Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in APA

How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in APA
In this citation guide, you will learn how to reference and cite an undergraduate thesis, master’s thesis, or doctoral dissertation. This guide will also review the differences between a thesis or dissertation that is published and one that has remained unpublished. The guidelines below come from the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (2020a), pages 333 and 334. Please note that the association is not affiliated with this guide.
Alternatively, you can visit EasyBib.com for helpful citation tools to cite your thesis or dissertation .
Guide Overview
Citing an unpublished thesis or dissertation, citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database, citing a thesis or dissertation published online but not from a database, citing a thesis or dissertation: reference overview, what you need.
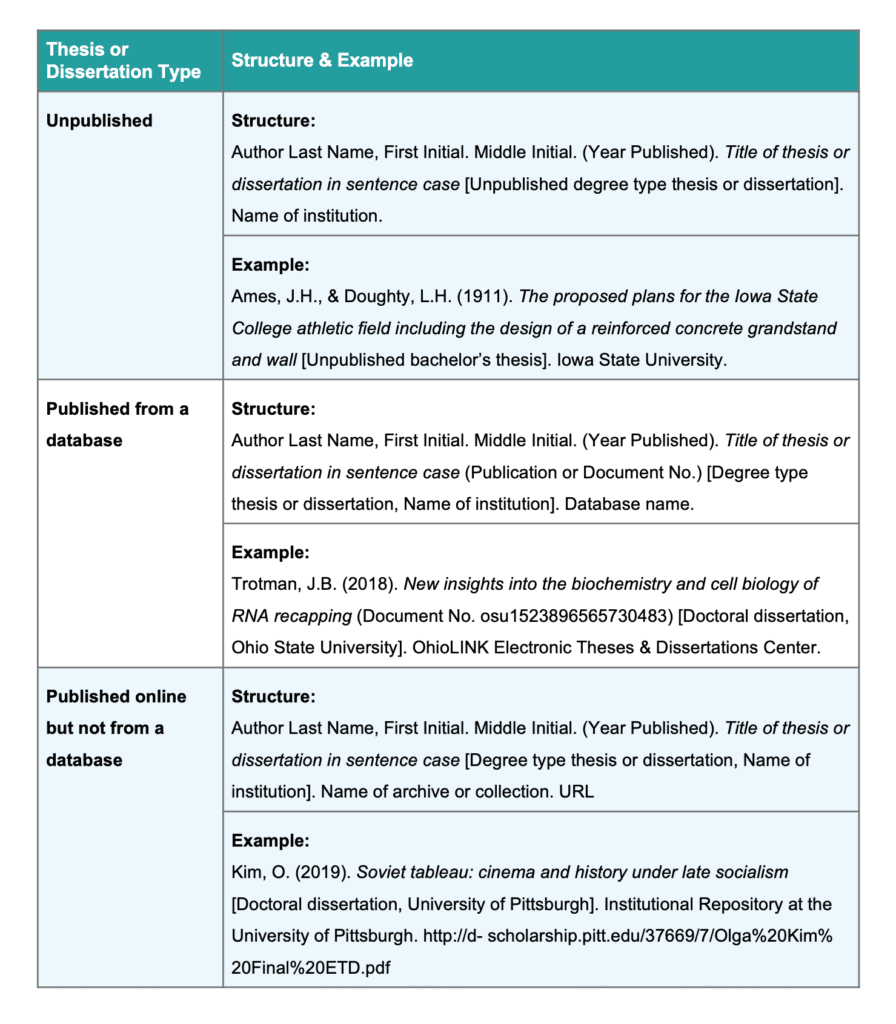
Since unpublished theses can usually only be sourced in print form from a university library, the correct citation structure includes the university name where the publisher element usually goes.
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year published). Title in sentence case [Unpublished degree type thesis or dissertation]. Name of institution.
Ames, J. H., & Doughty, L. H. (1911). The proposed plans for the Iowa State College athletic field including the design of a reinforced concrete grandstand and wall [Unpublished bachelor’s thesis]. Iowa State University.
In-text citation example:
- Parenthetical : (Ames & Doughty, 1911)
- Narrative : Ames & Doughty (1911)
If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It’s similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences:
- The institution is presented in brackets after the title
- The archive or database name is included
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year published). Title in sentence case (Publication or Document No.) [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Database name.
Examples 1:
Knight, K. A. (2011). Media epidemics: Viral structures in literature and new media (Accession No. 2013420395) [Doctoral dissertation, University of California, Santa Barbara]. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing.

Trotman, J.B. (2018). New insights into the biochemistry and cell biology of RNA recapping (Document No. osu1523896565730483) [Doctoral dissertation, Ohio State University]. OhioLINK Electronic Theses & Dissertations Center.
In the example given above, the dissertation is presented with a Document Number (Document No.). Sometimes called a database number or publication number, this is the identifier that is used by the database’s indexing system. If the database you are using provides you with such a number, then include it directly after the work’s title in parentheses.
If you are interested in learning more about how to handle works that were accessed via academic research databases, see Section 9.3 of the Publication Manual.
In-text citation examples :
- Parenthetical citation : (Trotman, 2018)
- Narrative citation : Trotman (2018)
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year Published). Title in sentence case [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Name of archive or collection. URL
Kim, O. (2019). Soviet tableau: cinema and history under late socialism [Doctoral dissertation, University of Pittsburgh]. Institutional Repository at the University of Pittsburgh. https://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/37669/7/Olga%20Kim%20Final%20ETD.pdf
Stiles, T. W. (2001). Doing science: Teachers’ authentic experiences at the Lone Star Dinosaur Field Institute [Master’s thesis, Texas A&M University]. OAKTrust. https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/ETD-TAMU-2001-THESIS-S745
It is important to note that not every thesis or dissertation published online will be associated with a specific archive or collection. If the work is published on a private website, provide only the URL as the source element.
In-text citation examples:
- Parenthetical citation : (Kim, 2019)
- Narrative citation : Kim (2019)
- Parenthetical citation : (Stiles, 2001)
- Narrative citation : Stiles (2001)
We hope that the information provided here will serve as an effective guide for your research. If you’re looking for even more citation info, visit EasyBib.com for a comprehensive collection of educational materials covering multiple source types.
If you’re citing a variety of different sources, consider taking the EasyBib citation generator for a spin. It can help you cite easily and offers citation forms for several different kinds of sources.
To start things off, let’s take a look at the different types of literature that are classified under Chapter 10.6 of the Publication Manual :
- Undergraduate thesis
- Master’s thesis
- Doctoral dissertation
You will need to know which type you are citing. You’ll also need to know if it is published or unpublished .
When you decide to cite a dissertation or thesis, you’ll need to look for the following information to use in your citation:
- Author’s last name, and first and middle initials
- Year published
- Title of thesis or dissertation
- If it is unpublished
- Publication or document number (if applicable; for published work)
- Degree type (bachelor’s, master’s, doctoral)
- Thesis or dissertation
- Name of institution awarding degree
- DOI (https://doi.org/xxxxx) or URL (if applicable)
Since theses and dissertations are directly linked to educational degrees, it is necessary to list the name of the associated institution; i.e., the college, university, or school that is awarding the associated degree.
To get an idea of the proper form, take a look at the examples below. There are three outlined scenarios:
- Unpublished thesis or dissertation
- Published thesis or dissertation from a database
- Thesis or dissertation published online but not from a database
American Psychological Association. (2020a). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
American Psychological Association. (2020b). Style-Grammar-Guidelines. https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/citations/basic-principles/parenthetical-versus-narrative
Published August 10, 2012. Updated March 24, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite a published thesis in APA style, it is important that you know some basic information such as the author, publication year, title of the thesis, institute name, archive name, and URL (uniform resource locator). The templates for an in-text citation and reference list entry of a thesis, along with examples, are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
Use the author surname and the publication year in the in-text citation.
Author Surname (Publication Year)
Cartmel (2007)
Parenthetical:
(Author Surname, Publication Year)
(Cartmel, 2007)
Reference list entry template and example:
The title of the thesis is set in sentence case and italicized. Enclose the thesis and the institute awarding the degree inside brackets following the publication year. Then add the name of the database followed by the URL.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the thesis [Master’s thesis, Institute Name]. Name of the Database. URL
Cartmel, J. (2007). Outside school hours care and schools [Master’s thesis, Queensland University of Technology]. EPrints. http://eprints.qut.edu.au/17810/1/Jennifer_Cartmel_Thesis.pdf
To cite an unpublished dissertation in APA style, it is important that you know some basic information such as the author, year, title of the dissertation, and institute name. The templates for in-text citation and reference list entry of an online thesis, along with examples, are given below:
Author Surname (Year)
Averill (2009)
(Author Surname, Year)
(Averill, 2009)
The title of the dissertation is set in sentence case and italicized. Enclose “Unpublished doctoral dissertation” inside brackets following the year. Then add the name of the institution awarding the degree.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the dissertation [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Name of the Institute.
Averill, R. (2009). Teacher–student relationships in diverse New Zealand year 10 mathematics classrooms: Teacher care [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Victoria University of Wellington.
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
How to Write a Thesis Bibliography: A Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a thesis bibliography can be a daunting task, especially if you’re not familiar with the process. however, with a step-by-step guide, you can navigate through this essential part of your thesis with ease. in this blog post, we will walk you through the process of writing a thesis bibliography, ensuring that your sources are appropriately cited..

What is a Thesis Bibliography?
A thesis bibliography is a list of all the sources you have cited or referenced in your thesis. It includes all the books, articles, research papers, websites, and any other resources you have used to support your research and arguments. The purpose of a bibliography is to give credit to the original authors and allow readers to locate the sources you have used.
Why is a Thesis Bibliography Important?
A thesis bibliography serves several important purposes:
- It demonstrates the depth of your research and shows the credibility of your thesis.
- It allows readers to verify your research and delve deeper into the sources you have used.
- It helps you avoid plagiarism by providing a clear list of the sources you have consulted.
- It showcases your academic integrity and commitment to acknowledging the work of others.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Thesis Bibliography
Now, let’s dive into the step-by-step process of writing a thesis bibliography:
Step 1: Understand the Citation Style Guidelines
Before you begin compiling your bibliography, familiarize yourself with the citation style required by your university or department. Common citation styles include APA, MLA, Chicago, and Harvard. Each style has specific formatting guidelines for different types of sources, such as books, journal articles, and websites. Make sure to follow the guidelines consistently throughout your bibliography.
Step 2: Collect and Organize Your Sources
Gather all the sources you have referenced or cited in your thesis. Make a list of books, articles, webpages, and any other relevant sources. Organize them in alphabetical order based on the author’s last name or the title of the source.
Step 3: Format Your Bibliography Entries
When formatting each entry in your bibliography, keep the following in mind:
- Book: Include the author’s name, publication year, title, place of publication, and publisher.
- Journal Article: Include the author’s name, publication year, article title, journal name, volume number, issue number, and page range.
- Website: Include the author’s name (if available), publication or last updated date, title of the webpage, URL, and the date you accessed the website.
Step 4: Verify Your Information
Double-check all the information in your bibliography entries to ensure accuracy. Pay close attention to spelling, punctuation, and formatting. Use reliable sources or citation generators to confirm the correct citation format for each source.
Step 5: Apply Consistent Formatting
Make sure your bibliography entries adhere to the formatting guidelines specified by your citation style. Consistency in formatting is crucial for the professional presentation of your thesis.
Step 6: Proofread
Once you have completed your bibliography, take the time to proofread it. Look for any typographical errors, missing information, or incorrect formatting. A well-organized and error-free bibliography adds to the professionalism of your thesis.
Writing a thesis bibliography doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By following this step-by-step guide, you can accurately list and cite all your sources, ensuring your thesis is well-supported and authoritative. Remember to always abide by the citation guidelines provided by your university or department, as they may have specific requirements. A meticulously crafted thesis bibliography adds credibility to your work and demonstrates your commitment to scholarly research.
For more assistance, feel free to consult your university’s writing center or reach out to your thesis advisor for guidance.
How helpful was this article?

- Future Students
- Parents and Families
College of Engineering
- Research and Facilities
- Departments
Guide to Writing Your Thesis in LaTeX
The bibliography and list of references.
The Graduate School requires a Bibliography which includes all the literature cited for the complete thesis or dissertation. Quoting from the Graduate School’s Guidelines for the Format of Theses and Dissertations :
“Every thesis in Standard Format must contain a Bibliography which lists all the sources used or consulted in writing the entire thesis and is placed at the very end of the work. The complete citations are arranged alphabetically by last name of the author. Individual citations are not numbered. No abbreviations in titles of published works will be accepted. The full title of a book, journal, website, proceedings, or any other published work must be italicized or underlined. Citations must follow standards set by the style manual that the student is using. The bibliography for URI theses is not broken into categories.”
The List of References is not required by the Graduate School, but is the style commonly used in Engineering, Mathematics, and many of the Sciences. It consists of a numbered list of the sources used or consulted in writing the thesis in the order that they are referenced in the text. There can be either one List of References for the entire thesis, or a List of References at the end of each chapter.
Both the Bibliography and the List of References will be generated by the urithesis LaTeX class. All you need to do is add information about your sources to the references.bib file, which is a database containing all of the necessary information about the references, then cite the reference in your thesis using the \cite{} command.
Generating the Bibliography and References
The bibliography and list of references are generated by running BibTeX. To generate the bibliography, load the file thesisbib.tex into your editor, then run BibTeX on it.
If each chapter has its own list of references, you will need to run BibTeX on each chapter to update its list of references. If there is one list of references for the whole thesis (because you used the oneref option, you will only need to run BibTeX on the top level file thesis.tex .
How to Add a Bibliography Entry
When we want to refer to a source in the thesis, we place an entry for that source in the file references.bib , then cite the source in the thesis with the \cite{LABEL} command. The syntax for an entry in the references.bib file is of the form:
ENTRYTYPE is the type of bibliographic entry such as Book , Article , or TechReport , that this entry describes. At the end of this page is a list of all possible entry types .
LABEL is a unique string that is used to refer to this entry in the body of the thesis when using the \cite{LABEL} command.
The FIELDNAMEn entries are the fields that describe this entry, (ie. author, title, pages, year, etc.). Each entry type has certain required fields and optional fields. See the list of all entry types for a description of the available fields.
As an example, suppose we have a paper from a conference proceedings that we want to cite. First we make an entry in the our references.bib file of the form:
We then cite this source in the text of our thesis with the command \cite{re:toolan:as03} . This will generate a Bibliography entry that looks something like:
and a List of References entry that looks something like:
Types of List of References
The Graduate School requires that the bibliography is always at the end of the thesis and sorted alphabetically by author, therefore there is no options that affect it. The list of references is optional, therefore there are a few different ways that it can created.
By default a separate list of references appears at the end of each chapter, and are sorted by the order that they are cited in that chapter. The option oneref (see options ) will create a single list of references for the whole thesis, which due to the requirements of the Graduate School, will appear after the last chapter and before any appendices.
The option aparefs will cite references using the APA style, which is the last name of the author and year of publication, such as (Toolan, 2006), instead of the default IEEE style, which is a number, such as [1]. This option will also sort the references alphabetically by author, instead of in order of citation. The options oneref and aparefs can be used together to create a single list of references using the APA style.
Supported Bibliography Entry Types
The following is a list of all the entry types that can be used. Click on the desired type to see a detailed description of how to use that type.
- Article – An article from a journal or magazine
- Book – A book with an explicit publisher
- InBook – A part of a book, such as a chapter or selected page(s)
- InCollection – A part of a book having its own title
- Booklet – Printed and bound works that are not formally published
- Manual – Technical documentation
- InProceedings – An article in a conference proceedings
- Proceedings – The entire proceedings of a conference
- MastersThesis – A Master’s thesis
- PhDThesis – A Ph.D. dissertation
- TechReport – A report published by a school or other institution
- Unpublished – A document that has not been formally published
- Electronic – An internet reference like a web page
- Patent – A patent or patent application
- Periodical – A magazine or journal
- Standard – Formally published standard
- Misc – For use when nothing else fits
Articles that have not yet been published can be handled as a misc type with a note. Sometimes it is desirable to put extra information into the month field such as the day, or additional months. This is accomplished by using the BIBTEX concatenation operator “#“:
Example .bib using this type:
Books may have authors, editors or both. Example .bib using this type:
Inbook is used to reference a part of a book, such as a chapter or selected page(s). The type field can be used to override the word chapter (for which IEEE uses the abbreviation “ch.”) when the book uses parts, sections, etc., instead of chapters
Incollection is used to reference part of a book having its own title. Like book , incollection supports the series, chapter and pages fields. Also, the type field can be used to override the word chapter.
Booklet is used for printed and bound works that are not formally published. A primary difference between booklet and unpublished is that the former is/was distributed by some means. Booklet is rarely used in bibliographies.
Technical documentation is handled by the manual entry type.
References of papers in conference proceedings are handled by the inproceedings or conference entry type. These two types are functionally identical and can be used interchangeably. Example .bib using this type:
It is rare to need to reference an entire conference proceedings, but, if necessary, the proceedings entry type can be used to do so.
Master’s (or minor) theses can be handled with the mastersthesis entry type. The optional type field can be used to override the words “Master’s thesis” if a different designation is desired:
The phdthesis entry type is used for Ph.D. dissertations (major theses). Like mastersthesis , the type field can be used to override the default designation. Example .bib using this type:
Techreport is used for technical reports. The optional type field can be used to override the default designation “Tech. Rep.” Example .bib using this type:
The unpublished entry type is used for documents that have not been formally published. IEEE typically just uses “unpublished” for the required note field.
The electronic entry type is for internet references. IEEE formats electronic references differently by not using italics or quotes and separating fields with periods rather than commas. Also, the date is enclosed within parentheses and is placed closer to the title. This is probably done to emphasize that electronic references may not remain valid on the rapidly changing internet. Note also the liberal use of the howpublished field to describe the form or category of the entries. The organization and address fields may also be used. Example .bib using this type:
The nationality field provides a means to handle patents from different countries
The nationality should be capitalized. The assignee and address (of the assignee) fields are not used, however, they are provided. The type field provides a way to override the “patent” description with other patent related descriptions such as “patent application” or “patent request”:
The periodical entry type is used for journals and magazines.
The standard entry type is used for formally published standards. Alternatively, the misc entry type, along with its howpublished field, can be used to create references of standards.
Misc is the most flexible type and can be used when none of the other entry types are applicable. The howpublished field can be used to describe what exactly (or in what form) the reference is (or appears as). Possible applications include technical-report-like entries that lack an institution, white papers and data sheets.
Additional Comments
Because we are effectively creating multiple bibliographies, (one for the actual bibliography, and one for each list of references), the two LATEX commands \bibliographystyle{} and \bibliography{} are not used. They have been redefined to do nothing, and the equivalent of these commands are done automatically when necessary.
When there is a reference that should be included in the bibliography, but does not need to be explicitly referenced in the thesis, use the \nocite{} command. This command works like the \cite{} command, except it does not put the citation in the list of references, only in the bibliography. The \nocite{} command must appear after the first \newchapter{} command, or it will be ignored.
When using the option aparefs , and a citation does not have an author, (such as often occurs with a web page), the key field can be used to specify what to use in the citation instead of the author’s name.
About the Bibliography Format
The bibliography format used by the urithesis class is based on the IEEE format. See the article “How to Use the IEEEtran BIBTEX Style” by Michael Shell for more details.
- AUT Library
- Library Guides
- Referencing styles and applications
APA 7th Referencing Style Guide
- Theses and dissertations
- Referencing & APA style
- In-text citation
- Elements of a reference
- Format & examples of a reference list
- Conferences
- Reports & grey literature
- Figures (graphs and images)
Terminology - Thesis, dissertation or exegesis?
Published theses and dissertations, unpublished theses and dissertations.
- Audio works
- Films, TV & video
- Visual works
- Computer software, games & apps
- Lecture notes & Intranet resources
- Legal resources
- Personal communications
- PowerPoint slides
- Social media
- Specific health examples
- Standards & patents
- Websites & webpages
- Footnotes and appendices
- Frequently asked questions
Thesis and dissertation can mean different things depending on where the degree is awarded. Always check the title page, or subsequent pages, to determine exactly what the work is and use the information for your reference.
Auckland University of Technology (and other NZ universities)
- Thesis is either for a doctoral or a master's degree.
- Dissertation is either for a master's or a bachelor's degree with honours.
- Exegesis is the written component of a practice-based thesis where the major output is a creative work; e.g., a film, artwork, novel.
Other parts of the world
- In North America and some other countries, dissertation is used for a doctoral degree and thesis for a master's degree.
Theses available in a database, a university archive or from a personal website.
Reference format
Theses published online (e.g. in institutional repositories), theses from proquest dissertations and theses global.
Find how to cite in text on the In-text citation page.
Unpublished thesis or dissertations are usually sourced directly from the university in print form.
Reference format
- << Previous: Tables
- Next: Audiovisual media >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 3:25 PM
- URL: https://aut.ac.nz.libguides.com/APA7th
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Published on 1 May 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 7 November 2022.
In Harvard style , the bibliography or reference list provides full references for the sources you used in your writing.
- A reference list consists of entries corresponding to your in-text citations .
- A bibliography sometimes also lists sources that you consulted for background research, but did not cite in your text.
The two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. If in doubt about which to include, check with your instructor or department.
The information you include in a reference varies depending on the type of source, but it usually includes the author, date, and title of the work, followed by details of where it was published. You can automatically generate accurate references using our free reference generator:
Harvard Reference Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Formatting a harvard style bibliography, harvard reference examples, referencing sources with multiple authors, referencing sources with missing information, frequently asked questions about harvard bibliographies.
Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading ‘Reference list’ or ‘Bibliography’ appears at the top.
Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used:

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Reference list or bibliography entries always start with the author’s last name and initial, the publication date and the title of the source. The other information required varies depending on the source type. Formats and examples for the most common source types are given below.
- Entire book
- Book chapter
- Translated book
- Edition of a book
Journal articles
- Print journal
- Online-only journal with DOI
- Online-only journal without DOI
- General web page
- Online article or blog
- Social media post
Newspapers and magazines
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
When a source has up to three authors, list all of them in the order their names appear on the source. If there are four or more, give only the first name followed by ‘ et al. ’:
Sometimes a source won’t list all the information you need for your reference. Here’s what to do when you don’t know the publication date or author of a source.
Some online sources, as well as historical documents, may lack a clear publication date. In these cases, you can replace the date in the reference list entry with the words ‘no date’. With online sources, you still include an access date at the end:
When a source doesn’t list an author, you can often list a corporate source as an author instead, as with ‘Scribbr’ in the above example. When that’s not possible, begin the entry with the title instead of the author:
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a difference in meaning:
- A reference list only includes sources cited in the text – every entry corresponds to an in-text citation .
- A bibliography also includes other sources which were consulted during the research but not cited.
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
In Harvard style referencing , to distinguish between two sources by the same author that were published in the same year, you add a different letter after the year for each source:
- (Smith, 2019a)
- (Smith, 2019b)
Add ‘a’ to the first one you cite, ‘b’ to the second, and so on. Do the same in your bibliography or reference list .
To create a hanging indent for your bibliography or reference list :
- Highlight all the entries
- Click on the arrow in the bottom-right corner of the ‘Paragraph’ tab in the top menu.
- In the pop-up window, under ‘Special’ in the ‘Indentation’ section, use the drop-down menu to select ‘Hanging’.
- Then close the window with ‘OK’.

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 07). Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/harvard-bibliography/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, harvard in-text citation | a complete guide & examples, referencing books in harvard style | templates & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


Thesis Preparation: Bibliography & Referencing
- Books about writing a thesis
- Literature Review
- Bibliography & Referencing
- Writing your thesis
- Your thesis in UL's Research Repository
- Research Services Guide This link opens in a new window
What is a bibliography
A bibliography, sometimes known as a “Reference List” is a list of all of the sources you have used (whether referenced or not) in the process of researching your work. In general, a bibliography should include:
- the authors' names
- the titles of the works
- the names of the publishers who published your sources and where they were published.
- the dates your sources were published
- the page numbers of your sources (if they are part of multi-source volumes)
When preparing your thesis, be aware of rules around using copyright restricted material in your submission. The library can advise you on these matters and in relation specifically to publishing and necessary embargoes that should be considered when you prepare your final document.
What is EndNote Online?
EndNote Online (formerly called EndNote Web) is available to all UL staff and students. It allows you to access your EndNote library from any PC with an Internet connection, to create bibliographies in Word and to share your library with group members.
Creating an EndNote Online account
When you first access EndNote Online you MUST Register. Please follow the instruction in the box opposite to ensure you register for EndNote Online correctly. If you do not register correctly you will not be able to access the Harvard UL referencing style.
Once you have created your account you will be able to use EndNote from anywhere once you have a PC with Internet access.
EndNote Online Cite While You Write plug-in for Word
To download the Cite While You Write (CWYW) plug-in for Microsoft Word go to the Downloads tab in EndNote Online.
If you experience any difficulties installing the EndNote CWYW plug-in, you can download and install this alternative version .
Cite it Right; an introduction to Referencing
Cite It Right 4th Edition
The Glucksman Library wrote a guide called Cite it Right: Guide to Harvard Referencing Style . To access the 4th edition of Cite It Right go to https://libguides.ul.ie/citeitright . A PDF version of the 4th edition can be accessed below:
- Cite It Right 4th Edition - Print optimised version This version of the Cite It Right 4th edition has been optimised for printing. For best results and to only use 13 sheets of paper: Print 2 pages per sheet; Print page border; Print on both sides of paper (i.e. double-sided); Flip on short edge.
Academic Writing and Referencing
- << Previous: Copyright
- Next: Writing your thesis >>
- Last Updated: Jan 18, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ul.ie/theses

Writing your Dissertation / Thesis
- Getting started
- Dissertations and theses
- Bibliographic research and literature review
- Citations and bibliography
- Copyright and plagiarism
- Ask a Librarian
Citation styles
A citation style provides a standardized system to format bibliographic references within the text and in the bibliography at the end of the essay. In particular, the style defines which elements to cite, in what order to cite them and with what punctuation.
There isn’t an official citation style used in Bocconi University. Since there are different citation styles, you will need to choose which one is right for you, taking into account the subject area and what you supervisor might suggest.
Some styles commonly used internationally are:
The APA style is an “author-date” citation system, with the author and date of the cited source appearing in the body of the text. You will need to add a bibliography at the end of the essay, with the full references alphabetically ordered by author’s name. It is mainly used in the social sciences.
The Chicago style uses two systems: "author-date" in the body of the text and bibliography at the end of the paper, or footnotes with bibliography.
To learn more about this style you can visit the official website with tutorials, webinars, examples and exercises accessible for free.
The Harvard style is an “author-date” citation, with the author and date of the cited source appearing in the body of the text. You must include a bibliography at the end of the text, with the full references alphabetically ordered by author’s name. It is used in the social sciences.
To learn more about this style you can visit the dedicated section of the Guides on citation styles prepared by Harvard Library staff.
The MLA style, developed by the Modern language Association, is an “author-page number” citation system appearing in the body of the text. You must include a bibliography at the end of the text, with the full references alphabetically ordered by author’s name. It is used in the social sciences and humanities.
The Oscola style, acronym for Oxford University Standard for Citation of Legal Authorities, is a citation system using footnotes and bibliography. It is used in law studies.
To learn more about this style you can read:
Faculty of Law, University of Oxford (2012) (ed.). OSCOLA. Oxford University Standard for the Citation of Legal Authorities (4. ed.)
OSCOLA Quick Reference Guide
The Bluebook style is a citation system used in the United States in a professional setting to cite legal sources.
To learn more about this style, we suggest you read the manual, in particular the Whitepages section, dedicated to academic citations and the Quick Style Guide where you will find examples of citations from non-US legal sources.
Here are some print books that you can find in the Library:
RefWorks is the bibliographic management tool (citation manager) supported by the Library. It helps you with keeping track of your sources as you search, with citing them correctly and creating a bibliography.
Further information on RefWorks .
Would you like to know more? The Library regularly organizes RefWorks workshops for students. Check the calendar on the yoU@B Student Diary (Library section) and sign up!
- << Previous: Bibliographic research and literature review
- Next: Copyright and plagiarism >>
- Last Updated: Jan 30, 2024 11:59 AM
- URL: https://unibocconi.libguides.com/dissertation
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Formatting and Style Guide (7th Edition)

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
In-Text Citations
Resources on using in-text citations in APA style
Reference List
Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats
Other APA Resources
How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper

Do not try to “wow” your instructor with a long bibliography when your instructor requests only a works cited page. It is tempting, after doing a lot of work to research a paper, to try to include summaries on each source as you write your paper so that your instructor appreciates how much work you did. That is a trap you want to avoid. MLA style, the one that is most commonly followed in high schools and university writing courses, dictates that you include only the works you actually cited in your paper—not all those that you used.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, assembling bibliographies and works cited.
- If your assignment calls for a bibliography, list all the sources you consulted in your research.
- If your assignment calls for a works cited or references page, include only the sources you quote, summarize, paraphrase, or mention in your paper.
- If your works cited page includes a source that you did not cite in your paper, delete it.
- All in-text citations that you used at the end of quotations, summaries, and paraphrases to credit others for their ideas,words, and work must be accompanied by a cited reference in the bibliography or works cited. These references must include specific information about the source so that your readers can identify precisely where the information came from.The citation entries on a works cited page typically include the author’s name, the name of the article, the name of the publication, the name of the publisher (for books), where it was published (for books), and when it was published.
The good news is that you do not have to memorize all the many ways the works cited entries should be written. Numerous helpful style guides are available to show you the information that should be included, in what order it should appear, and how to format it. The format often differs according to the style guide you are using. The Modern Language Association (MLA) follows a particular style that is a bit different from APA (American Psychological Association) style, and both are somewhat different from the Chicago Manual of Style (CMS). Always ask your teacher which style you should use.
A bibliography usually appears at the end of a paper on its own separate page. All bibliography entries—books, periodicals, Web sites, and nontext sources such radio broadcasts—are listed together in alphabetical order. Books and articles are alphabetized by the author’s last name.
Most teachers suggest that you follow a standard style for listing different types of sources. If your teacher asks you to use a different form, however, follow his or her instructions. Take pride in your bibliography. It represents some of the most important work you’ve done for your research paper—and using proper form shows that you are a serious and careful researcher.
Bibliography Entry for a Book
A bibliography entry for a book begins with the author’s name, which is written in this order: last name, comma, first name, period. After the author’s name comes the title of the book. If you are handwriting your bibliography, underline each title. If you are working on a computer, put the book title in italicized type. Be sure to capitalize the words in the title correctly, exactly as they are written in the book itself. Following the title is the city where the book was published, followed by a colon, the name of the publisher, a comma, the date published, and a period. Here is an example:
Format : Author’s last name, first name. Book Title. Place of publication: publisher, date of publication.
- A book with one author : Hartz, Paula. Abortion: A Doctor’s Perspective, a Woman’s Dilemma . New York: Donald I. Fine, Inc., 1992.
- A book with two or more authors : Landis, Jean M. and Rita J. Simon. Intelligence: Nature or Nurture? New York: HarperCollins, 1998.
Bibliography Entry for a Periodical
A bibliography entry for a periodical differs slightly in form from a bibliography entry for a book. For a magazine article, start with the author’s last name first, followed by a comma, then the first name and a period. Next, write the title of the article in quotation marks, and include a period (or other closing punctuation) inside the closing quotation mark. The title of the magazine is next, underlined or in italic type, depending on whether you are handwriting or using a computer, followed by a period. The date and year, followed by a colon and the pages on which the article appeared, come last. Here is an example:
Format: Author’s last name, first name. “Title of the Article.” Magazine. Month and year of publication: page numbers.
- Article in a monthly magazine : Crowley, J.E.,T.E. Levitan and R.P. Quinn.“Seven Deadly Half-Truths About Women.” Psychology Today March 1978: 94–106.
- Article in a weekly magazine : Schwartz, Felice N.“Management,Women, and the New Facts of Life.” Newsweek 20 July 2006: 21–22.
- Signed newspaper article : Ferraro, Susan. “In-law and Order: Finding Relative Calm.” The Daily News 30 June 1998: 73.
- Unsigned newspaper article : “Beanie Babies May Be a Rotten Nest Egg.” Chicago Tribune 21 June 2004: 12.
Bibliography Entry for a Web Site
For sources such as Web sites include the information a reader needs to find the source or to know where and when you found it. Always begin with the last name of the author, broadcaster, person you interviewed, and so on. Here is an example of a bibliography for a Web site:
Format : Author.“Document Title.” Publication or Web site title. Date of publication. Date of access.
Example : Dodman, Dr. Nicholas. “Dog-Human Communication.” Pet Place . 10 November 2006. 23 January 2014 < http://www.petplace.com/dogs/dog-human-communication-2/page1.aspx >
After completing the bibliography you can breathe a huge sigh of relief and pat yourself on the back. You probably plan to turn in your work in printed or handwritten form, but you also may be making an oral presentation. However you plan to present your paper, do your best to show it in its best light. You’ve put a great deal of work and thought into this assignment, so you want your paper to look and sound its best. You’ve completed your research paper!
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

APA Style 6th Edition: Citing Your Sources
- Basics of APA Formatting
- In Text Quick View
- Block Quotes
- Books & eBooks
- Thesis/Dissertation
Standard Format
Various examples.
- Conference Presentations
- Course Documents
- Social Media
- Government Documents
- Academic Integrity and Plagiarism
- Additional Resources
- Sample Reference Page
Dissertation or thesis available from a database service:
Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of publication). Title of dissertation or thesis (Doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis). Retrieved from Name of database. (Accession or Order No.)
For an unpublished dissertation or thesis:
Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of creation). Title of dissertation or thesis (Unpublished doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis). Name of Institution, Location.
See Ch 7 pp. 207-208 APA Manual for more examples and formatting rules
Formatting:
- Italicize the title
- Identify whether source is doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis in parentheses after the title
- << Previous: Articles
- Next: Websites >>
- Last Updated: Sep 22, 2022 11:20 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/APA-citation-style
Thesis and Dissertation Guide
- « Thesis & Dissertation Resources
- The Graduate School Home
- Introduction
- Copyright Page
- Dedication, Acknowledgements, Preface (optional)
- Table of Contents
- List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations
- List of Abbreviations
- List of Symbols
Non-Traditional Formats
Font type and size, spacing and indentation, tables, figures, and illustrations, formatting previously published work.
- Internet Distribution
- Open Access
- Registering Copyright
- Using Copyrighted Materials
- Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Submission Steps
- Submission Checklist
- Sample Pages

II. Formatting Guidelines
All copies of a thesis or dissertation must have the following uniform margins throughout the entire document:
- Left: 1″ (or 1 1/4" to ensure sufficient room for binding the work if desired)
- Right: 1″
- Bottom: 1″ (with allowances for page numbers; see section on Pagination )
- Top: 1″
Exceptions : The first page of each chapter (including the introduction, if any) begins 2″ from the top of the page. Also, the headings on the title page, abstract, first page of the dedication/ acknowledgements/preface (if any), and first page of the table of contents begin 2″ from the top of the page.
Non-traditional theses or dissertations such as whole works comprised of digital, artistic, video, or performance materials (i.e., no written text, chapters, or articles) are acceptable if approved by your committee and graduate program. A PDF document with a title page, copyright page, and abstract at minimum are required to be submitted along with any relevant supplemental files.
Fonts must be 10, 11, or 12 points in size. Superscripts and subscripts (e.g., formulas, or footnote or endnote numbers) should be no more than 2 points smaller than the font size used for the body of the text.
Space and indent your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- The text must appear in a single column on each page and be double-spaced throughout the document. Do not arrange chapter text in multiple columns.
- New paragraphs must be indicated by a consistent tab indentation throughout the entire document.
- The document text must be left-justified, not centered or right-justified.
- For blocked quotations, indent the entire text of the quotation consistently from the left margin.
- Ensure headings are not left hanging alone on the bottom of a prior page. The text following should be moved up or the heading should be moved down. This is something to check near the end of formatting, as other adjustments to text and spacing may change where headings appear on the page.
Exceptions : Blocked quotations, notes, captions, legends, and long headings must be single-spaced throughout the document and double-spaced between items.
Paginate your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:
- Use lower case Roman numerals (ii, iii, iv, etc.) on all pages preceding the first page of chapter one. The title page counts as page i, but the number does not appear. Therefore, the first page showing a number will be the copyright page with ii at the bottom.
- Arabic numerals (beginning with 1, 2, 3, 4, etc.) start at chapter one or the introduction, if applicable. Arabic numbers must be included on all pages of the text, illustrations, notes, and any other materials that follow. Thus, the first page of chapter one will show an Arabic numeral 1, and numbering of all subsequent pages will follow in order.
- Do not use page numbers accompanied by letters, hyphens, periods, or parentheses (e.g., 1., 1-2, -1-, (1), or 1a).
- Center all page numbers at the bottom of the page, 1/2″ from the bottom edge.
- Pages must not contain running headers or footers, aside from page numbers.
- If your document contains landscape pages (pages in which the top of the page is the long side of a sheet of paper), make sure that your page numbers still appear in the same position and direction as they do on pages with standard portrait orientation for consistency. This likely means the page number will be centered on the short side of the paper and the number will be sideways relative to the landscape page text. See these additional instructions for assistance with pagination on landscape pages in Microsoft Word .

Format footnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- Footnotes must be placed at the bottom of the page separated from the text by a solid line one to two inches long.
- Begin at the left page margin, directly below the solid line.
- Single-space footnotes that are more than one line long.
- Include one double-spaced line between each note.
- Most software packages automatically space footnotes at the bottom of the page depending on their length. It is acceptable if the note breaks within a sentence and carries the remainder into the footnote area of the next page. Do not indicate the continuation of a footnote.
- Number all footnotes with Arabic numerals. You may number notes consecutively within each chapter starting over with number 1 for the first note in each chapter, or you may number notes consecutively throughout the entire document.
- Footnote numbers must precede the note and be placed slightly above the line (superscripted). Leave no space between the number and the note.
- While footnotes should be located at the bottom of the page, do not place footnotes in a running page footer, as they must remain within the page margins.
Endnotes are an acceptable alternative to footnotes. Format endnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines:

- Always begin endnotes on a separate page either immediately following the end of each chapter, or at the end of your entire document. If you place all endnotes at the end of the entire document, they must appear after the appendices and before the references.
- Include the heading “ENDNOTES” in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the first page of your endnotes section(s).
- Single-space endnotes that are more than one line long.
- Number all endnotes with Arabic numerals. You may number notes consecutively within each chapter starting over with number 1 for the first note in each chapter, or you may number notes consecutively throughout the entire document.
- Endnote numbers must precede the note and be placed slightly above the line (superscripted). Leave no space between the number and the note.
Tables, figures, and illustrations vary widely by discipline. Therefore, formatting of these components is largely at the discretion of the author.
For example, headings and captions may appear above or below each of these components.
These components may each be placed within the main text of the document or grouped together in a separate section.
Space permitting, headings and captions for the associated table, figure, or illustration must be on the same page.
The use of color is permitted as long as it is consistently applied as part of the finished component (e.g., a color-coded pie chart) and not extraneous or unprofessional (e.g., highlighting intended solely to draw a reader's attention to a key phrase). The use of color should be reserved primarily for tables, figures, illustrations, and active website or document links throughout your thesis or dissertation.
The format you choose for these components must be consistent throughout the thesis or dissertation.
Ensure each component complies with margin and pagination requirements.
Refer to the List of Tables, Figures, and Illustrations section for additional information.
If your thesis or dissertation has appendices, they must be prepared following these guidelines:

- Appendices must appear at the end of the document (before references) and not the chapter to which they pertain.
- When there is more than one appendix, assign each appendix a number or a letter heading (e.g., “APPENDIX 1” or “APPENDIX A”) and a descriptive title. You may number consecutively throughout the entire work (e.g., 1, 2 or A, B), or you may assign a two-part Arabic numeral with the first number designating the chapter in which it appears, separated by a period, followed by a second number or letter to indicate its consecutive placement (e.g., “APPENDIX 3.2” is the second appendix referred to in Chapter Three).
- Include the chosen headings in all capital letters, and center them 1″ below the top of the page.
- All appendix headings and titles must be included in the table of contents.
- Page numbering must continue throughout your appendix or appendices. Ensure each appendix complies with margin and pagination requirements.
You are required to list all the references you consulted. For specific details on formatting your references, consult and follow a style manual or professional journal that is used for formatting publications and citations in your discipline.

Your reference pages must be prepared following these guidelines:
- If you place references after each chapter, the references for the last chapter must be placed immediately following the chapter and before the appendices.
- If you place all references at the end of the thesis or dissertation, they must appear after the appendices as the final component in the document.
- Select an appropriate heading for this section based on the style manual you are using (e.g., “REFERENCES”, “BIBLIOGRAPHY”, or “WORKS CITED”).
- Include the chosen heading in all capital letters, and center it 1″ below the top of the page.
- References must be single-spaced within each entry.
- Include one double-spaced line between each reference.
- Page numbering must continue throughout your references section. Ensure references comply with margin and pagination requirements.
In some cases, students gain approval from their academic program to include in their thesis or dissertation previously published (or submitted, in press, or under review) journal articles or similar materials that they have authored. For more information about including previously published works in your thesis or dissertation, see the section on Use of Your Own Previously Published Materials and the section on Copyrighting.
If your academic program has approved inclusion of such materials, please note that these materials must match the formatting guidelines set forth in this Guide regardless of how the material was formatted for publication.
Some specific formatting guidelines to consider include:

- Fonts, margins, chapter headings, citations, and references must all match the formatting and placement used within the rest of the thesis or dissertation.
- If appropriate, published articles can be included as separate individual chapters within the thesis or dissertation.
- A separate abstract to each chapter should not be included.
- The citation for previously published work must be included as the first footnote (or endnote) on the first page of the chapter.
- Do not include typesetting notations often used when submitting manuscripts to a publisher (i.e., insert table x here).
- The date on the title page should be the year in which your committee approves the thesis or dissertation, regardless of the date of completion or publication of individual chapters.
- If you would like to include additional details about the previously published work, this information can be included in the preface for the thesis or dissertation.
Previous: Order and Components
Next: Distribution
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
Published on March 9, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 23, 2022.
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that includes a short descriptive text (an annotation) for each source. It may be assigned as part of the research process for a paper , or as an individual assignment to gather and read relevant sources on a topic.
Scribbr’s free Citation Generator allows you to easily create and manage your annotated bibliography in APA or MLA style. To generate a perfectly formatted annotated bibliography, select the source type, fill out the relevant fields, and add your annotation.
An example of an annotated source is shown below:

Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Annotated bibliography format: apa, mla, chicago, how to write an annotated bibliography, descriptive annotation example, evaluative annotation example, reflective annotation example, finding sources for your annotated bibliography, frequently asked questions about annotated bibliographies.
Make sure your annotated bibliography is formatted according to the guidelines of the style guide you’re working with. Three common styles are covered below:
In APA Style , both the reference entry and the annotation should be double-spaced and left-aligned.
The reference entry itself should have a hanging indent . The annotation follows on the next line, and the whole annotation should be indented to match the hanging indent. The first line of any additional paragraphs should be indented an additional time.

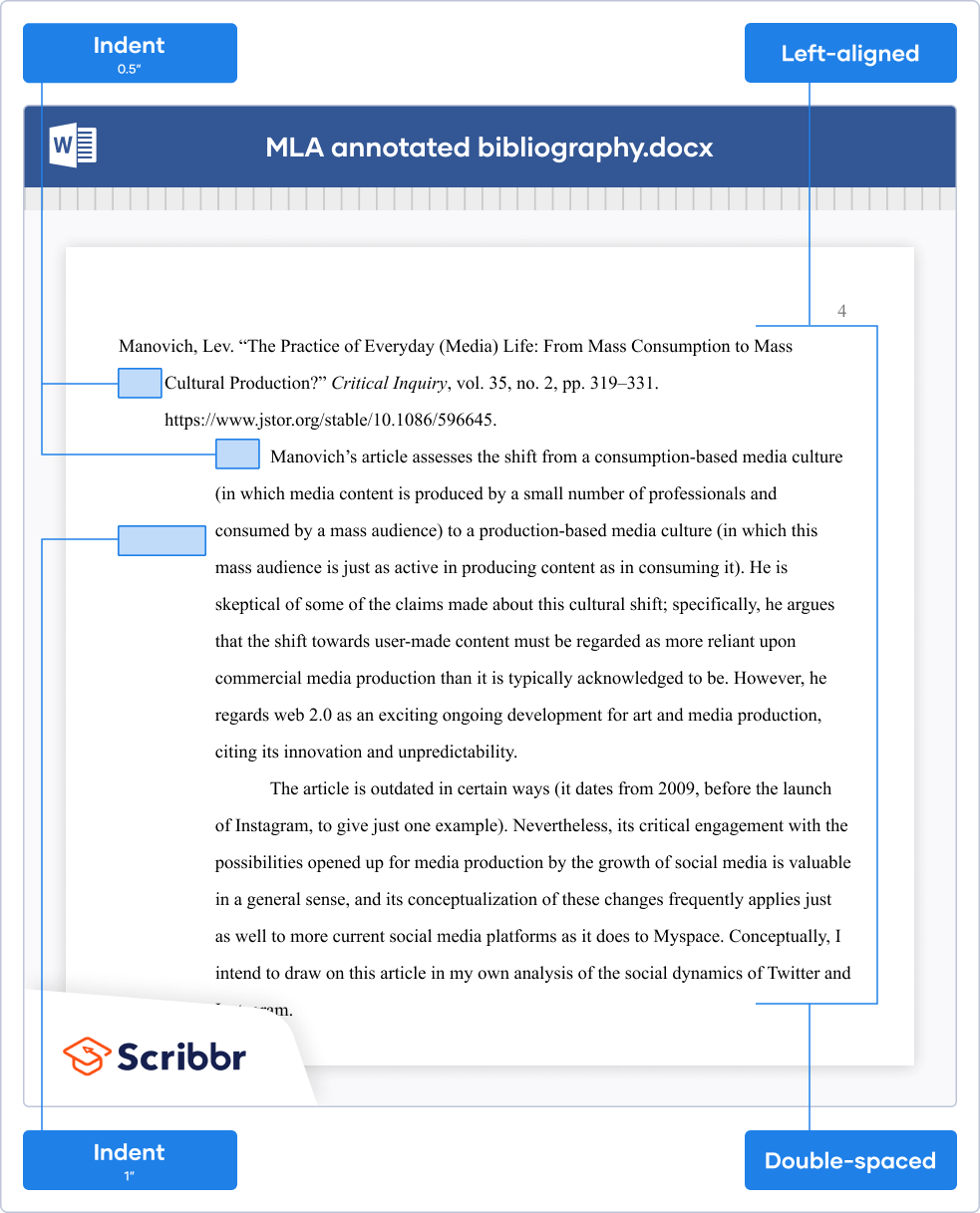
In an MLA style annotated bibliography , the Works Cited entry and the annotation are both double-spaced and left-aligned.
The Works Cited entry has a hanging indent. The annotation itself is indented 1 inch (twice as far as the hanging indent). If there are two or more paragraphs in the annotation, the first line of each paragraph is indented an additional half-inch, but not if there is only one paragraph.
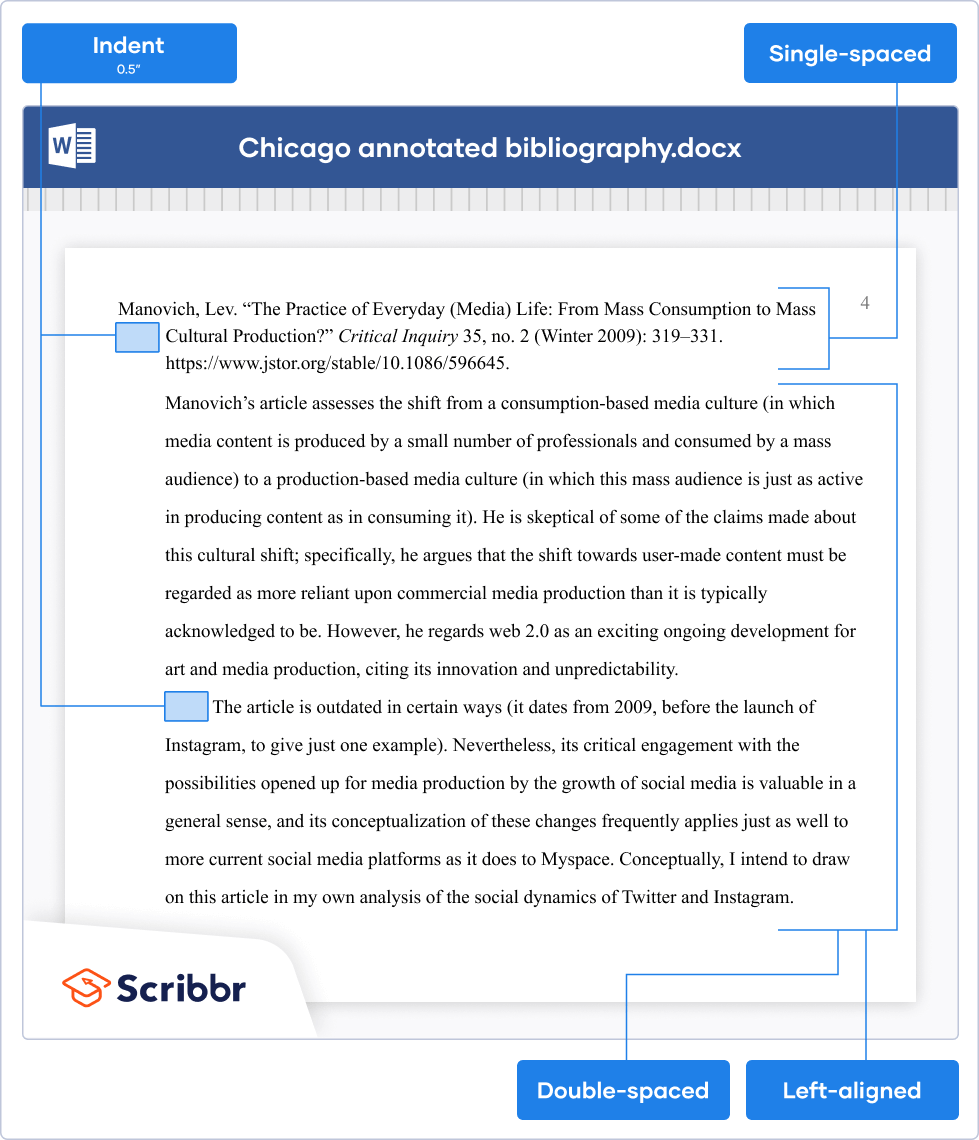
Chicago style
In a Chicago style annotated bibliography , the bibliography entry itself should be single-spaced and feature a hanging indent.
The annotation should be indented, double-spaced, and left-aligned. The first line of any additional paragraphs should be indented an additional time.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
For each source, start by writing (or generating ) a full reference entry that gives the author, title, date, and other information. The annotated bibliography format varies based on the citation style you’re using.
The annotations themselves are usually between 50 and 200 words in length, typically formatted as a single paragraph. This can vary depending on the word count of the assignment, the relative length and importance of different sources, and the number of sources you include.
Consider the instructions you’ve been given or consult your instructor to determine what kind of annotations they’re looking for:
- Descriptive annotations : When the assignment is just about gathering and summarizing information, focus on the key arguments and methods of each source.
- Evaluative annotations : When the assignment is about evaluating the sources , you should also assess the validity and effectiveness of these arguments and methods.
- Reflective annotations : When the assignment is part of a larger research process, you need to consider the relevance and usefulness of the sources to your own research.
These specific terms won’t necessarily be used. The important thing is to understand the purpose of your assignment and pick the approach that matches it best. Interactive examples of the different styles of annotation are shown below.
A descriptive annotation summarizes the approach and arguments of a source in an objective way, without attempting to assess their validity.
In this way, it resembles an abstract , but you should never just copy text from a source’s abstract, as this would be considered plagiarism . You’ll naturally cover similar ground, but you should also consider whether the abstract omits any important points from the full text.
The interactive example shown below describes an article about the relationship between business regulations and CO 2 emissions.
Rieger, A. (2019). Doing business and increasing emissions? An exploratory analysis of the impact of business regulation on CO 2 emissions. Human Ecology Review , 25 (1), 69–86. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26964340
An evaluative annotation also describes the content of a source, but it goes on to evaluate elements like the validity of the source’s arguments and the appropriateness of its methods .
For example, the following annotation describes, and evaluates the effectiveness of, a book about the history of Western philosophy.
Kenny, A. (2010). A new history of Western philosophy: In four parts . Oxford University Press.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
A reflective annotation is similar to an evaluative one, but it focuses on the source’s usefulness or relevance to your own research.
Reflective annotations are often required when the point is to gather sources for a future research project, or to assess how they were used in a project you already completed.
The annotation below assesses the usefulness of a particular article for the author’s own research in the field of media studies.
Manovich, Lev. (2009). The practice of everyday (media) life: From mass consumption to mass cultural production? Critical Inquiry , 35 (2), 319–331. https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/596645
Manovich’s article assesses the shift from a consumption-based media culture (in which media content is produced by a small number of professionals and consumed by a mass audience) to a production-based media culture (in which this mass audience is just as active in producing content as in consuming it). He is skeptical of some of the claims made about this cultural shift; specifically, he argues that the shift towards user-made content must be regarded as more reliant upon commercial media production than it is typically acknowledged to be. However, he regards web 2.0 as an exciting ongoing development for art and media production, citing its innovation and unpredictability.
The article is outdated in certain ways (it dates from 2009, before the launch of Instagram, to give just one example). Nevertheless, its critical engagement with the possibilities opened up for media production by the growth of social media is valuable in a general sense, and its conceptualization of these changes frequently applies just as well to more current social media platforms as it does to Myspace. Conceptually, I intend to draw on this article in my own analysis of the social dynamics of Twitter and Instagram.
Before you can write your annotations, you’ll need to find sources . If the annotated bibliography is part of the research process for a paper, your sources will be those you consult and cite as you prepare the paper. Otherwise, your assignment and your choice of topic will guide you in what kind of sources to look for.
Make sure that you’ve clearly defined your topic , and then consider what keywords are relevant to it, including variants of the terms. Use these keywords to search databases (e.g., Google Scholar ), using Boolean operators to refine your search.
Sources can include journal articles, books, and other source types , depending on the scope of the assignment. Read the abstracts or blurbs of the sources you find to see whether they’re relevant, and try exploring their bibliographies to discover more. If a particular source keeps showing up, it’s probably important.
Once you’ve selected an appropriate range of sources, read through them, taking notes that you can use to build up your annotations. You may even prefer to write your annotations as you go, while each source is fresh in your mind.
An annotated bibliography is an assignment where you collect sources on a specific topic and write an annotation for each source. An annotation is a short text that describes and sometimes evaluates the source.
Any credible sources on your topic can be included in an annotated bibliography . The exact sources you cover will vary depending on the assignment, but you should usually focus on collecting journal articles and scholarly books . When in doubt, utilize the CRAAP test !
Each annotation in an annotated bibliography is usually between 50 and 200 words long. Longer annotations may be divided into paragraphs .
The content of the annotation varies according to your assignment. An annotation can be descriptive, meaning it just describes the source objectively; evaluative, meaning it assesses its usefulness; or reflective, meaning it explains how the source will be used in your own research .
A source annotation in an annotated bibliography fulfills a similar purpose to an abstract : they’re both intended to summarize the approach and key points of a source.
However, an annotation may also evaluate the source , discussing the validity and effectiveness of its arguments. Even if your annotation is purely descriptive , you may have a different perspective on the source from the author and highlight different key points.
You should never just copy text from the abstract for your annotation, as doing so constitutes plagiarism .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, August 23). What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format. Scribbr. Retrieved April 13, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/annotated-bibliography/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, evaluating sources | methods & examples, how to find sources | scholarly articles, books, etc., hanging indent | word & google docs instructions, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database. If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It's similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences: Structure: Author's last name, F. M. (Year published).
Step 2: Collect and Organize Your Sources. Gather all the sources you have referenced or cited in your thesis. Make a list of books, articles, webpages, and any other relevant sources. Organize them in alphabetical order based on the author's last name or the title of the source.
The term "bibliography" is a catch-all for any list of sources cited at the end of an academic work. Certain style guides use different terminology to refer to bibliographies. For example, MLA format refers to a paper's bibliography as its Works Cited page. APA refers to it as the References page.
Thesis, from a commercial database. Lope, M. D. (2014). Perceptions of global mindedness in the international baccalaureate middle years programme: The relationship to student academic performance and teacher characteristics (Order No. 3682837) [Doctoral dissertation, University of Maryland].ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
In the square brackets, specify the type of dissertation or thesis and the university. As with other database sources, no URL or DOI is included. APA format. Author last name, Initials. ( Year ). Dissertation title (Publication No. Number) [ Type of dissertation/thesis, University Name ]. Database Name.
Chicago style bibliography examples. Bibliography entries vary in format depending on the type of source. Templates and examples for the most common source types are shown below. Book. Book chapter. Journal article. Website. Template. Author Last Name, First Name.
How to Add a Bibliography Entry. When we want to refer to a source in the thesis, we place an entry for that source in the file references.bib, then cite the source in the thesis with the \cite{LABEL} command. The syntax for an entry in the references.bib file is of the form: @ ENTRYTYPE { LABEL,
How to Cite a Dissertation or Thesis in APA 7th Edition. The APA dissertation or thesis citation isn't a one size fits all type of citation. The reason behind this is because APA offers a different format for a published and unpublished thesis or dissertation. However, you'll need to include information like: Author, A. A. (Year).
Auckland University of Technology (and other NZ universities) Thesis is either for a doctoral or a master's degree. Dissertation is either for a master's or a bachelor's degree with honours. Exegesis is the written component of a practice-based thesis where the major output is a creative work; e.g., a film, artwork, novel.
Formatting a Harvard style bibliography. Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading 'Reference list' or 'Bibliography' appears at the top. Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used: Harvard bibliography example.
Alphabetizing Your Reference List or Bibliography Formatting According to Your Discipline's Style Guidelines Using Endnote, Zotero, or Other Bibliographic Software Creating a Reference-Formatting System In this Guide This guide offers several tips for creating uniform, readable formatting in a bibliography or references list,
A bibliography, sometimes known as a "Reference List" is a list of all of the sources you have used (whether referenced or not) in the process of researching your work. In general, a bibliography should include: the authors' names; the titles of the works; the names of the publishers who published your sources and where they were published.
Full Citation Rules. Citing a thesis in APA on the References page follows the format for citing a dissertation. Author's Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year). Title of dissertation/thesis (Publication No. #) [Dissertation type, University]. Database.
The APA style is an "author-date" citation system, with the author and date of the cited source appearing in the body of the text. You will need to add a bibliography at the end of the essay, with the full references alphabetically ordered by author's name. It is mainly used in the social sciences. The Chicago style uses two systems ...
Basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper Author/Authors Rules for handling works by a single author or multiple authors that apply to all APA-style references in your reference list, regardless of the type of work (book, article, electronic resource, etc.)
Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles. Published on June 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on November 7, 2022. A citation style is a set of guidelines on how to cite sources in your academic writing.You always need a citation whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize a source to avoid plagiarism.How you present these citations depends on the style you follow.
Bibliography Entry for a Book. A bibliography entry for a book begins with the author's name, which is written in this order: last name, comma, first name, period. After the author's name comes the title of the book. If you are handwriting your bibliography, underline each title. If you are working on a computer, put the book title in ...
Dissertation or thesis available from a database service: Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of publication). Title of dissertation or thesis (Doctoral dissertation or master's thesis). Retrieved from Name of database. (Accession or Order No.) For an unpublished dissertation or thesis: Author Surname, First Initial. Second ...
model of an annotated bibliography. The annotated bibliography is simply a means to an end—namely, organizing your sources so you can make progress on your thesis. Provisional Argument At the top of your annotated bibliography, write one paragraph (anywhere from six to eight sentences) that summarizes the argument you plan to make in your thesis.
Footnotes. Format footnotes for your thesis or dissertation following these guidelines: Footnotes must be placed at the bottom of the page separated from the text by a solid line one to two inches long. Begin at the left page margin, directly below the solid line. Single-space footnotes that are more than one line long.
Published on March 9, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 23, 2022. An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that includes a short descriptive text (an annotation) for each source. It may be assigned as part of the research process for a paper, or as an individual assignment to gather and read relevant sources on a topic.