Ludwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer whose Symphony 5 is a beloved classic. Some of his greatest works were composed while Beethoven was going deaf.

(1770-1827)

Who Was Ludwig van Beethoven?
Ludwig van Beethoven was a German pianist and composer widely considered to be one of the greatest musical geniuses of all time. His innovative compositions combined vocals and instruments, widening the scope of sonata, symphony, concerto and quartet. He is the crucial transitional figure connecting the Classical and Romantic ages of Western music.
Beethoven’s personal life was marked by a struggle against deafness, and some of his most important works were composed during the last 10 years of his life, when he was quite unable to hear. He died at the age of 56.
Controversial Birthday
Beethoven was born on or about December 16, 1770, in the city of Bonn in the Electorate of Cologne, a principality of the Holy Roman Empire. Although his exact date of birth is uncertain, Beethoven was baptized on December 17, 1770.
As a matter of law and custom, babies at the time were baptized within 24 hours of birth, so December 16 is his most likely birthdate.
However, Beethoven himself mistakenly believed that he was born two years later, in 1772, and he stubbornly insisted on the incorrect date even when presented with official papers that proved beyond any reasonable doubt that 1770 was his true birth year.
Beethoven had two younger brothers who survived into adulthood: Caspar, born in 1774, and Johann, born in 1776. Beethoven's mother, Maria Magdalena van Beethoven, was a slender, genteel, and deeply moralistic woman.
His father, Johann van Beethoven, was a mediocre court singer better known for his alcoholism than any musical ability. However, Beethoven's grandfather, godfather and namesake, Kapellmeister Ludwig van Beethoven, was Bonn's most prosperous and eminent musician, a source of endless pride for young Beethoven.
Childhood Abuse
Sometime between the births of his two younger brothers, Beethoven's father began teaching him music with an extraordinary rigor and brutality that affected him for the rest of his life.
Neighbors provided accounts of the small boy weeping while he played the clavier, standing atop a footstool to reach the keys, his father beating him for each hesitation or mistake.
On a near daily basis, Beethoven was flogged, locked in the cellar and deprived of sleep for extra hours of practice. He studied the violin and clavier with his father as well as taking additional lessons from organists around town. Whether in spite of or because of his father's draconian methods, Beethoven was a prodigiously talented musician from his earliest days.
Meanwhile, the musical prodigy attended a Latin grade school named Tirocinium, where a classmate said, "Not a sign was to be discovered of that spark of genius which glowed so brilliantly in him afterwards."
Beethoven, who struggled with sums and spelling his entire life, was at best an average student, and some biographers have hypothesized that he may have had mild dyslexia. As he put it himself, "Music comes to me more readily than words."
In 1781, at the age of 10, Beethoven withdrew from school to study music full time with Christian Gottlob Neefe, the newly appointed Court Organist, and at the age of 12, Beethoven published his first composition, a set of piano variations on a theme by an obscure classical composer named Dressler.
By 1784, his alcoholism worsening and his voice decaying, Beethoven's father was no longer able to support his family, and Beethoven formally requested an official appointment as Assistant Court Organist. Despite his youth, his request was accepted, and Beethoven was put on the court payroll with a modest annual salary of 150 florins.
Beethoven and Mozart
There is only speculation and inconclusive evidence that Beethoven ever met with Mozart, let alone studied with him. In an effort to facilitate his musical development, in 1787 the court sent Beethoven to Vienna, Europe’s capital of culture and music, where he hoped to study with Mozart.
Tradition has it that, upon hearing Beethoven, Mozart said, "Keep your eyes on him; someday he will give the world something to talk about.”
After only a few weeks in Vienna, Beethoven learned that his mother had fallen ill and he returned home to Bonn. Remaining there, Beethoven continued to carve out his reputation as the city's most promising young court musician.
Early Career as a Composer
When the Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II died in 1790, a 19-year-old Beethoven received the immense honor of composing a musical memorial in his honor. For reasons that remain unclear, Beethoven's composition was never performed, and most assumed the young musician had proven unequal to the task.
However, more than a century later, Johannes Brahms discovered that Beethoven had in fact composed a "beautiful and noble" piece of music entitled Cantata on the Death of Emperor Joseph II . It is now considered his earliest masterpiece.
DOWNLOAD BIOGRAPHY'S LUDWIG VAN BEETHOVEN'S FACT CARD

Beethoven and Haydn
In 1792, with French revolutionary forces sweeping across the Rhineland into the Electorate of Cologne, Beethoven decided to leave his hometown for Vienna once again. Mozart had passed away a year earlier, leaving Joseph Haydn as the unquestioned greatest composer alive.
Haydn was living in Vienna at the time, and it was with Haydn that the young Beethoven now intended to study. As his friend and patron Count Waldstein wrote in a farewell letter, "Mozart's genius mourns and weeps over the death of his disciple. It found refuge, but no release with the inexhaustible Haydn; through him, now, it seeks to unite with another. By means of assiduous labor you will receive the spirit of Mozart from the hands of Haydn."
In Vienna, Beethoven dedicated himself wholeheartedly to musical study with the most eminent musicians of the age. He studied piano with Haydn, vocal composition with Antonio Salieri and counterpoint with Johann Albrechtsberger. Not yet known as a composer, Beethoven quickly established a reputation as a virtuoso pianist who was especially adept at improvisation.
Debut Performance
Beethoven won many patrons among the leading citizens of the Viennese aristocracy, who provided him with lodging and funds, allowing Beethoven, in 1794, to sever ties with the Electorate of Cologne. Beethoven made his long-awaited public debut in Vienna on March 29, 1795.
Although there is considerable debate over which of his early piano concerti he performed that night, most scholars believe he played what is known as his "first" piano concerto in C Major. Shortly thereafter, Beethoven decided to publish a series of three piano trios as his Opus 1, which were an enormous critical and financial success.
In the first spring of the new century, on April 2, 1800, Beethoven debuted his Symphony No. 1 in C major at the Royal Imperial Theater in Vienna. Although Beethoven would grow to detest the piece — "In those days I did not know how to compose," he later remarked — the graceful and melodious symphony nevertheless established him as one of Europe's most celebrated composers.
As the new century progressed, Beethoven composed piece after piece that marked him as a masterful composer reaching his musical maturity. His Six String Quartets, published in 1801, demonstrate complete mastery of that most difficult and cherished of Viennese forms developed by Mozart and Haydn.
Beethoven also composed The Creatures of Prometheus in 1801, a wildly popular ballet that received 27 performances at the Imperial Court Theater. It was around the same time that Beethoven discovered he was losing his hearing.
Personal Life
For a variety of reasons that included his crippling shyness and unfortunate physical appearance, Beethoven never married or had children. He was, however, desperately in love with a married woman named Antonie Brentano.
Over the course of two days in July of 1812, Beethoven wrote her a long and beautiful love letter that he never sent. Addressed "to you, my Immortal Beloved," the letter said in part, "My heart is full of so many things to say to you — ah — there are moments when I feel that speech amounts to nothing at all — Cheer up — remain my true, my only love, my all as I am yours."
The death of Beethoven's brother Caspar in 1815 sparked one of the great trials of his life, a painful legal battle with his sister-in-law, Johanna, over the custody of Karl van Beethoven, his nephew and her son.
The struggle stretched on for seven years, during which both sides spewed ugly defamations at the other. In the end, Beethoven won the boy's custody, though hardly his affection.
Despite his extraordinary output of beautiful music, Beethoven was lonely and frequently miserable throughout his adult life. Short-tempered, absent-minded, greedy and suspicious to the point of paranoia, Beethoven feuded with his brothers, his publishers, his housekeepers, his pupils and his patrons.
In one illustrative incident, Beethoven attempted to break a chair over the head of Prince Lichnowsky, one of his closest friends and most loyal patrons. Another time he stood in the doorway of Prince Lobkowitz's palace shouting for all to hear, "Lobkowitz is a donkey!"
For years, rumors have swirled that Beethoven had some African ancestry. These unfounded tales may be based on Beethoven's dark complexion or the fact that his ancestors came from a region of Europe that had once been invaded by the Spanish, and Moors from northern Africa were part of Spanish culture.
A few scholars have noted that Beethoven seemed to have an innate understanding of the polyrhythmic structures typical to some African music. However, no one during Beethoven's lifetime referred to the composer as Moorish or African, and the rumors that he was Black are largely dismissed by historians.
Was Beethoven Deaf?
At the same time as Beethoven was composing some of his most immortal works, he was struggling to come to terms with a shocking and terrible fact, one that he tried desperately to conceal: He was going deaf.
By the turn of the 19th century, Beethoven struggled to make out the words spoken to him in conversation.
Beethoven revealed in a heart-wrenching 1801 letter to his friend Franz Wegeler, "I must confess that I lead a miserable life. For almost two years I have ceased to attend any social functions, just because I find it impossible to say to people: I am deaf. If I had any other profession, I might be able to cope with my infirmity; but in my profession it is a terrible handicap."

Heiligenstadt Testament
At times driven to extremes of melancholy by his affliction, Beethoven described his despair in a long and poignant note that he concealed his entire life.
Dated October 6, 1802, and referred to as "The Heiligenstadt Testament," it reads in part: "O you men who think or say that I am malevolent, stubborn or misanthropic, how greatly do you wrong me. You do not know the secret cause which makes me seem that way to you and I would have ended my life — it was only my art that held me back. Ah, it seemed impossible to leave the world until I had brought forth all that I felt was within me."
Almost miraculously, despite his rapidly progressing deafness, Beethoven continued to compose at a furious pace.
Moonlight Sonata
From 1803 to 1812, what is known as his "middle" or "heroic" period, he composed an opera, six symphonies, four solo concerti, five string quartets, six-string sonatas, seven piano sonatas, five sets of piano variations, four overtures, four trios, two sextets and 72 songs.
The most famous among these were the haunting Moonlight Sonata, symphonies No. 3-8, the Kreutzer violin sonata and Fidelio , his only opera.
In terms of the astonishing output of superlatively complex, original and beautiful music, this period in Beethoven's life is unrivaled by any other composer in history.
Beethoven’s Music
Some of Beethoven’s best-known compositions include:
Eroica: Symphony No. 3
In 1804, only weeks after Napoleon Bonaparte proclaimed himself Emperor of France, Beethoven debuted his Symphony No. 3 in Napoleon's honor. Beethoven, like all of Europe, watched with a mixture of awe and terror; he admired, abhorred and, to an extent, identified with Napoleon, a man of seemingly superhuman capabilities, only one year older than himself and also of obscure birth.
Later renamed the Eroica Symphony because Beethoven grew disillusioned with Napoleon, it was his grandest and most original work to date.
Because it was so unlike anything heard before it, the musicians could not figure out how to play it through weeks of rehearsal. A prominent reviewer proclaimed "Eroica" as "one of the most original, most sublime, and most profound products that the entire genre of music has ever exhibited."
Symphony No. 5
One of Beethoven’s best-known works among modern audiences, Symphony No. 5 is known for its ominous first four notes.
Beethoven began composing the piece in 1804, but its completion was delayed a few times for other projects. It premiered at the same time as Beethoven’s Symphony No. 6, in 1808 in Vienna.
In 1810, Beethoven completed Fur Elise (meaning “For Elise”), although it was not published until 40 years after his death. In 1867, it was discovered by a German music scholar, however Beethoven’s original manuscript has since been lost.
Some scholars have suggested it was dedicated to his friend, student and fellow musician, Therese Malfatti, to whom he allegedly proposed around the time of the song’s composition. Others said it was for the German soprano Elisabeth Rockel, another friend of Beethoven’s.
Symphony No. 7
Premiering in Vienna in 1813 to benefit soldiers wounded in the battle of Hanau, Beethoven began composing this, one of his most energetic and optimistic works, in 1811.
The composer called the piece “his most excellent symphony." The second movement is often performed separately from the rest of the symphony and may have been one of Beethoven’s most popular works.
Missa Solemnis
Debuting in 1824, this Catholic mass is considered among Beethoven’s finest achievements. Just under 90 minutes in length, the rarely-performed piece features a chorus, orchestra and four soloists.
Ode to Joy: Symphony No. 9
Beethoven’s ninth and final symphony, completed in 1824, remains the illustrious composer's most towering achievement. The symphony's famous choral finale, with four vocal soloists and a chorus singing the words of Friedrich Schiller's poem "Ode to Joy," is perhaps the most famous piece of music in history.
While connoisseurs delighted in the symphony's contrapuntal and formal complexity, the masses found inspiration in the anthem-like vigor of the choral finale and the concluding invocation of "all humanity."
String Quartet No. 14
Beethoven’s String Quartet No. 14 debuted in 1826. About 40 minutes in length, it contains seven linked movements played without a break.
The work was reportedly one of Beethoven’s favorite later quartets and has been described as one of the composer’s most elusive compositions musically.
Beethoven died on March 26, 1827, at the age of 56, of post-hepatitic cirrhosis of the liver.
The autopsy also provided clues to the origins of his deafness: While his quick temper, chronic diarrhea and deafness are consistent with arterial disease, a competing theory traces Beethoven's deafness to contracting typhus in the summer of 1796.
Scientists analyzing a remaining fragment of Beethoven's skull noticed high levels of lead and hypothesized lead poisoning as a potential cause of death, but that theory has been largely discredited.
Beethoven is widely considered one of the greatest, if not the single greatest, composer of all time. Beethoven's body of musical compositions stands with William Shakespeare 's plays at the outer limits of human brilliance.
And the fact Beethoven composed his most beautiful and extraordinary music while deaf is an almost superhuman feat of creative genius, perhaps only paralleled in the history of artistic achievement by John Milton writing Paradise Lost while blind.
Summing up his life and imminent death during his last days, Beethoven, who was never as eloquent with words as he was with music, borrowed a tagline that concluded many Latin plays at the time. Plaudite, amici, comoedia finita est , he said. "Applaud friends, the comedy is over."
QUICK FACTS
- Name: Ludwig Beethoven
- Birth Year: 1770
- Birth date: December 16, 1770
- Birth City: Bonn
- Birth Country: Germany
- Gender: Male
- Best Known For: Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer whose Symphony 5 is a beloved classic. Some of his greatest works were composed while Beethoven was going deaf.
- Astrological Sign: Sagittarius
- Nacionalities
- Interesting Facts
- Beethoven's father was an alcoholic who beat his son into practicing music.
- Many of Beethoven's most accomplished works were created during the time he was deaf.
- Death Year: 1827
- Death date: March 26, 1827
- Death City: Vienna
- Death Country: Austria
We strive for accuracy and fairness.If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us !
CITATION INFORMATION
- Article Title: Ludwig van Beethoven Biography
- Author: Biography.com Editors
- Website Name: The Biography.com website
- Url: https://www.biography.com/musicians/ludwig-van-beethoven
- Access Date:
- Publisher: A&E; Television Networks
- Last Updated: July 13, 2021
- Original Published Date: April 3, 2014
- Never shall I forget the time I spent with you. Please continue to be my friend, as you will always find me yours.
- Anyone who tells a lie has not a pure heart and cannot make good soup.
- Love demands all and has a right to all.
- Recommend to your children virtues that alone can make them happy. Not gold.
- I shall seize fate by the throat.
- Music is the mediator between the spiritual and sensual life.
- To play without passion is inexcusable!
- Ever thine, ever mine, ever ours.
- Don't only practice your art, but force your way into its secrets, for it and knowledge can raise men to the divine.
- Music is a higher revelation than all wisdom and philosophy.
Classical Musicians

The True Story of Leonard Bernstein’s Marriage

Wolfgang Mozart

Johann Sebastian Bach

Richard Rodgers

Franz Joseph Haydn

Luciano Pavarotti

George Frideric Handel
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky

Hector Berlioz

Gustav Mahler
Biography Online

Beethoven Biography
Ludwig van Beethoven (1770 – 1827) is one of the most widely respected composers of classical music. He played a crucial role in the transition from classical to romantic music and is considered one of the greatest composers of all time.
“Music is … A higher revelation than all Wisdom and Philosophy”
– Beethoven

Beethoven was born 16 December 1770 in Bonn (now part of Germany) From an early age, Beethoven was introduced to music. His first teacher was his father who was also very strict. Beethoven was frequently beaten for his failure to practise correctly. Once his mother protested at his father’s violent beatings, but she was beaten too. It is said, Beethoven resolved to become a great pianist so his mother would never be beaten.
Beethoven’s talent as a piano virtuoso was recognised by Count Ferdinand Ernst Gabriel von Waldstein. He sponsored the young Beethoven and this enabled him to travel to Vienna, where Mozart resided. It was hoped Beethoven would be able to learn under the great Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart , but it is not clear whether the two ever met. Mozart was to die shortly, but Beethoven was able to spend time with the great composer Joseph Haydn, who taught him many things.
Rather than working for the church, Beethoven relied on private donations from various benefactors. However, while many loved his music, they were often not forthcoming with donations and Beethoven sometimes struggled to raise enough finance. He complained about the way artists like him were treated.
“One clashes with stupidity of all kinds. And then how much money must be spent in advance! The way in which artists are treated is really scandalous… Believe me, there is nothing to be done for artists in times like these.” – Beethoven
His situation was made more difficult by his mother’s early death and his father’s descent into alcoholism; this led to Beethoven being responsible for his two brothers.

Beethoven by August Klober, 1818
Beethoven was widely regarded as a great musician, though his habits were unconventional for the social circles which he moved in. He was untidy, clumsy and (by all accounts) ugly. All attempts to make Beethoven behave failed. On one occasion, Beethoven pushed his way up to the Archduke saying it was impossible for him to follow the many rules of social behaviour. The Archduke smiled and said – ‘we will have to accept Beethoven as he is.’ Beethoven himself had great faith in his own capacities, referring to the princes at court.
“There are and always will be thousands of princes, but there is only one Beethoven!”
Beethoven’s music was also unconventional, he explored new ideas and left behind the old conventions on style and form. His freer and explorative musical ideas caused estrangement with his more classical teachers like Haydn and Salieri.
From his early 20s, Beethoven experienced a slow deterioration in his hearing, which eventually left him completely deaf.
Beethoven once said:
“Music is the mediator between the spiritual and the sensual life.”

Beethoven by Mahler, 1815
Yet, despite his deafness and the frustration this caused him, Beethoven was still able to compose music of the highest quality. He was still able to inwardly hear the most sublime music. However, his deafness meant he struggled to perform with an orchestral backing, as he often fell out of time. This caused the great pianist to be ridiculed by the public, causing much distress. As a result, he retreated more into his private world of composition. Despite these later difficulties, his most widely admired works were composed in this difficult last 15 years. This included the great works Missa Solemnis and the Ninth Symphony – both finished shortly before his death. The Ninth Symphony was groundbreaking in creating a choral symphony from different voices singing separate lines to create a common symphony. The final part of the symphony (often referred to as “Ode to Joy”) is a symbolic musical representation of universal brotherhood. It was a fitting climax to Beethoven’s unique musical creativity and life. Beethoven considered music as one of the greatest contributors to a higher philosophy.
Beethoven was also a supporter of the Enlightenment movement sweeping Europe. He was going to dedicate a great symphony to Napoléon , whom Beethoven believed was going to defend the ideals of the French Republic. However, when Napoléon’s imperial ambitions were made known, Beethoven scratched out his name so powerfully, he tore a hole in the paper.
Religious views of Beethoven
Beethoven was born and raised a Catholic. His mother was a devout Catholic and sought to share her religious views with her children. Beethoven was considered a fairly moral person, he recommended the virtues of religion to those around him and encouraged his nephew to attend mass.
“Recommend to your children virtues, that alone can make them happy, not gold.”
In his mid-life, his deafness and stomach pains created something of a spiritual crisis in Beethoven. He stopped attending Mass regularly and looked to a wider source of spiritual inspiration. One of his favourite works was Reflections on the Works of God and His Providence Throughout All Nature by a Lutheran Pastor which praised the ‘romantic’ view of the value of nature. Beethoven also became interested in Hindu religious texts and expressed belief in a Supreme Being in a language which was not overtly Catholic. Beethoven wrote
” O God! – you have no threefold being and are independent of everything, you are the true, eternal, blessed, unchangeable light of all time and space.” – Beethoven’s Letters with explanatory notes by Dr. A.C. Kalischer (trans. J.S. Shedlock ), 1926.
Beethoven never formally left the Catholic Church, but some identify him more the tradition of Theists – those who believe in God but don’t follow a particular religion. Others suggest that Beethoven remained a Catholic, but he just redefined Catholicism in a more liberal understanding to accommodate the current enlightenment thinking and his own spiritual exploration of music. In terms of music, he did compose specific religious music such as Missa Solemnis – the great choral symphony. When asked whether he thought this work was intended for church or the concert hall, Beethoven replied that such a distinction was not so important.
“My chief aim was to awaken and permanently instill religious feelings not only into the singers but also into the listeners.” ( link )
- For piano: Sonata in C sharp minor, op. 27, nr. 2 “The Moonlight Sonata”
- For piano: Sonata in C minor, op. 13, “Pathetique”
- Symphony No. 3 “Eroica”; in E flat major (Op. 55)
- Symphony No. 5 in C minor
- Symphony No. 9 in D minor, including well known “Ode to Joy”.
- Missa Solemnis D Major, Op. 123
- Piano Concerto no. 5 “Emperor” in E flat major op. 73
Beethoven’s Death
For the last few months of his life, Beethoven was confined to his bed with illness. Amongst his last view visitors was the younger composer Franz Schubert , who had been deeply inspired by Beethoven. Beethoven, in return, expressed great admiration for the works of Schubert and said of him “Schubert has my soul.” Beethoven’s last words were reported to be:
“Plaudite, amici, comedia finita est. (Applaud, my friends, the comedy is over.) and Ich werde im Himmel hören! (I will hear in heaven!)”
He died on 26 March 1827, aged 56. The precise cause of death is uncertain, but, he had significant liver damage – due to either the accumulation of lead poisoning or excess alcohol consumption. Over 20,000 people are said to have lined the streets of Vienna for his funeral. Though Beethoven had a difficult temperament, and although his music was sometimes too visionary for the general public, Beethoven was deeply appreciated for his unique contribution to music.
Citation: Pettinger, Tejvan . “Biography of Beethoven”, Oxford, UK. www.biographyonline.net , 28th May 2008. Last updated 1 February 2020.
Greatest Hits Beethoven

Greatest Hits Beethoven at Amazon
Beethoven: The Man Revealed

Beethoven: The Man Revealed at Amazon
Related pages

Calm Classics with Myleene Klass 10pm - 1am
Now Playing
Serenade Melancolique Opus 26 Peter Ilich Tchaikovsky Download 'Serenade Melancolique Opus 26' on iTunes
Beethoven: Compositions, biography, siblings and more facts

He reinvented the symphony, reshaped string quartets, and redefined piano sonatas - but there's much more to learn about Ludwig van Beethoven, the deaf composer who changed music forever.
1. When is Beethoven's birthday?
Ludwig van Beethoven was born in Bonn, Germany in December 1770… but no one is sure of the exact date! He was baptised on 17 December, so he was probably born the day before. His birthplace (pictured) is now the Beethoven-Haus museum.
2. Beethoven's father creates a child prodigy
Never mind the exact date, the year of Beethoven’s birth is sometimes questioned, and for years the composer thought he was born in 1772, two years too late. This may have been a deliberate deception on the part of his father (pictured) to make the musical prodigy seem younger – and therefore, more advanced for his age – than he actually was.
3. Beethoven's siblings
Beethoven had seven sibings: Kaspar Anton Karl, Nikolaus Johann (pictured), Ludwig Maria, Maria Margarita, Anna Maria Francisca and Franz Georg van Beethoven, and Johann Peter Anton Leym.
4. Beethoven on the violin
As a young boy, Beethoven played the violin, often enjoying improvisation rather than reading the notes from a score. His father once asked: “What silly trash are you scratching together now? You know I can’t bear that – scratch by note, otherwise your scratching won’t amount to much.” How wrong he was…
5. Beethoven's first composition
There’s some speculation about when the young composer started setting his ideas on paper, but the only piece to date from as early as 1782 is a set of nine variations for piano. Beethoven set himself apart as a musical maverick even at the age of 12 – the music is in C minor, which is unusual for music of the time, and it’s fiendishly difficult to play!
6. Beethoven, Haydn and Mozart
After the death of Mozart in 1791, musicians in his hometown of Vienna were in need of a new genius. The Viennese Count Waldstein (pictured) told the young Beethoven if he worked hard enough he would receive ‘Mozart’s spirit through Haydn’s hands’. No pressure then.
7. Beethoven in Vienna
Finding a wig maker? Noting the address of a dance teacher? Oh, and finding a piano, of course. Beethoven kept a diary of his day-to-day activities when he moved to Vienna in 1792, giving us insights into his personality.
8. Beethoven and Bach
By 1793, aged just 22, Beethoven often played the piano in the salons of the Viennese nobility. He often performed the preludes and fugues from Bach’s Well Tempered Clavier and quickly established himself as a piano virtuoso.
9. Was Beethoven deaf?
Composing anything at all is a challenge, even for a musical genius. So when you consider Beethoven started to go deaf around 1796, aged just 25, it’s a wonder he managed to write any music at all. He communicated using conversation books, asking his friends to write down what they wanted to say so he could respond.
10. Beethoven's Symphony No. 1 – a musical joke?
Beethoven was 30 when his first symphony was first performed in the Burgtheater in Vienna (pictured), and it went where no symphony had ever gone before. Symphonies were seen to be pretty light-hearted works, but Beethoven took this one step further with the introduction, which sounds so musically off-beam it’s often considered to be a joke!
11. Deafness and despair: The Heiligenstadt Testament
Despite his increasing deafness, by 1802 Beethoven was almost at breaking point. On a retreat to Heiligenstadt, just outside Vienna, he wrote: “I would have ended my life – it was only my art that held me back. Ah, it seemed to me impossible to leave the world until I had brought forth all that I felt was within me.” It’s known as the ‘Heiligenstadt Testament’, and was published in 1828.
12. Beethoven’s three musical periods: early period
It's hard to split Beethoven’s music up into sections, but it’s generally agreed there are three different periods with three broad styles. The first is his early period, ending around 1802 after the Heiligenstadt Testament, and includes the first and second symphonies, a set of six string quartets, piano concerto no. 1 and 2, and around a dozen piano sonatas – including the 'Pathétique' sonata.
13. Beethoven’s three musical periods: ‘heroic’ middle period
After his personal crisis, it’s perhaps no surprise that Beethoven’s middle period works are more emotional. A lot of the music from this period expresses heroes and struggles – including Symphony No. 3, the last three piano concertos, five string quartets, Beethoven’s only opera, Fidelio, and piano sonatas including the ‘Moonlight’, ‘Waldstein’ and ‘Appassionata’.
14. Beethoven’s ‘Moonlight’ Sonata
It’s one of Beethoven’s great piano works, but he never knew the piece as the ‘Moonlight’ Sonata. He simply called it Piano Sonata No. 14, and it wasn’t given its poetic nickname until 1832, five years after Beethoven’s death. German poet Ludwig Rellstab said the first movement sounded like moonlight shining upon Lake Lucerne, and the name stuck.
15. Beethoven’s temper and Symphony No. 3 ‘Eroica’
Beethoven admired the ideals of the French Revolution, so he dedicated his third symphony to Napoleon Bonaparte… until Napoleon declared himself emperor. Beethoven then sprung into a rage, ripped the front page from his manuscript and scrubbed out Napoleon’s name. Some modern reproductions of the original title page have scrubbed out Napoleon’s name to create a hole for authenticity’s sake!
16. Beethoven’s opera: Fidelio
If a job’s worth doing, it’s worth doing properly. He may have only composed one opera, but Beethoven poured blood, sweat, and tears into revising and improving it. He reworked the whole opera over a ten year period, giving us the two act version performed today – the older version is sometimes known as Leonore.
17. Beethoven’s three musical periods: late period
Symphony No. 9 with its choral finale, the Missa Solemnis, late string quartets, and some of his greatest piano music including sonatas and the Diabelli variations – Beethoven’s late period is jam-packed with musical genius. Much of the music is characterised by its intellectual intensity, but it sounds just as wonderful to beginners and Beethoven-lovers alike.
18. Beethoven at the movies
The moving music from Beethoven’s Symphony No. 7 is a perfect soundtrack to 2010 blockbuster smash, The King’s Speech, as George VI makes his address to the nation. You’ll also find hints of his fifth symphony in unexpected places, if you listen carefully – have you watched Saturday Night Fever recently…?
19. Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony and the 'Ode to Joy'
Symphony No. 9 is often nicknamed the ‘choral’ symphony, but it’s only the finale that features a choir. Using singers in a symphony was a wild idea at the time, but it seems to have paid off – Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony changed the face of classical music forever, and continues to inspire listeners and composers to this day!
20. When and how did Beethoven die?
We all like a tipple, but Beethoven may have been more partial to a pint than most. He was once arrested for being a tramp by an unsuspecting policeman who didn’t recognise him! After his death in 1827, his autopsy revealed a shrunken liver due to cirrhosis.
21. Famous last words?
Just like Beethoven’s birth, his last words are also a bit of a mystery. It’s often thought his last words were ‘applaud friends, the comedy is ended’ (in Latin!) but his parting gift to the world was far less cerebral. After a publisher bought Beethoven 12 bottles of wine as a gift, the dying composer’s final words were: ‘Pity, pity, too late!’
Beethoven latest
See more Beethoven latest
Chopin and Beethoven’s music helps students pass exams, study finds
Remembering the great maurizio pollini with this intensely beautiful final beethoven sonata.
Maurizio Pollini
What is a symphony? We explain…
Discover Music
10 heart-melting quotations from composers’ love letters
10 epic pieces of classical music that will make you feel tiny in comparison, ‘pdq bach’ musical satirist has died – this beethoven 5 parody captures peter schickele’s rare genius, the 15 greatest violin concertos of all time, ranked, 15 timeless pieces to begin your journey into classical music, the new ai piano that allows disabled musicians to play beethoven in full harmony, 10 pieces of classical music that will 100% change your life, best classical music.
See more Best classical music
The 15 most famous tunes in classical music
The 15 greatest symphonies of all time, the 4 eras of classical music: a quick guide, the 25 greatest conductors of all time, 30 of the greatest classical music composers of all time, the 25 best pianists of all time, latest on classic fm, 75% of students agree, classical music is the best soundtrack to revision, miloš karadaglić: ‘picking up the guitar was a complete accident – it’s now my best friend’.
Miloš Karadaglić
Classical Pride returns with 5-day festival with media partner Classic FM
‘music is vital to her’ – how neurodivergent the piano star lucy speaks through the piano, operatic mezzo stuns with impromptu bizet ‘habanera’ in busy london restaurant, in historic first, a lord of the rings opera has been approved by the tolkien estate, new ‘amadeus’ tv series reveals mozart and salieri actors, musicians break guinness world record with 26-hour concert of music by women composers, why are orchestras arranged the way they are, russian republic announces ban on music that is too slow or too fast.
Culture History

Ludwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827) was a German composer and pianist, widely regarded as one of the greatest composers in the history of Western classical music. Born in Bonn, Beethoven displayed exceptional musical talent from a young age. He composed a vast and influential body of work, including symphonies, piano sonatas, string quartets, and more. Notably, Beethoven’s later compositions, created during a period of increasing deafness, are considered revolutionary for their emotional depth and innovative structures. His Ninth Symphony, featuring the “Ode to Joy,” is particularly celebrated. Beethoven’s legacy extends beyond his music, inspiring generations of composers and leaving an indelible mark on the world of classical music.
Beethoven’s early years were marred by adversity. Born into a musical family, his father, Johann van Beethoven, recognized young Ludwig’s musical talent and sought to mold him into a child prodigy like Mozart. However, the family faced financial hardships, exacerbated by Johann’s struggles with alcoholism. These challenges cast a shadow over Beethoven’s formative years.
In 1787, at the age of 17, Beethoven traveled to Vienna, the musical capital of Europe, to study under Joseph Haydn. Vienna, a vibrant hub of artistic and intellectual activity, provided the young composer with exposure to the leading musicians and thinkers of his time. Under Haydn’s guidance, Beethoven honed his craft and developed a mastery of classical forms.
Beethoven’s early compositions reflected the influence of his contemporaries, including Haydn and Mozart, but he quickly began to forge his own path. His compositions from this period, such as the Piano Sonata No. 1 in F minor, showcased a burgeoning musical voice marked by emotional depth and technical brilliance.
The turn of the century marked a significant shift in Beethoven’s life and career. Around 1800, he began to experience the first signs of hearing loss, a condition that would gradually worsen over the years. Despite this profound challenge, Beethoven continued to compose with unparalleled intensity, delving into new and innovative musical realms.
The early 1800s witnessed the emergence of Beethoven’s heroic period, characterized by compositions that exuded passion, drama, and a sense of triumph over adversity. One of the most iconic works from this period is the Symphony No. 3 in E-flat major, commonly known as the “Eroica.” Originally dedicated to Napoleon Bonaparte, Beethoven later withdrew the dedication, expressing disillusionment with Napoleon’s imperial ambitions.
During this period, Beethoven also composed a series of groundbreaking piano sonatas, including the famous “Moonlight Sonata” (Piano Sonata No. 14 in C-sharp minor) and the “Waldstein” Sonata (Piano Sonata No. 21 in C major). These works showcased Beethoven’s innovative use of form and harmonic language, pushing the boundaries of classical conventions.
As Beethoven’s hearing deteriorated, he grappled with the emotional toll of his affliction. In a poignant document known as the Heiligenstadt Testament, written in 1802 but discovered after his death, Beethoven revealed his despair and contemplation of suicide due to his increasing deafness. However, he found solace in his art, declaring his commitment to overcoming adversity and contributing to the world of music.
The middle period also gave birth to Beethoven’s only opera, “Fidelio.” Premiered in 1805, “Fidelio” explores themes of justice, freedom, and marital devotion. While not an immediate success, the opera underwent revisions and eventually found acclaim for its powerful narrative and musical innovation.
The late period of Beethoven’s life, marked by increasing isolation due to his hearing loss, produced some of his most profound and introspective works. The Ninth Symphony in D minor, completed in 1824, stands as a monumental achievement, incorporating a choral finale that includes the famous “Ode to Joy.” This symphony is a testament to Beethoven’s belief in the universal power of music to convey joy and humanity.
In the final years of his life, Beethoven continued to compose despite deteriorating health. His late string quartets, including the transcendent “Late Quartets” (Op. 127, 130, 131, 132, 133, and 135), are considered some of the most profound and forward-looking works in the chamber music repertoire. These compositions pushed the boundaries of tonality, structure, and expression, influencing generations of composers who followed.
Beethoven’s personal life was marked by his struggles with relationships, including unrequited love and failed romantic pursuits. His famous “Immortal Beloved” letter, discovered after his death, remains a source of speculation regarding the identity of the mysterious woman who captured his heart.
On March 26, 1827, Ludwig van Beethoven passed away in Vienna at the age of 56. His funeral was attended by a multitude of mourners, reflecting the profound impact of his music on both his contemporaries and future generations. Beethoven’s legacy extended far beyond the confines of his time, influencing the Romantic era and leaving an indelible mark on the course of classical music.
Beethoven’s impact on music extended beyond his compositions. His emphasis on individual expression, emotional depth, and innovation paved the way for the Romantic movement in music. Composers like Brahms, Wagner, and later figures like Mahler and Shostakovich drew inspiration from Beethoven’s groundbreaking approach to composition.
The deafness that plagued Beethoven’s later years did not silence his voice; rather, it fueled a creative fire that transcended the limitations of the physical world. His ability to channel personal turmoil into artistic expression remains an enduring testament to the transformative power of music.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Deceptive Cadence
- Issues & Ideas
- Music Makers
- Now Playing
- NPR Classical
Beethoven 250
Beethoven's life, liberty and pursuit of enlightenment.

Tom Huizenga

A portrait of Ludwig van Beethoven, painted in 1804 by W.J. Mähler. Wikimedia Commons hide caption
A portrait of Ludwig van Beethoven, painted in 1804 by W.J. Mähler.
Two-hundred-fifty years ago, a musical maverick was born. Ludwig van Beethoven charted a powerful new course in music. His ideas may have been rooted in the work of European predecessors Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Josef Haydn , but the iconic German composer became who he was with the help of some familiar American values: life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. That phrase, from the Declaration of Independence, is right out of the playbook of the Enlightenment, the philosophical movement that shook Europe in the 18th century.
"One way to look at it is what happened after Newton created the scientific revolution: Basically, people, for the first time, developed the idea that through reason and science, we can understand the universe and understand ourselves," says Jan Swafford, the author of Beethoven: Anguish and Triumph , a 1,000-page biography of the composer.

All Songs Considered
Let's celebrate beethoven's 250th.

Jonathan Biss: Tiny Desk Beethoven (Home) Concert
Swafford says the Enlightenment idea embodied in the Declaration of Independence is that the aim of life is to serve your own needs and your own happiness. "But you can only do that in a free society," he says. "So freedom is the first requirement of happiness."
Other key components of the Enlightenment — including a cult of personal freedom and the importance of heroes — were vibrating in the air in Beethoven's progressive hometown of Bonn when he was an impressionable teenager. "There was discussion of all these ideas in coffeehouses and wine bars and everywhere," Swafford adds. "Beethoven was absorbed into all that and he soaked it up like a sponge."
You can hear ideas from the Enlightenment in Beethoven's Third Symphony, nicknamed "Eroica" — heroic. "There's an amazing place near the end of the first movement of the 'Eroica' where you hear this theme which I think represents the hero," Swafford points out. "It starts playing in a horn, and then it's as if it leads the whole orchestra into a gigantic proclamation, as if that is the hero leading an army into the future."
The hero of the "Eroica" Symphony was originally Napoleon — until Beethoven found out he was just another brutal dictator, and tore up the dedication page of the score. Overall, the hero of much of Beethoven's music is humanity itself.
"He was a humanist, above all," says conductor Marin Alsop, who had planned to mount Beethoven's Ninth Symphony on six continents this year, before the pandemic hit. Beethoven, she says, believed that each of us can surmount any obstacle.
"You can hear his perspective on this new philosophy of the Enlightenment, because it's very personal to Beethoven," Alsop says. "Throughout all of his works, you have this sense of overcoming."
You can hear that journey from darkness to light in pieces like the "Eroica," in the famous Fifth Symphony — and, Alsop says, at the very beginning the groundbreaking Ninth Symphony.
"It opens in the most unexpected way for a piece that's about to make a huge statement," Alsop says. "You can't even tell if it's a major or a minor key. It's kind of fluttering with a tremolo sound in the strings. It's this idea of possibility, an empty slate."
From there, Alsop adds, "Beethoven builds this whole journey of empowerment of unity. There's a lot of unison where the orchestra shouts out as one."
Those unisons are the way Beethoven depicts the connections between people – a pretty important thing for a man who began to go deaf before he was 30. He's a perfect symbol for this era of COVID, Alsop says, because of his severe isolation. That solitude sent the composer out for long walks in the woods outside Vienna.
"Beethoven absolutely loved and cherished nature, and thought of nature as a holy thing," says conductor Roderick Cox, who led performances of Beethoven's Symphony No. 6, the "Pastorale," this fall in Fort Worth, Texas. "Those are some of the principles of Enlightenment, of this music, the liberation of the human mind."
Cox also points to another Beethoven obsession: freedom, which is captured on stage, he says, in the composer's politically fueled opera Fidelio . "It really is the epitome of this Enlightenment spirit: This governmental prisoner, speaking out against the government for individual rights and liberty, has been jailed." In the opera, when the chorus of political prisoners leave their dungeon cells for a momentary breath of fresh air, Beethoven has them sing the word "Freiheit" — freedom.
Two and a half centuries after his birth, Beethoven continues to loom large over today's composers — literally, in some cases. American composer Joan Tower has a picture of Beethoven over her desk, and says he even paid her a ghostly visit once while she was trying to write music.
"He walked into the room right away," Tower says," and I said, 'Listen, could you leave? I'm busy here.' He would not leave. So I said, 'OK, if you're going to stay, then I'm going to use your music.' " And she did, in her piano concerto: Dedicated to Beethoven, the piece borrows fragments from three of his piano sonatas, including his final sonata, No. 32 in C minor.
"The thing I relate to is the struggle, because I struggle the way he does," Tower adds. "He was slow, and I'm slow. So there are certain connections that I'm so happy to have with him."
Everyone can connect to Beethoven, according to Alsop. "This is art that defies time, that defies culture, that defies partisanship, that unifies. And it can speak to each individual differently, but it speaks loudly to each of us," she says.
It's music that speaks to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness — things we're all yearning for right now.
- Ludwig van Beethoven
- Marin Alsop
Biography of Ludwig van Beethoven, German Composer
no_limit_pictures / Getty Images
- Alternative Music
- Country Music
- Rap & Hip Hop
- Rhythm & Blues
- World Music
- Heavy Metal
- Latin Music
- B.A., Classical Music and Opera, Westminster Choir College of Rider University
Ludwig van Beethoven (December 16, 1770–March 26, 1827) was a German composer and musician. His work embraced a range of musical styles, from the classical to the romantic; although Beethoven composed music for a variety of settings, he is best known for his nine symphonies. His final symphony—featuring the "Ode to Joy" chorus—is one of the most famous works in Western music.

Fast Facts: Ludwig van Beethoven
- Known For : Beethoven is one of the most celebrated composers in the history of classical music; his symphonies are still performed throughout the world.
- Born : December 16, 1770 in Bonn, Electorate of Cologne
- Parents : Johann van Beethoven and Maria Magdalena Keverich
- Died : March 26, 1827 in Vienna, Austria
Beethoven's father Johann van Beethoven sang soprano in the electoral chapel where his father was Kapellmeister (chapel master). Johann eventually became proficient enough to teach violin, piano, and voice to earn a living. He married Maria Magdalena Keverich in 1767. Ludwig van Beethoven was baptized on December 17, 1770. Most scholars believe he was born the day before, as Catholic baptisms traditionally took place the day after birth. Maria later gave birth to five other children, but only two survived, Kaspar Anton Karl and Nikolaus Johann.
At a very early age, Beethoven received violin and piano lessons from his father. At the age of 8, he studied theory and keyboard with Gilles van den Eeden (a former chapel organist). He also studied with several local organists and received piano lessons from Tobias Friedrich Pfeiffer and violin and viola lessons from Franz Rovantini. Although Beethoven’s musical genius is often compared to that of Mozart , his education never exceeded the elementary level.
Teenage Years
As a teenager, Beethoven was the assistant and formal student of Christian Gottlob Neefe, the court organist of the city of Bonn. Beethoven performed more than he composed. In 1787, Neefe sent Beethoven to Vienna for reasons unknown, but many historians agree that while he was there he met and briefly studied with Mozart. Two weeks later, he returned home because his mother was ill with tuberculosis. She died in July. His father took to drink, and Beethoven, only 19 years old, petitioned to be recognized as the head of the house; he received half of his father's salary to support his family.
Music Career
In 1792, Beethoven moved to Vienna. His father died in December that same year. Beethoven studied with Austrian composer Joseph Haydn for less than a year; their personalities were evidently not a match for each other. Beethoven then studied with Johann Georg Albrechtsberger, the most famous teacher of counterpoint in Vienna. He studied counterpoint and contrapuntal exercises in free writing, in imitation, in two to four-part fugues, choral fugues, double counterpoint at different intervals, double fugue , triple counterpoint, and canon.
After establishing himself as a composer, Beethoven began writing more complex works. In 1800, he performed his first symphony and a septet. Publishers soon began to compete for the rights to his newest compositions. While still in his 20s, however, Beethoven began to suffer from hearing loss after a fall. His attitude and social life changed dramatically, as the composer wanted to hide his impairment from the world. Determined to overcome his disability, he wrote his second, third, and fourth symphonies before 1806. Symphony 3, ("Eroica") , was originally titled "Bonaparte" as a tribute to Napoleon.
Middle Period
In 1808, Beethoven completed his fifth symphony, whose opening notes are some of the most famous in all of classical music. This success was followed by several additional symphonies as well as string quartets and piano sonatas, including Fur Elise . During this time, Beethoven also premiered an early version of his opera "Fidelio." The production received poor reviews, and the composer continued to revise the work until 1814.
Beethoven's newfound fame began to pay off, and he soon found himself prosperous. His symphonic works were celebrated as masterpieces; critics cited Mozart, Haydn, and Beethoven as the greatest composers of their era. Nevertheless, Beethoven faced personal challenges during this time. He fell in love with a young countess, Julie Guicciardi, but could not marry her because he was from a lower social station. He later dedicated his "Moonlight Sonata" to her.
Beethoven's output suffered during the next decade, the result of several serious illnesses and the death of his brother Kaspar, whom Beethoven had cared for during his sickness. This was followed by a custody battle with his brother's wife over his nephew Karl. The case was eventually resolved in Beethoven's favor, and the composer became the guardian of his nephew. However, the two had a troubled relationship.
Late Period
During the last 15 years of his life, Beethoven's hearing continued to decline. Nevertheless, he did not cease work on his compositions, and in the years before his death, he finished two of his most ambitious pieces—the Missa Solemnis , a mass written for a small orchestra and mixed choir, and the Ninth Symphony, one of the earliest examples of a choral symphony. The latter features what is perhaps Beethoven's most enduring piece of music—a chorus set to words from Friedrich Schiller's poem "Ode to Joy." Beethoven also wrote several additional string quartets, even as his health began to decline.
In 1827, Beethoven died of dropsy. In a will written several days before his death, he left his estate to his nephew Karl, of whom he was the legal guardian after his brother Kaspar's death.
Beethoven remains one of the most popular classical composers of all time, and his major works are frequently performed throughout the world. By introducing new musical ideas, he inspired countless composers after him; indeed, his influence is so great that it is difficult to summarize. The Voyager Golden Record—a recording placed onboard the Voyager spacecraft—contains two pieces of music by Beethoven: the opening of the Fifth Symphony and String Quartet No. 13 in B flat.
- Grove, George. "Beethoven and His Nine Symphonies." Franklin Classics, 2018.
- Lockwood, Lewis. "Beethoven: the Music and the Life." Norton, 2003.
- Swafford, Jan. "Beethoven: Anguish and Triumph." Faber and Faber, 2014.
- The Greatest Composers of the Classical Period
- Top 24 Composers of the Romantic Era
- Biography of Franz Joseph Haydn, Austrian Composer
- Early Romantic Period Music Guide for Beginners
- A List of Beethoven's Music That Has Appeared in the Movies
- Top 10 Baroque Music Song Selections
- Top 10 Baroque Period Composers
- Famous Composers of the 20th Century
- Music Events During the Classical Period
- A Profile of Pyotr Tchaikovsky
- An Expert's Guide to Sergey Prokofiev's 'Dance of the Knights'
- Music History: Different Types of Music Over the Centuries
- Profile of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
- Top 10 Yo-Yo Ma Albums
- Beethoven's Eroica Symphony
- 'Fur Elise' by Beethoven
LVBEETHOVEN.COM
The biography of ludwig van beethoven.
Ludwig van Beethoven , a name synonymous with profound musical innovation, stands as one of the most influential composers in the annals of music history. Born in the late Classical period, his revolutionary compositions and personal resilience bridged the gap between the Classical and Romantic eras, reshaping the course of music. While other composers are praised for their dexterity or their inventiveness, Beethoven is revered for a combination of these traits, punctuated by an indomitable spirit that resonates through his pieces. His work, rich in texture and emotion, was unlike anything heard before, and it challenged the conventions of his time. This guide delves deep into the life, struggles, and monumental achievements of this titan of classical music, exploring how a man grappling with profound personal challenges could produce such timeless art.
Early Life and Beginnings
Ludwig van Beethoven was born in December 1770 in Bonn, situated in the Electorate of Cologne – a principal electorate of the Holy Roman Empire. The Beethoven household was deeply embedded in the world of music, with Ludwig’s grandfather being a musician at the court of Bonn and his father serving as a tenor in the electoral choir. It was evident from an early age that Ludwig had a prodigious musical talent.
Guided initially by his father’s rather strict hand, Beethoven’s early musical education was intensive. Johann van Beethoven, recognizing his son’s gift, envisioned a prodigious trajectory for him akin to the childhood of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. As Ludwig matured, he studied with several prominent musicians in Bonn, including Christian Gottlob Neefe, who introduced him to the works of Johann Sebastian Bach – a pivotal influence in Beethoven’s musical formation.
These formative years were instrumental in shaping the young Beethoven. They instilled in him not just the technical prowess for which he became renowned, but also a deep-seated appreciation for the profound emotional capabilities of music.
Transition to Vienna
By his early twenties, Beethoven recognized the limited opportunities Bonn offered for his burgeoning talents. Hence, in 1792, he made a life-altering decision to move to Vienna, the undisputed musical capital of Europe. Vienna was a city humming with artistic potential, where legends like Mozart and Haydn had crafted their masterpieces.
Rumors of a young prodigious pianist from Bonn had reached the Viennese elite, and Beethoven’s arrival was anticipated. Shortly after settling in Vienna, he began studying composition with Joseph Haydn. Their student-teacher relationship was not without its challenges, but it undoubtedly enriched Beethoven’s musical perspectives.
Vienna became Beethoven’s canvas, where he showcased his brilliance both as a pianist and an emerging composer. He quickly caught the attention of influential patrons, and soon, his compositions began to echo through the halls of the Viennese aristocracy. The city not only provided him with the ideal platform to hone his artistry but also became the backdrop against which many of his most celebrated works were composed.
Musical Innovations and Style
Ludwig van Beethoven’s musical innovations remain some of the most groundbreaking and significant in the history of classical music. As he transitioned from the Classical period’s poised structures into the emotive swells of the Romantic era, Beethoven expanded and transformed the very foundation of music.
One of Beethoven’s most notable innovations was his treatment of the sonata form, a structure central to Classical music. In pieces like the “Waldstein” and “Appassionata” sonatas, Beethoven stretched and expanded the typical boundaries of the form, introducing new thematic material and extending the development sections. This not only increased the length of individual movements but also augmented their emotional depth and complexity.
Rhythmically, Beethoven was a pioneer. He utilized unexpected syncopations, drastic changes in tempo, and expanded rhythmic motifs in ways that were unforeseen in his time. The famous opening four-note motif of Symphony No. 5 is a testament to his ability to generate vast landscapes from simple rhythmic ideas.
Harmonically, he was a trailblazer, often moving away from the traditional tonal centers and introducing remote modulations, chromaticism, and unexpected dissonances. These harmonic adventures can be seen in works like the “Grosse Fuge” for string quartet, where dissonance and counterpoint meld into a challenging but rewarding listening experience.
Lastly, Beethoven’s musical narratives often showcased a journey from struggle to triumph. This “heroic” style, evident in pieces like Symphony No. 3 “ Eroica ,” underscored a departure from the more balanced and reserved expressions of the Classical era. Through these innovations, Beethoven essentially set the stage for the Romantic era’s expansive, emotive compositions.
The Symphonies
Spanning Beethoven’s entire career, his nine symphonies are monumental pillars in the symphonic repertoire, each marking a distinct phase of his creative evolution.
Symphony No. 1 in C Major, though rooted in the Classical traditions of Mozart and Haydn, showed glimpses of Beethoven’s unique voice, particularly in its unexpected harmonic shifts.
Symphony No. 2 in D Major, still in the Classical vein, carries a vivacious energy, especially in its final movement. However, the undercurrents of Beethoven’s emerging individual style are unmistakably present.
Symphony No. 3 in E-flat Major, “Eroica” (Heroic), stands as a turning point. Originally dedicated to Napoleon Bonaparte, Beethoven’s disillusionment with the ruler led him to simply label it “Eroica.” With this symphony, he transcended Classical norms, presenting a grand narrative of struggle and victory.
Symphony No. 4 in B-flat Major, by contrast, is more introspective, with its mysterious introduction and spirited rhythms. It acts as a gentle interlude between the more forceful third and fifth symphonies.
Symphony No. 5 in C Minor is arguably his most iconic. Its dramatic four-note motif, representing “fate knocking at the door,” evolves throughout the symphony, culminating in a triumphant C Major finale.
Symphony No. 6 in F Major, “Pastoral,” is an ode to nature. A programmatic work, its five movements depict scenes like babbling brooks, merry gatherings, and stormy weather, presenting a picturesque landscape.
Symphony No. 7 in A Major is rhythmically vigorous and infectious. Particularly notable is the Allegretto, a movement of such profound emotion that it often overshadows the others in popularity.
Symphony No. 8 in F Major is Beethoven’s shortest symphony but by no means lacks depth. It’s a work brimming with humor, vitality, and joy.
Symphony No. 9 in D Minor, the “Choral” symphony, is Beethoven’s magnum opus. Integrating soloists and a choir into the final movement, it’s a powerful testament to the universal brotherhood of mankind, with the “Ode to Joy” theme representing a pinnacle in Western music.
Collectively, Beethoven’s symphonies changed the course of music history. They expanded the symphony’s scope, both in terms of structure and emotional depth, laying the groundwork for future composers to explore uncharted musical territories.
Beethoven’s Struggles with Hearing Loss
One of the most tragic ironies in the annals of music history is Beethoven’s deteriorating hearing. For a composer of such stature, whose life was interwoven with the intricacies of sound, this loss was akin to a painter losing their sight. Beginning in his late twenties, Beethoven started experiencing episodes of tinnitus, which progressively worsened. By the time he was in his late forties, he was almost completely deaf.
Throughout these distressing years, Beethoven grappled with feelings of despair, frustration, and isolation. The pivotal moment in understanding his emotional turmoil came in the form of the Heiligenstadt Testament, a letter written to his brothers in 1802. In it, Beethoven conveyed the depth of his anguish, even admitting contemplation of suicide. Yet, he resolved to continue living for and through his art.
His deafness brought about a change in his compositions. As external sounds dimmed, Beethoven turned inward, leading to a deepened introspection in his works. His music from this period exhibits a profound depth of emotion, ranging from the fiercest anger to the most tender expressions of love and yearning.
Remarkably, many of Beethoven’s most celebrated compositions, including his late symphonies, string quartets, and the monumental Ninth Symphony, were conceived when he was severely hard of hearing or entirely deaf. These works stand as a testament to his unparalleled inner musical ear and his unyielding spirit.
Late Period Masterpieces
Beethoven’s late period, roughly from 1815 onwards, is characterized by works of unparalleled depth, complexity, and introspection. While his earlier compositions revolutionized music, his late works transcended the norms and conventions of his time, pointing the way to future developments in Western classical music.
Among the jewels of this period are the last five piano sonatas. Pieces like the *Sonata No. 29 in B-flat Major, Op. 106* (commonly known as the “Hammerklavier”) are masterclasses in structure, thematic development, and expressiveness. This particular sonata is both technically challenging and emotionally draining, representing a summation of Beethoven’s pianistic innovations.
Equally significant are the late string quartets. Compositions like the *String Quartet No. 14 in C-sharp minor, Op. 131*, with its seven interlinked movements played without a break, are explorations of new musical territories. These quartets are dense, otherworldly, and at times, enigmatic, requiring intense engagement from both performers and listeners.
Another monumental achievement from this period is the *Missa Solemnis in D Major, Op. 123*. While it’s a religious work, Beethoven’s treatment goes beyond liturgical function. It’s a profound exploration of faith, doubt, and transcendence, written in his characteristically intricate style.
These late period masterpieces, often described as “ahead of their time,” baffled many of Beethoven’s contemporaries. Their complexity and depth were not fully appreciated until years after his death. Today, however, they are recognized as works of profound genius, where Beethoven, unburdened by the constraints of convention and unfettered by his physical limitations, reached the pinnacle of musical expression.
Personal Life and Challenges
Beyond the music sheets and grand performances, Beethoven’s personal life was fraught with challenges and heartaches. Born into a family where his father, Johann, was an alcoholic, young Ludwig often bore the weight of familial responsibilities. His relationships with his brothers were tumultuous, with Beethoven taking on a paternal role for his nephew, Karl, which resulted in prolonged legal battles and personal strife.
Romantically, Beethoven’s life was marked by unrequited loves and fleeting relationships. The mystery surrounding the identity of the “Immortal Beloved,” to whom he penned a series of passionate letters in 1812, remains one of music history’s tantalizing enigmas.
Beethoven also struggled with deteriorating health, which wasn’t limited to his hearing loss. He suffered from abdominal ailments, joint pain, and, in his final years, a series of illnesses that contributed to his death. These challenges, intertwined with his artistic journey, deeply influenced his musical narratives of struggle, resilience, and triumph.
Legacy and Influence
Beethoven’s impact on the world of music is monumental. His compositions set the stage for the Romantic era, allowing subsequent generations to explore richer emotional depths and thematic complexities. Composers like Brahms, Wagner, and Mahler owe a significant debt to Beethoven’s innovations.
More than just influencing composers, Beethoven reshaped public concerts. His works demanded larger orchestras and grander venues, indirectly contributing to the rise of the modern concert hall. His insistence on artistic integrity over catering to popular tastes set a precedent for composers as artists, rather than just entertainers.
Beyond classical music, traces of Beethoven’s influence can be found in contemporary genres. Rock bands, pop artists, and film scores have borrowed from his motifs, rhythms, and emotional intensity. His “Ode to Joy” from the Ninth Symphony, for example, has been adapted countless times, becoming a universal anthem for hope and unity.
Beethoven’s life story — one of overcoming personal adversities to achieve artistic greatness — continues to inspire not just musicians but individuals from all walks of life. His dedication to his art, despite overwhelming challenges, stands as a testament to human resilience and the indomitable spirit.
Final Thoughts
Ludwig van Beethoven, a titan of classical music, embodies the essence of artistic genius combined with unwavering human spirit. Through personal challenges that would have derailed many, he created masterpieces that continue to resonate with audiences around the world. From intimate piano sonatas to grand symphonies, his works tap into the universal human experiences of love, loss, struggle, and joy. In understanding Beethoven’s life and legacy, we gain insight not just into the evolution of music but also the profound depths of the human soul. As we look back on his monumental achievements, we are reminded of the timeless power of music and the enduring spirit of humanity.
Recommended Listening and Further Reading
1. Symphony No. 5 in C Minor 2. “Moonlight” Sonata No. 14 in C-sharp minor 3. String Quartet No. 14 in C-sharp minor, Op. 131 4. “Emperor” Piano Concerto No. 5 in E-flat Major
1. “ Beethoven: Anguish and Triumph ” by Jan Swafford 2. “ Beethoven: The Music and the Life ” by Lewis Lockwood 3. “ Beethoven’s Letters ” (translated by Emily Anderson) – a collection of Beethoven’s correspondence offering intimate insights into his mind.
For those eager to delve deeper into Beethoven’s world, these resources provide a gateway to understanding the maestro’s genius and humanity.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ludwig van Beethoven
Child Prodigy: Beethoven showed musical promise from a very young age. Under his father’s guidance, he gave his first public piano performance at the age of 7, showcasing his talent as a child prodigy, though not as precocious as Mozart.
Shift to Romanticism: Beethoven’s compositions bridged the Classical and Romantic periods in Western music. While he began his career composing in the Classical style, his later works exhibit the emotion, depth, and individualism characteristic of the Romantic era.
Heiligenstadt Testament: In 1802, amidst the despair of his worsening hearing loss, Beethoven penned the Heiligenstadt Testament. This deeply personal letter, addressed to his brothers, expressed his emotional anguish over his impending deafness and his determination to overcome it through his art.
Late Start on Symphonies: Unlike Mozart, who began composing symphonies as a child, Beethoven wrote his First Symphony when he was almost 30. However, he followed this with eight more, each distinct and revolutionary in its own way.
Dedicated Works: Many of Beethoven’s works were dedicated to patrons, lovers, and friends. One of the most famous dedications was to his patron and pupil, Archduke Rudolph, to whom he dedicated a number of major works, including the “Archduke” Piano Trio.
This is a common misconception. Beethoven was not blind; he was deaf. His hearing began to deteriorate in his late twenties and he became progressively more deaf as he aged. By the last decade of his life, he was almost completely deaf, a fact which makes his later compositions all the more remarkable. The confusion might arise because both Beethoven and the famous Baroque composer Johann Sebastian Bach faced significant health challenges. While Beethoven was deaf , Bach became blind in the last years of his life.
There is much speculation, but no concrete evidence, that Beethoven and Mozart met. Beethoven moved to Vienna in 1792, shortly after Mozart’s death in 1791. However, accounts suggest that Beethoven had visited Vienna a few years earlier, and during this time, he might have met Mozart.
Legend has it that Mozart, upon hearing the young Beethoven play, remarked, “Keep your eyes on him; someday he will give the world something to talk about.” However, this story, while romantic, is not substantiated by primary sources.
What is clear is that Beethoven greatly admired Mozart’s work. He was deeply influenced by Mozart’s compositions, especially his piano concertos and symphonies. In fact, Beethoven’s early works often drew comparisons to Mozart, highlighting both the inspiration and the shadow that Mozart cast over the young composer.
Ludwig van Beethoven’s gradual hearing loss is one of the most poignant aspects of his life story. Beginning in his late twenties, he experienced signs of auditory degradation, which worsened progressively. By his late forties, he was profoundly deaf. The exact cause remains uncertain, even after centuries of research and speculation.
Some medical historians suggest that lead poisoning may have been a significant contributor. This hypothesis is based on analyses of hair samples from Beethoven’s remains, which indicated elevated lead levels. The sources of this exposure might have ranged from contaminated wine, lead-based drinking vessels, or medications available in his era.
Alternative theories propose that autoimmune disorders, typhus, or even the numerous treatments he underwent (often involving heavy metals) might have led to his hearing loss.
Whatever the cause, Beethoven’s deafness added layers of both tragedy and triumph to his narrative, profoundly influencing his later works.
Yes, Beethoven continued to play and compose even after losing his hearing. As his condition deteriorated, he began relying more on the vibrations and sensations of the instruments to gauge sound. He would often place his ear close to the piano and, in some instances, used a special rod attached to the instrument to feel the vibrations.
His deafness did not deter his creativity. Arguably, some of his most profound compositions, including the late string quartets and the Ninth Symphony, were created when he was nearly or completely deaf. His ability to compose and engage with music without actively hearing it is a testament to his deep internal understanding of musical structures and his prodigious memory.
Beethoven’s contributions to classical music are vast, and he’s celebrated for several seminal works. His nine symphonies stand at the core of his legacy, with each representing a unique musical journey. The Symphony No. 5 in C Minor , with its instantly recognizable motif, and the Symphony No. 9 in D Minor with its “Ode to Joy”, are often heralded as pinnacle achievements in Western music.
Additionally, his 32 piano sonatas are cornerstones of the piano repertoire, with pieces like the “Moonlight” Sonata resonating across generations. His chamber music, especially the late string quartets, are revered for their complexity and depth.
Beyond compositions, Beethoven’s fearless innovation, bridging the Classical and Romantic eras, and his powerful narrative of personal struggle and artistic perseverance, make him a figure of enduring admiration.
Beethoven’s final years, though marked by personal and health challenges, were intensely creative. He composed some of his most introspective and revolutionary works during this period. The String Quartet No. 15 in A minor, Op. 132 , with its “Heiliger Dankgesang” movement, reflected his gratitude after recovering from an illness. Similarly, the Piano Sonata No. 32 in C minor, Op. 111 , his last piano sonata, showcased his evolving, boundary-pushing style.
While his health deteriorated, leading to his death in 1827, Beethoven remained artistically active, leaving behind sketches for further projects and a rich legacy of completed works. His resilience, in the face of mounting challenges, adds to the profound respect he commands in the annals of music history.
Yes, by the end of his life, Ludwig van Beethoven was almost completely deaf. His hearing issues began in his late twenties and progressed steadily. Despite this immense personal challenge, Beethoven continued to compose and create music, even as his ability to hear it diminished. By his mid-40s, he was profoundly deaf. Despite this handicap, or perhaps even because of it, he produced some of his most profound and innovative work during this period. His determination and resilience in the face of such adversity make his achievements all the more awe-inspiring.
While Beethoven composed many iconic pieces that are popularly recognized and loved, the Symphony No. 5 in C Minor is arguably his most famous. Recognizable from its opening four-note motif — short-short-short-long — this motif has been described as “fate knocking at the door.” The symphony is celebrated not just for its powerful beginning, but for its entire journey, which takes listeners from tension and conflict to triumphant resolution. It has been performed, studied, and admired extensively since its premiere and holds a significant place in Western music.
Despite his hearing loss, Beethoven continued to compose masterpieces. Among the many works he composed while partially or completely deaf are his later symphonies, notably the Ninth Symphony, also known as the “Choral” Symphony, which features the renowned “Ode to Joy.” Additionally, his late piano sonatas and string quartets, recognized for their depth and complexity, were written during this period of his life.
Beethoven’s Symphony No. 5 in C Minor is not only recognized for its unforgettable opening motif but also for the way it epitomizes Beethoven’s mastery of form, development, and expression. The symphony’s journey from its tumultuous beginning to its triumphant end represents a triumph over adversity, which many interpret as Beethoven’s personal narrative in battling his increasing deafness. Its recurring four-note motif, its intricate structures, and its emotional breadth make it a staple in concert halls worldwide and a representation of Beethoven’s genius.
“Für Elise” translates to “For Elise” in English. It’s one of Beethoven’s most popular and recognizable compositions, especially noted for its charming and simple melody. However, the identity of “Elise” remains a mystery. There has been much speculation about her identity — whether she was a lover, a friend, a student, or even a fictional or symbolic figure. Some theories suggest she might have been Therese Malfatti, a woman Beethoven reportedly proposed to. It’s believed that the title might have been mis-transcribed and originally could have been “Für Therese.” Regardless of the muse’s identity, the piece remains a beloved staple in piano repertoire and is often one of the first pieces aspiring pianists learn to play.
The true identity of “Elise” from “Für Elise” remains one of the most enduring mysteries in the realm of classical music. While the title translates to “For Elise”, historians and musicologists have not been able to conclusively determine who this Elise was. One popular theory posits that “Elise” might have been a transcription error and that the piece was originally dedicated to Therese Malfatti, a woman Beethoven reportedly proposed to. It’s suggested that an error in reading Beethoven’s handwriting might have turned “Therese” into “Elise.” Regardless of the actual identity of Elise or Therese, the piece itself has become one of the most recognizable and beloved compositions in the classical piano repertoire.
No, Ludwig van Beethoven never married. However, his personal letters and documented accounts of his life suggest that he had several romantic attachments and infatuations throughout his lifetime. One of the most profound mysteries surrounding his personal life is the identity of the “Immortal Beloved,” a name found in a love letter written by Beethoven. The identity of this woman has been the subject of much speculation, but her true identity remains uncertain.
The exact last words of Beethoven are a matter of some debate, as various accounts exist. According to one of his close friends, Anselm Hüttenbrenner, Beethoven’s last words were in response to the gift of twelve bottles of wine from his publisher. He reportedly said, “Pity, pity, too late!” However, this account might be apocryphal. Another version suggests that he expressed gratitude or made a gesture of affirmation right before his death. Given the varying narratives, it’s challenging to pinpoint his exact final words.
Beethoven’s personal life, particularly his romantic life, remains a subject of much intrigue. While he had several love interests throughout his life, the most intense and mysterious of his relationships is represented by the letters to his “Immortal Beloved.” In these letters, Beethoven expressed deep passion and longing for this unnamed woman. Various candidates have been suggested, including Antonie Brentano, Josephine Brunsvik, and Giulietta Guicciardi, among others. Given the lack of conclusive evidence, the identity of his greatest love remains speculative.
This question likely pertains to a famous scene from the movie “Immortal Beloved”, wherein Beethoven shares a passionate kiss with his love interest. In real life, Beethoven had romantic attachments and infatuations with several women, including Giulietta Guicciardi, to whom he dedicated his “Moonlight” Sonata. Given the private nature of personal relationships in his era, detailed accounts of intimate moments, like a kiss, are not well-documented. The portrayal of such moments in films or literature is often a blend of factual basis, interpretation, and artistic liberty.
- Analysis and Scholarship
- Beethoven and Culture
- Beethoven Books
- Beethoven Collections
- Beethoven Music
- Beethoven's Inspirations and Influence
- Beethoven's Works
- Community and Education
- Multimedia Gallery
- Performance and Recordings
- Uncategorized
- Beethoven: The Maestro of Musical Innovation
- Beethoven: A Symphony of Genius
- The Composer Who Defined an Era
- Beethoven’s Early Years: Childhood, Training, and Musical Legacy

30 Beethoven Facts – Interesting Facts About Ludwig van Beethoven

Here are the facts about the great composer – Beethoven (1770 – 1827). Real also the complete Beethoven Biography and the best of Beethoven works .
Facts About Ludwig van Beethoven:
- Beethoven died during a thunderstorm on the 29th March 1827 in Vienna.
- When he died, Beethoven’s headstone had only a single word – ‘Beethoven’. Such was his fame at the time it was all that was needed.
- It was reported that Beethoven often dipped his head in cold water before composing – neither he nor anyone else has given any reason why.
- For three years (early in his career), Beethoven earned his living playing the Viola in an orchestra – possibly one of the reasons he was said to compose for the piano ‘as if it was a stringed instrument’.
- Beethoven’s Sonata Opus 27 no. 1 (the one before the Moonlight Sonata) took over two years to compose because he had to write the Prometheus Ballet just after he’d started it; the Ballet was a commission so he had to finish that first before he could go back to the Sonata.
- After his mother died of consumption in 1787, and he was forced to look after his younger brothers, Beethoven took his responsibilities very seriously; to the point where he refused to allow them to marry women who he thought were unsuitable.
- Thomas Broadwood, the English piano builder, sent Beethoven one of his pianos as a gift in 1818. But, by the time he received it, he was profoundly deaf and wouldn’t have heard a note.
- We know a lot about how Beethoven composed from his sketchbooks that have mostly survived – all his ideas were written in these books first.
- In one of Beethoven’s letters, he said that he thought his deafness had started when he tripped and fell over after being startled. No one knows the real reason but it is believed to have been more likely to have been as a result of one of his many childhood illnesses – typhus, smallpox.
- Beethoven was always ill. The catalog of his ailments is long and his suffering would have been very real. During his life, he was known to have suffered from deafness, colitis, rheumatism, rheumatic fever, typhus, abscesses, ophthalmia, jaundice, chronic hepatitis, infections, and cirrhosis of the liver.
- Beethoven drunk a lot of alcohol; his father had been an alcoholic. He was once even arrested as a vagrant due to his drunkenness. The cirrhosis of his liver was only discovered after his death.
- Beethoven’s final words are believed to have been ‘Pity, pity, too late!’ Apparently, this was in response to having just received the gift of a case of wine from a music publisher.
- Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony is often known as the Choral Symphony – it was the first symphony ever to have parts for singers.
- A disco version of Beethoven’s Fifth Symphony arranged by Walter Murphy and called ‘A Fifth of Beethoven’, was used in the film Saturday Night Fever. The use of the word ‘Fifth’ in this context was referring to a bottle of liquor which was usually sold in bottles that contained a fifth of a gallon.
- The Seventh Symphony by Beethoven was used in the 2010 award-winning film, ‘The Kings Speech’.
- Beethoven’s father, a failed musician, was a bully. He realized his son’s talent and, seeing financial rewards for himself, decided that he should be the new Mozart – he made the young Ludwig practice for hours. He died in 1792 before Beethoven’s greatness was truly realized.
- Young Ludwig had to leave school aged only 11 to help with family duties. As a result, he never learned to do multiplication or division.
- Beethoven didn’t call his Sonata Opus 27, No. 2 the ‘Moonlight’ He called it No. 14. The name was penned by the German poet Ludwig Rellstab, some years after Beethoven had died. Apparently, the poet thought the music sounded like moonlight reflecting on Lake Lucerne. The name stuck.
- Beethoven’s Third Symphony, known as the Eroica, was initially dedicated to Napoleon Bonaparte, whose ideas were mightily respected by Beethoven. However, when Napoleon declared himself Emperor, Beethoven went into one of his rages, ripped off the front page of the score, and scribbled out Napoleon’s name from the work.
- Beethoven only wrote one opera, Fidelio. On the basis that took him over ten years of revisions, it’s not surprising that he didn’t write another. The original version is still occasionally performed and is known as Leonora.
- After realizing that his deafness was permanent and irreversible, Beethoven wrote a letter in 1802 to his two younger brothers – it is now known as the Heiligenstadt Testament – in which he faced up to his disability (surely the greatest a musician/composer can suffer) and announced his determination to overcome it. The letter was never sent and was found in his papers after his death in 1827.
- After becoming deaf he communicated with his friends with ‘conversation books’ where they would write down what they wanted to ask him.
- Deafness began to descend on Beethoven when he was only 25 years old – he suffered from tinnitus (ringing in his ears) for some years before it deteriorated completely.
- The date of Beethoven’s birth is not actually known. He was baptized on the 17th of December 1770, so it is usually assumed that he would have been born on the previous day – the 16th. Children at that time were usually baptized quickly on account that many of them didn’t survive very long.
- Beethoven taught for most of his life although he would only teach pupils if they had genuine talent or were pretty girls. The girls weren’t required to have any talent.
- Beethoven always fell in love with unobtainable women so never consummated his love or married.
- He fell in love with one of his pupils, Josephine Brunswick, in 1799; she was believed to be the intended recipient of his famous ‘immortal beloved’ love letter. She married a Count instead.
- Beethoven also fell in love with a girl called Julie – she was a Countess. However, she couldn’t marry him because he was deemed a commoner. He wrote 15 passionate and unrequited love letters to her.
- His first composition was written when he was only 12. It was a set of 9 variations for piano on a March by Ernst Christoph Dressler, in C minor. As a portent for what was to come, it was extremely difficult to play.
- The final movement of Beethoven’s Ninth Symphony is known as the ‘Ode to Joy’ – the words in the movement are sung to the poem of the same name written by Freidrich Schiller in 1785. The piece was subsequently adopted as the ‘National Anthem of Europe’ by the EU. Parts of it were also used in a Bruce Willis film (Die Hard) to accompany crooks cracking a safe, and Michaels Jackson’s 1993 single (Will You Be There).
Leave a Comment
Ludwig Van Beethoven
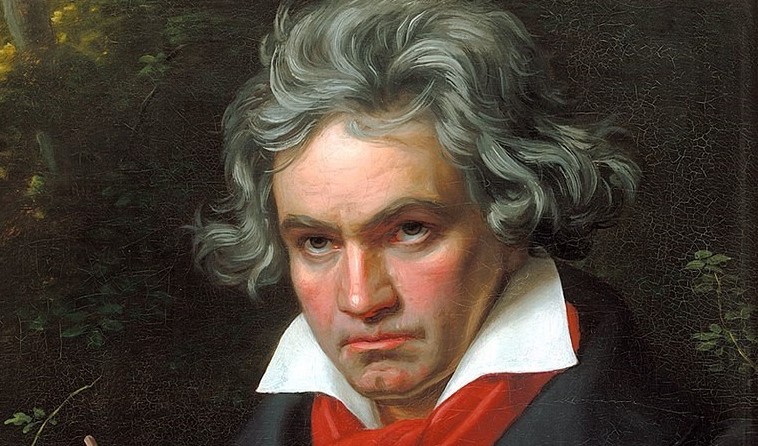

Ludwig Van Beethoven Biography
Ludwig Van Beethoven was a composer, pianist, and conductor, born in Bonn, Germany in 1770. Beethoven was baptized on December 17, 1770, which is why historians place his birth a day earlier, on December 16 of 1770. Ludwig Van Beethoven has been considered the greatest composer of all time by many specialized critics.
Beethoven was deaf and yet managed to compose the greatest symphonies in history. From an early age, he was an exceptional pianist and managed to elevate classical music like no one had ever done before.
Ludwig Van Beethoven was the first son of Johann Van Beethoven and Maria Magdalena Keverich, who had two more children: Karl Kaspar and Nikolaus Johann.
Beethoven’s childhood can be considered particularly difficult. He did not have a functional home, due to the father figure, who assumed dictatorial attitudes mired in alcoholism. His father had had a musical career without transcendence, so he managed in a despotic manner to force Beethoven to triumph in the musical field at a very early age.
Throughout history, not all the cases in which the parents pretend to satisfy their frustrations by influencing excessively in the life of their children have had remarkable results. However, and despite the constant pressure exerted by Beethoven’s father, Ludwig showed an innate talent, very exceptional, especially the with the piano.
In 1778, at the age of eight, Beethoven gave his first concert in Cologne, Germany, sponsored by the elector of the city, who at the same time gave him the job as the organist, where he began a childhood dedicated exclusively to music.
It is often said about Beethoven that he used to be lonely, romantic and hostile; and a great part of his personality was forged in the adolescence, time in which the music occupied his absolute dedication, moving away from the friends, the games, and immersed in a much more complex familiar atmosphere still.
“Consider difficulties as stepping stones to a better life.” Ludwig Van Beethoven.
In 1787, helped by the elector, Beethoven traveled to Vienna (Austria), a journey that would change the course of his life. Nevertheless, a great part of their aspirations undergoes a remarkable impact after the death of his mother they would go back to Bonn.
After his return to Bonn, Beethoven finds a Dantesque picture in his family. His father succumbed absolutely to alcohol, which did not let him keep a stable job and support his brothers. So then, Beethoven assumes the responsibilities of home, plays the violin and gives piano lessons to support his family, likewise accumulates for a little more than five years, a great resentment and a remarkable frustration.
For Ludwig Van Beethoven, Bonn represents his suffering, not only in childhood but also in adolescence. It symbolizes the pain of his mother and dreams of the possibility of traveling.
In 1792, the elector would finance Beethoven’s return to Vienna, which was known as “the European capital of music.” Beethoven in Vienna received classes from who was the teacher of the already consecrated Mozart, the famous composer Salieri . Also, he received classes from Haydn , considered a musical eminence.
At the age of twenty-five, Beethoven would compose his first considerable works: Pathetic and Moonlight , which catapulted him to the point of being able to offer for the first time a concert in public as a professional composer.
The success of Beethoven was already resounding in all Vienna and surroundings. The clergy, the nobility, and the court celebrated his compositions. Beethoven, concerned that his success will be eclipsed by the figure of his teacher Haydn, separated from his classes and begins to receive them in secret from Schenk and Albrechstberger. Regarding his style, Beethoven combined classicism and romanticism perfectly, in his intention to compose for the nobility and the church; already by those times, Beethoven thought about composing for himself, abandoning a little his style, acquiring an epic tone.
The fact that Mozart died years before immersed in the acutest poverty, motivated the Austrian aristocracy to protect Beethoven; to whom an annual annuity was assigned. In addition, the editors valued his works in high economic sums.
Ludwig Van Beethoven would begin to face two new ghosts: his constant amorous disappointments, and, a loss of auditory capacity that would become more severe until it became total deafness. Beethoven then is decidedly devoted to his career as a composer, leaving an invaluable legacy for history.
In 1805, he premiered his work Fidelio , his only composition for opera, which would not become popular until 1816. Three years later, Vienna and Europe celebrate his 5th Symphony , his supreme work.
“Without introduction, its four movements range from the tense construction of the first to the solemnity of the second, passing through the instrumental tension of the third and the apotheosis of the fourth, an unheard-of crescendo of more than 50 measures.”
In 1824, after having composed 8 symphonies, Beethoven successfully premiered his glorious and magnificent 9th symphony, the famous choral. “it is called choral because of the vocal choir of the 4th movement, the famous ode to joy, a poem by Schiller adapted by Beethoven.”
Ludwig Van Beethoven would pass away in Vienna on March 26, 1827 , at the age of 57.
- 1st Symphony (1800): Fresh and original.
- 2 nd Symphony (1803): Symphony in D major.
- 3rd Symphony (1805): Symphony in E flat major.
- 4th Symphony (1806): Symphony in B flat major.
- 5th Symphony (1808): Symphony in C minor.
- 6th Symphony (1808): Symphony in F major.
- 7th Symphony (1813): Symphony in A major.
- 8th Symphony (1814): Symphony in F major.
- 9th Symphony (1824): Choral.
Ludwig Van Beethoven not only wrote symphonies, he also wrote 32 sonatas, chamber works, overtures, quartets and much more.
“Those of you who think or say that I am malevolent, obstinate or misanthrope, how wrong they are about me” Beethoven.

You may like

Paul McCartney

Britney Spears

Romeo Santos
Fernando Botero

Fernando Botero Biography
Fernando Botero Angulo (April 19, 1932 – September 15, 2023) was a sculptor, painter, muralist, and draftsman, hailing from Medellín, Antioquia, Colombia. He was a Colombian artist known and celebrated for infusing a substantial volume to human and animal figures in his works.
Early Years and Beginnings
Fernando Botero was born into an affluent Paisa family , composed of his parents, David Botero and Flora Angulo, along with his older brother Juan David, who was four years his senior, and his younger brother, Rodrigo, who would be born four years after Fernando, in the same year that their father passed away. In 1938, he enrolled in primary school at the Ateneo Antioqueño and later entered the Bolivariana to continue his high school education. However, he was expelled from the institution due to an article he published in the newspaper El Colombiano about Picasso , as well as his drawings that were considered obscene. As a result, he graduated from high school at the Liceo of the University of Antioquia in 1950.
In parallel to his studies, Fernando attended a bullfighting school in La Macarena at the request of one of his uncles. However, due to an issue related to bullfighting, Botero left the bullring and embarked on a journey into painting. In 1948, he held his first exhibition in Medellín. Two years later, he traveled to Bogotá where he had two more exhibitions and had the opportunity to meet some intellectuals of the time. He then stayed at Isolina García’s boarding house in Tolú, which he paid for by painting a mural. Once again in Bogotá, he won the second prize at the IX National Artists Salon with his oil painting “Facing the Sea” .
“Ephemeral art is a lesser form of expression that cannot be compared to the concept of art conceived with the desire for perpetuity. What many people fail to understand is that Picasso is a traditional artist”- Fernando Botero
Due to the prize from the IX Salon and the sale of several of his works, Fernando Botero traveled to Spain in 1952 to enroll at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts of San Fernando in Madrid. There, he lived by selling drawings and paintings in the vicinity of the Prado Museum. In 1953, he went to Paris with filmmaker Ricardo Irrigarri, and later, they both traveled to Florence. Here, he entered the Academy of San Marco, where he was heavily influenced by Renaissance painters such as Piero della Francesca, Titian, and Paolo Uccello.
Career and Personal Life
In 1955, Botero returned to Colombia to hold an exhibition featuring several of his works created during his time in Europe, but it was met with a lukewarm reception from the public.

Woman With a Mirror / Foto:Luis García (Zaqarbal) / Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Spain (CC BY-SA 3.0 ES)
In 1956, he married Gloria Zea, with whom he would later have three children: Fernando, Juan Carlos, and Lina. The couple traveled to Mexico City, where Fernando Botero was eager to see the works of Mexican muralists, but this experience left him disillusioned. Consequently, he began searching for his own artistic style, drawing influence from both the Mexican artist Rufino Tamayo and the Colombian artist Alejandro Obregón . In this quest, he started experimenting with volume, initially in still lifes, and gradually extending this approach to other elements.
In 1957, he successfully exhibited in New York, showcasing his new artistic sensibility. The following year, he returned to Bogotá, where he was appointed as a professor at the School of Fine Arts at the National University of Colombia . He presented his work “La Camera Degli Sposi” at the X Colombian Artists Salon , winning the first prize and becoming the country’s most prominent painter. This piece sparked some controversy as it was initially censored for being almost a parody of Andrea Mantegna’s “La Cámara de los Esposos”. However, it was later reinstated in the exhibition on the advice of Marta Traba. Subsequently, Fernando Botero exhibited his works in various spaces in the United States, where a businessman from Chicago purchased “La Camera Degli Sposi” .
“Fernando Botero and his works are the finest ambassadors of our country in this land of navigators and discoverers, of poets and fado singers”- Juan Manuel Santos
In 1960, Botero separated from Gloria Zea and traveled to New York. He led a modest life here as the New York art scene was primarily inclined towards abstract expressionism. Consequently, Botero was influenced by artists like Pollock, which led him to experiment with color, brushwork, and format, to the point of nearly abandoning his distinctive style characterized by the manipulation of volume. Aware of this, Botero returned to his usual style of flat colors and figurative representations.
Starting in 1962, he began a series of exhibitions in both Europe and the United States, as well as in Colombia. By 1970, the year his son Pedro was born to his second wife, Cecilia Zambrano, Fernando Botero had already become the world’s most sought-after sculptor. However, in 1974, his son Pedro tragically died in a traffic accident, leading to his second divorce and leaving significant marks on his artistic endeavors.
In 1978, the Colombian painter married Sophia Vari , a renowned Greek artist with whom he shared a significant part of his life, until sadly, she passed away in May 2023.
Since 1983, Fernando Botero has been exhibiting his works and donating them to various cities around the world. As a result, we can find his pieces in the streets of Medellín, Barcelona, Oviedo, Singapore, and Madrid, among others. In 2008, the Autonomous University of Nuevo León in Mexico conferred upon him an honorary Doctorate.
Renowned Colombian artist, Fernando Botero, died on September 15, 2023 , in Monaco at the age of 91 due to pneumonia . His artistic legacy will endure forever. In his hometown, seven days of mourning were declared.

Pedrito a Caballo, Fernando Botero (1975).
Top 10 Famous works by Fernando Botero
Some of the most recognized works by Colombian painter and sculptor Fernando Botero:
- “Pedrito on Horseback” / “Pedrito a Caballo” (1974): This is an oil painting on canvas measuring 194.5 cm x 150.5 cm. For Botero, this work is his masterpiece and a refuge during a personal tragedy. The child depicted is Pedro, his son from his second marriage, who tragically passed away in an accident when he was young.
- “Mona Lisa at 12 Years Old” / “Mona lisa a los 12 años” (1978): This piece stands out as a unique version of Leonardo da Vinci’s famous painting, the Mona Lisa . Painted in oil on canvas and measuring 183 cm x 166 cm, Botero incorporates his characteristic style of voluptuous and rounded figures into this work, which has become one of his most distinctive pieces.
- “Woman’s Torso” / “Torso de Mujer” (1986): It is a majestic bronze sculpture that rises to an impressive height of approximately 2.48 meters. It is often affectionately referred to as “La Gorda” (“The Fat One”). This artwork finds its home in Parque de Berrío, located in the captivating city of Medellín.
- “Woman with Mirror” / “Mujer con Espejo” (1987): An imposing bronze sculpture weighing 1000 kg. It is located in Plaza de Colón, in the heart of Madrid, Spain. The artwork captivates the gaze with the portrayal of a woman peacefully lying face down on the ground, holding a mirror in her hands. Her expression reflects deep introspection and enigmatic melancholy.
- “The Orchestra” / “La Orquesta” (1991): In this oil on canvas artwork, measuring 200 cm x 172 cm, Botero presents a band of musicians with a singer, all immersed in a spirit of celebration. The artist aims to convey a sense of harmony and joy through his portrayal.
- “Woman Smoking” / “Mujer Fumando” (1994): It is a creation executed in watercolor, spanning dimensions of 122 cm x 99 cm. In this work, Maestro Botero skillfully captures the essence of a woman elegantly holding a cigarette between her fingers. His meticulous focus on voluptuous forms, posture, and the serene expression of the figure masterfully combine to emphasize the sensuality and profound intimacy of the moment captured in the artwork.
- “Man on Horseback” / “Hombre a Caballo” (1996): This bronze sculpture is one of the most iconic works in the artist’s career. It depicts a rider in a majestic and proud posture. Over the years, this imposing work has been exhibited in multiple cities around the world, solidifying its place as a prominent piece in the sculptor’s body of work.
- “The Horse” / “El Caballo” (1997): This iconic sculpture showcases a horse of majestic presence and a distinctive rounded form, sculpted in bronze and measuring approximately 3 meters in height. This masterpiece reflects Botero’s profound passion for horses while also serving as a powerful representation of the mythical Trojan Horse.
- “The Death of Pablo Escobar” / “La muerte de Pablo Escobar” (1999): This artwork, created using the oil on canvas technique, has dimensions of 58 cm x 38 cm. While not considered a masterpiece, this artistic piece represents one of the most significant moments in Colombia’s history. Fernando Botero captures, in his distinctive style, the moment of the death of the drug lord Pablo Escobar , addressing issues related to violence and criminality that have marked the country’s history. An interesting detail is that, although Pablo Escobar admired Fernando Botero’s art, it cannot be said that the admiration was mutual. The painter created two works depicting the death of the drug trafficker.
- “Boterosutra Series” / “Serie Boterosutra” (2011): This work by Botero is part of an erotic art collection called Boterosutra , marking a milestone in the history of Colombian art as the first artistic representation of sexual intimacy between lovers. This series comprises around 70 small-sized pieces created using various techniques, including colored drawings, watercolors, brushstrokes, and also black and white, all of which constitute one of the most contemporary works by the painter.
Ryan Reynolds

Biography of Ryan Reynolds
Ryan Rodney Reynolds was born on October 23, 1976 in Vancouver, Canada, and he is a well-known actor. When Ryan was born, his mother, Tammy, was a student and a salesperson, while his father, Jim, worked in wholesale food sales and also excelled as a semi-professional boxer. In addition, Ryan has three older siblings.
He studied in his hometown of Vancouver until 1994 when he decided to join a theater group as an extracurricular activity while attending Kwantlen College. However, his passion for acting became a vocation, and Ryan dropped out of college to devote all his time and energy to his acting career.
Debut as an actor
He quickly landed small roles in successful and memorable TV series such as “Sabrina the Teenage Witch” and “The X-Files”. In 1998, his big break came with the series “Two Guys, a Girl and a Pizza Place”, which ran until 2001 and catapulted him to fame. The show became very popular thanks to its great comedic content, an area where Reynolds demonstrated perfect skill, but this was not the first time that Ryan had made a name for himself in a Hollywood comedy, as he had already been in “Life During Wartime” in 1997.
After working in several minor jobs, Ryan got his first major role as a protagonist in the crazy “Van Wilder – Animal Party”, where he played a college party organizer. The success of the film opened doors for him to work alongside Michael Douglas in “Till Death Do Us Part”, support Wesley Snipes in “Blade Trinity” or star in the horror movie “The Amityville Horror”. However, at this stage of his career, Ryan stood out mainly as a protagonist in comedies such as “Just Friends”, “Waiting” and “Harold & Kumar Go to White Castle”. This led him to want to leave his comedic side behind, getting involved in different projects such as the thriller “Smokin’ Aces”, the independent film “Adventureland” and the action film “X-Men Origins: Wolverine”. Later on, he also participated in romantic films such as “The Proposal” and “Definitely, Maybe”. However, recognition of his acting ability did not come until Ryan was nominated for a Goya Award for his demanding role in “Buried”. It is worth noting that he also brought to life the comic book hero “Green Lantern” and the renowned “Deadpool”.
Contracts, curiosities
Prestigious brands like Hugo Boss have not been oblivious to Ryan Reynolds’ popularity, charisma, and good looks, offering him contracts to be the face of one of their fragrances : Boss Bottled Night, a fragrance that, through great advertising, managed to convey an irresistible seductive effect.
Two curiosities can be highlighted from his work: first, the nearly 10 kilos of solid muscle he gained thanks to rigorous physical training to bring Hannibal King to life in “Blade: Trinity”; and second, his appearance on the animated TV series Zeroman, in which he lent his voice to the character Ty Cheese. In addition, like many Hollywood stars, Ryan Reynolds has an eccentricity outside the world of entertainment: a great passion for motorcycles , of which he owns three collector’s items, one of which was designed exclusively for him and is none other than a Harley Davidson.
Romantic relationships
Regarding his personal life, Ryan Reynolds was in a romantic relationship with singer Alanis Morissette from 2002 to 2007. The couple got engaged in 2004, but in July 2006, People magazine reported that they had separated, although neither of them officially confirmed the news. Shortly after, in February 2007, they decided to end their engagement by mutual agreement. In May 2008, Reynolds announced his engagement to actress Scarlett Johansson , and they got married on September 27 of the same year. However, in December 2010, the couple announced in a statement to People magazine that they had decided to end their marriage.
So, on September 9, 2012, he married the actress Blake Lively in Mount Pleasant, South Carolina. In October 2014, they announced that they were expecting their first child, and in December of that same year, Ryan Reynolds and his wife Blake Lively became parents with the birth of their daughter: Ines. Later, on April 14, 2016, his wife’s second pregnancy was confirmed, and on September 30, 2016, he became a father for the second time to a boy named James.

Biography of Tom Hanks
Thomas Jeffrey Hanks, born July 9, 1956 in Concord, California, United States, is an actor known as Tom Hanks. Hanks was raised by his father Amos Mefford Hanks, who worked as a cook of English food, and his mother Janet Marylyn, a nurse. He was raised with the values of the Catholic and Mormon religion. During his time at Skyline High School in Oakland, he attended theater classes with his best friend. During his adolescence, Hanks demonstrated his acting talent and won the Best Theater Actor award at his institute. Later, he enrolled in Chabot College in Hayward, California and two years later did a exchange at California State University, Sacramento.
1981 – Debut as an actor
In 1979, the Hanks family moved to New York, which gave Tom the opportunity to debut as a supporting actor in the horror film “Sabe que estás sola” in 1981. Two years later, he landed a lead role in another film. Additionally, he did his first television work in the comedy series “Bosom Buddies.” Later, he decided to move to Los Angeles to participate in “Despedida de soltero” in 1984, although the film was not very successful, it allowed him to be discovered by Ron Howard, who later contacted him to offer a role in “Splash” in 1984.
Since then, Tom starred in several comedy films such as “Amigos del alma” (1980), “Esta casa es una ruina” (1986), “Big” (1988), “No matarás… al vecino” (1989), “Socios y sabuesos” (1989), and “Joe contra el volcán” (1990). His father was always very important in his career, constantly encouraging him to keep fighting for his dream. On several occasions, he helped him to get small roles. He also supported his participation in the Great Lakes Shakespeare Festival in Cleveland, Ohio. Tom had already made some appearances in series like “Vacaciones en el mar”, “Happy Days”, “Taxi”, or “Family Ties”.
“The King of Comedy”
After a small role in the horror film “He Knows You’re Alone” (1980) directed by Armand Mastroianni, he starred in several comedies that typecast him in comedic roles. His charming personality and natural talent contributed to his growing popularity. Definitely his consecration came in the eighties, he was cataloged as the king of comedy . Thanks to “Big” (1988), he achieved great success for his performance, receiving the Los Angeles Critics Award and an Oscar nomination . Although he had a bit of a downfall after that, he regained momentum as a disillusioned former baseball pitcher who trains a women’s team in “A League of Their Own” (1992).
Tom considered it appropriate to change direction and tackle other stories, to move away from comedy a little. So, he eagerly sought more intense themes where he could showcase his versatility. With his work in “The Bonfire of the Vanities” (1989), directed by Brian de Palma, he attempted to take the first step to break away from light comedies, but the result was not as expected. However, his career took off again with his portrayal of an AIDS-stricken lawyer in “Philadelphia” (1992), directed by Jonathan Demme, an intense character that was quite a challenge. His effort was rewarded with an Oscar. He renewed his commercial success with “Sleepless in Seattle” (1993), directed by Nora Ephron, where he teamed up with Meg Ryan, and worked with her again in “You’ve Got Mail” (1998).
Some of his most acclaimed performances
In the mid-90s, Hanks established himself as one of Hollywood’s brightest stars. It’s worth mentioning that his career enjoyed significant success. For his role in Robert Zemeckis’ “ Forrest Gump ” (1994), this has been one of the most striking films of the decade, he was again deserving of an Oscar , a prize that increased, turning him into one of the best-paid actors in Hollywood. With the comedy “The Wonders” (1996), he made his directorial debut.
Later, he did the same in the field of production with the TV series “From the Earth to the Moon,” a work that took him several years. Hanks had the lead role in the feature film “Saving Private Ryan” (1997), directed by Steven Spielberg , with this role he was nominated for the Academy Award, although the film received five Oscars. In 2000, he worked with Robert Zemeckis again in the film “Cast Away,” a film in which his solo performance was praised, for which he received an Oscar nomination.
Between 2003 and 2004, he repeated his collaboration with Spielberg in “Catch Me If You Can” and also in “The Terminal.” In 2006, he starred in the hit film “The Da Vinci Code,” the cinematic version of Dan Brown’s controversial work. Starting in 2014, Hanks’ films have grossed over 4.2 billion in countries such as the United States and Canada, and over 8.4 billion in the rest of the world, he is definitely an actor who ensures great success for films. His fame is such that the asteroid (12818) Tomhanks bears his name.
Marriages, children.
The actor has had several marriages throughout his life. His first marriage was to Samantha Lewes in 1978, from which two children were born: Colin Hanks in 1977 and Elisabeth Ann in 1982. However, the couple divorced in 1985. Later, in 1988, he married actress and producer Rita Wilson , with whom he had two additional children: Chester Marlon in 1991 and Truman Theodore in 1996. In recent years, the actor has been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, which requires a strict diet and daily care to maintain his health.
Marc Anthony

Biography of Marc Anthony
Marc Anthony (born September 16, 1968) is an American salsa singer and actor , born in New York. His real name is Marco Antonio Muñiz Rivera . From a young age, he has been involved in music, growing up with rock and rhythm & blues. His parents, Felipe Muñiz and Guillermina Rivera, discovered his passion and musical ability when he was a child. During his teenage years, to earn money, he began singing at bars and nightclubs , and quickly gained popularity. He was contacted by one of the members of the Latin Rascals group, and their producer Louie Vega invited him to record several albums with the Atlantic Records label.
Beginnings as a singer
One of Marc Anthony’s most successful musical products was the album “Rebel”, which achieved some success on the disco music charts. In 1992, his career in the salsa world took off when the famous Tito Puente took him as an opening act for a concert at Madison Square Garden. A year later, he recorded a salsa version of a song by Juan Gabriel that received excellent reviews and great popularity in the musical circles of New York. Soon, Marc Anthony appeared in several television productions and began to receive offers for concerts. After a few years, he was recognized as the new “king of salsa”. During the 1990s, his lyrics occupied the top position in Latin America and also in the United States.
The new “musical phenomenon”
Marc Anthony became a massively successful musical phenomenon , comparable to the success of Héctor Lavoe. At the same time, he continued to develop his acting career, appearing in films such as “Bringing out the Dead” directed by Martin Scorsese; “Big Night” directed by Stanley Tucci; “Hackers,” and “The Capeman,” a Broadway musical directed by singer and songwriter Paul Simon. He also performed the main theme of the soundtrack of “The Mask of Zorro” (1998), in which Antonio Banderas was the lead actor.
Third salsa album “Against the Stream”
That same year, he worked on the production of his third salsa album: “Contra la Corriente,” undoubtedly many salsa critics and aficionados affirm that it was the best album of his career, for which he received a Grammy for Best Latin-Tropical Album. In 1999, he released the album “Marc Anthony” to the market, this album undoubtedly demonstrates a new stage in his musical career, as it combined salsa with pop and also featured songs in English, in order to reach and conquer the Anglo-Saxon audience and market.
The first single, “I Need to Know,” put him in the top positions of the North American charts: it remained in the Top 10 of the Billboard for eleven weeks and eight more weeks in the Top 40. He also released the Spanish version, titled “Dímelo.” With this song, he won the Grammy for Best Latin Song of the Year and was number one on the Latin Billboard chart. He quickly released the second single, “You Sang to Me,” repeating the success of the previous one and selling over two million copies of the album.
Starting the new millennium, he released a greatest hits salsa album titled “Desde el principio.” After that, Marc Anthony went on a extensive tour that took him through the United States. All magazines and press talked about his triumphant concert at Madison Square Garden. Then he was in Canada and Central America. At that time, Marc Anthony received the admiration of his fans when he helped with his charitable work for the victims of Hurricane George, in sum, he founded a foundation that bears his name.
International tours
In 2011, he started the Dos Mundos Tour, with the company of Alejandro Fernández , a concert across Latin America. The following year, he was in Colombia at the Manacacías Summer Festival, many people from different parts of the country traveled to attend his concert. He had a significant participation in the 53rd International Song Festival of Viña del Mar, Chile, where he sang the song “¿Y cómo es él?” from his album “Iconos”. He received the highest distinction.
On March 3, 2012, Marc returned to Uruguay after 17 years and gave his performance at the Charrúa Stadium in Montevideo with an attendance of 25,000 spectators. In the GIGANT3S TOUR, he performed in several North American cities alongside Chayanne and Marco Antonio Solís . In 2013, he released his album 3.0. In 2014, he was the big winner of four of the five awards for which he was nominated at the Premios Lo Nuestro. Additionally, his career was recognized as one of the most successful Latin music artists. In 2016, he released a song called “Deja que te bese” with the collaboration of Spanish singer Alejandro Sanz, the song has over 50 million views on Youtube.
In September 2016, he carried out his “Marc Anthony Live” tour which included 5 dates at Radio City Music Hall. His private life has been somewhat controversial and has been exposed to various comments. He had his first daughter in 1994, Arianna Rosado-Muñiz, a product of his relationship with a former police officer from New York. In 2000 he married for the first time to Dayanara Torres, with whom he had two children. He later helped Jennifer Lopez in the production of the song “Sway” for the soundtrack of the movie Shall We Dance?. They then fell in love and after only one month of relationship, they got engaged in March 2004.
The couple had twins and Jennifer sold the exclusive photos of the children to People Magazine. However, after a few years, the couple decided to end their marriage on April 9, 2012. It is said that everything started when Jennifer Lopez met dancer Casper Smart and began a relationship with him two months after her separation from Marc. Later, Marc started a relationship with Venezuelan model Shannon de Lima, whom he married in 2014. Despite this, his relationship with Jennifer, the mother of his children, is harmonious, and he even participated in her song “Olvídame y pega la vuelta” in 2016. Two years earlier, the Puerto Rican singer made an impact with the hit song “Flor Pálida”.
On January 28, 2023, he married Nadia Ferreira in an incredible wedding surrounded by stars from film, music, and sports. The ceremony took place at the Perez Art Museum in Miami, with David Beckham as the best man.
Ver esta publicación en Instagram Una publicación compartida por Nadia Ferreira (@nadiatferreira)

Biography of Paul McCartney
Paul McCartney (born June 18, 1942) is a singer. He was born in Liverpool, England. His mother, Mary Patricia, was a nurse, while his father, James McCartney, was a volunteer firefighter. During Paul’s birth, his father was not present as he was fighting in the Battle of England during World War II. Paul grew up in a religious and strict environment, with his mother Catholic and his father Protestant, but later became agnostic. After returning from the war, his father devoted himself to selling cleaning products and, in his free time, played in bars.
Death of his mother
That’s why his son developed a deep love for music. He stood out in school for his intelligence and discipline and studied at Liverpool Institute secondary school, a good free secondary school. In 1954, he met George Harrison, with whom he quickly formed a strong friendship. At the time, McCartney’s mother was the one who kept the household and for work reasons they moved to Allerton, where they lived until 1964. On October 31, 1956, when McCartney was 14 years old, his mother died from a stroke.
After his mother’s death, McCartney was devastated. It took some time for him to return to normal. H is father saw music as a refuge to help his son feel better, so he took him to listen to the Jim Mac’s Jazz Band, where his father played trumpet or piano. He also gave him a trumpet, but when rock and roll became popular, he chose an acoustic guitar. The first song he composed was “I Lost My Little Girl” on that guitar, a Zenith. He also composed “When I’m Sixty-Four” on the home piano.
1957 – Met John Lennon
He met Lennon on July 6th, 1957. McCartney joined The Quarrymen, a school band led by Lennon, in 1958 as the lead guitarist. The band mixed rock and roll and skiffle, a popular music style, with jazz and blues. After several name changes, the band decided to call themselves The Beatles in August 1960 and recruited drummer Pete Best for their move to Hamburg. In 1961, one of its members, Sutcliffe, left the band and McCartney was forced to take over as bassist. They recorded as a backing band for English singer Tony Sheridan on the single My Bonnie.
1963 – “Beatlemania”
They managed to attract the attention of Brian Epstein, who became their manager in January 1962 and a key figure in their later success. With their first hit, “Love Me Do” in 1963, the “Beatlemania” began. John Lennon and Paul wrote a large number of songs together, but later their egos collided and they preferred to write separately. In 1970, The Beatles disbanded. But Paul continued his successful career with songs that reached number one. He recorded his first solo LP, “McCartney”, with songs very different from those that Lennon would write, with commercial melodies for varied tastes.
1980 – Paul McCartney Guinness Records
In 1980, he entered the Guinness Book of Records as the highest-selling songwriter in the world. His theme Yesterday , one of the most celebrated by The Beatles , has around 2,500 versions in the most diverse musical styles. Some of his solo hits are: Uncle Albert/Admiral Halsey, Live and Let Die for the James Bond film received the Oscar for best musical theme; Coming Up from his solo album Paul McCartney II. He joined George Martin and Ringo Starr in 1982 for the recording of Tug of War. On Press to play, his next album, was recorded with Eric Stewart.
Awards, arrest, record.
Winner of 18 Grammy Awards, including two Lifetime Achievement Grammy Awards (one with the Beatles and another as a solo artist). He is a vegetarian and an animal rights advocate. He was arrested for marijuana possession in Tokyo in 1980 and was briefly in jail. He participated in the “Live Aid” concert against hunger in Ethiopia in 1985. I n 1990, he achieved the record for the largest attendance at a concert with 184,000 people in Rio de Janeiro. Since 1997 he is Sir Paul McCartney, invested as a knight by Queen Elizabeth II.
2013 – Other awards, marriages.
On February 10, 2013, he received a Grammy for “Best Traditional Pop Album” for his album “Kisses On The Bottom”. Later, he received a special award from PRS for Music in commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the composition of his most famous song, “ Yesterday “. These songs, as well as “And I Love Her,” “You Will Not See Me,” and “I’m Looking Through You,” were written inspired by his relationship with British actress Jane Asher. After five years of engagement, the couple broke up due to his infidelity with Francie Schwartz. He married Linda Eastman on March 12, 1969, and together they formed the musical group Wings after the dissolution of the Beatles . In 1999, he presented his collection of poems entitled “Blackbird Singing: Poems and Lyrics (1965-1999)”. After the death of his wife, McCartney experienced deep sadness.
In 2002, Paul McCartney married former model Heather Mills in an Irish castle. After a long legal battle in the London Supreme Court, in 2008 Mills was authorized to collect one fifth of the 250 million dollars she had demanded from McCartney for their four-year marriage. In 2011, McCartney married Nancy Shevell in a civil ceremony in London on October 9th of that year.
Relevant aspects of his life and musical career
- With 60 gold records and the sale of over 100 million albums and singles as a solo artist and with The Beatles, McCartney is recognized as one of the most successful composers and artists of all time.
- As a solo artist in 1999 and as a member of The Beatles in 1988, he has been inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame twice.
- As a solo artist and with The Beatles, he has been recognized with twenty-one Grammy Awards.
- 32 of the songs that McCartney has written or co-written have reached number one on the Billboard Hot 100.
- As of 2014, he had sold over 15 million certified units by the RIAA in the United States.
- In 1997, McCartney was elevated to the rank of knight for his services to music.
- In 1965, McCartney, Lennon, Harrison and Starr were named members of the Order of the British Empire .
- He has been married three times and is the father of five children.
- He has participated in projects to help international charities related to issues such as animal rights, seal hunting, landmine cleaning, vegetarianism, poverty and musical education.
- He ranks 11th on Rolling Stone’s list of 100 Greatest Singers.
- He ranks first on Rolling Stone’s list of 100 Greatest Artists as a member of The Beatles.
- He ranks third on Rolling Stone’s list of 100 Greatest Bassists.
- Only surpassed by Bob Dylan , he ranks second on Rolling Stone’s list of 100 Greatest Songwriters.
Celebrities

Nicola Porcella
Nicola Porcella Biography Nicola Emilio Porcella Solimano (February 5, 1988), better known as Nicola Porcella, is an actor and TV...

Wendy Guevara
Wendy Guevara Biography Wendy Guevara Venegas (August 12, 1993), better known as Wendy Guevara, is an influencer, actress, singer, and...

Paris Hilton
Paris Hilton Biography Paris Whitney Hilton (February 17, 1981), better known as Paris Hilton, is a socialite, businesswoman, model, DJ,...

Leonardo DiCaprio
Biography of Leonardo DiCaprio Leonardo Wilhelm DiCaprio is a renowned actor and film producer who has won numerous awards within...

Denzel Washington
Biography of Denzel Washington Denzel Washington is an African American actor born on December 28, 1954 in Mount Vernon, New...

Biography of Ryan Reynolds Ryan Rodney Reynolds was born on October 23, 1976 in Vancouver, Canada, and he is a...

Biography of Brad Pitt William Bradley Pitt, better known as Brad Pitt, was born on December 18, 1963 in Shawnee,...
Entrepreneurs

Luciano Benetton
Luciano Benetton Biography Luciano Benetton (May 13, 1935) Born in Ponzano, Treviso, Italy. An Italian businessman and fashion designer, co-founder...

Louis Vuitton
Louis Vuitton Biography Louis Vuitton (August 4, 1821 – February 25, 1892) businessman and fashion designer. Founder of the leather...

Peter Drucker
Peter Drucker biography Peter Drucker (November 19, 1909 – November 11, 2005) writer, consultant, entrepreneur, and journalist. He was born...

Paul Allen biography Paul Gardner Allen (January 21, 1953) entrepreneur, business magnate, investor, and philanthropist. He was born in Seattle,...

Nik Powell biography Nik Powell (November 4, 1950) businessman and co-founder of the Virgin Group. He was born in Great...
Most Popular

Henri Fayol

Walt Disney

Taiichi Ohno

Philip B. Crosby

Kaoru Ishikawa

Ariana Grande

Adolf Hitler

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Excerpt from Violin Concerto in D Major, Opus 61, by Ludwig van Beethoven, with a pianist playing the orchestra's part. (more) Ludwig van Beethoven (baptized December 17, 1770, Bonn, archbishopric of Cologne [Germany]—died March 26, 1827, Vienna, Austria) German composer, the predominant musical figure in the transitional period between the ...
Birth Country: Germany. Gender: Male. Best Known For: Ludwig van Beethoven was a German composer whose Symphony 5 is a beloved classic. Some of his greatest works were composed while Beethoven was ...
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 1770 - 26 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire and span the transition from the Classical period to the Romantic era in classical music. Beethoven's career has conventionally been divided into ...
Beethoven Biography. Ludwig van Beethoven (1770 - 1827) is one of the most widely respected composers of classical music. He played a crucial role in the transition from classical to romantic music and is considered one of the greatest composers of all time. "Music is …. A higher revelation than all Wisdom and Philosophy".
Ludwig van Beethoven was born in Bonn, Germany, on 16 December 1770. His grandfather was the director of music ( Kapellmeister) to the Archbishop-Elector of Cologne at Bonn and his father, Johann van Beethoven (c. 1740-1792), worked at the same court as both an instrumentalist and tenor singer. Ludwig's mother was a head cook in the palace.
The first all-Beethoven concert at Carnegie Hall—given by the New York Philharmonic and conductor Anton Seidl on December 13, 1895 —celebrated the 125th anniversary of Beethoven's birth. Walter Damrosch and the New York Symphony Orchestra presented a Beethoven cycle in spring 1908 that included all nine symphonies.
Ludwig van Beethoven (1770-1827) was a German composer and pianist, who is arguably the defining figure in the history of Western music. Ludwig Van Beethoven was born in December 1770, but no-one is completely sure on which date. He was baptized on the 17th. The earliest recorded piece that Beethoven composed is a set of nine piano variations ...
Biography. Ludwig van Beethoven (1770-1827) was a German composer and pianist, who is arguably the defining figure in the history of Western music. ... Beethoven composed only one opera, Fidelio, which took years to get right. He re-wrote one aria no fewer than 18 times and came up with four different overtures before deciding upon the one he ...
Beethoven first publicly performed when he was eight years old. Kosovo and the Council of Europe adopted Beethoven's "Ode to Joy" as their anthems. After Napoleon crowned himself emperor of France, Beethoven erased a dedication to him so harshly that he ripped the manuscript. Beethoven's father advertised his son as the next musical child ...
Beethoven, Ludwig van, great German composer whose unsurpassed genius, expressed with supreme mastery in his syms., chamber music, concertos, and piano sonatas, revealing an extraordinary power of invention, marked a historic turn in the art of composition; b. Bonn, Dec. 15 or 16 (baptized, Dec. 17), 1770; d. Vienna, March 26, 1827.
Beethoven had seven sibings: Kaspar Anton Karl, Nikolaus Johann (pictured), Ludwig Maria, Maria Margarita, Anna Maria Francisca and Franz Georg van Beethoven, and Johann Peter Anton Leym. 4. Beethoven on the violin. As a young boy, Beethoven played the violin, often enjoying improvisation rather than reading the notes from a score.
Ludwig van Beethoven (1770-1827) was a German composer and pianist, widely regarded as one of the greatest composers in the history of Western classical music. Born in Bonn, Beethoven displayed exceptional musical talent from a young age.
Swafford says the Enlightenment idea embodied in the Declaration of Independence is that the aim of life is to serve your own needs and your own happiness. "But you can only do that in a free ...
Published September 29, 2020. 10 Revolutionary Beethoven Facts. Beethoven was born in December 1770 in Bonn, Germany. [6] Beethoven's father and grandfather were both performers in the state choir. [6] When Beethoven was 17, he performed for Mozart in Vienna. While no one is sure what was said, Mozart (who famously was unimpressed with other ...
Ludwig van Beethoven (December 16, 1770-March 26, 1827) was a German composer and musician. His work embraced a range of musical styles, from the classical to the romantic; although Beethoven composed music for a variety of settings, he is best known for his nine symphonies. His final symphony—featuring the "Ode to Joy" chorus—is one of ...
Ludwig van Beethoven is one of the most well-known composers close composerA person who writes music. of all time. He was born in 1770 in Germany and died in 1827. Beethoven started to go deaf at ...
Ludwig van Beethoven, a name synonymous with profound musical innovation, stands as one of the most influential composers in the annals of music history. Born in the late Classical period, his revolutionary compositions and personal resilience bridged the gap between the Classical and Romantic eras, reshaping the course of music.
Died At Age: 56. Family: father: Johann van Beethoven. mother: Maria Magdalena Keverich. siblings: Anna Maria Francisca van Beethoven, Franz Georg van Beethoven, Johann Peter Anton Leym, Kaspar Anton Karl van Beethoven, Ludwig Maria van Beethoven, Maria Margarita van Beethoven, Nikolaus Johann van Beethoven. Born Country: Germany.
Discover Ludwig van Beethoven facts through this Beethoven biography. Explore Beethoven's early life and the details of his career before and after becoming deaf. Updated: 11/21/2023
The composer Ludwig van Beethoven created some of the most influential music in history. He transformed many traditional forms of Western classical music . For example, he set new standards for the symphony, creating longer pieces that expressed important ideas and deep feelings rather than just serving as entertainment. His works include nine ...
Ludwig van Beethoven Facts. Here are the facts about the great composer - Beethoven (1770 - 1827). Real also the complete Beethoven Biography and the best of Beethoven works. Facts About Ludwig van Beethoven:
Ludwig Van Beethoven Biography Ludwig Van Beethoven was a composer, pianist, and conductor, born in Bonn, Germany in 1770. Beethoven was baptized on December 17, 1770, which is why historians place his birth a day earlier, on December 16 of 1770. Ludwig Van Beethoven has been considered the greatest composer of all time by many specialized […]
1. Beethoven was Forced to into Music. Beethoven's father, Johann van Beethoven, knew his son enjoyed playing the piano so, he took it upon himself to try to create a prodigy - like Mozart. It didn't matter what time, night or day, Beethoven was forced to practice until he could reach the prodigy level.