant availability. Other times the rationale is more obscure and buried within the research design. Common types of limitations and their ramifications include:
- Theoretical: limits the scope, depth, or applicability of a study.
- Methodological: limits the quality, quantity, or diversity of the data.
- Empirical: limits the representativeness, validity, or reliability of the data.
- Analytical: limits the accuracy, completeness, or significance of the findings.
- Ethical: limits the access, consent, or confidentiality of the data.
Regardless of how, when, or why they arise, limitations are a natural part of the research process and should never be ignored . Like all other aspects, they are vital in their own purpose.
Why is identifying limitations important?
Whether to seek acceptance or avoid struggle, humans often instinctively hide flaws and mistakes. Merging this thought process into research by attempting to hide limitations, however, is a bad idea. It has the potential to negate the validity of outcomes and damage the reputation of scholars.
By identifying and addressing limitations throughout a project, researchers strengthen their arguments and curtail the chance of peer censure based on overlooked mistakes. Pointing out these flaws shows an understanding of variable limits and a scrupulous research process.
Showing awareness of and taking responsibility for a project’s boundaries and challenges validates the integrity and transparency of a researcher. It further demonstrates the researchers understand the applicable literature and have thoroughly evaluated their chosen research methods.
Presenting limitations also benefits the readers by providing context for research findings. It guides them to interpret the project’s conclusions only within the scope of very specific conditions. By allowing for an appropriate generalization of the findings that is accurately confined by research boundaries and is not too broad, limitations boost a study’s credibility .
Limitations are true assets to the research process. They highlight opportunities for future research. When researchers identify the limitations of their particular approach to a study question, they enable precise transferability and improve chances for reproducibility.
Simply stating a project’s limitations is not adequate for spurring further research, though. To spark the interest of other researchers, these acknowledgements must come with thorough explanations regarding how the limitations affected the current study and how they can potentially be overcome with amended methods.
How to write limitations
Typically, the information about a study’s limitations is situated either at the beginning of the discussion section to provide context for readers or at the conclusion of the discussion section to acknowledge the need for further research. However, it varies depending upon the target journal or publication guidelines.
Don’t hide your limitations
It is also important to not bury a limitation in the body of the paper unless it has a unique connection to a topic in that section. If so, it needs to be reiterated with the other limitations or at the conclusion of the discussion section. Wherever it is included in the manuscript, ensure that the limitations section is prominently positioned and clearly introduced.
While maintaining transparency by disclosing limitations means taking a comprehensive approach, it is not necessary to discuss everything that could have potentially gone wrong during the research study. If there is no commitment to investigation in the introduction, it is unnecessary to consider the issue a limitation to the research. Wholly consider the term ‘limitations’ and ask, “Did it significantly change or limit the possible outcomes?” Then, qualify the occurrence as either a limitation to include in the current manuscript or as an idea to note for other projects.
Writing limitations
Once the limitations are concretely identified and it is decided where they will be included in the paper, researchers are ready for the writing task. Including only what is pertinent, keeping explanations detailed but concise, and employing the following guidelines is key for crafting valuable limitations:
1) Identify and describe the limitations : Clearly introduce the limitation by classifying its form and specifying its origin. For example:
- An unintentional bias encountered during data collection
- An intentional use of unplanned post-hoc data analysis
2) Explain the implications : Describe how the limitation potentially influences the study’s findings and how the validity and generalizability are subsequently impacted. Provide examples and evidence to support claims of the limitations’ effects without making excuses or exaggerating their impact. Overall, be transparent and objective in presenting the limitations, without undermining the significance of the research.
3) Provide alternative approaches for future studies : Offer specific suggestions for potential improvements or avenues for further investigation. Demonstrate a proactive approach by encouraging future research that addresses the identified gaps and, therefore, expands the knowledge base.
Whether presenting limitations as an individual section within the manuscript or as a subtopic in the discussion area, authors should use clear headings and straightforward language to facilitate readability. There is no need to complicate limitations with jargon, computations, or complex datasets.
Examples of common limitations
Limitations are generally grouped into two categories , methodology and research process .
Methodology limitations
Methodology may include limitations due to:
- Sample size
- Lack of available or reliable data
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic
- Measure used to collect the data
- Self-reported data

The researcher is addressing how the large sample size requires a reassessment of the measures used to collect and analyze the data.
Research process limitations
Limitations during the research process may arise from:
- Access to information
- Longitudinal effects
- Cultural and other biases
- Language fluency
- Time constraints

The author is pointing out that the model’s estimates are based on potentially biased observational studies.
Final thoughts
Successfully proving theories and touting great achievements are only two very narrow goals of scholarly research. The true passion and greatest efforts of researchers comes more in the form of confronting assumptions and exploring the obscure.
In many ways, recognizing and sharing the limitations of a research study both allows for and encourages this type of discovery that continuously pushes research forward. By using limitations to provide a transparent account of the project's boundaries and to contextualize the findings, researchers pave the way for even more robust and impactful research in the future.
Charla Viera, MS
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.
- The Scientist University
How to Present a Research Study’s Limitations
All studies have imperfections, but how to present them without diminishing the value of the work can be tricky..

Nathan Ni holds a PhD from Queens University. He is a science editor for The Scientist’s Creative Services Team who strives to better understand and communicate the relationships between health and disease.
View full profile.
Learn about our editorial policies.

Scientists work with many different limitations. First and foremost, they navigate informational limitations, work around knowledge gaps when designing studies, formulating hypotheses, and analyzing data. They also handle technical limitations, making the most of what their hands, equipment, and instruments can achieve. Finally, researchers must also manage logistical limitations. Scientists will often experience sample scarcity, financial issues, or simply be unable to access the technology or materials that they want.
All scientific studies have limitations, and no study is perfect. Researchers should not run from this reality, but engage it directly. It is better to directly address the specific limitations of the work in question, and doing so is actually a way to demonstrate an author’s proficiency and aptitude.
Do: Be Transparent
From a practical perspective, being transparent is the main key to directly addressing the specific limitations of a study. Was there an experiment that the researchers wanted to perform but could not, or a sample that existed that the scientists could not obtain? Was there a piece of knowledge that would explain a question raised by the data presented within the current study? If the answer is yes, the authors should mention this and elaborate upon it within the discussion section.
Asking and addressing these questions demonstrates that the authors have knowledge, understanding, and expertise of the subject area beyond what the study directly investigated. It further demonstrates a solid grasp of the existing literature—which means a solid grasp of what others are doing, what techniques they are using, and what limitations impede their own studies. This information helps the authors contextualize where their study fits within what others have discovered, thereby mitigating the perceived effect of a given limitation on the study’s legitimacy. In essence, this strategy turns limitations, often considered weaknesses, into strengths.
For example, in their 2021 Cell Reports study on macrophage polarization mechanisms, dermatologist Alexander Marneros and colleagues wrote the following. 1
A limitation of studying macrophage polarization in vitro is that this approach only partially captures the tissue microenvironment context in which many different factors affect macrophage polarization. However, it is likely that the identified signaling mechanisms that promote polarization in vitro are also critical for polarization mechanisms that occur in vivo. This is supported by our observation that trametinib and panobinostat inhibited M2-type macrophage polarization not only in vitro but also in skin wounds and laser-induced CNV lesions.
This is a very effective structure. In the first sentence ( yellow ), the authors outlined the limitation. In the next sentence ( green ), they offered a rationalization that mitigates the effect of the limitation. Finally, they provided the evidence ( blue ) for this rationalization, using not just information from the literature, but also data that they obtained in their study specifically for this purpose.

Don't: Be Defensive
It can feel natural to avoid talking about a study’s limitations. Scientists may believe that mentioning the drawbacks still present in their study will jeopardize their chances of publication. As such, researchers will sometimes skirt around the issue. They will present “boilerplate faults”—generalized concerns about sample size/diversity and time limitations that all researchers face—rather than honestly discussing their own study. Alternatively, they will describe their limitations in a defensive manner, positioning their problems as something that “could not be helped”—as something beyond what science can currently achieve.
However, their audience can see through this, because they are largely peers who understand and have experienced how modern research works. They can tell the difference between global challenges faced by every scientific study and limitations that are specific to a single study. Avoiding these specific limitations can therefore betray a lack of confidence that the study is good enough to withstand problems stemming from legitimate limitations. As such, researchers should actively engage with the greater scientific implications of the limitations that they face. Indeed, doing this is actually a way to demonstrate an author’s proficiency and aptitude.
In an example, neurogeneticist Nancy Bonini and colleagues, in their publication in Nature , discussed a question raised by their data that they have elected not to directly investigate in this study, writing “ Among the intriguing questions raised by these data is how senescent glia promote LDs in other glia. ” To show both the legitimacy of the question and how seriously they have considered it, the authors provided a comprehensive summary of the literature in the following seven sentences, offering two hypotheses backed by a combined eight different sources. 2 Rather than shying away from a limitation, they attacked it as something to be curious about and to discuss. This is not just a very effective way of demonstrating their expertise, but it frames the limitation as something that, when overcome, will build upon the present study rather than something that negatively affects the legitimacy of their current findings.
Striking the Right Balance
Scientists have to navigate the fine line between acknowledging the limitations of their study while also not diminishing the effect and value of their own work. To be aware of legitimate limitations and properly assess and dissect them shows a profound understanding of a field, where the study fits within that field, and what the rest of the scientific community are doing and what challenges they face.
All studies are parts of a greater whole. Pretending otherwise is a disservice to the scientific community.
Looking for more information on scientific writing? Check out The Scientist’ s TS SciComm section. Looking for some help putting together a manuscript, a figure, a poster, or anything else? The Scientist ’s Scientific Services may have the professional help that you need.
- He L, et al. Global characterization of macrophage polarization mechanisms and identification of M2-type polarization inhibitors . Cell Rep . 2021;37(5):109955.
- Byrns CN, et al. Senescent glia link mitochondrial dysfunction and lipid accumulation . Nature . 2024.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.9(8); 2017 Aug

Case Reports, Case Series – From Clinical Practice to Evidence-Based Medicine in Graduate Medical Education
Jerry w sayre.
1 Family Medicine, North Florida Regional Medical Center
Hale Z Toklu
2 Graduate Medical Education, North Florida Regional Medical Center
Joseph Mazza
3 Department of Clinical Research, Marshfield Clinic Research Foundation
Steven Yale
4 Internal Medicine, University of Central Florida College of Medicine
Case reports and case series or case study research are descriptive studies that are prepared for illustrating novel, unusual, or atypical features identified in patients in medical practice, and they potentially generate new research questions. They are empirical inquiries or investigations of a patient or a group of patients in a natural, real-world clinical setting. Case study research is a method that focuses on the contextual analysis of a number of events or conditions and their relationships. There is disagreement among physicians on the value of case studies in the medical literature, particularly for educators focused on teaching evidence-based medicine (EBM) for student learners in graduate medical education. Despite their limitations, case study research is a beneficial tool and learning experience in graduate medical education and among novice researchers. The preparation and presentation of case studies can help students and graduate medical education programs evaluate and apply the six American College of Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) competencies in the areas of medical knowledge, patient care, practice-based learning, professionalism, systems-based practice, and communication. A goal in graduate medical education should be to assist residents to expand their critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. These attributes are required in the teaching and practice of EBM. In this aspect, case studies provide a platform for developing clinical skills and problem-based learning methods. Hence, graduate medical education programs should encourage, assist, and support residents in the publication of clinical case studies; and clinical teachers should encourage graduate students to publish case reports during their graduate medical education.
Introduction
Case reports and case series or case study research are descriptive studies to present patients in their natural clinical setting. Case reports, which generally consist of three or fewer patients, are prepared to illustrate features in the practice of medicine and potentially create new research questions that may contribute to the acquisition of additional knowledge in the literature. Case studies involve multiple patients; they are a qualitative research method and include in-depth analyses or experiential inquiries of a person or group in their real-world setting. Case study research focuses on the contextual analysis of several events or conditions and their relationships [ 1 ]. In addition to their teaching value for students and graduate medical education programs, case reports provide a starting point for novice investigators, which may prepare and encourage them to seek more contextual writing experiences for future research investigation. It may also provide senior physicians with clues about emerging epidemics or a recognition of previously unrecognized syndromes. Limitations primarily involve the lack of generalizability and implications in clinical practice, which are factors extraneous to the learning model (Table (Table1 1 ).
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| One case to initiate a signal (case report) | No control (uncontrolled) |
| Provide stronger evidence with multiple cases (cases series) | Difficult to compare different cases |
| Observational | Cases may not be generalizable |
| Educational | Selection bias |
| Easy to do (fast and no financial support needed) | Unknown future outcome/follow-up |
| Identify rare manifestations of a disease or drug |
There is disagreement among physicians on the value of case reports in the medical literature and in evidence-based medicine (EBM) [ 2 ]. EBM aims to optimize decision-making by using evidence from well-conducted research. Therefore, not all data has the same value as the evidence. The pyramid (Figure (Figure1) 1 ) classifies publications based on their study outlines and according to the power of evidence they provide [ 2 - 3 ]. In the classical pyramid represented below, systematic reviews and a meta-analysis are expected to provide the strongest evidence. However, a recent modification of the pyramid was suggested by Murad et al. [ 2 ]: the meta-analysis and systematic reviews are removed from the pyramid and are suggested to be a lens through which evidence is viewed (Figure 1 ).

Modified from Murad et al. [ 2 ]
Because case reports do not rank highly in the hierarchy of evidence and are not frequently cited, as they describe the clinical circumstances of single patients, they are seldom published by high-impact medical journals. However, case reports are proposed to have significant educational value because they advance medical knowledge and constitute evidence for EBM. In addition, well-developed publication resources can be difficult to find, especially for medical residents; those that do exist vary in quality and may not be suitable for the aim and scope of the journals. Over the last several years, a number (approximately 160) of new peer-reviewed journals that focus on publishing case reports have emerged. These are mostly open-access journals with considerably high acceptance rates [ 4 ]. Packer et al. reported a 6% publication rate for case reports [ 5 ]; however, they did not disclose the number of papers submitted but rejected and neither did they state whether any of the reported cases were submitted to open-access journals.
The development of open-access journals has created a new venue for students and faculty to publish. In contrast to subscription-based and peer-reviewed e-journals, many of these new case report journals are not adequately reviewed and, instead, have a questionably high acceptance rate [ 4 ]. There, however, remains the issue of the fee-based publication of case reports in open-access journals without proper peer reviews, which increases the burden of scientific literature. Trainees should be made aware of the potential for academic dilution, particularly with some open-access publishers. While case reports with high-quality peer reviews are associated with a relatively low acceptance rate, this rigorous process introduces trainees to the experience and expectations of peer reviews and addresses other issues or flaws not considered prior to submission. We believe that these are important skills that should be emphasized and experienced during training, and authors should seek these journals for the submission of their manuscripts.
Importance of Case Reports and Case Series in Graduate Medical Education
The Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) has challenged faculties to adapt teaching methodologies to accommodate the different learning modalities of the next generation of physicians. As evidenced by its implementation by ACGME, competency-based medical education is rapidly gaining international acceptance, moving from classic didactic lectures to self-directed learning opportunities with experiential learning aids in the development of critical cognitive and scholarly skills. As graduate medical educators, we are in agreement with Packer et al. about the value of the educational benefits resulting from student-generated case reports [ 5 ]. Case study assignments help residents develop a variety of key skills, as previously described. EBM is an eventual decision-making process for executing the most appropriate treatment approach by using the tools that are compatible with the national health policy, medical evidence, and the personal factors of physician and patient (Figure (Figure2). The 2 ). The practice of identifying and developing a case study creates a learning opportunity for listening skills and appreciation for the patient’s narrative as well as for developing critical learning and thinking skills that are directly applicable to the practice of EBM. This critically important process simultaneously enhances both the medical and the humanistic importance of physician-patient interaction. In addition, case-based learning is an active learner-centered approach for medical students and residents. It serves as a curricular context, which can promote the retention of information and evidence-based thinking.

Modified from Toklu et al. 2015 [ 3 ]
The value of case studies in the medical literature is controversial among physicians. Despite their limitations, clinical case reports and case series are beneficial tools in graduate medical education. The preparation and presentation of case studies can help students and residents acquire and apply clinical competencies in the areas of medical knowledge, practice-based learning, systems-based practice, professionalism, and communication. In this aspect, case studies provide a tool for developing clinical skills through problem-based learning methods. As a result, journals should encourage the publication of clinical case studies from graduate medical education programs through a commonly applied peer-review process, and clinical teachers should promote medical residents to publish case reports during their graduate medical education.
The content published in Cureus is the result of clinical experience and/or research by independent individuals or organizations. Cureus is not responsible for the scientific accuracy or reliability of data or conclusions published herein. All content published within Cureus is intended only for educational, research and reference purposes. Additionally, articles published within Cureus should not be deemed a suitable substitute for the advice of a qualified health care professional. Do not disregard or avoid professional medical advice due to content published within Cureus.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
- Open access
- Published: 14 June 2024
Associations between deep venous thrombosis and thyroid diseases: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Lifeng Zhang 1 na1 ,
- Kaibei Li 2 na1 ,
- Qifan Yang 1 ,
- Yao Lin 1 ,
- Caijuan Geng 1 ,
- Wei Huang 1 &
- Wei Zeng 1
European Journal of Medical Research volume 29 , Article number: 327 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
199 Accesses
Metrics details
Some previous observational studies have linked deep venous thrombosis (DVT) to thyroid diseases; however, the findings were contradictory. This study aimed to investigate whether some common thyroid diseases can cause DVT using a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) approach.
This two-sample MR study used single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) identified by the FinnGen genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to be highly associated with some common thyroid diseases, including autoimmune hyperthyroidism (962 cases and 172,976 controls), subacute thyroiditis (418 cases and 187,684 controls), hypothyroidism (26,342 cases and 59,827 controls), and malignant neoplasm of the thyroid gland (989 cases and 217,803 controls. These SNPs were used as instruments. Outcome datasets for the GWAS on DVT (6,767 cases and 330,392 controls) were selected from the UK Biobank data, which was obtained from the Integrative Epidemiology Unit (IEU) open GWAS project. The inverse variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger and weighted median methods were used to estimate the causal association between DVT and thyroid diseases. The Cochran’s Q test was used to quantify the heterogeneity of the instrumental variables (IVs). MR Pleiotropy RESidual Sum and Outlier test (MR-PRESSO) was used to detect horizontal pleiotropy. When the causal relationship was significant, bidirectional MR analysis was performed to determine any reverse causal relationships between exposures and outcomes.
This MR study illustrated that autoimmune hyperthyroidism slightly increased the risk of DVT according to the IVW [odds ratio (OR) = 1.0009; p = 0.024] and weighted median methods [OR = 1.001; p = 0.028]. According to Cochran’s Q test, there was no evidence of heterogeneity in IVs. Additionally, MR-PRESSO did not detect horizontal pleiotropy ( p = 0.972). However, no association was observed between other thyroid diseases and DVT using the IVW, weighted median, and MR-Egger regression methods.
Conclusions
This study revealed that autoimmune hyperthyroidism may cause DVT; however, more evidence and larger sample sizes are required to draw more precise conclusions.
Introduction
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a common type of disease that occurs in 1–2 individuals per 1000 each year [ 1 ]. In the post-COVID-19 era, DVT showed a higher incidence rate [ 2 ]. Among hospitalized patients, the incidence rate of this disease was as high as 2.7% [ 3 ], increasing the risk of adverse events during hospitalization. According to the Registro Informatizado Enfermedad Tromboembolica (RIETE) registry, which included data from ~ 100,000 patients from 26 countries, the 30-day mortality rate was 2.6% for distal DVT and 3.3% for proximal DVT [ 4 ]. Other studies have shown that the one-year mortality rate of DVT is 19.6% [ 5 ]. DVT and pulmonary embolism (PE), collectively referred to as venous thromboembolism (VTE), constitute a major global burden of disease [ 6 ].
Thyroid diseases are common in the real world. Previous studies have focused on the relationship between DVT and thyroid diseases, including thyroid dysfunction and thyroid cancer. Some case reports [ 7 , 8 , 9 ] have demonstrated that hyperthyroidism is often associated with DVT and indicates a worse prognosis [ 10 ]. The relationship between thyroid tumors and venous thrombosis has troubled researchers for many years. In 1989, the first case of papillary thyroid carcinoma presenting with axillary vein thrombosis as the initial symptom was reported [ 11 ]. In 1995, researchers began to notice the relationship between thyroid tumors and hypercoagulability [ 12 ], laying the foundation for subsequent extensive research. However, the aforementioned observational studies had limitations, such as small sample sizes, selection bias, reverse causality, and confounding factors, which may have led to unreliable conclusions [ 13 ].
Previous studies have explored the relationship of thyroid disease and DVT and revealed that high levels of thyroid hormones may increase the risk of DVT. Hyperthyroidism promotes a procoagulant and hypofibrinolytic state by affecting the von Willebrand factor, factors VIII, IV, and X, fibrinogen, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 [ 14 , 15 ]. At the molecular level, researchers believe that thyroid hormones affect coagulation levels through an important nuclear thyroid hormone receptor (TR), TRβ [ 16 ], and participate in pathological coagulation through endothelial dysfunction. Thyroid hormones may have non-genetic effects on the behavior of endothelial cells [ 17 , 18 ]. In a study regarding tumor thrombosis, Lou [ 19 ] found that 303 circular RNAs were differentially expressed in DVT using microarray. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis revealed that the most significantly enriched pathways included thyroid hormone-signaling pathway and endocytosis, and also increased level of proteoglycans in cancer. This indicated that tumor cells and thyroid hormones might interact to promote thrombosis. Based on these studies, we speculated that thyroid diseases, including thyroid dysfunction and thyroid tumors, may cause DVT.
Mendelian randomization (MR) research is a causal inference technique that can be used to assess the causal relationship and reverse causation between specific exposure and outcome factors. If certain assumptions [ 20 ] are fulfilled, genetic variants can be employed as instrumental variables (IVs) to establish causal relationships. Bidirectional MR analysis can clarify the presence of reverse causal relationships [ 21 ], making the conclusions more comprehensive. Accordingly, we aimed to apply a two-sample MR strategy to investigate whether DVT is related to four thyroid diseases, including autoimmune hyperthyroidism, subacute thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, and thyroid cancer.
Study design
MR relies on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as IVs. The IVs should fulfill the following three criteria [ 22 ]: (1) IVs should be strongly associated with exposure. (2) Genetic variants must be independent of unmeasured confounding factors that may affect the exposure–outcome association. (3) IVs are presumed to affect the outcome only through their associations with exposure (Fig. 1 ). IVs that met the above requirements were used to estimate the relationship between exposure and outcome. Our study protocol conformed to the STROBE-MR Statement [ 23 ], and all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
The relationship between instrumental variables, exposure, outcome, and confounding factors
Data sources and instruments
Datasets (Table 1 ) in this study were obtained from a publicly available database (the IEU open genome-wide association studies (GWAS) project [ 24 ] ( https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk )). There was no overlap in samples between the data sources of outcome and exposures. Using de-identified summary-level data, privacy information such as overall age and gender were hidden. Ethical approval was obtained for all original work. This study complied with the terms of use of the database.
MR analysis was performed using the R package “TwoSampleMR”. SNPs associated with each thyroid disease at the genome-wide significance threshold of p < 5.0 × 10 –8 were selected as potential IVs. To ensure independence between the genetic variants used as IVs, the linkage disequilibrium (LD) threshold for grouping was set to r 2 < 0.001 with a window size of 10,000 kb. The SNP with the lowest p -value at each locus was retained for analyses.
Statistical analysis
Multiple MR methods were used to infer causal relationships between thyroid diseases and DVT, including the inverse variance weighted (IVW), weighted median, and MR-Egger tests, after harmonizing the SNPs across the GWASs of exposures and outcomes. The main analysis was conducted using the IVW method. Heterogeneity and pleiotropy were also performed in each MR analysis. Meanwhile, the MR-PRESSO Global test [ 25 ] was utilized to detect horizontal pleiotropy. The effect trend of SNP was observed through a scatter plot, and the forest plot was used to observe the overall effects. When a significant causal relationship was confirmed by two-sample MR analysis, bidirectional MR analysis was performed to assess reverse causal relationships by swapping exposure and outcome factors. Parameters were set the same as before. All abovementioned statistical analyses were performed using the package TwoSampleMR (version 0.5.7) in the R program (version 4.2.1).
After harmonizing the SNPs across the GWASs for exposures and outcomes, the IVW (OR = 1.0009, p = 0.024, Table 2 ) and weighted median analyses (OR = 1.001, p = 0.028) revealed significant causal effects between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and DVT risk. Similar results were observed using the weighted median approach Cochran’s Q test, MR-Egger intercept, and MR-PRESSO tests suggested that the results were not influenced by pleiotropy and heterogeneity (Table 2 ). However, the leave-one-out analysis revealed a significant difference after removing some SNPs (rs179247, rs6679677, rs72891915, and rs942495, p < 0.05, Figure S2a), indicating that MR results were dependent on these SNPs (Figure S2, Table S1). No significant effects were observed in other thyroid diseases (Table 2 ). The estimated scatter plot of the association between thyroid diseases and DVT is presented in Fig. 2 , indicating a positive causal relationship between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and DVT (Fig. 2 a). The forest plots of single SNPs affecting the risk of DVT are displayed in Figure S1.
The estimated scatter plot of the association between thyroid diseases and DVT. MR-analyses are derived using IVW, MR-Egger, weighted median and mode. By fitting different models, the scatter plot showed the relationship between SNP and exposure factors, predicting the association between SNP and outcomes
Bidirectional MR analysis was performed to further determine the relationship between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and DVT. The reverse causal relationship was not observed (Table S2), which indicated that autoimmune hyperthyroidism can cause DVT from a mechanism perspective.
This study used MR to assess whether thyroid diseases affect the incidence of DVT. The results showed that autoimmune hyperthyroidism can increase the risk of DVT occurrence, but a reverse causal relationship was not observed between them using bidirectional MR analysis. However, other thyroid diseases, such as subacute thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, and thyroid cancer, did not show a similar effect.
Recently, several studies have suggested that thyroid-related diseases may be associated with the occurrence of DVT in the lower extremities, which provided etiological clues leading to the occurrence of DVT in our subsequent research. In 2006, a review mentioned the association between thyroid dysfunction and coagulation disorders [ 26 ], indicating a hypercoagulable state in patients with hyperthyroidism. In 2011, a review further suggested a clear association between hypothyroidism and bleeding tendency, while hyperthyroidism appeared to increase the risk of thrombotic events, particularly cerebral venous thrombosis [ 27 ]. A retrospective cohort study [ 28 ] supported this conclusion, but this study only observed a higher proportion of concurrent thyroid dysfunction in patients with cerebral venous thrombosis. The relationship between thyroid function and venous thromboembolism remains controversial. Krieg VJ et al. [ 29 ] found that hypothyroidism has a higher incidence rate in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and may be associated with more severe disease, which seemed to be different from previous views that hyperthyroidism may be associated with venous thrombosis. Alsaidan [ 30 ] also revealed that the risk of developing venous thrombosis was almost increased onefold for cases with a mild-to-moderate elevation of thyroid stimulating hormone and Free thyroxine 4(FT4). In contrast, it increased twofold for cases with a severe elevation of thyroid stimulating hormone and FT4. Raised thyroid hormones may increase the synthesis or secretion of coagulation factors or may decrease fibrinolysis, which may lead to the occurrence of coagulation abnormality.
Other thyroid diseases are also reported to be associated with DVT. In a large prospective cohort study [ 31 ], the incidence of venous thromboembolism was observed to increase in patients with thyroid cancer over the age of 60. However, other retrospective studies did not find any difference compared with the general population [ 32 ]. In the post-COVID-19 era, subacute thyroiditis has received considerable attention from researchers. New evidence suggests that COVID-19 may be associated with subacute thyroiditis [ 33 , 34 ]. Mondal et al. [ 35 ] found that out of 670 COVID-19 patients, 11 presented with post-COVID-19 subacute thyroiditis. Among them, painless subacute thyroiditis appeared earlier and exhibited symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Another case report also indicated the same result, that is, subacute thyroiditis occurred after COVID-19 infection, accompanied by thyroid function changes [ 36 ]. This led us to hypothesize that subacute thyroiditis may cause DVT through alterations in thyroid function.
This study confirmed a significant causal relationship between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and DVT ( p = 0.02). The data were tested for heterogeneity and gene pleiotropy using MR-Egger, Cochran’s Q, and MR-PRESSO tests. There was no evidence that the results were influenced by pleiotropy or heterogeneity. In the leave-one-out analysis, four of the five selected SNPs showed significant effects of autoimmune hyperthyroidism on DVT, suggesting an impact of these SNPs on DVT outcome. Previous studies have focused on the relationship between hyperthyroidism and its secondary arrhythmias and arterial thromboembolism [ 37 , 38 ]. This study emphasized the risk of DVT in patients with hyperthyroidism, which has certain clinical implications. Prophylactic anticoagulant therapy was observed to help prevent DVT in patients with hyperthyroidism. Unfortunately, the results of this study did not reveal any evidence that suggests a relationship between other thyroid diseases and DVT occurrence. This may be due to the limited database, as this study only included the GWAS data from a subset of European populations. Large-scale multiracial studies are needed in the future.
There are some limitations to this study. First, it was limited to participants of European descent. Consequently, further investigation is required to confirm these findings in other ethnicities. Second, this study did not reveal the relationship between complications of hyperthyroidism and DVT. Additionally, this study selected IVs from the database using statistical methods rather than selecting them from the real population. This may result in weaker effects of the screened IVs and reduce the clinical significance of MR analysis. Moreover, the definitions of some diseases in this study were not clear in the original database, and some of the diseases were self-reported, which may reduce the accuracy of diagnosis. Further research is still needed to clarify the causal relationship between DVT and thyroid diseases based on prospective cohort and randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
This study analyzed large-scale genetic data and provided evidence of a causal relationship between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and the risk of DVT, Compared with the other thyroid diseases investigated. Prospective RCTs or MR studies with larger sample sizes are still needed to draw more precise conclusions.
Availability of data and materials
The IEU open gwas project, https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/
Ortel TL, Neumann I, Ageno W, et al. American society of hematology 2020 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Blood Adv. 2020;4(19):4693–738.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mehrabi F, Farshbafnadi M, Rezaei N. Post-discharge thromboembolic events in COVID-19 patients: a review on the necessity for prophylaxis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023;29:10760296221148476.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Loffredo L, Vidili G, Sciacqua A, et al. Asymptomatic and symptomatic deep venous thrombosis in hospitalized acutely ill medical patients: risk factors and therapeutic implications. Thromb J. 2022;20(1):72.
RIETE Registry. Death within 30 days. RIETE Registry. 2022[2023.8.23]. https://rieteregistry.com/graphics-interactives/dead-30-days/ .
Minges KE, Bikdeli B, Wang Y, Attaran RR, Krumholz HM. National and regional trends in deep vein thrombosis hospitalization rates, discharge disposition, and outcomes for medicare beneficiaries. Am J Med. 2018;131(10):1200–8.
Di Nisio M, van Es N, Büller HR. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 2016;388(10063):3060–73.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Aquila I, Boca S, Caputo F, et al. An unusual case of sudden death: is there a relationship between thyroid disorders and fatal pulmonary thromboembolism? A case report and review of literature. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2017;38(3):229–32.
Katić J, Katić A, Katić K, Duplančić D, Lozo M. Concurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism associated with hyperthyroidism: a case report. Acta Clin Croat. 2021;60(2):314–6.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hieber M, von Kageneck C, Weiller C, Lambeck J. Thyroid diseases are an underestimated risk factor for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Front Neurol. 2020;11:561656.
Pohl KR, Hobohm L, Krieg VJ, et al. Impact of thyroid dysfunction on short-term outcomes and long-term mortality in patients with pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res. 2022;211:70–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Sirota DK. Axillary vein thrombosis as the initial symptom in metastatic papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. Mt Sinai J Med. 1989;56(2):111–3.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Raveh E, Cohen M, Shpitzer T, Feinmesser R. Carcinoma of the thyroid: a cause of hypercoagulability? Ear Nose Throat J. 1995;74(2):110–2.
Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89–98.
Stuijver DJ, van Zaane B, Romualdi E, Brandjes DP, Gerdes VE, Squizzato A. The effect of hyperthyroidism on procoagulant, anticoagulant and fibrinolytic factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost. 2012;108(6):1077–88.
PubMed Google Scholar
Son HM. Massive cerebral venous sinus thrombosis secondary to Graves’ disease. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(3):273–80.
Elbers LP, Moran C, Gerdes VE, et al. The hypercoagulable state in hyperthyroidism is mediated via the thyroid hormone β receptor pathway. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016;174(6):755–62.
Davis PJ, Sudha T, Lin HY, et al. Thyroid hormone, hormone analogs, and angiogenesis. Compr Physiol. 2015;6(1):353–62.
Mousa SA, Lin HY, Tang HY, et al. Modulation of angiogenesis by thyroid hormone and hormone analogues: implications for cancer management. Angiogenesis. 2014;17(3):463–9.
Lou Z, Li X, Li C, et al. Microarray profile of circular RNAs identifies hsa_circ_000455 as a new circular RNA biomarker for deep vein thrombosis. Vascular. 2022;30(3):577–89.
Hemani G, Bowden J, Davey SG. Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in Mendelian randomization studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(R2):R195–208.
Zhang Z, Li L, Hu Z, et al. Causal effects between atrial fibrillation and heart failure: evidence from a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16(1):187.
Emdin CA, Khera AV, Kathiresan S. Mendelian randomization. JAMA. 2017;318(19):1925–6.
Skrivankova VW, Richmond RC, Woolf BAR, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614–21.
Hemani G, Zheng J, Elsworth B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. 2018;7: e34408.
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693–8.
Franchini M. Hemostatic changes in thyroid diseases: haemostasis and thrombosis. Hematology. 2006;11(3):203–8.
Franchini M, Lippi G, Targher G. Hyperthyroidism and venous thrombosis: a casual or causal association? A systematic literature review. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2011;17(4):387–92.
Fandler-Höfler S, Pilz S, Ertler M, et al. Thyroid dysfunction in cerebral venous thrombosis: a retrospective cohort study. J Neurol. 2022;269(4):2016–21.
Krieg VJ, Hobohm L, Liebetrau C, et al. Risk factors for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension—importance of thyroid disease and function. Thromb Res. 2020;185:20–6.
Alsaidan AA, Alruwiali F. Association between hyperthyroidism and thromboembolism: a retrospective observational study. Ann Afr Med. 2023;22(2):183–8.
Walker AJ, Card TR, West J, Crooks C, Grainge MJ. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer—a cohort study using linked United Kingdom databases. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(6):1404–13.
Ordookhani A, Motazedi A, Burman KD. Thrombosis in thyroid cancer. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2017;16(1): e57897.
Ziaka M, Exadaktylos A. Insights into SARS-CoV-2-associated subacute thyroiditis: from infection to vaccine. Virol J. 2023;20(1):132.
Henke K, Odermatt J, Ziaka M, Rudovich N. Subacute thyroiditis complicating COVID-19 infection. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2023;16:11795476231181560.
Mondal S, DasGupta R, Lodh M, Ganguly A. Subacute thyroiditis following recovery from COVID-19 infection: novel clinical findings from an Eastern Indian cohort. Postgrad Med J. 2023;99(1172):558–65.
Nham E, Song E, Hyun H, et al. Concurrent subacute thyroiditis and graves’ disease after COVID-19: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(18): e134.
Mouna E, Molka BB, Sawssan BT, et al. Cardiothyreosis: epidemiological, clinical and therapeutic approach. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2023;17:11795468231152042.
Maung AC, Cheong MA, Chua YY, Gardner DS. When a storm showers the blood clots: a case of thyroid storm with systemic thromboembolism. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2021;2021:20–0118.
Download references
Not applicable.
Author information
Lifeng Zhang and Kaibei Li have contributed equally to this work and share the first authorship.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Vascular Surgery, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 39, Shierqiao Road, Jinniu District, Chengdu, 610072, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China
Lifeng Zhang, Qifan Yang, Yao Lin, Caijuan Geng, Wei Huang & Wei Zeng
Disinfection Supply Center, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 39, Shierqiao Road, Jin Niu District, Chengdu, 610072, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conception and design: LFZ and WZ. Analysis and interpretation: LFZ, KBL and WZ. Data collection: LFZ, QFY, YL, CJG and WH. Writing the article: LFZ, KBL. Critical revision of the article: LFZ, GFY and WZ. Final approval of the article: LFZ, KBL, YL, CJG, WH, QFY and WZ. Statistical analysis: YL, QFY.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Wei Zeng .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was obtained in all original studies. This study complies with the terms of use of the database.
Competing interests
Additional information, publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhang, L., Li, K., Yang, Q. et al. Associations between deep venous thrombosis and thyroid diseases: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Med Res 29 , 327 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-024-01933-1
Download citation
Received : 12 September 2023
Accepted : 09 June 2024
Published : 14 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-024-01933-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Deep venous thrombosis
- Thyroid diseases
- Mendelian randomization analysis
European Journal of Medical Research
ISSN: 2047-783X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
A study on the willingness of “generation z” consumers to use online virtual try-on shopping services based on the s-o-r framework.

Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Jiang, Q. A Study on the Willingness of “Generation Z” Consumers to Use Online Virtual Try-On Shopping Services Based on the S-O-R Framework. Systems 2024 , 12 , 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12060217
Wang Z, Jiang Q. A Study on the Willingness of “Generation Z” Consumers to Use Online Virtual Try-On Shopping Services Based on the S-O-R Framework. Systems . 2024; 12(6):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12060217
Wang, Zhicheng, and Qianling Jiang. 2024. "A Study on the Willingness of “Generation Z” Consumers to Use Online Virtual Try-On Shopping Services Based on the S-O-R Framework" Systems 12, no. 6: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12060217
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Feds well-positioned to provide slavery reparations, Harvard study finds
New research shows there is “a moral case, societal norm, and governmental precedent for paying reparations” to Black Americans for continuing harms resulting in the racial wealth gap.

When President Biden proclaimed Wednesday as Juneteenth Day of Observance, he called on Americans to “recognize how the impact of America’s original sin remains.”
He listed his administration’s accomplishments of particular interest to Black America, including “one of my proudest,” signing 2021 legislation making Juneteenth, which marks the end of slavery in Texas, a federal holiday.
One item not on Biden’s list is reparations, the long overdue but still controversial payments to the descendants of enslaved people in compensation for that original sin. Reparations proposals are controversial because of people like Sen. Mitch McConnell (R-Ky.), the chamber’s Republican leader, who in 2019 said “none of us currently living are responsible” for slavery.
Now, a couple of Harvard University professors, Linda J. Bilmes and Cornell William Brooks, a White woman and a Black man, refute McConnell’s argument and related ones in a detailed, well-documented academic paper timed for this week’s Juneteenth observance.
In convincing fashion, the two authors — one of European descent, the other a great-great-great-grandson of an enslaved man — write in The Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences that the federal government “already has the norm, precedent, expertise, and resources to provide reparations to Black Americans.”
Washington has funded many and varied “reparatory compensation programs,” their research shows, demonstrating “that reparations for nonracial harms is regular and routine” and “that America provides reparations to nearly everyone but Black Americans, even for comparably severe harms.”
Although the politically contentious word is not commonly used to describe these forms of compensation, Bilmes and Brooks said “reparations are surprisingly commonplace practices in the federal government’s role of compensating harms.”
The reparations list goes well beyond often cited payments to Jewish victims of the Holocaust and Japanese Americans incarcerated in World War II internment camps.
“Categories of those harmed who have been compensated include,” they wrote, “coal miners; farmers whose crops have failed; workers whose companies have gone bankrupt; victims of terrorism and natural disasters; people exposed to nuclear radiation; military veterans; individuals wrongfully convicted in the legal system; people denied earnings on tribal lands; fishermen facing depleted fish stocks; individuals harmed by pesticides, toxins, vaccines, or medical devices; workers and businesses affected by U.S. trade agreements; depositors in banks; and numerous other categories.”
The authors did not estimate the cost or mechanisms of a slavery reparations program. But “a key finding,” Bilmes and Brooks said, is “the federal government draws on designated fees, trust funds, excise taxes, subsidized insurance premiums, and customized financial arrangements to help pay for the wide system of reparatory compensation.”
One thing they recommended is a presidentially appointed national commission to study reparations, similar to one previously proposed by former Rep. John Conyers Jr. (D-Mich.) and in legislation, H.R. 40 , offered by Rep. Sheila Jackson Lee (D-Tex.) in 2021. The professors also suggested an audit of federal reparatory compensation programs to gather more information about them.
Although the House and Senate have not voted on the 2021 bill, that doesn’t mean action on reparations is stalled.
To the contrary, said Ron Daniels, convener of the National African American Reparations Commission . The issue is “on fire” around the country, he added, citing “Reparations on Fire ,” a 2022 book by D.C. lawyer Nkechi Taifa. Daniels, a longtime political activist, said he has “never, ever, ever seen a more robust” time for reparations advocacy. He pointed to the 196 co-sponsors on the House bill (the Senate legislation has 22) and scores, “maybe a couple hundred” of state and local actions related to reparations.
Evanston, Ill., is a leader on that front. As my colleague Emmanuel Felton reported earlier this month, the Chicago suburb is credited with the nation’s first government-funded reparations program. Over the past two years, it paid almost $5 million to nearly 200 Black residents. Evanston’s program now is threatened by Judicial Watch, a conservative organization suing to stop the program, because, it said, the “race-based eligibility requirement” violates the Constitution.
The lawsuit is part of a much broader attack on affirmative action, following a Supreme Court decision last year against related college admission programs. The attack extends to the fundamental — and once widely praised — American values of diversity and inclusion. Last week, Senate and House Republicans introduced the “Dismantle DEI Act” to outlaw federal programs that promote diversity, equity and inclusion — a keystone of Biden’s administration.
Mike Gonzalez, a senior fellow with the conservative Heritage Foundation, said the Harvard professors’ arguments “do not pass the test of justice, morality, logic, ethics or efficacy” and “establish collective guilt … They mete out collective punishment and hand out collective rewards, nearly 160 years after the Civil War ended and the 13th Amendment abolished slavery.”
But the continuing impact of slavery has not been abolished.
Because of “major racial harms precipitated or aggravated by actions involving the federal government,” there is, Bilmes and Brooks wrote, “a moral case, societal norm, and governmental precedent for paying reparations for these harms and the resulting racial wealth gap.”
Compensating those harmed by slavery’s legacy is “based on this norm of generosity and the idea that America as a whole is better off if we do this,” Bilmes, a former Commerce Department chief financial officer and assistant secretary, said by email.
But as the legislation outlawing federal DEI programs demonstrates, that “norm of generosity,” or even basic fairness, stops for many people where programs to right past wrongs against African Americans begin.
To answer reparations opponents like McConnell, whose “two great-great-grandfathers, James McConnell and Richard Daley,” according to NBC News , “owned a total of at least 14 enslaved people in Limestone County, Alabama,” the article presents a list of issues to demonstrate “complex, interlocking, and compounding racial harms to Black Americans spanning centuries” that followed slavery and continue “into the present moment.”
The authors argue that because “Black Americans have long been deprived of the ability to accumulate wealth,” it is consistent with American norms, precedent and practice to compensate them “for unpaid contributions to the country and in recognition of the suffering endured” during slavery and since.
“Not only are reparations regular and routine,” Brooks, a former NAACP CEO and president, said in an interview, “but we actually have the experience, the expertise and the resources to do it.”

Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Household Pulse Survey

As part of an ongoing partnership with the Census Bureau, the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) recently added questions to assess the prevalence of post-COVID-19 conditions (long COVID), on the experimental Household Pulse Survey. This 20-minute online survey was designed to complement the ability of the federal statistical system to rapidly respond and provide relevant information about the impact of the coronavirus pandemic in the U.S. Data collection began on April 23, 2020.
Beginning in Phase 3.5 (on June 1, 2022), NCHS included questions about the presence of symptoms of COVID that lasted three months or longer. Beginning in Phase 3.6 (on September 14, 2022), NCHS included a question about whether long-term symptoms among those reporting symptoms lasting three months or longer reduced the ability to carry out day-to-day activities compared with the time before having COVID-19. Phase 3.6 will continue with a two-weeks on, two-weeks off collection and dissemination approach.
Estimates on this page are derived from the Household Pulse Survey and show the following outcomes for adults aged 18 and over:
- The percentage of all U.S. adults who EVER experienced post-COVID conditions (long COVID). These adults had COVID and had some symptoms that lasted three months or longer.
- The percentage of adults who EVER experienced post-COVID conditions (long COVID) among those who ever had COVID .
- The percentage of all U.S. adults who are CURRENTLY experiencing post-COVID conditions (long COVID). These adults had COVID, had long-term symptoms, and are still experiencing symptoms.
- The percentage of adults who are CURRENTLY experiencing post-COVID conditions (long COVID) among those who ever had COVID.
Beginning in Phase 3.6:
- The percentage of any activity limitations (either ‘yes, a little’ or ‘yes, a lot’ responses) from long COVID, among adults who are currently experiencing long COVID and among all adults
- The percentage of significant activity limitations (‘yes, a lot’ response) from long COVID, among adults who are currently experiencing long COVID and among all adults
The percentage of all U.S. adults who ever said they had COVID is also included to provide context for the other percentages. It should be noted that the percentage of adults who said they ever had COVID based on the Household Pulse Survey is lower than other estimates based on seroprevalence studies .
See the technical notes for more information on these measures.
Questions on post-COVID conditions (long COVID) were also included on the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) in 2022. The NHIS, conducted by NCHS, is the major source for high-quality data used to monitor the nation’s health. NHIS data collection will continue through December 2024.
- Anxiety and Depression
- Health Insurance Coverage
- Lack of Social Connection
- Functioning and Disability
- Telemedicine Use
- Mental Health Care
- Reduced Access to Care
Long COVID or Post COVID Conditions
Use the drop-down menus to show data for selected indicators or categories. Select the buttons at the bottom of the dashboard to view national and state estimates. The data table may be scrolled horizontally and vertically to view additional estimates.
Access Dataset on Data.CDC.gov (Export to CSV, JSON, XLS, XML) [?]
Beginning in Phase 4.1 (April 2, 2024) of data collection and reporting, the answer choices for the third question in the series changed to Yes, my symptoms lasted between 3 and 6 months; Yes, my symptoms lasted 6 months to a year; Yes, my symptoms lasted more than a year; No. The definitions of ever and currently have Long COVID remain the same.
Technical Notes
Survey questions.
Have you ever tested positive for COVID-19 (using a rapid point-of-care test, self-test, or laboratory test) or been told by a doctor or other health care provider that you have or had COVID-19?
Answer Choices: yes, no
How would you describe your coronavirus symptoms when they were at their worst?
Answer choices: I had no symptoms, I had mild symptoms, I had moderate symptoms, I had severe symptoms.
Did you have any symptoms lasting 3 months or longer that you did not have prior to having coronavirus or COVID-19?
Long term symptoms may include: Tiredness or fatigue, difficulty thinking, concentrating, forgetfulness, or memory problems (sometimes referred to as “brain fog”), difficulty breathing or shortness of breath, joint or muscle pain, fast-beating or pounding heart (also known as heart palpitations), chest pain, dizziness on standing, menstrual changes, changes to taste/smell, or inability to exercise.
Answer choices: yes, no
Do you have symptoms now?
Do these long-term symptoms reduce your ability to carry out day-to-day activities compared with the time before you had COVID-19?
Answer choices: Yes, a lot; Yes, a little; Not at all
Data Source
The U.S. Census Bureau, in collaboration with multiple federal agencies, launched the Household Pulse Survey to produce data on the social and economic impacts of COVID-19 on American households. The Household Pulse Survey was designed to gauge the impact of the pandemic on employment status, consumer spending, food security, housing, education disruptions, and dimensions of physical and mental wellness.
The survey was designed to meet the goal of accurate and timely weekly estimates. It was conducted by an internet questionnaire, with invitations to participate sent by email and text message. The sample frame is the Census Bureau Master Address File Data. Housing units linked to one or more email addresses or cell phone numbers were randomly selected to participate, and one respondent from each housing unit was selected to respond for him or herself. Estimates are weighted to adjust for nonresponse and to match Census Bureau estimates of the population by age, sex, race and ethnicity, and educational attainment. All estimates shown meet the NCHS Data Presentation Standards for Proportions .
Limitations
The Household Pulse Survey is different from other surveys. NCHS, the Census Bureau, and other federal statistical agencies are considered the preeminent source of the nation’s most important benchmark surveys. Many of these surveys have been in production for decades and provide valuable insight on health, social, and economic trends. However, the production of benchmark data requires a relatively long lead time, and personal interviews (face-to-face or telephone) require additional time. While efforts are underway to introduce COVID-19 questions into these surveys, that process can take months, sometimes years, before data are made available.
The Household Pulse Survey is different: It was designed to go into the field quickly, to be administered via the web, and to disseminate data in near real-time, providing data users with information they can use now to help ease the burden on American households and expedite post-pandemic recovery. The Census Bureau is fielding the Household Pulse Survey as a demonstration project, with data released as part of its Experimental Statistical Products Series.
Confidence intervals included in the tables on this page only reflect the potential for sampling error. Nonsampling errors can also occur and are more likely for surveys that are implemented quickly, achieve low response rates, and rely on online response. Nonsampling errors for the Household Pulse Survey may include:
- Measurement error: The respondent provides incorrect information, or an unclear survey question is misunderstood by the respondent. The Household Pulse Survey schedule offered only limited time for testing questions.
- Coverage error: Individuals who otherwise would have been included in the survey frame were missed. The Household Pulse Survey only recruited households for which an email address or cell phone number could be identified.
- Nonresponse error: Responses are not collected from all those in the sample or the respondent is unwilling to provide information. The response rate for the Household Pulse Survey was substantially lower than most federally sponsored surveys.
- Processing error: Forms may be lost, data may be incorrectly keyed, coded, or recoded. The real-time dissemination of the Household Pulse Survey provided limited time to identify and fix processing errors.
For more information on nonresponse bias for the Household Pulse Survey, please visit https://www2.census.gov/programs-surveys/demo/technical-documentation/hhp/2020_HPS_NR_Bias_Report-final.pdf .
For more information on the Household Pulse Survey, please visit https://www.census.gov/data/experimental-data-products/household-pulse-survey.html .
Suggested Citation
National Center for Health Statistics. U.S. Census Bureau, Household Pulse Survey, 2022–2024. Long COVID. Generated interactively: from https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/covid19/pulse/long-covid.htm
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Having elucidated the defining principles of the single case study approach, the paper now turns to an overview of its main benefits. As noted above, a lack of consensus still exists within the wider social science literature on the principles and purposes - and by extension the advantages and limitations - of case study research.
Advantages. 1. In-depth analysis of complex phenomena. Case study design allows researchers to delve deeply into intricate issues and situations. By focusing on a specific instance or event, researchers can uncover nuanced details and layers of understanding that might be missed with other research methods, especially large-scale survey studies.
Case study research also has methodological limitations. Case study has been criticized for its perceived lack of rigor and/or quality, lack of consensus on design methods, as well as its ...
Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment. Limitations of Case Study Research. There are several limitations of case study research, including:
Definitions of qualitative case study research. Case study research is an investigation and analysis of a single or collective case, intended to capture the complexity of the object of study (Stake, 1995).Qualitative case study research, as described by Stake (), draws together "naturalistic, holistic, ethnographic, phenomenological, and biographic research methods" in a bricoleur design ...
Limitations of Case Studies In order to balance this account, it is necessary to examine, if more briefly, some of the limitations of case study research. There is too much data for easy analysis. All case study researchers are conscious of being swamped in data. For example, our Training Credits study generated 198 taped interviews.
The definitions of case study evolved over a period of time. Case study is defined as "a systematic inquiry into an event or a set of related events which aims to describe and explain the phenomenon of interest" (Bromley, 1990).Stoecker defined a case study as an "intensive research in which interpretations are given based on observable concrete interconnections between actual properties ...
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table 5 ), the ...
Tylenol - Disadvantages. The main disadvantage is that the study cannot be recreated, and what happens in one industry, doesn't necessarily resonate in other industries. Case study method is responsible for intensive study of a unit. It is the investigation and exploration of an event thoroughly and deeply.
Observations published can generate ideas and be a trigger for further studies. For instance, a case series consisting of several similar cases in a short period can make up the case-group for a case-control study . Clinicians could do the observation and publish the case series while the case-control study could be left to the academics.
A case study is a type of qualitative research that examines one particular case (or several cases) in-depth. It is often used for exploring a single phenomenon or event, such as a successful marketing campaign, a product, or a service. Case study researchers collect data through a variety of methods, such as interviews, document analysis, and ...
The case study is not a research method in and of itself; rather, researchers select methods for data collection and analysis that will result in case study-worthy data. Limitations of Case Studies. There is insufficient scientific rigour and no basis for extending findings to a broader population. The researchers could inject their personal ...
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
Summary: No study is expected to be flawless. Research is like building blocks and each new study is rooted in a limitation that existed in a previous study. It is important to communicate the limitations to your readers as they provide direction for future research. Hiding the limitations only draws more attention to them and additionally ...
Even interviews can be conducted over the phone. That means this method is good for formative research that is exploratory in nature, even if it must be completed from a remote location. 6. It is inexpensive. Compared to other methods of research, the case study method is rather inexpensive.
In this section, we provide a summary of each approach, including its particular strengths or limitations. ... A case study can be a complete research project in itself, such as in the study of a particular organization, community, or program. Case studies are also often used for evaluation purposes, for example, in an external review. In ...
The fact is that stories (individual, collective, institutional) have a vital role to play in the world of research. And to play the specific v. general card against case study design suggests a tendency towards forms of research fundamentalism as opposed to any kind of rational and objective take on case study's strengths and limitations.
This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research. Benefits include the following: Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in ...
The case study method uses investigatory research as a way to collect data about specific demographics. This approach can apply to individuals, businesses, groups, or events. ... Without this limitation in place, the results of the study cannot be guaranteed because of the presence of bias. 4. It is a subjective method to use for research.
Common types of limitations and their ramifications include: Theoretical: limits the scope, depth, or applicability of a study. Methodological: limits the quality, quantity, or diversity of the data. Empirical: limits the representativeness, validity, or reliability of the data. Analytical: limits the accuracy, completeness, or significance of ...
All scientific studies have limitations, and no study is perfect. Researchers should not run from this reality, but engage it directly. It is better to directly address the specific limitations of the work in question, and doing so is actually a way to demonstrate an author's proficiency and aptitude. Do: Be Transparent
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table.
Despite their limitations, case study research is a beneficial tool and learning experience in graduate medical education and among novice researchers. The preparation and presentation of case studies can help students and graduate medical education programs evaluate and apply the six American College of Graduate Medical Education (ACGME ...
Data sources and instruments. Datasets (Table 1) in this study were obtained from a publicly available database (the IEU open genome-wide association studies (GWAS) project [] (https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk)).There was no overlap in samples between the data sources of outcome and exposures. Using de-identified summary-level data, privacy information such as overall age and gender were hidden.
To address this theoretical gap, this study employs the Stimulus-Organism-Response (S-O-R) theory as its research framework, using online virtual shoe try-on services as a case study. Focusing on "Generation Z" consumers, this study utilizes literature review, user research, factor analysis, and linear regression to establish a user ...
2.1. Study areas. The study area, Jiuzhaigou County, is located in the northern part of Aba Prefecture, Sichuan Province, with a total area of approximately 541.61 km 2.Positioned in the transitional zone from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau to the Sichuan Basin, the area undergoes abrupt changes in topography (Xiao Citation 2019) (Figure 1).The region exhibits well-developed fold and fault ...
The purpose of case studies is not to generalize, but to generate knowledge about unique conditions and experiences in specific contexts. 23 Although the number of cases is small, this study has triangulated methods, employing both qualitative and quantitative approaches to obtain nuanced and detailed insights, 51 which are further reflected in ...
New research shows there is "a moral case, societal norm, and governmental precedent for paying reparations" to Black Americans for continuing harms resulting in the racial wealth gap.
As part of an ongoing partnership with the Census Bureau, the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) recently added questions to assess the prevalence of post-COVID-19 conditions (long COVID), on the experimental Household Pulse Survey. This 20-minute online survey was designed to complement the ability of the federal statistical system to rapidly respond and provide relevant information ...