
- High contrast
- Press Centre

Search UNICEF
The state of the global education crisis, a path to recovery.
The global disruption to education caused by the COVD-19 pandemic is without parallel and the effects on learning are severe. The crisis brought education systems across the world to a halt, with school closures affecting more than 1.6 billion learners. While nearly every country in the world offered remote learning opportunities for students, the quality and reach of such initiatives varied greatly and were at best partial substitutes for in-person learning. Now, 21 months later, schools remain closed for millions of children and youth, and millions more are at risk of never returning to education. Evidence of the detrimental impacts of school closures on children’s learning offer a harrowing reality: learning losses are substantial, with the most marginalized children and youth often disproportionately affected.
The State of the Global Education Crisis: A Path to Recovery charts a path out of the global education crisis and towards building more effective, equitable and resilient education systems.

Files available for download
Related topics, more to explore, global deployment of rapid diagnostic tests to boost fight against cholera, six grave violations against children in times of war.
How children have become frontline targets in armed conflicts
Millions at risk from cholera due to lack of clean water, soap and toilets, and shortage of cholera vaccine
Water and the climate crisis: 10 things you should know.
The world needs to get water smart. Everyone has a role to play, and we cannot afford to wait

The global education crisis – even more severe than previously estimated
Ellinore carroll, joão pedro azevedo, jessica bergmann, matt brossard, gwang- chol chang, borhene chakroun, marie-helene cloutier, suguru mizunoya, nicolas reuge, halsey rogers.

In our recent The State of the Global Education Crisis: A Path to Recovery report (produced jointly by UNESCO, UNICEF, and the World Bank), we sounded the alarm: this generation of students now risks losing $17 trillion in lifetime earnings in present value, or about 14 percent of today’s global GDP, because of COVID-19-related school closures and economic shocks. This new projection far exceeds the $10 trillion estimate released in 2020 and reveals that the impact of the pandemic is more severe than previously thought .
The pandemic and school closures not only jeopardized children’s health and safety with domestic violence and child labor increasing, but also impacted student learning substantially. The report indicates that in low- and middle-income countries, the share of children living in Learning Poverty – already above 50 percent before the pandemic – could reach 70 percent largely as a result of the long school closures and the relative ineffectiveness of remote learning.
Unless action is taken, learning losses may continue to accumulate once children are back in school, endangering future learning.
Figure 1. Countries must accelerate learning recovery
Severe learning losses and worsening inequalities in education
Results from global simulations of the effect of school closures on learning are now being corroborated by country estimates of actual learning losses. Evidence from Brazil , rural Pakistan , rural India , South Africa , and Mexico , among others, shows substantial losses in math and reading. In some low- and middle-income countries, on average, learning losses are roughly proportional to the length of the closures—meaning that each month of school closures led to a full month of learning losses (Figure 1, selected LMICs and HICs presents an average effect of 100% and 43%, respectively), despite the best efforts of decision makers, educators, and families to maintain continuity of learning.
However, the extent of learning loss varies substantially across countries and within countries by subject, students’ socioeconomic status, gender, and age or grade level (Figure 1 illustrates this point, note the large standard deviation, a measure which shows data are spread out far from the mean). For example, results from two states in Mexico show significant learning losses in reading and in math for students aged 10-15. The estimated learning losses were greater in math than reading, and they disproportionately affected younger learners, students from low-income backgrounds, and girls.
Figure 2. The average learning loss standardized by the length of the school closure was close to 100% in Low- and Middle-Income countries, and 43% in High-Income countries, with a standard deviation of 74% and 30%, respectively.
While most countries have yet to measure learning losses, data from several countries, combined with more extensive evidence on unequal access to remote learning and at-home support, shows the crisis has exacerbated inequalities in education globally.
- Children from low-income households, children with disabilities, and girls were less likely to access remote learning due to limited availability of electricity, connectivity, devices, accessible technologies as well as discrimination and social and gender norms.
- Younger students had less access to age-appropriate remote learning and were more affected by learning loss than older students. Pre-school-age children, who are at a pivotal stage for learning and development, faced a double disadvantage as they were often left out of remote learning and school reopening plans.
- Learning losses were greater for students of lower socioeconomic status in various countries, including Ghana , Mexico , and Pakistan .
- While the gendered impact of school closures on learning is still emerging, initial evidence points to larger learning losses among girls, including in South Africa and Mexico .
As a result, these children risk missing out on much of the boost that schools and learning can provide to their well-being and life chances. The learning recovery response must therefore target support to those that need it most, to prevent growing inequalities in education.
Beyond learning, growing evidence shows the negative effects school closures have had on students’ mental health and well-being, health and nutrition, and protection, reinforcing the vital role schools play in providing comprehensive support and services to students.
Critical and Urgent Need to Focus on Learning Recovery
How should decision makers and the international community respond to the growing global education crisis?
Reopening schools and keeping them open must be the top priority, globally. While nearly every country in the world offered remote learning opportunities for students, the quality and reach of such initiatives varied, and in most cases, they offered a poor substitute for in-person instruction. Stemming and reversing learning losses, especially for the most vulnerable students, requires in-person schooling. Decision makers need to reassure parents and caregivers that with adequate safety measures, such as social distancing, masking, and improved ventilation, global evidence shows that children can resume in-person schooling safely.
But just reopening schools with a business-as-usual approach won’t reverse learning losses. Countries need to create Learning Recovery Programs . Three lines of action will be crucial:
- Consolidating the curriculum – to help teachers prioritize essential material that students have missed while out of school, even if the content is usually covered in earlier grades, to ensure the curriculum is aligned to students’ learning levels. As an example, Tanzania consolidated its curriculum for grade 1 and 2 in 2015, reducing the number of subjects taught and increasing time on ensuring the acquisition of foundational numeracy and literacy.
- Extending instructional time – by extending the school day, modifying the academic calendar to make the school year longer, or by offering summer school for all students or those in need. In Mexico , the Ministry of Public Education announced planned extensions to the academic calendar to help recovery. In Madagascar , the government scaled up an existing two-month summer “catch-up” program for students who reintegrate into school after having left the system.
- Improving the efficiency of learning – by supporting teachers to apply structured pedagogy and targeted instruction. A structured pedagogy intervention in Kenya using teachers guides with lesson plans has proven to be highly effective. Targeted instruction, or aligning instruction to students’ learning level, has been successfully implemented at scale in Cote D’Ivoire .
Finally, the report emphasizes the need for adequate funding. As of June 2021, the education and training sector had been allocated less than 3 percent of global stimulus packages. Much more funding will be needed for immediate learning recovery if countries are to avert the long-term damage to productivity and inclusion that they now face.
Learning Recovery as a Springboard to an Accelerated Learning Trajectory
Accelerating learning recovery has benefits that go well beyond short-term gains: it can give children the necessary foundations for a lifetime of learning, and it can help countries increase the efficiency, equity, and resilience of schooling. This can be achieved if countries build on investments made and lessons learned during the crisis—most notably, with a focus on six areas:
- Assessing student learning so instruction can be targeted to students’ learning levels and specific needs.
- Investing in digital learning opportunities for all students, ensuring that technology is fit for purpose and focused on enhancing human interactions.
- Reinforcing support that leverages the role of parents, families, and communities in children’s learning.
- Ensuring that teachers are supported and have access to practical, high-quality professional development opportunities, teaching guides and learning materials.
- Increasing the share of education in the national budget allocation of stimulus packages and tying it to investments mentioned above that can accelerate learning.
- Investing in evidence building - in particular, implementation research, to understand what works and how to scale what works to the system level.
It is time to shift from crisis response to learning recovery. We must make sure that investments and actions for learning recovery lay the foundations for more efficient, equitable, and resilient education systems—systems that truly deliver learning and well-being for all children and youth. Only then can we ensure learning continuity in the face of future disruption.
The report was produced as part of the Mission: Recovering Education 2021 , through which the World Bank , UNESCO , and UNICEF are focused on three priorities: bringing all children back to schools, recovering learning losses, and preparing and supporting teachers.

Young Professional

Lead Economist

Education Researcher – UNICEF Office of Research-Innocenti

Chief, Education – UNICEF Office of Research-Innocenti

Chief of Education Policy Section, Division of Policies and Lifelong Learning Systems, UNESCO Education Sector

Director, Division for Policies and Lifelong Learning Systems, UNESCO Education Sector

Senior Economist

Senior Advisor, Statistics and Monitoring (Education) – UNICEF New York HQ

Senior Adviser Education, UNICEF Headquarters

Lead Economist, Education Global Practice
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
The global education challenge: Scaling up to tackle the learning crisis
- Download the policy brief
Subscribe to Global Connection
Alice albright alice albright chief executive officer - global partnership for education @alicealbright.
July 25, 2019
The following is one of eight briefs commissioned for the 16th annual Brookings Blum Roundtable, “2020 and beyond: Maintaining the bipartisan narrative on US global development.”
Addressing today’s massive global education crisis requires some disruption and the development of a new 21st-century aid delivery model built on a strong operational public-private partnership and results-based financing model that rewards political leadership and progress on overcoming priority obstacles to equitable access and learning in least developed countries (LDCs) and lower-middle-income countries (LMICs). Success will also require a more efficient and unified global education architecture. More money alone will not fix the problem. Addressing this global challenge requires new champions at the highest level and new approaches.
Key data points
In an era when youth are the fastest-growing segment of the population in many parts of the world, new data from the UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) reveals that an estimated 263 million children and young people are out of school, overwhelmingly in LDCs and LMICs. 1 On current trends, the International Commission on Financing Education Opportunity reported in 2016 that, a far larger number—825 million young people—will not have the basic literacy, numeracy, and digital skills to compete for the jobs of 2030. 2 Absent a significant political and financial investment in their education, beginning with basic education, there is a serious risk that this youth “bulge” will drive instability and constrain economic growth.
Despite progress in gender parity, it will take about 100 years to reach true gender equality at secondary school level in LDCs and LMICs. Lack of education and related employment opportunities in these countries presents national, regional, and global security risks.
Related Books
Amar Bhattacharya, Homi Kharas, John W. McArthur
November 15, 2023
Geoffrey Gertz, Homi Kharas, Johannes F. Linn
September 12, 2017
Esther Care, Patrick Griffin
April 11, 2017
Among global education’s most urgent challenges is a severe lack of trained teachers, particularly female teachers. An additional 9 million trained teachers are needed in sub-Saharan Africa by 2030.
Refugees and internally displaced people, now numbering over 70 million, constitute a global crisis. Two-thirds of the people in this group are women and children; host countries, many fragile themselves, struggle to provide access to education to such people.
Highlighted below are actions and reforms that could lead the way toward solving the crisis:
- Leadership to jump-start transformation. The next U.S. administration should convene a high-level White House conference of sovereign donors, developing country leaders, key multilateral organizations, private sector and major philanthropists/foundations, and civil society to jump-start and energize a new, 10-year global response to this challenge. A key goal of this decadelong effort should be to transform education systems in the world’s poorest countries, particularly for girls and women, within a generation. That implies advancing much faster than the 100-plus years required if current programs and commitments remain as is.
- A whole-of-government leadership response. Such transformation of currently weak education systems in scores of countries over a generation will require sustained top-level political leadership, accompanied by substantial new donor and developing country investments. To ensure sustained attention for this initiative over multiple years, the U.S. administration will need to designate senior officials in the State Department, USAID, the National Security Council, the Office of Management and Budget, and elsewhere to form a whole-of-government leadership response that can energize other governments and actors.
- Teacher training and deployment at scale. A key component of a new global highest-level effort, based on securing progress against the Sustainable Development Goals and the Addis 2030 Framework, should be the training and deployment of 9 million new qualified teachers, particularly female teachers, in sub-Saharan Africa where they are most needed. Over 90 percent of the Global Partnership for Education’s education sector implementation grants have included investments in teacher development and training and 76 percent in the provision of learning materials.
- Foster positive disruption by engaging community level non-state actors who are providing education services in marginal areas where national systems do not reach the population. Related to this, increased financial and technical support to national governments are required to strengthen their non-state actor regulatory frameworks. Such frameworks must ensure that any non-state actors operate without discrimination and prioritize access for the most marginalized. The ideological divide on this issue—featuring a strong resistance by defenders of public education to tap into the capacities and networks of non-state actors—must be resolved if we are to achieve a rapid breakthrough.
- Confirm the appropriate roles for technology in equitably advancing access and quality of education, including in the initial and ongoing training of teachers and administrators, delivery of distance education to marginalized communities and assessment of learning, strengthening of basic systems, and increased efficiency of systems. This is not primarily about how various gadgets can help advance education goals.
- Commodity component. Availability of appropriate learning materials for every child sitting in a classroom—right level, right language, and right subject matter. Lack of books and other learning materials is a persistent problem throughout education systems—from early grades through to teaching colleges. Teachers need books and other materials to do their jobs. Consider how the USAID-hosted Global Book Alliance, working to address costs and supply chain issues, distribution challenges, and more can be strengthened and supported to produce the model(s) that can overcome these challenges.
Annual high-level stock take at the G-7. The next U.S. administration can work with G-7 partners to secure agreement on an annual stocktaking of progress against this new global education agenda at the upcoming G-7 summits. This also will help ensure sustained focus and pressure to deliver especially on equity and inclusion. Global Partnership for Education’s participation at the G-7 Gender Equality Advisory Council is helping ensure that momentum is maintained to mobilize the necessary political leadership and expertise at country level to rapidly step up progress in gender equality, in and through education. 3 Also consider a role for the G-20, given participation by some developing country partners.
Related Content
Jenny Perlman Robinson, Molly Curtiss Wyss
July 3, 2018
Michelle Kaffenberger
May 17, 2019
Ramya Vivekanandan
February 14, 2019
- “263 Million Children and Youth Are Out of School.” UNESCO UIS. July 15, 2016. http://uis.unesco.org/en/news/263-million-children-and-youth-are-out-school.
- “The Learning Generation: Investing in education for a changing world.” The International Commission on Financing Global Education Opportunity. 2016. https://report.educationcommission.org/downloads/.
- “Influencing the most powerful nations to invest in the power of girls.” Global Partnership for Education. March 12, 2019. https://www.globalpartnership.org/blog/influencing-most-powerful-nations-invest-power-girls.
Global Education
Global Economy and Development
Elyse Painter, Emily Gustafsson-Wright
January 5, 2024
Online only
9:00 am - 10:00 am EST
Nariman Moustafa
October 20, 2023

Global Education
By Hannah Ritchie, Veronika Samborska, Natasha Ahuja, Esteban Ortiz-Ospina and Max Roser
A good education offers individuals the opportunity to lead richer, more interesting lives. At a societal level, it creates opportunities for humanity to solve its pressing problems.
The world has gone through a dramatic transition over the last few centuries, from one where very few had any basic education to one where most people do. This is not only reflected in the inputs to education – enrollment and attendance – but also in outcomes, where literacy rates have greatly improved.
Getting children into school is also not enough. What they learn matters. There are large differences in educational outcomes : in low-income countries, most children cannot read by the end of primary school. These inequalities in education exacerbate poverty and existing inequalities in global incomes .
On this page, you can find all of our writing and data on global education.
Key insights on Global Education
The world has made substantial progress in increasing basic levels of education.
Access to education is now seen as a fundamental right – in many cases, it’s the government’s duty to provide it.
But formal education is a very recent phenomenon. In the chart, we see the share of the adult population – those older than 15 – that has received some basic education and those who haven’t.
In the early 1800s, fewer than 1 in 5 adults had some basic education. Education was a luxury; in all places, it was only available to a small elite.
But you can see that this share has grown dramatically, such that this ratio is now reversed. Less than 1 in 5 adults has not received any formal education.
This is reflected in literacy data , too: 200 years ago, very few could read and write. Now most adults have basic literacy skills.
What you should know about this data
- Basic education is defined as receiving some kind of formal primary, secondary, or tertiary (post-secondary) education.
- This indicator does not tell us how long a person received formal education. They could have received a full program of schooling, or may only have been in attendance for a short period. To account for such differences, researchers measure the mean years of schooling or the expected years of schooling .
Despite being in school, many children learn very little
International statistics often focus on attendance as the marker of educational progress.
However, being in school does not guarantee that a child receives high-quality education. In fact, in many countries, the data shows that children learn very little.
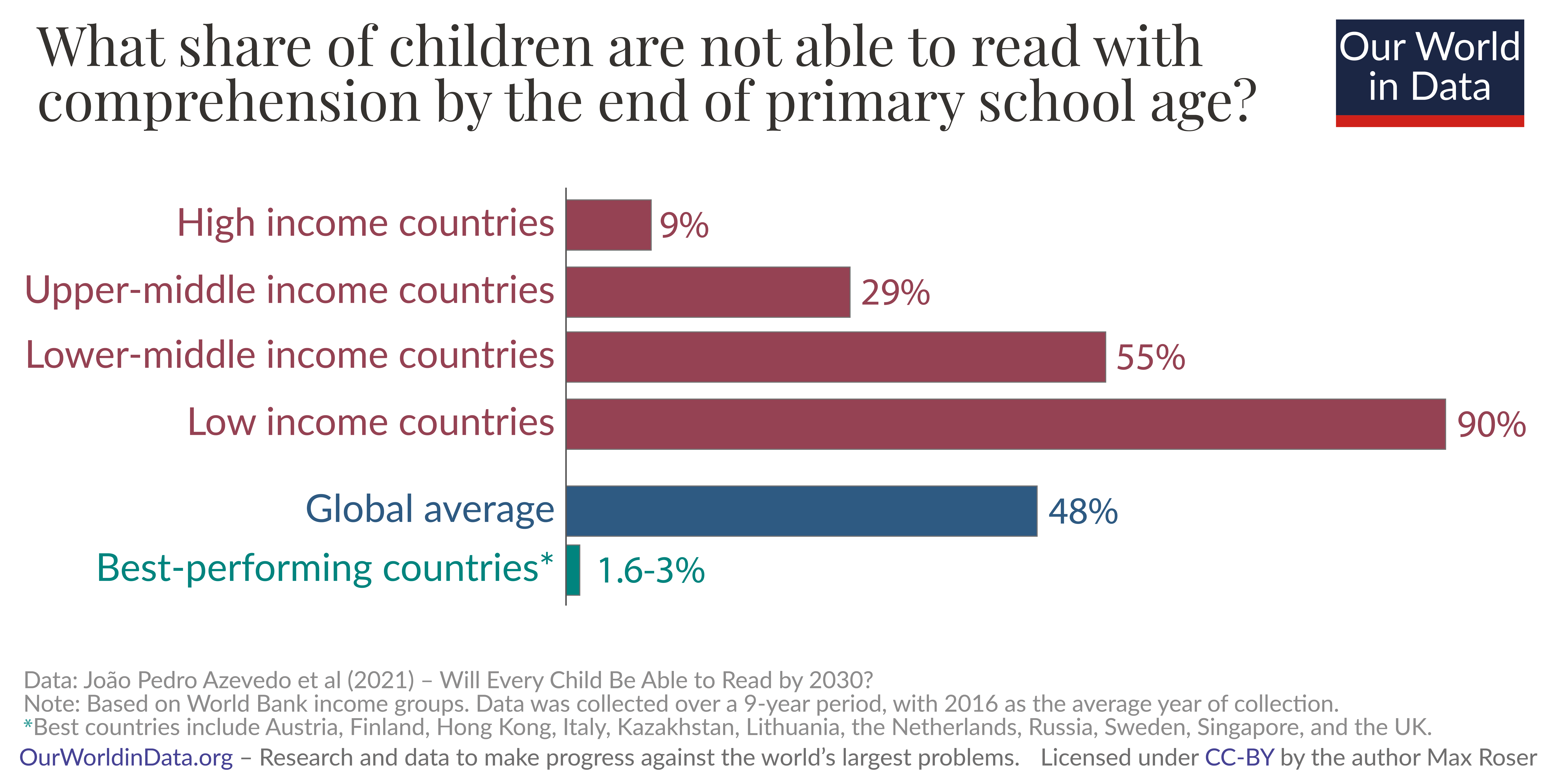
Just half – 48% – of the world’s children can read with comprehension by the end of primary school. It’s based on data collected over a 9-year period, with 2016 as the average year of collection.
This is shown in the chart, where we plot averages across countries with different income levels. 1
The situation in low-income countries is incredibly worrying, with 90% of children unable to read by that age.
This can be improved – even among high-income countries. The best-performing countries have rates as low as 2%. That’s more than four times lower than the average across high-income countries.
Making sure that every child gets to go to school is essential. But the world also needs to focus on what children learn once they’re in the classroom.

Millions of children learn only very little. How can the world provide a better education to the next generation?
Research suggests that many children – especially in the world’s poorest countries – learn only very little in school. What can we do to improve this?
- This data does not capture total literacy over someone’s lifetime. Many children will learn to read eventually, even if they cannot read by the end of primary school. However, this means they are in a constant state of “catching up” and will leave formal education far behind where they could be.
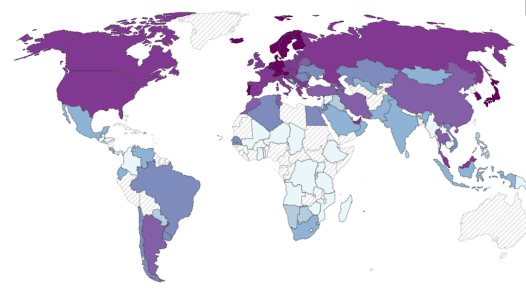
Children across the world receive very different amounts of quality learning
There are still significant inequalities in the amount of education children get across the world.
This can be measured as the total number of years that children spend in school. However, researchers can also adjust for the quality of education to estimate how many years of quality learning they receive. This is done using an indicator called “learning-adjusted years of schooling”.
On the map, you see vast differences across the world.
In many of the world’s poorest countries, children receive less than three years of learning-adjusted schooling. In most rich countries, this is more than 10 years.
Across most countries in South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa – where the largest share of children live – the average years of quality schooling are less than 7.
- Learning-adjusted years of schooling merge the quantity and quality of education into one metric, accounting for the fact that similar durations of schooling can yield different learning outcomes.
- Learning-adjusted years is computed by adjusting the expected years of school based on the quality of learning, as measured by the harmonized test scores from various international student achievement testing programs. The adjustment involves multiplying the expected years of school by the ratio of the most recent harmonized test score to 625. Here, 625 signifies advanced attainment on the TIMSS (Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study) test, with 300 representing minimal attainment. These scores are measured in TIMSS-equivalent units.
Hundreds of millions of children worldwide do not go to school
While most children worldwide get the opportunity to go to school, hundreds of millions still don’t.
In the chart, we see the number of children who aren’t in school across primary and secondary education.
This number was around 260 million in 2019.
Many children who attend primary school drop out and do not attend secondary school. That means many more children or adolescents are missing from secondary school than primary education.

Access to basic education: almost 60 million children of primary school age are not in school
The world has made a lot of progress in recent generations, but millions of children are still not in school.
The gender gap in school attendance has closed across most of the world
Globally, until recently, boys were more likely to attend school than girls. The world has focused on closing this gap to ensure every child gets the opportunity to go to school.
Today, these gender gaps have largely disappeared. In the chart, we see the difference in the global enrollment rates for primary, secondary, and tertiary (post-secondary) education. The share of children who complete primary school is also shown.
We see these lines converging over time, and recently they met: rates between boys and girls are the same.
For tertiary education, young women are now more likely than young men to be enrolled.
While the differences are small globally, there are some countries where the differences are still large: girls in Afghanistan, for example, are much less likely to go to school than boys.
Research & Writing
Talent is everywhere, opportunity is not. We are all losing out because of this.
Access to basic education: almost 60 million children of primary school age are not in school, interactive charts on global education.
This data comes from a paper by João Pedro Azevedo et al.
João Pedro Azevedo, Diana Goldemberg, Silvia Montoya, Reema Nayar, Halsey Rogers, Jaime Saavedra, Brian William Stacy (2021) – “ Will Every Child Be Able to Read by 2030? Why Eliminating Learning Poverty Will Be Harder Than You Think, and What to Do About It .” World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 9588, March 2021.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this topic page, please also cite the underlying data sources. This topic page can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
- Side Hustles
- Power Players
- Young Success
- Save and Invest
- Become Debt-Free
- Land the Job
- Closing the Gap
- Science of Success
- Pop Culture and Media
- Psychology and Relationships
- Health and Wellness
- Real Estate
- Most Popular
Related Stories
- Raising Successful Kids 5 ways parents can help their kids be more successful than most
- Health and Wellness The No. 1 thing that leads to happiness can also help your business excel
- Raising Successful Kids 3 simple ways to teach your kid about money and 'change their life'
- Psychology and Relationships We've studied over 30,000 couples—here are 6 phrases you'll hear in the most successful relationships
- Raising Successful Kids Want to raise successful kids? Teach them how to get angry, psychologist says
'Our future as humanity is in peril': UNESCO report says education should focus on these 4 problems

For the past two years, the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, known as UNESCO, developed a report to define international education goals.
The report , titled "Reimagining Our Futures Together: a New Social Contract for Education" identifies key issues that all countries should center their educational systems around.
"The main problems we're trying to fix are climate change, democratic backsliding, growing social inequality, and growing social fragmentation. And the report is saying this is the business of educational institutions," says Fernando Reimers, director of the Global Education Innovation Initiative at Harvard University and member of UNESCO's commission on the Futures of Education. "Unless educational institutions intentionally align what they do with these four challenges, our future as humanity is in peril."
Unfortunately, Reimers says that the United States' education system is not currently designed to address these challenges. "I'm very concerned, frankly, for the disconnect between education in America and the big challenges of America," he warns.

The report comes shortly after the COP26 summit in which 200 countries approved a U.N.-brokered pact that critics say falls short of limiting global warming after delegates struggled to resolve major sticking points , such as phasing out coal, fossil fuel subsidies and financial support to low-income countries.
To help address climate change, Reimers says research universities should partner with elementary, middle and high schools to develop curriculum for the next generation of climate scientists and should open access to available research and data.
"We call on the 28,000 universities of the world to partner with school systems for the purpose of collaborating, of sharing what they know, and in building curriculum," he says. "How can you hope that a teacher by herself in her classroom can design the most effective climate change curriculum, when the science of climate change is in research universities, in laboratories, in departments of physics, of chemistry and so on? We need to find ways to connect those dots and to create collaborations."
And Reimers says collaboration between schools and business sectors can help address many of the other concerns raised by the international community.
"Integrate schools with other schools, in partnerships with universities, in partnerships with organizations of civil society, in partnerships with businesses, for the purpose of providing students the experiences that they will need to develop the capacity to address these challenges," argues Reimers. "And that is a tall order, we realize, because the [common] model of education is one where a little school with their teacher, in her classroom, or in his classroom, can solve all the problems in the world. And we just don't see that happening, given the scale of the problem."
The report points out that poverty and poor educational opportunities are often interconnected and claims that collaboration between businesses and schools may help address growing inequality in wealth.
The report also comes after the United States, for the first time in history , was added to a list of "backsliding democracies" by the International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance, an organization based in Sweden.
"The National Defense Council produces a report every four years on the main challenges to our democracy. The report they released this March said that the main challenge to American democracy is growing social fragmentation. If we don't figure out a way to bridge our divides, and to agree, this democracy may not survive," says Reimers, pointing to the Jan 6. insurrection at the Capitol as an example of the U.S. educational system failing to produce citizens that address their concerns through democratic means. He also mentions anti-democratic violence in countries such as Turkey, Poland and Russia.
"In a society that is governed by law, individuals shouldn't resort to violence to resolve their differences," says Reimers. "In a number of countries, you now have regimes who unabashedly see no problem in using violence as an instrument to maintain political control and to advance political ideas. And of course, that means the end of the world that was built after World War II, ruled on the notion of human rights. And I hope we don't want to live to see that world. That's why this is a call to action to educators saying, 'The stakes are very high.' If we want human rights to actually mean something, we better examine whether we are preparing students to understand these rights and to live in a manner that these rights actually have any reality in their own lives."
He says including topics of human rights in curriculums, as defined by the United Nations in 1948 , could help education systems around the world avoid democratic backsliding and social fragmentation.
"It is very important that educational institutions help individuals think about purposes bigger than themselves, not as an idea, but as a practice, to help [students] understand that the business of addressing climate change is our business, that the business of making democracy work is our business, that the business of growing inequality is everybody's business," says Reimers. "The truth is, we have curricula, and we have the knowledge about how to develop these capacities in children."
"But in the United States, we have a huge problem in that our growing social fragmentation and political polarization is invading our schools, our school boards, and making it even harder to tackle these challenges."
Don't miss:
- You're more likely to have your FAFSA verified than to have your taxes audited—here's why
- 3 things student loan borrowers should know before the end of the year
- College tuition increased at historically low rates this year—why that's 'good news' for students

The Education Crisis: Being in School Is Not the Same as Learning

First grade students in Pakistan’s Balochistan Province are learning the alphabet through child-friendly flash cards. Their learning materials help educators teach through interactive and engaging activities and are provided free of charge through a student’s first learning backpack. © World Bank
THE NAME OF THE DOG IS PUPPY. This seems like a simple sentence. But did you know that in Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda, three out of four third grade students do not understand it? The world is facing a learning crisis . Worldwide, hundreds of millions of children reach young adulthood without even the most basic skills like calculating the correct change from a transaction, reading a doctor’s instructions, or understanding a bus schedule—let alone building a fulfilling career or educating their children. Education is at the center of building human capital. The latest World Bank research shows that the productivity of 56 percent of the world’s children will be less than half of what it could be if they enjoyed complete education and full health. For individuals, education raises self-esteem and furthers opportunities for employment and earnings. And for a country, it helps strengthen institutions within societies, drives long-term economic growth, reduces poverty, and spurs innovation.


One of the most interesting, large scale educational technology efforts is being led by EkStep , a philanthropic effort in India. EkStep created an open digital infrastructure which provides access to learning opportunities for 200 million children, as well as professional development opportunities for 12 million teachers and 4.5 million school leaders. Both teachers and children are accessing content which ranges from teaching materials, explanatory videos, interactive content, stories, practice worksheets, and formative assessments. By monitoring which content is used most frequently—and most beneficially—informed decisions can be made around future content.
In the Dominican Republic, a World Bank supported pilot study shows how adaptive technologies can generate great interest among 21st century students and present a path to supporting the learning and teaching of future generations. Yudeisy, a sixth grader participating in the study, says that what she likes doing the most during the day is watching videos and tutorials on her computer and cell phone. Taking childhood curiosity as a starting point, the study aimed to channel it towards math learning in a way that interests Yudeisy and her classmates.

Yudeisy, along with her classmates in a public elementary school in Santo Domingo, is part of a four-month pilot to reinforce mathematics using software that adapts to the math level of each student. © World Bank
Adaptive technology was used to evaluate students’ initial learning level to then walk them through math exercises in a dynamic, personalized way, based on artificial intelligence and what the student is ready to learn. After three months, students with the lowest initial performance achieved substantial improvements. This shows the potential of technology to increase learning outcomes, especially among students lagging behind their peers. In a field that is developing at dizzying speeds, innovative solutions to educational challenges are springing up everywhere. Our challenge is to make technology a driver of equity and inclusion and not a source of greater inequality of opportunity. We are working with partners worldwide to support the effective and appropriate use of educational technologies to strengthen learning.
When schools and educations systems are managed well, learning happens
Successful education reforms require good policy design, strong political commitment, and effective implementation capacity . Of course, this is extremely challenging. Many countries struggle to make efficient use of resources and very often increased education spending does not translate into more learning and improved human capital. Overcoming such challenges involves working at all levels of the system.
At the central level, ministries of education need to attract the best experts to design and implement evidence-based and country-specific programs. District or regional offices need the capacity and the tools to monitor learning and support schools. At the school level, principals need to be trained and prepared to manage and lead schools, from planning the use of resources to supervising and nurturing their teachers. However difficult, change is possible. Supported by the World Bank, public schools across Punjab in Pakistan have been part of major reforms over the past few years to address these challenges. Through improved school-level accountability by monitoring and limiting teacher and student absenteeism, and the introduction of a merit-based teacher recruitment system, where only the most talented and motivated teachers were selected, they were able to increase enrollment and retention of students and significantly improve the quality of education. "The government schools have become very good now, even better than private ones," said Mr. Ahmed, a local villager.
The World Bank, along with the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and the UK’s Department for International Development, is developing the Global Education Policy Dashboard . This new initiative will provide governments with a system for monitoring how their education systems are functioning, from learning data to policy plans, so they are better able to make timely and evidence-based decisions.
Education reform: The long game is worth it
In fact, it will take a generation to realize the full benefits of high-quality teachers, the effective use of technology, improved management of education systems, and engaged and prepared learners. However, global experience shows us that countries that have rapidly accelerated development and prosperity all share the common characteristic of taking education seriously and investing appropriately. As we mark the first-ever International Day of Education on January 24, we must do all we can to equip our youth with the skills to keep learning, adapt to changing realities, and thrive in an increasingly competitive global economy and a rapidly changing world of work.
The schools of the future are being built today. These are schools where all teachers have the right competencies and motivation, where technology empowers them to deliver quality learning, and where all students learn fundamental skills, including socio-emotional, and digital skills. These schools are safe and affordable to everyone and are places where children and young people learn with joy, rigor, and purpose. Governments, teachers, parents, and the international community must do their homework to realize the promise of education for all students, in every village, in every city, and in every country.
The Bigger Picture: In-depth stories on ending poverty
4 trends that will shape the future of higher education

Higher education needs to address the problems it faces by moving towards active learning, and teaching skills that will endure in a changing world. Image: Vasily Koloda for Unsplash
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Diana El-Azar

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Education is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
Listen to the article
- Measures adopted during the pandemic do not address the root causes of the problems facing higher education.
- Institutions need to undertake true reform, moving towards active learning, and teaching skills that will endure in a changing world.
- Formative assessment is more effective than high-stakes exams in equipping students with the skills they need to succeed.
Since the onset of the recent pandemic, schools and universities have been forced to put a lot of their teaching online. On the surface, this seems to have spurred a series of innovations in the education sector. Colleges around the world embraced more flexibility, offering both virtual and physical classrooms. Coding is making its way into more school curricula , and the SAT exam for college admission in the US has recently been shortened and digitized , making it easier to take and less stressful for students.
These changes might give the illusion that education is undergoing some much-needed reform. However, if we look closely, these measures do not address the real problems facing higher education. In most countries, higher education is inaccessible to the socio-economically underprivileged, certifies knowledge rather than nurtures learning, and focuses on easily-outdated knowledge. In brief, it is failing on both counts of quality and access.
Have you read?
Four ways universities can future-proof education, the global education crisis is even worse than we thought. here's what needs to happen, covid-19’s impact on jobs and education: using data to cushion the blow, higher education trends.
In the last year, we have started to see examples of true reform, addressing the root causes of the education challenge. Below are four higher education trends we see taking shape in 2022.
1. Learning from everywhere
There is recognition that as schools and universities all over the world had to abruptly pivot to online teaching, learning outcomes suffered across the education spectrum . However, the experiment with online teaching did force a reexamination of the concepts of time and space in the education world. There were some benefits to students learning at their own pace, and conducting science experiments in their kitchens . Hybrid learning does not just mean combining a virtual and physical classroom, but allowing for truly immersive and experiential learning, enabling students to apply concepts learned in the classroom out in the real world.
So rather than shifting to a “learn from anywhere ” approach (providing flexibility), education institutions should move to a “learn from everywhere ” approach (providing immersion). One of our partners, the European business school, Esade, launched a new bachelor’s degree in 2021, which combines classes conducted on campus in Barcelona, and remotely over a purpose-designed learning platform, with immersive practical experiences working in Berlin and Shanghai, while students create their own social enterprise. This kind of course is a truly hybrid learning experience.

2. Replacing lectures with active learning
Lectures are an efficient way of teaching and an ineffective way of learning. Universities and colleges have been using them for centuries as cost-effective methods for professors to impart their knowledge to students.
However, with digital information being ubiquitous and free, it seems ludicrous to pay thousands of dollars to listen to someone giving you information you can find elsewhere at a much cheaper price. School and college closures have shed light on this as bad lectures made their way into parents’ living rooms, demonstrating their ineffectiveness.
Education institutions need to demonstrate effective learning outcomes, and some are starting to embrace teaching methods that rely on the science of learning. This shows that our brains do not learn by listening, and the little information we learn that way is easily forgotten (as shown by the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve , below). Real learning relies on principles such as spaced learning, emotional learning, and the application of knowledge.

The educational establishment has gradually accepted this method, known as 'fully active learning'. There is evidence that it not only improves learning outcomes but also reduces the education gap with socio-economically disadvantaged students. For example, Paul Quinn College, an HBCU based in Texas, launched an Honors Program using fully active learning in 2020, combined with internships at regional employers. This has given students from traditionally marginalised backgrounds the opportunity to apply the knowledge gained at university in the real world.
3. Teaching skills that remain relevant in a changing world
According to a recent survey, 96% of Chief Academic Officers at universities think they are doing a good job preparing young people for the workforce . Less than half (41%) of college students and only 11% of business leaders shared that view. Universities continue to focus on teaching specific skills involving the latest technologies, even though these skills and the technologies that support them are bound to become obsolete. As a result, universities are forever playing catch up with the skills needed in the future workplace.
What we need to teach are skills that remain relevant in new, changing, and unknown contexts. For example, journalism students might once have been taught how to produce long-form stories that could be published in a newspaper; more recently, they would have been taught how to produce shorter pieces and post content for social media. More enduring skills would be: how to identify and relate to readers, how to compose a written piece; how to choose the right medium for your target readership. These are skills that cross the boundaries of disciplines, applying equally to scientific researchers or lawyers.
San Francisco-based Minerva University, which shares a founder with the Minerva Project, has broken down competencies such as critical thinking or creative thinking into foundational concepts and habits of mind . It teaches these over the four undergraduate years and across disciplines, regardless of the major a student chooses to pursue.

4. Using formative assessment instead of high-stake exams
If you were to sit the final exam of the subject you majored in today, how would you fare? Most of us would fail, as that exam did not measure our learning, but rather what information we retained at that point in time. Equally, many of us hold certifications in subject matters we know little about.
Many people gain admission to higher education based on standardized tests that skew to a certain socio-economic class , rather than measure any real competency level. Universities then try to rectify this bias by imposing admission quotas, rather than dissociating their evaluation of competence from income level. Many US universities are starting to abandon standardized tests, with Harvard leading the charge , and there have been some attempts to replace high-stake exams with other measures that not only assess learning outcomes but actually improve them.
Formative assessment, which entails both formal and informal evaluations through the learning journey, encourages students to actually improve their performance rather than just have it evaluated. The documentation and recording of this assessment includes a range of measures, replacing alphabetical or numerical grades that are uni-dimensional.
The COVID-19 pandemic and recent social and political unrest have created a profound sense of urgency for companies to actively work to tackle inequity.
The Forum's work on Diversity, Equality, Inclusion and Social Justice is driven by the New Economy and Society Platform, which is focused on building prosperous, inclusive and just economies and societies. In addition to its work on economic growth, revival and transformation, work, wages and job creation, and education, skills and learning, the Platform takes an integrated and holistic approach to diversity, equity, inclusion and social justice, and aims to tackle exclusion, bias and discrimination related to race, gender, ability, sexual orientation and all other forms of human diversity.
The Platform produces data, standards and insights, such as the Global Gender Gap Report and the Diversity, Equity and Inclusion 4.0 Toolkit , and drives or supports action initiatives, such as Partnering for Racial Justice in Business , The Valuable 500 – Closing the Disability Inclusion Gap , Hardwiring Gender Parity in the Future of Work , Closing the Gender Gap Country Accelerators , the Partnership for Global LGBTI Equality , the Community of Chief Diversity and Inclusion Officers and the Global Future Council on Equity and Social Justice .
The International School in Geneva just launched its Learner Passport that includes measures of creativity, responsibility and citizenship. In the US, a consortium of schools have launched the Mastery Transcript Consortium that has redesigned the high school transcript to show a more holistic picture of the competencies acquired by students.
Education reform requires looking at the root cause of some of its current problems. We need to look at what is being taught (curriculum), how (pedagogy), when and where (technology and the real world) and whom we are teaching (access and inclusion). Those institutions who are ready to address these fundamental issues will succeed in truly transforming higher education.
Don't miss any update on this topic
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Education .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

How universities can use blockchain to transform research
Scott Doughman
March 12, 2024

Empowering women in STEM: How we break barriers from classroom to C-suite
Genesis Elhussein and Julia Hakspiel
March 1, 2024

Why we need education built for peace – especially in times of war
February 28, 2024

These 5 key trends will shape the EdTech market upto 2030
Malvika Bhagwat
February 26, 2024

With Generative AI we can reimagine education — and the sky is the limit
Oguz A. Acar
February 19, 2024

How UNESCO is trying to plug the data gap in global education
February 12, 2024
Education 2030: topics and issues

The debates included the following sessions:
Providing meaningful learning opportunities to out-of-school children
In this session a panel of experts explored the changes needed in countries which have large out-of-school children populations as well as examples from countries which are ‘in the final mile’. “They are all different, they don’t fit into one box” said Mary Joy Pigozzi, Director of Educate A Child (EAC). Ms Pigozzi emphasized the need for attention to children who are displaced, conflict affected, working children, and so on. Mr Albert Montivans, Head of Education Indicators and Data Analysis at UNESCO Institute for Statistics added: “one of the priorities is to better the disadvantaged”.
The session was also attended by the Minister of Education, Haiti, Nesmy Manigat, the CEO of Global Partnership for Education Alice Albright, and the Director-General in the Romanian Ministry of Education, Liliana Preoteasa. The panelists raised their voices on ‘inclusion’, ‘partnership’, ‘financing’, and ‘sustainable planning’ in order to pull youngsters into the schooling system. The session concluded with further food for thought from Mr Nesmy Manigat, the Minister of Education,Haiti: “Let’s also talk about the children who are in school, yet they do not learn. Teach them what the meaning of school is - what do we need to do in school and not only focus on the policies”.
Mobilizing Business to Realize the 2030 Education Agenda
Representatives from business and education organizations gathered at a parallel session on mobilizing business to realize the 2030 agenda. Chaired by Justin van Fleet, Chief of Staff for the UN Special Envoy for Global Education, the session established a business case to invest in education and focused on how business can coordinate action with other stakeholders. The lively discussion saw questions from the floor around ICT’s, but also issues of trust; with a representative from the Philippines asking the panel whether business cares about education or is simply benefiting from it. The President of Lego Education, Mr Jacob Kragh, said there was a sincere objective from the company “to pursue the benefit of the children and make sure they get the chance to be the best they can in life”. He said that "taking over education was by no means the objective of the private sector", and reiterated the importance of working closely with governments and the public sector. Panelists also included Vikas Pota from GEMS Education, Martina Roth from Intel Corporation and Jouko Sarvi from the Asian Development Bank.
In parallel, Argentina’s Minister of Education, Alberto Sileoni, was joined by UNESCO Director, David Atchoarena, and UN Special Advisor on Post-2015 Development Planning, Amina Mohammed, at a session on Global and regional coordination and monitoring mechanisms. The session dealt with the importance of having robust mechanisms for coordination and monitoring. Session participants looked at how global and regional mechanisms for education should work alongside the new mechanisms for the overall Sustainable Development Goal, with Mr Atchoarena pointing out that the focus on ‘country-level’ monitoring and review was much stronger in the new education agenda.
Effective Governance and Accountability
In this group session, the panelists suggested the right direction for contemporary national education governance. Namely the key policies and strategies to construct a pragmatic governance framework that is both regulatory and collaborative were suggested throughout the discussion.
The chair, Mr. Gwang-Jo Kim, Director of UNESCO’s regional office in Bangkok, Thailand, posed three questions before the discussion: How can we define the term “effective governance”. What would be the role of the private sector and how to balance between autonomy resulting from decentralization, and accountability. The panels and the participants engaged in a lively debate: “Governance should focus on dialogue between communities in society so that private sector can become stakeholders to invest in education,” stated the Minister of Education, Bolivia, Roberto Aguilar, as an answer to the second question. He also gave an example from his country where education campaigns are usually funded by private institutions, saying it is social responsibility for private entities to participate actively in the effective governance framework.
The Minster of Education, Democratic Republic of Congo,Maker Mwangu Famba, said the core elements of effective governance were transparency and responsibility.
How does education contribute to sustainable development post 2015?
Sustainable development is not just about technological solutions, political regulation or financial instruments alone. The realization of the transformative power of education and the importance of cross-sectoral approaches need to be taken into account. This was the message given by Ms Amina Mohammed, Special Advisor to the UN Secretary-General on Post 2015 Development Planning, as she said that education was not simply about learning, it is about empowerment and key in the sustainable development agenda. In this session, the panel members discussed how education can address global challenges, in particular how education contributes to addressing climate change and health issues and poverty reduction.
Education is one of the most powerful tools for people to be informed about diseases, take preventative measures, recognize signs of illness early and be informed to use health care services, the speakers highlighted. Mr Mark Brown, the Minister of Finance in Cook Islands, said that current knowledge as well as new knowledge should reach not only school children but also adults, as they are the educators.
The growing interaction between education and climate change cannot be neglected, Ms Kandia Camara, Minister of National Education, Cote d’lvoire, said: “There are school programs to teach healthy lifestyles and the importance of forests,” actions are being taken to ensure climate-safe and climate-friendly school environments.
Furthermore, Mr Renato Janine Ribeiro, Minister of Education in Brazil, expressed the difficulty of eradicating poverty, “the challenge we face is ‘hunger, they live in places that are very difficult to access”, he said. Hence, geographic placement poses as a barrier to accessibility. Yet, in order to mitigate the problem with a collective effort, he asserted that Brazil would be happy to share its valuable experience on education for sustainable development with any country in order to bolster efforts.
Towards the end of the session, the CEO of the Campaign for Popular Education, Bangladesh, Ms Rasheda Choudhury, firmly stated: “The two nonnegotiable principles are: first, education is a fundamental human right and second, it is the state’s responsibility to provide education to their every single citizen”.

Other recent news

Peter DeWitt's
Finding common ground.
A former K-5 public school principal turned author, presenter, and leadership coach, DeWitt provides insights and advice for education leaders. He can be found at www.petermdewitt.com . Read more from this blog .
11 Critical Issues Facing Educators in 2023

- Share article
For several years, I wrote a list of 10, 11, or even 15 critical issues facing education at the end of a year to give a glimpse into issues to consider for the following year. Then COVID happened and blew my last list of issues up. Why? Because it never occurred to me to put a pandemic on the list of critical issues in 2019.
We have educational issues to consider every year that also highlight what teachers, leaders, and students face. Education has often been a dumping ground for criticism of educators who are tasked with teaching children content, feeding them when they come in hungry because they live in poverty or are homeless, and, at the same time, practicing school safety drills because students and teachers have to prepare for fending off the next school shooter.
Television shows and movies poke fun at educators and school, politicians have “plans” about how they can do it better, although the large majority of them ever step foot in a school since they graduated. During all of that “entertainment,” educators are supposed to just go in and do their jobs for the love of education and children.
And that’s exactly what they do.
11 Issues for 2023
These issues were chosen based on the number of times they came up in stories on Education Week or in workshops and coaching sessions that I do in my role as a leadership coach and workshop facilitator.
For full disclosure, some of the issues will be difficult to read, but they are the reality for teachers, leaders, staff, and students around the country. With that being said, the issues on the list are not exhaustive, and as always, if you have an issue to add to the list, find me on social media and let me know which ones are a top priority for you.
Guns – Recent research from the Centers for Disease Control shows that firearms are the leading cause of death for children. This research study cites the CDC report and says there were 45,222 total firearm-related deaths in the United States in 2020, and around 10% of those were children and teens . Just to be intentional, because people will accuse me of a political argument, what this has to do with schools is the fact that the children who are killed or injured are our students. These deaths and this topic have an enormous impact on schools.
Politics in education – In the last couple of years, school leaders and teachers have had to fight rumors about teaching critical race theory, and we know states like Arkansas, Oklahoma, and Florida have governors or secretaries of education who want to ban conversations around equity, race, and social-emotional learning. Politics have always been a part of education, but the last few years have brought an increased level of it into our classrooms and schools.
Social-emotional learning – Critics believe that social-emotional learning is about indoctrinating students, which is wholly inaccurate. Social-emotional learning is about teaching students about empathy and how to self-regulate their behavior so they can better deal with stress and anxiety. This will continue to be an issue playing out in schools, and we will see work by researchers like Marc Brackett and his team at Yale be at the forefront of this issue.
The Flu – I’m not putting this on the list because I didn’t anticipate COVID in 2019. It’s on the list because, according to the CDC , there are millions of children each year who get the flu. Currently, we know that the respiratory virus RSV has affected millions of children under the age of 5, which does impact preschool- and kindergarten-age children, as well as their siblings or grandparents. Between the flu and RSV, schools will continue to see an increase in student absenteeism. Considering the COVID learning-loss debate that hit schools after COVID, that discourse will only continue. Here’s a recent story written by my Ed Week colleague Evie Blad covering student absences.
De-implementation – This is not as self-serving as it may seem. I say that because I have done a great deal of research on the topic of de-implementation and written a book about it . It’s on the list because it is a topic that school leaders are exploring. No longer should the conversation about workload be one that we push to the side, and de-implementing ineffective practices is a way to make the workload more manageable. Here is a YouTube video with 5 areas to consider when de-implementing.
Substitute teachers – In many states, it is no longer required that substitute teachers have an associate degree. There are states that have lowered the requirement to a high school diploma, yet there is still a shortage of substitute teachers. The lesser standard also brings into question the ability of substitute teachers to cover important core content for students.
Poverty – According to the National Center for Children Living in Poverty, there are 11 million children in that situation. Countless schools around the country are tasked not only with educating students but also feeding them breakfast and lunch as well. During COVID, school leaders, teachers, and staff made bag lunches for these students on a daily basis.
Teacher shortage – My Ed Week colleague Madeline Will recently wrote a story highlighting just how bad the teacher shortage is in the United States . However, this is not just a problem in the United States. Countries around the world are experiencing the same issue. Please check out this article by Ed Week reporter Caitlynn Peetz for the sobering statistics behind this issue.
Teacher-prep programs – Not only should there be conversations about how colleges and universities are preparing our nation’s teachers, but a big issue for 2023 is how those same colleges and universities are recruiting prospective teachers to enter the profession in the first place.
Tutoring programs – With a lot of coverage about COVID learning loss, tutoring as a means of “catching kids up” is going to be a big topic in 2023. Education Week is planning to do a series of articles and provide research on the topic, and I will be moderating a conversation on the topic for A Seat at the Table in 2023.
A love for learning – I know this sounds hokey, but it’s not. There are countless teachers, leaders, and staff trying to inspire a love for learning for themselves and their students. Too often, education is seen as a system of compliance rather than an institution of inspiration and creativity. We need to change that in 2023. Will the political rhetoric allow us to do that?
The opinions expressed in Peter DeWitt’s Finding Common Ground are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
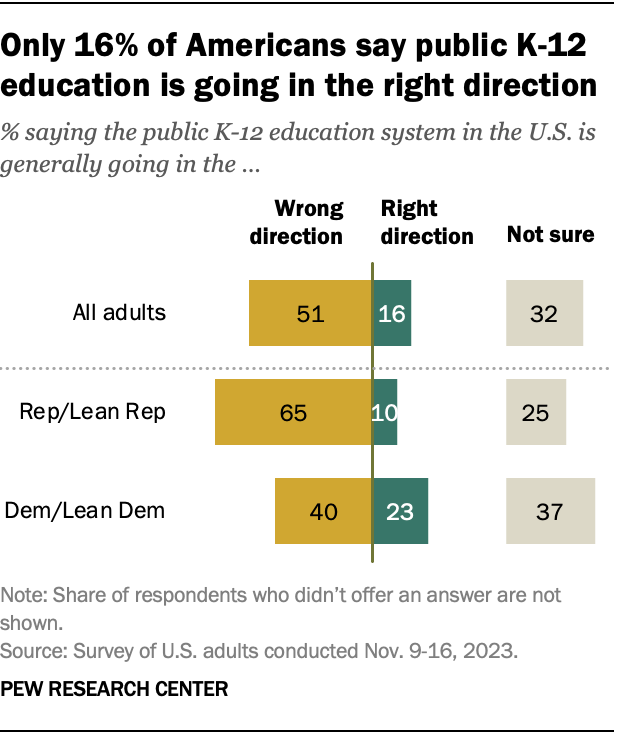
About half of americans say public k-12 education is going in the wrong direction.

About half of U.S. adults (51%) say the country’s public K-12 education system is generally going in the wrong direction. A far smaller share (16%) say it’s going in the right direction, and about a third (32%) are not sure, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in November 2023.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand how Americans view the K-12 public education system. We surveyed 5,029 U.S. adults from Nov. 9 to Nov. 16, 2023.
The survey was conducted by Ipsos for Pew Research Center on the Ipsos KnowledgePanel Omnibus. The KnowledgePanel is a probability-based web panel recruited primarily through national, random sampling of residential addresses. The survey is weighted by gender, age, race, ethnicity, education, income and other categories.
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and the survey methodology .
A majority of those who say it’s headed in the wrong direction say a major reason is that schools are not spending enough time on core academic subjects.
These findings come amid debates about what is taught in schools , as well as concerns about school budget cuts and students falling behind academically.
Related: Race and LGBTQ Issues in K-12 Schools
Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say the public K-12 education system is going in the wrong direction. About two-thirds of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents (65%) say this, compared with 40% of Democrats and Democratic leaners. In turn, 23% of Democrats and 10% of Republicans say it’s headed in the right direction.
Among Republicans, conservatives are the most likely to say public education is headed in the wrong direction: 75% say this, compared with 52% of moderate or liberal Republicans. There are no significant differences among Democrats by ideology.
Similar shares of K-12 parents and adults who don’t have a child in K-12 schools say the system is going in the wrong direction.
A separate Center survey of public K-12 teachers found that 82% think the overall state of public K-12 education has gotten worse in the past five years. And many teachers are pessimistic about the future.
Related: What’s It Like To Be A Teacher in America Today?
Why do Americans think public K-12 education is going in the wrong direction?
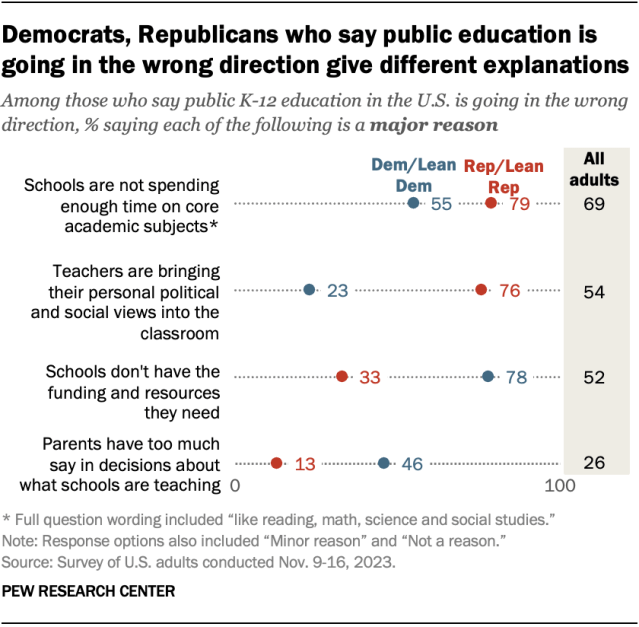
We asked adults who say the public education system is going in the wrong direction why that might be. About half or more say the following are major reasons:
- Schools not spending enough time on core academic subjects, like reading, math, science and social studies (69%)
- Teachers bringing their personal political and social views into the classroom (54%)
- Schools not having the funding and resources they need (52%)
About a quarter (26%) say a major reason is that parents have too much influence in decisions about what schools are teaching.
How views vary by party
Americans in each party point to different reasons why public education is headed in the wrong direction.
Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say major reasons are:
- A lack of focus on core academic subjects (79% vs. 55%)
- Teachers bringing their personal views into the classroom (76% vs. 23%)
In turn, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to point to:
- Insufficient school funding and resources (78% vs. 33%)
- Parents having too much say in what schools are teaching (46% vs. 13%)
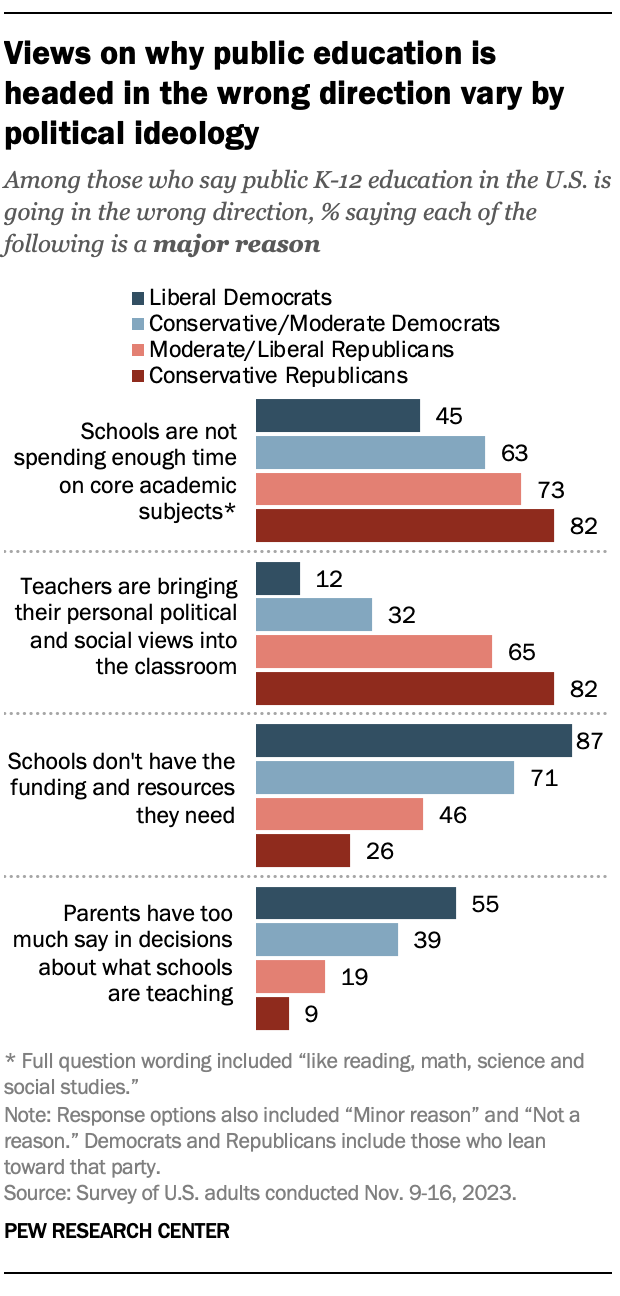
Views also vary within each party by ideology.
Among Republicans, conservatives are particularly likely to cite a lack of focus on core academic subjects and teachers bringing their personal views into the classroom.
Among Democrats, liberals are especially likely to cite schools lacking resources and parents having too much say in the curriculum.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and the survey methodology .

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
‘Back to school’ means anytime from late July to after Labor Day, depending on where in the U.S. you live
Among many u.s. children, reading for fun has become less common, federal data shows, most european students learn english in school, for u.s. teens today, summer means more schooling and less leisure time than in the past, about one-in-six u.s. teachers work second jobs – and not just in the summer, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
We couldn’t find any results matching your search.
Please try using other words for your search or explore other sections of the website for relevant information.
We’re sorry, we are currently experiencing some issues, please try again later.
Our team is working diligently to resolve the issue. Thank you for your patience and understanding.
News & Insights

Crude Oil News Today: Bullish Forecast Amid Global Developments
April 05, 2024 — 05:57 am EDT
Written by James Hyerczyk for FX Empire ->
Crude Oil Market Overview
Mixed signals emerge in the crude oil futures market this Friday, presenting a contrast to the significant advances seen earlier in the week. While geopolitical concerns and supply issues have previously fueled gains, the current market pause reflects anticipation of the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls report’s potential impact on Federal Reserve policies and crude oil demand.
At 09:44 GMT, Light Crude Oil Futures are trading $86.55, down $0.04 or -0.05%. This is down from an intraday high of $87.07.
Geopolitical and Supply Influences
This week’s upward trend in oil prices, marking a second successive weekly gain, can be attributed to heightened geopolitical tensions in Europe and the Middle East, combined with concerns over tightening supplies. Both Brent and WTI have reached their highest levels since October, signaling a strong bullish momentum.
More Price Appreciation Expected
The immediate outlook suggests a continued rise in oil prices. Economic optimism, persistent supply constraints, and increasing geopolitical risks are converging to push prices upward. Analysts have revised their short-term Brent price target to $95 per barrel, reflecting these factors. WTI is forecast to overcome $90 per barrel.
Key Developments in Geopolitics and Supply
Recent events in the Middle East and Russia are significantly impacting the oil market. Iran’s response to an attack attributed to Israel and ongoing Ukrainian drone strikes on Russian refineries, reportedly disrupting significant production capacity, are critical elements in the current supply tightness.
OPEC+ Stance and Heavy Oil Supply
OPEC+ maintains a firm stance on its supply policy, urging better compliance with output cuts. This approach, along with decreased heavy oil exports from Mexico and the UAE, is leading to a tighter global heavy oil market.
Demand Growth and Economic Indicators
The demand for oil continues its strong growth trajectory, with a notable increase in the first quarter. High-frequency indicators suggest a March consumption rate higher than expected, aligning with a strengthening global economic recovery. The upcoming U.S. employment report is keenly awaited for insights into economic health and future monetary policy.
Short-Term Forecast
The confluence of geopolitical instability, supply concerns, and strong demand growth points to a bullish short-term outlook for crude oil. These factors are expected to drive further price increases, making market conditions favorable for continued upward movement.
Technical Analysis
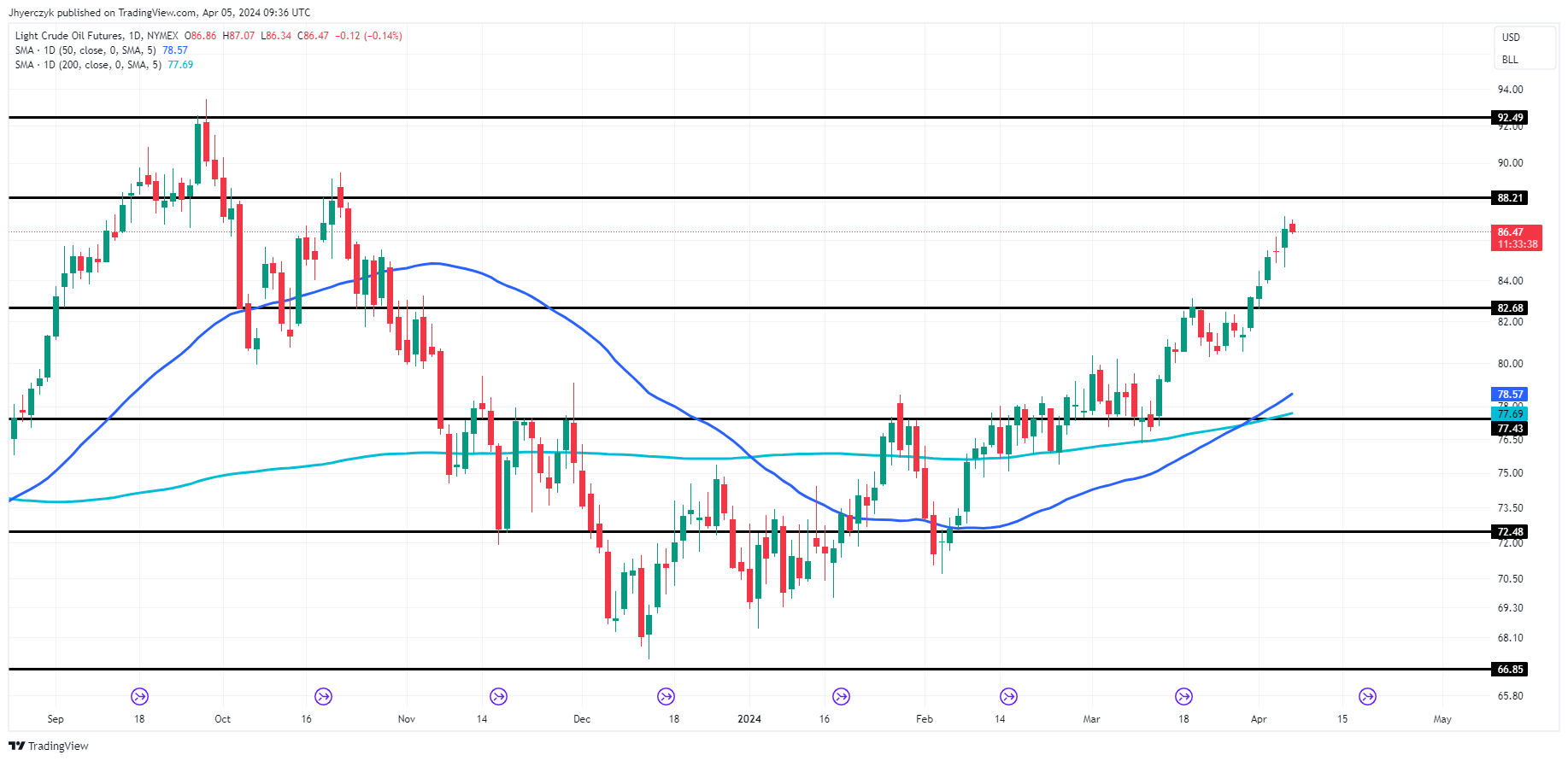
Despite today’s mild setback, Light Crude Oil Futures bulls are eyeing the $88.21 to $89.49 area as their next upside target zone.
While the fundamentals favor a further extension of the rally, some technical traders are calling the market overbought. A short-term reversal top won’t change the trend, but it could alleviate some of the upside pressure. Prices could begin to weaken under $84.64.
This article was originally posted on FX Empire
More From FXEMPIRE:
- Bitcoin Weekly Price Forecast – Bitcoin Continues to Consolidate After Its Big Move
- Natural Gas Weekly Price Forecast – Natural Gas Continues to Build a Base
- Silver Is Heading Towards The $30.00 Level
The views and opinions expressed herein are the views and opinions of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Nasdaq, Inc.

More Related Articles
This data feed is not available at this time.
Sign up for the TradeTalks newsletter to receive your weekly dose of trading news, trends and education. Delivered Wednesdays.
To add symbols:
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to My Quotes by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
- Copy and paste multiple symbols separated by spaces.
These symbols will be available throughout the site during your session.
Your symbols have been updated
Edit watchlist.
- Type a symbol or company name. When the symbol you want to add appears, add it to Watchlist by selecting it and pressing Enter/Return.
Opt in to Smart Portfolio
Smart Portfolio is supported by our partner TipRanks. By connecting my portfolio to TipRanks Smart Portfolio I agree to their Terms of Use .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The global disruption to education caused by the COVD-19 pandemic is without parallel and the effects on learning are severe. The crisis brought education systems across the world to a halt, with school closures affecting more than 1.6 billion learners. While nearly every country in the world offered remote learning opportunities for students ...
We focused on neuroscience, the role of the private sector, education technology, inequality, and pedagogy. Unfortunately, we think the four biggest problems facing education today in developing countries are the same ones we have identified in the last decades. 1. The learning crisis was made worse by COVID-19 school closures.
Photo credit: Shutterstock In our recent The State of the Global Education Crisis: A Path to Recovery report (produced jointly by UNESCO, UNICEF, and the World Bank), we sounded the alarm: this generation of students now risks losing $17 trillion in lifetime earnings in present value, or about 14 percent of today's global GDP, because of COVID-19-related school closures and economic shocks.
At the Center for Universal Education, this means strengthening our work with local leaders in girls' education: promoting gender-transformative research through the Echidna Global Scholars ...
The 2020 Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report urges countries to focus on those left behind as schools reopen so as to foster more resilient and equal societies. To rise to the challenges of our time, a move towards more inclusive education is imperative. Rethinking the future of education is all the more important following the Covid-19 ...
Among global education's most urgent challenges is a severe lack of trained teachers, particularly female teachers. An additional 9 million trained teachers are needed in sub-Saharan Africa by ...
2022 was a year that witnessed major milestones in the global movement to transform education. Against a backdrop of an alarming learning, and budgetary crisis, UNESCO's call for a global mobilization to place education at the top of the political agenda resonated across the world with renewed national and global commitments. And three UNESCO World Conferences focusing on early childhood ...
Transforming education requires a significant increase in investment in quality education, a strong foundation in comprehensive early childhood development and education, and must be underpinned by strong political commitment, sound planning, and a robust evidence base. Learning and skills for life, work and sustainable development.
Hundreds of millions of children worldwide do not go to school. While most children worldwide get the opportunity to go to school, hundreds of millions still don't. In the chart, we see the number of children who aren't in school across primary and secondary education. This number was around 260 million in 2019.
Learning poverty, post-pandemic, is still on the increase worldwide. Policy-makers must begin to incorporate solutions pioneered by educators on the ground. If teachers are heeded, the innovations that work can be systematized. World leaders gathered this September to grapple with the global learning crisis at the UN's Transforming Education ...
Analysis has already revealed deep losses, with international reading scores declining from 2016 to 2021 by more than a year of schooling. These losses may translate to a 0.68 percentage point in global GDP growth. The staggering effects of school closures reach beyond learning. This generation of children could lose a combined total of US$21 ...
The report, titled "Reimagining Our Futures Together: a New Social Contract for Education" identifies key issues that all countries should center their educational systems around. "The main ...
areas. Education must therefore address key issues such as climate change, poverty and sustainable production. ESD promotes the integration of these critical sustainability issues in local and global contexts into the curriculum to prepare learners to understand and respond to the changing world. ESD
The first edition of Trends Shaping Education was published in 2008 and subsequent editions appeared in 2010, 2013, 2016 and 2019. The 2022 edition contains 25 trend areas each illustrated by two figures. This content is organised in five chapters: growth, living and working, knowledge and power, identity and belonging, and our changing nature.
The 2020 Global Education Monitoring (GEM) Report shows that inequalities will have deepened during the pandemic: 40% of countries worldwide have not supported learners at risk during the crisis. It calls on the region to foster more resilient and equal societies by concentrating on those being left behind as schools re-group.
Trends Shaping Education is a triennial report examining major economic, political, social and technological trends affecting education. ... It includes a specific focus on the impact of COVID‑19 on global trends, and new futures thinking sections inviting readers to reflect on how the future might differ from our current expectations. This ...
In rural India, nearly three-quarters of third graders cannot solve a two-digit subtraction problem such as 46 minus 17, and by grade five — half still cannot do so. The world is facing a learning crisis. While countries have significantly increased access to education, being in school isn't the same thing as learning.
Global Education: Current Issues Today Barbara Perry Otago Polytechnic, New Zealand Abstract This article is based on the findings of a workshop held at the London International Conference in Education, November, 2016, where a group of researchers met to share new and emerging issues in global education and collaborate together.
Below are four higher education trends we see taking shape in 2022. 1. Learning from everywhere. There is recognition that as schools and universities all over the world had to abruptly pivot to online teaching, learning outcomes suffered across the education spectrum. However, the experiment with online teaching did force a reexamination of ...
Education Debates: A Breakdown. Rapid changes in the global economy and within education are sparking fierce battles over the future of public schools in statehouses and cities across the country.
Education 2030: topics and issues. The debates included the following sessions: Providing meaningful learning opportunities to out-of-school children. In this session a panel of experts explored the changes needed in countries which have large out-of-school children populations as well as examples from countries which are 'in the final mile'.
11 Issues for 2023. These issues were chosen based on the number of times they came up in stories on Education Week or in workshops and coaching sessions that I do in my role as a leadership coach ...
Related: Race and LGBTQ Issues in K-12 Schools. Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say the public K-12 education system is going in the wrong direction. About two-thirds of Republicans and Republican-leaning independents (65%) say this, compared with 40% of Democrats and Democratic leaners.
Despite today's mild setback, Light Crude Oil Futures bulls are eyeing the $88.21 to $89.49 area as their next upside target zone. While the fundamentals favor a further extension of the rally ...