Research Paper Writing Checklist
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A research paper checklist is an essential tool because the task of putting together a quality paper involves many steps. Nobody writes a perfect report in one sitting!
Before you get started on your project, you should review the checklist on research ethics .
Later, once you have finished the final draft of your research paper, you can use this checklist to make sure that you have remembered all the details.

Research Paper Checklist
- How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline
- What Is a Research Paper?
- How to Organize Research Notes
- Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- Explore and Evaluate Your Writing Process
- Self-Evaluation of Essays
- German Grammar Checklist
- How to Outline and Organize an Essay
- 14 Ways to Write Better in High School
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- Documentation in Reports and Research Papers
- Creating a Table of Contents
- Abstract Writing for Sociology
- What Is a Literature Review?
- Brainstorming Techniques for Students
- Writing Worksheets and Other Writing Resources
- Research Paper
Checklist for Research Papers
About the slc.
- Our Mission and Core Values

- Do I have a sufficient number of sources?
- Are a significant number of my sources critical sources (e.g., from academic journals)?
- Are my sources integrated smoothly into the paper?
- Is there a dialogue between my own analysis of the text and the research I'm including?
- Is my own scholarly opinion strongly present in the research paper, rather than the paper reading like a review of the opinions of other scholars?
- Have I cited all sources I draw from?
- If my paper is a revision, have I considered the changes I want to make, the comments of my peers, and the instructor's comments towards the end of significantly improving on the previous version of this paper?
María Villaseñor
Student Learning Center, University of California, Berkeley
© 2002 UC Regents
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1918 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,450 quotes across 1918 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Writing Tips / Research Paper Checklist
Research Paper Checklist
Research papers are hard. As tempting as it may be to just hand in your paper the second you finish that last citation, it is super important to review everything to make sure you don’t have any silly mistakes!
Use this 10-step checklist to make sure your paper is in top-notch form:
- Credit and cite all information from other sources.
- Place direct quotes from other sources between quotation marks.
- Add all appropriate in-text citations or footnotes.
- All in-text citations/footnotes have a matching citation in the bibliography.
- Alphabetize bibliography and check formatting/ capitalization of titles .
- The thesis statement (purpose of the paper) is clearly stated.
- The paper has a clear conclusion/closing statement.
- Check for spelling and grammatical errors.
- Check for slang words or contractions in writing.
- The title page is properly formatted (when required by your instructor).
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
Research Paper Writing: A 15-Point Academic Writing Checklist

Research paper writing can be a challenging task for PhD students, early career researchers, and even some more experienced academics. When writing a research paper, authors need to be able to present their work in a compelling, easy to understand way, and in doing so demonstrate a deep understanding of their subject. This requires a structured process, a proper approach, careful attention to detail, meticulous planning, excellent writing skills and a significant amount of effort. In this article, we will outline the key elements of a good research paper and provide researchers with a 15-point research paper writing checklist to streamline the process.
Key elements of research paper writing
The research paper writing process requires you to include some essential elements to deliver a well-written, complete manuscript.
- An engaging title: Ensuring that the title of your research paper is concise, impactful, and engaging is important as it is the first thing that readers will see. It should be able to convey the subject of your research paper clearly and simply.
- Well-articulated research questions : Research paper writing is incomplete without a well-defined thesis statement or research question that clearly conveys the purpose and scope of the research.
- Thorough literature reviews: This key element in research paper writing covers a comprehensive overview of existing research in the field, which helps researchers identify and address potential gaps in knowledge.
- Structured methodology: A good research paper must present a detailed description of the methodology used to collect and analyze data as part of their study. This allows readers to assess the validity and reliability of the research.
- Accurate results : Communicating the results accurately and logically is an important element of research paper writing. Use graphs, tables and other visual aids as needed to organize and present your findings in an easy-to-understand way.
- Analysis and discussion: In research paper writing, this isthe section that helps readers evaluate, discuss, and understand the relevance, significance, and implications of the research being done.
- Strong conclusion : A well-rounded conclusion summarizes the key research findings and provides a clear, concise answer to the research question or thesis statement.
- Citations and references: A good research paper writing practice is to ensure you have got the citations and references right; this establishes your expertise and adds credibility to your work.
THE academic writing checklist for researchers
Now that you know the key elements to include in your research paper writing process, it’s time to get started. If it seems like a lot, don’t worry. Follow this 15-point academic writing checklist to ensure that all the key research paper writing elements have been included and carefully checked before you submit.
- Assess the research paper title to see if it clearly conveys the focus of the research paper, has relevant keywords, and is engaging enough to attract reader attention.
- Read the abstract to make sure that it contains the aims and objectives of the study, the research design and methodology, the main findings, and final conclusions.
- Ensure the introduction is well structured and addresses key issues like the aim, research questions, and arguments made in the research paper.
- Present a clear statement of the rationale for the study in the introduction and ensure that relevant literature is cited as it relates to the study.
- Ensure that the research paper is well structured and organized with sub-sections and paragraphs and presented in a logical flow; this will aid reader comprehension.
- Craft short, engaging paragraphs that communicate often complex ideas clearly; use appropriate transitional phrases or words to connect paragraphs and sub-sections smoothly.
- Provide relevant headings for sub-sections to improve overall readability and convey important points quickly.
- Ensure that the conclusion summarizes and clearly communicates the findings and analysis of the research problem. Remember not to introduce any new ideas or findings that are nor reflected in the main body of the text.
- Avoid repetition – differentiate the results from the discussion section; the former should present the findings, while the latter evaluates how the study adds to existing knowledge, practice and/or policy formulation.
- Check the citations follows the target journal’s style guidelines. Make sure that in-text citations match the references and bibliography.
- Check that the guidelines for formatting provided by the target journal have been strictly followed. Page numbers must be provided in the proper format, line spacing must be even, and tables and figures should be given titles and numbers that match with the references.
- Proofread several times to ensure that your final manuscript duly addresses and resolves all the feedback comments and recommendations shared by the supervisor/reviewer/editor.
- Check for possible plagiarism by checking and properly citing all the sources used for research paper writing; use the appropriate citation style (APA, MLA, etc.) preferred by your journal.
- Make sure that the research paper adheres to the recommended word count and length specified by the journal. Check abbreviations have been provided in full at least once and a glossary has been provided, where necessary. Any non-English language should be accurately translated.
- Include an acknowledgement section mentioning and thanking individuals or teams who have helped and supported you with the research study.
The research paper writing process requires careful attention to detail and adherence to academic standards. By following this comprehensive 15-point academic writing checklist, PhD students and researchers can optimize their research paper writing and ensure they consistently deliver coherent, well-structured manuscripts that meet the high standards expected by journal editors.
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed. Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks, submission readiness and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$12 a month !
Related Reads:
- Top 5 Ethical Considerations in Research
- Good Writing Habits: 7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing
- Self-Plagiarism in Research: What it is and How to Avoid It
- How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)
How to Ask a Journal Editor About Manuscript Status (Email Template Included)
Are you using the right verbs in your research paper, you may also like, measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., 9 steps to publish a research paper, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how..., 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their....

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Research Paper Checklist For Academic Success
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Embarking on the journey of writing a research paper can be a daunting task. To aid in this process and ensure thoroughness, we’ve curated an article titled ‘Research Paper Checklist.’ This guide is designed to provide step-by-step essentials to guarantee the quality and rigor of your research paper. In this article, we’ll look at how you can formulate a workable research paper checklist to help you with your dissertations.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Research Paper Checklist – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Research paper checklist
- 3 The importance of a research paper checklist
- 4 Research paper checklist
- 5 Research paper checklist: The benefits
Research Paper Checklist – In a Nutshell
- A research paper checklist is a document that lists the required criteria for writing a thesis.
- It is a guiding tool that allows you to express your research ideas logically and systematically.
- A research paper checklist provides an overview of the writing process, enabling proper planning.
Definition: Research paper checklist
A research paper checklist is a document that briefly highlights the scope and structure of a research report in point form. It provides step-by-step instructions that you can use to complete a given task, which in this case is drafting a research thesis.
Ideally, the checklist enables you to ascertain that you meet all the requirements when writing and submitting a dissertation. It also allows you to achieve a coherent flow of opinions when discussing a given topic.
The importance of a research paper checklist
All these elements can be overwhelming to remember, so it is advisable to use a checklist.
A research paper checklist is a general guideline on the most crucial aspects of writing a report. It clarifies what to prioritize in your thesis; where, when, and why. It also allows you to break down the writing process into bite-sized chunks that you can tackle easily without feeling overwhelmed by the overall workload. Additionally, the research paper checklist assists you in comprehensively adhering to report writing criteria before presenting your work.
A typical research report provides in-depth information that accounts for the flow of events when studying a particular subject. It features organized documents containing defined elements, including the:
- introduction
- literature review
- methodology
- recommendations
- conclusions
A research paper checklist is a general guideline on the most crucial aspects of writing a report. It clarifies what to prioritize in your thesis; where, when, and why.
It also allows you to break down the writing process into bite-sized chunks that you can tackle easily without feeling overwhelmed by the overall workload.
Additionally, the research paper checklist assists you in comprehensively adhering to report writing criteria before presenting your work.
Research paper checklist
As discussed, a research paper checklist lets you write an adequate research report.
Here are some pointers you can use to guide you when drafting your thesis:
- What is the required writing style for the research paper?
- Does the report have a title?
- Is the title clear and specific?
- Are my transitions smooth and coherent?
- Does the research paper have adequate source citations?
- Are all the sources listed in the bibliography?
- Are most, if not all, of the source citations derived from critical sources?
- Do the source citations listed adhere to the prevailing writing format?
- Are there spelling issues and grammatical errors in the report?
- Does the research report risk having stylistic problems that can obscure meaning?
- Does the text contain overused words or phrases?
- Do paragraphs adhere to effective paragraphing criteria?
- Does the overall report depict a coherent flow of ideas?
- Is the content thoroughly addressing the subject matter?
- Do the summary and recommendations relate to the topic in question?
- Are the examples used relevant to the research paper?
- Does the summary restate the thesis briefly and conclusively?
- Do the number of pages of the report compare appropriately with the subject matter?

Research paper checklist: The benefits
A research report checklist is essential in helping you write a well-organized thesis.
It can be beneficial in the following ways:
- A research paper checklist allows you to express your thoughts and ideas in a concise flow that readers can comprehend effortlessly.
- It helps you limit your ideas and discussion to the scope of the subject matter.
- You can use it to strategically approach the writing process without feeling overwhelmed.
- A research paper checklist lets you put together and submit a high-quality report that sufficiently addresses the topic in question.
- It also acts as an evaluation document to help you ascertain that you considered all the essential aspects of your report, like the writing style.
- Additionally, a report-writing checklist minimizes the time needed to write a research paper.
What is a research paper checklist?
A research paper checklist is a document that provides a detailed overview of essential factors to consider and prioritize when writing a research report.
Why should you use a research paper checklist?
A research paper checklist helps you define your workload. In doing so, you can strategize how to approach the task accordingly and achieve timely delivery.
How do you formulate a research paper checklist?
Start by considering the scope of the topic in question and the style guidelines required to write the report, and then create a list that prominently highlights the major focus areas .
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2020
- Volume 36 , pages 909–913, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Clara Busse ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-1000 1 &
- Ella August ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5151-1036 1 , 2
269k Accesses
15 Citations
719 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Similar content being viewed by others

How to design bibliometric research: an overview and a framework proposal

Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice
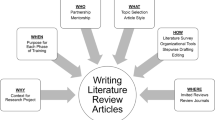
Why, When, Who, What, How, and Where for Trainees Writing Literature Review Articles
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.
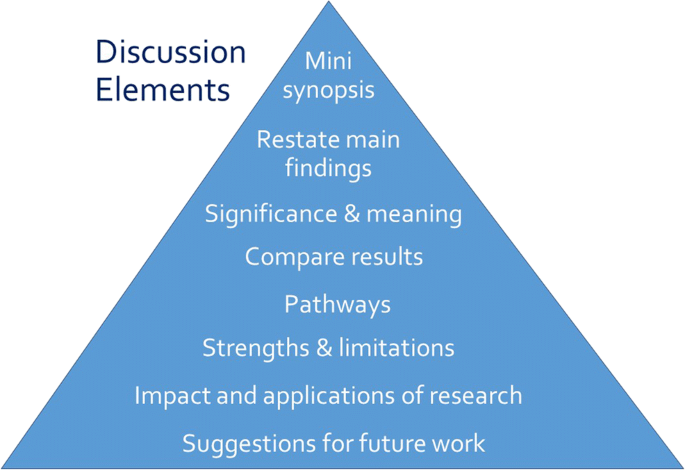
Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
Data Availability
Michalek AM (2014) Down the rabbit hole…advice to reviewers. J Cancer Educ 29:4–5
Article Google Scholar
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributors: who is an author? http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authosrs-and-contributors.html . Accessed 15 January, 2020
Vetto JT (2014) Short and sweet: a short course on concise medical writing. J Cancer Educ 29(1):194–195
Brett M, Kording K (2017) Ten simple rules for structuring papers. PLoS ComputBiol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005619
Lang TA (2017) Writing a better research article. J Public Health Emerg. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Download references
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Clara Busse & Ella August
Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109-2029, USA
Ella August
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ella August .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
(PDF 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Busse, C., August, E. How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal. J Canc Educ 36 , 909–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Download citation
Published : 30 April 2020
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Manuscripts
- Scientific writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Check List for Research Papers
Statement of purpose, review of literature, transitions..
We have discussed the topic of code-switching in Swahili from what might be termed the point of view of the mechanics of code-switching; i.e. how it operates in Swahili; let us now examine its function in Swahili linguistic culture, i.e. why Swahili speakers choose to code-switch, and when. We will then show how code-switching is used in popular media, print advertising, and other genres.
No discussion of print-medium advertising in Swahili would be complete without a discussion of another, related phenomenon, which is the use of language(s) and varieties in comic books. Particularly instructive are Swahili renditions of Tarzan comics, which depict Tarzan as fluent in Swahili and English, while other characters are depicted only as speaking English inadequately.
"The work of Ferguson (Ferguson 1959:32) is crucial for our understanding of the concept of diglossia."
"No discussion of language maintenance would be complete without the work of Fishman (1959, 1960, 1963, 1966, 1972, [...])"
Most researchers on the subject of bilingualism accept the notion that one language or code will be dominant, i.e. they assume that individual speakers have more facility, or higher proficiency, in one language than in another; that is, the so-called balanced bilingual is a rare phenomenon. I will follow this practice, but will also point out examples where this has been shown to be problematical.
Which sounds better, `English's worldwide spread' or `the worldwide spread of English'? `The Queen of England's unruly children' vs. the unruly children of the Q of England'? Spelling problems are marked in margins etc. with "sp" Stylistic problems are given alternative suggestions. (sometimes marked in margin "awk" for awkward.) If some words or phrases are repeated or overused, the mark repet for `repetitious' may appear in the margin. If the symbol PP appears, it means "start a new paragraph". Content I stated at the beginning of the course ("Helpful Hints...") that I would like your paper to reflect issues and problems we have discussed in various ways during the class. I will not try to summarize these here, but I would like to see evidence that these ideas have been considered, and brought to bear on the material you are discussing. I do not expect you to parrot what others say, or what I have said; I expect you to contrast different ideas and weigh them; or bring two disparate opinions or approaches together and show how the conjunction of these ideas throws new light on the subject. Example: Much has been written about the status of French in France, and much has also been written about French attempts to control the corpus of Standard French. What has not often been made clear is how the French themselves do not usually distinguish between corpus and status issues, and that is what I wish to focus on in this paper. As such I introduce no new facts into the situation, but I do introduce a new interpretation of existing facts.
I have discussed in this paper how such issues as code-switching, code-shifting, and bilingualism in Swahili linguistic culture are manifested in print-medium advertising in East Africa. I have attempted to describe in a general way both the mechanics of these phenomena, as well as the social motivation for them, and how advertisers use these techniques for their own means in advertising.
In the process I have attempted to demonstrate that these phenomena are intricately interwoven with social forces identified by various writers as modernization, power-relations, and gender relations in East African society. They do not constitute in any way a failure of the linguistic code, but are in fact a manifestation of shifting identities in the culture.
My own contribution, if any, has been to bring in the work of A, B, and C, and relate their research to the ideas presented by X, Y, and Z, who are the acknowledged primary researchers in this field.
Example: In the process of this review, an attempt to define the role of language in the definition of ethnicity, I have to conclude that many researchers seem to define ethnicity in a circular or tautological way, i.e., as a constellation of factors involving language, race, descent, culture, history, etc. but often with one or more of these factors missing. Some researchers act as if ethnicity were a given, something that must be present in society, rather than a construct they themselves have invented. And, they often act as if all languages are equal in their impact on ethnicity, or as if any `language' at all would do for their definition of ethnicity , with no sense of the complexity of any one language. My conclusion, therefore, is that ethnicity is a problematical construct, and that in the society I examined, Eastern Rumelia, ethnicity indeed seems to involve a language factor, but having said this, I am unable to state what ethnicity actually means to the Rumelians. Perhaps this is a factor of the recent political shift in eastern Europe, but in any event, the concept of ethnicity seems to be in a very fluid state. Much more work, beyond the scope of this paper, is obviously required.
Entertainment Value

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Checklist: Research paper 0 / 14. I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet. My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information.. My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement.. My paper is logically organized using paragraphs and (if relevant) section headings.
Research paper checklist. Checklist: Research paper 0 / 14. I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet. My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information. My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement.
How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline. Before you get started on your project, you should review the checklist on research ethics . Later, once you have finished the final draft of your research paper, you can use this checklist to make sure that you have remembered all the details.
This checklist corresponds to the writing and formatting guidelines described in full in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Refer to the following chapters for specific information: paper elements and format in Chapter 2. writing style and grammar in Chapter 4. bias-free language in Chapter 5.
Checklist: Research paper 0 / 14. I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet. My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information.. My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement.. My paper is logically organized using paragraphs and (if relevant) section headings.
Checklist: Writing a Research Article. The title emphasizes what is most important about the paper (often the main conclusion but sometimes also the methods used) The results are described in a logical order that fits into a scientific narrative (and not necessarily the order with which you performed the experiments) The abstract reads like a ...
Checklist for Research Papers. Do I have a sufficient number of sources? Are a significant number of my sources critical sources (e.g., from academic journals)? Are my sources integrated smoothly into the paper? Is there a dialogue between my own analysis of the text and the research I'm including?
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment. "Research Paper Planner" (UCLA) UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
Research papers are hard. As tempting as it may be to just hand in your paper the second you finish that last citation, it is super important to review everything to make sure you don't have any silly mistakes! Use this 10-step checklist to make sure your paper is in top-notch form: Credit and cite all information from other sources.
This checklist is to help you along your research paper writing process. Make sure you read and understand the specific requirements and instructions that are specific to your paper. It is a good idea to have professional paper editors review your work, to make sure you submit original content and that your work is formatted correctly and free ...
Use this checklist to help you write a beginner-friendly student paper in seventh edition APA Style, consisting of a title page, text, and reference list. If your paper has more elements, such as tables and figures, use the Publication Manual checklist or the Concise Guide checklist. Links in this checklist lead to free resources on the APA ...
Research Paper Checklist Below is a checklist for completing a research paper. You should remember that the process of researching and writing is very malleable. It depends on many factors: the assignment requirements, the field of study, the topic, and your personal preferences. This checklist is designed to give you a basic overview of the ...
The research paper writing process requires careful attention to detail and adherence to academic standards. By following this comprehensive 15-point academic writing checklist, PhD students and researchers can optimize their research paper writing and ensure they consistently deliver coherent, well-structured manuscripts that meet the high ...
Use this article submission checklist to find out. By the time you're ready to submit your paper to a journal, there are a lot of things you'll need to have checked, understood, and incorporated into your article. We've created this checklist to help you make sure that you don't miss anything important, both in writing and preparing ...
Research Paper Checklist - In a Nutshell. A research paper checklist is a document that lists the required criteria for writing a thesis.; It is a guiding tool that allows you to express your research ideas logically and systematically.; A research paper checklist provides an overview of the writing process, enabling proper planning.
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common ...
I have a minimum of ___ facts/ notes from sources to use in my paper. 22. Each fact/note is written on the sheet and the location (page number, source, etc.) is clearly identified (if required by teacher). DEVELOPMENT / ORGANIZATION: 23. Everything in my paper relates to my thesis statement. 24.
Many research papers suffer from rough transitions; they shift from one topic to another abruptly, without adequately warning the reader that a transition is about to take place. Or, a ... This abbreviated checklist incorporates the detailed items in the above list, and is what I will hand back to you with your various writing samples, to give ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Ethical approval by an appropriate body. A statement on the ethical approval process followed should be in the report. 10. Relationship of conclusions to analysis, or interpretation of the data. This criterion concerns the relationship between the findings reported and the views or words of study participants.
eligibility, confirmed eligible, included in the study, completing follow-up, and analyzed. (b) Give reasons for nonparticipation at each stage. (c) Consider use of a flow diagram. Descriptive ...
Do not use a period after your title or after any heading in the paper (e.g., Works Cited). Begin your text on a new, double-spaced line after the title, indenting the first line of the paragraph half an inch from the left margin. Fig. 1. The top of the first page of a research paper.