Seventy-Five Scientific Research Projects You Can Contribute to Online
From astrophysicists to entomologists, many researchers need the help of citizen scientists to sift through immense data collections
:focal(300x157:301x158)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/e2/ca/e2ca665f-77b7-4ba2-8cd2-46f38cbf2b60/citizen_science_mobile.png)
Rachael Lallensack
Former Assistant Editor, Science and Innovation
If you find yourself tired of streaming services, reading the news or video-chatting with friends, maybe you should consider becoming a citizen scientist. Though it’s true that many field research projects are paused , hundreds of scientists need your help sifting through wildlife camera footage and images of galaxies far, far away, or reading through diaries and field notes from the past.
Plenty of these tools are free and easy enough for children to use. You can look around for projects yourself on Smithsonian Institution’s citizen science volunteer page , National Geographic ’s list of projects and CitizenScience.gov ’s catalog of options. Zooniverse is a platform for online-exclusive projects , and Scistarter allows you to restrict your search with parameters, including projects you can do “on a walk,” “at night” or “on a lunch break.”
To save you some time, Smithsonian magazine has compiled a collection of dozens of projects you can take part in from home.
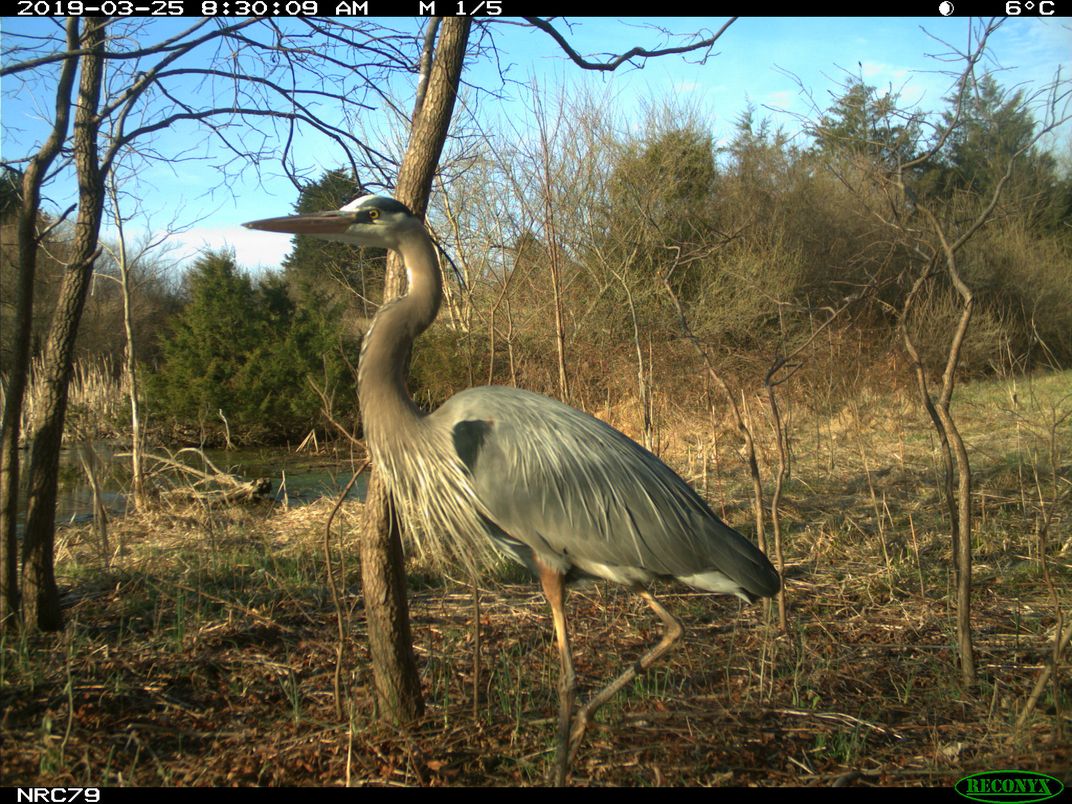


American Wildlife
If being home has given you more time to look at wildlife in your own backyard, whether you live in the city or the country, consider expanding your view, by helping scientists identify creatures photographed by camera traps. Improved battery life, motion sensors, high-resolution and small lenses have made camera traps indispensable tools for conservation.These cameras capture thousands of images that provide researchers with more data about ecosystems than ever before.
Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute’s eMammal platform , for example, asks users to identify animals for conservation projects around the country. Currently, eMammal is being used by the Woodland Park Zoo ’s Seattle Urban Carnivore Project, which studies how coyotes, foxes, raccoons, bobcats and other animals coexist with people, and the Washington Wolverine Project, an effort to monitor wolverines in the face of climate change. Identify urban wildlife for the Chicago Wildlife Watch , or contribute to wilderness projects documenting North American biodiversity with The Wilds' Wildlife Watch in Ohio , Cedar Creek: Eyes on the Wild in Minnesota , Michigan ZoomIN , Western Montana Wildlife and Snapshot Wisconsin .
"Spend your time at home virtually exploring the Minnesota backwoods,” writes the lead researcher of the Cedar Creek: Eyes on the Wild project. “Help us understand deer dynamics, possum populations, bear behavior, and keep your eyes peeled for elusive wolves!"
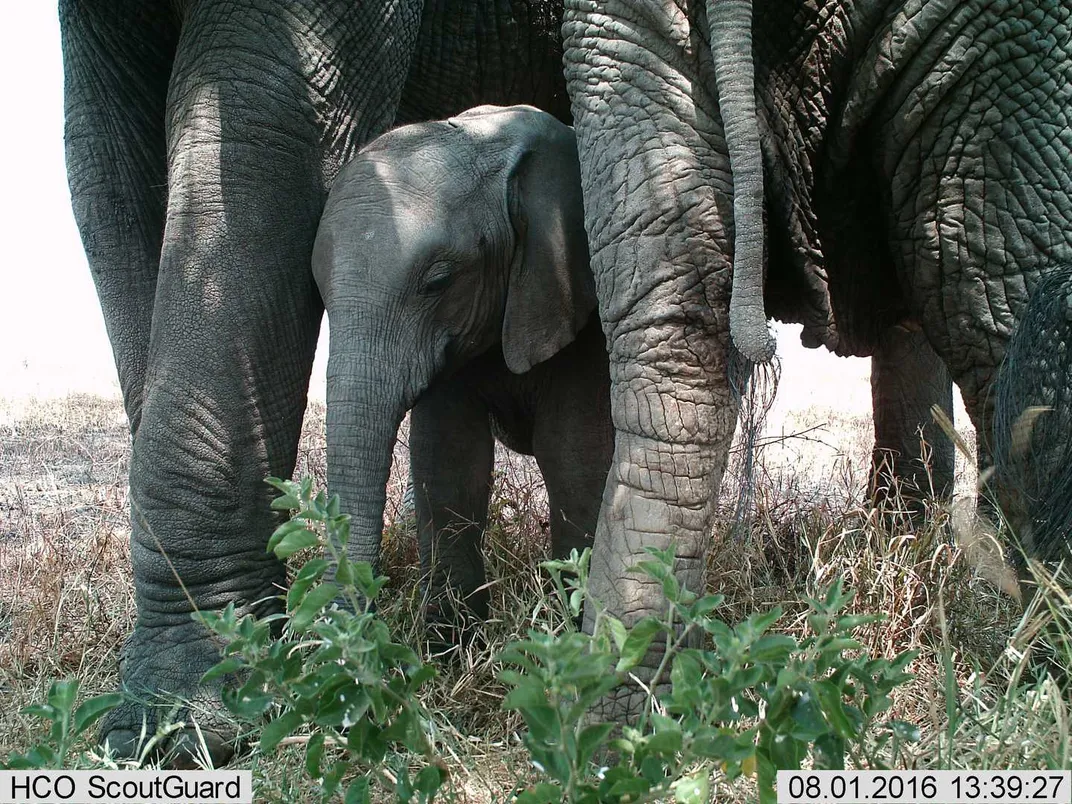

If being cooped up at home has you daydreaming about traveling, Snapshot Safari has six active animal identification projects. Try eyeing lions, leopards, cheetahs, wild dogs, elephants, giraffes, baobab trees and over 400 bird species from camera trap photos taken in South African nature reserves, including De Hoop Nature Reserve and Madikwe Game Reserve .
With South Sudan DiversityCam , researchers are using camera traps to study biodiversity in the dense tropical forests of southwestern South Sudan. Part of the Serenegeti Lion Project, Snapshot Serengeti needs the help of citizen scientists to classify millions of camera trap images of species traveling with the wildebeest migration.
Classify all kinds of monkeys with Chimp&See . Count, identify and track giraffes in northern Kenya . Watering holes host all kinds of wildlife, but that makes the locales hotspots for parasite transmission; Parasite Safari needs volunteers to help figure out which animals come in contact with each other and during what time of year.
Mount Taranaki in New Zealand is a volcanic peak rich in native vegetation, but native wildlife, like the North Island brown kiwi, whio/blue duck and seabirds, are now rare—driven out by introduced predators like wild goats, weasels, stoats, possums and rats. Estimate predator species compared to native wildlife with Taranaki Mounga by spotting species on camera trap images.
The Zoological Society of London’s (ZSL) Instant Wild app has a dozen projects showcasing live images and videos of wildlife around the world. Look for bears, wolves and lynx in Croatia ; wildcats in Costa Rica’s Osa Peninsula ; otters in Hampshire, England ; and both black and white rhinos in the Lewa-Borana landscape in Kenya.
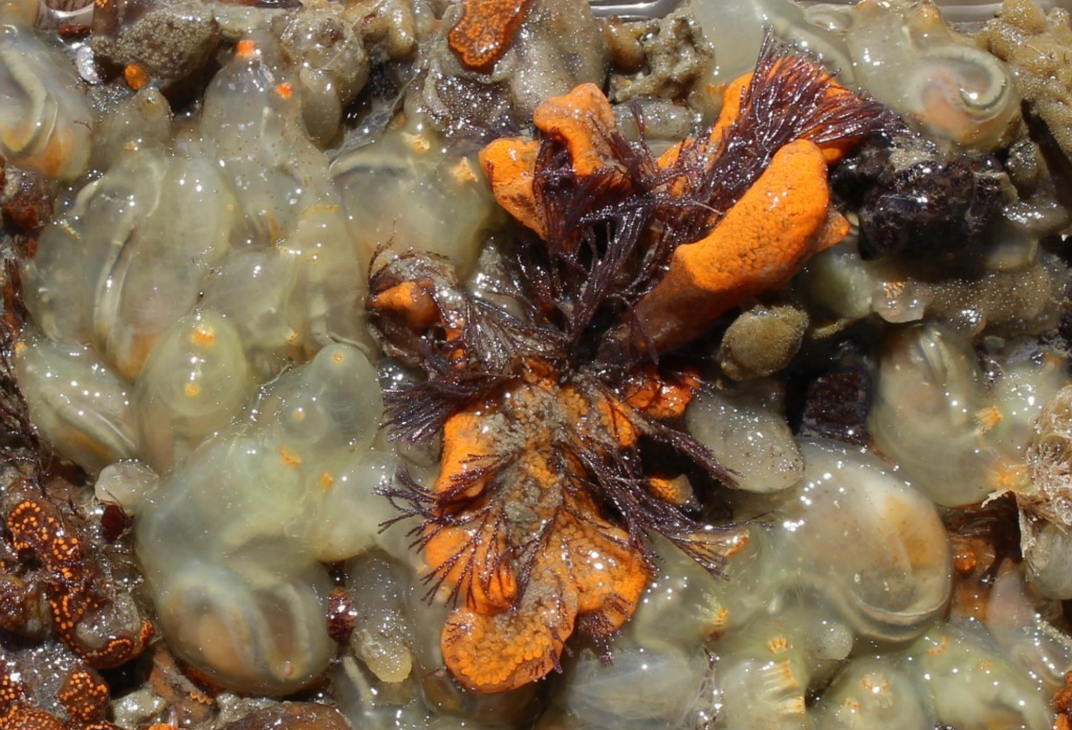

Under the Sea
Researchers use a variety of technologies to learn about marine life and inform conservation efforts. Take, for example, Beluga Bits , a research project focused on determining the sex, age and pod size of beluga whales visiting the Churchill River in northern Manitoba, Canada. With a bit of training, volunteers can learn how to differentiate between a calf, a subadult (grey) or an adult (white)—and even identify individuals using scars or unique pigmentation—in underwater videos and images. Beluga Bits uses a “ beluga boat ,” which travels around the Churchill River estuary with a camera underneath it, to capture the footage and collect GPS data about the whales’ locations.
Many of these online projects are visual, but Manatee Chat needs citizen scientists who can train their ear to decipher manatee vocalizations. Researchers are hoping to learn what calls the marine mammals make and when—with enough practice you might even be able to recognize the distinct calls of individual animals.
Several groups are using drone footage to monitor seal populations. Seals spend most of their time in the water, but come ashore to breed. One group, Seal Watch , is analyzing time-lapse photography and drone images of seals in the British territory of South Georgia in the South Atlantic. A team in Antarctica captured images of Weddell seals every ten minutes while the seals were on land in spring to have their pups. The Weddell Seal Count project aims to find out what threats—like fishing and climate change—the seals face by monitoring changes in their population size. Likewise, the Año Nuevo Island - Animal Count asks volunteers to count elephant seals, sea lions, cormorants and more species on a remote research island off the coast of California.
With Floating Forests , you’ll sift through 40 years of satellite images of the ocean surface identifying kelp forests, which are foundational for marine ecosystems, providing shelter for shrimp, fish and sea urchins. A project based in southwest England, Seagrass Explorer , is investigating the decline of seagrass beds. Researchers are using baited cameras to spot commercial fish in these habitats as well as looking out for algae to study the health of these threatened ecosystems. Search for large sponges, starfish and cold-water corals on the deep seafloor in Sweden’s first marine park with the Koster seafloor observatory project.
The Smithsonian Environmental Research Center needs your help spotting invasive species with Invader ID . Train your eye to spot groups of organisms, known as fouling communities, that live under docks and ship hulls, in an effort to clean up marine ecosystems.
If art history is more your speed, two Dutch art museums need volunteers to start “ fishing in the past ” by analyzing a collection of paintings dating from 1500 to 1700. Each painting features at least one fish, and an interdisciplinary research team of biologists and art historians wants you to identify the species of fish to make a clearer picture of the “role of ichthyology in the past.”
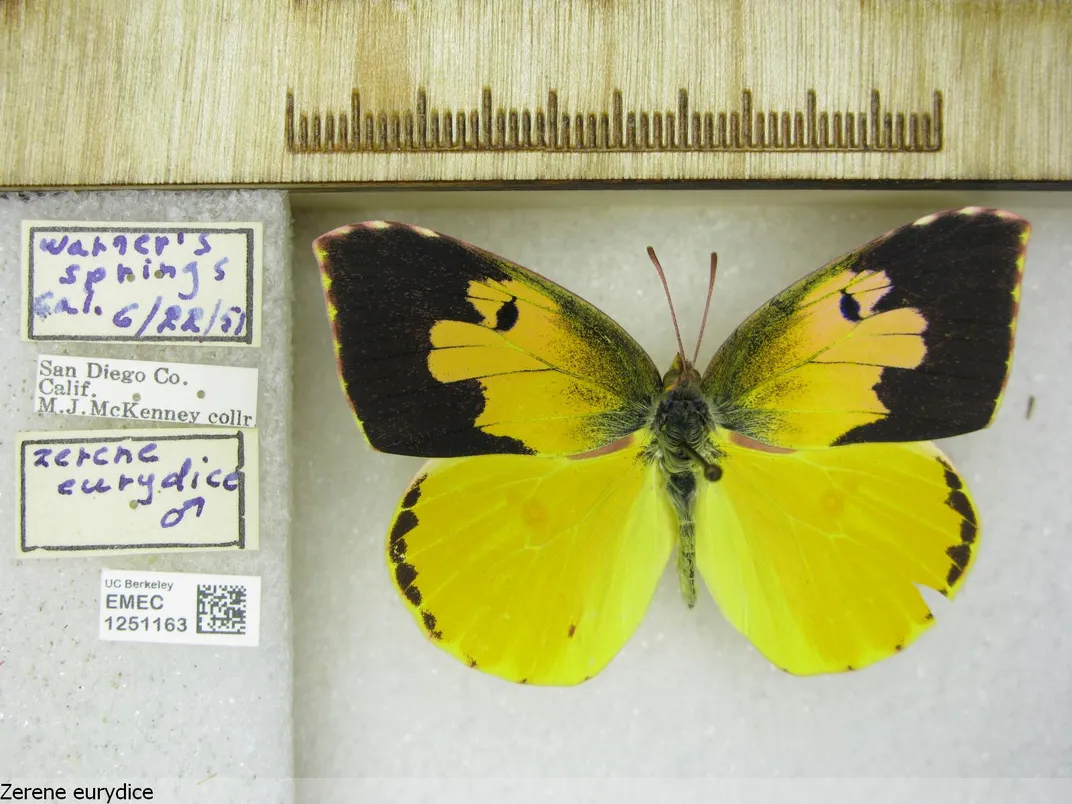

Interesting Insects
Notes from Nature is a digitization effort to make the vast resources in museums’ archives of plants and insects more accessible. Similarly, page through the University of California Berkeley’s butterfly collection on CalBug to help researchers classify these beautiful critters. The University of Michigan Museum of Zoology has already digitized about 300,000 records, but their collection exceeds 4 million bugs. You can hop in now and transcribe their grasshopper archives from the last century . Parasitic arthropods, like mosquitos and ticks, are known disease vectors; to better locate these critters, the Terrestrial Parasite Tracker project is working with 22 collections and institutions to digitize over 1.2 million specimens—and they’re 95 percent done . If you can tolerate mosquito buzzing for a prolonged period of time, the HumBug project needs volunteers to train its algorithm and develop real-time mosquito detection using acoustic monitoring devices. It’s for the greater good!
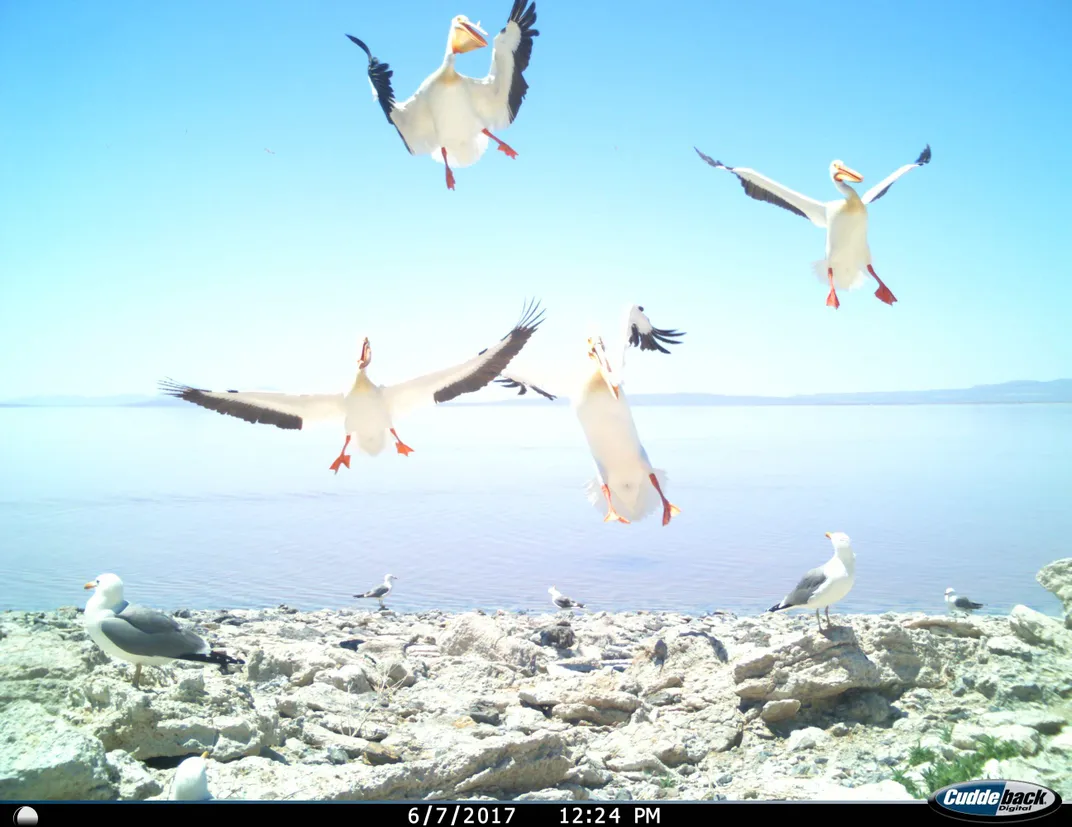

For the Birders
Birdwatching is one of the most common forms of citizen science . Seeing birds in the wilderness is certainly awe-inspiring, but you can birdwatch from your backyard or while walking down the sidewalk in big cities, too. With Cornell University’s eBird app , you can contribute to bird science at any time, anywhere. (Just be sure to remain a safe distance from wildlife—and other humans, while we social distance ). If you have safe access to outdoor space—a backyard, perhaps—Cornell also has a NestWatch program for people to report observations of bird nests. Smithsonian’s Migratory Bird Center has a similar Neighborhood Nest Watch program as well.
Birdwatching is easy enough to do from any window, if you’re sheltering at home, but in case you lack a clear view, consider these online-only projects. Nest Quest currently has a robin database that needs volunteer transcribers to digitize their nest record cards.
You can also pitch in on a variety of efforts to categorize wildlife camera images of burrowing owls , pelicans , penguins (new data coming soon!), and sea birds . Watch nest cam footage of the northern bald ibis or greylag geese on NestCams to help researchers learn about breeding behavior.
Or record the coloration of gorgeous feathers across bird species for researchers at London’s Natural History Museum with Project Plumage .

Pretty Plants
If you’re out on a walk wondering what kind of plants are around you, consider downloading Leafsnap , an electronic field guide app developed by Columbia University, the University of Maryland and the Smithsonian Institution. The app has several functions. First, it can be used to identify plants with its visual recognition software. Secondly, scientists can learn about the “ the ebb and flow of flora ” from geotagged images taken by app users.
What is older than the dinosaurs, survived three mass extinctions and still has a living relative today? Ginko trees! Researchers at Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History are studying ginko trees and fossils to understand millions of years of plant evolution and climate change with the Fossil Atmospheres project . Using Zooniverse, volunteers will be trained to identify and count stomata, which are holes on a leaf’s surface where carbon dioxide passes through. By counting these holes, or quantifying the stomatal index, scientists can learn how the plants adapted to changing levels of carbon dioxide. These results will inform a field experiment conducted on living trees in which a scientist is adjusting the level of carbon dioxide for different groups.
Help digitize and categorize millions of botanical specimens from natural history museums, research institutions and herbaria across the country with the Notes from Nature Project . Did you know North America is home to a variety of beautiful orchid species? Lend botanists a handby typing handwritten labels on pressed specimens or recording their geographic and historic origins for the New York Botanical Garden’s archives. Likewise, the Southeastern U.S. Biodiversity project needs assistance labeling pressed poppies, sedums, valerians, violets and more. Groups in California , Arkansas , Florida , Texas and Oklahoma all invite citizen scientists to partake in similar tasks.
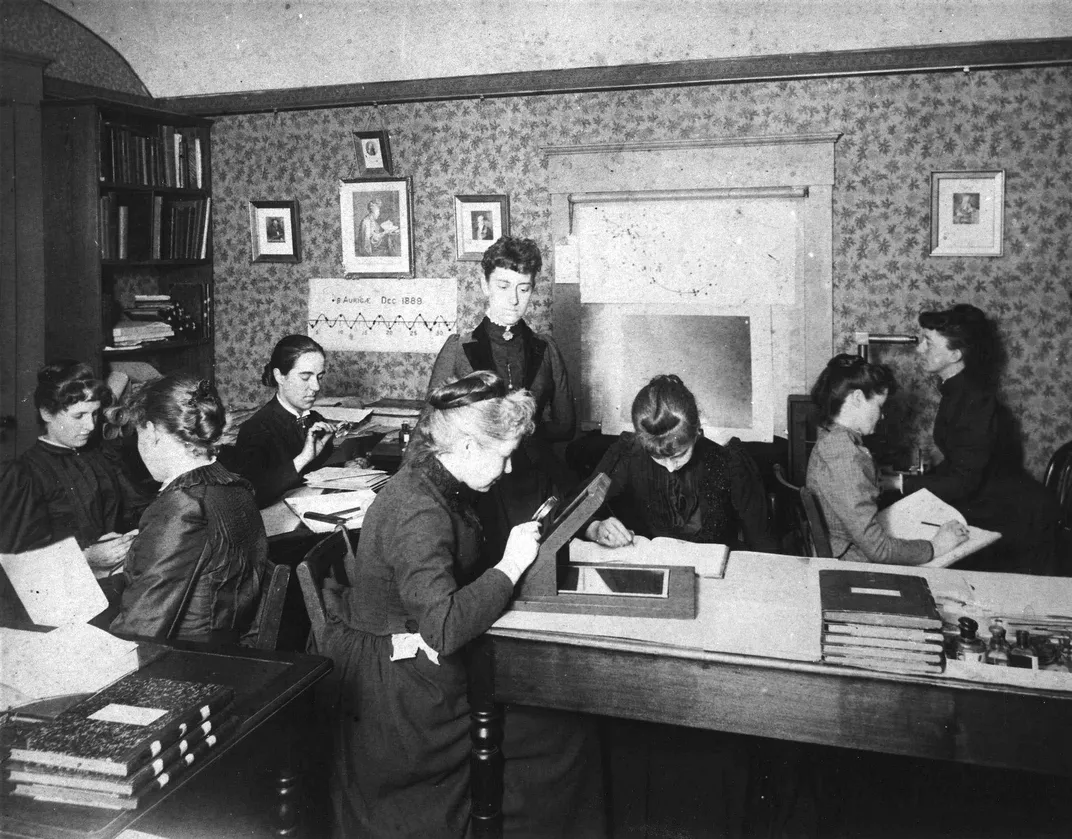

Historic Women in Astronomy
Become a transcriber for Project PHaEDRA and help researchers at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics preserve the work of Harvard’s women “computers” who revolutionized astronomy in the 20th century. These women contributed more than 130 years of work documenting the night sky, cataloging stars, interpreting stellar spectra, counting galaxies, and measuring distances in space, according to the project description .
More than 2,500 notebooks need transcription on Project PhaEDRA - Star Notes . You could start with Annie Jump Cannon , for example. In 1901, Cannon designed a stellar classification system that astronomers still use today. Cecilia Payne discovered that stars are made primarily of hydrogen and helium and can be categorized by temperature. Two notebooks from Henrietta Swan Leavitt are currently in need of transcription. Leavitt, who was deaf, discovered the link between period and luminosity in Cepheid variables, or pulsating stars, which “led directly to the discovery that the Universe is expanding,” according to her bio on Star Notes .
Volunteers are also needed to transcribe some of these women computers’ notebooks that contain references to photographic glass plates . These plates were used to study space from the 1880s to the 1990s. For example, in 1890, Williamina Flemming discovered the Horsehead Nebula on one of these plates . With Star Notes, you can help bridge the gap between “modern scientific literature and 100 years of astronomical observations,” according to the project description . Star Notes also features the work of Cannon, Leavitt and Dorrit Hoffleit , who authored the fifth edition of the Bright Star Catalog, which features 9,110 of the brightest stars in the sky.
Microscopic Musings
Electron microscopes have super-high resolution and magnification powers—and now, many can process images automatically, allowing teams to collect an immense amount of data. Francis Crick Institute’s Etch A Cell - Powerhouse Hunt project trains volunteers to spot and trace each cell’s mitochondria, a process called manual segmentation. Manual segmentation is a major bottleneck to completing biological research because using computer systems to complete the work is still fraught with errors and, without enough volunteers, doing this work takes a really long time.
For the Monkey Health Explorer project, researchers studying the social behavior of rhesus monkeys on the tiny island Cayo Santiago off the southeastern coast of Puerto Rico need volunteers to analyze the monkeys’ blood samples. Doing so will help the team understand which monkeys are sick and which are healthy, and how the animals’ health influences behavioral changes.
Using the Zooniverse’s app on a phone or tablet, you can become a “ Science Scribbler ” and assist researchers studying how Huntington disease may change a cell’s organelles. The team at the United Kingdom's national synchrotron , which is essentially a giant microscope that harnesses the power of electrons, has taken highly detailed X-ray images of the cells of Huntington’s patients and needs help identifying organelles, in an effort to see how the disease changes their structure.
Oxford University’s Comprehensive Resistance Prediction for Tuberculosis: an International Consortium—or CRyPTIC Project , for short, is seeking the aid of citizen scientists to study over 20,000 TB infection samples from around the world. CRyPTIC’s citizen science platform is called Bash the Bug . On the platform, volunteers will be trained to evaluate the effectiveness of antibiotics on a given sample. Each evaluation will be checked by a scientist for accuracy and then used to train a computer program, which may one day make this process much faster and less labor intensive.
Out of This World
If you’re interested in contributing to astronomy research from the comfort and safety of your sidewalk or backyard, check out Globe at Night . The project monitors light pollution by asking users to try spotting constellations in the night sky at designated times of the year . (For example, Northern Hemisphere dwellers should look for the Bootes and Hercules constellations from June 13 through June 22 and record the visibility in Globe at Night’s app or desktop report page .)
For the amateur astrophysicists out there, the opportunities to contribute to science are vast. NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mission is asking for volunteers to search for new objects at the edges of our solar system with the Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 project .
Galaxy Zoo on Zooniverse and its mobile app has operated online citizen science projects for the past decade. According to the project description, there are roughly one hundred billion galaxies in the observable universe. Surprisingly, identifying different types of galaxies by their shape is rather easy. “If you're quick, you may even be the first person to see the galaxies you're asked to classify,” the team writes.
With Radio Galaxy Zoo: LOFAR , volunteers can help identify supermassive blackholes and star-forming galaxies. Galaxy Zoo: Clump Scout asks users to look for young, “clumpy” looking galaxies, which help astronomers understand galaxy evolution.
If current events on Earth have you looking to Mars, perhaps you’d be interested in checking out Planet Four and Planet Four: Terrains —both of which task users with searching and categorizing landscape formations on Mars’ southern hemisphere. You’ll scroll through images of the Martian surface looking for terrain types informally called “spiders,” “baby spiders,” “channel networks” and “swiss cheese.”
Gravitational waves are telltale ripples in spacetime, but they are notoriously difficult to measure. With Gravity Spy , citizen scientists sift through data from Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, or LIGO , detectors. When lasers beamed down 2.5-mile-long “arms” at these facilities in Livingston, Louisiana and Hanford, Washington are interrupted, a gravitational wave is detected. But the detectors are sensitive to “glitches” that, in models, look similar to the astrophysical signals scientists are looking for. Gravity Spy teaches citizen scientists how to identify fakes so researchers can get a better view of the real deal. This work will, in turn, train computer algorithms to do the same.
Similarly, the project Supernova Hunters needs volunteers to clear out the “bogus detections of supernovae,” allowing researchers to track the progression of actual supernovae. In Hubble Space Telescope images, you can search for asteroid tails with Hubble Asteroid Hunter . And with Planet Hunters TESS , which teaches users to identify planetary formations, you just “might be the first person to discover a planet around a nearby star in the Milky Way,” according to the project description.
Help astronomers refine prediction models for solar storms, which kick up dust that impacts spacecraft orbiting the sun, with Solar Stormwatch II. Thanks to the first iteration of the project, astronomers were able to publish seven papers with their findings.
With Mapping Historic Skies , identify constellations on gorgeous celestial maps of the sky covering a span of 600 years from the Adler Planetarium collection in Chicago. Similarly, help fill in the gaps of historic astronomy with Astronomy Rewind , a project that aims to “make a holistic map of images of the sky.”
Get the latest Science stories in your inbox.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/rachael.png)
Rachael Lallensack | READ MORE
Rachael Lallensack is the former assistant web editor for science and innovation at Smithsonian .
- Open access
- Published: 21 January 2022
Behind every great research project is great data management
- Samantha Kanza ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4831-9489 1 na1 &
- Nicola J. Knight ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8286-3835 1 na1
BMC Research Notes volume 15 , Article number: 20 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
11k Accesses
8 Citations
24 Altmetric
Metrics details
Research data management (RDM) is the cornerstone of a successful research project, and yet it often remains an underappreciated art that gets overlooked in the hustle and bustle of everyday project management even when required by funding bodies. If researchers are to strive for reproducible science that adheres to the principles of FAIR, then they need to manage the data associated with their research projects effectively. It is imperative to plan your RDM strategies early on, and setup your project organisation before embarking on the work. There are several different factors to consider: data management plans, data organisation and storage, publishing and sharing your data, ensuring reproducibility and adhering to data standards. Additionally it is important to reflect upon the ethical implications that might need to be planned for, and adverse issues that may need a mitigation strategy. This short article discusses these different areas, noting some best practices and detailing how to incorporate these strategies into your work. Finally, the article ends with a set of top ten tips for effective research data management.
Introduction
A research project without proper research data management (RDM) is akin to building a house without laying the foundations. Good RDM is critical to the success of a research project; however, it is an element that is often neglected even when required by funding bodies. Planning your RDM needs to take into account not just the current moment, but considering how you will look back on your information in several years or how you might be able to share the information with colleagues, possibly across multiple disciplines, in a form that they can easily understand. There are many aspects involved in the data research lifecycle that will help a research project and its data to be findable, accessible, interoperable and re-useable (FAIR) [ 1 ]. In this short article we are going to discuss some of the key areas involved in RDM including: Organising, storing and sharing your data, creating data management plans and ensuring that any research conducted is both ethical and reproducible. We discuss why these areas are important and how they might be incorporated in your work and conclude with a list of our top ten tips for how to manage your research data.
Data organisation and storage
How you organise and store your data will shape your capacity to find, manage, publish and re-use it at a later date [ 2 ]. The first person likely to benefit from a sensible organisational system is your future self. Using sensible easy to follow folder and file structures will enable you to easily locate different pieces of your data. Just randomly naming files and putting in a haphazard folder structure will not benefit either you or anyone looking to use your data in the future. Another potential consideration is being aware of restrictions on where you are permitted to store your research data, such as institutional requirements or specific collaborator requirements related to security and international transfer of data.
This should be something that you think about at the very beginning of your work, as it is much simpler to add to an existing structure than having to go back and rework years of files at the end of the project (if you can even remember what each file referred to). If you are storing lots of similar types of data then you might want to consider making template folders that you can use each time you create a new dataset. When working in a collaborative research project it is also important that the organisational strategies are agreed upon as a group at the start to ensure consistency across the team with respect to both where and how team members are storing and organising the project data.
It is also worth identifying which aspects of your data you will need to store for the short term and long term, and how you are going to store the data. Further, it is worth considering the trade-off between data storage and recreating data, as data that is expensive to store but easy to re-create doesn’t necessarily need to be stored [ 3 ].
If your data is being produced in a proprietary format, then you need to work out how to store it in an accessible way that you and others can use it later down the line even if you don’t have access to the software that produced it. One way of ensuring the longevity of your data is to save it in a .txt file, meaning that even if the proprietary files become unusable, the data still remains in a readable and editable format. However, this strategy should only be employed alongside saving the data in the original data formats as opposed to relying on this as the primary storage method. Additionally, when doing this, it is important to supply context alongside the data potentially in the form of a README data description file or as additional metadata as merely saving the data in raw text files isn’t very helpful when it comes to sharing or understanding it later down the line.
It is also worth remembering that if you are working on collaborative research projects, then a key aspect of organising your data is communication. Even with the most organised group members, projects and data cannot be effectively managed unless all group members are communicating and have agreed on who is doing what with the different pieces of data [ 4 ]. The more data, and the more complex the data, the more time you need to devote to planning the organisation and communication of the data.
Data management
Poor data management can lead to data breaches and subsequently, unsuccessful and potentially harmful research projects. Managing your data well and planning how to achieve this from the start is absolutely key to a successful research project and is often a requirement of Research Application Funding Bodies. In order to achieve this, a Data Management Plan (DMP) should be created which outlines how the data is going to be managed throughout the entire project lifecycle. Many universities have their own internal resources for creating these plans, but there are also templates available from DMP Online [ 5 ].
A DMP should be an active document that is referred to throughout the project and used to measure whether it is on track. It is essential that these documents are updated throughout the project to reflect any changes, and data managers should be consulted with respect to the DMP throughout the entire project lifecycle, rather than only at the beginning. Further, in collaborative data projects these plans become even more essential as all group members should be collecting and handling data in the same way.
Another core aspect of data management is version control. All the work associated with a research project should be backed up, but versions should also be kept such that changes can be recorded and documents or data can be rolled back to a previous version if necessary. There are a number of ways to version data depending on the nature of the data and the project teams expertise. There are version control systems such as GitHub [ 6 ] for code or datasets. For documents, you can use integrated track changes, alternatively separate files can be created with version numbers, or version control tables can be added at the top of documents to record in document changes.
Data publication and sharing
Publishing your data and making it shareable is an important outcome for any successful research project. Ultimately it is desirable to disseminate the useful and relevant outputs of a research project to those who might be interested in reading or using them. It is important to give careful consideration to what parts of the project are published, and where they are published. Ultimately, the choice of what to publish and where to publish might be a requirement of the research funding, in which case that should be adhered to. If there is no specific data mandate, then publishing data in an open access repository that is relevant and well used within the research domain is advisable.
Data should always be published with suitable metadata, README files, and it should adhere to the FAIR standards of being findable, accessible, interoperable and re-useable [ 1 ]. Ideally, the datasets would have their own DOI and would be published under a license that enables their re-use. When considering what extent of the data and descriptions to publish, it is worth establishing what level of data (and methods) needs to be shared in order for the project results to be reproduced. Depending on the nature of your data (e.g. if it contains any sensitive or personal data) it may be necessary to anonymise and or aggregate the data before making it available [ 7 ].
Data reproducibility
Reproducibility (or the lack thereof) is a significant problem in scientific research in the 21st Century, as in order to allow other scientists to assess your work and also use it in the advancement of scientific knowledge it is crucial that the work can be reproduced. There are unfortunately a large number of peer reviewed scientific studies that are not reproducible [ 8 , 9 ], which could be due to lack of availability of raw data, poor methodological explanations, missing data, and a number of other considerations. There are so many factors, parameters and methods that can be used on data, right from the point of acquisition, through analysis, up to the visualisation of outputs. All of these changes can affect the data findings, and it essential that these are all captured alongside the data if it is to stand a chance of being reproducible.
There are a number of steps that can be taken to aid with facilitating reproducibility. One of the crucial elements in reproducibility is sharing your data provenance, that could be pointing researchers to specific datasets, if using existing data, or your detailed protocols if you collected the data yourself. It is also becoming increasingly important to share your code and detailed methods alongside the data used in the analysis, as this enables other researchers to understand the processes that were undertaken and attempt to reproduce them. It is worth considering using an electronic lab notebook (ELN) System or a notebook that can combine commentary and analysis code such as Jupyter Notebooks [ 10 ]. Additionally, using version control systems for your documents and code will allow others to see any changes that you have made, and specific versions can be viewed and used. Ultimately, if you yourself could not reproduce the project results from the data and documents that you have shared, then you cannot expect another researcher to be able to. This is something that should be considered and evaluated before finalising what data to share.
- Data ethics
Data ethics is another vital aspect of responsible research. In most jurisdictions any study that involves humans (whether through direct data generation, the use of their tissue/cells, or the use of their previously generated data e.g. tweets or online contributions) will need specific ethics approval [ 11 ], but ethical considerations should apply generally as well.
The core requirements of an ethics application are to lay out the purposes of the study, what data you are collecting and why, and to ensure that participants are fully informed about their involvement [ 12 ]. Consent needs to be obtained from any active participants (and that includes the researchers themselves), and researchers need to make a data protection plan and devise a risk assessment to ensure that the research is being conducted safely, with mitigated risks, and that the data collected is going to be adequately protected.
If you are working with personal data then there are ethical considerations around collection of the appropriate amount of data to collect and ensuring that it is anonymised as soon as possible. It is also worth remembering that, even when projects are not working with personal data there are ethical considerations around the potential effects of your research and possible unintended consequences to the communities involved [ 13 ].
The biggest piece of advice that we can give to improve your data management is start early! Don’t leave thinking about this until the project wraps up, or when writing up your results, think about it when you start out, and continue to evolve this as your project matures. Don’t be afraid to ask for advice, as there is lots of expertise out there, and remember that changes can always be made. It is obviously preferable to start out with an optimum data management plan, but it is much better to change a system that isn’t working or to make improvements than to just stick to a plan that isn’t working. Making small steps towards better overall data handling is better than not taking any steps.
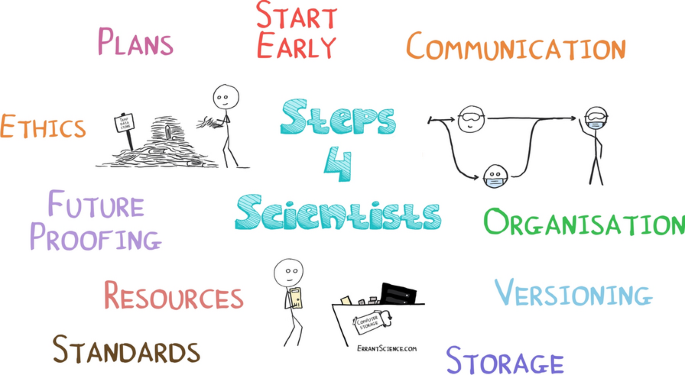
Top ten tips for good research data management
To help with this here are our top ten tips for good research data management as shown in Fig. 1 .
Start early: Plan your data management strategy right from the start, think about every aspect of your project from the data collection, organisation, storage, and even where you are planning on publishing and sharing the results.
Data management plan: Make one of these right at the beginning and refer to it and improve it throughout the entire project life cycle.
Organisation is key: Use sensible folder/file structures that have been agreed with the entire team.
Version control your work: Decide on what version control systems you are going to use and implement these plans from the beginning.
Storage strategy: Consider your long term and short term data storage. And implement the 321 data storage rule: (3 copies of the data, within 2 types of media, with 1 stored at a separate site), and NEVER rely on USB sticks.
Remember your standards and be FAIR: Think about what standards you are going to make your data available in. Data should be Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Re-useable.
Consider ethics: If you are interacting with human data in any way, you will need ethics! These applications can take a while to write and obtain approval for, so start straight away!
Factor in resources: Time and costs should be factored in for all required resources, including your data management!
Future proof your data: Metadata alone will not future proof your data, you should get DOI’s for your datasets and include relevant README’s and description files.
Communicate: If you are working on collaborative research projects then communication is key both in setting up the initial organisational strategies, and throughout the entire project life cycle to ensure that team members are working consistently with respect to data collection, organisation, storage etc.
These tips and the content of this article was collated from our own research, and through the results of running our “Failed it to Nailed it Getting Data Sharing Right” and “Skills4Scientists” series. More information on these series including links to videos can be found here: http://www.ai3sd.org/fi2ni and http://www.ai3sd.org/s4s .
Availability of data and materials
These tips and the content of this article was collated from our own research, and through the results of running our “Failed it to Nailed it Getting Data Sharing Right” and “Skills4Scientists” series. All referenced videos have already been published on YouTube and deposited in the Southampton ePrints repository with a CC-BY 4.0 License. More information on these series including links to videos can be found here: http://www.ai3sd.org/fi2ni and http://www.ai3sd.org/s4s .
Abbreviations
- Research data management
Findable, accessible, interoperable, reusable
Data management plan
Digital object identifier
Electronic lab notebook
Wilkinson MD, Dumontier M, Aalbersberg IJ, Appleton G, Axton M, Baak A, Blomberg N, Boiten J-W, da Silva Santos LB, Bourne PE, Bouwman J, Brookes AJ, Clark T, Crosas M, Dillo I, Dumon O, Edmunds S, Evelo CT, Finkers R, Gonzalez-Beltran A, Gray AJG, Groth P, Goble C, Grethe JS, Heringa J, ’t Hoen PAC, Hooft R, Kuhn T, Kok R, Kok J, Lusher SJ, Martone ME, Mons A, Packer AL, Persson B, Rocca-Serra P, Roos M, van Schaik R, Sansone S-A, Schultes E, Sengstag T, Slater T, Strawn G, Swertz MA, Thompson M, van der Lei J, van Mulligen E, Velterop J, Waagmeester A, Wittenburg P, Wolstencroft K, Zhao J, Mons B. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci Data. 2016;3(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.18 .
Article Google Scholar
Kanza S, Knight N. Failed it to nailed it! Getting data sharing right: event 1 report - dealing with data: tips and tricks. University of Southampton; 2020. p. 16. https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0032 . https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/445061/ . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
Stark I. AI3SD video: love notes to the future: the importance of metadata. In: Kanza S, Frey JG, Hooper V, Knight N, editors. 2020. https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0067 . https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/447529/ . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
Kanza S. AI3SD video: collaborative data management. In: Knight N, Frey JG, editors. 2021. https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0115 . https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/450268/ . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
DMPonline. https://dmponline.dcc.ac.uk/ . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
GitHub: where the world builds software. https://github.com/ . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
Kanza S, Knight N. Failed it to nailed it! Getting data sharing right: event 3 report—responsible data management. University of Southampton; 2020. p. 40. https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0034 . https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/447534/ . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
McNutt M. Reproducibility. Science. 2014;343(6168):229–229. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1250475 .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Miyakawa T. No raw data, no science: another possible source of the reproducibility crisis. Mol Brain. 2020;13(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-020-0552-2 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Project Jupyter. https://www.jupyter.org . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
Craigon P. AI3SD video: intro to ethics. In: Kanza S, Frey JG, Knight N, editors. 2021. https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0147 . https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/451137/ . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
Kanza S. AI3SD video: writing an ethics application. In: Frey JG, Knight N, editors. 2021. https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0148 . https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/451154/ . Accessed 13 Oct 2021.
Kanza S, Knight N. Failed it to nailed it! Getting data sharing right: event 2 report - data standards. University of Southampton; 2020. p. 23. https://doi.org/10.5258/SOTON/P0033 . https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/445483/ . Accessed 17 Aug 2021.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We wish to acknowledge Professor Jeremy Frey and Dr Sarah Callaghan for their support in planning and organising the event series and for proof-reading our article. We also extend our heartfelt thanks to all our speakers and contributors who participated in our Failed it to nailed it and Skills4Scientists series.
This work was funded by EPSRC through grants EP/S000356/1-AI3SD Network+ (Artificial Intelligence and Augmented Intelligence for Automated Investigations for Scientific Discovery) and EP/S020357/1-PSDS (Physical Sciences Data science Service).
Author information
Samantha Kanza and Nicola J. Knight contributed equally to this work
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences, University of Southampton, University Road, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, UK
Samantha Kanza & Nicola J. Knight
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SK and NK jointly organised and co-ordinated the survey and event series that provided the basis for this commentary. The article was also written and edited jointly. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Samantha Kanza .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The survey used in the design of our event series was approved by University of Southampton ethics panel ERGO No: 57287.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kanza, S., Knight, N.J. Behind every great research project is great data management. BMC Res Notes 15 , 20 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-022-05908-5
Download citation
Received : 01 December 2021
Accepted : 11 January 2022
Published : 21 January 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-022-05908-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Data management plans
- Data organisation
- Data sharing
- Reproducibility
BMC Research Notes
ISSN: 1756-0500
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Research articles

Scuttle fly Megaselia scalaris (Loew) (Diptera: Phoridae) endoparasitoid as a novel biocontrol agent against adult American cockroaches ( Periplaneta americana )
- Esraa A. Arafat
- Lamia M. El-Samad
- Mohamed A. Hassan
Predictive value of lactate dehydrogenase for Mycoplasma pneumoniae necrotizing pneumonia in children based on decision curve analysis and dose–response analysis
- Ren Yanhong
- Sun Xiaomin
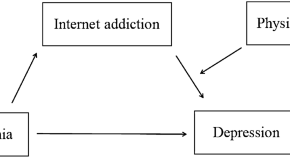
The mediating effect of internet addiction and the moderating effect of physical activity on the relationship between alexithymia and depression
- Liangfan Duan
- Tiancheng Zhang
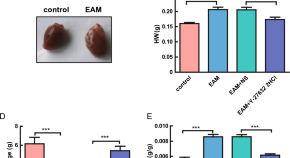
Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 downregulates IL-1β expression in mice with experimental autoimmune myocarditis
- Yuxing Wang
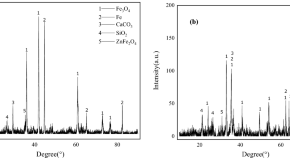
Process and mechanism of preparing metallized blast furnace burden from metallurgical dust and sludge
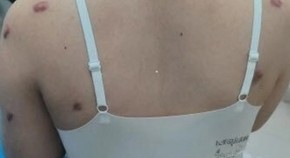
The clinical efficacy of single-hole punch excision combined with intralesional steroid injection for nodular keloid treatment: a self-controlled trial
- Bingbing Liu
- Haoying Lin
- Minghai Zhang
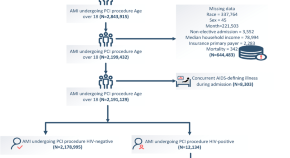
Symptomatic HIV infection and in-hospital outcomes for patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention from national inpatient sample
- Mingzhi Cui
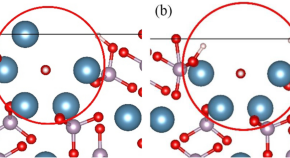
- Guangzhi Cong
The impact of hydroxyapatite crystal structures and protein interactions on bone's mechanical properties

Passive high explosive neutron inspection (PHENIX): a new method to confirm the presence or absence of high explosives for nuclear treaty verification
- David L. Chichester
- James T. Johnson
- Edward H. Seabury
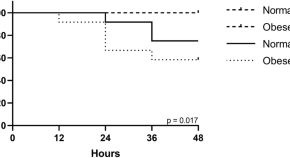
Obesity aggravates acute kidney injury resulting from ischemia and reperfusion in mice
- Igor Oliveira da Silva
- Nicole K. de Menezes
- Lucia Andrade
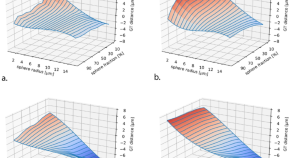
A novel imaging marker of cortical “cellularity” in multiple sclerosis patients
- Muhamed Barakovic
- Matthias Weigel
- Cristina Granziera
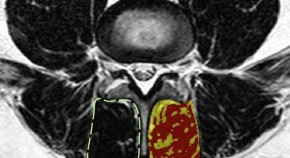
Spinal degeneration and lumbar multifidus muscle quality may independently affect clinical outcomes in patients conservatively managed for low back or leg pain
- Jeffrey R. Cooley
- Tue S. Jensen
- Jeffrey J. Hebert
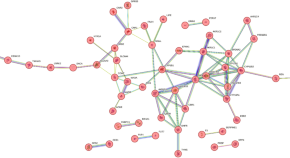
Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental verification to elucidate the effect of flavan-3-ols and aromatic resin on anxiety
- Ansari Vikhar Danish Ahmad
- Subur W. Khan
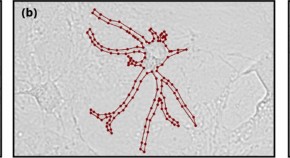
Machine learning approach for recognition and morphological analysis of isolated astrocytes in phase contrast microscopy
- Egor V. Yakovlev
- Ivan V. Simkin
- Nikita P. Kryuchkov
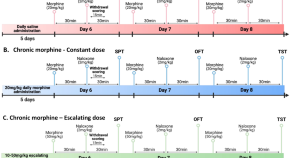
Model of negative affect induced by withdrawal from acute and chronic morphine administration in male mice
- Dersu Ozdemir
- Judith Meyer
- Emmanuel Darcq
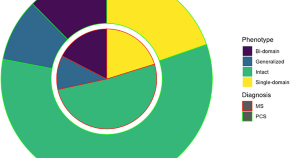
Cognitive profile in multiple sclerosis and post-COVID condition: a comparative study using a unified taxonomy
- Cristina Delgado-Alonso
- Alfonso Delgado-Alvarez
- Jordi A. Matias-Guiu
Lead and copper removal from sterile dumps by phytoremediation with Robinia pseudoacacia
- Adriana Mihaela Chirilă Băbău
- Valer Micle
- Ioana Monica Sur
Use of a natural rock material as a precursor to inhibit corrosion of Ti alloy in an aggressive phosphoric acid medium
- Amany M. Fekry
- Inna V. Filippova
- Lev O. Filippov
Effects of trimer repeats on Psidium guajava L. gene expression and prospection of functional microsatellite markers
- Giovanna Pinto Pires
- Vinicius Sartori Fioresi
- Marcia Flores da Silva Ferreira
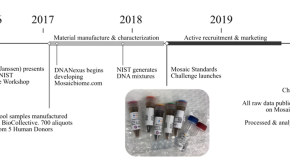
Variability and bias in microbiome metagenomic sequencing: an interlaboratory study comparing experimental protocols
- Samuel P. Forry
- Stephanie L. Servetas
- Scott A. Jackson
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Get Started With a Research Project
Last Updated: October 3, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Chris Hadley, PhD . Chris Hadley, PhD is part of the wikiHow team and works on content strategy and data and analytics. Chris Hadley earned his PhD in Cognitive Psychology from UCLA in 2006. Chris' academic research has been published in numerous scientific journals. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 311,924 times.
You'll be required to undertake and complete research projects throughout your academic career and even, in many cases, as a member of the workforce. Don't worry if you feel stuck or intimidated by the idea of a research project, with care and dedication, you can get the project done well before the deadline!

Development and Foundation

- Don't hesitate while writing down ideas. You'll end up with some mental noise on the paper – silly or nonsensical phrases that your brain just pushes out. That's fine. Think of it as sweeping the cobwebs out of your attic. After a minute or two, better ideas will begin to form (and you might have a nice little laugh at your own expense in the meantime).

- Some instructors will even provide samples of previously successful topics if you ask for them. Just be careful that you don't end up stuck with an idea you want to do, but are afraid to do because you know someone else did it before.

- For example, if your research topic is “urban poverty,” you could look at that topic across ethnic or sexual lines, but you could also look into corporate wages, minimum wage laws, the cost of medical benefits, the loss of unskilled jobs in the urban core, and on and on. You could also try comparing and contrasting urban poverty with suburban or rural poverty, and examine things that might be different about both areas, such as diet and exercise levels, or air pollution.

- Think in terms of questions you want answered. A good research project should collect information for the purpose of answering (or at least attempting to answer) a question. As you review and interconnect topics, you'll think of questions that don't seem to have clear answers yet. These questions are your research topics.

- Don't limit yourself to libraries and online databases. Think in terms of outside resources as well: primary sources, government agencies, even educational TV programs. If you want to know about differences in animal population between public land and an Indian reservation, call the reservation and see if you can speak to their department of fish and wildlife.
- If you're planning to go ahead with original research, that's great – but those techniques aren't covered in this article. Instead, speak with qualified advisors and work with them to set up a thorough, controlled, repeatable process for gathering information.

- If your plan comes down to “researching the topic,” and there aren't any more specific things you can say about it, write down the types of sources you plan to use instead: books (library or private?), magazines (which ones?), interviews, and so on. Your preliminary research should have given you a solid idea of where to begin.
Expanding Your Idea with Research

- It's generally considered more convincing to source one item from three different authors who all agree on it than it is to rely too heavily on one book. Go for quantity at least as much as quality. Be sure to check citations, endnotes, and bibliographies to get more potential sources (and see whether or not all your authors are just quoting the same, older author).
- Writing down your sources and any other relevant details (such as context) around your pieces of information right now will save you lots of trouble in the future.

- Use many different queries to get the database results you want. If one phrasing or a particular set of words doesn't yield useful results, try rephrasing it or using synonymous terms. Online academic databases tend to be dumber than the sum of their parts, so you'll have to use tangentially related terms and inventive language to get all the results you want.

- If it's sensible, consider heading out into the field and speaking to ordinary people for their opinions. This isn't always appropriate (or welcomed) in a research project, but in some cases, it can provide you with some excellent perspective for your research.
- Review cultural artifacts as well. In many areas of study, there's useful information on attitudes, hopes, and/or concerns of people in a particular time and place contained within the art, music, and writing they produced. One has only to look at the woodblock prints of the later German Expressionists, for example, to understand that they lived in a world they felt was often dark, grotesque, and hopeless. Song lyrics and poetry can likewise express strong popular attitudes.

Expert Q&A

- Start early. The foundation of a great research project is the research, which takes time and patience to gather even if you aren't performing any original research of your own. Set aside time for it whenever you can, at least until your initial gathering phase is complete. Past that point, the project should practically come together on its own. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- When in doubt, write more, rather than less. It's easier to pare down and reorganize an overabundance of information than it is to puff up a flimsy core of facts and anecdotes. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

- Respect the wishes of others. Unless you're a research journalist, it's vital that you yield to the wishes and requests of others before engaging in original research, even if it's technically ethical. Many older American Indians, for instance, harbor a great deal of cultural resentment towards social scientists who visit reservations for research, even those invited by tribal governments for important reasons such as language revitalization. Always tread softly whenever you're out of your element, and only work with those who want to work with you. Thanks Helpful 8 Not Helpful 2
- Be mindful of ethical concerns. Especially if you plan to use original research, there are very stringent ethical guidelines that must be followed for any credible academic body to accept it. Speak to an advisor (such as a professor) about what you plan to do and what steps you should take to verify that it will be ethical. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 2
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/research/research_paper.html
- ↑ https://www.nhcc.edu/academics/library/doing-library-research/basic-steps-research-process
- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185905
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/using-an-interview-in-a-research-paper
- ↑ https://www.science.org/content/article/how-review-paper
About This Article

The easiest way to get started with a research project is to use your notes and other materials to come up with topics that interest you. Research your favorite topic to see if it can be developed, and then refine it into a research question. Begin thoroughly researching, and collect notes and sources. To learn more about finding reliable and helpful sources while you're researching, continue reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jun 30, 2016
Did this article help you?

Maooz Asghar
Aug 14, 2016
Jun 27, 2016
Calvin Kiyondi
Apr 24, 2017
Nov 2, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- OU Homepage
- The University of Oklahoma
Researchers Earn $2.3 Million Grant to Study Generational Cycle of Maternal Obesity, Liver Disease

Project includes testing an antioxidant for improving metabolic health
OKLAHOMA CITY, OKLA. – Research increasingly suggests that when a woman with obesity becomes pregnant, a process of “fetal reprogramming” increases the risk that her baby will face problems like obesity, Type 2 diabetes and liver disease earlier in life.
To better understand how that reprogramming occurs, University of Oklahoma researchers recently earned a $2.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health. They also will study whether an antioxidant called PQQ given to the mother can lower the risk of future metabolic problems for her offspring.
“Today in the United States, more than 40% of women of childbearing age are overweight or obese,” said OU College of Medicine researcher Karen Jonscher, Ph.D., who is leading the work of the grant with Dean Myers, Ph.D. “Research has shown that people whose mothers were obese during pregnancy have a higher risk for developing metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, a fatty liver disease that becomes progressively worse and can result in the need for a transplant. However, in offspring, it happens earlier in life and with more severe problems. The whole process seems to be accelerated in children who are born to mothers with obesity.”
Much of America’s obesity problem is attributed to eating a “Western-style” diet that is heavy on fats. However, even if a woman with obesity eats healthier during pregnancy, her offspring still face a higher risk of disease. Jonscher and Myers believe the key may be what is happening in the placenta — the interface between mother and fetus.
Obesity is essentially a low-grade, chronic inflammatory disease. Fat cells cause inflammation, which means the body’s white blood cells are in a constant state of activation and can damage other cells and tissues. Cholesterol and triglyceride levels rise, and blood pressure increases. Jonscher hypothesizes that the inflammation in pregnant women with obesity prompts the placenta to send a signal to the fetus’s stem cells, telling them to reprogram themselves to become more susceptible to the inflammation’s harmful effects.
“There is even some evidence that inflammation changes how nutrients are transported to the fetus so that fat is preferentially transported rather than the building blocks of proteins,” said Jonscher, an associate professor of biochemistry and physiology.
With the grant, Jonscher and Myers will try to prove that hypothesis. In addition, they will test an antioxidant called pyrroloquinoline quinone, or PQQ, for its ability to block or reverse fetal reprogramming. PQQ, found in fruits and vegetables, has anti-inflammatory properties, but if a person doesn’t eat a healthy diet, they are less likely to have adequate levels of PQQ.
In their preliminary studies in a preclinical research model, the researchers found that when PQQ is given to obese mothers, their offspring are protected from fatty liver disease in adulthood. Because women are generally advised not to take weight loss drugs during pregnancy due to potential harm to the fetus, the researchers hope PQQ is both safe and effective.
“Based on the data we have gathered so far, we believe that PQQ will create a healthier pregnancy,” Myers said. “The mother may still have a high body mass index, but PQQ appears able to lower inflammation and improve cholesterol and lipid levels. If we can improve the mother's health, we are also improving the function of the placenta, which will protect the fetus in a positive way. And if we can protect the placenta, nutrient transport will be improved with more amino acids and protein building blocks reaching the fetus instead of fats, as well as better oxygen flow.”
Myers, who is a professor in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, often talks with his clinical colleagues who are caring for women with obesity during their pregnancies. Exercising and eating a healthy diet can be difficult for all people, pregnant or not, and physicians need another tool to help women become more metabolically healthy while pregnant.
“Our goal is to create a less-inflamed, healthier placenta,” he said. “Hopefully, PQQ will help the mother, too, because women with obesity who are pregnant have an increased risk for gestational diabetes. If our research with this grant is successful, we hope to move PQQ into clinical trials in a few years.”
About the University of Oklahoma
Founded in 1890, the University of Oklahoma is a public research university located in Norman, Oklahoma. As the state’s flagship university, OU serves the educational, cultural, economic and health care needs of the state, region and nation. OU was named the state’s highest-ranking university in U.S. News & World Report’s most recent Best Colleges list . For more information about the university, visit ou.edu .
Recent News
University of oklahoma receives $4m grant for supply chain resiliency research.
The University of Oklahoma has received a nearly $4 million congressional appropriation for supply chain risk management research from the 448th Supply Chain Management Wing of the U.S. Air Force Sustainment Center.

OU Student Named Pulitzer Reporting Fellow
Maddy Keyes, a senior from the Gaylord College of Journalism and Mass Communication, has been chosen as a Pulitzer Center Reporting Fellow to explore the ecological grief caused by climate change for the Inuit in Greenland.

University of Oklahoma Contributes to National Strategy for Suicide Prevention, Released This Week
This week, the Biden-Harris Administration, through the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, announced its federal action plan to carry out the work of the new National Strategy for Suicide Prevention — a structure developed with expertise from the University of Oklahoma.

More OU News

- Accessibility
- Sustainability
- OU Job Search
- Legal Notices
- Resources and Offices
- OU Report It!

Local news, paywall-free.
MinnPost’s timely reporting is available for free, all year round. But our work isn’t free to produce. Help sustain our nonprofit newsroom with a monthly donation today.

Nonprofit, independent journalism. Supported by readers.
- Research project that found elevated food insecurity levels in Stevens County expands to a five-county region
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)

Stay in the know.
MinnPost’s top stories delivered straight to your inbox Monday through Saturday.
After seeing the economic pressures people were facing during the COVID-19 pandemic, the Center for Small Towns – an organization connected to the University of Minnesota – Morris – began looking into what challenges their community faced when it came to food security.
The team found that many people in Stevens County experienced food insecurity. Separate data showed that between 2016 and 2020, more than 250 households in the county received SNAP benefits and free and reduced lunch rates ranged from 16%-45% in the local school districts.
Of 237 people surveyed in the spring of 2022, at least 22% were food insecure to some degree. The researchers defined food security as “a situation in which an individual or household always has access to sufficient nutritious and culturally acceptable foods that enable a healthy, active lifestyle.”
Two-thirds of survey respondents indicated they experienced at least one barrier to food access with the top barrier being the time of year (availability of garden produce) followed by distance to food sources. After better understanding the factors behind food insecurity in Stevens County, this year, the center sought to conduct similar surveys and analyses of Stevens and its neighboring counties: Traverse, Douglas, Grant and Polk.
Grocery store affordability and access
The center’s first food assessment compared the prices of a supermarket in town to Walmart over three different occasions, purchasing items on the USDA’s Thrifty Food plan, which is the USDA’s guideline for a nutritious, practical, cost-effective diet for a family of four. The store in town, Willie’s SuperValu, had significantly higher prices than Walmart, which is more than 45 minutes away, and the research found that the people who were identified as food insecure were less likely than other respondents to shop at Willie’s SuperValu. Its prices for the thrifty food plan at the time were 5-10% higher than the national average, and the weekly trip at Walmart was around 33% lower than Willie’s SuperValu, the study found.
For most people who live in Morris, there is a grocery store within two miles of their home. But residents of other cities, like Alberta, Donnelly, Hancock and Chokio have to travel more miles to get to a store. The research found that the transit options in Morris did not provide sufficient access to grocery stores, as some of them, like Rainbow Rider, a public transit system in several West Central counties, have fewer operational hours on weekends.
“We have a bus system in Morris that can take you to the local grocery store but if students need to go to Walmart or Aldi’s for an expanded selection or cheaper prices, the closest Walmart to Morris is an hour away and the bus doesn’t go from Morris to there, so there’s no immediate access to an expanded grocery store,” said Danny Kenyon, who was an AmeriCorps VISTA team member on the first food assessment.
Kenyon, who had gone to college in Morris and was familiar with the food shelves in the area, didn’t realize how big of an issue food insecurity was for her county until she worked on this project.
“I lived there for four years. But when you’re living on campus … a lot of your life is basically in that same five-block perimeter. I realized I didn’t actually know a lot about the community that I’ve been living in,” she said. “I realized both how many people were struggling, but also how many people that were struggling weren’t getting help. We found a lot of people that were making poverty level income or lower according to the census; those numbers did not at all match up with people on SNAP benefits or on WIC benefits or going to the food shelf. There was just a huge difference there between people that really needed help, but weren’t using the resources.”
She said the food shelf had some people who came more regularly, but many times there would be people who had to pay unexpected bills for one month, which meant they didn’t have money for groceries that week.
And at the food shelves, certain high-demand items would quickly go.
“We’d often get milk in and it’d be gone in two days. And then we wouldn’t have another (shipment) for two weeks,” she said.
Solutions
Based on the first food assessment, the researchers came up with areas of improvement to address the food insecurity their community was facing, including finding ways to increase access to affordable groceries (including reducing food waste), finding ways to connect residents without stable transportation to food resources, increasing the availability of culturally appropriate foods and creating spaces for more locally grown fresh produce.
- SBA recognizes SMSU grad Layne Lozinski as Young Entrepreneur of the Year
- Providing some care for the caregiver
This summer, there will be a community garden near the county’s soil and water conservation district office in Morris. It’ll be around 2,000 square feet and will grow things like tomatoes, potatoes, onions, zucchinis, tomatillos and peppers, said Annabelle Scafe, the Americorps VISTA on this project.
Through this project, Scafe has a better understanding of how neighboring counties have also approached this issue. Traverse County, for example, has a community garden where people buy plots and can use them during the summer, she said.
“We decided the best kind of model for that would be, you can go and get whatever you want from the garden at any time and all of the remaining produce and everything will be donated to the food shelf so that hopefully more people can access it,” Scafe said.
Expanding to five counties
The research that’s been going on this year began in September and is examining food insecurity in Traverse, Douglas, Grant, Polk and Stevens counties throughout an eight-month period. That means comparing prices across different grocery stores in those counties and also doing the survey to understand what the barriers are to food access.
“(The team is) looking at two things, one: item availability, they have their list of items. So staples that people would eat, like their milk, grains, vegetables, canned goods, that kind of thing. Are they in the store? And two is what’s the price?,” said Ed Brands, a professor at Morris and project co-lead.
The survey on barriers closes on May 1. The team is encouraging residents of those counties who are 18 years and older to submit responses.

Ava Kian Ava Kian is MinnPost’s Greater Minnesota reporter. Follow her on Twitter @kian_ava or email her at [email protected] .
Thanks to our major sponsors

We've recently sent you an authentication link. Please, check your inbox!
Sign in with a password below, or sign in using your email .
Get a code sent to your email to sign in, or sign in using a password .
Enter the code you received via email to sign in, or sign in using a password .
Subscribe to our newsletters:
- Daily Newsletter MinnPost's top stories delivered to your inbox Monday through Saturday.
- Events & member benefits Be the first to know about opportunities around MinnPost membership & events.
Sign in with your email
Lost your password?
Try a different email
Send another code
Sign in with a password
Privacy Policy
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Transformations That Work
- Michael Mankins
- Patrick Litre

More than a third of large organizations have some type of transformation program underway at any given time, and many launch one major change initiative after another. Though they kick off with a lot of fanfare, most of these efforts fail to deliver. Only 12% produce lasting results, and that figure hasn’t budged in the past two decades, despite everything we’ve learned over the years about how to lead change.
Clearly, businesses need a new model for transformation. In this article the authors present one based on research with dozens of leading companies that have defied the odds, such as Ford, Dell, Amgen, T-Mobile, Adobe, and Virgin Australia. The successful programs, the authors found, employed six critical practices: treating transformation as a continuous process; building it into the company’s operating rhythm; explicitly managing organizational energy; using aspirations, not benchmarks, to set goals; driving change from the middle of the organization out; and tapping significant external capital to fund the effort from the start.
Lessons from companies that are defying the odds
Idea in Brief
The problem.
Although companies frequently engage in transformation initiatives, few are actually transformative. Research indicates that only 12% of major change programs produce lasting results.
Why It Happens
Leaders are increasingly content with incremental improvements. As a result, they experience fewer outright failures but equally fewer real transformations.
The Solution
To deliver, change programs must treat transformation as a continuous process, build it into the company’s operating rhythm, explicitly manage organizational energy, state aspirations rather than set targets, drive change from the middle out, and be funded by serious capital investments.
Nearly every major corporation has embarked on some sort of transformation in recent years. By our estimates, at any given time more than a third of large organizations have a transformation program underway. When asked, roughly 50% of CEOs we’ve interviewed report that their company has undertaken two or more major change efforts within the past five years, with nearly 20% reporting three or more.
- Michael Mankins is a leader in Bain’s Organization and Strategy practices and is a partner based in Austin, Texas. He is a coauthor of Time, Talent, Energy: Overcome Organizational Drag and Unleash Your Team’s Productive Power (Harvard Business Review Press, 2017).
- PL Patrick Litre leads Bain’s Global Transformation and Change practice and is a partner based in Atlanta.
Partner Center
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
U.S. centenarian population is projected to quadruple over the next 30 years

The number of Americans ages 100 and older is projected to more than quadruple over the next three decades, from an estimated 101,000 in 2024 to about 422,000 in 2054, according to projections from the U.S. Census Bureau. Centenarians currently make up just 0.03% of the overall U.S. population, and they are expected to reach 0.1% in 2054.
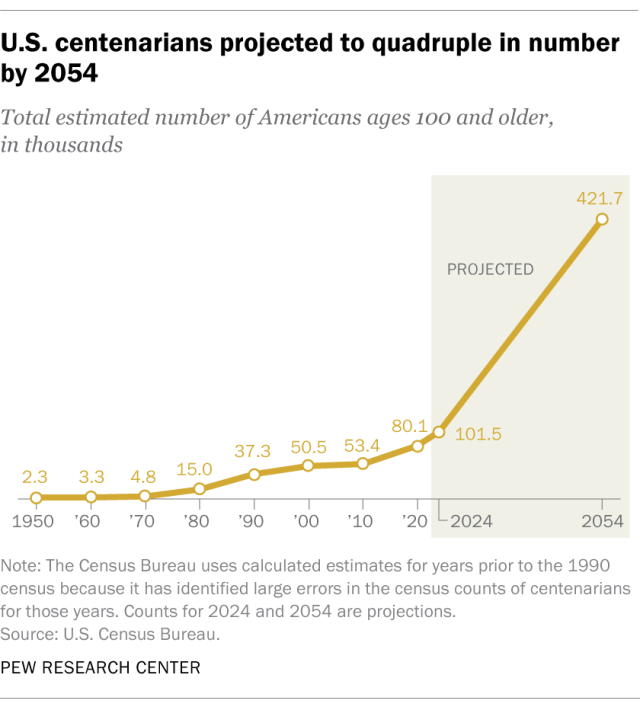
The number of centenarians in the United States has steadily ticked up since 1950, when the Census Bureau estimates there were just 2,300 Americans ages 100 and older. (The Census Bureau uses calculated estimates for years prior to the 1990 census because it has identified large errors in the census counts of centenarians for those years.)
In the last three decades alone, the U.S. centenarian population has nearly tripled. The 1990 census counted around 37,000 centenarians in the country.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand how the population of Americans ages 100 and older looks today, and how it is expected to change in the next 30 years. U.S. population estimates come from the U.S. Census Bureau , and global projections are drawn from the United Nations’ population projections under its medium variant scenario .
All racial groups are single-race and non-Hispanic. Hispanics are of any race.
Today, women and White adults make up the vast majority of Americans in their 100s. This trend is largely projected to continue, though their shares will decrease:
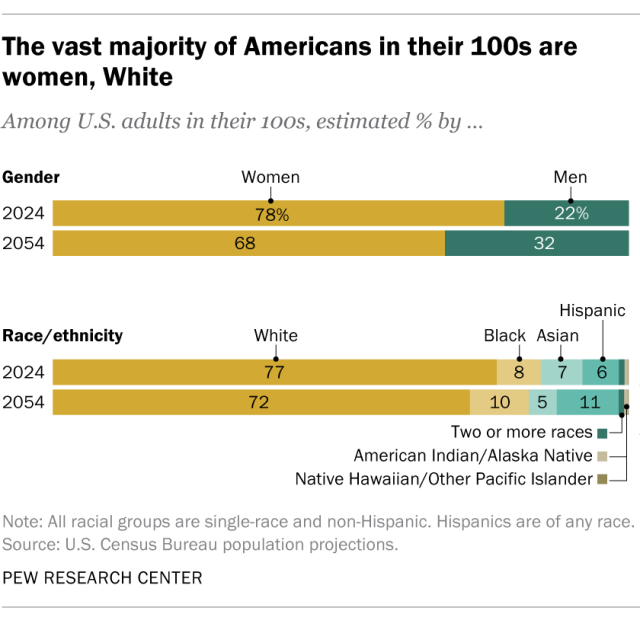
- In 2024, 78% of centenarians are women, and 22% are men. In 30 years, women are expected to make up 68% of those ages 100 and older, while 32% will be men.
- 77% of today’s centenarians are White. Far fewer are Black (8%), Asian (7%) or Hispanic (6%). And 1% or fewer are multiracial; American Indian or Alaska Native; or Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander. By 2054, White and Asian adults are projected to make up smaller shares of centenarians (72% and 5%, respectively), while the shares who are Hispanic (11%) or Black (10%) will be larger. (All racial categories here are single-race and non-Hispanic. Hispanics are of any race.)
The U.S. population overall is expected to trend older in the coming decades as life expectancies increase and the birth rate declines. There are currently roughly 62 million adults ages 65 and older living in the U.S., accounting for 18% of the population. By 2054, 84 million adults ages 65 and older will make up an estimated 23% of the population.
Even as the 65-and-older population continues to grow over the next 30 years, those in their 100s are projected to roughly double as a percentage of that age group, increasing from 0.2% of all older Americans in 2024 to 0.5% in 2054.
Centenarians around the world
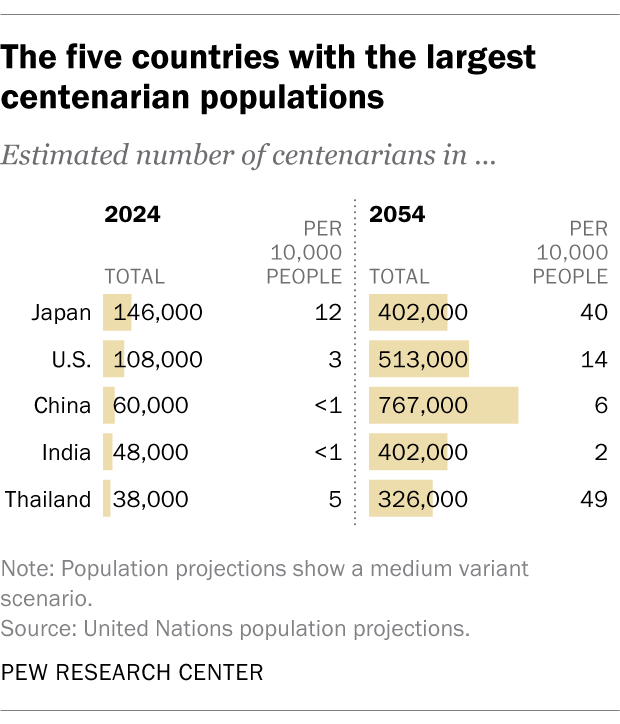
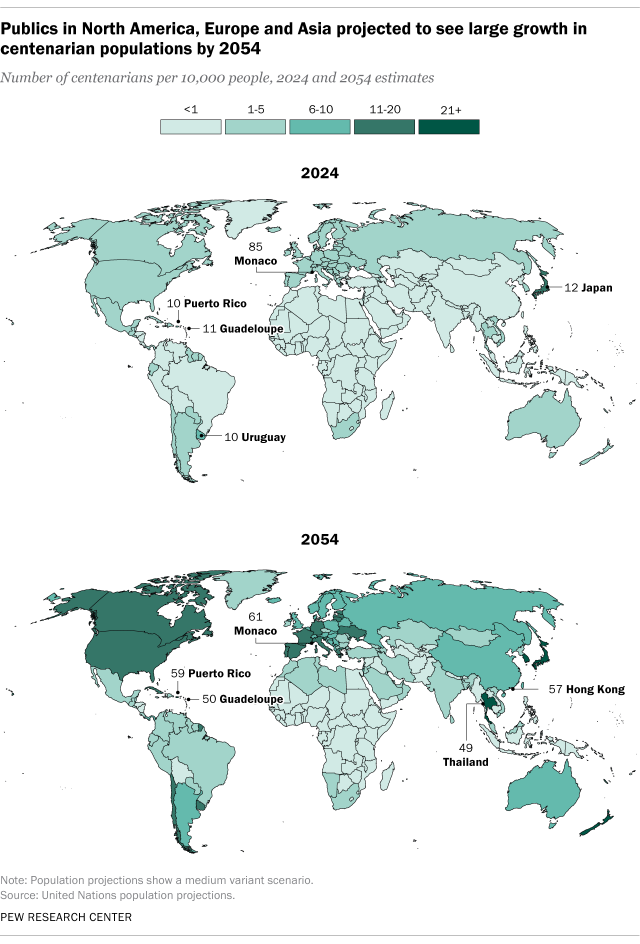
The world is home to an estimated 722,000 centenarians, according to the United Nations’ population projections for 2024. The U.S. centenarian population is the world’s second largest – the UN estimates it at 108,000, slightly larger than the Census Bureau’s estimate.
Japan is the country with the greatest number of people in their 100s, at 146,000. China (60,000), India (48,000) and Thailand (38,000) round out the top five.
In each of these countries, centenarians make up less than 1% of the overall population, but combined, they account for more than half (55%) of the world’s population ages 100 and older.
Looked at another way, centenarians make up a bigger proportion of the total population in Japan, Thailand and the U.S., and smaller shares in China and India, which have large but relatively young populations. There are about 12 centenarians for every 10,000 people in Japan, five for every 10,000 in Thailand and three for every 10,000 in the U.S. That compares with fewer than one centenarian for every 10,000 people in China and India.
By 2054, the global centenarian population is projected to grow to nearly 4 million. China is expected to have the largest number of centenarians, with 767,000, followed by the U.S., India, Japan and Thailand. As a proportion, centenarians are projected to account for about 49 out of every 10,000 people in Thailand, 40 of every 10,000 in Japan and 14 of every 10,000 in the U.S. Six out of every 10,000 people in China will be centenarians, as will about two of every 10,000 in India.
- Older Adults & Aging

Katherine Schaeffer is a research analyst at Pew Research Center
How Teens and Parents Approach Screen Time
Older workers are growing in number and earning higher wages, teens, social media and technology 2023, dating at 50 and up: older americans’ experiences with online dating, about half of americans say the best age for a u.s. president is in their 50s, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
New Group Joins the Political Fight Over Disinformation Online
The group intends to fight what its leader, Nina Jankowicz, and others have described as a coordinated campaign by conservatives and their allies to undermine researchers who study disinformation.

By Steven Lee Myers and Jim Rutenberg
Two years ago, Nina Jankowicz briefly led an agency at the Department of Homeland Security created to fight disinformation — the establishment of which provoked a political and legal battle over the government’s role in policing lies and other harmful content online that continues to reverberate.
Now she has re-entered the fray with a new nonprofit organization intended to fight what she and others have described as a coordinated campaign by conservatives and others to undermine researchers, like her, who study the sources of disinformation.
Already a lightning rod for critics of her work on the subject, Ms. Jankowicz inaugurated the organization with a letter accusing three Republican committee chairmen in the House of Representatives of abusing their subpoena powers to silence think tanks and universities that expose the sources of disinformation.
“These tactics echo the dark days of McCarthyism, but with a frightening 21st-century twist,” she wrote in the letter on Monday with the organization’s co-founder Carlos Álvarez-Aranyos, a public-relations consultant who in 2020 was involved in efforts to defend the integrity of the American voting system.
The inception of the group, the American Sunlight Project, reflects how divisive the issue of identifying and combating disinformation has become as the 2024 presidential election approaches. It also represents a tacit admission that the informal networks formed at major universities and research organizations to address the explosion of disinformation online have failed to mount a substantial defense against a campaign, waged largely on the right, depicting their work as part of an effort to silence conservatives.
Taking place in the courts, in conservative media and on the Republican-led House Judiciary Select Subcommittee on the Weaponization of the Federal Government, the campaign has largely succeeded in eviscerating efforts to monitor disinformation, especially around the integrity of the American election system.
Many of the nation’s most prominent researchers, facing lawsuits, subpoenas and physical threats, have pulled back.
“More and more researchers were getting swept up by this, and their institutions weren’t either allowing them to respond or responding in a way that really just was not rising to meet the moment,” Ms. Jankowicz said in an interview. “And the problem with that, obviously, is that if we don’t push back on these campaigns, then that’s the prevailing narrative.”
That narrative is prevailing at a time when social media companies have abandoned or cut back efforts to enforce their own policies against certain types of content.
Many experts have warned that the problem of false or misleading content is only going to increase with the advent of artificial intelligence.
“Disinformation will remain an issue as long as the strategic gains of engaging in it, promoting it and profiting from it outweigh consequences for spreading it,” Common Cause, the nonpartisan public interest group, wrote in a report published last week that warned of a new wave of disinformation around this year’s vote.
Ms. Jankowicz said her group would run advertisements about the broad threats and effects of disinformation and produce investigative reports on the backgrounds and financing of groups conducting disinformation campaigns — including those targeting the researchers.
She has joined with two veteran political strategists: Mr. Álvarez-Aranyos, formerly a communications strategist for Protect Democracy, a nonpartisan group that seeks to counter domestic authoritarian threats, and Eddie Vale, formerly of American Bridge, a liberal group devoted to gathering opposition research into Republicans.
The organization’s advisory board includes Katie Harbath, a former Facebook executive who was previously a top digital strategist for Senate Republicans; Ineke Mushovic, a founder of the Movement Advancement Project , a think tank that tracks threats to democracy and gay, lesbian and transgender issues; and Benjamin Wittes, a national security legal expert at the Brookings Institution and editor in chief of Lawfare .
“We need to be a little bit more aggressive about how we think about defending the research community,” Mr. Wittes said in an interview, portraying the attacks against it as part of “a coordinated assault on those who have sought to counter disinformation and election interference.”
In the letter to congressional Republicans, Ms. Jankowicz noted the appearance of a fake robocall in President Biden’s voice discouraging voters in New Hampshire from voting in the state’s primary and artificially generated images of former President Donald J. Trump with Black supporters, as well as renewed efforts by China and Russia to spread disinformation to American audiences.
The American Sunlight Project has been established as a nonprofit under the section of the Internal Revenue Code that allows it greater leeway to lobby than tax-exempt charities known as 501(c)(3)s. It also does not have to disclose its donors, which Ms. Jankowicz declined to do, though she said the project had initial commitments of $1 million in donations.
The budget pales in comparison with those behind the counteroffensive like America First Legal, the Trump-aligned group that, with a war chest in the tens of millions of dollars, has sued researchers at Stanford and the University of Washington over their collaboration with government officials to combat misinformation about voting and Covid-19.
The Supreme Court is expected to rule soon in a federal lawsuit filed by the attorneys general of Missouri and Louisiana accusing government agencies of using the researchers as proxies to pressure social media platforms to take down or restrict the reach of accounts.
The idea for the American Sunlight Project grew out of Ms. Jankowicz’s experience in 2022 when she was appointed executive director of a newly created Disinformation Governance Board at the Department of Homeland Security.
From the instant the board became public, it faced fierce criticism portraying it as an Orwellian Ministry of Truth that would censor dissenting voices in violation of the First Amendment, though in reality it had only an advisory role and no enforcement authority.
Ms. Jankowicz, an expert on Russian disinformation who once served as an adviser to Ukraine’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, stepped down shortly after her appointment. Even then, she faced such a torrent of personal threats online that she hired a security consultant. The board was suspended and then, after a short review, abolished.
“I think we’re existing in an information environment where it is very easy to weaponize information and to make it seem sinister,” Mr. Álvarez-Aranyos said. “And I think we’re looking for transparency. I mean, this is sunlight in the very literal sense.”
Ms. Jankowicz said that she was aware that her involvement with the new group would draw out her critics, but that she was well positioned to lead it because she had already “gone through the worst of it.”
Steven Lee Myers covers misinformation and disinformation from San Francisco. Since joining The Times in 1989, he has reported from around the world, including Moscow, Baghdad, Beijing and Seoul. More about Steven Lee Myers
Jim Rutenberg is a writer at large for The Times and The New York Times Magazine and writes most often about media and politics. More about Jim Rutenberg
About Project Reports
NSF requires that NSF-funded researchers regularly report on the progress of supported projects and the way funds are used.
- Only Principal Investigators (PIs) and co-PIs can create, edit and submit project reports
- Sponsored Projects Office (SPO) staff and administrative users with read-only access can view project reports
Sign In to create, edit and submit reports Find project outcomes reports
The 4 types of project reports are:
- Annual report
- Interim report
- Final report
- Project outcomes report
Annual, Interim and Final Reports Annual project reports are required for all standard and continuing grants and cooperative agreements. Final reports are required for all standard and continuing grants, cooperative agreements and fellowships. Interim project reports are not required and are used to update the progress of a project any time during or before the award period expires
All submitted annual and final reports must be approved by an NSF Program Officer to meet the submission requirements.
Key features of Project Reporting System in Research.gov:
- A consolidated project reporting dashboard that includes annual, final, interim, and project outcomes report
- Ability to deposit published journal articles and juried conference papers in NSF Public Access Repository to be compliant with the Public Access requirement. PIs and co-PIs can also submit publications in the NSF’s Public Access repository through their project reports and comply with the Public Access requirement.Refer to Public Access page for additional information
- Upload multiple Products via BibTex upload feature
Project Outcome Reports (for general public) The Project Outcomes Report is a report written for new and existing awards, specifically for the public, that provides insight into the outcomes of NSF-funded research. Project Outcome Reports can be viewed through Research.gov’s Research Spending & Results search service.
Note: Project Outcome Reports are not reviewed or approved by NSF
More Information
- About Public Access
- Example Project Reports (Demo site)
Project Report Screenshots and Instructions
Project reports template
Project Reporting Getting Started Guide
Project Reporting FAQ's
Project Reports and Reminder Email Schedule Tip Sheet
For additional information on Project Reports, please visit the Help section .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.20; 2019 Oct 25
Managing Ideas, People, and Projects: Organizational Tools and Strategies for Researchers
Samuel pascal levin.
1 Beverly, MA 01915, USA
Michael Levin
2 Allen Discovery Center at Tufts University, Suite 4600, 200 Boston Avenue, Medford, MA 02155-4243, USA
Primary Investigators at all levels of their career face a range of challenges related to optimizing their activity within the constraints of deadlines and productive research. These range from enhancing creative thought and keeping track of ideas to organizing and prioritizing the activity of the members of the group. Numerous tools now exist that facilitate the storage and retrieval of information necessary for running a laboratory to advance specific project goals within associated timelines. Here we discuss strategies and tools/software that, together or individually, can be used as is or adapted to any size scientific laboratory. Specific software products, suggested use cases, and examples are shown across the life cycle from idea to publication. Strategies for managing the organization of, and access to, digital information and planning structures can greatly facilitate the efficiency and impact of an active scientific enterprise. The principles and workflow described here are applicable to many different fields.
Graphical Abstract

Information Systems; Knowledge Management
Introduction
Researchers, at all stages of their careers, are facing an ever-increasing deluge of information and deadlines. Additional difficulties arise when one is the Principal Investigator (PI) of those researchers: as group size and scope of inquiry increases, the challenges of managing people and projects and the interlocking timelines, finances, and information pertaining to those projects present a continuous challenge. In the immediate term, there are experiments to do, papers and grants to write, and presentations to construct, in addition to teaching and departmental duties. At the same time, however, the PI must make strategic decisions that will impact the future direction(s) of the laboratory and its personnel. The integration of deep creative thought together with the practical steps of implementing a research plan and running a laboratory on a day-to-day basis is one of the great challenges of the modern scientific enterprise. Especially difficult is the fact that attention needs to span many orders of scale, from decisions about which problems should be pursued by the group in the coming years and how to tackle those problems to putting out regular “fires” associated with the minutiae of managing people and limited resources toward the committed goals.
The planning of changes in research emphasis, hiring, grant-writing, etc. likewise occur over several different timescales. The optimization of resources and talent toward impactful goals requires the ability to organize, store, and rapidly access information that is integrated with project planning structures. Interestingly, unlike other fields such as business, there are few well-known, generally accepted guidelines for best practices available to researchers. Here we lay out a conceptual taxonomy of the life cycle of a project, from brainstorming ideas through to a final deliverable product. We recommend methods and software/tools to facilitate management of concurrent research activities across the timeline. The goal is to optimize the organization, storage, and access to the necessary information in each phase, and, crucially, to facilitate the interconnections between static information, action plans, and work product across all phases. We believe that the earlier in the career of a researcher such tools are implemented and customized, the more positive impact they will exert on the productivity of their enterprise.
This overview is intended for anyone who is conducting research or academic scholarship. It consists of a number of strategies and software recommendations that can be used together or independently (adapted to suit a given individual's or group's needs). Some of the specific software packages mentioned are only usable on Apple devices, but similar counterparts exist in the Windows and Linux ecosystems; these are indicated in Table 1 (definitions of special terms are given in Table 2 ). These strategies were developed (and have been continuously updated) over the last 20 years based on the experiences of the Levin group and those of various collaborators and other productive researchers. Although very specific software and platforms are indicated, to facilitate the immediate and practical adoption by researchers at all levels, the important thing is the strategies illustrated by the examples. As software and hardware inevitably change over the next few years, the fundamental principles can be readily adapted to newer products.
Software Packages and Alternatives
A Glossary of Special Terms
Basic Principles
Although there is a huge variety of different types of scientific enterprises, most of them contain one or more activities that can be roughly subsumed by the conceptual progression shown in Figure 1 . This life cycle progresses from brainstorming and ideation through planning, execution of research, and then creation of work products. Each stage requires unique activities and tools, and it is crucial to establish a pipeline and best practices that enable the results of each phase to effectively facilitate the next phase. All of the recommendations given below are designed to support the following basic principles:
- • Information should be easy to find and access, so as to enable the user to have to remember as little as possible—this keeps the mind free to generate new, creative ideas. We believe that when people get comfortable with not having to remember any details and are completely secure in the knowledge that the information has been offloaded to a dependable system and will be there when they need it, a deeper, improved level of thinking can be achieved.
- • Information should be both organized hierarchically (accessible by drill-down search through a rational structure) and searchable by keywords.
- • Information should be reachable from anywhere in the world (but secure and access restricted). Choose software that includes a cell phone/tablet platform client.
- • No information should ever be lost—the systems are such that additional information does not clog up or reduce efficiency of use and backup strategies ensure disaster robustness; therefore, it is possible to save everything.
- • Software tools optimized for specific management tasks should be used; select those tools based on interoperability, features, and the ability to export into common formats (such as XML) in case it becomes expedient someday to switch to a newer product.
- • One's digital world should be organized into several interlocking categories, which utilize different tools: activity (to-dos, projects, research goals) and knowledge (static information).
- • One's activity should be hierarchically organized according to a temporal scale, ranging from immediate goals all the way to career achievement objectives and core mission.
- • Storage of planning data should allow integration of plans with the information needed to implement them (using links to files and data in the various tools).
- • There should be no stored paper—everything should be obtained and stored in a digital form (or immediately digitized, using one of the tools described later in this document).
- • The information management tasks described herein should not occupy so much time as to take away from actual research. When implemented correctly, they result in a net increase in productivity.

The Life Cycle of Research Activity
Various projects occupy different places along a typical timeline. The life cycle extends from creative ideation to gathering information, to formulating a plan, to the execution for the plan, and then to producing a work product such as a grant or paper based on the results. Many of these phases necessitate feedback to a prior phase, shown in thinner arrows (for example, information discovered during a literature search or attempts to formalize the work plan may require novel brainstorming). This diagram shows the product (end result) of each phase and typical tools used to accomplish them.
These basic principles can be used as the skeleton around which specific strategies and new software products can be deployed. Whenever possible, these can be implemented via external administration services (i.e., by a dedicated project manager or administrator inside the group), but this is not always compatible with budgetary constraints, in which case they can readily be deployed by each principal investigator. The PIs also have to decide whether they plan to suggest (or insist) that other people in the group also use these strategies, and perhaps monitor their execution. In our experience, it is most essential for anyone leading a complex project or several to adopt these methods (typically, a faculty member or senior staff scientist), whereas people tightly focused on one project and with limited concurrent tasks involving others (e.g., Ph.D. students) are not essential to move toward the entire system (although, for example, the backup systems should absolutely be ensured to be implemented among all knowledge workers in the group). The following are some of the methods that have proven most effective in our own experience.
Information Technology Infrastructure
Several key elements should be pillars of your Information Technology (IT) infrastructure ( Figure 2 ). You should be familiar enough with computer technology that you can implement these yourself, as it is rare for an institutional IT department to be able to offer this level of assistance. Your primary disk should be a large (currently, ∼2TB) SSD drive or, better, a disk card (such as the 2TB SSD NVMe PCIe) for fast access and minimal waiting time. Your computer should be so fast that you spend no time (except in the case of calculations or data processing) waiting for anything—your typing and mouse movement should be the rate-limiting step. If you find yourself waiting for windows or files to open, obtain a better machine.

Schematic of Data Flow and Storage
Three types of information: data (facts and datasets), action plans (schedules and to-do lists), and work product (documents) all interact with each other in defining a region of work space for a given research project. All of this should be hosted on a single PC (personal computer). It is accessed by a set of regular backups of several types, as well as by the user who can interact with raw files through the file system or with organized data through a variety of client applications that organize information, schedules, and email. See Table 2 for definitions of special terms.
One key element is backups—redundant copies of your data. Disks fail—it is not a question of whether your laptop or hard drive will die, but when. Storage space is inexpensive and researchers' time is precious: team members should not tolerate time lost due to computer snafus. The backup and accessibility system should be such that data are immediately recoverable following any sort of disaster; it only has to be set up once, and it only takes one disaster to realize the value of paranoia about data. This extends also to laboratory inventory systems—it is useful to keep (and back up) lists of significant equipment and reagents in the laboratory, in case they are needed for the insurance process in case of loss or damage.
The main drive should be big enough to keep all key information (not primary laboratory data, such as images or video) in one volume—this is to facilitate cloning. You should have an extra internal drive (which can be a regular disk) of the same size or bigger. Use something like Carbon Copy Cloner or SuperDuper to set up a nightly clone operation. When the main disk fails (e.g., the night before a big grant is due), boot from the clone and your exact, functioning system is ready to go. For Macs, another internal drive set up as a Time Machine enables keeping versions of files as they change. You should also have an external drive, which is likewise a Time Machine or a clone: you can quickly unplug it and take it with you, if the laboratory has to be evacuated (fire alarm or chemical emergency) or if something happens to your computer and you need to use one elsewhere. Set a calendar reminder once a month to check that the Time Machine is accessible and can be searched and that your clone is actually updated and bootable. A Passport-type portable drive is ideal when traveling to conferences: if something happens to the laptop, you can boot a fresh (or borrowed) machine from the portable drive and continue working. For people who routinely install software or operating system updates, I also recommend getting one disk that is a clone of the entire system and applications and then set it to nightly clone the data only , leaving the operating system files unchanged. This guarantees that you have a usable system with the latest data files (useful in case an update or a new piece of software renders the system unstable or unbootable and it overwrites the regular clone before you notice the problem). Consider off-site storage. CrashPlan Pro is a reasonable choice for backing up laboratory data to the cloud. One solution for a single person's digital content is to have two extra external hard drives. One gets a clone of your office computer, and one is a clone of your home computer, and then you swap—bring the office one home and the home one to your office. Update them regularly, and keep them swapped, so that should a disaster strike one location, all of the data are available. Finally, pay careful attention (via timed reminders) to how your laboratory machines and your people's machines are being backed up; a lot of young researchers, especially those who have not been through a disaster yet, do not make backups. One solution is to have a system like CrashPlan Pro installed on everyone's machines to do automatic backup.
Another key element is accessibility of information. Everyone should be working on files (i.e., Microsoft Word documents) that are inside a Dropbox or Box folder; whatever you are working on this month, the files should be inside a folder synchronized by one of these services. That way, if anything happens to your machine, you can access your files from anywhere in the world. It is critical that whatever service is chosen, it is one that s ynchronizes a local copy of the data that live on your local machine (not simply keeps files in the cloud) —that way, you have what you need even if the internet is down or connectivity is poor. Tools that help connect to your resources while on the road include a VPN (especially useful for secure connections while traveling), SFTP (to transfer files; turn on the SFTP, not FTP, service on your office machine), and Remote Desktop (or VNC). All of these exist for cell phone or tablet devices, as well as for laptops, enabling access to anything from anywhere. All files (including scans of paper documents) should be processed by OCR (optical character recognition) software to render their contents searchable. This can be done in batch (on a schedule), by Adobe Acrobat's OCR function, which can be pointed to an entire folder of PDFs, for example, and left to run overnight. The result, especially with Apple's Spotlight feature, is that one can easily retrieve information that might be written inside a scanned document.
Here, we focus on work product and the thought process, not management of the raw data as it emerges from equipment and experimental apparatus. However, mention should be made of electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs), which are becoming an important aspect of research. ELNs are a rapidly developing field, because they face a number of challenges. A laboratory that abandons paper notebooks entirely has to provide computer interfaces anywhere in the facility where data might be generated; having screens, keyboards, and mice at every microscope or other apparatus station, for example, can be expensive, and it is not trivial to find an ergonomically equivalent digital substitute for writing things down in a notebook as ideas or data appear. On the other hand, keeping both paper notebooks for immediate recording, and ELNs for organized official storage, raises problems of wasted effort during the (perhaps incomplete) transfer of information from paper to the digital version. ELNs are also an essential tool to prevent loss of institutional knowledge as team members move up to independent positions. ELN usage will evolve over time as input devices improve and best practices are developed to minimize the overhead of entering meta-data. However, regardless of how primary data are acquired, the researcher will need specific strategies for transitioning experimental findings into research product in the context of a complex set of personal, institutional, and scientific goals and constraints.
Facilitating Creativity
The pipeline begins with ideas, which must be cultivated and then harnessed for subsequent implementation ( Altshuller, 1984 ). This step consists of two components: identifying salient new information and arranging it in a way that facilitates novel ideas, associations, hypotheses, and strategic plans for making impact.
For the first step, we suggest an automated weekly PubCrawler search, which allows Boolean searches of the literature. Good searches to save include ones focusing on specific keywords of interest, as well as names of specific people whose work one wants to follow. The resulting weekly email of new papers matching specific criteria complements manual searches done via ISI's Web of Science, Google Scholar, and PubMed. The papers of interest should be immediately imported into a reference manager, such as Endnote, along with useful Keywords and text in the Notes field of each one that will facilitate locating them later. Additional tools include DevonAgent and DevonSphere, which enable smart searches of web and local resources, respectively.
Brainstorming can take place on paper or digitally (see later discussion). We have noticed that the rate of influx of new ideas is increased by habituating to never losing a new idea. This can be accomplished by establishing a voicemail contact in your cell phone leading to your own office voicemail (which allows voice recordings of idea fragments while driving or on the road, hands-free) and/or setting up Endnote or a similar server-synchronized application to record (and ideally transcribe) notes. It has been our experience that the more one records ideas arising in a non-work setting, the more often they will pop up automatically. For notes or schematics written on paper during dedicated brainstorming, one tool that ensures that nothing is lost is an electronic pen. For example, the Livescribe products are well integrated with Evernote and ensure that no matter where you are, anything you write down becomes captured in a form accessible from anywhere and are safe no matter what happens to the original notebook in which they were written.
Enhancing scientific thought, creative brainstorming, and strategic planning is facilitated by the creation of mind maps: visual representations of spatial structure of links between concepts, or the mapping of planned activity onto goals of different timescales. There are many available mind map software packages, including MindNode; their goal is to enable one to quickly set down relationships between concepts with a minimum of time spent on formatting. Examples are shown in Figures 3 A and 3B. The process of creating these mind maps (which can then be put on one's website or discussed with the laboratory members) helps refine fuzzy thinking and clarifies the relationships between concepts or activities. Mind mappers are an excellent tool because their light, freeform nature allows unimpeded brainstorming and fluid changes of idea structure but at the same time forces one to explicitly test out specific arrangements of plans or ideas.

Mind Mapping
(A and B) The task of schematizing concepts and ideas spatially based on their hierarchical relationships with each other is a powerful technique for organizing the creative thought process. Examples include (A), which shows how the different projects in our laboratory relate to each other. Importantly, it can also reveal disbalances or gaps in coverage of specific topics, as well as help identify novel relationships between sub-projects by placing them on axes (B) or even identify novel hypotheses suggested by symmetry.
(C) Relationships between the central nervous system (CNS) and regeneration, cancer, and embryogenesis. The connecting lines in black show typical projects (relationships) already being pursued by our laboratory, and the lack of a project in the space between CNS and embryogenesis suggests a straightforward hypothesis and project to examine the role of the brain in embryonic patterning.
It is important to note that mind maps can serve a function beyond explicit organization. In a good mapped structure, one can look for symmetries (revealing relationships that are otherwise not obvious) between the concepts involved. An obvious geometric pattern with a missing link or node can help one think about what could possibly go there, and often identifies new relationships or items that had not been considered ( Figure 3 C), in much the same way that gaps in the periodic table of the elements helped identify novel elements.
Organizing Information and Knowledge
The input and output of the feedback process between brainstorming and literature mining is information. Static information not only consists of the facts, images, documents, and other material needed to support a train of thought but also includes anything needed to support the various projects and activities. It should be accessible in three ways, as it will be active during all phases of the work cycle. Files should be arranged on your disk in a logical hierarchical structure appropriate to the work. Everything should also be searchable and indexed by Spotlight. Finally, some information should be stored as entries in a data management system, like Evernote or DevonThink, which have convenient client applications that make the data accessible from any device.
Notes in these systems should include useful lists and how-to's, including, for example:
- • Names and addresses of experts for specific topics
- • Emergency protocols for laboratory or animal habitats
- • Common recipes/methods
- • Lists and outlines of papers/grants on the docket
- • Information on students, computers, courses, etc.
- • Laboratory policies
- • Materials and advice for students, new group members, etc.
- • Lists of editors, and preferred media contacts
- • Lists of Materials Transfer Agreements (MTAs), contract texts, info on IP
- • Favorite questions for prospective laboratory members
Each note can have attachments, which include manuals, materials safety sheets, etc. DevonThink needs a little more setup but is more robust and also allows keeping the server on one's own machine (nothing gets uploaded to company servers, unlike with Evernote, which might be a factor for sensitive data). Scientific papers should be kept in a reference manager, whereas books (such as epub files and PDFs of books and manuscripts) can be stored in a Calibre library.
Email: A Distinct Kind of Information
A special case of static information is email, including especially informative and/or actionable emails from team members, external collaborators, reviewers, and funders. Because the influx of email is ever-increasing, it is important to (1) establish a good infrastructure for its management and (2) establish policies for responding to emails and using them to facilitate research. The first step is to ensure that one only sees useful emails, by training a good Bayesian spam filter such as SpamSieve. We suggest a triage system in which, at specific times of day (so that it does not interfere with other work), the Inbox is checked and each email is (1) forwarded to someone better suited to handling it, (2) responded quickly for urgent things that need a simple answer, or (3) started as a Draft email for those that require a thoughtful reply. Once a day or a couple of times per week, when circumstances permit focused thought, the Draft folder should be revisited and those emails answered. We suggest a “0 Inbox” policy whereby at the end of a day, the Inbox is basically empty, with everything either delegated, answered, or set to answer later.
We also suggest creating subfolders in the main account (keeping them on the mail server, not local to a computer, so that they can be searched and accessed from anywhere) as follows:
- • Collaborators (emails stating what they are going to do or updating on recent status)
- • Grants in play (emails from funding agencies confirming receipt)
- • Papers in play (emails from journals confirming receipt)
- • Waiting for information (emails from people for whom you are waiting for information)
- • Waiting for miscellaneous (emails from people who you expect to do something)
- • Waiting for reagents (emails from people confirming that they will be sending you a physical object)
Incoming emails belonging to those categories (for example, an email from an NIH program officer acknowledging a grant submission, a collaborator who emailed a plan of what they will do next, or someone who promised to answer a specific question) should be sorted from the Inbox to the relevant folder. Every couple of weeks (according to a calendar reminder), those folders should be checked, and those items that have since been dealt with can be saved to a Saved Messages folder archive, whereas those that remain can be Replied to as a reminder to prod the relevant person.
In addition, as most researchers now exchange a lot of information via email, the email trail preserves a record of relationships among colleagues and collaborators. It can be extremely useful, even years later, to be able to go back and see who said what to whom, what was the last conversation in a collaboration that stalled, who sent that special protocol or reagent and needs to be acknowledged, etc. It is imperative that you know where your email is being stored, by whom, and their policy on retention, storage space limits, search, backup, etc. Most university IT departments keep a mail server with limited storage space and will delete your old emails (even more so if you move institutions). One way to keep a permanent record with complete control is with an application called MailSteward Pro. This is a front-end client for a freely available MySQL server, which can run on any machine in your laboratory. It will import your mail and store unlimited quantities indefinitely. Unlike a mail server, this is a real database system and is not as susceptible to data corruption or loss as many other methods.
A suggested strategy is as follows. Keep every single email, sent and received. Every month (set a timed reminder), have MailSteward Pro import them into the MySQL database. Once a year, prune them from the mail server (or let IT do it on their own schedule). This allows rapid search (and then reply) from inside a mail client for anything that is less than one year old (most searches), but anything older can be found in the very versatile MailStewardPro Boolean search function. Over time, in addition to finding specific emails, this allows some informative data mining. Results of searches via MailStewardPro can be imported into Excel to, for example, identify the people with whom you most frequently communicate or make histograms of the frequency of specific keywords as a function of time throughout your career.
With ideas, mind maps, and the necessary information in hand, one can consider what aspects of the current operations plan can be changed to incorporate plans for new, impactful activity.
Organizing Tasks and Planning
A very useful strategy involves breaking down everything according to the timescales of decision-making, such as in the Getting Things Done (GTD) philosophy ( Figure 4 ) ( Allen, 2015 ). Activities range from immediate (daily) tasks to intermediate goals all the way to career-scale (or life-long) mission statements. As with mind maps, being explicit about these categories not only force one to think hard about important aspects of their work, but also facilitate the transmission of this information to others on the team. The different categories are to be revisited and revised at different rates, according to their position on the hierarchy. This enables you to make sure that effort and resources are being spent according to priorities.

Scales of Activity Planning
Activities should be assigned to a level of planning with a temporal scale, based on how often the goals of that level get re-evaluated. This ranges from core values, which can span an entire career or lifetime, all the way to tactics that guide day-to-day activities. Each level should be re-evaluated at a reasonable time frame to ensure that its goals are still consistent with the bigger picture of the level(s) above it and to help re-define the plans for the levels below it.
We also strongly recommend a yearly personal scientific retreat. This is not meant to be a vacation to “forget about work” but rather an opportunity for freedom from everyday minutiae to revisit, evaluate, and potentially revise future activity (priorities, action items) for the next few years. Every few years, take more time to re-map even higher levels on the pyramid hierarchy; consider what the group has been doing—do you like the intellectual space your group now occupies? Are your efforts having the kind of impact you realistically want to make? A formal diagram helps clarify the conceptual vision and identify gaps and opportunities. Once a correct level of activity has been identified, it is time to plan specific activities.
A very good tool for this purpose, which enables hierarchical storage of tasks and subtasks and their scheduling, is OmniFocus ( Figure 5 ). OmniFocus also enables inclusion of files (or links to files or links to Evernote notes of information) together with each Action. It additionally allows each action to be marked as “Done” once it is complete, providing not only a current action plan but a history of every past activity. Another interesting aspect is the fact that one can link individual actions with specific contexts: visualizing the database from the perspective of contexts enables efficient focus of attention on those tasks that are relevant in a specific scenario. OmniFocus allows setting reminders for specific actions and can be used for adding a time component to the activity.

Project Planning
This figure shows a screenshot of the OmniFocus application, illustrating the nested hierarchy of projects and sub-projects, arranged into larger groups.
The best way to manage time relative to activity (and to manage the people responsible for each activity) is to construct Gantt charts ( Figure 6 ), which can be used to plan out project timelines and help keep grant and contract deliverables on time. A critical feature is that it makes dependencies explicit, so that it is clear which items have to be solved/done before something else can be accomplished. Gantt charts are essential for complex, multi-person, and/or multi-step projects with strict deadlines (such as grant deliverables and progress reports). Software such as OmniPlanner can also be used to link resources (equipment, consumables, living material, etc.) with specific actions and timelines. Updating and evaluation of a Gantt chart for a specific project should take place on a time frame appropriate to the length of the next immediate phase; weekly or biweekly is typical.

Timeline Planning
This figure shows a screenshot of a typical Gantt chart, in OmniPlan software, illustrating the timelines of different project steps, their dependencies, and specific milestones (such as a due date for a site visit or grant submission). Note that Gantt software automatically moves the end date for each item if its subtasks' timing changes, enabling one to see a dynamically correct up-to-date temporal map of the project that adjusts for the real-world contingencies of research.
In addition to the comprehensive work plan in OmniFocus or similar, it is helpful to use a Calendar (which synchronizes to a server, such as Microsoft Office calendar with Exchange server). For yourself, make a task every day called “Monday tasks,” etc., which contains all the individual things to be accomplished (which do not warrant their own calendar reminder). First thing in the morning, one can take a look at the day's tasks to see what needs to be done. Whatever does not get done that day is to be copied onto another day's tasks. For each of the people on your team, make a timed reminder (weekly, for example, for those with whom you meet once a week) containing the immediate next steps for them to do and the next thing they are supposed to produce for your meeting. Have it with you when you meet, and give them a copy, updating the next occurrence as needed based on what was decided at the meeting to do next. This scheme makes it easy for you to remember precisely what needs to be covered in the discussion, serves as a record of the project and what you walked about with whom at any given day (which can be consulted years later, to reconstruct events if needed), and is useful to synchronize everyone on the same page (if the team member gets a copy of it after the meeting).
Writing: The Work Products
Writing, to disseminate results and analysis, is a central activity for scientists. One of the OmniFocus library's sections should contain lists of upcoming grants to write, primary papers that are being worked on, and reviews/hypothesis papers planned. Microsoft Word is the most popular tool for writing papers—its major advantage is compatibility with others, for collaborative manuscripts (its Track Changes feature is also very well implemented, enabling collaboration as a master document is passed from one co-author to another). But Scrivener should be seriously considered—it is an excellent tool that facilitates complex projects and documents because it enables WYSIWYG text editing in the context of a hierarchical structure, which allows you to simultaneously work on a detailed piece of text while seeing the whole outline of the project ( Figure 7 ).

Writing Complex Materials
This figure shows a screenshot from the Scrivener software. The panel on the left facilitates logical and hierarchical organization of a complex writing project (by showing where in the overall structure any given text would fit), while the editing pane on the right allows the user to focus on writing a specific subsection without having to scroll through (but still being able to see) the major categories within which it must fit.
It is critical to learn to use a reference manager—there are numerous ones, including, for example, Endnote, which will make it much easier to collaborate with others on papers with many citations. One specific tip to make collaboration easier is to ask all of the co-authors to set the reference manager to use PMID Accession Number in the temporary citations in the text instead of the arbitrary record number it uses by default. That way, a document can have its bibliography formatted by any of the co-authors even if they have completely different libraries. Although some prefer collaborative editing of a Google Doc file, we have found a “master document” system useful, in which a file is passed around among collaborators by email but only one can make (Tracked) edits at a time (i.e., one person has the master doc and everyone makes edits on top of that).
One task most scientists regularly undertake is writing reviews of a specific subfield (or Whitepapers). It is often difficult, when one has an assignment to write, to remember all of the important papers that were seen in the last few years that bear on the topic. One method to remedy this is to keep standing document files, one for each topic that one might plausibly want to cover and update them regularly. Whenever a good paper is found, immediately enter it into the reference manager (with good keywords) and put a sentence or two about its main point (with the citation) into the relevant document. Whenever you decide to write the review, you will already have a file with the necessary material that only remains to be organized, allowing you to focus on conceptual integration and not combing through literature.
The life cycle of research can be viewed through the lens of the tools used at different stages. First there are the conceptual ideas; many are interconnected, and a mind mapper is used to flesh out the structure of ideas, topics, and concepts; make it explicit; and share it within the team and with external collaborators. Then there is the knowledge—facts, data, documents, protocols, pieces of information that relate to the various concepts. Kept in a combination of Endnote (for papers), Evernote (for information fragments and lists), and file system files (for documents), everything is linked and cross-referenced to facilitate the projects. Activities are action items, based on the mind map, of what to do, who is doing what, and for which purpose/grant. OmniFocus stores the subtasks within tasks within goals for the PI and everyone in the laboratory. During meetings with team members, these lists and calendar entries are used to synchronize objectives with everyone and keep the activity optimized toward the next step goals. The product—discovery and synthesis—is embodied in publications via a word processor and reference manager. A calendar structure is used to manage the trajectory from idea to publication or grant.
The tools are currently good enough to enable individual components in this pipeline. Because new tools are continuously developed and improved, we recommend a yearly overview and analysis of how well the tools are working (e.g., which component of the management plan takes the most time or is the most difficult to make invisible relative to the actual thinking and writing), coupled to a web search for new software and updated versions of existing programs within each of the categories discussed earlier.
A major opportunity exists for software companies in the creation of integrated new tools that provide all the tools in a single integrated system. In future years, a single platform will surely appear that will enable the user to visualize the same research structure from the perspective of an idea mind map, a schedule, a list of action items, or a knowledge system to be queried. Subsequent development may even include Artificial Intelligence tools for knowledge mining, to help the researcher extract novel relationships among the content. These will also need to dovetail with ELN platforms, to enable a more seamless integration of project management with primary data. These may eventually become part of the suite of tools being developed for improving larger group dynamics (e.g., Microsoft Teams). One challenge in such endeavors is ensuring the compatibility of formats and management procedures across groups and collaborators, which can be mitigated by explicitly discussing choice of software and process, at the beginning of any serious collaboration.
Regardless of the specific software products used, a researcher needs to put systems in place for managing information, plans, schedules, and work products. These digital objects need to be maximally accessible and backed up, to optimize productivity. A core principle is to have these systems be so robust and lightweight as to serve as an “external brain” ( Menary, 2010 )—to maximize creativity and deep thought by making sure all the details are recorded and available when needed. Although the above discussion focused on the needs of a single researcher (perhaps running a team), future work will address the unique needs of collaborative projects with more lateral interactions by significant numbers of participants.
Acknowledgments
We thank Joshua Finkelstein for helpful comments on a draft of the manuscript. M.L. gratefully acknowledges support by an Allen Discovery Center award from the Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group (12171) and the Barton Family Foundation.
- Allen D. Revised edition. Penguin Books; 2015. Getting Things Done: The Art of Stress-free Productivity. [ Google Scholar ]
- Altshuller G.S. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers; 1984. Creativity as an Exact Science: The Theory of the Solution of Inventive Problems. [ Google Scholar ]
- Menary R. MIT Press; 2010. The Extended Mind. [ Google Scholar ]
Minnesota Sea Grant
A Systemwide Program of the University of Minnesota
Minnesota Sea Grant: Two Aquatic Research Technician Position Job Openings

Minnesota Sea Grant is hiring two Aquatic Research Technicians! Application review begins May 10, 2024.
The Minnesota Sea Grant Aquatic Research Technician will be working on the e nhancing habitat and diversity in invasive cattail-dominated shorelines project. Invasive, hybrid cattails have expanded into Minnesota nearshore lake zones, altering habitat for fishes and displacing native plant species. The objective of MNSG's cattail project is to understand the effects of hybrid cattail invasion on the ecological dynamics of nearshore lake communities across Minnesota. The project team will compare regional effects of cattail removal on nearshore lake ecosystems in lakes across Minnesota by measuring water quality variables, identifying plants, and sampling and identifying fishes.
Quick Links & Instructions
Applications must be submitted online.
- To apply for this position, go to https://hr.umn.edu/Jobs/Find-Job
- In the the "Search Jobs" field, enter "360868." This is the job ID #.
- Or go directly to MNSG Aquatic Research Technician posting
- Cover letter
- Resume or curriculum vitae
- Contact information for three professional references
- Who’s hiring : The University of Minnesota Sea Grant College Program
- Job Title : Aquatic Research Technician
- Job ID : 360868
- Location : St. Paul, MN. But travel throughout Minnesota is required.
- Full or part time: Approximately 40 hours per week. Work days and hours may vary and may include weekends.
- Term of service: June 2024 through late August 2024.
- Compensation: $15 per hour.
- Application open date: 4/26/2024
- Application close date: Reviews will begin May 10, 2024.
- Questions: If you have questions about this position contact MNSG Extension Program Leader Amy Schrank at [email protected].
- Go to https://humanresources.umn.edu/content/find-job .
- Select "students.”
- Enter 360868 (Job ID number)
About the Position
Primary duties:.
- Travel to lakes across Minnesota throughout the summer for extensive field work.
- Set and retrieve minnow traps to collect and identify fishes.
- Help identify and enumerate nearshore plant species.
- Measure water quality and other physical habitat variables in the field.
- Collect and record accurate, detailed field data and notes.
- Properly care for all sampling equipment, follow safety procedures, and follow animal use permit requirements.
Skills required:
- Must be organized, responsible, detail oriented, and willing to work as a team member.
- Must be able to conduct field work under all outdoor conditions (rain, heat, wind, bugs).
- Must be able to hike 4 miles carrying up to 40 lbs of equipment over uneven and/or steep terrain.
- Must have a valid driver’s license and good driving record.
- Must be comfortable working in/around water and canoeing/kayaking to some sites.
- Must be comfortable camping for at least two weeks.
- Must have a positive attitude and eagerness to learn.
Preferred skills and attributes:
- Past experience with fish and/or plant identification/sampling.
- Past field work/research/outdoor experience.
- Experience using a hand-held GPS.
Who is Sea Grant?
Minnesota Sea Grant (MNSG) is a systemwide program of the University of Minnesota and one of 34 federal-university Sea Grant partnerships across the country that bring applied water science to communities. MNSG’s extension educators, researchers and communicators work with community members, local decision-makers, policy leaders, and personnel from resource agencies, business and industry to protect, enhance and restore habitats, ecosystems and the services those ecosystems provide. We are what makes the University of Minnesota a Sea Grant institution.
If you have questions about this position contact Minnesota Sea Grant Extension Program Leader Amy Schrank
Image credit: Amy Schrank/MNSG
Departments
- Special Request
- What is Sea Grant?
- Advisory Board
- People Directory
- Partners & Collaborators
- Reports & Plans
- News Overview
- Featured Stories
- Newsletter Archive
- News Releases
- Sea Grant in the News
- Staff Publications
- Outreach Materials
- Programs Overview
- Coastal Hazards of Superior - Community of Practice
- Partnering with Local Governments for Climate Adaptation
- Great Lakes One Water Resilient Future
- One Block at a Time
- The Watershed Game
- Twin Ports Climate Conversations
- Bugs Below Zero
- Center for Great Lakes Literacy
- Shipboard Science Workshops
- Students Ask Scientists
- Aquaculture 101
- Aquaculture Market Study
- Aquaculture Regulations
- Consumer Education Resources
- Egg-to-Market Yellow Perch Project
- Steelhead or Salmon? Which Did You Catch?
- Increasing Golden Shiner Bait Production in Minnesota
- Great Lakes Aquaculture Collaborative
- Great Lakes FreshFishFinder.org Website
- Kids Cooking Seafood with Spark-Y
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Supply Chain
- Clean Sweep Program
- Field Guide for Maintaining Rural Roadside Ditches
- Habitat Management in the St. Louis River Estuary Workshop
- Invasive Cattail-Dominated Shorelines
- Regional Stormwater Protection Team (RSPT)
- Twin Ports Freshwater Folk
- Wild Rice - Manoomin
- Great Lakes Shipping 101
- Hazardous Material Transport Outreach Network
- Drowning Hotspots in the St. Louis River Estuary
- Hypothermia: Understanding and Prevention
- Minnesota Lake Ice-Out Clock
- Paddle Safe Twin Ports
- Research Overview
- Research Projects
- Scholarly Articles
- Biennial Request for Proposals (RFP)
- Joint MN-WI-OH Sea Grant RFP
- Marine Debris Challenge Competition
- Marine Debris Community Action Coalitions
- Translating Coastal Research Into Application
- Fast-Track Grants
- Knauss Fellowship
- National Marine Fisheries-Sea Grant Joint Fellowship
- NOAA Hollings Undergraduate Scholarship
- NOAA Coastal Management Fellowship
- Proposal Forms and Documents

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Completing any research project requires meticulous planning, experimental design and execution, and compilation and publication of findings in the form of a research paper. All of these are often unfamiliar to naïve researchers; thus, the purpose of this workshop was to teach participants to master the critical steps involved in the ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Students pursuing studies in academic institutions (particularly, universities) both at the undergraduate and postgraduate levels are required to conduct an independent piece of research and present in the form of a dissertation or thesis as part of the requirements for awarding academic degrees.
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
INTRODUCTION. A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under 'Research methodology II' section [Table 1] in this issue of IJA) and to ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Science | June 15, 2020. Seventy-Five Scientific Research Projects You Can Contribute to Online. From astrophysicists to entomologists, many researchers need the help of citizen scientists to sift ...
Step 1: Consider your aims and approach. Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Step 3: Identify your population and sampling method. Step 4: Choose your data collection methods. Step 5: Plan your data collection procedures. Step 6: Decide on your data analysis strategies. Other interesting articles.
Research data management (RDM) is the cornerstone of a successful research project, and yet it often remains an underappreciated art that gets overlooked in the hustle and bustle of everyday project management even when required by funding bodies. If researchers are to strive for reproducible science that adheres to the principles of FAIR, then they need to manage the data associated with ...
Background: Every research project faces challenges regarding how to achieve its goals in a timely and effective manner. The purpose of this paper is to present a project evaluation methodology gathered during the implementation of the Participation to Healthy Workplaces and Inclusive Strategies in the Work Sector (the EU PATHWAYS Project). The PATHWAYS project involved multiple countries and ...
A project can end for various reasons, including getting scooped by competitors or when funding runs out. In Argentina, we often face limited research funding compared with other regions of the ...
Methodology - the methods you will use for your primary research. Findings and results - presenting the data from your primary research. Discussion - summarising and analysing your research and what you have found out. Conclusion - how the project went (successes and failures), areas for future study.
Development and preliminary validation of a prediction formula of sodium and sodium-to-potassium ratio based on multiple regression using 24-h urines. Marina Yamagishi. Ribeka Takachi. Norie ...
Just be careful that you don't end up stuck with an idea you want to do, but are afraid to do because you know someone else did it before. 4. Think from all angles. If you have at least a little direction based on the project guidelines, take that basic direction and start turning it over and over in your mind.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Project Management Journal® is the academic and research journal of the Project Management Institute and features state-of-the-art research, techniques, theories, ... Research article. First published Nov 6, 2023. Interorganizational Design for Collaborative Governance in Co-Owned Major Projects: An Engaged Scholarship Approach ...
Here are some simple steps that may contribute to an organised start on the project. You need a protocol but first you must be clear about what the project will involve. Undertake a literature search on the suggested topic. Read all the papers from the last ten years and summarise them on a single page of A4.
Research increasingly suggests that when a woman with obesity becomes pregnant, a process of "fetal reprogramming" increases the risk that her baby will face problems like obesity, Type 2 diabetes and liver disease earlier in life. To better understand how that reprogramming occurs, University of Oklahoma researchers recently earned a $2.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health.
Research project that found elevated food insecurity levels in Stevens County expands to a five-county region SBA recognizes SMSU grad Layne Lozinski as Young Entrepreneur of the Year Providing ...
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Bioenergy Technologies Office (BETO) hosted the 2023 Project Peer Review in April 2023 in Denver, Colorado. During the event, new research and development (R&D) projects from 11 technology areas within BETO's portfolio were presented to external subject-matter experts from industry, academia, and federal agencies. Experts reviewed the research and provided ...
The Problem. Although companies frequently engage in transformation initiatives, few are actually transformative. Research indicates that only 12% of major change programs produce lasting results.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand how the population of Americans ages 100 and older looks today, and how it is expected to change in the next 30 years. U.S. population estimates come from the U.S. Census Bureau , and global projections are drawn from the United Nations' population projections under its medium variant ...
What is a research project? A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question.Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative, descriptive, longitudinal, experimental, or correlational.What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
Such research may pose challenges related to ethics in relation to the social and cultural milieu. Biomedical research related to human genetics and transplantation research poses an increased threat to ethical concerns, especially after the success of the human genome project (HGP) in the year 2000.
The American Sunlight Project has been established as a nonprofit under the section of the Internal Revenue Code that allows it greater leeway to lobby than tax-exempt charities known as 501(c)(3)s.
Project Outcome Reports (for general public) The Project Outcomes Report is a report written for new and existing awards, specifically for the public, that provides insight into the outcomes of NSF-funded research. Project Outcome Reports can be viewed through Research.gov's Research Spending & Results search service. Note: Project Outcome ...
The Life Cycle of Research Activity. Various projects occupy different places along a typical timeline. The life cycle extends from creative ideation to gathering information, to formulating a plan, to the execution for the plan, and then to producing a work product such as a grant or paper based on the results. Many of these phases necessitate ...
SummaryThe Minnesota Sea Grant Aquatic Research Technician will be working on the enhancing habitat and diversity in invasive cattail-dominated shorelines project. Invasive, hybrid cattails have expanded into Minnesota nearshore lake zones, altering habitat for fishes and displacing native plant species. The objective of MNSG's cattail project is to understand the effects of hybrid cattail ...