- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for April 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
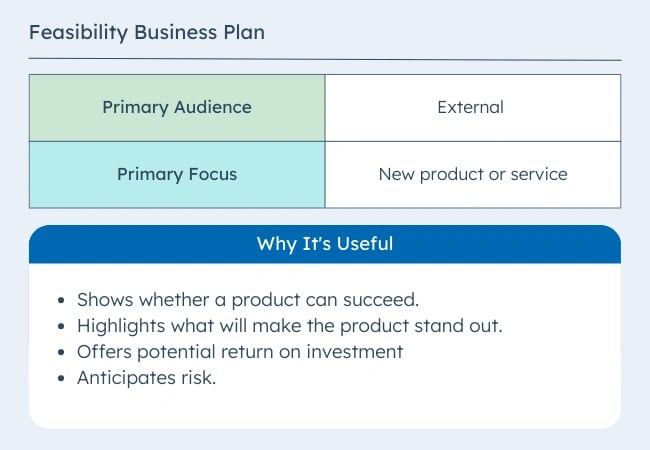
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![business plan definition and meaning How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![business plan definition and meaning 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![business plan definition and meaning The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.

Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated April 17, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Laundromat Business Plan + Example Templates

13 Min. Read
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

6 Min. Read
How to Do a SWOT Analysis for Better Strategic Planning

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Business Plan
By Entrepreneur Staff
Business Plan Definition:
A written document describing the nature of the business, the sales and marketing strategy, and the financial background, and containing a projected profit and loss statement
A business plan is also a road map that provides directions so a business can plan its future and helps it avoid bumps in the road. The time you spend making your business plan thorough and accurate, and keeping it up-to-date, is an investment that pays big dividends in the long term.
Your business plan should conform to generally accepted guidelines regarding form and content. Each section should include specific elements and address relevant questions that the people who read your plan will most likely ask. Generally, a business plan has the following components:
Title Page and Contents A business plan should be presented in a binder with a cover listing the name of the business, the name(s) of the principal(s), address, phone number, e-mail and website addresses, and the date. You don't have to spend a lot of money on a fancy binder or cover. Your readers want a plan that looks professional, is easy to read and is well-put-together.
Include the same information on the title page. If you have a logo, you can use it, too. A table of contents follows the executive summary or statement of purpose, so that readers can quickly find the information or financial data they need.
Executive Summary The executive summary, or statement of purpose, succinctly encapsulates your reason for writing the business plan. It tells the reader what you want and why, right up front. Are you looking for a $10,000 loan to remodel and refurbish your factory? A loan of $25,000 to expand your product line or buy new equipment? How will you repay your loan, and over what term? Would you like to find a partner to whom you'd sell 25 percent of the business? What's in it for him or her? The questions that pertain to your situation should be addressed here clearly and succinctly.
The summary or statement should be no more than half a page in length and should touch on the following key elements:
- Business concept describes the business, its product, the market it serves and the business' competitive advantage.
- Financial features include financial highlights, such as sales and profits.
- Financial requirements state how much capital is needed for startup or expansion, how it will be used and what collateral is available.
- Current business position furnishes relevant information about the company, its legal form of operation, when it was founded, the principal owners and key personnel.
- Major achievements points out anything noteworthy, such as patents, prototypes, important contracts regarding product development, or results from test marketing that have been conducted.
Description of the Business The business description usually begins with a short explanation of the industry. When describing the industry, discuss what's going on now as well as the outlook for the future. Do the necessary research so you can provide information on all the various markets within the industry, including references to new products or developments that could benefit or hinder your business. Base your observations on reliable data and be sure to footnote and cite your sources of information when necessary. Remember that bankers and investors want to know hard facts--they won't risk money on assumptions or conjecture.
When describing your business, say which sector it falls into (wholesale, retail, food service, manufacturing, hospitality and so on), and whether the business is new or established. Then say whether the business is a sole proprietorship, partnership, C or Sub chapter S corporation. Next, list the business' principals and state what they bring to the business. Continue with information on who the business' customers are, how big the market is, and how the product or service is distributed and marketed.
Description of the Product or Service The business description can be a few paragraphs to a few pages in length, depending on the complexity of your plan. If your plan isn't too complicated, keep your business description short, describing the industry in one paragraph, the product in another, and the business and its success factors in two or three more paragraphs.
When you describe your product or service, make sure your reader has a clear idea of what you're talking about. Explain how people use your product or service and talk about what makes your product or service different from others available in the market. Be specific about what sets your business apart from those of your competitors.
Then explain how your business will gain a competitive edge and why your business will be profitable. Describe the factors you think will make it successful. If your business plan will be used as a financing proposal, explain why the additional equity or debt will make your business more profitable. Give hard facts, such as "new equipment will create an income stream of $10,000 per year" and briefly describe how.
Other information to address here is a description of the experience of the other key people in the business. Whoever reads your business plan will want to know what suppliers or experts you've spoken to about your business and their response to your idea. They may even ask you to clarify your choice of location or reasons for selling this particular product.
Market Analysis A thorough market analysis will help you define your prospects as well as help you establish pricing, distribution, and promotional strategies that will allow your company to be successful vis-à-vis your competition, both in the short and long term.
Begin your market analysis by defining the market in terms of size, demographics, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. Next, determine how often your product or service will be purchased by your target market. Then figure out the potential annual purchase. Then figure out what percentage of this annual sum you either have or can attain. Keep in mind that no one gets 100 percent market share, and that a something as small as 25 percent is considered a dominant share. Your market share will be a benchmark that tells you how well you're doing in light of your market-planning projections.
You'll also have to describe your positioning strategy. How you differentiate your product or service from that of your competitors and then determine which market niche to fill is called "positioning." Positioning helps establish your product or service's identity within the eyes of the purchaser. A positioning statement for a business plan doesn't have to be long or elaborate, but it does need to point out who your target market is, how you'll reach them, what they're really buying from you, who your competitors are, and what your USP (unique selling proposition) is.
How you price your product or service is perhaps your most important marketing decision. It's also one of the most difficult to make for most small business owners, because there are no instant formulas. Many methods of establishing prices are available to you, but these are among the most common.
- Cost-plus pricing is used mainly by manufacturers to assure that all costs, both fixed and variable, are covered and the desired profit percentage is attained.
- Demand pricing is used by companies that sell their products through a variety of sources at differing prices based on demand.
- Competitive pricing is used by companies that are entering a market where there's already an established price and it's difficult to differentiate one product from another.
- Markup pricing is used mainly by retailers and is calculated by adding your desired profit to the cost of the product.
You'll also have to determine distribution, which includes the entire process of moving the product from the factory to the end user. Make sure to analyze your competitors' distribution channels before deciding whether to use the same type of channel or an alternative that may provide you with a strategic advantage.
Finally, your promotion strategy should include all the ways you communicate with your markets to make them aware of your products or services. To be successful, your promotion strategy should address advertising, packaging, public relations, sales promotions and personal sales.
Competitive Analysis The purpose of the competitive analysis is to determine:
- the strengths and weaknesses of the competitors within your market.
- strategies that will provide you with a distinct advantage.
- barriers that can be developed to prevent competition from entering your market.
- any weaknesses that can be exploited in the product development cycle.
The first step in a competitor analysis is to identify both direct and indirect competition for your business, both now and in the future. Once you've grouped your competitors, start analyzing their marketing strategies and identifying their vulnerable areas by examining their strengths and weaknesses. This will help you determine your distinct competitive advantage.
Whoever reads your business plan should be very clear on who your target market is, what your market niche is, exactly how you'll stand apart from your competitors, and why you'll be successful doing so.
Operations and Management The operations and management component of your plan is designed to describe how the business functions on a continuing basis. The operations plan highlights the logistics of the organization, such as the responsibilities of the management team, the tasks assigned to each division within the company, and capital and expense requirements related to the operations of the business.
Financial Components of Your Business Plan After defining the product, market and operations, the next area to turn your attention to are the three financial statements that form the backbone of your business plan: the income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
The income statement is a simple and straightforward report on the business' cash-generating ability. It is a scorecard on the financial performance of your business that reflects when sales are made and when expenses are incurred. It draws information from the various financial models developed earlier such as revenue, expenses, capital (in the form of depreciation), and cost of goods. By combining these elements, the income statement illustrates just how much your company makes or loses during the year by subtracting cost of goods and expenses from revenue to arrive at a net result, which is either a profit or loss. In addition to the income statements, include a note analyzing the results. The analysis should be very short, emphasizing the key points of the income statement. Your CPA can help you craft this.
The cash flow statement is one of the most critical information tools for your business, since it shows how much cash you'll need to meet obligations, when you'll require it and where it will come from. The result is the profit or loss at the end of each month and year. The cash flow statement carries both profits and losses over to the next month to also show the cumulative amount. Running a loss on your cash flow statement is a major red flag that indicates not having enough cash to meet expenses-something that demands immediate attention and action.
The cash flow statement should be prepared on a monthly basis during the first year, on a quarterly basis for the second year, and annually for the third year. The following 17 items are listed in the order they need to appear on your cash flow statement. As with the income statement, you'll need to analyze the cash flow statement in a short summary in the business plan. Once again, the analysis doesn't have to be long and should cover highlights only. Ask your CPA for help.
The last financial statement you'll need is a balance sheet. Unlike the previous financial statements, the balance sheet is generated annually for the business plan and is, more or less, a summary of all the preceding financial information broken down into three areas: assets, liabilities and equity.
Balance sheets are used to calculate the net worth of a business or individual by measuring assets against liabilities. If your business plan is for an existing business, the balance sheet from your last reporting period should be included. If the business plan is for a new business, try to project what your assets and liabilities will be over the course of the business plan to determine what equity you may accumulate in the business. To obtain financing for a new business, you'll need to include a personal financial statement or balance sheet.
In the business plan, you'll need to create an analysis for the balance sheet just as you need to do for the income and cash flow statements. The analysis of the balance sheet should be kept short and cover key points.
Supporting Documents In this section, include any other documents that are of interest to your reader, such as your resume; contracts with suppliers, customers, or clients, letters of reference, letters of intent, copy of your lease and any other legal documents, tax returns for the previous three years, and anything else relevant to your business plan.
Some people think you don't need a business plan unless you're trying to borrow money. Of course, it's true that you do need a good plan if you intend to approach a lender--whether a banker, a venture capitalist or any number of other sources--for startup capital. But a business plan is more than a pitch for financing; it's a guide to help you define and meet your business goals.
Just as you wouldn't start off on a cross-country drive without a road map, you should not embark on your new business without a business plan to guide you. A business plan won't automatically make you a success, but it will help you avoid some common causes of business failure, such as under-capitalization or lack of an adequate market.
As you research and prepare your business plan, you'll find weak spots in your business idea that you'll be able to repair. You'll also discover areas with potential you may not have thought about before--and ways to profit from them. Only by putting together a business plan can you decide whether your great idea is really worth your time and investment.
More from Business Plans
Financial projections.
Estimates of the future financial performance of a business
Financial Statement
A written report of the financial condition of a firm. Financial statements include the balance sheet, income statement, statement of changes in net worth and statement of cash flow.
Executive Summary
A nontechnical summary statement at the beginning of a business plan that's designed to encapsulate your reason for writing the plan
Latest Articles
Passengers are now entitled to a full cash refund for canceled flights, 'significant' delays.
The U.S. Department of Transportation announced new rules for commercial passengers on Wednesday.
Franchising Is Not For Everyone. Explore These Lucrative Alternatives to Expand Your Business.
Not every business can be franchised, nor should it. While franchising can be the right growth vehicle for someone with an established brand and proven concept that's ripe for growth, there are other options available for business owners.
Elon Musk Tells Investors Cheaper Tesla Electric Cars Should Arrive Ahead of Schedule
On an earnings call, Musk told shareholders that Tesla could start producing new, affordable electric cars earlier than expected.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
What Is a Business Plan?
Definition and Examples of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Morsa Images / Getty Images
A business plan is a document that summarizes the operational and financial objectives of a business. It is a business's road map to success with detailed plans and budgets that show how the objectives will be realized.
Keep reading to learn the basic components of a business plan, why they're useful , and how they differ from an investment plan.
A business plan is a guide for how a company will achieve its goals. For anyone starting a business , crafting a business plan is a vital first step. Having these concrete milestones will help track the business's success (or lack thereof). There are different business plans for different purposes, and the best business plans are living documents that respond to real-world factors as quickly as possible.
In a nutshell, a business plan is a practice in due diligence. When it's done well, it will prevent entrepreneurs from wasting time and money on a venture that won't work.
How Does a Business Plan Work?
If you have an idea for starting a new venture, a business plan can help you determine if your business idea is viable. There's no point in starting a business if there is little or no chance that the business will be profitable, and a business plan helps to figure out your chances of success.
In many cases, people starting new businesses don't have the money they need to start the business they want to start. If start-up financing is required, you must have an investor-ready business plan to show potential investors that demonstrates how the proposed business will be profitable.
Since the business plan contains detailed financial projections, forecasts about your business's performance, and a marketing plan, it's an incredibly useful tool for everyday business planning. To be as effective as possible, it should be reviewed regularly and updated as required.
Business owners have leeway when crafting their business plan outline. They can be short or long, and they can include whatever detail you think will be useful. There are basic templates you can work from, and you'll likely notice some common elements if you look up examples of business plans.
Market Analysis
The market analysis will reveal whether there is sufficient demand for your product or service in your target market . If the market is already saturated, your business model will need to be changed (or scrapped).
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis will examine the strengths and weaknesses of the competition and help direct your strategy for garnering a share of the market in your marketing plan . If the existing market is dominated by established competitors, for instance, you will have to come up with a marketing plan to lure customers from the competition (lower prices, better service, etc.).
Management Plan
The management plan outlines your business structure, management, and staffing requirements. If your business requires specific employee and management expertise, you will need a strategy for finding and hiring qualified staff and retaining them.
Operating Plan
The operating plan describes your facilities, equipment, inventory, and supply requirements. Business location and accessibility are critical for many businesses. If this is the case for your business, you will need to scout potential sites. If your proposed business requires parts or raw materials to produce goods to be sold to customers, you will need to investigate potential supply chains.
Financial Plan
The financial plan is the determining factor as to whether your proposed business idea is likely to be a success. If financing is required, your financial plan will determine how likely you are to obtain start-up funding in the form of equity or debt financing from banks, angel investors , or venture capitalists . You can have a great idea for a business, along with excellent marketing, management, and operational plans, but if the financial plan shows that the business will not be profitable enough, then the business model is not viable and there's no point in starting that venture.
Business Plan vs. Investment Proposal
A business plan is similar to an investment proposal. In fact, investment proposals are sometimes called investor-ready business plans . Generally speaking, they both have the same contents. You can think of an investment proposal as a business plan with a different audience.
The business plan is largely an internal document, intended to guide the decisions of executives, managers, and employees. The investment proposal, on the other hand, is designed to be presented to external agencies.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a detailed road map that explains what the company's goals are and how it will achieve them.
- The exact details of a business plan will depend on the intended audience and the nature of the business.
- It's a good idea to regularly revisit your business plan so you know it's as accurate, realistic, and detailed as possible.

Try for free
Business Plan
Who should write a business plan, pros and cons of a business plan, the anatomy of a business plan, .css-uphcpb{position:absolute;left:0;top:-87px;} what is a business plan, definition of a business plan.
A business plan is a strategic document which details the strategic objectives for a growing business or startup, and how it plans to achieve them.
In a nutshell, a business plan is a written expression of a business idea and will describe your business model, your product or service, how it will be priced, who will be your target market, and which tactics you plan to use to reach commercial success.
Whilst every enterprise should have a plan of some sort, a business plan is of particular importance during the investment process. Banks, venture capitalists, and angel investors alike will need to see a detailed plan in order to make sound investment decisions — think of your plan as a way of convincing them your idea is worth their resources.
Roadmapping From A to Z

Business plans can also be useful as a guide to keeping a new business on track, especially in the first few months or years when the road ahead isn’t too clear.
Starting a business isn’t an exact science. Some companies organically develop out of trial and error, while others are plotted out from start to finish.
So if you’re asking whether your company needs a lengthy business plan, the answer would be ‘no’. That said, there are definitely a few situations in which writing a plan makes sense and can help increase the chances of a business becoming successful:
In situations when the market is new and untested — or simply volatile — it can be very helpful to have a business plan to refer back to when the road ahead isn’t clear.
For those who have an exciting business idea but haven’t necessarily distilled it down into black-and-white. Writing a business plan is a great way to look at a concept from all angles and spot any potential pitfalls.
How to write a business plan?
The most important step in writing a business plan is to identify its purpose.
Who are you trying to attract with it, and why?
Here are a few key pointers for writing a business plan:
Are you looking to secure a bank loan, get funding from private investors, or to lure skilled professionals to join you?
Include a brief history of your business, the concept, and the products or services. Keep it professional and transparent.
Don’t exaggerate your experience or skills, and definitely don’t leave out information investors need to know. They’ll find out at some point, and if they discover you lied, they could break off their involvement. Trust is crucial.
Explain what the product or service your business offers in simplistic terms.
Watch out for complex language and do whatever you can to prevent readers from becoming confused.
Focus on the benefits the business offers, how it solves the core audience’s problem(s), and what evidence you have to prove that there is a space in the market for your idea. It’s important to touch on the market your business will operate in, and who your main competitors are.
Another essential aspect of writing an effective business plan is to keep it short and sweet. Just focus on delivering the crucial information the reader has to know in order to make a decision. They can always ask you to elaborate on certain points later.
Still, deciding whether or not a business plan will benefit you at this stage of your venture?
Let’s look at a few reasons why you might (or might not) want to write a business plan.
A business plan will help you to secure funding even when you have no trading history. At the seed stage, funding is all-important — especially for tech and SaaS companies. It’s here that a business plan can become an absolute lifesaver.
Your business plan will maintain a strategic focus as time goes on. If you’ve ever heard of “mission creep”, you’ll know how important an agreed can be — and your business plan serves exactly that purpose.
Having a plan down in black and white will help you get other people on board . Again, with no trading history, it can be hard to convince new partners that you know what you’re doing. A business plan elegantly solves this problem.
Your business plan can cause you to stop looking outward. Sometimes, especially in business, you need to be reactive to market conditions. If you focus too much on your original business plan, you might make mistakes that can be costly or miss golden opportunities because they weren’t in the plan.
A lot of time can be wasted analyzing performance. It’s easy to become too focused on the goals and objectives in your business plan — especially when you’re not achieving them. By spending too much time analyzing past performance and looking back, you may miss out on other ways to push the business forward.
A business plan is out of date as soon as it’s written. We all know how quickly market conditions change. And, unfortunately, certain elements in your business plan may have lost relevance by the time you’re ready to launch. But there is another way — by transferring your strategic plan into an actionable roadmap , you can get the best of both worlds. The business plan contains important detail that is less likely to change, such as your mission statement and target audience, and the roadmap clarifies a flexible, adaptable, route forward.
So, you’ve decided to write a business plan — a great choice!
But now comes the tricky task of actually writing it.
This part can be a little frustrating because there is no one-size-fits-all template appropriate for all business plans. The best approach, in fact, is to look at common ingredients of a business plan and pick out the ones that make sense for your venture.
The key elements of a great business plan include:
An overview of the business concept . This is sometimes referred to as an executive summary and it’s essentially the elevator pitch for your business.
A detailed description of the product or service. It’s here that you’ll describe exactly what your core offering will be — what’s your USP , and what value do you deliver?
An explanation of the target audience. You need a good understanding of who you’ll be selling your product or service to, backed up by recent market research.
Your sales and marketing strategy. Now that you know who you’re targeting, how do you plan to reach them? Here you can list primary tactics for finding and maintaining an engaged client base.
Your core team . This section is all about people: do you have a team behind you already? If not, how will you build this team and what will the timeline be? Why are you the right group of people to bring this idea to the market? This section is incredibly important when seeking external investment — in most cases, passion can get you much further than professional experience.
Financial forecasts . Some investors will skim the executive summary and skip straight to the finances — so expect your forecasts to be scrutinized in a lot of detail. Writing a business plan for your eyes only? That’s fine, but you should still take time to map out your financial requirements: how much money do you need to start? How do you plan to keep money coming in? How long will it take to break even ? Remember, cash is king. So you need a cash flow forecast that is realistic, achievable and keeps your business afloat, especially in the tricky first few years.

General FAQ
Glossary categories.

Feedback Management

Prioritization

Product Management

Product Strategy

Roadmapping
Build great roadmaps
Book a demo
Experience the new way of doing product management


What is a Business Plan?
Home › Business Management › What is a Business Plan?
Definition: A business plan is a detailed written steps and goals defined to guide a business’ course of action from its initial stages. A business plan provides a complete description and projection of the company as well as its core strategies and expected results.
- What Does Business Plan Mean?
The creation of a new organization or a new business requires coherent actions in order to achieve the desired outcomes. Following a business plan allows to link actions and resources to objectives and measurable goals. This plan can be used internally like a roadmap for the owner but also can be a requirement when looking for funding or partners.
A business plan is generally a precise, short document that commonly contains the following sections: executive summary, business description with its products or services, marketing plan, operational plan and financial plan with its forecasted financial statements for the first years of operation, often five to ten years. The initial business plan is later substituted by annual or bi-annual strategic plans.
Mark Tilson is a young professional that wants to start a new business. He has the idea of providing an innovative maintenance service to medium-size manufacturing companies but he needs funds to implement it. Mr. Tilson therefore decided to write a business plan to present the idea to some potential capital partners. He though that the ideas were already clear but soon realized that more analysis and pre-launching work was required.
How many employees the company will have? How the company will market its services? How much money the initial investment requires? How much profit the company is expected to generate at the end of the fifth year of operation? These and other questions must be answered and coherently written in the business plan. Finally, Mr. Tilson improved his ideas, presented the plan and found the required partner.

Accounting & CPA Exam Expert
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.
Search 2,000+ accounting terms and topics.
- Basic Accounting Course
- Financial Accounting Basics
- Accounting Principles
- Accounting Cycle
- Financial Statements
- Financial Ratio
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of business plan in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- make time idiom
- set the agenda idiom
- slot someone/something in
- social calendar
- spread something over something
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
business plan | Business English
Examples of business plan, translations of business plan.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
anonymously
without the name of someone who has done a particular thing being known or made public

Dead ringers and peas in pods (Talking about similarities, Part 2)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- Business Noun
- Translations
- All translations
To add business plan to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add business plan to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
What the New Overtime Rule Means for Workers

One of the basic principles of the American workplace is that a hard day’s work deserves a fair day’s pay. Simply put, every worker’s time has value. A cornerstone of that promise is the Fair Labor Standards Act ’s (FLSA) requirement that when most workers work more than 40 hours in a week, they get paid more. The Department of Labor ’s new overtime regulation is restoring and extending this promise for millions more lower-paid salaried workers in the U.S.
Overtime protections have been a critical part of the FLSA since 1938 and were established to protect workers from exploitation and to benefit workers, their families and our communities. Strong overtime protections help build America’s middle class and ensure that workers are not overworked and underpaid.
Some workers are specifically exempt from the FLSA’s minimum wage and overtime protections, including bona fide executive, administrative or professional employees. This exemption, typically referred to as the “EAP” exemption, applies when:
1. An employee is paid a salary,
2. The salary is not less than a minimum salary threshold amount, and
3. The employee primarily performs executive, administrative or professional duties.
While the department increased the minimum salary required for the EAP exemption from overtime pay every 5 to 9 years between 1938 and 1975, long periods between increases to the salary requirement after 1975 have caused an erosion of the real value of the salary threshold, lessening its effectiveness in helping to identify exempt EAP employees.
The department’s new overtime rule was developed based on almost 30 listening sessions across the country and the final rule was issued after reviewing over 33,000 written comments. We heard from a wide variety of members of the public who shared valuable insights to help us develop this Administration’s overtime rule, including from workers who told us: “I would love the opportunity to...be compensated for time worked beyond 40 hours, or alternately be given a raise,” and “I make around $40,000 a year and most week[s] work well over 40 hours (likely in the 45-50 range). This rule change would benefit me greatly and ensure that my time is paid for!” and “Please, I would love to be paid for the extra hours I work!”
The department’s final rule, which will go into effect on July 1, 2024, will increase the standard salary level that helps define and delimit which salaried workers are entitled to overtime pay protections under the FLSA.
Starting July 1, most salaried workers who earn less than $844 per week will become eligible for overtime pay under the final rule. And on Jan. 1, 2025, most salaried workers who make less than $1,128 per week will become eligible for overtime pay. As these changes occur, job duties will continue to determine overtime exemption status for most salaried employees.

The rule will also increase the total annual compensation requirement for highly compensated employees (who are not entitled to overtime pay under the FLSA if certain requirements are met) from $107,432 per year to $132,964 per year on July 1, 2024, and then set it equal to $151,164 per year on Jan. 1, 2025.
Starting July 1, 2027, these earnings thresholds will be updated every three years so they keep pace with changes in worker salaries, ensuring that employers can adapt more easily because they’ll know when salary updates will happen and how they’ll be calculated.
The final rule will restore and extend the right to overtime pay to many salaried workers, including workers who historically were entitled to overtime pay under the FLSA because of their lower pay or the type of work they performed.
We urge workers and employers to visit our website to learn more about the final rule.
Jessica Looman is the administrator for the U.S. Department of Labor’s Wage and Hour Division. Follow the Wage and Hour Division on Twitter at @WHD_DOL and LinkedIn . Editor's note: This blog was edited to correct a typo (changing "administrator" to "administrative.")
- Wage and Hour Division (WHD)
- Fair Labor Standards Act
- overtime rule
SHARE THIS:


An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Take action
- Report an antitrust violation
- File adjudicative documents
- Find banned debt collectors
- View competition guidance
- Competition Matters Blog
New HSR thresholds and filing fees for 2024
View all Competition Matters Blog posts
We work to advance government policies that protect consumers and promote competition.
View Policy
Search or browse the Legal Library
Find legal resources and guidance to understand your business responsibilities and comply with the law.
Browse legal resources
- Find policy statements
- Submit a public comment

Vision and Priorities
Memo from Chair Lina M. Khan to commission staff and commissioners regarding the vision and priorities for the FTC.
Technology Blog
Consumer facing applications: a quote book from the tech summit on ai.
View all Technology Blog posts
Advice and Guidance
Learn more about your rights as a consumer and how to spot and avoid scams. Find the resources you need to understand how consumer protection law impacts your business.
- Report fraud
- Report identity theft
- Register for Do Not Call
- Sign up for consumer alerts
- Get Business Blog updates
- Get your free credit report
- Find refund cases
- Order bulk publications
- Consumer Advice
- Shopping and Donating
- Credit, Loans, and Debt
- Jobs and Making Money
- Unwanted Calls, Emails, and Texts
- Identity Theft and Online Security
- Business Guidance
- Advertising and Marketing
- Credit and Finance
- Privacy and Security
- By Industry
- For Small Businesses
- Browse Business Guidance Resources
- Business Blog
Servicemembers: Your tool for financial readiness
Visit militaryconsumer.gov
Get consumer protection basics, plain and simple
Visit consumer.gov
Learn how the FTC protects free enterprise and consumers
Visit Competition Counts
Looking for competition guidance?
- Competition Guidance
News and Events
Latest news, ftc expands patent listing challenges, targeting more than 300 junk listings for diabetes, weight loss, asthma and copd drugs.
View News and Events
Upcoming Event
Older adults and fraud: what you need to know.
View more Events
Sign up for the latest news
Follow us on social media
--> --> --> --> -->

Playing it Safe: Explore the FTC's Top Video Game Cases
Learn about the FTC's notable video game cases and what our agency is doing to keep the public safe.
Latest Data Visualization
FTC Refunds to Consumers
Explore refund statistics including where refunds were sent and the dollar amounts refunded with this visualization.
About the FTC
Our mission is protecting the public from deceptive or unfair business practices and from unfair methods of competition through law enforcement, advocacy, research, and education.
Learn more about the FTC

Meet the Chair
Lina M. Khan was sworn in as Chair of the Federal Trade Commission on June 15, 2021.
Chair Lina M. Khan
Looking for legal documents or records? Search the Legal Library instead.
- Cases and Proceedings
- Premerger Notification Program
- Merger Review
- Anticompetitive Practices
- Competition and Consumer Protection Guidance Documents
- Warning Letters
- Consumer Sentinel Network
- Criminal Liaison Unit
- FTC Refund Programs
- Notices of Penalty Offenses
- Advocacy and Research
- Advisory Opinions
- Cooperation Agreements
- Federal Register Notices
- Public Comments
- Policy Statements
- International
- Office of Technology Blog
- Military Consumer
- Consumer.gov
- Bulk Publications
- Data and Visualizations
- Stay Connected
- Commissioners and Staff
- Bureaus and Offices
- Budget and Strategy
- Office of Inspector General
- Careers at the FTC
Fact Sheet on FTC’s Proposed Final Noncompete Rule
- Competition
- Office of Policy Planning
- Bureau of Competition
The following outline provides a high-level overview of the FTC’s proposed final rule :
- Specifically, the final rule provides that it is an unfair method of competition—and therefore a violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act—for employers to enter into noncompetes with workers after the effective date.
- Fewer than 1% of workers are estimated to be senior executives under the final rule.
- Specifically, the final rule defines the term “senior executive” to refer to workers earning more than $151,164 annually who are in a “policy-making position.”
- Reduced health care costs: $74-$194 billion in reduced spending on physician services over the next decade.
- New business formation: 2.7% increase in the rate of new firm formation, resulting in over 8,500 additional new businesses created each year.
- This reflects an estimated increase of about 3,000 to 5,000 new patents in the first year noncompetes are banned, rising to about 30,000-53,000 in the tenth year.
- This represents an estimated increase of 11-19% annually over a ten-year period.
- The average worker’s earnings will rise an estimated extra $524 per year.
The Federal Trade Commission develops policy initiatives on issues that affect competition, consumers, and the U.S. economy. The FTC will never demand money, make threats, tell you to transfer money, or promise you a prize. Follow the FTC on social media , read consumer alerts and the business blog , and sign up to get the latest FTC news and alerts .
Press Release Reference
Contact information, media contact.
Victoria Graham Office of Public Affairs 415-848-5121
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government, request access.
Due to aggressive automated scraping of FederalRegister.gov and eCFR.gov, programmatic access to these sites is limited to access to our extensive developer APIs.
If you are human user receiving this message, we can add your IP address to a set of IPs that can access FederalRegister.gov & eCFR.gov; complete the CAPTCHA (bot test) below and click "Request Access". This process will be necessary for each IP address you wish to access the site from, requests are valid for approximately one quarter (three months) after which the process may need to be repeated.
An official website of the United States government.
If you want to request a wider IP range, first request access for your current IP, and then use the "Site Feedback" button found in the lower left-hand side to make the request.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you'll write, it's the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company's mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals. 3.
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse ...
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a business's operations, finances, and goals. It guides the business's day-to-day decisions. A business plan is necessary for your company's success, as it creates a path to scalability. There are two main types of business plans: a traditional business plan and a lean startup plan.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
To get a better sense of what a 21st century business plan is, it's best to look at what it's not. Or, more specifically, what it's not anymore. When most people think about a business plan, the first thing that usually comes to mind is an incredibly dense, 50-plus-page manifesto that's as hard to write as it is to read.
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan. 2.
Business Plan Definition: A written document describing the nature of the business, the sales and marketing strategy, and the financial background, and containing a projected profit and loss statement
A business plan is a detailed road map that explains what the company's goals are and how it will achieve them. The exact details of a business plan will depend on the intended audience and the nature of the business. It's a good idea to regularly revisit your business plan so you know it's as accurate, realistic, and detailed as possible.
Clawback. v. t. e. A business plan is a formal written document containing the goals of a business, the methods for attaining those goals, and the time-frame for the achievement of the goals. It also describes the nature of the business, background information on the organization, the organization's financial projections, and the strategies it ...
A business plan is an executive document that acts as a blueprint or roadmap for a business. It is quite necessary for new ventures seeking capital, expansion activities, or projects requiring additional capital. It is also important to remind the management, employees, and partners of what they represent. You are free to use this image on your ...
business plan: A business plan is a document demonstrating the feasibility of a prospective new business and providing a roadmap for its first several years of operation.
A business plan is a strategic document which details the strategic objectives for a growing business or startup, and how it plans to achieve them. In a nutshell, a business plan is a written expression of a business idea and will describe your business model, your product or service, how it will be priced, who will be your target market, and ...
Definition: A business plan is a detailed written steps and goals defined to guide a business' course of action from its initial stages. A business plan provides a complete description and projection of the company as well as its core strategies and expected results. ... A business plan is generally a precise, short document that commonly ...
BUSINESS PLAN meaning: 1. a detailed plan describing the future plans of a business 2. a detailed plan describing the…. Learn more.
Business plan definition: a detailed plan setting out the objectives of a business, the strategy and tactics planned to achieve them, and the expected profits, usually over a period of three to ten years. See examples of BUSINESS PLAN used in a sentence.
BUSINESS PLAN definition: 1. a detailed plan describing the future plans of a business 2. a detailed plan describing the…. Learn more.
Nation-building definition. Nation-building is a significant undertaking that governments employ to develop political, economic, security, and social institutions in other countries—especially those emerging from conflict. Governments conduct those activities abroad to secure their own national interests.
The Federal Trade Commission on Tuesday voted to ban for-profit US employers from making employees sign agreements with noncompete clauses. Such a ban could affect tens of millions of workers.
As Pro-Palestinian protests continue to sweep across major US universities, a unifying message has emerged.
Over the past few years, people have thrown around the term "fascism" pretty loosely. It has been used to criticize any number of issues—stay-at-home orders during a global pandemic, proposed environmental regulations aimed at curbing greenhouse gas emissions, and even legislation limiting the size of sodas. But the origins of the term point to something far more serious than Big Gulps.
One of the basic principles of the American workplace is that a hard day's work deserves a fair day's pay. Simply put, every worker's time has value.
New business formation: 2.7% increase in the rate of new firm formation, resulting in over 8,500 additional new businesses created each year. Rise in innovation: an average of 17,000-29,000 more patents each year for the next ten years.
Butlin's advertises its camps as sunny havens for holidaymakers seeking to escape the routine of everyday life. But guests experienced the polar opposite last September when its biggest camp in ...
To ensure that the definition is readily and more broadly accessible for those seeking requirements related to network-based plans, we proposed in the December 2022 proposed rule (87 FR 79569) to move the definition of a network-based plan from § 422.114(a)(3)(ii) to the definitions section in § 422.2. Further, we proposed that the PFFS ...